- 1Department of Pediatric Surgery, Hong Qi Hospital Affiliated to Mudanjiang Medical University, Mudanjiang, Heilongjiang, China
- 2Surgical Teaching and Research Section, The First Clinical Medical College of Mudanjiang Medical University, Mudanjiang, Heilongjiang, China
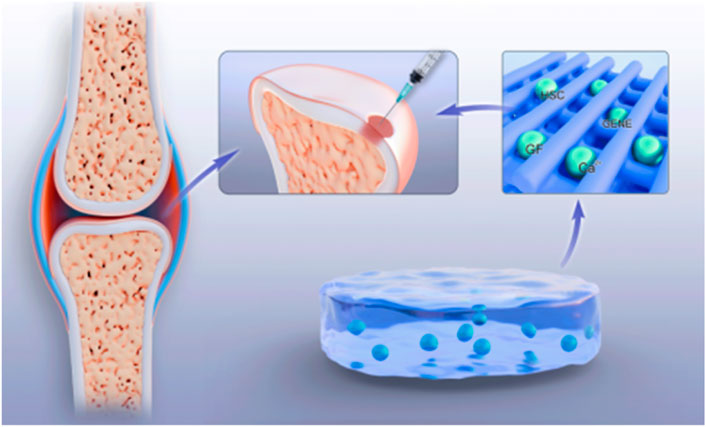
Articular cartilage injury is an important challenge in the field of orthopedics. Due to its unique characteristics of being vascularless, neuralless, and without lymphoid tissue, as well as the poor proliferation and migration ability of chondrocytes, the self-repair ability of cartilage after injury is limited. In recent years, with the development of tissue engineering, temperature-sensitive hydrogels, a new type of biomedical material, have unique temperature-responsive phase transition characteristics (such as a phase transition critical point close to the physiological temperature) that enable them to rapidly form a stable three-dimensional porous structure triggered by body temperature after being injected into the joint cavity. The material is injectable, will form a gel in situ, and can construct a dynamic bionic extracellular matrix (ECM) microenvironment. Compared with chemically cross-linked hydrogels, this material can achieve precise spatiotemporal control without introducing exogenous stimuli, significantly reducing the risk of cytotoxicity. Through adjustable mechanical properties, highly efficient loading, and release of bioactive factors, as well as viscoelastic characteristics similar to natural cartilage matrices, it has shown great potential in the repair of articular cartilage injuries. This article reviews the research progress of temperature-sensitive hydrogels in the repair of articular cartilage injuries from aspects such as biological characteristics, mechanism of action, clinical applications, and challenges faced, providing new ideas and possibilities for cartilage injury repair.
1 Introduction
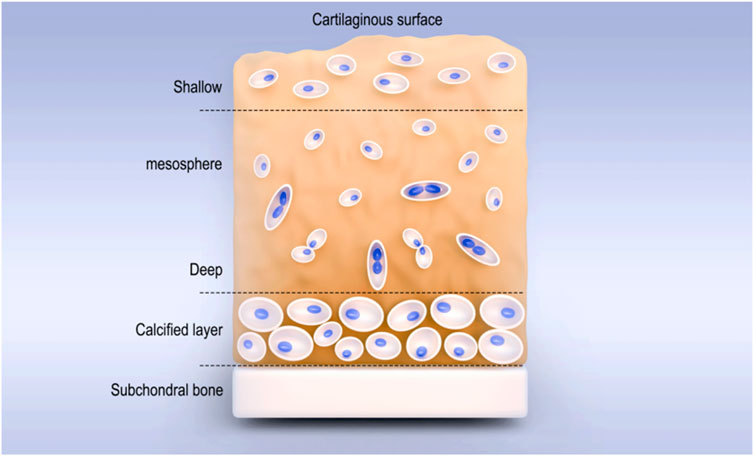
Articular cartilage is a smooth and elastic connective tissue located on the surface of the articular bone and consistent in shape with the articular surface of the bone. It includes the superficial (outer) layer, the middle layer (central area), the deep layer, and the calcified area (Figure 1). The thickness of different articular cartilages depends on the content, the structure of the extracellular matrix (ECM), and the state of chondrocytes (Rahvar et al., 2024). As hyaline cartilage, its ECM is composed of type II collagen (COLII) fibers (15%–25%), proteoglycans (5%–10%), and water (5%–10%) (Li H. S. et al., 2023; Wang Z. W. et al., 2024), and it has functions such as buffering pressure and vibration, reducing friction (Karan et al., 2022), secreting synovial fluid, lubricating, protecting subchondral bone, and load transmission (Liu et al., 2024). However, due to the lack of tissues such as blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves (Song et al., 2023; Xi et al., 2023), once the articular cartilage is damaged, its self-repair ability is extremely limited. When the full-thickness cartilage is defective and the range is greater than 4 mm3, it cannot repair spontaneously (Benmassaoud et al., 2020). Traditional surgical methods such as drilling, microfracture, and cartilage transplantation can promote cartilage repair to a certain extent. However, the repaired tissue is often fibrocartilage, which has lower mechanical properties than hyaline cartilage and is prone to the occurrence of osteoarthritis (Sang et al., 2022; Marcus et al., 2021). Therefore, it is particularly important to find more effective methods for cartilage injury repair.
Temperature-sensitive hydrogels, a kind of intelligent responsive biomaterial, have the core advantage that the phase transition temperature can be precisely controlled to around 37°C through molecular design, and they can undergo sol–gel phase transformation at physiological temperatures. This enables the gel to precisely fill the irregular defect area through minimally invasive injection in the liquid state, and immediately transform into a solid gel under the effect of body temperature, perfectly adhering to the injured area (Jin et al., 2024) and restoring the anatomical shape. The formed three-dimensional network structure not only simulates the porosity and compression modulus of natural cartilage ECM (Kalantarnia et al., 2025) but can also guide the polar arrangement of chondrocytes through topological structure, maintain the cell phenotype, and promote the expression of COLⅡ/aggrecan genes. Compared with photocurable or pH-sensitive hydrogels, the characteristics of no initiator residue and no local pH disturbance are more in line with the physiological environment requirements of the joint cavity.
In terms of controlled drug release, the 177Lu-nucleotide coordination polymer thermosensitive hydrogel reported by Liu P. et al. (2025) achieved dual sustained release of radionuclides and anti-inflammatory factors. Real-time PET-CT monitoring confirmed that its retention time in the joint cavity was prolonged to 21 days. Integrating growth factors such as TGF-β3/BMP-2, mechanical support, and temporal regulation of biological signals can be achieved simultaneously through the temperature-controlled sustained-release system (Zou et al., 2024). The introduction of 4D printing technology enables gradient thermosensitive hydrogel scaffolds to undergo pre-programmed morphological remodeling with temperature changes. For instance, the GelMA/F127DA dual-responsive hydrogel designed by Sun et al. (2025a) can dynamically release MMP inhibitors in response to the mechanical stress generated by joint movement while triggering gelation with body temperature. These innovative achievements have laid a new technical foundation for the precise application of temperature-sensitive hydrogels in cartilage repair and have shown broad application prospects in the repair of articular cartilage injuries.
2 Characteristics and response principles of temperature-sensitive hydrogels
A temperature-sensitive hydrogel is a kind of soft polymer material with a three-dimensional network structure, which can quickly sense and respond to temperature changes, and has hydrophilic swelling properties (Pearce et al., 2022), biomechanical properties (Sun et al., 2025b), and plastic deformability (Mohammad et al., 2020). It is an intelligent, responsive material that can change its physical state in response to variations in internal and external environmental temperatures. In the human body, phase changes can occur along with variations in body temperature, thereby achieving precise filling and fixation of the injured area. Temperature-sensitive hydrogels not only have temperature-sensitive properties but also have good biocompatibility, degradability, and injectability, providing the possibility for the repair of articular cartilage injuries.
