- 1Department of Orthopedics, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China
- 2Key Laboratory for Regenerative Medicine of the Ministry of Education of China, School of Biomedical Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, Hong Kong SAR, China
- 3National Center for Orthopaedics, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 4Beijing Key Lab of Regenerative Medicine in Orthopedics, Key Laboratory of Musculoskeletal Trauma & War Injuries PLA, Institute of Orthopedics, The First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
- 5Department of Orthopedics, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China
- 6Institute of Hemu Biotechnology, Beijing Hemu Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China
Tendinopathy treatment is hindered by persistent inflammation and irreversible matrix degradation, with current therapies offering transient symptom relief without addressing disease progression. Here, we developed an mRNA-based anti-inflammatory strategy utilizing SM102 lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to deliver interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (Il1rn) mRNA for tendon repair. SM102-LNPs demonstrated efficient transfection of primary tendon stem cells, sustaining IL-1RA protein expression for over 72 h and neutralizing IL-1β-induced inflammatory cascades. In vitro, IL-1RA suppressed pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, iNOS), restored collagen I/III balance, and enhanced cell migration. In collagenase-induced tendinopathy mice, a single SM102-Il1rn mRNA injection attenuated inflammation, reduced MMP1/13 expression, and improved collagen alignment within 1 week. By 4 weeks, treated tendons exhibited functional recovery with normalized gait patterns. Transcriptomics revealed dual modulation of IL-1 signaling and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling pathways, alongside macrophage polarization and oxidative stress regulation. Systemic safety was confirmed by unaltered serum biomarkers and organ histology. This SM102-Il1rn mRNA therapy enables spatiotemporally controlled anti-inflammatory therapy, providing a promising non-surgical solution for refractory tendinopathies. Its adaptable design allows expansion to other regenerative targets, advancing precision treatment for musculoskeletal degeneration.
1 Introduction
Tendinopathy, as a common degenerative disease in the musculoskeletal system, has a high incidence rate among professional athletes and the elderly population (Kwan et al., 2023; Loiacono et al., 2019). Its pathological features are characterized by abnormal activation of pro-inflammatory factors, accelerated degradation of type I collagen due to upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases, and elevated expression of fibrosis-related genes (Loiacono et al., 2019; Millar et al., 2021; Riley, 2008; Morita et al., 2017). Disordered collagen structure and loss of biomechanical function of the tendon triggered clinical symptoms such as pain and swelling (Millar et al., 2021). The main clinical treatments for tendinopathy include NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, and physical therapy, but this therapy can only provide short-term symptom relief and cannot reverse the degenerative process (Andres and Murrell, 2008; Adjei-Sowah et al., 2024). Moreover, pieces of evidence supported that the use of NSAIDs and glucocorticoids may elevate the risk of tendon rupture and toxic tendinopathy (Coombes et al., 2010; Canosa-Carro et al., 2022).
In recent years, the regulation of the inflammatory microenvironment has become an important direction in tendon repair research (Chisari et al., 2020). The interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA), as an endogenous anti-inflammatory protein, blocks the IL-1β signaling pathway by competitively binding to IL-1R1 receptors (Arend, 1993; Gabay et al., 2010). Clinical and pre-clinical studies have shown the good safety and efficacy of recombinant IL-1RA (commercially known as “anakinra”) in treating osteoarthritis (Iqbal and Fleischmann, 2007; Pelletier et al., 1997; Nuki et al., 2002; Fleischmann et al., 2006). In the field of tendon diseases, local injection of recombinant IL-1RA protein can significantly improve the pathological process of rat tendonitis models (Berkoff et al., 2016; Eskildsen et al., 2019). However, this protein has limitations such as a short half-life (4–6 h), poor stability, and susceptibility to degradation, necessitating frequent injections (Nuki et al., 2002; Fleischmann et al., 2006; Tarighi et al., 2021; Dahlén et al., 2008; Yang et al., 2019).
Recent advancements in regenerative approaches have highlighted the potential of nucleic acid-based interventions, with mRNA delivery platforms demonstrating particular promise as clinically applicable treatment strategies (Balmayor, 2022). Compared with traditional DNA therapy, mRNA can be translated and expressed without entering the cell nucleus, fundamentally avoiding the risk of genome integration (Hou et al., 2021; Sahin et al., 2014). Its time-limited expression feature (usually lasting for several days) and dose controllability are particularly suitable for the treatment of inflammatory diseases that require precise regulation (Hou et al., 2021; Sahin et al., 2014; Weissman, 2015). In selecting delivery systems, lipid nanoparticles (LNP) stand out due to their mature preparation process and verified safety (Sahin et al., 2014). The core component, ionizable lipid SM102, promotes endosomal escape through a pH-responsive mechanism, and its delivery efficiency has been confirmed in the muscle tissue transfection of the COVID-19 vaccine (Schoenmaker et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2023). However, the potential application of this delivery system in tendon tissues still needs to be verified.
Our study was the first to demonstrate that mRNA delivery mediated by SM102-LNP can be used to treat tendinitis. In vitro experiments have shown that SM102-LNP can efficiently transfect primary tendon stem cells and maintain the expression of target genes for at least 72 h. Meanwhile, tendon stem cells transfected with SM102- Il1rn mRNA can synthesize and secrete bioactive IL-1RA and provide a protective effect on tendon stem cells under IL-1β stimulation. In vivo experiments have proved that a single injection of SM102 LNPs/mRNA complex can successfully deliver mRNA to tendon tissue cells. Local injection of SM102- Il1rn mRNA at the tendon site could inhibit inflammation, accelerate the repair of tendon tissue structure and function, and exhibit good biological safety. The SM102 LNPs delivery system has the advantage of modular design. By replacing the coding sequence, it can be flexibly expanded to deliver other anti-inflammatory factors such as IL-10 and TGF-β inhibitors. In the future, by optimizing the tendon targeting of LNP, this strategy is expected to provide a new non-surgical intervention scheme for refractory tendon diseases and has important clinical application prospects.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 mRNA synthesis
The mRNA (GFP or mouse Il1rn)was synthesized via in vitro transcription (IVT). Briefly, the coding sequence (CDS) of EGFP or mouse Il1rn was inserted into the IVT template plasmid. The CDS was flanked by a T7 promoter and a poly(A) tail sequence. The plasmid was linearized through restriction enzyme digestion, and the mRNA was transcribed. After purification, the size and purity of the synthesized mRNA were analyzed by denaturing agarose gel electrophoresis. The concentration of mRNA was determined by Nanodrop (A260/A280 ratio ∼2.0).
2.2 SM102 lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulation and mRNA encapsulation
The SM102-LNP formulation was prepared as previously described (Hassett et al., 2019). Briefly, ionizable lipid (SM102), Phospholipid (DSPC) Cholesterol, and PEGylated lipid (DMG-PEG2000) were dissolved in ethanol with a mass ratio of 50:10:38.5:1.5. The LNPs containing mRNA were assembled via the microfluidic device. RNA was dissolved in citrate buffer (pH 4.0, 50 mM) and the aqueous phase and organic phase were combined at a 3:1 volumetric ratio, achieving rapid mixing in a staggered herringbone micromixer. The SM102-LNP/mRNA complexes were diluted in RNase-free PBS buffer and purified using a cutoff membrane (30 kDa). The final concentration of mRNA was 60 μg/mL and the sucrose in PBS was 10%. Efficiency was determined by Quant-iT RiboGreen RNA Assay Kit according to the user’s instructions. Particle Size and Polydispersity Index (PDI, DLS) were measured by Dynamic light scattering. The morphology of SM102 LNPs-Il1rn was observed using transmission electron microscopy (JEOL).
2.3 Cell culture and transfection
Mouse primary tendon stem cells (purchased from Wuhan Pricella Biotechnology Co., Ltd., CP-M176) and HEK293T (purchased from Bkmam Holdings Co., Ltd., CL0005) were cultured in complete growth medium (DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin) at 37°C with 5% CO2. Cells were seeded at an appropriate density. On the 2nd day, the cells were incubated with SM102 LNPs-GFP mRNA. The GFP signals were checked under fluorescent microscopy at the indicated time point post-transfection. For flow cytometry, at 48 h post-transfection, cells were trypsinized, and the GFP+ cell populations were quantified. Untransfected cells served as negative controls.
2.4 IL-1RA expression analysis
Mouse primary tendon stem cells or HEK293T cells were seeded cells in 12-well plates (1 × 105 cells/well) and were incubated with SM102 LNPs- l1rn mRNA with indicated dosage. Supernatants were collected at the indicated time point post-transfection and IL-1RA levels were quantified by ELISA (ABclonal, RK04182) following kit instructions. The size of IL-1RA secreted by transfected cells was analyzed by Western blotting, with Recombinant Human IL-1ra Protein Standard (Abcam, ab316382) used as a positive control.
