- 1Department of Orthopaedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Naval Medical University (Second Military Medical University), Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, College of Basic Medical Sciences, Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China
- 3Spine Tumor Center, Changzheng Hospital, Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China
Spinal cord injury is a severe neurological condition that frequently. Results in lasting motor and sensory dysfunction. Traditional drug therapies have shown limited efficacy in addressing the complexities of spinal cord injury. This limitation highlighting the urgent need for innovative treatment strategies. In recent years, nanocarrier-mediated systems have garnered significant attention due to their superior drug delivery capabilities and targeting precision. This review summarizes the latest advancements in the application of nanocarriers for the treatment of spinal cord injuries, discussing various types of nanocarriers, drug loading and capacity and release profiles, as well as targeted delivery strategies. The insights aim to establish a theoretical foundation for future research and clinical applications in this critical area of medicine.
Introduction
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) is a traumatic disruption of spinal cord integrity, resulting in transient or permanent functional alterations of motor, sensory, and autonomic nervous systems, with profound consequences for patient quality of life (Eckert and Martin, 2017; McDonald and Sadowsky, 2002). As the most prevalent cause of disability among spinal disorders, SCI pathophysiology comprises two distinct phases:primary injury from mechanical trauma and subsequent secondary injury driven by molecular cascades (Jendelova, 2018; Chay and Kirshblum, 2020). In most injuries the spinal cord is compressed and the extent of the damage depends primarily on the force of the compression directly causing damage to the spinal cord tissue and nerve cells necrosis (Zheng and Tuszynski, 2023; Dams-O'Connor et al., 2023). Secondary injury refers to additional damage caused by local ischemia, edema, and inflammation. These processes affect the normal tissues surrounding the lesion. This impairs the normal delivery of nutrients and oxygen to cells, leading to the release of toxic chemicals for excitotoxicity, disrupting the integrity of adjacent cells, and further spreading and exacerbating the spinal cord injury (Ambrozaitis et al., 2006; Sterner and Sterner, 2022; Gao W. et al., 2022) (Figure 1). SCI can cause fatal or long-term disabilities, including paralysis, sensory loss, organ dysfunction, mental disorders, and behavioral complications such as drug abuse and self-injury, which greatly affect the patient’s quality of life. (Anjum et al., 2020). SCI also has varying degrees of impact on a patients’ occupation, family, and economy (Radhakrishna et al., 2014; Malekzadeh et al., 2022). Therefore, effective treatment of SCI is crucial. Even with the continuous efforts of scientists, although many neuroprotective and neuroregenerative therapies have entered preclinical trials, there are currently no approved drugs for the treatment of spinal cord injury. While nano-drug delivery systems hold great potential in spinal cord injury treatment, further research is needed to optimize design, improve delivery efficiency, and ensure safety. Future research and clinical trials should validate the application prospects of nano-drug delivery systems in spinal cord injury treatment.
