- 1Department of Orthopedics, the Fourth People’s Hospital of Shenyang, Shenyang, China
- 2Department of Orthopedics, Qianjiang People’s Hospital, Qianjiang, China
- 3College of Exercise and Health, Shenyang Sport University, Shenyang, China
The meniscus, an important fibrocartilaginous structure within the knee joint, plays essential roles in shock absorption, joint stabilization, and the optimization of mechanical force transmission. Meniscus injuries are common among athletes, middle-aged and elderly individuals, and those engaged in heavy physical labor. Both conservative and surgical treatments currently have limitations, making it difficult to achieve complete repair and functional restoration of meniscal tissue. In recent years, hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogel has shown broad potential in meniscus repair due to its excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability. As a cell carrier, this material not only promotes cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation but also mimics the biomechanical properties of the meniscus, regulates the inflammatory environment, and facilitates angiogenesis, thereby creating favorable conditions for tissue regeneration. This review summarizes the mechanisms, current applications, and research advances of HA hydrogel in meniscus repair, aiming to provide new theoretical foundations and technical support for meniscus injury treatment and to promote clinical translation and development in this field.
1 Introduction
The meniscus (Figure 1) is one of the most important components of the human knee joint (Pasiński et al., 2023), playing a critical role in shock absorption, enhancing joint stability, lubricating joint surfaces, and optimizing force transmission (Mameri et al., 2022; Adams et al., 2021). Meniscus injury remains a pervasive and costly clinical challenge, burden increasingly amplified by aging global populations experiencing natural tissue degeneration and rising rates of sports participation and associated trauma, together driving significant and escalating demand for effective interventions (Adams et al., 2021). Currently, meniscus injury treatments primarily include conservative and surgical approaches (Giuffrida et al., 2020), against this backdrop, conventional treatments present persistent limitations that fail to adequately address the scope of the problem. Conservative approaches like physical therapy offer symptomatic relief but fundamentally cannot initiate biological repair of torn tissue (Sari and Kurniawati, 2022). Surgical options represent a historical compromise: partial meniscectomy removes damaged sections to alleviate pain (Wang H. et al., 2024a) but inevitably diminishes the meniscus’s vital biomechanical functions, inevitably accelerating joint degeneration and osteoarthritis risk (McDermott and Amis, 2006). While suturing aims for anatomical repair, its utility is severely constrained by factors like tear location (particularly in the poorly vascularized inner zones), chronicity, and patient age, leading to variable success rates, complex recovery periods, and procedural risks like infection and non-union (Popper et al., 2023); crucially, even successful repair often cannot fully restore the native tissue’s complex structure and function, representing a significant therapeutic gap. Motivated precisely by these long-standing inadequacies–the unmet need to achieve biological healing of tears (especially in challenging zones) and restore functional, protective meniscus tissue to halt the cascade towards osteoarthritis-research has increasingly focused on tissue engineering and regenerative medicine strategies (Bian et al., 2022; Lombardo et al., 2021). Stem cell therapy and novel biomaterials hold theoretical promise. However, practical translation faces formidable barriers, including identifying reliable cell sources, designing scaffolds that effectively mimic the anisotropic biomechanical properties of the native meniscus while supporting cellular integration and tissue formation, and ensuring long-term safety and efficacy (Li et al., 2023); It is within this specific context of unresolved needs and defined knowledge gaps that Hyaluronic Acid (HA) hydrogel has emerged as a compelling solution (Li et al., 2019). Its inherent high biocompatibility and biodegradability provide a foundation. Functionally, HA hydrogel offers potential as an injectable cell or bioactive factor carrier, fostering cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation directly at the injury site (Gupta et al., 2019; Teng et al., 2021). Critically, it represents a platform uniquely positioned to address the core limitations identified above: by potentially matching biomechanical cues, regulating the local inflammatory milieu, encouraging controlled vascular in-growth specifically where beneficial, and providing structural support, HA hydrogel aims to create the precisely tailored microenvironment necessary for functional meniscus regeneration (Li et al., 2024).
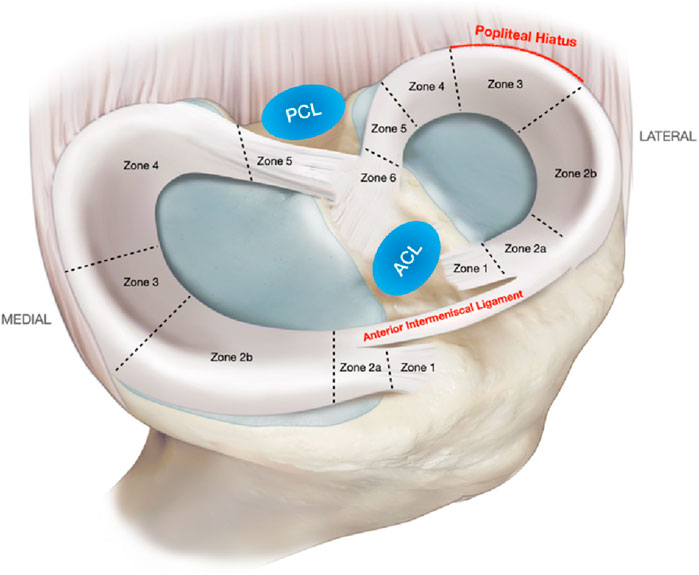
Figure 1. Medial and lateral meniscus zones and relevant anatomical relations. ACL, anterior cruciate ligament; PCL, posterior cruciate ligament. Reproduced with permission from ref Mameri et al. (2022). Copyright © 2022, The Author(s).
This review will summarize research advances in HA hydrogel for meniscus repair. By examining its mechanism of action, application value, and current research status, it aims to provide a new theoretical foundation and technical pathway for meniscus injury treatment. Moreover, it will guide clinical applications and future research, holding significant importance in advancing meniscus repair therapies.
2 HA hydrogel
HA (HA), as a naturally occurring polysaccharide, has garnered significant attention in the biomedical field due to its unique structure and diverse functions (Yasin et al., 2022). From its chemical structure and biocompatibility to its mechanical properties, the characteristics of HA endow it with great potential for applications in tissue engineering (Tsanaktsidou et al., 2022), drug delivery (Buckley et al., 2022), and joint lubrication (Su et al., 2023). The following sections provide a detailed overview of the structure and properties of HA from three perspectives: chemical structure, biocompatibility and biodegradability, as well as mechanical properties and viscoelasticity.
2.1 Structure and properties of HA
HA is a naturally occurring linear polysaccharide, whose chemical structure (Figure 2) consists of repeating disaccharide units of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine linked by β-1,3 and β-1,4 glycosidic bonds (Marinho et al., 2021). This structure is simple yet highly regular, with molecular chains rich in hydroxyl and carboxyl groups, endowing HA with pronounced hydrophilicity and a strong negative charge (Laffleur et al., 2025). HA forms hydrogen bonds with water molecules, creating a highly hydrated network structure that results in excellent water retention capacity and lubricating properties (Yasin et al., 2022). In addition, the molecular weight of HA spans a broad range, from several thousand to several million Daltons, and HA of different molecular weights exhibits significant differences in biological functions and applications. High molecular weight HA typically provides greater water retention and viscoelasticity, while low molecular weight HA more readily penetrates tissues to exert specific biological effects (Jabbari et al., 2023). This structural diversity gives HA broad application potential in the biomedical field.
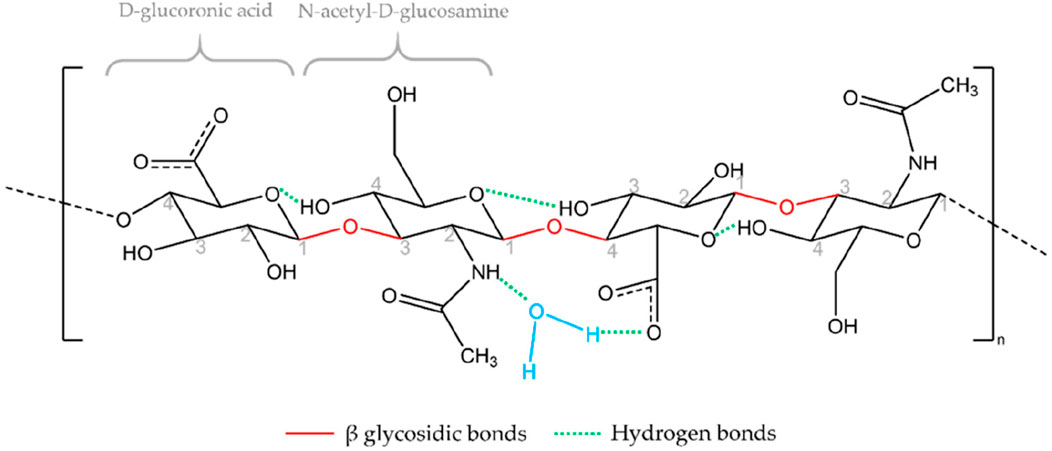
Figure 2. Chemical structure of HA. Reproduced with permission from ref Marinho et al. (2021). Copyright © 2021, The Author(s).
