- 1Department of General Practice, Jinshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 2Center of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Jinshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 3Research Center for Chemical Injury, Emergency and Critical Medicine of Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 4Key Laboratory of Chemical Injury, Emergency and Critical Medicine of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission, Shanghai, China
Pneumonia remains a significant global health challenge due to its high incidence, mortality rates, and the limitations of conventional therapies, such as antibiotic resistance and inefficient drug delivery. In recent years, hydrogels have emerged as a promising biomaterial platform for pneumonia treatment, offering exceptional biocompatibility, tunable physicochemical properties, and multifunctionality. This review comprehensively examines the recent advancements in hydrogel applications for pneumonia therapy. It focuses on their roles as drug delivery vehicles, anti-inflammatory agents, and facilitators of tissue repair and regeneration. Hydrogels enable targeted and sustained release of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and bioactive molecules, enhancing local drug concentrations while minimizing systemic side effects. Their ability to mimic the extracellular matrix (ECM) supports lung tissue repair and regeneration, addressing the long-term complications of pneumonia, such as fibrosis. Additionally, hydrogels can be engineered to respond to specific physiological conditions, such as pH or enzyme activity, allowing for intelligent drug release profiles tailored to the pulmonary microenvironment. Despite these promising developments, challenges related to material safety, drug loading efficiency, and scalability of manufacturing processes must be addressed to facilitate clinical translation. This review highlights the therapeutic potential of hydrogels in pneumonia treatment and provides insights into future research directions, aiming to bridge the gap between laboratory innovations and clinical applications.
1 Introduction
Pneumonia, a prevalent respiratory infection, presents a complex etiology involving various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Characterized by symptoms such as cough, fever, chest pain, dyspnea, and fatigue (Scott et al., 2008), this disease has emerged as a critical global health challenge, affecting approximately 300 million individuals annually (Li et al., 2021) and directly causing over three million deaths worldwide (Ching and Pedersen, 2025). The burden disproportionately impacts vulnerable populations: elderly patients (>75 years) face high hospitalization mortality rates (30.3%) (Hespanhol and Barbara, 2020), while neonates account for 750,000–1.2 million annual deaths, representing 10% of global child mortality (Nissen, 2007).
Conventional therapeutic approaches, primarily comprising antibiotic therapy, respiratory support, and symptomatic treatment (Prina et al., 2015), face three major limitations. First, antibiotic therapy is increasingly compromised by the rise of multidrug-resistant pathogens (Cilloniz et al., 2021). A multi-country analysis estimates that the average prevalence of multiple-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Asian hospitals reached 67.4% (Laxminarayan et al., 2016). Second, oxygen therapy fails to address underlying tissue hypoxia in severe cases (Klitgaard et al., 2023), while mechanical ventilation carries risks of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) and barotrauma (Walter, 2021). Third, current symptomatic treatments (e.g., antipyretics, bronchodilators) merely alleviate symptoms without modulating the excessive inflammatory response that drives lung injury (Meijvis et al., 2012). Additionally, these approaches share systemic shortcomings: (1) inefficient drug delivery to infected alveoli due to poor pulmonary penetration and mucus barriers (Bassetti et al., 2020); (2) failure to promote alveolar repair (Singh et al., 2023), leading to long-term fibrosis in 28%–53% of survivors (Tran et al., 2022); and (3) inadequate coverage for viral and fungal pathogens, which account for 80% of cases in American children but lack targeted therapies (Jain et al., 2015). These limitations underscore the urgent need for novel therapeutic strategies to enhance pneumonia treatment outcomes (Doroudian et al., 2019).
In recent years, hydrogels have garnered substantial attention in biomedical research as a promising biomaterial platform, owing to their exceptional biocompatibility, tunable physicochemical properties, and multifunctionality. Composed of hydrophilic polymers forming three-dimensional networks through physical or chemical crosslinking, hydrogels can absorb and retain substantial amounts of water while mimicking the native tissue microenvironment (Cao et al., 2021). These unique characteristics have demonstrated remarkable potential in diverse applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine. Particularly in pulmonary disease management, hydrogels have emerged as a promising therapeutic tool due to their excellent mucoadhesive properties, controllable biodegradability, and capacity for localized sustained drug release (Wan et al., 2023).
In the context of pneumonia treatment, hydrogel-based strategies have demonstrated significant potential through several mechanisms: Firstly, hydrogels serve as efficient drug delivery vehicles, enabling targeted transport of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, or bioactive molecules to infected pulmonary regions, thereby enhancing local drug concentrations while minimizing systemic side effects (Oliva et al., 2017). Secondly, their inherent physicochemical properties, including pH-responsiveness and enzyme-sensitivity, facilitate intelligent drug release profiles that can adapt to the complex pulmonary microenvironment (Ding et al., 2022; Hu et al., 2012). Furthermore, hydrogels can promote the repair and regeneration of damaged lung tissue by mimicking the structural and functional characteristics of the extracellular matrix (ECM) (Brown et al., 2022).
Despite these promising advances in hydrogel-based pneumonia therapeutics, several challenges must be addressed before clinical translation, including material safety concerns (Souto et al., 2024), drug loading efficiency optimization (Chen et al., 2024), and scalability of manufacturing processes (Bernal et al., 2019). This review aims to comprehensively examine recent progress in hydrogel applications for pneumonia treatment, analyzing their mechanisms of action, therapeutic advantages, and future development directions, thereby providing both theoretical foundations and practical guidance for further research in this field (Figure 1).
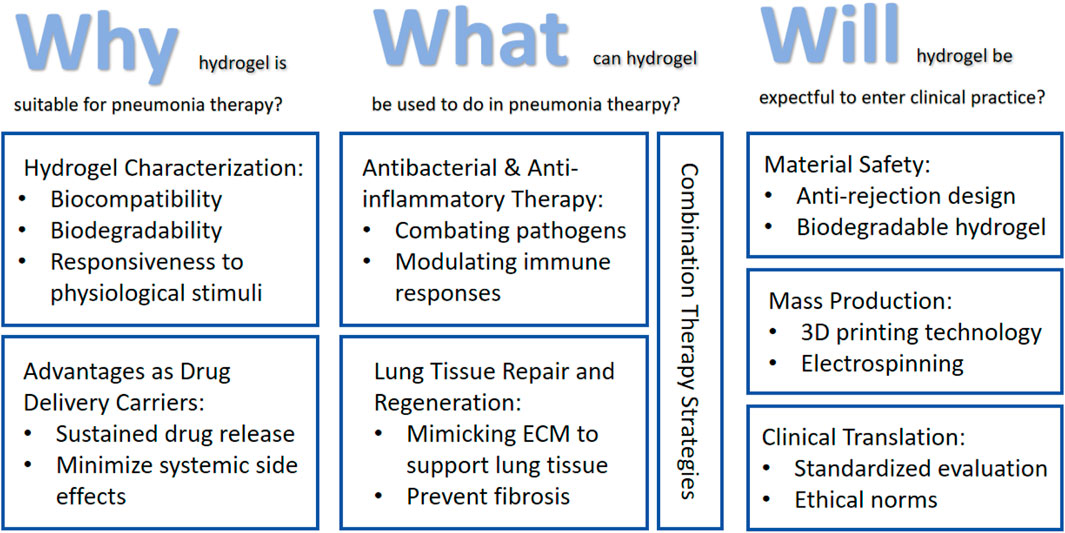
Figure 1. Roadmap of the main content discussed in this review: (1) Discuss the suitability of hydrogels for pneumonia treatment based on their intrinsic properties and advantages as drug delivery carriers; (2) Applications of hydrogels in pneumonia treatment encompass antimicrobial therapy, anti-inflammatory intervention, tissue regeneration, and comprehensive combination therapies; (3) Current limitations and challenges in hydrogel applications for pneumonia treatment, along with potential future improvement strategies.
2 Characterization of hydrogels and their suitability for pneumonia treatment
Hydrogels represent a unique class of crosslinked hydrophilic polymer networks with intrinsic porous structures that exhibit exceptional water retention capacity and closely mimic the natural extracellular matrix microenvironment (Zhu et al., 2023). Their distinctive architecture, combining high water content (often >90%) with tunable mechanical properties and biocompatibility, has driven remarkable progress in biomedical applications since their first clinical use in 1960s contact lenses (PHEMA hydrogel) (Mester, 1979). Over decades of development, hydrogels have evolved from passive biomaterials (Guowei et al., 2007) to sophisticated systems capable of stimuli-responsive behavior (e.g., pH-, temperature-, or enzyme-triggered changes) (Tian and Liu, 2023), enabling transformative applications ranging from targeted drug delivery (Mikhail et al., 2023) to advanced tissue engineering (Rastogi and Kandasubramanian, 2019) and bioelectronic interfaces (Yuk et al., 2019). The continuous innovation in hydrogel technology - from early wound dressings (Yang et al., 2021) to current self-healing formulations (Bertsch et al., 2023) and organ-on-a-chip platforms (Gnatowski et al., 2025) - demonstrates their unparalleled versatility as biomimetic materials that bridge materials science and cutting-edge medical therapies.
Pneumonia’s unique pathophysiology—including viscous mucus obstruction, acidic infection sites, alveolar barrier damage, biofilm resistance, and dysregulated inflammation (Bohn et al., 2020; Lim and Siow, 2018)—makes hydrogel-based therapies particularly advantageous. Their high water content hydrates and loosens mucus (Hong et al., 2022), while pH-responsive swelling enables targeted antibiotic release in infected areas (Zhang et al., 2019). Hydrogels also mimic the lung’s ECM to support tissue repair, sustain drug delivery to overcome biofilm resistance, and modulate excessive immune responses (van Os et al., 2023). By combining mucolytic, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory functions in a single biocompatible platform, hydrogels outperform conventional treatments by providing localized, prolonged, and pathology-responsive therapy tailored to pneumonia’s complex biological mechanisms (Xiao et al., 2021) (Figure 2).