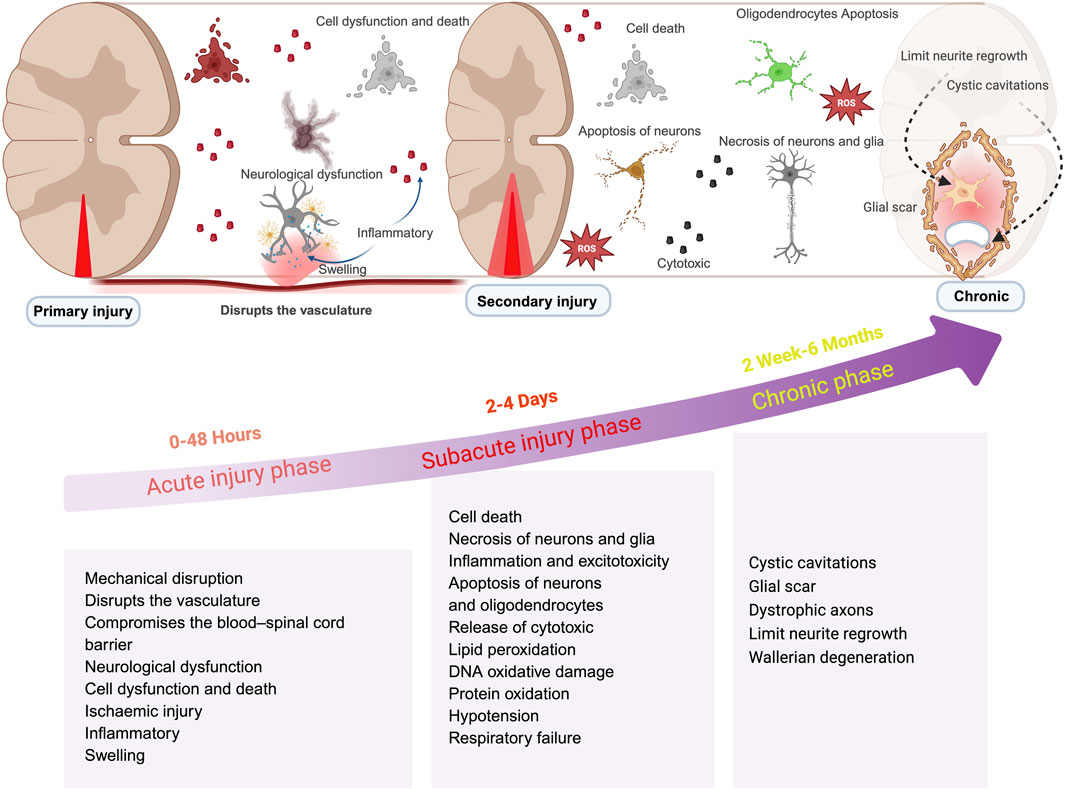
Figure 1. Schematic illustrations of changes in spinal cord injury at different phase. This illustration is organized into three distinct stages: acute, subacute, and chronic. The acute phase, occurring within 0–48 h, is characterized by cascades of secondary injury; the subacute phase, spanning from 2 to 4 days, is defined by prolonged inflammation; while the chronic phase, extending beyond 2 weeks, is identified by the maturation of glial scars and additional pathological alterations. (created with https://biorender.com).
The field of spinal cord injury treatment has seen the application of nanomedicine technology in recent years, which brings new hope for spinal cord injury treatment (Wang et al., 2024; Liang et al., 2024; Prakash, 2023). Nano-drug delivery systems utilizes nanoparticles to deliver therapeutic drugs to the spinal cord injury site in a targeted manner. This systems have advantages of: controlled release, enhanced drug stability, breaking through the blood-brain barrier, and combination therapy (Gao et al., 2016; Meyer et al., 2015; Feliu and Parak, 2024). These nanocarriers can enhance the bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of drugs, potentially transforming the therapeutic landscape for SCI. This review aims to explore the applications and future prospects of nanocarrier-mediated drug delivery systems in the context of spinal cord injury treatment (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Schematic overview of Nanocarrier-mediated delivery strategies to treat spinal cord injury. Nanocarrier -mediated delivery strategies include the delivery of bioactive substances regulating and cell therapy, applied from different perspectives to repair spinal cord injury and associated molecular changes. (created with https://biorender.com).
Hydrogel-based nano-biomaterials for SCI treatment
Hydrogels are three-dimensional networks of crosslinked polymers that can hold a large amount of water. Nanoparticles can be incorporated into hydrogels to improve their mechanical properties, drug-delivery capabilities, and cellular interactions. These hydrogels can provide a supportive environment for cell growth, facilitate neural tissue regeneration, and deliver therapeutic agents at the injury site (Zhu et al., 2023; Yin et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2022). When combined with nanomaterials, hydrogels can form a versatile platform for drug delivery and tissue regeneration in SCI treatment (Anderson et al., 2018; Koffler et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2023). The main advantages of using hydrogel-based nano-biomaterials is their ability to provide localized and sustained drug release. By encapsulating therapeutic agents within the hydrogel matrix, drugs can be released in a controlled manner, allowing for long-term treatment and minimizing side effects (Fan et al., 2022; Wang S. et al., 2023).