2.1 Temperature sensitivity
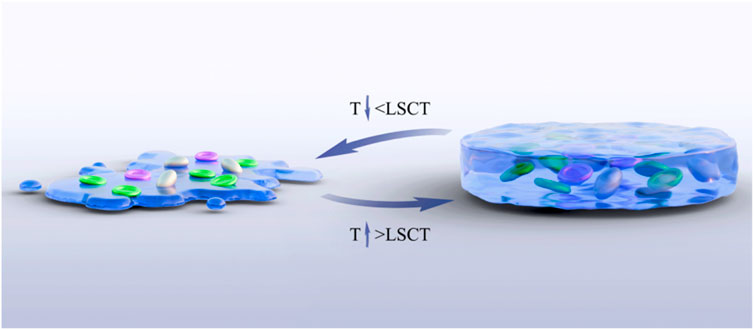
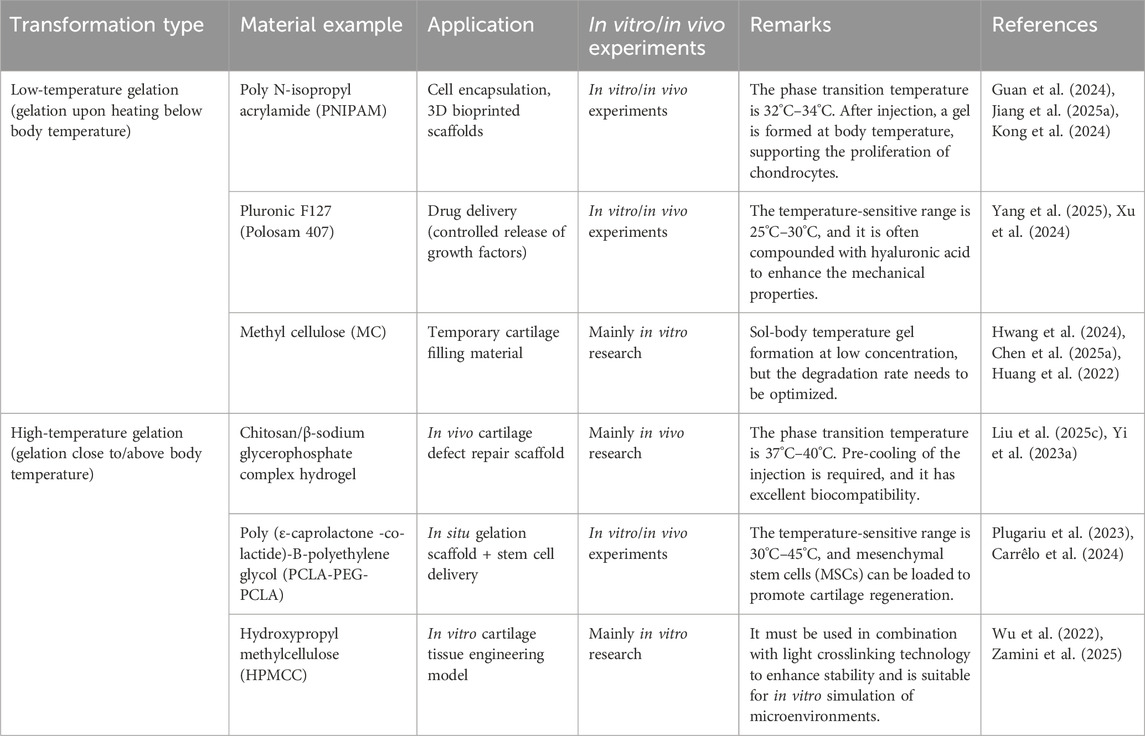
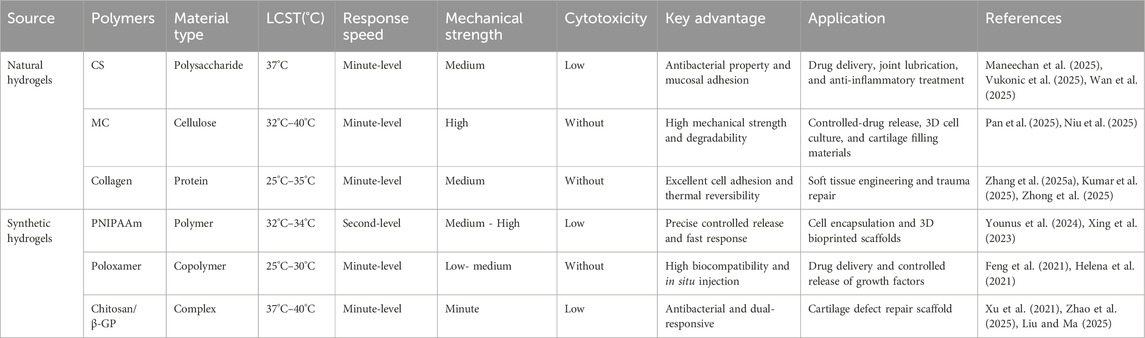
The temperature-sensitive performance of temperature-sensitive hydrogels is one of their most significant and critical characteristics. Copolymers can undergo phase transformation through appropriate temperature changes, and this appropriate temperature is the lower critical solution temperature (LCST) (Moon et al., 2024). This temperature is usually close to the human body temperature, that is, between 32.0°C and 37.0°C. Under LCST, a reversible sol–gel phase transformation occurs (Figure 2). When the temperature is lower than LCST, it presents a sol state, with good fluidity and injectability. When the temperature increases above the LCST, the hydrogel rapidly transforms into a gel state, forming a stable three-dimensional network structure. This phase change behavior is usually caused by the hydrophilic–hydrophobic equilibrium change of the hydrogel polymer chain (Sun T. C. et al., 2024). The porous structure enables the joint to have high water content and remain moist, reducing the friction between the joints and allowing the diffusion and absorption of various solutes and nutrients (Liu et al., 2021; Liu Y. et al., 2025). Liu D. et al. (2025) developed a multifunctional temperature-sensitive hydrogel based on chitosan (CS), using chitosan (CS)/β-glycerophosphate (β-GP) as the main body of the hydrogel. The gelation transformation was achieved at physiological temperature, and the physical properties changed accordingly, promoting the repair of bone and cartilage. Han et al. (2024) confirmed through rat experiments that heterogeneous DNA hydrogels loaded with tetrahedral skeletal nucleic acids modified by Apt02 could effectively promote the injury repair of bone and cartilage in the physiological temperature environment of the human body and achieved good results. Temperature-sensitive hydrogels are classified according to the transformation type, as detailed in Table 1, and according to the source of materials, as detailed in Table 2.
2.2 Biocompatibility
Biocompatibility refers to whether the interaction between the applied material and the organism will cause adverse immune responses or toxic reactions while being able to support the growth, proliferation, and functional expression of cells (Hennig et al., 2025). Good biocompatibility is a key prerequisite for the application of hydrogels in the biomedical field. Temperature-sensitive hydrogels can interact with cells and tissues in vivo and can be gradually degraded in vivo without causing obvious immune responses and cytotoxicity (Pandya et al., 2025), avoiding the potential risks brought by long-term implantation. Meanwhile, the three-dimensional network structure of hydrogels can provide a suitable microenvironment for chondrocytes or mesenchymal stem cells, etc., promoting cell adhesion, proliferation, differentiation, and metabolism. This can also enable the temperature-sensitive hydrogel to regulate the inflammatory response and reduce tissue damage during the process of cartilage injury repair. It has been proved through in vivo and in vitro experiments on rats that an injectable thermosensitive chitosan hydrogel has good biocompatibility and biodegradability (Alyeh et al., 2023; Westin et al., 2020), and such materials are often used in the regeneration and repair of bones, cartilage, hearts, wounds, and other diseases.
2.3 Controllability
Thermosensitive hydrogels not only have adjustable temperature but also play a role in precisely regulating aspects such as gelation time, mechanical properties, solubility and swelling, degradation rate, controlled drug release, and microenvironment (Hanafy and El-Ganainy, 2020). Their behavior can be regulated by changing the composition, structure, and preparation process of the material. For example, the performance of hydrogels can be optimized by adjusting the length of the polymer chains and the crosslinking density and introducing specific functional groups. Stable molecular chains and more crosslinking sites can increase the crosslinking degree of hydrogels, promote higher compressive strength, and regulate the mechanical properties and swelling properties of hydrogels (Huang C. J. et al., 2024). At the same time, the gel can carry targeted treatments such as drugs, ions, and stem cells to meet the repair needs of different articular cartilage injuries.
The regulation of mechanical properties of temperature-sensitive hydrogels is the key to their adaptation to cartilage repair, and the compressive modulus and dynamic viscoelasticity of natural articular cartilage are the core of its mechanical characteristics (Venkata and Ravi, 2023). Natural articular cartilage can withstand repeated cyclic stress during the gait cycle, while thermosensitive hydrogels repeatedly rub and squeeze in the joints, causing fatigue wear or modulus decrease, resulting in structural collapse (Sergi et al., 2024). Moreover, after long-term immersion in joint fluid, the lubricating performance is significantly reduced. In future research, the mechanical stability should be improved through topological structure optimization to enable the hydrogel to exert a lasting effect and be regulated in real time according to the damage condition and in vivo regulation.
3 The application of thermosensitive hydrogel in the repair of articular cartilage injury
3.1 Cell carrier
Thermosensitive hydrogels can be used as cell carriers to load and encapsulate seed cells such as chondrocytes or bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMMSCs) into a three-dimensional hydrogel network and deliver them to the site of articular cartilage injury by injection (Jiang J. et al., 2025; Xiao et al., 2025), making them more targeted, controllable, and intelligent. At the liquid precursor stage, where the temperature is lower than the LCST, the hydrogel presents a low-viscosity sol state. Its molecular chains are highly hydrated with water molecules through hydrogen bonds, giving Newtonian fluid-like properties. The surface tension of the sol state is low, and it has high compatibility with the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane. Cells can be dispersed into a single-cell suspension by vortex or micropipette (Suljovrujic et al., 2023). The material itself carries a negative charge. For example, the potential of chitosan is approximately −25 mV. Through electrostatic repulsion, it prevents cell aggregation and sedimentation. At the same time, the osmotic pressure matches the cytoplasm to avoid osmotic stress (Liu H. Y. et al., 2025). When the temperature rises above the LCST, the molecular conformation changes, and the hydrophobic groups of the polymer dehydrate to form physical crosslinking points, establishing a three-dimensional network (In and Crespy, 2025). During the gelation process, the hydrated layer gradually contracts to generate microchannels of approximately 1–5μm, guiding the cells to the center of the pores through fluid shear force (Li L. et al., 2025). The result is the formation of a gel that is close to the ECM of cartilage and has a viscoelastic modulus, which not only limits cell displacement (mobility <5 μm/h) but also allows nutrient diffusion (Ks et al., 2025; Deng et al., 2023). Hydrogels can provide a scaffold protection for cells, preventing them from being damaged during the injection process, and at the same time, offer a suitable microenvironment for cell growth and differentiation. At body temperature, hydrogels change from liquid to gel state, fixing cells at the damaged site and promoting cell proliferation and differentiation. The hydrogel can be implanted into the joint cavity by injection, rapidly forming a gel in the body to fill the cartilage defect area, avoiding complex surgical operations and the problem of implant fixation. Studies have shown that after the thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with chondrocytes is injected into the cartilage defect model, the cells can adhere and proliferate within the gel, secrete extracellular matrix, inhibit cartilage degradation and inflammatory responses, and promote the repair of cartilage tissue. In addition, MSCs have multi-directional differentiation potential and can secrete COLⅡ and various cytokines (Zhang B. K. et al., 2025), such as chemokines, growth factors, colony-stimulating factors, tumor necrosis factors, and interferons. Under the appropriate microenvironment, they can differentiate into chondrocytes and promote the expression of cartilage-specific genes. The combination of mesenchymal stem cells and temperature-sensitive hydrogels can achieve more effective repair of articular cartilage injuries.
3.2 Delivery system
The repair process of articular cartilage injury requires the participation of various growth factors and drugs to promote cell proliferation, differentiation, and the synthesis of extracellular matrix. Thermosensitive hydrogels, as delivery systems, can load growth factors, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc., inside the hydrogels (Inoue et al., 2025; Liao et al., 2024) (Figure 3). Anggelia et al. (2024) demonstrated that materials such as pomeroxam, collagen, and PLGA, as carriers, can effectively maintain the structural integrity of drugs, hormones, and growth factors as delivery systems in animal models. When the ambient temperature is low, the release of drugs is mainly driven by the concentration difference between the internal and external solutions of the hydrogel. As the temperature rises, the hydrogen bonds inside the hydrogel break and the network structure collapses, promoting the release of the carried factors, drugs, etc. (Duan et al., 2024). By controlling the release rate and amount, with the slow degradation of the hydrogel, drugs or bioactive substances such as growth factors and genes are gradually released (Yi H. Y. et al., 2023), continuously exerting their effects to achieve precise and continuous treatment of the injured areas of articular cartilage. This drug delivery method avoids the risks of infection and pain caused by multiple injections and greatly reduces the economic burden on patients.