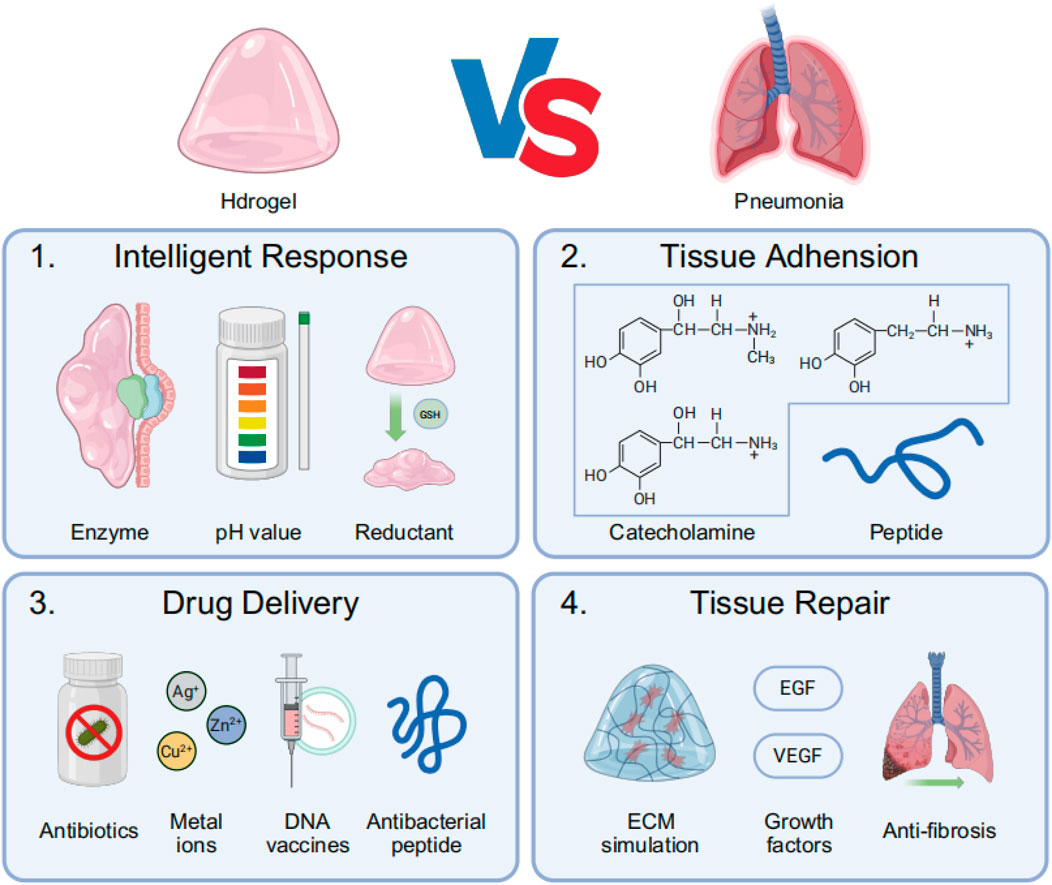
Figure 2. The main process of treating pneumonia with hydrogel: (1) Intelligent response: Hydrogels respond to infection-related local specific enzymes, low pH environments, or specific reductants such as glutathione (GSH); (2) Hydrogels achieve tissue adhesion through the conjugation of catecholamines and lung-targeting peptide motifs; (3) Hydrogels exert therapeutic effects by delivering antimicrobial agents, including antibiotics, metal ions, DNA vaccines, and antimicrobial peptides (AMPs); (4) Hydrogels promote post-infection lung tissue repair by mimicking the ECM while releasing growth factors and anti-fibrotic drugs.
2.1 Physicochemical properties of hydrogels
Hydrogels are typically fabricated from natural or synthetic polymers, such as hyaluronic acid, chitosan, and polyethylene glycol (PEG) (Goor et al., 2017). These materials exhibit excellent biocompatibility and can interact favorably with lung tissue, thereby minimizing immune rejection (Nasra et al., 2023). For instance, a nanostructured hydrogel self-assembled from ciprofloxacin and tripeptide significantly reduced drug cytotoxicity while effectively killing Gram-negative bacteria (Marchesan et al., 2013). Another bioadhesive hydrogel (SHIELD) developed for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) treatment showed no histological or functional damage in both in vitro and in vivo experiments (Mei et al., 2023). Unfortunately, at present, the research of this hydrogel mostly involves non-human primates with a small sample size, and the future clinical transformation is still far away. Furthermore, the biodegradable nature of hydrogels allows them to be gradually absorbed by the body after completing drug delivery or tissue repair, eliminating the need for metabolic detoxification or secondary surgical removal. A notable example is MICP-1, a mucin-based synthetic hydrogel that can block herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) airway infection and rapidly degrade under reduced GSH treatment due to its abundant disulfide bonds (Bej et al., 2024).
The high water content of hydrogels (typically exceeding 90%) endows them with softness and elasticity similar to biological tissues, effectively mimicking the mechanical environment of the lungs (Shamskhou et al., 2019). Compared to artificial elastic membranes (e.g., polydimethylsiloxane, PDMS) used in traditional chip-based lungs, the F127-DA hydrogel component demonstrates a composition and stiffness more akin to human alveolar extracellular matrix (Shen et al., 2023). Additionally, when bovine lung extract-derived pulmonary surfactant was applied to a Carbopol hydrogel surface, it exhibited viscoelastic properties resembling natural, healthy tracheobronchial mucus (Schenck and Fiegel, 2016). These characteristics not only reduce mechanical damage to lung tissue but also provide a foundation for uniform distribution and adhesion in the lungs. However, the authors also admitted that they were still unable to fully control the factors affecting the pulmonary surfactant tension caused by Carbopol hydrogel.
The mechanical properties (e.g., elastic modulus, viscoelasticity), degradation rate, and drug release behavior of hydrogels can be precisely controlled by adjusting crosslinking density, polymer types, and functional modifications. For example, the FK-MEM@CMCO-CS hydrogel coating demonstrated optimal pH 5.0-dependent release of its conjugated AMP FK13-a1 and effectively controlled inflammatory factor production in a VAP rat model (Zhu B. et al., 2024). Notably, since a ventilator is a device requiring continuous use, this study did not address the long-term effects of the coating on host immune responses and the microbiome. Nadia A Mohamed et al. synthesized four novel crosslinked chitosan hydrogels (H1-H4) that showed significantly lower minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) against various common pneumonia pathogens compared to chitosan, all exhibiting pH and temperature responsiveness (Mohamed et al., 2019). Kasula Nagaraja et al. developed a pH-responsive TMGA-Ag nanocomposite hydrogel that effectively inactivated multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains (Nagaraja et al., 2021a).
Hydrogels can achieve specific adhesion to lung tissue through surface modification or functional design. For instance, hydrogels conjugated with polyphenol-based adhesion-triggering molecules such as catechol or pyrogallol groups can form strong bonds with pulmonary mucosa, thereby prolonging drug retention at infection sites. Nathan Gasek et al. developed two dopamine-conjugated hydrogels (ALG-MA-DA and GEL-MA-DA) that demonstrated excellent viscoelastic properties in ex vivo and in vivo preclinical pleural and tracheal injury models (Gasek et al., 2021). The authors claimed they were unsure why dopamine binding affects tensile strength and called for further mechanistic studies in the future. Another catechol-conjugated alginate (C-ALG) hydrogel localized around lung tissue within 5 min of in vivo injection and showed good cytocompatibility (Ji et al., 2021). Researchers also developed a tannic acid adhesion-triggering solution that, when combined with synthetic polyacrylamide-alginate (PAM/Alg) hydrogel, enhanced adhesion to porcine lung tissue by 45-fold (Li et al., 2024). Moreover, hydrogels can achieve targeted drug delivery by loading targeting molecules (e.g., antibodies, peptides). C16-ceramide, a unique receptor in pulmonary vascular endothelium, can be specifically recognized by hydrogels conjugated with endothelial lung-homing peptide (CGSPGWVRC) (Staquicini et al., 2023). Although the receptor protein of pulmonary vascular endothelium had individual heterogeneity, this study provided a new idea for targeting hydrogels. The advent of functionalized DNA hydrogels represents a groundbreaking development, as they can specifically recognize SARS-CoV-2 RNA signals in infected lung epithelial cells through transfer RNA (tRNA) triggered cascade signal amplification, releasing encapsulated particles that convert and amplify signals into colorimetric and temperature readouts for viral detection (Jiao et al., 2025).
2.2 Advantages of hydrogels as pulmonary drug delivery carriers
Hydrogels possess the unique capability to encapsulate drugs within their three-dimensional networks and facilitate controlled drug release through diffusion, swelling, or degradation mechanisms. This characteristic not only enhances local drug concentration in the lungs but also minimizes systemic exposure, thereby reducing side effects. For instance, antibiotic-loaded hydrogels can be delivered to the lungs via nebulization or direct injection, enabling sustained treatment or even prophylactic protection of infected areas. Khojasteh Shirkhani et al. developed a polymethacrylic acid (PMA) based anionic hydrogel capable of delivering amphotericin B (AmB) for effective treatment of aspergillus pneumonia (Shirkhani et al., 2015). The hydrogel nebulization route achieved a daily dosage of 135 μg/kg, demonstrating higher 8-day survival rates (100% vs. 80%) with only 75% of the conventional nebulization dose, proving to be a simple and cost-effective pre-exposure prophylaxis method (Schmitt et al., 1988). An agarose saline spray supplemented with 1% hydrogel significantly enhanced drug delivery to the posterior nasal region and effectively blocked SARS-CoV-2 binding to alveolar epithelial type II cells (AECII), providing short-term protection (Seifelnasr et al., 2024). Although the anthelmintic drug niclosamide shows therapeutic potential against respiratory viral infections such as SARS-CoV-2, respiratory syncytial virus, and influenza, its systemic side effects have limited its use. However, localized aerosol delivery through small PEG coating has enabled its deposition on airway epithelium (Ousingsawat et al., 2022). Furthermore, an injectable DNA hydrogel (NT-CpG) loaded with nano-toxoid was shown to promote Th1/Th17-biased immune responses, protecting mice from MRSA pneumonia and addressing antibiotic resistance (Guo et al., 2023).