2.5 Quantitative PCR assay
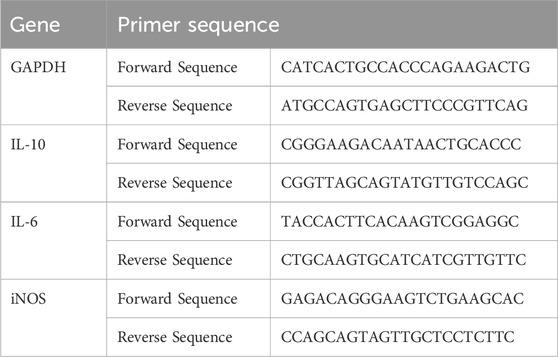
Mouse primary tendon stem cells were seeded at an appropriate density and transfected with SM102-IL-1RA. At 24 h post transfection, the transfected cells were incubated in the presence or absence of 10 ng/mL recombinant mouse IL-1β (SinoBiological, 10139-HNAE). At 24 h post stimulation, the total RNA was extracted using Trizol for qPCR analysis. Primer sequences are listed below:
2.6 Immunofluorescent assay
Primary tendon stem cells were seeded in 24-well plates (2 × 104 cells/well). The cells were incubated with the indicated dose of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA for 24 h. Then the cells with or without transfection were stimulated with 10 ng/mL recombinant mouse IL-1β (SinoBiological, 10139-HNAE) for 24 h. Then the cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 for 10 min, and blocked with 5% BSA for 1 h. Subsequently, cells were incubated with anti-COL1A1 antibody (ABclonal, A24112) or anti-COL3A1 (ABclonal, A3795) at 4°C overnight. After washing, ABflo® 555-conjugated Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H + L) (ABclonal, AS058) (1:500) was added and incubated at room temperature for 1 h. Actin-Tracker Green-488 (C2201S) was then applied at room temperature for 40 min, followed by two PBS washes. Finally, DAPI (1:1000) was incubated in the dark at room temperature for 10 min. Images were captured using a confocal microscope, and fluorescence intensity is quantified with ImageJ.
2.7 Cell scratch assay
The primary tendon stem cells were seeded in 6-well plates, and when the fusion degree reached 90%, a scratch was made using the tip of a 200 μL pipette. Images were taken at fixed positions using an inverted microscope at the indicated time points. The migration rate was calculated as: (initial area - remaining area)/initial area × 100%.
2.8 Establishment of the mouse tendinitis model
Figure 1 illustrated the group designment, details of treatments, and animal experiments timelines. To establish the mouse tendinitis model, 10-week-old male C57BL/6J mice were chosen to receive two injections of 20 μL of collagenase I (5 mg/mL, Gibco, Cat# 17100017) at the midpoint of the right Achilles tendon 7 days and 4 days before the experiment, respectively. Before experiments, the clinical assessments were performed to confirm the induction of tendinitis of the right Achilles tendon. The mice were randomly divided into the untreat group and SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA group (2 µg of RNA per mouse). Healthy mice were used as the control group. Animals were euthanized at the respective endpoints (week 1 and week 4), and the tissue was collected for follow-up analysis. All animal trials received approval from the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of PLA General Hospital (SCXK No. 2019–0018).
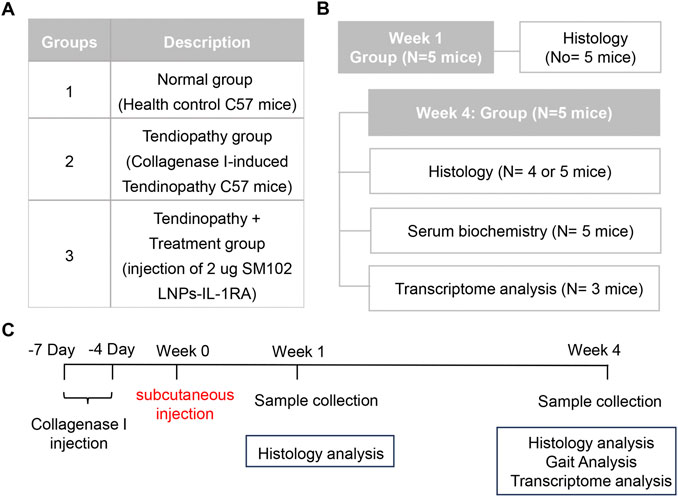
Figure 1. Animal experiment design. (A) A table illustrating group assignments and details of treatments. (B) A table illustrating the number of mice used for each measurement. (C) A diagram demonstrating treatment timelines for groups 2 and 3.
2.9 In vivo fluorescence imaging and analysis
For in vivo imaging, C57BL/6 mice (20–25 g) were anesthetized with isoflurane, and 2 μg of SM102 LNPs-luciferase mRNA were injected into the Achilles tendon using a 30G needle. At indicated timepoints post-injection, D-luciferin (150 mg/kg in PBS) was intraperitoneally administered, followed by bioluminescence imaging of with an IVIS Spectrum system (40 s exposure, region-of-interest analysis). Immediately following live IVIS imaging, heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney were harvested and imaged ex-vivo. Data were quantified as fluorescent intensity at the region of interest.
2.10 Histological and immunofluorescent assessment
Tendon samples were collected and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight. After dehydration and embedding in paraffin, 5 μm paraffin sections were prepared for Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), Masson’s trichrome and Sirius Red staining. For immunofluorescent analysis, sections were blocked at room temperature after antigen retrieval, followed by overnight incubation at 4°C with the indicated primary antibodies [anti-COL1A1 antibody (ABclonal, A24112), anti-COL3A1 antibody (ABclonal, A3795), or anti iNOS antibody (ABclonal, A3774)] and secondary antibodies. The collagen or fluorescent positive area was quantified using ImageJ software.
2.11 ELISA assay on tendon tissue
Tendon tissue was collected and rinsed in cold PBS to remove blood contaminants. Then, the samples were minced into small fragments and incubated into 250 μL RIPA Lysis Buffer (Beyotime, P0038) with protease inhibitors (Beyotime, P1046). Then the mixture was centrifuged for supernatant collection. The ELISA assays for detection of IL-6 (ABclonal, RK04845) and IL-10 (ABclonal, RK04490) were performed according to the user’s instruction.
2.12 Gait analysis
At week 4 after treatment, gait analysis was performed using the CatWalk XT system (Noldus). In brief, the mice were placed on a glass walking platform and their walking sequences were recorded (step speed range 10–30 cm/s).
2.13 Transcriptome analysis on tendon tissue
At the end of the animal experiment, the tendon samples were collected and snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. Then the frozen samples were homogenized in TRIzol reagent for total RNA extraction. RNA sequencing was performed using the Illumina sequencing platform. Reads were aligned to the mouse reference genome (mm39). Differential gene expression analysis was performed with DESeq2 (adjusted p-value <0.05, |log2 fold change| >1). Functional enrichment of pathways was analyzed using the Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) databases. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was used to determine the predefined gene sets that were significantly enriched in the treatment group. All computational workflows were executed on Novogene’s online platform (NovoMagic), accessed via https://magic-plus.novogene.com/#/, and default parameters were used. Raw sequencing data were deposited in the NCBI SRA under accession number SUB15328155.
2.14 Biological safety evaluation
Blood serum samples were collected and immediately analyzed using an automatic biochemical analyzer (BIOBASE, BK280) to assess metabolic parameters, including alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin (TBIL), direct bilirubin (DBIL), creatinine (CREA), and urea. Additionally, the heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney were fixed in paraffin, sectioned, and subjected to hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining for histological evaluation of tissue morphology.
2.15 Statistical analysis
All data were presented as the mean ± Standard Error of the Mean (SEM). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA or two way ANOWA with Fisher’s LSD test using GraphPad Prism 9. P < 0.05 was considered significant.
3 Results
3.1 Assessment of the in vitro transfection efficiency of mRNA mediated by SM102 LNPs
The physicochemical characterization and representative transmission electron microscopy images of SM102-based nano-liposome particles (LNPs)-mRNA was shown in Figures 2A–C. The denaturing agarose gel electrophoresis showed that the size of Il1rn mRNA before and after encapsulation was approximately 900 bp, which was consistent with the expected size (Figure 2D; Supplementary Figure S1). Co-incubation of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA with HEK293T cells for 48 h and the total protein was extracted to detect the expression of IL-1RA. The result indicated a protein band in the co-incubation group but not in the negative control (Figure 2E). The molecular weight of the band was around 20 kDa, which is comparable with the positive control (Figure 2E; Supplementary Figure S2). In addition, the delivery of GFP mRNA to HEK293T using SM102 LNPs enabled robust protein expression for at least 48 h (Figure 2F). To further evaluate the SM102 LNPs-mediated mRNA transfection efficiency on primary tendon stem cells, SM102 LNPs-GFP mRNA was used for co-incubation. At 48 h post-incubation, flow cytometry analysis showed that the proportion of GFP-positive cells in the treatment group was 74.9% (Figure 2G). Under fluorescence microscopy, significant GFP fluorescence signals were observed in the treatment group from 24 to 72 h post-transfection (Figure 2H). Quantification analysis indicated that the fluorescence intensity of GFP was significantly increased during the 3 days post transfection (Figure 2I). Similarly, ELISA assay showed that the expression of IL-1RA in the supernatant of the SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA treatment group was significantly higher than that of the untreated group from 24 to 72 h (Figure 2J). These results implied the therapeutic time windows of the exogenous protein expression were around 72 h. Additionally, the transfected tendon cells could secrete IL-1RA in a dosage dependent manner (Figure 2K). The above results indicated that SM102 LNPs could efficiently transfect primary tendon stem cells and achieve functional protein expression for at least 72 h.