Due to its natural presence in human tissues, such as synovial fluid, skin, and the vitreous body-HA exhibits excellent biocompatibility (Valachová and Šoltés, 2021). It does not trigger immune rejection and can interact with cell surface receptors (such as CD44 and RHAMM), participating in various biological processes including cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation (Rosales et al., 2024). In vivo, HA can be degraded by hyaluronidase and reactive oxygen species (Weber et al., 2019; Šoltés et al., 2006), with its degradation rate depending on molecular weight, degree of crosslinking, and local enzymatic activity. This tunable degradability provides HA with broad application prospects in tissue engineering and drug delivery.
The mechanical properties and viscoelasticity of HA are among its most important characteristics. Due to the flexibility of its polymer chains and its highly hydrated nature, HA exhibits pronounced viscoelastic behavior in solution (Fundarò et al., 2022). Its viscosity increases significantly with higher concentration and molecular weight, enabling it to form highly viscous, gel-like structures. This viscoelasticity allows HA to serve as a lubricant and shock absorber in synovial fluid, reducing friction and wear of articular cartilage (Zhang and Christopher, 2015). Additionally, the mechanical properties of HA can be tuned through chemical crosslinking or by combining it with other biomaterials to meet the requirements of various applications (Khanlari et al., 2015; Kong et al., 2020). Crosslinked HA hydrogels possess greater mechanical strength and stability, allowing them to withstand certain mechanical loads in the body while retaining their bioactivity and degradability (Khunmanee et al., 2017). For example, in joint injections, crosslinked HA can provide prolonged lubrication and help delay joint degeneration (Qiu et al., 2023).
2.2 Mechanism of HA in the meniscal repair
The underlying mechanism by which hyaluronic acid (HA) facilitates meniscal healing has been increasingly elucidated. Research demonstrates that HA promotes human meniscus regeneration, primarily through inhibiting apoptosis, enhancing cell migration, and accelerating cell proliferation. Murakami et al. (2019) specifically examined the effects of HA on prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)-induced apoptosis and gene expression in meniscus cells. Their findings confirmed that HA concentration-dependently increases both cell migration and proliferation in both the inner and outer regions of the meniscus. Crucially, these beneficial effects were blocked by an anti-CD44 antibody, indicating the essential role of the CD44 receptor. Further mechanistic insight revealed that HA activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, activation which was also prevented by anti-CD44 antibody treatment. This strongly suggests HA acts via the CD44 receptor to stimulate the PI3K/MAPK pathway. Additionally, HA was found to upregulate the mRNA levels of Collagen Type II Alpha 1 Chain (COL2A1) and Aggrecan (ACAN) specifically in inner meniscus cells. Based on these results, Murakami et al. concluded that HA holds promise for clinical application in managing meniscal injuries. Furthermore, the well-established anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of HA (Salathia et al., 2023) are also considered critical for supporting overall meniscus repair.
2.3 Preparation methods of HA hydrogels
The preparation methods of HA hydrogels mainly include chemical crosslinking, physical crosslinking, and composite preparation with other biomaterials. Each method has its own characteristics and can be used to adjust the mechanical properties, degradation rate, and biological activity of the hydrogel according to specific application requirements. By selecting different preparation methods, it is possible to meet the needs of various application scenarios ranging from tissue engineering to drug delivery.
2.3.1 Chemical crosslinking
Chemical crosslinking involves the formation of covalent bonds between HA molecular chains through chemical reactions (Wang et al., 2022), thereby constructing a stable three-dimensional network structure. Commonly used chemical crosslinking agents include Glutaraldehyde (GTA), divinyl sulfone (DVS), adipic acid dihydrazide (ADH), and carbodiimides (EDC). These crosslinking agents react with hydroxyl or carboxyl groups on HA molecular chains to form stable crosslinking points (Luo et al., 2023; Khunmanee et al., 2017). Hydrogels prepared by chemical crosslinking possess higher mechanical strength and stability, allowing them to withstand certain mechanical loads in vivo (Fuchs et al., 2020). Furthermore, the degree of crosslinking can be precisely controlled by adjusting the concentration of crosslinking agents and reaction conditions, thereby regulating the degradation rate of the hydrogel. For example, by increasing the concentration of crosslinking agents or extending the reaction time, the crosslinking density of the hydrogel can be enhanced (Nasution et al., 2022), improving its mechanical strength and stability. However, chemical crosslinking processes may introduce residual crosslinking agents (Sapuła et al., 2023), necessitating rigorous purification to ensure biosafety. To reduce the residual crosslinking agents, mild crosslinking conditions can be adopted or more biocompatible crosslinking agents can be used, such as natural crosslinking agents (like genipin) or photo-crosslinking agents (like methacrylates) (Yang et al., 2023). Additionally, chemical crosslinking methods can be combined with other techniques, such as microfluidic technology, to prepare hydrogels with complex structures and functions (Chen et al., 2021).
2.3.2 Physical crosslinking
Physical interactions, including electrostatic interactions, chain entanglement, hydrophobic self-assembly, hydrophobic/hydrophilic interactions, and hydrogen bonds, have been developed as common crosslinking strategies for the preparation of HA-based hydrogels (Faivre et al., 2021). Physical crosslinking normally leads to a rapid polymerization behavior under relatively mild conditions and needs no toxic crosslinkers or catalysts, decreasing potential cytotoxicity (Huang et al., 2017; Baek et al., 2018). However, physically crosslinked hydrogels typically have lower mechanical strength and poorer stability (Xu et al., 2021), which may limit their use in certain high-load applications.
2.3.3 Composite preparation with other biomaterials
To enhance the properties of HA hydrogels, they are often combined with other biomaterials such as collagen, chitosan (Wang et al., 2024b). Composite hydrogels integrate the excellent biocompatibility and lubricating properties of HA with the mechanical strength and functional characteristics of other materials. For example, combining HA with collagen can improve the hydrogel’s cell adhesion and tissue regeneration capabilities (Hwang et al., 2022); blending with chitosan can enhance the hydrogel’s antibacterial properties (Bai et al., 2023). The design of composite hydrogels can be flexibly adjusted according to the requirements of specific applications, allowing for precise control of their mechanical properties, degradation rate, and bioactivity to meet diverse clinical needs. For instance, in tissue engineering, composite hydrogels can serve as scaffold materials to support cell growth and tissue regeneration (Wang et al., 2021; Liang et al., 2023); in drug delivery, composite hydrogels can act as carriers, enabling sustained and targeted release of therapeutic agents (Svarca et al., 2022; Rong et al., 2023).
2.4 Intelligent responsive HA hydrogels
Intelligent Responsive HA Hydrogels are advanced biomaterials engineered by combining the inherent, advantageous properties of the natural biopolymer HA, namely, its outstanding biocompatibility, biodegradability, and ease of chemical modification with functional groups that exhibit sensitivity to external physical or chemical stimuli [e.g., pH (Qian et al., 2019), temperature (Ha et al., 2006), enzymes (Tam et al., 2017), light (Tam et al., 2017; Zhao et al., 2020), glucose (Xu et al., 2022), redox status (Zhang et al., 2017; Huang et al., 2022; Shi et al., 2024)]. This integration enables the dynamic environmental responsiveness and significant physicochemical property transitions characteristic of these materials; their sensitivities can be strategically combined to achieve multi-responsiveness tailored for precise interaction within complex pathological microenvironments. Demonstrating significant potential in medical applications, these smart materials facilitate on-demand drug release within lesion sites (such as acidic (Qian et al., 2019), highly reducing (Zhang et al., 2017), or enzymatic tumor microenvironments (Yang et al., 2015)) or via external triggers (e.g., light/heat) (Ha et al., 2006; Xu et al., 2020) in drug delivery, significantly improving targetability and minimizing side effects. Within tissue engineering, serving as intelligent scaffolds, they regulate cellular behavior and guide tissue regeneration through responsive degradation and signaling factor release (Lam et al., 2014). Furthermore, in wound repair, they not only manage a moist environment but also respond to variations in exudate pH or infection-related protease levels to release antibacterial or anti-inflammatory agents, promoting healing (Mohammed et al., 2022). Despite facing challenges concerning in vivo enzymatic stability, manufacturing standardization, complex system characterization, and precise in vivo control, intelligent responsive HA hydrogels, leveraging their engineerable dynamic responsiveness, multifunctional integration capacity, and HA’s inherent biological merits, are emerging as key Frontier materials driving advancements in precision drug delivery, intelligent tissue regeneration, and diagnostic/therapeutic integration.
