- 1Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering and PolitoBIOMed Lab, Politecnico di Torino, Turin, Italy
- 2Interuniversity Center for the Promotion of the 3Rs Principles in Teaching and Research, Turin, Italy
Bone fractures and cartilage pathologies represent a heavy socioeconomic burden for the national healthcare systems worldwide. Pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) stimulation has become a widely recognized treatment for enhancing bone fracture healing and reducing tissue inflammation, thereby supporting bone tissue regeneration. More recently, its effectiveness in treating cartilage degeneration and osteoarthritis has also been demonstrated. However, the effects of PEMF, particularly the underlying mechanisms related to the activation of specific signaling pathways, are not yet fully known neither correlated with the specific PEMF parameters applied. As a result, standardized protocols for PEMF treatment are lacking in clinical practice, leading to empirical application of PEMF stimulation and heterogeneity in treatment protocols. For these reasons, over the past three decades, the biological effects of PEMF on bone and cartilage tissues have been extensively investigated through both in vitro and in vivo experiments. The aim of this review is to provide a detailed overview of the performed studies, focusing on the applied PEMF stimulation parameters and the induced effects on bone and cartilage tissues. Furthermore, to enable comparisons across various published protocols and to aid in understanding the correlation between applied PEMF parameters and their resulting biological effects, we propose, for the first time, a quantitative descriptor for PEMF stimulation, termed PEMF dose, which accounts for magnetic field intensity, stimulation waveform, and exposure duration. The use of this comprehensive descriptor enabled the identification of common features across different studies and, in the future, it could serve as a valuable tool for refining PEMF stimulation protocols and establishing standardized guidelines to support bone and cartilage repair.
1 Introduction
Bone fragility fractures and osteoarthritis (OA) are two of the most prevalent disorders and among the primary causes of disability worldwide, with a significant impact on the socio-economic landscape (Borgström et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2021). In 2019, considering the European Union, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom, 25.5 million women and 6.5 million men over 50 years of age were estimated to have osteoporosis, with total direct costs associated with osteoporotic fractures accounting for € 57 billion. Moreover, 4.3 million new osteoporosis-related fractures were registered in 2019, with an expected increase of 25% in the number of fractures by 2034 (Kanis et al., 2021; Willers et al., 2022; IOF, 2024). Concerning OA, it was estimated that it afflicts over 500 million individuals worldwide (Hunter et al., 2020), with estimates indicating that, by 2032, 45% of adults over the age of 45 will be affected by OA (Miguel et al., 2022). These projections can be attributed to several interactive factors, primarily population aging combined with the rising prevalence of risk factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyle, tobacco consumption (Amini et al., 2013; Suryani et al., 2019), and the prolonged use of medications known to affect musculoskeletal health, including glucocorticoids, certain anticonvulsants, and hormonal contraceptives (Ampatzis et al., 2022).
Although bone has an intrinsic capacity for regeneration and functional recovery through self-healing mechanisms (Salhotra et al., 2020; Varani et al., 2021), certain fractures exhibit delayed healing or complications such as non-unions, often resulting in chronic pain and significant impairment (Freeman et al., 2015). In contrast, cartilage injuries do not undergo spontaneous regeneration due to the avascularity and complex zonal architecture of the tissue (Gu et al., 2023). The gold standard interventions for repairing bone and cartilage defects—particularly in cases of trauma or sports injuries—rely on surgical procedures involving the implantation of autografts or allografts, frequently supplemented with biophysical therapies. Nonetheless, these approaches are associated with clinical limitations, including donor site morbidity in autografts and immunogenic or infectious risks in allografts (Bentley et al., 2012; Gaspar et al., 2012). In the context of osteoarthritis (OA), however, therapeutic strategies vary according to disease stage, with early management typically centered on pharmacological pain control and lifestyle modifications, while surgical interventions such as microfracture or joint replacement are considered for advanced stages (McAlindon et al., 2014).
Beside conventional surgical procedures, bone and cartilage tissue engineering (TE) approaches are emerging as promising strategies to promote the healing process (Daher et al., 2009; Amini et al., 2013; Langer and Vacanti, 2016; Pedrero et al., 2021; Miguel et al., 2022). Ideally, TE aims to generate three-dimensional (3D) functional substitutes for implantation, designed to mimic the architecture, composition, biology, and mechanical cues of the native tissue. However, the clinical translation of TE approaches remains constrained by scientific, technical, and regulatory challenges (Davies et al., 2014; Mittwede et al., 2018). As a result, TE constructs are primarily used as biomimetic tissue models for in vitro research and pre-clinical studies (Quarto and Giannoni, 2016). Moreover, for advancing the understanding of tissue behavior, significant progress has been made in developing bioreactors for biophysical stimulation, enabling the investigation of cellular and tissue responses to physical stimuli (Lanza et al., 2000; Massai et al., 2013). When cultured within bioreactors, biomimetic tissue models can be studied in a monitored and controlled environment, allowing for the exploration of complex cellular behaviors under various biophysical conditions. Over the past decade, several in vitro models and bioreactors have been used to investigate the influence of different physical stimulations—including mechanical loading (Hoenig et al., 2011; Matziolis et al., 2011; Hoffmann et al., 2015; Ravichandran et al., 2017; Lovecchio et al., 2019), fluid shear stress (Bancroft et al., 2002; Wendt et al., 2003; Datta et al., 2006; Du et al., 2009; Li et al., 2009; da Silva et al., 2010; Kavlock and Goldstein, 2011; Beşkardeş et al., 2018; Engel et al., 2021; Gabetti et al., 2022; Yamada et al., 2022), ultrasounds (Claes and Willie, 2007; Lim et al., 2013; Zhou X. et al., 2016; Ricotti et al., 2024), and electrical fields (Wiesmann et al., 2001; Dauben et al., 2016; Jing et al., 2019; Leppik et al., 2019; Portan et al., 2019)—on bone and cartilage tissues. Through these studies, researchers have gained valuable insights into how specific biophysical stimulations can enhance cellular responses, such as osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation, matrix mineralization, and tissue remodeling, with the final aim to optimize the biophysical treatments.
Among the biophysical stimulations explored to promote bone and cartilage healing, electrical and electromagnetic fields have been used in clinical settings for over 40 years; however, detailed characterization of the signaling pathways they activate has become the subject of intense investigation only recently. Indeed, since bone and cartilage are characterized by piezoelectric properties (Jacob et al., 2018)—meaning that mechanical deformations generate electrical polarization in these tissues, known to play a key role in maintaining or repairing tissue (Fukada and Yasuda, 1957)—it has been hypothesized that external electrical or electromagnetic fields can enhance the body’s natural repair mechanisms (Barker and Lunt, 1983). For the application of these stimulations, three main techniques have been proposed (Kuzyk and Schemitsch, 2009; Leppik et al., 2020): direct current (DC), capacitive coupling (CC), and inductive coupling (IC). In DC stimulation, electrodes are placed in direct contact with the tissue to generate an electric current. This invasive method is commonly employed in research and clinical settings, but it is susceptible to complications, including issues related to electrode insertion, electrode corrosion, and the release of metallic ions. CC represents a non-invasive alternative, in which the target tissue is placed between two electrodes that are in mechanical contact with the skin but electrically insulated, avoiding flow of direct current between the electrodes and the tissue. However, achieving the same level of effectiveness as DC typically requires the application of higher voltages. Alternatively, IC offers a further non-invasive option that employs pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF). The PEMF stimulation is obtained by imposing an alternating current along a single solenoid or a pair of Helmholtz coils and positioning the target near the solenoid or between the coils. The alternating current generates a time-varying magnetic field that induces a time-varying electric field in the tissue, as demonstrated by Faraday and Lenz. The magnitude and frequency of the induced electric field are dependent on the variation of the magnetic flux in the tissue and on tissue properties. IC mode operates at low frequencies (6–500 Hz) and low intensities (0.1–30 mT), making it less energy-intensive than CC and more suitable for clinical and home use (Hu et al., 2020).
The main effect of such stimulations is to induce a time-varying electric field in the exposed tissue, like the one naturally generated during movement (Varani et al., 2021). This secondary electric field depolarizes cell membranes, initiating ionic currents that activate signaling pathways responsible for tissue regeneration (Markov, 2007). Since the Food and Drugs Administration (FDA) approval in 1979 for the treatment of non-union fractures, backed by pioneering studies (Andrew et al., 1974; Bassett et al., 1977; Friedenberg and Brighton, 1974; Brighton et al., 1975), PEMF stimulation has gained increasing importance in orthopedic clinical practice (Nelson et al., 2013). Several studies demonstrated its potential in enhancing bone endogenous healing processes (Chalidis et al., 2011; Daish et al., 2018; Cadossi et al., 2020) and for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis (Wang et al., 2021), osteonecrosis (Massari et al., 2006) and OA (Veronesi et al., 2014). Moreover, several clinical trials have shown the efficacy of PEMF therapy in the treatment of numerous conditions, including non-union bone fractures (NCT01574833 (XIONG, 2012)), osteoporosis (NCT04608162 (El-Shamy, 2020)), and OA (NCT04106986 (Jordan University of Science and Technology, 2021); NCT01877278 (Bagnato et al., 2016)).
Indeed, clinical studies performed using different devices showed biological effectiveness when applying PEMF with exposure times of 3–8 h per day from 3 to 10 months to treat fracture non-unions or pseudoarthrosis (Garland et al., 1991; Massari et al., 2006; Cebrián et al., 2010; Faldini et al., 2010). However, due to the different device operating parameters—such as intensity, frequency, waveform—standardized guidelines have not been defined yet (Hu et al., 2020). Furthermore, although numerous PEMF stimulation devices are commercially available and widely used in clinical practice, it is important to note that the European regulation for the market authorization of medical devices has long required only the verification of electrical safety, with the risk of exposing patients to ineffective devices. It was only in 1993 that the European directive came into effect, mandating manufacturers to provide evidence demonstrating the effectiveness of medical devices before they could be commercialized (Massari et al., 2011). Given the heterogeneity of parameters used, the regulatory requirements, and the consistently positive effects reported in literature, further research on PEMF stimulation is essential, together with strategies for enabling comparability.
This review aims to illustrate the advancements made over the past three decades in understanding the effects of PEMF stimulation on bone and cartilage tissues, with a particular focus on findings from both in vitro and in vivo studies. Moreover, we introduced, for the first time, the quantitative descriptor PEMF dose. This is a comprehensive metric based on PEMF stimulation parameters (i.e., magnetic field intensity, stimulation waveform, and exposure duration) which was crucial for comparing the protocols and outcomes obtained using different PEMF stimulators and applying different operating parameters and for identifying quantitative thresholds for biological responses.
2 Background to composition and electroactive properties of bone and articular cartilage tissues
Bone and articular cartilage are connective tissues composed predominantly by their respective resident cells embedded in a dense extracellular matrix (ECM). While articular cartilage is uniquely composed of chondrocytes, bone tissue resident cells include osteoblasts (bone ECM production), osteoclasts (bone resorption), osteocytes (terminally differentiated mature bone cells and main mechanoreceptors of the tissue), and bone lining cells (Schaffler and Kennedy, 2012). For both bone and cartilage tissues, collagen is the main constituent of their ECM. Once the collagen fibers are exposed to mechanical stress due to daily movement, its macromolecules, which are highly composed by glycine, proline and hydroxyproline residues (with NH and CO units), experience reorientation towards the protein long axis and magnitude change of their dipole moment (Zhou Z. et al., 2016). Such responses to mechanical stimuli are responsible for the intrinsic piezoelectricity of collagen, which plays a crucial role in influencing the endogenous bioelectric signaling and electrical features of bone and cartilage tissues (Chen et al., 2024). However, bone and cartilage respond differently to PEMF stimulation due to their distinct resident cell populations, biological functions, composition, structure, and mechanical and electroactive properties (summarized in Table 1). The following sections offer insights into the composition and associated electroactive properties of bone and cartilage tissues.
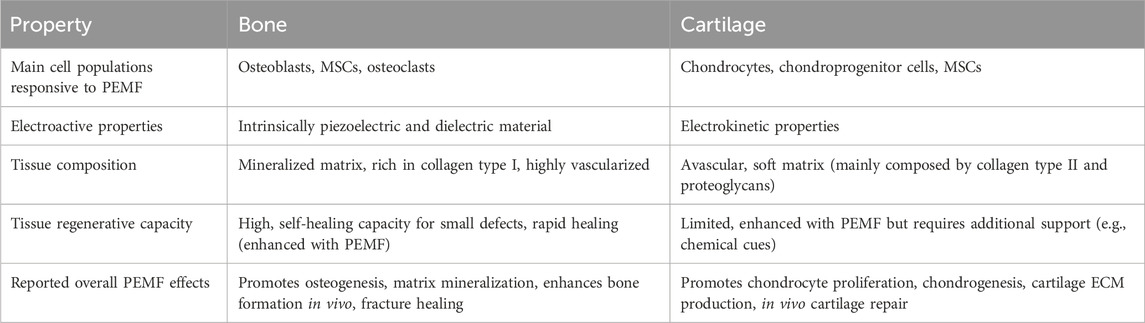
Table 1. Summary of the main differences observed between bone and cartilage tissues in terms of their response to PEMF stimulation.
2.1 Bone
Bone tissue is considered a composite material consisting of an inorganic (65%) and organic (35%) phase. The bone organic phase consists mainly (90%) in collagen type I (COL1) organized in fibrils, providing the tissue its high tensile mechanical strength. The inorganic phase consists mainly in calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite nanocrystals deposited within the collagen fibrils, being responsible for mineral exchange and for the high compressive strength (Baxter et al., 2010; Domingues et al., 2024). Macroscopically, bone tissue can be categorized into two main types: compact (also known as cortical) bone and cancellous (also known as spongy or trabecular) bone. Compact bone constitutes approximately 80% of the human skeleton, serving as a hard, dense protective outer layer that envelops long bones throughout the body. Cancellous bone (20%), which is less dense (high porosity – 50%–90%) than the compact bone and includes the inner layer of irregular bones, contributes to the load absorption and metabolic exchange capacities of the tissue (Collins et al., 2021). Moreover, cancellous bone comprises most of the human body’s bone marrow, which is responsible for the production of blood cells and harbors many stem cells involved in bone repair and remodeling processes. In particular, the human bone marrow-derived stem/stromal cells (hBMMSCs) have been considered the “gold standard” cell source for cell therapy and TE strategies for bone regeneration, mainly due to their superior tissue-specific potential for osteogenesis, high in vitro proliferation capacity, and advantageous trophic/immunomodulatory properties (Silva et al., 2021; Zha et al., 2022; Rossi et al., 2023).
The dielectric and piezoelectric features of natural bone, responsible for the bioelectric signaling occurring within the tissue regulating its remodeling and homeostasis, have been previously demonstrated (Wang et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2024). The bone dielectric properties, i.e., its capacity to undergo electric polarization, resulting from charge displacement and the formation of dipoles, arise from the separation of hydrogen bonds present in its main components, collagen and hydroxyapatite (Jacob et al., 2018; Amin et al., 2019). The dielectric constant of bone tissue depends strongly on the water content and frequency of the applied electric field, with a value of 10 being reported for hydrated bone within the frequency range of 1–100 kHz (Bai et al., 2024). Previous studies have demonstrated a correlation between the dielectric coefficient of bone tissue and its elastic modulus and mineral density, suggesting that the mechanical performance and health condition of bone can be evaluated through the assessment of its dielectric properties (Sierpowska et al., 2003). Moreover, as a result of the bone tissue’s high degree of anisotropy, its conductivity value is highly dependent on the direction of the electrical flow through the tissue (Chen et al., 2024).
The primary origin of bone piezoelectricity arises from the non-centrosymmetric structure of COL1 fibers that, upon mechanical stimulation, slide over each other, creating a separation and polarization of charged groups, subsequently generating a physiologic electric potential (piezoelectric effect) (Barbosa et al., 2022; Bai et al., 2024). The piezoelectric coefficient of bone tissue has been reported to lie within the range of 0.7–2.3 pC/N, however, due to the tissue’s inherent anisotropy, these values vary across different regions (Chen et al., 2024). Importantly, the piezoelectric effect of bone tissue has been shown to induce polarization by converting mechanical loads in electrical signals, which, in turn, supports osteogenesis, bone growth, maintenance and healing (Rajabi et al., 2015). Accordingly, bone tissue has the capacity of regulating its metabolism and function through the conversion of mechanical loads into electrical signals, triggering several signaling cascades promoting cell osteogenic differentiation, tissue formation, and bone remodeling (Barbosa et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2024).
2.2 Articular cartilage
Articular cartilage is a highly specialized and complex connective tissue consisting in chondrocytes embedded in a dense ECM mainly composed by collagen type II (COL2) fibrils intertwined with proteoglycans—i.e., a core protein with covalently attached glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) (Sophia Fox et al., 2009). The cartilage tissue exhibits a multilayered gradient structure, where each distinct zone—superficial, middle, and deep—possesses unique characteristics tailored to its functional role (Gu et al., 2023). The superficial zone contains a high density of flattened chondrocytes, high water content, and an ECM rich in COL2 fibers arranged parallel to the surface, resulting in a smooth surface for reducing friction and high tensile strength to withstand shear forces. The middle zone contains rounded chondrocytes that are more sparsely distributed. Its ECM has a lower collagen concentration, with fibers that are organized in a more random orientation, and a higher proportion of proteoglycans, contributing to its ability to absorb compressive forces. Finally, the deep zone is characterized by the lowest chondrocyte density and water concentration. Here, the ECM is dominated by vertically aligned collagen fibers and a high concentration of proteoglycans, responsible for the tissue’s resistance to compressive loads.
Articular cartilage tissue has been shown to regulate its own metabolism through physical phenomena, namely, through physical interactions (electrical or mechanical signals) between the resident cells (chondrocytes and cartilage progenitor cells) and the surrounding ECM (Guilak et al., 2009). Such physical signals can induce and act synergistically with biochemical signals to modulate cartilage tissue formation and maintenance (Mow et al., 1999). In fact, such observations have motivated the combination of dynamic mechanical loading with chondrogenic growth factors (e.g., TGF-β) to promote cartilage ECM biosynthesis towards improved tissue engineering strategies (Mauck et al., 2003).
