- 1College of Life Science, Linyi University, Linyi, Shandong, China
- 2Agricultural Comprehensive Law Enforcement Team, Agricultural and Rural Affairs Bureau of Lanshan District, Linyi, Shandong, China
- 3Linyi Vocational University of Science and Technology, Linyi, Shandong, China
This experiment evaluated the impact of varying ratios of dietary metabolic energy: lysine (ME: Lys) in the diet on egg production, egg quality, and feed intake of laying hens. A total of 432 Hy-line brown laying hens, aged 55 wk, were reared over a period of 11 weeks. Hens were individually assigned to a basal standard diet with a ME to Lys ratio of 275:64 kcal/mg, along with five additional ratio types: 270:74 kcal/mg, 275:74 kcal/mg, 280:74 kcal/mg, 285:74 kcal/mg, and 290:74 kcal/mg. Feed and fecal digestibility were determined and egg quality were assayed on wk 1, 5, 9 and 11. The results indicated that an ME/Lys ratio of 285:74 kcal/mg improved yolk color pigment during weeks 9 and 11. Additionally, a ratio of 290:74 kcal/mg contributed to higher Hastelloy unit measurements during weeks 5, 9, and 11. In summary, while different ME/Lys ratios had no impact on overall egg production, both the 285:74 and 290:74 kcal/mg ratios demonstrated positive effects on deeper yolk color pigment and higher Hastelloy unit values.
Introduction
Eggs are globally recognized as a high quality, cost-effective protein source that offers nutritional and health benefits, leading to a 40% increase in consumption over the past 20 years. Accumulated evidence has demonstrated that the egg production and quality are affected by dietary metabolic energy (ME) and amino acids. The NRC (1994) recommends the optimal ME and protein levels in layer hens under ideal environment and management. For brown laying hens, the NRC (1994) recommends an ME level of 2,860 kcal/kg and a crude protein (CP) content of 16%. However, evidence from various studies indicates that the optimal levels of ME and CP may differ during different phases, significantly impacting egg production and quality (Junqueira et al., 2006; Li et al., 2023; Li et al., 2024). For feed formulation, the ME level and the protein content are the two major nutritional parameters to consider (Ding et al., 2016), which mainly consist of corn, wheat, and soybean meal. Wu et al. (2005) indicated that increasing the ME from 2,719 to 2,956 kcal/kg resulted in the reduction of feed intake from 107.6 to 101.1 g/hen per day while increasing the egg weight. Kim and Kang (2022) reported that the feed intake of Hy-Line Brown laying hens (30–50 weeks) decreased when the dietary ME increased from 2,700 to 2,800 kcal/kg in the diet. However, recent findings by Li et al. (2024) illustrated that ME at 2,800 kcal/kg decreased the feed intake and elevated the cholesterol content, but failed to change the egg mass, egg weight, and quality. This discrepancy in research outcomes highlights the current lack of consensus on the optimal ME levels for Hy-Line Brown layers during their post-peak production phase.
In addition to energy, amino acids play a significant role in influencing egg quality and production. Lysine (Lys), recognized as the second limiting amino acid in poultry nutrition, has contradictory effects on both egg production and quality (Kakhki et al., 2016). The NRC (1994) lists a Lys requirement of 690 mg/bird per day for white egg-laying hens. Affected by variety, age, and genetic selection, the Lys requirements were 860, 700, and 820 mg/bird per day in a previous research (Al Bustany and Elwinger, 1987). More recent research by Silva et al. (2015) found that Dekalb White hens achieved the optimum economic Lys intake with 699, 658, and 667 mg Lys per bird per day at 37–40, 41–44, and 45–48 weeks of age, respectively. A linear effect was found between the Lys levels (550–755 mg) and both egg weight and production in hens at 54–70 weeks of age (Edwiney et al., 2009). In the latest studies, Scappaticcio et al. (2021) indicated that laying hens require digestible Lys below 744 mg/day at 19–59 weeks old, with higher levels positively influencing egg mass and shell strength. Their study also found that apparent ME (2,680 and 2,780 kcal/kg) and standard ileal digestible Lys (680, 720, and 800 mg) had no effect on the egg quality and production. Nevertheless, discrepancies remain with regard to the optimal ME/Lys ratio, particularly for Hy-Line Brown hens during the post-peak laying phase.
During the late egg-laying stage, Hy-Line Brown hens experience a decline in both production performance and egg quality (Molnar et al., 2016; Alfonso-Carrillo et al., 2021). Although the egg weight, the thin-shelled egg rate, and the malformed egg rate increased with hen age, the Haugh unit, yolk color, and eggshell-breaking strength decreased (Ketta and Tumova, 2016; Molnar et al., 2016). While ME and Lys are known to influence layer performance, their optimal levels remain controversial, particularly for modern Hy-Line Brown strains during post-peak production (37–72 weeks). Therefore, in the current study, we designed the dietary 2,700–2,900 kcal/kg ME and 640–740 mg/kg digestible Lys combination and hypothesized that this maintains the same level of protein for maximizing the egg mass and egg quality of Hy-Line brown layer hens.