New types of nano-biological materials have become highly promising tools for the treatment of spinal cord injury (SCI) (Afsartala et al., 2023; Sun et al., 2023). These materials combine the advantages of nanotechnology and biomaterials, which create a supportive environment for tissue nerve regeneration, and functional recovery at the spinal cord injury site. Among these, Among them, hydrogels stand out due to their softness, flexible responsiveness, exceptional absorbency, biocompatibility, chemical stability, and potential applications in tissue engineering (Afsartala et al., 2023; Guan et al., 2024). Hydrogels are classified into two main types: traditional and responsive. Responsive hydrogels react to stimuli such as light, temperature, magnetism, pH, ultrasound, ionic strength, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and glutathione. They can be designed to respond to one or multiple stimuli as a trigger response for controlled drug delivery. They can mimic the three-dimensional structure and scaffolding function of the extracellular matrix. This supports stem cell attachment, proliferation, and differentiation, as well as the release of growth factors, which helps improve the microenvironment after spinal cord injury. Hence, It promots nerve regeneration and acts as a local reservoir for sustained release of drugs or growth factors, continuously enhancing neuronal and tissue regeneration, as well as synaptic regeneration (Han et al., 2022; Roh et al., 2023; Grijalvo et al., 2019). Recently, they have found widespread use in tissue engineering, biomedical, and pharmaceutical field. So providing effective carriers for minimally invasive treatments, precisely filling defects to adapt to the shape and size of injuries, thus promoting tissue repair and inducing regeneration of damaged areas in the body (Yuan et al., 2022; Assuncao-Silva et al., 2015).
Stem cell transplantation using biomaterial scaffolds holds promise for treating SCI. Biomaterial scaffolds can provide a 3D growth environment for mesenchymal stem cells and promote tissue regeneration (Yuan et al., 2022; Qiu et al., 2023). Hyaluronic acid (HA), which is derived from the natural extracellular matrix (ECM), can inhibit glial scar formation, which is beneficial for spinal cord tissue repair. HA hydrogels have a porous structure and a texture similar to spinal cord tissue, giving researchers enough room to design and build three-dimensional cross-linked networks, endowing them with various regulatory functions (Fan et al., 2024; Duarte et al., 2024). Researchers introduced manganese dioxide nanoparticles (MnO2NPs) into HA-peptide hydrogels, utilizing the property of MnO2, which decomposes hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to produce oxygen (O2), thereby improving the oxidative stress environment and effectively increasing the survival rate of stem cells. Biomimetic hydrogels based on hyaluronic acid and silk fibroin can keep releasing neurotrophic factors, which really helps to improve recovery after spinal cord injuries (Li et al., 2019). Hydrogels are widely used to construct nerve guidance conduits (NGCs) that direct peripheral nerve repair. Studies have found that conduits combining black phosphorus hydrogels with nerve growth factor (NGF-1) can significantly enhance peripheral nerve regeneration. These conduits strongly induce cell growth, promote Schwann cell proliferation, and facilitate nerve branching. (Hopf et al., 2020; Luo et al., 2021). Hydrogels also play an important role in the repair of spinal cord injuries. By embedding polypyrrole nanoparticles with antioxidant and conductive functions into bioactive hydrogels, the transmission of bioelectrical signals can be restored effectively, promoting nerve regeneration and functional recovery (Luo et al., 2021). Additionally, a temperature-responsive hydrogel system has been developed that can continuously release extracellular vesicles from adipose-derived stem cells in vivo. This can greatly boost the movement and growth of Schwann cells, thereby improving the efficiency of nerve regeneration (Zhu et al., 2023; Hopf et al., 2020). The design of hydrogels can also achieve functionalization by adjusting their chemical composition. For example, hydrogels constructed from amino acid derivatives exhibit good biocompatibility and neuroprotective effects, effectively promoting the growth and differentiation of nerve cells (Park et al., 2010; Chen et al., 2024).
In the treatment of spinal cord injuries, dendritic polymers not only serve as drug carriers but also enhance treatment outcome by regulating the drug release rate. For instance, some studies have created hydrogel systems using dendritic polymers that allow for sustained drug release, which boosts the drug concentration at the target site and lowers the chances of systemic side effects (Woerly et al., 2001; Paleos et al., 2007). Additionally, dendritic polymers can work alongside other treatments, such as gene therapy, to improve nerve repair and regeneration after a spinal cord injury.
Furthermore, the application of conductive hydrogels has shown promising prospects in nerve regeneration, as these materials can promote the growth and functional recovery of nerve cells by mimicking the transmission of bioelectrical signals. In terms of wound healing and hemostasis for spinal cord injuries, as well as antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects to reduce postoperative infection complications, organic gels can be used for long-acting drug formulations to improve drug bioavailability and control drug release, which is very important and has a lot of potential use in long-lasting drug delivery systems.
