- 1Department of Surgical Anesthesia, First Affiliated Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 2Basic Medical College, Army Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 3First Affiliated Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 4Department of Orthopaedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing, China
Bone infection is an infectious disease characterized by the accumulation of various pathogens in bone tissue, often causing significant suffering to patients. Current therapeutic approaches for bone infections predominantly rely on the postoperative application of implantable antibacterial materials, highlighting their essential role in clinical treatment. In this review, we systematically analyze research progress in antibacterial implant materials for Bone infection from 2019 to 2025. Materials are classified into four categories based on matrix composition: metal-based composite implants, bioceramic-based composite implants, polymer-based composite implants, and other composite implant materials, with dedicated focus on the limitations of each material type. The deterioration effects of these materials are also thoroughly analyzed. Finally, we present our own insights regarding future development directions of antibacterial implant materials. This review aims to provide practical references and research perspectives for advancing antibacterial implant material development.
1 Introduction
Bone infection represents a devastating condition characterized by bacterial or other pathogenic invasions into bone tissue, often leading to bone destruction and subsequent bone defects (Porrino et al., 2020). Severe trauma, such as open fractures of extremities, carries a 30% probability of progressing to infectious osteomyelitis, if prompt debridement is not performed, frequently resulting in substantial patient suffering (Metsemakers et al., 2017). The incidence of secondary bone defects caused by surgical resection (e.g., radical tumor excision) has also been increasing (Driscoll et al., 2020; Pazarçeviren et al., 2020). In recent years, with the widespread adoption of joint replacement surgeries, implant-related infections have shown a year-on-year rise, emerging as one of the primary complications within 3 months postoperatively for both knee and hip arthroplasty, and contributing to elevated mortality rates (Rennert-May et al., 2018; Scialla et al., 2021).
According to previous epidemiological investigations, Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) remains the predominant pathogen in bone infections (Kong et al., 2022), Oxacillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) produces lethal toxins and exhibits high drug resistance, accounting for over 50% of S. aureus-related infections (Dudareva et al., 2019). Other pathogens, including Escherichia coli (E. coil), Cutibacterium acnes, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, can also induce bone infections. S. aureus-mediated bone infections primarily involve four mechanisms: intracellular infection, osteocyte lacuna-canalicular network (OLCN) invasion, biofilm formation, and abscess development (Libraty et al., 2012; de Mesy Bentley et al., 2017) (detailed in Section 2). These mechanisms collectively enable S. aureus to colonize and persist within bone tissue, resulting in protracted osteomyelitis. Consequently, S. aureus-induced bone infections are particularly severe and clinically challenging to manage.
Current therapeutic approaches for bone infections primarily involve surgical intervention and antimicrobial administration. Surgical techniques are based on classical Ilizarov and Masquelet methods (Hatashita et al., 2021; Szelerski et al., 2021). Both of which present limitations including joint stiffness, delayed union, or nonunion at defect sites (Aktuglu et al., 2019). Concurrently, the rising bacterial minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) compromises the efficacy of locally or systemically administered antibiotics (Satola et al., 2011; Aljohani et al., 2020). Consequently, contemporary treatment protocols combine surgical debridement with localized application of antibacterial materials and adjunctive systemic antibiotic therapy. This underscores the critical importance of advanced antibacterial materials in bone infection management, representing both a pivotal strategy for therapeutic improvement and an emerging focus in this field (Ding et al., 2022). Currently approved orthopedic antibacterial implants include: antimicrobial metal-coated implants (e.g., those containing bioactive metals like silver (Ag), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu)); absorbable magnesium (Mg) alloy antibacterial screws; antibiotic-loaded bone cement (gentamicin- polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)cement); bioceramic composites; and dynamically responsive smart implants. Most of these materials are composite systems, as single-type matrix materials typically exhibit both advantages and limitations. Combining multiple materials (e.g., Mg alloy/graphene oxide (GO)/hydroxyapatite (HAP) composite coatings that inhibit bacterial adhesion through synergistic effects between magnesium hydroxide and GO (Yuan et al., 2022)), enables enhanced functionality, such as smart antibacterial materials capable of autonomously regulating local temperature and pH levels (Frazar et al., 2020; Li et al., 2020; Nagase, 2021). These systems achieve optimal transitions between bactericidal activity and sustained release during different infection phases. Material modifications also address historical limitations: PMMA remains a clinically established bone filler, yet its polymerization process generates substantial heat, imposing thermal stability requirements on incorporated antibiotics (Lai et al., 2013). This exothermic reaction typically causes burst antibiotic release rather than sustained antimicrobial action. To overcome this, researchers have developed PMMA composites incorporating silica particle-gentamicin complexes, achieving prolonged antibiotic release post-implantation (Al Thaher et al., 2018). Surface modifications and doping techniques have been extensively applied to inert metal implants (predominantly titanium [Ti] implants) (Yu et al., 2023; Hou et al., 2025; Tan et al., 2025), alongside emerging materials controllable via photoelectric, photothermal, and magnetic field effects. The antibacterial mechanisms of materials can be broadly categorized into bactericidal and bacteriostatic effects, both contributing positively to bone infection management. Antimicrobial efficacy is achieved through two primary pathways: direct antimicrobial action from material properties, or indirect immune cell modulation via material-tissue interactions. Regardless of the antimicrobial approach employed, effective treatment necessitates defect filling to restore bone continuity, making the selection of appropriate implant matrices critical. Current implant matrices predominantly utilize inert materials, classified as: metal-based composite implants, bioceramic-based composite implants, polymer-based composite implants, and other composite systems. Following this classification framework, we review representative advancements in antibacterial implant materials, analyze associated degenerative issues, and propose countermeasures, aiming to provide systematic references for current research progress in bone infection therapeutic materials.
2 Mechanisms of bacterial-induced bone infection
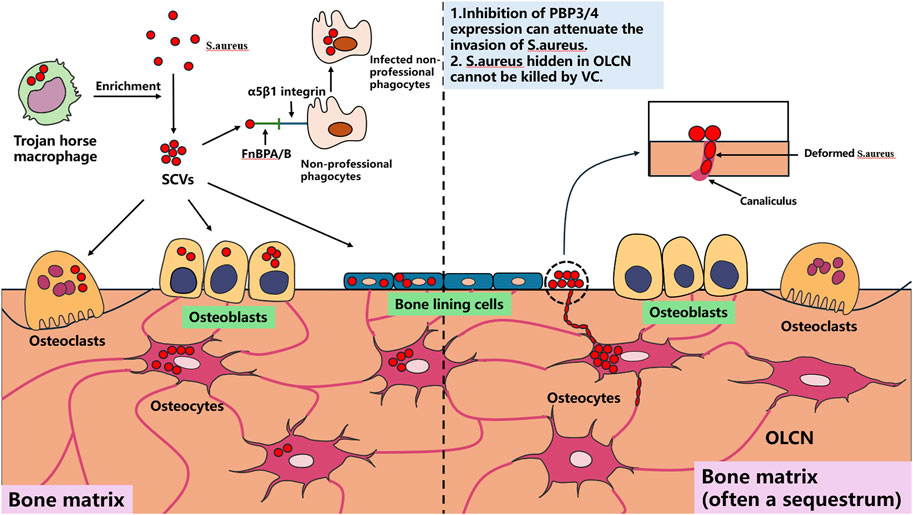
Using S. aureus as the primary example, most current implantable antibacterial materials target this pathogen. Understanding its cellular infection mechanisms is essential for rational material design. S. aureus can persistently survive intracellularly within macrophages (Garzoni and Kelley, 2011), keratinocytes (Kintarak et al., 2004), epithelial cells, and endothelial cells (Dziewanowska et al., 1999; Edwards et al., 2010). Macrophages harboring intracellular S. aureus are termed “Trojan horse” macrophages, which critically facilitate infection dissemination and enrichment of small colony variants (SCVs) (Garzoni and Kelley, 2011). SCVs, a specialized S. aureus phenotype, are primarily responsible for chronic recurrent infections. Within bone tissue, S. aureus demonstrates persistent survival in osteocytes, osteoclasts (OCs), and osteoblasts (OBs) (Josse et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2018; Krauss et al., 2019). Direct osteocyte infection constitutes a pivotal mechanism in bone infection progression, primarily through S. aureus-induced cytokine production by OCs that drives pathological bone loss.
Notably, S. aureus employs amoeboid motility to invade and persist within the confined to OLCN (Yu et al., 2020), a process mechanistically linked to PBP3 and/or PBP4 gene expression (da Costa et al., 2018). Suppressing the expression of these two genes may provide novel insights for developing implantable therapeutic materials against bone infections. Bacterial biofilm formation constitutes a critical step in bone infection pathogenesis, as established biofilms impede antibiotic penetration and immune cell infiltration into deep infection sites while resisting mechanical disruption, frequently leading to therapeutic failure (Masters et al., 2019).
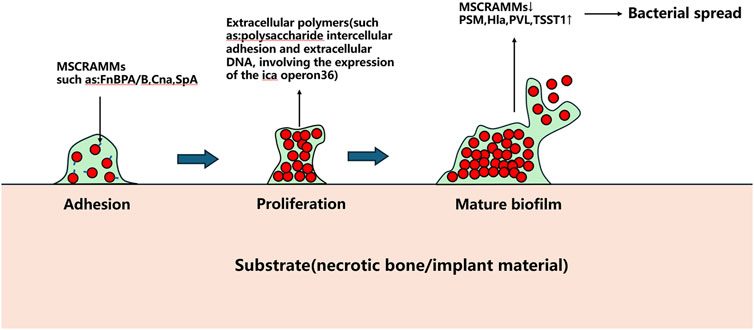
The Agr quorum sensing system serves as a key regulator of S. aureus biofilm development. Under low cell density conditions, S. aureus expresses microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules (MSCRAMMs), such as fibronectin-binding proteins A and B (FnBPA and FnBPB), collagen adhesin (Cna), and staphylococcal protein A (SpA), which facilitate bacterial adhesion to abiotic surfaces (Patti et al., 1994). Following adhesion, bacterial proliferation commences. Upon reaching critical population density, the Agr system downregulates MSCRAMMs expression while producing phenol-soluble modulins (PSMs) and virulence factors including α-haemolysin (Hla), Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL), and toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST1), triggering biofilm dispersal (Patti et al., 1994).
Beyond biofilms, S. aureus forms staphylococcal abscess communities (SACs) that contribute to chronic osteomyelitis and peri-implant chronic inflammation progression. SACs persistently acquire iron through iron-scavenging proteins (IdA, IsdB, IsdH) by binding hemoglobin and extracting heme iron for metabolic utilization (Kim et al., 2010). This iron sequestration concurrently compromises local blood supply, exacerbating infection severity (Carek et al., 2001; Kavanagh et al., 2018). Currently, surgical excision remains the sole effective SACs management approach, as these structures demonstrate remarkable resistance to antibiotics and immune attacks. The pathogenic mechanisms of S. aureus in bone infections are schematically summarized in Figures 1, 2.
3 Advances in antibacterial materials with different matrix types
3.1 Metal-based composite implant materials
Clinically utilized metal-based composite implant materials predominantly include: medical-grade stainless steel (316L stainless steel and its low-nickel high-nitrogen modified variants) with superior mechanical properties; wear-resistant cobalt-based alloys (Co-Cr-Mo, Co-Cr-W-Ni alloys); widely applied Ti and its alloys; biodegradable metals (Mg alloys, Zn alloys); and shape-memory alloys (notably nitinol, along with other noble/rare metals primarily employed in dental applications and sensor technologies) (Piñera-Avellaneda et al., 2024).
