- Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, The Affiliated Panyu Central Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Objectives: This study aimed to comprehensively analyze the postural control characteristics of middle-aged and elderly patients with cervicogenic dizziness from both dynamic and static balance perspectives.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted involving 20 patients with cervicogenic dizziness (dizziness group) and 20 healthy individuals (health group). Using the Prokin Balance Instrument, we conducted static balance and limits of stability tests on both groups. Key metrics such as average speed of sway, standard deviation of sway, average center of pressure, Romberg’s ratio, and limits of stability values were recorded.
Results: With the exception of the standard deviation of mediolateral sway in the healthy group, the values of static balance indices were higher in the eyes-closed condition compared to the eyes-open condition for both groups (|Z| > 2.068, P < 0.05). Except for the average speed of mediolateral sway in both the eyes-open and eyes-closed conditions and the length of body sway in the eyes-open condition, the remaining static balance index values were higher in the dizziness group than in the healthy group (|Z| > 2.077, P < 0.05). Compared to the healthy group, the Romberg ratio was significantly higher in the dizziness group, while the values of the limits of stability were significantly lower (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the average center of pressure along the X and Y-axes exhibited a dispersed distribution pattern away from the axis in the dizziness group, in contrast to the healthy group, which demonstrated a concentrated distribution pattern close to the axis.
Conclusion: Middle-aged and elderly patients with cervicogenic dizziness demonstrate postural control abnormalities, including decreased static balance, reduced limits of stability, increased center of gravity sway, reliance on visual compensation for postural control, and an elevated risk of falls.
1 Introduction
Cervicogenic dizziness is a prevalent clinical condition characterized by dizziness and balance disorders resulting from neck issues. As a significant component of dizziness-related disorders, cervicogenic dizziness accounts for approximately 89% of all dizziness cases (Takahashi, 2018; Chu et al., 2023). Epidemiological studies indicate a prevalence of 10% in adults, with a higher incidence in the elderly population, affecting about 30% of this group (Yao et al., 2020; Li et al., 2022). Retrospective studies in otorhinolaryngology report non-traumatic cervicogenic dizziness rates ranging from 5.42% to 7.5% (Polaczkiewicz and Olszewski, 2019; Ardiç et al., 2006). A prospective multicenter study further corroborated a prevalence of 6.4% (Lüscher et al., 2014). These data suggest a notable prevalence of cervicogenic dizziness among dizziness patients, although exact figures may vary based on population and study methodology. Importantly, with the increasing use of electronic devices and lifestyle changes, the incidence of cervicogenic dizziness is rising annually, and the age of onset is decreasing (Takahashi, 2018; Tardov et al., 2022). Typical symptoms include dizziness, neck pain, limited mobility, and abnormal postural control (Micarelli et al., 2021; Végh et al., 2019), with severe cases potentially leading to complications such as fractures and stroke (Xie et al., 2020).
Among these symptoms, decreased postural stability is considered the most frequent and consistent clinical feature of cervicogenic dizziness (Knapstad et al., 2019). The pathogenesis of these postural abnormalities remains unclear, though several hypotheses have been proposed, including vascular compression, sympathetic nerve stimulation, cervical proprioceptive disturbances, and migraine-related mechanisms (Végh et al., 2019). The cervical proprioceptive disorder hypothesis is the most widely accepted (Végh et al., 2019). Given that balance is primarily regulated by vision, proprioception, and vestibular sensation, any abnormalities in proprioception can disrupt balance control (Cao et al., 2021). Therefore, characterizing postural control in patients with cervicogenic dizziness is crucial for understanding its pathogenesis and developing targeted therapeutic strategies.
Previous studies, such as the one by Micarelli et al., utilized the postural picture test to evaluate the balance function of patients with cervicogenic dizziness and confirmed that these patients exhibited significant increases in classic postural picture parameters (such as area and length) (Micarelli et al., 2021). However, this study relied on a single balance parameter and lacked high-sensitivity balance measures such as center of gravity sway frequency, amplitude, and limits of stability, thus offering limited insight into balance characteristics. Additionally, research by Micarelli and colleagues using the Dizziness Disorder Scale revealed higher balance scale scores in cervicogenic dizziness patients compared to healthy individuals, reflecting not only limited balance function but also psychological factors like depression and fear (Micarelli et al., 2020). However, this study lacked dynamic balance assessment and employed a highly subjective balance scale, limiting its objectivity. Despite the significant impact of postural control deficits on the quality of life in cervicogenic dizziness patients, there remains a paucity of studies characterizing their balance function. Most clinical studies rely on scales like Berg and Tinetti, or single balance parameters, which are cumbersome and limited in accuracy and objectivity (Taghavi Azar Sharabiani et al., 2024; Chen et al., 2024; Rivolta et al., 2019).
Recently, balance testers have emerged as a preferred tool for balance function research due to their objectivity, accuracy, and ease of use. These devices quantitatively assess static and dynamic balance abilities and identify the degree, type, or cause of balance impairments (Lin et al., 2020). The Prokin Balance tester has been extensively utilized in research across a variety of diseases. For instance, Zhang et al. engaged 20 healthy volunteers to participate in a balance test aimed at investigating postural control in patients with chronic low back pain. The findings revealed that the Prokin Balance tester exhibited excellent intra-rater reliability (Zhang et al., 2020). In a separate study examining dynamic and static balance in stroke patients, researchers compared the Prokin Balance tester with traditional tools like the widely used Berg Balance Scale. The results demonstrated that the Prokin Balance tester offers superior effectiveness and advantages in posture assessment (Lin et al., 2020). Furthermore, in studies exploring postural control in conditions such as acromegaly, migraine, and stroke, the Prokin Balance tester effectively differentiated balance disparities between patients and healthy individuals (Haliloglu et al., 2019; Dumanlidağ and Milanlioğlu, 2021; Lin et al., 2020).
In light of this, we employed the highly reliable and efficient Prokin Balance Instrument (TECNOBODY, Italy, Model 252) to accurately measure and analyze postural control in cervicogenic dizziness patients (Meier et al., 2016). The aim of this study is to elucidate the postural control characteristics of cervicogenic dizziness patients, providing a new perspective and scientific basis for the assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of cervicogenic dizziness, ultimately improving clinical treatment effectiveness and patient quality of life.
