- 1Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zigong First People’s Hospital, Zigong, China
- 2Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Dazhou Dachuan District People’s Hospital (Dazhou Third People’s Hospital), Dazhou, China
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, West China Hospital, Sichuan Clinical Research Center for Laboratory Medicine, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 4Department of Clinical Medicine, North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China
- 5Department of Oncology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Since the lungs are directly connected to the external environment and have a rich blood supply, they are susceptible to damage and tumor growth. However, the pharmacokinetics of traditional drugs in the lungs are limited when administered orally or intravenously, posing challenges for clinical treatment. Compared to traditional drug delivery methods, nano-based drug delivery systems (NDDSs) have the advantages of high drug loading capacity, strong targeting, low cellular toxicity, and extended circulation time in the blood. Stimuli-responsive materials, often referred to as “smart” materials, are a class of functional materials that can change their properties in response to various stimuli in both internal and external environments. Therefore, stimuli-responsive materials have gradually become promising candidates for NDDSs. To date, many stimuli-responsive NDDSs have been developed for treating lung diseases. Our review primarily summarizes the novel NDDSs that have emerged in recent years for treating common benign and malignant lesions in the lungs, based on stimuli-responsive materials. Finally, we discussed the existing issues in stimuli-responsive NDDSs and looked forward to their future development prospects.
1 Introduction
Lung diseases encompass a variety of conditions affecting the lungs, which can arise from multiple factors, including infections, environmental influences, genetic predispositions, and others (Odendaal et al., 2024; Wang T. et al., 2024). Among these, the inhalation of external microorganisms and the dysregulation of the lungs’ internal microbiota are important factors leading to lung infections (Li R. et al., 2024; Natalini et al., 2023). Lung cancer (LC) is typically classified into small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), with NSCLC accounting for more than 85% of all cases (Leiter et al., 2023). As environmental pollution, food safety issues, and exposure to volatile chemicals in daily life increase, the risk of lung problems is also on the rise (Liang et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2023).
Due to the complexity of the respiratory system and the challenges posed by traditional treatment methods, there is an urgent need to develop innovative treatment strategies. In recent years, with the rapid advancement of science and technology, nanomaterials have provided a viable platform for drug loading and delivery. Nano-based drug delivery systems (NDDSs) are considered an effective approach for treating lung diseases because they can overcome the limitations of traditional treatments (Nayak et al., 2025). Stimuli-responsive nanomaterials can experience controllable changes in their physicochemical properties when exposed to various environmental conditions, including physiological stimuli such as pH, enzymes, and redox potential, as well as external energy stimuli like light, magnetic fields, and ultrasound (Wang et al., 2022; Wei et al., 2023). Compared to traditional drug delivery nanosystems, stimuli-responsive NDDSs offer many advantages, such as high sensitivity, broad applicability to various diseases, and diverse functionalities (Wei et al., 2023). In particular, the use of multi-stimuli responsive strategies to achieve sequential or cascade drug delivery has attracted significant attention. In recent years, researchers have reported a series of stimuli-responsive NDDSs for lung diseases, including polymer vesicles, dendrimers, hydrogel capsules, metal nanoparticles (NPs), and lipid NPs (Su et al., 2023; Huang et al., 2022; Fischer et al., 2023; Li H. et al., 2024; Reczyńska et al., 2020).
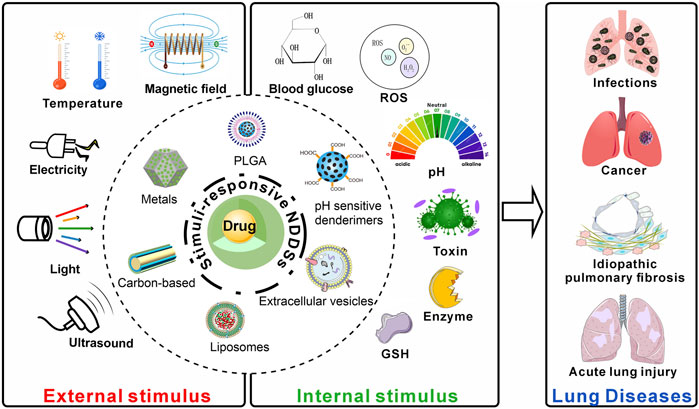
Our review primarily focuses on summarizing the stimuli-responsive NDDSs that have been developed recently for treating lung infections, LC, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), and acute lung injury (ALI) (Figure 1). Following that, the review discusses the challenges in the clinical translation of these NDDSs and looks ahead to their future application prospects.
2 An introduction to stimuli-responsive NDDSs
The internal microenvironment of the human body is complex, and the pathological microenvironment affects the occurrence and development of diseases. Within this microenvironment, the pH levels of pathological sites, such as infections, inflammation, and tumors, differ from those of normal tissues (Feng et al., 2024). When the pH changes, stimuli-responsive NDDSs can respond by expanding, contracting, or cleaving their functional groups, thereby releasing the encapsulated drugs (Lv et al., 2024; Fan et al., 2021; Wang S. et al., 2024). In addition, enzymes play an important role in the human body. The assembled responsive NDDSs can be transformed by enzymes into detachable structures, leading to a reduction in size that facilitates penetration into diseased and injured tissues, as well as the release of encapsulated drugs (Chen et al., 2024). External stimuli, such as light, ultrasound, magnetic fields, temperature, and radiation, offer more precise spatiotemporal adjustability and can be added or removed based on the treatment needs (Wei et al., 2023; Ding et al., 2024). Many pulmonary diseases (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, and lung infections) are characterized by excessive mucus production, which can hinder the delivery of drugs to the target site. Stimuli-responsive NDDSs can be designed with specific trigger mechanisms (such as pH sensitivity, enzyme sensitivity, or temperature sensitivity, etc.) to release drugs upon encountering mucus, thereby effectively penetrating the mucus barrier (Yu et al., 2025; Wang et al., 2024a; Wang et al., 2024b). Immunotherapy has emerged as a significant tumor treatment strategy following the clinical application of targeted therapies. However, due to tumor heterogeneity and the low immunogenicity of the tumor microenvironment (TME), only a small fraction of tumors are sensitive to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Therefore, it is crucial to develop nanocarriers that selectively activate various innate immune pathways, enhance innate immune responses, and reduce side effects. In particular, the use of nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery, combined with the research on environmentally responsive NPs, offers new perspectives for the immunotherapy of NSCLC (Li Y. et al., 2024; Li M. et al., 2024).