Materials and methods
Ethics statement
The experimental protocols describing the management and care of animals were reviewed and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Linyi University (protocol no. LYU20240103). This trial obeyed animal ethical approval to avoid animal abuse and stress during the period.
Animals and housing
A total of 432 Hy-Line Brown laying hens (385 days old) with similar body weights were acquired for this study. Each group consisted of six replicates (72 chickens), with two hens housed together in each cage (38 cm × 50 cm × 40 cm). The birds were housed in a temperature-controlled environment maintained at 23°C for an 11-week experimental period.
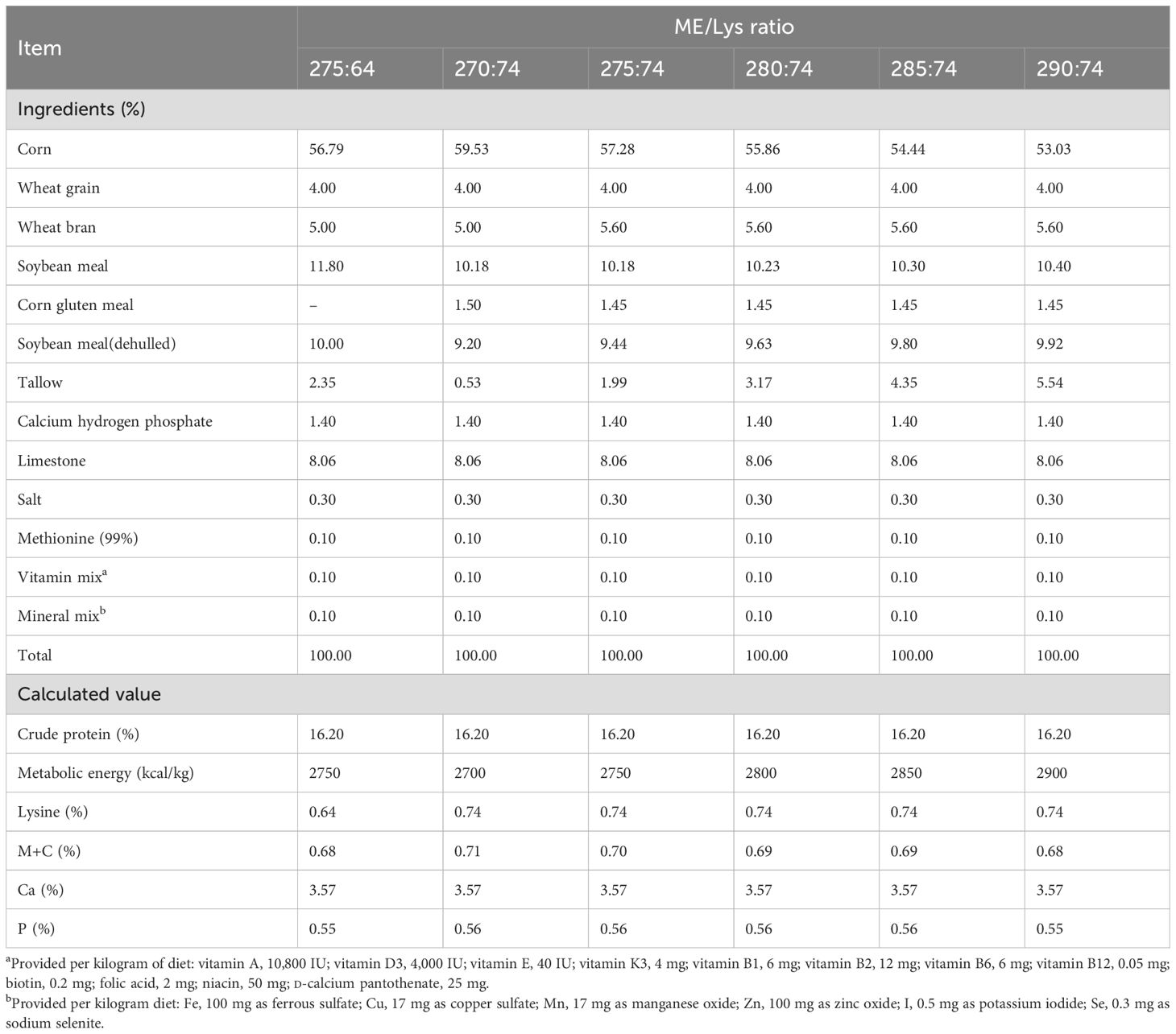
The hens were randomly allocated into six dietary treatment groups based on the following ME/Lys ratios: 275:64, 270:74, 275:74, 280:74, 285:74, and 290:74 kcal/mg. Six experimental diets contained 16.2 g/kg protein, as shown in Table 1. Throughout the 11-week study period, the animals received 8 h of daily lighting and 16 h of darkness. The environmental conditions were carefully maintained, with ambient temperature ranging between 20°C and 22°C and relative humidity at 60%–70%.
