- 1Laboratoire des Symbioses Tropicales et Méditerranéenne (LSTM), Univ. Montpellier, Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD), Centre de coopération Internationale en Recherche Agronomique pour le développement (CIRAD), Institut National de Recherche pour l’Agriculture, l’Alimentation et l’Environnement (INRAE), Institut Agro Montpellier, Montpellier, France
- 2Société Agronutrition, Carbonne, France
- 3Laboratoire de Biotechnologie et Physiologie Végétales, Faculté des Sciences, Université Mohammed V de Rabat, Maroc/Laboratoire Mixte International - Laboratoire Mixte International (LMI) AMIR, Rabat, Morocco
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are major components of soil microbiota and mainly interact with other microorganisms in the rhizosphere. Mycorrhiza establishment impacts the plant physiology and some nutritional and physical properties of the rhizospheric soil. These effects alter the development of the root or mycorrhizas resulting from the activity of soil microorganisms. The rhizosphere of mycorrhizal plants (mycorrhizosphere), is inhabited by large microbial activities responsible for several key ecosystem processes. This review is focused on the microbial interactions between mycorrhizal fungi and components of rhizosphere microbiota and highlight the agronomic potentialities of the Mycorrhiza Helper Bacteria on mycorrhiza formation. The main conclusion is that this MHB effect in the rhizosphere of mycorrhizal plants, enhance plant fitness and soil quality and are of great interest to ensure sustainable agricultural development and ecosystem functioning.
Introduction
By 2050, and in order to cope with the increase in the number of the world’s population which will reach 9 billion people according to the FAO, agricultural production needs to be doubled in developing countries and increased by 70% in the rest of the word (1). The major challenge is to occur a world food security but in the last decades, agricultural lands have been severely impacted by human over-exploitation of the naturelle resources, and the abusive use of fields, resulting in land degradation and desertification (2). Soil erosion and desertification have reduced by 50% the productivity of some lands (3). In Africa, fertile yield decrease is estimated from 2 to 40%, with a mean loss of 8.2% for the continent. Both processes are commonly related to an alteration of the plant cover (species diversity, abundance) but they also affect the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of soils (soil structure, nutrient bioavailability, microbial activity, etc) (4, 5). In agriculture, the adoption of high-input farming practices is dependent to the use of resources such as, mineral nutrients, soil, or water, known to become limiting soon. Hence, the use of fertilizer application will decrease due to increasing costs of mineral fertilizer (6, 7), and the environmental damages (8, 9). This projection will be aggravated by the environmental conditions predicted by current climate change scenarios (10) allowing to a worsening of the impact of abiotic stress on agricultural productivity. At the same time, the demand for food from an over-increasing world population will also be greater, leading to a large imbalance between supply and demand, whose resolution will be a major challenge in defining the basis for an environmentally friendly and productive agriculture.
In order to deal with these increasing agricultural problems, it has been suggested to integrate key processes from natural ecosystems in agricultural practices (2, 3). In many cases, non-degraded ecosystems ensure a high plant and soil health (11). Among all these natural processes, the potentialities of arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM), associations between plant roots and fungi belonging to the phylum Glomeromycota (12) into three classes (Glomeromycetes, Archaeosporomycetes, and Paraglomeromycetes), with almost 250 species distributed across 11 families and 25 genera (13, 14), have been highlighted. They are of particular interest to promote the productivity, stability and resistance of agricultural systems. A recent study has reported that AMF accounted for about one-third of the maize grain production in a medium input field showing the great importance of this biological process in crop yield (15). Mycorrhizal symbiosis is the most common beneficial mutualistic association between fungal symbionts and plant roots (16, 17). This fun gal symbiosis can also be considered as an indicator of soil health (18). There are different forms of mycorrhizal symbiosis depending on the type of fungus and the mode of association: (i) arbuscular mycorrhizae; (ii) ectendomycorrhizae: and (iii) ectomycorrhizae.
It has been well demonstrated that these microorganisms play a main role in improving the water, trophic nutrition and enhance plant defenses against root pathogens and root browsing and can also impair the performance of their host plant by colonizing and exploiting a large surface of the soil invaded by roots alone (17).
There are more than 90% of terrestrial plants whose roots are colonized by mycorrhizal fungi. This association contributes to a succession of physiological and morphological changes in the roots of host plants, thus inducing healthy plant growth. Hence mycorrhizae could be used in agriculture, forestry to ensure better restoration to improve yield. Indeed, the ability of mycorrhizal fungi is not only reduced to their ability to improve the nutrition of plants or to strengthen their immune system, but also have an ability to accumulate metals making them potential candidates for the restoration and remediation of diseases. polluted environments (17, 19, 20). Many studies confirm the interest of the use of mycorrhizal fungi to assess soil and plant health. Gupta et al. (2020) (18) argue in their review that mycorrhizae are not only as indicators but also as determining organisms of soil health. The interaction between the plant species considered and the symbiotic fungus confers multiple advantages for the plant, including the improved of plant nutrition by allowing better uptake of water, P, Cu, Zn and nitrogen (21–23), release of carbonaceous compounds forming the mycorrhizosphere (24); stimulation of the production of phytohormones such as abscisic acid (25); improving plant resistance to (a)biotic stresses (26) and improving soil structure and stability (21). Tahat et al. (2020) (27) highlight that AMF (arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi) improve the functions of the rhizospheric part of the soil. Mahmoudi et al. (2021) (28) also showed that AMF are indicators of soil multifunctionality. Indeed, the multifunctionality of the soil is strongly dependent on the mycorrhizal traits and the mycorrhizal intensity is more correlated with the multifunctional character of the soil than the mycorrhizal frequency. These fungal symbionts are also involved in the biological processes that impact plant community productivity and plant-plant interactions (29).
Nutrient cycling and biological diversity are considered as the main differences between natural ecosystems and agrosystems resulting from the high-input of fertilizers to ensure the high crop productivity. Two different technical ways could be considered to integrate the AMF in agricultural practices: (i) the “reductionist” approach where specialized fungal inocula adapted to the given condition are mixed to the cultured soil (also named controlled mycorrhization) and (ii) the “holistic” approach where the main objective is to conserve, promote or restore native AMF diversity (Figure 1).