3 Preclinical studies
HA hydrogels demonstrate diverse application prospects in the field of meniscal injury repair. For instance, a decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM)-based hydrogel system incorporating methacrylated hyaluronic acid (meHA) (Figure 3) has been developed for the precision repair of meniscal injuries (Lee et al., 2025). In vivo tests confirmed the biocompatibility of hydrogels and their integration with native meniscus tissues. Furthermore, advanced 3D bioprinting techniques enabled the fabrication of hybrid hydrogels with biomaterial and mechanical gradients, effectively emulating the zonal properties of meniscus tissue and enhancing cell integration (Figure 4). This study represents a significant advance in meniscus tissue engineering, providing a promising platform for customized regenerative therapies across a range of heterogeneous fibrous connective tissues. This innovative system represents a significant advancement in meniscal repair, effectively addressing the challenges posed by heterogeneous meniscal injuries. The study points out that traditional repair strategies often fail to replicate the complex zonal characteristics of meniscal tissue, resulting in suboptimal healing outcomes. However, although this novel hydrogel system shows promise for precision repair, the research did not investigate the potential long-term effects or durability of engineered tissues in clinical applications, which may constrain the translational relevance of the findings.
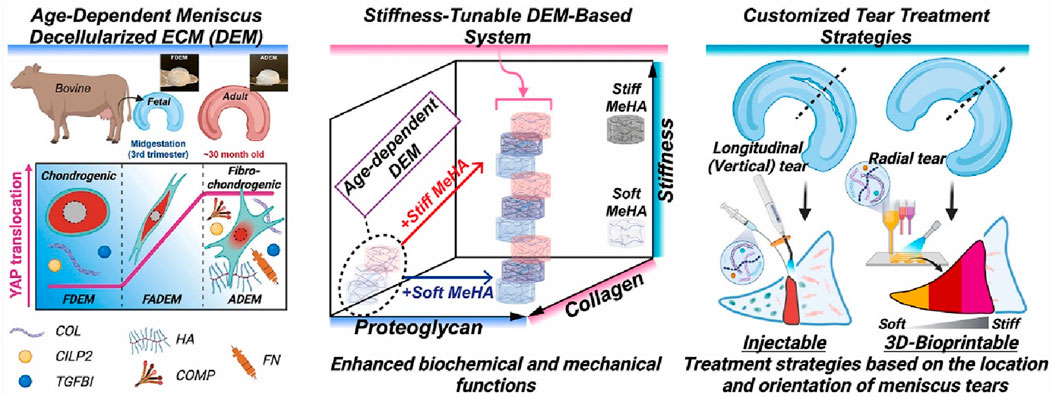
Figure 3. Precision repair of zone-specific meniscal injuries using decellularized extracellular matrix-based hydrogel system incorporating methacrylated hyaluronic acid. Reproduced with permission from ref Lee et al. (2025). Copyright © 2025, The Author(s).
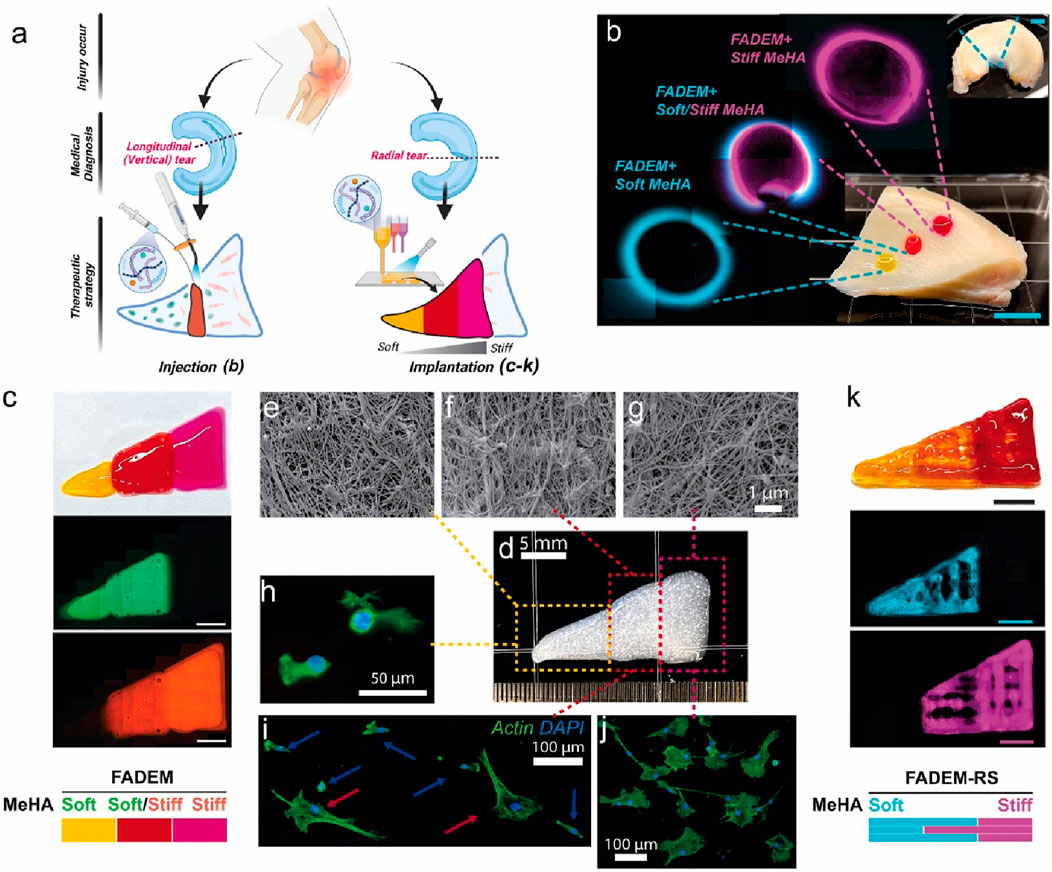
Figure 4. Targeted Meniscus Repair Using Stiffness-Tunable DEM-Based Hydrogels. (a) Illustration of the application of the system. Injection method: (b) injected stiffness-modulated FADEM-based hydrogel in defects in different meniscus zones (scale bar: 5 mm). Implantation method using 3D printed hybrid constructs: (c) images of a bioprinted stiffness-modulated FADEM-based hydrogel. (e–g) Representative FE-SEM images of fibrous structure of printed FADEM-based hydrogels. (h–j) F-actin staining of MSCs cultured on the zone-dependent printed FADEM-based hydrogels. (k) 3D printed lattices of zone-specific FADEM-based hydrogels with the addition of ruthenium/sodium persulfate (scale bars: 5 mm). Reproduced with permission from ref Lee et al. (2025). Copyright © 2025, The Author(s).
In exploring microenvironmental regulation mechanisms, the pentenoic acid-functionalized hyaluronic acid (PHA) hydrogel system provides a platform for investigating mechanotransduction cues in meniscal fibrochondrocytes (MFCs) within the context of meniscal injury repair (Burkey et al., 2023). By modulating the degree of substitution (DoS) of reactive alkene groups, researchers achieved tunable crosslinking density and physical properties (including hydrogel crosslinking density, swelling ratio, and compressive modulus), which subsequently influenced MFC morphology and promoted regenerative phenotypes. This approach highlights the potential of PHA hydrogels for optimizing cellular microenvironments to enhance post-injury meniscal tissue regeneration. The study also indicates that while the developed HA hydrogel system possesses adjustable crosslinked network properties, its degradation rate is inversely correlated with DoS levels (lower DoS = faster degradation), which may compromise long-term structural integrity in physiological environments. Crucially, regulating the surface elastic modulus of these hydrogels was proven to modulate MFC morphology, suggesting that softer hydrogels preferentially induce an inner meniscus-like phenotype. However, the engineered mechanical properties may not fully recapitulate the complex biomechanical niche of the native meniscus, potentially limiting their efficacy in driving functional tissue regeneration.