The electrical properties of the cartilage tissue arise from the flow of free cations—such as K+, Ca2+, and Na+—interacting with the fixed negative charges present on the carboxyl and sulfate groups attached to the main cartilage GAGs (i.e., chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid). This interaction creates a dynamic environment where ions flow and diffuse, generating electrical phenomena such as diffusion and Donnan potentials (Farooqi et al., 2019; Miguel et al., 2022). Due to the high presence of COL2 fibers in its composition, cartilage also exhibits piezoelectric features, with a reported piezoelectric charge coefficient between 0.2 and 0.7 pC/N (Kapat et al., 2020). In comparison to bone, cartilage has a lower piezoelectric coefficient, possibly due to differences in the structure of the different collagen types as well as in the tissues’ dielectric properties (Denning et al., 2014). Notably, as in bone, the piezoelectricity of cartilage is crucial for the tissue’s maintenance and function. When cartilage is exposed to mechanical stress, the endogenous electrical signals generated by the COL2 fibers trigger key processes such as cell growth, differentiation and ECM production, thus promoting the tissue’s regeneration and mechanical performance (Poillot et al., 2021; Barbosa et al., 2022).
3 PEMF stimulators
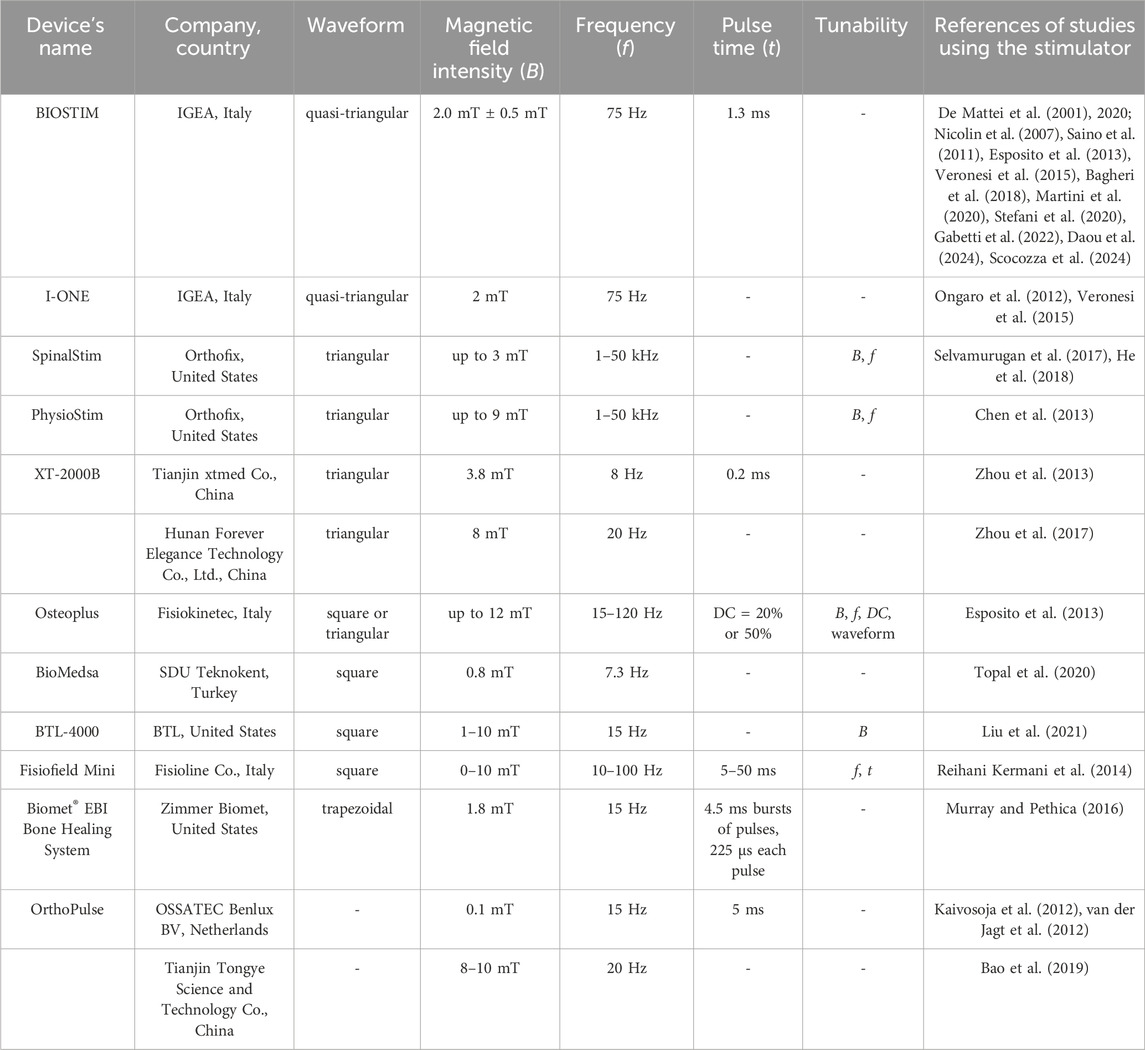
Several PEMF stimulators, both commercially available and custom-made, were used in the reported studies. In general, a PEMF device consists of a power supply connected to a single solenoid or a pair of Helmholtz’s coils (Figure 1A). In Figures 1B–D are reported examples of PEMF systems for stimulating 2D and 3D cell culture and animal models, respectively. According to Ampere’s law, these coils generate a time-varying electromagnetic field when powered with alternating current. By controlling the current that flows through the coils, a variety of PEMF stimulation waveforms can be generated, including triangular, square, sinusoidal, and trapezoidal waveforms (Hu et al., 2020). Just few PEMF stimulators are tunable in terms of magnetic field intensity (B), frequency (f), duty cycle (DC), pulse time (t), and/or waveform. In particular, the majority of the commercial devices (listed in Table 2) deliver a triangular or quasi-triangular waveform, with magnetic field intensity and frequency values varying, depending on the device, from 1.5 to 12 mT and from 8 Hz to 50 kHz, respectively. Some devices, such as the OrthoPulse (OSSATEC Benlux, Netherlands) and a stimulator by Tianjin Tongye (China), do not provide information about the waveform. It is noteworthy that the Biomet EBI Bone Healing System (Zimmer Biomet, United States), which was the first device obtaining the FDA pre-market approval in 1979 (at the time under the name Bio Osteogen System 204) (Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation Devices Panel, 2020), employs the sinusoidal waveform. The heterogeneity among available PEMF stimulators complicates direct comparisons of outcomes, making challenging to draw definitive conclusions or to establish consistent correlations between specific PEMF settings and their biological effects across different studies.
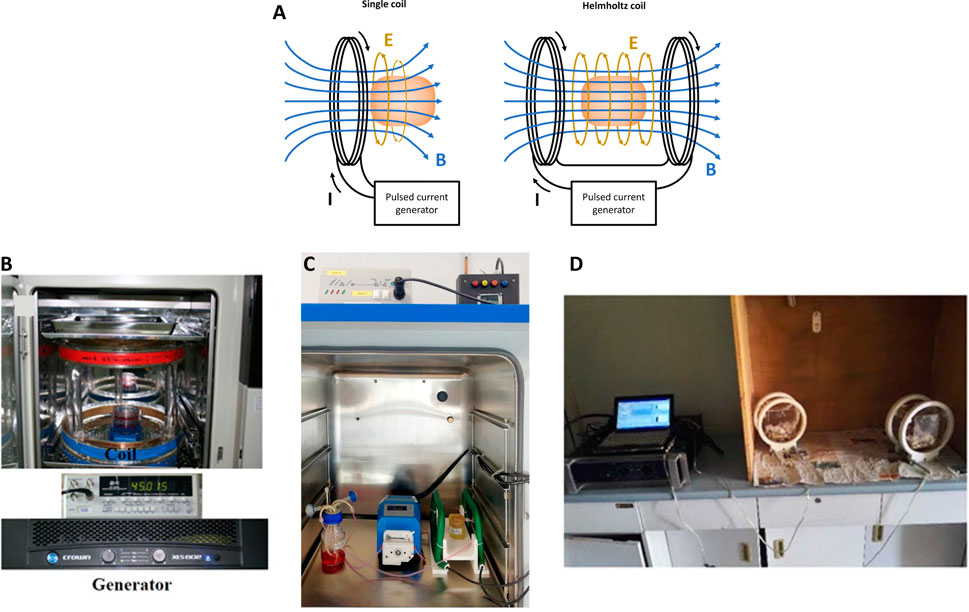
Figure 1. (A) Schematic representation of a general PEMF stimulator, composed of a single coil or a pair of Helmholtz’s coils; (B) Example of PEMF stimulation of 2D in vitro culture with custom-made device. Reproduced with permission from Kim et al, J Orthop Res. 39,8 (2021). Copyright 2020 Authors, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license; (C) Example of PEMF stimulation of 3D in vitro culture with IGEA BIOSTIM device. Reproduced with permission from Gabetti et al., Sci. Rep. 12, 13,859 (2022). Copyright 2022 Authors, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license; (D) Example of PEMF stimulation of in vivo culture with custom-made device. Reproduced with permission from Lei et al., Sci. Rep. 7,1 553 (2017). Copyright 2017 Authors, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
4 Quantitative descriptor for comparing PEMF stimulation protocols
To address the challenge of comparing PEMF stimulation protocols and biological outcomes obtained using different PEMF stimulators and applying different operating parameters, we propose the use of a dedicated quantitative descriptor. The specifically developed descriptor is the PEMF dose, a comprehensive metric that integrates the magnetic field intensity, the stimulation waveform, and the exposure duration to the magnetic field. In detail, we calculated the PEMF dose (D), expressed in mT⋅h, as in Equation 1:
where Brms is the root mean square value of the magnetic field intensity (in mT), and texp is the total exposure duration (in h) to the PEMF stimulation. For the different stimulation waveforms, Brms was calculated from the peak amplitude of the magnetic field intensity (Bpeak) and the duty-cycle (DC), i.e., the fraction over one period of stimulation during which the stimulation is active, as shown in Table 3. Due to the variety of stimulating setups, for each study the DC was specifically calculated based on the reported PEMF waveform parameters.
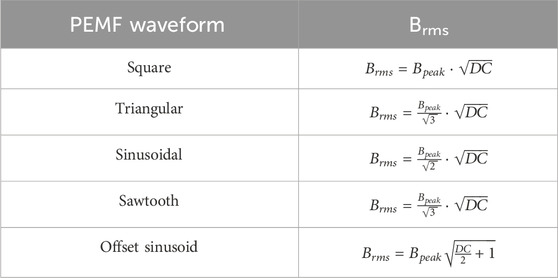
Table 3. Formulas adopted for the calculation of Brms depending on the waveform. Bpeak is the peak intensity of the PEMF waveform, DC is the waveform duty cycle.
The texp was calculated as in Equation 2:
where EDday is the daily exposure duration to the PEMF stimulation (h/day), EDweek is the number of days of the week in which PEMF stimulation is applied (day/week), and nweek is the duration of the experiment expressed in weeks.
In Sections 5, 6, the PEMF dose has been calculated only for the studies that provided all the parameters needed for the evaluation (Bpeak, waveform, DC, texp) while excluding the studies that did not provide information on the complete parameter set. The results are presented in Brms–D graphs. This visualization enables to appreciate the various PEMF stimulation protocols adopted, highlighting the contribution of the combined PEMF parameters (Brms) with respect to the total delivered stimulation (D). This method enabled a quantitative comparison of the effects of PEMF stimulation on bone and cartilage tissues for both in vitro and in vivo studies.
In addition, for visually representing and using the PEMF dose descriptor, we propose a log-log graph of Brms versus texp, where isolines of constant D values appear as straight lines (Figure 2). Since the operating parameters of PEMF stimulators typically fall within a specific range of Brms values, this graph enables the extraction of the corresponding texp value needed to achieve a target D value. Practically, starting from the Brms value of the selected PEMF stimulator and tracing a horizontal line to intersect the desired D isoline, the corresponding texp value is extracted by drawing a vertical line downward to the texp–axis, yielding the exposure duration required to deliver the target dose (Figure 2).
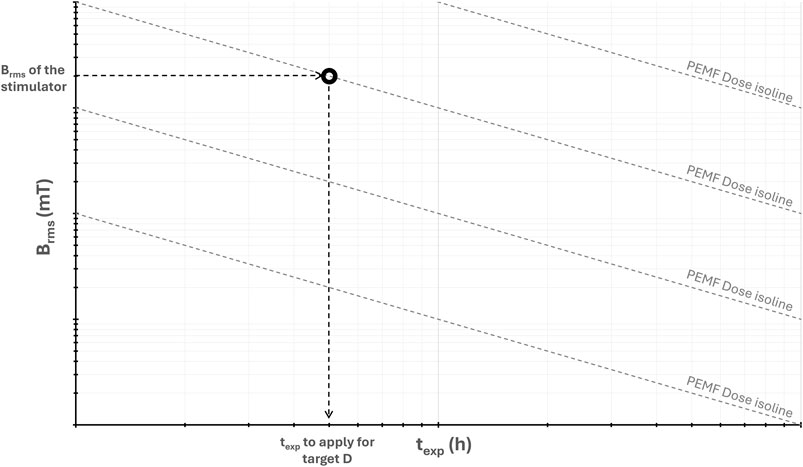
Figure 2. Log-log graph of the root mean square value of the magnetic field intensity (Brms) versus the total exposure duration (texp), showing isolines of constant PEMF dose (D) and the procedure for extracting the value of texp for achieving the desired D value.
5 In vitro PEMF studies
Over the past few decades, numerous in vitro experiments have been conducted on bone and cartilage cells, as well as on 3D tissue models, to investigate the effects of PEMF stimulation and the associated activation of signaling pathways. In the following sections, these studies are presented based on the specific type of tissue stimulated.
5.1 Bone
For investigating the effects of PEMF stimulation on bone stem cells, differentiated cells, or even 3D constructs, the literature reports a wide range of values for each PEMF stimulation parameter. In particular, magnetic field intensity (B) values ranging from 0.1 to 20 mT and frequency (f) values ranging from 0.2 to 150 Hz were used, with variations in pulse time (t), duty cycle (DC), and waveform types (see Table 4).
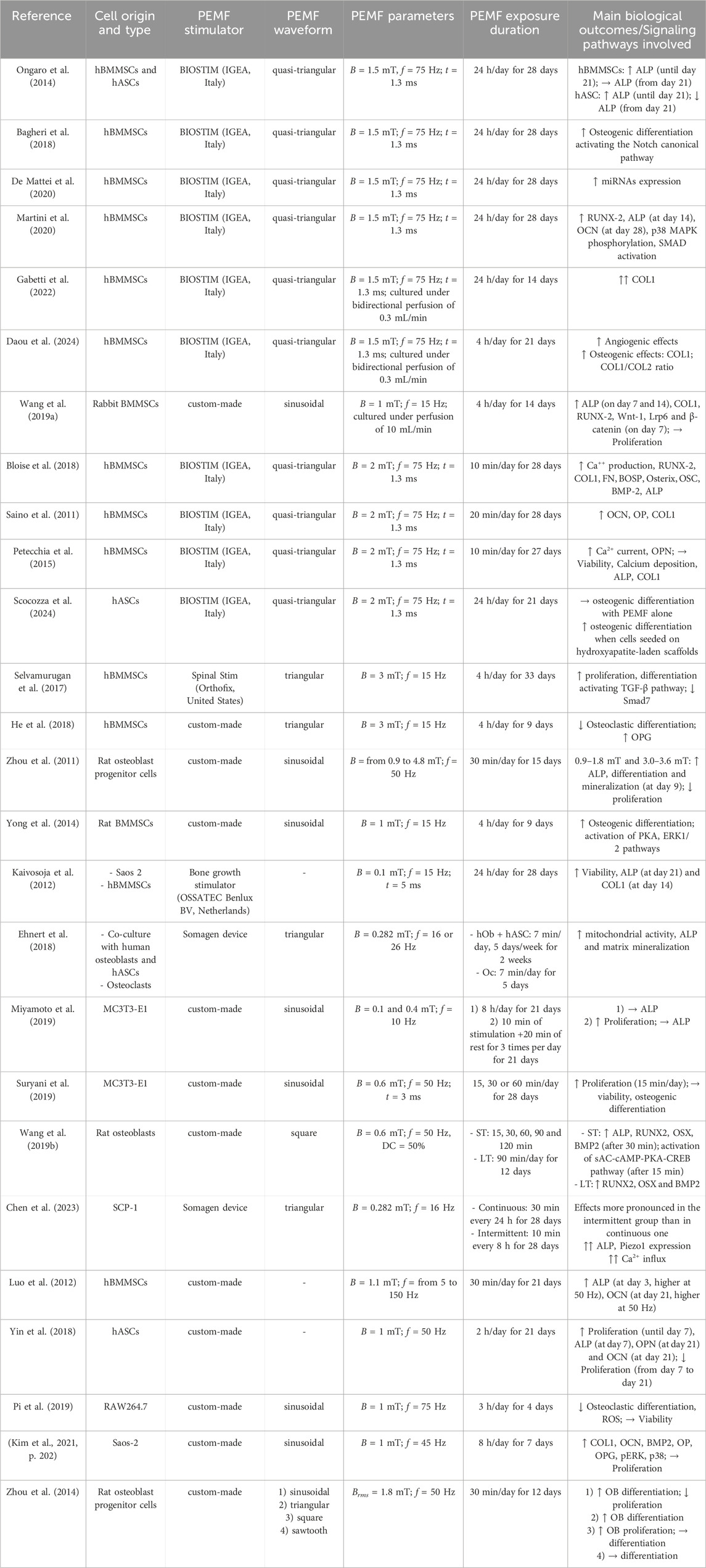
Several researchers adopted a specific PEMF parameter combination (B = 1.5 mT, f = 75 Hz, t = 1.3 ms, and a quasi-triangular waveform), which can be obtained using the commercially available PEMF stimulator BIOSTIM (IGEA, Italy). These studies demonstrated that exposing hBMMSCs to this PEMF protocol effectively promoted their commitment to the osteogenic lineage (Ongaro et al., 2014; Bagheri et al., 2018; De Mattei et al., 2020; Martini et al., 2020; Gabetti et al., 2022; Daou et al., 2024). Adopting the same protocol, monolayers of hBMMSCs and human adipose-derived stem/stromal cells (hASCs) exposed to PEMF for 24 h/day over 28 days resulted in an increase in alkaline phosphatase (ALP) expression until day 21. Subsequently, ALP levels remained stable in hBMMSCs but decreased in hASCs (Ongaro et al., 2014). Martini and colleagues later demonstrated that ALP expression peaked at day 14, accompanied by increased expression of runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) and osteocalcin (OCN) genes. In addition, the same PEMF protocol was shown to activate the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway, leading to increased expression of the receptors ALK2, phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), and activation of Smad 1/5/8, a transcription factor closely associated with the BMP2 pathway (Martini et al., 2020). In addition, it was demonstrated that this PEMF parameter combination applied on hBMMSCs modulated the Notch genes involved in osteogenic differentiation, and increased microRNA and the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression, which are both essential for promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis (Bagheri et al., 2018; De Mattei et al., 2020). To explore the effects of PEMF stimulation on a more realistic model, some of the authors used the same PEMF protocol, (for 24 h/day over 14 days) for stimulating a 3D construct consisting of a porous scaffold seeded with hBMMSCs and cultured within a perfusion bioreactor. The combination of PEMF stimulation and bi-directional direct perfusion, this latter providing physiological shear stress stimuli, resulted in a synergistic effect, with enhanced expression of COL1, ALP, and RUNX2 (Gabetti et al., 2022), in accordance with (Wang H. et al., 2019). Using the same bioreactor and PEMF stimulation set-up, Daou and colleagues demonstrated through transcriptomics analysis that PEMF stimulation promoted the expressions of angiogenesis and osteogenesis upstream regulators and activated immune response pathways, effectively replicating in vitro the dynamic interplay of biological processes developing during bone healing (Daou et al., 2024). Imposing the same frequency, pulse time, and waveform, but increasing the magnetic field intensity (2 mT), comparable effects on hBMMSCs were observed. In particular, calcium production and the expression of genes such as OCN, osteopontin (OP), COL1, RUNX2, fibronectin (FN), bone sialoprotein (BOSP), osterix (OSX), BMP2, and ALP increased after 28 days of PEMF stimulation for either 10 min/day (Bloise et al., 2018) or 20 min/day (Saino et al., 2011). Interestingly, despite using the same PEMF protocol, two studies reported no changes in calcium deposition, ALP, or COL1 expression (Petecchia et al., 2015; Scocozza et al., 2024).