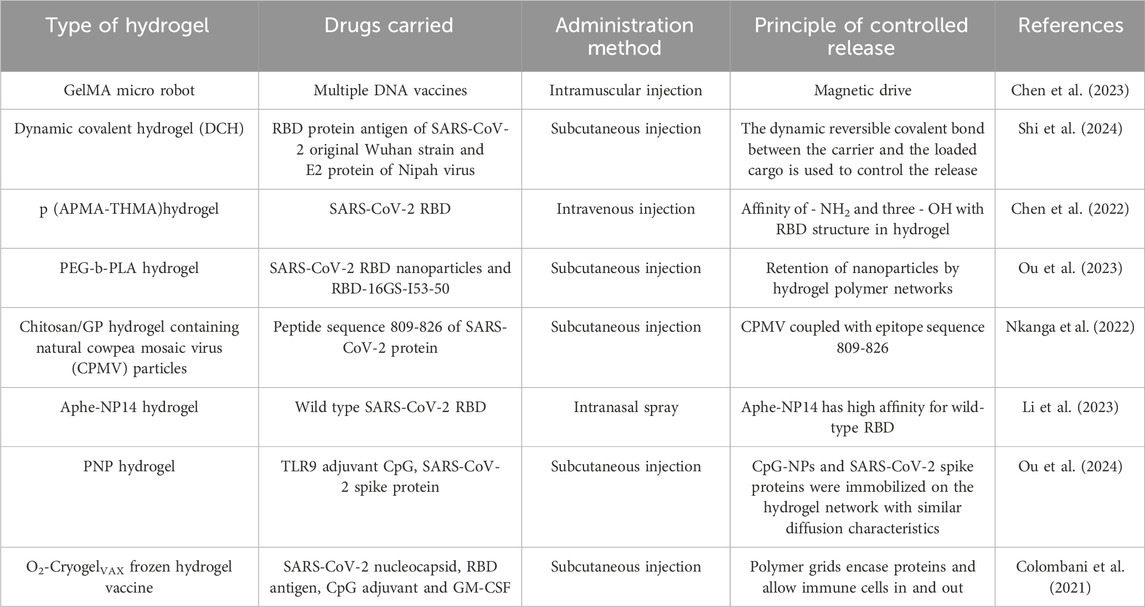
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has significantly accelerated the development of hydrogel-based vaccines (Table 1). Several injectable hydrogel vaccines incorporating the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein have been developed, including a polymer-nanoparticle (PNP) hydrogel system encapsulating RBD (Ou BS et al.) (Ou et al., 2023) and a hydrogel scaffold for prolonged poly (I: C)-adjuvanted RBD delivery (Chen J et al.) (Chen et al., 2022). A single-dose administration of these two systems in murine models induced sustained elevation of specific IgG titers for up to 28 days and enhanced gene expression lasting 185 days, respectively, demonstrating their capacity to elicit durable and effective humoral immune responses.
In addition to traditional single-drug hydrogel systems, hydrogels can also simultaneously load multiple drugs or bioactive molecules (such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, growth factors, etc.), enabling synergistic therapy. As previously mentioned, FK-MEM@CMCO-CS can co-load meropenem (MEM) and FK13-a1 AMP, significantly reducing the required antibiotic dosage in the treatment of VAP (Zhu B. et al., 2024). Similarly, in tuberculosis treatment, an amphiphilic hydrogel drug delivery system, TB-Gel, can encapsulate a mixture of four first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs, achieving therapeutic efficacy equivalent to oral administration with only half the dosage (Pal et al., 2021).
The three-dimensional network structure of hydrogels can protect drugs from enzymatic degradation or pH variations, thereby enhancing drug stability. For instance, hydrogels loaded with protein or peptide drugs can prevent their rapid degradation in the pulmonary environment, prolonging their duration of action. For example, a hydrogel system synthesized by Christian Isalomboto Nkanga et al., coated with the SARS-CoV-2 protein peptide sequence 809-826, demonstrated stable release of 10%–12% over 21 days, in contrast to 100% release observed in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) (Nkanga et al., 2022). Additionally, Zhiyuan Shi et al. designed a dynamic covalent hydrogel (DCH) that achieved sustained release of loaded recombinant protein antigens for up to 30 days, while eliciting neutralizing antibody titers 150-fold higher than conventional Alum-adjuvanted vaccines (Shi et al., 2024).
Beyond serving as drug delivery vehicles, hydrogels can mimic the structure and function of the ECM, providing support for lung tissue repair. For example, hydrogels loaded with growth factors (such as VEGF, FGF) can promote angiogenesis and tissue regeneration, accelerating the repair of lung injuries. Chuang Hu et al. developed an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-loaded hydrogel (EGF@PP), which, when delivered as a dry powder via bronchoscopy to the injured site in a rabbit model, effectively accelerated airway epithelial repair (Hu et al., 2023). The bronchoscopy scores demonstrated 1.60-fold and 1.38-fold improvements over the control group on days 7 and 10, respectively. Another alginate/hyaluronic acid hydrogel loaded with basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), when injected directly into the larynx of aged rats, demonstrated a 1.5-fold increase in laryngeal muscle cross-sectional area after 12 weeks compared to controls (Choi et al., 2019). These findings suggest its potential for restoring swallowing function and preventing aspiration pneumonia in the elderly.
3 Advances in hydrogel applications for pneumonia treatment
Hydrogels, owing to their unique physicochemical properties and multifunctionality, have shown broad application prospects in pneumonia treatment. Below, we review recent research progress in this field from four aspects: antibacterial therapy, anti-inflammatory therapy, tissue repair and regeneration, and combination therapy strategies.
3.1 Antibacterial therapy
A key pathological feature of pneumonia is the colonization and proliferation of pathogens (such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses) in the lungs. As carriers for antibacterial drugs, hydrogels can significantly enhance local drug concentrations and prolong their duration of action, effectively inhibiting pathogen growth.
Hydrogels can load antibiotics (such as vancomycin, gentamicin, and ciprofloxacin) through physical encapsulation or chemical bonding, achieving sustained drug release via controlled mechanisms. For example, a hydrogel based on Methocel (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) has been used to load amoxicillin, which, when administered orally to mice, significantly increased drug retention time and antibacterial efficacy at the infection site (Xu et al., 2017). Pradeep A et al. developed a chitosan hydrogel loaded with colistimethate sodium (a high-end antibiotic), which not only directly kills pathogenic bacteria but also effectively inhibits biofilm formation, reducing bacterial colonization potential (Pradeep et al., 2022). A novel hydrogel application strategy involves coating ventilator tubes with gentamicin-loaded hydrogel, greatly reducing the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia (Jones et al., 2015). Beyond traditional antibiotics, newly synthesized halogenated dopamine methacrylamides (DMA), particularly chlorinated DMA, when used in hydrogels, copolymers, and coatings, exhibit broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria, including MRSA, multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PAER), and carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) (Liu et al., 2021). Metal ions, due to their direct penetration of bacterial membranes, serve as excellent non-traditional “antibiotics.” Their ease of cross-linking with hydrogels has led to the development of numerous nanocomposites, such as Si@Ni (Gwon et al., 2024), Si@NiO-hydrogel (Gwon et al., 2022), ODHCs/CuONPs (Mohamed, 2024), and silver-coated hydrogels (Olson et al., 2002), which utilize metal ions as antibacterial components.
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are small peptides with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity but suffer from poor stability and short half-lives in vivo. Hydrogels can protect AMPs from enzymatic degradation and enable their sustained release, enhancing therapeutic efficacy. For example, a polymyxin B (PMB) peptide-containing antibacterial hydrogel coating on ventilator tubes extended the release and antibacterial cycle to at least 42 days (Wouters et al., 2024). Similarly, applying a hydrogel containing neuranidase (CSA-131) to tracheal tubes has shown promising results in preventing VAP (Hashemi et al., 2018). A supramolecular nanogel structure formed by self-assembly of a poorly soluble antibiotic (ciprofloxacin) and a hydrophobic tripeptide ((D)Leu-Phe-Phe) demonstrated strong antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and K. pneumoniae in mice (Marchesan et al., 2013).
3.2 Anti-inflammatory therapy
Pneumonia is often accompanied by severe inflammatory responses, leading to lung tissue damage and dysfunction. Hydrogels can effectively mitigate inflammation and promote tissue repair by loading anti-inflammatory drugs or modulating the immune microenvironment.
Hydrogels can be loaded with glucocorticoids (e.g., dexamethasone), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., ibuprofen), or cytokine inhibitors (e.g., IL-6 inhibitors), achieving sustained drug release through controlled mechanisms. For instance, Zhen Wang et al. developed hyaluronic acid methacrylate hydrogel microspheres combined with genetically engineered membranes overexpressing angiotensin-converting enzyme II (ACEII) receptors. These microspheres compete with the SARS-CoV-2 virus for ACE2 binding, neutralizing pro-inflammatory cytokines, and calming the cytokine storm (Wang et al., 2022). In addition to their aforementioned antibacterial properties, the immunostimulatory effects of Ag + have also been extensively studied. Ag + can stimulate the production of a large number of leukocytes in the early stages of wound healing, generating synergistic antibacterial activity, followed by a rapid reduction in leukocyte count. This results in a shorter duration of inflammation compared to the normal process, minimizing tissue damage caused by inflammation (Zhang et al., 2023; Liang et al., 2024). Leveraging this property, a series of hydrogel materials embedded with silver nanoparticles have been developed, including TGIAVE-Ag (Nagaraja et al., 2021b), TMGA-Ag (Nagaraja et al., 2021a), and AgNPs-loaded CS/PVA hydrogels (Suflet et al., 2021). Furthermore, researchers have explored natural extracts for their anti-inflammatory potential. For example, hydrogels containing sea buckthorn extract not only exhibit strong antibacterial activity against Streptococcus pneumoniae but also possess anti-inflammatory properties (Nowak et al., 2022). Emulsified grape seed oil incorporated into hydrogels has shown inhibitory effects on Cyclooxygenase-1/2 (COX-1/2), with a predominant effect on COX-1 (Eid et al., 2025).