Current evidence suggests that HA hydrogels hold therapeutic potential for diverse cartilage-related injuries, including meniscal pathologies, through enhanced tissue preservation and mitigation of inflammation-associated damage. However, traditional articular cartilage repair strategies primarily provide short-term symptomatic relief while failing to regenerate functional hyaline cartilage, leading to repaired tissues and adjacent healthy tissues being susceptible to progressive degeneration and mechanical wear over time (Kowalski et al., 2022). Although the developed HA hydrogel shows promise in restoring compromised cartilage biomechanics and suppressing chondrocyte catabolic activity, critical gaps remain in its clinical translation. Relevant studies lack longitudinal data on hydrogel efficacy under physiological loading environments and have not addressed potential limitations across varying injury severities (e.g., focal defects vs advanced degeneration). Furthermore, the interplay between hydrogel degradation kinetics and sustained biomechanical support in weight-bearing joints remains uncharacterized.
In animal model validation, the hyaluronic acid/hydroxypropyl chitin (HA/HPCH) thermosensitive hydrogel demonstrated superior efficacy in promoting the repair of full-thickness meniscal tears in a rabbit model (Wang et al., 2024b) compared to other treatment groups, exhibiting excellent temperature sensitivity, biocompatibility, and enhanced capacity to promote cellular proliferation and migration (Figure 5). The study found that the 2% HA-chitin hydrogel containing transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) displayed the highest glycosaminoglycan (GAG) production, indicating its enhanced ability for matrix formation. After injecting this hydrogel into a rabbit model of full-thickness meniscal tears, at 12 weeks post-implantation, the TGF-β1 + HA/HPCH composite hydrogel showed significantly improved meniscal repair outcomes (Figure 6). The newly formed tissue closely resembled normal meniscal tissue in both structural and biochemical characteristics, outperforming other tested hydrogel formulations and control groups.
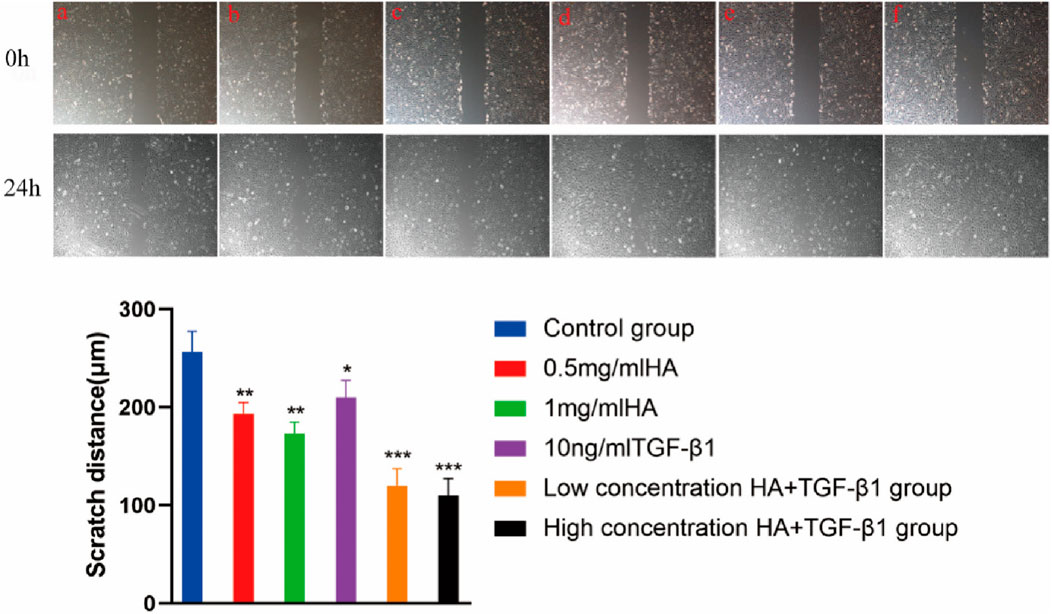
Figure 5. Scratch test image. a Control group; b 0.5 mg/mL HA; c 1 mg/mL HA; d 10 ng/mL TGF-β1; e low concentration HA + TGF-β1; f high concentration HA + TGF-β1. Magnification, Scale bar, 100 µm. Reproduced with permission from ref Wang. et al. (2024b). Copyright© 2024, The Author(s).
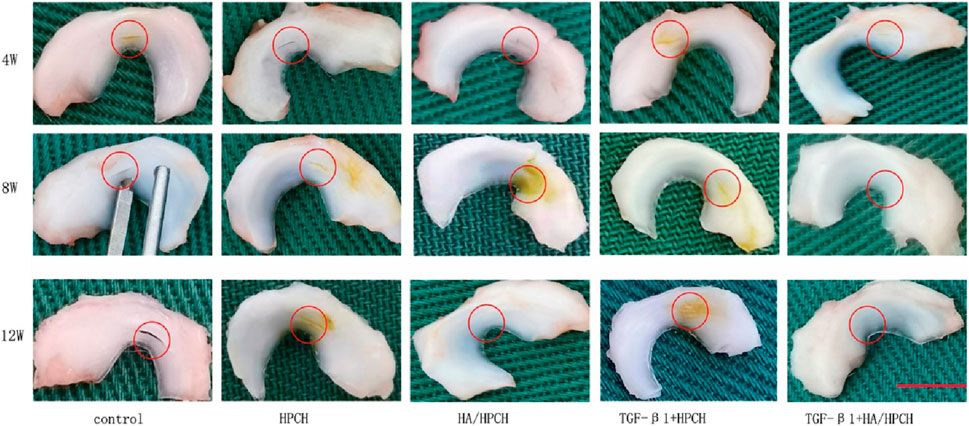
Figure 6. Hyaluronic acid/chitin thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with TGF-β1 promotes meniscus repair in rabbit meniscus full-thickness tear model after (a) 4 weeks, (b) 8 weeks and (c) 12 weeks. Reproduced with permission from ref Wang et al. (2024b). Copyright© 2024, The Author(s).
Another class of promising materials is the polyvinyl alcohol/tannic acid/gelatin/HA (PTGH) hydrogel, which demonstrates favorable mechanical properties and biocompatibility for cartilage tissue engineering applications (Xiang et al., 2023). Although the study primarily focused on articular cartilage repair, the incorporation of HA suggests potential applicability in meniscal injury repair. In vitro cell culture results indicated that PTGH hydrogels exert no negative impact on chondrocyte viability and proliferation, supporting their utility in tissue regeneration contexts, including meniscal injury. However, the biocompatibility of gelatin- and hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels is compromised by rapid degradation kinetics, which may diminish their effectiveness as tissue-engineered scaffolds for cartilage repair and regeneration. Additionally, traditional gelatin and HA hydrogels exhibit suboptimal mechanical properties, limiting their application in load-bearing tissues such as articular cartilage.
HA hydrogels themselves can serve as scaffolds for cell-based therapies to promote meniscal injury repair. These hydrogels support cell culture, improve the microenvironment of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and facilitate effective tissue regeneration. Findings from preclinical studies suggest that combining hydrogels with cell-based treatments may improve the outcomes of meniscus repair strategies (Li et al., 2023). The review highlighted significant variability in cell doses used in clinical trials (ranging from 16 × 106 to 150 × 106 cells), which may affect the consistency and comparability of results across studies. The average dose was found to be 41.52 × 106 cells, indicating a lack of standardized dosing protocols that could impact the efficacy of cell-based therapies for meniscus regeneration. The study notes that while various therapeutic strategies, including co-culture systems and composite materials, show promise for meniscus tissue regeneration, the selection of appropriate strategies must be tailored to the specific nature of the injury. This suggests that no universal approach exists, and the complexity of injury patterns may limit the generalizability of preclinical findings to clinical applications.
To further enhance cellular function, one study investigated the effects of meniscal fibrochondrocyte-derived conditioned medium (CM) and transforming growth factor-β3 (TGF-β3) on transduced mesenchymal stem cells (t-MSCs) (Koh et al., 2017), aiming to enhance their chondrogenic potential for effective meniscal tissue engineering. The methodology involved expanding t-MSCs in CM and encapsulating them within a riboflavin-induced photo-crosslinked collagen-hyaluronic acid (COL-RF-HA) hydrogel, which functions as a cell-supportive scaffold to facilitate tissue regeneration. In vitro results demonstrated that the combination of CM and TGF-β3 significantly upregulated fibrocartilage-associated gene expression (e.g., COL2, SOX9, ACAN, and COL1) and enhanced the production of extracellular matrix (ECM) components critical for tissue repair. In vivo evaluations further revealed that CM-expanded t-MSCs treated with TGF-β3 exhibited optimal performance in cell proliferation, glycosaminoglycan (GAG) accumulation, and collagen deposition, achieving complete regeneration in a meniscal defect model. The study concludes that integrating CM with innovative biomaterial design substantially enhances the chondrogenic differentiation capacity of t-MSCs, thereby promoting meniscal regeneration. This research provides a promising approach to improving meniscal repair strategies, with the potential to improve clinical outcomes for patients with meniscal injuries. However, it should be noted that although the study demonstrated the effects of conditioned medium (CM) and transforming growth factor-β3 (TGF-β3) on transduced mesenchymal stem cells (t-MSCs), it provided limited insights into the molecular-level interaction mechanisms of these factors. The long-term implications of this therapeutic approach, including the durability of regenerated tissue and potential late-onset complications, remain unassessed, constraining the understanding of the proposed method’s long-term efficacy and safety. Furthermore, no direct comparative analysis was conducted between the proposed strategy and established meniscus repair techniques, such as allografts or synthetic implants.