Besides the differentiation of hBMMSCs toward osteoblasts, it was also demonstrated that imposing a specific PEMF stimulation (B = 3 mT, f = 15 Hz, triangular waveform) may reduce osteoclastic differentiation (Selvamurugan et al., 2017; He et al., 2018). Optimal ALP expression and mineralization were also observed in rat osteoblast progenitor cells imposing B = 3.0–3.6 mT (Zhou et al., 2011). Although characterized by a lower magnetic field intensity, the PEMF stimulation protocol (B = 1 mT, f = 15 Hz, sinusoidal waveform, for 4 h/day) applied on rat BMMSCs activated, after 9 days, osteogenic pathways, including MEK/ERK and PKA-ERK1/2 pathways (Song et al., 2014; Yong et al., 2014). For lower magnetic field intensity values (0.1–0.6 mT), there is no agreement regarding the efficacy for osteogenic differentiation (Kaivosoja et al., 2012; Ehnert et al., 2018; Miyamoto et al., 2019; Suryani et al., 2019; Wang Y. et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2023). Concerning the frequency parameter, the cell osteogenic differentiation has been promoted when compared to a non-stimulated control when similar PEMF intensities (1–1.1 mT) were applied, despite different frequency values (45, 50, or 75 Hz) (Luo et al., 2012; Yin et al., 2018; Pi et al., 2019; Kim et al., 2021).
Interestingly, Zhou and colleagues demonstrated that cell proliferation can be affected by PEMF stimulation by varying the waveform type. Imposing a specific PEMF stimulation protocol (Brms = 1.8 mT, f = 50 Hz) with a sinusoidal waveform, the proliferation of rat osteoblast progenitor cells was observed to decrease in favor of differentiation, while using a square waveform the cell proliferation was enhanced (Zhou et al., 2014). These findings were partially confirmed by two further studies, where PEMF stimulation at B = 1 mT with sinusoidal waveforms at different frequencies (f = 15 and 45 Hz, respectively) were applied, without significant changes in proliferation rates during the experimental time (Wang H. et al., 2019; Kim et al., 2021). Additionally, a triangular waveform has been shown to promote the proliferation of bone progenitor cells (Selvamurugan et al., 2017; Miyamoto et al., 2019).
In summary, although the high variability in operating parameters, it is interesting to note that PEMF stimulation applied on bone stem cells generally induces osteogenic differentiation, which is associated with the activation of various signaling pathways. These pathways are known to be closely linked with the expression of specific osteogenic markers. In detail, the reviewed studies indicate that PEMF affects adenosine receptors and calcium channels which play a key role in the activation and mediation of the downstream osteogenic effects. In fact, PEMF stimulation enhances the expression and activity of adenosine A2A/A3 receptors on MSCs and osteoblasts, which are key resident cells involved in bone remodeling. The activation of A2A/A3 receptors triggers the sAC-cAMP-PKA-CREB pathway, which promotes the expression of the osteogenic transcription factors osterix (OSX) and RUNX2, which in turn enhance the synthesis of bone ECM proteins (e.g., osteocalcin and collagen type I) while suppressing the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, both favoring bone formation (Kar et al., 2021). In addition, PEMF enhances the levels of intracellular calcium ions by the modulation of two types of calcium channels, voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs) and store-operated calcium channels (SOCs). Then, the elevated calcium levels trigger both the MAPK/ERK, Wnt/β-catenin, and Calmodulin/CaMK pathways, all of which are known to enhance ALP activity, osteoblast proliferation, MSC osteogenic differentiation and ECM mineralization (Gavazzo et al., 2021). Furthermore, as also recently reported by Kaadan and colleagues (Kaadan et al., 2024) PEMF stimulation activates the Notch canonical, MAPK-ERK1/2, Wnt, mTOR, and sAC-cAMP-PKA-CREB pathways (Supplementary Table S1), which play a pivotal role in bone formation. The synthesis of ECM proteins is also enhanced by various activated growth factors, including IGF and TGF-β. Concurrently, PEMF stimulation inhibits osteoclastogenesis initiated by RANK pathways, thereby reducing the rate of bone resorption.
5.2 Quantitative comparison among in vitro studies on PEMF stimulation for bone tissue
Figure 3 shows the distribution of the root mean square values of the magnetic field intensity (Brms) and the PEMF dose (D) values (in logarithmic scale) for some of the in vitro studies performed imposing PEMF stimulation on bone cells or constructs and described in the previous section. The distribution reflects the wide range of parameters and exposure durations that were adopted, resulting in PEMF dose values ranging from 10–2 to 2⋅102 mT·h.
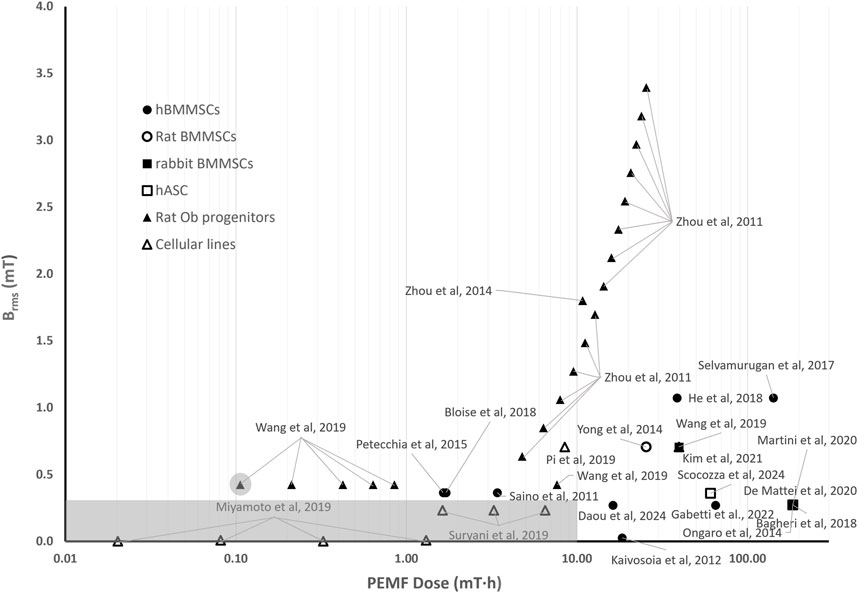
Figure 3. Distribution of the root mean square value of the magnetic field intensity (Brms) and the PEMF dose (D) value for the in vitro studies performed imposing PEMF stimulation on bone cells/tissues. The grey rectangle represents the threshold region for the Brms and D values, within which the likelihood of observing an osteogenic effect induced by PEMF stimulation is lower. The different symbols refer to different cell types.
Interestingly, in studies where the applied Brms was below 0.3 mT and the resulting D value was less than 10 mT∙h (grey rectangle in Figure 3), a delay in ALP expression or even no ALP expression was observed. In detail, Miyamoto and colleagues, who exposed osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells to Brms values equal to 0.002 mT and 0.008 mT (f = 10 Hz) with D values ranging from 0.02 to 1.3 mT·h (Miyamoto et al., 2019), did not register any increase in ALP expression applying either a short term (30 min/day) or a long-term (8 h/day) exposure. Accordingly, Suryani et al., who applied to MC3T3-E1 cells a Brms value equal to 0.232 mT (f = 50 Hz) associated with PEMF dose values (D = 1.6, 3.2, 6.5 mT·h) lower than 10 mT∙h, did not observe increase in ALP expression for any of the applied exposure durations (Suryani et al., 2019). Overall, the results of different studies suggest that, when Brms values lower than 0.3 mT are adopted, it is fundamental to increase the delivered PEMF dose above 10 mT∙h for observing osteogenic behaviors. In particular, an increase in osteogenic markers after 21 days of stimulation when hBMMSCs were exposed to low-intensity PEMFs (Brms = 0.027 mT, f = 15 Hz) but with a total PEMF dose of 18.4 mT∙h was reported (Kaivosoja et al., 2012). Similarly, when a Brms value of 0.27 mT (f = 75 Hz) was applied, enhanced osteogenic differentiation was observed in both static monolayer cultures of hBMMSCs or hASCs, characterized by a PEMF dose of 184 mT∙h (Ongaro et al., 2014; Bagheri et al., 2018; De Mattei et al., 2020; Martini et al., 2020), as well as in hBMMSCs-seeded scaffolds cultured under perfusion with PEMF doses of 64.9 mT∙h (Gabetti et al., 2022) and 16.3 mT∙h (Daou et al., 2024).
Remarkably, for Brms values above 0.3 mT, intensity-dependent effects could not be observed, but from the literature studies analyzed it appears that a minimum value of PEMF dose should be delivered. Specifically, Wang and colleagues, who applied to rat osteoblasts a square PEMF waveform (B = 0.6 mT, f = 50 Hz, DC = 50%, varying the exposure from 15 to 120 min) resulting in Brms = 0.424 mT, found that the group exposed to 15 min of PEMF (corresponding to D = 0.11 mT∙h) did not show any significant differences in comparison to the untreated group. Differently, the experimental groups subjected to longer exposure durations, thus receiving higher PEMF doses (with D ranging from 0.21 to 7.64 mT∙h), reported increased osteogenic differentiation (Wang Y. et al., 2019). This was confirmed by Zhou et al. that exposed rat osteoblastic progenitor cells to sinusoidal PEMFs of different intensities (B = 0.9–4.8 mT, f = 50 Hz, for 30 min/day for 15 days) (Zhou et al., 2011), corresponding to Brms values ranging from 0.64 to 3.40 mT with PEMF dose values ranging from 4.77 to 25.46 mT∙h. All stimulation protocols promoted differentiation and mineralization of osteoblasts and increased osteogenesis-related gene expression (Zhou et al., 2011). Overall, in studies in which Brms values above 0.3 mT and D values equal or above 0.21 mT∙h were applied, the authors reported increased osteogenic differentiation (Saino et al., 2011; Ongaro et al., 2014; Yong et al., 2014; Petecchia et al., 2015; Selvamurugan et al., 2017; Bagheri et al., 2018; Bloise et al., 2018; De Mattei et al., 2020; Martini et al., 2020; Kim et al., 2021; Scocozza et al., 2024) or decreased osteoclastic differentiation (He et al., 2018; Pi et al., 2019) on a wide variety of cell types (Figure 3).
To sum up, the proposed quantitative comparison made it possible to deduce that, for low Brms values (<0.3 mT), the exposure duration plays a crucial role, as enhanced osteogenic differentiation was observed only when a PEMF dose above 10 mT∙h was reached. When higher magnetic field intensities (Brms ≥ 0.3 mT) are provided, the exposure duration becomes less relevant, although a minimum PEMF dose threshold (D ≥ 0.21 mT∙h) is required to induce osteogenic effects.
5.3 Cartilage
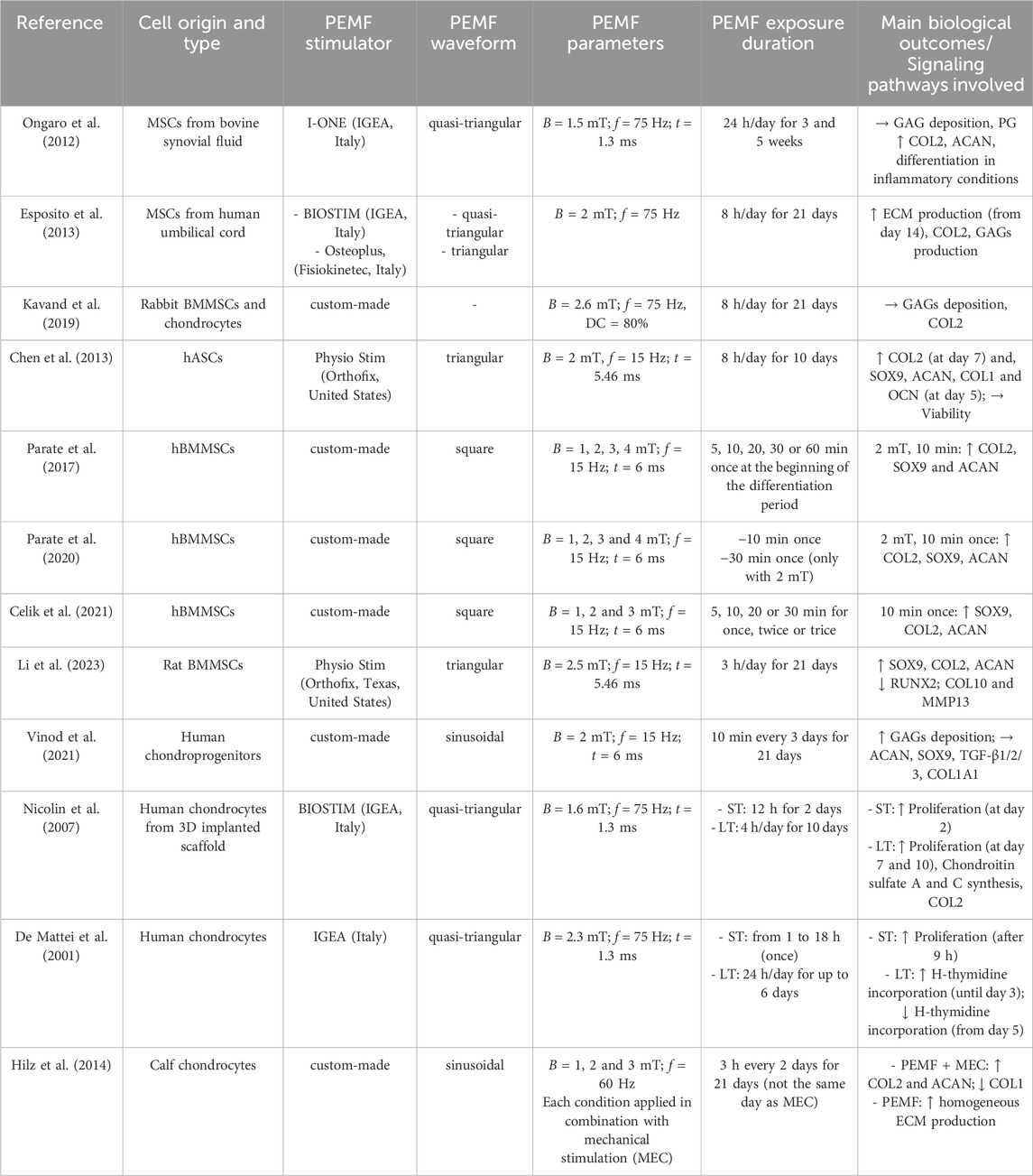
PEMF stimulation has recently gained attention also as a promising non-invasive treatment for enhancing the clinical outcome of cartilage repair procedures, showing both anti-inflammatory and chondrogenic effects on chondrocyte cultures (Ongaro et al., 2012; Varani et al., 2021). Analogously to PEMF studies for bone tissue, the stimulation parameters applied for investigating the PEMF effects on cartilage cells encompass a wide range of values, from 1 to 4 mT for the magnetic field intensity and from 15 to 75 Hz for the frequency (see Table 5). Moreover, different culture techniques have been employed, including the conventional monolayer culture method, the cultivation of cells as 3D pellets for mimicking the native cell condensation during chondrogenensis, and 3D cartilage constructs based on cell-seeded scaffolds. In particular, the application of PEMF stimulation (B = 1.5 mT, f = 75 Hz, quasi-triangular waveform, for 24 h/day) to 3D pellets of MSCs derived from bovine synovial fluid and treated with interleukin (IL-1β) resulted in an increase in COL2 and aggrecan (ACAN) gene expression after 5 weeks of treatment. This demonstrated the promotion of the MSCs chondrogenic differentiation even under inflammatory conditions (Ongaro et al., 2012). Similarly, PEMF treatment (B = 2 mT, f = 75 Hz, quasi-triangular waveform, for 8 h/day) applied to human umbilical cord derived MSCs was observed to significantly enhance COL2 expression, with no differences between the devices utilized (Esposito et al., 2013). Differently, stimulating 3D pellets of rabbit BMMSCs with a similar protocol (i.e., B = 1.8 mT, f = 75 Hz for 8 h/day) resulted in no changes in COL2 expression and GAGs production (Kavand et al., 2019). Concerning hASCs, Chen et al. observed that exposing 3D pellets to PEMF stimulation (B = 2 mT, f = 15 Hz, triangular waveform, for 8 h/day) led to an increase in the expression of transcription factor SOX9, ACAN, COL1, and OCN after 5 days and enhanced COL2 expression after 7 days of culture (Chen et al., 2013). Even shorter exposure durations (i.e., 3 h/day or 10 min applied once with B = 1–4 mT and f = 15 Hz, square waveform) could be sufficient to enhance the expression of COL2, SOX9, and ACAN genes in human (Parate et al., 2017; 2020; Celik et al., 2021) and rat BMMSCs (Li et al., 2023). However, the application of PEMF stimulation (B = 2 mT, f = 15 Hz, sinusoidal waveform) to chondroprogenitors harvested from non-diseased human knee joints for 10 min every 3 days over a period of 21 days did not result in any significant increase in the expression of chondrogenic markers (Vinod et al., 2021). This discrepancy could be attributed to differences in experimental protocols, such as the cell type, the duration and frequency of stimulation, or the specific waveform adopted. Applying a different stimulation protocol (B = 1.6 mT, f = 75 Hz, sinusoidal waveform) for 4 h/day for 10 days to human matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation (MACI)-derived cells, it was shown that cell proliferation could be increased until day 7, as well as the synthesis of COL2 (Nicolin et al., 2007). Similarly, De Mattei and colleagues demonstrated that for increasing the proliferation rate of human articular chondrocytes at least 9 h of PEMF stimulation (B = 2.3 mT, f = 75 Hz, quasi-triangular waveform) are necessary. Moreover, they observed that PEMF can induce cell proliferation of low density chondrocyte cultures for a long time (6 days) only when fresh serum is added again in the culture medium. In other words, the PEMF exposure seemed to accelerate the consumption of growth factors and therefore the proliferation rate (De Mattei et al., 2001). Finally, Hilz et al. demonstrated that exposing 3D cartilage constructs, based on polyurethane scaffolds seeded with articular chondrocytes from bovine fetlock joints, to combined PEMF stimulation (B = 1–3 mT, f = 60 Hz, sinusoidal waveform, for 3 h every 2 days) and mechanical stimulation led to higher levels of GAG content and COL2, cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP), SOX9, proteoglycan-4 (PRG-4) and matrix metalloproteinase 3 and 13 (MMP-3 and 13) expressions in comparison to PEMF stimulation alone (Hilz et al., 2014).