Sampling and measurements
Feed placement and surplus were recorded using a cage unit on weeks 1, 5, 9, and 11. Daily records were maintained for the egg mass and egg weight. Egg quality analysis was conducted on the final day of each week by randomly selecting five eggs per treatment. Soft and broken eggs were excluded from the analysis. Egg weight was determined individually using a digital electronic scale (0.01–1 g). The egg yolk and albumen were separated with a commercial handheld egg separator. Paper napkins were used to eliminate adherent albumen residues from the yolks, and the yolks were then weighed. The fresh eggshells were washed with water, dried for 48 h, and weighed. The eggshell thickness was measured using a micrometer apparatus (0.001-mm; Model 293–240 mitutoyo co, ltd Kanagawa, Japan) at three disparate sites (top, middle, and bottom), which were averaged to calculate the overall eggshell thickness. The Haugh unit was calculated according to the following formula: Haugh units=100×log[albumen height(mm)+7.57−1.7× (egg weight^0.037)]. (Gunawardana et al., 2008). Egg production was determined by dividing the total number of picked eggs by the number of layers in each treatment group throughout the testing period. The results were expressed as a percentage.
Statistical analyses
The data were analyzed using Shapiro–Wilk in SAS (SAS Institute, 1996) to assess the data heterogeneity. The egg weight at weeks 9 and 11 and the yolk color at week 5 did not conform to normal distribution, and these were analyzed using a non-parametric one-way ANOVA. For other data, a parametric one-way ANOVA was used. Differences were assessed utilizing Duncan’s multiple-range tests. Variability was expressed as the standard error of the mean (SEM), and a p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
The feed consumption data for weeks 1–11 are presented in Table 2. Diets with an ME/Lys ratio of 270:74 mg/kg promoted a higher feed intake compared with those using the ratios 280:74, 285:74, and 290:74 kcal/mg (p = 0.01). When ME was maintained at 2,750 kcal/kg, the average daily feed intake (ADFI) of laying hens remained consistent across weeks.
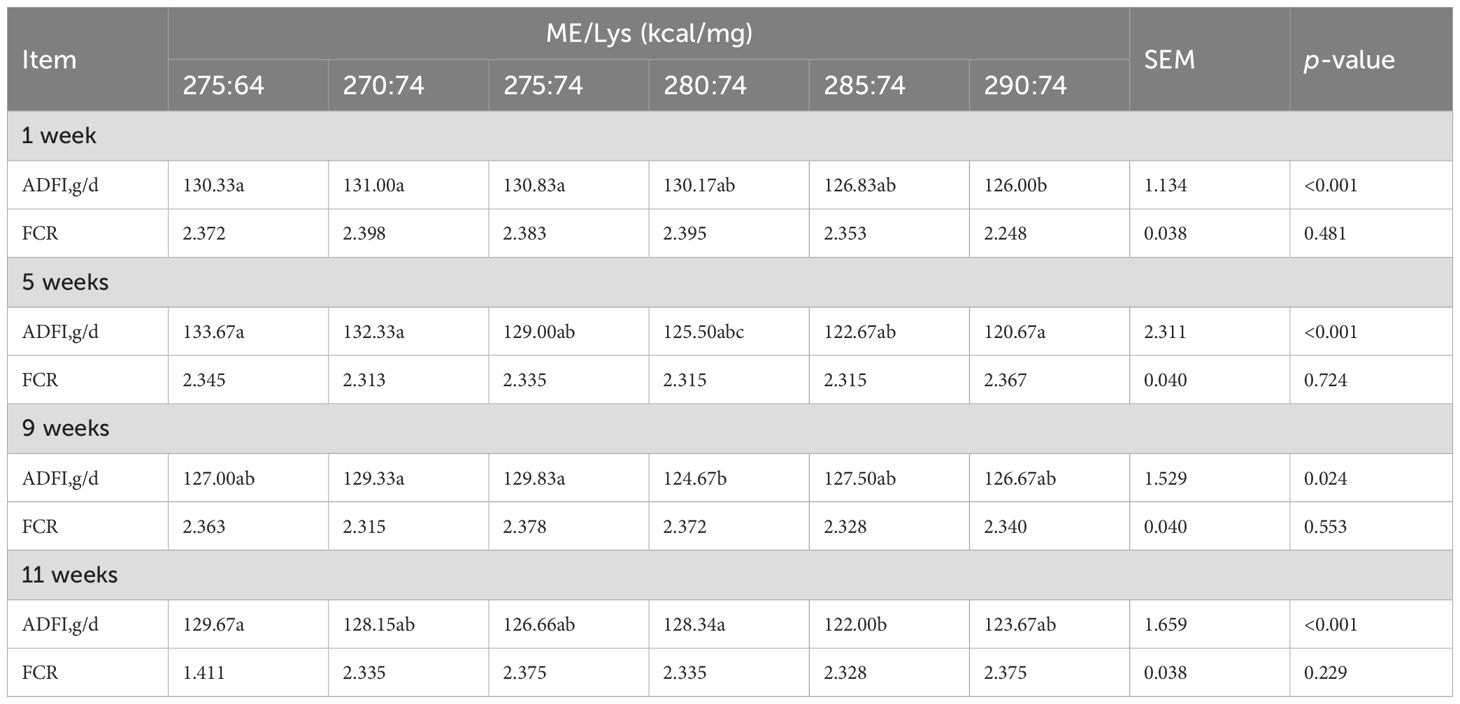
Table 2. Influence of dietary metabolizable energy-to-lysine ratios on the feed intake of laying hens.