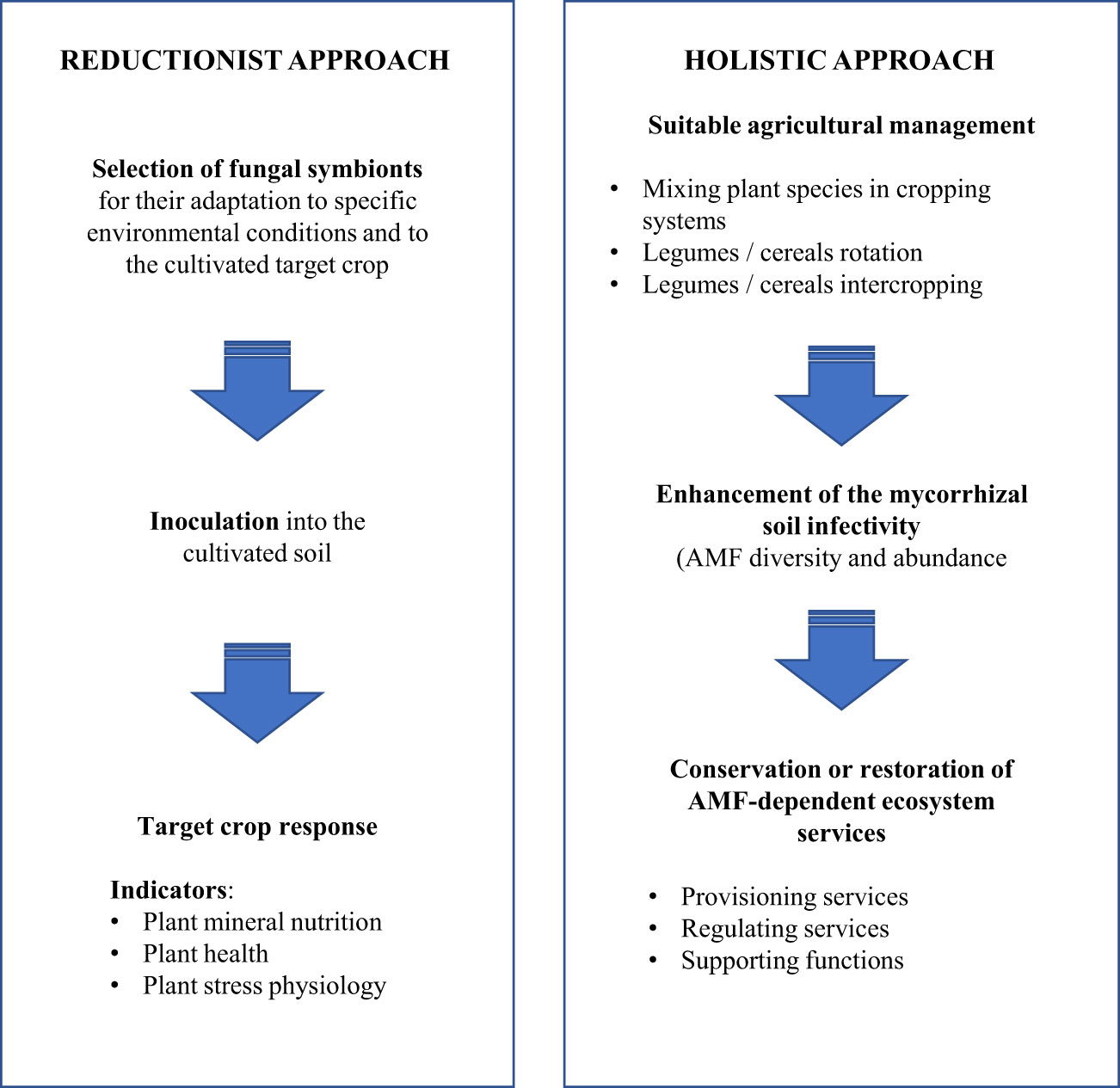
Figure 1 Technical approaches to ensure the AMF integration in agricultural practices (Adapted from Fester & Sawers (2011).
The potentialities of using single AMF strains to restore or conserve the whole range of ecosystem services resulting from the AM symbiosis could be challenging. Although numerous studies have been published on AMF symbiosis, data on the “reductionist” management of AMF in field conditions remain scarce (30).
Several scientifical studies conducted on the mycorrhizal symbiosis have been limited to the interactions between each biological component (host plant/AMF) resulting to bipartite interaction investigation. However, and in natural conditions, plants are in constant selection of their microbial host from different surrounding microbial reservoirs (11, 17). The “Plants/Microorganisms” associations are not randomly established. They are controlled by many conditions and multiple factors. Plant microbiota is in fact influenced by (i) soil type, (ii) plant immune system, (iii) stage of plant development, (iv) season and genotype and (v) the host specie (11). Furthermore, it is now well established that several communities of bacteria and fungi interact with the establishment and functioning at the metabolic level of the mycorrhizal association. For instance, it has been reported that AMF spores hosted some bacteria within or on their spore walls or in the cytoplasm (31). In order to optimize establishment and effectiveness of artificial fungal inocula under field conditions, a promising way of research could be envisaged by designing complex inoculants combining strains of mycorrhizal fungi and microbial biofertilizers (30). Hence, the associated microbial biofertilizers are generally selected for their agronomic features of interest (i.e. P solubilizers, N-fixers, etc) but their impacts the fungal symbionts and/or the AM establishment and functioning are generally not considered. One of the strategies would be to select bacterial strains capable to promote the establishment and functioning of the mycorrhizal symbiosis and thus optimize the performance of the AMF introduction on plant development (14, 15).
This review covers the specificity and mechanism of action of MHB, through which they positively impact the functioning of AMF as bioenhancers and play key roles in mycorrhizal symbiosis.