Briefly, several studies demonstrated that PEMF may have beneficial influence for cartilage regeneration, particularly promoting the differentiation of stem cells towards chondrocytes, enhancing the expression of COL2, SOX9, ACAN genes, and increasing the production and deposition of GAGs, as well as the synthesis of cartilage-like ECM through adenosine receptors.
5.4 Quantitative comparison among in vitro studies on PEMF stimulation for cartilage tissue
Similarly to what was reported for the in vitro studies on bone cells, the wide PEMF parameter variation that characterize the in vitro studies for cartilage tissue results in Brms values ranging from 0.25 to 2.1 mT and D values ranging from 2∙10–2 to 3∙102 mT·h (Figure 4). Depending on the stimulated cells and on the combinations of Brms and D values, different responses can be observed. In particular, the study conducted by De Mattei and co-workers, who subjected chondrocytes to PEMF (B = 2.3 mT, f = 75 Hz) resulting in Brms value equal to 0.42 mT, led to chondrocyte proliferation imposing either 18 h (D = 7.56 mT∙h) or 6 days (D = 60.47 mT·h) of exposure duration (De Mattei et al., 2001). Increased chondrocyte proliferation was also observed when imposing a lower intensity PEMF stimulation (B = 1.6 mT, f = 75 Hz) (Nicolin et al., 2007), resulting in a Brms value equal to 0.29 mT and D values ranging from 3.51 to 8.18 mT·h. These findings suggest that Brms values equal to or greater than 0.3 mT associated with D values above 3.5 mT·h could be effective for inducing the proliferation of chondrocytes. Further studies exposing different types of stem cells to PEMF stimulation with Brms values above 0.25 mT and D values higher than 26.02 mT∙h demonstrated increased chondrogenic differentiation (Ongaro et al., 2012; Chen et al., 2013; Esposito et al., 2013; Li et al., 2023).
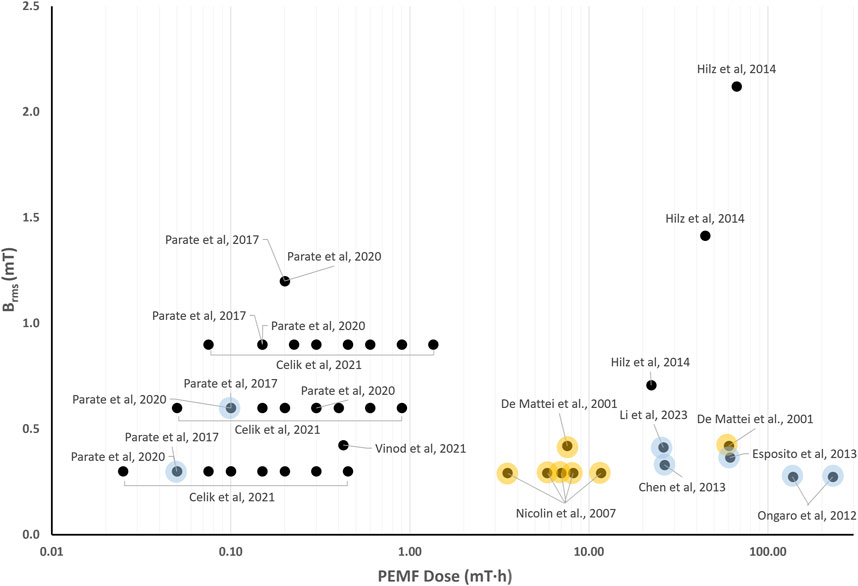
Figure 4. Distribution of the root mean square value of the magnetic field intensity (Brms) and the PEMF dose (D) value for the in vitro studies performed imposing PEMF stimulation on cartilage cells/tissues. The colored dots refer to studies reporting enhanced chondrocyte proliferation (yellow dots) or promoted chondrogenic differentiation (light blue dots).
In contrast, for D values below 3.5 mT∙h, no clear relationship between PEMF parameters and biological effects could be established. Recently, hBMMSCs were exposed to square PEMF waveform varying the intensity (B = 1–4 mT, f = 15 Hz) and the exposure duration (from 5 to 60 min). Chondrogenic differentiation was obtained only when B = 2 mT for 10 min was applied (Parate et al., 2017; 2020), corresponding to Brms = 0.6 mT and D = 0.1 mT·h. However, in a subsequent study, the same combination applied to the same cell type proved ineffective, with chondrogenic differentiation observed only when B = 1 mT was imposed for 10 min (Celik et al., 2021), resulting in Brms = 0.3 mT and D = 0.007 mT·h. In case of chondroprogenitors, exposed to a sinusoidal PEMF waveform (B = 2 mT, f = 15 Hz) resulting in Brms = 0.424 mT and D = 0.424 mT·h, no effects on chondrogenic differentiation were detected (Vinod et al., 2021).
Overall, the quantitative comparison of in vitro studies applying PEMF stimulation to cartilage cells indicates that the exposure duration might be a crucial parameter, indeed increased chondrocyte proliferation was observed when applying D above 3.5 mT∙h and enhanced chondrogenic differentiation when applying D above 26.02 mT∙h. When lower PEMF doses were provided, the available studies reported different combinations of parameters for chondrogenic differentiation.
6 In vivo animal studies
The effects of PEMF stimulation on bone, cartilage, and osteochondral tissues have also been widely investigated in vivo through a considerable number of animal studies. The studies involved the use of a great variety of models, which differ for the investigated pathology (i.e., fracture healing, osteoporosis, bone resorption, and OA), for the selected animal (i.e., mice, rats, rabbits, guinea pigs, and dogs), and for the technique used to induce pathological conditions. Animals have been subjected to PEMF stimulation using either commercially available devices or custom-made setups, and, depending on the animal’s size, the stimulation was applied to a specific body district or to the whole body. The following sections recapitulate the main findings, depending on the specific type of tissue stimulated.
6.1 Bone
Analogously to in vitro studies, the in vivo investigation of the effects of PEMF stimulation on bone tissue also shows variations in the applied PEMF parameters among the studies, with magnetic field intensity ranging from 0.1 to 12.4 mT and frequency ranging from 1 to 100 Hz (see details in Table 6).
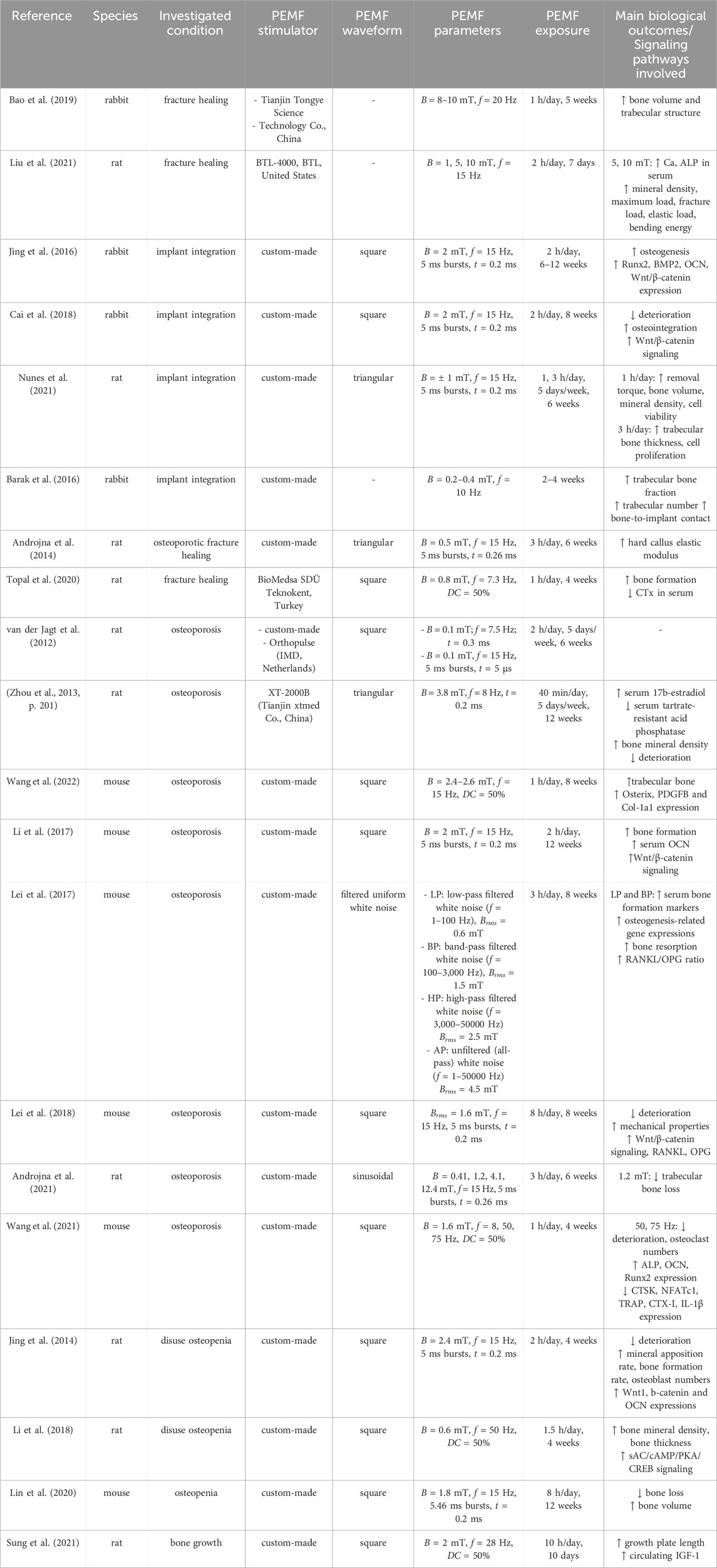
As regards the treatment of bone fractures, in 1974 Bassett and Pawluk conducted the first pioneering study, in which pulsing electromagnetic fields have been inductively coupled to dog bone, resulting in improved organization and increased strength of the repaired tissue after fracture (Andrew et al., 1974). Subsequent experiments further validated these findings (Bassett et al., 1977; 1978), ultimately leading in 1979 to the first pre-market approval by the FDA for a PEMF stimulator designed for fracture healing (Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation Devices Panel, 2020). This milestone spurred extensive development of PEMF devices and broadened the clinical application of PEMF stimulation for treating fracture healing. More recently, Bao et al. explored the so-called combined magnetic field (CMF) stimulation, combining static magnetic field and PEMF stimulations. In detail, they implanted intramedullary magnets in rabbit femurs to treat osteotomies and then exposed the animals to PEMF stimulation (B = 8–10 mT, f = 20 Hz, for 1 h/day) for 5 weeks. The CMF group exhibited increased bone volume and improved trabecular structure, at faster rates, in comparison to both the control and the PEMF-only treated groups (Bao et al., 2019). In 2021, Liu et al. investigated the effect of different intensities of PEMF stimulation (B = 1, 5, 10 mT), on rats with osteotomized femurs, showing that higher magnetic field intensity values led to better regeneration outcomes. Namely, rats that received 5 and 10 mT pulses presented higher release of Ca and ALP in the serum, as well as increased bone density, maximum load, fracture load, elastic load, and bending energy of the callus compared to rats exposed to 1 mT (Liu et al., 2021).
Recently, PEMF stimulation has also been explored as a potential adjuvant therapy to enhance implant osseointegration. In case of rabbit bone defects treated with titanium implants, it was reported that PEMF stimulation (B = 2 mT, f = 15 Hz, square waveform, for 2 h/day for either 6 or 12 weeks) resulted in enhanced bone formation around the implants and upregulated gene expressions in the femoral region, including RUNX2, BMP2, OCN, and Wnt/β-catenin signaling (Jing et al., 2016). In a subsequent study, the same PEMF protocol was delivered for 8 weeks to rabbits with type 1 diabetes and porous titanium implants. The PEMF stimulation mitigated bone deterioration and promoted both osseointegration and bone ingrowth into implant pores, reducing bone loss by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling (Cai et al., 2018). Concerning the stability of the implant, Nunes et al. tested on rats with titanium implants the effects of two different PEMF exposure regimens (1 and 3 h/day, B = ± 1 mT, f = 15 Hz, triangular waveform). A peculiar dependence on the exposure duration was observed, as 1 h/day resulted in better outcomes in removal torque tests, bone volume and mineral density, cell viability, total protein content, and mineralization nodules in comparison to the 3 h/day regimen, while this latter protocol yielded higher trabecular bone thickness and cell proliferation (Nunes et al., 2021). Adopting a different approach, Barak and co-workers developed a miniaturized PEMF stimulator embedded in a commercially available dental implant, which was implanted in rabbit tibiae. Already after 2 weeks of continuous exposure (B = 0.2–0.4 mT, f = 10 Hz), test implants showed a significantly higher trabecular bone fraction, enhanced connectivity, and higher bone-to-implant contact as compared to the control group (Barak et al., 2016).
Over the past decade, researchers have also focused on exploring the potential of PEMF stimulation as a treatment for osteoporosis, for which mice or rats have been used as animal models suitable for delivering whole-body treatments. Regarding osteoporotic fractures, in 2014, Androjna and co-workers performed fibular osteotomies on female rats with osteopenia and subjected them to PEMF treatment (B = 0.5 mT, f = 15 Hz, triangular waveform, for 3 h/day over 6 weeks), observing increased elastic modulus of the hard callus across fibula fractures (Androjna et al., 2014). Moreover, PEMF treatment (B = 0.8 mT, f = 7.3 Hz, square waveform, for 1 h/day for 28 days) increased new bone formation and reduced bone degradation markers in rats with heparin-induced osteoporosis (Topal et al., 2020). Concerning the direct treatment of osteoporosis, Van der Jagt et al. did not observe significant differences in female rats with ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis when exposing them to different PEMF stimulations (B = 0.1 mT, f = 15 or 7.5 Hz, t = 0.3 or 5 ms burst, square waveform, for 2 h/day for 5 days/week over 6 weeks) in comparison to unstimulated controls (van der Jagt et al., 2012). However, adopting the same animal model but using different PEMF parameters with higher B values (i.e., B = 3.8 mT (Zhou et al., 2013); B = 2.4–2.6 mT (Wang et al., 2022)), significant improvements were observed in bone mineral density, trabecular bone amount, serum 17β-estradiol levels, and inhibition of bone microarchitecture deterioration. Recently, the application of PEMF (B = 2 mT, f = 15 Hz, square waveform, for 3 h/day) on diabetic osteoporotic mice was demonstrated to enhance bone formation through upregulation of osteoblastogenesis-related genes via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, while no significant effects on osteoclastogenesis-related genes were observed (Li et al., 2017). Similarly, Lei and colleagues demonstrated that exposing ovariectomized mice to PEMF stimulation (B = 0.6 and 1.5 mT, f = 1–3,000 Hz, for 3 h/day over 8 weeks) significantly increased bone formation markers and osteogenic gene expression, while higher B values (B = 2.5 and 4.5 mT, f = 3,000–50,000 Hz) reduced these effects. Additional findings showed improved trabecular architecture and mechanical properties, with upregulation of Wnt/β-catenin, RANKL, and OPG, though the RANKL/OPG mRNA ratio remained unchanged (Lei et al., 2017; 2018). Further studies focused on the impact of different magnetic field intensity and frequency values. Namely, in 2021, Androjna and co-workers compared four different PEMF protocols (B = 0.41, 1.2, 4.1, and 12.4 mT, f = 15 Hz, sinusoidal waveform, for 3 h/day over 6 weeks) with the efficacy of the alendronate drug, used to prevent or treat osteoporosis. The authors found that PEMF stimulation with B = 1.2 mT was nearly as effective as alendronate in reducing trabecular bone loss. Moreover, PEMF with B = 1.2 mT and 4.1 mT altered lacuno-canalicular features, suggesting osteocyte sensitivity to PEMF (Androjna et al., 2021). In the same year, Wang et al. applied to ovariectomized mice PEMF stimulation (B = 1.6 mT, square waveform, for 1 h/day over 4 weeks) at different frequencies (f = 8, 50, 75 Hz). At high frequencies (i.e., 50 and 75 Hz), they observed improved bone microarchitecture, decreased osteoclast numbers, promoted osteoblast-related gene expression (ALP, OCN, RUNX2), and inhibited osteoclast-related genes (CTSK, NFATc1, TRAP) and bone resorption markers like CTX-I and IL-1β (Wang et al., 2021).