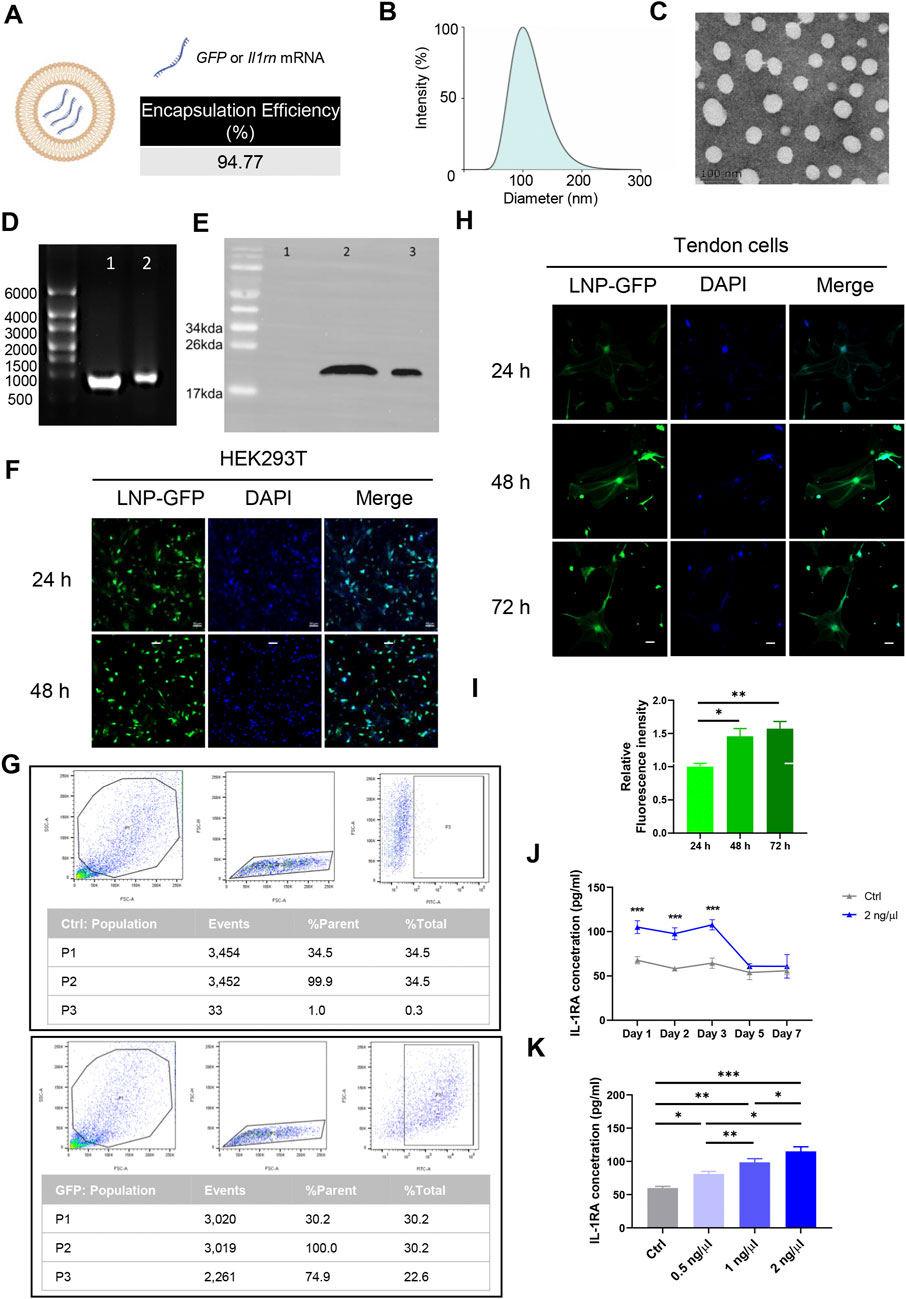
Figure 2. Assessment of the in vitro transfection efficiency of mRNA mediated by SM102 LNPs. (A) Schematic diagram of SM102 LNPs. (B) Dynamic light scattering distribution plot of SM102 LNPs-Il1rn. (C) Representative transmission electron microscopy image of SM102 LNPs-Il1rn. (D) Denaturing agarose gel electrophoresis of Il1rn mRNA before (lane 1) and after (lane 2) SM102 LNPs encapsulation. (E) Detection of IL-1RA protein in HEK293T cells treated with (lane 2) or without (lane 1) SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA. Lane 3 was the positive control (Commercially available human IL-1RA protein) (F) Representative images showing the SM102 LNPs-mediated transfection of GFP mRNA in HEK293T cells. Scale bar: 50 μm. (G) Flow cytometry results of GFP positive cells for the control group (upper panel) and transfection group (Lower panel) at 48 h post-treatment. (H) Representative images showing the SM102 LNPs-mediated transfection of GFP mRNA in primary tendon stem cells. Scale bar: 50 μm. (I) Quantification of the fluorescence intensity of GFP from 24 h to 72 h post-transfection. (J) ELISA assay for detection of IL-1RA levels in the culture medium of tendon cells treated with 2 ng/μL SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA from Day 1 to Day 7 post-transfection. (K) ELISA assay for detection of IL-1RA levels in the culture medium of tendon cells treated with different concentration of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA at 24 h post-transfection. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; n = 3; All data are shown as the mean ± Standard Error of the Mean (SEM); Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test.
3.2 In vitro anti-inflammatory effect of IL-1RA in tendon cells
Inflammatory responses alter the tendon microenvironment (Chisari et al., 2020). Existing evidence indicates that exogenous supplementation of IL-1β will increase the expression of a series of genes such as Interleukin 6 (Il10) in tendon cells (Tsuzaki et al., 2003; Vinhas et al., 2020). To verify the anti-inflammatory effect of IL-1RA, tendon stem cells transfected with or without SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA were stimulated with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 24 h qPCR results showed that IL-1β significantly upregulated Il6, inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase 2 (Nos2) and downregulated Interleukin 10 (Il10) (Figure 3A). Overexpression of IL-1RA could partially reverse the abnormal changes of the inflammatory-related genes (Figure 3A). Normal tendon ECM is mainly composed of collagen I (Col1), while in tendon lesions, the deposition of disordered collagen III (Col3) significantly increases, and the imbalance of Col3/Col1 ratio becomes a characteristic pathological marker (Tu et al., 2023; Franchi et al., 2007). Immunofluorescence staining confirmed that IL-1β treatment significantly decreased the Col I expression, increased the Col III expression and Col III/Col I in tendon stem cells, while overexpression of IL-1RA in tendon stem cells restored their expression levels comparable to the normal mice (Figures 3B–F). In addition, the effects of IL-1RA on tendon cell migration under IL-1β stimulation were evaluated by cell scratch assays. Scratch assays indicated that IL-1β significantly reduced migration of tendon stem cells at 12 and 24 h, while overexpression of IL-1RA significantly inhibited this effect (Figures 3G,H).
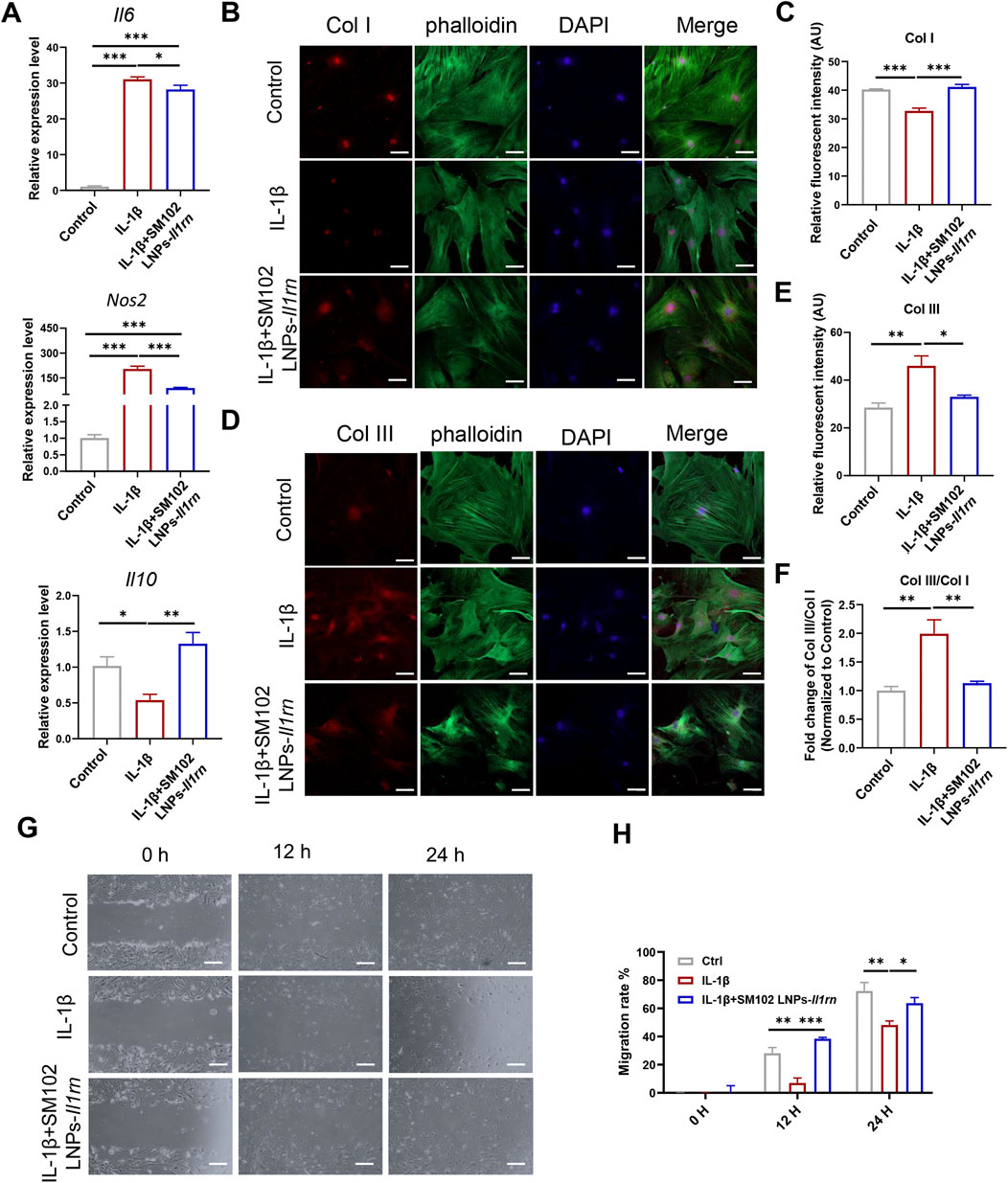
Figure 3. In vitro anti-inflammation property of IL-1RA on tendon stem cells. (A) qPCR results of Il6 (upper), Nos2 (middle) and Il10 (Lower) in control, IL-1β and SM102 LNPs-Il1rn group. (B) Representative images showing the Col I expression in control, IL-1β, and IL-1β+SM102 LNPs-Il1rn group. Col I (Red); phalloidin (Green); Nucleus (Blue). Scale bar = 100 μm (C) Quantification analysis of Col I expression in control, IL-1β and IL-1β+ SM102 LNPs-Il1rn group. (D) Representative images showing the Col III expression in control, IL-1β and IL-1β+ SM102 LNPs-Il1rn group. Col III (Red); phalloidin (Green); Nucleus (Blue). Scale bar = 100 μm (E) Quantification analysis of Col III expression in control, IL-1β, and IL-1β+ SM102 LNPs-Il1rn group. (F) Quantification analysis of Col III/Col I expression in control, IL-1β, and IL-1β+ SM102 LNPs-Il1rn group. (G) Representative microscopic images showing the scratch closure in control, IL-1β, and IL-1β+ SM102 LNPs-Il1rn group at 0 h, 12 h, and 24 h. Scale bar = 200 μm (H) Quantification of scratch closure in different groups at 0 h, 12 h, and 24 h *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; n = 3; All data are shown as the mean ± Standard Error of the Mean (SEM); Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test (A,C,E); Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test (G).