Mycorrhizae helper bacteria: A tripartite symbiosis
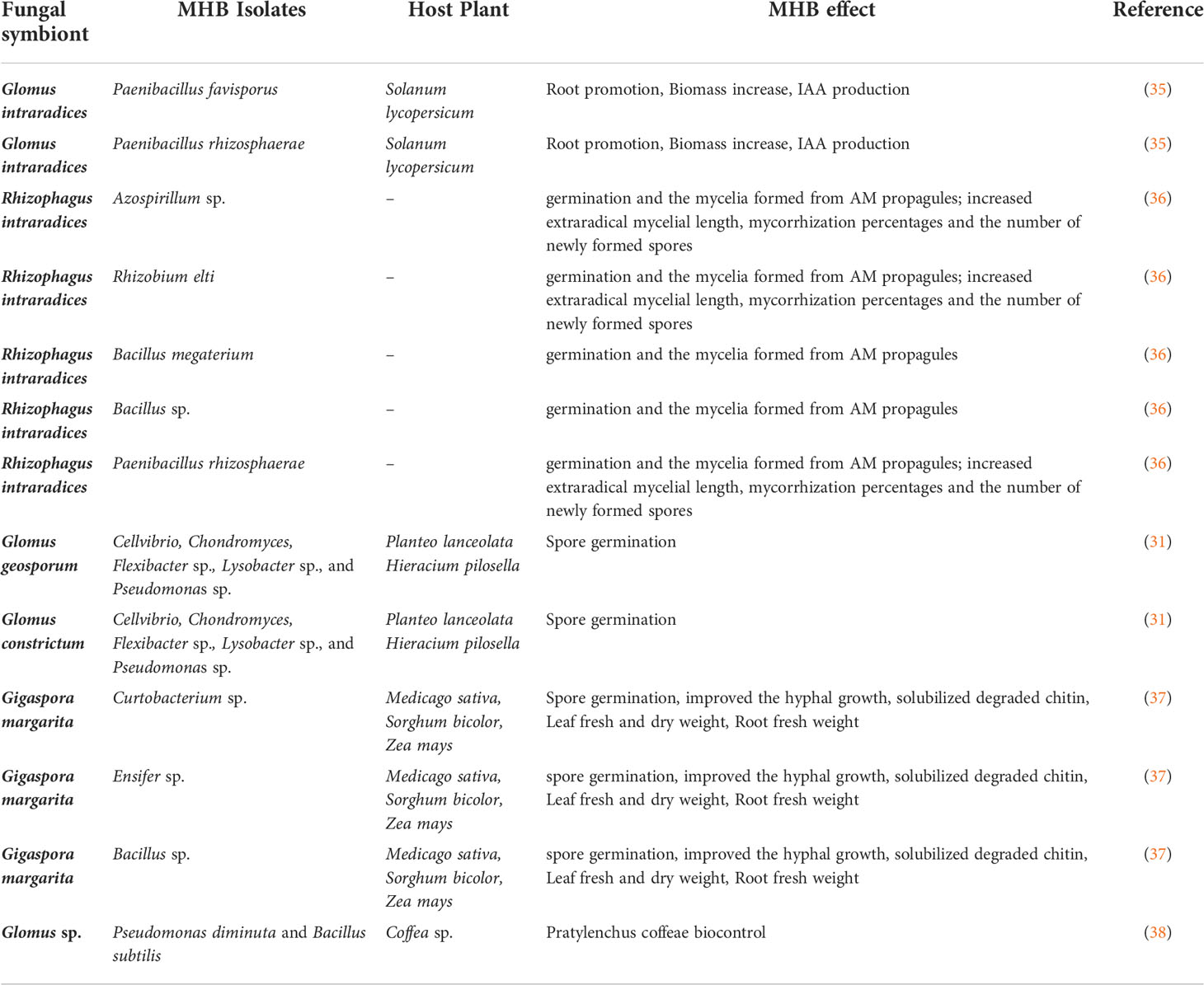
The concept of “Mycorrhizae Helper Bacteria” refers to bacteria that have the ability to promote the establishment of the “Root-Mycorrhizal Fungus” interaction, or bacteria associated with roots and mycorrhizal fungi and which will selectively promote the development of this mycorrhizal symbiosis. Two groups of MHB have been distinguished according to their functional action (32): (i) mycorrhiza helper bacteria that impact the functions of an already established AMF symbiosis and (ii) mycorrhization helper bacteria that stimulate the establishment of the fungal symbionts on the host plants. Both groups are generally named MHB but they can be discriminated according to their natural location around the root systems such as hyphosphere, mycorrhizosphere and sporocarps (Figure 2). Some MHB have been first observed in the AMF Rhizophagus (33, 34). Since this report, numerous examples of positive interactions between AMF and bacteria have been documented (Table 1). Bacteria with MHB-like properties are classified into two groups: Gram-negative Proteobacteria (Agrobacterium,
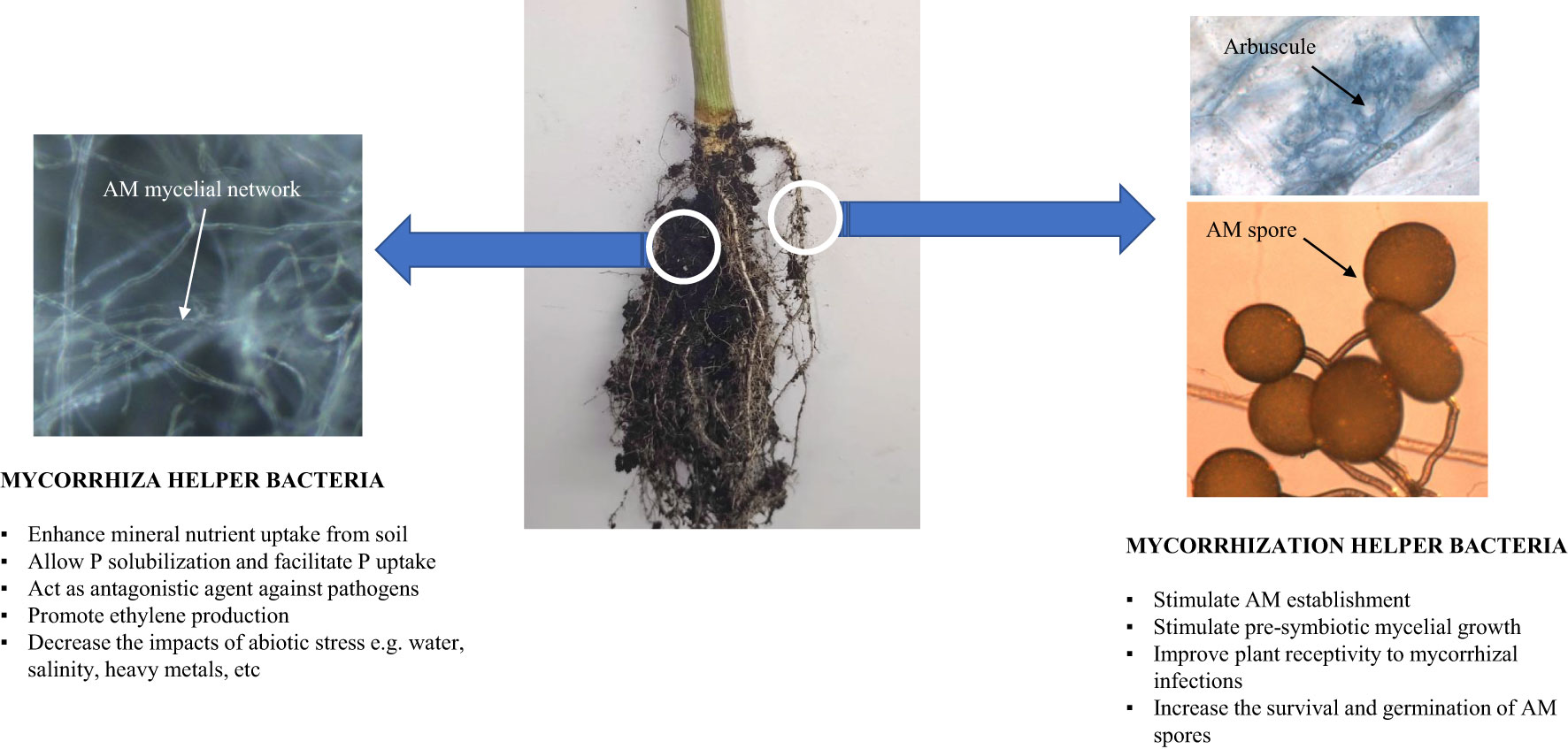

Figure 2 Spatial distribution and functions of Mycorrhiza Helper Bacteria and Mycorrhization Helper Bacteria.
Azospirillum, Azotobacter, Burkholderia, Bradyrhizobium, Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, and Rhizobium), Gram-positive Actinobacteria (Rhodococcus, Streptomyces, and Arthrobacter), and Firmicutes (Bacillus, Brevibacillus, and Paenibacillus). It has been also suggested that this MHB effect could result from plant growth promoting (PGP) activities (39)
Microbe-microbe interaction
In order to facilitate co-habitation of different microbial species under the same habitat, many mechanisms are established to permit a healthy growth of different microbe profile. One of the most important aspects is the communication among several microbial species (40). The intraspecies an interspecies microbial communication is made possible by several chemical secretion that regulate microbial interactions in numerous ecological environment and that is also known as Quorum sensing (QS) (41).
Microbes have the ability to create and detect tiny molecule signals in QS, in response to this phenomena, the expression levels of several genes can change and be modified. Autoinducers, or QS signals, may gather surrounding the cell and convey information about ambient conditions, transport dynamics, and the quantity and identity of microbial neighbors (42).
These autoinducers can modify the transcription of multiple QS-regulated genes that take part in the biofilm formation and other factors (43).