Shi et al. (2021) inserted circRNA3503 loaded with a temperature-sensitive hydrogel, which could effectively promote the proliferation and migration of chondrocytes and simultaneously inhibit the inflammatory response, into the site of a cartilage injury. The research team of Alizadeh et al. (2025) loaded transforming growth factor -β3 (TGF-β3) or recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) into temperature-sensitive hydrogels, which could form local high-concentration areas at the injury site and be slowly released over several weeks, stimulating the proliferation, differentiation, and extracellular matrix synthesis of chondrocytes. Meanwhile, the sustained release of drugs can also reduce the dosage of drugs and systemic side effects, improve the safety and effectiveness of treatment, and significantly promote cartilage repair. Thermosensitive hydrogels are helpful in reducing the inflammatory response within joints (Han et al., 2025; Liu H. et al., 2025). Tian et al. (2024) confirmed through experiments on rats that thermosensitive hydrogels have antibacterial properties, achieving an antibacterial rate against Escherichia coli of 87.17% ± 2.48%, which was significantly higher than the 54.41% ± 4.29% rate of the control group. Thermosensitive hydrogels can also reduce the catabolism of chondrocytes under inflammatory conditions, inhibit inflammatory responses, and create a relatively stable internal environment for cartilage repair.
3.3 Cartilage tissue engineering scaffold
By adjusting the material composition and crosslinking degree, temperature-sensitive hydrogels serve as tissue engineering scaffolds (Ren et al., 2025) and simulate the extracellular matrix of natural cartilage as well as its mechanical properties and biological activities using a three-dimensional network structure to provide support for cell growth and tissue construction. After being combined with chondrocytes or bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, the material is implanted into the injured area of articular cartilage. Especially for irregular injuries, the effect of restoring the integrity and smoothness of the joint surface is better. The temperature-sensitive hydrogel scaffold provides a favorable growth environment for cells, promotes stem cell recruitment and cartilage differentiation, and maintains the original structure and function of cartilage tissue at the same time. The mechanical properties of the scaffold can also be further enhanced by adding bioactive molecules and nanomaterials, such as hydroxyapatite (Jahangir et al., 2023), to activate the biological activity and promote the differentiation and proliferation of chondrocytes (Zigan et al., 2024). With the development of 3D printing technology, personalized hydrogel scaffolds can be precisely prepared based on the shape and area of articular cartilage injuries, achieving more accurate repair and treatment.
At present, the most common temperature-sensitive hydrogels include blocks of PNIPAM (Qian et al., 2024) and polyethylene glycol (PEG), CS (Fan et al., 2025) hydrogels, sodium hyaluronate hydrogels, polyoxide–polyoxide–polyethylene oxide (PEO-PO-PEO) hydrogels, stereocomposite polylactic acid temperature-sensitive hydrogels, etc. Among them, the most common ones are PNIPAM and PEG blocks (Gao et al., 2021; Zhang X. Y. et al., 2025). PNIPAM is a heat-sensitive polymer material that has been used in some studies for the repair of articular cartilage. Its temperature-sensitive properties contribute to good operation and adaptation to the in vivo environment. Mixing chondrocytes or BMMSCs with PNIPAM solution and injecting them into the cartilage defect site can trigger gelation at body temperature (37.0°C), fix the cells, and form a porous three-dimensional scaffold, which helps reduce the load on the joint and minimize secondary injuries. PEG is temperature-sensitive and degradable. The degradation rate can be regulated by adjusting the molecular weight (Liu and Zhou, 2025). It can provide mechanical support in the early stage of injection and implantation injury site and is gradually replaced by extracellular matrix in the later stage, matching the degradation rate with the cartilage regeneration rate. Moreover, through the relaxation characteristics of hydrogel, it promotes the conduction of mechanical signals to seed cells and accelerates injury repair. CS hydrogel utilizes its natural antibacterial properties to prevent infection (Tu et al., 2024), and, at the same time, loads BMMSCs to promote cartilage regeneration.
Complex exosomes or miRNAs regulate the inflammatory microenvironment and promote cartilage differentiation through a sustained-release gel system. It is possible to form a pH/temperature dual-responsive gel by introducing temperature-sensitive components such as sodium β -glycerophosphate (β-GP) (Pham et al., 2025). Jiang et al. (2024) added magnesium particles (MPs) to glycerophosphate solution and mixed it with CS solution to prepare porous injectable thermosensitive hydrogels containing magnesium ions. The incorporation of MPs formed interconnected pores in the hydrogel, demonstrating high cytocompatibility and maintaining cell viability, proliferation, diffusion, and osteogenesis in vitro. The pore size can allow the migration, proliferation, and differentiation of cells in the hydrogel scaffold. However, an increase in porosity will reduce the mechanical properties of the scaffold, while insufficient porosity will lead to poor regeneration (Mo et al., 2021). Sodium hyaluronate hydrogel is the sodium salt form of hyaluronic acid. As a natural component of human joint fluid and cartilage, it has excellent biocompatibility and degradability, reducing the risk of immune rejection (Hanyu et al., 2024). A three-dimensional network structure is formed through physical crosslinking, with a high water content of approximately 74 wt%, simulating cartilage ECM and providing a suitable microenvironment for cells (Zhou et al., 2025). The gel interface can enhance the combination with the surrounding cartilage tissue through physical crosslinking, reducing the risk of detachment (Xiang et al., 2024; Li G. F. et al., 2024). Hydrogels can enhance the viscoelasticity of joint fluid, improve joint range of motion, relieve pain, and promote cartilage repair through multi-dimensional mechanisms (Steale et al., 2025). PEO-PPO-PEO hydrogel is a temperature-sensitive triblock copolymer that can form a physically cross-linked gel at body temperature, providing a three-dimensional porous structure similar to that of natural cartilage ECM and promoting the adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation of chondrocytes. The inflammatory microenvironment of the joint cavity can be alleviated by loading anti-inflammatory drugs or directly regulating the polarization of macrophages through the surface properties of the materials. Inhibit the excessive proliferation of fibroblasts, reduce the formation of scar tissue (Zhang F. et al., 2025), promote the regeneration of hyaline cartilage rather than fibrocartilage, and avoid the recurrence of fibrocartilage fragmentation during joint movement. By adjusting the molecular weight and proportion of the copolymer, such as the PEO/PPO ratio, the mechanical strength can be regulated to simulate the elasticity and compressive resistance of cartilage and provide temporary mechanical support for the damaged area (Rick, 2021). The steric composite polylactic acid (sc-PLA) thermosensitive hydrogel is formed by the intermolecular hydrogen bonds of L-polylactic acid (PLLA) and d-polylactic acid (PDLA) to create a steric composite structure. It has a higher melting point (220°C), mechanical strength (modulus up to 10 GPa), and hydrolysis resistance (Park et al., 2025). The degradation rate can be regulated by the three-dimensional composite ratio to avoid the problem of too fast or too slow degradation of a single PLA and better match the cartilage regeneration cycle. It also promotes cartilage regeneration through the synergy of multiple mechanisms such as mechanical support, cell delivery, and factor sustained release.
3.4 Unique effects at the cellular and tissue levels
3.4.1 Cellular level
Thermosensitive hydrogels, such as PNIPAM, are liquid at low temperatures and can be uniformly mixed with cells. When the temperature rises to the physiological temperature, a gel network is rapidly formed, enveloping the cells in a three-dimensional structure. The cell survival rate is high (Thanh et al., 2024). The enveloping process does not require ultraviolet light or chemical crosslinking, reducing cell stress and toxic damage to the cells, achieving mild cell enveloping and protection (Constantin et al., 2025). By adjusting the hydrophilicity, hydrophobicity, and porosity of temperature-sensitive hydrogels, the exposure of cell adhesion proteins (such as fibronectin and laminin) can be controlled, affecting cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation. By altering the temperature to induce changes in gel strength (Li Y. F. et al., 2024), the mechanical microenvironment of stem cells can be regulated, guiding their differentiation toward specific lineages, such as osteogenic and cartilaginous differentiation, and dynamically regulating cell behavior. Thermosensitive hydrogels can be used as sustained-release carriers to encapsulate growth factors (such as VEGF or TGFβ) or small-molecule drugs (Liu Q. Y. et al., 2025). By triggering the swelling/contraction of the gel through temperature changes, the drug is released on demand, and the cellular signaling pathways are precisely regulated. At the same time, the material can provide a bionic three-dimensional microenvironment, support intercellular interactions and organoid formation, and realistically simulate the physiological conditions in vivo.
3.4.2 Organizational level
Thermosensitive hydrogels can be directly injected into the body by injecting liquid precursors at the site of cartilage defects. They can form gels in situ at body temperature and fill irregular tissue defects without surgical intervention. The mechanical properties, such as the elastic modulus and pore structure of hydrogels, can simulate natural ECM, promoting cell infiltration and tissue regeneration. When there is often an increase in local temperature at the site of inflammation or lesion, thermosensitive hydrogels can release anti-inflammatory drugs or recruit repair cells, such as MSCs, through temperature response to achieve intelligent responsive treatment (Bucatariu et al., 2024). Moreover, by regulating the degradation rate, angiogenic factors can be gradually released to promote the growth of new blood vessels in the soft tissues within the joint (Yang et al., 2024), increase local blood circulation, and facilitate the rapid repair of combined injuries. Temperature-sensitive hydrogels exhibit unique regulatory effects at the cellular and tissue levels through the construction of dynamic bionic microenvironments that are distinct from traditional scaffolds.
3.5 Combined application
Temperature-sensitive hydrogels can also be combined with other biomaterials or therapeutic methods (Gao et al., 2025). For example, in some special injuries or severe traumas that cause irregular or large-area defects of articular cartilage, traditional drilling surgery, microfracture surgery, and cartilage transplantation surgery combined with temperature-sensitive hydrogels can be used for treatment to make up for each other’s deficiencies and maximize the therapeutic effect. It is also possible to combine and adapt various repair materials that promote the proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes (Qian et al., 2025) or carry multiple therapeutic drugs and factors in the same hydrogel. Sobrino et al. (2024a) successfully transplanted and re-cultured osteoblast membranes rich in type I collagen using nanoparticle technology loaded with icariin, maintaining the optimal ECM composition and promoting the repair of cartilage damage. The material can also be combined with nanomaterials, conductive polymers, or bioactive glass composites (SiCong et al., 2024) to enhance mechanical properties, electrical activity, or osteogenic ability and jointly exert therapeutic effects. The hydrogel can be made to fit the missing area perfectly, like natural cartilage, and maximize the repair effect.