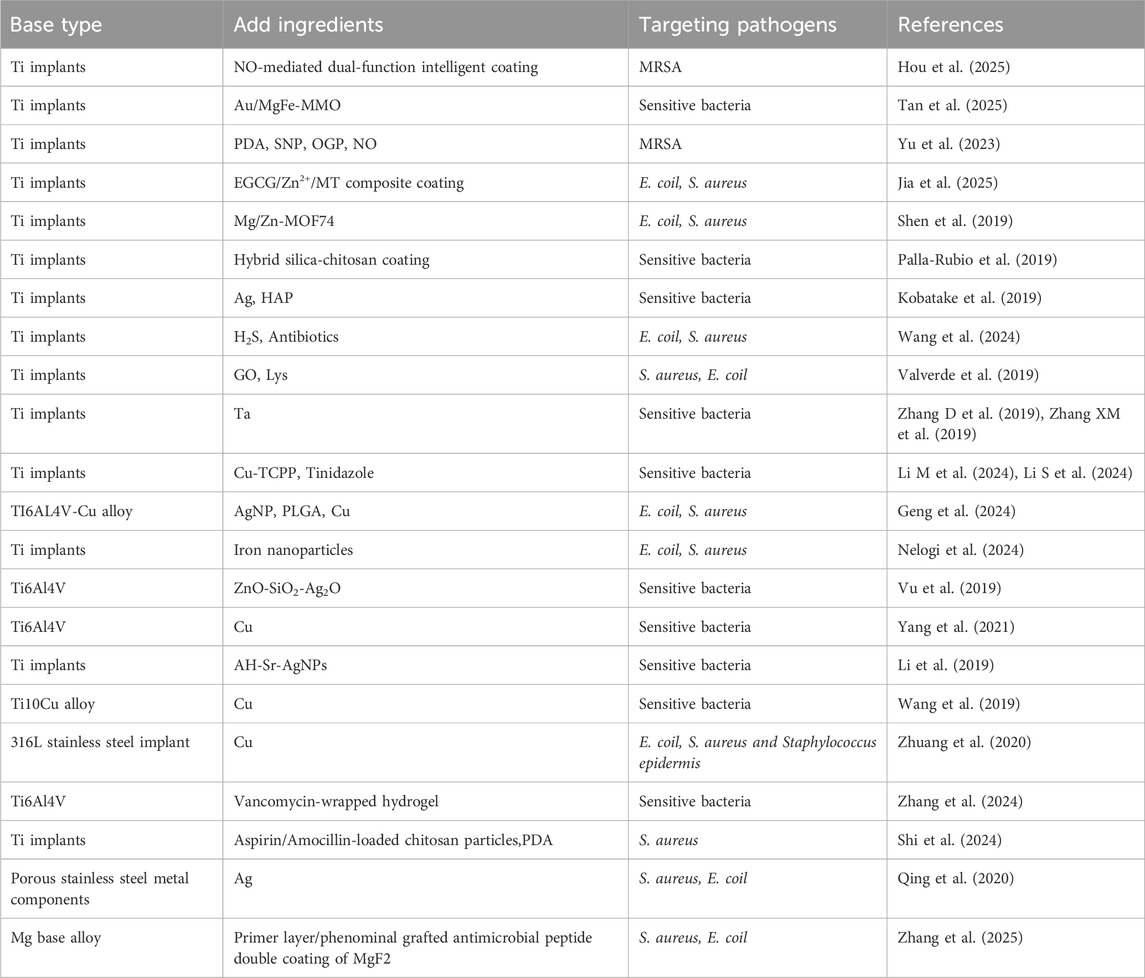
Ti implants currently represent the most widely used metallic matrix in orthopedic applications. However, challenges persist regarding their osseointegration and interfacial adhesion, making Ti-based implant modification a major focus in materials research with various innovative approaches being proposed (Uicich et al., 2024). Hou et al. developed a nitric oxide (NO)-mediated dual-functional smart Ti implant coating. This system achieves antibacterial efficacy through rapid high-dose NO release in response to infectious microenvironments and near-infrared stimulation, exhibiting antibacterial rates of 97.84% against MRSA and 97.18% against its biofilms. Once infection resolves and physiological conditions normalize, the coating gradually releases low-dose NO to enhance osseointegration (Hou et al., 2025). Hou et al. developed a nitric oxide (NO)-mediated dual-functional smart Ti implant coating. This system achieves antibacterial efficacy through rapid high-dose NO release in response to infectious microenvironments and near-infrared stimulation, exhibiting antibacterial rates of 97.84% against MRSA and 97.18% against its biofilms. Once infection resolves and physiological conditions normalize, the coating gradually releases low-dose NO to enhance osseointegration (Tan et al., 2025). Yu et al. proposed an interfacial functionalization strategy by integrating mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles (PDA), nitric oxide (NO)-releasing donor sodium nitroprusside (SNP), and osteogenic growth peptide (OGP) onto Ti implants (Ti-PDA@SNP-OGP). Under near-infrared irradiation, this system demonstrated synergistic photothermal and NO-dependent antibacterial effects against MRSA. Through reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated oxidative stress induction, it disrupted bacterial membrane integrity, caused intracellular component leakage, and effectively eradicated established MRSA biofilms (Yu et al., 2023). Another study constructed an EGCG/Zn2+/MT composite coating on Ti surfaces by loading melatonin (MT), polyphenol (EGCG), and Zn2+, achieving 97% and 81% inhibition rates against E. coil and S. aureus respectively. This coating regulated macrophage (RAW264.7) polarization toward M2 phenotype, induced angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), and promoted osteogenic differentiation of pre-osteoblasts (MC3T3-E1) (Jia et al., 2025). Shen’s team developed Mg/Zn-metal-organic framework (Mg/Zn-MOF74) composite coatings on Ti implants via alkaline thermal treatment. These coatings demonstrated structural stability and pH-responsive degradation in acidic microenvironments generated during bacterial proliferation. The degraded MOF74 coating exhibited potent antibacterial activity against E. coil and S. aureus. Ti implants with this novel coating showed enhanced early-stage antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties in vivo, significantly improving peri-implant new bone formation in both non-infected and infected femoral regions (Shen et al., 2019). Similarly, B. Palla-Rubio et al. fabricated hybrid silica-chitosan coatings on Ti implants via sol-gel method. Silicon (Sr), a crucial element for osteogenesis, is continuously released post-implantation, while chitosan exerts bacteriostatic effects (Palla-Rubio et al., 2019). Tomoki Kobatake’s group developed silver (Ag)- HAP coatings on pure Ti implants, demonstrating reduced bacterial burden in femoral bone infections after 14 days, though specific antibacterial mechanisms remain undetermined (Kobatake et al., 2019). Wang et al. engineered a responsive coating on Ti implants that achieves on-demand release of therapeutic hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and antibiotics to enhance osseointegration and eradicate infections. This coating sustains low-dose H2S release to promote osteogenic differentiation and cellular migration. Bacterial invasion disrupts the dense H2S donor layer, triggering rapid antibiotic release for infection prevention. The system exhibits effective antibacterial activity against E. coil and S. aureus through coordinated H2S/antibiotic delivery (Wang et al., 2024). Li et al. employed a layer-by-layer (LBL) assembly technique to sequentially deposit GO and lysozyme (Lys) onto Ti implants, forming an ultrathin film. This film demonstrated effective bactericidal activity against both S. aureus and E. coil while promoting osteoblast (OB) differentiation, showing promising clinical potential. Other researchers developed hyaluronic acid (HA)/chitosan polyelectrolyte multilayer films on Ti alloy surfaces. The chitosan component prevents bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation through its dense positive charge, while simultaneously serving as a reservoir for antimicrobial triclosan (TRI) (Valverde et al., 2019). Tantalum (Ta) coatings have demonstrated notable antibacterial properties. Zhang’s team modified Ti implants with Ta coatings, where micro-galvanic couples formed between Ta and Ti consume bacterial intracellular protons, reducing ATP synthesis while promoting ROS generation. This process downregulates bacterial virulence genes associated with cellular adhesion, invasion, and viability (Zhang D et al., 2019; Zhang XM et al., 2019). Li’s group engineered a sonosensitive metal-organic framework coating on Ti implants, comprising Cu-TCPP (tetrakis (4-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin) nanosheets and tinidazole-doped outer membrane vesicles (OMVs). Through high-penetration sonodynamic therapy (SDT), Cu-TCPP converts O2 to cytotoxic singlet oxygen (1O2) under normoxic conditions, exacerbating hypoxic microenvironments. Bacterial membrane disruption enhances Cu(I) transporter activity, obstructing the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and inducing Cu(I) overload, ultimately causing copper-toxicity-mediated bacterial death (Li M et al., 2024; Li S et al., 2024). Ti and Cu can form alloys, where Cu incorporation results in the formation of Cu-rich phases (Ti2Cu phase), which is critical for Cu2+ release in Ti-Cu alloys. For instance, Geng et al. developed a novel antibacterial osteogenic NSPTICU implant by coating nano-silver particles/poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) onto Ti6Al4V-Cu surfaces via solvent casting. This system leverages synergistic effects between silver nanoparticles and Cu2+, significantly reducing E. coil and S. aureus colony counts while demonstrating favorable osteogenic properties (Geng et al., 2024). Nelogi et al. constructed iron nanoparticle coatings on Ti implants, which respond to magnetic fields to enhance ROS generation, exhibiting potent antibacterial activity against E. coil and S. aureus (Nelogi et al., 2024). Nelogi et al. constructed iron nanoparticle coatings on Ti implants, which respond to magnetic fields to enhance ROS generation, exhibiting potent antibacterial activity against E. coil and S. aureus (Vu et al., 2019). Yang et al. fabricated and evaluated Ti6Al4V-6.5wt%Cu alloy, experimentally confirming its bactericidal action through electrostatic interactions with bacterial positive charges. This alloy accelerates biofilm aging and degradation, reduces C-reactive protein and leukocyte levels, and suppresses local inflammatory responses (Yang et al., 2021). Li et al. constructed a dual drug delivery system (denoted as AH-Sr- silver nanoparticles (AgNPs)) on Ti surfaces capable of independently releasing Sr2+ and Ag+. This system promoted M2 macrophage polarization for pathogen clearance, partially activated osteoblasts (OBs), and established a pro-healing microenvironment for bone infection resolution (Li et al., 2019). Wang et al. investigated the antibacterial properties of Ti10Cu alloy, demonstrating significantly lower local leukocyte counts and bacterial colony numbers in the Ti10Cu group compared to controls post-implantation, confirming its enhanced antibacterial efficacy (Wang et al., 2019). Zhang’s team integrated vancomycin-loaded hydrogels onto micro-arc oxidized 3D-printed porous Ti6Al4V implants, achieving controlled antibiotic release for precise bacterial proliferation inhibition (Zhang et al., 2024). Shi et al. developed aspirin/amoxicillin-loaded chitosan microparticles combined with PDA-modified Ti implants, experimentally verifying their capacity to suppress S. aureus proliferation through antimicrobial action (Shi et al., 2024).
Other modifications have been applied to stainless steel implants. Zhuang et al. developed a Cu-containing 316L stainless steel implant (316L-Cu SS) that demonstrates stable Cu release post-implantation, exhibiting significant antibacterial effects against E. coil (95.2% reduction), S. aureus (94.8% reduction), and Staphylococcus epidermidis (94.1% reduction), demonstrating potential for preventing implant-related infections (IRI) (Zhuang et al., 2020). Qing’s group fabricated Ag-containing coatings on porous stainless steel substrates via 3D printing combined with in situ hydrothermal crystallization. The released Ag+ effectively inhibits S. aureus and E. coil growth while maintaining excellent compatibility with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) (Qing et al., 2020). Mg-based alloys are considered promising biodegradable orthopedic implants, yet their clinical application is limited by rapid degradation rates and insufficient osteogenic/antibacterial performance. Zhang et al. engineered a dual-layer coating system on Mg alloys comprising an MgF2 primer layer and phenolic-amine grafted antimicrobial peptides. This system enhances corrosion resistance, promotes osteogenesis, and achieves over 85% antibacterial rates against both S. aureus and E. coil (Zhang et al., 2025). Metal-based composite implant materials are systematically summarized in Table 1.