Table 3 shows that the egg production, the egg breaking rate, and the egg weight rate >60 g (p > 0.05) were not affected by dietary ME/Lys supplementation throughout the experiment.
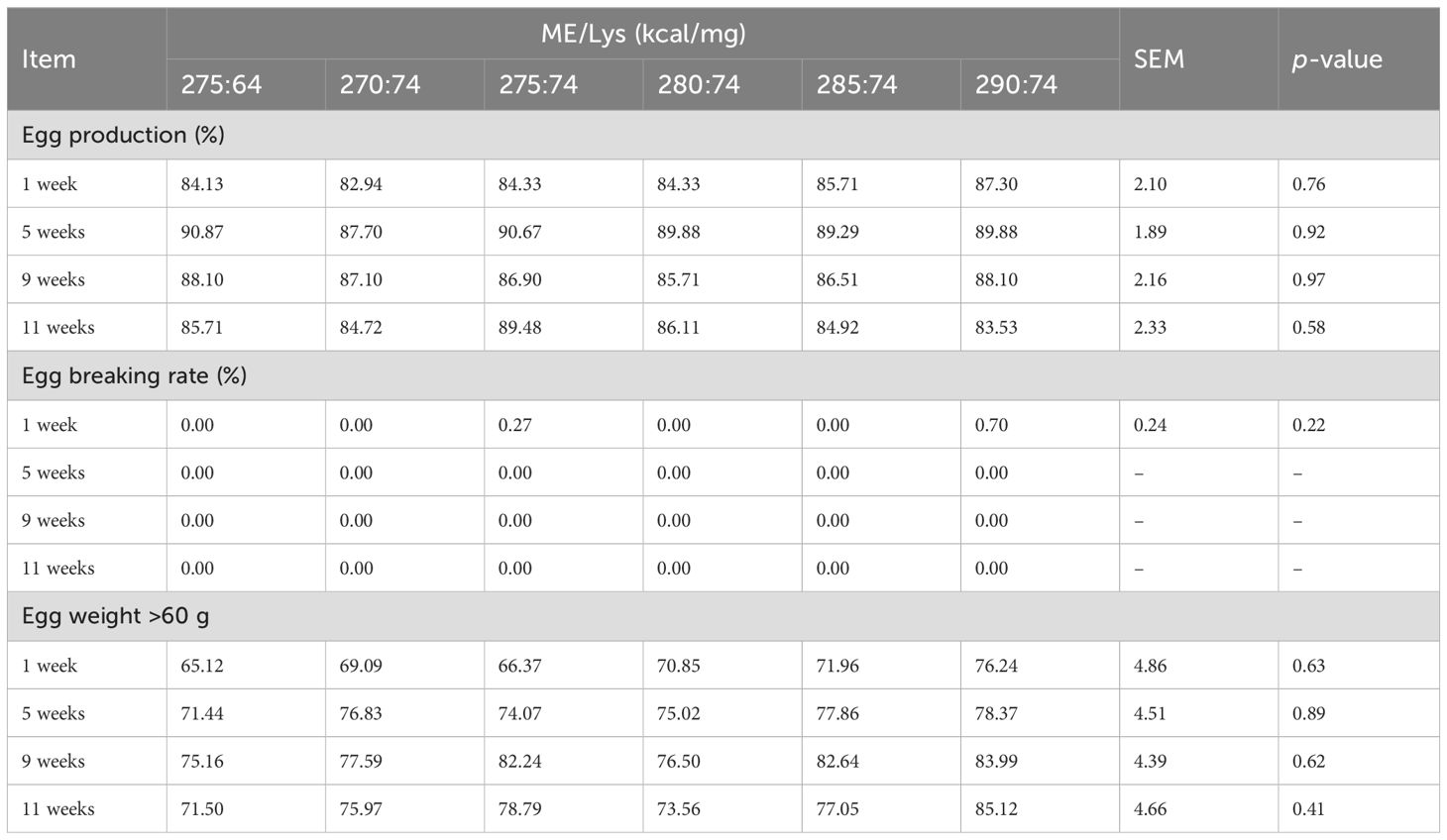
Table 3. Influence of dietary metabolizable energy-to-lysine ratios on the feed intake of laying hens.