Micelles systems for SCI treatment
Micelles are one of the earliest carriers among in drug delivery systems (Dutt et al., 2023; Bose et al., 2021). Currently, the micelles mostly studied are formed from amphiphilic polymer materials and are also known as polymeric micelles (PMs) (Ghezzi et al., 2021). As a type of freely assembled colloid, micelles have a wide range of applications in drug delivery. In recent years, designing polymer materials as carriers for poorly soluble drugs have become hot research topics. With the development of various new amphiphilic block copolymers, micelle-based drug delivery systems have emerged as one of the best options for treating spinal cord injuries (Liu et al., 2017; Feng et al., 2023).
The particle size of micelles generally ranges from 10 to 100 nm. Because of their size and flexibility, they are not easily recognized or captured by the endoplasmic reticulum system (ERS) in the bloodstream. This helps increase the drug’s circulation half-life and prolongs the carrier’s retention time in the blood. They also target the site of spinal cord injury using the Enhanced Permeability and Retention Effect (EPR) effect (Qian et al., 2023; Movassaghian et al., 2015). Polyethylene glycol (PEG), known for its good solubility, is commonly used as an outer protective layer to extend circulation time and create a hydrophilic shell for the micelles (Rasoulianboroujeni et al., 2022; Gill et al., 2015).
Disguising nanomedicine systems as neurotransmitters allows for their delivery to neurons. Researchers coupled the drug CLP-257 with GABA and dopamine (Zuo et al., 2023). CLP-257 is a potassium chloride co-transporter 2 (KCC2) activator that can reduce intracellular chloride ion concentration and decrease neuronal excitability, which reportedly plays a crucial role in motor control. To facilitate minimally invasive delivery and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive release, researchers designed and synthesized amphiphilic block copolymers with PEG hydrophilic segments and hydrophobic segments containing boronic acid ROS scavengers, which encapsulate hydrophobic prodrugs. These micelle-based drugs can be administered intravenously, triggering ROS responses to accumulate and release prodrugs at the injury site (Zuo et al., 2023). This pharmacological approach can target neurons in SCI rat contusion model. It increase axon numbers, further offering neuroprotective effects and enhancing lower limb motor function, bringing new hope for the treatment of SCI and other neurological diseases. Minocycline (MC) has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic effects in the context of spinal cord injury and also plays a significant role in secondary injury. Polysialic acid (PSA) can promote cell migration and facilitate neuronal and synaptic reconstruction. Polysialic acid-modified (PSM) can significantly protect neurons and myelin from damage, reduce glial scar formation, and recruit endogenous neural stem cells to the lesion site. Thus promoting neuronal regeneration and extending axons, significantly improving rats’ motor function and demonstrating therapeutic efficacy (Wang et al., 2021). Notably, using minocycline alone can lead to hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic effects; however, the PMS drug delivery system avoids these side effects and effectively reduces toxicity. The application of micelle drug delivery systems in spinal cord injury SCI offers a new strategy for drug therapy, with the potential to enhance treatment efficacy and improve patients’ quality of life.
Nanoparticles systems for SCI treatment
The non-specific distribution and uncontrolled release efficiency of drugs in conventional drug delivery systems (CDDSs) have prompted the design and development of smart drug delivery systems (SDDSs) (Adepu and Ramakrishna, 2021; Hossen et al., 2019). Nanodrug delivery systems can selectively deliver drugs to the site of spinal cord injury, significantly improving drug concentration distribution and release efficiency. Drugs can achieve controlled release in terms of timing and location, and nanodrug delivery systems can enhance drug loading efficiency and bioavailability in vivo, improve drug solubility, and reduce side effects. They can also achieve targeted delivery through various administration routes, such as local injection, intravenous injection, and biomaterial-assisted delivery (Rossi et al., 2013; Liu et al., 2020; De Jong and Borm, 2008).
The blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB) represents a distinct adaptation of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) specifically within the spinal cord area. It is formed by spinal microvascular endothelial cells that are interconnected through tight junctions, along with a basement membrane, pericytes, and the end-feet of astrocytes. The BSCB meticulously controls the ingress and egress of various substances into the spinal parenchyma via a mechanism of selective permeability, thereby preserving the proper functioning of neurons (Rust et al., 2025). Surface modification is also one effective strategy to enhance targeting. Researchers have used human mesenchymal stem cell membrane modification that can effectively penetrate the blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB) and release drugs at the injury site, promoting axon regeneration and improving the inflammatory environment (Blagovic et al., 2013).