We hypothesize that both healthy individuals and patients with cervicogenic dizziness will exhibit higher static balance index values with eyes-closed compared to eyes-open. However, the disparity between these conditions is expected to be significantly more pronounced in patients with cervicogenic dizziness than in the healthy population, as indicated by higher Romberg ratios (the ratio of the eyes-closed condition to the eyes-open condition). Furthermore, patients with cervicogenic dizziness are anticipated to demonstrate markedly reduced limits of stability, greater oscillation amplitude of the center of plantar pressure, and an increased risk of falls compared to healthy subjects.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Participants
The sample size estimation for this study was conducted with a significance level of 0.05, a power of 0.8, and an effect size of 0.9, based on insights from prior research (Yahia et al., 2009). Consequently, the study enrolled 20 middle-aged and elderly patients diagnosed with cervicogenic dizziness by a surgeon (dizziness group) at the Affiliated Panyu Central Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University. Concurrently, 20 healthy individuals were recruited as the control group during the same timeframe.
Inclusion Criteria: Participants were selected based on the following criteria (Lin et al., 2020): (a) aged between 46 and 70 years, with stable vital signs and no cognitive impairments; (b) experiencing recurrent episodes of dizziness, neck pain, and restricted mobility; (c) symptoms that are exacerbated by changes in body position or neck movement, which may be persistent or intermittent; (d) imaging studies revealing altered cervical spine curvature, osteophytes at the intervertebral joints, vertebral instability, atlantoaxial subluxation, or disc herniation.
Exclusion Criteria: Participants were excluded if they had: (a) deformities, fractures, trauma, or surgeries of the trunk and limbs; (b) conditions such as pregnancy, lactation, menstruation, or chronic dysmenorrhea; (c) severe cardiovascular, cerebral, hepatic, renal, or psychiatric disorders; (d) cerebral, otogenic, ophthalmic, or other diseases.
Healthy individuals were selected based on the absence of dizziness symptoms and related conditions, with demographic characteristics matched to those of the cervicogenic dizziness patients.The study received approval from the Ethics Committee of Guangzhou Panyu District Central Hospital (PYRC-2021–077), and informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to testing. Anthropometric parameters, including age, height, weight, and body mass index (BMI), showed no significant differences between the two groups (P > 0.05). See Table 1 for details.
2.2 Test program
2.2.1 Testing instruments and requirements
The study utilized the Model 252 Prokin Balance Instrument (TECNOBODY, Italy) for postural assessment. This instrument has been validated in previous studies as a highly reliable and efficient tool for evaluating postural control (Dumanlidağ and Milanlioğlu, 2021).
Previous studies have demonstrated that the Model 252 Prokin Balance is capable of detecting subtle nuances or impairments that traditional clinical scales might overlook (Lin et al., 2020). This capability effectively mitigates the ceiling effect commonly associated with scale-based assessments. This distinctive attribute was a crucial factor in our selection of the Prokin Balance as the testing instrument for this study.
Prior to the assessment, the testing environment was maintained in a quiet state. The researcher provided the participants with detailed explanations regarding the purpose, procedures, and precautions of the assessment to ensure the process proceeded smoothly.
To minimize potential external influences such as environmental conditions and clothing, participants were instructed to wear loose-fitting attire and perform one or two pre-test exercises. Additionally, a quiet testing environment was maintained. These measures were implemented to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data collected.
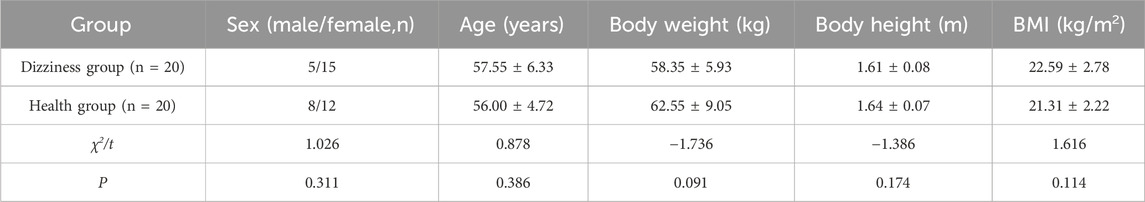
Participants were instructed to adopt a standard standing position for the posture assessment. This involved standing barefoot on the pressure platform of the balance instrument, with feet apart and symmetrically aligned along the center axis (A1-A5). The feet were positioned together, with the second toe of the left foot pointing to A8 and the second toe of the right foot pointing to A2. The heels were aligned along the same transverse axis, and the inner ankles crossed the A3-A7 transverse axes. Participants were required to place their hands naturally at their sides and focus their gaze straight ahead on a 1-m achromatic target. See Figure 1 for reference.
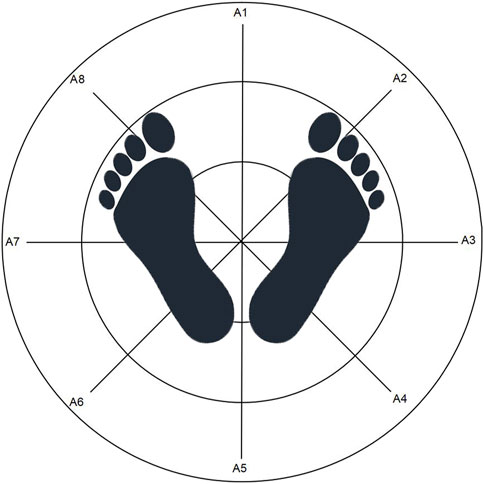
Figure 1. Schematic diagram illustrating the top-down view of a subject in the standard standing position.
2.2.2 Test composition
The postural control assessment comprised a static balance test and a dynamic balance test (limits of stability). The static balance test included two visual input conditions: eyes-open and eyes-closed, each lasting 30 s (Zhang et al., 2020; Paillard and Noé, 2015). Participants were instructed to remain as still as possible during the test. Repeat each test twice. Figure 2 displays the statokinesiogram during the static balance test.
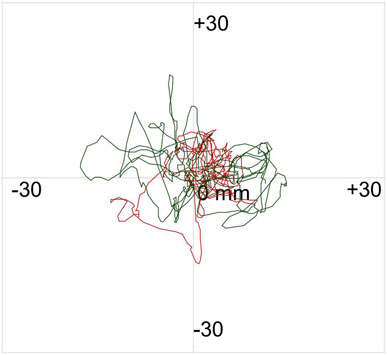
Figure 2. Statokinesiogram of the subject during the static balance test. The red and green lines depict the trajectory of the center of pressure swing with eyes open and closed, respectively.