Hydrogels can exert anti-inflammatory effects by modulating macrophage polarization (e.g., promoting M2 macrophage activation) or inhibiting the release of inflammatory mediators. For example, a hydrogel carrying Y-27632, a Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor, within CeO2-Y@ZIF-8@Gel, can repair damaged mitochondrial DNA, reduce the leakage of Ox-mtDNA, and downregulate the cGAS-STING pathway. This promotes macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype and enhances the production of anti-inflammatory factors (He et al., 2024). Another example is MNPs/Alg hydrogel, which inhibits oxidative stress damage by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and promotes macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype (Zhou et al., 2021). Although numerous hydrogels based on macrophage polarization modulation have been developed, their application in anti-inflammatory therapy for pneumonia remains underexplored. Therefore, this represents a promising direction for future research in the field of hydrogel-based pneumonia treatment.
3.3 Tissue repair
Lung tissue damage and fibrosis caused by pneumonia are among the most challenging aspects of treatment. Hydrogels, by mimicking the structure and function of the ECM, provide critical support for lung tissue repair.
The three-dimensional network structure of hydrogels can simulate the ECM of lung tissue, offering an optimal microenvironment for cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation. Current research has demonstrated that hydrogels derived from decellularized porcine lung ECM outperform traditional type I collagen and Matrigel in supporting cell adhesion, distribution, viability, and proliferation, making them a superior platform for three-dimensional cell culture and drug screening (Yan et al., 2022). Xinglong Zhu et al. developed a decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM) hydrogel, which was found to reverse pulmonary fibrosis in a mouse model by downregulating the ficolin signaling pathway and inhibiting M2 macrophage polarization (Zhu X. et al., 2024). Similarly, ECM hydrogels prepared from human lung fibroblast-derived matrix (hFDM) have shown significant potential for wound healing, although the underlying mechanisms remain incompletely understood (Savitri et al., 2020). Studies in rats have shown that ECM-derived hydrogels protect against lung injury through multiple mechanisms, including reducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), inflammation, and oxidative damage (Zhou et al., 2020). Additionally, gelatin hydrogels that control the release of macrophage-regulating cytokines have successfully shifted macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype, promoting ECM structural and compositional changes and enhancing downstream remodeling potential (Witherel et al., 2021).
Hydrogels can be loaded with growth factors (e.g., VEGF, FGF, EGF) and promote angiogenesis and tissue regeneration through sustained release mechanisms. Functionalized dextran (FD), an anionic water-soluble polymer capable of binding transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), has been used to prepare dextran hydrogels that retain up to 88% of rhTGF-β1 (Maire et al., 2005). In a three-dimensional co-culture model of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and lung fibroblasts, a hybrid network of polycaprolactone-collagen (PCL/Col) and hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogels loaded with VEGF supported not only cell attachment but also cell infiltration and the formation of primitive capillary networks within the scaffold structure (Ekaputra et al., 2011). Keiichi Hirose et al. synthesized micro-gelatin hydrogel microspheres containing bFGF, which, when administered intratracheally to rats, significantly increased pulmonary vascular density and improved hemodynamics (Hirose et al., 2008). Similarly, Qing Ban et al. modified an ordered colloidal crystal scaffold (CCS) made from chitosan and gelatin with bFGF, which greatly promoted the proliferation of lung epithelial cells and elicited only mild inflammatory responses when implanted into SD rats (Ban et al., 2019). Beyond direct growth factor delivery, encapsulating low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) in hydrogels has been shown to promote the expression of angiogenic factors and enhance compensatory lung growth in a mouse model of unilateral pneumonectomy (Mammoto et al., 2019). In addition to direct growth factor delivery, small interfering RNA (siRNA) inhalation therapy to activate endogenous regenerative programs is noteworthy. Hydrogels have effectively addressed the low intracellular delivery efficiency of siRNA. For example, hydrogel nanocomplexes combined with surfactant protein B (SP-B) have been reported as effective siRNA delivery enhancers, demonstrating efficacy in a mouse model of lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced lung injury (Merckx et al., 2018).
Hydrogels can inhibit pulmonary fibrosis by loading antifibrotic drugs (e.g., pirfenidone) or modulating the TGF-β signaling pathway. For instance, Elya A. Shamskhou et al. demonstrated that a hydrogel system based on hyaluronic acid and heparin, leveraging heparin’s reversible binding to Interleukin-10 (IL-10), could inhibit TGF-β-driven collagen production by lung fibroblasts and myofibroblasts (Shamskhou et al., 2019). Stem cell therapy holds significant promise for lung fibrosis regeneration but faces limitations, particularly the rapid clearance of implanted cells by the host. Hydrogel-based microcapsules for stem cell delivery have been shown to significantly prolong the persistence of donor mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in the host while enhancing their therapeutic functions, including immunomodulation and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-mediated ECM remodeling (Zhang et al., 2025).
3.4 Combination therapy strategies
The complex composition and multifunctionality of hydrogels enable the tailored construction of drug carriers based on the properties of the drugs. Through meticulous design and synthesis, hydrogels can easily integrate multiple drugs, combining antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and tissue repair functions to achieve comprehensive pneumonia treatment.
The fundamental challenge of differing drug solubilities has been addressed, with novel hydrogels capable of accommodating both water-soluble and lipid-soluble drugs now reported. For example, a chitosan-crosslinked dialdehyde xanthan gum interpenetrating hydroxypropyl methylcellulose hydrogel has been developed for the controlled delivery of various antibiotics, including ampicillin, minocycline, and rifampicin (Ngwabebhoh et al., 2021). Researchers have also explored the use of adjuvants to enhance drug delivery. Paeoniflorin analog 1, a linear lipopeptide, significantly enhances the antibacterial activity of clarithromycin. Sun Hee Moon et al. co-encapsulated these agents in a hydrogel, achieving effective killing of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and K. pneumoniae (Moon et al., 2021). To comprehensively target different subtypes of the same pathogen, Yoshikazu Yuki and his team combined three pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA) fusion antigen monovalent formulations into a trivalent nanogel (Yuki et al., 2021). Additionally, the incorporation of toll-like receptors 9 (TLR9), which activate dendritic cells (DCs), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), which stimulates various immune cells, significantly increased antibody titers (Colombani et al., 2021).
Hydrogels can be combined with nanomaterials such as nanoparticles, liposomes, or exosomes to further enhance drug delivery efficiency and therapeutic efficacy. Beyond the traditional approach of integrating SARS-CoV-2 RBD domain nanoparticles with injectable polymer hydrogel systems (Ou et al., 2023), Ben S. Ou et al. designed a hydrogel-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccine by incorporating CpG nanoparticles (CpG-NPs), a potent TLR9 agonist, which greatly amplified the magnitude and duration of the antibody response (Ou et al., 2024). Another emerging area of research involves embedding vaccine silver nanocomposites into polymer matrices. Unlike the previously mentioned direct crosslinking of metal ions, Yi-Syuan Wei et al. developed a composite hydrogel containing only silver monomers, which not only exhibited excellent antibacterial properties but also demonstrated strong water absorption capabilities (Wei et al., 2016). Additionally, the combination of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) with hydrogels produced rGO@LNP, which exhibited both direct killing and adsorption effects against K. pneumoniae and Enterococcus faecalis (Sohni et al., 2023). In summary, the inherent versatility of hydrogels makes them a natural “adhesive,” offering researchers endless possibilities to harness the strengths of various materials.
4 Challenges and limitations
Despite the immense potential exhibited by hydrogels in the treatment of pneumonia, their practical application still faces numerous challenges and limitations. These issues encompass material safety, drug delivery efficiency, large-scale production, and clinical translation, among other aspects, all of which require further research and technological breakthroughs for resolution.
The biosafety of hydrogels in pulmonary drug delivery is a primary concern. Although most hydrogel materials, such as hyaluronic acid and chitosan, possess good biocompatibility, their long-term retention in the lungs may trigger local or systemic immune responses. For instance, certain synthetic polymeric materials, like polyacrylamide, may elicit inflammatory reactions or cytotoxicity (despite being useful in cancer treatment) (Bloch et al., 2017). Furthermore, prolonged retention of hydrogels in the lungs may affect lung function and even lead to fibrosis or other complications (Harding and Reynolds, 2014).
The physical properties of hydrogels, such as viscoelasticity and degradation rate, significantly influence their distribution in the lungs and drug release behavior. For example, higher viscoelasticity has been shown to reduce cell dispersion (Charrier et al., 2018) and may be difficult to uniformly distribute via nebulization inhalation; whereas hydrogels with too low viscosity may fail to effectively adhere to lung tissue (Lou et al., 2018). Furthermore, the degradation rate of hydrogels needs to match and remain constant with the drug release kinetics. Rapid degradation may lead to drug bolus release, while slow degradation may prevent the drug from reaching therapeutic concentrations. A notable example is the pulsatile release of parathyroid hormone, which stimulates bone formation, whereas continuous release leads to bone loss (Li et al., 2017).
The clinical translation of hydrogels faces numerous challenges, including the feasibility of large-scale production, drug loading efficiency and stability, and the realization of personalized treatment. The preparation process of hydrogels is complex and requires strict quality control standards, posing challenges for large-scale production. For instance, although microfluidic technology can produce uniform hydrogels, its production efficiency is low and difficult to meet clinical demands (Tien and Dance, 2021). Additionally, the drug loading efficiency of hydrogels may be affected by material properties, drug characteristics, and preparation processes, while drug stability within hydrogels (such as maintaining the activity of protein drugs) is also a critical issue (Lee et al., 2024). Finally, the etiology and pathological mechanisms of pneumonia are complex and diverse, and different patients may require different treatment regimens.
As a novel drug delivery system, the clinical translation of hydrogels requires rigorous regulatory approval (e.g., FDA, EMA). However, current regulatory standards for hydrogels are not yet comprehensive, adding uncertainty to their approval process (Wang et al., 2024). Currently approved medical tissue “adhesives”, including fibrin glue (Atrah, 1994) and cyanoacrylate (Trott, 1997), are not suitable for applications involving drug delivery. Furthermore, the long-term safety of hydrogels in pulmonary drug delivery has not been fully elucidated, which may raise ethical concerns. For example, in elderly patients or those with weakened immune function, the application of hydrogels may pose additional infection risks, requiring greater caution (Beattie et al., 2003; Lebaudy et al., 2021).