These results proved that IL-1RA can regulate inflammatory levels, improve ECM metabolic imbalance, and inhibit abnormal cell behaviors induced by IL-1β.
3.3 Therapeutic efficacy of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA in tendinopathy mice model
Before evaluating the therapeutic efficacy of SM102 LNPs-Il1rn mRNA, we first injected Luciferase mRNA into the tendon region of mice to determine whether SM102 LNPs could effectively deliver mRNA in vivo. Imaging was performed at 1-, 3-, and 7-day post-injection (Supplementary Figure S3A). Fluorescent signals indicated the successful delivery of mRNA to the tendon tissue by SM102 LNPs (Supplementary Figure S3A). Quantification analysis confirmed significantly higher signal levels in injected mice compared to control mice, persisting for 3 days, which is consistent with the in vitro data (Supplementary Figure S3B). To investigate the biodistribution of luciferase protein, major organs were dissected for imaging at 24 h post-injection. Luciferase signals were detectable in typical storage organs such as the liver and spleen (Rosanaly et al., 2025). However, the signal intensity in these organs was significantly lower, accounting for approximately 10% (liver) and 0.5% (spleen) of that observed in tendon tissue (1.7E+05) (Supplementary Figure S3C).
A murine model of tendinopathy was established via type I collagenase injection to evaluate the anti-inflammatory efficacy of SM102 LNPs-IL-1RA in vivo (Figure 4A). Histopathological analysis at 1-week post-treatment revealed that untreated tendons exhibited disorganized extracellular matrix (ECM) architecture, whereas SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA treatment restored regular fiber alignment (Figure 4B). Masson’s trichrome and Sirius red staining demonstrated excessive collagen deposition in the untreated group, which was significantly attenuated by SM102 LNPs-Il1rn mRNA treatment (Figures 4C,D). Immunofluorescence analysis further indicated elevated expression of pro-inflammatory IL-6, matrix-degrading enzymes MMP1/MMP13, and suppressed IL-10 levels in untreated tendons, consistent with sustained inflammation and ECM catabolism. These pathological markers were normalized to near-physiological levels in the treatment group (Figures 4E–I). The ELISA analysis revealed a comparable expression profile for IL-6 and IL-10 in tendon tissues to the immunofluorescence results (Figure 4J). Furthermore, IL-1RA treatment significantly reduced iNOS expression in the tendon tissue of tendinopathy mice (Figures 4K,L).
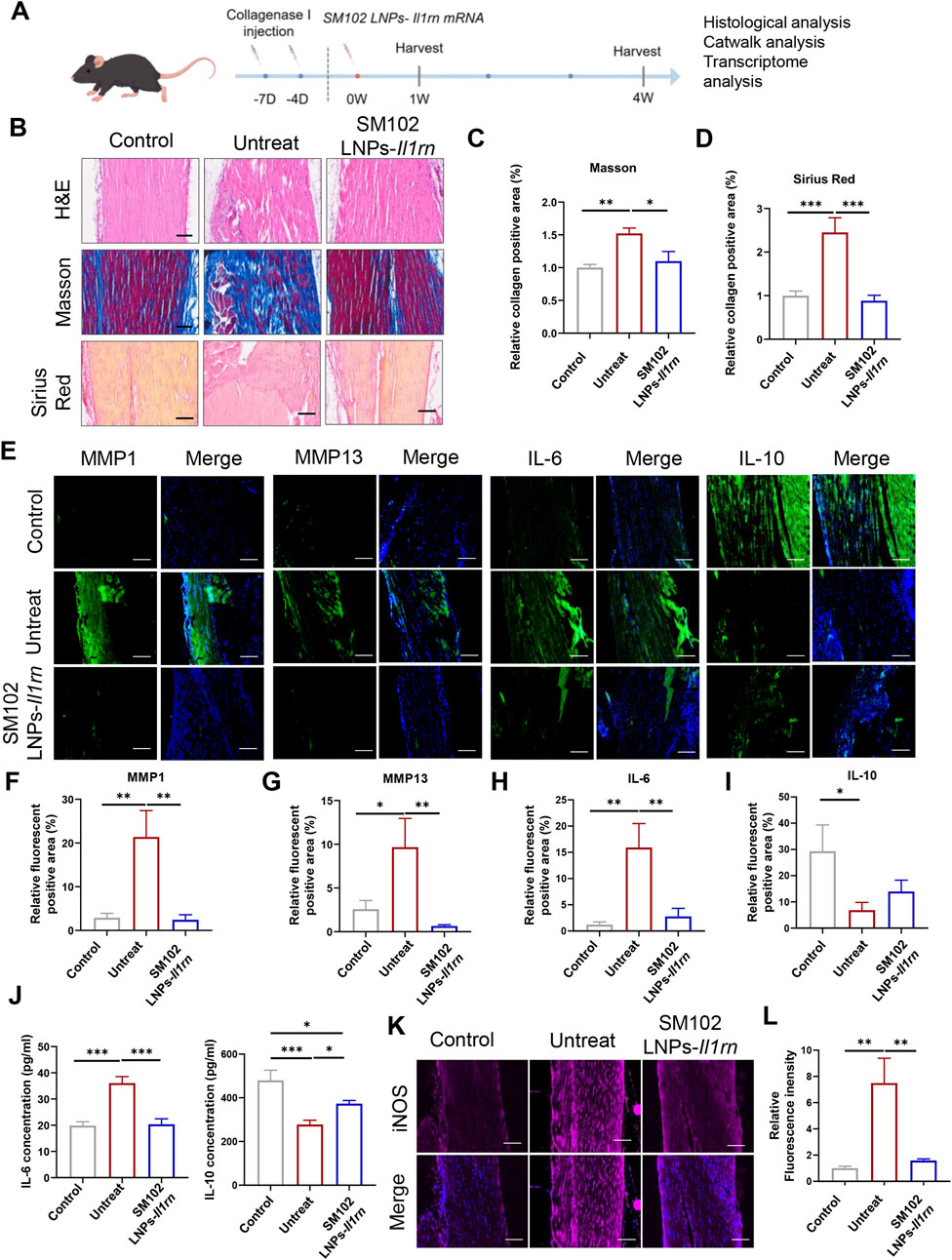
Figure 4. In vivo therapeutic effects of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA on tendon tissues at week 1. (A) Scheme of animal experiment design (By Figdraw). (B) Representative images of H&E staining (upper panel), Masson’s trichrome staining (middle panel), and Sirius red staining (lower panel) of tendons from different groups in the first week postoperatively. Scale bar = 100 µm (C,D) Quantification analysis of Masson’s trichrome staining (C) and Sirius red staining (D). (E) Representative images of immunofluorescent staining of MMP1, MMP13, IL-6, and IL-10 of sections of each group in the first week postoperatively. Scale bar = 100 µm (F–I) Quantification of MMP1, MMP13, IL-6, and IL-10 expression in different groups. (J) Elisa assay for detection of IL-6 (Left) and IL-10 (Right) expression level in tendon tissue from different groups. (K) Representative images of immunofluorescent staining of iNOS of sections of each group in the first week postoperatively. Scale bar = 100 µm (L) Quantification of iNOS expression in different groups. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n = 5; All data are shown as the mean ± Standard Error of the Mean (SEM). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test.
At 4 weeks post-treatment, untreated tendons persistently displayed disordered collagen architecture and hyperdeposition, while M102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA- treated mice exhibited mitigated pathological features (Figures 5A–C). Quantitative immunofluorescence analysis of collagen subtypes revealed a marked decrease in Col I and an increase in Col III and the Col III/Col I ratio in tendinopathy mice (Figures 5D–H). In contrast, SM102 LNPs-Il1rn mRNA treatment reversed this imbalance, significantly downregulating Col I, upregulating Col III, and increasing the Col III/Col I ratio compared to the untreated group (Figures 5D–H).