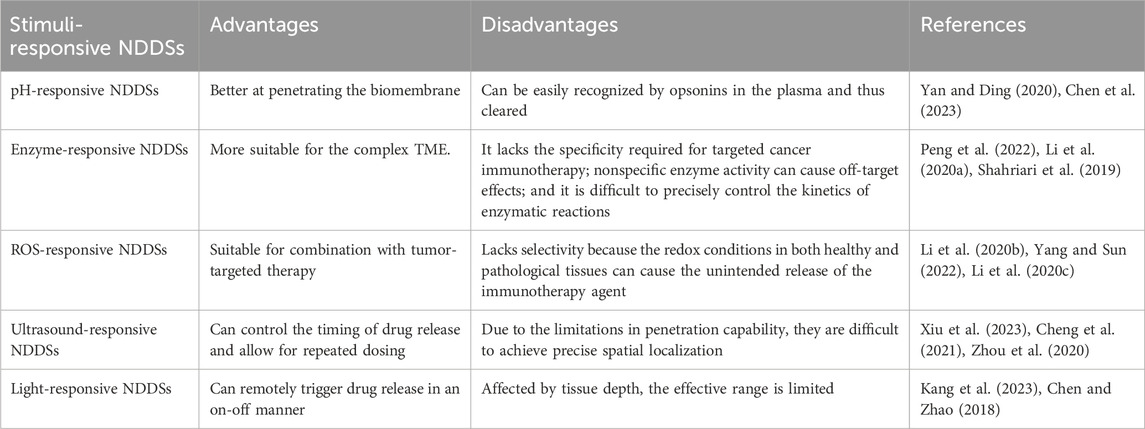
In recent years, stimuli-responsive nanocarriers have experienced rapid development in areas such as cancer treatment, anti-inflammatory therapy, and antimicrobial applications (Zhang et al., 2023; Yu et al., 2024; Peng et al., 2024). Currently, research on stimuli-responsive nanocarriers is primarily focused on synthetic polymers and biomaterials. Compared to synthetic polymers, biomaterials and their derivatives are gaining increasing attention due to their unique advantages, such as biodegradability, biocompatibility, natural abundance, and unique chemical structures (Datta et al., 2020). In particular, stimuli-responsive NDDSs based on biomaterials have the potential to address issues such as poor water solubility, less precise targeting, limited dispersibility, and high toxicity, which are difficult to overcome in traditional drug delivery systems. However, various types of stimuli-responsive NDDSs exhibit distinct advantages and disadvantages (Table 1). These nanocomposites offer new options for effective disease treatment.
3 Stimuli-responsive NDDSs for anti-lung infection
Lung infection refers to the inflammatory response caused by the invasion of pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi into the lungs (Pettigrew et al., 2021). For lower respiratory tract infections caused by bacteria, systemic antibiotic administration is commonly used in clinical treatment (Lalmohamed et al., 2024). However, systemic drug administration has characteristics such as low drug utilization, significant toxicity to surrounding tissues, and a tendency to induce bacterial resistance (Pani and Mohapatra, 2024). Moreover, due to the unique pathological environment of the lower respiratory tract, it is more challenging to efficiently deliver drugs to eliminate bacteria within the lung mucous layer and biofilms. These NDDSs have been extensively validated for safety and efficacy in animal models of pulmonary infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus).
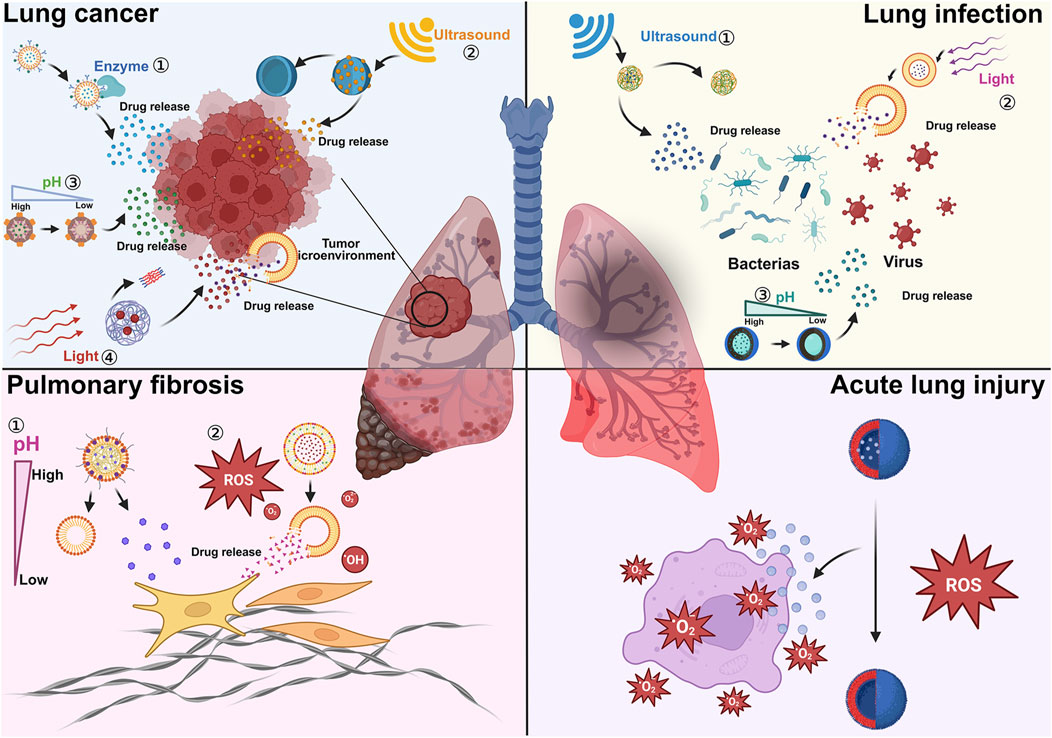
PA is an important pathogen in respiratory tract infections, particularly in the lower respiratory tract (Weimann et al., 2024). The cell membrane of PA can hinder drug penetration and the phagocytosis of immune cells. The bacterium produces virulence factors that inhibit the host’s immune response, leading to antibiotic tolerance and immune evasion (Du Toit, 2024). A responsive NDDS prepared from dimethylmaleic anhydride (DA) and azithromycin (AZI), epsilon-poly (l-lysine) (DA-AZI NPs). Acidic conditions can promote the penetration of DA-AZI NPs through mucus and biofilms, ultimately allowing the carried antibiotics to better exert effects against PA infections (Li R. et al., 2024). Curcumin (Cur) and dimethylmaleic anhydride (DA) were modified with anti-CD54 to form anti-CD54@Cur-DA NPs. The release of Cur from Cur-DA NPs at acidic pH results in charge reversal and size reduction, which facilitates increased penetration of PA biofilms and enhances the antibacterial effects of the antibiotics (Chen et al., 2023). In addition, some stimulus-responsive NDDSs rely on external physical stimuli. In recent years, there have been many breakthroughs in ultrasound-stimulated (US) responsive NDDSs. Chlorin e6 (Ce6) and metronidazole (MNZ) were incorporated into liposome (Lip) NPs encapsulating perfluoropentane (PFP), ultimately forming PLCM NPs. Under US, Ce6 and MNZ are more easily released from PLCM NPs, which induces the formation of numerous pores in the PA cell membrane, thus enhancing the antibiotic’s bactericidal effect (Xiu et al., 2024). Another team utilized Fe3O4 NPs and the antibiotic piperacillin (Pip) to construct ultrasound-responsive catalytic microbubbles (MB-Pip). Under ultrasound, MB-Pip disrupt the biofilm structure through mechanical effects and release Fe3O4 NPs, which degrade the extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) matrix. This results in physical and chemical biofilm disruption, enhancing the drug’s penetration and antibacterial performance (Xiu et al., 2023). A human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell membrane (MSCm) modified with the bacterial targeting peptide UBI29-41, ZIF-8 metal-organic framework, and organic silica NPs makes up PMZMU. Upon activation by ultrasound, PMZMU can eliminate bacterial biofilms, as confirmed in a PA-induced mouse pneumonia model study (Huang J. et al., 2024). In addition to ultrasound, new research results have also been reported on responsive NDDSs activated by physical radiation. The photosensitizer black phosphorus quantum dots (BPQDs) and the antibiotic amikacin (AM) were loaded into a biomimetic liposome (AB@LRM) constructed by fusing red blood cell membranes and macrophage cell membranes, resulting in the synthesis of AB@LRM NPs. Under near-infrared (NIR) radiation, BPQDs generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) and heat, which enhance the thermal sensitivity of PA cell membranes, disrupt their structure, and improve the antibacterial effect (Liu et al., 2024). In addition to directly damaging the cell membrane, reversing the resistance conditions of dormant PA biofilms for infection treatment is also an effective approach. Composed of maltahexose (GP), catalase, and gallium ions, the nanosystem (MCPGaGP) is capable of awakening the metabolism of PA within the biofilm. Finally, by activating the secretion of more iron ion uptake channels in PA, this nanosystem enhances the self-destructive absorption of the nutrient iron-gallium analog (He et al., 2024).