5 Future research priorities and potential innovations
To address the biosafety issues, researchers may attempt various approaches, including drug-eluting coatings (Farah et al., 2019), hydrophilic (Gudipati et al., 2005) or zwitterionic polymer coatings (Zhang et al., 2013), active surfaces (Dolan et al., 2019), and controlling material stiffness (Noskovicova et al., 2021) and/or size (Veiseh et al., 2015). Notably, Xuanhe Zhao and his team developed a hydrogel made of cross-linked polymers that effectively suppresses immune cell attacks on implants, a groundbreaking achievement published in Nature. Additionally, designing degradable hydrogels that can be naturally cleared by the body after completing drug delivery or tissue repair is also a crucial strategy to enhance their safety (Tian and Liu, 2023; Chen et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2023).
As for how to enhance the controlled release of hydrogel, researchers are optimizing the viscoelasticity of hydrogels by adjusting their cross-linking density or polymer concentration (Song et al., 2012; Wang and Windbergs, 2019) and achieving precise control over degradation rate and drug release through rational design of the hydrogel’s cross-linked network or introduction of stimuli-responsive groups (Numata et al., 2012; Hu et al., 2022). By optimizing the chemical structure of hydrogels, such as introducing protective groups to couple drugs (Nkanga et al., 2022) or adopting nanoparticle composite technology (Choi and Kohane, 2024), the drug loading efficiency and stability can be improved. These plans are all selective to drugs and lack simple, standardized synthesis methods. Although some novel materials supporting multimodal drug release have been reported (Day et al., 2022), there are still requirements for the standardization and large-scale production process of hydrogels in the future. To address this, researchers are developing efficient, low-cost preparation processes such as 3D printing (Mandrycky et al., 2016) and electrospinning (Xie et al., 2021), and establishing standardized quality control systems.
Finally, the booming development of molecular medicine research has raised new demands for personalized treatment. The development of smart responsive hydrogels, such as pH-responsive (Liang et al., 2022) and enzyme-responsive (Shigemitsu et al., 2020) hydrogels, or the integration of precision medicine technologies like genetic testing (Mo et al., 2021), can enable the individualized design of hydrogels to meet clinical needs. For these innovative personalized medications, Strengthening communication with regulatory bodies and establishing standardized evaluation systems for hydrogels are crucial for accelerating their clinical translation (James et al., 2023). Strict adherence to ethical norms in clinical trials and thorough assessment of the potential risks and benefits of hydrogels are essential prerequisites for ensuring their safe application.
Author contributions
JW: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. PW: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review and editing. KL: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review and editing. DH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (Grant No. 202040174), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant No. 22Y11900800) and the Key Discipline of Shanghai Health System (Grant No. 2024ZDXK0012).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ban, Q., Chen, W., Du, S., Wang, H., Li, J., You, R., et al. (2019). The preparation of the ordered pores colloidal crystal scaffold and its role in promoting growth of lung cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 173, 907–917. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.10.055
Bassetti, M., Vena, A., Russo, A., and Peghin, M. (2020). Inhaled liposomal antimicrobial delivery in lung infections. Drugs 80 (13), 1309–1318. doi:10.1007/s40265-020-01359-z
Beattie, T. K., Tomlinson, A., McFadyen, A. K., Seal, D. V., and Grimason, A. M. (2003). Enhanced attachment of acanthamoeba to extended-wear silicone hydrogel contact lenses: a new risk factor for infection? Ophthalmology 110 (4), 765–771. doi:10.1016/s0161-6420(02)01971-1
Bej, R., Stevens, C. A., Nie, C., Ludwig, K., Degen, G. D., Kerkhoff, Y., et al. (2024). Mucus-inspired self-healing hydrogels: a protective barrier for cells against viral infection. Adv. Mater. 36 (32), e2401745. doi:10.1002/adma.202401745
Bernal, P. N., Delrot, P., Loterie, D., Li, Y., Malda, J., Moser, C., et al. (2019). Volumetric bioprinting of complex living-tissue constructs within seconds. Adv. Mater. 31 (42), e1904209. doi:10.1002/adma.201904209
Bertsch, P., Diba, M., Mooney, D. J., and Leeuwenburgh, S. C. G. (2023). Self-healing injectable hydrogels for tissue regeneration. Chem. Rev. 123 (2), 834–873. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00179
Bloch, M. B. D., Yavin, E., Nissan, A., Ariel, I., Kenett, R., Brass, D., et al. (2017). The effect of linker type and recognition peptide conjugation chemistry on tissue affinity and cytotoxicity of charged polyacrylamide. J. Control Release 257, 102–117. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.06.038
Bohn, M. K., Hall, A., Sepiashvili, L., Jung, B., Steele, S., and Adeli, K. (2020). Pathophysiology of COVID-19: mechanisms underlying disease severity and progression. Physiol. (Bethesda) 35 (5), 288–301. doi:10.1152/physiol.00019.2020
Brown, M., Li, J., Moraes, C., Tabrizian, M., and Li-Jessen, N. Y. (2022). Decellularized extracellular matrix: new promising and challenging biomaterials for regenerative medicine. Biomaterials 289, 121786. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121786
Cao, H., Duan, L., Zhang, Y., Cao, J., and Zhang, K. (2021). Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 6 (1), 426. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00830-x
Charrier, E. E., Pogoda, K., Wells, R. G., and Janmey, P. A. (2018). Control of cell morphology and differentiation by substrates with independently tunable elasticity and viscous dissipation. Nat. Commun. 9 (1), 449. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-02906-9
Chen, J., Luo, J., Feng, J., Wang, Y., Lv, H., and Zhou, Y. (2024). Spatiotemporal controlled released hydrogels for multi-system regulated bone regeneration. J. Control Release 372, 846–861. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.06.065
Chen, J., Wang, B., Caserto, J. S., Shariati, K., Cao, P., Pan, Y., et al. (2022). Sustained delivery of SARS-CoV-2 RBD subunit vaccine using a high affinity injectable hydrogel scaffold. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 11 (2), e2101714. doi:10.1002/adhm.202101714
Chen, S., Tan, Z., Liao, P., Li, Y., Qu, Y., Zhang, Q., et al. (2023). Biodegradable microrobots for DNA vaccine delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 12 (21), e2202921. doi:10.1002/adhm.202202921
Ching, P. R., and Pedersen, L. L. (2025). Severe pneumonia. Med. Clin. North Am. 109 (3), 705–720. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2024.12.011
Choi, W., and Kohane, D. S. (2024). Hybrid nanoparticle-hydrogel systems for drug delivery depots and other biomedical applications. ACS Nano 18 (34), 22780–22792. doi:10.1021/acsnano.4c06888
Choi, Y. H., Kim, S. H., Kim, I. G., Lee, J. H., and Kwon, S. K. (2019). Injectable basic fibroblast growth factor-loaded alginate/hyaluronic acid hydrogel for rejuvenation of geriatric larynx. Acta Biomater. 89, 104–114. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2019.03.005
Cilloniz, C., Torres, A., and Niederman, M. S. (2021). Management of pneumonia in critically ill patients. BMJ 375, e065871. doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-065871
Colombani, T., Eggermont, L. J., Rogers, Z. J., McKay, L. G. A., Avena, L. E., Johnson, R. I., et al. (2021). Biomaterials and oxygen join forces to shape the immune response and boost COVID-19 vaccines. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 8 (18), 2100316. doi:10.1002/advs.202100316
Day, N. B., Dalhuisen, R., Loomis, N. E., Adzema, S. G., Prakash, J., and Shields IV, C. W. (2022). Tissue-adhesive hydrogel for multimodal drug release to immune cells in skin. Acta Biomater. 150, 211–220. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2022.07.053
Ding, H., Tan, P., Fu, S., Tian, X., Zhang, H., Ma, X., et al. (2022). Preparation and application of pH-responsive drug delivery systems. J. Control Release 348, 206–238. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.056
Dolan, E. B., Varela, C. E., Mendez, K., Whyte, W., Levey, R. E., Robinson, S. T., et al. (2019). An actuatable soft reservoir modulates host foreign body response. Sci. Robot. 4 (33), eaax7043. doi:10.1126/scirobotics.aax7043
Doroudian, M., MacLoughlin, R., Poynton, F., Prina-Mello, A., and Donnelly, S. C. (2019). Nanotechnology based therapeutics for lung disease. Thorax 74 (10), 965–976. doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2019-213037
Eid, A. M., Al-Hawari, H., Nazzal, S., and Khudarieh, S. (2025). Development of Vitis vinifera nanoemulgel and evaluation of its potential anticancer, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 25 (1), 47. doi:10.1186/s12906-025-04804-2
Ekaputra, A. K., Prestwich, G. D., Cool, S. M., and Hutmacher, D. W. (2011). The three-dimensional vascularization of growth factor-releasing hybrid scaffold of poly (epsilon-caprolactone)/collagen fibers and hyaluronic acid hydrogel. Biomaterials 32 (32), 8108–8117. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.07.022
Farah, S., Doloff, J. C., Müller, P., Sadraei, A., Han, H. J., Olafson, K., et al. (2019). Long-term implant fibrosis prevention in rodents and non-human Primates using crystallized drug formulations. Nat. Mater. 18 (8), 892–904. doi:10.1038/s41563-019-0377-5
Gasek, N., Park, H. E., Uriarte, J. J., Uhl, F. E., Pouliot, R. A., Riveron, A., et al. (2021). Development of alginate and gelatin-based pleural and tracheal sealants. Acta Biomater. 131, 222–235. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2021.06.048
Gnatowski, P., Ansariaghmiuni, M., Piłat, E., Poostchi, M., Kucińska-Lipka, J., Yazdi, M. K., et al. (2025). Hydrogel membranes in organ-on-a-chip devices: a review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 251, 114591. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2025.114591
Goor, O., Hendrikse, S. I. S., Dankers, P. Y. W., and Meijer, E. W. (2017). From supramolecular polymers to multi-component biomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46 (21), 6621–6637. doi:10.1039/c7cs00564d