Metal-based composite implant materials exhibit several critical limitations: (1) Antimicrobial metal ions (e.g., Ag+, Cu2+) have been demonstrated to induce cellular protein dysfunction, activate ROS generation, deplete intracellular antioxidants, and cause membrane damage. Systemic accumulation of these ions/particles in lymphatic and circulatory systems may lead to persistent cytotoxicity and increased carcinogenic risks (Teske and Detweiler, 2015). Additionally, nickel-containing alloys pose allergic reaction risks, with cobalt-chromium alloys exhibiting higher allergenic potential. (2) The elastic modulus of metallic materials (e.g., Ti alloys, stainless steel) significantly exceeds that of natural bone, resulting in ineffective load transfer to surrounding bone tissue. This mismatch induces stress shielding effects, triggering bone resorption and osteoporosis, which may ultimately cause implant loosening or fracture. (3) Although inert matrices like commercially pure Ti (cp-Ti) demonstrate mechanical strength, their poor biocompatibility often leads to fibrous encapsulation, compromising long-term osseointegration. (4) Metallic implants generate substantial imaging artifacts in CT/MRI examinations, obscuring critical postoperative evaluations such as bone healing status or tumor recurrence. (5) High manufacturing costs associated with precision forging or 3D printing technologies make metallic implants economically burdensome compared to polymeric/ceramic alternatives.
3.2 Bioceramic-based composite implant materials
Bioceramic matrix materials, including bioactive glass (BG), calcium phosphate, and silicate ceramics, exhibit exceptional osteoconductivity, osteoinductivity, favorable cytocompatibility, low immunogenicity, controllable degradability, multifunctionality, and intrinsic antibacterial properties in certain formulations (Nguyen et al., 2024). Current research focuses on three primary directions: functionalized surface modifications (e.g., coralline alumina), development of multicomponent systems (e.g., HAP/collagen composites), and synergistic integration of antibacterial and therapeutic functions (e.g., nanosilver/hydroxyapatite composites (Bee et al., 2021)). The developmental trajectory of bioceramic-based implant materials is illustrated in Figure 3.
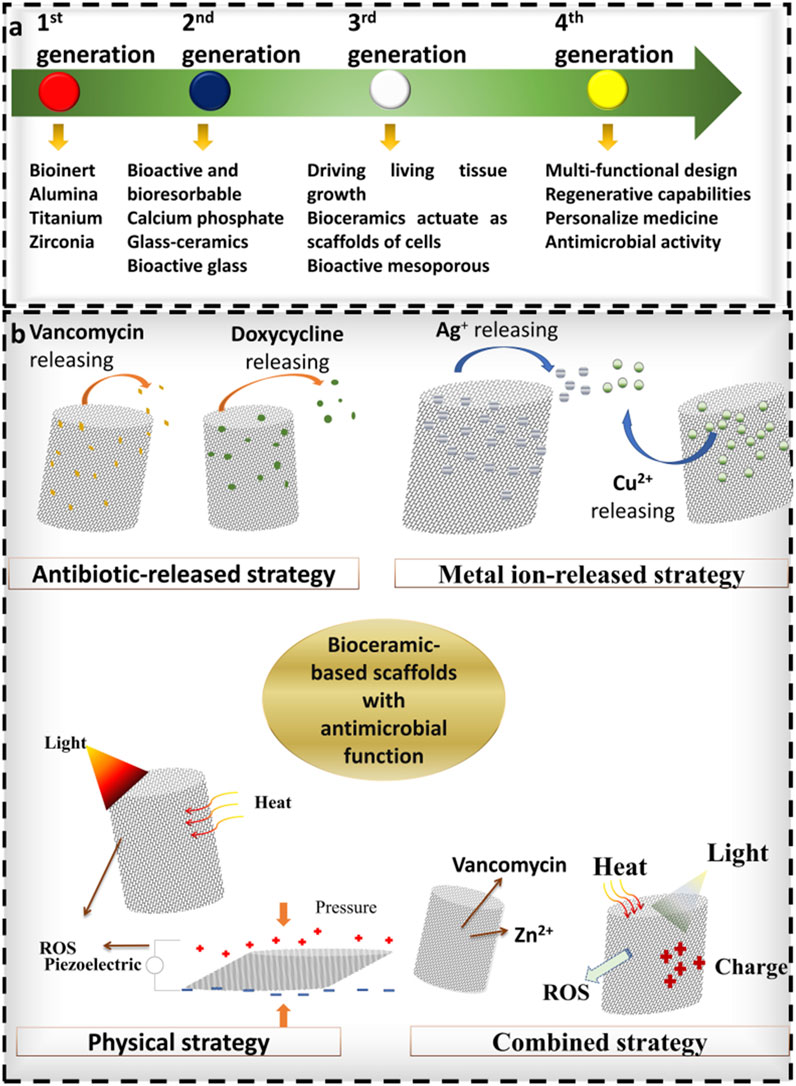
Figure 3. Illustrates the development of bioceramic-based materials, reproduced from (Nguyen et al., 2024) with permission.
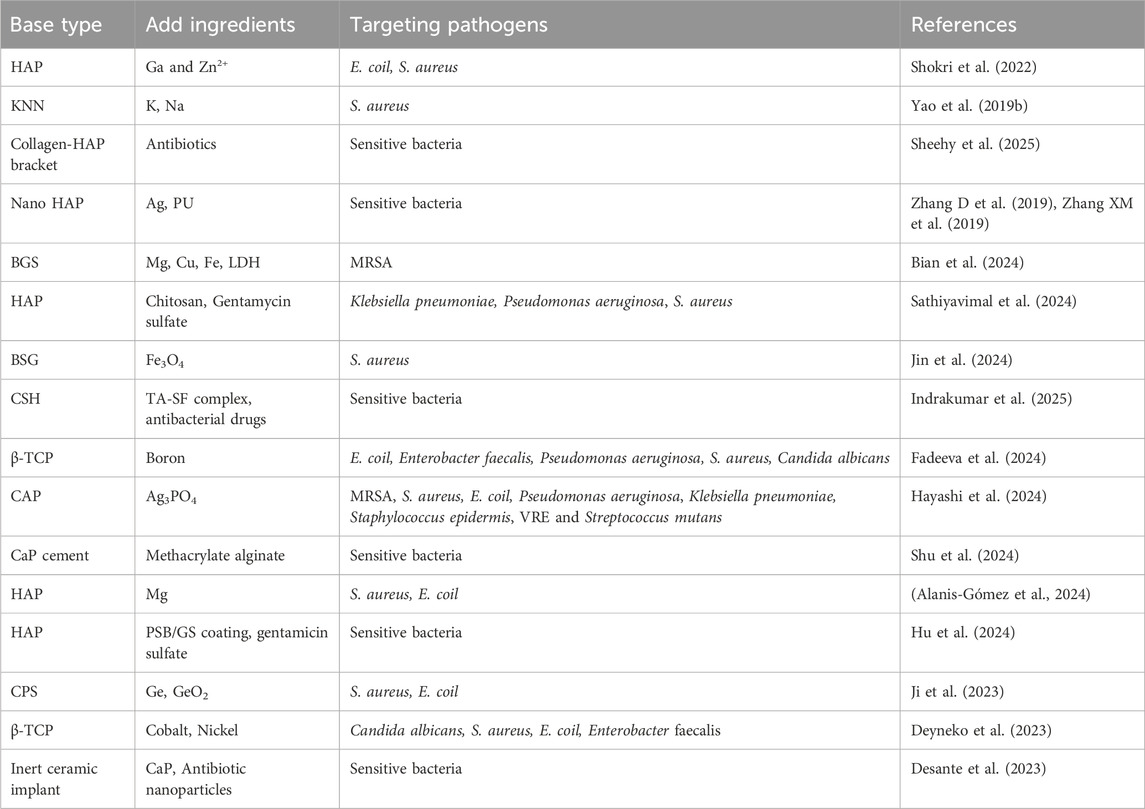
Mahshid Shokri et al. incorporated gallium (Ga) and zinc ions (Zn2+) into HAP matrices. The modified material demonstrated >60% antibacterial rates against both E. coil and S. aureus, while maintaining non-cytotoxicity toward bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs). Co-culture with BMSCs significantly enhanced alkaline phosphatase activity and mineralization capacity, indicating robust osteogenic promotion (Shokri et al., 2022). Yao et al. developed potassium-sodium niobate piezoelectric ceramics (K0.5Na0.5NbO3, KNN) and evaluated their biocompatibility and antibacterial efficacy. Results revealed substantial reductions in S. aureus colony counts and enhanced proliferation of rat BMSCs (rBMSCs), with mechanisms potentially linked to the surface positive charge of piezoelectric ceramics (Yao T. et al., 2019). Eamon J Sheehy et al. engineered an antibiotic-eluting collagen-HAP scaffold featuring a hierarchical dual-release system. This design enables initial rapid antibiotic release for infection eradication, followed by sustained controlled release to prevent recurrence. The system demonstrates compatibility with gentamicin, vancomycin, and other antibiotics (Sheehy et al., 2025). Zhang et al. synthesized nano-HAP composites containing 3% silver-doped polyurethane (PU) (3% Ag/nHAP/PU), demonstrating controlled Ag+ release with effective bactericidal activity. Subsequent studies revealed optimal bone defect repair, moderate scaffold degradation rates, and favorable cytocompatibility in the 3% Ag/nHAP/PU group (Zhang D et al., 2019; Zhang XM et al., 2019). Mg-doped HAP (HAP-Mg) nanofibers, structurally analogous to bone mineral with enhanced biocompatibility and antibacterial performance, were investigated by Ricardo Pascual Alanis-Gómez et al. Their findings revealed dose-dependent inhibitory effects of HAP-Mg nanoparticles against S. aureus and E. coil. This antibacterial mechanism correlates with Mg2+ release, which alters the structural integrity of bacterial cell walls/membranes and induces ROS generation, ultimately leading to bacterial death (Alanis-Gómez et al., 2024). Sathiyavimal et al. fabricated HAP composites using natural waste materials, combined with chitosan and gentamicin sulfate antibiotics (HAP/CS-GA). Experimental results demonstrated potent antibacterial activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and S. aureus (Sathiyavimal et al., 2024). Hu et al. designed a pH-responsive smart zwitterionic antibacterial coating (PSB/GS coating) deposited on HAP. During initial implantation, the hydrophilic zwitterionic polymer exhibited anti-bacterial adhesion properties, achieving over 90% reduction in protein and bacterial adhesion. Subsequent bacterial proliferation lowered the microenvironmental pH, triggering hydrolysis of acid-sensitive Schiff base bonds to release gentamicin sulfate on-demand, effectively enhancing antibiofilm performance (Hu et al., 2024).