At present, bilayer hydrogels with bionic mechanical gradients are being developed (Zhang T. et al., 2025), such as the combination of a surface highly cross-linked PLGA layer and a bottom temperature-sensitive gelatin layer, which greatly enhances the interfacial shear strength. The RGD peptide and TGF-β1 microarray were fixed in the interface area by photografting technology, which significantly increased the migration rate of chondrocytes (K et al., 2020). Polypyrrole nanowires can also be doped to generate a local electric field through the piezoelectric effect (Li M. et al., 2024), promoting the vertical directional growth of COLII fibers, achieving precise integration of biological activity and electrical activity, and facilitating rapid repair of damaged areas (Du et al., 2024). Kang et al. (2023) used an oxygenated thermosensitive hydrogel containing 1-bromosefluorooctane in the repair of femoral condylar bone defects in a rabbit experiment. It effectively promoted the formation of new bone, increased tissue vascular differentiation at the same time, and was more conducive to the repair of surface cartilage injury Table 3.
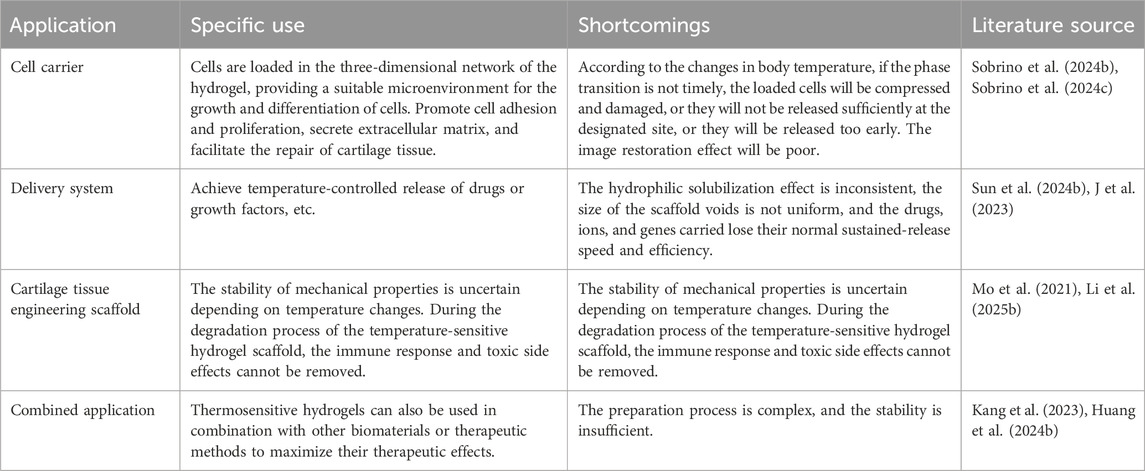
Table 3. Summary of applications of temperature-sensitive hydrogel in repairing articular cartilage injury.
4 The shortcomings of temperature-sensitive hydrogels
In practical applications, temperature-sensitive hydrogels have many deficiencies that need to be further optimized. In terms of temperature control, it is difficult to precisely control the phase transition temperature of temperature-sensitive hydrogels based on LCST, especially in deep tissues, in high-cold regions, or under pathological conditions such as inflammation and trauma. The body temperature changes due to the different degrees of blood flow richness in local areas, causing the gel cure to be delayed or premature, resulting in a mismatch of gel morphology in the defect area (Colombo et al., 2025). The thermal conductivities of different tissues (such as subchondral bone, synovium, and fat pads) vary. After injection, the hydrogel may form “cold zones” or “hot zones” due to the differences in thermal conduction of the surrounding tissues, resulting in uneven porosity or crosslinking density within the gel (Wang et al., 2025; Li D. P. et al., 2025). Deep tissues (such as acetabular cartilage defects) have a lower temperature than superficial tissues (such as knee cartilage), and gradient LCST materials must be designed to meet the requirements of different depths (Stanzione et al., 2024).
In terms of drug sustained release, the hydrophilic swelling performance of hydrogels varies, and the internal circulation and water content within the joints of different populations also differ, resulting in uneven swelling effects. This leads to different pore sizes of hydrogel scaffolds, causing the drugs, ions, and genes they carry to lose their normal sustained-release speed and efficiency (Guo et al., 2023). The PNIPAM thermosensitive hydrogel still has disadvantages such as a low swelling ratio, a small re-swelling rate, and poor mechanical strength (Jiang et al., 2025c). In terms of degradation, the mismatch between the degradation rate of the hydrogel and the tissue regeneration rate during the degradation process, as well as the degradation products generated, increase the immune response during the absorption process (Li M. Y. et al., 2023).
Although chitosan (CS), a natural polysaccharide, has good biocompatibility, when its concentration is too high, its degradation product glucosamine can be metabolized into urea and carbon dioxide in the body, which may cause an increase in the secretion of TNF-α by macrophages and lead to a local mild inflammatory response (Pitrolino et al., 2024; Chen et al., 2025b). When the concentration of the residual unreacted monomer (N-isopropyl acrylamide) in the PNIPAM system is too high, it can significantly inhibit the gene expression of chondrocytes, and the low-molecular-weight oligomer produced by its degradation has a half-life of up to 28 days in synovial fluid, which can affect cell adhesion (Rauer et al., 2024; Komarova et al., 2025). The mechanical strength of thermosensitive hydrogels still lags behind that of natural cartilage. The persistent friction and compression caused by daily activities such as walking, running, and jumping are difficult to withstand, and joints are under complex stress, resulting in fatigued fragmentation of hydrogels or immune responses, etc. (Liu et al., 2020a; Liu et al., 2020b). Existing studies have fully verified the advantages of temperature-sensitive hydrogels in terms of injectability, minimal invasiveness, and the construction of dynamic microenvironments (Khan et al., 2024). However, although rapid gelation is beneficial for morphological fixation, the high shear force environment leads to a decrease in the survival rate of MSCs. Enhancing mechanical properties is often accompanied by an prolonged degradation cycle, which is inconsistent with the matching time of the cartilage regeneration cycle (Hu et al., 2025; Wang J. S. et al., 2024). The increase in the encapsulation rate of growth factors instead leads to a decrease in biological activity, reducing the accuracy of controlled drug release and bioavailability.
In response to these issues, in future research, we still need to verify and improve the deficiencies of temperature-sensitive hydrogels through more animal experiments and clinical trials so as to enhance their mechanical properties, histocompatibility, and biodegradability; maintain the stability of temperature-sensitive hydrogels under the physiological and pathological conditions of the organism; and fully exert their good biological efficacy. Genetic engineering technology can be combined to develop intelligent hydrogels with intrinsic biological activities that enable them to play a greater role in the repair of articular cartilage.
5 Summary and prospect
Temperature-sensitive hydrogels, which are intelligent biomaterials, have shown great potential in the repair of articular cartilage injuries. They share commonalities with other hydrogels and have their own characteristics. Their unique temperature response characteristics, good biocompatibility, and controllable degradation performance can be used for filling, protecting, and lubricating scaffolds and material exchange at cartilage injury sites. The sol–gel transformation occurs at body temperature, forming a gel scaffold with a three-dimensional network structure, providing a favorable growth microenvironment for chondrocytes and promoting cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and matrix secretion. They can simultaneously carry cells, drugs, genes, growth factors, etc. Changing the pore size and gel phase of the hydrogel scaffold adjusts the release rate of these carried materials, achieving good in situ retention and efficient delivery, and improving cell survival rate, drug delivery efficiency, and repair effect.
Based on its injectable and in situ gelation characteristics, through minimally invasive injection assisted by arthroscopy, precise filling of cartilage defects in complex anatomical sites, such as the posterior condyle of the knee joint, the acetabular fossa, and the ankle joint, can be achieved in the future. Combined with medical image navigation techniques such as intraoperative ultrasound or fluorescence labeling, the distribution and gelation state of hydrogels at the defect site can be monitored in real time to ensure the anatomical matching degree between the three-dimensional morphology and natural cartilage. Patient-specific temperature-sensitive hydrogel stents have been prepared by 3D printing technology. The three-dimensional model of the defect was reconstructed using preoperative CT/MRI data, and personalized stents with bionic gradient pores and mechanical gradients were designed.
In time, a treatment team will construct a multimodal combined treatment plan, establish a “hydrogel + clinical” plan, combine shock wave therapy, and enhance the penetration depth of growth factors in the hydrogel through a cavitation effect. Combined with methods such as gene editing, the gene expression is continuously upregulated in the defect area to promote the synthesis of COLII. Through interdisciplinary collaboration and technological innovation, temperature-sensitive hydrogels are expected to become standardized treatment plans for cartilage repair, promoting the transformation of regenerative medicine from the model of “structural substitution” to that of “functional reconstruction.”
With the continuous cross-integration of multiple disciplines such as materials science and biomedical engineering, temperature-sensitive types have broad application prospects in cartilage regeneration. Future research should focus on the following aspects: First, develop new temperature-sensitive materials with a wider temperature response range, faster response speed, and better biocompatibility, and conduct in-depth studies on the relationship between the microstructure and performance of hydrogels to better understand their temperature response mechanism and optimize their performance. Research simpler and more efficient hydrogel preparation methods and more precise characterization techniques to meet the needs of damage repair in different parts of the body. Second, conduct in-depth research on the interaction mechanism between hydrogels and mesenchymal stem cells and tissues, optimizing the loading mode of cells and drugs, and improving the repair effect. Third, strengthen basic research and clinical trials to promote the early clinical transformation and wide application of temperature-sensitive hydrogels. At the same time, enhance research on special injury types such as epiphyseal injuries in children and injuries at the cartilage-bone junction. Fourth, multiple stimulus response factors such as temperature, pH value, light, and enzymes can be combined to develop dual-sensitive or multi-sensitive response materials with multiple functionalization. The fifth research focus is to develop mature temperature-sensitive hydrogel products with independent packaging that can be directly applied in clinical practice. With the continuous development of 4D printing technology and artificial intelligence (AI) technology, AI technology may be applied to precisely regulate the composition and parameter adjustment of temperature-sensitive hydrogels, establish a multi-scale evaluation system, and integrate molecular dynamics simulation, organ-chips, and AI-assisted clinical decision-making systems. Develop new types of hydrogels with body temperature feedback functions, such as integrating temperature sensors, to achieve real-time temperature regulation. These would enable real-time monitoring and dynamic adjustment during the process of cartilage injury repair, reducing treatment costs, shortening treatment time, and efficiently utilizing thermosensitive hydrogels. Through continuous improvement and optimization, the hydrogel can play a greater role in the repair of cartilage damage and approach the performance of natural cartilage to the greatest extent. These characteristics make hydrogels an ideal repair material for cartilage injury repair that could be widely applied.
