- 1College of Innovative Technology and Engineering, Dhurakij Pundit University, Bangkok, Thailand
- 2Faculty of business administration for society, Srinakharinwirot University, Bangkok, Thailand
- 3Department of Forest Biomaterials and Technology, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala, Sweden
This research aims to extract a grouped semantic-feature relation, particularly a PlantPart-MedicinalPropertyGroup relation which is a semantic relation between an element of a plant-part concept set and a group of medicinal-property concept features of various herbs or medicinal plants, including indigenous medicinal plants, to graphically represent medicinal-plant property knowledge from documents available on pharmacy academic websites. The medicinal-plant property knowledge representation particularly benefits native users and patients seeking alternative medical therapies during pandemics, such as COVID-19, due to limited access to medicines, physicians and hospitals. Medicinal-property expressions on the documents, particularly in Thai, are often structured as event expressions conveyed through verb phrases within Elementary Discourse Units (EDUs) or simple sentences. There are three research problems in extracting the PlantPart-MedicinalPropertyGroup relations from the documents: how to identify EDU occurrences with medicinal-property concepts, how to extract medicinal-property concept features from medicinal-property concept EDU occurrences without concept annotations, and how to extract the PlantPart-MedicinalPropertyGroup relation without relation-class labeling from the documents with the high dimensional and correlated feature consideration. To address these problems, we apply a Solving-Verb Concept set primarily sourced from translated terms on HerbMed, an American Botanical Council resource, to identify a medicinal-property concept EDU. Additionally, a word co-occurrence (word-co) pattern is applied as a compound variable on the translated terms to construct a medicinal-property-concept (MPC) table. The MPC table is employed to extract the medicinal-property concept features from the medicinal-property concept EDUs through a string-matching method. We then propose using structural equation modeling to automatically extract the PlantPart-MedicinalPropertyGroup relations from the documents. Thus, the proposed approach enables the extraction of PlantPart-MedicinalPropertyGroup relations with high qualities to represent medicinal-plant property knowledge on social media.
1 Introduction
During a pandemic, e.g., the COVID-19 pandemic, indigenous medicinal plants from various countries were considered as herbal medicines in an alternative medical therapy (Nelson and Perrone, 2000) due to the limited availability of conventional medicines, physicians and hospitals. The majority of herbal medicine usages from indigenous medicinal plants are formed through herbal-indigenous knowledge, where indigenous knowledge is the systematic body of knowledge acquired by local people through the accumulation of experiences, informal experiments, and an intimate understanding of the environment in a given culture (Rajasekaran, 1993). A combination of indigenous medicinal plants was used synergistically in COVID-19 symptom treatment. Synergistic effects are the combined effects of at least two different medicinal plants/plant-parts with different phytochemicals or biological structures that have a greater influence than either one of them could have individually (Prasathkumar et al., 2021; Ali et al., 2022; Intharuksa et al., 2022). Regarding (Rajasekaran, 1993; Yuan et al., 2006; Itharat et al., 2021; Petrovska, 2012), the awareness of plant-part usage from medicinal plants as a natural product is a result of many years of struggles against illnesses. Additionally, the medicinal properties in various parts (i.e., roots, rhizomes, leaves, flowers, seeds, etc.) of the plant vary in contents and percentages of the plant-part phytochemicals. These phytochemicals not only protect plants from competitors, pathogens, or predators, but also protect humans and animals against certain diseases (Parihar and Balekar, 2016; Osman et al., 2020; Rabizadeh et al., 2022) that result in similar or different properties (Agidew, 2022). There are about 200 different medicinal plants in Thailand with various medicinal properties found in different plant parts, as documented by the Plant Genetic Conservation Project under the royal initiative of Her Highness Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn (http://www.rspg.or.th/; accessed on 18 August 2024; Singhabutra, 1992) in cooperation with the Pharmacy Division of the Department of Health, Thailand. However, it is time consuming to read all of the medicinal properties of all medicinal plants from documents to find each semantic relation which is the logical or conceptual relation expressed in a sentence or sentences in the text (Khoo and Na, 2006). The semantic relation pertinent to our research is a grouped semantic-feature relation connecting an element of a semantic-feature set to a group of related semantic features. Specifically, it involves a PlantPart-MedicinalPropertyGroup relation (called a “pp-mpG” relation) which is a semantic relation connecting a ppi feature (ppi ∈ PP which is a plant-part concept set) to mpGg—a group of related medicinal-property concept features where mpGg ⊂ MPG which is a set of medicinal-property concept groups from the medicinal plants. Thus, determining the grouped semantic-feature relation, i.e., the “pp-mpG” relation, from downloaded Thai documents for graphical representation of medicinal-plant property knowledge on social media is a challenge. Moreover, Khoo and Na (2006) also stated that “the sematic relation is the cement linking up the concepts into the knowledge structures.”
Numerous previous studies (Khoo and Na, 2006; Fang et al., 2008; Choi and Lee, 2015; Behera and Mahalakshmi, 2019; Cho et al., 2020; Yoo et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020; Jia et al., 2022; Braik et al., 2023; Pechsiri and Piriyakul, 2016; see Table A.1) determined or computerized a relation, particularly a semantic relation as a traditional relation linking a medicinal-plant name (which is a medicinal-plant/herbal name concept) to a medicinal property (a medicinal-property/phytochemical-activity concept) for disease prevention and/or treatment from the corpus by manually or semi-automatically annotating the relation without concerning the high dimensional and correlated feature space of various medicinal properties (see Section 2). According to Salmerón-Manzano et al. (2020), it is estimated that globally there are ~350,000–1,000,000 plant species used for medicinal purposes, highlighting the vast scope of this domain. Our research observations reveal significant correlation occurrences among medicinal-property concepts that depend on various plant names or plant-part concepts; for instance, both “antiviral” and “anti-inflammatory” concepts frequently co-occur in medicinal plant names such as “curcumin,” “ginger,” and “lemongrass,” whilst “antipyretic,” “antitussive,” and “expectorant” concepts also appear together in some plant-part concepts like lemon fruit and miracle tree. These correlation patterns demonstrate the complex, interconnected nature of medicinal property concepts across different plant species, necessitating sophisticated analytical approaches to properly model these multidimensional relationships in medicinal plant research. Therefore, this research aims to automatically extract the grouped semantic-feature relation as the pp-mpG relation which occurs as a common relation (see Figure 1) between ppi and mpGg of various hk from the Thai documents downloaded from several web sites of organizations involving in herb and medicinal plant researches, e.g., Herbal Information Center at the Faculty of Pharmacy-Mahidol University (https://medplant.mahidol.ac.th/document/inews.asp; accessed on 18 August 2024), Faculty of Pharmacy-Silpakorn University (https://pharmacy.su.ac.th/herbmed/herb/text/; accessed on 18 August 2024), and (http://www.rspg.or.th/; accessed on 18 August 2024) where:
1) hk is a medicinal-plant name concept which is also used as a document file name, k = 1,2,.., numOfHerbalNameConcepts.
2) ppi is a plant-part concept feature which is an element of a plant-part concept set (PP), ppi ∈ PP; PP = {“root,” “rhizome,” “leaf,” “flower,” “seed,”...}, and i = 1,2,.., numOfPlantPartConcepts in PP; -
3) mpj is a medicinal-property concept element, particularly the medicinal-action/activity concept element such as “anti-inflammation,” “wound healing,” “anti-virus growth,” etc., and mpj ∈ MP where MP is the universal medicinal-property concept set having j = 1,2,.., numOfMedicinalPropertyConcepts in MP;
4) mpGg is a group of medicinal-property concept features having some correlations among their features.
mpGg = {mp1, mp2,…, mplast−g} which contains several mpj features having some mpj features that are correlated, and g = 1,2,.., numOfmpG in MPG;
mpGg ⊂ MPG on which MPG is a set of medicinal-property concept groups from these medicinal plants; MPG = {mpG1,mpG2,..mpGnumOfmpG};
5) mpG1 ∪ mpG2…∪ mpGnumOfmpG = MP; mpGg and mpGq are mutually exclusive for g ≠ q; and 1 ≤ q ≤ numOfmpG.
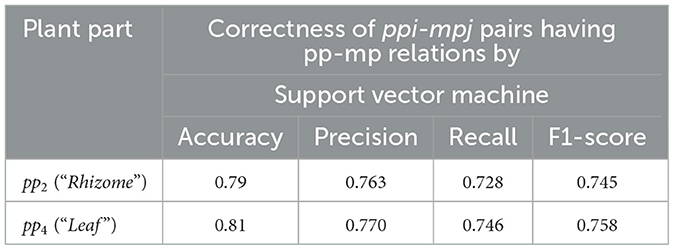
Figure 1. A graphical representation of the pp-mpG relations including Plant Table for finding plant names by ppi and/or mpj where all pp1-mpG1, pp1-mpG2, pp1-mpGnumOfmpG, pp2-mpG1, pp2-mpG2, pp2-mpGnumOfmpG, …, ppnum-mpG1, ppnum-mpG2, ppnum-mpGnumOfmpG relations are the pp-mpG relations connecting ppi (a plant-part concept feature, i = 1,2,..,num) to mpGg (a group of medicinal-property concept features, g = 1,2,.., numOfmpG in MPG which is a set of medicinal-property concept groups).
Each pp-mpG relation is involved with the high dimensional and correlated features of medicinal-property concepts.
Figure 1 presents a representation of medicinal-plant property knowledge where each pp-mpG relation as a linkage is represented by an arrow connecting a ppi feature node to a mpGg node, which consists of several mpj features nodes with some correlations among the mpj features; i = 1, 2, ..., num (num is numOfPlantPartConcepts); numa, numb, numc, numd, nume, numf, and numg are different numbers of j. Figure 1 also includes a Plant table (Plant Table) consisting of PlantName or hk, Plant-Part or ppi, and MedicinalProperty or mpj collected from the documents. The Plant table is used to decide whether to list either the hk features along with ppi features with the same mpj feature or vice versa. Moreover, the synergistic effect typically occurs if the particular mpGg node is linked to different ppi features.
Thus, the pp-mpG relations shown in Figure 1 present the medicinal-plant property knowledge for potential usage in an alternative medical therapy through social media. The medicinal-plant property knowledge representation benefits individuals and communities with limited access to medical facilities and modern treatments. The usage of mixing medicinal plants not only has a synergistic effect, but also has low cost and minimal side effects compared to certain western medicines (Behera and Mahalakshmi, 2019).
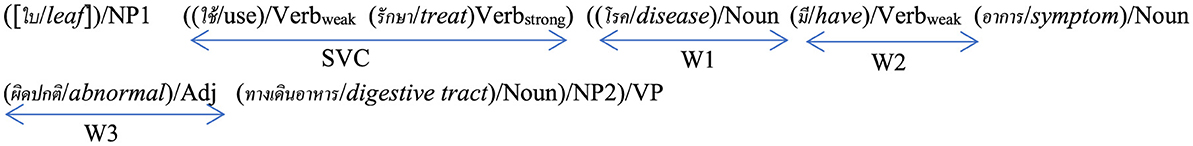
The mpj feature expression on the documents is mostly based on an event expression of a medicinal-property activity on an elementary discourse unit (EDU), which is defined as a simple sentence or a clause by Carlson et al. (2003). The event expression is explained by a verb with the event semantic (Pustejovsky, 1991) on the EDU's verb phrase wherein each EDU expression is based on a general linguistic expression, e.g., a general Thai linguistic expression (see Figure 2a) after stemming words and eliminating stop words.

Figure 2. Example: a medicinal plant or herb document, e.g., “Thai basil,” based on (a) a general Thai linguistic expression including Thai-to-English translation by Lexitron Dictionary and WordNet where NP1 and NP2 are noun phrases; VP is a verb phrase; Verb is a verb term, Verbstrong is a strong-verb concept set, Verbweak is a weak-verb concept set, Adv is an adverb concept set, Adj is an adjective concept set, and Noun is a noun concept set. (b) An explanation by several EDUs with medicinal property concepts where a [...] symbol means a word/words ellipsis.
In addition, the medicinal property concepts of our research rely on HerbMed (provided by the American Botanical Council; https://www.herbalgram.org/resources/terminology/; accessed on 18 August 2024) including the medical-symptom term list on the Wikipedia web site (https://en.wikipedia. https://www.org/wiki/List_of_medical_symptoms; accessed on 18 August 2024). Each medicinal property concept by HerbMed and each medical-symptom-term concept by Wikipedia is presented in English as either a noun term or a noun phrase expression. In contrast, the corresponding concepts in Thai are expressed by an EDU or an EDU's verb phrase. The noun or noun phrase representing either a medicinal property concept from HerbMed or a medical symptom concept from Wikipedia is translated into a Thai term represented by an EDUtmt—a translated EDU expression in Thai, derived from the English translation of the corresponding concept in HerbMed or Wikipedia, using Lexitron, a Thai-English machine-readable dictionary developed by NECTEC (the National Electronics and Computer Technology Center of Thailand; http://lexitron.nectec.or.th/, accessed on 20 August 2024; Trakultaweekoon et al., 2007). The reason for using the medical-symptom term list is because some medicinal-property terms do not occur in HerbMed as it only presents the most common terms of the medicinal properties of plants. The EDUtmt expressions are then segmented by the Thai word segmentation tool (Sudprasert and Kawtrakul, 2003) which yields the elements, including the element concepts of the Verbweak, Verbstrong, Adv, Adj, and Noun sets in Figure 2a where the element concepts are determined by the Thai-to-English translation with Lexitron including WordNet (Miller, 1995).