As shown in Table 4, the egg weight, the eggshell strength, and the eggshell thickness did not differ significantly among the groups throughout the experimental period (p > 0.05). However, the yolk color was significantly deeper in the group administered 285:74 kcal/mg ME/Lys compared with the other ME/Lys ratio groups at weeks 9 and 11 (p < 0.01). When ME was maintained at 2,750 kcal/kg, a dietary Lys level of 740 or 640 mg/kg had no significant effect on the yolk color (p > 0.05). The Haugh unit remained consistent across weeks 1, 5, and 11, except at week 9, where it was significantly higher in the 290:74 kcal/mg group than that in the other groups (p < 0.05).
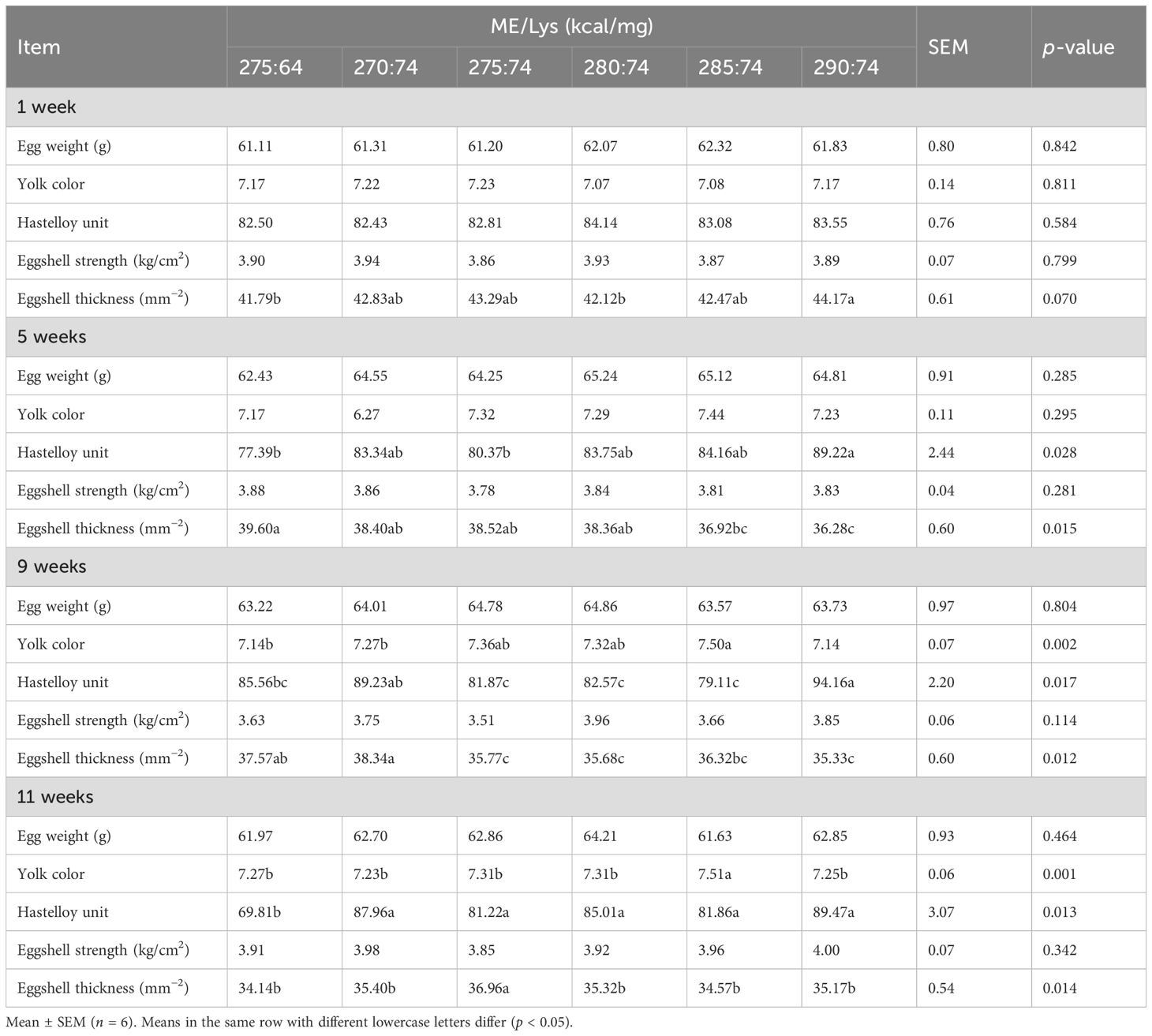
Table 4. Influence of dietary metabolizable energy-to-lysine ratios on the feed intake of laying hens.