Author contributions
LY: writing – original draft. KS: writing – original draft and resources. RH: writing – original draft and resources. QX: supervision and writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alizadeh, S., Ezzatpour, S., Zarkesh, I., Vazquez, H., Lopez, G., Mirsalehi, M., et al. (2025). Fabrication of injectable dexamethasone-loaded hydrogel microparticle via microfluidic technique for biomedical applications. J. Eur. Polym. J. 225, 113740–113753. doi:10.1016/J.EURPOLYMJ.2025.113740
Alyeh, A., Atefeh, M., Sadat, M. R., Mojgan, S., Koorosh, A., Zahra, R., et al. (2023). The recent advancement in the chitosan-based thermosensitive hydrogel for tissue regeneration. J. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 86, 1–14. doi:10.1016/J.JDDST.2023.104627
Anggelia, R. M., Cheng, Y. H., and Lin, H. C. (2024). Thermosensitive hydrogels as targeted and controlled drug delivery systems: potential applications in transplantation. J. Macromol. Biosci. 24 (10), e2400064. doi:10.1002/MABI.202400064
Benmassaoud, M. M., Gultian, K. A., Di, C. M., and Vega, S.L. (2020). Hydrogel screening approaches for bone and cartilage tissue regeneration. J. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1460 (1), 25–42. doi:10.1111/nyas.14247
Bucatariu, S., Cosman, B., Constantin, M., Ailiesei, G. L., Rusu, D., and Fundueanu, G. (2024). Thermally solvent-free cross-linked pH/Thermosensitive hydrogels as smart drug delivery systems. J. Gels 10 (12), 834–852. doi:10.3390/GELS10120834
Carrêlo, H., Rosado, J. M., Vieira, T., Da Rosa, R. R., Perez-Puyana, V. M., Silva, J. C., et al. (2024). A thermoresponsive injectable drug delivery system of chitosan/β-glycerophosphate with gellan gum/alginate microparticles. J. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 271 (P1), 131981–131992. doi:10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2024.131981
Chen, S., Hou, Z., Xiao, M., Wu, P., Yang, Y., Han, S., et al. (2025b). Quaternized chitosan-based photothermal antibacterial hydrogel with pro-vascularization and on-demand degradation properties for enhanced infected wound healing. J. Carbohydr. Polym. 355, 123350–123367. doi:10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2025.123350
Chen, S., Hu, C., Lu, W., and Zhang, J. (2025a). A lubcan cross-linked polyethylene glycol dimethyl ether hydrogel for hyaluronic acid replacement as soft tissue engineering fillers. J. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 298, 140061–140074. doi:10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2025.140061
Colombo, G., Lehéricey, P., Müller, J. F., Majji, M. V., Vutukuri, H. R., Swan, J. W., et al. (2025). Kinetic pathways to gelation and effects of flow-induced structuring in depletion gels. J. Industrial and Eng. Chem. Res. 64 (8), 4581–4595. doi:10.1021/ACS.IECR.4C03873
Constantin, M., Bucatariu, S., and Fundueanu, G. (2025). A potential self-regulated drug delivery system actuated by a simple and double command. J. Sensors and actuators: b. Chemical 432, 137493–137504. doi:10.1016/J.SNB.2025.137493
Deng, M., Xia, G. H., Liu, F., Li, J. L., and Wang, B. (2023). In vitro bioactivity of growth factor-loaded hydrogels. J. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. 49 (05), 581–588. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-3851(n).2023.05.006
Du, C., Zhang, S. B., and Zhang, M. (2024). An injectable piezoelectric PLLA/mXene nanofiber hydrogel composite for osteogenesis promotion. J. J. Med. Biomechanics. 39 (S1), 538.
Duan, X. H., Ma, H., Shang, H. Z., Liu, H. D., Wei, D. X., and Qiao, N. (2024). Advances in the application of smart hydrogels in biomedicine. J. Chin. J. Hosp. Pharm. 44 (16), 1950–1955+1959. doi:10.13286/j.1001-5213.2024.16.17
Fan, Y., Yan, J., Zhao, X., Wang, W., Gao, C., Lin, X., et al. (2025). In situ polysaccharide-based double-network hydrogels as a sustained kartogenin delivery system for cartilage tissue engineering. J. React. Funct. Polym. 214, 106335–106350. doi:10.1016/J.REACTFUNCTPOLYM.2025.106335
Feng, T. Q., Wang, C. L., and Wang, S. Y. (2021). Preparation of chitosan/poloxam composite thermosensitive hydrogel. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 43 (06), 679–684.
Gao, J., Li, M., Chen, H., Xu, Z., and Kong, Y. (2025). Synthesis of stimuli-responsive copolymeric hydrogels for temperature, reduction and pH-controlled drug delivery. J. J. Industrial Eng. Chem. 143, 252–261. doi:10.1016/J.JIEC.2024.08.027
Gao, J. P., Li, M., and Tang, P. F. (2021). Stimuli-responsive hydrogels for bone repair: a review. J. Acad. J. Chin. PLA Med. Sch. 42 (08), 873–877.
Guan, Z., Katla, K. S., Dahanayake, V., and Bae, J. (2024). 3D printable Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel suspensions with temperature-dependent rheological responses. J. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 6 (23), 14095–14105. doi:10.1021/ACSAPM.3C03230
Guo, Z., Zhao, Z. D., Gao, H. Y., and Li, Z. L. (2023). Effects of intra-articular injection of thermosensitive hydroxybutyl chitosan hydrogel loaded with Dickkopf-3 on osteoarthritis in rats. J. Acad. J. Chin. PLA Med. Sch. 44 (07), 787–793. doi:10.12435/j.issn.2095-5227.2023.023
Han, J., Liu, H., Cheng, J., Wang, X., Xu, C., Zhang, F., et al. (2025). A chondroitin sulfate-based temperature-responsive hydrogel with antimicrobial properties for epidermal wound repair in diabetic patients. J. Eur. Polym. J. 222, 113588–113597. doi:10.1016/J.EURPOLYMJ.2024.113588
Han, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, F., Li, G., Wang, J., Wu, X., et al. (2024). Heterogeneous DNA hydrogel loaded with Apt02 modified tetrahedral framework nucleic acid accelerated critical-size bone defect repair. J. Bioact. Mater. 35, 1–16. doi:10.1016/J.BIOACTMAT.2024.01.009
Hanafy, S. A., and El-Ganainy, O. S. (2020). Thermoresponsive hyalomer intra-articular hydrogels improve monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats. J. Int. J. Pharm. 573, 118859–118869. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118859
Hanyu, R., Andi, G., and Chunhui, L. (2024). Sandwich hydrogel to realize cartilage-mimetic structures and performances from polyvinyl alcohol, chitosan and sodium hyaluronate. J. Carbohydr. Polym. 328, 121738–121749. doi:10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2023.121738
Helena, M. N. D. M., Nogueira, F. A., Carajiliascov, D. F., Windisch-Neto, H., Querobino, S. M., Nascimento-Sales, M., et al. (2021). Sulforaphane-loaded hyaluronic acid-poloxamer hybrid hydrogel enhances cartilage protection in osteoarthritis models. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 128 (prepublish), 112345–112360. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2021.112345
Hennig, K., Vacun, G., Thude, S., and Meyer, W. (2025). Photocurable crosslinker from bio-based non-isocyanate poly(hydroxyurethane) for biocompatible hydrogels. J. Polym. 17 (9), 1285–1297. doi:10.3390/POLYM17091285
Hu, W. T., Zhou, H. D., Fan, S. Y., and Shan, J. C. (2025). Research advances in novel biomaterials for articular cartilage repair: a multidimensional analysis from material design to clinical applications. J/OL. J. Air Force Med. Univ. 1-17. Available online at: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1526.R.20250318.0946.002.html.
Huang, C. J., Lei, H., and Tang, X. J. (2024a). EDC/NHS-crosslinked recombinant collagen hydrogel for repairing articular cartilage defects. J. Mater. China 43 (04), 344–354.