In other hand, “Cross feeding” is an important mechanism in microbe–microbe interactions to stabilize cooperation and to reach a maximum growth under different environment conditions (44). For example, in a Pande et al. study in 2013 (45), the combining of two, non-amino acids producing, Escherichia coli mutants can complement each other by overproducing the amino acid. Also, they showed a higher fitness when grown together compared to E. coli wildtype alone.
Other studies, shown that this complementarity can also be seen in a bacteria-fungus combination and not only in a bacteria-bacteria coexisting (46).
These strategies permit to microbes to survive and persist in the most unfavorable environment (47).
MHB- microbe interaction
The MHB-microbes interaction, and as cited above, is no different from the microbes-microbes interaction.
For the MHB-microbes interaction, the communication is also due to chemical secretion (41).
As an example, Pseudomonas fluorescens BBc6R8 (Considered as an MHB) secrete a chemical component: Thiamine, that helps with the growth of mycorrhizal fungus: Laccaria bicolor S238. In the other hand, The mycorrhizal fungus releases trehalose that serve as chemoattractant for the Mycorrhiza Helper Bacteria (MHB) Pseudomonas fluorescens BBc6R8 (41).
The MHB and AMF interaction
Factors affecting MHB and AMF colonization
Mycorrhizal symbiosis is generally influenced by the presence of other microorganisms, and particularly bacteria in the rhizosphere. These bacteria develop mechanisms of selective interaction with the rhizospheric microbiome and exert neutral, negative, or positive effects on the development and establishment of mycorrhizal associations. Given the positive effect exerted by some bacteria on mycorrhization, the term ‘mycorrhization helper bacteria’ was first used by Duponnois & Garbaye in 1991 (48) describing bacteria that promote the establishment of the root–fungus symbiosis.
Numerous factors can affect the MHB/AMF colonization. The affinity between the AMF and the MHB is influenced by the specificity between the mycorrhizal and bacterial (i) species and strains, (ii) plant roots, (iii) soil structure, (iv) biotic and abiotic stresses, (v) nutrient competition and soil microbiome composition (49, 26).
A heat shock can also disturbed the MHB/AMF colonization due to the alteration of soil microbiomes that influence directly the tripartite association “Plant/AMF/MHB” (49)
It has also been reported in several studies, that MHB have also the ability to produce molecule signals that influence and regulate the fungal gene networks under the AMF symbiosis (50, 51). Some reports have highlighted the role of MHB associated with AMF spores in contracting the symbiotic relationship of AMF with its host plant by increasing spore germination, growth of AMF hyphae, and root colonization (36, 52).
Indeed, the complexity of this tripartite association needs to be more explored (53).