Among the pathogens causing lung infections, S. aureus is also a key bacterium of concern for clinical practitioners (Zaghen et al., 2023). The nanosystem consists of D-alanine functionalized gold NPs (DAu NPs) encapsulated by a macrophage membrane (MM) coating, known as MM@DAu NPs. After exposure to NIR, the accumulation of DAu NPs around the bacteria within the cells induces localized hyperthermia, enabling precise eradication of S. aureus within lung cells (Xiong et al., 2024). Pure ciprofloxacin NPs (NanoCip) integrated with PBP2a antibody-modified membrane nanovesicles (AMVs) form a novel biomimetic nanomedicine known as AMV@NanoCip. After US, this NDDS exhibits significant S. aureus-targeting affinity in both in vitro and in vivo models, thereby greatly enhancing its antibacterial activity (Ding et al., 2024). Li et al. developed a novel nanodelivery system by combining bovine serum albumin, polydopamine, and Ag2O2, known as Ag2O2@BP-MT@MM. This system effectively eliminates the activity of metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) by replacing the Zn2+ cofactor in MBL with Ag+, thereby demonstrating effective bactericidal properties (Li H. et al., 2024).
4 Stimuli-responsive NDDSs for anti-LC
LC is one of the most lethal cancers globally, with NSCLC being the most common type, but it has a low overall survival rate (Tammemägi et al., 2024). Due to the characteristics of the TME, stimulus-responsive polymers specifically targeting the TME have been widely used to prepare intelligent nanocarriers for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents and diagnostic reagents to tumor tissues. Compared to traditional NDDSs, stimulus-responsive NDDSs have many advantages, such as high sensitivity, broad applicability across different tumors, multifunctionality, and improved biosafety.
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) belong to the family of zinc-dependent endopeptidases and are one of the commonly overexpressed enzymes in the TME. The research team utilized MMP2-responsive peptides to construct a complex conjugated with miR-126-3p (MAIN) and further disguised it with red blood cell (RBC) membranes (named REMAIN), targeting the overexpressed MMP2 in the TME. REMAIN can effectively transduce miRNA into LC cells, releasing the miRNA in response to MMP2, and ultimately induce apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells (Liang et al., 2022). In addition, micro-NPs (GSC) made from silk fibroin (SF) and gelatin were prepared for MMP9 in the TME, which were fabricated to load paclitaxel (PTX@GSC), PD-L1 antibodies (αPD-L1@GSC), and PD-L1 small interfering RNA (siPD-L1@GSC) respectively. These stimulus-responsive NDDSs require prolonged exposure to a high MMP-9 environment to release the drugs, which increases the specificity and targeting of the anti-tumor effects (Gou et al., 2023). To enhance the immune response to NSCLC, a team of scientists in China has developed a folic acid-modified liposomal nano-bubble for precise delivery of PFH, STAT3 siRNA, and Fe3O4 to the TME. These nano-bubbles can undergo phase transition and release Fe3O4 under low-intensity focused ultrasound (LIFU), which can activate the IRF5 signaling pathway. This ultimately promotes the transformation of M2-type macrophages into M1-type while simultaneously inhibiting the polarization of M2-type macrophages (Li P. et al., 2024).
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is the most common mutation site in NSCLC, and there are currently several targeted drugs available for this mutation (Pan et al., 2024). Recent studies have shown that stimulus-responsive NDDSs play a positive role in targeted therapy. A NDDS composed of hyaluronic acid (HA), boron dipyrromethene (BPY), adamantane, the peptide sequence GFLG, and gefitinib (Gef) is termed HA-BPY-GEF-NPs. HA-BPY-GEF-NPs generate ROS upon NIR stimulation, which directly eliminate tumor cells. Subsequently, under the stimulation of enzyme (cathepsin B), this nanodrug delivery system releases Gef in a targeted manner (Huang Q. et al., 2024). Another research team utilized dendrimer-based NPs to target the co-delivery of Gef and YAP gene-silencing siRNA (YAP-siRNA). In a reducting environment, this NDDS releases Gef and YAP-siRNA. Additionally, under laser irradiation, the NPs can produce strong antitumor effects without causing significant toxicity (Huang et al., 2022).
LC is prone to metastasis, which is closely associated with poor prognosis. Therefore, recent studies have focused on exploring NDDSs aimed at blocking metastasis (Li et al., 2021; Fan et al., 2023). A recent study reported a pH-responsive NDDS based on DNA tetrahedral framework nucleic acids for the simultaneous delivery of immunomodulatory CpG oligonucleotides and PD-L1-targeting antagonistic DNA aptamers, which effectively treats lung metastatic cancer (Fan et al., 2023).