For example: HerbMed term, e.g., “carminative” is translated to the Thai language as “ขับลม/hạblm” which is an EDUtmt expression. The result of the (“ขับลม/hạblm”)/EDUtmt segmentation including a part of speech notification is ((“ขับ/hạb”/expel/Verbstrong “ลม/lm”/gas/Noun)/VP)/EDUtmt which conveys the same concept as “carminative” (see Section 3.2).
Regarding the automatic extraction of the grouped semantic-feature relation (the pp-mpG relation) from the documents, e.g., the Thai basil document in Figure 2b, there are three main research problems.
1) How to automatically identify several EDU occurrences with medicinal-property concepts scattered throughout the downloaded documents, which are mostly semi-structure data. For example: several EDU occurrences (EDUr; r = 1,2,..,numOfDocumentEDUs) in Figure 2b have 15 different mpj feature expressions based on verb phrases of EDU3-EDU11, EDU14, EDU17, EDU19-EDU21, and EDU24, where a [..] symbol means an ellipsis of a word or words inside the symbol.
2) How to extract the mpj features from the medicinal-property concept EDU occurrences without annotating the concepts of the mpj features on the EDU occurrences.
3) How to extract the grouped semantic-feature relation, which is the pp-mpG relation/linkage between ppi and mpGg involving the high dimensional and correlated feature space of the mpj features.
In order to fulfill the aim of automatically extracting a grouped semantic-feature relation from the documents, this paper will conduct the following:
1) Use a Solving-Verb Concept set (SVC), {“แก้,รักษา/cure,treat,remedy,” “ลด/reduce,” “บรรเทา/relieve,” “เป็น/be+ยา/medicine,” “ช่วย/help+ขับ/excrete,”…}, to identify each medicinal-property concept EDU from the documents. According to the general Thai linguistic expression on Figure 2a, SVC is a verb set with the solving concept, formed by the verb term (Verb) consisting Verbstrong, Verbstrong + Word1, or Verbweak + Word1. This contrasts with previous research (Behera and Mahalakshmi, 2019) which used terms based on noun expressions from MeSH to identify phytochemical-property/medicinal-property sentences from PubMedCloud.
2) Apply a compound variable, i.e., a word co-occurrence (called word-co) to represent the medicinal-property term concepts and the medical-symptom term concepts from HerbMed and Wikipedia, respectively. The word-co expression relies on the following word-co pattern (called “WCPattern”) on which WCPattern is the verb-based word-co pattern to represent events on the EDUtmt after stemming words and stop word removal. WCPattern is then used to construct a medicinal-property-concept (MPC) table from the translated terms of HerbMed and Wikipedia. The MPC table is used to extract mpj features from medicinal-property concept EDUs by a string-matching method.
where: regarding the Verbweak, Verbstrong, Adv, Adj, and Noun sets on Figure 2, W1, W2, and W3 are the problem/symptom-word concept sets and exist right after SVC in sequence where (w1 ∈ W1) ≠ (w2 ∈ W2) ≠ (w3 ∈ W3); W1, W2, and W3 = Noun∪Adj∪Adv∪Verbstrong. If ((vstrong ∈ SVC) ∨ (vweak + wrd) ∈ SVC)) + a “อาการ/symptom” word, then the next word right after the “อาการ/symptom” word is w1, followed by w2 and w3 in sequence where vstrong ∈ Verbstrong, vweak ∈ Verbweak, and wrd ∈ Word1. And, if w1, w2, or w3 does not exist, then w1, w2, or w3 is null, respectively. For example, “แก้/ cure” + “อาการ/symptom” + “ปวด/pain” + “กล้ามเนื้อ/muscle” = “แก้/cure” + “ปวด/pain” + “กล้ามเนื้อ/muscle.”
3) Propose a statistical-based approach by using structural equation modeling (SEM), a multivariate statistical analysis technique (Schumacker and Lomax, 2004) to extract the pp-mpG relation on the high dimensional and correlated mpj features from the downloaded documents to represent the medicinal-plant property knowledge on social media without relation-class annotation on the documents. The neural network is more complicated than SEM and requires relation-class annotation or labeling. Generally, machine-learning techniques, except neural networks, without considering the feature correlation between either dependent variables or independent variables, are not suitable for our corpus in extracting the pp-mpG relation. Moreover, most of the traditional relation approaches to relation classification and extraction heavily rely on rule bases and machine learning techniques without concerning the correlation among features (Detroja et al., 2023). Therefore, our research approach both a proposed SEM technique and a machine-learning technique, particularly a support vector machine (SVM; Cristianini and Shawe-Taylor, 2000), to observe the quantitative and qualitative differences between the extracted relations/linkages on the correlated features in the documents by SEM and SVM techniques. According to this research, SVM determines and extracts several ppi-mpj pairs with pp-mp relations between ppi features and mpj features having the same ppi feature. SEM is applied to determine and extract the pp-mpG relations from the documents after applying hierarchical factor analysis, which consists of two levels: a first-order factor model and a higher-order factor model, where each level is a part of the general linear model used to reduce numerous variables/features into fewer numbers of factors without information loss (Kim and Mueller, 1978).
Moreover, the following are key terminologies used in this paper.
• EDU is an elementary discourse unit which is defined as a simple sentence or a clause.
• EDUtmt is a translated EDU expression by translating the medicinal-property/medical-symptom terms on HerbMed/the Wikipedia, respectively, from English to Thai by Lexitron.
• MPC Table is Medicinal-Property-Concept Table.
• pp-mpG is a semantic relation linking an element of plant-part concept set to a group of related medicinal-property concept features.
• pp-mp is a semantic relation between a ppi feature and various mpj features on ppi-mpj pairs with the same ppi feature.
• SEM is Structural Equation Modeling.
• SVC is a verb set with the solving concept; an SVC element is formed by the verb term (Verb) consisting Verbstrong, Verbstrong + Word1, or Verbweak + Word1 on the EDUtmt occurrence.
• SVM is Support Vector Machine.
• word-co is a word co-occurrence.
• WCPattern is the verb-based word-co pattern on the translated EDU expression (EDUtmt) of events after stemming words and stop word removal.
Our research is organized into five sections. In Section 2, related works are summarized. Our methodology shows a system framework for extracting the pp-mpG relations and pp-mp relations in Section 3. We evaluate our proposed model including discussion in Section 4. Finally, in Section 5, the conclusions are provided.
2 Related works
Most of the previous research studies (Fang et al., 2008; Choi and Lee, 2015; Behera and Mahalakshmi, 2019; Cho et al., 2020; Yoo et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020; Jia et al., 2022; Braik et al., 2023; Pechsiri and Piriyakul, 2016) attempted to determine a relation or association between the medicinal plants in an herbal category and their medicinal properties or between phytochemical activities and diseases in the documents, including medical entity recognition.
Fang et al. (2008) used TCM (Traditional Chinese Medicine) names involving natural products that included many effective chemical components from herbs, gene names, disease names, TCM ingredients, and effects from a TCMGeneDIT database to annotate the PubMed literature corpus by employing an NLP (Natural Language Processing) tool. They found various associations, including (TCM, gene), (TCM, disease), (TCM, gene, disease), (TCM, ingredient), (TCM, effect), and (gene, ingredient), by applying rule-based information extraction to extract the relations between effecters and effects from the corpus and also the transitive association based on the Swanson's ABC model. The average precision result of the associations was 0.91 at 95% minimum confidence without emphasizing the high dimensional feature space on (TCM, disease), (TCM, ingredient), and (TCM, effect).
Choi and Lee (2015) applied a rule-based text mining model to infer herb-chemical relationships from a corpus of 245 PubMed abstracts that were annotated as herb–chemical relation by three annotators. The F-measure of the rule-based model for identifying herb-chemical relationships was 0.749 by testing with the PubMed abstracts.
Behera and Mahalakshmi (2019) applied text mining techniques to biomedical literatures on PubMed Cloud to reveal information concerning the curing of disease based upon the phytochemical properties of medicinal plants. The diseases and the phytochemical properties based on noun expressions were identified from the literature by using selected terms based on the probabilistic term frequency of MeSH thesaurus in research articles from PubMed. The result of identifying an informative sentence pertaining to cure/treat disease, have side effects and prevent relationship types by a trained probabilistic classifier displayed 73% accuracy where the positions of the disease feature and the phytochemical property feature occurred anywhere in the sentence.
Cho et al. (2020) sought medicinal herbs for skincare by applying a data mining technique to investigate associations between medicinal herbs and skincare-related functions based on 26 skin-related keywords (SRKs) from Donguibogam texts as classical texts. The SRKs as medicinal properties were set up by several experts from the classical texts. Using a term frequency-inverse document frequency approach, they mined and extracted 52 candidate medicinal herbs by assessing herbal characteristics on the co-occurrence frequencies in which each candidate medicinal herb had least one of the 26 SRKs with tf-idf index p-values < 0.05 without concerning the high dimensional and correlated features of skin-related terms as medicinal herb properties. Their results showed that only 46 herbs out of 52 candidate medicinal herbs had skincare-related effects by employing bio-medicinal evaluation.
Yoo et al. (2020) proposed a deep learning-based approach to identify the medicinal uses (which were a part of medicinal properties) of natural compounds exploiting massive and heterogeneous drug and natural compound data involving structured and unstructured data from which they generated the three main feature groups: latent knowledge features (about 101 features) by text mining, molecular interaction features from protein-protein interactions (as a structured data base) via principal component analysis (PCA) to reduce the protein feature dimensionality from 4,487 to 285 features, and chemical property features (about 300 features) containing physiological and physicochemical properties with feature scaling by applying Z-score normalization. The result of an average AUROC value of their proposed method of identifying the medicinal uses in diseases related to the natural compounds was 0.90.
Zhang et al. (2020) assigned two different labels for the named-entity tagging scheme on the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) book: a named-entity type label and a “Tie or Break” label, for neural network learning of the named-entity type prediction and the named-entity boundary detection, respectively. The results of named entity classification based on a multiclass model, i.e., Symptom, Chinese Medicine, Prescription, etc., had precision, recall and an F1 scores of 0.73, 0.67, and 0.70, respectively.
Jia et al. (2022) continued working on the named-entity recognition (NER) task by proposing a span-level distantly supervised approach to extract TCM medical entities from the TCM book by using a simple multilayer neural network as a classifier for multiclass classification, where the distant supervision used knowledge bases, domain ontologies and journals to automatically generate annotated datasets. Their proposed method was able to correctly classify the named entities with an F1 score of 0.77. Therefore, the previous works (Yoo et al., 2020; Jia et al., 2022) on determining named entities, e.g., Chinese medicines, applied the neural network learning technique by manual class labeling (Yoo et al., 2020) and automatic class labeling (Jia et al., 2022) to determine the named entities while the mpj features were automatically determined by mainly using HerbMed and dictionaries.
Braik et al. (2023) worked on the feature selection by applying the basic capuchin search algorithm (CSA) for lowering the feature dimensionality in ML tasks for classification purposes on various data sets, including COVID-19 dataset as the structure data. They proposed using three methods of exponential CSA, power CSA, and S-shaped CSA, based on binary data to improve CSA in selecting the features with time consuming. One of their classification results on the COVID-19 datasets was an average accuracy rate of 95.9% after applying CSA with the low fitness value of 0.04. Their Feature selection techniques can reduce the dimensionality of the features but loss of information whereas the dimensionality reduction by SEM as wrapper-based method proposed in our research aim to minimize information loss.
Pechsiri and Piriyakul (2016) worked on automatically extracting a semantic relation between two event-explanation groups as a Problem-Solving relation, for example a DiseaseSymptom-Treatment relation from hospital-web-board documents. Each Problem or DiseaseSymptom group and each Solving or Treatment group were represented by a vector of problem-event features and a vector of solving-event features, respectively, where each event feature relied on a verb phrase expression. The feature extraction was based on the word cooccurrence extraction where the word cooccurrence consisted of two words (one word was a verb; and another word was a word right after the verb) to represent each event feature. They applied the simple k-means clustering method to object clustering and feature clustering for reducing the object and feature dimensions before learning the relation by Naïve Bayes. Their F1 score of the a DiseaseSymptom-Treatment relation extraction was 0.81.
The previous studies determined either the relation/association between the medicinal plants and the medicinal properties or the phytochemical activities related to the diseases with direct relation, indirect relation as a transitive relation, or part of a series effects without concerning the high dimensional and correlated features except (Yoo et al., 2020; Braik et al., 2023; Pechsiri and Piriyakul, 2016), and the grouped semantic-feature relation as the common relation. However, the pp-mpG relation extraction as the grouped semantic-feature relation extraction involves the high dimensional and correlated features from the documents to represent the medicinal-plant property knowledge on social media, which results in both potential remedy common ailments in the form of primary or supplementary treatments and using the medicinal plants as alternative medical therapy.