The mycorrhization helper bacteria and AMF spore germination
Some bacteria are strictly associated with AMF spores (54, 55). Using both culture-dependent and culture-independent methods, they have been identified as Pseudomonas, Flexibacter, Cellvibrio, Chondromyces, and Lysobacter (31) or Bacillales, Burkholderiales, Actinomycetales, Rhizobiales, and Pseudomonadales. It has also been reported the presence of several genera inside AMF spores such as Bacillus, Paenibacillus, Rhizobium, Sinorhizobium, Arthrobacter, Streptomyces, Pseudomonas, Herbaspirillum and Massilia (56, 57), MHB were also detected in the layers of the spore cell wall of Glomus clarum NT4, Glomus versiforme (58, 59), Gigaspora margarita (60), Funneliformis mosseae, and Rhizophagus intraradices (53, 55). One of the well-documented effect of MHB on mycorrhizal establishment is related to the stimulation of the spore germination. The first report on this mode of action showed that that the fungal spore germination of Funneliformis mosseae was stimulated by MHB and their culture filtrates (33). Other mechanisms have been then suggested such as:
- MHB production of several volatile and non-volatile compounds, e.g., CO2 and 2-methylisoborneol regulating the germination of spores (54). This mechanism has been also described with different species of Streptomyces that increase the germination of Funneliformis mosseae spores.
- A specific sugar (raffinose) excreted by Paenibacillus validus could stimulate the germination of Rhizophagus irregularis spores (61).
- The growth, development, and early sporulation of Rhizophagus irregularis was also facilitated by a strain of Paenibacillus validus that exhibited nitrogen fixation and P solubilization (60).
- The importance of direct physical interaction. has been also emphasized in the MHB positive effect on spore germination (59, 62).
- MHB enzymatic production (i.e. cell-wall degrading enzymes including cellulase, chitinase,
protease) could also enhance spore germination (63). For instance, the main component of the fungal spore cell wall role of chitinase was degraded by chitinase produced by actinomycete strains (37).
Other mechanisms have been suggested to explain the MHB effects on mycorrhizal establishment such as the stimulation of root receptivity to AMF by increasing the infection sites where plants and fungi interact (64). Other reports have identified signal molecules
produced by MHB, which regulate the fungal gene networks underlying the AMF symbiosis (65). It has been also well demonstrated that the co-culture of Glomus fistulosum and the MHB Pseudomonas putida or its culture supernatant resulted to a higher growth of the fungal symbiont (66).
MHB and impact on soil
The practice of intensive agriculture reducing the density of AMF in agricultural soils (67), the introducing af the MHB can promote the ecosystem services rendered by fungal symbiot by improving rhizospheric soil functions leading to better soil properties and increased yield (68).
MHB have an indirect effect on soil fertility due to the release of chemical substances necessary for communication between the different microbial communities present in the soil. These molecular exchanges induce a difference in soil properties (69)
Formulation of AMF inocula embedded with MHB strains in field conditions
Data showing the beneficial effects on plant growth resulting from the association of MHB and mycorrhizal fungi are scarce. Duponnois & Garbaye (1991) and Garbaye et al. (1992) (48, 70), showed that a MHB strain (Fluorescent pseudomonads) could reduce the amount of ectomycorrhizal inoculum (Laccaria bicolor) inoculated to the cultural soil with the same beneficial effect on Douglas-fir growth than that obtained with a higher rate of inoculation. Most of the available data have been recorded from glasshouse experiments. Hence it has been demonstrated that Bradyrhizobium japonicum was able to positively influence and establish symbiosis with G.mosseae and synergistically effectively act as “mycorrhiza helper bacteria” (MHB) when both were co-inoculated in Bambara plant. The use of Phosphate solubilizing bacteria as mycorrhiza helper bacteria promoted a higher colonization rate and spore number of AMF which increased the solubilization of a mineral phosphate and allowed a sustainable nutrient supply to Sesamum indicum L for higher yield (71).
In 2009, a study conducted by Gamalero and his team, proved that the interaction of the MHB strain Pseudomonas putida UW4 and the AMF strain Grigaspora rosea BEG9, affected positively the growth of cucumber under a sever soil salinity conditions (72).
On the same pattern, in 2016, the combined use of both AMF and it associated MHB isolated from a salt affected soil, has significantly improves the soil salinity tolerance of maize plants (73). In fact, the co-inoculation of AMf and it associated MHB strain, has improved the soil salinity tolerance of maize plants by impacting the plant root colonization and the efficiency of the nutrient use of the maize plants. A tripartite interaction between the AMF, the MHB isolated and the maize plants has been assessed.
Another example of the MHB/AMF field use; in a recent 2021 study, the beneficial effect of the co-inoculation using AMF and MHB strains was demonstrated (64). The use of this consortium has significantly improved the growth of plants and enhance their biomass. The co-inoculation has significantly improved both the nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition.
In a 2019 review, the interaction between AMF and Bacillus spp. Strains in order to promote field plant growth has been explained (74). The synergically acting between both the AMf and MHB strains was define as the key of yield field enhancement.
Mycorrhization helper bacteria could play the role of environmental probiotics or ecosystem catalysts by exerting a positive influence on the intensity of mycorrhization. Indeed, the practice of intensive agriculture reducing the density of AMF in agricultural soils, the use of these auxiliary bacteria could make it possible to promote the ecosystem services rendered by fungal symbionts such as improved rhizospheric soil functions (Figure 3).
Conclusion and further prospects
Mycorrhizal helper bacteria are currently used in some practices in agriculture and forestry. Indeed, these microorganisms would represent an opportunity to optimize the mycorrhizal effects within agrosystems for the benefit of agriculture. According to Garbaye (48), mycorrhizal helper bacteria are not plant-specific, but are selected according to the fungal species, and are therefore specific to the mycorrhizal fungus genus. MHB include a wide range of Gram-negative and Gram-positive species (49). Among the fungi described as interacting with MHB, we note the basidiomycetes belonging to the ectomycorrhizae and the arbuscular mycorrhizae (48).
According to several studies, these MHB would act (i) by improving the receptivity and recognition of the fungal partner by the root, (ii) by improving the growth of the mycorrhizal fungus, (iii) by bringing about certain modifications at the level of the rhizosphere or (iv) by improving the germination of fungal propagules (15, 48, 49).
With all these advantages in the service of the ecosystem, MHB have a large agro-industrial potential (49). These bacteria having the possibility to positively influence the abundance of mycorrhizal propagules, their introduction into the soil will allow obtaining a significant improvement of the physico-chemical properties of the soil and therefore of the agricultural yield (51).