4 Clinical application research
HA hydrogels, distinguished by their exceptional biocompatibility, tunable mechanical properties, and ability to promote tissue regeneration, have emerged as highly promising ideal materials for meniscus repair, with significant progress also achieved in related clinical applications. Taking Hymovis® (manufactured by Fidia Farmaceutici SPA) as an example, it is a hexadecylamide derivative of hyaluronic acid, formulated as a sterile, pyrogen-free, viscoelastic hydrogel for intra-articular injection. It has been used for treating patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis (Pavelka et al., 2020), hip osteoarthritis (Migliore et al., 2020), and meniscal lesions (Zorzi et al., 2014). Clinical trials have substantiated the positive clinical efficacy of such viscosupplements in patients undergoing arthroscopic partial meniscectomy. Studies have demonstrated that intra-articular injection of Hymovis® effectively alleviates patient pain, improves joint mobility, and reduces the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The specific advances of Hymovis® in the clinical application of meniscus repair will be detailed in the following section.
4.1 clinical efficacy evaluation
The clinical efficacy of HA hydrogels in meniscus repair is reflected in improved symptoms, enhanced tissue regeneration, and restored joint function. Clinical studies demonstrate that intra-articular HA hydrogel injections significantly reduce pain, improve joint mobility, and enhance patients’ quality of life (Zorzi et al., 2014). Supporting this, Zorzi et al. recruited 50 participants with degenerative meniscal tears and conducted a single-centre, observer-blinded, parallel-group clinical study to investigate the efficacy of Hymovis® in the management of meniscal tears and meniscal tear repair (Zorzi et al., 2015). Clinical outcomes included pain reduction (Visual Analogue Scale), improved knee function (WOMAC questionnaire), reduced meniscal tear length and depth (MRI-confirmed), and SF-36 questionnaire scores. Clinical assessments were conducted at baseline, as well as on days 14, 30, and 60, to evaluate multiple outcome measures. Results showed that the HYADD4® group exhibited significant pain reduction by day 14 (p < 0.001), with sustained improvements in subsequent follow-ups. Compared to the control group, the HYADD4® group demonstrated significant reductions in meniscal lesion length and depth (p < 0.001). These findings suggest that HYADD4® may represent a novel therapeutic option for the conservative management of patients with painful meniscal tears. MRI data further indicated that this hydrogel formulation might actively contribute to the healing process of meniscal lesions. In conclusion, HYADD4® significantly alleviated pain, improved knee function, and promoted meniscal lesion repair through iA administration, offering a potentially effective treatment strategy for meniscal tear patients. However, limitations of this study include the involvement of a limited number of participants, where the small sample size may compromise the reliability of conclusions. The relatively short follow-up period restricted the ability to assess long-term therapeutic efficacy and safety. Despite demonstrating clinical benefits, the study did not explore the biological mechanisms underlying the observed improvements.
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) and meniscal tears (MT) are two of the most common knee injuries, significantly impacting patients’ quality of life (QoL). A non-interventional, prospective, multicenter study involving 165 patients with KOA and/or MT evaluated the effects of intra-articular Hymovis® injection on QoL, physical mobility, and satisfaction levels in patients with isolated KOA, isolated MT, or both conditions (Balius et al., 2023). Results demonstrated significant QoL improvement (>80%) across all three patient groups, with statistically significant improvements (p < 0.001) in both KOOS and WOMAC scores compared to baseline; post-treatment enhancements were observed in physical activity levels, sports and recreational capacity, and treatment satisfaction (p < 0.001), while pain symptoms also significantly improved (p < 0.05) across all groups, collectively demonstrating that Hymovis® intra-articular injection improves quality of life, physical function, and clinical outcomes in patients with KOA, MT, or both comorbidities.
Degenerative meniscus lesion (DML) presents in adult patients (35–65 years of age) who have not had a trauma and consists in a progressive delamination and surface fibrillation. Bertondenet et al. evaluated the clinical efficacy and healing effects of conservative management of DMLs with Hymovis® (Berton et al., 2020). Significant improvements were observed between baseline and follow-up in WOMAC scores, physical function, patient global assessment (ptGA), clinician global assessment (CoGA), and SF-36 indices (Lam et al., 2014). The treatment demonstrated good tolerability, with only one patient requiring further surgical intervention (arthroscopic partial meniscectomy) 1 year post-treatment. This study supports the use of HA in the conservative management of DML, as evidenced by T2 measurements in MRI scans, indicating HA’s clinical efficacy in enhancing meniscal healing processes. A major limitation highlighted is the lack of evaluation correlating treatment outcomes with the degree of meniscal degeneration. HA’s therapeutic effects may vary depending on the severity of degeneration, and the high degenerative status of enrolled patients may influence the observed results.
4.2 Safety
Hyaluronan-based hydrogels demonstrate good safety and tolerance profiles, with a low incidence of adverse events reported in clinical applications (Migliore et al., 2009; Humphries et al., 2025). This is supported by multiple meta-analyses that have evaluated the differences in safety between intra-articular hyaluronic acid (IAHA) and intra-articular placebo control (Bellamy et al., 2006; Bannuru et al., 2015). A Cochrane review encompassing 76 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) was unable to draw definitive conclusions regarding the safety of HA products due to sample size limitations; however, it found no serious safety concerns. Furthermore, IAHA demonstrated efficacy comparable to systemic therapies (such as oral NSAIDs), though with a higher incidence of local reactions and a lower incidence of systemic adverse events (Bellamy et al., 2006). Reinforcing this view, multiple other meta-analyses also consistently conclude that HA demonstrates good tolerance, with a low incidence of adverse events and an absence of serious risk (Strand et al., 2015; Bannuru et al., 2016a; Bannuru et al., 2016b). However, it is noteworthy that most previous meta-analyses on the safety of IAHA relied solely on published data, where underreporting of safety data is common. Furthermore, these analyses did not adequately account for the concurrent use of oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) by patients in some clinical trials. Both factors may have compromised the accuracy of the safety assessments. Additionally, a contrasting finding comes from a 2012 meta-analysis which reported that IAHA may be associated with an increased risk of serious adverse events (Rutjes et al., 2012).
4.3 Combined therapeutic strategies
The combined application of hyaluronan-based hydrogels with other therapeutic approaches demonstrates synergistic effects in meniscus injury repair, leading to further enhanced treatment outcomes. Firstly, hyaluronan hydrogels serve as effective carriers for stem cells, promoting their colonization and differentiation at the injury site, thereby augmenting tissue regeneration. For example, studies indicate that combined therapy utilizing hyaluronan hydrogels and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) significantly improves the regenerative capacity and functional recovery of meniscal tissue (Rhim et al., 2021). Secondly, hyaluronan hydrogels possess the ability to adsorb and provide sustained release of bioactive factors, such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), enhancing their biological activity. Illustrating this, combination therapy employing hyaluronan hydrogels with TGF-β has been shown to significantly promote the synthesis and remodeling of the meniscal ECM (Ding et al., 2022). Thirdly, hyaluronan hydrogel treatment combined with physical therapy modalities, including functional exercises and electrical stimulation, can further improve joint function and alleviate pain. For instance, clinical research demonstrates that the combination of hyaluronan hydrogels and physical therapy significantly enhances patients’ knee joint functional scores and quality of life (Onu et al., 2024).