3 Methodology
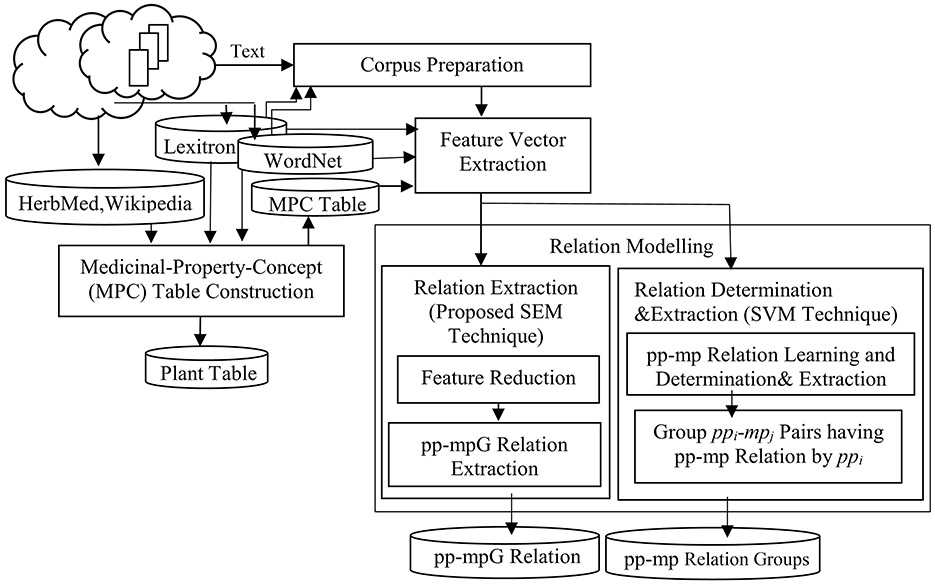
There are four main steps within our framework: Corpus Preparation, Medicinal-Property-Concept (MPC) Table Construction, Feature Vector Extraction, and Relation Modeling. Relation modeling consists of two difference techniques, Extraction by Proposed SEM Technique (which consists of Feature Reduction, and pp-mpG Relation Extraction), and Relation Determination & Extraction by SVM technique (which consists of pp-mp Relation Learning and Determination & Extraction and Group ppi-mpj Pairs having pp-mp Relations by ppi; see Figure 3).
3.1 Corpus preparation
From a total of 128 Thai research organization websites, this research selected 97 units using simple random sampling to ensure adequate statistical representation with an error rate not exceeding 5% (n ≥ N/(1+N*e2)), employing this approach due to the homogeneous nature of the sample units. The Thai-herbal-plant corpus preparation involved extracting 20,000 Elementary Discourse Units (EDUs) from 259 downloaded documents sourced from pharmacy academic websites (Table A.2), encompassing 50 distinct herbal-name concepts (hk) predominantly related to COVID-19 symptoms and Thai cooking ingredients, with document sizes varying from 20 to 130 EDUs per document. The corpus was strategically partitioned into two components: 5,000 EDUs from 64 documents for corpus behavior study and 15,000 EDUs from 195 documents for mpj feature vector extraction, specifically targeting potential disease remedies analysis excluding body nourishment considerations, incorporating relation extraction using both the proposed SEM technique and the SVM technique. The preprocessing pipeline employed Thai word segmentation tools (Sudprasert and Kawtrakul, 2003) and named-entity recognition tools (Chanlekha and Kawtrakul, 2004; Tongtep and Theeramunkong, 2010) based on Lexitron and WordNet lexical resources, followed by EDU segmentation (Chareonsuk et al., 2005; Ketui et al., 2013) to achieve standardized discourse unit identification across the corpus for subsequent analytical procedures.
3.2 Medicinal-property-concept (MPC) table construction
It is necessary to collect the sets of terminal symbols, i.e., the Verbweak, Verbstrong, Adv, Adj, and Noun sets as shown in Figure 2a, by the following method to construct the MPC table based on the WCPattern.
It is necessary to collect the sets of terminal symbols, i.e., the Verbweak, Verbstrong, Adv, Adj, and Noun sets as shown in Figure 2a, by the following method to construct the MPC table based on the WCPattern.
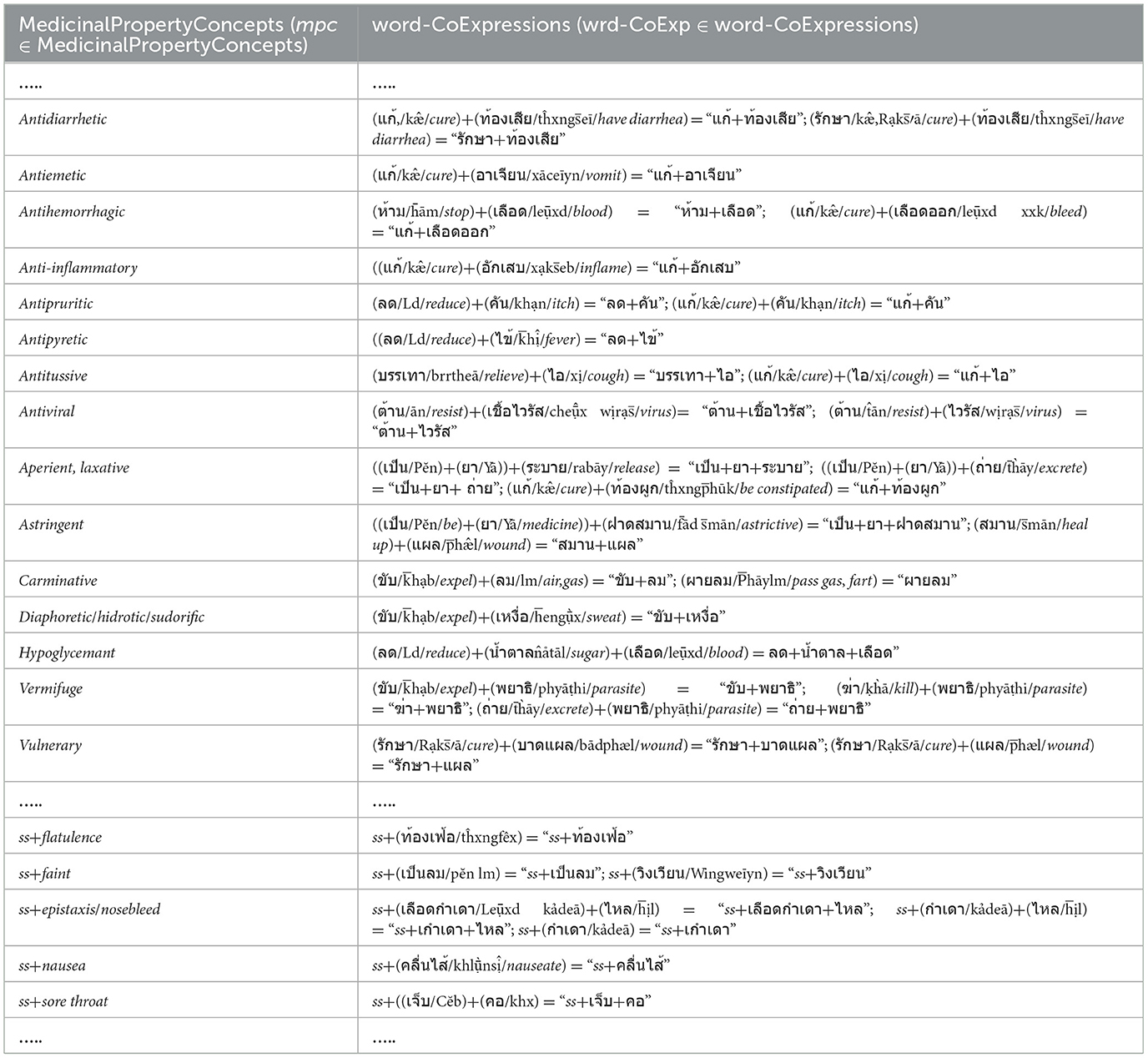
a) The elements of the Verbstrong, Verbweak, Noun, Adj, and Adv sets including the concepts of the elements in Figure 2a, are prepared and collected from the EDUtmt expressions of HerbMed/Medical-Symptom Term List after word segmentation (see Table 1 presenting examples of herbal terms with medicinal-property concepts from HerbMed and Table 2 presenting terms with medical-symptom concepts from the Medical-Symptom Term List). The concepts of the segmented words as the element concepts after stemming words and eliminating stop words are determined by the Thai-to-English translation based on Lexitron and WordNet, as shown in Tables 1, 2. If any entities from Tables 1, 2 have the same element concept, they will be collected as one entity, e.g., “aperient” and “laxative” in Table 1. The examples in Tables 1, 2 also include the phonetic expression by http://translate.google.com/ (accessed on 23 August 2024).
b) If there is more than one sense/concept of an element from the Thai-to-English translation by Lexitron, we use WordNet to select the sense that contains the following elements of wrdSet, {“patient,” “healthy,” “illness,” “body,” “wound”}, on its description by WordNet. For example, “(ถ่าย/T̄h̀āy)/Vstrong” has three senses by Lexitron, “โยกย้าย/transfer,” “ถ่ายอุจจาระ/excrete,” and “ถ่ายภาพ/photograph.” The “excrete” sense is selected by the system because the description of “excrete” by WordNet is “excrete, egest, eliminate, pass—(eliminate from the body; ‘Pass a kidney stone'),” which contains “body” as the element of wrdSet.
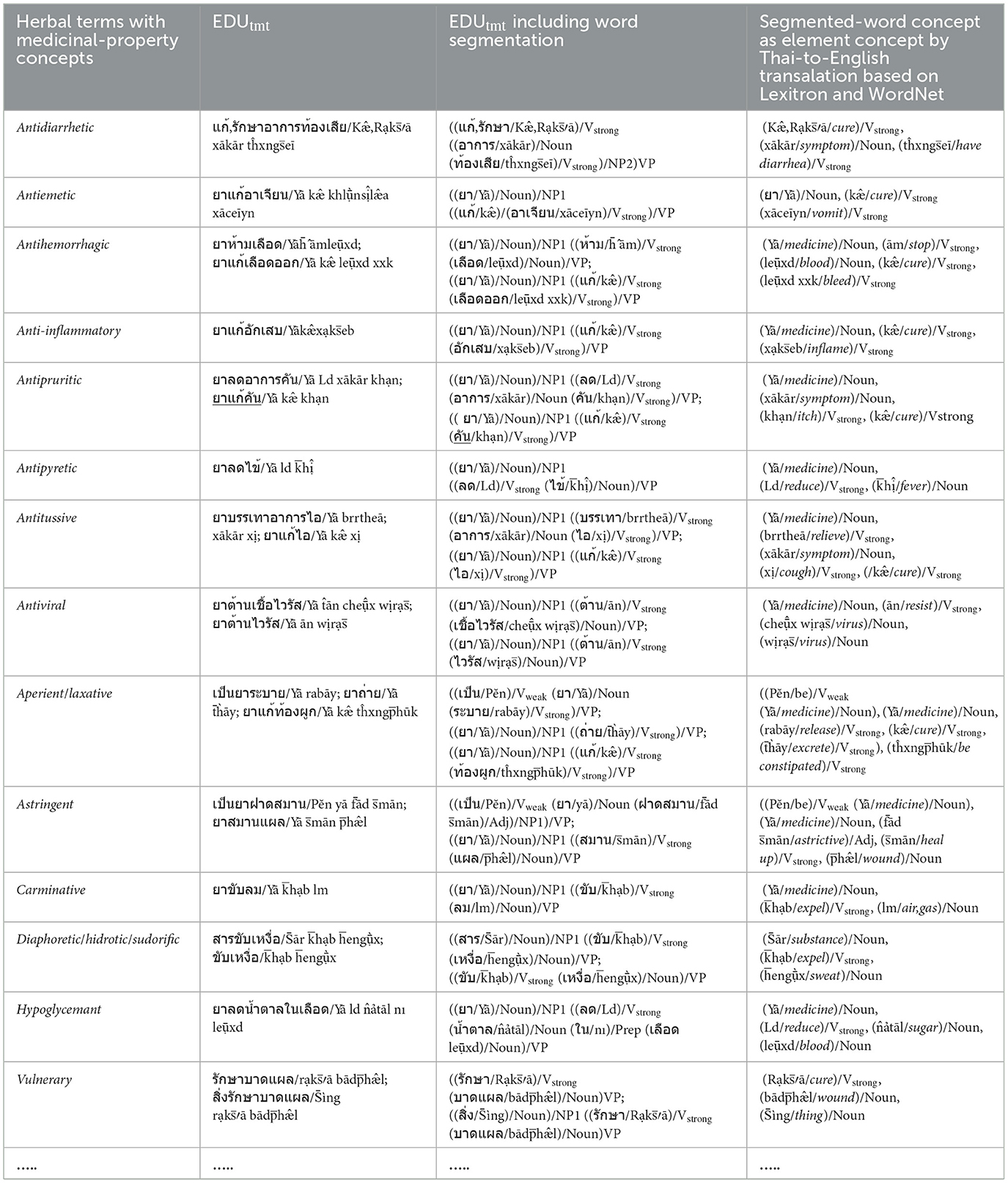
Table 1. Example: Herbal terms with medicinal-property concepts from HerbMed are translated to Thai as EDUtmt expressions by Lexitron.