5 Stimulus-responsive NDDSs for IPF
IPF is a chronic, progressive, and highly lethal lung disease with a short average survival period following diagnosis (Wijsenbeek and Cottin, 2020). It is characterized by damage to alveolar epithelial cells (AECs), accompanied by enhanced activation/stimulation of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, leading to the accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) in the alveolar walls (Podolanczuk et al., 2023). Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) transplantation has been proven to be an effective treatment for IPF (Averyanov et al., 2020). However, the poor microenvironment caused by inflammation, fibrosis, and high levels of ROS in IPF leads to low survival rates and poor function of transplanted MSCs, significantly impacting their therapeutic efficacy. Additionally, the mechanism of action for MSCs in treating IPF is not yet fully understood, greatly limiting the clinical translation of stem cell therapy. Therefore, removing excess intracellular ROS and imaging tracking have become important strategies to protect MSCs. Metal NPs are widely used in biomedical applications related to pulmonary fibrosis. Their antioxidant properties and ability to enhance imaging functions have shown great potential in treating IPF and in sensors for detecting specific biomarkers of IPF. By combining zinc ions and 7,8-dihydroxyflavone with fasudil (a ROCK inhibitor), ZDFPR NPs can reduce mechanical tension in type II alveolar epithelial cells (AEC II) and disrupt the ROCK signaling pathway, thereby reducing the formation of ROS after aerosol inhalation (Li X. N. et al., 2024). By encapsulating copper-based nanozymes (CuxO NPs) and gold NPs (AuNPs) in oxidation-sensitive dextran (Oxi-Dex), ROS-responsive nanocomposites (RSNPs) were successfully created. This nanosystem can eliminate ROS and enable long-term CT imaging tracking of MSCs, thereby allowing a deeper understanding of the cellular therapy mechanisms (Li et al., 2023). Additionally, a pH-sensitive Au nanotracer (CPP-PSD@Au) was prepared by combining AuNPs with sulfonamide-based polymers (PSD) and cell-penetrating peptides (CPP). It can monitor MSCs via CT imaging for up to 35 days after transplantation into the lungs of IPF mice (Yu et al., 2021). Bao et al. prepared a non-viral bifunctional nanocarrier using AuNPs stabilized by protamine sulfate, which can be used for simultaneous IPF treatment and the monitoring the biological behavior of MSCs (Bao et al., 2022). Furthermore, the team subsequently developed a tri-metallic nanocarrier (TBNCs) with similar functionality, using protamine sulfate and three metals: gold (Au), platinum (Pt), and cobalt (Co) (Bao et al., 2024).
6 Stimulus-responsive NDDSs for ALI
ALI is caused by various factors that lead to damage of alveolar epithelial cells and capillary endothelial cells, and is associated with uncontrolled inflammatory responses of the host immune system (Guo et al., 2021; Meyer et al., 2021). According to recent studies, early inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine release and the formation of ROS may be a promising therapy for ALI. Dexamethasone (Dex) was encapsulated into a poly (thioketone) polymer to form polymeric NPs (PTKNPs@Dex). In a ROS environment, the NPs can degrade responsively, releasing the drug and thereby reducing oxidative tissue damage (Zhai et al., 2022). Bilirubin (Br) and Atorvastatin (As) were encapsulated into the smart ROS-responsive nanocarrier DSPE-TK-PEG (DPTP), forming the NDDS (BA@DPTP). The high levels of ROS in ALI tissues trigger the drug release from BA@DPTP, thereby reducing ALI (Xia et al., 2024). A synergistic NDDS (AZI + IBF@NP) composed of ROS-responsive polymer (PFTU), antibiotics (Azithromycin, AZI), and anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, IBF) was developed. ROS can be effectively cleared by this system in both in vitro and in vivo experiments (Muhammad et al., 2023). A nanosystem composed of oxidation-sensitive chitosan (Ox-CS), cerium nanoparticles (Ce NPs), and resatorvid (Ox-CS/CeRT NPs) has been developed. In vitro experiments have shown that Ox-CS/CeRT NPs can reduce ROS and inflammatory factors, thereby alleviating lung damage (Wu et al., 2023).
7 A clinical perspective on NDDSs for lung diseases
Currently, most approved or clinically developed nanomedicines are liposomal nanomedicines, polymeric nanomedicines, nanocrystal drugs, micellar nanomedicines, protein-based nanomedicines, or inorganic nanomedicines (Fernández-García and Fraguas-Sánchez, 2024). Nanocurcumin, prepared using nanotechnology, has shown positive effects in the treatment of various diseases (Yan et al., 2025). In a clinical study involving patients with COPD, nanocurcumin demonstrated an improvement in lung function (Zare’i et al., 2024). In another randomized controlled trial involving COVID-19 patients, nanocurcumin exhibited a positive effect on regulating inflammatory factors (Valizadeh et al., 2020). In LC patients, a recent clinical study has shown that nanoselenium significantly increases blood selenium levels in NSCLC patients and reduces the toxic side effects of chemotherapy (Song et al., 2021). In summary, NDDSs offer more hope for patients, but currently, the number of NDDSs entering clinical studies remains limited.
8 Discussion
With the continuous development of nanotechnology and polymer materials technology, research on stimulus-responsive strategies based on nanomaterials for pulmonary diseases has become increasingly in-depth. Due to the inherent ability of stimulus-responsive biomaterials to interact with the biological environment, they can be used as drug delivery carriers (Dou et al., 2020; Han et al., 2024; Wen et al., 2023). These “smart” biomaterials can respond to signals in the environment through mechanisms such as swelling/contraction, bond cleavage, surface changes, and structural changes. Drug release within NDDSs can be achieved through self-regulation or by direct or gradual activation via external or internal stimuli. By responding to specific stimulus signals, NDDSs can release drugs at the site of the lesion, ensuring that the highest concentration of the drug is achieved where it is most needed. This not only increases the local concentration of the drug but also prolongs its duration of action, thereby enhancing its efficacy. Additionally, this precise release of drugs under specific conditions can significantly reduce the required drug dosage (Li and Kataoka, 2021). Lower drug doses not only minimize toxic side effects but also lower treatment costs. Traditional drug delivery systems may require frequent dosing, whereas stimulus-responsive NDDSs can achieve prolonged drug release, reducing the frequency of patient dosing and thereby improving patient compliance. In summary, the development and application of stimulus-responsive NDDSs provide new approaches and methods for the treatment of lung diseases. By precisely controlling the timing and location of drug release, these “smart” biomaterials can significantly enhance drug efficacy, reduce toxicity, and improve patient compliance.
The advantages of endogenous stimulus-responsive NDDSs lie in their ability to utilize intrinsic stimuli within the body to regulate drug release, thereby achieving precise targeted therapy for diseased areas. This method reduces the need for external interventions, minimizes trauma to the body, and is more suitable for personalized medical strategies. However, endogenous stimulus-responsive NDDSs face challenges in precisely controlling their drug release behavior in vivo, and since not all internal stimuli are disease-specific, this can lead to unintended drug release in non-lesional areas. Additionally, different tumor types, physiological stages, and individual variations limit the clinical application of endogenous stimulus-responsive NDDSs. Currently, pH-responsive and enzyme-responsive NDDSs are widely studied, but these carriers still face difficulties in precisely controlling drug release at the lesion site and exhibit poor reproducibility, with few such drugs advancing to the clinical stage.
