- 1Regenerative Medicine and Wound Repair Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
- 2Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
- 3Department of Joint Surgery, People’s Hospital of Liaoning Province, Shenyang, China
- 4Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University Department of Radiology, Shenyang, China
Background: Foot and ankle diseases significantly impact quality of life, with regenerative medicine emerging as a promising approach. A comprehensive evaluation of both efficacy and safety is paramount for its clinical translation.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed using keywords “regenerative medicine” and “foot and ankle” (as of 31 December 2024). Studies were categorized by technology and disease.
Results: PRP and HA showed short-term efficacy in talar cartilage repair; stem cells enhanced functional recovery in ankle osteoarthritis. 3D printing enabled personalized implants. Exosomes and AI were identified as future directions. However, the reporting of safety data was often sporadic and non-standardized, highlighting the need for more systematic monitoring in future studies.
Conclusion: Regenerative therapies demonstrate potential but require further validation through robust trials that prioritize standardized safety reporting alongside efficacy outcomes. Gaps in exosome isolation, long-term safety, and clinical translation need addressing.
1 Introduction
Foot and ankle disorders, stemming from their complex anatomy and weight-bearing function (Riddick et al., 2019; Brockett and Chapman, 2016), represent a significant clinical challenge worldwide (Lin et al., 2006). Current foot and ankle treatments include surgical and conservative options, with the latter often offering lower risk and cost alongside better structural preservation (Donken et al., 2012; Kerkhoffs et al., 2007; Ramelli et al., 2024; Lan et al., 2021a). Therefore, exploring more effective treatment methods, such as regenerative medicine, is crucial for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Regenerative medicine focuses on structural and functional restoration primarily through pharmacological activation of endogenous repair, cell-based replacement therapies, and bioengineered tissue constructs (Bajaj et al., 2014). This review performs a scoping analysis of several key approaches (e.g., stem cells (Golchin, 2022), PRP (Everts et al., 2020),3D printing, (Tack et al., 2016),and exosomes (Lai et al., 2022)) and their translational applications in foot and ankle pathology.
Despite rapid advancements, the evidence for these regenerative applications remains fragmented. A comprehensive synthesis that maps the current landscape, evaluates the efficacy and safety of different technologies across specific pathologies, and identifies key future directions is required. Consequently, this scoping review aims to critically explore the applications of bone regenerative medicine in the foot and ankle. We systematically categorize and evaluate the evidence for key technologies—including stem cells, platelet-rich plasma, hyaluronic acid, hypertonic glucose, placental tissues, 3D printing, exosomes, and AI—in managing major conditions such as talar osteochondral lesions, ankle osteoarthritis, Achilles tendon injuries, plantar fasciitis, and ligament injuries. This review seeks to provide a clear overview of the state of the art, discuss translational challenges, and inform future clinical research and practice.
2 Materials
This scoping review was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines and followed the methodological framework proposed by Arksey and O’Malley. The protocol was registered in advance. The methodology comprised five key stages: (1) identifying the research questions, (2) identifying relevant studies, (3) study selection, (4) charting the data, and (5) collating, summarizing, and reporting the results.
Step 1: Identifying the Research Questions
The primary objectives of this scoping review were as follows:
1. To map the key regenerative medicine technologies (e.g., stem cells, platelet-rich plasma, 3D printing) used in the treatment of common foot and ankle diseases.
2. To examine and describe the application and scope of these technologies in specific foot and ankle disorders, including talar cartilage injuries, ankle osteoarthritis, Achilles tendon injuries, plantar fasciitis, and ligament injuries.
3. To synthesize and report the main research outcomes and findings of various regenerative therapies in clinical applications.
4. To identify emerging technological trends (e.g., exosomes, artificial intelligence) and research gaps in the current literature, and to suggest directions for future research.
Step 2: Identifying Relevant Studies
A comprehensive literature search was performed in PubMed from inception to 31 December 2024. The search strategy combined Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and free-text terms related to regenerative medicine and foot and ankle pathologies. The search terms included but were not limited to: “regenerative medicine,” “stem cells,” “platelet-rich plasma,” “PRP,” “3D printing,” “biomaterials,” “exosomes,” “growth factors,” “talus cartilage injuries,” “ankle osteoarthritis,” “Achilles tendon injury,” “plantar fasciitis,” and “ligament injury.” The full search strategy for PubMed is illustrated in Table 1. The search was limited to English-language publications. Additionally, the reference lists of included studies were manually screened to identify any potentially relevant articles.
The PICOS framework (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Study Design) was applied to define eligibility criteria, as detailed in Table 2.
Studies were excluded if they were: (1) non-English publications; (2) non-peer-reviewed articles (e.g., editorials, commentaries, conference abstracts); (3) protocols or studies with unavailable full text; or (4) irrelevant to regenerative medicine or foot and ankle diseases.
Step 3: Study Selection
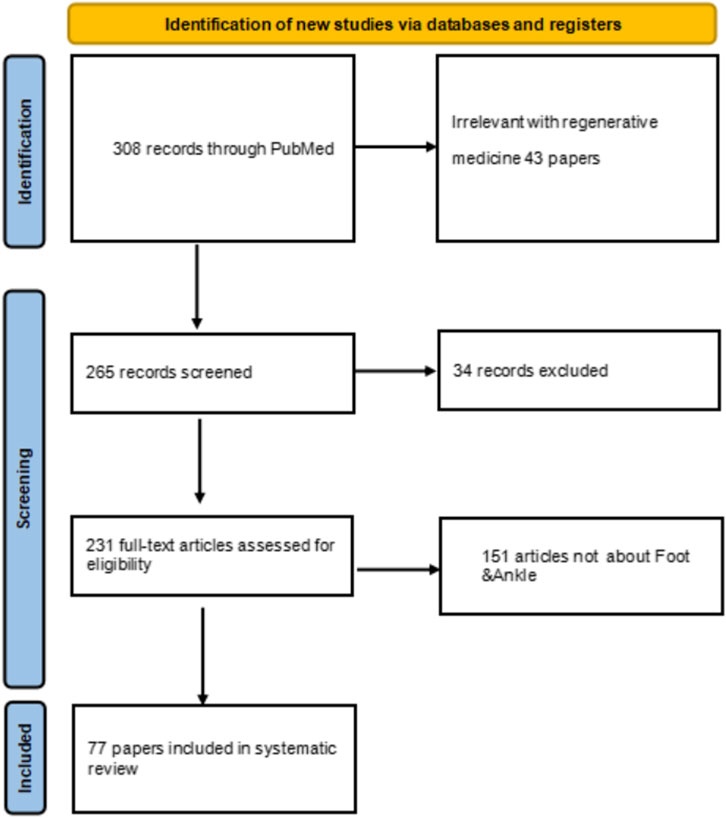
The study selection process involved two phases. First, two reviewers independently screened titles and abstracts against the eligibility criteria. Second, the full texts of potentially eligible studies were retrieved and assessed independently by the same reviewers. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion or by a third reviewer. The study selection process is summarized in a PRISMA flow diagram, which outlines the number of records identified, included, and excluded at each stage.
Step 4: Charting the Data
A standardized data extraction form was developed and piloted to document key information from included studies. Data were extracted by one reviewer and verified by another. The extracted items included: first author, publication year, study design, sample size, patient/model characteristics, intervention details (type, preparation, dosage, etc.), comparator, follow-up duration, and main outcomes/findings, as shown in Table 3.
Step 5: Collating, Summarizing, and Reporting Results
The extracted data were summarized quantitatively (e.g., frequency analysis) and qualitatively (narrative synthesis). The analysis aimed to describe the characteristics, scope, and trends of regenerative therapies in foot and ankle disorders. Results were presented in tables and narrative form.
Consistent with the purpose of a scoping review, no formal quality assessment of included studies was conducted, as the goal was to map the evidence rather than evaluate intervention efficacy.
3 Results
A systematic search of the PubMed database yielded 308 records for initial screening. Following the removal of duplicates, 265 records remained for title and abstract screening. During this stage, 154 records were excluded as they were deemed irrelevant to the focus on foot and ankle diseases. Subsequently, 111 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility. Of these, 43 articles were excluded for not meeting the regenerative medicine intervention criteria, and 34 articles were excluded due to unavailability of full text or being non-peer-reviewed publications. Ultimately, a total of 77 studies were included in the qualitative synthesis and descriptive analysis presented in this scoping review (see flow diagram in Figure 1). The included studies were further categorized and mapped based on the specific regenerative technology and foot/ankle disorder investigated (see study classification in Figure 2).
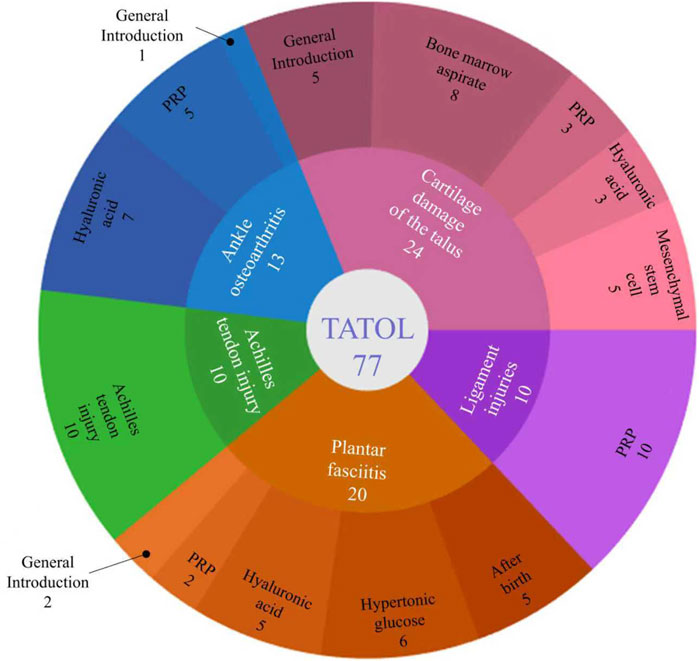
Figure 2. Number of references in each section of this paper regarding the application of regenerative medicine to diseases.