Huang, K., Du, J., Xu, J., Wu, C., Chen, C., Chen, S., et al. (2022). Tendon-bone junction healing by injectable bioactive thermo-sensitive hydrogel based on inspiration of tendon-derived stem cells. J. Mater. Today Chem. 23, 100720–100733. doi:10.1016/J.MTCHEM.2021.100720
Huang, Y. N., Wang, Y., Wang, X. B., Li, Z., Hao, T. N., and Zhou, X. (2024b). Applications of intelligent delivery systems in gene drug therapy. J. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 41 (04), 482–492. doi:10.14066/j.cnki.cn21-1349/r.2023.0395
Hwang, M. S., Kim, E., Wu, J., Lee, H., and Park, W. H. (2024). Temperature- and pH-induced dual-crosslinked methylcellulose/chitosan-gallol conjugate composite hydrogels with improved mechanical, tissue adhesive, and hemostatic properties. J. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 277 (P1), 134098–134115. doi:10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2024.134098
In, B. S., and Crespy, D. (2025). Multiple-temperature-responsive double- and triple-network hydrogels. J. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 46 (9), 2570030–2570037. doi:10.1002/MARC.202570030
Inoue, S., Yoshimura, M., Haraguchi, R., Oishi, Y., and Narita, T. (2025). Temperature-responsive self-adhesive particles for targeted agent delivery in dynamic fluid environments. J. Mater. Today Chem. 44, 102589–102600. doi:10.1016/J.MTCHEM.2025.102589
Jahangir, S., Vecstaudza, J., Augurio, A., Canciani, E., Stipniece, L., Locs, J., et al. (2023). Cell-laden 3D printed GelMA/HAp and THA hydrogel bioinks:development of osteochondral tissue-like bioinks. J. Mater. 16 (22), 7214–7218. doi:10.3390/MA16227214
Jiang, J., Tian, Y., Wu, X., Zeng, M., Wu, C., Wei, D., et al. (2025b). Temperature and light dual-responsive hydrogels for anti-inflammation and wound repair monitoring. J. J. Mater. chemistry.B. 13, 2855–2870. doi:10.1039/D4TB02555E
Jiang, Y., Wei, F. J., and Wu, Y. Y. (2025a). Research progress in thermosensitive poly(n-isopropylacrylamide)-based hydrogels. J. Packag. Eng. 46 (07), 24–33. doi:10.19554/j.cnki.1001-3563.2025.07.004
Jiang, Y., Wu, Y. Y., Wei, F. J., and Liu, H. (2025c). Preparation and properties of novel highly absorbent PGA/PEG-crosslinked PNIPAM hydrogels. J/OL. New Chem. Mater. 1-7. doi:10.19817/j.cnki.issn1006-3536.2025.04.049
Jiang, Z., Qin, S., Wang, W., Du, T., Zang, Y., He, Y., et al. (2024). Investigating the anti-inflammatory and bone repair-promoting effects of an injectable porous hydrogel containing magnesium ions in a rat periodontitis mode. J. Smart Mater. Med. 5 (2), 207–220. doi:10.1016/J.SMAIM.2023.12.002
Jiao, H., Wu, C. W., Chi, H. T., and Zhang, W. (2023). Research progress in hydrogels for osteoarthritis treatment. J. Sci. and Technol. Rev. 41 (18), 72–83. doi:10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2023.18.010
Jin, S., Cao, J., Li, K., Xiao, H., and Wu, P. (2024). Injectable polyvinylpyrrolidone/tannic acid multifunctional hydrogel coating with excellent self-healing and adhesive properties for application in tissue engineering. J. Prog. Org. Coatings 189, 108334–108347. doi:10.1016/J.PORGCOAT.2024.108334
Kalantarnia, F., Maleki, S., Shamloo, A., Akbarnataj, K., and Tavoosi, S. N. (2025). A thermo-responsive chitosan-based injectable hydrogel for delivery of curcumin-loaded polycaprolactone microspheres to articular cartilage: in-vitro and in-vivo assessments. J. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 9, 100678–100691. doi:10.1016/J.CARPTA.2025.100678
Kang, Q. J., Liu, G. H., Liu, C. G., Ren, W., and Wang, Y. (2023). Temperature-sensitive,1-bromoheptafluorooctane-containing hydrogels in repairing bone defect in rabbits. J. Arabian J. Chem. 16 (11), 105202–105208. doi:10.1016/J.ARABJC.2023.105202
Karan, V., Scott, M., and J, L. B. (2022). Polyacrylamide hydrogel lubricates cartilage after biochemical degradation and mechanical injury. J. J. Orthop. research:official Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 41 (1), 63–71. doi:10.1002/JOR.25340
Khan, D. U. M., Afzaal, A., Shahnaz, S., Gilani, M. A., Perveen, S., Sharif, F., et al. (2024). Synergistic utilization of cost-effective glycerophosphate and biologically active zein for innovative minimally invasive smart thermo-responsive hydrogels for potential hard tissue engineering applications. J. Smart Mater. Struct. 33 (8), 085007–085022. doi:10.1088/1361-665X/AD57A4
K, L., Viji, S. C. K. B., Balagangadharan, K., and Selvamurugan, N. (2020). Temperature- and pH-responsive chitosan-based injectable hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 111 (prepublish), 110862–110874. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2020.110862
Komarova, A. G., Kozhunova, Y. E., Gumerov, A. R., Potemkin, I. I., and Nasimova, I. R. (2025). Effect of polymer network architecture on adsorption kinetics at liquid–liquid interfaces: a comparison between Poly(NIPAM-co-AA) copolymer microgels and interpenetrating network microgels. J. Gels. 11 (1), 58–72. doi:10.3390/GELS11010058
Kong, X., Tian, L., Li, W., and Han, T. (2024). Preparation and properties of biomimetic bone repair hydrogel with sandwich structure. J. J. biomaterials Appl. 39 (5), 455–465. doi:10.1177/08853282241268676
Ks, S., Rout, S., and Jacob, R. A. (2025). Revisiting crosslinking density effects on pNIPAM microgel properties: size, electrophoretic mobility, and transition temperatures. J. J. Chem. Phys. 162 (18), 184903–184920. doi:10.1063/5.0269885
Kumar, G. A., Nair, A., Sreejith, S., Adithya, D., Jose, J., Vinod Thazhenandayipurath, V., et al. (2025). Biocompatible PVA–Chitosan hydrogel enriched with collagen hydrolysate and Couroupita guianensis flower extract for enhanced wound-healing and antibacterial activity. Polym. Bull. (prepublish), 1–23. doi:10.1007/s00289-025-05806-3
Li, A. K., Zhou, Z. M., Wu, L. B., Yue, Y., H., Weng, J., Yu, F., et al. (2025b). Research progress on hydrogel scaffolds for cartilage repair. Chin. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 18 (02), 177–183. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-9958.2025.02.13
Li, D. P., Li, Y., Zhou, X. L., Makesh, M., Lei, T. D., Chen, K., et al. (2025c). Hydrogel fibers: morphological evolution, mechanical properties and moisture absorption behavior. J/OL. Sci. China Mater. 1-20. Available online at: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/10.1236.tb.20250507.1329.016.html.
Li, G. F., Liang, J. L., Guo, S. R., Jing, Z. X., Li, Y., et al. (2024a). Construction of double-network hydrogels and their applications in biomedicine. J. Eng. Plast. Appl. 52 (12), 165–170.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2024.12.023
Li, H. S., Yan, X., Yu, H., Cui, J., Jing, Z., Li, D., et al. (2023a). Collagen-based hydrogels for cartilage regeneration. J. Orthop. Surg. 15 (12), 3026–3045. doi:10.1111/OS.13884
Li, L., Luo, W. H., and Cui, H. J. (2025a). Research progress on silk fibroin hydrogels in tissue regeneration and repair. J. Newsl. Sericultural Sci. 45 (01), 13–23. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-0561.2025.01.006
Li, M., Liu, X. F., Li, L. Y., Zhang, W., Hu, X. T., and Ma, C. F (2024c). Research progress on piezoelectric hydrogel materials for bone tissue engineering applications. J. Chin. J. Pract. Stomatology. 7 (06), 709–715. doi:10.19538/j.kq.2024.06.012
Li, M. Y., Zheng, G. S., Yang, J. H., Chen, X. F., Xu, J. F., and Zhao, D. W. (2023b). Construction strategies and application advances in bone/cartilage immunomodulatory hydrogels. Chin. J. Reparative Reconstr. Surg. 37 (11), 1423–1430. doi:10.7507/1002-1892.202305081
Li, Y. F., Wang, Y., Bai, T. N., Dong, S., Wang, K. K., and Sun, H. J. (2024b). Preparation and characterization of thermosensitive chitosan/κ-carrageenan oligosaccharide hydrogels. J. Polym. Bull. 37 (10), 1428–1437. doi:10.14028/j.cnki.1003-3726.2024.24.010
Liao, J., Wu, Z., Qiu, Y., Xue, F., Gong, K., Duan, Y., et al. (2024). Injectable thermosensitive microsphere-hydrogel composite system: combined therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma by remodeling tumor immune microenvironment. J. Sci. China Mater. (prepublish) 67, 3379–3391. doi:10.1007/S40843-024-3001-3
Liu, D., Chen, J., Gao, L., Chen, X., Lin, L., Liu, Y., et al. (2025c). Nano Sim@ZIF8@PDA modified injectable temperature sensitive nanocomposite hydrogel for photothermal/drug therapy for peri-implantitis. J. Carbohydr. Polym. 354, 123327–123345. doi:10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2025.123327
Liu, H., Wang, M., Wang, Q., Guo, J., Chen, W., Ming, Y., et al. (2025e). Promoting scarless wound closure utilizing an injectable thermosensitive hydrogel with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and scar formation inhibiting properties. J. Biomater. Adv. 173, 214295–214311. doi:10.1016/J.BIOADV.2025.214295
Liu, H. Y., Huang, F. X., Chen, B. Q., and Yan, Y. (2025d). Preparation of chitosan/hyaluronic acid composite nanoparticles and their application in siRNA delivery. J. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 41 (04), 1340–1353. doi:10.13345/j.cjb.240600
Liu, J., Fang, Q., Lin, H., Yu, X., Zheng, H., and Wan, Y. (2020b). Alginate-Poloxamer/Silk fibroin hydrogels with covalently and physically cross-linked networks for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Carbohydr. Polym. 247, 116593–116628. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116593
Liu, J., Yang, B., Li, M., Li, J., and Wan, Y. (2020a). Enhanced dual network hydrogels consisting of thiolated chitosan and silk fibroin for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Carbohydr. Polym. 227, 115335–11548. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115335
Liu, J. J., Qu, S. X., Suo, Z. G., and Yang, W. (2021). Functional hydrogel coatings. J. Natl. Sci. Rev. 8 (2), nwaa254. doi:10.1093/NSR/NWAA254
Liu, P., Zhou, M., Luo, Z., Hao, L., Hsu, J. C., Cai, W., et al. (2025a). A 177Lu-nucleotide coordination polymer-incorporated thermosensitive hydrogel with anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective capabilities for osteoarthritis treatment. J. Biomater. 317, 123098–123111. doi:10.1016/J.BIOMATERIALS.2025.123098
Liu, Q. Y., Guo, Y. H., Ou, Y., Hu, C. Y., and Xu, X. (2025f). Mechanically tough thermo-responsive hydrogel reinforced by Quaternary ammonium chitosan/silver nanoparticle as potential controlled drug carriers. J. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 711, 136289–136305. doi:10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2025.136289