Metal nanoparticles, such as gold nanoparticles, iron oxide nanoparticles, and manganese nanoparticles, have also shown great potential in targeted therapy and imaging. You can achieve high-sensitivity imaging of cells in spinal cord injury models (Chomoucka et al., 2010; Mousavi et al., 2020). Additionally, gold nanoparticles can generate hydrogen gas through catalytic reactions and possess selective antioxidant properties, which help with inflammation during the acute phase of spinal cord injury, thereby improving and enhancing motor function (You et al., 2024). Iron nanoparticles have magnetic properties, and iron oxide nanoparticles containing strontium can improve the imaging quality of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The advantage of iron nanoparticles as drug carriers is their ability to enable targeted drug release through an external magnetic field, reducing the impact on healthy tissues. They also have a thermal effect that, when used with photothermal therapy, can boost treatment effectiveness (Dadfar et al., 2019). Manganese nanoparticles can deliver poorly soluble resveratrol to the site of spinal cord injury, and experimental results show that they can inhibit inflammatory factors and apoptotic factors, thereby further promoting motor function in mice. Biocompatible manganese-iron Prussian blue nanoparticles are a new kind of drug carrier and have also demonstrated good immunotherapy effects (Jiang et al., 2022). TiO2/iron nanocomposites are used to load antibiotics and other drugs to make them more bioavailable and targeted. Studies have shown that antibiotics encapsulated in TiO2/iron nanocomposites exhibit excellent antibacterial activity in in vitro experiments, effectively inhibiting the growth of multidrug-resistant bacteria (Zafar et al., 2022; Koli et al., 2016).
Lipid nanoparticle systems for SCI treatment
Nanoliposomes are nanoscale carriers composed of lipid bilayers, which mainly consist of phospholipids, cholesterol, and other surfactants (Talens-Visconti et al., 2022; Tereshkina et al., 2022). The choice of phospholipids significantly affects the stability, drug encapsulation capacity, and release characteristics of nanoliposomes. The structure of nanoliposomes is typically spherical, with a diameter generally ranging from 50 to 200 nm, exhibiting good biocompatibility and adjustable drug release properties (Mozafari, 2010). Additionally, the surface of nanoliposomes can be chemically modified to enhance their targeting and biocompatibility, for example, by using amino acids or polymer coatings to improve their stability and cellular uptake in biological environments. The breakdown products of nanoliposomes are typically non-toxic and can be safely eliminated from the body, thus providing assurance for their promotion in clinical applications (Hallaj-Nezhadi and Hassan, 2015; Zoghi et al., 2018).
In the treatment of spinal cord injuries, lipid nanoparticle delivery systems are advantageous because they improve drug solubility and bioavailability, overcoming the limitations of traditional drug delivery methods. The design of lipid nanoparticles allows for prolonged drug release in vivo, reducing toxic reactions and achieving targeted delivery directly to the injured tissue. These nanoparticles can deliver not only small molecule drugs but also large biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids to promote nerve regeneration and repair (Yin et al., 2023). Furthermore, lipid nanoparticle delivery systems also help regulate the microenvironment following spinal cord injury. Research has shown that delivering anti-inflammatory proteins or neurotrophic factors via lipid nanoparticles can significantly reduce the inflammatory response at the injury site, promoting the survival and regeneration of nerve cells (Gao X. et al., 2022). For example, lipid nanoparticles that encapsulate mRNA for human interleukin-10 (hIL-10) can effectively promote neuroprotection and functional recovery. This new delivery system not only improves targeted drug delivery efficiency but also offers new strategies for treating spinal cord injuries. Effectively encapsulating siRNA in nanoliposomes allows for sustained gene silencing at the injury site, thereby regulating the regeneration and repair mechanisms of nerve cells (Gal et al., 2023).