3.1 Applications in disease management
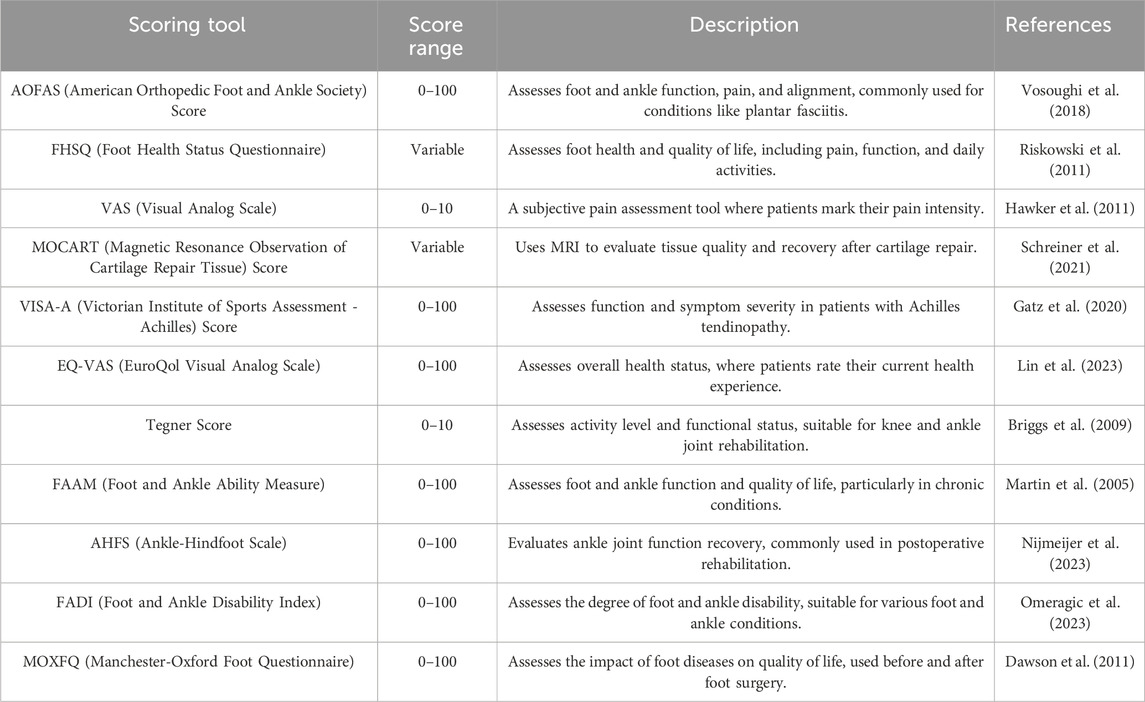
The standardized scoring tools commonly used for postoperative assessment of foot and ankle diseases and their clinical characteristics are summarized in Table 4. These tools cover multiple dimensions of evaluation, including pain, function, and imaging. Among them, the MOCART score provides a quantitative basis for evaluating cartilage repair efficacy through objective imaging parameters, while the VISA-A and Tegner scores focus on longitudinal monitoring of functional recovery in sports activities.
3.1.1 Talus cartilage injuries
Osteochondral lesions of the talus (OLT) refer to localized damage to the articular cartilage and its underlying subchondral bone, including cartilage tears, subchondral bone fractures, bone marrow edema, and subchondral cysts. These injuries are of significant concern in ankle joint pathology, commonly occurring following sprains, dislocations, or fractures (Cheng and Wang, 2024). Studies report that approximately 40% of patients with ankle sprains experience long-term instability and recurrent sprains, which can further lead to cartilage damage. (Wang et al., 2020). Treatment largely depends on clinical symptoms, the location of the lesions, and imaging findings. For lesions located medially or laterally with no radiological evidence of cartilage fragment detachment, conservative treatment may be considered. Conservative options include rest, casting or bracing, weight-bearing restrictions, and the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Surgical treatments encompass arthroscopic debridement, bone marrow stimulation or microfracture, osteochondral autograft transplantation, autologous chondrocyte implantation, and allograft osteochondral transplantation, among other techniques (Bruns et al., 2021). Among these, microfracture has traditionally been considered the “gold standard” for initial treatment as it promotes the formation of fibrocartilage at cartilage defects (Nguyen et al., 2024). According to the German Society for Orthopedics and Trauma Surgery, BMS is recommended for lesions with an area smaller than 1.5 cm2 and a depth less than 5 mm (Walther et al., 2024).
3.1.1.1 PRP
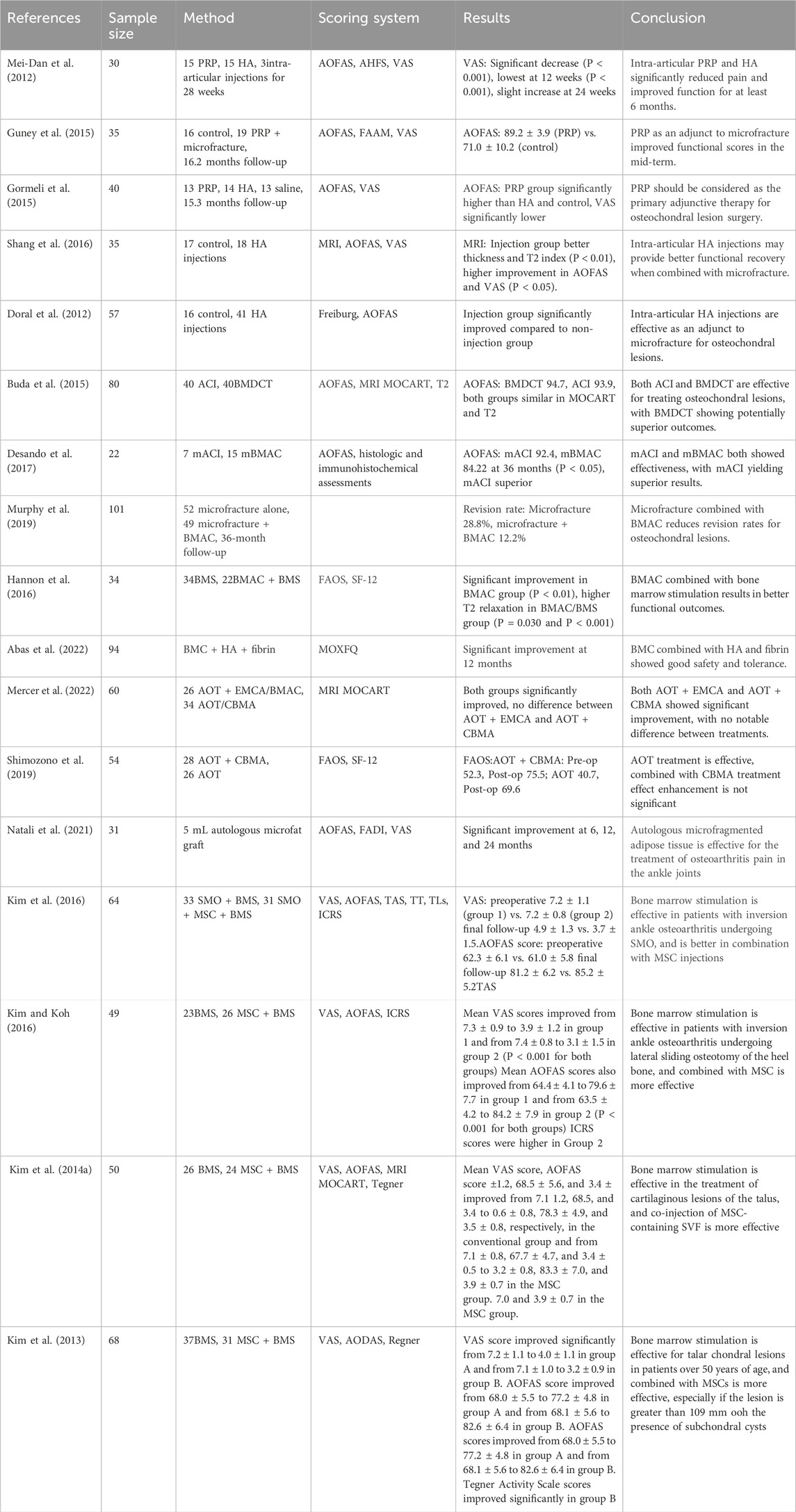
Intra-articular injection of PRP has been used in the treatment of talus cartilage lesions and has shown a significant reduction in pain scores, with functional improvement lasting for at least 6 months (Mei-Dan et al., 2012). When combined with arthroscopic microfracture surgery, PRP further enhances functional scores for mid-stage osteochondral lesions (Guney et al., 2015). Moreover, PRP is increasingly considered a primary adjunctive treatment after OCL surgery (Gormeli et al., 2015).
3.1.1.2 HA
Hyaluronic acid (HA), a nonsulfated linear polysaccharide comprising repeating disaccharides, exhibits tissue-specific molecular weight variations and high hydration in vivo (Prestwich, 2011). Its physicochemical properties are tunable via crosslinking/degradation, facilitating angiogenesis, osteointegration, and cellular homeostasis (Allison and Grande-Allen, 2006). Intra-articular injection of HA is another effective treatment for talus cartilage lesions, significantly reducing pain scores and improving functional status for at least 6 months (Mei-Dan et al., 2012). HA has also shown superior healing effects when used as an adjunct to arthroscopic microfracture surgery for osteochondral lesions (Shang et al., 2016), contributing to better outcomes in cartilage healing (Doral et al., 2012), and joint function recovery.
3.1.1.3 BMAC
Bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC) transplantationhas proven to be an effective regenerative technique for talus cartilage defects (Buda et al., 2015; Desando et al., 2017), with clinical outcomes slightly better than those of autologous chondrocyte implantation (Buda et al., 2015). BMAC, when used in combination with microfracture surgery, significantly reduces the recurrence rate of osteochondral lesions (Murphy et al., 2019). BMAC combined with arthroscopic microfracture surgery provides better functional improvement in the medium term. When combined with HA and fibrin, BMAC significantly enhances ankle joint cartilage function (Abas et al., 2022). However, not all combination therapies yield favorable clinical results, as seen in studies combining extracellular matrix allografts with cBMA (Mercer et al., 2022) or cBMA with autologous bone tissue grafts, which showed no significant benefits (Shimozono et al., 2019).
3.1.1.4 Adipose-derived MSCs and stromal vascular fraction
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells have shown promising results in treating talus cartilage lesions and have been shown to be safe in the treatment of ankle osteoarthritis pain (Natali et al., 2021). In patients with ankle osteoarthritis undergoing subtalar medial oblique osteotomy or calcaneal sliding osteotomy, additional mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) injection combined with bone marrow stimulation significantly improved VAS and AOFAS scores in the short-term follow-up (Kim et al., 2016; Kim and Koh, 2016). In combination therapies, MSCs have been widely applied. Kim et al. (2014a) compared the effects of bone marrow stimulation alone with bone marrow stimulation combined with MSC-containing stromal vascular fraction injections. The results indicated that the combined therapy of MSC-SVF and bone marrow stimulation significantly improved VAS, AOFAS, Tegner, and MOCART scores compared to bone marrow stimulation alone. Kim et al. (2013) found that combined treatment with MSCs had better results in the treatment of OLT in patients over 50 years of age by comparing MSC injection plus arthroscopic bone marrow stimulation versus arthroscopic bone marrow stimulation alone for the treatment of OLT in elderly patients.
The main information of Talus Cartilage Injuries included literature is shown in Table 5.
3.1.2 Ankle osteoarthritis
Ankle osteoarthritis (OA) is less common than knee and hip OA, with 75%–80% of clinical cases being trauma-related, typically resulting from ligament or bone injuries to the ankle. Conservative treatment for ankle OA currently focuses on pain relief, while surgical treatments for end-stage ankle OA are primarily centered around ankle arthrodesis and total ankle replacement (Anastasio et al., 2024).