Discussion
“Chickens eat for energy” has been proven in this trial as the hens fed relatively less on the high-energy (2,900 kcal/kg) than the low-energy diet (2,700 kcal/kg), as demonstrated in numerous studies (Wu et al., 2005; Kingori et al., 2014; Classen, 2017; Ahiwe et al., 2018). Independent of the protein levels, layer hens had a lower feed intake of the high-energy diet than the low-energy diet (Ding et al., 2016; Li et al., 2013; Kim and Kang, 2022) as per the 100-kcal/kg ME difference reduction. It was also found that, under the same 2,750 kcal/kg of ME, hens had the same feed intake of any diet containing 740 or 640 mg/kg Lys from 56 to 67 weeks of age. In contrast, 650 mg/kg Lys contributed to more feed intake than 670 mg/kg Lys in the diet only for 1 week at 65 weeks of age (Sharif et al., 2020).
Extra supplementation of corn and poultry oils contributed to greater egg weights (Bohnsack et al., 2002; Reda et al., 2020). However, in this study, the egg production, the egg breaking rate, and the egg weight remained unaffected by the varying ME/Lys ratios. Evidence indicated that the low energy, temperature, and breed may be related to the egg weight and mass, except for sufficient Lys level (van Eck et al., 2024). Our findings align with those of studies demonstrating no difference in the egg production when the energy levels were 2,519, 2,798, and 3,078 kcal/kg or when the ME deceased from 3,002 to 2,447 kcal/kg (Mathlouthi et al., 2002; Wu et al., 2005; Li et al., 2025). Contrasting results were indicated by Mathlouthi et al. (2002) and Rao et al. (2011), where the decrease in ME in brown layer hens from 2,753 to 2,653 kcal/kg and from 2,800 to 2,300 kcal/kg decreased the egg mass. With Lys levels of 716 and 750–950 mg/kg, the egg production and egg mass were not different (Novak et al., 2004; Fouad et al., 2018).
The egg parameters such as yolk color, albumen, eggshell, and the Hastelloy unit are key indicators of egg quality and are easily affected by major dietary elements (Novak et al., 2004; Shim et al., 2013). Pastore et al. (2018) proposed that Lys primarily supports egg production and modulates the synthesis of egg components. In the present study, there was no significant difference in the Haugh unit values observed between dietary Lys levels of 640 and 740 mg/kg. The Haugh unit serves as an indicator of egg protein quality, reflecting the degree of thick albumen thinning, with values below 60 indicating poor protein consistency. However, in this study, the Haugh unit value exceeded 79, suggesting superior protein quality, which may be attributed to the optimal ME/Lys ratio of 290:74 kcal/mg.
Interestingly, the yolk color increased as the dietary ME increased (Gunawardana et al., 2008). In this study, 2,850 kcal/kg, and not 2,900 kcal/kg, ME resulted in deeper yolk color pigment. A likely explanation is that, as xanthophylls are fat soluble, more xanthophylls may have been deposited in the egg yolk as pigments with the increase in dietary fat (Gunawardana et al., 2008; Ortiz et al., 2021). In Dekalb Delta hens, Lys at 716 mg/day had no effect on the egg production and feed intake at age 43 weeks (Novak et al., 2004).