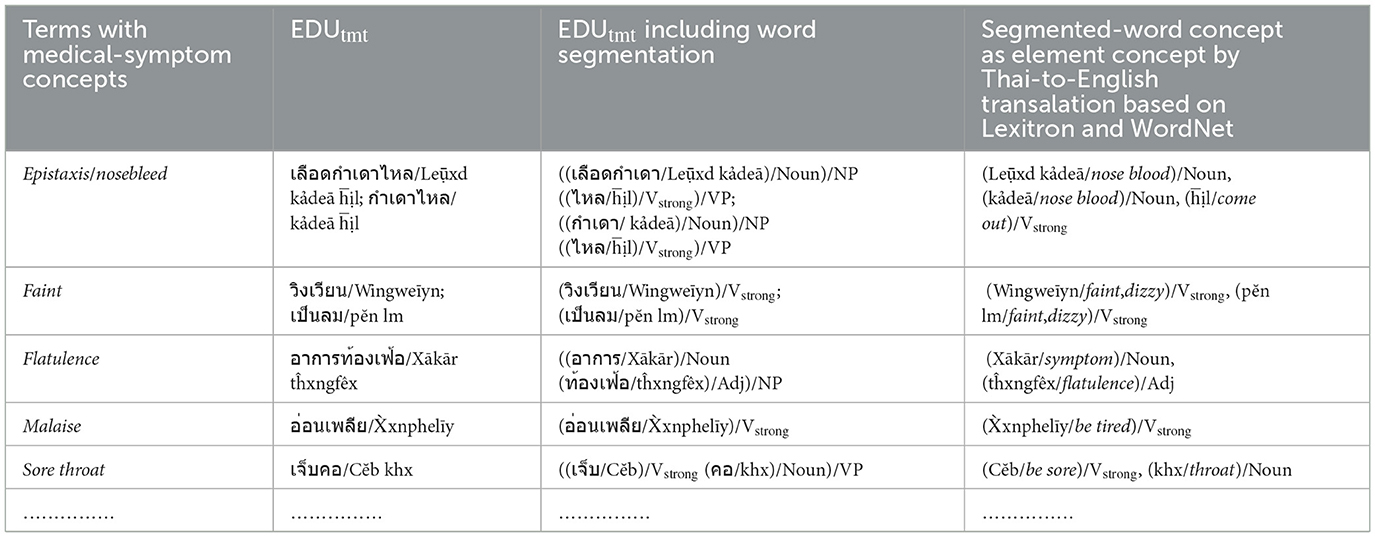
Table 2. Example: terms with medical-symptom concepts from medical-symptom term list (Wikipedia) are translated to Thai as EDUtmt expressions by Lexitron.
As shown in Table 1, we determine the word-co expressions based on WCPattern on EDUtmt, after the word segmentation followed by stemming words and eliminating stop words. The determined word-co expressions on EDUtmt and their corresponding term in the Herbal Terms with Medicinal-Property Concepts column are the wrd-CoExp elements and the mpc elements, respectively (wrd-CoExp∈word-CoExpressions, mpc∈ MedicinalPropertyConcepts) as shown in Table 3 with the phonetic expression.
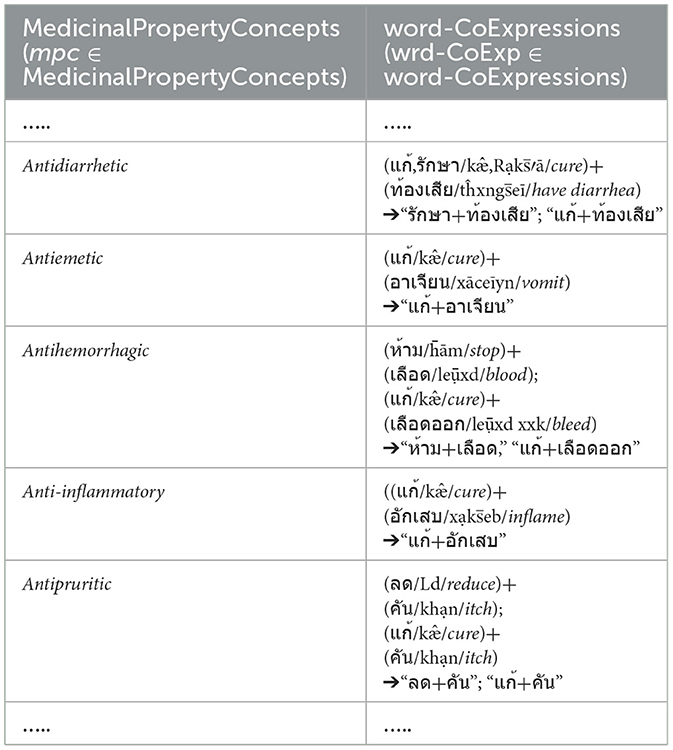
Table 3. Show word-co expressions on the segmented EDUtmt expressions aligned with medicinal property concepts from HerbMed.
In addition to Table 2, each word sequence (w1, w2, w3) of WCPattern that is determined from EDUtmt after the word segmentation followed by stemming words and eliminating stop words is then added ss (where ss ∈ SVCsub; SVCsub ⊂ SVC; SVCsub = {“แก้,รักษา/cure, treat, remedy,” “ห้าม/stop,” “เพิ่ม/increase,” “ลด/reduce,” “บรรเทา/relieve,” “ขจัด/expel, anti-,” “ทำให้/cause”}) in front of both the word sequence (ss + “w1, w2, w3”) and its corresponding term in the “Terms with Medical-Symptom Concepts” column of Table 2 to form a wrd-CoExp element and a mpc element, respectively, as shown in Table 4.
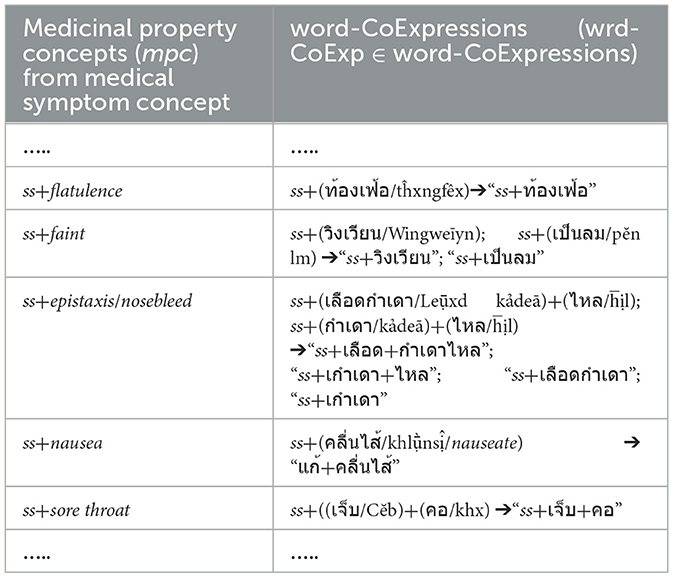
Table 4. Show ss plus word-co expressions on the segmented EDUtmt expressions aligned with ss plus medicinal property concepts from medical-symptom concept term in Wikipedia where ss ∈ SVCsub; SVCsub ⊂ SVC.
Thus, Table 3 is appended by the formations of the mpc elements and the corresponding wrd-CoExp elements from Table 4 to generate the MPC table (Table 5) including the phonetic expressions. Further, if any entities from Table 5 have the same wrd-CoExp element, they will be collected into one entity for redundancy elimination.
3.3 Feature vector extraction
The example of the corpus preparation from Section 3.1 for Figure 2a is shown in the following for the feature vector extraction.
Example of Corpus Preparation (where the [..] sympbol means ellipsis; the underline on an EDU expression shows a word-co expression based on WCPattern of the corpus's EDU expression).
File name: “กะเพรา/Thai basil”
Sub-topic name: (ใบ/Leaf)/NP1
EDU1: “([((ใบ/leaf)/Noun)/NP1] ((มี/have)/Verbweak (รส/ taste/Noun) (เผ็ดร้อน/spicy)/Adj)/VP)/EDU”
“[A leaf] has a spicy taste.”
EDU2: “(((ต้ม/boil)/Verbstrong (เอา/get)/Verbwerk) (น้ำดื่ม/ drinking water)/Noun)/VP)/EDU”
“Boil to get the water for drinking.”
EDU3: “(([(ดื่ม/drink)/Verbstrong] (เป็น/be)/Verbweak (ยา/ medicine)/Noun (ขับ/pass)/Verbstrong(ลม/gas)/Noun)/VP)/EDU”
“[Drink] as a carminative.”
EDU4: “(((แก้/treat)/Verbstrong (ท้องอืด, ท้องเฟ้อ/bloat)/Adv)/VP)/EDU”
“Treat Bloating or flatulence.”
EDU 5: “(((แก้/treat)/Verbstrong (ปวด/pain)/Verbstrong (ท้อง/abdomend)/Noun)/VP)/EDU”
“Relieve stomach pain.”
EDU 6: “(((แก้/treat)/Verbstrong (จุกเสียด/be colic)/Verbstrong)/VP)/EDU”
“Cure colic.”
EDU7: “(((แก้/treat)/Verbstrong (คลื่นเหียนอาเจียน, คลื่นไส้/ nauseate)/Verbstrong)/ VP)/EDU”
“Cure nausea and vomit.”
EDU 8: “(((ขับ/excrete)/Verbstrong (เสมหะ/phlegm)Noun)/VP)/EDU”
“Excrete phlegm.”
…………………….
EDU12: “(((นำ/use)/Verbweak (ใบ/leaf)/Noun (สด/fresh)/Adj (บีบคั้น/squeeze)/Verbstrong (น้ำ/water)/Noun)/VP)/EDU”
“Use/bring fresh leaves to squeeze juice.”
EDU13: “(((ทา/apply)/Verbstrong)/VP)/EDU”
“Apply.”
EDU14: “(((แก้/cure)/Verbstrong (โรคผิวหนัง/Skin Disease)/Noun)/ VP)/EDU”
“Cure skin disease.”
Regarding Figure 4, the FeatureVector_Extraction algorithm consists of the following 4 main steps after initializing the symbolic-feature vectors (such as sbvector, sbv, line, Plant, and Bvector) represented by an array of a string vector, e.g., sbvector[b]; b = 1,2,..,numofsbvectors) that consists of the determined features as follows: the herbal-name concept (hname) feature the plant-part concept (ppart) feature including the medicinal-property concept (medp) features of each ppart feature from the hname document:
Step1 Load MPC table: this step is to load the MPC table file into line[].
Step2 Process each document of 195 herb document:
While numberOfDocuments (D) is not equal to 195
// this step is carried out to extract several symbolic-feature vectors (sbvector) from the 195 downloaded documents as the document files shown in the following steps within the while loop
Begin-WhileLoop-jnStep2
Open a data file of a herb document as DocumentD.txt
e.g., Basil1.txt, Basil2.txt, Ginger1.txt, etc. or the document topic names determined by named-entity recognition (Chanlekha and Kawtrakul, 2004; Tongtep and Theeramunkong, 2010) based on Lexitron.
After the hname feature is determined and extracted from the document file name in the corpus, L (the number of EDUs in the document file name) is determined.
Step2.1 Skip irrelevant EDUs within the current document:
While sLength[L]
Begin-WhileLoop-inStep2.1
Skip irrelevant EDUs of the current document
Step2.2 Identify relevant plant part:
- The ppart feature is determined from EDUs.NP1.noun/ EDUsNP2.noun (which is the noun (or Noun in Figure 2a) of NP1/NP2, respectively, in EDUs; s = 1, 2, ..., numofEDUinAhkDocument) as the element of PP where
PP = {“ทั้งต้น/WholePlant,” “ลำต้นใต้ดิน/Rhizome,” “เปลือกต้น/Bark,” “ใบและก้าน/LeafandBranch,” “ดอก/Flower,” “ผล/Fruit,” “เมล็ด/Seed,” “ราก/Root,” “หน่อ/Shoot”}.
- In addition, the section name or the sub-section name of the corpus document is also represented by an EDUs where EDUs.VP (VP of EDUs) is equal to null.
- The determined ppart feature involves the various medp features on several EDU occurrences where one medp feature occurs in one EDU occurrence.
- SVC is used to identify a medicinal-property concept EDUs to extract a medp feature in Step2.3. If the medicinal-property concept EDUs is found, the flag is set to 1 and a b increment occurs.
SVC = {“แก้,รักษา/cure,treat,remedy,” “ห้าม/stop,” “เพิ่ม/increase,” “ลด/reduce,” “บรรเทา/relieve,” “ขับ/release,” “สมาน/heel,” “ขจัด/expel, anti-,” “ขับถ่าย,ถ่าย,ระบาย/excrete,” “เป็น/be+ยา/medicine,” “ช่วย/help+ขับ/excrete” “ใช้/use-for+รักษา/remedy”}
Step2.3 If relevant data found, build feature entry:
- This step of the medp feature extraction occurs if flag = 1.
- The medp feature is determined by extracting wcs (which is EDUs.wc or a word-co expression based on WCPattern in EDUs). If MPC.wrd-CoExp has a string matching to wcs, then medp of wcsis the mpc of MPC.wrd-CoExp in line[count]..
- Add the feature entry into sbvector[b]
- Flag is set to 0; a s increment occurs.