3.1.2.1 PRP
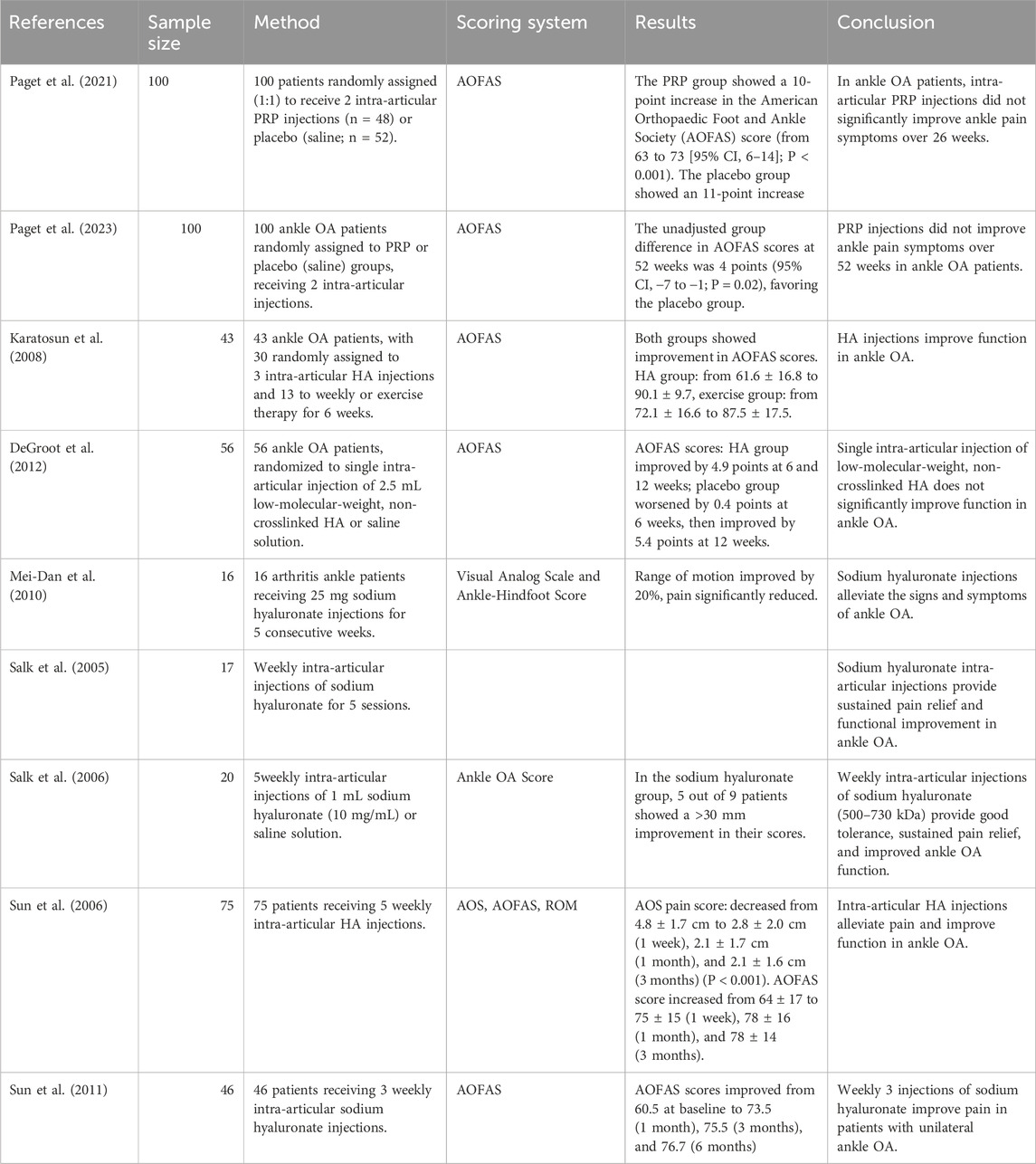
PRP injection therapy has been shown to improve the function and activity of ankle OA and has significant analgesic effects (Evans et al., 2020; Xiong et al., 2023), with particularly notable results in the short term (Laohajaroensombat et al., 2023). However, in long-term treatments (26 weeks (Paget et al., 2021) and 52 weeks (Paget et al., 2023)), the therapeutic effects do not show significant improvements.
3.1.2.2 HA
HA injections improve the function of patients with ankle OA (Karatosun et al., 2008), but require long-term administration. A single intra-articular injection of low-molecular-weight, non-crosslinked hyaluronic acid does not show significant functional improvements (DeGroot et al., 2012). For long-term injections, a regimen of 25 mg sodium hyaluronate injected intra-articularly over 5 consecutive weeks can alleviate the signs and symptoms of ankle OA (Mei-Dan et al., 2010). Weekly intra-articular injections of sodium hyaluronate for 5 weeks also show good results (Salk et al., 2005). Injections of sodium hyaluronate with a molecular weight of 500–730 kDa are well tolerated (Salk et al., 2006), and studies suggest that clinical benefits can be observed as early as 1 week, potentially lasting for 6 months or longer (Sun et al., 2006). Additionally, injecting hyaluronic acid three times per week also provides excellent clinical outcomes (Sun et al., 2011).
The main information of Ankle Osteoarthritis included literature is shown in Table 6.
3.1.3 Achilles tendon injury
Achilles tendon rupture (ATR) is the most common type of tendon rupture, accounting for 10.7% of all tendon and ligament injuries. In North America and Europe, the annual incidence of ATR ranges from 2.5 to 47 per 100,000 people (Briggs-Price et al., 2024). 60.1% of cases are secondary to sports-related mechanisms. Basketball is the most common sport-related mechanism, accounting for 36.6% of cases (Lyons et al., 2024). Heterotopic ossification (HO) occurs relatively frequently following Achilles tendon rupture. A clinical study indicated that nearly 20% of patients who underwent surgical repair of Achilles tendon rupture exhibited some degree of HO within the healing tendon (Sullivan et al., 2021). HO can lead to pain and functional impairment (Sullivan et al., 2021); however, it cannot be prevented through early rehabilitation (Guyton, 2020).
There is some evidence supporting the efficacy of a single PRP injection in treating chronic Achilles tendinopathy (AT). Monto (2012) treated 30 patients with chronic AT, who had failed 6 months of conservative treatment, with a single ultrasound-guided PRP injection. Three months post-treatment, the average AOFAS score improved from 34 to 92, with 88 points remaining at 24 months. Imaging showed resolution of Achilles tendon abnormalities in 27 of the 29 patients after 6 months. Clinical success was achieved in 28 of 30 patients. Krogh et al. (2016) studied 24 patients with a median disease duration of 33 months and treated them with blinded PRP (n = 12) or saline (n = 12). There were no differences in the VISA-A scores, but the PRP group showed tendon thickening. Boesen et al. (2017) indicated that PRP combined with eccentric training could reduce pain, improve activity levels, and reduce tendon thickness.
Regarding the long-term efficacy of PRP, repeated PRP injections show better outcomes. After three bi-weekly ultrasound-guided injections, the VISA-A score increased from baseline 49.9 ± 18.1 to 62.9 ± 19.8 at 2 months (Filardo et al., 2014).
However, the application of PRP in ATR patients shows limited effectiveness (Boesen et al., 2020; Schepull et al., 2011; Keene et al., 2022), and in non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy, the combination of endoscopic debridement with PRP shows limited results (Thermann et al., 2023).
3.1.4 Plantar fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is a common musculoskeletal injury, especially among runners, affecting approximately 17.4% of runners (Rhim et al., 2021). Risk factors include restricted ankle dorsiflexion, increased body mass index, and prolonged standing. Treatment should begin with stretching the plantar fascia, icing, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Refractory plantar fasciitis may require injections, extracorporeal shock wave therapy, or surgical intervention (Trojian and Tucker, 2019).
3.1.4.1 PRP
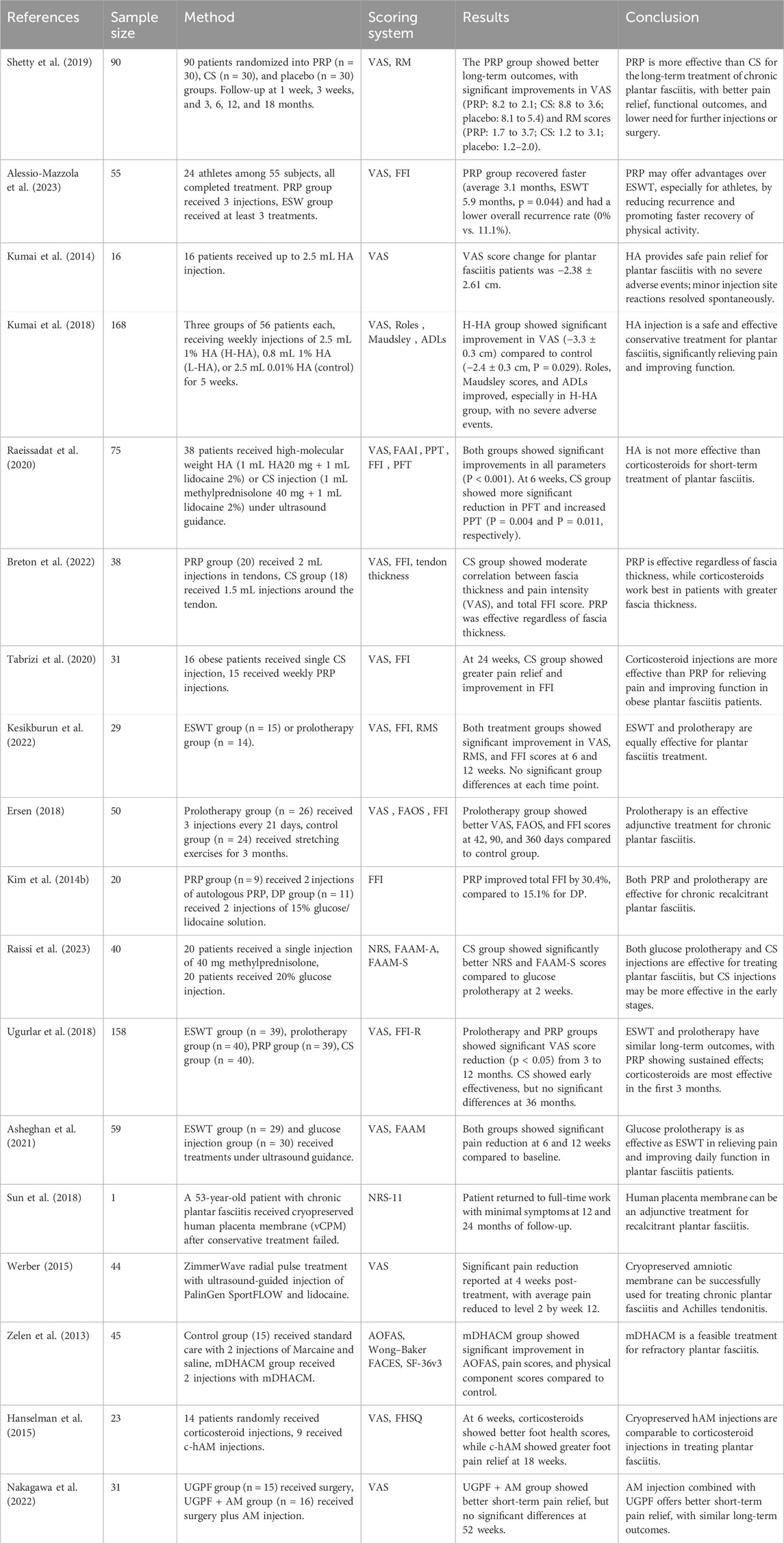
PRP injections are widely used in the treatment of plantar fasciitis, with studies assessing pain relief and reduction in fascia thickness using VAS, FADI, and AOFAS scores. Compared to corticosteroids, PRP treatment is more effective in relieving pain and restoring function, with longer-lasting effects (Shetty et al., 2019). For specific populations such as athletes, PRP injections can also accelerate functional recovery (Alessio-Mazzola et al., 2023).
3.1.4.2 HA
HA is used as a non-surgical treatment for knee OA and persistent shoulder pain, and its anti-inflammatory effects hold promise for treating plantar fasciitis. Studies suggest that HA injections are a safe and effective conservative treatment option for plantar fasciitis, significantly alleviating pain and improving function, with no severe adverse events; mild injection site reactions resolve spontaneously (Kumai et al., 2014; Kumai et al., 2018). However, other studies have pointed out that HA is less effective than corticosteroids for short-term treatment of plantar fasciitis (Raeissadat et al., 2020). Regarding the choice between PRP and corticosteroids, Breton et al. (2022) and others suggest that the treatment method should be based on initial fascia thickness. For patients with an initial fascia thickness greater than 7 mm, corticosteroids are recommended. Tabrizi et al. (2020) suggest that for obese patients with a BMI ≥30 kg/m2, corticosteroids should be preferred.