In contrast, the primary advantage of exogenous stimulus-responsive NDDSs is their remote controllability. By triggering drug release through external signals such as temperature, light, magnetic fields, and ultrasound, these carriers offer the potential for precise disease treatment. However, exogenous stimulus-responsive NDDSs also have some drawbacks. First, the spatiotemporal positioning of exogenous stimuli is difficult to accurately control, necessitating the introduction of localization components, which increases the complexity of carrier design. Second, the tissue penetration depth of exogenous stimuli also limits their applicability. Currently, more research is based on mouse models, which have limited in vivo validation. Furthermore, while some stimulus-responsive NDDSs have shown promising targeting effects in animal model experiments, delivering drugs precisely to the diseased area, they often exhibit off-target effects in clinical trials, thereby affecting treatment efficacy. The transition from basic research to clinical application requires further optimization of carrier design and functionality.
Despite many studies on stimulus-responsive delivery systems being reported, only a few of these systems have been tested in vivo in preclinical models, and even fewer have entered clinical phases. The biocompatibility, biodegradability, nontoxicity, and safer elimination from the biological system of stimulus-responsive carriers are important limitations that need to be considered before designing NDDSs. Different carrier materials can affect biocompatibility, and materials with good biocompatibility should be selected. For example, liposomes and polymer NPs are carrier materials that exhibit low toxicity and immunogenicity in the body. The microstructure and composition of nanomedicines are complex, and their construction process often involves multiple steps or sophisticated techniques, leading to poor reproducibility in preparation and making large-scale production extremely challenging. Additionally, the use of different analytical tools and testing methods by various research groups, coupled with the lack of standardized procedures for characterizing nanomedicine formulations, further complicates the research efforts. This inconsistency makes it difficult to conduct comprehensive comparative evaluations. Currently, the lack of animal models that accurately simulate human tumor conditions is a recognized deficiency in the field, resulting in weak correlations between preclinical studies and clinical trial outcomes (such as pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and safety). Furthermore, regulatory frameworks struggle to keep pace with rapid technological advancements, creating a complex approval environment. Future research should focus on designing NDDSs with characteristics such as biocompatibility, biodegradability, and nontoxicity. To achieve better clinical translation, there is a need for more reproducible and scalable NDDSs and the development of in vitro and in vivo models that accurately reflect clinical characteristics. Novel equipment and technologies need to be accelerated and promoted to enable industrial-scale production of nanomedicines, ensuring they meet Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards. Additionally, further improvements are needed in the evaluation systems for these drugs and the optimization of the approval processes for clinical trials.
9 Conclusion
Stimuli-responsive NDDSs have raised higher expectations for the treatment of lung diseases. Current research has focused more on animal models and has demonstrated their efficacy and safety, but lacks human trials. The preparation of economically viable and scalable nanomedicine systems is urgently needed. In conclusion, with the rapid development of nanomedicine, the continuous integration of basic and clinical research, and the collaborative efforts of researchers from various fields, these challenges are expected to be overcome. We believe that stimulus-responsive NDDSs for the treatment of pulmonary diseases will ultimately be successfully applied in clinical settings.
Author contributions
WL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. QH: Writing – original draft. ML: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. YW: Writing – original draft. ZC: Writing – original draft. YF: Writing – original draft. CS: Writing – review and editing. CG: Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Conceptualization. YL: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Methodology. ZD: Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the Zigong Academy of Medical Sciences 2022 (ZGYKY22KF002, ZGYKY22KF003 and ZGYKY22KF005); Zigong Science and Technology Program 2023 (2023YKY07); Zigong First People’s Hospital 2024 (2024GZL06); Science and Technology Foundation of Sichuan Province of China (2024NSFSC1922) and joint supported by Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation and Hengrui pharmaceutical innovation and development of China (2025AFD820).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Averyanov, A., Koroleva, I., Konoplyannikov, M., Revkova, V., Lesnyak, V., Kalsin, V., et al. (2020). First-in-human high-cumulative-dose stem cell therapy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with rapid lung function decline. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 9 (1), 6–16. doi:10.1002/sctm.19-0037
Bao, H., Cheng, S., Li, X., Li, Y., Yu, C., Huang, J., et al. (2022). Functional Au nanoparticles for engineering and long-term CT imaging tracking of mesenchymal stem cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis treatment. Biomaterials 288, 121731. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121731
Bao, H., Wu, M., Xing, J., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Wu, A., et al. (2024). Enzyme-like nanoparticle-engineered mesenchymal stem cell secreting HGF promotes visualized therapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in vivo. Sci. Adv. 10 (34), eadq0703. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adq0703
Chen, H., and Zhao, Y. (2018). Applications of light-responsive systems for cancer theranostics. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 10 (25), 21021–21034. doi:10.1021/acsami.8b01114
Chen, X., Yang, Y., Mai, Q., Ye, G., Liu, Y., and Liu, J. (2024). Pillar arene Se nanozyme therapeutic systems with dual drive power effectively penetrated mucus layer combined therapy acute lung injury. Biomaterials 304, 122384. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122384
Chen, Y., Gao, Y., Huang, Y., Jin, Q., and Ji, J. (2023). Inhibiting quorum sensing by active targeted pH-sensitive nanoparticles for enhanced antibiotic therapy of biofilm-associated bacterial infections. ACS Nano 17 (11), 10019–10032. doi:10.1021/acsnano.2c12151
Cheng, D., Wang, X., Zhou, X., and Li, J. (2021). Nanosonosensitizers with ultrasound-induced reactive oxygen species generation for cancer sonodynamic immunotherapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9, 761218. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2021.761218