5 Limitations and future perspectives
Despite demonstrating significant potential in meniscal injury repair, current research on hyaluronan-based hydrogels faces limitations in three key aspects: material properties, clinical study design, and scope of application. Firstly, insufficient mechanical strength (as mentioned in section 2.2.2), uncontrolled degradation rates, and functional simplicity hinder their ability to meet the demands of complex injury repair. Secondly, clinical studies are commonly constrained by small sample sizes, short follow-up periods, and a lack of rigorous control groups, compromising the reliability and generalizability of findings. Finally, their applicability remains limited primarily to mild-to-moderate injuries, with further restrictions imposed by individual variability and high costs, presenting barriers to personalized treatment and widespread clinical adoption. Therefore, the development of personalised treatment and the clinical translation of HA hydrogels in this field still face two core obstacles. One of these challenges stems from the complex anatomical structure and dynamic biological environment of the meniscus. The precise dimensions, curvature, and mechanical gradients of the injured area must be customised using high-precision MRI data, but the degradation rate of the hydrogel is difficult to match the highly variable concentrations of synovial inflammatory factors in individual patients. Additionally, biofunctional customisation faces a dilemma: high cross-linking density can bear weight but inhibits cell migration, while low cross-linking promotes regeneration but may cause rapid collapse. The practical requirement for low viscosity during arthroscopic injection further complicates the balance of material properties. On the other hand, cost and manufacturing bottlenecks permeate the entire chain from R&D to payment. Personalised manufacturing relies on expensive raw materials and processes, with regulatory and clinical translation costs being particularly prominent. Long-term MRI follow-up and cold chain transportation continue to drive up expenses.
Future research should prioritize optimizing the mechanical properties, degradation kinetics, and functional diversity of hyaluronan hydrogels; conducting large-scale, multi-center randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with extended follow-up to comprehensively evaluate efficacy and safety; and exploring their potential for complex injuries while integrating complementary therapeutic approaches to enhance repair outcomes. Additionally, refining manufacturing processes to reduce costs is essential to facilitate broader clinical implementation, thereby enabling safe and effective treatment for more patients.
Looking further ahead, future development directions for hyaluronan hydrogels in meniscal repair encompass three domains: 1) Materials science innovation (developing smart hydrogels responsive to pH/temperature/enzymes, functionalizing with cell-adhesive peptides or growth factor binding sites, and creating composites with collagen/chitosan to enhance mechanical strength, bioactivity, and multifunctionality); 2) Personalized medicine strategies (designing precision treatment plans based on individual patient profiles, utilizing biomarkers to assess injury severity and repair progression, and developing tailored delivery systems); and 3) Novel technologies/methods (leveraging gene editing like CRISPR-Cas9 to modulate cellular regeneration, integrating mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) into hydrogel composite systems, and employing advanced imaging such as MRI for real-time repair monitoring). These innovations will drive efficient and precise applications of hyaluronan hydrogels, offering safer and more personalized therapeutic solutions.
6 Conclusion
Hyaluronan-based hydrogels exhibit substantial promise for meniscal injury repair and cell culture applications. Their capacity to mimic the native ECM, support cellular growth and differentiation, and deliver therapeutic agents establishes them as invaluable tools in tissue engineering. Despite persistent challenges, ongoing research and advancements in hydrogel technology hold significant potential to overcome current limitations, paving the way for clinical translation and widespread adoption in meniscal repair.
Author contributions
GW: Writing – original draft. XL: Writing – original draft. XZ: Writing – review and editing. MH: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research work was supported by the Shenyang Bureau of Science and Technology (No.24-214-3-129).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adams, B. G., Houston, M. N., and Cameron, K. L. (2021). The epidemiology of meniscus injury. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 29 (3), e24–e33. doi:10.1097/jsa.0000000000000329
Baek, J., Fan, Y., Jeong, S. H., Lee, H. Y., Jung, H. D., Kim, H. E., et al. (2018). Facile strategy involving low-temperature chemical cross-linking to enhance the physical and biological properties of hyaluronic acid hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 202, 545–553. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.014
Bai, Q., Gao, Q., Hu, F., Zheng, C., Chen, W., Sun, N., et al. (2023). Chitosan and hyaluronic-based hydrogels could promote the infected wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 232, 123271. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123271
Balius, R., Guillermo, Á. R., Fernando, B. P., Miguel, D. M., Enrique, G. O., Alberto, G. M., et al. (2023). Evaluation of quality-of-life following treatment with hymovis in patients with knee osteoarthritis and/or meniscal tear.
Bannuru, R. R., Brodie, C. R., Sullivan, M. C., and McAlindon, T. E. (2016b). Safety of repeated injections of sodium hyaluronate (SUPARTZ) for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cartilage 7 (4), 322–332. doi:10.1177/1947603516642271
Bannuru, R. R., Osani, M., Vaysbrot, E. E., and McAlindon, T. (2016a). Comparative safety profile of hyaluronic acid products for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 24 (12), 2022–2041. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2016.07.010
Bannuru, R. R., Schmid, C. H., Kent, D. M., Vaysbrot, E. E., Wong, J. B., and McAlindon, T. E. (2015). Comparative effectiveness of pharmacologic interventions for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 162 (1), 46–54. doi:10.7326/m14-1231
Bellamy, N., Campbell, J., Welch, V., Gee, T. L., Bourne, R., and Wells, G. A. (2006). Viscosupplementation for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014 (2), CD005321. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd005321.pub2
Berton, A., Longo, U. G., Candela, V., Greco, F., Martina, F. M., Quattrocchi, C. C., et al. (2020). Quantitative evaluation of meniscal healing process of degenerative meniscus lesions treated with hyaluronic acid: a clinical and MRI study. J. Clin. Med. 9 (7), 2280. doi:10.3390/jcm9072280
Bian, Y., Wang, H., Zhao, X., and Weng, X. (2022). Meniscus repair: up-to-date advances in stem cell-based therapy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 13 (1), 207. doi:10.1186/s13287-022-02863-7
Buckley, C., Murphy, E. J., Montgomery, T. R., and Major, I. (2022). Hyaluronic acid: a review of the drug delivery capabilities of this naturally occurring polysaccharide. Polymers 14 (17), 3442. doi:10.3390/polym14173442
Burkey, K., Castillo, K., Elrod, P., Suekuni, M. T., Aikman, E., Gehrke, S., et al. (2023). Modulating pentenoate-functionalized hyaluronic acid hydrogel network properties for meniscal fibrochondrocyte mechanotransduction. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 111 (10), 1525–1537. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.37551
Chen, M., Bolognesi, G., and Vladisavljević, G. T. (2021). Crosslinking strategies for the microfluidic production of microgels. Molecules 26 (12), 3752. doi:10.3390/molecules26123752
Ding, G., Du, J., Hu, X., and Ao, Y. (2022). Mesenchymal stem cells from different sources in meniscus repair and regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 796367. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.796367
Faivre, J., Pigweh, A. I., Iehl, J., Maffert, P., Goekjian, P., and Bourdon, F. (2021). Crosslinking hyaluronic acid soft-tissue fillers: current status and perspectives from an industrial point of view. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 18 (12), 1175–1187. doi:10.1080/17434440.2021.2014320
Fuchs, S., Shariati, K., and Ma, M. (2020). Specialty tough hydrogels and their biomedical applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9 (2), 1901396, doi:10.1002/adhm.201901396
Fundarò, S. P., Salti, G., Malgapo, D. M. H., and Innocenti, S. (2022). The rheology and physicochemical characteristics of hyaluronic acid fillers: their clinical implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (18), 10518. doi:10.3390/ijms231810518
Giuffrida, A., Di Bari, A., Falzone, E., Iacono, F., Kon, E., Marcacci, M., et al. (2020). Conservative vs. surgical approach for degenerative meniscal injuries: a systematic review of clinical evidence. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24 (6), 2874–2885. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202003_20651