3.1.4.3 Hypertonic glucose
Hypertonic glucose injections mediate tissue repair through local initiation of wound healing phases (formation, inflammation, remodeling) and extracellular matrix synthesis (Kesikburun et al., 2022). Proposed mechanisms include VEGF pathway activation and cytokine modulation, though precise proliferative actions require further elucidation (Chutumstid et al., 2023).
Hypertonic glucose injection therapy is highly effective in treating plantar fasciitis (Kesikburun et al., 2022; Ersen, 2018; Kim et al., 2014b; Raissi et al., 2023; Ugurlar et al., 2018; Asheghan et al., 2021). Glucose prolotherapy has comparable efficacy to radial shock wave therapy in alleviating pain, improving daily function, and reducing plantar fascia thickness in plantar fasciitis patients (Kesikburun et al., 2022; Asheghan et al., 2021), although its effect is less pronounced than corticosteroid injection in the early stages (Raissi et al., 2023; Ugurlar et al., 2018).
3.1.4.4 Placenta
In the treatment of plantar fasciitis, Sun XP et al. found that human placenta membrane, cryopreserved and intact, could serve as an adjunctive treatment and significantly relieve pain (Sun et al., 2018). Amnion is a component of the human placenta membrane. Werber (2015) found that a single injection of human amniotic tissue-amniotic fluid significantly alleviated pain caused by plantar fasciitis. Zelen et al. (2013) observed that micro-powdered dehydrated human amniotic membrane improved symptoms and function in chronic plantar fasciitis after 8 weeks. Hanselman et al. (2015) compared cryopreserved human amniotic membrane injections with corticosteroid treatment for plantar fasciitis. After 12 weeks of follow-up, both groups showed similar results on the Foot Health Status Questionnaire and VAS scores. Nakagawa et al. (2022) found that combining amniotic membrane allograft injections with ultrasound-guided percutaneous plantar fascia release resulted in better early pain relief.
The main information of Plantar Fasciitis included literature is shown in Table 7.
3.1.5 Ligament injury
Acute ankle injuries are among the most common musculoskeletal injuries and are often accompanied by intra-articular damage (Bsoul et al., 2024). Ankle sprains typically cause pain, leading to missed work and/or restricted daily activities, and may result in ankle instability and other functional impairments (Kemler et al., 2011). The ankle complex consists of the ankle joint (subtalar joint), the tibiofibular joint (talus), and the transverse tarsal joint (ankle joint). The Achilles tendon attaches to the calcaneus and provides stability to the tibiofibular joint through the interosseous tibiofibular ligament, lateral collateral ligament, anterior talofibular ligament, and the tibionavicular ligament of the deltoid ligament (Lp et al., 2023). For ligament injuries, conservative treatment can also be effective. Compared to conservative treatment, surgical intervention has not shown clear advantages in the repair of these ligaments, particularly in recovery time and complication rates, thus surgery is not recommended (Lim et al., 2019). PRP treatment has proven effective in alleviating pain and promoting functional recovery during the healing process of ankle injuries (Zhang et al., 2022). For grade II lateral ankle sprain patients, PRP treatment significantly reduced pain and promoted functional recovery at 8 weeks (Blanco-Rivera et al., 2020). In athletes with high-grade ankle sprains, PRP helps stabilize the syndesmosis joint and reduce long-term residual pain (Laver et al., 2015). For chronic ankle sprains, especially in chronic lateral ankle instability patients, PRP also shows significant efficacy, effectively improving symptoms and function (Medina-Porqueres et al., 2024), and two consecutive PRP injections may yield better outcomes (Zhang et al., 2022). However, the effectiveness of PRP for treating ankle injuries remains debated. Rowden et al. (2015) noted that PRP did not show significant efficacy in treating acute ankle sprains. Similarly, Sabaghzadeh et al. (2023) found that PRP did not significantly improve function when used post-MBG surgery.
3.2 Key technological platforms in regenerative medicine
This section outlines the key technological platforms underpinning regenerative medicine applications in the foot and ankle, ranging from established cell-based therapies to emerging engineering and computational approaches.
3.2.1 Stem cell-based therapies
Stem cells form a cornerstone of regenerative medicine due to their defining capacities for self-renewal and multi-lineage differentiation. These cells are broadly categorized by their developmental potential: pluripotent stem cells (including embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells), multipotent stem cells, and unipotent stem cells (Kimbrel and Lanza, 2020). While embryonic stem cells represent a source of natural pluripotency, their clinical application is constrained by ethical considerations and risks of immune rejection (Liu et al., 2020). Induced pluripotent stem cells, generated by reprogramming somatic cells, offer a patient-specific alternative but face challenges such as a bias toward fetal-state differentiation and incompletely defined molecular mechanisms.
In clinical practice for foot and ankle disorders, MSCs are the most widely utilized adult stem cell type. MSCs demonstrate the ability to differentiate into osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic lineages (Qin et al., 2023), and their therapeutic effect is further enhanced through the secretion of paracrine factors that modulate the local microenvironment (Pittenger et al., 1999). Common clinical sources of MSCs include:Bone Marrow: BMAC contains a heterogeneous mixture of cellular components, including platelets, monocytes, and MSCs, providing a rich regenerative milieu (Lan et al., 2021b). Adipose Tissue: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) possess multi-lineage differentiation potential and robust regenerative capabilities. Compared to bone marrow-derived MSCs, ADSCs offer advantages of higher accessibility, greater abundance, and lower donor site morbidity (Yuan et al., 2024). Placental and Amniotic Tissues: The human amniotic membrane (hAM) is considered an important source of stem cells (Igura et al., 2004; Hu et al., 2023) and contains multiple bioactive factors that synergistically promote tissue repair and regeneration (Parolini et al., 2009).
3.2.2 3D printing
3D printing technology constructs objects layer by layer based on digital models and has been widely adopted in the biomedical field, particularly in personalized medicine. In the treatment of ankle disorders, its value is primarily demonstrated in: (1) fabricating customized implants for bone repair, such as talar prostheses (Giannotti et al., 2023; Gatz et al., 2020; Hannon et al., 2016); (2) producing physical anatomical models for preoperative planning of complex surgeries [72,147,148]; and (3) manufacturing patient-matched surgical guides and orthotic devices (Gormeli et al., 2015; Sun et al., 2018; Briggs et al., 2009) (e.g., AFOs). However, it must be noted that most existing studies supporting these applications are relatively small in scale, and many conclusions regarding the functional advantages of “personalized implants” are derived from case reports or small case series. Therefore, such claims should be interpreted with caution, and their clinical benefits require further validation. The general challenges facing the technology mainly involve printing accuracy and biomimeticity, material biocompatibility and regulatory compliance, as well as performance limitations of bioinks (Li et al., 2022). Specifically, in applications such as surgical guides, additional constraints include limited material options, suboptimal cost and time efficiency, insufficient long-term clinical evidence, and a lack of industry standards and regulations (Meng et al., 2022).
3.2.3 Exosomes
Exosomes are nanoscale extracellular vesicles actively secreted by cells, with a diameter of 30–150 nm, encased in a lipid bilayer membrane, containing proteins, nucleic acids, and other active molecules. The production process involves cell endocytosis, forming early endosomes, which mature into multivesicular bodies under the action of endosomal sorting complexes, eventually being released extracellularly. Exosomes play a critical role in intercellular communication, substance transport, immune regulation, tumor development, and tissue repair and regeneration (Doyle and Wang, 2019; Zhang et al., 2015). Although exosomes theoretically offer numerous benefits, research on exosomes remains confined to laboratory animal models. Exosome-based therapies for ankle repair show immense promise, leveraging their ability to promote osteogenesis, angiogenesis, and chondrogenesis. For instance, exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and other sources enhance tissue repair by delivering key regulatory molecules (e.g., miR-126, miR-140-5p) (Yu et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2020; Behera et al., 2021). (Wu et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2018). However, the transition from promising research to clinical application faces significant hurdles. Key challenges include the lack of standardized methods for exosome isolation, quantification, and drug loading, which impacts batch-to-batch consistency and therapeutic reproducibility (Rezaie et al., 2022; Tian et al., 2023). Furthermore, critical translational barriers must be addressed, such as establishing clear regulatory pathways (e.g., FDA/EMA classification as a biologic or drug product), implementing Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance for production, ensuring quality control, and navigating ethical requirements for informed consent and long-term patient follow-up in clinical trials.
3.2.4 Artificial intelligence
AI has emerged as a pivotal enabler in the advancement of regenerative medicine. Central to this role are machine learning—which identifies patterns from datasets—and deep learning—which excels at processing complex, high-dimensional data. Together, these methodologies constitute the analytical foundation of predictive regenerative medicine. AI is transforming the field across several critical fronts: it significantly enhances the discovery, development, and manufacturing of biotherapeutics, including cell and gene therapies, while also providing robust decision support in clinical trial design, patient stratification, and dynamic treatment assessment. These advances collectively contribute to improved diagnostic accuracy, research and development (R&D) efficiency, and therapeutic outcomes. However, the predictive performance and generalizability of AI models are heavily contingent upon the quality and comprehensiveness of the training data. Consequently, the successful implementation of such approaches necessitates unprecedented levels of accuracy, standardization, and consistency in multi-source clinical data—encompassing genomic profiles, medical histories, and imaging data—obtained from collaborative research and clinical centers. Inadequate data governance and quality control remain significant impediments to the widespread adoption of this research paradigm (Garmany and Terzic, 2024).
4 Discussion
This scoping review synthesizes regenerative medicine advancements for five major foot/ankle pathologies: ligament injuries, talar cartilage defects, ankle osteoarthritis, Achilles tendinopathy, and plantar fasciitis. Although significant methodological variations and ongoing debates regarding efficacy exist, current evidence indicates a trend toward the clinical potential of regenerative therapies in areas such as pain relief, functional recovery, and tissue repair. Nonetheless, the observed heterogeneity among studies highlights the need for further rigorously designed trials.