Datta, L. P., Manchineella, S., and Govindaraju, T. (2020). Biomolecules-derived biomaterials. Biomaterials 230, 119633. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119633
Ding, L., Liang, X., Ma, J., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Long, Q., et al. (2024). Sono-triggered biomimetically nanoantibiotics mediate precise sequential therapy of MRSA-Induced lung infection. Adv. Mater 36 (46), e2403612. doi:10.1002/adma.202403612
Dou, Y., Li, C., Li, L., Guo, J., and Zhang, J. (2020). Bioresponsive drug delivery systems for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. J. Control Release 327, 641–666. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.09.008
Du Toit, A. (2024). Bacterial architects build the biofilm structures. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 22 (4), 187. doi:10.1038/s41579-024-01020-6
Fan, L., He, Z., Peng, X., Xie, J., Su, F., Wei, D. X., et al. (2021). Injectable, intrinsically antibacterial conductive hydrogels with self-healing and pH stimulus responsiveness for epidermal sensors and wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 13 (45), 53541–53552. doi:10.1021/acsami.1c14216
Fan, Q., Li, Z., Yin, J., Xie, M., Cui, M., Fan, C., et al. (2023). Inhalable pH-responsive DNA tetrahedron nanoplatform for boosting anti-tumor immune responses against metastatic lung cancer. Biomaterials 301, 122283. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122283
Feng, Q., Bennett, Z., Grichuk, A., Pantoja, R., Huang, T., Faubert, B., et al. (2024). Severely polarized extracellular acidity around tumour cells. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 8 (6), 787–799. doi:10.1038/s41551-024-01178-7
Fernández-García, R., and Fraguas-Sánchez, A. I. (2024). Nanomedicines for pulmonary drug delivery: overcoming barriers in the treatment of respiratory infections and lung cancer. Pharmaceutics 16 (12), 1584. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics16121584
Fischer, A., Ehrlich, A., Plotkin, Y., Ouyang, Y., Asulin, K., Konstantinos, I., et al. (2023). Stimuli-responsive hydrogel microcapsules harnessing the COVID-19 immune response for cancer therapeutics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 62 (43), e202311590. doi:10.1002/anie.202311590
Gou, S., Wang, G., Zou, Y., Geng, W., He, T., Qin, Z., et al. (2023). Non-pore dependent and MMP-9 responsive gelatin/silk fibroin composite microparticles as universal delivery platform for inhaled treatment of lung cancer. Adv. Mater 35 (42), e2303718. doi:10.1002/adma.202303718
Guo, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, S., Xu, W., Li, Y., Zhao, P., et al. (2021). Oxidative stress-induced FABP5 S-glutathionylation protects against acute lung injury by suppressing inflammation in macrophages. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 7094. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-27428-9
Han, J., Sheng, T., Zhang, Y., Cheng, H., Gao, J., Yu, J., et al. (2024). Bioresponsive immunotherapeutic materials. Adv. Mater 36 (43), e2209778. doi:10.1002/adma.202209778
He, J., Lin, X., Zhang, D., Hu, H., Chen, X., Xu, F., et al. (2024). Wake biofilm up to enhance suicidal uptake of gallium for chronic lung infection treatment. Biomaterials 310, 122619. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122619
Huang, J., Hong, X., Chen, S., He, Y., Xie, L., Gao, F., et al. (2024a). Biomimetic metal-organic framework gated nanoplatform for sonodynamic therapy against extensively drug resistant bacterial lung infection. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 11 (33), e2402473. doi:10.1002/advs.202402473
Huang, J., Zhuang, C., Chen, J., Chen, X., Li, X., Zhang, T., et al. (2022). Targeted drug/gene/photodynamic therapy via a stimuli-responsive dendritic-polymer-based nanococktail for treatment of EGFR-TKI-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. Adv. Mater 34 (27), e2201516. doi:10.1002/adma.202201516
Huang, Q., Ding, C., Wang, W., Yang, L., Wu, Y., Zeng, W., et al. (2024b). An “AND” logic gate-based supramolecular therapeutic nanoplatform for combatting drug-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Adv. 10 (39), eadp9071. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adp9071
Kang, W., Liu, Y., and Wang, W. (2023). Light-responsive nanomedicine for cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 13 (6), 2346–2368. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2023.05.016
Lalmohamed, A., Venekamp, R. P., Bolhuis, A., Souverein, P. C., van de Wijgert, J., Gulliford, M. C., et al. (2024). Within-episode repeat antibiotic prescriptions in patients with respiratory tract infections: a population-based cohort study. J. Infect. 88 (4), 106135. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106135
Leiter, A., Veluswamy, R. R., and Wisnivesky, J. P. (2023). The global burden of lung cancer: current status and future trends. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 20 (9), 624–639. doi:10.1038/s41571-023-00798-3
Li, D., Zhang, R., Liu, G., Kang, Y., and Wu, J. (2020c). Redox-responsive self-assembled nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater 9 (20), e2000605. doi:10.1002/adhm.202000605
Li, H., Duan, S., Li, L., Zhao, G., Wei, L., Zhang, B., et al. (2024b). Bio-responsive sliver peroxide-nanocarrier serves as broad-spectrum metallo-β-lactamase inhibitor for combating severe pneumonia. Adv. Mater 36 (11), e2310532. doi:10.1002/adma.202310532
Li, J., Ge, Z., Toh, K., Liu, X., Dirisala, A., Ke, W., et al. (2021). Enzymatically transformable polymersome-based nanotherapeutics to eliminate minimal relapsable cancer. Adv. Mater 33 (49), e2105254. doi:10.1002/adma.202105254
Li, J., and Kataoka, K. (2021). Chemo-physical strategies to advance the in vivo functionality of targeted nanomedicine: the next generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143 (2), 538–559. doi:10.1021/jacs.0c09029
Li, L., Zou, J., Dai, Y., Fan, W., Niu, G., Yang, Z., et al. (2020b). Burst release of encapsulated annexin A5 in tumours boosts cytotoxic T-cell responses by blocking the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 4 (11), 1102–1116. doi:10.1038/s41551-020-0599-5
Li, M., Li, Y., Zheng, J., Ma, Z., Zhang, J., Wu, H., et al. (2024d). Ultrasound-responsive nanocarriers with siRNA and Fe(3)O(4) regulate macrophage polarization and phagocytosis for augmented non-small cell lung cancer immunotherapy. J. Nanobiotechnology 22 (1), 605. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02883-w
Li, M., Zhao, G., Su, W. K., and Shuai, Q. (2020a). Enzyme-responsive nanoparticles for anti-tumor drug delivery. Front. Chem. 8, 647. doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.00647
Li, P., Pan, J., Dong, Y., Sun, Y., Wang, Y., Liao, K., et al. (2024e). Microenvironment responsive charge-switchable nanoparticles act on biofilm eradication and virulence inhibition for chronic lung infection treatment. J. Control Release 365, 219–235. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.11.032