Bian’s team developed a bioactive glass scaffold (BGS) functionalized with MgCuFe-layered double hydroxide (LDH)-derived sulfide nanosheets (BGS/MCFS). This system directly inhibits MRSA energy metabolism, disrupts bacterial membranes, and eliminates peri-implant infections through near-infrared photothermal properties (Bian et al., 2024). As previously described, S. aureus residing within OLCN and SACs presents significant therapeutic challenges, with conventional surgical irrigation proving ineffective and contributing to recurrent osteomyelitis. To address this, Jin et al. engineered a borosilicate bioactive glass (BSG) scaffold integrated with 5% ferroferric oxide (Fe3O4) magnetic nanoparticles. The BSG+5%Fe3O4 composite enhanced antibacterial immune responses, promoted osteogenic differentiation and mineralization of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and upregulated gene expression of nod-like receptors and TNF pathways in MSCs. Concurrently, it increased osteogenic factor expression (RUNX2, ALP, OCN) while elevating anti-inflammatory genes (TGF-β1, IL-1Ra) and suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β) in macrophages. Under alternating magnetic fields, complete eradication of SACs and bacteria within OLCN was achieved after 42 days of treatment (Jin et al., 2024). Indrakumar developed a drug delivery platform incorporating tannic acid (TA)-silk fibroin (SF) composites into calcium sulfate hemihydrate (CSH). Compared to pure CSH particles, the composite demonstrated a 7.5-fold increase in antioxidant activity and extended antibacterial efficacy by 13 days (Indrakumar et al., 2025). Inna V Fadeeva incorporated boron into β-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) bioceramics, revealing that 30% boron-loaded TCP exhibited inhibitory effects against multiple pathogens: 30.9% for Escherichia coli, 36.4% for Enterococcus faecalis, 37.8% for Pseudomonas aeruginosa, 46.8% for S. aureus, and 38.8% for Candida albicans (Fadeeva et al., 2024). Hayashi et al. developed a carbonate apatite (CAP) matrix with osteoconductivity and biodegradability, partially substituting its surface with Ag3PO4. This material demonstrated antibacterial activity values exceeding 2 (corresponding to 99% lethality) against MRSA, S. aureus, E. coil, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus epidermidis, VRE, and Streptococcus mutans under in vitro shaking conditions, exhibiting potent bactericidal efficacy without significant cytotoxicity (Hayashi et al., 2024). Shu et al. fabricated photo-crosslinked methacrylated alginate-co-calcium phosphate cement (PMA-co-PCPC) with antibacterial properties. By employing CuCl2 and SrCl2 as inhibitors and CaCl2 as an activator, the system achieved precisely regulated antimicrobial activity (Shu et al., 2024). Ji et al. leveraged the antibacterial properties of germanium (Ge) and GeO2 to augment silicon carbonate (CPS). Results demonstrated that Ge-CPS effectively inhibited S. aureus and E. coil proliferation. Sustained Ge release during bioceramic degradation ensured prolonged antibacterial activity (Ji et al., 2023). Dina V Deyneko conducted supplementary studies on β-TCP doped with cobalt and nickel. Nickel incorporation exhibited dose-dependent inhibitory effects against Candida albicans, S. aureus, E. coil, and Enterococcus faecalis, while showing ambiguous efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Deyneko et al., 2023). Gaëlle Desante et al. proposed biomimetic calcium phosphate (CaP) coatings encapsulating antibiotic-loaded nanoparticles (gentamicin or bacitracin) to multifunctionalize inert ceramic implants. This approach enhanced both bioactivity and antibacterial efficacy (Desante et al., 2023). Table 2 summarizes bioceramic-based composite implant materials.
The defects of bioceramic-based composite implant materials are mainly as follows: (1) Fragile. Although their hardness is high, bioceramic-based materials are prone to fracture under high stress conditions (such as the fragmentation rate is as high as 15% during inlay repair), and this risk will further increase during large-scale repair applications; (2) The elastic modulus is mismatched, such as zirconia (elastic modulus about 200 GPa) is much higher than that of human bone (7–30 GPa), which may lead to stress shielding effect, and long-term implantation triggers bone resorption; (3) Poor fatigue resistance, and under repeated stress environments (such as artificial joints), ceramic materials are prone to failure due to microcrack propagation, and need to be improved through toughening technology (such as nanocomposite). (4) The rate of degradation in vivo may not match the rate of bone growth, resulting in the risk of repair failure; (5) Risk of biocompatibility. A few patients may have allergies or local inflammatory reactions to ceramic components (such as certain phosphates or metal ions doping) (the incidence rate is about 1%–3%), and there is also the possibility of bioceramic-based materials that cannot be integrated with human bones, and long-term stress weakness may occur. (6) The production cost of bioceramic-based materials is relatively high and processing is difficult. These limit the widespread application of bioceramic-based materials in clinical practice. At present, various ways have been improved to address these problems of bioceramic-based implant materials, such as making composite materials by doping nanomaterials for increasing toughness treatment. Some researchers have also combined Mg alloys or polymers with bioceramic materials to balance the relationship between material strength and degradation rate.
3.3 Polymer-based composite implant materials
Polymer-based implants represent another major category for bone infection defect repair, including classical materials such as PMMA (Ghavimi et al., 2019), polyetheretherketone (PEEK) (Zheng et al., 2024), polylactic acid (PLA), PU (Hu et al., 2014), and polyethylene. These materials generally exhibit favorable biocompatibility. Certain formulations, notably PEEK, possess elastic moduli comparable to human bone, thereby mitigating stress shielding-induced bone resorption. PEEK is regarded as the most viable alternative to Ti. However, these polymers inherently lack antibacterial activity. Functional enhancements can be achieved through chemical modifications or composite material incorporation to improve mechanical properties (e.g., hardness, fatigue resistance), osteoconductivity, and antimicrobial performance.
Similar to Ti-based implants, surface modification of PEEK remains a key focus in polymer-based implant research. Zhao et al. loaded L-arginine onto sulfonated PEEK (SPEEK). Under infectious conditions, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) catalyzes L-arginine to generate NO and ROS, exerting bactericidal effects. Additionally, this system induces macrophage polarization toward M1 and M2 phenotypes, providing indirect antibacterial action (Zhao et al., 2024). Chen et al. developed a hydrogel coating (GPL) composed of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA), methacrylamide-modified ε-polylysine (ε-PLMA), and laponite, crosslinked onto PEEK via UV irradiation. This surface modification enhances osteogenic capacity while maintaining antibacterial activity against S. aureus and E. coil until complete hydrogel hydrolysis (Chen et al., 2023). Han et al. applied the natural antimicrobial agent paclitaxel as a coating on fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D-printed PEEK. At a paclitaxel concentration of 10 mg/mL, the coating exhibited contact-killing effects that inhibited biofilm development (Han et al., 2024). Wei et al. modified SPEEK surfaces with Ag+-incorporated GO films. The modified material inhibited proliferation of S. aureus, E. coil, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Candida albicans, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, while reducing bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. GO incorporation enhanced Ag+ release, optimizing bactericidal efficacy (Wei et al., 2024). Sun et al. fabricated gentamicin-loaded chitosan coatings on porous PEEK fixation plates, demonstrating superior antibacterial activity against S. aureus and E. coil (Sun et al., 2025). Notably, Liu et al. innovatively immobilized siRNA onto PEEK surfaces using antimicrobial polyphenol tannic acid (pTAN). pTAN inhibits bacterial adhesion by suppressing glycosyltransferase activity, increases membrane permeability, and ultimately induces cytoplasmic leakage leading to bacterial death (Liu et al., 2024). Şakir Altınsoy et al. incorporated AgNPs and copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) onto PEEK surfaces for evaluation. Results demonstrated that AgNPs exhibited superior antioxidant properties compared to CuNPs, significantly enhancing PEEK’s surface activity and antibacterial performance (Altınsoy et al., 2024).
Carbon fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone (CFRPEEK), a modified PEEK variant, is considered a promising biomedical implant material. However, its inertness and insufficient antibacterial activity limit clinical utility. Wang et al. modified CFRPEEK via Ti plasma immersion ion implantation and hybridization with PDA@ZnO-EDN1 nanoparticles. The modified CFRPEEK effectively inhibited S. aureus and E. coil adhesion/aggregation, significantly increasing bacterial membrane permeability. Subsequent leakage of intracellular components (e.g., proteins and adenosine triphosphate, ATP) induced bacterial death (Wang J et al., 2023; Wang X et al., 2023). Diabetic patients frequently suffer from comorbid bone infections, where the diabetic infection microenvironment (DIME) – characterized by hyperglycemia and peri-implant pathogenic infections–often leads to bone repair failure. To address this, He et al. engineered a glucose-responsive orthopedic implant comprising PEEK, a copper-chelated metal-polyphenol network (hauberk coating), and glucose oxidase (GOx). Within DIME, GOx continuously consumes glucose to generate H2O2, while the hauberk coating releases Cu to catalyze H2O2 into highly bactericidal hydroxyl radicals (•OH). Subsequent photo-enhanced chemodynamic therapy eradicates pathogens, offering a novel strategy for refractory diabetic Bone infection (He et al., 2023). Li et al. developed a dual-functional surface modification strategy by achieving sustained release of chondroitin sulfate (CS) and levofloxacin (LVFX) from a bio-inspired PDA coating on PEEK. LVFX release provided localized bactericidal effects and promoted bone defect repair (Li M et al., 2024; Li S et al., 2024). Gao et al. immobilized the antimicrobial peptide HHC36 onto the three-dimensional porous structure of SPEEK and conducted characterization. Experiments demonstrated sustained HHC36 release over 10 days from SPEEK, reducing planktonic bacterial survival rates, suppressing peri-sample bacterial growth, and inhibiting surface biofilm formation (Gao et al., 2023). Enhancements have also been designed for other materials.
Fan et al. incorporated BSG into low-dose gentamicin sulfate-loaded PMMA cement to create an intelligent antibiotic release system. This strategy synergistically eradicated bacteria and promoted osseointegration by disrupting bacterial cell wall/membrane integrity, inhibiting ATP synthesis via respiratory chain and glycogen metabolism interference, and elevating ROS levels through depletion of antioxidant components (peroxisomes and carotenoids), achieving efficient bacterial killing and biofilm eradication (Fan et al., 2025). Ankita Negi et al. fixed citric acid-conjugated chitosan onto oxygen plasma-etched 3D-printed PLA scaffolds via EDC-NHS coupling. Compared to unmodified oxygen plasma-etched PLA scaffolds, the surface-modified scaffolds exhibited superior antibacterial activity against S. aureus and E. coil (Negi et al., 2024). Mohammad Reza Shafiei et al. incorporated rifampicin-loaded mesoporous silica into acrylic bone cement to address antimicrobial resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococcal biofilms. Results demonstrated that the modified cement enhanced mechanical strength and optimized drug release kinetics, achieving bactericidal efficacy while minimizing resistance development (Shafiei et al., 2025). Olga Bakina et al. developed novel PMMA-based HAP/ZnFe2O4/ZnO composites using ZnFe2O4/ZnO heterostructures as antibacterial agents. The material exhibited >99% inhibition against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, S. aureus, and MRSA, with 100% efficacy against Candida albicans. This activity likely stems from ZnFe2O4/ZnO-induced oxidative damage to cell membranes, proteins, and DNA, coupled with electrostatic gradient disruption leading to bacterial inactivation (Bakina et al., 2023). Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) represents an emerging matrix material. Mehmet D Asik et al. blended submicron gentamicin sulfate particles into UHMWPE, demonstrating significantly higher and sustained antibiotic release rates alongside improved mechanical properties, suggesting potential for IRI management (Asik et al., 2025). Li et al. fabricated a multifunctional gelatin methacryloyl/methacrylated dopamine adhesive hydrogel coating containing polydopamine-protected 2D black phosphorus (BP) nanoparticles via photocrosslinking, modifying polyarylethernitrileketone (PPENK) implant surfaces. The system enables photothermal-controlled drug delivery (e.g., doxorubicin hydrochloride) and photodynamic bacterial eradication. pBP’s photothermal effects regulate drug release via electrostatic interactions while generating ROS for bactericidal action, with ROS scavenging capabilities preventing normal cell apoptosis (Li J et al., 2023; Li Y et al., 2023). Table 3 summarizes Polymer-based composite implant materials.
Polymer-based composite implants are not without limitations. These materials exhibit limited load-bearing capacity due to elastic moduli that, while similar to skin and bone, remain significantly lower than those of metallic and ceramic-based materials, posing fracture risks in weight-bearing applications. Long-term use of UHMWPE may generate wear particles through oxidative degradation, potentially leading to osteolysis, prosthetic loosening, and revision surgeries. Biocompatibility challenges persist, including insufficient osseointegration of PEEK implants and non-specific protein adsorption that activates macrophages to release pro-inflammatory factors, exacerbating postoperative inflammation. Degradable polymers like PLA and PLGA face mismatched degradation-osteogenesis rates, while localized accumulation of degradation products may exacerbate bacterial-induced acidic microenvironments, potentially inhibiting OB activity. Additionally, complex manufacturing processes and high R&D costs hinder clinical translation, exemplified by the substantially higher development costs of fourth-generation ceramic-reinforced PEEK compared to metallic alternatives. Current strategies focus on nanocomposite integration (e.g., CFRPEEK) to enhance mechanical strength while preserving PEEK’s inherent advantages, surface functionalization to develop smart responsive materials, and 3D printing-based.