Since osteopenia and osteoporosis can also result from disuse conditions, such as prolonged bed rest, immobilization after injury, or exposure to altered gravity in space travel, the potential of PEMF stimulation as a treatment for bone loss was investigated. In 2014, Jing et al. revealed that applying PEMF stimulation (B = 2.4 mT, f = 15 Hz, square waveform, for 2 h/day over 4 weeks) to hindlimb-unloaded rats prevented the deterioration of bone microarchitecture and promoted bone formation, with increased expression of Wnt1, β-catenin, and osteocalcin genes (Jing et al., 2014). Similarly, it was reported that PEMF treatment (B = 0.6 mT, f = 50 Hz, square waveform, for 1.5 h/day for 4 weeks) helped to maintain bone mineral density and cortical bone thickness in suspended rats, likely through activation of the sAC/cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway (Li et al., 2018). In 2020, Lin et al. induced disuse osteopenia in mice and then applied either PEMF stimulation (B = 1.8 mT, f = 15 Hz, square waveform, for 8 h/day over 12 weeks) or single-pulsed electromagnetic field (SPEMF) stimulation (B = 1 T, f = 0.2 Hz, asymmetrical half-sine waveform, for 3 min/day over 12 weeks). SPEMF significantly reversed bone loss as early as 6 weeks post-treatment, while PEMF reversed bone loss after 8 weeks, with a significant increase in bone volume for both groups in comparison to unstimulated mice (Lin et al., 2020). Finally, the effect of PEMF on bone growth without the presence of any altered condition was investigated by Sung et al., in 2021, exposing rats to PEMF stimulation (B = 2 mT, f = 28 Hz, square waveform, for 10 h/day along 10 days) and then analyzing the animals’ tibiae. In treated rats, the length of the growth plate resulted significantly higher, as well as the levels of circulating IGF-1 (Sung et al., 2021).
Overall, these studies suggest that PEMF can promote bone health by modulating osteogenesis and bone resorption pathways across various pathological conditions, including implant osseointegration, osteoporosis, and inactivity-related bone loss. However, the PEMF efficacy depends on specific parameters, emphasizing the need for further research to optimize therapeutic protocols.
6.2 Quantitative comparison among in vivo studies on PEMF stimulation for bone tissue
The in vivo investigations of the effects of PEMF stimulation on bone tissue report a wide range of PEMF stimulation parameters (B = 0.1–12.4 mT, f = 1–100 Hz), with studies lasting from 10 days to 12 weeks and exposure durations ranging from 40 min/day to 10 h/day. Therefore, this results in Brms values ranging from 0.005 to 4.5 mT and D values ranging from 2∙10–2–103 mT·h. Figure 5 shows the distribution of the Brms and D values for the in vivo experiments focusing on the use of PEMF for the treatment of pathological conditions related to osteoporosis, such as osteoporotic fractures, disuse osteopenia, and osteoporosis.
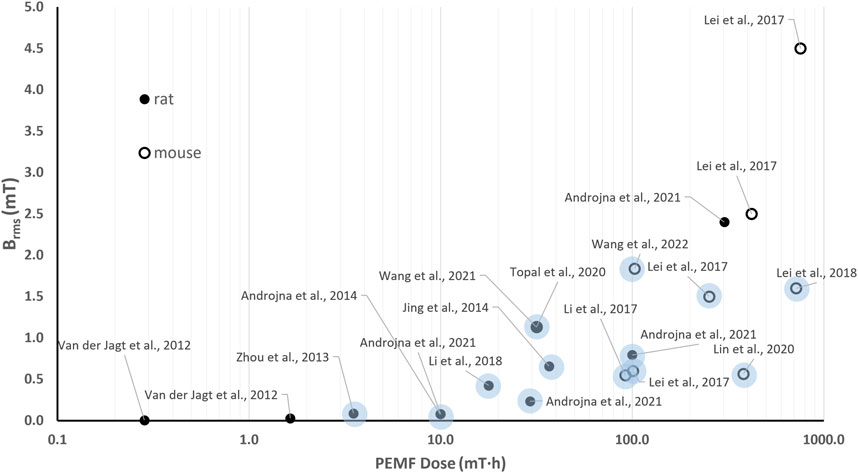
Figure 5. Distribution of the root mean square value of the magnetic field intensity (Brms) and the PEMF dose (D) value for the in vivo studies performed imposing PEMF stimulation on bone tissue. The light dots refer to studies reporting positive effects of PEMF stimulation on pathological conditions related to osteoporosis. The different symbols refer to different animal models.
Interestingly, regarding the use of PEMF for the treatment of osteoporosis-related pathologies, all the reported studies delivered whole-body PEMF stimulation to either rats or mice, enhancing the consistency of the proposed comparison. In particular, no significant PEMF effects were observed on rat osteoporotic bone when low-intensity PEMF (B = 0.1 mT) was imposed, corresponding to Brms values equal to 0.005 mT (f = 7.5 Hz, t = 0.3 ms) and 0.027 mT (f = 15 Hz, burst duration = 0.5 ms) for the two tested groups (van der Jagt et al., 2012). The received PEMF doses (D = 0.29 mT·h and D = 1.65 mT·h, respectively) proved insufficient to trigger a response. Adopting the same animal model, Zhou and co-workers applied a higher peak intensity (B = 3.8 mT, f = 8 Hz) and found positive effects of PEMF stimulation in terms of inhibited deterioration of bone microarchitecture (Zhou et al., 2013). Indeed, although the applied stimulation resulted in a low Brms value (0.088 mT), this was for a longer exposure duration, leading to a higher total PEMF dose equal to 3.51 mT·h. Two comparative studies, conducted independently in 2017 (Lei et al., 2017) and in 2021 (Androjna et al., 2021), offer further insights on the correlation between the applied Brms and D and the biological effects. In detail, Lei et al. subjected ovariectomized osteoporotic mice to 4 different PEMF stimulation protocols, based on uniform white noise filtered at different frequencies, for 3 h/day over 8 weeks. Interestingly, only two stimulation protocols, resulting in Brms values of 0.6 mT and 1.5 mT and PEMF dose values of 100.8 and 252 mT·h, respectively, significantly increased serum bone formation markers and osteogenesis-related gene expressions in comparison to controls. The other tested protocols, characterized by higher Brms and D values, did not prove as effective (Lei et al., 2017). In parallel, Androjna and co-workers compared four different PEMF protocols (B = 0.41, 1.2, 4.1, and 12.4 mT, f = 15 Hz, sinusoidal waveform, for 3 h/day over 6 weeks) with the efficacy of the alendronate drug (Androjna et al., 2021). The most effective protocols were characterized by Brms values equal to 0.23 and 0.79 mT and D values equal to 29.3 mT·h and 100 mT·h, respectively. The other protocols, characterized by the lowest Brms value (0.08 mT) and D equal to 10 mT·h or by the highest Brms value (2.4 mT) with D = 302.6 mT·h, were not effective.
Notably, most of the studies that reported positive effects of in vivo PEMF stimulation on pathological conditions related to osteoporosis (Jing et al., 2014; Li et al., 2017; Lei et al., 2018; Lin et al., 2020; Topal et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021) are characterized by Brms values lower than 1.84 mT and D values higher than 3.51 mT·h (light blue dots in Figure 5). When higher Brms values were provided, the corresponding protocols did not prove effective, regardless of the high PEMF dose associated (Lei et al., 2017; Androjna et al., 2021).
6.3 Cartilage and osteochondral tissue
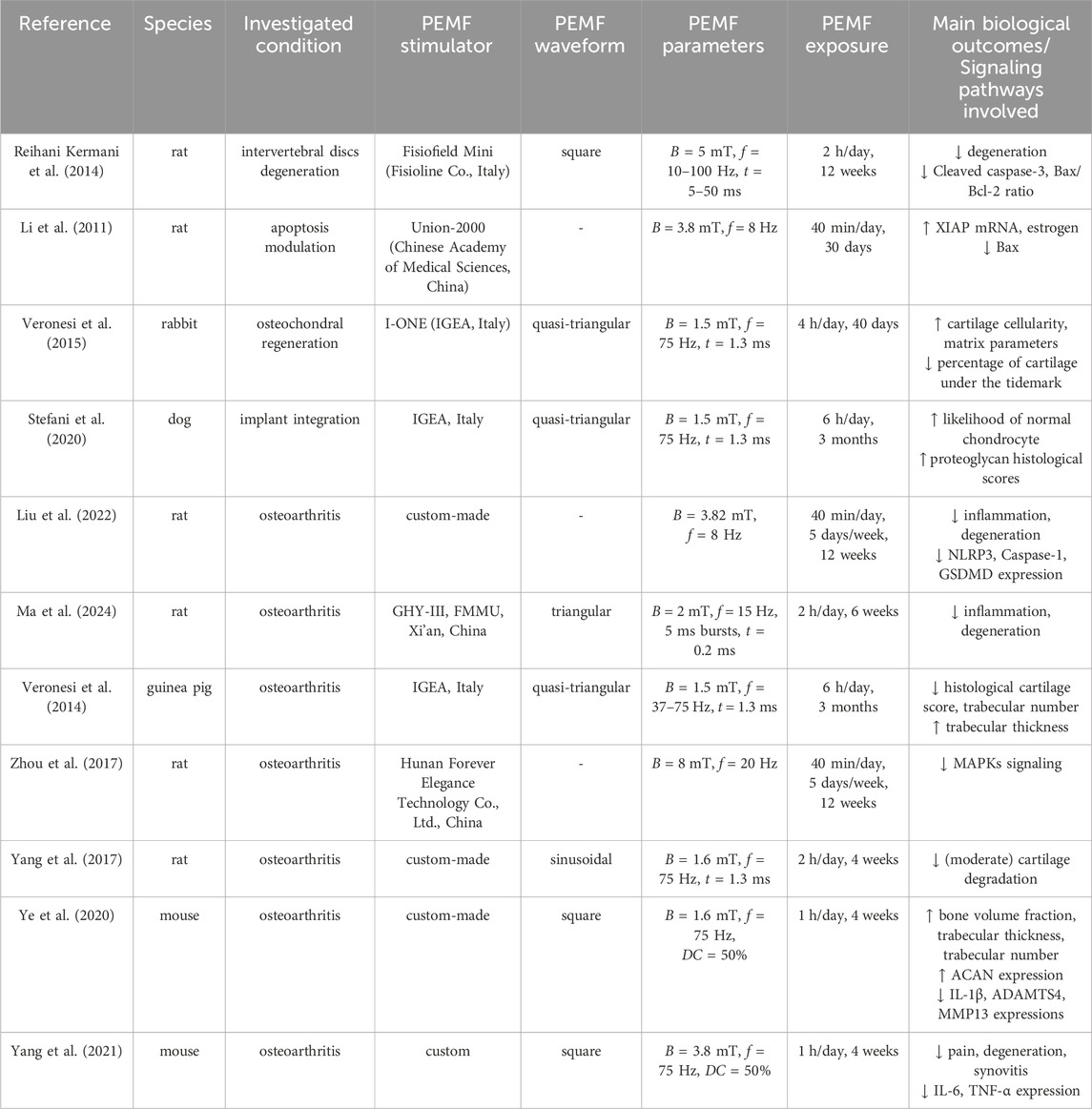
The promising results of in vitro application of PEMF on cartilage regeneration have prompted investigations into its in vivo effects, with a particular focus on cartilage degeneration and OA in different articular districts (see Table 7). As regards the intervertebral disc, in 2014, rats with surgically induced degeneration were treated with PEMF imposing the same magnetic field intensity (B = 5 mT, square waveform) and two different frequencies (f = 10, 100 Hz) for 2 h/day over 12 weeks. Both PEMF protocols attenuated intervertebral degenerative processes, with a significant decrease of Cleaved caspase-3 and Bax/Bcl-2 ratio compared to the untreated group (Reihani Kermani et al., 2014). Many more studies investigated PEMF impact on knee articular defects. In 2011, Li and co-workers exposed rats with ovariectomy-induced knee cartilage apoptosis to PEMF stimulation (B = 3.8 mT, f = 8 Hz, for 40 min/day along 30 days), observing significantly upregulated X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) mRNA and estrogen and downregulated Bax in knee joint cartilage (Li et al., 2011). In 2015, Veronesi et al. created surgical lesions in both knees of 10 rabbits and implanted a collagen scaffold in one lesion and a collagen scaffold seeded with bone marrow cells in the other. Afterwards, they provided PEMF stimulation (B = 1.5 mT, f = 75 Hz, quasi-triangular waveform, for 4 h/day over 40 days) on half of the animals. PEMF alone improved both cartilage cell and matrix parameters compared with scaffold alone. Additionally, the combination of cell-seeded scaffold and PEMF further improved osteochondral regeneration in terms of cartilage cellularity, matrix parameters, and reduced percentage of cartilage under the tidemark (Veronesi et al., 2015). A similar approach was adopted in 2020, when engineered osteochondral constructs were implanted in focal cartilage defects created in the stifle joints of eight dogs. After 3 months of PEMF stimulation (B = 1.5 mT, f = 75 Hz, quasi-triangular waveform, for 6 h/day), treated animals were less likely to have proteoglycan- and chondrocyte-related pathology than control, with tissue-engineered repair integration improved by PEMF, although not significantly (Stefani et al., 2020). Recent studies confirmed that PEMF can inhibit cartilage degradation, reducing the upregulation of pro-inflammatory and degradative factors in synovium (Liu et al., 2022; Ma et al., 2024).
Regarding the direct treatment of OA, Veronesi and colleagues exposed guinea pigs with OA to PEMF stimulation (B = 1.3 mT for 6 h/day over 3 months) imposing two different frequencies (f = 37 or 75 Hz). PEMF significantly reduced histological cartilage score, fibrillation index, subchondral bone thickness, and trabecular number while increased trabecular thickness and separation in comparison to the untreated group. Moreover, stimulation at 75 Hz significantly improved the histological score (Veronesi et al., 2014). In 2017, Zhou et al. treated an experimental rat model of OA with PEMF stimulation (B = 8 mT, f = 20 Hz, for 40 min/day for 5 days/week over 12 weeks) and observed partially prevented cartilage destruction, with inhibition of MAPKs signaling pathway (Zhou et al., 2017). In parallel, Yang and coworkers investigated the effect of the time of delivery of PEMF stimulation (B = 1.6 mT, f = 75 Hz, for 2 h/day over 4 weeks) on rats with induced knee OA, finding that timing is crucial. Pre-emptive PEMF maintained the microarchitecture of subchondral trabecular bone and partial chondroprotective properties were observed in pre-emptive and early PEMF treatment groups (Yang et al., 2017). Recently, the efficacy of PEMF for treating OA was also compared to the whole-body vibration treatment in mice with knee OA. Both PEMF stimulation (B = 1.6 mT, f = 75 Hz, square waveform, for 1 h/day) and vibration treatment (frequency = 5 Hz, amplitude = 4 mm, gravitational acceleration = 0.3 g, for 20 min/day) were applied over 4 weeks, leading to increased bone volume fraction, trabecular thickness, and trabecular number. In addition, the expression of ACAN was promoted, while the surface to volume ratio of bone was reduced, complemented by inhibited expressions of inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1 (IL-1β), and downregulated expression of the catabolic factor MMP13, with better results observed in PEMF-treated mice (Ye et al., 2020). Based on these results, in 2021, the abovementioned animal models were treated with PEMF with increased magnetic field intensity (B = 3.8 mT), resulting in a beneficial effect on pain, cartilage degeneration, synovitis, and trabecular bone microarchitecture. Moreover, PEMF slowed the structural and functional progression of OA by inhibiting TNF-α and IL-6 signaling and ameliorated cartilage matrix, reducing chondrocyte apoptosis and autophagy (Yang et al., 2021).
In summary, it has been demonstrated that PEMF treatment can improve cartilage health, enhance matrix parameters, and inhibit degenerative processes in osteochondral tissue. In addition, PEMF can modulate inflammatory pathways (Supplementary Table S1), reduce cartilage destruction, and improve bone and joint health in OA models. These findings suggest that PEMF may be an effective non-invasive treatment for OA, particularly when applied at specific intensities and frequencies.
6.4 Quantitative comparison among in vivo studies on PEMF stimulation for cartilage and osteochondral tissue
Besides variations in the intensity of the imposed magnetic field (resulting in Brms values ranging from 0.19 to 5.66 mT, Figure 6), in vivo studies on PEMF stimulation investigating its effects on cartilage and osteochondral repair are distinguished by PEMF dose values ranging from 19.8 to 594 mT·h. All studies reported the attenuation of degenerative processes in cartilage via the inhibition of pathways related to inflammatory response and apoptosis. Interestingly, the study on guinea pigs with OA exposed to PEMF stimulation adopting two different frequency values (B = 1.3 mT, f = 37 or 75 Hz) found positive effects with both protocols, but better histological score was obtained when the highest frequency was used, which also corresponds to the highest PEMF dose (D = 104.6 mT·h for f = 37 Hz and D = 147.9 mT·h for f = 75 Hz) (Veronesi et al., 2014). However, given the limited number of available studies, no clear correlations between PEMF parameters and biological responses can be established from this analysis.
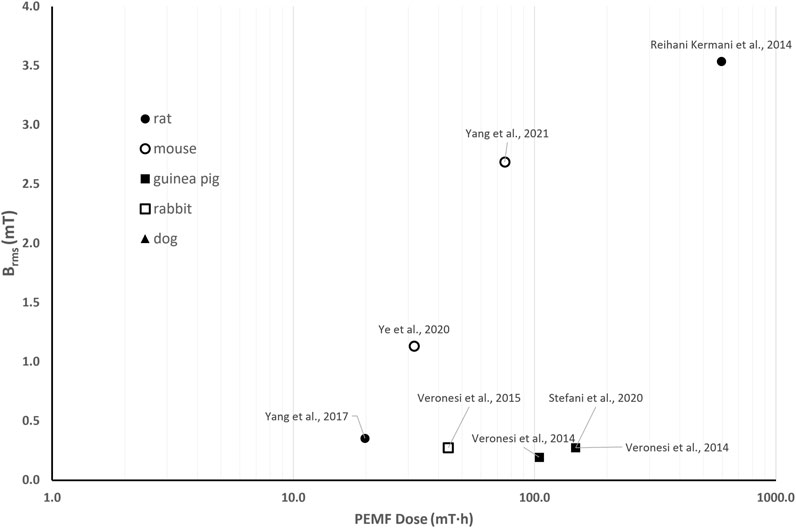
Figure 6. Distribution of the root mean square value of the magnetic field intensity (Brms) and the PEMF dose (D) value for the in vivo studies performed imposing PEMF stimulation on cartilage and osteochondral tissues. The different symbols refer to different animal models.