Li, R., Li, J., and Zhou, X. (2024a). Lung microbiome: new insights into the pathogenesis of respiratory diseases. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 9 (1), 19. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01722-y
Li, X., Li, Y., Yu, C., Bao, H., Cheng, S., Huang, J., et al. (2023). ROS-Responsive janus Au/mesoporous silica core/shell nanoparticles for drug delivery and long-term CT imaging tracking of MSCs in pulmonary fibrosis treatment. ACS Nano 17 (7), 6387–6399. doi:10.1021/acsnano.2c11112
Li, X. N., Lin, Y. P., Han, M. M., Fang, Y. F., Xing, L., Jeong, J. H., et al. (2024f). Modulating fibrotic mechanical microenvironment for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis therapy. Adv. Mater 36 (50), e2407661. doi:10.1002/adma.202407661
Li, Y., Li, M., Zheng, J., Ma, Z., Yu, T., Zhu, Y., et al. (2024c). Ultrasound-responsive nanocarriers delivering siRNA and Fe(3)O(4) nanoparticles reprogram macrophages and inhibit M2 polarization for enhanced NSCLC immunotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 16 (42), 56634–56652. doi:10.1021/acsami.4c10036
Liang, H., Zhou, X., Zhu, Y., Li, D., Jing, D., Su, X., et al. (2023). Association of outdoor air pollution, lifestyle, genetic factors with the risk of lung cancer: a prospective cohort study. Environ. Res. 218, 114996. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2022.114996
Liang, L., Cen, H., Huang, J., Qin, A., Xu, W., Wang, S., et al. (2022). The reversion of DNA methylation-induced miRNA silence via biomimetic nanoparticles-mediated gene delivery for efficient lung adenocarcinoma therapy. Mol. Cancer 21 (1), 186. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01651-4
Liu, H., Tang, L., Yin, Y., Cao, Y., Fu, C., Feng, J., et al. (2024). Photoresponsive multirole nanoweapon camouflaged by hybrid cell membrane vesicles for efficient antibacterial therapy of pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected pneumonia and wound. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 11 (35), e2403101. doi:10.1002/advs.202403101
Lv, X., Min, J., Huang, J., Wang, H., Wei, S., Huang, C., et al. (2024). Simultaneously controlling inflammation and infection by smart nanomedicine responding to the inflammatory microenvironment. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 11 (39), e2403934. doi:10.1002/advs.202403934
Meyer, N. J., Gattinoni, L., and Calfee, C. S. (2021). Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet 398 (10300), 622–637. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00439-6
Muhammad, W., Zhang, Y., Zhu, J., Xie, J., Wang, S., Wang, R., et al. (2023). Co-delivery of azithromycin and ibuprofen by ROS-Responsive polymer nanoparticles synergistically attenuates the acute lung injury. Biomater. Adv. 154, 213621. doi:10.1016/j.bioadv.2023.213621
Natalini, J. G., Singh, S., and Segal, L. N. (2023). The dynamic lung microbiome in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 21 (4), 222–235. doi:10.1038/s41579-022-00821-x
Nayak, T. R., Chrastina, A., Valencia, J., Cordova-Robles, O., Yedidsion, R., Buss, T., et al. (2025). Rapid precision targeting of nanoparticles to lung via caveolae pumping system in endothelium. Nat. Nanotechnol. 20 (1), 144–155. doi:10.1038/s41565-024-01786-z
Odendaal, M. L., de Steenhuijsen Piters, W. A. A., Franz, E., Chu, M., Groot, J. A., van Logchem, E. M., et al. (2024). Host and environmental factors shape upper airway microbiota and respiratory health across the human lifespan. Cell 187 (17), 4571–4585.e15. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2024.07.008
Pan, K., Owens, J., Elamin, Y., Lu, C., Routbort, M., Zhang, J., et al. (2024). Mutational characteristics and clinical outcomes for lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR germline mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 19 (10), 1438–1448. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2024.06.004
Pani, S., and Mohapatra, S. S. (2024). Phenotypic heterogeneity in bacteria: the rise of antibiotic persistence, clinical implications, and therapeutic opportunities. Arch. Microbiol. 206 (11), 446. doi:10.1007/s00203-024-04173-3
Peng, S., Xiao, F., Chen, M., and Gao, H. (2022). Tumor-microenvironment-responsive nanomedicine for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 9 (1), e2103836. doi:10.1002/advs.202103836
Peng, X., Chen, J., Gan, Y., Yang, L., Luo, Y., Bu, C., et al. (2024). Biofunctional lipid nanoparticles for precision treatment and prophylaxis of bacterial infections. Sci. Adv. 10 (14), eadk9754. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adk9754
Pettigrew, M. M., Tanner, W., and Harris, A. D. (2021). The lung microbiome and pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 223 (12 Suppl. 2), S241–s245. doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa702
Podolanczuk, A. J., Thomson, C. C., Remy-Jardin, M., Richeldi, L., Martinez, F. J., Kolb, M., et al. (2023). Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: state of the art for 2023. Eur. Respir. J. 61 (4), 2200957. doi:10.1183/13993003.00957-2022
Reczyńska, K., Marchwica, P., Khanal, D., Borowik, T., Langner, M., Pamuła, E., et al. (2020). Stimuli-sensitive fatty acid-based microparticles for the treatment of lung cancer. Mater Sci. Eng. C Mater Biol. Appl. 111, 110801. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2020.110801
Shahriari, M., Zahiri, M., Abnous, K., Taghdisi, S. M., Ramezani, M., and Alibolandi, M. (2019). Enzyme responsive drug delivery systems in cancer treatment. J. Control Release 308, 172–189. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.07.004
Song, Z., Luo, W., Zheng, H., Zeng, Y., Wang, J., and Chen, T. (2021). Translational nanotherapeutics reprograms immune microenvironment in malignant pleural effusion of lung adenocarcinoma. Adv. Healthc. Mater 10 (12), e2100149. doi:10.1002/adhm.202100149
Su, Z., Dong, S., Chen, Y., Huang, T., Qin, B., Yang, Q., et al. (2023). Microfluidics-enabled nanovesicle delivers CD47/PD-L1 antibodies to enhance antitumor immunity and reduce immunotoxicity in lung adenocarcinoma. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 10 (20), e2206213. doi:10.1002/advs.202206213
Tammemägi, M. C., Darling, G. E., Schmidt, H., Walker, M. J., Langer, D., Leung, Y. W., et al. (2024). Risk-based lung cancer screening performance in a universal healthcare setting. Nat. Med. 30 (4), 1054–1064. doi:10.1038/s41591-024-02904-z
Valizadeh, H., Abdolmohammadi-Vahid, S., Danshina, S., Ziya Gencer, M., Ammari, A., Sadeghi, A., et al. (2020). Nano-curcumin therapy, a promising method in modulating inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 patients. Int. Immunopharmacol. 89 (Pt B), 107088. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107088
Wang, S., Liu, L., Tian, L., Xu, P., Li, S., Hu, L., et al. (2024d). Elucidation of spatial cooperativity in chemo-immunotherapy by a sequential dual-ph-responsive drug delivery system. Adv. Mater 36 (26), e2403296. doi:10.1002/adma.202403296