3.4 Other composite materials
Beyond the aforementioned three matrix types, other composite materials have achieved notable research progress. Addressing PLA’s limitations, Hyun Lee et al. developed PLA/Mg composites combining Mg with PLA. The composite retains PLA’s biodegradability while incorporating Mg’s intrinsic antibacterial properties and NIR-induced photothermal effects, synergistically minimizing IRI (Lee et al., 2023). Cheng et al. uniformly distributed silver nanoparticles within PLA/gelatin composite fibers via co-electrospinning. The composite demonstrated >97% antibacterial rates against Candida albicans, S. aureus, E. coil, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, alongside enhanced adhesion and proliferation of MSCs and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), indicating robust osteogenic activity (Cheng et al., 2020). Liu et al. constructed PDA self-polymerized films on PLA/HAP nanofibers, followed by stable silver nanoparticle coatings for controlled release. The composite fibers exhibited excellent physiological stability, 100% antibacterial efficacy against S. aureus and E. coil, and favorable osteoblast compatibility (Liu et al., 2020). Shi et al. engineered an infection-responsive guided tissue regeneration (GTR)/guided bone regeneration (GBR) membrane based on electrospun nanofibers. Metronidazole (MNA) was esterified and covalently linked via ester bonds to modified polycaprolactone (PCL) nanofiber mats. Under infection, cholesterol esterase (CE) secreted by macrophages hydrolyzes these ester bonds to release MNA, with CE concentrations correlating to bacterial infection severity, enabling infection-responsive drug release (Shi et al., 2019). Tang et al. developed nano zinc magnesium silicate (nZMS)/PK bioactive composites (nZPC). Increasing nZMS content significantly enhanced MC3T3-E1 cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation on nZPC. Maximum inhibition against E. coil was achieved at 50% nZMS loading (Tang et al., 2019).
Huang et al. designed a nanoreactor integrating piezoelectric barium titanate with PDA and Cu. Ultrasound activation generates piezoelectric hot carriers transferred by PDA to Cu, promoting ROS generation and Cu2+/Cu+ interconversion. This facilitates hydroxyl radical (•OH) production via Cu+-catalyzed chemodynamic reactions. Elevated ROS levels induce bacterial membrane disruption, DNA damage, and Cu overload-mediated TCA cycle inhibition, culminating in copper-toxicity-like bacterial death (Huang et al., 2024). Ujjayan Majumdar designed a Ti6Al4V disk coated with HAP, featuring a dual drug delivery system with curcumin in the lower layer and vitamin C in the upper layer. Curcumin and vitamin C releases demonstrated 94% and 98.6% antibacterial efficiency against S. aureus, respectively. Bacteria exposed to these agents exhibited either expanded membranes or compromised cellular integrity, confirming bactericidal efficacy of the implant design (Majumdar and Bose, 2024). Xie et al. developed a multifunctional collagen composite scaffold (CUR-GO-COL) by freeze-drying crosslinked curcumin-loaded GO and collagen. The composite achieved sustained curcumin release in vitro, reducing S. aureus and E. coil colony counts. This activity likely stems from GO’s edge-induced mechanical membrane damage and curcumin’s inherent antibacterial properties, synergistically compromising bacterial structural integrity and viability (Xie et al., 2024). Weronika Bodylska et al. combined biocompatible HAP with Ti-based metal-organic framework MIL-125(Ti)-NH2, impregnated with gentamicin to form a novel composite. Gentamicin integration significantly enhanced bactericidal effects against S. aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, highlighting metal-organic framework (MOF)-based composites as emerging research frontiers (Bodylska et al., 2024). Mansi Uday Joshi et al. engineered a pH-responsive alginate composite delivery system for tobramycin. Acidic infection microenvironments triggered responsive drug release, achieving >84% inhibition against S. aureus within 30 min (Joshi et al., 2023).
Researchers have also fabricated antibacterial materials by combining alginate with Zn, lactate, HAP, and other components. These composites exhibit excellent antibacterial performance and moderate osteogenic promotion capabilities (Suo et al., 2020; Beheshtizadeh et al., 2023; Tanadchangsaeng et al., 2024). Li et al. developed a hydrogel delivery vehicle loaded with DNase I and vancomycin. After implantation in rats, the system initially co-released DNase I and vancomycin, followed by sustained vancomycin release for up to 14 days, thus effectively eliminating MRSA infections, preventing biofilm formation, and providing a sterile microenvironment conducive to healing fracture-associated infections (Li J et al., 2023; Li Y et al., 2023). Wang et al. incorporated HAP microspheres into GelMA hydrogels via photocrosslinking to create multifunctional injectable hydrogels. These materials demonstrated enhanced flexural strength, cell adhesion sites, and antibacterial functionality through metal ion incorporation. The Ag-incorporated HAP/GelMA hydrogel showed significant inhibition against Escherichia coli but weaker efficacy against S. aureus, likely attributable to the thicker cell walls and inherent antimicrobial resistance of Gram-positive bacteria (Wang J et al., 2023; Wang X et al., 2023). Abdullah Mohammed et al. proposed a novel PLA/calcium peroxide (PLA/CPO) composite filament for 3D-printed scaffolds. Calcium and oxygen released from the material exhibited antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, which may be attributed to residual hydrogen peroxide generated during CPO decomposition (Mohammed et al., 2023).
4 Degradation effects and impacts of antimicrobial implant materials
Similar to materials utilized in other fields, antimicrobial implants cannot persist indefinitely in a pristine state post-implantation, as degradation ensures following introduction into the biological environment. The degradation effects refer to the progressive deterioration of antimicrobial efficacy and other material properties under physicochemical influences in vivo. These degradation manifestations primarily include: Uncontrolled release of antimicrobial agents, Biotoxicity of degradation byproducts, Decline/loss of mechanical strength and Delamination and functional loss of surface structures. Existing experimental evidence confirms multiple adverse impacts of degradation effects on host tissues. The uncontrolled release of antimicrobial agents may elevate local concentrations to cytotoxic levels, thereby compromising osteogenic activities (Feng et al., 2018). Current antimicrobial implants often incorporate AgNPs. Prolonged bacterial exposure to sublethal AgNP concentrations may activate the bacterial SOS repair system (Janion, 2008), potentially leading to enhanced biofilm formation and genetic mutations. Rapid degradation of Mg alloys can elevate local pH levels, creating alkaline microenvironments that induce tissue damage while prematurely compromising antimicrobial efficacy (Jin et al., 2014). Degradation-released metal ions (e.g., Ag+, Ni2+) may accumulate in organs such as the liver and kidneys, causing systemic toxicity. Circulating nickel ions may trigger allergic responses. Mechanical strength deterioration risks stress shielding effects or implant fracture, which could catastrophically result in secondary fractures and osseointegration failure for bone defect patients. Under stress conditions, carbon fiber-reinforced composites subjected to prolonged stress release particulate debris, exacerbating localized inflammatory responses (Kang et al., 2012). Furthermore, antimicrobial coatings represent a critical surface modification strategy for diverse implant materials. However, coating delamination can diminish or abolish antimicrobial efficacy. For instance, PDA-mediated Mg2+/ceria oxide coatings may prematurely exhaust antibacterial payloads in acidic infectious microenvironments due to pH-responsive release mechanism failure (Aurore et al., 2018). Degradation of photothermal-responsive materials (e.g., Au@ZIF-8) diminishes photocatalytic ROS generation capacity (Ortiz-Benítez et al., 2019). Residual bacteria not fully eradicated by degraded photodynamic coatings may induce chronic infections (Yao T. et al., 2019), complicating subsequent therapeutic interventions.
5 Summary and perspectives
Although bone infection remains a devastating skeletal disease, novel intelligent materials continue to emerge. This review systematically categorizes antimicrobial implant materials for bone infection defect repair (2019–2025, with emphasis on 2024–2025) based on matrix types, encompassing both newly developed materials and enhanced traditional systems. Most materials exhibit multifunctionality, integrating antibacterial efficacy with osteogenic promotion and immunomodulatory capabilities. We comprehensively discuss advances in: Antimicrobial metal-based composite implants, antimicrobial bioceramic-based composite implants, antimicrobial polymer-based composite implants and other specialized antimicrobial composite systems. Concurrent attention is given to material degradation effects. Despite inherent application-specific limitations, encouraging progress is evident. Emerging research prioritizes: Functional integration: Transition from single antibacterial functions to synergistic antibacterial-osteogenic systems; Intelligent responsiveness: pH-/photothermal-responsive materials; Bioinspired precision: Bacteria-responsive antimicrobial release mimicking physiological immune environments. These developments expand therapeutic options for bone infection management.
The future development of various materials mainly includes the following directions. For metal-based composite implant materials, the first direction is the potential transition from mechanical adaptation to controllable degradation. The developed Ti-Ta and Ti-niobium (Ti-Nb) low-modulus alloys and gradient porous structures (e.g., 3D-printed porousTi) (Sun et al., 2023) are designed to address the mismatch between elastic modulus and bone. Additionally, regulating the degradation rate by adding rare metal elements to Mg alloys and Zn alloys may enable dynamic matching between degradation rates and bone regeneration in the future, or accelerate the release of antibacterial metal ions under infectious microenvironments. Finally, functionalized surface modifications can enhance osseointegration capacity, promote the role of local immune cells, and reduce the likelihood of local allergic reactions (Zhang et al., 2023). For bioceramic-based composite implant materials, the focus lies in nanocomposite reinforcement, degradation regulation, intelligent responsiveness (pH- or enzyme-responsive ceramics), and functional structural design (4D-printed bioceramic materials, shape-memory ceramics (zirconia-based bioceramic materials)), aiming to transform bioceramics from inert materials into intelligent responsive materials. The development of polymer-based composite implant materials also follows the directions of nanoscale engineering, intelligent responsiveness, and controlled degradation rates. Meanwhile, most composite materials are no longer simple combinations of components but emphasize synergistic interactions, gradient composites, and biomimetic multimodal development. Materials are no longer limited to antibacterial properties but strive to design multifunctional implants (Zhang et al., 2023). While retaining antibacterial capabilities, electrical stimulation can be applied to promote osteogenesis at bone defect sites. Furthermore, advancements in novel technologies such as 4D printing technology (a printing technology capable of manufacturing “dynamic” objects responsive to external stimuli), 3D bioprinting technology, and in situ manufacturing technology are shifting implant materials from standardized mass production toward personalized designs. For example, some studies integrate 4D printing with smart materials to create antibacterial implants that adapt to anatomical structures (Zhou et al., 2023). The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) enables material production machines to intelligently learn parameters, optimize cost and quality issues during manufacturing, and reduce the usage costs of antimicrobial materials. Current research on antibacterial materials involves interdisciplinary collaborations. By combining single-cell sequencing with bone infection models, researchers aim to elucidate the regulatory mechanisms of OB competitive adhesion on material surface topologies (e.g., nanopillar arrays), guiding the design of multifunctional antibacterial surfaces.
In summary, the development of novel antibacterial materials is still ongoing. We earnestly hope that future antibacterial implant materials for bone defects can maintain implantation performance and localized antibacterial efficacy over the long term, ultimately achieving permanent implantation.