For the Limits of Stability Test, participants were tasked with moving a cursor as quickly and accurately as possible from the center of a computer screen to one of eight targets, arranged at 45-degree intervals around the center and highlighted sequentially. Participants were instructed to keep their feet stationary, avoid falling, and refrain from touching the bar during the test. They were also required to return the cursor to the center before the next target appeared. The test concluded once all eight targets had been displayed. This test was also repeated twice. Figure 3 illustrates the motion trajectory diagram of the subject during the limits of stability test.
Figure 3. Motion trajectory diagram of the subject during the limits of stability test. The red line illustrates the movement trajectory of the human body’s center of pressure during limits of stability testing.
2.2.3 Observation indicators
Drawing upon insights from prior research (Sarabon et al., 2013; Hébert-Losier and Murray, 2020; Thomsen et al., 2017), we identified the following highly reliable and sensitive parameters as the primary observables for this study:
(a) Static balance: During the static balance test, the following parameters were recorded: average center of pressure X, average center of pressure Y, standard deviation of anteroposterior sway, standard deviation of mediolateral sway, average speed of anteroposterior sway (mm/s), average speed of mediolateral sway (mm/s), length of body sway (mm), and area of body sway (mm2). Larger values indicate poorer static balance stability (Walia et al., 2021).
(b) Romberg’s Ratio: This ratio primarily reflects the patient’s reliance on vision for postural control. In this study, we calculated the Romberg’s ratio using both the area and length of body sway, defined as the ratio of eyes-closed to eyes-open. A larger ratio signifies a higher degree of visual dependence (Dunn et al., 2024; Anagnostou et al., 2024).
(c) Limits of Stability: This was assessed by recording the total percentage of completion after the participant achieved the eight targets. A higher percentage indicates stronger limits of stability and a reduced risk of falls (Tomita et al., 2024).
2.2.4 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS 21.0 software. Data conforming to a normal distribution were expressed as mean ± SD and analyzed using paired t-tests within groups and independent samples t-tests between groups. Data not conforming to a normal distribution were expressed as median and Interquartile range (IQR), with the Wilcoxon signed-rank test used for two related samples within groups, and the Mann-Whitney U test used between groups. Effect size (r) was used to calculate the power of the nonparametric tests. The significance level was set at α = 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Comparison of static balance results between the two groups
In the dizziness group, all static balance indices were significantly higher when participants' eyes were closed compared to when their eyes were open (P < 0.05). Similarly, in the healthy group, static balance indices were also significantly elevated in the eyes-closed condition compared to the eyes-open condition, with the exception of the standard deviation of mediolateral sway (P > 0.05). Refer to Table 2 for detailed comparisons.
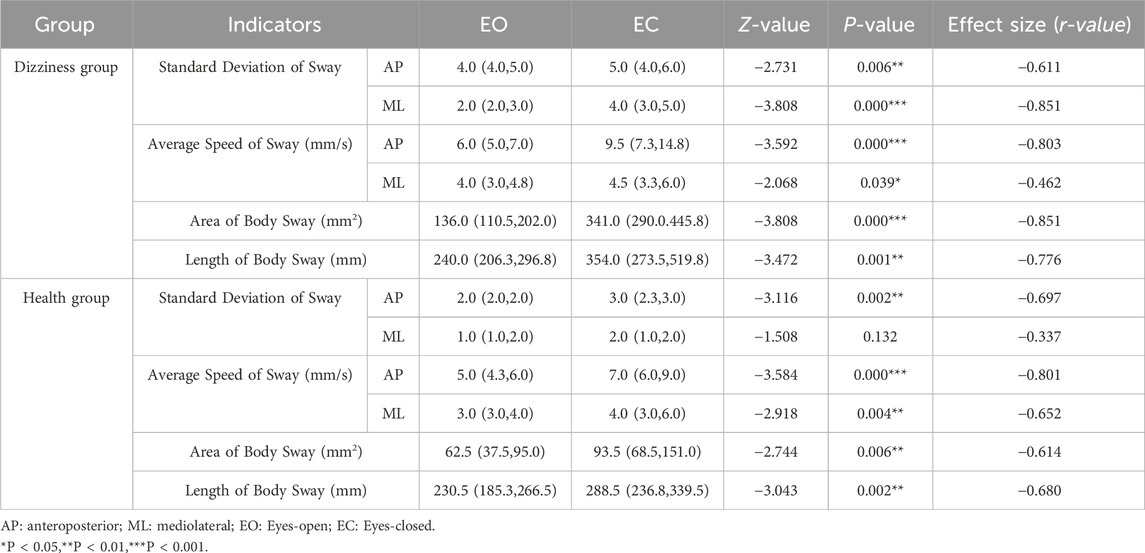
Table 2. Comparison of intra-group static balance test results for two groups of subjects with eyes open and closed within each group (Median (IQR)).
Under the eyes-open condition, except for the average speed of mediolateral sway and the length of body sway (P > 0.05), all other static balance indices in the dizziness group were significantly higher than those in the healthy group (P < 0.05). In the eyes-closed condition, with the exception of the average speed of mediolateral sway (P > 0.05), the indices in the dizziness group were also significantly higher than those in the healthy group (P < 0.05). Refer to Table 3 for detailed comparisons.
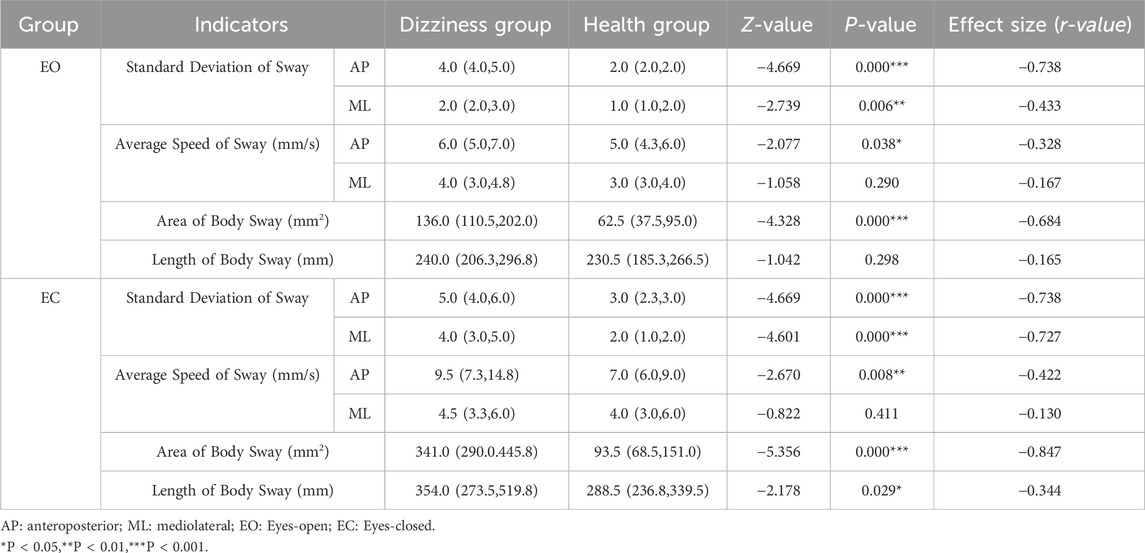
Table 3. Comparison of inter-group static balance test results for two groups of subjects with eyes open or closed (Median (IQR)).