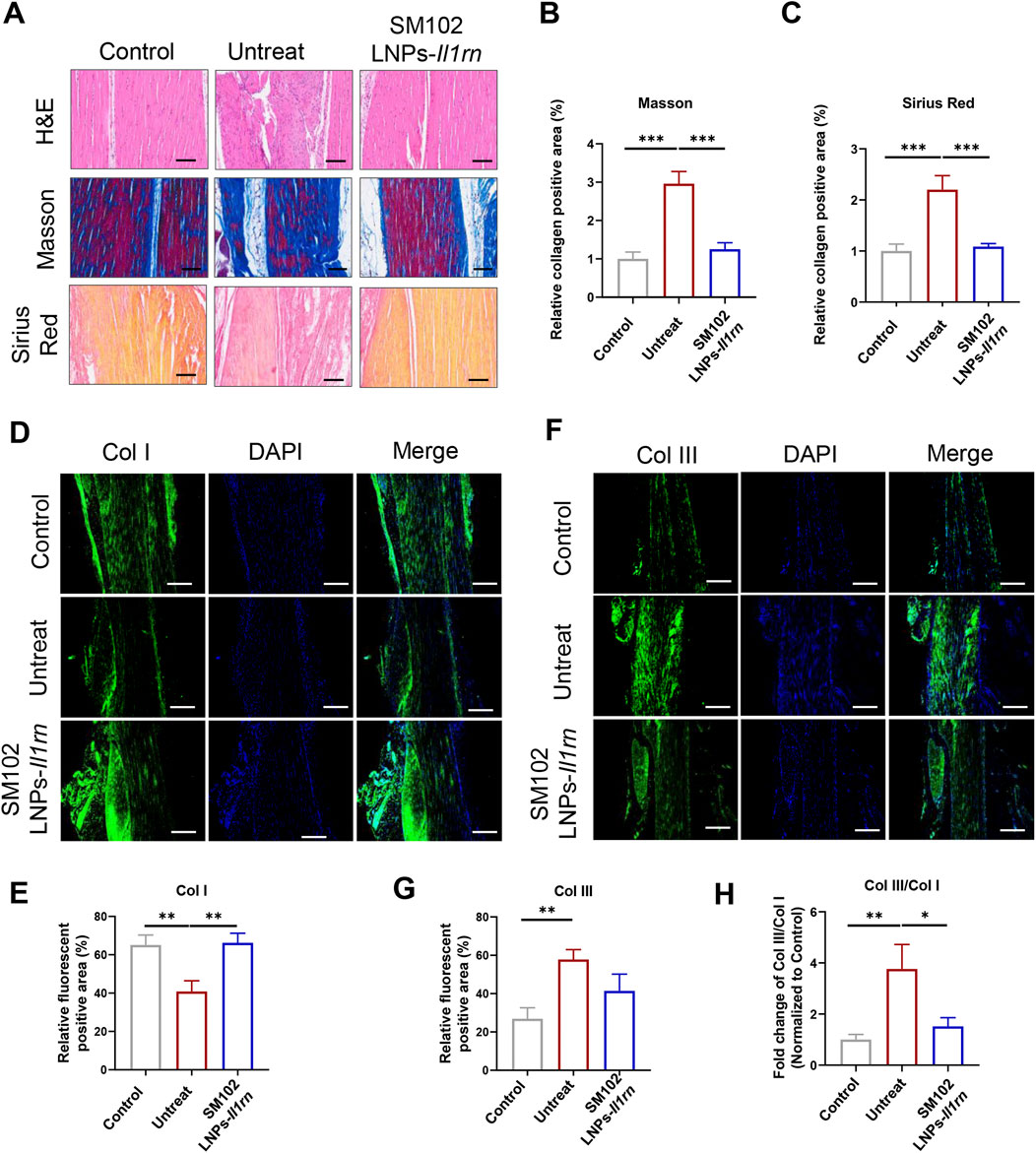
Figure 5. In vivo therapeutic effects of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA on tendon tissues at week 4. (A) Representative images of H&E staining (upper panel), Masson’s trichrome staining (middle panel), and Sirius red staining (lower panel) of tendons from different groups in the fourth week postoperatively. Scale bar = 100 µm (B,C) Quantification analysis of Masson’s trichrome staining (B) and Sirius red staining (C). (D) Representative images of immunofluorescent staining of Col I of sections of each group in the fourth week postoperatively. Scale bar = 100 µm (E) Quantification Col I expression in different groups. (F) Representative images of immunofluorescent staining of Col III of sections of each group in the fourth week postoperatively. Scale bar = 100 µm (G) Quantification Col III expression in different groups. (H) Quantification Col III/Col I expression in different groups. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n = 5; All data are shown as the mean ± Standard Error of the Mean (SEM). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test.
Functional recovery was assessed via 3D gait analysis. The treatment group displayed a footprint intensity map resembling healthy controls (Figure 6A), with quantitative analysis confirming significant improvement in gait patterns and near-restoration to control levels (Figure 6B). For instance, tendinopathy mice exhibited significantly smaller contact areas and lower intensity values than the control group (Figure 6B), indicating pain-induced unloading of the affected limb to minimize mechanical pressure. Conversely, the restoration of these parameters to near-normal levels in the IL-1RA treatment group demonstrates that local IL-1 blockade effectively reverses tendon damage-induced dysfunction. These results demonstrate that SM102 LNPs-IL-1RA alleviates tendinopathy by resolving inflammation, normalizing collagen composition, and restoring motor function.
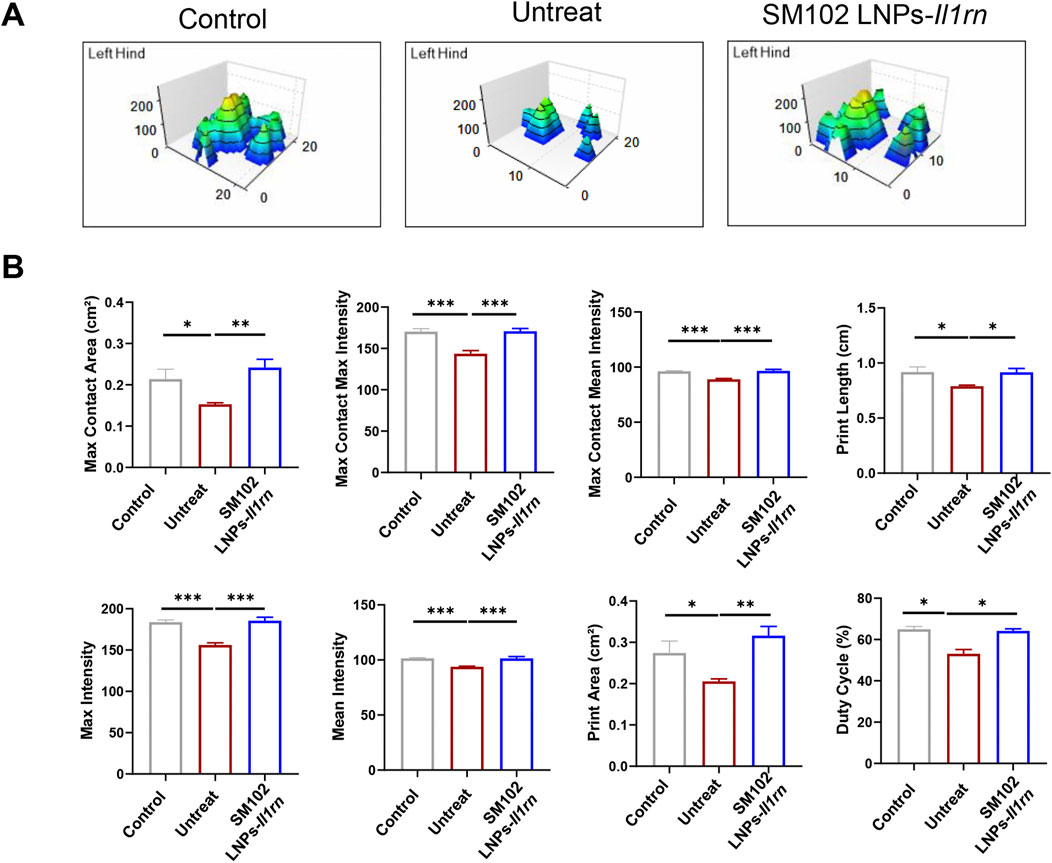
Figure 6. Catwalk for gait analysis after SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA treatment. (A) Representative 3D footprint intensity images of control (left panel), untreated (middle panel), and treated (right panel) groups at 4 weeks after treatment. (B) The quantification analysis of the catwalk for gait analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; n = 5; All data are shown as the mean ± Standard Error of the Mean (SEM). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test.
3.4 Transcriptome analysis on SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA-mediated therapeutic effect in tendinopathy mice model
RNA sequencing analysis of mouse tendon tissues revealed 447 downregulated genes and 317 upregulated genes (|Log2FoldChange| ≥1, Padj ≤0.05) in the SM102 LNPs-Il1rn mRNA group compared to controls (Figure 7A). Differential gene expression analysis (Figure 7B) and Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment (Figure 7E) demonstrated that SM102 LNPs-Il1rn mRNA treatment specifically modulated cellular responses to IL-1 and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling (e.g., regulation of collagen metabolic processes and collagen trimer formation), suggesting that the therapy suppresses inflammation by blocking IL-1 signaling while promoting collagen synthesis and ECM repair. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis further supported these findings, showing regulation of inflammatory signaling pathways such as NF-κB and IL-17 signaling in the treatment group (Figures 7C, D). The enrichment of the MAPK signaling pathway aligned with Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) results (Figure 7E). In addition, GSEA analysis also found enhanced macrophage differentiation and hydrogen peroxide metabolism in treatment groups (Figure 7E).