PRP is an autologous blood-derived product processed to concentrate platelets and related growth factors (Carr, 2022). PRP therapy is based on platelet-derived growth factors that support the three stages of wound healing and repair: inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling (Everts et al., 2020). PRP contains a large number of growth factors and cytokines that promote tissue regeneration, accelerate wound healing, and reduce inflammation. Due to its theoretical potential to repair tissues with poor healing capabilities, PRP is increasingly used in the treatment of various musculoskeletal diseases (Martinez-Martinez et al., 2018). In addition to PRP, platelet derivatives such as platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and concentrated growth factors (CGF) have different clinical effects (Giannotti et al., 2023). However, the translation of this strong theoretical foundation into consistent clinical evidence faces significant challenges. Current evidence on PRP therapy in the foot and ankle field indicates that the methodological quality of randomized controlled trials is generally low to moderate (Bennell et al., 2017), with limitations such as inadequate blinding and small sample sizes. Therefore, conclusions from any single study should be interpreted with caution. The core issue has shifted from “whether PRP is effective” to “how to define and standardize PRP to enable meaningful comparisons and optimization” (Kieb et al., 2017). Considerable variations exist across studies regarding the number and timing of injections. Some researchers adopt repeated injection protocols based on the rationale of sustaining growth factor release to enhance efficacy (Filardo et al., 2014). Such fundamental discrepancies in treatment protocols lead to inconsistent conclusions and pose challenges for evidence synthesis. Moreover, the efficacy of PRP is influenced by multiple factors. First, platelet concentration has an “optimal window”: insufficient concentration may fail to deliver adequate growth factors (e.g., TGF-β1, PDGF), while excessive concentration may trigger exaggerated inflammatory responses and impair healing (Sánchez-González et al., 2012). Second, leukocytes exhibit a complex dual role in PRP. On one hand, they help remove necrotic tissue and secrete specific cytokines to initiate repair; on the other hand, excessive activation may release pro-inflammatory mediators, aggravating local inflammation and potentially leading to adverse outcomes (Dohan Ehrenfest et al., 2012). Furthermore, leukocyte content affects the release kinetics of growth factors: high-leukocyte PRP tends to form more stable fibrin scaffolds enabling sustained release, which may be more suitable for chronic injuries; whereas low-leukocyte PRP is characterized by a rapid, burst-like release of growth factors (Calciolari et al., 2025). Finally, the preparation technique (e.g., centrifugation conditions) profoundly influences the structure of the fibrin matrix and the release kinetics of growth factors, thereby modulating the overall biological effects of PRP (Giannotti et al., 2023). Even the use of activators (e.g., Ca2+) is not merely for accelerating activation but also regulates the release pattern of growth factors (Steller et al., 2019). Therefore, there is currently no universally accepted standardized protocol for PRP. Its definition remains ambiguous, encompassing a range of unresolved variables such as platelet and leukocyte concentrations, activation methods and agents, anticoagulant use, and final product form (Anitua et al., 2022). In the treatment of foot and ankle disorders (such as Achilles tendinopathy, ligament injuries, and osteoarthritis),PRP represents an emerging biological therapy. However, it must be clearly recognized that PRP is not a single, standardized “drug.” Therefore, in the absence of specific clinical practice guidelines for PRP, management should adhere to existing general guidelines. We anticipate that more standardized, high-quality studies will emerge in the future to refine its treatment protocols and provide more definitive and reliable conclusions for clinical practice.
HO is an aberrant regenerative process characterized by the pathological deposition of bone tissue within soft tissues where it does not normally occur, such as tendon regions following Achilles tendon rupture (Lin et al., 2010; Lui et al., 2009). The precise mechanisms underlying its formation remain incompletely elucidated; it is generally regarded as a pathological wound healing response subsequent to musculoskeletal trauma, involving both local and systemic inflammatory processes (Kraft et al., 2016). This process is potentially associated with the differentiation of stem or tendon cells into chondrocytes, followed by chondral hypertrophy and calcification, ultimately leading to osteogenesis (Lui et al., 2009). Li and Tuan (2020) proposed that muscle injury-induced upregulation of local BMP-7 levels, combined with a systemic downregulation of TGF-β1 caused by glucocorticoid excess, may represent a critical pathogenic mechanism in traumatic HO (tHO) formation. Current management of traumatic HO remains predominantly prophylactic. Conventional strategies include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, e.g., celecoxib, which has been demonstrated to inhibit HO formation in rat models (Zhang et al., 2013) and glucocorticoids. However, celecoxib is ineffective against the progression of already initiated HO (Li et al., 2019). Recent investigations have revealed that a synergistic strategy combining engineered exosomes with 3D-printed scaffolds shows significant promise. This approach primarily entails (Xu et al., 2025): (1) pre-treating the cell source with a BMP signaling pathway inhibitor (e.g., LDN-193189) to endow the secreted exosomes with intrinsic “anti-osteogenic” activity; (2) engineering the exosomal membrane (e.g., by incorporating RGD peptides) to enhance its targeting capability and retention at the injury site; and (3) loading the modified exosomes onto a biodegradable 3D-printed sustained-release scaffold, which provides structural support while enabling the long-term controlled release of bioactive molecules. In rigorous animal models, this strategy not only significantly promoted tendon-like tissue regeneration and the restoration of biomechanical function but also, more importantly, effectively inhibited heterotopic ossification formation as confirmed by micro-CT and histological analyses.
The clinical translation of stem cells faces several challenges, including the need to optimize cell sources, differentiation protocols, and delivery methods to ensure treatment safety, efficacy, and reproducibility. Furthermore, post-transplant immune rejection responses and other potential adverse events require rigorous evaluation and long-term monitoring (Rahimi Darehbagh et al., 2024).
Author contributions
YaL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Project administration. YiL: Investigation, Data curation, Writing – review and editing. TW: Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing – review and editing. ZZ: Investigation, Resources, Validation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. WL: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. JL: Investigation, Data curation, Writing – review and editing. HC: Investigation, Data curation, Writing – review and editing ZQ: Formal analysis, Writing – review and editing. XW: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. WB: Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. HL: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This review was supported by the Dalian Medical Science Research Program [21Z12006] and the ‘1+X’ Program Clinical Technology Level Improvement Project Task Book of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University [2022LCJSYS17].
Acknowledgements
We thank Untitled (https://www.figdraw.com/static/index.html#/ for providing us with a drawing platform.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2025.1653964/full#supplementary-material
References
Abas, S., Kuiper, J. H., Roberts, S., McCarthy, H., Williams, M., Bing, A., et al. (2022). Osteochondral lesions of the ankle treated with bone marrow concentrate with hyaluronan and fibrin: a single-centre study. Cells 11 (4), 629. doi:10.3390/cells11040629
Alessio-Mazzola, M., Stambazzi, C., Ursino, C., Tagliafico, A., Trentini, R., and Formica, M. (2023). Ultrasound-guided autologous platelet-rich plasma injections versus focal ultrasound-guided extracorporeal shockwave therapy for plantar fasciitis in athletes and nonathletes: a retrospective comparative study with minimum 2-year follow-up. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 62 (3), 417–421. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2022.10.005
Allison, D. D., and Grande-Allen, K. J. (2006). Review. Hyaluronan: a powerful tissue engineering tool. Tissue Eng. 12 (8), 2131–2140. doi:10.1089/ten.2006.12.2131
Anastasio, A. T., Lau, B., and Adams, S. (2024). Ankle osteoarthritis. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 32 (16), 738–746. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-23-00743
Anitua, E., Zalduendo, M., Troya, M., Alkhraisat, M. H., and Blanco-Antona, L. A. (2022). Platelet-rich plasma as an alternative to xenogeneic sera in cell-based therapies: a need for standardization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (12), 6552. doi:10.3390/ijms23126552
Asheghan, M., Hashemi, S. E., Hollisaz, M. T., Roumizade, P., Hosseini, S. M., and Ghanjal, A. (2021). Dextrose prolotherapy versus radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Foot Ankle Surg. 27 (6), 643–649. doi:10.1016/j.fas.2020.08.008
Bajaj, P., Schweller, R. M., Khademhosseini, A., West, J. L., and Bashir, R. (2014). 3D biofabrication strategies for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 16, 247–276. doi:10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071813-105155
Behera, J., Kumar, A., Voor, M. J., and Tyagi, N. (2021). Exosomal lncRNA-H19 promotes osteogenesis and angiogenesis through mediating Angpt1/Tie2-NO signaling in CBS-heterozygous mice. Theranostics 11 (16), 7715–7734. doi:10.7150/thno.58410
Bennell, K. L., Hunter, D. J., and Paterson, K. L. (2017). Platelet-rich plasma for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 19 (5), 24. doi:10.1007/s11926-017-0652-x
Blanco-Rivera, J., Elizondo-Rodriguez, J., Simental-Mendia, M., Vilchez-Cavazos, F., Pena-Martinez, V. M., and Acosta-Olivo, C. (2020). Treatment of lateral ankle sprain with platelet-rich plasma: a randomized clinical study. Foot Ankle Surg. 26 (7), 750–754. doi:10.1016/j.fas.2019.09.004
Boesen, A. P., Hansen, R., Boesen, M. I., Malliaras, P., and Langberg, H. (2017). Effect of high-volume injection, platelet-rich plasma, and sham treatment in chronic midportion achilles tendinopathy: a randomized double-blinded prospective study. Am. J. Sports Med. 45 (9), 2034–2043. doi:10.1177/0363546517702862
Boesen, A. P., Boesen, M. I., Hansen, R., Barfod, K. W., Lenskjold, A., Malliaras, P., et al. (2020). Effect of platelet-rich plasma on nonsurgically treated acute achilles Tendon ruptures: a randomized, double-blinded prospective study. Am. J. Sports Med. 48 (9), 2268–2276. doi:10.1177/0363546520922541
Breton, A., Leplat, C., Picot, M. C., Aouinti, S., Taourel, P., Laffont, I., et al. (2022). Prediction of clinical response to corticosteroid or platelet-rich plasma injection in plantar fasciitis with MRI: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. Diagn Interv. Imaging 103 (4), 217–224. doi:10.1016/j.diii.2021.10.008
Briggs, K. K., Lysholm, J., Tegner, Y., Rodkey, W. G., Kocher, M. S., and Steadman, J. R. (2009). The reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the lysholm score and tegner activity scale for anterior cruciate ligament injuries of the knee: 25 years later. Am. J. Sports Med. 37 (5), 890–897. doi:10.1177/0363546508330143
Briggs-Price, S., Mangwani, J., Houchen-Wolloff, L., Modha, G., Fitzpatrick, E., Faizi, M., et al. (2024). Incidence, demographics, characteristics and management of acute achilles tendon rupture: an epidemiological study. PLoS One 19 (6), e0304197. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0304197