- End-WhileLoop-inStep2.1
Close a data file; a D increment occurs; s is set to 1
End-WhileLoop-inStep2.
In conclusion, sbvector[b], which is a symbolic vector, consists of the extracted features with the comma separator as follows: the hname/hk feature and the ppart/ppi feature including the medp/mpj features of the corresponding ppart/ppi feature. Moreover, the extracted features are also collected into Plant[num] which consists of three attributes: the hk feature, the ppi feature, and the mpj feature. Plant[num] is used to provide the medicinal-plant name of the certain the pp-mpG relation.
Step3 Post processing
After all symbolic-feature vectors (sbvector) have been extracted from the corpus, all features of sbvector except the hkfeature are converted into binary-feature vectors (BVector). BVector, represented by an array of binary vectors as BVector[b] having b = 1,2,..,numofBVectors, consists of the following features: ppi (i = 1,2,…, numOfPlantPartConcepts or 9) and mpj [j = 1,2,…, MedicinalPropertyConcepts or m which is mpSet.size() and is equal to 88 (see Table A.3); and mpSet is a medicinal-property concept set].
Moreover, Plant[num] is converted to a comma delimited file (a CSV file named “PlantF”). The redundancy occurrences in PlantF are eliminated to become the plant file named PlantFile.
Step4 Return output:
Return Bvector, PlantFile
3.4 Relation modeling
There are two relation modeling techniques for the relation extraction: SEM and SVM.
3.4.1 Relation extraction (proposed SEM technique)
SEM combines aspects of factor analysis to reduce features in the first step and multiple regression into one comprehensive model in the second step as follow.
3.4.1.1 Feature reduction
The extracted BVector[b], < pp1,pp2,..pp9, mp1,mp2,..mpm>[b], from the previous step contains a medicinal-property concept vector (MPvector[b]), < mp1,mp2,..mpm>[b], with m = 88 as the high-dimensional feature space. The hierarchical factor analysis technique (Kim and Mueller, 1978; Brunner et al., 2011), a common factor analysis method at the first-order factor model, is then applied to reduce the mpj features on MPvector by using covariance matrices to determine which variables have the highest correlation and then groups those variables together into a factor as follows. According to the extraction of the MPvector[b] occurrences (with b = 1,2,..,617), the medicinal-property concept feature matrix (MPmatrix) is then rotated to group the medicinal-property concept features of the vector into separated feature groups with the minimum number of separated feature groups where each separated feature group is called “Fgroupz”; z = 1,2,...,numofFeatureGroups which is less than m. After the medicinal-property concept feature vector rotation, a feature loading weight from an eigenvector for the mpj feature is determined according to Fgroupz. The high feature loading weight of mpj to Fgroupz infers that the correlation between mpj and Fgroupz is high. The different mpj feature elements with the high feature loading weights in a certain Fgroupz are wrapped to become a factor (called “Factorz”) including its factor score (called “FactorScorez”) determined by Equation 1 from the feature loading weights of the wrapped mpj feature elements.
where:
wj is a feature loading weight of mpj from an eigenvector in Factorz;
mpj is an element of the medicinal-property concept feature within Factorz; j = 1,2,…,kz;
kz is the number of different medicinal-property concept features in Factorz;
xc is an original value of the number of each mpj with its mean, , and standard deviation, SDj
At the first level of the factor analysis or the first-order factor model, the common factor analysis method (based on IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 21.0) is used to reduce the number of m features of the vector of the medicinal-property concept features by wrapping each mpj feature element with the feature loading weight from the eigenvector ≥|0.4| based on our corpus within the corresponding Fgroupz to become Factorz (z = 1,2,..., numofFeatureGroups which is 15). Each Factorz contains several elements of the different mpj features. One mpj feature can exist in only one Factorz. At the second level of the factor analysis or the higher-order factor model, Factor1, Factor2, …, Factor15 are grouped or wrapped by the common factor analysis method into core factors for the pp-mpG relation determination and extraction in the next step (pp-mpG relation extraction).
The application of Factor Analysis principles for dimensionality reduction of medicinal properties effectively addresses both high-dimensionality and redundancy issues, which constitute NP-hard computational problems; Alweshah et al., 2016, particularly within NLP contexts, while utilizing unsupervised data and offering superior advantages when integrated with Machine Learning approaches to examine plant component-medicinal property relationships through Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). This methodology delivers three critical computational cost advantages: first, enhanced computational time efficiency through initial Distributed Processing followed by Centralized Processing for result compilation and synthesis; second, significant relationship testing time reduction achieved by transforming the original number of medicinal property variables (n) to reduced factor dimensions (k, where k<n), exemplified by a seven-fold analysis time reduction when n = 21 and k = 3; and third, substantial reduction in supervised data processing time requirements and associated computational overhead. These combined computational efficiencies render this approach highly advantageous for large-scale medicinal property analysis applications while preserving analytical rigor, statistical validity, and predictive accuracy across diverse plant-based pharmaceutical research domains.
3.4.1.2 pp-mpG relation extraction
Concerning (Schumacker and Lomax, 2004), structural equation modeling (SEM) serves as a robust statistical framework that encompasses multiple regression analysis and factor analysis, designed to unveil and elucidate relationships among antecedent and consequent factors (variables). SEM is used to analyze structural relationships, i.e., the pp-mpG relation. SEM analyzes the structural relationship between measured variables, i.e., the ppi features, and latent constructs, i.e., the core factors. Additionally, SEM comprises two primary categories: variance-based SEM and covariance-based SEM (CB SEM). According to Petrovska (2012) and Parihar and Balekar (2016), explanations of plant parts related to medicinal properties, CB SEM is applied to provide direct relevance when examining the pp-mpG relation as the actual relation occurrences between the plant-part concept feature and the medicinal-property concept features.
The data analysis in this study falls into two distinct phases. In Step 1, we initiate a hierarchical feature reduction process, initially reducing 88 features to 15 factors. Subsequently, these 15 factors (denoted as AC1 to AC15) are further streamlined into the three core factors (FA, FB, FC). Consequently, a four-dimensional dataset emerges and is represented as X = f(FA, FB, FC) where X = {pp1, pp2,...,ppnumOfPlantPartConcepts}. This framework facilitates the extraction of the relation between X and f(FA, FB, FC) through the utilization of structural equations and an indicator framework. The relation can be expressed through Equation 2:
Additionally, the measurement models are structured across two levels:
The first level (in the previous step of Feature Reduction) for z = 1…, 15; j = 1 to 88
The second level for l = A, B, C:
These structural equations and measurement models collectively constitute the analytical framework (in Figure A.1) for the pp-mpG relation determination.
Moreover, FA, FB, and FC are then named according to their mpj features having FScorez ≥ 0.5 as follows: “beCarminative_beAntiemetic_excreteWaste_beVulnerary_beAnti Inflamation_beAntiVirus_relieveCold_relieve Pain_haveImmunity_haveDermatitisCare,” “beAntiFungi&Bac_reduceBloodlipidsBloodPressure &Bloodsugar_treatGingivitis &Scurvy_treatUrinarytract &RespiratoryDiseases_relieveSorethroat &Headache_beAntitussive,” and “reduceFever_reduceDizziness &Faint_releieveBruise_beAstringent_beExpectorant_releieveDiarrhea &Constipation_cureHemorrhoidsDisease_cureEye Disease,” respectively.
3.4.2 Relation extraction (SVM technique)
There are the various mpj occurrences (88 different mpj features) on BVector which has 617 extracted feature vectors, and the number of different mpj occurrences for the certain ppi occurrence in the hk document varies from 1 to 24. We then learn each ppi-mpj pair having the pp-mp relation by SVM with supervise learning on the 617 extracted feature vectors (based on 10-fold cross validation). Moreover, there are plenty of pp2 (“Rhizome”) and pp4 (“Leaf ”) occurrences in the extracted feature vectors as 137 extracted feature vectors of pp2 and 95 extracted feature vectors of pp4. Therefore, we randomly selected 100 extracted feature vectors with pp2 or pp4 as test sample from 617 ones.
3.4.2.1 pp-mp relation learning and extraction
SVM learning (Cristianini and Shawe-Taylor, 2000) with the linear kernel: The linear function, y = f(x), y is a binary vector, of the input x = (x1…xn) assigned to the positive class if f(x) ≥ 0, and otherwise to the negative class if f(x) < 0, can be written as follows:
where: x is a dichotomous vector; w is a weight vector; b is a bias; and (w,b) ∈ Rn × R are the parameters that control the function.
Regarding our learning samples, SVM is applied to determine that a ppi feature is related to a mpj feature by the pp-mp relation. The SVM learning then determines wt and b for ppi and mpj features (xt) in each ppi-mpj pair with either the positive class (pp-mp_Rel, yu= 1, u = 1,2,..,9*88 which is 792) or the negative class (non_pp-mp_Rel, yu= 0) which relies on the supervised learning instances. For example (see Table A.5): the negative class of a ppi-mpj pair occcurs if the extracted mpj feature is unclear because of the noun ellipsis, e.g., the extracted mpj feature is “(แก้/relieve)/Verbstrong (ปวด/pain)/Verbstrong”(“relieve pain”) instead of “(แก้/relieve)/Verbstrong (ปวด/pain)/Verbstrong [(ท้อง/abdomen)/Noun]”(“relieve abdominal pain”).
Determination and extraction of the ppi-mpj pairs having the pp-mp relation from the test sample containing pp2 or pp4 is determined by the weight vector from ppi and mpj features. The weight vector and the bias obtained from the SVM learning through Weka (Eibe et al., 2016) are used to test or determine and extract the ppi-mpj pair with a pp-mp_Rel class (which is a pp-mp relation) by Equation 3. If f(x) ≥ 0, the ppi-mpj pair with a pp-mp_Rel class (Positive-Class) as a pp-mp relation/linkage occurs, otherwise the non-pp-mp relation/linkage (Negative-Class) occurs. The ppi-mpj pairs with Positive-Class from the test sample are collected for grouping ppi-mpj pairs in the next step.
3.4.2.2 Group ppi-mpj pairs having pp-mp relations by ppi
Each correct extracted ppi-mpj pair having the pp-mp relation/linkage is collected into a group/set of ppi-mpj pairs having the pp-mp relations with the same ppi as shown in Figure 5.
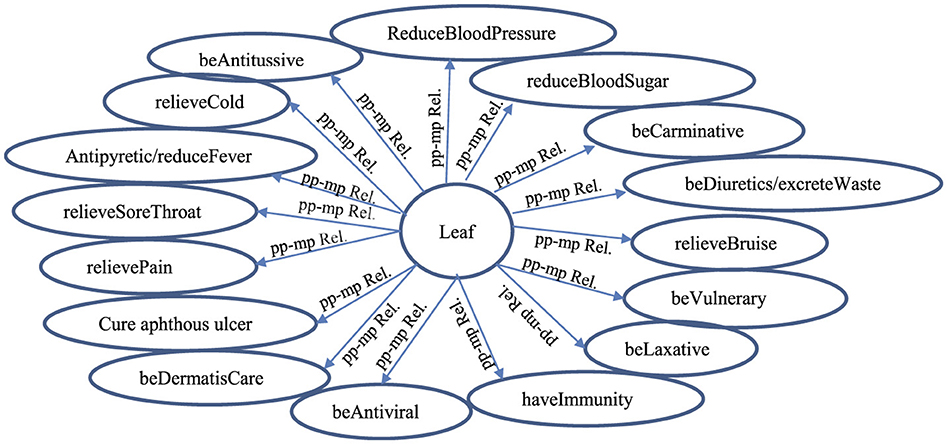
Figure 5. A group of ppi-mpj pairs having pp-mp relations/linkages (pp-mp Rel) between the mpj features and the ppi features by SVM determination (i = 2; pp2 = “Leaf ”).
4 Results and discussion
The 617 extracted feature vectors from 15,000 EDU corpus are employed to evaluate the proposed SEM for the pp-mpG relation extraction through the medicinal-property concept EDU identification including the mpj feature extraction whilst the test sample of randomly selected 100 extracted feature vectors of pp2 and pp4 from the 617 ones are used to evaluate or test the ppi-mpj pairs having the pp-mp relation by the SVM determination. There are four evaluations: (1) medicinal-property concept EDU identification, (2) mpj feature extraction, (3) pp-mpG relation extraction by SEM and pp-mp relation determination and extraction by SVM, and (4) the evaluation of a concise and comprehensible representation of medicinal-plant property knowledge by graphical representation of pp-mpG relations.
4.1 Medicinal-property concept EDU identification
The medicinal-property concept EDU identification is evaluated by the percentage accuracy of the identification based on three experts with max win voting. The evaluation result of the medicinal-property concept EDU identification by SVC is 97% accurate where each medicinal-property concept is based on the VP of an EDU expression. However, there are a few medicinal-property concepts expressed within several EDU occurrences that cannot be identified by SVC, as in the following example.
EDU1: “ผู้ป่วยโควิด-19 มีอาการปอดบวม/A COVID-19 patient has pneumonia”
EDU1: “หลังจาก ผู้ป่วยได้รับยาฟ้าทะลายโจร/After the patient has received Andrographis paniculata.”
EDU2: “[ผู้ป่วย]ก็รู้สึกดีขึ้น/[The patient] feels better.”