3.2 Comparison of scatterplot results for the average center of plantar pressure between the two groups
Whether the eyes were open or closed, the average displacement of the center of foot pressure in the dizziness group exhibited a wide dispersion, deviating significantly from the central axis. In contrast, the distribution in the healthy group was more concentrated around the central axis. For further details, please refer to Figure 4.
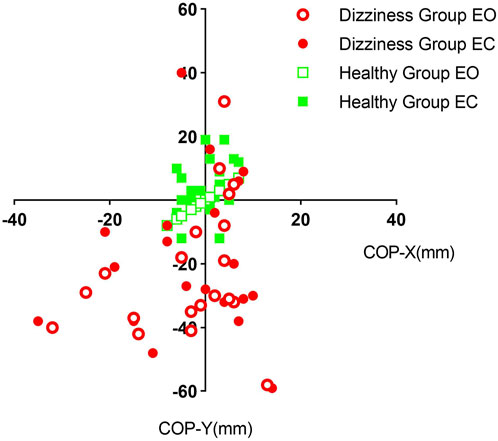
Figure 4. Scatter plots depicting the average pressure center distribution on the soles of the feet for the two groups of subjects with their eyes open and closed, respectively. EO: Eyes-open; EC: Eyes-closed; COP-X: average center of pressure X; COP-Y: average center of pressure Y.
3.3 Comparison of limits of stability and Romberg’s ratio between the two groups
When compared to the healthy group, the dizziness group showed significantly greater area and length ratios (P < 0.05). Conversely, the percentage values for limits of stability were significantly lower in the dizziness group than in the healthy group (P < 0.05). See Figure 5 for detailed results.
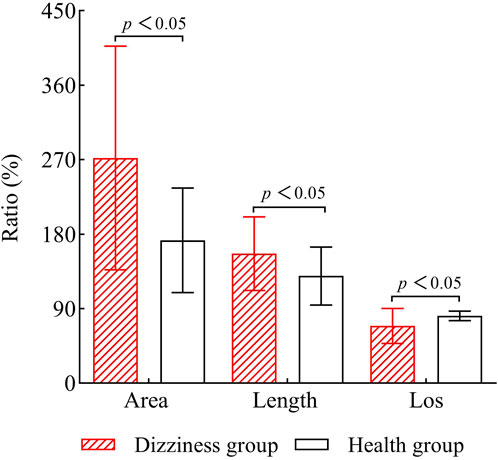
Figure 5. Comparison of Romberg’s ratio and limits of stability (LOS) between the two groups. LOS: Limits of Stability.
4 Discussion
In this study, we conducted an in-depth analysis of the postural control characteristics in patients with cervicogenic dizziness using the highly reliable and efficient Prokin balance instrument. Our findings robustly support the hypothesis that static balance index values are higher in the eyes-closed condition compared to the eyes-open condition, both in healthy individuals and in patients with cervicogenic dizziness. Notably, the disparity in balance index values between these conditions, as well as the Romberg ratios, were significantly elevated in patients with cervicogenic dizziness compared to healthy participants. This indicates that individuals with cervicogenic dizziness exhibit poorer balance maintenance and a greater reliance on visual input when visual cues are removed, relative to their healthy counterparts. Additionally, the study revealed that patients with cervicogenic dizziness have a markedly reduced range of limits of stability and a significantly larger range of oscillations in the center of plantar pressure than the healthy population. These findings suggest that cervicogenic dizziness patients experience a restricted range of safe mobility during daily activities, diminished physical dexterity and adaptability, and a significantly heightened risk of falls. These findings provide crucial evidence for the development of targeted balance training programs. Leveraging this evidence, more effective training regimens can be designed to enhance patients' balance abilities and effectively prevent falls.
Cervicogenic dizziness, a condition resulting from functional or organic changes in neck structures, is primarily characterized by dizziness and impaired postural control (Micarelli et al., 2020). Epidemiological studies indicate that annually, approximately 15%–35% of patients seeking medical care report dizziness, a condition particularly prevalent among middle-aged and elderly populations (Koukoulithras et al., 2022). The increasing use of electronic devices has contributed to a rise in the incidence of cervicogenic dizziness within these age groups (Takahashi, 2018), which in turn exacerbates the global prevalence of fall incidents, imposing a substantial burden on patients' quality of life, physical and mental health, and socio-economic systems. Consequently, it is crucial to explore preventive strategies for falls in middle-aged and elderly patients with cervicogenic dizziness. A fundamental step is to thoroughly understand the balance and postural control characteristics in these patients, thereby guiding researchers in developing effective interventions, which hold significant implications for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of cervicogenic dizziness.
While previous studies have primarily investigated the balance function in patients with cervicogenic dizziness using methods such as the Balance Scale, these studies are limited in several ways. The balance parameters observed are relatively narrow and lack highly sensitive indices. Additionally, the procedures are cumbersome and exhibit deficiencies in accuracy and objectivity (Yahia, et al., 2009; Micarelli, et al., 2020). Consequently, these studies struggle to accurately, objectively, and comprehensively capture the characteristics of postural control disorders in patients with cervicogenic dizziness. Previous studies have investigated various parameters for assessing balance posture. For instance, the elliptical area is frequently employed to quantify balance posture performance, as it encompasses 90% or 95% of the total area in both the anterior-posterior and lateral directions, serving as a reliable indicator of overall posture performance. Typically, a smaller elliptical area signifies better postural stability (Asseman et al., 2004). Additionally, path length is regarded as an effective outcome measurement parameter, with smaller values indicating greater postural stability (Donath et al., 2012). Swing speed reflects the efficiency of the postural control system and characterizes the net neuromuscular activity required to maintain balance, making it the most reliable measurement method in experimental settings (Duarte and Freitas, 2010). Swing amplitude is also a dependable parameter and has been extensively utilized to analyze postural deficits in patients with neuromotor disorders, such as cerebral palsy, particularly when examining left-right directional movements (Pavão et al., 2014). However, some studies have noted that parameters like frequency and capture time exhibit relatively low sensitivity, especially when less influenced by visual cues, and their performance is not as significant as the aforementioned indicators (Sarabon et al., 2013).