7 Concluding remarks
Over the past three decades, due to its non-invasiveness and promising outcomes, PEMF stimulation has gained widespread adoption as a clinical intervention for enhancing the treatment of various bone and cartilage disorders, including non-union bone fractures, osteoporosis, and OA (Haddad et al., 2007; Court-Brown et al., 2017). Additionally, PEMF has garnered attention as a potential countermeasure for mitigating the adverse effects of disuse conditions, including those caused by altered gravity during space travel, as evidenced by two NASA patents (Goodwin and Parker, 2007; Goodwin and Shackelford, 2014). However, despite the increasing availability of PEMF devices on the market and their growing use in clinical practice, the PEMF stimulation parameters are largely applied empirically with a persistent lack of standardization (Yuan et al., 2018). As illustrated in Table 2, there is substantial heterogeneity among commercially available PEMF stimulators, with significant variation in key parameters. Moreover, the absence of standardization has led to a multitude of studies, both in vitro (Tables 4, 5) and in vivo (Tables 6, 7), with the aim of elucidating the biological phenomena induced by PEMF at cellular and tissue levels.
However, this variability in experimental set-ups and imposed PEMF parameters complicates the direct comparison of outcomes across studies. This challenge is further compounded by inconsistencies in device specifications and experimental protocols, which introduce confounding factors that obscure the interpretation of results. Moreover, the lack of tunability in the parameters of most commercial devices imposes limitations on the capacity of research groups to conduct comparative studies, to vary the stimulation conditions, and to replicate the set-ups adopted by other researchers. Consequently, for the advancement of PEMF research, it would be highly desirable to adopt, at least in the early stages, standardized stimulation parameters to facilitate comparability across studies. Although standardization remains a significant challenge in the field, it is noteworthy that a limited number of research efforts have followed a rigorous translational approach, consistently applying identical PEMF parameters across in vitro (Saino et al., 2011; Ongaro et al., 2012), in vivo (Veronesi et al., 2015; Stefani et al., 2020), and clinical investigations (Massari et al., 2006). This methodological coherence not only strengthens the reliability of the findings but also supports the generation of clinical evidence with greater translational relevance. These examples demonstrate that it is indeed feasible to design and implement protocols that maintain parameter fidelity throughout the translational pipeline, ultimately contributing to the development of clinically validated therapeutic applications.
To facilitate the comparability of past and future research, here we proposed a quantitative approach based on the calculation of the PEMF dose—a comprehensive metric that integrates magnetic field intensity, stimulation waveform and exposure duration. Thanks to this method, we were able to highlight some common outcomes among different studies. Concerning bone tissue, from the comparison of the in vitro studies (Figure 3) we concluded that, for low Brms values (<0.3 mT), the exposure duration plays a crucial role and a minimum PEMF dose of 10 mT∙h should be guaranteed for promoting osteogenic differentiation. While, when higher magnetic field intensities (Brms ≥ 0.3 mT) are provided, a lower minimum PEMF dose threshold (D ≥ 0.21 mT∙h) is required to induce osteogenic effects. Comparing the in vivo animal studies on osteoporosis (Figure 5), the best results were obtained exploiting Brms values below 1.84 mT and D values above 3.51 mT·h (light blue dots in Figure 5). Regarding cartilage tissue, in vitro investigations suggest that the PEMF dose is a pivotal factor in determining whether the PEMF stimulation favors cell proliferation or differentiation (Figure 4). Specifically, it was observed that with D ranging from 3.5 to 26 mT·h, cell proliferation was induced (yellow dots in Figure 4), while at PEMF doses exceeding 26.02 mT·h, a shift towards chondrogenic differentiation was promoted (light blue dots in Figure 4). Concerning in vivo studies, given the low number of studies available in literature, the proposed quantitative approach did not lead to the extraction of significant evidence (Figure 6).
The method proposed for quantitative comparison is affected by some limitations. In the PEMF dose calculation, the frequency and pulse duration parameters are combined in the duty cycle and do not account separately, although the adopted frequency could be an important factor to consider for osteogenic differentiation (Luo et al., 2012; Poh et al., 2018). Additionally, only studies that explicitly reported all relevant PEMF parameters were included in the PEMF dose calculation for the quantitative comparison, as the absence of such data precludes PEMF dose estimation. Furthermore, the proposed approach does not account for cell type or animal models, factors that could influence the observed effects of PEMF stimulation. Despite these limitations, the synthesized findings provide valuable insights that can guide the refinement of future research on the biological effects of PEMF stimulation.
For the future of PEMF research, it would be desirable to use, at least initially, the same parameters to ensure better comparability. Subsequently, it would make sense to systematically vary the various parameters individually until the best possible combination is achieved (Flatscher et al., 2023). To support parameter selection for comparative studies and assist in the design of new experiments, the proposed log-log graph of Brms versus texp (Figure 2) represents a valuable tool. Indeed, by displaying PEMF dose values as straight isolines and incorporating the Brms value of a given PEMF stimulator, this graphical approach enables researchers to determine the corresponding texp values relevant for future investigations. Log-log graphs of Brms versus texp for the studies analyzed in the quantitative sections are provided in the Supplementary Material (Supplementary Figures S1–S4). Moreover, in order to perform more realistic in vitro studies, the use of 3D biomimetic tissue models cultured in bioreactors could offer significant potential to refine experiments and overcome the limitations of the conventional static 2D cultures. In the reviewed literature, only three studies have used 3D in vitro tissue models cultured in bioreactors (Wang H. et al., 2019; Gabetti et al., 2022; Daou et al., 2024), although the results suggest that bioreactors could represent powerful tools for in depth investigating the cell and tissue behavior under PEMF treatment. Furthermore, adopting more descriptive and reliable models would enable the refinement of the tested conditions and the reduction of the number of animals for the in vivo experiments, which often fail to provide directly translatable predictions for human outcomes. This approach also aligns with the 3R principles, promoting more ethical and efficient research methodologies.
In conclusion, this review provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of the art of in vitro and in vivo experiments investigating the biological effects of PEMF stimulation on bone and cartilage, underscoring the great variability in the models and conditions employed across studies. By introducing a method for quantitatively comparing the reviewed studies, we aim to foster the refinement of future research and support the development of standardized guidelines for PEMF treatment. Future investigations should prioritize the identification of optimal PEMF parameters, including amplitude, frequency, waveform, and exposure duration, through harmonized and reproducible methodologies. Establishing consensus on experimental models, outcome measures, and stimulation protocols is essential to improve comparability across studies and to generate robust, translatable data. These would be crucial for deepening the understanding of cellular responses and for establishing optimal PEMF treatment protocols to promote effective bone and cartilage repair.
Author contributions
BM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SG: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. JS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. GP: Writing – original draft. SI: Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Visualization. CB: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. DM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was carried out within the scope of: 1) the BIGMECH project funded by European Union–Next-Generation EU within the PRIN 2022 program (D.D. 104–02/02/2022 Ministero dell’Università e della Ricerca); 2) the SYNERGIES project funded by the European Union through the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions Individual Postdoctoral Fellowship 2023 (awarded to João C. Silva, HORIZON-MSCA-2023-PF-01, Project No. 101155027). This manuscript reflects only the authors’ views and opinions and both the Italian Ministry of the University and Research, and the European Union cannot be considered responsible for them.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Prof. Aldo Canova for technical explanations about PEMF generation and to Simona Salati from IGEA S.p.A. for the fruitful and valuable discussions on the perspectives of PEMF stimulation for cartilage tissue.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2025.1557572/full#supplementary-material
References
Amin, B., Elahi, M. A., Shahzad, A., Porter, E., and O’Halloran, M. (2019). A review of the dielectric properties of the bone for low frequency medical technologies. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 5, 022001. doi:10.1088/2057-1976/aaf210
Amini, A. R., Laurencin, C. T., and Nukavarapu, S. P. (2013). Bone tissue engineering: recent advances and challenges. 59.
Ampatzis, C., Zervoudis, S., Iatrakis, G., and Mastorakos, G. (2022). Effect of oral contraceptives on bone mineral density. Acta Endocrinol. (Buchar) 18, 355–360. doi:10.4183/aeb.2022.355
Andrew, C., Bassett, L., Pawluk, R. J., and Pilla, A. A. (1974). Augmentation of bone repair by inductively coupled electromagnetic fields. Science 184, 575–577. doi:10.1126/science.184.4136.575
Androjna, C., Fort, B., Zborowski, M., and Midura, R. J. (2014). Pulsed electromagnetic field treatment enhances healing callus biomechanical properties in an animal model of osteoporotic fracture: PEMF enhances OVX fracture healing. Bioelectromagnetics 35, 396–405. doi:10.1002/bem.21855
Androjna, C., Yee, C. S., White, C. R., Waldorff, E. I., Ryaby, J. T., Zborowski, M., et al. (2021). A comparison of alendronate to varying magnitude PEMF in mitigating bone loss and altering bone remodeling in skeletally mature osteoporotic rats. Bone 143, 115761. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2020.115761
Bagheri, L., Pellati, A., Rizzo, P., Aquila, G., Massari, L., De Mattei, M., et al. (2018). Notch pathway is active during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by pulsed electromagnetic fields. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 12, 304–315. doi:10.1002/term.2455
Bagnato, G. L., Miceli, G., Marino, N., Sciortino, D., and Bagnato, G. F. (2016). Pulsed electromagnetic fields in knee osteoarthritis: a double blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Rheumatology 55, 755–762. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kev426
Bai, Y., Li, X., Wu, K., Heng, B. C., Zhang, X., and Deng, X. (2024). Biophysical stimuli for promoting bone repair and regeneration. Med. Rev. 5, 1–22. doi:10.1515/mr-2024-0023
Bancroft, G. N., Sikavitsas, V. I., van den Dolder, J., Sheffield, T. L., Ambrose, C. G., Jansen, J. A., et al. (2002). Fluid flow increases mineralized matrix deposition in 3D perfusion culture of marrow stromal osteoblasts in a dose-dependent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99, 12600–12605. doi:10.1073/pnas.202296599
Bao, Z., Fan, M., Ma, L., Duan, Q., and Jiang, W. (2019). The effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields combined with a static magnetic intramedullary implant on the repair of bone defects: a preliminary study. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 38, 210–217. doi:10.1080/15368378.2019.1625785
Barak, S., Neuman, M., Iezzi, G., Piattelli, A., Perrotti, V., and Gabet, Y. (2016). A new device for improving dental implants Anchorage: a histological and micro-computed tomography study in the rabbit. Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 27, 935–942. doi:10.1111/clr.12661
Barbosa, F., Ferreira, F. C., and Silva, J. C. (2022). Piezoelectric electrospun fibrous scaffolds for bone, articular cartilage and osteochondral tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 2907. doi:10.3390/ijms23062907
Barker, A. T., and Lunt, M. J. (1983). The effects of pulsed magnetic fields of the type used in the stimulation of bone fracture healing. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. 4, 1–27. doi:10.1088/0143-0815/4/1/002
Bassett, C. A., Mitchell, S. N., Norton, L., and Pilla, A. (1978). Repair of non-unions by pulsing electromagnetic fields. Acta Orthop. Belg 44, 706–724.
Bassett, C. A., Pilla, A. A., and Pawluk, R. J. (1977). A non-operative salvage of surgically-resistant pseudarthroses and non-unions by pulsing electromagnetic fields. A preliminary report. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res., 128–143. doi:10.1097/00003086-197705000-00017
Baxter, F. R., Bowen, C. R., Turner, I. G., and Dent, A. C. E. (2010). Electrically active bioceramics: a review of interfacial responses. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38, 2079–2092. doi:10.1007/s10439-010-9977-6
Bentley, G., Biant, L. C., Vijayan, S., Macmull, S., Skinner, J. A., and Carrington, R. W. J. (2012). Minimum ten-year results of a prospective randomised study of autologous Chondrocyte implantation versus mosaicplasty for symptomatic articular cartilage lesions of the knee. J. Bone and Jt. Surg. Br. 94-B, 504–509. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.94B4.27495
Beşkardeş, I. G., Aydın, G., Bektaş, Ş., Cengiz, A., and Gümüşderelioğlu, M. (2018). A systematic study for optimal cell seeding and culture conditions in a perfusion mode bone-tissue bioreactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 132, 100–111. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2018.01.006
Bloise, N., Petecchia, L., Ceccarelli, G., Fassina, L., Usai, C., Bertoglio, F., et al. (2018). The effect of pulsed electromagnetic field exposure on osteoinduction of human mesenchymal stem cells cultured on nano-TiO2 surfaces. PLoS ONE 13, e0199046. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0199046
Borgström, F., Karlsson, L., Ortsäter, G., Norton, N., Halbout, P., Cooper, C., et al. (2020). Fragility fractures in Europe: burden, management and opportunities. Arch. Osteoporos. 15, 59. doi:10.1007/s11657-020-0706-y
Brighton, C. T., Friedenberg, Z. B., Zemsky, L. M., and Pollis, P. R. (1975). Direct-current stimulation of non-union and congenital pseudarthrosis. Exploration of its clinical application. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 57, 368–377. doi:10.2106/00004623-197557030-00015
Cadossi, R., Massari, L., Racine-Avila, J., and Aaron, R. K. (2020). Pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation of bone healing and joint preservation: cellular mechanisms of skeletal response. JAAOS Glob. Res. Rev. 4, e19.00155. doi:10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-19-00155
Cai, J., Li, W., Sun, T., Li, X., Luo, E., and Jing, D. (2018). Pulsed electromagnetic fields preserve bone architecture and mechanical properties and stimulate porous implant osseointegration by promoting bone anabolism in type 1 diabetic rabbits. Osteoporos. Int. 29, 1177–1191. doi:10.1007/s00198-018-4392-1
Cebrián, J. L., Gallego, P., Francés, A., Sánchez, P., Manrique, E., Marco, F., et al. (2010). Comparative study of the use of electromagnetic fields in patients with pseudoarthrosis of tibia treated by intramedullary nailing. Int. Orthop. 34, 437–440. doi:10.1007/s00264-009-0806-1
Celik, C., Franco-Obregón, A., Lee, E. H., Hui, J. H., and Yang, Z. (2021). Directionalities of magnetic fields and topographic scaffolds synergise to enhance MSC chondrogenesis. Acta Biomater. 119, 169–183. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2020.10.039
Chalidis, B., Sachinis, N., Assiotis, A., Maccauro, G., and Graziani, F. (2011). Stimulation of bone formation and fracture healing with pulsed electromagnetic fields: biologic responses and clinical implications. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 24, 17–20. doi:10.1177/03946320110241S204
Chen, C.-H., Lin, Y.-S., Fu, Y.-C., Wang, C.-K., Wu, S.-C., Wang, G.-J., et al. (2013). Electromagnetic fields enhance chondrogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells in a chondrogenic microenvironment in vitro. J. Appl. Physiology 114, 647–655. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01216.2012
Chen, L., Yang, J., Cai, Z., Huang, Y., Xiao, P., Wang, J., et al. (2024). Electroactive biomaterials regulate the electrophysiological microenvironment to promote bone and cartilage tissue regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34, 2314079. doi:10.1002/adfm.202314079
Chen, Y., Braun, B. J., Menger, M. M., Ronniger, M., Falldorf, K., Histing, T., et al. (2023). Intermittent exposure to a 16 Hz extremely low frequency pulsed electromagnetic field promotes osteogenesis in vitro through activating piezo 1-Induced Ca2+ influx in osteoprogenitor cells. JFB 14, 165. doi:10.3390/jfb14030165
Claes, L., and Willie, B. (2007). The enhancement of bone regeneration by ultrasound. Prog. Biophysics Mol. Biol. 93, 384–398. doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2006.07.021
Collins, M. N., Ren, G., Young, K., Pina, S., Reis, R. L., and Oliveira, J. M. (2021). Scaffold fabrication technologies and structure/function properties in bone tissue engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2010609. doi:10.1002/adfm.202010609
Court-Brown, C. M., Clement, N. D., Duckworth, A. D., Biant, L. C., and McQueen, M. M. (2017). The changing epidemiology of fall-related fractures in adults. Injury 48, 819–824. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2017.02.021
Daher, R. J., Chahine, N. O., Greenberg, A. S., Sgaglione, N. A., and Grande, D. A. (2009). New methods to diagnose and treat cartilage degeneration. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 5, 599–607. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2009.204
Daish, C., Blanchard, R., Fox, K., Pivonka, P., and Pirogova, E. (2018). The application of pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs) for bone fracture repair: past and perspective findings. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 46, 525–542. doi:10.1007/s10439-018-1982-1
Daou, F., Masante, B., Gabetti, S., Mochi, F., Putame, G., Zenobi, E., et al. (2024). Unraveling the transcriptome profile of pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation in bone regeneration using a bioreactor-based investigation platform. Bone 182, 117065. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2024.117065
da Silva, H. M., Mateescu, M., Damia, C., Champion, E., Soares, G., and Anselme, K. (2010). Importance of dynamic culture for evaluating osteoblast activity on dense silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 80, 138–144. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.05.040
Datta, N., Pham, Q. P., Sharma, U., Sikavitsas, V. I., Jansen, J. A., and Mikos, A. G. (2006). In vitro generated extracellular matrix and fluid shear stress synergistically enhance 3D osteoblastic differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103, 2488–2493. doi:10.1073/pnas.0505661103
Dauben, T. J., Ziebart, J., Bender, T., Zaatreh, S., Kreikemeyer, B., and Bader, R. (2016). A novel in vitro system for comparative analyses of bone cells and bacteria under electrical stimulation. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 1–12. doi:10.1155/2016/5178640
Davies, B. M., Rikabi, S., French, A., Pinedo-Villanueva, R., Morrey, M. E., Wartolowska, K., et al. (2014). Quantitative assessment of barriers to the clinical development and adoption of cellular therapies: a pilot study. J. Tissue Eng. 5, 2041731414551764. doi:10.1177/2041731414551764
De Mattei, M., Caruso, A., Pezzetti, F., Pellati, A., Stabellini, G., Sollazzo, V., et al. (2001). Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on human articular chondrocyte proliferation. Connect. Tissue Res. 42, 269–279. doi:10.3109/03008200109016841
De Mattei, M., Grassilli, S., Pellati, A., Brugnoli, F., De Marchi, E., Contartese, D., et al. (2020). Pulsed electromagnetic fields modulate miRNAs during osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells: a possible role in the osteogenic-angiogenic coupling. Stem Cell Rev Rep 16, 1005–1012. doi:10.1007/s12015-020-10009-6
Denning, D., Kilpatrick, J. I., Hsu, T., Habelitz, S., Fertala, A., and Rodriguez, B. J. (2014). Piezoelectricity in collagen type II fibrils measured by scanning probe microscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 116, 066818. doi:10.1063/1.4891400
Domingues, M. F., Silva, J. C., and Sanjuan-Alberte, P. (2024). From spheroids to bioprinting: a literature review on biomanufacturing strategies of 3D in vitro osteosarcoma models. Adv. Ther. 7, 2400047. doi:10.1002/adtp.202400047
Du, D., Furukawa, K. S., and Ushida, T. (2009). 3D culture of osteoblast-like cells by unidirectional or oscillatory flow for bone tissue engineering. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 102, 1670–1678. doi:10.1002/bit.22214
Ehnert, S., van Griensven, M., Unger, M., Scheffler, H., Falldorf, K., Fentz, A.-K., et al. (2018). Co-Culture with human osteoblasts and exposure to extremely low frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields improve osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. IJMS 19, 994. doi:10.3390/ijms19040994
El-Shamy, S. M. (2020). Long-term effect of electromagnetic field in treatment of patients with osteopenia or osteoporosis. A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04608162 (Accessed December 31, 2024).