However, Behera and Mahalakshmi (2019) used the selected terms based on noun expressions with word size ≤ 2 from MeSH and the PubMed research articles to identify each informative sentence containing a phytochemical property feature and a target disease feature by the trained probabilistic classifier with 73% accuracy without considering the part of speech on the features since their feature positions occurred anywhere in the sentence.
4.2 mpj feature extraction
The evaluation results of extracting the mpj features, which are based on the WCPattern of the medicinal-property concept EDUs after stemming words and stop word removal, by the string-matching method to wrd-CoExp ∈ word-CoExpressions of the MPC table (without the medicinal-property concept annotation) have precision of 0.91, a recall of 0.84, and an F1 score of 0.86, which are based on three experts employing max win voting. The low recall is due to the WCPattern being insufficient in covering the medicinal-property concept, i.e., the word-CoExpressions set of the MPC table is unable to match WCPattern of the following EDU.
EDU: “[ใบ] ใช้รักษาโรค มี อาการ ผิดปกติ ทางเดินอาหาร/[A Leaf] is used to treat diseases with gastrointestinal disorders.”
WCPattern = SVC + W1 + W2 + W3
However, Cho et al. (2020) used the skin-related keywords (SRKs) and data mining to extract skincare-related terms of the skincare-function categories (the medicinal properties) and medicinal herbs (at the p-value < 0.05) from the prescriptions. The SRKs are selected from classical texts by several experts in discussions and judgments which are time consuming and involve some subjective ideas from various references. Moreover, Jia et al. (2022) applied neural network classification as the multiclass classifier on a span-level distantly supervised named-entity recognition based on their Chinese herbal dictionary to correctly classify or predict from several classes of TCM medical named entities, e.g., symptoms, Chinese medicines, prescriptions, etc., with an F1 score of 0.77. However, the neural network classification requires the class labeling and is more complicated than using the regular dictionary and HerbMed, including the medical-symptom term list on Wikipedia, to determine our mpj features without concept annotation from the documents.
4.3 pp-mpG relation extraction by SEM and pp-mp relation extraction by SVM
4.3.1 pp-mpG relation extraction (grouped semantic-feature relation extraction)
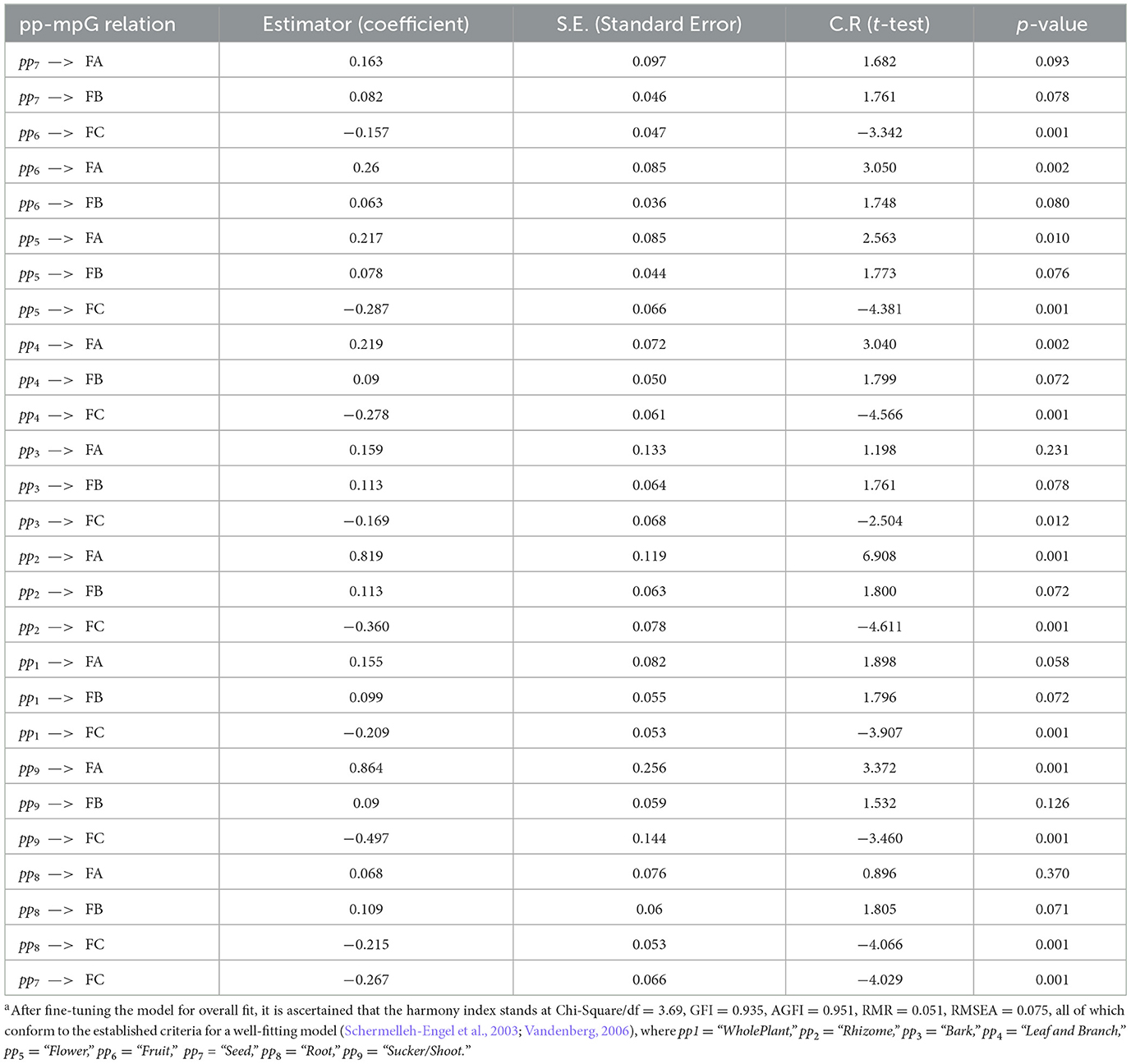
The evaluation results of the pp-mpG relation extraction as the grouped semantic-feature relation extraction by SEM are based on the p-value < 0.05 or 95% accuracy with 588 pp-mpG relations correctly determined from 617 extracted binary-feature vectors from the corpus with high dimensional and correlated mpj features in 50 different plant-name concepts as shown in Table 6 (by using the IBM SPSS Statistics Version 21.0 for Windows).
From Table 6, in regard to a p-value < 0.05, the determined pp-mpG relation with (1) the positive estimator describes increasing the number of times using ppi results in increasing the improved symptom(s) by FA, FB, or FC; and (2) the negative estimator describes increasing the number of times using ppi results in decreasing the symptom(s) by FA, FB, or FC. For example, (1) pp2 —> FA (with Estimator = 0.819) describes that “increasingthenumberoftimesusingpp2 results in increasing the improved symptom(s) by FA.” (2) pp2 —> FC (with Estimator = −0.360) describes that “increasingthenumberoftimesusingpp2 results in decreasing the degree of symptom(s) by FC.” However, ppi – > FB cannot be determined at the p-value < 0.05 because most medicinal plants including indigenous medicinal plants in our corpus relate to COVID-19 remedies, which mostly exist in FA and FC. For example: leaves (of Andrographis, lemon glass, and holy basil) and rhizomes (of ginger, finger root, and galangal) that have common medicinal properties such as anti-inflammatory, antiviral, immunity and antiemetic properties conform with (Jamshidi and Cohen, 2017; Ding et al., 2019; Homnan et al., 2020; Kanjanasirirat et al., 2020; Jafarzadeh et al., 2021; Yearsley, 2021). Thus, our proposed SEM automatically extracts the grouped semantic-feature relation, especially the pp-mpG relation as the common relation which relies on 50 different herbal-name concepts and the high dimensionality of 88 mpj features from the documents without involving the experts to label the relation class and to annotate the mpj concepts. However, Cho et al. (2020) applied a data mining technique with skin-related keywords (SRKs), which were selected and judged by several experts, to discover medicinal herbs. SRKs were used to extract 46 medicinal herbs associated with the skincare-related terms (p-values < 0.05) from prescriptions of the Donguibogam text with 626 herbs without concerning the high dimensional and correlated features and also the common relation. Regarding the feature reduction, our proposed SEM to extract the pp-mpG relation reduces the mpj feature dimensionality from 88 mpj features to three core factors (which is reduced by 29 times) as the correlated mpj feature groups (i.e., FA, FB, FC) with minimizing information loss while (Yoo et al., 2020) applied PCA (Principal Component Analysis) to reduce the protein feature dimensionality from 4,487 to 285 features (which is reduced by 16 times) as one part of all features used in deep learning to identify the medicinal uses related to the natural compounds without presenting feature correlations effect to the medicinal-use identification. According to the machine learning techniques, Pechsiri and Piriyakul (2016) applied the clustering technique to generalize the feature vector concepts as the object reduction and the feature reduction for determining a group-pair relation by Naïve Bayes from documents with 0.80 F1 score. Moreover, Braik et al. (2023) worked on the feature selection on several structural data set by the capuchin search algorithm which resulted in the information loss whilst the SEM technique for extracting the pp-mpG relation by dimensionality reduction in the mpj features with minimized information loss.
The pp-mpG relations that have the p-value < 0.05 (Table 6) are then presented by the graphical representation to represent the medicinal-plant property knowledge (Figure 6) where Leaf-FA Relation, Leaf-FC Relation, Rhizome-FA Relation, and Rhizome-FC Relation are the pp-mpG relations/linkages, and num is numOfPlantPartConcepts. Figure 6 also includes the Plant Table collection, which is used to list the hk features along with the ppi and mpj features.
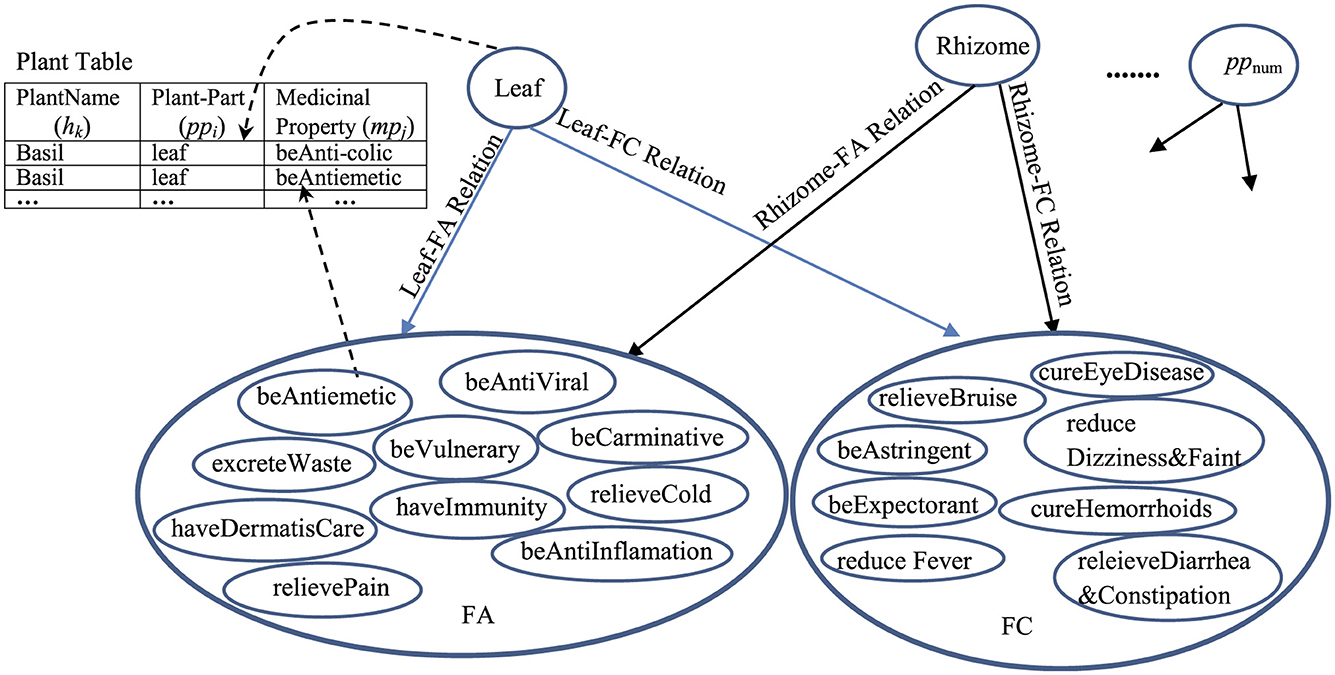
Figure 6. The graphical representation of the pp-mpG relations to represent the medicinal-plant property knowledge. For example: the pp-mpG relations, e.g., Leaf-FA Relation connecting a Leaf node (a pp4 node) to a FA node (which consists of various mpj features) where the Leaf node and each mpj feature in the FA node can access to the Plant table to find the certain hk features as follow: (1) “Leaf” and “Antiemetic” are found in the following plant names: “Basil,” “Andrographis paniculata,” and “Cinnamon”; (2) “Leaf” and “relieveCold” are found in the following plant names: “Basil,” “Andrographis paniculata,” “Fish mint,” and “Lemonglass.”