Advanced balance instrumentation provides a quantitative analysis of the body’s balance function under both dynamic and static conditions, uncovering issues that traditional observational methods and scale evaluations might miss. This allows for an accurate and objective assessment of a patient’s balance status (Haliloglu et al., 2019). This technology has been successfully applied to the assessment and training of balance functions in patients with diabetes and stroke, demonstrating its efficacy. (Reyhanıoglu et al., 2024; Lin et al., 2020). In this study, we utilized the Model 252 balancing instrument from Italy to evaluate the static balance and stabilization limits of middle-aged and elderly patients with cervicogenic dizziness. The balance instrument offers a comprehensive evaluation of balance issues from both static and dynamic perspectives and includes the highly reliable and sensitive balance indicator parameters previously mentioned. This study’s implementation will effectively address the constraints of prior research and conventional methodologies in evaluating postural disorders in individuals with cervicogenic dizziness.
Our findings demonstrate that both healthy individuals and patients with cervicogenic dizziness exhibit diminished static balance in the eyes-closed condition compared to the eyes-open condition, underscoring the moderating effect of visual input on static balance. Regardless of visual input, all static balance indices were significantly higher in patients with cervicogenic dizziness than in healthy subjects, indicating significant static balance dysfunction in these patients that is independent of visual input. Furthermore, the Romberg ratios for body sway length and area were significantly elevated in patients with cervicogenic dizziness compared to healthy subjects, suggesting a greater visual dependency in static balance regulation among the cervicogenic dizziness.
The Romberg ratio is a classic and well-established parameter in neurological assessments, though its sensitivity remains a topic of debate within academic circles, with scholars expressing differing views. Our research findings align with those of Putri et al., suggesting that the Romberg ratio can, to some extent, reflect a patient’s postural balance ability (Putri and Komalasari, 2025), despite differences in the patient populations studied. Additionally, Tjernström et al. questioned the reliability and validity of the Romberg ratio as an assessment tool for postural control in healthy young adults (Tjernström et al., 2015). We speculate that this discrepancy may be due to the influence of disease factors. The presence of disease may amplify changes in the Romberg ratio, a hypothesis that warrants further investigation in future studies.
Despite this increased visual reliance, static balance dysfunction persists in middle-aged and elderly patients with cervicogenic dizziness. This may be attributed to disturbances in neck proprioception, as balance control heavily depends on the integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive inputs (Cao et al., 2021). When proprioception is compromised, the body compensates by relying more on other senses, yet increased visual dependence often falls short of fully compensating for proprioceptive deficits (Meier et al., 2016). This explains why patients with cervicogenic dizziness, despite their increased visual dependence, demonstrate inferior static balance capabilities compared to healthy individuals.
In the discussion of the pathogenesis of cervicogenic dizziness, although four main types were initially proposed, subsequent research has refuted the existence of neurosympathetic cervicogenic dizziness, and rotational vertebral artery cervicogenic dizziness is now considered extremely rare. Migraine-type cervicogenic dizziness still requires further investigation and validation. In contrast, proprioceptive cervicogenic dizziness has emerged as the most common and widely accepted mechanism (Li and Peng, 2015). This underscores the central role of proprioceptive dysfunction in the pathogenesis of cervicogenic dizziness and its significant impact on postural control disorders.
Proprioceptive information, transmitted by proprioceptors located in joints, muscles, and tendons, is crucial for perceiving body position and movement (Riemann and Lephart, 2002; Tuthill and Azim, 2018). In the cervical region, approximately 50% of proprioceptors are distributed in the C1-C3 joint capsules (Hulse, 1983), highlighting the significant role of the upper cervical spine in proprioceptive regulation (McLain, 1994; Pettorossi and Schieppati, 2014). The upper cervical spine (including the atlanto-occipital and atlanto-axial joints) is responsible for the majority of flexion and rotational movements of the neck (Li and Peng, 2015; Savitz and Caplan, 2005; Swartz et al., 2005), with its mobility dependent on the synergistic action of ligaments and muscles. Ligaments such as the transverse ligament primarily maintain the stability of the upper cervical spine (Steilen et al., 2014), while muscle groups like the suboccipital muscles not only regulate neck motion (Yamauchi et al., 2017) but also serve as sensory receptors due to their high density of muscle spindles, playing a crucial role in postural adjustment (Kulkarni et al., 2001). Therefore, cumulative abnormal stimuli from prolonged poor posture, as well as trauma and degenerative changes, may affect the structural function of the upper cervical spine, subsequently impairing proprioception, leading to dizziness and postural abnormalities (Chu et al., 2020; L'Heureux-Lebeau et al., 2014).
Based on the aforementioned anatomical and physiological evidence, as well as the positive effects of proprioceptive training on postural stability in patients with cervicogenic headaches and healthy elderly individuals (Martínez-Amat et al., 2013; Emam et al., 2024), the findings of this study may offer a new perspective for the rehabilitative treatment of cervicogenic dizziness. Proprioceptive training could be equally applicable to patients with cervicogenic dizziness, potentially enhancing their perception of head position and movement, thereby improving their postural control and reducing symptoms of dizziness.
It is important to note that cervical pain is not only a symptom of cervicogenic dizziness but may also be a contributing factor, with a close association between the two. Nearly half of patients with neck pain experience cervicogenic dizziness (Vural et al., 2021). Neck pain is a symptom with high specificity (100%) but low sensitivity (68%) for cervicogenic dizziness (L'Heureux-Lebeau et al., 2014). However, pain itself may negatively impact cervical proprioception. Pioneering studies have found that individuals with cervical spine pain exhibit impaired sensorimotor control (Treleaven, 2008), a phenomenon particularly pronounced in patients with chronic pain (Lee et al., 2008). These findings support the notion that pain may alter cervical spine proprioception and afferent signals, leading to sensory mismatch.