Liu, S., and Ma, L. (2025). Therapeutic effects of chitosan/β-glycerophosphate/collagen hydrogel combined with MSCs on chronic achilles tendon injury via the Akt/GSK-3β pathway. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 20 (1), 204–213. doi:10.1186/s13018-025-05607-4
Liu, X. X., and Zhou, G. Y. (2025). Polyethylene glycol-based double-network hydrogel as cartilage-like material. J. J. Hunan Univ. Technol. 39 (05), 67–73. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-9833.2025.05.010
Liu, X. Y., Wang, Q. B., and Sun, L. Y. (2024). Research progress on hydrogel-loaded extracellular vesicles in tissue engineering applications. J. China Med. Pharm. 14 (15), 40–44. doi:10.20116/j.issn2095-0616.2024.15.10
Liu, Y., Yang, J. L., Wang, W. L., Chui, Y. Y., Sun, Q. H., and Li, Y. (2025b). Application characteristics of temperature-responsive hydrogels in bone tissue engineering. J. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 29 (28), 6094–6100. doi:10.12307/2025.468
Maneechan, W., Khumfu, P., Charoensit, P., Tuanchai, A., Ross, S., Ross, G. M., et al. (2025). Bioactive hydrogel scaffolds integrating chitosan, silk fibroin, and Aloe vera extract for enhanced cartilage tissue regeneration. Polymers 17 (10), 1409–1429. doi:10.3390/polym17101409
Marcus, D., Parssa, G., Dartora Vanessa, F. C., Christiansen, B. A., and Panitch, A. (2021). Hyaluronic acid-binding, anionic, nanoparticles inhibit ECM degradation and restore compressive stiffness in aggrecan-depleted articular cartilage explants. J. Pharm. 13 (9), 1503–1524. doi:10.3390/PHARMACEUTICS13091503
Mohammad, M., Ashveen, N., Mohammadreza, A., and Ramezani, M. (2020). Mechanical and microscopical characterisation of bilayer hydrogels strengthened by TiO2 nanoparticles as a cartilage replacement candidate. Mater. Today Commun. 25, 101279–101293. doi:10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101279
Mojgan, G., Masoud, S., Fatemeh, M., Firouzi, Z., and Mousavi, S. D. (2021). The impact of zirconium oxide nanoparticles content on alginate dialdehyde-gelatin scaffolds in cartilage tissue engineering. J. J. Mol. Liq. 335, 116531–116538. doi:10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2021.116531
Moon, H. S., Park, J. S., Lee, W. Y., and Yang, Y. J. (2024). LCST/UCST behavior of polysaccharides for hydrogel fabrication. J. RSC Adv. 14 (48), 35754–35768. doi:10.1039/D4RA06240J
Niu, S., Liu, C., Sun, A., Zhang, Q., Yan, J., Fu, J., et al. (2025). Preparation and characterization of thermosensitive phase-transition hydrogel based on decanoic acid-modified chitosan and methyl cellulose for wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 308 (Pt4), 142725. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.142725
Pan, Z. R., Zhang, H. L., Qi, Z., Wu, H. M., Liang, J., Ding, M. C., et al. (2025). Research progress of cellulose-based composite hydrogels in the medical field. Cellul. Sci. Technol. 33 (01), 59–67. doi:10.16561/j.cnki.xws.2025.01.03
Pandya, T., Joshi, D., Presswala, Z., Kulkarni, M., Patel, R., Patel, S., et al. (2025). Advanced therapeutic strategies using Thermo-sensitive chitosan/pectin hydrogel in the treatment of multiple cancers. J. Carbohydr. Polym. 357, 123454–123476. doi:10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2025.123454
Park, J. S., Lim, K. H., Lee, J. S., Jung, Y., Lee, J. M., Jung, Y., et al. (2025). Enhancing biodegradable bone plate performance: Stereocomplex polylactic acid for improved mechanical properties and near-infrared transparency. Biomacromolecules 26 (4), 2390–2401. doi:10.1021/ACS.BIOMAC.4C01768
Pearce, H. A., Swain, J. W. R., Hector, L. V., Hogan, K. J., Jiang, E. Y., Bedell, M. L, et al. (2022). Thermogelling hydrogel charge and lower critical solution temperature influence cellular infiltration and tissue integration in an ex vivo cartilage explant model. J. J. Biomed. Mater. research. Part A 111 (1), 15–34. doi:10.1002/JBM.A.37441
Pham, M. H., Joo, C., Ferdous, J. M., Ali, I., Kang, S. W., and Huh, K. M. (2025). Synthesis and characterization of N-octanoyl glycol chitosan as a novel temperature and pH-sensitive injectable hydrogel for biomedical applications. J. Mater. and Des. 254, 114052–114065. doi:10.1016/J.MATDES.2025.114052
Pitrolino, K., Felfel, R., Roberts, G., Scotchford, C., Grant, D., and Sottile, V. (2024). In vitrodegradation of a chitosan-based osteochondral construct points to a transient effect on cellular viability. J. Biomed. Mater. Bristol, Engl. 19 (5), 055025–055040. doi:10.1088/1748-605X/AD6547
Plugariu, A. I., Gradinaru, M. L., Avadanei, M., Rosca, I., Nita, L. E., Maxim, C., et al. (2023). Thermosensitive polyurethane-based hydrogels as potential vehicles for meloxicam delivery. J. Pharm. 16 (11), 1510–1529. doi:10.3390/PH16111510
Qian, Y., Tong, F. Z., Zhang, K. Q., and Zhang, J. (2024). 4D printed thermosensitive drug-controlled release gel scaffold. J. Mod. Silk Sci. Technol. 39 (02), 38–42.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-8433.2024.02.009
Qian, Z., Qi, S., and Yuan, W. (2025). Injectable, self-healing and phase change nanocomposite gels loaded with two nanotherapeutic agents for mild-temperature, precise and synergistic photothermal-thermodynamic tumor therapy. J. J. Colloid And Interface Sci. 683 (P2), 877–889. doi:10.1016/J.JCIS.2024.12.235
Rahvar, T. P., Abdekhodaie, J. M., Jooybar, E., and Benjamin, G. (2024). An enzymatically crosslinked collagen type II/hyaluronic acid hybrid hydrogel: a biomimetic cell delivery system for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 279 (P1), 134614. doi:10.1016/J.ijbiomac.19987
Rauer, B. S., Stüwe, L., Steinbeck, L., de Toledo, M. A. S., Fischer, G., Wennemaring, S., et al. (2024). Cell adhesion and local cytokine control on protein-functionalized PNIPAM-co-AAc hydrogel microcarriers. J. Small Weinheim der Bergstrasse, Ger. 21 (2), e2404183. doi:10.1002/SMLL.202404183
Ren, B., Tang, Y. L., Li, N., and Liu, B. D (2025). Thermosensitive antibacterial hydrogel for treating infectious bone defects. J. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 29 (34), 7269–7277. doi:10.12307/2025.498
Rick, S. W. (2021). Insights into the thermal response of a poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) triblock polymer in water. J. J. Phys. chemistry.B. 125 (8), 2167–2173. doi:10.1021/ACS.JPCB.0C11279
Sang, X. H., Zhao, X. H., Yan, L. Q., Jin, X., Wang, X., Wang, J., et al. (2022). Thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with primary chondrocyte-derived exosomes promotes cartilage repair by regulating macrophage polarization in osteoarthritis. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 19 (3), 629–642. doi:10.1007/S13770-022-00437-5
Sergi, R. S., Hastie, J. J., Smith, M. J. F., Devlin, A. G., Bury, E. G., Paterson, M. L., et al. (2024). Swelling-shrinking behavior of a hydrogel with a CO2-Switchable volume phase transition temperature. J. Macromol. rapid Commun. 46 (8), e2400772. doi:10.1002/MARC.202400772
Shi, C. T., Ji-Yan, H., Yuan, G., Li, Z. X., Wei, Z. Y., Dawes, H., et al. (2021). Small extracellular vesicles in combination with sleep-related circRNA3503:A targeted therapeutic agent with injectable thermosensitive hydrogel to prevent osteoarthritis. J. Bioact. Mater. 6 (12), 4455–4469. doi:10.1016/J.BIOACTMAT.2021.04.031
SiCong, L., Lei, L., Wang, Q., Deng, Z., and ChanYuan, J. (2024). Synergistic injection of the thermosensitive hydrogel and Bi-based alloy bone cement for orthopaedic repair. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 67 (7), 2153–2163. doi:10.1007/S11431-023-2609-6
Sobrino, G. R., Blas, R. I., García, C., Reinecke, H., Elvira, C., Hernández, R .J., et al. (2024b). Hydrogels with dual sensitivity to temperature and pH in physiologically relevant ranges as supports for versatile controlled cell detachment. J. Biomater. Adv. 159, 213826–213837. doi:10.1016/J.BIOADV.2024.213826
Sobrino, G. R., García, C., Basteiro, L. P., Reinecke, H., Elvira, C., and Hernández, R. J. (2024c). Cell harvesting on robust smart thermosensitive pseudo-double networks prepared by one-step procedure. J. Eur. Polym. J. 209, 112925–112936. doi:10.1016/J.EURPOLYMJ.2024.112925
Sobrino, G. R., Losada, C. I., Caltagirone, C., Crespo, G. A., García, C., Hernández, R. J., et al. (2024a). Osteoblastic cell sheet engineering using P(VCL-HEMA)-Based thermosensitive hydrogels doped with pVCL@Icariin nanoparticles obtained with supercritical CO2-SAS. J. Pharm. 16 (8), 1063–1082. doi:10.3390/PHARMACEUTICS16081063
Song, X. B., Gu, L. L., Yang, Q. M., Wu, J., Chen, J., Tian, X., et al. (2023). Thermosensitive injectable hydrogel loaded with hypoxia-induced exosomes maintains chondrocyte phenotype through NDRG3-mediated hypoxic response. J. Chin. Chem. Lett. 34 (8), 108079–5. doi:10.1016/J.CCLET.2022.108079
Stanzione, A., Polini, A., Scalera, F., Gigli, G., Moroni, L., and Gervaso, F. (2024). Photo/Thermo-Sensitive chitosan and gelatin-based interpenetrating polymer network for mimicking muscle tissue extracellular matrix. J. Heliyon 10 (21), 39820–39833. doi:10.1016/J.HELIYON.2024.E39820
Stealey, S., Dharmesh, E., Bhagat, M., Tyagi, A. M., Schab, A., Hong, M., et al. (2025). Super-lubricous polyethylene glycol hydrogel microspheres for use in knee osteoarthritis treatments. J. npj Biomed. Innov. 2 (1), 11–23. doi:10.1038/S44385-025-00011-3
Suljovrujic, E., Krstic, M., Rogic, M. Z., Petrovic, S., Leskovac, A., and Stamboliev, G (2023). Optimization of thermoresponsive hydrogels based on oligomers with lower critical solution temperature (LCST) far below/above physiological temperatures for biomedical applications. J. React. Funct. Polym. 189, 105612–105624. doi:10.1016/J.REACTFUNCTPOLYM.2023.105612
Sun, M., Sun, H., Jiang, S., Tian, Y., Liu, Y., and Li, M. (2024b). Research progress and applications of polysaccharide-based thermosensitive injectable hydrogels. J. Fine Chem. 41 (08), 1679–1692. doi:10.13550/j.jxhg.20230931
Sun, Q., Zhang, Y., Hu, B., Feng, Q., Xia, Y., Yu, L., et al. (2025a). Development of a dual-responsive injectable GelMA/F127DA hydrogel for enhanced cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis: harnessing MMP-Triggered and mechanical stress-induced release of therapeutic agents. J. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 304 (P1), 140823. doi:10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2025.140823