However, as it has been well established that the potential practical application of MHB in agriculture and forestry was great, new screening criteria are needing that will facilitate a performant selection of efficient bacterial isolates (75). The screening strategies used so far are too time‐consuming. Therefore, there is a need to identify fungal marker genes specific for the mycorrhiza helper effect. This knowledge will have major practical outputs, more particularly for the improvement of crop yields in degraded soils.
In addition, and from a practical point of view, more data have to be obtained from field experiment using innovative microbial inoculum formulations which allow the expected impacts from the MHB/interaction on plant and soil health.
Author contributions
NB: realization of the experiments and manuscript redaction. DR: redaction and proof-reading of the manuscript FH: proof-reading of the manuscript. SA: proof-reading of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was carried out as part of a joint thesis with co-funding from ANRT (France) and CNRST (Morocco).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. L’Hoir M, Nasslahsen B, Ferhout H, Prin Y, Smouni A, Walker V, et al. Endophytic seed bacteria: A relevant pool of microorganisms with the ability to promote plant growth. In: Arora NK, Bouizgarne B, editors. Microbial BioTechnology for sustainable agriculture volume 1. Singapore: Springer Nature (2022). p. 105−41. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-4843-4_3
2. Vu QM, Le QB, Frossard E, Vlek PLG. Socio-economic and biophysical determinants of land degradation in Vietnam: An integrated causal analysis at the national level. Land Use Policy (2014) 36:605−617. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2013.10.012
3. Eswaran H, Lal R, Reich PF. Land degradation: An overview. CRC Press (2019). p. 20−35. doi: 10.1201/9780429187957-4
4. Garcia C, Hernandez T, Roldan A, Albaladejo J. Biological and biochemical quality of a semiarid soil after induced devegetation. J Environ Qual (1997) 26:1116−1122. doi: 10.2134/jeq1997.00472425002600040024x
5. Requena N, Perez-Solis E, Azcón-Aguilar C, Jeffries P, Barea J-M. Management of indigenous plant-microbe symbioses aids restoration of desertified ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol (2001) 67:495−498. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.2.495-498.2001
6. Cordell D, Drangert J-O, White S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Glob Environ Change (2009) 19:292−305. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2008.10.009
8. Janzen HH, Beauchemin KA, Bruinsma Y, Campbell CA, Desjardins RL, Ellert BH, et al. The fate of nitrogen in agroecosystems: An illustration using Canadian estimates. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst (2003) 67:85−102. doi: 10.1023/A:1025195826663
9. Mishima S, Endo A, Kohyama K. Recent trends in phosphate balance nationally and by region in Japan. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst (2010) 86:69−77. doi: 10.1007/s10705-009-9274-7
10. Battisti DS, Naylor RL. Historical warnings of future food insecurity with unprecedented seasonal heat. Science (2009) 323:240−44. doi: 10.1126/science.1164363
11. Ewel JJ. Natural systems as models for the design of sustainable systems of land use. Agrofor Syst (1999) 45:1−21. doi: 10.1023/A:1006219721151
12. SCHÜßLER A, Schwarzott D, Walker C. A new fungal phylum, the glomeromycota: phylogeny and evolution. Mycol Res (2001) 105:1413−1421. doi: 10.1017/S0953756201005196
13. Spatafora JW, Chang Y, Benny GL, Gryganskyi A, James TY, O'Donnell K, et al. A phylum-level phylogenetic classification of zygomycete fungi based on genome-scale data. Mycologia (2016) 108:1028−46. doi: 10.3852/16-042
14. Tedersoo L, Sánchez-Ramírez S, Kõljalg U, Bahram M, Döring M, Schigel D, et al. High-level classification of the fungi and a tool for evolutionary ecological analyses. Fungal Divers (2018) 90:135−59. doi: 10.1007/s13225-018-0401-0
15. Ramírez-Flores MR, Perez-Limon S, Li M, Barrales-Gamez B, Albinsky D, Paszkowski U, et al. The genetic architecture of host response reveals the importance of arbuscular mycorrhizae to maize cultivation. eLife (2020) 9:e61701. doi: 10.7554/eLife.61701
16. Garbaye J. La symbiose mycorhizienne: Une association entre les plantes et les champignons. Editions Quae (2013).
18. Gupta MM. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: The potential soil health indicators. In: Giri B, Varma A, editors. Soil health. Cham: Springer International Publishing (2020). p. 183−95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-44364-1_11
19. Jakobsen I, Gazey C, Abbott LK. Phosphate transport by communities of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in intact soil cores. New Phytol (2001) 149:95−103. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.2001.00006.x
20. Dighton J. Mycorrhizae. Encycl Microbiol (2009) 3:153−162. doi: 10.1016/B978-012373944-5.00327-8
21. Marschner H, Dell B. Nutrient uptake in mycorrhizal symbiosis. Plant Soil (1994) 159:89−102. doi: 10.1007/BF00000098
22. Abdelhameid NM. Effect of mycorrhizal inoculation and potassium fertilization on grain yield and nutrient uptake of sweet sorghum cultivated under water stress in calcareous soil. Egypt J Soil Sci (2020) 60:17−29. doi: 10.21608/ejss.2019.17512.1312
23. Chalot M, Javelle A, Blaudez D, Lambilliote R, Cooke R, Sentenac H, et al. An update on nutrient transport processes in ectomycorrhizas. In: Diversity and integration in mycorrhizas. Dordrecht: Springer (2002). p. 165−75. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-1284-2_16
24. Linderman RG. Mycorrhizal interactions in the rhizosphere. In: Keister DL, Cregan PB, editors. The rhizosphere and plant growth. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands (1991). p. 343−48. doi: 10.1007/978-94-011-3336-4_73
25. Cassán F, Perrig D, Sgroy V, Luna V. Basic and technological aspects of phytohormone production by microorganisms: Azospirillum sp. as a model of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. In: Maheshwari DK, editor. Bacteria in agrobiology: Plant nutrient management. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer (2011). p. 141−82. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-21061-7_7
26. Basu S, Rabara RC, Negi S. AMF: The future prospect for sustainable agriculture. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol (2018) 102:36−45. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2017.11.007