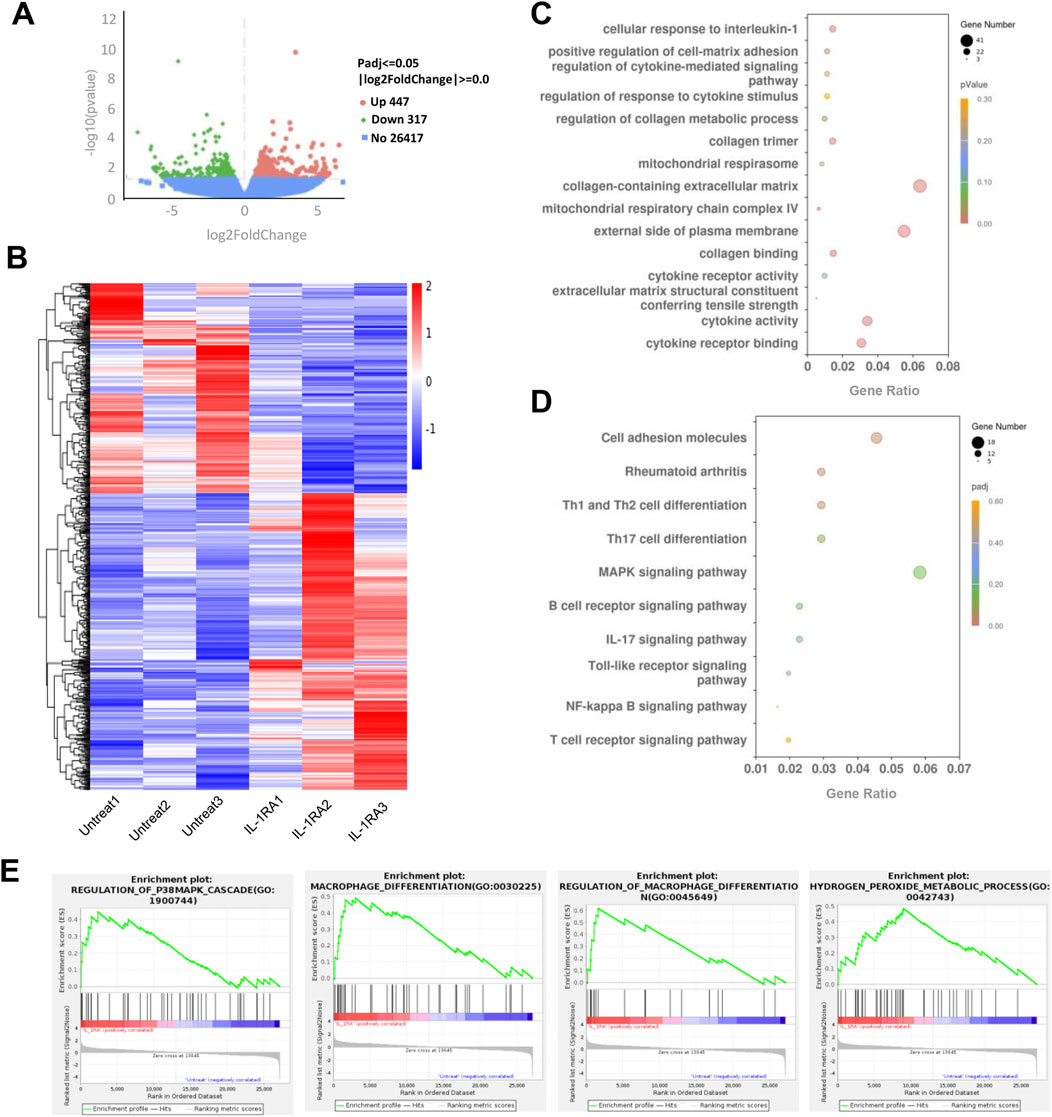
Figure 7. Transcriptome analysis of tendon tissues between the untreated and treated groups. (A) Volcano plot of gene expression (Treated versus Untreated; fold change, ≥1; q value <0.05). (B) Heat map of differentiated expression genes. (C) GO analysis of differentially expressed genes. (D) KEGG analysis of differentially expressed genes in the treatment group. (E) GSEA plot of the genes associated with P38MAPK signaling, microphage differentiation, and hydrogen peroxide metabolic process. FDR <0.25.
Collectively, these transcriptomic findings suggest that SM102 LNPs-Il1rn mRNA exerts dual therapeutic effects in tendinitis by targeting IL-1 signaling—simultaneously inhibiting inflammatory cascades and activating collagen-driven ECM restoration. The coordinated modulation of MAPK signaling, macrophage polarization, and H2O2 metabolism may further contribute to reestablishing tissue homeostasis.
3.5 Body safety evaluation
The safety of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA was evaluated by H&E staining of major organs and serum biochemical indicators (Figure 8A). Histological analysis showed that the structures of organs such as the heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney in the treatment group were intact, and no degenerative changes or inflammatory cell infiltration were observed. Also, there was no significant difference in serum biochemical parameters (such as liver and kidney function indicators) between the treatment group and the control group, confirming the good biological safety of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA treatment (Figure 8B).
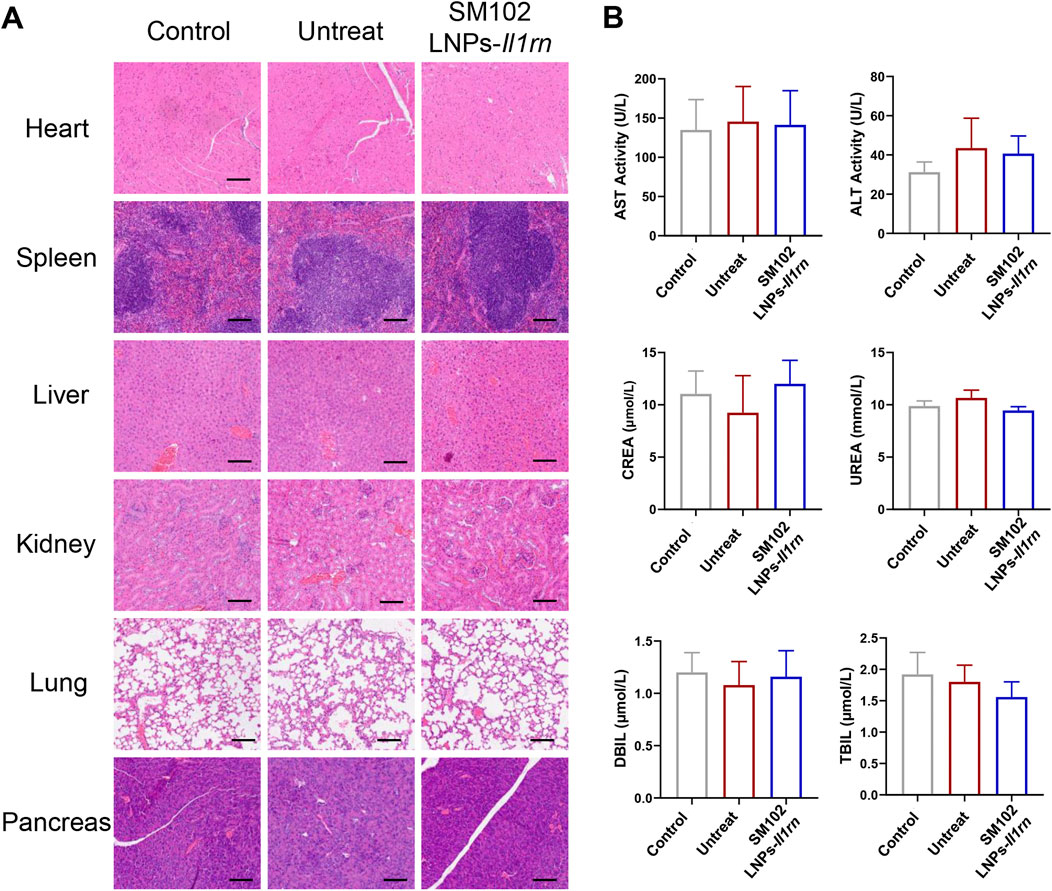
Figure 8. Evaluation of Biosafety of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA treatment. (A) H&E-stained sections of rat heart, spleen, liver, kidney, lung, and pancreas from Control, Untreated, and Treated groups after a 4-week intervention. Scale bar = 100 µm (B) Biochemical analysis of serum markers indicating organ function in different groups. The panels display levels of AST, ALT, CREA, UREA, DBIL, and TBIL. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n = 5; All data are shown as the mean ± Standard Error of the Mean (SEM). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test.
4 Discussion
Tendinopathy is a disease characterized by chronic inflammation and matrix degeneration as its core pathological features (Lipman et al., 2018; Rees et al., 2006). There were two challenges in the treatment: how to effectively block matrix degradation mediated by pro-inflammatory signals and achieve precise drug delivery and sustained action of therapeutic drugs. In this study, SM102 lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) were used for the local delivery of Il1rn mRNA to the tendon tissue. We systematically investigated the anti-inflammatory, pro-healing effects and biological safety of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA in vitro and in vivo (Figure 9).