Sun, Q., Zhang, Y., Hu, B., Feng, Q., Xia, Y., Yu, L., et al. (2025b). Development of a dual-responsive injectable GelMA/F127DA hydrogel for enhanced cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis:harnessing MMP-Triggered and mechanical stress-induced release of therapeutic agents. J. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 304 (P1), 140823–140836. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140823
Sun, T. C., Chen, X. S., Xu, X., Wang, J., Ning, R. D., Li, Q., et al. (2024a). Temperature-responsive hydrogels for biological applications. J. Anhui Chem. Eng. 50 (04), 15–18+22. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-553X.2024.04.004
Thanh, T. T. H., Maddison, L., Hongmanlin, Z., Martinez, F., Lee, Y., and Jang, Y. C. (2024). Designing biofunctional hydrogels for stem cell biology and regenerative medicine applications. J. J. Industrial Eng. Chem. 129, 69–104. doi:10.1016/J.JIEC.2023.08.042
Tian, Y., Cui, Y., Ren, G., Fan, Y., Dou, M., Li, S., et al. (2024). Dual-functional thermosensitive hydrogel for reducing infection and enhancing bone regeneration in infected bone defects. J. Mater. Today Bio 25, 100972–100987. doi:10.1016/J.MTBIO.2024.100972
Tu, Q., Jiang, D., Hu, R., Liu, Y., Fu, X., Chen, W., et al. (2024). An injectable CS-hydrogel incorporating TPGS for cartilage repair. J. Mater. and Des. 241, 112894–112907. doi:10.1016/J.MATDES.2024.112894
Venkata, D. K., and Ravi, M. S. (2023). Bioinspired artificial synovial fluid for in vitro frictional behavior of bovine articular cartilage and auxiliary biomaterials. J. J. Mol. Liq. 388, 122836–122852. doi:10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2023.122836
Vukonic, L., Nothnagel, M. R., Groß, F., Bauer, C., Fritz, J., Thurner, P., et al. (2025). Cartilage-inspired biocompatible double network PVA based hydrogels: a critical comparison of the role of agarose, chitosan, and silk fibroin additives. Mater. Today Commun. 45, 112318–112332. doi:10.1016/j.mtcomm.2025.112318
Wan, J., Jiang, J., Yu, X., Zhou, J., Wang, Y., Fu, S., et al. (2025). Injectable biomimetic hydrogel based on modified chitosan and silk fibroin with decellularized cartilage extracellular matrix for cartilage repair and regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 298, 140058. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140058
Wang, J. S., Deng, H. R., Song, H. C., Yuan, F. Z., Li, P. Q., Cao, X. Y., et al. (2024b). Biomechanically matched and multistage hybrid porous scaffolds for stem cell-based osteochondral regeneration. J. Nano Today 59, 102539–102554. doi:10.1016/J.NANTOD.2024.102539
Wang, Y., Zhou, X., Jiang, J., Zhao, T., Dang, J., Hu, R., et al. (2025). Carboxymethyl chitosan-enhanced multi-level microstructured composite hydrogel scaffolds for bone defect repair. J. Carbohydr. Polym. 348 (PB), 122847–122860. doi:10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2024.122847
Wang, Z. W., Li, C. Z., Liu, J. H., Li, Y. C., Wu, M. J., Chui, Y., et al. (2024a). Preparation methods and advantages/disadvantages of cartilage scaffold materials. J. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 28 (15), 2404–2409. doi:10.12307/2024.378
Westin, C. B., Nagahara, M. H. T., Decarli, M. C., Kelly, D. J., and Moraes, Â. M. (2020). Development and characterization of carbohydrate-based thermosensitive hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Eur. Polym. J. 129 (prepublish), 109637–109648. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.109637
Wu, D., Wang, P., Lei, C., Wu, W., Ma, S. S., Tang, C. B., et al. (2022). Preparation and properties of thermosensitive hydrogels loaded with antimicrobial peptides. J. J. Nanjing Med. Univ. Nat. Sci. 42 (07), 957–964. doi:10.7655/NYDXBNS20220707
Xi, Y., Wang, J. L., Yang, Y., Huang, L., Zhou, C., Su, J., et al. (2023). Thermosensitive hydrogel for cartilage regeneration via synergistic delivery of SDF-1α like polypeptides and kartogenin. J. Carbohydr. Polym. 304, 120492–120505. doi:10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2022.120492
Xiang, C., Guo, Z., Zhang, Q., Wang, Z., Li, X., Chen, W., et al. (2024). Physically crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol)-based hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Mater. and Des. 243, 113048–113062. doi:10.1016/J.MATDES.2024.113048
Xiao, P., Liu, J., Du, C., Cheng, S., Liu, S., Liu, J., et al. (2025). Injectable mineralized hydrogel microspheres for accelerated osteocyte network reconstruction and intelligent bone regeneration. J. J. Control. release official J. Control. Release Soc. 380, 240–255. doi:10.1016/J.JCONREL.2025.02.002
Xing, Y. H., Zhi, Y. W., Huai, Y. W., Chen, D., and Tong, L. (2023). Novel strategies for the treatment of osteoarthritis based on biomaterials and critical molecular signaling. J. Mater. Sci. and Technol. 149, 42–55. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2022.11.027
Xu, H., Wei, Y., Xu, S. M., Su, H., Li, H. Q., Huang, L, et al. (2021). Study on cell surface encapsulation based on chitosan/β-Glycerophosphate sodium (CS/β-GP) thermosensitive hydrogel and its effect on cancer cell behavior. Funct. Mater. 52 (05), 5121–5126. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2021.05.018
Xu, Z., Gao, J., Zhang, H., Zheng, G., Hu, J., Li, J., et al. (2024). A thermosensitive hydrogel based arginine grafted chitosan and poloxamer 407 for wound healing. J. Eur. Polym. J. 213, 113129–113139. doi:10.1016/J.EURPOLYMJ.2024.113129
Yang, J., Zhao, Q., Lu, B., Lv, Y., Jiang, W., Chen, X., et al. (2025). Injectable thermosensitive hydrogel based on hyaluronic acid and poloxamer for sustained bupivacaine release and prolonged analgesia. J. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 309 (Pt2), 142845–142859. doi:10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2025.142845
Yang, S., Zhu, Y., Ji, C., Zhu, H., Lao, A., Zhao, R., et al. (2024). A five-in-one novel MOF-Modified injectable hydrogel with thermo-sensitive and adhesive properties for promoting alveolar bone repair in periodontitis: antibacterial, hemostasis, immune reprogramming, pro-osteo-/angiogenesis and recruitment. J. Bioact. Mater. 41, 239–256. doi:10.1016/J.BIOACTMAT.2024.07.016
Yi, H. Y., Guo, C., Song, G., Li, Z. H., Tian, L.Z., Yu, X. W., et al. (2023b). Injectable temperature-sensitive hydrogel loaded with IL-36Ra for the relief of osteoarthritis. J. ACS biomaterials Sci. and Eng. 9 (3), 1672–1681. doi:10.1021/ACSBIOMATERIALS.2C01144
Yi, Z. W., Zhan, F. K., Chen, Y. J., Zhang, R., and Zhao, L. (2023a). An electroconductive hydrogel with injectable and self-healing properties accelerates peripheral nerve regeneration and motor functional recovery. J. Chem. Eng. J. 478, 147261–147277. doi:10.1016/J.CEJ.2023.147261
Younus, M. Z., Ahmed, I., Roach, P., and Forsyth, N. R. (2024). A phosphate glass reinforced composite acrylamide gradient scaffold for osteochondral interface regeneration. Biomaterials Biosyst. 15, 100099–100112. doi:10.1016/j.bbiosy.2024.100099
Zamini, N., Mirzadeh, H., Solouk, A., and Shafipour, R. (2025). Injectable in situ forming hydrogel based on carboxymethyl chitosan for sustained release of hyaluronic acid: a viscosupplement for biomedical applications. J. Carbohydr. Polym. 352, 123227–123239. doi:10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2025.123227
Zhang, B. K., Li, H. K., Xia, W., Zhang, C., Yang, R. Y., Zheng, J. H., et al. (2025b). Kartogenin induces chondrogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes cartilage defect repair. J. J. Trauma. Surg. 27 (02), 141–148+158. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-4237.2025.02.010
Zhang, F., Zhang, H., Wang, S., Gao, M., Du, K., Chen, X., et al. (2025d). A dynamically phase-adaptive regulating hydrogel promotes ultrafast anti-fibrotic wound healing. J. Nat. Commun. 16 (1), 3738–3758. doi:10.1038/S41467-025-58987-W
Zhang, T., Zhong, C. X., Feng, X. Z., Lin, X. Y., Chen, C. Y., Wang, X. W., et al. (2025e). An active shrinkage and antioxidative hydrogel with biomimetic mechanics functions modulates inflammation and fibrosis to promote skin regeneration. J. Bioact. Mater. 45, 322–344. doi:10.1016/J.BIOACTMAT.2024.11.028
Zhang, X. Y., Wang, J., Wang, X. F., He, L. Y., Wang, H. J., Yang, R., et al. (2025c). Research progress in stimuli-responsive drug carriers and their materials. J. Prog. Pharm. Sci. 49 (02), 111–125. doi:10.20053/j.issn1001-5094.2025.02.004
Zhang, Z., Hu, X., Yao, H., and Wang, D. A (2025a). Application progress of collagen scaffolds in articular cartilage repair. J. Orthop. Clin. Res. 10 (02), 109–114. doi:10.19548/j.2096-269x.2025.02.008
Zhao, Z. B., Li, C. X., Dou, C. L., Ma, N., and Zhou, G. J. (2025). Anti-inflammatory and osteogenic effects of chitosan/sodium glycerophosphate/sodium alginate/motherwort alkali hydrogel. Res. Organ. Eng. China 29 (04), 678–685. doi:10.12307/2025.264
Zhong, G., Luo, Y., Wang, M., Yu, Z., Zou, X., Wang, G., et al. (2025). Transcript-activated collagen matrix for enhanced bone marrow stem cell differentiation and osteochondral repair. Eng. Regen. 6, 111–120. doi:10.1016/j.engreg.2025.03.002
Zhou, D., Wang, W., Ma, W., Xian, Y., Zhang, Z., Pan, Z., et al. (2025). Cartilage-adaptive hydrogels via the synergy strategy of protein templating and mechanical training. J. Adv. Mater. Deerf. Beach, Fla. 37 (19), e2414081. doi:10.1002/ADMA.202414081
Zigan, C., Alston, B. C., Chatterjee, A., Solorio, L., and Chan, D. D. (2024). Characterization of composite agarose–collagen hydrogels for chondrocyte culture. J. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 53 (1), 1–13. doi:10.1007/S10439-024-03613-X
Keywords: temperature-sensitive hydrogel, response principle, cartilage injury, regenerative medicine, clinical application
Citation: Yu L, She K, He R and Xu Q (2025) Application and progress of temperature-sensitive hydrogels in cartilage injury repair. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1602303. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1602303
Received: 07 April 2025; Accepted: 30 June 2025;
Published: 06 August 2025.
Edited by:
Cheng Hu, Sichuan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Sunho Park, Pusan National University, Republic of KoreaRaj Hazra, North Dakota State University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Yu, She, He and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qingyu Xu, MzU4MjUzNTAxQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Long Yu1,2
Long Yu1,2 Qingyu Xu
Qingyu Xu