Gudipati, C. S., Finlay, J. A., Callow, J. A., Callow, M. E., and Wooley, K. L. (2005). The antifouling and fouling-release perfomance of hyperbranched fluoropolymer (HBFP)−Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) composite coatings evaluated by adsorption of biomacromolecules and the green fouling alga ulva. Langmuir 21 (7), 3044–3053. doi:10.1021/la048015o
Guo, Z., Zhou, J., Yu, Y., Krishnan, N., Noh, I., Zhu, A. T., et al. (2023). Immunostimulatory DNA hydrogel enhances protective efficacy of nanotoxoids against bacterial infection. Adv. Mater. 35 (31), e2211717. doi:10.1002/adma.202211717
Guowei, D., Adriane, K., Chen, X., Jie, C., and Yinfeng, L. (2007). PVP magnetic nanospheres: biocompatibility, in vitro and in vivo bleomycin release. Int. J. Pharm. 328 (1), 78–85. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.07.042
Gwon, K., Park, J. D., Lee, S., Choi, W. I., Hwang, Y., Mori, M., et al. (2022). Injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogel encapsulated with Si-based NiO nanoflower by visible light cross-linking: its antibacterial applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 208, 149–158. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.03.051
Gwon, K., Park, J. D., Lee, S., Yu, J. S., and Lee, D. N. (2024). Fabrication of silicon-based nickel nanoflower-encapsulated gelatin microspheres as an active antimicrobial carrier. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 264 (Pt 2), 130617. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130617
Harding, J. L., and Reynolds, M. M. (2014). Combating medical device fouling. Trends Biotechnol. 32 (3), 140–146. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.12.004
Hashemi, M. M., Rovig, J., Bateman, J., Holden, B. S., Modelzelewski, T., Gueorguieva, I., et al. (2018). Preclinical testing of a broad-spectrum antimicrobial endotracheal tube coated with an innate immune synthetic mimic. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 73 (1), 143–150. doi:10.1093/jac/dkx347
He, S., Li, Z., Wang, L., Yao, N., Wen, H., Yuan, H., et al. (2024). A nanoenzyme-modified hydrogel targets macrophage reprogramming-angiogenesis crosstalk to boost diabetic wound repair. Bioact. Mater. 35, 17–30. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.01.005
Hespanhol, V., and Barbara, C. (2020). Pneumonia mortality, comorbidities matter? Pulmonology 26 (3), 123–129. doi:10.1016/j.pulmoe.2019.10.003
Hirose, K., Marui, A., Arai, Y., Kushibiki, T., Kimura, Y., Sakaguchi, H., et al. (2008). Novel approach with intratracheal administration of microgelatin hydrogel microspheres incorporating basic fibroblast growth factor for rescue of rats with monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc Surg. 136 (5), 1250–1256. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2008.05.038
Hong, Y., Lin, Z., Yang, Y., Jiang, T., Shang, J., and Luo, Z. (2022). Biocompatible conductive hydrogels: applications in the field of biomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (9), 4578. doi:10.3390/ijms23094578
Hu, C., Ji, H., Gong, Y., Yang, X., Jia, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2023). Wet-adhesive γ-PGA/ε-PLL hydrogel loaded with EGF for tracheal epithelial injury repair. J. Mater Chem. B 11 (36), 8666–8678. doi:10.1039/d3tb01550e
Hu, J., Zhang, G., and Liu, S. (2012). Enzyme-responsive polymeric assemblies, nanoparticles and hydrogels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41 (18), 5933–5949. doi:10.1039/c2cs35103j
Hu, S., Zhi, Y., Shan, S., and Ni, Y. (2022). Research progress of smart response composite hydrogels based on nanocellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 275, 118741. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118741
Jain, S., Williams, D. J., Arnold, S. R., Ampofo, K., Bramley, A. M., Reed, C., et al. (2015). Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. children. N. Engl. J. Med. 372 (9), 835–845. doi:10.1056/nejmoa1405870
James, J. R., Curd, J., Ashworth, J. C., Abuhantash, M., Grundy, M., Seedhouse, C. H., et al. (2023). Hydrogel-based pre-clinical evaluation of repurposed FDA-approved drugs for AML. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (4), 4235. doi:10.3390/ijms24044235
Ji, Y. R., Young, T. H., Tsai, T. Y., Chen, J. S., and Chen, K. C. (2021). Dopamine-modified alginate hydrogel with effectiveness and safety for preoperative localization of lung nodules. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 7 (9), 4637–4644. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c00512
Jiao, J. B., Kang, Q., Cui, S. x., Cao, J. l., Lin, T., Ma, C. j., et al. (2025). Target-driven functionalized DNA hydrogel capillary sensor for SARS-CoV-2 dual-mode detection. Talanta 285, 127342. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2024.127342
Jones, D. S., McCoy, C. P., Andrews, G. P., McCrory, R. M., and Gorman, S. P. (2015). Hydrogel antimicrobial capture coatings for endotracheal tubes: a pharmaceutical strategy designed to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia. Mol. Pharm. 12 (8), 2928–2936. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00208
Klitgaard, T. L., Schjørring, O. L., Nielsen, F. M., Meyhoff, C. S., Perner, A., Wetterslev, J., et al. (2023). Higher versus lower fractions of inspired oxygen or targets of arterial oxygenation for adults admitted to the intensive care unit. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 9 (9), CD012631. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd012631.pub3
Laxminarayan, R., Matsoso, P., Pant, S., Brower, C., Røttingen, J. A., Klugman, K., et al. (2016). Access to effective antimicrobials: a worldwide challenge. Lancet 387 (10014), 168–175. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(15)00474-2
Lebaudy, E., Fournel, S., Lavalle, P., Vrana, N. E., and Gribova, V. (2021). Recent advances in antiinflammatory material design. Adv. Healthc. Mater 10 (1), e2001373. doi:10.1002/adhm.202001373
Lee, S., Choi, S., and Kim, M. S. (2024). Intra-articular hydrogel formulation prolongs the in vivo stability of toll-like receptor antagonistic peptides for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. J. Control Release 372, 467–481. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.06.034
Li, B., Zhao, Y., Wu, X., Wu, H., Tang, W., Yu, X., et al. (2023). Abiotic synthetic antibody inhibitor with broad-spectrum neutralization and antiviral efficacy against escaping SARS-CoV-2 variants. ACS Nano 17 (7), 7017–7034. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c02050
Li, J., Celiz, A. D., Yang, J., Yang, Q., Wamala, I., Whyte, W., et al. (2017). Tough adhesives for diverse wet surfaces. Science 357 (6349), 378–381. doi:10.1126/science.aah6362
Li, L., An, J., Lin, Z., Liu, L., and Liu, Q. (2024). A rapid and robust organ repair polyacrylamide/alginate adhesive hydrogel mediated via interfacial adhesion-trigger molecules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 281 (Pt 2), 135681. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135681
Li, Z. J., Zhang, H. Y., Ren, L. L., Lu, Q. B., Ren, X., Zhang, C. H., et al. (2021). Etiological and epidemiological features of acute respiratory infections in China. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 5026. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-25120-6
Liang, X., Ding, L., Ma, J., Li, J., Cao, L., Liu, H., et al. (2024). Enhanced mechanical strength and sustained drug release in carrier-free silver-coordinated anthraquinone natural antibacterial anti-inflammatory hydrogel for infectious wound healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13 (23), e2400841. doi:10.1002/adhm.202400841
Liang, Y., Li, M., Yang, Y., Qiao, L., Xu, H., and Guo, B. (2022). pH/Glucose dual responsive metformin release hydrogel dressings with adhesion and self-healing via dual-dynamic bonding for athletic diabetic foot wound healing. ACS Nano 16 (2), 3194–3207. doi:10.1021/acsnano.1c11040
Lim, T. K., and Siow, W. T. (2018). Pneumonia in the tropics. Respirology 23 (1), 28–35. doi:10.1111/resp.13137
Liu, B., Zhou, C., Zhang, Z., Roland, J. D., and Lee, B. P. (2021). Antimicrobial property of halogenated catechols. Chem. Eng. J. 403, 126340. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.126340
Liu, S., Yu, Q., Guo, R., Chen, K., Xia, J., Guo, Z., et al. (2023). A biodegradable, adhesive, and stretchable hydrogel and potential applications for allergic rhinitis and epistaxis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 12 (29), e2302059. doi:10.1002/adhm.202302059
Lou, J., Stowers, R., Nam, S., Xia, Y., and Chaudhuri, O. (2018). Stress relaxing hyaluronic acid-collagen hydrogels promote cell spreading, fiber remodeling, and focal adhesion formation in 3D cell culture. Biomaterials 154, 213–222. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.11.004
Maire, M., Logeart-Avramoglou, D., Degat, M. C., and Chaubet, F. (2005). Retention of transforming growth factor β1 using functionalized dextran-based hydrogels. Biomaterials 26 (14), 1771–1780. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.06.003
Mammoto, A., Muyleart, M., and Mammoto, T. (2019). LRP5 in age-related changes in vascular and alveolar morphogenesis in the lung. Aging (Albany NY) 11 (1), 89–103. doi:10.18632/aging.101722
Mandrycky, C., Wang, Z., Kim, K., and Kim, D. H. (2016). 3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues. Biotechnol. Adv. 34 (4), 422–434. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.12.011
Marchesan, S., Qu, Y., Waddington, L. J., Easton, C. D., Glattauer, V., Lithgow, T. J., et al. (2013). Self-assembly of ciprofloxacin and a tripeptide into an antimicrobial nanostructured hydrogel. Biomaterials 34 (14), 3678–3687. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.01.096
Mei, X., Li, J., Wang, Z., Zhu, D., Huang, K., Hu, S., et al. (2023). An inhaled bioadhesive hydrogel to shield non-human Primates from SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Mater. 22 (7), 903–912. doi:10.1038/s41563-023-01475-7
Meijvis, S. C., van de Garde, E. M. W., Rijkers, G. T., and Bos, W. J. W. (2012). Treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs in community-acquired pneumonia. J. Intern. Med. 272 (1), 25–35. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2012.02554.x
Merckx, P., De Backer, L., Van Hoecke, L., Guagliardo, R., Echaide, M., Baatsen, P., et al. (2018). Surfactant protein B (SP-B) enhances the cellular siRNA delivery of proteolipid coated nanogels for inhalation therapy. Acta Biomater. 78, 236–246. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2018.08.012