Brockett, C. L., and Chapman, G. J. (2016). Biomechanics of the ankle. Orthop. Trauma 30 (3), 232–238. doi:10.1016/j.mporth.2016.04.015
Bruns, J., Habermann, C., and Werner, M. (2021). Osteochondral lesions of the talus: a review on talus osteochondral injuries, including osteochondritis dissecans. Cartilage 13 (1_Suppl. l), 1380S–1401S. doi:10.1177/1947603520985182
Bsoul, N., Ning, L., Cai, L., Mazmanyan, D., and Porter, D. (2024). Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for the management of acute ankle injuries according to: a PRISMA systematic review and quality appraisal with AGREE II. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 25 (1), 523. doi:10.1186/s12891-024-07655-z
Buda, R., Vannini, F., Castagnini, F., Cavallo, M., Ruffilli, A., Ramponi, L., et al. (2015). Regenerative treatment in osteochondral lesions of the talus: autologous chondrocyte implantation versus one-step bone marrow derived cells transplantation. Int. Orthop. 39 (5), 893–900. doi:10.1007/s00264-015-2685-y
Calciolari, E., Dourou, M., Akcali, A., and Donos, N. (2025). Differences between first- and second-generation autologous platelet concentrates. Periodontol 97 (1), 52–73. doi:10.1111/prd.12550
Carr, B. J. (2022). Platelet-rich plasma as an orthobiologic: clinically relevant considerations. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 52 (4), 977–995. doi:10.1016/j.cvsm.2022.02.005
Cheng, L., and Wang, X. (2024). Advancements in the treatment of osteochondral lesions of the talus. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 19 (1), 827. doi:10.1186/s13018-024-05314-6
Chutumstid, T., Susantitaphong, P., and Koonalinthip, N. (2023). Effectiveness of dextrose prolotherapy for the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PM R. 15 (3), 380–391. doi:10.1002/pmrj.12807
Dawson, J., Boller, I., Doll, H., Lavis, G., Sharp, R., Cooke, P., et al. (2011). The MOXFQ patient-reported questionnaire: assessment of data quality, reliability and validity in relation to foot and ankle surgery. Foot (Edinb) 21 (2), 92–102. doi:10.1016/j.foot.2011.02.002
DeGroot, H., Uzunishvili, S., Weir, R., Al-omari, A., and Gomes, B. (2012). Intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid is not superior to saline solution injection for ankle arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 94 (1), 2–8. doi:10.2106/JBJS.J.01763
Desando, G., Bartolotti, I., Vannini, F., Cavallo, C., Castagnini, F., Buda, R., et al. (2017). Repair potential of matrix-induced bone marrow aspirate concentrate and matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation for talar osteochondral repair: patterns of some catabolic, inflammatory, and pain mediators. Cartilage 8 (1), 50–60. doi:10.1177/1947603516642573
Dohan Ehrenfest, D. M., Bielecki, T., Jimbo, R., Barbé, G., Del Corso, M., Inchingolo, F., et al. (2012). Do the fibrin architecture and leukocyte content influence the growth factor release of platelet concentrates? An evidence-based answer comparing a pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) gel and a leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 13 (7), 1145–1152. doi:10.2174/138920112800624382
Donken, C. C., Al-Khateeb, H., Verhofstad, M. H., and van Laarhoven, C. J. (2012). Surgical versus conservative interventions for treating ankle fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012 (8), CD008470. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008470.pub2
Doral, M. N., Bilge, O., Batmaz, G., Donmez, G., Turhan, E., Demirel, M., et al. (2012). Treatment of osteochondral lesions of the talus with microfracture technique and postoperative hyaluronan injection. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 20 (7), 1398–1403. doi:10.1007/s00167-011-1856-7
Doyle, L. M., and Wang, M. Z. (2019). Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells 8 (7), 727. doi:10.3390/cells8070727
Ersen, O. (2018). A randomized-controlled trial of prolotherapy injections in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. Turk J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 64 (1), 59–65. doi:10.5606/tftrd.2018.944
Evans, A., Ibrahim, M., Pope, R., Mwangi, J., Botros, M., Johnson, S. P., et al. (2020). Treating hand and foot osteoarthritis using a patient's own blood: a systematic review and meta-analysis of platelet-rich plasma. J. Orthop. 18, 226–236. doi:10.1016/j.jor.2020.01.037
Everts, P., Onishi, K., Jayaram, P., Lana, J. F., and Mautner, K. (2020). Platelet-rich plasma: new performance understandings and therapeutic considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (20), 7794. doi:10.3390/ijms21207794
Filardo, G., Kon, E., Di Matteo, B., Di Martino, A., Tesei, G., Pelotti, P., et al. (2014). Platelet-rich plasma injections for the treatment of refractory achilles tendinopathy: results at 4 years. Blood Transfus. 12 (4), 533–540. doi:10.2450/2014.0289-13
Garmany, A., and Terzic, A. (2024). Artificial intelligence powers regenerative medicine into predictive realm. Regen. Med. 19 (12), 611–616. doi:10.1080/17460751.2024.2437281
Gatz, M., Betsch, M., Dirrichs, T., Schrading, S., Tingart, M., Michalik, R., et al. (2020). Eccentric and isometric exercises in achilles tendinopathy evaluated by the VISA-A score and shear wave elastography. Sports Health 12 (4), 373–381. doi:10.1177/1941738119893996
Giannotti, L., Di Chiara Stanca, B., Spedicato, F., Nitti, P., Damiano, F., Demitri, C., et al. (2023). Progress in regenerative medicine: exploring autologous platelet concentrates and their clinical applications. Genes (Basel) 14 (9), 1669. doi:10.3390/genes14091669
Golchin, A. (2022). Stem cell technology and skin disorders: from stem cell biology to clinical applications. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 18 (6), 1881–1882. doi:10.1007/s12015-022-10381-5
Gormeli, G., Karakaplan, M., Gormeli, C. A., Sarikaya, B., Elmali, N., and Ersoy, Y. (2015). Clinical effects of platelet-rich plasma and hyaluronic acid as an additional therapy for talar osteochondral lesions treated with microfracture surgery: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Foot Ankle Int. 36 (8), 891–900. doi:10.1177/1071100715578435
Guney, A., Akar, M., Karaman, I., Oner, M., and Guney, B. (2015). Clinical outcomes of platelet rich plasma (PRP) as an adjunct to microfracture surgery in osteochondral lesions of the talus. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 23 (8), 2384–2389. doi:10.1007/s00167-013-2784-5
Guyton, G. P. (2020). CORR insights®: heterotopic ossification after an achilles tendon rupture cannot be prevented by early functional rehabilitation: a cohort study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 478 (5), 1109–1110. doi:10.1097/corr.0000000000001200
Hannon, C. P., Ross, K. A., Murawski, C. D., Deyer, T. W., Smyth, N. A., Hogan, M. V., et al. (2016). Arthroscopic bone marrow stimulation and concentrated bone marrow aspirate for osteochondral lesions of the talus: a case-control study of functional and magnetic resonance observation of cartilage repair tissue outcomes. Arthroscopy 32 (2), 339–347. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2015.07.012
Hanselman, A. E., Tidwell, J. E., and Santrock, R. D. (2015). Cryopreserved human amniotic membrane injection for plantar fasciitis: a randomized, controlled, double-blind pilot study. Foot Ankle Int. 36 (2), 151–158. doi:10.1177/1071100714552824
Hawker, G. A., Mian, S., Kendzerska, T., and French, M. (2011). Measures of adult pain: visual analog scale for pain (VAS pain), numeric rating scale for pain (NRS pain), McGill pain questionnaire (MPQ), short-form McGill pain questionnaire (SF-MPQ), chronic pain grade Scale (CPGS), short Form-36 bodily pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and measure of intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res. Hob. 63 (Suppl. 11), S240–S252. doi:10.1002/acr.20543
Hu, Z., Luo, Y., Ni, R., Hu, Y., Yang, F., Du, T., et al. (2023). Biological importance of human amniotic membrane in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Mater Today Bio 22, 100790. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100790
Igura, K., Zhang, X., Takahashi, K., Mitsuru, A., Yamaguchi, S., and Takashi, T. A. (2004). Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal progenitor cells from chorionic villi of human placenta. Cytotherapy 6 (6), 543–553. doi:10.1080/14653240410005366-1
Jiang, Y., Zhang, J., Li, Z., and Jia, G. (2020). Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-25 regulates the ubiquitination and degradation of Runx2 by SMURF1 to promote fracture healing in mice. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 7, 577578. doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.577578
Karatosun, V., Unver, B., Ozden, A., Ozay, Z., and Gunal, I. (2008). Intra-articular hyaluronic acid compared to exercise therapy in osteoarthritis of the ankle. A prospective randomized trial with long-term follow-up. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 26 (2), 288–294.
Keene, D. J., Alsousou, J., Harrison, P., O’Connor, H. M., Wagland, S., Dutton, S. J., et al. (2022). Platelet-rich plasma injection for acute achilles tendon rupture: two-year follow-up of the PATH-2 randomized, placebo-controlled, superiority trial. Bone Jt. J. 104-B (11), 1256–1265. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.104B11.BJJ-2022-0653.R1
Kemler, E., van de Port, I., Backx, F., and van Dijk, C. N. (2011). A systematic review on the treatment of acute ankle sprain: brace versus other functional treatment types. Sports Med. 41 (3), 185–197. doi:10.2165/11584370-000000000-00000
Kerkhoffs, G. M., Handoll, H. H., de Bie, R., Rowe, B. H., and Struijs, P. A. (2007). Surgical versus conservative treatment for acute injuries of the lateral ligament complex of the ankle in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (2), CD000380. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000380.pub2
Kesikburun, S., Uran San, A., Kesikburun, B., Aras, B., Yasar, E., and Tan, A. K. (2022). Comparison of ultrasound-guided prolotherapy versus extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis: a randomized clinical trial. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 61 (1), 48–52. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2021.06.007
Kieb, M., Sander, F., Prinz, C., Adam, S., Mau-Möller, A., Bader, R., et al. (2017). Platelet-rich plasma powder: a new preparation method for the standardization of growth factor concentrations. Am. J. Sports Med. 45 (4), 954–960. doi:10.1177/0363546516674475
Kim, Y. S., and Koh, Y. G. (2016). Injection of mesenchymal stem cells as a supplementary strategy of marrow stimulation improves cartilage regeneration after lateral sliding calcaneal osteotomy for varus ankle osteoarthritis: clinical and second-look arthroscopic results. Arthroscopy 32 (5), 878–889. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2016.01.020
Kim, Y. S., Park, E. H., Kim, Y. C., and Koh, Y. G. (2013). Clinical outcomes of mesenchymal stem cell injection with arthroscopic treatment in older patients with osteochondral lesions of the talus. Am. J. Sports Med. 41 (5), 1090–1099. doi:10.1177/0363546513479018
Kim, Y. S., Lee, H. J., Choi, Y. J., Kim, Y. I., and Koh, Y. G. (2014a). Does an injection of a stromal vascular fraction containing adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells influence the outcomes of marrow stimulation in osteochondral lesions of the talus? A clinical and magnetic resonance imaging study. Am. J. Sports Med. 42 (10), 2424–2434. doi:10.1177/0363546514541778
Kim, E., and Lee, J. H. (2014b). Autologous platelet-rich plasma versus dextrose prolotherapy for the treatment of chronic recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. PM R. 6 (2), 152–158. doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2013.07.003
Kim, Y. S., Lee, M., and Koh, Y. G. (2016). Additional mesenchymal stem cell injection improves the outcomes of marrow stimulation combined with supramalleolar osteotomy in varus ankle osteoarthritis: short-term clinical results with second-look arthroscopic evaluation. J. Exp. Orthop. 3 (1), 12. doi:10.1186/s40634-016-0048-2