Wang, T., Duan, W., Jia, X., Huang, X., Liu, Y., Meng, F., et al. (2024c). Associations of combined phenotypic ageing and genetic risk with incidence of chronic respiratory diseases in the UK biobank: a prospective cohort study. Eur. Respir. J. 63 (2), 2301720. doi:10.1183/13993003.01720-2023
Wang, X., Shan, M., Zhang, S., Chen, X., Liu, W., Chen, J., et al. (2022). Stimuli-responsive antibacterial materials: molecular structures, design principles, and biomedical applications. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 9 (13), e2104843. doi:10.1002/advs.202104843
Wang, Y., Ding, Q., Ma, G., Zhang, Z., Wang, J., Lu, C., et al. (2024b). Mucus-penetrable biomimetic nanoantibiotics for pathogen-induced pneumonia treatment. ACS Nano 18 (45), 31349–31359. doi:10.1021/acsnano.4c10837
Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Liu, Y., Yue, X., Han, K., Kong, Z., et al. (2024a). Realveolarization with inhalable mucus-penetrating lipid nanoparticles for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Sci. Adv. 10 (24), eado4791. doi:10.1126/sciadv.ado4791
Wei, D., Sun, Y., Zhu, H., and Fu, Q. (2023). Stimuli-responsive polymer-based nanosystems for cancer theranostics. ACS Nano 17 (23), 23223–23261. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c06019
Weimann, A., Dinan, A. M., Ruis, C., Bernut, A., Pont, S., Brown, K., et al. (2024). Evolution and host-specific adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Science 385 (6704), eadi0908. doi:10.1126/science.adi0908
Wen, P., Ke, W., Dirisala, A., Toh, K., Tanaka, M., and Li, J. (2023). Stealth and pseudo-stealth nanocarriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 198, 114895. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2023.114895
Wijsenbeek, M., and Cottin, V. (2020). Spectrum of fibrotic lung diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 383 (10), 958–968. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2005230
Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., Tang, X., Ye, S., Shao, J., Tu, L., et al. (2023). Synergistic anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of ceria/resatorvid co-decorated nanoparticles for acute lung injury therapy. J. Nanobiotechnology 21 (1), 502. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-02237-y
Xia, D., Lu, Z., Li, S., Fang, P., Yang, C., He, X., et al. (2024). Development of an intelligent reactive oxygen species-responsive dual-drug delivery nanoplatform for enhanced precise therapy of acute lung injury. Int. J. Nanomedicine 19, 2179–2197. doi:10.2147/ijn.S442727
Xiong, J., Tang, H., Sun, L., Zhu, J., Tao, S., Luo, J., et al. (2024). A macrophage cell membrane-coated cascade-targeting photothermal nanosystem for combating intracellular bacterial infections. Acta Biomater. 175, 293–306. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2023.12.045
Xiu, W., Dong, H., Chen, X., Wan, L., Lu, L., Yang, K., et al. (2024). Metabolic modulation-mediated antibiotic and immune activation for treatment of chronic lung infections. ACS Nano 18 (23), 15204–15217. doi:10.1021/acsnano.4c03527
Xiu, W., Ren, L., Xiao, H., Zhang, Y., Wang, D., Yang, K., et al. (2023). Ultrasound-responsive catalytic microbubbles enhance biofilm elimination and immune activation to treat chronic lung infections. Sci. Adv. 9 (4), eade5446. doi:10.1126/sciadv.ade5446
Yan, Y., and Ding, H. (2020). pH-Responsive nanoparticles for cancer immunotherapy: a brief review. Nanomater. (Basel) 10 (8), 1613. doi:10.3390/nano10081613
Yan, Y., Sun, Y., Li, Y., Wang, Z., and Xue, L. (2025). Advancing cancer therapy: nanomaterial-Based encapsulation strategies for enhanced delivery and efficacy of curcumin. Mater Today Bio 33, 101963. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101963
Yang, Y., and Sun, W. (2022). Recent advances in redox-responsive nanoparticles for combined cancer therapy. Nanoscale Adv. 4 (17), 3504–3516. doi:10.1039/d2na00222a
Yu, C., Chen, Z., Li, X., Bao, H., Wang, Y., Zhang, B., et al. (2021). PH-triggered aggregation of gold nanoparticles for enhanced labeling and long-term CT imaging tracking of stem cells in pulmonary fibrosis treatment. Small 17 (33), e2101861. doi:10.1002/smll.202101861
Yu, H., Gao, R., Liu, Y., Fu, L., Zhou, J., and Li, L. (2024). Stimulus-responsive hydrogels as drug delivery systems for inflammation targeted therapy. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 11 (1), e2306152. doi:10.1002/advs.202306152
Yu, Q., Zhang, Q., Zhu, J., Pan, F., Zhang, H., Chen, L., et al. (2025). Inhalable neutrophil-mimicking nanoparticles for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treatment. J. Control Release 381, 113648. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.113648
Zaghen, F., Sora, V. M., Meroni, G., Laterza, G., Martino, P. A., Soggiu, A., et al. (2023). Epidemiology of antimicrobial resistance genes in staphyloccocus aureus isolates from a public database in a one health perspective-sample characteristics and isolates' sources. Antibiot. (Basel) 12 (7), 1225. doi:10.3390/antibiotics12071225
Zare'i, M., Rabieepour, M., Ghareaghaji, R., Zarrin, R., and Faghfouri, A. H. (2024). Nanocurcumin supplementation improves pulmonary function in severe COPD patients: a randomized, double blind, and placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 38 (3), 1224–1234. doi:10.1002/ptr.8114
Zhai, Z., Ouyang, W., Yao, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., Xu, F., et al. (2022). Dexamethasone-loaded ROS-Responsive poly(thioketal) nanoparticles suppress inflammation and oxidative stress of acute lung injury. Bioact. Mater 14, 430–442. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.01.047
Zhang, Q., Kuang, G., Li, W., Wang, J., Ren, H., and Zhao, Y. (2023). Stimuli-responsive gene delivery nanocarriers for cancer therapy. Nanomicro Lett. 15 (1), 44. doi:10.1007/s40820-023-01018-4
Zhou, L. Q., Li, P., Cui, X. W., and Dietrich, C. F. (2020). Ultrasound nanotheranostics in fighting cancer: advances and prospects. Cancer Lett. 470, 204–219. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.034
Keywords: stimuli-responsive materials, NDDSs, internal and external environments, lung diseases, treatment
Citation: Li W, Huang Q, Li M, Wen Y, Chen Z, Fan Y, Shen C, Gong C, Luo Y and Deng Z (2025) Research progress of nano-based drug delivery systems based on stimuli-responsive materials for the treatment of lung diseases. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1644007. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1644007
Received: 09 June 2025; Accepted: 21 July 2025;
Published: 31 July 2025.
Edited by:
Junjie Li, Kyushu University, JapanReviewed by:
Hailiang Wu, University of California, San Francisco, United StatesChangyuan Qin, The University of Chicago, United States
Copyright © 2025 Li, Huang, Li, Wen, Chen, Fan, Shen, Gong, Luo and Deng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhiping Deng, ZGVuZ3pwMTAxNkAxNjMuY29t; Yao Luo, bHVveWFvQHNjdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Wenqiang Li
Wenqiang Li Qian Huang
Qian Huang Mei Li
Mei Li Youli Wen
Youli Wen Zhao Chen
Zhao Chen Yuting Fan1,4
Yuting Fan1,4 Chen Shen
Chen Shen Chen Gong
Chen Gong Yao Luo
Yao Luo Zhiping Deng
Zhiping Deng