27. Tahat MM, Alananbeh KM, Othman YA, Leskovar DI. Soil health and sustainable agriculture. Sustainability (2020) 12:4859. doi: 10.3390/su12124859
28. Mahmoudi N, Caeiro MF, Mahdhi M, Tenreiro R, Ulm F, Mars M, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal traits are good indicators of soil multifunctionality in drylands. Geoderma (2021) 397:115099. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.115099
29. Wagg C, Jansa J, Schmid B, van der Heijden MGA. Belowground biodiversity effects of plant symbionts support aboveground productivity. Ecol Lett (2011) 14:1001−9. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01666.x
30. Thangavel P, Anjum NA, Muthukumar T, Sridevi G, Vasudhevan P, Maruthupandian A. Arbuscular mycorrhizae: natural modulators of plant–nutrient relation and growth in stressful environments. Arch Microbiol (2022) 204:64. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-02882-1
31. Roesti D, Ineichen K, Braissant O, Redecker D, Wiemken A, Aragno M. Bacteria associated with spores of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi Glomus geosporum and Glomus constrictum. Appl Environ Microbiol (2005) 71:6673−79. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.11.6673-6679.2005
32. Frey-Klett P, Garbaye J, Tarkka M. The mycorrhiza helper bacteria revisited. New Phytol (2007) 176:22−36. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02191.x
33. Mosse B. The establishment of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza under aseptic conditions. Microbiology (1962) 27:509−20. doi: 10.1099/00221287-27-3-509
34. Choudhary DK, Varma A, Tuteja N. Mycorrhizal helper bacteria: Sustainable approach. In: Varma A, Prasad R, Tuteja N, editors. Mycorrhiza - function, diversity, state of the art. Cham: Springer International Publishing (2017). p. 61−74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53064-2_5
35. Bidondo LF, Silvani V, Colombo R, Pérgola M, Bompadre J, Godeas A. Pre-symbiotic and symbiotic interactions between glomus intraradices and two paenibacillus species isolated from AM propagules. In vitro and in vivo assays with soybean (AG043RG) as plant host. Soil Biol Biochem (2011) 43:1866−72. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.05.004
36. Fernández Bidondo L, Colombo R, Bompadre J, Benavides M, Scorza V, Silvani V, et al. Cultivable bacteria associated with infective propagules of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. implications for mycorrhizal activity. Appl Soil Ecol (2016) 105:86−90. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.04.013
37. Long L, Lin Q, Yao Q, Zhu H. Population and function analysis of cultivable bacteria associated with spores of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus gigaspora margarita. 3 Biotech (2017) 7:8. doi: 10.1007/s13205-017-0612-1
38. Asyiah IN, Hindersah R, Harni R, Fitriatin BN, Anggraeni W. Mycorrhizal fungi Glomus spp. propagation in zeolite enriched with mycorrhiza helper bacteria for controlling nematode in coffee. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci (2021). doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/883/1/012021
40. Scherlach K, Hertweck C. Mediators of mutualistic microbe–microbe interactions. Nat Prod Rep (2018) 35:303−8. doi: 10.1039/C7NP00035A
41. Pantigoso HA, Newberger D, Vivanco JM. The rhizosphere microbiome: Plant–microbial interactions for resource acquisition. J Appl Microbiol (2022) 133:2864–76. doi: 10.1111/jam.15686
42. Boedicker J, Nealson K. Microbial communication via quorum sensing. IEEE Trans Mol Biol Multi-Scale Commun (2015) 1:310−20. doi: 10.1109/TMBMC.2016.2587629
43. Venturi V, Keel C. Signaling in the rhizosphere. Trends Plant Sci (2016) 21:187−98. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2016.01.005
44. Kemen E. Microbe–microbe interactions determine oomycete and fungal host colonization. Curr Opin Plant Biol (2014) 20:75−81. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2014.04.005
45. Pande S, Merker H, Bohl K, Reichelt M, Schuster S, de Figueiredo LF, et al. Fitness and stability of obligate cross-feeding interactions that emerge upon gene loss in bacteria. ISME J (2014) 8:953–62. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.211
46. Kamei I, Yoshida T, Enami D, Meguro S. Coexisting curtobacterium bacterium promotes growth of white-rot fungus stereum sp. Curr Microbiol (2012) 64:173−78. doi: 10.1007/s00284-011-0050-y
47. Hassani MA, Durán P, Hacquard S. Microbial interactions within the plant holobiont. Microbiome (2018) 6:58. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0445-0
48. Duponnois R, Garbaye J. Mycorrhization helper bacteria associated with the Douglas fir-laccaria laccata symbiosis: effects in aseptic and in glasshouse conditions. Ann Sci For (1991) 48:239−51. doi: 10.1051/forest:19910301
49. Arruda B, George PBL, Robin A, Mescolotti DLC, Herrera WFB, Jones DL, et al. Manipulation of the soil microbiome regulates the colonization of plants by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhiza (2021) 31:545−58. doi: 10.1007/s00572-021-01044-3
50. Frey-Klett P, Garbaye J. Mycorrhiza helper bacteria: A promising model for the genomic analysis of fungal-bacterial interactions. New Phytol (2005) 168:4−8. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01553.x
51. Lies A, Delteil A, Prin Y, Duponnois R. Using mycorrhiza helper microorganisms (MHM) to improve the mycorrhizal efficiency on plant growth. In: Meena VS, editor. Role of rhizospheric microbes in soil: Volume 1: Stress management and agricultural sustainability. Singapore: Springer (2018). p. 277−98. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-8402-7_11
52. Salvioli A, Chiapello M, Fontaine J, Hadj-Sahraoui AL, Grandmougin-Ferjani A, Lanfranco L, et al. Endobacteria affect the metabolic profile of their host gigaspora margarita, an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. Environ Microbiol (2010) 12:2083−95. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02246.x
53. Bharadwaj DP, Lundquist P-O, Alström S. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore-associated bacteria affect mycorrhizal colonization, plant growth and potato pathogens. Soil Biol Biochem (2008) 40:2494−501. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.06.012