Mester, U. (1979). Tierexperimentelle Ergebnisse mit Hydrogel-Keratoprothesen unterschiedlichen Wassergehaltes. Ophthalmologica 179 (1), 62–69. doi:10.1159/000308865
Mikhail, A. S., Morhard, R., Mauda-Havakuk, M., Kassin, M., Arrichiello, A., and Wood, B. J. (2023). Hydrogel drug delivery systems for minimally invasive local immunotherapy of cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 202, 115083. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2023.115083
Mo, F., Jiang, K., Zhao, D., Wang, Y., Song, J., and Tan, W. (2021). DNA hydrogel-based gene editing and drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 168, 79–98. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2020.07.018
Mohamed, N. A. (2024). Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of in vitro potential antimicrobial efficiency of new chitosan hydrogels and their CuO nanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 276 (Pt 2), 133810. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133810
Mohamed, N. A., Al-Harby, N. F., and Almarshed, M. S. (2019). Synthesis and characterization of novel trimellitic anhydride isothiocyanate-cross linked chitosan hydrogels modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes for enhancement of antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 132, 416–428. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.195
Moon, S. H., Kaufmann, Y., Fujiwara, R., and Huang, E. (2021). Enzymatically-crosslinked gelatin hydrogels containing paenipeptin and clarithromycin against carbapenem-resistant pathogen in murine skin wound infection. BMC Microbiol. 21 (1), 326. doi:10.1186/s12866-021-02383-z
Nagaraja, K., Krishna Rao, K. S. V., Zo, S., Soo Han, S., and Rao, K. M. (2021a). Synthesis of novel tamarind gum-co-poly(acrylamidoglycolic acid)-based pH responsive Semi-IPN hydrogels and their Ag nanocomposites for controlled release of chemotherapeutics and inactivation of multi-drug-resistant bacteria. Gels 7 (4), 237. doi:10.3390/gels7040237
Nagaraja, K., Rao, K. M., Reddy, G. V., and Rao, K. K. (2021b). Tragacanth gum-based multifunctional hydrogels and green synthesis of their silver nanocomposites for drug delivery and inactivation of multidrug resistant bacteria. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 174, 502–511. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.203
Nasra, S., Patel, M., Shukla, H., Bhatt, M., and Kumar, A. (2023). Functional hydrogel-based wound dressings: a review on biocompatibility and therapeutic efficacy. Life Sci. 334, 122232. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122232
Ngwabebhoh, F. A., Zandraa, O., Patwa, R., Saha, N., Capáková, Z., and Saha, P. (2021). Self-crosslinked chitosan/dialdehyde xanthan gum blended hypromellose hydrogel for the controlled delivery of ampicillin, minocycline and rifampicin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 167, 1468–1478. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.100
Nissen, M. D. (2007). Congenital and neonatal pneumonia. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 8 (3), 195–203. doi:10.1016/j.prrv.2007.07.001
Nkanga, C. I., Ortega-Rivera, O. A., Shin, M. D., Moreno-Gonzalez, M. A., and Steinmetz, N. F. (2022). Injectable slow-release hydrogel formulation of a plant virus-based COVID-19 vaccine candidate. Biomacromolecules 23 (4), 1812–1825. doi:10.1021/acs.biomac.2c00112
Noskovicova, N., Schuster, R., van Putten, S., Ezzo, M., Koehler, A., Boo, S., et al. (2021). Suppression of the fibrotic encapsulation of silicone implants by inhibiting the mechanical activation of pro-fibrotic TGF-β. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 5 (12), 1437–1456. doi:10.1038/s41551-021-00722-z
Nowak, A., Zagórska-Dziok, M., Perużyńska, M., Cybulska, K., Kucharska, E., Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P., et al. (2022). Assessment of the anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and anti-aging properties and possible use on the skin of hydrogels containing Epilobium angustifolium L. extracts. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 896706. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.896706
Numata, K., Yamazaki, S., and Naga, N. (2012). Biocompatible and biodegradable dual-drug release system based on silk hydrogel containing silk nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 13 (5), 1383–1389. doi:10.1021/bm300089a
Oliva, N., Conde, J., Wang, K., and Artzi, N. (2017). Designing hydrogels for On-Demand therapy. Acc. Chem. Res. 50 (4), 669–679. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00536
Olson, M. E., Harmon, B. G., and Kollef, M. H. (2002). Silver-coated endotracheal tubes associated with reduced bacterial burden in the lungs of mechanically ventilated dogs. Chest 121 (3), 863–870. doi:10.1378/chest.121.3.863
Ou, B. S., Baillet, J., Picece, V. C. T. M., Gale, E. C., Powell, A. E., Saouaf, O. M., et al. (2024). Nanoparticle-conjugated toll-like receptor 9 agonists improve the potency, durability, and breadth of COVID-19 vaccines. ACS Nano 18 (4), 3214–3233. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c09700
Ou, B. S., Saouaf, O. M., Yan, J., Bruun, T. U. J., Baillet, J., Zhou, X., et al. (2023). Broad and durable humoral responses following single hydrogel immunization of SARS-CoV-2 subunit vaccine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 12 (28), e2301495. doi:10.1002/adhm.202301495
Ousingsawat, J., Centeio, R., Cabrita, I., Talbi, K., Zimmer, O., Graf, M., et al. (2022). Airway delivery of hydrogel-encapsulated niclosamide for the treatment of inflammatory airway disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (3), 1085. doi:10.3390/ijms23031085
Pal, S., Soni, V., Kumar, S., Jha, S. K., Medatwal, N., Rana, K., et al. (2021). A hydrogel-based implantable multidrug antitubercular formulation outperforms oral delivery. Nanoscale 13 (31), 13225–13230. doi:10.1039/d0nr08806d
Pradeep, A., Ashok, N., Priya, V., Pillai, A. V., Menon, R. R., Kumar, V. A., et al. (2022). Colistimethate sodium-chitosan hydrogel for treating Gram-negative bacterial wound infections. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 214, 610–616. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.113
Prina, E., Ranzani, O. T., and Torres, A. (2015). Community-acquired pneumonia. Lancet 386 (9998), 1097–1108. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(15)60733-4
Rastogi, P., and Kandasubramanian, B. (2019). Review of alginate-based hydrogel bioprinting for application in tissue engineering. Biofabrication 11 (4), 042001. doi:10.1088/1758-5090/ab331e
Savitri, C., Ha, S. S., Liao, E., Du, P., and Park, K. (2020). Extracellular matrices derived from different cell sources and their effect on macrophage behavior and wound healing. J. Mater Chem. B 8 (42), 9744–9755. doi:10.1039/d0tb01885f
Schenck, D. M., and Fiegel, J. (2016). Tensiometric and phase domain behavior of lung surfactant on mucus-like viscoelastic hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 (9), 5917–5928. doi:10.1021/acsami.6b00294
Schmitt, H. J., Bernard, E. M., Häuser, M., and Armstrong, D. (1988). Aerosol amphotericin B is effective for prophylaxis and therapy in a rat model of pulmonary aspergillosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 32 (11), 1676–1679. doi:10.1128/aac.32.11.1676
Scott, J. A., Brooks, W. A., Peiris, J. M., Holtzman, D., and Mulhollan, E. K. (2008). Pneumonia research to reduce childhood mortality in the developing world. J. Clin. Invest. 118 (4), 1291–1300. doi:10.1172/jci33947
Seifelnasr, A., Talaat, M., Si, X. A., and Xi, J. (2024). Delivery of agarose-aided sprays to the posterior nose for mucosa immunization and short-term protection against infectious respiratory diseases. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 25 (6), 787–798. doi:10.2174/1389201024666230801142913
Shamskhou, E. A., Kratochvil, M. J., Orcholski, M. E., Nagy, N., Kaber, G., Steen, E., et al. (2019). Hydrogel-based delivery of Il-10 improves treatment of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. Biomaterials 203, 52–62. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.02.017
Shen, C., Yang, H., She, W., and Meng, Q. (2023). A microfluidic lung-on-a-chip based on biomimetic hydrogel membrane. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 120 (7), 2027–2038. doi:10.1002/bit.28426
Shi, Z., Gao, Z., Zhuang, X., Si, X., Huang, Z., Di, Y., et al. (2024). Dynamic covalent hydrogel as a single-dose vaccine adjuvant for sustained antigen release and significantly elevated humoral immunity. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13 (23), e2400886. doi:10.1002/adhm.202400886
Shigemitsu, H., Kubota, R., Nakamura, K., Matsuzaki, T., Minami, S., Aoyama, T., et al. (2020). Protein-responsive protein release of supramolecular/polymer hydrogel composite integrating enzyme activation systems. Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 3859. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17698-0
Shirkhani, K., Teo, I., Armstrong-James, D., and Shaunak, S. (2015). Nebulised amphotericin B-polymethacrylic acid nanoparticle prophylaxis prevents invasive aspergillosis. Nanomedicine 11 (5), 1217–1226. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2015.02.012
Singh, S. J., Baldwin, M. M., Daynes, E., Evans, R. A., Greening, N. J., Jenkins, R. G., et al. (2023). Respiratory sequelae of COVID-19: pulmonary and extrapulmonary origins, and approaches to clinical care and rehabilitation. Lancet Respir. Med. 11 (8), 709–725. doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(23)00159-5
Sohni, S., Hassan, T., Khan, S. B., Akhtar, K., Bakhsh, E. M., Hashim, R., et al. (2023). Lignin nanoparticles-reduced graphene oxide based hydrogel: a novel strategy for environmental applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 225, 1426–1436. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.11.200
Song, B., Wu, C., and Chang, J. (2012). Dual drug release from electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/mesoporous silica nanoparticles composite mats with distinct release profiles. Acta Biomater. 8 (5), 1901–1907. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2012.01.020
Souto, E. B., Blanco-Llamero, C., Krambeck, K., Kiran, N. S., Yashaswini, C., Postwala, H., et al. (2024). Regulatory insights into nanomedicine and gene vaccine innovation: safety assessment, challenges, and regulatory perspectives. Acta Biomater. 180, 1–17. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2024.04.010