Kimbrel, E. A., and Lanza, R. (2020). Next-generation stem cells - ushering in a new era of cell-based therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 19 (7), 463–479. doi:10.1038/s41573-020-0064-x
Kraft, C. T., Agarwal, S., Ranganathan, K., Wong, V. W., Loder, S., Li, J., et al. (2016). Trauma-induced heterotopic bone formation and the role of the immune system: a review. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 80 (1), 156–165. doi:10.1097/ta.0000000000000883
Krogh, T. P., Ellingsen, T., Christensen, R., Jensen, P., and Fredberg, U. (2016). Ultrasound-guided injection therapy of achilles tendinopathy with platelet-rich plasma or saline: a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 44 (8), 1990–1997. doi:10.1177/0363546516647958
Kumai, T., Muneta, T., Tsuchiya, A., Shiraishi, M., Ishizaki, Y., Sugimoto, K., et al. (2014). The short-term effect after a single injection of high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid in patients with enthesopathies (lateral epicondylitis, patellar tendinopathy, insertional achilles tendinopathy, and plantar fasciitis): a preliminary study. J. Orthop. Sci. 19 (4), 603–611. doi:10.1007/s00776-014-0579-2
Kumai, T., Samoto, N., Hasegawa, A., Noguchi, H., Shiranita, A., Shiraishi, M., et al. (2018). Short-term efficacy and safety of hyaluronic acid injection for plantar fasciopathy. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 26 (3), 903–911. doi:10.1007/s00167-017-4467-0
Lai, J. J., Chau, Z. L., Chen, S., Hill, J. J., Korpany, K. V., Liang, N., et al. (2022). Exosome processing and characterization approaches for research and technology development. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 9 (15), e2103222. doi:10.1002/advs.202103222
Lan, T., McCarthy, H. S., Hulme, C. H., Wright, K. T., and Makwana, N. (2021a). The management of talar osteochondral lesions - current concepts. J. Arthrosc. Jt. Surg. 8 (3), 231–237. doi:10.1016/j.jajs.2021.04.002
Lan, T., Luo, M., and Wei, X. (2021b). Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 14 (1), 195. doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01208-w
Laohajaroensombat, S., Prusmetikul, S., Rattanasiri, S., Thakkinstian, A., and Woratanarat, P. (2023). Platelet-rich plasma injection for the treatment of ankle osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 18 (1), 373. doi:10.1186/s13018-023-03828-z
Laver, L., Carmont, M. R., McConkey, M. O., Palmanovich, E., Yaacobi, E., Mann, G., et al. (2015). Plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF) as a treatment for high ankle sprain in elite athletes: a randomized control trial. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 23 (11), 3383–3392. doi:10.1007/s00167-014-3119-x
Li, L., and Tuan, R. S. (2020). Mechanism of traumatic heterotopic ossification: in search of injury-induced osteogenic factors. J. Cell Mol. Med. 24 (19), 11046–11055. doi:10.1111/jcmm.15735
Li, F., Mao, D., Pan, X., Zhang, X., Mi, J., and Rui, Y. (2019). Celecoxib cannot inhibit the progression of initiated traumatic heterotopic ossification. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 28 (12), 2379–2385. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2019.08.013
Li, B., Zhang, M., Lu, Q., Zhang, B., Miao, Z., Li, L., et al. (2022). Application and development of modern 3D printing technology in the field of orthopedics. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 8759060. doi:10.1155/2022/8759060
Lim, W. L., Liau, L. L., Ng, M. H., Chowdhury, S. R., and Law, J. X. (2019). Current progress in tendon and ligament tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 16 (6), 549–571. doi:10.1007/s13770-019-00196-w
Lin, C. F., Gross, M. L., and Weinhold, P. (2006). Ankle syndesmosis injuries: anatomy, biomechanics, mechanism of injury, and clinical guidelines for diagnosis and intervention. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 36 (6), 372–384. doi:10.2519/jospt.2006.2195
Lin, L., Shen, Q., Xue, T., and Yu, C. (2010). Heterotopic ossification induced by achilles tenotomy via endochondral bone formation: expression of bone and cartilage related genes. Bone 46 (2), 425–431. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2009.08.057
Lin, D. Y., Cheok, T. S., Kaambwa, B., Samson, A. J., Morrison, C., Chan, T., et al. (2023). Evaluation of the EQ-5D-5L, EQ-VAS stand-alone component and Oxford knee score in the Australian knee arthroplasty population utilising minimally important difference, concurrent validity, predictive validity and responsiveness. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 21 (1), 41. doi:10.1186/s12955-023-02126-w
Liu, Y., Lin, L., Zou, R., Wen, C., Wang, Z., and Lin, F. (2018). MSC-derived exosomes promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis of chondrocytes via lncRNA-KLF3-AS1/miR-206/GIT1 axis in osteoarthritis. Cell Cycle 17 (21-22), 2411–2422. doi:10.1080/15384101.2018.1526603
Liu, G., David, B. T., Trawczynski, M., and Fessler, R. G. (2020). Advances in pluripotent stem cells: history, mechanisms, technologies, and applications. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 16 (1), 3–32. doi:10.1007/s12015-019-09935-x
Lp, M. R. L., and Agrawal, D. K. (2023). Biomechanical forces in the tissue engineering and regeneration of shoulder, hip, knee, and ankle joints. J. Biotechnol. Biomed. 6 (4), 491–500. doi:10.26502/jbb.2642-91280111
Lui, P. P., Chan, L. S., Cheuk, Y. C., Lee, Y. W., and Chan, K. M. (2009). Expression of bone morphogenetic protein-2 in the chondrogenic and ossifying sites of calcific tendinopathy and traumatic tendon injury rat models. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 4, 27. doi:10.1186/1749-799x-4-27
Lyons, J. G., Berkay, F. B., and Minhas, A. (2024). Epidemiology of sports-related tendon ruptures presenting to emergency departments in the United States. Am. J. Sports Med. 52 (13), 3396–3403. doi:10.1177/03635465241284644
Martin, R. L., Irrgang, J. J., Burdett, R. G., Conti, S. F., and Van Swearingen, J. M. (2005). Evidence of validity for the foot and ankle ability measure (FAAM). Foot Ankle Int. 26 (11), 968–983. doi:10.1177/107110070502601113
Martinez-Martinez, A., Ruiz-Santiago, F., and Garcia-Espinosa, J. (2018). Platelet-rich plasma: myth or reality? Radiol. Engl. Ed. 60 (6), 465–475. doi:10.1016/j.rx.2018.08.006
Medina-Porqueres, I., Martin-Garcia, P., Sanz-De-Diego, S., Reyes-Eldblom, M., Moya-Torrecilla, F., Mondragon-Cortes, R., et al. (2024). Platelet-rich plasma injections in chronic lateral ankle instability: a case series. Biomedicines 12 (5), 963. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12050963
Mei-Dan, O., Kish, B., Shabat, S., Masarawa, S., Shteren, A., Mann, G., et al. (2010). Treatment of osteoarthritis of the ankle by intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid: a prospective study. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 100 (2), 93–100. doi:10.7547/1000093
Mei-Dan, O., Carmont, M. R., Laver, L., Mann, G., Maffulli, N., and Nyska, M. (2012). Platelet-rich plasma or hyaluronate in the management of osteochondral lesions of the talus. Am. J. Sports Med. 40 (3), 534–541. doi:10.1177/0363546511431238
Meng, M., Wang, J., Sun, T., Zhang, W., Zhang, J., Shu, L., et al. (2022). Clinical applications and prospects of 3D printing guide templates in orthopaedics. J. Orthop. Transl. 34, 22–41. doi:10.1016/j.jot.2022.03.001
Mercer, N. P., Samsonov, A. P., Dankert, J. F., and Kennedy, J. G. (2022). Outcomes of autologous osteochondral transplantation with and without extracellular matrix cartilage allograft augmentation for osteochondral lesions of the talus. Am. J. Sports Med. 50 (1), 162–169. doi:10.1177/03635465211057117
Monto, R. R. (2012). Platelet rich plasma treatment for chronic achilles tendinosis. Foot Ankle Int. 33 (5), 379–385. doi:10.3113/FAI.2012.0379
Murphy, E. P., McGoldrick, N. P., Curtin, M., and Kearns, S. R. (2019). A prospective evaluation of bone marrow aspirate concentrate and microfracture in the treatment of osteochondral lesions of the talus. Foot Ankle Surg. 25 (4), 441–448. doi:10.1016/j.fas.2018.02.011
Nakagawa, H., Sung, K., Ashkani-Esfahani, S., Waryasz, G., May, T., and Sussman, W. I. (2022). Plantar fasciitisc: a comparison of ultrasound-guided fasciotomy with or without amniotic membrane allograft injection. Regen. Med. 17 (12), 931–940. doi:10.2217/rme-2022-0094
Natali, S., Screpis, D., Farinelli, L., Iacono, V., Vacca, V., Gigante, A., et al. (2021). The use of intra-articular injection of autologous micro-fragmented adipose tissue as pain treatment for ankle osteoarthritis: a prospective not randomized clinical study. Int. Orthop. 45 (9), 2239–2244. doi:10.1007/s00264-021-05093-3
Nguyen, K., Cooperman, S., and Ng, A. (2024). Osteochondral injuries of the talus. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 41 (3), 437–450. doi:10.1016/j.cpm.2024.01.004
Nijmeijer, W. S., Voorthuis, B. J., Groothuis-Oudshoorn, C. G. M., Würdemann, F. S., van der Velde, D., Vollenbroek-Hutten, M. M. R., et al. (2023). The prediction of early mortality following hip fracture surgery in patients aged 90 years and older: the Almelo Hip Fracture Score 90 (AHFS(90)). Osteoporos. Int. 34 (5), 867–877. doi:10.1007/s00198-023-06696-9
Omeragic, V. Z., Tanovic, E., Mesanovic, E., and Pecar, M. (2023). Fadi evaluation of the effects of kinesitherapy after ankle fracture. Acta Clin. Croat. 62 (2), 270–276. doi:10.20471/acc.2023.62.02.03
Paget, L. D. A., Reurink, G., de Vos, R. J., Weir, A., Moen, M. H., Bierma-Zeinstra, S. M. A., et al. (2021). Effect of platelet-rich plasma injections vs placebo on ankle symptoms and function in patients with ankle osteoarthritis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 326 (16), 1595–1605. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.16602
Paget, L. D. A., Reurink, G., de Vos, R. J., Weir, A., Moen, M. H., Bierma-Zeinstra, S. M., et al. (2023). Platelet-rich plasma injections for the treatment of ankle osteoarthritis. Am. J. Sports Med. 51 (10), 2625–2634. doi:10.1177/03635465231182438
Parolini, O., Soncini, M., Evangelista, M., and Schmidt, D. (2009). Amniotic membrane and amniotic fluid-derived cells: potential tools for regenerative medicine? Regen. Med. 4 (2), 275–291. doi:10.2217/17460751.4.2.275
Pittenger, M. F., Mackay, A. M., Beck, S. C., Jaiswal, R. K., Douglas, R., Mosca, J. D., et al. (1999). Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284 (5411), 143–147. doi:10.1126/science.284.5411.143
Prestwich, G. D. (2011). Hyaluronic acid-based clinical biomaterials derived for cell and molecule delivery in regenerative medicine. J. Control Release 155 (2), 193–199. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.04.007
Qin, Y., Ge, G., Yang, P., Wang, L., Qiao, Y., Pan, G., et al. (2023). An update on adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine: where challenge meets opportunity. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 10 (20), e2207334. doi:10.1002/advs.202207334
Raeissadat, S. A., Nouri, F., Darvish, M., Esmaily, H., and Ghazihosseini, P. (2020). Ultrasound-guided injection of high molecular weight hyaluronic acid versus corticosteroid in management of plantar fasciitis: a 24-Week randomized clinical trial. J. Pain Res. 13, 109–121. doi:10.2147/JPR.S217419
Rahimi Darehbagh, R., Seyedoshohadaei, S. A., Ramezani, R., and Rezaei, N. (2024). Stem cell therapies for neurological disorders: current progress, challenges, and future perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Res. 29 (1), 386. doi:10.1186/s40001-024-01987-1
Raissi, G., Arbabi, A., Rafiei, M., Forogh, B., Babaei-Ghazani, A., Khalifeh Soltani, S., et al. (2023). Ultrasound-guided injection of dextrose versus corticosteroid in chronic plantar Fasciitis management: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Foot Ankle Spec. 16 (1), 9–19. doi:10.1177/1938640020980924