Engel, N., Fechner, C., Voges, A., Ott, R., Stenzel, J., Siewert, S., et al. (2021). An optimized 3D-printed perfusion bioreactor for homogeneous cell seeding in bone substitute scaffolds for future chairside applications. Sci. Rep. 11, 22228. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-01516-8
Esposito, M., Lucariello, A., Costanzo, C., Fiumarella, A., Giannini, A., Riccardi, G., et al. (2013). Differentiation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells, WJ-MSCs, into chondrogenic cells in the presence of pulsed electromagnetic fields. vivo 6.
Faldini, C., Cadossi, M., Luciani, D., Betti, E., Chiarello, E., and Giannini, S. (2010). Electromagnetic bone growth stimulation in patients with femoral neck fractures treated with screws: prospective randomized double-blind study. Curr. Orthop. Pract. 21, 282–287. doi:10.1097/BCO.0b013e3181d4880f
Farooqi, A. R., Bader, R., and van Rienen, U. (2019). Numerical study on electromechanics in cartilage tissue with respect to its electrical properties. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 25, 152–166. doi:10.1089/ten.teb.2018.0214
Flatscher, J., Pavez Loriè, E., Mittermayr, R., Meznik, P., Slezak, P., Redl, H., et al. (2023). Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF)—Physiological response and its potential in trauma treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 11239. doi:10.3390/ijms241411239
Freeman, M. F. E., Haugh, D. M. G., and McNamara, D. L. (2015). An in vitro bone tissue regeneration strategy combining chondrogenic and vascular priming enhances the mineralisation potential of MSCs in vitro whilst also allowing for vessel formation. Tissue Eng. Part A 21, 46. doi:10.1089/ten.TEA.2014.0249
Friedenberg, Z. B., and Brighton, C. T. (1974). Electrical fracture healing. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 238, 564–574. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb26822.x
Fukada, E., and Yasuda, I. (1957). On the piezoelectric effect of bone. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 12, 1158–1162. doi:10.1143/JPSJ.12.1158
Gabetti, S., Masante, B., Cochis, A., Putame, G., Sanginario, A., Armando, I., et al. (2022). An automated 3D-printed perfusion bioreactor combinable with pulsed electromagnetic field stimulators for bone tissue investigations. Sci. Rep. 12, 13859. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-18075-1
Garland, D. E., Moses, B., and Salyer, W. (1991). Long-term follow-up of fracture nonunions treated with PEMFs. Contemp. Orthop. 22, 295–302.
Gaspar, D. A., Gomide, V., and Monteiro, F. J. (2012). The role of perfusion bioreactors in bone tissue engineering. Biomatter 2, 167–175. doi:10.4161/biom.22170
Gavazzo, P., Viti, F., Donnelly, H., Oliva, M. A. G., Salmeron-Sanchez, M., Dalby, M. J., et al. (2021). Biophysical phenotyping of mesenchymal stem cells along the osteogenic differentiation pathway. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 37, 915–933. doi:10.1007/s10565-020-09569-7
Goodwin, T. J., and Parker, C. R. (2007). Apparatus and method for enhancing tissue repair in mammals. Washington, DC (US): U.S. Patent No 2007/100195 A1.
Goodwin, T. J., and Shackelford, L. C. (2014). Modifying the genetic regulation of bone and cartilage cells and associated tissue by EMF stimulation fields and uses thereof. Washington, DC (US): U.S. Patent No 8,795,147 B1.
Gu, Z., Wang, J., Fu, Y., Pan, H., He, H., Gan, Q., et al. (2023). Smart biomaterials for articular cartilage repair and regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2212561. doi:10.1002/adfm.202212561
Guilak, F., Cohen, D. M., Estes, B. T., Gimble, J. M., Liedtke, W., and Chen, C. S. (2009). Control of stem cell fate by physical interactions with the extracellular matrix. Cell Stem Cell 5, 17–26. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2009.06.016
Haddad, J. B., Obolensky, A. G., and Shinnick, P. (2007). The biologic effects and the therapeutic mechanism of action of electric and electromagnetic field stimulation on bone and cartilage: new findings and a review of earlier work. J. Altern. Complementary Med. 13, 485–490. doi:10.1089/acm.2007.5270
He, Z., Selvamurugan, N., Warshaw, J., and Partridge, N. C. (2018). Pulsed electromagnetic fields inhibit human osteoclast formation and gene expression via osteoblasts. Bone 106, 194–203. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2017.09.020
Hilz, F. M., Ahrens, P., Grad, S., Stoddart, M. J., Dahmani, C., Wilken, F. L., et al. (2014). Influence of extremely low frequency, low energy electromagnetic fields and combined mechanical stimulation on chondrocytes in 3-D constructs for cartilage tissue engineering: EMF ± mechanical stimulus on chondrocytes. Bioelectromagnetics 35, 116–128. doi:10.1002/bem.21822
Hoenig, E., Winkler, T., Mielke, G., Paetzold, H., Schuettler, D., Goepfert, C., et al. (2011). High amplitude direct compressive strain enhances mechanical properties of scaffold-free tissue-engineered cartilage. Tissue Eng. Part A 17, 1401–1411. doi:10.1089/ten.tea.2010.0395
Hoffmann, W., Feliciano, S., Martin, I., de Wild, M., and Wendt, D. (2015). Novel perfused compression bioreactor system as an in vitro model to investigate fracture healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 3, 10. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2015.00010
Hu, H., Yang, W., Zeng, Q., Chen, W., Zhu, Y., Liu, W., et al. (2020). Promising application of pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs) in musculoskeletal disorders. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 131, 110767. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110767
Hunter, D. J., March, L., and Chew, M. (2020). Osteoarthritis in 2020 and beyond: a lancet commission. Lancet 396, 1711–1712. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32230-3
IOF (2024). International osteoporosis foundation. Available online at: https://www.osteoporosis.foundation/facts-statistics/key-statistic-for-europe.
Jacob, J., More, N., Kalia, K., and Kapusetti, G. (2018). Piezoelectric smart biomaterials for bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Inflamm. Regen. 38, 2. doi:10.1186/s41232-018-0059-8
Jing, D., Cai, J., Wu, Y., Shen, G., Li, F., Xu, Q., et al. (2014). Pulsed electromagnetic fields partially preserve bone mass, microarchitecture, and strength by promoting bone formation in hindlimb-suspended rats: PEMF partially promote bone formation and bone quality in disuse rats. J. Bone Min. Res. 29, 2250–2261. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2260
Jing, D., Zhai, M., Tong, S., Xu, F., Cai, J., Shen, G., et al. (2016). Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote osteogenesis and osseointegration of porous titanium implants in bone defect repair through a Wnt/β-catenin signaling-associated mechanism. Sci. Rep. 6, 32045. doi:10.1038/srep32045
Jing, W., Huang, Y., Wei, P., Cai, Q., Yang, X., and Zhong, W. (2019). Roles of electrical stimulation in promoting osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs on conductive fibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 107, 1443–1454. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.36659
Jordan University of Science and Technology (2021). The effect of pulsed electromagnetic field and progressive resistance exercise on knee osteoarthritis. Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04106986 (Accessed December 31, 2024).
Kaadan, A., Salati, S., Setti, S., and Aaron, R. (2024). Augmentation of deficient bone healing by pulsed electromagnetic fields—from mechanisms to clinical outcomes. Bioeng. (Basel) 11, 1223. doi:10.3390/bioengineering11121223
Kaivosoja, E., Sariola, V., Chen, Y., and Konttinen, Y. T. (2012). The effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields and dehydroepiandrosterone on viability and osteo-induction of human mesenchymal stem cells: effect of PEMF and DHEA on MSC viability and osteoinduction. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 9, 31–40. doi:10.1002/term.1612
Kanis, J. A., Norton, N., Harvey, N. C., Jacobson, T., Johansson, H., Lorentzon, M., et al. (2021). SCOPE 2021: a new scorecard for osteoporosis in Europe. Arch. Osteoporos. 16, 82. doi:10.1007/s11657-020-00871-9
Kapat, K., Shubhra, Q. T. H., Zhou, M., and Leeuwenburgh, S. (2020). Piezoelectric nano-biomaterials for biomedicine and tissue regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1909045. doi:10.1002/adfm.201909045
Kar, N. S., Ferguson, D., Zhang, N., Waldorff, E. I., Ryaby, J. T., and DiDonato, J. A. (2021). Pulsed-electromagnetic-field induced osteoblast differentiation requires activation of genes downstream of adenosine receptors A2A and A3. PLOS ONE 16, e0247659. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0247659
Kavand, H., Lintel, H., and Renaud, P. (2019). Efficacy of pulsed electromagnetic fields and electromagnetic fields tuned to the ion cyclotron resonance frequency of Ca 2+ on chondrogenic differentiation. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 13, 799–811. doi:10.1002/term.2829
Kavlock, K. D., and Goldstein, A. S. (2011). Effect of pulse frequency on the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in a pulsatile perfusion bioreactor. J. Biomech. Eng. 133, 091005–NaN. doi:10.1115/1.4004919
Kim, Y., Lim, H., Lee, E., Ki, G., and Seo, Y. (2021). Synergistic effect of electromagnetic fields and nanomagnetic particles on osteogenesis through calcium channels and p-ERK signaling. J. Orthop. Res. 39, 1633–1646. doi:10.1002/jor.24905
Kuzyk, P., and Schemitsch, E. (2009). The science of electrical stimulation therapy for fracture healing. Indian J. Orthop. 43, 127. doi:10.4103/0019-5413.50846
Langer, R., and Vacanti, J. (2016). Advances in tissue engineering. J. Pediatr. Surg. 51, 8–12. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2015.10.022
Lanza, R., Langer, R., and Vacanti, J. (2000). Principle of tissue engineering. San Diego: Second. Accademic Press.
Lei, T., Li, F., Liang, Z., Tang, C., Xie, K., Wang, P., et al. (2017). Effects of four kinds of electromagnetic fields (EMF) with different frequency spectrum bands on ovariectomized osteoporosis in mice. Sci. Rep. 7, 553. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-00668-w
Lei, T., Liang, Z., Li, F., Tang, C., Xie, K., Wang, P., et al. (2018). Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) attenuate changes in vertebral bone mass, architecture and strength in ovariectomized mice. Bone 108, 10–19. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2017.12.008
Leppik, L., Bhavsar, M. B., Oliveira, K. M. C., Eischen-Loges, M., Mobini, S., and Barker, J. H. (2019). Construction and use of an electrical stimulation chamber for enhancing osteogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in vitro. JoVE J. Vis. Exp., e59127. doi:10.3791/59127
Leppik, L., Oliveira, K. M. C., Bhavsar, M. B., and Barker, J. H. (2020). Electrical stimulation in bone tissue engineering treatments. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 46, 231–244. doi:10.1007/s00068-020-01324-1
Li, D., Tang, T., Lu, J., and Dai, K. (2009). Effects of flow shear stress and mass transport on the construction of a large-scale tissue-engineered bone in a perfusion bioreactor. Tissue Eng. Part A 15, 2773–2783. doi:10.1089/ten.tea.2008.0540
Li, J., Zeng, Z., Zhao, Y., Jing, D., Tang, C., Ding, Y., et al. (2017). Effects of low-intensity pulsed electromagnetic fields on bone microarchitecture, mechanical strength and bone turnover in type 2 diabetic Db/Db mice. Sci. Rep. 7, 10834. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-11090-7
Li, S., Luo, Q., Huang, L., Hu, Y., Xia, Q., and He, C. (2011). Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on cartilage apoptosis signalling pathways in ovariectomised rats. Int. Orthop. (SICOT) 35, 1875–1882. doi:10.1007/s00264-011-1245-3
Li, W.-Y., Li, X.-Y., Tian, Y.-H., Chen, X.-R., Zhou, J., Zhu, B.-Y., et al. (2018). Pulsed electromagnetic fields prevented the decrease of bone formation in hindlimb-suspended rats by activating sAC/cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling pathway: pulsed electromagnetic fields prevented the decrease. Bioelectromagnetics 39, 569–584. doi:10.1002/bem.22150
Li, Y., Li, L., Li, Y., Feng, L., Wang, B., Wang, M., et al. (2023). Enhancing cartilage repair with optimized supramolecular hydrogel-based scaffold and pulsed electromagnetic field. Bioact. Mater. 22, 312–324. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.10.010
Lim, K., Kim, J., Seonwoo, H., Park, S. H., Choung, P.-H., and Chung, J. H. (2013). In vitro effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound stimulation on the osteogenic differentiation of human alveolar bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells for tooth tissue engineering. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 1–15. doi:10.1155/2013/269724
Lin, C.-C., Chang, Y.-T., Lin, R.-W., Chang, C.-W., Wang, G.-J., and Lai, K.-A. (2020). Single pulsed electromagnetic field restores bone mass and microarchitecture in denervation/disuse osteopenic mice. Med. Eng. and Phys. 80, 52–59. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2019.10.004
Liu, J., Huang, X., Zhou, J., Li, L., Xiao, H., Qu, M., et al. (2022). Pulsed electromagnetic field alleviates synovitis and inhibits the NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway in osteoarthritis rats. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 41, 101–107. doi:10.1080/15368378.2021.2021933
Liu, Y., Hao, L., Jiang, L., and Li, H. (2021). Therapeutic effect of pulsed electromagnetic field on bone wound healing in rats. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 40, 26–32. doi:10.1080/15368378.2020.1851252
Lovecchio, J., Gargiulo, P., Vargas Luna, J. L., Giordano, E., and Sigurjónsson, Ó. E. (2019). A standalone bioreactor system to deliver compressive load under perfusion flow to hBMSC-seeded 3D chitosan-graphene templates. Sci. Rep. 9, 16854. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-53319-7
Luo, F., Hou, T., Zhang, Z., Xie, Z., Wu, X., and Xu, J. (2012). Effects of pulsed electromagnetic field frequencies on the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Orthopedics 35, e526–e531. doi:10.3928/01477447-20120327-11
Ma, Y., He, F., Chen, X., Zhou, S., He, R., Liu, Q., et al. (2024). Low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields alleviate the condylar cartilage degeneration and synovitis at the early stage of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. J. Oral Rehabilitation 51, 666–676. doi:10.1111/joor.13636
Markov, M. S. (2007). Pulsed electromagnetic field therapy history, state of the art and future. Environmentalist 27, 465–475. doi:10.1007/s10669-007-9128-2
Martini, F., Pellati, A., Mazzoni, E., Salati, S., Caruso, G., Contartese, D., et al. (2020). Bone morphogenetic Protein-2 signaling in the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by pulsed electromagnetic fields. IJMS 21, 2104. doi:10.3390/ijms21062104
Massai, D., Cerino, G., Gallo, D., Pennella, F., Deriu, M., Rodriguez, A., et al. (2013). Bioreactors as engineering support to treat cardiac muscle and vascular disease. J. Healthc. Eng. 4, 329–370. doi:10.1260/2040-2295.4.3.329
Massari, L., Benazzo, F., Moretti, B., Dallari, D., Perugia, D., Meani, E., et al. (2011). Stimolazione elettrica dell’osteogenesi: efficacia e tecnologie a confronto. GIOT 37, 1–8.
Massari, L., Fini, M., Cadossi, R., Setti, S., and Traina, G. C. (2006). Biophysical stimulation with pulsed electromagnetic fields in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. JBJS 88, 56–60. doi:10.2106/JBJS.F.00536
Matziolis, D., Tuischer, J., Matziolis, G., Kasper, G., Duda, G., and Perka, C. (2011). Osteogenic predifferentiation of human bone marrow-derived stem cells by short-term mechanical stimulation. Open Orthop. J. 5, 1–6. doi:10.2174/1874325001105010001
Mauck, R. L., Nicoll, S. B., Seyhan, S. L., Ateshian, G. A., and Hung, C. T. (2003). Synergistic action of growth factors and dynamic loading for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. 9, 597–611. doi:10.1089/107632703768247304
McAlindon, T. E., Bannuru, R. R., Sullivan, M. C., Arden, N. K., Berenbaum, F., Bierma-Zeinstra, S. M., et al. (2014). OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 22, 363–388. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2014.01.003
Miguel, F., Barbosa, F., Ferreira, F. C., and Silva, J. C. (2022). Electrically conductive hydrogels for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Gels 8, 710. doi:10.3390/gels8110710
Mittwede, P. N., Gottardi, R., Alexander, P. G., Tarkin, I. S., and Tuan, R. S. (2018). Clinical applications of bone tissue engineering in orthopedic trauma. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 6, 99–108. doi:10.1007/s40139-018-0166-x
Miyamoto, H., Sawaji, Y., Iwaki, T., Masaoka, T., Fukada, E., Date, M., et al. (2019). Intermittent pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation activates the mTOR pathway and stimulates the proliferation of osteoblast-like cells. Bioelectromagnetics 40, 412–421. doi:10.1002/bem.22207
Mow, V. C., Wang, C. C., and Hung, C. T. (1999). The extracellular matrix, interstitial fluid and ions as a mechanical signal transducer in articular cartilage. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 7, 41–58. doi:10.1053/joca.1998.0161
Murray, H., and Pethica, B. (2016). A follow-up study of the in-practice results of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy in the management of nonunion fractures. ORR 8, 67–72. doi:10.2147/ORR.S113756
Nelson, F. R., Zvirbulis, R., and Pilla, A. A. (2013). Non-invasive electromagnetic field therapy produces rapid and substantial pain reduction in early knee osteoarthritis: a randomized double-blind pilot study. Rheumatol. Int. 33, 2169–2173. doi:10.1007/s00296-012-2366-8
Nicolin, V., Ponti, C., Baldini, G., Gibellini, D., Bortul, R., Zweyer, M., et al. (2007). In vitro exposure of human chondrocytes to pulsed electromagnetic fields. Eur. J. Histochem 51, 203–212.