Synergistic multi-target strategies for SCI treatment
In the treatment of spinal cord injury, traditional therapeutic strategies have often focused on single-target interventions, such as administering anti-inflammatory drugs or neurotrophic factors. While this approach can alleviate post-injury inflammation or promote nerve regeneration to some extent, these isolated interventions frequently fail to fully address the complex pathological processes involved in spinal cord injury. Such injuries not only cause direct mechanical damage but also trigger a cascade of secondary injuries, including oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and disruption of the blood-spinal cord barrier. These pathophysiological changes mutually interact and exacerbate the extent of neural damage (Xiong et al., 2024; Zuo et al., 2023). Therefore, current therapeutic strategies need to shift toward comprehensive and multi-target interventions, combining different drugs or treatment approaches to effectively intervene at various pathological stages of spinal cord injury (Shi et al., 2025; Qin et al., 2024). Additionally, strategies combining small-molecule drugs and cell therapy have demonstrated potential for improving functional recovery following spinal cord injury. The approach of using small-molecule therapeutics (e.g., antioxidants) in conjunction with stem cell transplantation can effectively mitigate oxidative stress and inflammatory responses while promoting nerve regeneration and functional restoration (Cui et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2023). Research indicates that stem cells possess the potential for self-renewal and differentiation into multiple cell types, enabling them to promote nerve regeneration and functional recovery following spinal cord injury. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) can enhance neuronal survival through the secretion of neurotrophic factors and improve motor function after spinal cord injury (Somredngan et al., 2023). In addition, hUC-MSCs can promote the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells through specific signaling pathways, such as the Wnt signal pathway, thereby enhancing the effect of nerve regeneration (Wang X. et al., 2023). In addition, using biomaterials as scaffolds not only provides structural support but also continuously releases growth factors, thereby generating positive biological responses in the local microenvironment and promoting cell survival and regeneration (Zhang et al., 2024).
The treatment of spinal cord injury is shifting towards acellular strategies, with engineered extracellular vesicles (EVs) emerging as promising candidates due to their low toxicity, immunogenicity, and ability to transport bioactive molecules across the blood-spinal cord barrier (Qin et al., 2024; Jiang et al., 2020; Kong et al., 2025).
Gene silencing tools play an important role in the treatment of spinal cord injury, especially small interfering RNA (siRNA) and the CRISPR-Cas9 system. They can target and inhibit the expression of specific genes through specific mechanisms, thereby alleviating pathological changes after spinal cord injury. Hydrogel-loaded mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and siRNA targeting glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). This combination not only inhibits scar formation but also promotes neurogenesis, thereby creating a more favorable microenvironment for the regeneration of nerve cells and enhancing the therapeutic effect on the injured area (Zhang et al., 2025; Kim et al., 2021).
Clinical translational bottlenecks and strategies
In the clinical translation of nanoparticle delivery systems, several key factors affect their efficacy. Firstly, the biocompatibility and safety of nanoparticles are fundamental requirements for clinical applications. Research shows that the composition, surface properties, and release characteristics of nanoparticles can influence their behavior in vivo (Matson et al., 2022). Therefore, selecting appropriate biomaterials as nanoparticle carriers and functionalizing their surfaces to enhance their stability and targeting in vivo is one of the optimization strategies (Zhu et al., 2025).
In the treatment of spinal cord injury, multi-modal therapeutic strategies are gradually emerging. Methods such as stem cell therapy, biomaterial scaffolds, nano-delivery systems, and targeted molecular therapy show good potential for clinical application. These strategies not only promote the regeneration and repair of neurons but also improve the microenvironment, making the recovery process at the injury site smoother. The results of clinical trial NCT01321333 indicate that the safety of using stem cell therapy for SCI has been preliminarily validated, but the efficacy still needs further confirmation (Guo et al., 2021). However, there may be controversies regarding the results and opinions of different studies on therapeutic effects, as some therapies have not been as effective as expected in certain clinical trials.
Additionally, the drug loading efficiency and release mechanism are also important factors affecting therapeutic effects. By optimizing the preparation process of nanoparticles, large-scale production, and quality control, the drug encapsulation rate can be improved, ensuring that sufficient drug concentration reaches the target. Furthermore, adjusting the release rate of nanoparticles to match the pathological process is also an effective optimization strategy (Wang and Bai, 2024).