Author contributions
BX: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JJ: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review and editing. HW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – review and editing. LS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. This work was strictly limited to grammatical corrections, terminology and other wording accuracy improvements, and adaptation of phrasing conventions to meet English language requirements. We declare that no AI involvement occurred during generating core textual content, developing research topics, conducting data analysis, or creating tables and figures.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aktuglu, K., Erol, K., and Vahabi, A. (2019). Ilizarov bone transport and treatment of critical-sized tibial bone defects: a narrative review. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 20, 22. doi:10.1186/s10195-019-0527-1
Alanis-Gómez, R. P., Hernández-Rosas, F., Olivares-Hernández, J. D., Rivera-Muñoz, E. M., Zapatero-Gutiérrez, A., Méndez-Lozano, N., et al. (2024). Magnesium-doped hydroxyapatite nanofibers for medicine applications: characterization, antimicrobial activity, and cytotoxicity study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (22), 12418. doi:10.3390/ijms252212418
Aljohani, S., Layqah, L., Masuadi, E., Al Alwan, B., Baharoon, W., Gramish, J., et al. (2020). Occurrence of vancomycin MIC creep in methicillin resistant isolates in Saudi Arabia. J. Infect. Public Health 13, 1576–1579. doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.008
Al Thaher, Y., Yang, L., Jones, S. A., Perni, S., and Prokopovich, P. (2018). LbL-assembled gentamicin delivery system for PMMA bone cements to prolong antimicrobial activity. PLoS One 13, e0207753. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0207753
Altınsoy, Ş., Kızılbey, K., and İlim, H. B. (2024). Green synthesis of Ag and Cu nanoparticles using E. telmateia ehrh extract: coating, characterization, and bioactivity on PEEK polymer substrates. Mater. (Basel) 17 (22), 5501. doi:10.3390/ma17225501
Asik, M. D., Walsh-Rock, E., Inverardi, N., Nepple, C., Zhao, T., Sekar, A., et al. (2025). Enhanced antibiotic release and mechanical strength in UHMWPE antibiotic blends: the role of submicron gentamicin sulfate particles. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 107 (6), 586–593. doi:10.2106/jbjs.24.00689
Aurore, V., Caldana, F., Blanchard, M., Kharoubi Hess, S., Lannes, N., Mantel, P. Y., et al. (2018). Silver-nanoparticles increase bactericidal activity and radical oxygen responses against bacterial pathogens in human osteoclasts. Nanomedicine 14, 601–607. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2017.11.006
Bakina, O., Svarovskaya, N., Ivanova, L., Glazkova, E., Rodkevich, N., Evstigneev, V., et al. (2023). New PMMA-based Hydroxyapatite/ZnFe(2)O(4)/ZnO composite with antibacterial performance and low toxicity. Biomimetics (Basel) 8 (6), 488. doi:10.3390/biomimetics8060488
Bee, S. L., Bustami, Y., Ul-Hamid, A., Lim, K., and Abdul Hamid, Z. A. (2021). Synthesis of silver nanoparticle-decorated hydroxyapatite nanocomposite with combined bioactivity and antibacterial properties. J. Mater Sci. Mater Med. 32, 106. doi:10.1007/s10856-021-06590-y
Beheshtizadeh, N., Farzin, A., Rezvantalab, S., Pazhouhnia, Z., Lotfibakhshaiesh, N., Ai, J., et al. (2023). 3D printing of complicated GelMA-coated Alginate/tri-Calcium silicate scaffold for accelerated bone regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 229, 636–653. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.267
Bian, Y., Hu, T., Zhao, K., Cai, X., Li, M., Tan, C., et al. (2024). A LDH-derived metal sulfide nanosheet-functionalized bioactive glass scaffold for vascularized osteogenesis and periprosthetic infection prevention/treatment. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 11 (39), e2403009. doi:10.1002/advs.202403009
Bodylska, W., Junka, A., Brożyna, M., Bartmański, M., Gadzała-Kopciuch, R., Jaromin, A., et al. (2024). New biocompatible Ti-MOF@hydroxyapatite composite boosted with gentamicin for postoperative infection control. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 10 (12), 7555–7565. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.4c01230
Carek, P. J., Dickerson, L. M., and Sack, J. L. (2001). Diagnosis and management of osteomyelitis. Am. Fam. Physician 63, 2413–2420.
Chen, Y., Chen, Y., Han, T., Xie, Z., Yang, Y., Chen, S., et al. (2023). Enhanced osteogenic and antibacterial properties of polyetheretherketone by ultraviolet-initiated grafting polymerization of a gelatin methacryloyl/epsilon-poly-L-lysine/laponite hydrogel coating. J. Biomed. Mater Res. A 111 (11), 1808–1821. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.37589
Cheng, X., Wei, Q., Ma, Y., Shi, R., Chen, T., Wang, Y., et al. (2020). Antibacterial and osteoinductive biomacromolecules composite electrospun fiber. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 143, 958–967. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.156
da Costa, T. M., de Oliveira, C. R., Chambers, H. F., and Chatterjee, S. S. (2018). PBP4: a new perspective on Staphylococcus aureus β-Lactam resistance. Microorganisms 6, 57. doi:10.3390/microorganisms6030057
de Mesy Bentley, K. L., Trombetta, R., Nishitani, K., Bello-Irizarry, S. N., Ninomiya, M., Zhang, L., et al. (2017). Evidence of Staphylococcus aureus deformation, proliferation, and migration in canaliculi of live cortical bone in murine models of osteomyelitis. J. Bone Min. Res. 32, 985–990. doi:10.1002/jbmr.3055
Desante, G., Pudełko, I., Krok-Borkowicz, M., Pamuła, E., Jacobs, P., Kazek-Kęsik, A., et al. (2023). Surface multifunctionalization of inert ceramic implants by calcium phosphate biomimetic coating doped with nanoparticles encapsulating antibiotics. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 15 (17), 21699–21718. doi:10.1021/acsami.3c03884
Deyneko, D. V., Lebedev, V. N., Barbaro, K., Titkov, V. V., Lazoryak, B. I., Fadeeva, I. V., et al. (2023). Antimicrobial and cell-friendly properties of cobalt and nickel-doped tricalcium phosphate ceramics. Biomimetics (Basel) 9 (1), 14. doi:10.3390/biomimetics9010014
Ding, J., Xiao, H., and Chen, X. (2022). Advanced biosafety materials for prevention and theranostics of biosafety issues. Biosaf. Health 4, 59–60. doi:10.1016/j.bsheal.2022.03.011
Driscoll, J. A., Lubbe, R., Jakus, A. E., Chang, K., Haleem, M., Yun, C., et al. (2020). 3D-Printed ceramic-demineralized bone matrix hyperelastic bone composite scaffolds for spinal fusion. Tissue Eng. Part A 26, 157–166. doi:10.1089/ten.tea.2019.0166
Dudareva, M., Hotchen, A. J., Ferguson, J., Hodgson, S., Scarborough, M., Atkins, B. L., et al. (2019). The microbiology of chronic osteomyelitis: changes over ten years. J. Infect. 79, 189–198. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2019.07.006
Dziewanowska, K., Patti, J. M., Deobald, C. F., Bayles, K. W., Trumble, W. R., and Bohach, G. A. (1999). Fibronectin binding protein and host cell tyrosine kinase are required for internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 67, 4673–4678. doi:10.1128/iai.67.9.4673-4678.1999
Edwards, A. M., Potts, J. R., Josefsson, E., and Massey, R. C. (2010). Staphylococcus aureus host cell invasion and virulence in sepsis is facilitated by the multiple repeats within FnBPA. PLoS Pathog. 6, e1000964. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000964
Fadeeva, I. V., Barbaro, K., Altigeri, A., Forysenkova, A. A., Gafurov, M. R., Mamin, G. V., et al. (2024). Exploring borate-modified calcium phosphate ceramics: antimicrobial potential and cytocompatibility assessment. Nanomater. (Basel) 14 (6), 495. doi:10.3390/nano14060495
Fan, M., Ren, Y., Zhu, Y., Zhang, H., Liu, C., Lv, H., et al. (2025). Borosilicate bioactive glass synergizing low-dose antibiotic loaded implants to combat bacteria through ATP disruption and oxidative stress to sequentially achieve osseointegration. Bioact. Mater 44, 184–204. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.10.009
Feng, Y., Zhu, S., Wang, L., Chang, L., Hou, Y., and Guan, S. (2018). Fabrication and characterization of biodegradable Mg-Zn-Y-Nd-Ag alloy: microstructure, mechanical properties, corrosion behavior and antibacterial activities. Bioact. Mater 3 (3), 225–235. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2018.02.002
Frazar, E. M., Shah, R. A., Dziubla, T. D., and Hilt, J. Z. (2020). Multifunctional temperature-responsive polymers as advanced biomaterials and beyond. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 137, 48770. doi:10.1002/app.48770
Gao, W., Han, X., Sun, D., Li, Y., Liu, X., Yang, S., et al. (2023). Antibacterial properties of antimicrobial peptide HHC36 modified polyetheretherketone. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1103956. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1103956
Garzoni, C., and Kelley, W. L. (2011). Return of the trojan horse: intracellular phenotype switching and immune evasion by Staphylococcus aureus. EMBO Mol. Med. 3, 115–117. doi:10.1002/emmm.201100123
Geng, Z., Dong, R., Li, X., Xu, X., Chen, L., Han, X., et al. (2024). Study on the antibacterial activity and bone inductivity of Nanosilver/PLGA-Coated TI-CU implants. Int. J. Nanomedicine 19, 6427–6447. doi:10.2147/ijn.s456906
Ghavimi, S., Lungren, E. S., Faulkner, T. J., Josselet, M. A., Wu, Y., Sun, Y., et al. (2019). Inductive co-crosslinking of cellulose nanocrystal/chitosan hydrogels for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 130, 88–98. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.02.086
Han, X., Sharma, N., Xu, Z., Krajewski, S., Li, P., Spintzyk, S., et al. (2024). A balance of biocompatibility and antibacterial capability of 3D printed PEEK implants with natural totarol coating. Dent. Mater 40 (4), 674–688. doi:10.1016/j.dental.2024.02.011
Hatashita, S., Kawakami, R., Ejiri, S., Sasaki, N., Toshiki, N., Ito, M., et al. (2021). Acute masquelet technique for reconstructing bone defects of an open lower limb fracture. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 47, 1153–1162. doi:10.1007/s00068-019-01291-2
Hayashi, K., Shimabukuro, M., Zhang, C., Taleb Alashkar, A. N., Kishida, R., Tsuchiya, A., et al. (2024). Silver phosphate-modified carbonate apatite honeycomb scaffolds for anti-infective and pigmentation-free bone tissue engineering. Mater Today Bio 27, 101161. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101161
He, M., Wang, H., Han, Q., Shi, X., He, S., Sun, J., et al. (2023). Glucose-primed PEEK orthopedic implants for antibacterial therapy and safeguarding diabetic osseointegration. Biomaterials 303, 122355. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122355
Hou, Z., Wang, K., Liu, G., Yuan, Z., Peng, H., Yuan, Y., et al. (2025). Nitric oxide-mediated dual-functional smart titanium implant coating for antibacterial and osseointegration promotion in implant-associated infections. Adv. Healthc. Mater 14, e2500997. doi:10.1002/adhm.202500997
Hu, G., Wang, H., Yao, X., Bi, D., Zhu, G., Tang, S., et al. (2014). Development of nanofluorapatite polymer-based composite for bioactive orthopedic implants and prostheses. Int. J. Nanomedicine 9, 3875–3884. doi:10.2147/IJN.S65682
Hu, Q., Du, Y., Bai, Y., Xing, D., Wu, C., Li, K., et al. (2024). Smart zwitterionic coatings with precise pH-responsive antibacterial functions for bone implants to combat bacterial infections. Biomater. Sci. 12 (17), 4471–4482. doi:10.1039/d4bm00932k
Huang, Y., Wan, X., Su, Q., Zhao, C., Cao, J., Yue, Y., et al. (2024). Ultrasound-activated piezo-hot carriers trigger tandem catalysis coordinating cuproptosis-like bacterial death against implant infections. Nat. Commun. 15 (1), 1643. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45619-y
Indrakumar, S., Gugulothu, S. B., Joshi, A., Dash, T. K., Mishra, V., Tandon, B., et al. (2025). Silk composite-based multifunctional pellets for controlled release. Macromol. Biosci. 25 (2), e2400410. doi:10.1002/mabi.202400410
Janion, C. (2008). Inducible SOS response system of DNA repair and mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 4 (6), 338–344. doi:10.7150/ijbs.4.338