Nunes, C. M. M., Ferreira, C. L., Bernardo, D. V., Lopes, C. C. R., Collino, L., da Silva Lima, V. C., et al. (2021). Evaluation of pulsed electromagnetic field protocols in implant osseointegration: in vivo and in vitro study. Clin. Oral Invest 25, 2925–2937. doi:10.1007/s00784-020-03612-x
Ongaro, A., Pellati, A., Bagheri, L., Fortini, C., Setti, S., and De Mattei, M. (2014). Pulsed electromagnetic fields stimulate osteogenic differentiation in human bone marrow and adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells: PEMFs on osteogenic differentiation of MSCs. Bioelectromagnetics 35, 426–436. doi:10.1002/bem.21862
Ongaro, A., Pellati, A., Setti, S., Masieri, F. F., Aquila, G., Fini, M., et al. (2012). Electromagnetic fields counteract IL-1β activity during chondrogenesis of bovine mesenchymal stem cells. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 9, E229–E238. doi:10.1002/term.1671
Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation Devices Panel (2020). Bone growth stimulators executive summary | FDA. U. S. Food Drug Adm. Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/media/141850 (Accessed December 30, 2024).
Parate, D., Franco-Obregón, A., Fröhlich, J., Beyer, C., Abbas, A. A., Kamarul, T., et al. (2017). Enhancement of mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis with short-term low intensity pulsed electromagnetic fields. Sci. Rep. 7, 9421. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-09892-w
Parate, D., Kadir, N. D., Celik, C., Lee, E. H., Hui, J. H. P., Franco-Obregón, A., et al. (2020). Pulsed electromagnetic fields potentiate the paracrine function of mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage regeneration. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 11, 46. doi:10.1186/s13287-020-1566-5
Pedrero, S. G., Llamas-Sillero, P., and Serrano-López, J. (2021). A multidisciplinary journey towards bone tissue engineering. Materials 14, 4896. doi:10.3390/ma14174896
Petecchia, L., Sbrana, F., Utzeri, R., Vercellino, M., Usai, C., Visai, L., et al. (2015). Electro-magnetic field promotes osteogenic differentiation of BM-hMSCs through a selective action on Ca2+-related mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 5, 13856. doi:10.1038/srep13856
Pi, Y., Liang, H., Yu, Q., Yin, Y., Xu, H., Lei, Y., et al. (2019). Low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic field inhibits RANKL-Induced osteoclastic differentiation in RAW264.7 cells by scavenging reactive oxygen species. Mol. Med. Rep. 19, 4129–4136. doi:10.3892/mmr.2019.10079
Poh, P. S. P., Seeliger, C., Unger, M., Falldorf, K., Balmayor, E. R., and van Griensven, M. (2018). Osteogenic effect and cell signaling activation of extremely low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields in adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 1–11. doi:10.1155/2018/5402853
Poillot, P., Le Maitre, C. L., and Huyghe, J. M. (2021). The strain-generated electrical potential in cartilaginous tissues: a role for piezoelectricity. Biophys. Rev. 13, 91–100. doi:10.1007/s12551-021-00779-9
Portan, D. V., Deligianni, D. D., Papanicolaou, G. C., Kostopoulos, V., Psarras, G. C., and Tyllianakis, M. (2019). Combined optimized effect of a highly self-organized nanosubstrate and an electric field on osteoblast bone cells activity. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 1–8. doi:10.1155/2019/7574635
Quarto, R., and Giannoni, P. (2016). “Bone tissue engineering: past–present–future,” in Mesenchymal stem cells: methods and protocols. Editor M. Gnecchi (New York, NY: Springer), 21–33. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-3584-0_2
Rajabi, A. H., Jaffe, M., and Arinzeh, T. L. (2015). Piezoelectric materials for tissue regeneration: a review. Acta Biomater. 24, 12–23. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2015.07.010
Ravichandran, A., Lim, J., Chong, M. S. K., Wen, F., Liu, Y., Pillay, Y. T., et al. (2017). In vitro cyclic compressive loads potentiate early osteogenic events in engineered bone tissue. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomaterials 105, 2366–2375. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.33772
Reihani Kermani, H., Pourghazi, M., and Mahani, S. E. (2014). Effects of pulsed electromagnetic field on intervertebral disc cell apoptosis in rats. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 33, 246–249. doi:10.3109/15368378.2013.843059
Ricotti, L., Cafarelli, A., Manferdini, C., Trucco, D., Vannozzi, L., Gabusi, E., et al. (2024). Ultrasound stimulation of piezoelectric nanocomposite hydrogels boosts chondrogenic differentiation in vitro, in both a normal and inflammatory milieu. ACS Nano 18, 2047–2065. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c08738
Rossi, N., Hadad, H., Bejar-Chapa, M., Peretti, G. M., Randolph, M. A., Redmond, R. W., et al. (2023). Bone marrow stem cells with tissue-engineered scaffolds for large bone segmental defects: a systematic review. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 29, 457–472. doi:10.1089/ten.teb.2022.0213
Saino, E., Fassina, L., Van Vlierberghe, S., Avanzini, M. A., Dubruel, P., Magenes, G., et al. (2011). Effects of electromagnetic stimulation on osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells seeded onto gelatin cryogel. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 24, 1–6. doi:10.1177/03946320110241S201
Salhotra, A., Shah, H. N., Levi, B., and Longaker, M. T. (2020). Mechanisms of bone development and repair. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 696–711. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-00279-w
Schaffler, M. B., and Kennedy, O. D. (2012). Osteocyte signaling in bone. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 10, 118–125. doi:10.1007/s11914-012-0105-4
Scocozza, F., Bina, V., Caliogna, L., Brancato, A. M., Mosconi, M., Fassina, L., et al. (2024). Effect of hydroxyapatite and pulsed electromagnetic field on osteogenic differentiation of human stem cells seeded onto 3D-printed polycaprolactone scaffolds for future bone graft transplantation. Polym. Adv. Technol. 35, e6386. doi:10.1002/pat.6386
Selvamurugan, N., He, Z., Rifkin, D., Dabovic, B., and Partridge, N. C. (2017). Pulsed electromagnetic field regulates MicroRNA 21 expression to activate TGF- β signaling in human bone marrow stromal cells to enhance osteoblast differentiation. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 1–17. doi:10.1155/2017/2450327
Sierpowska, J., Töyräs, J., Hakulinen, M. A., Saarakkala, S., Jurvelin, J. S., and Lappalainen, R. (2003). Electrical and dielectric properties of bovine trabecular Bone—Relationships with mechanical properties and mineral density. Phys. Med. Biol. 48, 775–786. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/48/6/306
Silva, J. C., Moura, C. S., Borrecho, G., Alves de Matos, A. P., Cabral, J. M. S., Linhardt, R. J., et al. (2021). Effects of glycosaminoglycan supplementation in the chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow- and synovial-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells on 3D-extruded poly (ε-caprolactone) scaffolds. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomaterials 70, 207–222. doi:10.1080/00914037.2019.1706511
Song, M., Zhao, D., Wei, S., Liu, C., Liu, Y., Wang, B., et al. (2014). The effect of electromagnetic fields on the proliferation and the osteogenic or adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells modulated by dexamethasone: effect of EMF on MSC modulated by DEX. Bioelectromagnetics 35, 479–490. doi:10.1002/bem.21867
Sophia Fox, A. J., Bedi, A., and Rodeo, S. A. (2009). The basic science of articular cartilage: structure, composition, and function. Sports Health 1, 461–468. doi:10.1177/1941738109350438
Stefani, R. M., Barbosa, S., Tan, A. R., Setti, S., Stoker, A. M., Ateshian, G. A., et al. (2020). Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote repair of focal articular cartilage defects with engineered osteochondral constructs. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 117, 1584–1596. doi:10.1002/bit.27287
Sung, Y.-Y., Shin, J.-W., Yang, W.-K., Kim, M.-J., Koo, J.-I., Noh, E.-M., et al. (2021). Effect of pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation on the growth plate of the tibia bone of rats: an in vivo study. Appl. Sci. 11, 7571. doi:10.3390/app11167571
Suryani, L., Too, J. H., Hassanbhai, A. M., Wen, F., Lin, D. J., Yu, N., et al. (2019). Effects of electromagnetic field on proliferation, differentiation, and mineralization of MC3T3 cells. Tissue Eng. Part C. Methods 25, 114–125. doi:10.1089/ten.tec.2018.0364
Topal, O., Çina Aksoy, M., Ciriş, İ. M., Doğuç, D. K., Sert, S., and Çömlekçi, S. (2020). Assessment of the effect of pulsed electromagnetic field application on the healing of bone defects in rats with heparin-induced osteoporosis. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 39, 206–217. doi:10.1080/15368378.2020.1762636
van der Jagt, O. P., van der Linden, J. C., Waarsing, J. H., Verhaar, J. A. N., and Weinans, H. (2012). Systemic treatment with pulsed electromagnetic fields do not affect bone microarchitecture in osteoporotic rats. Int. Orthop. (SICOT) 36, 1501–1506. doi:10.1007/s00264-011-1471-8
Varani, K., Vincenzi, F., Pasquini, S., Blo, I., Salati, S., Cadossi, M., et al. (2021). Pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation in osteogenesis and chondrogenesis: signaling pathways and therapeutic implications. IJMS 22, 809. doi:10.3390/ijms22020809
Veronesi, F., Cadossi, M., Giavaresi, G., Martini, L., Setti, S., Buda, R., et al. (2015). Pulsed electromagnetic fields combined with a collagenous scaffold and bone marrow concentrate enhance osteochondral regeneration: an in vivo study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 16, 233. doi:10.1186/s12891-015-0683-2
Veronesi, F., Torricelli, P., Giavaresi, G., Sartori, M., Cavani, F., Setti, S., et al. (2014). In vivo effect of two different pulsed electromagnetic field frequencies on osteoarthritis: PEMF FREQUENCY RESPONSE IN OA. J. Orthop. Res. 32, 677–685. doi:10.1002/jor.22584
Vinod, E., Kachroo, U., Rebekah, G., Thomas, S., and Ramasamy, B. (2021). In vitro chondrogenic differentiation of human articular cartilage derived chondroprogenitors using pulsed electromagnetic field. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 14, 22–28. doi:10.1016/j.jcot.2020.09.034
Wang, H., Tang, X., Li, W., Chen, J., Li, H., Yan, J., et al. (2019a). Enhanced osteogenesis of bone marrow stem cells cultured on hydroxyapatite/collagen I scaffold in the presence of low-frequency magnetic field. J. Mater Sci. Mater Med. 30, 89. doi:10.1007/s10856-019-6289-8
Wang, L., Li, Y., Xie, S., Huang, J., Song, K., and He, C. (2021). Effects of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy at different frequencies on bone mass and microarchitecture in osteoporotic mice. Bioelectromagnetics 42, 441–454. doi:10.1002/bem.22344
Wang, Q., Zhou, J., Wang, X., Xu, Y., Liang, Z., Gu, X., et al. (2022). Coupling induction of osteogenesis and type H vessels by pulsed electromagnetic fields in ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in mice. Bone 154, 116211. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2021.116211
Wang, X., Dai, X., and Chen, Y. (2023). Sonopiezoelectric nanomedicine and materdicine. Small 19, 2301693. doi:10.1002/smll.202301693
Wang, Y., Pu, X., Shi, W., Fang, Q., Chen, X., Xi, H., et al. (2019b). Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote bone formation by activating the sAC–cAMP–PKA–CREB signaling pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 234, 2807–2821. doi:10.1002/jcp.27098
Wendt, D., Marsano, A., Jakob, M., Heberer, M., and Martin, I. (2003). Oscillating perfusion of cell suspensions through three-dimensional scaffolds enhances cell seeding efficiency and uniformity. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 84, 205–214. doi:10.1002/bit.10759
Wiesmann, H.-P., Hartig, M., Stratmann, U., Meyer, U., and Joos, U. (2001). Electrical stimulation influences mineral formation of osteoblast-like cells in vitro. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Res. 1538, 28–37. doi:10.1016/S0167-4889(00)00135-X
Willers, C., Norton, N., Harvey, N. C., Jacobson, T., Johansson, H., Lorentzon, M., et al. (2022). Osteoporosis in Europe: a compendium of country-specific reports. Arch. Osteoporos. 17, 23. doi:10.1007/s11657-021-00969-8
Wu, A.-M., Bisignano, C., James, S. L., Abady, G. G., Abedi, A., Abu-Gharbieh, E., et al. (2021). Global, regional, and national burden of bone fractures in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis from the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2, e580–e592. doi:10.1016/S2666-7568(21)00172-0
Xiong, J. (2012). Phase 4 study of early applied pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postoperative delayed union of long-bone fractures. Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01574833 (Accessed December 31, 2024).
Yamada, S., Yassin, M. A., Schwarz, T., Mustafa, K., and Hansmann, J. (2022). Optimization and validation of a custom-designed perfusion bioreactor for bone tissue engineering: flow assessment and optimal culture environmental conditions. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 811942. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.811942
Yang, X., Guo, H., Ye, W., Yang, L., and He, C. (2021). Pulsed electromagnetic field attenuates osteoarthritis progression in a murine destabilization-induced model through inhibition of TNF-α and IL-6 signaling. CARTILAGE 13, 1665S–1675S. doi:10.1177/19476035211049561
Yang, X., He, H., Zhou, Y., Zhou, Y., Gao, Q., Wang, P., et al. (2017). Pulsed electromagnetic field at different stages of knee osteoarthritis in rats induced by low-dose monosodium iodoacetate: effect on subchondral trabecular bone microarchitecture and cartilage degradation. Bioelectromagnetics 38, 227–238. doi:10.1002/bem.22028
Ye, W., Guo, H., Yang, X., Yang, L., and He, C. (2020). Pulsed electromagnetic field versus whole body vibration on cartilage and subchondral trabecular bone in mice with knee osteoarthritis. Bioelectromagnetics 41, 298–307. doi:10.1002/bem.22263
Yin, Y., Chen, P., Yu, Q., Peng, Y., Zhu, Z., and Tian, J. (2018). The effects of a pulsed electromagnetic field on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 24, 3274–3282. doi:10.12659/MSM.907815
Yong, Y., Ming, Z. D., Feng, L., Chun, Z. W., and Hua, W. (2014). Electromagnetic fields promote osteogenesis of rat mesenchymal stem cells through the PKA and ERK1/2 pathways. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 10, E537–E545. doi:10.1002/term.1864
Yuan, J., Xin, F., and Jiang, W. (2018). Underlying signaling pathways and therapeutic applications of pulsed electromagnetic fields in bone repair. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 46, 1581–1594. doi:10.1159/000489206
Zha, K., Tian, Y., Panayi, A. C., Mi, B., and Liu, G. (2022). Recent advances in enhancement strategies for osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in bone tissue engineering. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 10, 824812. doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.824812
Zhou, J., Chen, S., Guo, H., Xia, L., Liu, H., Qin, Y., et al. (2013). Pulsed electromagnetic field stimulates osteoprotegerin and reduces RANKL expression in ovariectomized rats. Rheumatol. Int. 33, 1135–1141. doi:10.1007/s00296-012-2499-9
Zhou, J., Liao, Y., Xie, H., Liao, Y., Liu, H., Zeng, Y., et al. (2017). Pulsed electromagnetic field ameliorates cartilage degeneration by inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinases in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Phys. Ther. Sport 24, 32–38. doi:10.1016/j.ptsp.2016.10.003
Zhou, J., Ming, L.-G., Ge, B.-F., Wang, J.-Q., Zhu, R.-Q., Wei, Z., et al. (2011). Effects of 50Hz sinusoidal electromagnetic fields of different intensities on proliferation, differentiation and mineralization potentials of rat osteoblasts. Bone 49, 753–761. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2011.06.026
Zhou, J., Wang, J.-Q., Ge, B.-F., Ma, X.-N., Ma, H.-P., Xian, C. J., et al. (2014). Different electromagnetic field waveforms have different effects on proliferation, differentiation and mineralization of osteoblasts in vitro: effects of electromagnetic fields on Osteoblasts. Bioelectromagnetics 35, 30–38. doi:10.1002/bem.21794
Zhou, X., Castro, N. J., Zhu, W., Cui, H., Aliabouzar, M., Sarkar, K., et al. (2016a). Improved human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis in 3D bioprinted tissue scaffolds with low intensity pulsed ultrasound stimulation. Sci. Rep. 6, 32876. doi:10.1038/srep32876
Keywords: pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF), bone, cartilage, bone fractures, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, fracture healing, quantitative comparison
Citation: Masante B, Gabetti S, Silva JC, Putame G, Israel S, Bignardi C and Massai D (2025) Insights into bone and cartilage responses to pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation: a review with quantitative comparisons. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1557572. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1557572
Received: 08 January 2025; Accepted: 24 June 2025;
Published: 10 July 2025.
Edited by:
Roland Wohlgemuth, Lodz University of Technology, PolandReviewed by:
Ezhaveni Sathiyamoorthi, Yeungnam University, Republic of KoreaAryan Morita, Gadjah Mada University, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Masante, Gabetti, Silva, Putame, Israel, Bignardi and Massai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Diana Massai, ZGlhbmEubWFzc2FpQHBvbGl0by5pdA==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Beatrice Masante
Beatrice Masante Stefano Gabetti
Stefano Gabetti Joao C. Silva
Joao C. Silva Giovanni Putame
Giovanni Putame Simone Israel
Simone Israel Cristina Bignardi
Cristina Bignardi Diana Massai
Diana Massai