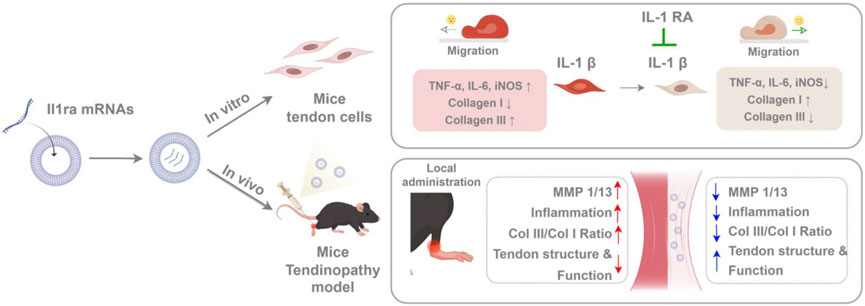
Figure 9. Schematic illustrating SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA-mediated therapeutic mechanisms against tendinopathy through coordinated modulation of inflammation, MMPs expression, collagen synthesis, and tenocyte migration (By Figdraw).
The low vascularization characteristic of tendon tissue limits the efficiency of drug delivery (Loiacono et al., 2019). Although various delivery systems have been developed for local treatment strategies for tendon diseases, their clinical translation still faces challenges (Adjei-Sowah et al., 2024; Han et al., 2024; Beldjilali-Labro et al., 2018). The success of the COVID-19 vaccine has verified the feasibility of lipid nanoparticles for delivering mRNA. The application of this technology in musculoskeletal diseases (especially tendon diseases) is in the exploration stage (Sun et al., 2022; López-Cerdá et al., 2024; Parchi et al., 2016; Huang et al., 2025). Ionizable lipid SM102 undergoes protonation in the acidic endosome environment, promoting mRNA escape to the cytoplasm, thereby achieving efficient expression (Schoenmaker et al., 2021; Hassett et al., 2019; Maier et al., 2013; Corbett et al., 2020). Our study found that SM102-LNPs can efficiently transfect primary tendon stem cells. Notably, our experiments demonstrated that SM102 LNPs-mediated delivery of mRNA achieved sustained expression of exogenous IL-1RA protein for approximately 72 h in tendon tissue. In contrast, literature reports indicate that subcutaneously administered recombinant proteins (molecular weight range: 23–149 kDa) are largely cleared from the injection site within 24 h, with clearance rates inversely correlating with molecular weight (Wu et al., 2012). These data support that mRNA therapy provides an extended therapeutic window compared to protein therapy. Our experiments demonstrated a clear dose-response relationship in SM102 LNPs-mediated exogenous gene expression, indicating that treatment effects can be precisely controlled by dose adjustment. This finding provides critical evidence for developing customized clinical therapies.
IL-1β is one of the key factors contributing to the development of tendon disorders (Morita et al., 2017). It drives the expression of pro-inflammatory factors and matrix metalloproteinases, leading to collagen degradation and fibrosis (Morita et al., 2017). To evaluate the anti-inflammatory function of SM 102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA. Primary tendon stem cells were incubated with IL-1β. And the results illustrated that the external IL-1β could stimulate the expression of IL-6 and TNF-α in tendon stem cells, which is consistent with a previous study (Vinhas et al., 2020). In addition, we also found that IL-1β could induce iNOS expression in primary tendon stem cells, similar to skeletal myoblasts (Adams et al., 2002). In vitro application of SM 102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA on tendon stem cells reversed the activation of these target genes. Also, our findings demonstrated that IL-1RA reduced the IL-1β induced imbalance of Col III/Col I and the inhibition of tendon cell migration. These in vitro data helped to explain the therapeutic efficacy of SM 102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA in the mouse model of tendinopathy.
Inflammation is a natural response to injury, and it plays a central role in the development of tendon disorders. Previous studies found that interleukin-1 (IL-1) significantly increased in the stress-shielded achilles tendons of rats, and the application of IL-1RA could prevent the morphological deterioration of tendons via inhibiting the elevation of MMP1, and improving collagen metabolism (Ma et al., 2012). Similarly, our experiments also demonstrated that the single injection of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA could modulate the inflammatory-matrix-degrading axis by increasing anti-inflammatory factors (e.g., IL-10), suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6), reducing matrix-degrading enzymes (e.g., MMP1/13) and downregulating Inflammatory marker iNOS within the first week post-treatment. At 4 weeks post-injection, treated mice exhibited significantly improved tendon fiber alignment compared to the tendinitis control group, with collagen I and III expression and the Col III/I ratio restored to baseline levels, a recovery pattern correlated with enhanced motor function in gait analyses.
The RNA-seq analysis further emphasized the regulating effect of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA in inflammation, ECM homeostasis, and collagen synthesis. It is worth noting that existing evidence indicates that the anabolic effects (such as the downregulation of type I collagen and the upregulation of MMP) of IL-1β in human tendon fibroblasts were mediated via the p38 MAPK signaling cascade (Chen et al., 2024). In our study, the relationship between p38 MAPK signaling and the effect of SM102 LNPs- Il1rn mRNA was also confirmed by KEGG pathway analysis and GSEA analysis.
In conclusion, this study has demonstrated that the Il1rn mRNA therapy based on SM102-LNPs can effectively inhibit inflammation, reverse matrix degradation, and promote functional recovery through efficient delivery, transient expression, and multi-target regulation mechanisms (Figure 9). Its modular design supports the flexible substitution of other therapeutic mRNAs (such as anti-fibrotic or pro-angiogenic factors), providing a new strategy for the precise treatment of tendon diseases and other degenerative disorders of soft tissues. With the optimization of mRNA delivery technology and the advancement of clinical translation, this method is expected to become a new alternative to traditional surgery and hormone therapy.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA1264510.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of PLA General Hospital. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YuZ: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. XL: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Investigation. HL: Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Investigation. RZ: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Investigation. TZ: Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Methodology, Formal Analysis. TJ: Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Formal Analysis. YoZ: Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology. QG: Writing – review and editing, Supervision. HZ: Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision. YC: Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the following funding sources: Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. L242040 and 7254434); Beijing JST Research Funding (code: No. JSTYC202403 and ZR-2024); National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)/Hong Kong Research Grants Council (RGC) Joint Research Scheme (Project Code: N_CUHK439/24); and the Innovation and Technology Fund of Hong Kong (ITS/020/22MS).
Conflict of interest
Author YZ was employed by Beijing Hemu Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2025.1641236/full#supplementary-material
References
Adams, V., Nehrhoff, B., Späte, U., Linke, A., Schulze, P. C., Baur, A., et al. (2002). Induction of iNOS expression in skeletal muscle by IL-1beta and NFkappaB activation: an in vitro and in vivo study. Cardiovasc Res. 54 (1), 95–104. doi:10.1016/s0008-6363(02)00228-6
Adjei-Sowah, E., Chandrasiri, I., Xiao, B., Liu, Y., Ackerman, J. E., Soto, C., et al. (2024). Development of a nanoparticle-based tendon-targeting drug delivery system to pharmacologically modulate tendon healing. Sci. Adv. 10 (25), eadn2332. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adn2332
Andres, B. M., and Murrell, G. A. (2008). Treatment of tendinopathy: what works, what does not, and what is on the horizon. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 466 (7), 1539–1554. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0260-1
Arend, W. P. (1993). Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Adv. Immunol. 54, 167–227. doi:10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60535-0
Balmayor, E. R. (2022). Synthetic mRNA – emerging new class of drug for tissue regeneration. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 74, 8–14. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2021.10.015
Beldjilali-Labro, M., Garcia Garcia, A., Farhat, F., Bedoui, F., Grosset, J. F., Dufresne, M., et al. (2018). Biomaterials in tendon and skeletal muscle tissue engineering: current trends and challenges. Mater. (Basel) 11 (7), 1116. doi:10.3390/ma11071116
Berkoff, D. J., Kallianos, S. A., Eskildsen, S. M., and Weinhold, P. S. (2016). Use of an IL1-receptor antagonist to prevent the progression of tendinopathy in a rat model. J. Orthop. Res. 34 (4), 616–622. doi:10.1002/jor.23057
Canosa-Carro, L., Bravo-Aguilar, M., Abuín-Porras, V., Almazán-Polo, J., García-Pérez-de-Sevilla, G., Rodríguez-Costa, I., et al. (2022). Current understanding of the diagnosis and management of the tendinopathy: an update from the lab to the clinical practice. Disease-a-Month 68 (10), 101314. doi:10.1016/j.disamonth.2021.101314
Chen, R., Ai, L., Zhang, J., and Jiang, D. (2024). Dendritic cell-derived exosomes promote tendon healing and regulate macrophage polarization in preventing tendinopathy. Int. J. Nanomedicine 19, 11701–11718. doi:10.2147/ijn.s466363
Chisari, E., Rehak, L., Khan, W. S., and Maffulli, N. (2020). The role of the immune system in tendon healing: a systematic review. Br. Med. Bull. 133 (1), 49–64. doi:10.1093/bmb/ldz040
Coombes, B. K., Bisset, L., and Vicenzino, B. (2010). Efficacy and safety of corticosteroid injections and other injections for management of tendinopathy: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Lancet 376 (9754), 1751–1767. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(10)61160-9