Ji, Y., Yang, S., Sun, J., and Ning, C. (2023). Realizing both antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility in silicocarnotite bioceramic via germanium incorporation. J. Funct. Biomater. 14 (3), 154. doi:10.3390/jfb14030154
Jia, F., Guan, J., Wang, J., Li, M., Zhang, Y., Xie, L., et al. (2025). Zinc and melatonin mediated antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant coatings accelerate bone defect repair. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 245, 114335. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2024.114335
Jin, G., Qin, H., Cao, H., Qian, S., Zhao, Y., Peng, X., et al. (2014). Synergistic effects of dual Zn/Ag ion implantation in osteogenic activity and antibacterial ability of titanium. Biomaterials 35 (27), 7699–7713. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.05.074
Jin, Y., Liu, H., Chu, L., Yang, J., Li, X., Zhou, H., et al. (2024). Initial therapeutic evidence of a borosilicate bioactive glass (BSG) and Fe(3)O(4) magnetic nanoparticle scaffold on implant-associated staphylococcal aureus bone infection. Bioact. Mater 40, 148–167. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.05.040
Joshi, M. U., Kulkarni, S. P., Choppadandi, M., Keerthana, M., and Kapusetti, G. (2023). Current state of art smart coatings for orthopedic implants: a comprehensive review. Smart Mater. Med. 4, 661–679. doi:10.1016/j.smaim.2023.06.005
Josse, J., Velard, F., and Gangloff, S. C. (2015). Staphylococcus aureus vs. osteoblast: relationship and consequences in osteomyelitis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 5, 85. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2015.00085
Kang, B. J., Ryu, H. H., Park, S. S., Kim, Y., Woo, H. M., Kim, W. H., et al. (2012). Effect of matrigel on the osteogenic potential of canine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 74 (7), 827–836. doi:10.1292/jvms.11-0484
Kavanagh, N., Ryan, E. J., Widaa, A., Sexton, G., Fennell, J., O'Rourke, S., et al. (2018). Staphylococcal osteomyelitis: disease progression, treatment challenges, and future directions. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 31, e00084-17–00017. doi:10.1128/cmr.00084-17
Kim, H. K., DeDent, A., Cheng, A. G., McAdow, M., Bagnoli, F., Missiakas, D. M., et al. (2010). IsdA and IsdB antibodies protect mice against Staphylococcus aureus abscess formation and lethal challenge. Vaccine 28, 6382–6392. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.02.097
Kintarak, S., Whawell, S. A., Speight, P. M., Packer, S., and Nair, S. P. (2004). Internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by human keratinocytes. Infect. Immun. 72, 5668–5675. doi:10.1128/iai.72.10.5668-5675.2004
Kobatake, T., Miyamoto, H., Hashimoto, A., Ueno, M., Nakashima, T., Murakami, T., et al. (2019). Antibacterial activity of Ag-Hydroxyapatite coating against hematogenous infection by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the rat femur. J. Orthop. Res. 37 (12), 2655–2660. doi:10.1002/jor.24431
Kong, P., Ren, Y., Yang, J., Fu, W., Liu, Z., Li, Z., et al. (2022). Relapsed boyhood tibia polymicrobial osteomyelitis linked to dermatophytosis: a case report. BMC Surg. 22 (1), 156. doi:10.1186/s12893-022-01600-4
Krauss, J. L., Roper, P. M., Ballard, A., Shih, C. C., Fitzpatrick, J. A. J., Cassat, J. E., et al. (2019). Staphylococcus aureus infects osteoclasts and replicates intracellularly. mBio 10, e02447-19–02419. doi:10.1128/mbio.02447-19
Lai, P. L., Chen, L. H., Chen, W. J., and Chu, I. M. (2013). Chemical and physical properties of bone cement for vertebroplasty. Biomed. J. 36, 162–167. doi:10.4103/2319-4170.112750
Lee, H., Shin, D. Y., Na, Y., Han, G., Kim, J., Kim, N., et al. (2023). Antibacterial PLA/Mg composite with enhanced mechanical and biological performance for biodegradable orthopedic implants. Biomater. Adv. 152, 213523. doi:10.1016/j.bioadv.2023.213523
Li, D., Li, Y., Shrestha, A., Wang, S., Wu, Q., Li, L., et al. (2019). Effects of programmed local delivery from a Micro/nano-hierarchical surface on titanium implant on infection clearance and osteogenic induction in an infected bone defect. Adv. Healthc. Mater 8, e1900002. doi:10.1002/adhm.201900002
Li, D., Wei, Q., Wu, C., Zhang, X., Xue, Q., Zheng, T., et al. (2020). Superhydrophilicity and strong salt-affinity: zwitterionic polymer grafted surfaces with significant potentials particularly in biological systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 278, 102141. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2020.102141
Li, J., Leung, S., Chung, Y. L., Chow, S. K. H., Alt, V., Rupp, M., et al. (2023). Hydrogel delivery of DNase I and liposomal vancomycin to eradicate fracture-related methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus infection and support osteoporotic fracture healing. Acta Biomater. 164, 223–239. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2023.03.044
Li, M., Liu, J., Li, Y., Chen, W., Yang, Z., Zou, Y., et al. (2024). Enhanced osteogenesis and antibacterial activity of dual-functional PEEK implants via biomimetic polydopamine modification with chondroitin sulfate and levofloxacin. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 35 (18), 2790–2806. doi:10.1080/09205063.2024.2390745
Li, S., Yue, Y., Wang, W., Han, M., Wan, X., Li, Q., et al. (2024). Ultrasound-activated probiotics vesicles coating for titanium implant infections through bacterial Cuproptosis-Like death and immunoregulation. Adv. Mater 36 (44), e2405953. doi:10.1002/adma.202405953
Li, Y., Liu, C., Cheng, X., Wang, J., Pan, Y., Liu, C., et al. (2023). PDA-BPs integrated mussel-inspired multifunctional hydrogel coating on PPENK implants for anti-tumor therapy, antibacterial infection and bone regeneration. Bioact. Mater 27, 546–559. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.04.020
Libraty, D. H., Patkar, C., and Torres, B. (2012). Staphylococcus aureus reactivation osteomyelitis after 75 years. N. Engl. J. Med. 366, 481–482. doi:10.1056/nejmc1111493
Liu, F., Wang, X., Chen, T., Zhang, N., Wei, Q., Tian, J., et al. (2020). Hydroxyapatite/silver electrospun fibers for anti-infection and osteoinduction. J. Adv. Res. 21, 91–102. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2019.10.002
Liu, Z., Yang, L., Ni, Y., Chen, K., Yan, Q., Zhao, Z., et al. (2024). Enhanced bacteriostasis and osseointegrative properties of SiRNA-modified polyetheretherketone surface for implant applications. PLoS One 19 (12), e0314091. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0314091
Majumdar, U., and Bose, S. (2024). Curcumin and vitamin C dual release from hydroxyapatite coated Ti6Al4V discs enhances in vitro biological properties. Mater Chem. Phys. 313, 128622. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.128622
Masters, E. A., Trombetta, R. P., de Mesy Bentley, K. L., Boyce, B. F., Gill, A. L., Gill, S. R., et al. (2019). Evolving concepts in bone infection: redefining “biofilm”, “acute vs. chronic osteomyelitis”, “the immune proteome” and local antibiotic therapy. Bone Res. 7, 20. doi:10.1038/s41413-019-0061-z
Metsemakers, W. J., Onsea, J., Neutjens, E., Steffens, E., Schuermans, A., McNally, M., et al. (2017). Prevention of fracture-related infection: a multidisciplinary care package. Int. Orthop. 41, 2457–2469. doi:10.1007/s00264-017-3607-y
Mohammed, A., Saeed, A., Elshaer, A., Melaibari, A. A., Memić, A., Hassanin, H., et al. (2023). Fabrication and characterization of oxygen-generating polylactic acid/calcium peroxide composite filaments for bone scaffolds. Pharm. (Basel). 16 (4), 627. doi:10.3390/ph16040627
Nagase, K. (2021). Thermoresponsive interfaces obtained using poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based copolymer for bioseparation and tissue engineering applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 295, 102487. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2021.102487
Negi, A., Verma, A., Garg, M., Goswami, K., Mishra, V., Singh, A. K., et al. (2024). Osteogenic citric acid linked chitosan coating of 3D-printed PLA scaffolds for preventing implant-associated infections. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 282 (Pt 3), 136968. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136968
Nelogi, S., Kumarpatil, A., Chowdhary, R., and Roy, R. (2024). Optimising titanium implant stability and infection resistance through iron nanoparticle coatings: a preclinical investigation. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 126 (6), 102155. doi:10.1016/j.jormas.2024.102155
Nguyen, N. H., Lu, Z., Elbourne, A., Vasilev, K., Roohani, I., Zreiqat, H., et al. (2024). Engineering antibacterial bioceramics: design principles and mechanisms of action. Mater Today Bio 26, 101069. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101069
Ortiz-Benítez, E. A., Velázquez-Guadarrama, N., Durán Figueroa, N. V., Quezada, H., and Olivares-Trejo, J. J. (2019). Antibacterial mechanism of gold nanoparticles on Streptococcus pneumoniae. Metallomics 11, 1265–1276. doi:10.1039/c9mt00084d
Palla-Rubio, B., Araújo-Gomes, N., Fernández-Gutiérrez, M., Rojo, L., Suay, J., Gurruchaga, M., et al. (2019). Synthesis and characterization of silica-chitosan hybrid materials as antibacterial coatings for titanium implants. Carbohydr. Polym. 203, 331–341. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.064
Patti, J. M., Allen, B. L., McGavin, M. J., and Höök, M. (1994). MSCRAMM-mediated adherence of microorganisms to host tissues. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 48, 585–617. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.48.1.585
Pazarçeviren, A. E., Dikmen, T., Altunbaş, K., Yaprakçı, V., Erdemli, Ö., Keskin, D., et al. (2020). Composite clinoptilolite/PCL-PEG-PCL scaffolds for bone regeneration: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 14, 3–15. doi:10.1002/term.2938
Piñera-Avellaneda, D., Buxadera-Palomero, J., Delint, R. C., Dalby, M. J., Burgess, K. V., Ginebra, M. P., et al. (2024). Gallium and silver-doped titanium surfaces provide enhanced osteogenesis, reduce bone resorption and prevent bacterial infection in co-culture. Acta Biomater. 180, 154–170. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2024.04.019
Porrino, J., Wang, A., Moats, A., Mulcahy, H., and Kani, K. (2020). Prosthetic joint infections: diagnosis, management, and complications of the two-stage replacement arthroplasty. Skelet. Radiol. 49, 847–859. doi:10.1007/s00256-020-03389-w
Qing, Y., Li, K., Li, D., and Qin, Y. (2020). Antibacterial effects of silver incorporated zeolite coatings on 3D printed porous stainless steels. Mater Sci. Eng. C Mater Biol. Appl. 108, 110430. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2019.110430
Rennert-May, E. D., Conly, J., Smith, S., Puloski, S., Henderson, E., Au, F., et al. (2018). The cost of managing complex surgical site infections following primary hip and knee arthroplasty: a population-based cohort study in Alberta, Canada. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 39, 1183–1188. doi:10.1017/ice.2018.199
Sathiyavimal, S., Vasantharaj, S., Mattheos, N., Pugazhendhi, A., and Subbalekha, K. (2024). Mussel shell-derived biogenic hydroxyapatite as reinforcement on chitosan-loaded gentamicin composite for antibacterial activity and bone regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 278 (Pt 2), 134143. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134143
Satola, S. W., Farley, M. M., Anderson, K. F., and Patel, J. B. (2011). Comparison of detection methods for heteroresistant vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus, with the population analysis profile method as the reference method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 49, 177–183. doi:10.1128/jcm.01128-10
Scialla, S., Martuscelli, G., Nappi, F., Singh, S. S. A., Iervolino, A., Larobina, D., et al. (2021). Trends in managing cardiac and orthopaedic device-associated infections by using therapeutic biomaterials. Polym. (Basel) 13, 1556. doi:10.3390/polym13101556