Gupta, R. C., Lall, R., Srivastava, A., and Sinha, A. (2019). Hyaluronic acid: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic trajectory. Front. Veterinary Sci. 6, 192. doi:10.3389/fvets.2019.00192
Ha, D. I., Lee, S. B., Chong, M. S., Lee, Y. M., Kim, S. Y., and Park, Y. H. (2006). Preparation of thermo-responsive and injectable hydrogels based on hyaluronic acid and poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) and their drug release behaviors. Macromol. Res. 14, 87–93. doi:10.1007/bf03219073
Huang, L., Wang, J., Kong, L., Wang, X., Li, Q., Zhang, L., et al. (2022). ROS-responsive hyaluronic acid hydrogel for targeted delivery of probiotics to relieve colitis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 222, 1476–1486. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.09.247
Huang, Q., Zou, Y., Arno, M. C., Chen, S., Wang, T., Gao, J., et al. (2017). Hydrogel scaffolds for differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46 (20), 6255–6275. doi:10.1039/c6cs00052e
Humphries, D., Baria, M., and Fitzpatrick, J. (2025). Severe acute localized reactions after intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections: a narrative review and physician’s guide to incidence, prevention, and management of these adverse reactions. J. Cartil. Jt. Preserv. 5 (1), 100187. doi:10.1016/j.jcjp.2024.100187
Hwang, J., Kiick, K. L., and Sullivan, M. O. (2022). Modified hyaluronic acid-collagen matrices trigger efficient gene transfer and prohealing behavior in fibroblasts for improved wound repair. Acta Biomater. 150, 138–153. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2022.07.039
Jabbari, F., Babaeipour, V., and Saharkhiz, S. (2023). Comprehensive review on biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with different molecular weights and its biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 240, 124484. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124484
Khanlari, A., Schulteis, J. E., Suekama, T. C., Detamore, M. S., and Gehrke, S. H. (2015). Designing crosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties for biomedical applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 132 (22). doi:10.1002/app.42009
Khunmanee, S., Jeong, Y., and Park, H. (2017). Crosslinking method of hyaluronic-based hydrogel for biomedical applications. J. Tissue Eng. 8, 2041731417726464. doi:10.1177/2041731417726464
Koh, R. H., Jin, Y., Kang, B. J., and Hwang, N. S. (2017). Chondrogenically primed tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in riboflavin-induced photocrosslinking collagen-hyaluronic acid hydrogel for meniscus tissue repairs. Acta Biomater. 53, 318–328. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2017.01.081
Kong, W., Gao, Y., Liu, Q., Dong, L., Guo, L., Fan, H., et al. (2020). The effects of chemical crosslinking manners on the physical properties and biocompatibility of collagen type I/hyaluronic acid composite hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 160, 1201–1211. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.208
Kowalski, M. A., Fernandes, L. M., Hammond, K. E., Labib, S., Drissi, H., and Patel, J. M. (2022). Cartilage-penetrating hyaluronic acid hydrogel preserves tissue content and reduces chondrocyte catabolism. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 16 (12), 1138–1148. doi:10.1002/term.3352
Laffleur, F., Bachleitner, K., Millotti, G., Lagast, J., Veider, F., and Bernkop-Schnürch, A. (2025). The progress of hyaluronic acid’s application in therapeutic delivery. Ther. Deliv. 16, 673–685. doi:10.1080/20415990.2025.2483150
Lam, J., Truong, N. F., and Segura, T. (2014). Design of cell–matrix interactions in hyaluronic acid hydrogel scaffolds. Acta biomater. 10 (4), 1571–1580. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2013.07.025
Lee, S. H., Li, Z., Zhang, E. Y., Kim, D. H., Huang, Z., Heo, Y., et al. (2025). Precision repair of zone-specific meniscal injuries using a tunable extracellular matrix-based hydrogel system. Bioact. Mater. 48, 400–413. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.02.013
Li, C., Deng, R., Yang, M., Yuan, F., Zhang, C., and Yu, J. (2024). Advanced hydrogel material for meniscus repair. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34 (16), 2312276. doi:10.1002/adfm.202312276
Li, H., Qi, Z., Zheng, S., Chang, Y., Kong, W., Fu, C., et al. (2019). The application of hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels in bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 1–12. doi:10.1155/2019/3027303
Li, X., Li, D., Li, J., Wang, G., Yan, L., Liu, H., et al. (2023). Preclinical studies and clinical trials on cell-based treatments for meniscus regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 29 (6), 634–670. doi:10.1089/ten.teb.2023.0050
Liang, M., Dong, L., Guo, Z., Liu, L., Fan, Z., Wei, C., et al. (2023). Collagen–hyaluronic acid composite hydrogels with applications for chronic diabetic wound repair. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 9 (9), 5376–5388. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c00695
Lombardo, M. D. M., Mangiavini, L., and Peretti, G. M. (2021). Biomaterials and meniscal lesions: current concepts and future perspective. Pharmaceutics 13 (11), 1886. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13111886
Luo, Z., Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Wang, J., and Yu, Y. (2023). Modification and crosslinking strategies for hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel biomaterials. Smart Med. 2 (4), e20230029. doi:10.1002/smmd.20230029
Mameri, E. S., Dasari, S. P., Fortier, L. M., Verdejo, F. G., Gursoy, S., Yanke, A. B., et al. (2022). Review of meniscus anatomy and biomechanics. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 15 (5), 323–335. doi:10.1007/s12178-022-09768-1
Marinho, A., Nunes, C., and Reis, S. (2021). Hyaluronic acid: a key ingredient in the therapy of inflammation. Biomolecules 11 (10), 1518. doi:10.3390/biom11101518
McDermott, I. D., and Amis, A. A. (2006). The consequences of meniscectomy. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 88 (12), 1549–1556. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.88b12.18140
Migliore, A., Frediani, B., Gigliucci, G., Foti, C., Crimaldi, S., De Lucia, O., et al. (2020). Efficacy of a single intra-articular HYMOVIS ONE injection for managing symptomatic hip osteoarthritis: a 12-month follow-up retrospective analysis of the ANTIAGE register data. Orthop. Res. Rev. 12, 19–26. doi:10.2147/orr.s239355
Migliore, A., Massafra, U., Bizzi, E., Vacca, F., Martin-Martin, S., Granata, M., et al. (2009). Comparative, double-blind, controlled study of intra-articular hyaluronic acid (Hyalubrix®) injections versus local anesthetic in osteoarthritis of the hip. Arthritis Res. Ther. 11, R183. doi:10.1186/ar2875
Mohammed, M., Devnarain, N., Elhassan, E., and Govender, T. (2022). Exploring the applications of hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles for diagnosis and treatment of bacterial infections. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechn. 14 (4), e1799. doi:10.1002/wnan.1799
Murakami, T., Otsuki, S., Okamoto, Y., Nakagawa, K., Wakama, H., Okuno, N., et al. (2019). Hyaluronic acid promotes proliferation and migration of human meniscus cells via a CD44-dependent mechanism. Connect. tissue Res. 60 (2), 117–127. doi:10.1080/03008207.2018.1465053
Nasution, H., Harahap, H., Dalimunthe, N. F., Ginting, M. H. S., Jaafar, M., Tan, O. O. H., et al. (2022). Hydrogel and effects of crosslinking agent on cellulose-based hydrogels: a review. Gels 8 (9), 568. doi:10.3390/gels8090568
Onu, I., Gherghel, R., Nacu, I., Cojocaru, F. D., Verestiuc, L., Matei, D. V., et al. (2024). Can combining hyaluronic acid and physiotherapy in knee Osteoarthritis improve the physicochemical properties of synovial fluid? Biomedicines 12 (2), 449. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12020449
Pasiński, M., Zabrzyńska, M., Adamczyk, M., Sokołowski, M., Głos, T., Ziejka, M., et al. (2023). A current insight into human knee menisci. Transl. Res. Anat. 32, 100259. doi:10.1016/j.tria.2023.100259
Pavelka, K., Bernetti, A., Giordan, N., Dokoupilová, E., and Santilli, V. (2020). Dose-response of hyaluronate-based viscoelastic hydrogels for the treatment of knee osteoarthrosis: a prospective, randomized, comparative clinical trial. Minerva Ortop. Traumatol. 71 (2), 44–55. doi:10.23736/s0394-3410.20.03967-3
Popper, H. R., Fliegel, B. E., Elliott, D. M., and Su, A. W. (2023). Surgical management of traumatic meniscus injuries. Pathophysiology 30 (4), 618–629. doi:10.3390/pathophysiology30040044
Qian, C., Zhang, T., Gravesande, J., Baysah, C., Song, X., and Xing, J. (2019). Injectable and self-healing polysaccharide-based hydrogel for pH-responsive drug release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 123, 140–148. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.048
Qiu, H., Deng, J., Wei, R., Wu, X., Chen, S., Yang, Y., et al. (2023). A lubricant and adhesive hydrogel cross-linked from hyaluronic acid and chitosan for articular cartilage regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 243, 125249. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125249