4.3.2 pp-mp relation extraction
The evaluation results of the pp-mp relation extraction by SVM with the automatic-supervised learning is evaluated in terms of an F1-score on the test sample (e.g., 350 ppi-mpj pair instances having pp2 or pp4) based on three experts with max win voting as shown in Table 7. The correctness of extracted ppi-mpj pairs having the pp-mp relation with an average accuracy of pp2 and pp4 is 0.80 and an average F1-score of pp2 and pp4 is 0.752, which result from having some ppi-mpj pairs existing in both positive and negative instances of the learning example. The correct extracted ppi-mpj pairs having the pp-mp relations also result in the correct group of ppi-mpj pairs having pp-mp relations with the same ppi (see Figure 5).
Regarding Figures 5, 6, the quantitative difference between the extracted relations/linkages by applying SEM and SVM is the number of relation/linkages connecting a certain plant-part concept to a group of different medicinal-property concepts. For example: the number of the pp-mpG relations/linkages (i.e., “Leaf-FA Relation” and “Leaf-FC Relation” (Figure 6) connect “Leaf” to FA and FC, respectively) determined and extracted by SEM is two linkages whereas the number of pp-mp relations/linkages (i.e., each “pp-mp Rel” linkage (Figure 5) connects “Leaf” to different mpj features) extracted by SVM is 16 linkages. This results in the time-consuming extraction the relations/linkages. The qualitative difference between the extracted relations/linkages by SEM and SVM is that the pp-mpG relations/linkages extracted by SEM have the correlated mpj feature occurrences within the medicinal-property concept group (e.g., FA, FC in Figure 6) whereas there is no correlation occurrence among the mpj features in a group of extracted pp-mp relations/linkages with the same ppi feature by SVM as shown in Figure 5. Other than SVM, using the neural network technique as deep learning to extract the medicinal uses in diseases related to the natural compounds is inadequate (Yoo et al., 2020) as it cannot present the feature-correlation occurrences among their independent variables/features (e.g., chemical property features in the natural compounds) of the extracted relations.
However, the extracted pp-mpG relations by SEM result in the synergistic effects when using different ppi features, e.g., using “Leaf” and “Rhizome” together for cold relief as shown in Figure 6 where both “Leaf-FA Relation” and “Rhizome-FA Relation” connect to FA containing the correlated mpj features “beAntiViral” and “relieveCold.” Thus, Figure 6 provides the medicinal-plant property knowledge for potential usages in the alternative medical therapy for synergistically solving the general health problems/symptoms.
In summary, the fundamental principle for proving the relationship linkage between SEM and SVM methodologies demonstrates that when there are n plant components and k medicinal-plant properties, the relationship testing requires n*k connections, whereas if we reduce the dimension k to only m = k/c (where c > 0), this results in the linkage analysis requiring only n*m connections (where n*m < n*k). This dimensional reduction approach significantly decreases computational complexity by reducing the total number of relationship pathways that need to be analyzed, thereby improving processing efficiency while maintaining the integrity of the plant component-medicinal property relationship modeling framework through the integrated SEM-SVM methodology.
4.4 Evaluation of concise and comprehensible representation of medicinal-plant property knowledge by graphical representation of pp-mpG relations
We evaluate the concise and comprehensible representations of the medicinal-plant property knowledge by the graphical representation of the pp-mpG relations in terms of a Likert scale (1–5). The evaluation results with the average scores based on the Likert scale of the concise and comprehensible representations of Doc (which is the documents from the pharmacy academic websites) and Graph (which is the graphical representation of the pp-mpG relations) by the 30 end-users (who are non-professional persons) are presented in Figure 7, where the average scores of the concise representation by Graph and Doc are 4.5 and 2.9, respectively, and where the average scores of the comprehensible representation by Graph and Doc are 4.0 and 3.1, respectively.

Figure 7. Box plot of the concise and comprehensible representations by Doc and Graph with the Likert scale 1–5.
Therefore, the contribution of our research, particularly Figure 6, can enhance the ability of non-professional persons in exploiting the potential of using herbal medicines or medicinal plant property knowledge as an alternative medical therapy through social media.
Moreover, we also collect the reviews/comments on the community forums (https://community.breastcancer.org/en/discussion/827489/turmeric-curcumin-yes-or-no; accessed on 30 August 2024; https://www.mtbr.com/threads/turmeric-im-a-believer.1202573/; accessed on 30 August 2024) of general users about the usefulness of using a certain medicinal plant, e.g., turmeric/curcumin as an alternative medical therapy to solve their health problems according to the various information on a particular medicinal plant on social media. In relation to the review/comment collection, we randomly select 30 reviews/comments from different users in using turmeric/curcumin as an alternative medical therapy for both cancer pains and inflammation or joint/muscle pains, to determine a sentiment score, a magnitude value, and a sentiment intensity (Lamba and Madhusudhan, 2022; Rutkowska and Szyszko, 2024) of each user review (30 user reviews/comments) by using text2data (https://www.text2data.com) as shown in Table A.4. The text2data software is a dictionary-based analyzer. The sentiment score is a numerical value ranging from −1.0 (extremely negative) to +1.0 (extremely positive), reflecting the overall emotional polarity expressed in a given text, indicating whether the expressed opinion is generally negative, neutral, or positive. In contrast, the sentiment magnitude measures the strength or intensity of the sentiment, regardless of polarity; it is a non-negative value that increases with the emotional expressiveness of the content, with higher magnitude values indicating more emotionally charged language (Lin et al., 2020). We also present a sentiment score graph and a sentiment intensity graph with the averages of the sentiment score and the sentiment intensity as 0.56, and 0.81, respectively, as shown in Figure 8a and a perceive usefulness graph between the sentiment scores and the sentiment intensity values as shown in Figure 8b.
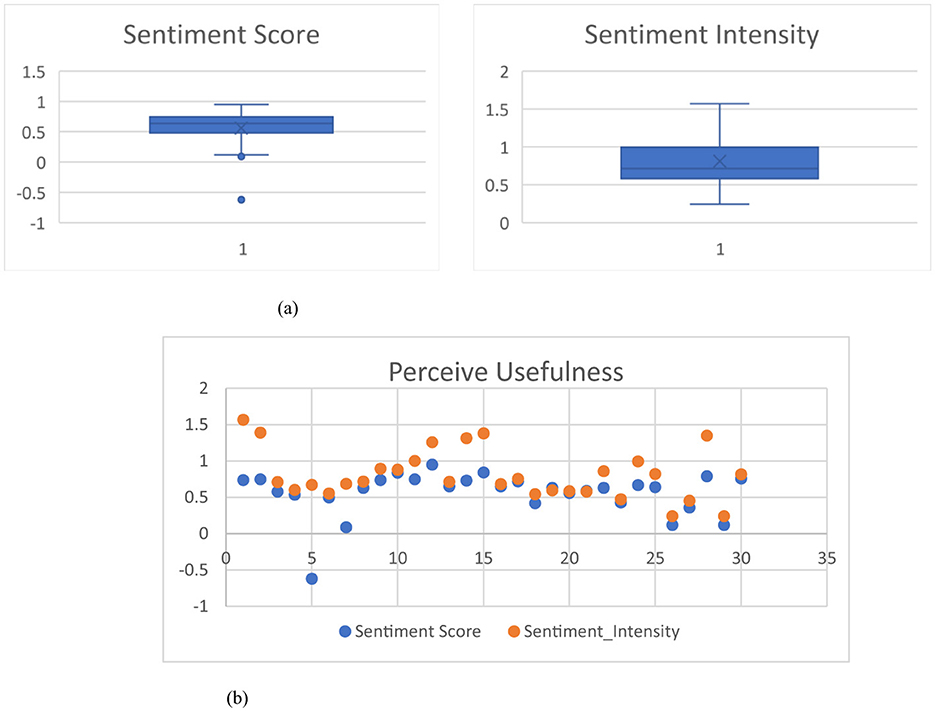
Figure 8. The sentiment graphs of 30 user reviews. (a) Box plot of sentiment score and sentiment intensity. (b) Scatter plot between sentiment score and sentiment intensity.
Figure 8b shows that most of the scatter plots are higher than 0.5 which means “Usefulness” or “Satisfaction” on using the medicinal-plant properties as a herbal medicine through the information on the networks, where a positive score means “Usefulnesss,” a zero score means neutral, and a negative score means “Dissatisfaction.” Thus, the medicinal-plant property knowledge representation in Figure 6 through social media can potentially enhance positive Usefulness to be the higher than the current one.
4.5 Limitations of study
This study explores the potential use of SEM as a statistical approach and SVM as the machine learning technique to extract the semantic relation from the corpus of the downloaded documents on the Thai pharmacy academic websites as the sources of data. The limitations of our research rely on the corpus behavior study which remains crucial for selecting the most effective techniques to address a research gap because different domains (like news, academic writing, fiction, etc.) have distinct patterns of language use. A word's frequency, collocations, grammatical patterns, and even its overall significance can all change when moving from one domain to another. For example, according to the Thai-herbal-plant corpus of the herbal domain, the medicinal-property concept feature (mpj) based on WCPattern within five words on an EDU verb phrase. In contrast to the plant-disease corpus of the agriculture domain, a plant-disease symptom concept is represented by an effect verb concept of an EDU's verb phrase (Pechsiri and Piriyakul, 2010), e.g., EDU: “ใบหงิก/Leaves shrink” (“(((ใบ/leaves)/noun)/NP ((หงิก/shrink)/verb)/VP)/EDU”) where (หงิก/shrink)/verb is the plant-symptom concept. In addition, a human symptom concept in the healthcare domain requires at least a 2-word cooccurrence to represent the symptom concept, e.g., EDU: “[ผู้ป่วย]ปวดศรีษะ/A patient feels headache” (“([((ผู้ป่วย/patient)/noun)/NP] ((ปวด/pain)/verb (ศรีษะ/head)/noun)VP)/EDU”) where (ปวด/pain)/verb+(ศรีษะ/head)/noun is a 2-word cooccurrence (verb+noun) having a symptom concept; Pechsiri and Piriyakul, 2016). Moreover, our herbal data source is provided by academic pharmacy organizations to ensure the accuracy of the information. Therefore, the corpus behaviors can influence the performance for use of statistical approach and also machine learning approach. Further exploration also needs to be made on the use of such approaches in other diagnostic cases [e.g., LCA study (Pechsiri et al., 2025)] to evaluate the potential use for other real-world applications.
5 Conclusion
This research applied word-co expression as the compound variable based on WCPattern (which is the verb-based word-co pattern) to determine the mpj features to extract the grouped semantic-feature relations (the pp-mpG relations) without the relational-class labeling and the pp-mp relations on supervised learning from the downloaded documents on the pharmacy academic websites. The limitations of our mpj feature extraction are (1) the mpj feature needs to be expressed within a single EDU occurrence, and (2) the medicinal-property concept feature needs to be expressed within five words on an EDU verb phrase. The extraction of the pp-mpG relations and the pp-mp relations from the documents relies on (1) the medicinal-property concept EDU identification by SVC collected from the verb-phrases of the EDUtmt expressions from HerbMed and Wikipedia; (2) the mpj feature extraction (without annotating concepts) by using the MPC table based on WCPattern to HerbMed and Wikipedia, and (3) the pp-mpG relation extraction by SEM involving the feature correlation among dependent variables (i.e., the mpj features) with high dimensionality. The result of each extracted pp-mpG relation as a linkage connecting a ppi feature node to the certain mpGg nodes from the documents has become the graphical representation of the medicinal-plant property knowledge. The relation/linkage qualities, e.g., the number of linkages (which affect the time it takes to extract the relations/linkages) and the correlated mpj feature expressions (which result in remedy enhancement with the supplementary treatment), of the pp-mpG relations by the proposed SEM technique are superior to the pp-mp relations extracted by SVM with supervised learning. However, the dominant mpj feature of mpGg in each disease remedy should be determined in future research. Thus, the graphical representation of the pp-mpG relations including Plant Table (Figure 6) provides concise and comprehensible representations of the medicinal-plant property knowledge for the potential enhancement of usefulness in alternative medical therapy through social media. Furthermore, the alternative medicinal usages can benefit users in terms of low cost, fewer side effects or a complete lack of side effects, and synergistic effects (Behera and Mahalakshmi, 2019). Finally, the grouped medicinal-plant property relation can be applied to several languages, particularly in East and Southeast Asia such as Tibetan, Loa, Japanese, and Chinese, having the similar behaviors of the Thai language, e.g., noun phrase ellipsis and lack of a sentence or word delimiter which affect computational tasks in natural language processing to handle these textual data effectively. Furthermore, integrating the grouped medicinal-plant property relation into the healthcare system establishes an enhanced problem-solving framework. Moreover, our grouped semantic-feature relation method can be applied not only to the grouped medicinal-plant property relation, but also to the other business areas, e.g., customer's behavior relates to various groups of product attributes on the social medias. The customer behavior is then influenced by the social medias containing various groups of product attributes. Finally, these attributes shape how consumers evaluate, choose, and ultimately purchase products.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Source of data as open source
Plant Genetic Conservation Project under the royal initiative of Her Highness Princes Maha Chakri Sirindhorn (http://www.rspg.or.th/), Medicinal Plant Information by Faculty of Pharmacy at Silpakorn University (https://pharmacy.su.ac.th/herbmed/herb/text/), Herbal Information Center in Faculty of Pharmacy Mahidol University (https://medplant.mahidol.ac.th/document/inews.asp), and the community forums (https://community.breastcancer.org/en/discussion/827489/turmeric-curcumin-yes-orno; https://www.mtbr.com/threads/turmeric-im-a-believer.1202573/).