Corbett, K. S., Edwards, D. K., Leist, S. R., Abiona, O. M., Boyoglu-Barnum, S., Gillespie, R. A., et al. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine design enabled by prototype pathogen preparedness. Nature 586 (7830), 567–571. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2622-0
Dahlén, E., Karin, B., Daniel, H., Patrik, H., Marie, K., Lill, L., et al. (2008). Development of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist mutants with enhanced antagonistic activity in vitro and improved therapeutic efficacy in collagen-induced arthritis. J. Immunotoxicol. 5 (2), 189–199. doi:10.1080/15476910802131477
Eskildsen, S. M., Berkoff, D. J., Kallianos, S. A., and Weinhold, P. S. (2019). The use of an IL1-receptor antagonist to reverse the changes associated with established tendinopathy in a rat model. Scand. J. Med. and Sci. Sports 29 (1), 82–88. doi:10.1111/sms.13310
Fleischmann, R. M., Tesser, J., Schiff, M. H., Schechtman, J., Burmester, G. R., Bennett, R., et al. (2006). Safety of extended treatment with anakinra in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 65 (8), 1006–1012. doi:10.1136/ard.2005.048371
Franchi, M., Trirè, A., Quaranta, M., Orsini, E., and Ottani, V. (2007). Collagen structure of tendon relates to function. ScientificWorldJournal 7, 404–420. doi:10.1100/tsw.2007.92
Gabay, C., Lamacchia, C., and Palmer, G. (2010). IL-1 pathways in inflammation and human diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 6 (4), 232–241. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2010.4
Han, Q., Bai, L., Qian, Y., Zhang, X., Wang, J., Zhou, J., et al. (2024). Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory injectable hydrogel microspheres for in situ treatment of tendinopathy. Regen. Biomater. 11, rbae007. doi:10.1093/rb/rbae007
Hassett, K. J., Benenato, K. E., Jacquinet, E., Lee, A., Woods, A., Yuzhakov, O., et al. (2019). Optimization of lipid nanoparticles for intramuscular administration of mRNA vaccines. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 15, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2019.01.013
Hou, X., Zaks, T., Langer, R., and Dong, Y. (2021). Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6 (12), 1078–1094. doi:10.1038/s41578-021-00358-0
Huang, M., Li, W., Sun, Y., Dong, J., Li, C., Jia, H., et al. (2025). Janus piezoelectric adhesives regulate macrophage TRPV1/Ca2+/cAMP axis to stimulate tendon-to-bone healing by multi-omics analysis. Bioact. Mater. 50, 134–151. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.03.029
Iqbal, I., and Fleischmann, R. (2007). Treatment of osteoarthritis with anakinra. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 9 (1), 31–35. doi:10.1007/s11926-007-0019-9
Kwan, K. Y. C., Ng, K. W. K., Rao, Y., Zhu, C., Qi, S., Tuan, R. S., et al. (2023). Effect of aging on tendon biology, biomechanics and implications for treatment approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (20), 15183. doi:10.3390/ijms242015183
Lipman, K., Wang, C., Ting, K., Soo, C., and Zheng, Z. (2018). Tendinopathy: injury, repair, and current exploration. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 12, 591–603. doi:10.2147/dddt.s154660
Loiacono, C., Palermi, S., Massa, B., Belviso, I., Romano, V., Gregorio, A. D., et al. (2019). Tendinopathy: pathophysiology, therapeutic options, and role of nutraceutics. A narrative literature review. Med. Kaunas. 55 (8), 447. doi:10.3390/medicina55080447
López-Cerdá, S., Molinaro, G., Tello, R. P., Correia, A., Waris, E., Hirvonen, J., et al. (2024). Antifibrotic and pro-regenerative effects of SMAD3 siRNA and collagen I mRNA-loaded lipid nanoparticles in human tenocytes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 7 (15), 17736–17747. doi:10.1021/acsanm.4c02996
Ma, Y., Yan, X., Zhao, H., and Wang, W. (2012). Effects of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist on collagen and matrix metalloproteinases in stress-shielded achilles tendons of rats. Orthopedics 35 (8), e1238–e1244. doi:10.3928/01477447-20120725-26
Maier, M. A., Jayaraman, M., Matsuda, S., Liu, J., Barros, S., Querbes, W., et al. (2013). Biodegradable lipids enabling rapidly eliminated lipid nanoparticles for systemic delivery of RNAi therapeutics. Mol. Ther. 21 (8), 1570–1578. doi:10.1038/mt.2013.124
Millar, N. L., Silbernagel, K. G., Thorborg, K., Kirwan, P. D., Galatz, L. M., Abrams, G. D., et al. (2021). Tendinopathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 7 (1), 1. doi:10.1038/s41572-020-00234-1
Morita, W., Dakin, S. G., Snelling, S. J. B., and Carr, A. J. (2017). Cytokines in tendon disease. Bone and Jt. Res. 6 (12), 656–664. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.612.bjr-2017-0112.r1
Nuki, G., Bresnihan, B., Bear, M. B., and McCabe, D. (2002). Long-term safety and maintenance of clinical improvement following treatment with anakinra (recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: extension phase of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis and Rheumatism 46 (11), 2838–2846. doi:10.1002/art.10578
Parchi, P. D., Vittorio, O., Andreani, L., Battistini, P., Piolanti, N., Marchetti, S., et al. (2016). Nanoparticles for tendon healing and regeneration: literature review. Front. Aging Neurosci. 8, 202. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2016.00202
Pelletier, J.-P., Caron, J. P., Evans, C., Robbins, P. D., Georgescu, H. I., Jovanovic, D., et al. (1997). In vivo suppression of early experimental osteoarthritis by interleukin-1 receptor antagonist using gene therapy. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 40 (6), 1012–1019. doi:10.1002/art.1780400604
Rees, J. D., Wilson, A. M., and Wolman, R. L. (2006). Current concepts in the management of tendon disorders. Rheumatol. Oxf. 45 (5), 508–521. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kel046
Riley, G. (2008). Tendinopathy—from basic science to treatment. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 4 (2), 82–89. doi:10.1038/ncprheum0700
Rosanaly, S., Apalama, M. L., Bringart, M., Giraud, P., Allard, B., Veeren, B., et al. (2025). Production, characterization and biodistribution of therapeutic high-density lipoprotein-like nanoparticles reconstituted with or without histidine-tagged recombinant ApoA1. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 1870 (3), 159606. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2025.159606
Sahin, U., Karikó, K., and Türeci, Ö. (2014). mRNA-based therapeutics — developing a new class of drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 13 (10), 759–780. doi:10.1038/nrd4278
Schoenmaker, L., Witzigmann, D., Kulkarni, J. A., Verbeke, R., Kersten, G., Jiskoot, W., et al. (2021). mRNA-lipid nanoparticle COVID-19 vaccines: structure and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 601, 120586. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120586
Sun, Y., Luo, Z., Chen, Y., Lin, J., Zhang, Y., Qi, B., et al. (2022). si-Tgfbr1-loading liposomes inhibit shoulder capsule fibrosis via mimicking the protective function of exosomes from patients with adhesive capsulitis. Biomaterials Res. 26 (1), 39. doi:10.1186/s40824-022-00286-2
Tarighi, P., Eftekhari, S., Chizari, M., Sabernavaei, M., Jafari, D., and Mirzabeigi, P. (2021). A review of potential suggested drugs for coronavirus disease (COVID-19) treatment. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 895, 173890. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173890
Tsuzaki, M., Guyton, G., Garrett, W., Archambault, J. M., Herzog, W., Almekinders, L., et al. (2003). IL-1β induces COX2, MMP-1, -3 and -13, ADAMTS-4, IL-1β and IL-6 in human tendon cells. J. Orthop. Res. 21 (2), 256–264. doi:10.1016/s0736-0266(02)00141-9
Tu, T., Shi, Y., Zhou, B., Wang, X., Zhang, W., Zhou, G., et al. (2023). Type I collagen and fibromodulin enhance the tenogenic phenotype of hASCs and their potential for tendon regeneration. npj Regen. Med. 8 (1), 67. doi:10.1038/s41536-023-00341-z
Vinhas, A., Rodrigues, M. T., Gonçalves, A. I., Reis, R. L., and Gomes, M. E. (2020). Pulsed electromagnetic field modulates tendon cells response in IL-1β-conditioned environment. J. Orthop. Res. 38 (1), 160–172. doi:10.1002/jor.24538
Weissman, D. (2015). mRNA transcript therapy. Expert Rev. Vaccines. 14 (2), 265–281. doi:10.1586/14760584.2015.973859
Wu, F., Bhansali, S. G., Law, W. C., Bergey, E. J., Prasad, P. N., and Morris, M. E. (2012). Fluorescence imaging of the lymph node uptake of proteins in mice after subcutaneous injection: molecular weight dependence. Pharm. Res. 29 (7), 1843–1853. doi:10.1007/s11095-012-0708-6
Yang, B. B., Gozzi, P., and Sullivan, J. T. (2019). Pharmacokinetics of anakinra in subjects of heavier vs. Lighter body weights. Clin. Transl. Sci. 12 (4), 371–378. doi:10.1111/cts.12622
Keywords: tendinopathy, mRNA therapy, SM102 lipid nanoparticles, interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, anti-inflammatory therapy
Citation: Zhang Y, Li X, Li H, Zhang R, Zhang T, Juma T, Zhou Y, Guo Q, Zhao H and Cao Y (2025) Anti-inflammatory therapy for tendinopathy using Il1rn mRNA encapsulated in SM102 lipid nanoparticles. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1641236. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1641236
Received: 06 June 2025; Accepted: 29 July 2025;
Published: 12 August 2025.
Edited by:
Michele Iafisco, National Research Council (CNR), ItalyReviewed by:
Chenzhen Zhang, Northeastern University, United StatesWenjuan Chen, Nankai University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Li, Li, Zhang, Zhang, Juma, Zhou, Guo, Zhao and Cao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongping Cao, ZnJlZWhvcnNlNjZAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Hui Zhao, emhhb2h1aUBjdWhrLmVkdS5oaw==; Quanyi Guo, ZG9jdG9yZ3VvXzMwMUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors share first authorship
 Yuan Zhang1,2†
Yuan Zhang1,2† Xu Li
Xu Li Hao Li
Hao Li Ti Zhang
Ti Zhang Quanyi Guo
Quanyi Guo Hui Zhao
Hui Zhao Yongping Cao
Yongping Cao