54. Battini F, Cristani C, Giovannetti M, Agnolucci M. Multifunctionality and diversity of culturable bacterial communities strictly associated with spores of the plant beneficial symbiont rhizophagus intraradices. Microbiol Res (2016) 183:68−79. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2015.11.012
55. Turrini A, Avio L, Giovannetti M, Agnolucci M. Functional complementarity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and associated microbiota: The challenge of translational research. Front Plant Sci (2018) 9:1407. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01407
56. Lecomte J, St-Arnaud M, Hijri M. Isolation and identification of soil bacteria growing at the expense of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. FEMS Microbiol Lett (2011) 317:43−51. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02209.x
57. Agnolucci M, Battini F, Cristani C, Giovannetti M. Diverse bacterial communities are recruited on spores of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal isolates. Biol Fertil Soils (2015) 51:379−89. doi: 10.1007/s00374-014-0989-5
58. Mayo K, Davis RE, Motta J. Stimulation of germination of spores of glomus versiforme by spore-associated bacteria. Mycologia (1986) 78:426−31. doi: 10.1080/00275514.1986.12025265
59. Xie ZP, Staehelin C, Vierheilig H, Wiemken A, Jabbouri S, Broughton WJ, et al. Rhizobial nodulation factors stimulate mycorrhizal colonization of nodulating and nonnodulating soybeans. Plant Physiol (1995) 108:1519−25. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.4.1519
60. Cruz AF, Horii S, Ochiai S, Yasuda A, Ishii T. Isolation and analysis of bacteria associated with spores of gigaspora margarita. J Appl Microbiol (2008) 104:1711−7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03695.x
61. Hildebrandt U, Ouziad F, Marner F-J, Bothe H. The bacterium Paenibacillus validus stimulates growth of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices up to the formation of fertile spores. FEMS Microbiol Lett (2006) 254:258−67. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2005.00027.x
62. Sundram S, Meon S, Seman IA, Othman R. Symbiotic interaction of endophytic bacteria with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and its antagonistic effect on ganoderma boninense. J Microbiol (2011) 49:551. doi: 10.1007/s12275-011-0489-3
63. Selvakumar G, Krishnamoorthy R, Kim K, Sa T-M. Genetic diversity and association characters of bacteria isolated from arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore walls. PloS One (2016) 11:e0160356. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160356
64. Sangwan S, Prasanna R. Mycorrhizae helper bacteria: Unlocking their potential as bioenhancers of plant–arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal associations. Microb Ecol (2021) 84:1–10. doi: 10.1007/s00248-021-01831-7
65. Frey-Klett P, Garbaye J. Mycorrhiza helper bacteria: a promising model for the genomic analysis of fungal–bacterial interactions. New Phytol (2005) 168:4−8. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01553.x
66. Vosátka M, Gryndler M. Treatment with culture fractions from pseudomonas putida modifies the development of glomus fistulosum mycorrhiza and the response of potato and maize plants to inoculation. Appl Soil Ecol (1999) 11:245−51. doi: 10.1016/S0929-1393(98)00151-6
67. Panwar J, Yadav RS, Yadav BK, Tarafdar JC. Arbuscular mycorrhizae: A dynamic microsymbiont for sustainable agriculture. In: Siddiqui ZA, Akhtar MS, Futai K, editors. Mycorrhizae: Sustainable agriculture and forestry. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands (2008). p. 159−76. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-8770-7_6
68. Heidari M, Karami V. Effects of different mycorrhiza species on grain yield, nutrient uptake and oil content of sunflower under water stress. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci (2014) 13:9−13. doi: 10.1016/j.jssas.2012.12.002
69. Bourles A, Guentas L, Charvis C, Gensous S, Majorel C, Crossay T, et al. Co-Inoculation with a bacterium and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improves root colonization, plant mineral nutrition, and plant growth of a cyperaceae plant in an ultramafic soil. Mycorrhiza (2020) 30:121−31. doi: 10.1007/s00572-019-00929-8
70. Garbaye J, Churin J-L, Duponnois R. Effects of substrate sterilization, fungicide treatment, and mycorrhization helper bacteria on ectomycorrhizal formation of pedunculate oak (Quercus robur) inoculated with laccaria laccata in two peat bare-root nurseries. Biol Fertil Soils (1992) 13:55−57. doi: 10.1007/BF00337239
71. Sab S, Lackshman HC. Effect of rock phosphate solubilization using mycorrhizal fungi and phosphobacteria on two high yielding varieties of sesamum indicum l. World J Agric Sci (2009) 5:470–9.
72. Gamalero E, Lingua G, Berta G, Glick BR. Beneficial role of plant growth promoting bacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on plant responses to heavy metal stress. Can J Microbiol (2009) 55:501−14. doi: 10.1139/W09-010
73. Krishnamoorthy R, Kim K, Subramanian P, Senthilkumar M, Anandham R, Sa T. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and associated bacteria isolated from salt-affected soil enhances the tolerance of maize to salinity in coastal reclamation soil. Agric Ecosyst Environ (2016) 231:233−9. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2016.05.037
74. Nanjundappa A, Bagyaraj DJ, Saxena AK, Kumar M, Chakdar H. Interaction between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and bacillus spp. in soil enhancing growth of crop plants. Fungal Biol Biotechnol (2019) 6:23. doi: 10.1186/s40694-019-0086-5
Keywords: biostimulant, biofertilizer, mycorrhizal symbiosis, mycorrhiza helper bacteria, sustainable agriculture
Citation: Nasslahsen B, Prin Y, Ferhout H, Smouni A and Duponnois R (2022) Mycorrhizae helper bacteria for managing the mycorrhizal soil infectivity. Front. Soil Sci. 2:979246. doi: 10.3389/fsoil.2022.979246
Received: 27 June 2022; Accepted: 25 October 2022;
Published: 15 November 2022.
Edited by:
Jay Prakash Verma, Banaras Hindu University, IndiaReviewed by:
Jitendra Mishra, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University, IndiaSunita K. Meena, Dr. Rajendra Prasad Central Agricultural University, India
Copyright © 2022 Nasslahsen, Prin, Ferhout, Smouni and Duponnois. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Robin Duponnois, Um9iaW4uRHVwb25ub2lzQGlyZC5mcg==
 Bouchra Nasslahsen
Bouchra Nasslahsen Yves Prin1
Yves Prin1 Hicham Ferhout
Hicham Ferhout Robin Duponnois
Robin Duponnois