In this study, we observed that the average center of plantar pressure in patients with cervicogenic dizziness exhibited a widely dispersed distribution in both eyes-open and eyes-closed conditions, whereas healthy individuals showed concentrations near the axis. This finding indicates that patients with cervicogenic dizziness experience greater shifts in their center of gravity during static balance assessments, reflecting poorer balance control compared to healthy individuals. Furthermore, dynamic balance stability was also compromised in patients with cervicogenic dizziness, as evidenced by the Limits of Stability Test results. Middle-aged and elderly patients with cervicogenic dizziness demonstrated reduced limits of stability in all eight directions, coupled with an increased risk of falling compared to their healthy counterparts.
Notably, in the comparison between patients with cervicogenic dizziness and healthy individuals, we found that the disparities in the average speed of anteroposterior sway were more pronounced than those in the mediolateral direction. This pattern was consistent across both eyes-open and eyes-closed conditions. Similar findings have been reported in patients with low back pain and cervical spine disorders (Soliman et al., 2017; Field et al., 2008). This may be due to the involvement of the hip, knee, ankle, and lumbar spine joints during anterior-posterior movements in the sagittal plane, which allows for a greater range of motion. In contrast, lateral movements in the frontal plane primarily involve only the hip, ankle, and lumbar spine joints.
Alternatively, the simplicity of static balance tests may not be sufficient to reveal balance differences, as significant variations in balance function are often more apparent during complex movements (Promsri et al., 2020). The Limits of Stability Test represents such a complex task, suggesting that it may serve as a more precise assessment tool for detecting balance discrepancies.
5 Limitations
This study has several inherent limitations. Firstly, while it primarily focuses on analyzing the static and dynamic balance characteristics of patients with cervicogenic dizziness, it does not explore the specific causes and mechanisms underlying these balance characteristics, leaving room for speculation. Secondly, the study predominantly targets middle-aged and elderly populations, where prevalence is high, without distinguishing among other age groups or genders. This limitation restricts the generalizability of the findings across different ages and genders. Lastly, although cervicogenic dizziness remains a diagnosis of exclusion, the study by Treleaven et al. demonstrated that a positive response to the modified cervical torsion test and the head-neck differentiation test can significantly enhance the diagnostic accuracy for cervicogenic dizziness (Treleaven et al., 2020). While our study employed similar methods, the modified testing protocols proposed by Treleaven et al. exhibit superior scientific rigor and standardization. Existing research suggests that gender differences may influence balance function (Ozcan Kahraman et al., 2018), indicating that further studies with gender differentiation could more accurately elucidate the balance function characteristics in patients with cervicogenic dizziness.
6 Conclusion
In conclusion, middle-aged and elderly patients with cervicogenic dizziness exhibit marked impairments in postural control, as demonstrated by significant reductions in static balance and limits of stability, as well as increased and dispersed center of gravity sway. These factors collectively indicate a heightened risk of falling. Additionally, maintaining postural control appears to rely, to some extent, on visual compensatory mechanisms, indicating a degree of visual dependence that may relate to disruptions in neck proprioceptive function.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Guangzhou Panyu District Central Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
WL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. YM: Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Supervision. PC: Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Visualization. HL: Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Validation. ZL: Writing – review and editing, Project administration. JS: Writing – review and editing. TZ: Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study received support from the Intramural Research Fund Project of Panyu Central Hospital affiliated with Guangzhou Medical University (PY-2024-006), the Health Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou Municipality (20251A011120), and the Science and Technology Plan Project of Panyu District, Guangzhou City (2024-Z04-042).
Acknowledgments
We are very appreciative of all the authors who participated in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Anagnostou, E., Kouvli, M., Karagianni, E., Gamvroula, A., Kalamatianos, T., Stranjalis, G., et al. (2024). Romberg's test revisited: changes in classical and advanced sway metrics in patients with pure sensory neuropathy. Neurophysiol. Clin. 54 (5), 102999. doi:10.1016/j.neucli.2024.102999
Ardiç, F. N., Topuz, B., and Kara, C. O. (2006). Impact of multiple etiology on dizziness handicap. Otol. Neurotol. 27 (5), 676–680. doi:10.1097/01.mao.0000226292.49789.c9
Asseman, F., Caron, O., and Crémieux, J. (2004). Is there a transfer of postural ability from specific to unspecific postures in elite gymnasts? Neurosci. Lett. 358 (2), 83–86. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2003.12.102
Cao, Z., Zhu, C., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, M., Ju, Y., et al. (2021). Risk factors related balance disorder for patients with dizziness/vertigo. Bmc. Neurol. 21 (1), 186. doi:10.1186/s12883-021-02188-7
Chen, P. T., Hsueh, I. P., Lee, S. C., Lee, M. L., Twu, C. W., and Hsieh, C. L. (2024). Test-retest reliability and responsiveness of the machine learning-based short-form of the berg balance scale in persons with stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. S0003-9993 (24), 880–886. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2024.10.013
Chu, E. C., Lin, A. F. C., Cheung, G., and Huang, K. H. K. (2023). Cervicogenic dizziness after self-manipulation of the cervical spine. Cureus 15 (4), e37051. doi:10.7759/cureus.37051
Chu, E. C. P., Lo, F. S., and Bhaumik, A. (2020). Plausible impact of forward head posture on upper cervical spine stability. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 9 (5), 2517–2520. doi:10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_95_20
Donath, L., Roth, R., Zahner, L., and Faude, O. (2012). Testing single and double limb standing balance performance: comparison of COP path length evaluation between two devices. Gait. posture. 36 (3), 439–443. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2012.04.001
Duarte, M., and Freitas, S. M. (2010). Revisão sobre posturografia baseada em plataforma de força para avaliação do equilíbrio. Rev. Bras. Fisioter. 14 (3), 183–192. doi:10.1590/s1413-35552010000300003
Dumanlidağ, S., and Milanlioğlu, A. (2021). Comparison of static and dynamic balance measurements among chronic and episodic migraine patients. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 79 (5), 399–406. doi:10.1590/0004-282X-ANP-2020-0319
Dunn, R., Stepanek, J., Eboka, R., and Pradhan, G. N. (2024). Effects of acute hypocapnia on postural standing balance measured by sharpened romberg testing (SRT) in healthy subjects. Wilderness. Environ. Med. 35 (4), 417–421. doi:10.1177/10806032241282320
Emam, M. A., Hortobágyi, T., Horváth, A. A., Ragab, S., and Ramadan, M. (2024). Proprioceptive training improves postural stability and reduces pain in cervicogenic headache patients: a randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Med. 13 (22), 6777. doi:10.3390/jcm13226777
Field, S., Treleaven, J., and Jull, G. (2008). Standing balance: a comparison between idiopathic and whiplash-induced neck pain. Man. Ther. 13 (3), 183–191. doi:10.1016/j.math.2006.12.005
Haliloglu, O., Topsakal, N., Camliguney, F., Polat Korkmaz, O., Sahin, S., Cotuk, B., et al. (2019). Static and dynamic balances of patients with acromegaly and impact of exercise on balance. Pituitary 22 (5), 497–506. doi:10.1007/s11102-019-00979-3
Hébert-Losier, K., and Murray, L. (2020). Reliability of centre of pressure, plantar pressure, and plantar-flexion isometric strength measures: a systematic review. Gait Posture 75, 46–62. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2019.09.027
Hulse, M. (1983). Disequelibrium caused by a functional disturbance of the upper cervical spine, clinical aspects and differential diagnosis. Man. Med. 1, 18–23.