Ramelli, L., Docter, S., Kim, C., Sheth, U., and Park, S. S. (2024). Single-row repair versus double-row repair in the surgical management of achilles insertional tendinopathy: a systematic review. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 12 (8), 23259671241262772. doi:10.1177/23259671241262772
Rezaie, J., Feghhi, M., and Etemadi, T. (2022). A review on exosomes application in clinical trials: perspective, questions, and challenges. Cell Commun. Signal 20 (1), 145. doi:10.1186/s12964-022-00959-4
Rhim, H. C., Kwon, J., Park, J., Borg-Stein, J., and Tenforde, A. S. (2021). A systematic review of systematic reviews on the epidemiology, evaluation, and treatment of plantar fasciitis. Life (Basel) 11 (12), 1287. doi:10.3390/life11121287
Riddick, R., Farris, D. J., and Kelly, L. A. (2019). The foot is more than a spring: human foot muscles perform work to adapt to the energetic requirements of locomotion. J. R. Soc. Interface 16 (150), 20180680. doi:10.1098/rsif.2018.0680
Riskowski, J. L., Hagedorn, T. J., and Hannan, M. T. (2011). Measures of foot function, foot health, and foot pain: American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons Lower Limb Outcomes Assessment: Foot and Ankle Module (AAOS-FAM), Bristol Foot Score (BFS), Revised Foot Function Index (FFI-R), Foot Health Status Questionnaire (FHSQ), Manchester Foot Pain and Disability Index (MFPDI), Podiatric Health Questionnaire (PHQ), and Rowan Foot Pain Assessment (ROFPAQ). Arthritis Care Res. Hob. 63 (Suppl. 11), S229–S239. doi:10.1002/acr.20554
Rowden, A., Dominici, P., D'Orazio, J., Manur, R., Deitch, K., Simpson, S., et al. (2015). Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled Study evaluating the use of platelet-rich plasma therapy (PRP) for acute ankle sprains in the emergency department. J. Emerg. Med. 49 (4), 546–551. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2015.03.021
Sabaghzadeh, A., Zarei Kurdkandi, H., Ebrahimpour, A., Biglari, F., and Jafari Kafiabadi, M. (2023). Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for chronic lateral ankle instability after modified Brostrom-Gould surgery: a randomized, Single-Blinded, prospective controlled trial. Foot Ankle Orthop. 8 (2), 24730114231168633. doi:10.1177/24730114231168633
Salk, R., Chang, T., D'Costa, W., Soomekh, D., and Grogan, K. (2005). Viscosupplementation (hyaluronans) in the treatment of ankle osteoarthritis. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 22 (4), 585–597. doi:10.1016/j.cpm.2005.07.007
Salk, R. S., Chang, T. J., D'Costa, W. F., Soomekh, D. J., and Grogan, K. A. (2006). Sodium hyaluronate in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the ankle: a controlled, randomized, double-blind pilot study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 88 (2), 295–302. doi:10.2106/JBJS.E.00193
Sánchez-González, D. J., Méndez-Bolaina, E., and Trejo-Bahena, N. I. (2012). Platelet-rich plasma peptides: key for regeneration. Int. J. Pept. 2012, 532519. doi:10.1155/2012/532519
Schepull, T., Kvist, J., Norrman, H., Trinks, M., Berlin, G., and Aspenberg, P. (2011). Autologous platelets have no effect on the healing of human achilles tendon ruptures: a randomized single-blind study. Am. J. Sports Med. 39 (1), 38–47. doi:10.1177/0363546510383515
Schreiner, M. M., Raudner, M., Marlovits, S., Bohndorf, K., Weber, M., Zalaudek, M., et al. (2021). The MOCART (Magnetic Resonance Observation of Cartilage Repair Tissue) 2.0 knee Score and Atlas. Cartilage 13 (1_Suppl. l), 571S–587S. doi:10.1177/1947603519865308
Shang, X. L., Tao, H. Y., Chen, S. Y., Li, Y. X., and Hua, Y. H. (2016). Clinical and MRI outcomes of HA injection following arthroscopic microfracture for osteochondral lesions of the talus. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 24 (4), 1243–1249. doi:10.1007/s00167-015-3575-y
Shetty, S. H., Dhond, A., Arora, M., and Deore, S. (2019). Platelet-rich plasma has better long-term results than corticosteroids or placebo for chronic plantar fasciitis: randomized control trial. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 58 (1), 42–46. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2018.07.006
Shimozono, Y., Yasui, Y., Hurley, E. T., Paugh, R. A., Deyer, T. W., and Kennedy, J. G. (2019). Concentrated bone marrow aspirate may decrease postoperative cyst occurrence rate in autologous osteochondral transplantation for osteochondral lesions of the talus. Arthroscopy 35 (1), 99–105. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2018.06.047
Steller, D., Herbst, N., Pries, R., Juhl, D., and Hakim, S. G. (2019). Impact of incubation method on the release of growth factors in non-Ca(2+)-activated PRP, Ca(2+)-activated PRP, PRF and A-PRF. J. Craniomaxillofac Surg. 47 (2), 365–372. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2018.10.017
Sullivan, D., Pabich, A., Enslow, R., Roe, A., Borchert, D., Barr, K., et al. (2021). Extensive ossification of the achilles tendon with and without acute fracture: a scoping review. J. Clin. Med. 10 (16), 3480. doi:10.3390/jcm10163480
Sun, S. F., Chou, Y. J., Hsu, C. W., Hwang, C. W., Hsu, P. T., Wang, J. L., et al. (2006). Efficacy of intra-articular hyaluronic acid in patients with osteoarthritis of the ankle: a prospective study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 14 (9), 867–874. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.03.003
Sun, S. F., Hsu, C. W., Sun, H. P., Chou, Y. J., Li, H. J., and Wang, J. L. (2011). The effect of three weekly intra-articular injections of hyaluronate on pain, function, and balance in patients with unilateral ankle arthritis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 93 (18), 1720–1726. doi:10.2106/JBJS.J.00315
Sun, X. P., Wilson, A. G., and Michael, G. M. (2018). Open surgical implantation of a viable intact cryopreserved human placental membrane for the treatment of recalcitrant plantar fasciitis: case report with greater than 2-Year Follow-Up duration. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 57 (3), 583–586. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2017.09.007
Tabrizi, A., Dindarian, S., and Mohammadi, S. (2020). The effect of corticosteroid local injection versus platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of plantar fasciitis in Obese patients: a single-blind, randomized clinical trial. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 59 (1), 64–68. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2019.07.004
Tack, P., Victor, J., Gemmel, P., and Annemans, L. (2016). 3D-printing techniques in a medical setting: a systematic literature review. Biomed. Eng. Online 15 (1), 115. doi:10.1186/s12938-016-0236-4
Thermann, H., Fischer, R., Gougoulias, N., Cipollaro, L., and Maffulli, N. (2023). Endoscopic debridement for non-insertional achilles tendinopathy with and without platelet-rich plasma. J. Sport Health Sci. 12 (2), 275–280. doi:10.1016/j.jshs.2020.06.012
Tian, J., Han, Z., Song, D., Peng, Y., Xiong, M., Chen, Z., et al. (2023). Engineered exosome for drug delivery: recent development and clinical applications. Int. J. Nanomedicine 18, 7923–7940. doi:10.2147/IJN.S444582
Ugurlar, M., Sonmez, M. M., Ugurlar, O. Y., Adiyeke, L., Yildirim, H., and Eren, O. T. (2018). Effectiveness of four different treatment modalities in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis during a 36-Month Follow-Up period: a randomized controlled trial. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 57 (5), 913–918. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2018.03.017
Vosoughi, A. R., Roustaei, N., and Mahdaviazad, H. (2018). American orthopaedic foot and Ankle society ankle-hindfoot scale: a cross-cultural adaptation and validation study from Iran. Foot Ankle Surg. 24 (3), 219–223. doi:10.1016/j.fas.2017.02.007
Walther, M., Gottschalk, O., and Aurich, M. (2024). Operative management of osteochondral lesions of the talus: 2024 recommendations of the working group ‘clinical tissue regeneration’ of the German society of orthopedics and traumatology (DGOU). EFORT Open Rev. 9 (3), 217–234. doi:10.1530/EOR-23-0075
Wang, D. Y., Jiao, C., Ao, Y. f., Yu, J. k., Guo, Q. w., Xie, X., et al. (2020). Risk factors for osteochondral lesions and osteophytes in chronic lateral ankle instability: a case series of 1169 patients. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 8 (5), 2325967120922821. doi:10.1177/2325967120922821
Werber, B. (2015). Amniotic tissues for the treatment of chronic plantar fasciosis and achilles tendinosis. J. Sports Med. 2015, 1–6. doi:10.1155/2015/219896
Wu, J., Kuang, L., Chen, C., Yang, J., Zeng, W. N., Li, T., et al. (2019). miR-100-5p-abundant exosomes derived from infrapatellar fat pad MSCs protect articular cartilage and ameliorate gait abnormalities via inhibition of mTOR in osteoarthritis. Biomaterials 206, 87–100. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.03.022
Xiong, Y., Gong, C., Peng, X., Liu, X., Su, X., Tao, X., et al. (2023). Efficacy and safety of platelet-rich plasma injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 10, 1204144. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1204144
Xu, Y., Huang, J., Mai, Y., Zhang, Z., Li, S., Lin, H., et al. (2025). CBD-conjugated BMP-inhibiting exosomes on collagen scaffold dual-target Achilles tendon repair: synergistic regeneration and heterotopic ossification prevention. Mater Today Bio 32, 101790. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101790
Yu, H., Zhang, J., Liu, X., and Li, Y. (2021). microRNA-136-5p from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes facilitates fracture healing by targeting LRP4 to activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Bone Jt. Res. 10 (12), 744–758. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.1012.BJR-2020-0275.R2
Yuan, C., Song, W., Jiang, X., Wang, Y., Li, C., Yu, W., et al. (2024). Adipose-derived stem cell-based optimization strategies for musculoskeletal regeneration: recent advances and perspectives. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 15 (1), 91. doi:10.1186/s13287-024-03703-6
Zelen, C. M., Poka, A., and Andrews, J. (2013). Prospective, randomized, blinded, comparative study of injectable micronized dehydrated amniotic/chorionic membrane allograft for plantar fasciitis--a feasibility study. Foot Ankle Int. 34 (10), 1332–1339. doi:10.1177/1071100713502179
Zhang, K., Wang, L., Zhang, S., Yu, B., Liu, F., Cui, Z., et al. (2013). Celecoxib inhibits the heterotopic ossification in the rat model with Achilles tenotomy. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 23 (2), 145–148. doi:10.1007/s00590-012-0944-9
Zhang, J., Li, S., Li, L., Li, M., Guo, C., Yao, J., et al. (2015). Exosome and exosomal microRNA: trafficking, sorting, and function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinforma. 13 (1), 17–24. doi:10.1016/j.gpb.2015.02.001
Zhang, S., Chuah, S. J., Lai, R. C., Hui, J. H. P., Lim, S. K., and Toh, W. S. (2018). MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing proliferation, attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune reactivity. Biomaterials 156, 16–27. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.11.028
Keywords: regenerative medicine, foot and ankle diseases, platelet-rich plasma, stem cells, 3D bioprinting
Citation: Yang L, Li Y, Wang T, Zhao Z, Li W, Lv J, Chen H, Qi Z, Wang X, Bao W and Liang H (2025) Applications of bone regenerative medicine in the foot and ankle: mechanisms, technologies, and therapeutic advances. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1653964. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1653964
Received: 25 June 2025; Accepted: 14 November 2025;
Published: 02 December 2025.
Edited by:
Yan Xu, Peking University Third Hospital, ChinaReviewed by:
Girish Pattappa, University of Wurzburg, GermanyBerivan Cecen, New Jersey Institute of Technology, United States
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Li, Wang, Zhao, Li, Lv, Chen, Qi, Wang, Bao and Liang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haidong Liang, am9obmxoZGRtdUBvdXRsb29rLmNvbQ==
 Lianbo Yang
Lianbo Yang Yijie Li
Yijie Li Tianqi Wang
Tianqi Wang Zhuo Zhao
Zhuo Zhao Wang Li
Wang Li Jinghang Lv
Jinghang Lv Haoran Chen
Haoran Chen Zhaodong Qi
Zhaodong Qi Xinming Wang
Xinming Wang Wenchi Bao
Wenchi Bao Haidong Liang
Haidong Liang