Author contributions
CP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. IP: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JP: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Uraiwan Janviriyasopak and Asst. Prof. Suntaree Vitayanatpaisal for pharmacology and phytochemical discussion.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frai.2025.1579357/full#supplementary-material
References
Agidew, M. G. (2022). Phytochemical analysis of some selected traditional medicinal plants in Ethiopia. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 46:87. doi: 10.1186/s42269-022-00770-8
Ali, H., Ali, D., Almutairi, B. O., Kumar, G., Karga, G. A., Masi, C., et al. (2022). Synergistic effect of conventional medicinal herbs against different pharmacological activity. Biomed Res. Int. 2022:7337261. doi: 10.1155/2022/7337261
Alweshah, M., Alzubi, O. A., Alzubi, J. A., and Alaqeel, S. (2016). Solving attribute reduction problem using wrapper genetic programming. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 16, 77–84.
Behera, N. K., and Mahalakshmi, G. S. (2019). A cloud based knowledge discovery framework for medicinal plants from PubMed literature. Inf. Med. Unlocked 16:100226. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2019.100226
Braik, M., Awadallah, M. A., Al-Betar, M., Hammouri, A. I., and Alzubi, O. A. (2023). Cognitively enhanced versions of capuchin search algorithm for feature selection in medical diagnosis: a COVID-19 case study. Cogn. Comput. 15, 1884–1921. doi: 10.1007/s12559-023-10149-0
Brunner, M., Nagy, G., and Wilhelm, O. A. (2011). Tutorial on Hierarchically Structured Constructs. J. Pers. 80, 796–846. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.2011.00749.x
Carlson, L., Marcu, D., and Okurowski, M. E. (2003). “Building a discourse-tagged corpus in the framework of rhetorical structure theory,” in Current and New Directions in Discourse and Dialogue (Dordrecht: Springer), 85–112. Available online at: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-010-0019-2_5 (Accessed September 1, 2023).
Chanlekha, H., and Kawtrakul, A. (2004). “Thai named entity extraction by incorporating maximum entropy model with simple heuristic information,” in Proceedings of the IJCNLP 2004, Hainan Island, China, March 22–24, 1–7. Available online at: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary (Accessed September 1, 2023).
Chareonsuk, J., Sukvakree, T., and Kawtrakul, A. (2005). “Elementary discourse unit segmentation for Thai using discourse cue and syntactic information,” in Proceedings of the NCSEC 2005, Bangkok, Thailand, October 27–28, 85–90.
Cho, G., Park, H.-M., Jung, W.-M., Cha, W., Lee, D., and Chae, Y. (2020). Identification of candidate medicinal herbs for skincare via data mining of the classic Donguibogam text on Korean medicine. Integrative Med. Res. 9:100436. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2020.100436
Choi, W., and Lee, H. (2015). “A text mining approach for identifying herb-chemical relationships from biomedical articles,” in Proceedings of the ACM Ninth International Workshop on Data and Text Mining in Biomedical Informatics – DTMBIO (New York, NY), 25–25. doi: 10.1145/2811163.2811178
Cristianini, N., and Shawe-Taylor, J. (2000). An Introduction to Support Vector Machines. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Detroja, K., Bhensdadia, C. K., and Bhatt, B. S. (2023). A survey on relation extraction. Intell. Syst. Appl. 19:200244. doi: 10.1016/j.iswa.2023.200244
Ding, P., Yang, L., Feng, C., and Xian, J.-C.. (2019). Research and application of Alpinia officinarum in medicinal field. Chinese Herbal Med. 11, 132–140. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2019.04.003
Eibe, F., Hall, M. A., and Witten, I. H. (2016). The WEKA Workbench. Online Appendix for Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques. Morgan Kaufmann. [Online]. Available online at: https://www.cs.waikato.~ac.nz/ml/weka/ (Accessed September 1, 2023).
Fang, Y. C., Huang, H. C., Chen, H. H., and Juan, H. F. (2008). TCMGeneDIT: a database for associated traditional Chinese medicine, gene and disease information using text mining. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 8, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-8-58
Homnan, N., Thongpraditchote, S., Chomnawang, M., and Thirapanmethee, K. (2020). In vitro anti-inflammatory effects of Thai herb essential oils. Pharm. Sci. Asia 47, 153–163. doi: 10.29090/psa.2020.02.019.0020
Intharuksa, A., Arunotayanun, W., Yooin, W., and Sirisa-Ard, P. A. (2022). Comprehensive review of Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) nees and its constituents as potential lead compounds for COVID-19 drug discovery. Molecules 27:4479. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144479
Itharat, A., Tiyao, V., Sutthibut, K., and Davies, N. M. (2021). Potential Thai herbal medicines for COVID-19. Asian Med. J. Alternative Med. 21, S58–S73.
Jafarzadeh, A., Jafarzadeh, S., and Nemati, M. (2021). Therapeutic potential of ginger against COVID-19: is there enough evidence?. J. Traditional Chinese Med. Sci. 8, 267–279. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcms.2021.10.001
Jamshidi, N., and Cohen, M. M. (2017). The clinical efficacy and safety of Tulsi in humans: a systematic review of the literature. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2017:9217567. doi: 10.1155/2017/9217567
Jia, Q., Zhang, D., Xu, H., and Xie, Y. (2022). Extraction of traditional Chinese medicine entity: design of a novel span-level named entity recognition method with distant supervision. JMIR Med. 9:e28219. doi: 10.2196/28219
Kanjanasirirat, P., Suksatu, A., Manopwisedjaroen, S., Munyoo, B., Tuchinda, P., Jearawuttanakul, K., et al. (2020). A high-content screening of Thai medicinal plants reveals Boesenbergia rotunda extract and its component Panduratin A as anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents. Sci. Rep. 10:19963. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77003-3
Ketui, N., Theeramunkong, T., and Onsuwan, C. (2013). Thai elementary discourse unit analysis and syntactic-based segmentation. Information 16, 7423–7436. Available online at: https://ndlsearch.ndl.go.jp/books/R000000004-I032131044
Khoo, C., and Na, J. C. (2006). Semantic relations in information science. Annu. Rev. Inf. Sci. Technol. 40, 157–228. doi: 10.1002/aris.1440400112
Kim, J.-O., and Mueller, C. W. (1978). Introduction to Factor Analysis: What it is and How to do it. Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications. doi: 10.4135/9781412984652
Lamba, M., and Madhusudhan, M. (2022). “Sentiment analysis,” in Text Mining for Information Professionals (Cham: Springer), 191–211. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-85085-2
Lin, H. C. K., Wang, T. H., Lin, G. C., Cheng, S. C., Chen, H. R., Huang, Y. M., et al. (2020). Applying sentiment analysis to automatically classify consumer comments concerning marketing 4Cs aspects. Appl. Soft Comput. 97:106755. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106755
Miller, G. A. (1995). WordNet: a lexical database for English. Commun. ACM 38, 39–41. doi: 10.1145/219717.219748
Nelson, L., and Perrone, J. (2000). Herbal and alternative medicine. Emerg. Med. Clin. North Am. 18, 709–722. doi: 10.1016/S0733-8627(05)70154-1
Osman, A., Sbhatu, D. B., and Giday, M. (2020). Medicinal plants used to manage human and livestock ailments in Raya Kobo District of Amhara Regional State, Ethiopia. Evid. Based Complement. Alternative Med. 2020:1329170. doi: 10.1155/2020/1329170
Parihar, G., and Balekar, N. (2016). Calotropis procera: a phytochemical and pharmacological review. Thai J. Pharm. Sci. 40, 115–131. doi: 10.56808/3027-7922.1918
Pechsiri, C., and Piriyakul, R. (2010). Explanation knowledge graph construction through causality extraction from texts. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 25, 1055–1070. doi: 10.1007/s11390-010-9387-0
Pechsiri, C., and Piriyakul, R. (2016). Extraction of a group-pair relation: problem-solving relation from web-board documents. Springerplus 5:1265. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-2864-3
Pechsiri, J. S., Souza, A., Pechsiri, C., Shigwedha, P. K., Katjouanga, U., Mapani, B., et al. (2025). Exploring the use of a machine assisted goal and scope in a Life Cycle Studies to understand stakeholder interest and priorities. Clean. Environ. Syst. 18:100288. doi: 10.1016/j.cesys.2025.100288
Petrovska, B. B. (2012). Historical review of medicinal plants' usage. Pharmacogn. Rev. 6, 1–5. doi: 10.4103/0973-7847.95849
Prasathkumar, M., Anisha, S., Dhrisya, C., Becky, R., and Sadhasivam, S. (2021). Therapeutic and pharmacological efficacy of selective Indian medicinal plants–a review. Phytomed. Plus 1:100029. doi: 10.1016/j.phyplu.2021.100029
Pustejovsky, J. (1991). The syntax of event structure. Cognition 41, 47–81. doi: 10.1016/0010-0277(91)90032-Y
Rabizadeh, F., Mirian, M. S., Doosti, R., Kiani-Anbouhi, R., and Eftekhari, E. (2022). Phytochemical classification of medicinal plants used in the treatment of kidney disease based on traditional persian medicine. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022:8022599. doi: 10.1155/2022/8022599
Rajasekaran, B. A. (1993). Framework for incorporating indigenous knowledge system into agricultural research and extension organizations for sustainable agricultural development in India (Ph.D. Dissertation). Iowa State University, Iowa.
Rutkowska, A., and Szyszko, M. (2024). Dictionary-based sentiment analysis of monetary policy communication: on the applicability of lexicons. Qual. Quant. 58, 5421–5444. doi: 10.1007/s11135-024-01896-9
Salmerón-Manzano, E., Garrido-Cardenas, J. A., and Manzano-Agugliaro, F. (2020). Worldwide research trends on medicinal plants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17:3376. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17103376
Schermelleh-Engel, K., Moosbrugger, H., and Müller, H. (2003). Evaluating the fit of structural equation models: tests of significance and descriptive goodness-of-fit measures. Methods Psychol. Res. Online 8, 23–74. doi: 10.23668/psycharchives.12784
Schumacker, R. E., and Lomax, R. G. (2004). A Beginner's Guide to Structural Equation Modeling, 2nd Edn. London: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9781410610904
Singhabutra, S. (1992). Use of 200 Medicine Plants. Bangkok: Kune. Available online at: http://www.rspg.or.th/; https://www.rspg.or.th/plants_data/herbs/herbs_200.htm (Accessed August 18, 2024).
Sudprasert, S., and Kawtrakul, A. (2003). “Thai word segmentation based on global and local unsupervised earning,” in Proceedings of the NCSEC 2003, Chonburi, Thailand, October 28–30, 1–8.
Tongtep, N., and Theeramunkong, T. (2010). Pattern-based extraction of named entities in Thai News documents. Thammasat. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 15, 70–81.
Trakultaweekoon, K., Porkaew, P., and Supnithi, T. (2007). “LEXiTRON vocabulary suggestion system with recommendation and vote mechanism,” in 7th International Symposium on Natural Language Processing (SNLP) 2007, Pattaya, Thailand, 43–48.
Vandenberg, R. J. (2006). Introduction: statistical and methodological myths and urban legends: where, pray tell, did they get this idea? Organ. Res. Methods 9, 194–201. doi: 10.1177/1094428105285506
Yearsley, C. (2021). Thailand approves Asian herb andrographis to treat COVID-19. HerbalGram J. Am. Botanical Council 129, 35–36.
Yoo, S., Yang, H. C., Lee, S., Shin, J., Min, S., Lee, E., et al. (2020). Deep learning-based approach for identifying the medicinal uses of plant-derived natural compounds. Front. Pharmacol. 11:584875. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.584875
Yuan, G., Wahlqvist, M. L., He, G., Yang, M., and Li, D. (2006). Natural products and anti-inflammatory activity. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 15, 143–152.
Keywords: grouped semantic-feature relation, word co-occurrence, structural equation modeling, natural language processing (computer science), artificial intelligence
Citation: Pechsiri C, Piriyakul I and Pechsiri JS (2025) Grouped semantic-feature relation extraction from texts to represent medicinal-plant property knowledge on social media. Front. Artif. Intell. 8:1579357. doi: 10.3389/frai.2025.1579357
Received: 19 February 2025; Accepted: 24 June 2025;
Published: 08 August 2025.
Edited by:
Lina F. Soualmia, Université de Rouen, FranceReviewed by:
Omar A. Alzubi, Al-Balqa Applied University, JordanFilippos Ventirozos, Manchester Metropolitan University, United Kingdom
Nada Ayman GabAllah, Coventry University, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2025 Pechsiri, Piriyakul and Pechsiri. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Joseph Santhi Pechsiri, anNwZWNoc2lyaUBvdXRsb29rLmNvbQ==
 Chaveevan Pechsiri1
Chaveevan Pechsiri1 Joseph Santhi Pechsiri
Joseph Santhi Pechsiri