Rhim, H. C., Jeon, O. H., Han, S. B., Bae, J. H., Suh, D. W., and Jang, K. M. (2021). Mesenchymal stem cells for enhancing biological healing after meniscal injuries. World J. Stem Cells 13 (8), 1005–1029. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v13.i8.1005
Rong, L., Liu, Y., Fan, Y., Xiao, J., Su, Y., Lu, L., et al. (2023). Injectable nano-composite hydrogels based on hyaluronic acid-chitosan derivatives for simultaneous photothermal-chemo therapy of cancer with anti-inflammatory capacity. Carbohydr. Polym. 310, 120721. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120721
Rosales, P., Vitale, D., Icardi, A., Sevic, I., and Alaniz, L. (2024). Role of hyaluronic acid and its chemical derivatives in immunity during homeostasis, cancer and tissue regeneration. Seminars Immunopathol. 46 (5), 15. doi:10.1007/s00281-024-01024-7
Rutjes, A. W. S., Jüni, P., da Costa, B. R., Trelle, S., Nüesch, E., and Reichenbach, S. (2012). Viscosupplementation for osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 157 (3), 180–191. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-157-3-201208070-00473
Salathia, S., Gigliobianco, M. R., Casadidio, C., Di Martino, P., and Censi, R. (2023). Hyaluronic acid-based nanosystems for CD44 mediated anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (8), 7286. doi:10.3390/ijms24087286
Sapuła, P., Białik-Wąs, K., and Malarz, K. (2023). Are natural compounds a promising alternative to synthetic cross-linking agents in the preparation of hydrogels? Pharmaceutics 15 (1), 253. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15010253
Sari, M. A. I. P., and Kurniawati, I. (2022). Physiotherapy management in meniscus injury. Kinesiol. Physiother. Compr. 1 (1), 19–21. doi:10.62004/kpc.v1i1.4
Shi, C., Zhang, Y., Wu, G., Zhu, Z., Zheng, H., Sun, X., et al. (2024). Hyaluronic acid-based reactive oxygen species-responsive multifunctional injectable hydrogel platform accelerating diabetic wound healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13 (4), 2302626. doi:10.1002/adhm.202302626
Šoltés, L., Mendichi, R., Kogan, G., Schiller, J., Stankovská, M., and Arnhold, J. (2006). Degradative action of reactive oxygen species on hyaluronan. Biomacromolecules 7 (3), 659–668. doi:10.1021/bm050867v
Strand, V., McIntyre, L. F., Beach, W. R., and Block, J. (2015). Safety and efficacy of US-approved viscosupplements for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, saline-controlled trials. J. Pain Res. 8, 217–228. doi:10.2147/jpr.s83076
Su, C. Y., Lu, Y. F., Lu, Y. C., Huang, C. H., and Fang, H. W. (2023). Potential lubricating mechanism of hyaluronic acid for a reduction of albumin-mediated friction in the artificial joint system. Lubricants 11 (5), 210. doi:10.3390/lubricants11050210
Svarca, A., Grava, A., Dubnika, A., Ramata-Stunda, A., Narnickis, R., Aunina, K., et al. (2022). Calcium phosphate/hyaluronic acid composite hydrogels for local antiosteoporotic drug delivery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 917765. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.917765
Tam, R. Y., Smith, L. J., and Shoichet, M. S. (2017). Engineering cellular microenvironments with photo-and enzymatically responsive hydrogels: toward biomimetic 3D cell culture models. Accounts Chem. Res. 50 (4), 703–713. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00543
Teng, B., Zhang, S., Pan, J., Zeng, Z., Chen, Y., Hei, Y., et al. (2021). A chondrogenesis induction system based on a functionalized hyaluronic acid hydrogel sequentially promoting hMSC proliferation, condensation, differentiation, and matrix deposition. Acta Biomater. 122, 145–159. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2020.12.054
Tsanaktsidou, E., Kammona, O., and Kiparissides, C. (2022). Recent developments in hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering applications. Polymers 14 (4), 839. doi:10.3390/polym14040839
Valachová, K., and Šoltés, L. (2021). Hyaluronan as a prominent biomolecule with numerous applications in medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (13), 7077. doi:10.3390/ijms22137077
Wang, H., Wu, J., Yang, L., Liu, S., Sui, X., Guo, Q., et al. (2024a). Surgical therapy and tissue engineering for meniscal repair. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 31 (3), 284–296. doi:10.1089/ten.teb.2024.0060
Wang, S., Tavakoli, S., Parvathaneni, R. P., Nawale, G. N., Oommen, O. P., Hilborn, J., et al. (2022). Dynamic covalent crosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogels and nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Biomaterials Sci. 10 (22), 6399–6412. doi:10.1039/d2bm01154a
Wang, Y., Wen, F., Yao, X., Zeng, L., Wu, J., He, Q., et al. (2021). Hybrid hydrogel composed of hyaluronic acid, gelatin, and extracellular cartilage matrix for perforated TM repair. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9, 811652. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2021.811652
Wang, Z., Huang, W., Jin, S., Gao, F., Sun, T., He, Y., et al. (2024b). Hyaluronic acid/chitin thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with TGF-β1 promotes meniscus repair in rabbit meniscus full-thickness tear model. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 19 (1), 683. doi:10.1186/s13018-024-05144-6
Weber, G. C., Buhren, B. A., Schrumpf, H., Wohlrab, J., and Gerber, P. A. (2019). “Clinical applications of hyaluronidase,” in Therapeutic enzymes: function and clinical implications. Editor M. Eghtedari (Singapore: Springer), 255–277.
Xiang, C., Guo, Z., Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Chen, W., Li, X., et al. (2023). Fabrication and characterization of porous, degradable, biocompatible poly (vinyl alcohol)/tannic acid/gelatin/hyaluronic acid hydrogels with good mechanical properties for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Biomaterials Sci. Polym. Ed. 34 (16), 2198–2216. doi:10.1080/09205063.2023.2230855
Xu, Q., Torres, J. E., Hakim, M., Babiak, P. M., Pal, P., Battistoni, C. M., et al. (2021). Collagen-and hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels and their biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 146, 100641. doi:10.1016/j.mser.2021.100641
Xu, X., Zeng, Z., Huang, Z., Sun, Y., Huang, Y., Chen, J., et al. (2020). Near-infrared light-triggered degradable hyaluronic acid hydrogel for on-demand drug release and combined chemo-photodynamic therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 229, 115394. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115394
Xu, Z., Liu, G., Liu, P., Hu, Y., Chen, Y., Fang, Y., et al. (2022). Hyaluronic acid-based glucose-responsive antioxidant hydrogel platform for enhanced diabetic wound repair. Acta biomater. 147, 147–157. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2022.05.047
Yang, C., Wang, X., Yao, X., Zhang, Y., Wu, W., and Jiang, X. (2015). Hyaluronic acid nanogels with enzyme-sensitive cross-linking group for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 205, 206–217. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.02.008
Yang, X., Li, X., Wu, Z., and Cao, L. (2023). Photocrosslinked methacrylated natural macromolecular hydrogels for tissue engineering: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 246, 125570. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125570
Yasin, A., Ren, Y., Li, J., Sheng, Y., Cao, C., and Zhang, K. (2022). Advances in hyaluronic acid for biomedical applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 910290. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.910290
Zhang, R., Li, X., He, K., Sheng, X., Deng, S., Shen, Y., et al. (2017). Preparation and properties of redox responsive modified hyaluronic acid hydrogels for drug release. Polym. Adv. Technol. 28 (12), 1759–1763. doi:10.1002/pat.4059
Zhang, Z., and Christopher, G. F. (2015). The nonlinear viscoelasticity of hyaluronic acid and its role in joint lubrication. Soft Matter 11 (13), 2596–2603. doi:10.1039/c5sm00131e
Zhao, W., Li, Y., Zhang, X., Zhang, R., Hu, Y., Boyer, C., et al. (2020). Photo-responsive supramolecular hyaluronic acid hydrogels for accelerated wound healing. J. Control. release 323, 24–35. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.04.014
Zorzi, C., Rigotti, S., Giordan, N., Madonna, V., Condello, V., Cortese, F., et al. (2014). Randomized, single center, observer-blind, parallel-group trial to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of HYADD® 4-G a viscoelastic hydrogel, for the treatment of meniscus tear. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 22, S194. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2014.02.369
Keywords: meniscus injury, hyaluronic acid hydrogel, meniscus repair, cell carrier, tissue engineering, regenerative medicine
Citation: Wang G, liu XJ, Zhang X-a and Hu M (2025) Advances in hyaluronic acid hydrogel for meniscus repair. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1639034. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1639034
Received: 01 June 2025; Accepted: 02 July 2025;
Published: 21 July 2025.
Edited by:
Dan Li, Jinzhou Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Wang, liu, Zhang and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mingjie Hu, aG1qODExMTE5QDE2My5jb20=; Xin-an Zhang, emhhbmd4YTI3MjVAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Guangxin Wang
Guangxin Wang Xiao Jun liu2
Xiao Jun liu2 Xin-an Zhang
Xin-an Zhang Mingjie Hu
Mingjie Hu