Staquicini, D. I., Cardó-Vila, M., Rotolo, J. A., Staquicini, F. I., Tang, F. H. F., Smith, T. L., et al. (2023). Ceramide as an endothelial cell surface receptor and a lung-specific lipid vascular target for circulating ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 120 (34), e2220269120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2220269120
Suflet, D. M., Popescu, I., Pelin, I. M., Ichim, D. L., Daraba, O. M., Constantin, M., et al. (2021). Dual cross-linked Chitosan/PVA hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial properties. Pharmaceutics 13 (9), 1461. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13091461
Tian, B., and Liu, J. (2023). Smart stimuli-responsive chitosan hydrogel for drug delivery: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 235, 123902. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123902
Tien, J., and Dance, Y. W. (2021). Microfluidic biomaterials. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 10 (4), e2001028. doi:10.1002/adhm.202001028
Tran, S., Ksajikian, A., Overbey, J., and Li, Y. (2022). Pathophysiology of pulmonary fibrosis in the context of COVID-19 and implications for treatment: a narrative review. Cells 11 (16), 2489. doi:10.3390/cells11162489
Trott, A. T. (1997). Cyanoacrylate tissue adhesives. An advance in wound care. JAMA 277 (19), 1559–1560. doi:10.1001/jama.1997.03540430071037
van Os, L., Yeoh, J., Witz, G., Ferrari, D., Krebs, P., Chandorkar, Y., et al. (2023). Immune cell extravasation in an organ-on-chip to model lung inflammation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 187, 106485. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106485
Veiseh, O., Doloff, J. C., Ma, M., Vegas, A. J., Tam, H. H., Bader, A., et al. (2015). Size- and shape-dependent foreign body immune response to materials implanted in rodents and non-human Primates. Nat. Mater. 14 (6), 643–651. doi:10.1038/nmat4290
Wan, Q., Zhang, X., Zhou, D., Xie, R., Cai, Y., Zhang, K., et al. (2023). Inhaled nano-based therapeutics for pulmonary fibrosis: recent advances and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnology 21 (1), 215. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-01971-7
Wang, J., and Windbergs, M. (2019). Controlled dual drug release by coaxial electrospun fibers - impact of the core fluid on drug encapsulation and release. Int. J. Pharm. 556, 363–371. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.12.026
Wang, P., Cai, F., Li, Y., Yang, X., Feng, R., Lu, H., et al. (2024). Emerging trends in the application of hydrogel-based biomaterials for enhanced wound healing: a literature review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 261 (Pt 1), 129300. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129300
Wang, Z., Xiang, L., Lin, F., Cai, Z., Ruan, H., Wang, J., et al. (2022). Inhaled ACE2-engineered microfluidic microsphere for intratracheal neutralization of COVID-19 and calming of the cytokine storm. Matter 5 (1), 336–362. doi:10.1016/j.matt.2021.09.022
Wei, Y. S., Chen, K. S., and Wu, L. T. (2016). In situ synthesis of high swell ratio polyacrylic acid/silver nanocomposite hydrogels and their antimicrobial properties. J. Inorg. Biochem. 164, 17–25. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2016.08.007
Witherel, C. E., Sao, K., Brisson, B. K., Han, B., Volk, S. W., Petrie, R. J., et al. (2021). Regulation of extracellular matrix assembly and structure by hybrid M1/M2 macrophages. Biomaterials 269, 120667. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120667
Wouters, M., Van Moll, L., De Vooght, L., Choińska, E., Idaszek, J., Szlązak, K., et al. (2024). Polymyxin B peptide hydrogel coating: a novel approach to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (19), 10269. doi:10.3390/ijms251910269
Xiao, Q., Li, X., Li, Y., Wu, Z., Xu, C., Chen, Z., et al. (2021). Biological drug and drug delivery-mediated immunotherapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 11 (4), 941–960. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2020.12.018
Xie, R., Liang, Z., Ai, Y., Zheng, W., Xiong, J., Xu, P., et al. (2021). Composable microfluidic spinning platforms for facile production of biomimetic perfusable hydrogel microtubes. Nat. Protoc. 16 (2), 937–964. doi:10.1038/s41596-020-00442-9
Xu, K., Li, L., Cui, M., Han, Y., Karahan, H. E., Chow, V. T. K., et al. (2017). Cold chain-free storable hydrogel for infant-friendly oral delivery of amoxicillin for the treatment of pneumococcal pneumonia. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9 (22), 18440–18449. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b01462
Yan, J., Zhai, W., Li, Z., Ding, L., You, J., Zeng, J., et al. (2022). ICH-LR2S2: a new risk score for predicting stroke-associated pneumonia from spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Transl. Med. 20 (1), 193. doi:10.1186/s12967-022-03389-5
Yang, Z., Huang, R., Zheng, B., Guo, W., Li, C., He, W., et al. (2021). Highly stretchable, adhesive, biocompatible, and antibacterial hydrogel dressings for wound healing. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 8 (8), 2003627. doi:10.1002/advs.202003627
Yuk, H., Lu, B., and Zhao, X. (2019). Hydrogel bioelectronics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 48 (6), 1642–1667. doi:10.1039/c8cs00595h
Yuki, Y., Uchida, Y., Sawada, S. i., Nakahashi-Ouchida, R., Sugiura, K., Mori, H., et al. (2021). Characterization and specification of a trivalent protein-based pneumococcal vaccine formulation using an adjuvant-free nanogel nasal delivery system. Mol. Pharm. 18 (4), 1582–1592. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c01003
Zhang, C. Y., Lin, W., Gao, J., Shi, X., Davaritouchaee, M., Nielsen, A. E., et al. (2019). pH-Responsive nanoparticles targeted to lungs for improved therapy of acute lung inflammation/injury. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 (18), 16380–16390. doi:10.1021/acsami.9b04051
Zhang, L., Cao, Z., Bai, T., Carr, L., Ella-Menye, J. R., Irvin, C., et al. (2013). Zwitterionic hydrogels implanted in mice resist the foreign-body reaction. Nat. Biotechnol. 31 (6), 553–556. doi:10.1038/nbt.2580
Zhang, Y., Kang, J., Chen, X., Zhang, W., Zhang, X., Yu, W., et al. (2023). Ag nanocomposite hydrogels with immune and regenerative microenvironment regulation promote scarless healing of infected wounds. J. Nanobiotechnology 21 (1), 435. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-02209-2
Zhang, Y., Zhao, Y., An, C., Guo, Y., Ma, Y., Shao, F., et al. (2025). Material-driven immunomodulation and ECM remodeling reverse pulmonary fibrosis by local delivery of stem cell-laden microcapsules. Biomaterials 313, 122757. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122757
Zhou, J., Liu, W., Zhao, X., Xian, Y., Wu, W., Zhang, X., et al. (2021). Natural melanin/alginate hydrogels achieve cardiac repair through ROS scavenging and macrophage polarization. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 8 (20), e2100505. doi:10.1002/advs.202100505
Zhou, J., Wu, P., Sun, H., Zhou, H., Zhang, Y., and Xiao, Z. (2020). Lung tissue extracellular matrix-derived hydrogels protect against radiation-induced lung injury by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell Physiol. 235 (3), 2377–2388. doi:10.1002/jcp.29143
Zhu, B., Xin, H., Yang, M., Pan, L., Zou, X., Lv, Z., et al. (2024a). Visualized and pH-responsive hydrogel antibacterial coating for ventilator-associated pneumonia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 178, 117224. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117224
Zhu, H., Zheng, J., Oh, X. Y., Chan, C. Y., Low, B. Q. L., Tor, J. Q., et al. (2023). Nanoarchitecture-integrated hydrogel systems toward therapeutic applications. ACS Nano 17 (9), 7953–7978. doi:10.1021/acsnano.2c12448
Zhu, X., Yang, Y., Mao, S., Liu, Q., Li, Y., Yang, Y., et al. (2024b). Lung dECM matrikine-based hydrogel reverses bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing M2 macrophage polarization. Biofabrication 17 (1), 015037. doi:10.1088/1758-5090/ada092
Glossary
MRSA Multiple-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
VAP Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia
ECM Extracellular Matrix
PEG Polyethylene Glycol
SARS-CoV-2 Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus two
HSV-1 Herpes Simplex Virus-1
GSH Glutathione
PDMS polydimethylsiloxane
MIC Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
MDR Multidrug-Resistant
C-ALG Catechol-conjugated Alginate
PAM/Alg Polyacrylamide-Alginate
tRNA Transfer RNA
PMA Polymethacrylic Acid
AmB Amphotericin B
AECII Alveolar Epithelial type II Cells
RBD Receptor-Binding Domain
PNP Polymer-Nanoparticle
MEM Meropenem
PBS Phosphate Buffer Saline
DCH Dynamic Covalent Hydrogel
EGF Epidermal Growth Factor
bFGF basic Fibroblast Growth Factor
DMA Dopamine Methacrylamides
PAER Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
CRKP Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae
AMP Antimicrobial Peptide
PMB Polymyxin B
ACEII Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme II
COX-1/2 Cyclooxygenase-1/2
ROS Reactive Oxygen Species
hFDM human lung Fibroblast-Derived Matrix
EMT Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
FD Functionalized Dextran
TGF-β1 Transforming Growth Factor-β1
PCL/Col Polycaprolactone-Collagen
HA Hyaluronic Acid
CCS Colloidal Crystal Scaffold
LRP5 Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein five
siRNA small interfering RNA
SP-B Surfactant Protein B
LPS Lipopolysaccharides
IL-10 Interleukin-10
MSC Mesenchymal Stem Cell
MMP Matrix Metalloproteinase
PspA Pneumococcal surface protein A
TLR9 Toll Like Receptors nine
DC Dendritic Cells
GM-CSF Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
rGO reduced Graphene Oxide
Keywords: pneumonia, hydrogels, drug delivery, biocompatibility, intelligent responsiveness
Citation: Wang J, Wang P, Liao K and He D (2025) Hydrogel applications: a promising frontier in pneumonia therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1602259. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1602259
Received: 29 March 2025; Accepted: 12 June 2025;
Published: 20 June 2025.
Edited by:
Xu Zhang, Peking University Hospital of Stomatology, ChinaReviewed by:
Wan Khartini Wan Abdul Khodir, International Islamic University Malaysia, MalaysiaYijiang Chen, Stanford University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wang, Liao and He. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Daikun He, ZGFpa3VuX2hlQDEyNi5jb20=
 Junming Wang
Junming Wang Pengfei Wang2,3,4
Pengfei Wang2,3,4 Daikun He
Daikun He