Conclusion
In summary, in the present study, a Lys level of 640 or 740 mg/kg did not affect the ADFI, egg production, or quality. Only the 285:74 kcal/mg ME/Lys ratio improved the yolk color pigment in the later stages of the trial. Based on the feed savings and experimental results, we recommend a ME/Lys ratio of 285:74 mg/kg for 55-week-old Hy-Line brown layer hens. Due to the limitation of the starting point of high energy and high protein level, ME/Lys at 270:64, 270:74, 275:74, 280:74, and 290:74 mg/kg had no benefits on the egg production or mass.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
All experimental and animal management procedures were implemented according to the Guide of Laboratory Animals provided by the Institutional Animal Care Advisory Committee for Linyi University (Protocol number: LYU20240103). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. The animal study was approved by All experimental and animal management procedures were implemented according to the Guide of Laboratory Animals provided by the Institutional Animal Care Advisory Committee for Linyi University (Protocol number: LYU20240103). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
JZ: Investigation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Conceptualization. JD: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Writing – original draft. RZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YZ: Investigation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. YW: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Supervision. YL: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Investigation. QZ: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was mainly financially supported by the following grants: Shandong Province Central Guide Local Science and Technology Development Fund Project (YDZX2023081), Linyi Key Research and Development Project (2020ZX028), Doctoral research project of Linyi University (LYDX2020BS025).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahiwe E. U., Omede A. A., Abdallh M. B., and Iji P. A. (2018). Managing dietary energy intake by broiler chickens to reduce production costs and improve product quality. Anim. husbandry Nutr. 115, 115–145. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.76972
Al Bustany Z. and Elwinger K. (1987). Response of laying hens to different dietary lysine intakes: A comparison of some commercial hybrids with strains selected on a low protein diet. Acta Agr. Scand. 37, 27–40. doi: 10.1080/00015128709436541
Alfonso-Carrillo C., Benavides-Reyes C., Mozos J. D. L., Dominguez-Gasca N., and Rodriguez-Navarro A. B. J. A. (2021). Relationship between bone quality, egg production and eggshell quality in laying hens at the end of an extended production cycle (105 Weeks). Animals. 11, 623. doi: 10.3390/ani11030623
Bohnsack C. R., Harms R. H., Merkel W. D., and Russell G. B. (2002). Performance of commercial layers when fed diets with four levels of corn oil or poultry fat. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 11, 68–76. doi: 10.1093/japr/11.1.68
Classen H. L. (2017). Diet energy and feed intake in chickens. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 233, 13–21. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2016.03.004
Ding Y., Bu X., Zhang N., Li L., and Zou X. (2016). Effects of metabolizable energy and crude protein levels on laying performance, egg quality and serum biochemical indices of Fengda-1 layers. Anim. Nutr. 2, 93–98. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2016.03.006
Edwiney S. C., Paulo C. G., Luiz F. T. A., Juarez L. D., Heloisa H. C. M., Schmidt M., et al. (2009). Digestible lysine requirements of laying hens from 54 to 70 weeks of age. Rev. Bras. Zootecn. 11, 102–107. doi: 10.1590/S1516-35982009000300012
Fouad A. M., Chen W., Ruan D., Wang S., and Zheng C. (2018). Effects of dietary lysine supplementation on performance, egg quality, and development of reproductive system in egg-laying ducks. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 46, 386–391. doi: 10.1080/09712119.2017.1308868
Gunawardana P., Roland D. A., and Bryant M. M. (2008). Effect of energy and protein on performance, egg components, egg solids, egg quality, and profits in molted hy-line w-36 hens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 17, 432–439. doi: 10.3382/japr.2007-00085
Junqueira O. M., De Laurentiz A. C., da Silva Filardi R., Rodrigues E. A., and Casartelli E. M. C. (2006). Effects of energy and protein levels on egg quality and performance of laying hens at early second production cycle. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 15, 110–115. doi: 10.1093/japr/15.1.110
Kakhki R. A., Golian A., and Zarghi H. (2016). Effect of dietary digestible lysine concentration on performance, egg quality, and blood metabolites in laying hens. J. Appl. Poultry Res. 5, 506–517. doi: 10.3382/japr/pfw032
Ketta M. and Tumova E. (2016). Eggshell structure, measurements, and quality-affecting factors in laying hens: a review. Czech J.Anim. Sci. 61, 299–309. doi: 10.17221/46/2015-CJAS
Kim C. H. and Kang H. K. (2022). Effects of energy and protein levels on laying performance, egg quality, blood parameters, blood biochemistry, and apparent total tract digestibility on laying hens in an aviary system. Animals 12, 3513. doi: 10.3390/ani12243513
Kingori A. M., Wachira A. M., and Tuitoek J. K. (2014). Influence of energy intake on egg production and weight in indigenous chickens of Kenya. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 13, 151. doi: 10.3923/ijps.2014.151.155