Shafiei, M. R., Nezafati, N., Karbasi, S., and Kharazi, A. Z. (2025). Rifampin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles improved physical and mechanical properties and biological response of acrylic bone cement. J. Med. Signals Sens. 15, 9. doi:10.4103/jmss.jmss_52_24
Sheehy, E. J., von Diemling, C., Ryan, E., Widaa, A., O’ Donnell, P., Ryan, A., et al. (2025). Antibiotic-eluting scaffolds with responsive dual-release kinetics facilitate bone healing and eliminate S. aureus infection. Biomaterials 313, 122774. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122774
Shen, X., Zhang, Y., Ma, P., Sutrisno, L., Luo, Z., Hu, Y., et al. (2019). Fabrication of magnesium/zinc-metal organic framework on titanium implants to inhibit bacterial infection and promote bone regeneration. Biomaterials 212, 1–16. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.05.008
Shi, R., Ye, J., Li, W., Zhang, J., Wu, C., Xue, J., et al. (2019). Infection-responsive electrospun nanofiber mat for antibacterial guided tissue regeneration membrane. Mater Sci. Eng. C Mater Biol. Appl. 100, 523–534. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2019.03.039
Shi, Y., Lai, Y., Guo, Y., Cai, Z., Mao, C., Lu, M., et al. (2024). Aspirin/amoxicillin loaded chitosan microparticles and polydopamine modified titanium implants to combat infections and promote osteogenesis. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 7624. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-57156-1
Shokri, M., Kharaziha, M., Tafti, H. A., Eslaminejad, M. B., and Aghdam, R. M. (2022). Synergic role of zinc and gallium doping in hydroxyapatite nanoparticles to improve osteogenesis and antibacterial activity. Biomater. Adv. 134, 112684. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2022.112684
Shu, X., Liao, J., Wang, Q., Wang, L., Shi, Q., and Xie, X. (2024). Enhanced osteogenic and bactericidal performance of premixed calcium phosphate cement with photocrosslinked alginate thin film. J. Biomed. Mater Res. A 112 (7), 1057–1069. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.37688
Sun, J., Li, J., Shan, A., Wang, L., Ye, J., Li, S., et al. (2025). A novel multifunctional PEEK internal fixation plate regulated by gentamicin/chitosan coating. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 245, 114316. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2024.114316
Sun, L., Chen, X., Ma, K., Chen, R., Mao, Y., Chao, R., et al. (2023). Novel Titanium implant: a 3D multifunction Architecture with charge-trapping and piezoelectric self-stimulation. Adv. Healthc. Mater 12 (11), e2202620. doi:10.1002/adhm.202202620
Suo, H., Li, L., Zhang, C., Yin, J., Xu, K., Liu, J., et al. (2020). Glucosamine-grafted methacrylated gelatin hydrogels as potential biomaterials for cartilage repair. J. Biomed. Mater Res. B Appl. Biomater. 108 (3), 990–999. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.34451
Szelerski, Ł., Pajchert Kozłowska, A., Żarek, S., Górski, R., Mochocki, K., Dejnek, M., et al. (2021). A new criterion for assessing ilizarov treatment outcomes in nonunion of the tibia. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 141, 879–889. doi:10.1007/s00402-020-03571-8
Tan, J., Zhang, H., Liu, Y., Hou, Z., Wang, D., Zhou, J., et al. (2025). Interfering with proton and electron transfer enables antibacterial starvation therapy. Sci. Adv. 11 (12), eadt3159. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adt3159
Tanadchangsaeng, N., Pasanaphong, K., Tawonsawatruk, T., Rattanapinyopituk, K., Tangketsarawan, B., Rawiwet, V., et al. (2024). 3D bioprinting of fish skin-based gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) bio-ink for use as a potential skin substitute. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 23240. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-73774-1
Tang, X., Dai, J., Sun, H., Nabanita, S., Petr, S., Wang, D., et al. (2019). Mechanical strength, surface properties, cytocompatibility and antibacterial activity of nano zinc-magnesium silicate/polyetheretherketone biocomposites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 19 (12), 7615–7623. doi:10.1166/jnn.2019.16727
Teske, S. S., and Detweiler, C. S. (2015). The biomechanisms of metal and metal-oxide nanoparticles' interactions with cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 12, 1112–1134. doi:10.3390/ijerph120201112
Uicich, F. C., Merlo, J. L., Redersdorff, I. E., Herrera Seitz, M. K., Pastore, J. I., and Ballarre, J. (2024). Optimized electrophoretic deposition of chitosan/mesoporous glass nanoparticles with gentamicin on titanium implants: enhancing hemocompatibility and antibacterial activity. ACS Appl. Bio Mater 7 (7), 4642–4653. doi:10.1021/acsabm.4c00488
Valverde, A., Pérez-Álvarez, L., Ruiz-Rubio, L., Pacha Olivenza, M. A., García Blanco, M. B., Díaz-Fuentes, M., et al. (2019). Antibacterial hyaluronic acid/chitosan multilayers onto smooth and micropatterned titanium surfaces. Carbohydr. Polym. 207, 824–833. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.039
Vu, A. A., Robertson, S. F., Ke, D., Bandyopadhyay, A., and Bose, S. (2019). Mechanical and biological properties of ZnO, SiO(2), and Ag(2)O doped plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coating for orthopaedic and dental applications. Acta Biomater. 92, 325–335. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.020
Wang, J., Wang, X., Liang, Z., Lan, W., Wei, Y., Hu, Y., et al. (2023). Injectable antibacterial Ag-HA/GelMA hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1219460. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1219460
Wang, K., Rong, F., Peng, H., Yuan, Z., Huo, J., Liu, P., et al. (2024). Infection microenvironment-responsive coating on titanium surfaces for On-Demand release of therapeutic gas and antibiotic. Adv. Healthc. Mater 13 (18), e2304510. doi:10.1002/adhm.202304510
Wang, X., Dong, H., Liu, J., Qin, G., Chen, D., and Zhang, E. (2019). In vivo antibacterial property of Ti-Cu sintered alloy implant. Mater Sci. Eng. C Mater Biol. Appl. 100, 38–47. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2019.02.084
Wang, X., Pan, L., Zheng, A., Cao, L., Wen, J., Su, T., et al. (2023). Multifunctionalized carbon-fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone implant for rapid osseointegration under infected environment. Bioact. Mater 24, 236–250. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.12.016
Wei, W., Zhu, J., Liu, Y., Chen, L., Ji, H., Cheng, Z., et al. (2024). Graphene oxide-silver-coated sulfonated polyetheretherketone (Ag/GO-SPEEK): a broad-spectrum antibacterial artificial bone implants. ACS Appl. Bio Mater 7 (6), 3981–3990. doi:10.1021/acsabm.4c00338
Xie, Q., Wang, T., He, L., Liang, H., Sun, J., Huang, X., et al. (2024). Biological and structural properties of curcumin-loaded graphene oxide incorporated collagen as composite scaffold for bone regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 12, 1505102. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2024.1505102
Yang, D., Wijenayaka, A. R., Solomon, L. B., Pederson, S. M., Findlay, D. M., Kidd, S. P., et al. (2018). Novel insights into Staphylococcus aureus deep bone infections: the involvement of osteocytes. mBio 9, e00415–e00418. doi:10.1128/mbio.00415-18
Yang, J., Qin, H., Chai, Y., zhang, P., Chen, Y., Yang, K., et al. (2021). Molecular mechanisms of osteogenesis and antibacterial activity of Cu-bearing Ti alloy in a bone defect model with infection in vivo. J. Orthop. Transl. 27, 77–89. doi:10.1016/j.jot.2020.10.004
Yao, T., Chen, J., Wang, Z., Zhai, J., Li, Y., Xing, J., et al. (2019a). The antibacterial effect of potassium-sodium niobate ceramics based on controlling piezoelectric properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 175, 463–468. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.12.022
Yao, T. T., Wang, J., Xue, Y. F., Yu, W. j., Gao, Q., Ferreira, L., et al. (2019b). A photodynamic antibacterial spray-coating based on the host-guest immobilization of the photosensitizer methylene blue. J. Mater Chem. B 7 (33), 5089–5095. doi:10.1039/c9tb01069f
Yu, B., Pacureanu, A., Olivier, C., Cloetens, P., and Peyrin, F. (2020). Assessment of the human bone lacuno-canalicular network at the nanoscale and impact of spatial resolution. Sci. Rep. 10, 4567. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-61269-8
Yu, Y. L., Wu, J. J., Lin, C. C., Qin, X., Tay, F. R., Miao, L., et al. (2023). Elimination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms on titanium implants via photothermally-triggered nitric oxide and immunotherapy for enhanced osseointegration. Mil. Med. Res. 10 (1), 21. doi:10.1186/s40779-023-00454-y
Yuan, B., Chen, H., Zhao, R., Deng, X., Chen, G., Yang, X., et al. (2022). Construction of a magnesium hydroxide/graphene oxide/hydroxyapatite composite coating on mg-ca-zn-ag alloy to inhibit bacterial infection and promote bone regeneration. Bioact. Mater 18, 354–367. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.02.030
Zhang, D., Liu, W., Wu, X. D., He, X., Lin, X., Wang, H., et al. (2019). Efficacy of novel nano-hydroxyapatite/polyurethane composite scaffolds with silver phosphate particles in chronic osteomyelitis. J. Mater Sci. Mater Med. 30, 59. doi:10.1007/s10856-019-6261-7
Zhang, H., Zhang, P., Shen, X., Han, J., Wang, H., Qin, H., et al. (2025). A cross-linked coating loaded with antimicrobial peptides for corrosion control, early antibacterial, and sequential osteogenic promotion on a magnesium alloy as orthopedic implants. Acta Biomater. 193, 604–622. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2024.12.046
Zhang, L., Dai, W., Gao, C., Wei, W., Huang, R., Zhang, X., et al. (2023). Multileveled hierarchical hydrogel with continuous biophysical and biochemical gradients for enhanced repair of full-thickness osteochondral defect. Adv. Mater 35 (19), e2209565. doi:10.1002/adma.202209565
Zhang, T., Zhou, W., Yang, W., Bi, J., Li, H., Gao, X., et al. (2024). Vancomycin-encapsulated hydrogel loaded microarc-oxidized 3D-printed porous Ti6Al4V implant for infected bone defects: reconstruction, anti-infection, and osseointegration. Bioact. Mater 42, 18–31. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.07.035
Zhang, X. M., Li, Y., Gu, Y. X., Zhang, C. N., Lai, H. C., and Shi, J. Y. (2019). Ta-Coated titanium surface with superior bacteriostasis and osseointegration. Int. J. Nanomedicine 14, 8693–8706. doi:10.2147/ijn.s218640
Zhao, T., Liu, X., Chu, Z., Zhao, J., Jiang, D., Dong, X., et al. (2024). L-arginine loading porous PEEK promotes percutaneous tissue repair through macrophage orchestration. Bioact. Mater 40, 19–33. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.05.025
Zheng, X., Luo, H., Li, J., Yang, Z., Zhuan, X., Li, X., et al. (2024). Zinc-doped bioactive glass-functionalized polyetheretherketone to enhance the biological response in bone regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater Res. A 112 (9), 1565–1577. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.37710
Zhou, Q., Su, X., Wu, J., Zhang, X., Su, R., Ma, L., et al. (2023). Additive manufacturing of bioceramic implants for restoration bone engineering: technologies, advances, and future perspectives. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 9 (3), 1164–1189. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c01164
Keywords: bone infection, implantable materials, antibacterial treatment, composite materials, material matrix
Citation: Xiang B, Jiang J, Wang H and Song L (2025) Research progress of implantable materials in antibacterial treatment of bone infection. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1586898. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1586898
Received: 03 March 2025; Accepted: 07 July 2025;
Published: 16 July 2025.
Edited by:
Jangho Kim, Chonnam National University, Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
Bin Liu, The First Hospital of Jilin University, ChinaRaj Hazra, North Dakota State University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Xiang, Jiang, Wang and Song. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lei Song, Y29iaXNvbmdsZWlAdG1tdS5lZHUuY24=
 Binqing Xiang1
Binqing Xiang1 Heng Wang
Heng Wang