Knapstad, M. K., Nordahl, S. H. G., and Goplen, F. K. (2019). Clinical characteristics in patients with cervicogenic dizziness: a systematic review. Health. Sci. Rep. 2 (9), e134. doi:10.1002/hsr2.134
Koukoulithras, I., Drousia, G., Kolokotsios, S., Plexousakis, M., Stamouli, A., Roussos, C., et al. (2022). A holistic approach to a dizzy patient: a practical update. Cureus 14 (8), e27681. doi:10.7759/cureus.27681
Kulkarni, V., Chandy, M. J., and Babu, K. S. (2001). Quantitative study of muscle spindles in suboccipital muscles of human foetuses. Neurol. India. 49 (4), 355–359.
Lee, H. Y., Wang, J. D., Yao, G., and Wang, S. F. (2008). Association between cervicocephalic kinesthetic sensibility and frequency of subclinical neck pain. Man. Ther. 13 (5), 419–425. doi:10.1016/j.math.2007.04.001
Li, Y., and Peng, B. (2015). Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of cervical vertigo. Pain physician 18 (4), E583–E595.
Li, Y., Yang, L., Dai, C., and Peng, B. (2022). Proprioceptive cervicogenic dizziness: a narrative review of pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Clin. Med. 11 (21), 6293. doi:10.3390/jcm11216293
Lin, Q., Zheng, Y., Lian, P., Guo, Y., Huang, H., Luo, Z., et al. (2020). Quantitative static and dynamic assessment of balance control in stroke patients. J. Vis. Exp. 159. doi:10.3791/60884
Lüscher, M., Theilgaard, S., and Edholm, B. (2014). Prevalence and characteristics of diagnostic groups amongst 1034 patients seen in ENT practices for dizziness. J. Laryngol. Otol. 128 (2), 128–133. doi:10.1017/S0022215114000188
L’Heureux-Lebeau, B., Godbout, A., Berbiche, D., and Saliba, I. (2014). Evaluation of paraclinical tests in the diagnosis of cervicogenic dizziness. Otol. Neurotol. 35 (10), 1858–1865. doi:10.1097/MAO.0000000000000506
Martínez-Amat, A., Hita-Contreras, F., Lomas-Vega, R., Caballero-Martínez, I., Alvarez, P. J., and Martínez-López, E. (2013). Effects of 12-week proprioception training program on postural stability, gait, and balance in older adults: a controlled clinical trial. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 27 (8), 2180–2188. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31827da35f
McLain, R. F. (1994). Mechanoreceptor endings in human cervical facet joints. Spine 19 (5), 495–501. doi:10.1097/00007632-199403000-00001
Meier, M. L., Stämpfli, P., Vrana, A., Humphreys, B. K., Seifritz, E., and Hotz-Boendermaker, S. (2016). Neural correlates of fear of movement in patients with chronic low back pain vs. pain-free individuals. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 10, 386. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2016.00386
Micarelli, A., Viziano, A., Augimeri, I., Micarelli, B., Capoccia, D., and Alessandrini, M. (2021). Diagnostic route of cervicogenic dizziness: usefulness of posturography, objective and subjective testing implementation and their correlation. Disabil. Rehabil. 43 (12), 1730–1737. doi:10.1080/09638288.2019.1680747
Micarelli, A., Viziano, A., Carlino, P., Granito, I., Micarelli, R. X., and Alessandrini, M. (2020). Reciprocal roles of joint position error, visual dependency and subjective perception in cervicogenic dizziness. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 37 (4), 262–270. doi:10.1080/08990220.2020.1803257
Ozcan Kahraman, B., Kahraman, T., Kalemci, O., and Salik Sengul, Y. (2018). Gender differences in postural control in people with nonspecific chronic low back pain. Gait Posture 64, 147–151. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2018.06.026
Paillard, T., and Noé, F. (2015). Techniques and methods for testing the postural function in healthy and pathological subjects. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 891390. doi:10.1155/2015/891390
Pavão, S. L., Nunes, G. S., Santos, A. N., and Rocha, N. A. (2014). Relationship between static postural control and the level of functional abilities in children with cerebral palsy. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 18 (4), 300–307. doi:10.1590/bjpt-rbf.2014.0056
Pettorossi, V. E., and Schieppati, M. (2014). Neck proprioception shapes body orientation and perception of motion. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 8, 895. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2014.00895
Polaczkiewicz, L., and Olszewski, J. (2019). Analyze causes and results of VNG examinations in patients with vertigo and balance disorders in the private ENT practice. Otolaryngol. Pol. 74 (2), 1–5. doi:10.5604/01.3001.0013.4374
Promsri, A., Haid, T., and Federolf, P. (2020). Complexity, composition, and control of bipedal balancing movements as the postural control system adapts to unstable support surfaces or altered feet positions. Neuroscience 430, 113–124. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.01.031
Putri, F., and Komalasari, D. (2025). Validity and reliability testing of the romberg test using a methodological approach in stroke patients. MIFI 13 (1), 32. doi:10.24843/mifi.2025.v13.i01.p07
Reyhanıoglu, D. A., Yıldırım, G., Sengun, I. Ş., and Kara, B. (2024). Effects of computer-based balance exercises on balance, pain, clinical presentation and nerve function in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomized controlled study. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal. Interact. 24, 168–177.
Riemann, B. L., and Lephart, S. M. (2002). The sensorimotor system, part I: the physiologic basis of functional joint stability. J. Athl. Train. 37 (1), 71–79.