Li W., Kai L., Shen Y., Su W., Fan Y., Wang Y., et al. (2024). Effects of dietary metabolizable energy and crude protein levels on laying performance, egg quality and fecal microbiota of Taihe Silky Fowl during the peak laying period. Anim. Biosci. 38, 539. doi: 10.5713/ab.24.0446
Li W., Kai L., Shen Y., Su W., Fan Y., Wang Y., et al. (2025). Effects of dietary metabolizable energy and crude protein levels on laying performance, egg quality and fecal microbiota of Taihe Silky Fowl during the peak laying period. Anim. Biosci. 38, 539–550. doi: 10.5713/ab.24.0446
Li F., Zhang L. M., Wu X. H., Li C. Y., Yang X. J., Dong Y., et al. (2013). Effects of metabolizable energy and balanced protein on egg production, quality, and components of Lohmann Brown laying hens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 22, 36–46. doi: 10.3382/japr.2012-00568
Mathlouthi N., Larbier M., Mohamed M. A., and Lessire M. (2002). Performance of laying hens fed wheat, wheatbarley or wheat-barley-wheat bran based diets supplemented with xylanase. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 82, 193–199. doi: 10.4141/A01-047
Molnar A., Maertens L., Ampe B., Buyse J., Kempen I., Zoons J., et al. (2016). Changes in egg quality traits during the last phase of production: is there potential for an extended laying cycle? Brit. Poult Sci. 57, 842–847. doi: 10.1080/00071668.2016.1209738
Novak C., Yakout H., and Scheideler S. (2004). The combined effects of dietary lysine and total sulfur amino acid level on egg production parameters and egg components in dekalb delta laying hens. Poult. Sci. 83, 977–981. doi: 10.1093/ps/83.6.977
Ortiz D., Lawson T., Jarrett R., Ring A., Scoles K. L., Hoverman L., et al. (2021). Biofortified orange corn increases xanthophyll density and yolk pigmentation in egg yolks from laying hens. Poult. Sci. 100, 101117. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101117
Pastore S. M., Gomes P. C., da Silva Viana G., da Silva E. A., de Oliveira W. P., Barbosa L. V. S., et al. (2018). Standardized ileal digestible lysine requirement of white commercial layers in peak egg production. Bio. Sci. J. 34, 186–193. doi: 10.14393/BJ-v34n1a2018-37205
Rao S. V. R., Ravindran V., Srilatha T., Panda A. K., and Raju M. V. L. N. (2011). Effect of dietary concentrations of energy, crude protein, lysine and methionine on the performance of White Leghorn layers in the tropics. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 20, 528–541. doi: 10.3382/japr.2011-00355
Reda F. M., El-Kholy M. S., Abd El-Hack M. E., Taha A. E., Othman S. I., Allam A. A., et al. (2020). Does the use of different oil sources in quail diets impact their productive and reproductive performance, egg quality, and blood constituents? Poult Sci. 99, 3511–3518. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.03.054
SAS Institute. (1996). SAS/STAT software: changes and enhancements for release 6.12. (sas Institute).
Scappaticcio R., García J., Fondevila G., de Juan A. F., Cámara L., and Mateos G. G. (2021). Influence of the energy and digestible lysine contents of the diet on performance and egg quality traits of brown-egg laying hens from 19 to 59 weeks of age. Poult. Sci. 100, 101211. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101211
Sharif M., Ali A., Anwar U., Chisti F. A., Jameel S., Bilal M. Q., et al. (2020). Effect of different levels of energy and lysine on the production performance of laying hens. Pak. J. Agr. Sci. 57 (6). doi: 10.21162/PAKJAS/20.963
Shim M. Y., Song E., Billard L., Aggrey S. E., Pesti G. M., and Sodsee P. (2013). Effects of balanced dietary protein levels on egg production and egg quality parameters of individual commercial layers. Poultry science. 92, 2687–2696. doi: 10.3382/ps.2012-02569
Silva E. P., Malheiros E. B., Sakomura N. K., Venturini K. S., Hauschild L., Dorigam J. C., et al. (2015). Lysine requirements of laying hens. Livest. Sci. 173, 69–77. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2015.01.005
van Eck L., Chen H., Carvalhido I., Enting H., and Kwakkel R. (2024). The influence of breed, dietary energy and lysine on laying persistency and body composition of laying hens. Poult. Sci. 103, 104124. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104124
Keywords: metabolic energy, lysine, egg quality, egg production, laying hens
Citation: Du J, Zhuang R, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Liu Y, Zhang Q and Zhang J (2025) Dietary metabolic energy/lysine ratios improve the yolk color and Hastelloy unit without affecting the egg performance of brown laying hens. Front. Anim. Sci. 6:1638293. doi: 10.3389/fanim.2025.1638293
Received: 30 May 2025; Accepted: 13 June 2025;
Published: 07 August 2025.
Edited by:
Petru Alexandru Vlaicu, National Research Development Institute for Animal Biology and Nutrition, RomaniaReviewed by:
Sohail Ahmad, University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, PakistanMuhammad Thohawi Elziyad Purnama, Airlangga University, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Du, Zhuang, Zhang, Wang, Liu, Zhang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qianqian Zhang, emhhbmdxaWFucWlhbkBseXUuZWR1LmNu; Jianying Zhang, emhhbmdqaWFueWluZ0BseXUuZWR1LmNu
 Jiagang Du
Jiagang Du Rufei Zhuang
Rufei Zhuang Yuanju Zhang1
Yuanju Zhang1 Yunguo Liu
Yunguo Liu Jianying Zhang
Jianying Zhang