Rivolta, M. W., Aktaruzzaman, M., Rizzo, G., Lafortuna, C. L., Ferrarin, M., Bovi, G., et al. (2019). Evaluation of the tinetti score and fall risk assessment via accelerometry-based movement analysis. Artif. Intell. Med. 95, 38–47. doi:10.1016/j.artmed.2018.08.005
Sarabon, N., Rosker, J., Loefler, S., and Kern, H. (2013). The effect of vision elimination during quiet stance tasks with different feet positions. Gait Posture 38 (4), 708–711. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2013.03.005
Savitz, S. I., and Caplan, L. R. (2005). Vertebrobasilar disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 352 (25), 2618–2626. doi:10.1056/NEJMra041544
Soliman, E. S., Shousha, T. M., and Alayat, M. S. (2017). The effect of pain severity on postural stability and dynamic limits of stability in chronic low back pain. J. Back. Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 30 (5), 1023–1029. doi:10.3233/BMR-169588
Steilen, D., Hauser, R., Woldin, B., and Sawyer, S. (2014). Chronic neck pain: making the connection between capsular ligament laxity and cervical instability. Open. Orthop. J. 8, 326–345. doi:10.2174/1874325001408010326
Swartz, E. E., Floyd, R. T., and Cendoma, M. (2005). Cervical spine functional anatomy and the biomechanics of injury due to compressive loading. J. Athl. Train. 40 (3), 155–161.
Taghavi Azar Sharabiani, P., Mehdizadeh, M., Goudarzi, S., Jamali, S., Mazhar, F. N., Heidari, M., et al. (2024). Minimal important difference of berg balance scale, performance-oriented mobility assessment and dynamic gait index in chronic stroke survivors. J. Stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 33 (11), 107930. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2024.107930
Takahashi, S. (2018). Importance of cervicogenic general dizziness. J. Rural. Med. 13 (1), 48–56. doi:10.2185/jrm.2958
Tardov, M. V., Boldin, A. V., and Razumov, A. N. (2022). Cervicogenic vertigo. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. S. S. Korsakova 122 (12), 50–56. doi:10.17116/jnevro202212212150
Thomsen, M. H., Støttrup, N., Larsen, F. G., Pedersen, A. S. K., Poulsen, A. G., and Hirata, R. P. (2017). Four-way-leaning test shows larger limits of stability than a circular-leaning test. Gait Posture 51, 10–13. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2016.09.018
Tjernström, F., Björklund, M., and Malmström, E. M. (2015). Romberg ratio in quiet stance posturography-Test to retest reliability. Gait posture 42 (1), 27–31. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2014.12.007
Tomita, H., Asai, H., Ogawa, Y., Kawamata, N., and Hayashi, H. (2024). Fingertip light touch contact increases anteroposterior limits of stability in healthy young and older adults. Gait Posture 114, 28–34. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2024.08.081
Treleaven, J. (2008). Sensorimotor disturbances in neck disorders affecting postural stability, head and eye movement control. Man. Ther. 13 (1), 2–11. doi:10.1016/j.math.2007.06.003
Treleaven, J., Joloud, V., Nevo, Y., Radcliffe, C., and Ryder, M. (2020). Normative responses to clinical tests for cervicogenic dizziness: clinical cervical torsion test and head-neck differentiation test. Phys. Ther. 100 (1), 192–200. doi:10.1093/ptj/pzz143
Tuthill, J. C., and Azim, E. (2018). Proprioception. Curr. Biol. CB 28 (5), R194–R203. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2018.01.064
Végh, I., Harmat, K., and Gerlinger, I. (2019). Cervicalis vertigo – Létező kórkép vagy fikció? [cervical vertigo - reality or fiction?]. Orv. Hetil. 160 (25), 967–972. doi:10.1556/650.2019.31409
Vural, M., Karan, A., Albayrak Gezer, I., Çalışkan, A., Atar, S., Yıldız Aydın, F., et al. (2021). Prevalence, etiology, and biopsychosocial risk factors of cervicogenic dizziness in patients with neck pain: A multi-center, cross-sectional study. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 67 (4), 399–408. doi:10.5606/tftrd.2021.7983
Walia, S., Kumar, P., and Kataria, C. (2021). Efficacy of electrical stimulation-augmented virtual reality training in improving balance in individuals with incomplete spinal cord injury: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial. Asian. Spine. J. 15 (6), 865–873. doi:10.31616/asj.2020.0047
Xie, R., You, J., Liu, L., Huang, C., and Liang, Y. (2020). Acupotomy therapy for cervical vertigo: a protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 99, e20662. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000020662
Yahia, A., Ghroubi, S., Jribi, S., Mâlla, J., Baklouti, S., Ghorbel, A., et al. (2009). Chronic neck pain and vertigo: is a true balance disorder present? Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 52 (7-8), 556–567. doi:10.1016/j.rehab.2009.07.033
Yamauchi, M., Yamamoto, M., Kitamura, K., Morita, S., Nagakura, R., Matsunaga, S., et al. (2017). Morphological classification and comparison of suboccipital muscle fiber characteristics. Anat. Cell. Biol. 50 (4), 247–254. doi:10.5115/acb.2017.50.4.247
Yao, M., Tang, Z. Y., Cui, X. J., Sun, Y. L., Ye, X. L., Wang, P., et al. (2020). Shi-style cervical mobilizations versus massage for cervical vertigo: a multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 26 (1), 58–66. doi:10.1089/acm.2019.0113
Keywords: middle-aged and elderly, cervicogenic dizziness, postural control, static balance, limits of stability
Citation: Luo W, Min Y, Chen P, Li H, Long Z, Sun J and Zhong T (2025) Dual analysis of postural control in middle-aged and elderly patients with cervicogenic dizziness: Dynamic and static balance perspectives. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1622648. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1622648
Received: 04 May 2025; Accepted: 11 July 2025;
Published: 22 July 2025.
Edited by:
Bernardo Innocenti, Université libre de Bruxelles, BelgiumReviewed by:
Conde-Vázquez Orlando, University of Vigo, SpainQihan Guo, Capital Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Luo, Min, Chen, Li, Long, Sun and Zhong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tao Zhong, emhvbmd0YW9AcHlob3NwaXRhbC5jb20uY24=; Wei Luo, bHVvd2VpMUBweWhvc3BpdGFsLmNvbS5jbg==
 Wei Luo
Wei Luo Yu Min
Yu Min Peishun Chen
Peishun Chen