Moreover, the design and implementation of clinical trials are also key to achieving the clinical transformation of nanotechnology. It is necessary to design reasonable clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of nanodelivery systems, while considering individual differences among patients. At the same time, integrating the advantages of biomedical engineering, medicinal chemistry, and clinical medicine through interdisciplinary collaboration will help promote the application of nanotechnology in the treatment of spinal cord injuries (Matson et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2025).
Finally, market access and regulatory approval are also important factors affecting the clinical application of nanodelivery systems. With the rapid development of nanotechnology, relevant regulatory policies and standards need to be continuously updated to ensure the safety and efficacy of nanomedicines, paving the way for clinical applications (Wang and Bai, 2024). In the future, the field of spinal cord injury treatment needs to strengthen the integration of mechanism analysis and clinical translation. By deeply exploring the molecular mechanisms after injury and the mechanisms of different treatment strategies, clearer guidance can be provided for clinical practice. At the same time, optimizing treatment plans to maximize the recovery of function in spinal cord injury patients is a common goal for researchers. Only through interdisciplinary collaboration and continuous exploration can more effective treatment options and better prognoses be provided for spinal cord injury patients.
Conclusion
SCI is a series of complex and dynamic changes, with high diversity for different patients. Changes in the post-injury microenvironment has yielded information showing the value and essential role played by neuroprotective and neurodegenerative therapies for clinical and basic research. In the future, we should comprehensively utilize multi-target positioning strategies that address both inherently edematous conditions and the complex disease processes associated with SCI. This includes targeting external cellular pathways and mediators within the SCI microenvironment to develop personalized treatment programs.
In recent years, nanomaterials have shown exceptional potential and high probability for applications in the field of SCI. These materials, through their unique physicochemical properties, can effectively promote cell regeneration, improve the inflammatory microenvironment, and enhance motor function, offering new hope for treatment of patients with SCI. Various methods, including cell-targeted drug delivery, tissue-specific targeting, and receptor-mediated endocytosis, can effectively increase drug selectivity. These methods also help reduce the impact on healthy cells. Cell-targeted drug delivery refers to the direct delivery of drugs or therapeutic substances into specific types of cells via specific carriers or molecules. For example, using stem cells or immune cells as drug carriers can achieve precise delivery by specifically binding to target cells. Tissue-specific targeting refers to optimizing the properties of drug carriers so that they can selectively accumulate in specific tissues or organs. Receptor-mediated endocytosis is the process by which cells recognize and uptake exogenous molecules through specific receptors. This mechanism is very important in drug delivery, especially in targeted therapy. By designing drug carriers that can specifically bind to receptors on the surface of target cells, effective endocytosis and cell uptake can be achieved. For instance, using antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) allows for direct delivery of drugs into cancer cells, thereby enhancing therapeutic effects and reducing damage to normal cells. With the rapid development of research technologies and the deep integration of medical and engineering disciplines, various new nanodrug delivery systems have emerged. These will surely play an important role in the future of the spinal cord injuries.
Author contributions
YC: Writing – review and editing. RW: Writing – original draft. XZ: Validation, Writing – original draft. HJ: Writing – original draft. ML: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. XW: Project administration, Investigation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Foundation of 2019-QH-17.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adepu, S., and Ramakrishna, S. (2021). Controlled drug delivery systems: current status and future directions. Molecules 26 (19), 5905. doi:10.3390/molecules26195905
Afsartala, Z., Hadjighassem, M., Shirian, S., Ebrahimi-Barough, S., Gholami, L., Parsamanesh, G., et al. (2023). The effect of collagen and fibrin hydrogels encapsulated with adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for treatment of spinal cord injury in a rat model. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 21, e3505. doi:10.30498/ijb.2023.362229.3505
Ambrozaitis, K. V., Kontautas, E., Spakauskas, B., and Vaitkaitis, D. (2006). Pathophysiology of acute spinal cord injury. Medicina 42, 255–261.
Anderson, M. A., O'Shea, T. M., Burda, J. E., Ao, Y., Barlatey, S. L., Bernstein, A. M., et al. (2018). Required growth facilitators propel axon regeneration across complete spinal cord injury. Nature 561, 396–400. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0467-6
Anjum, A., Yazid, M. D., Fauzi Daud, M., Idris, J., Ng, A. M. H., Selvi Naicker, A., et al. (2020). Spinal cord injury: pathophysiology, multimolecular interactions, and underlying recovery mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 7533. doi:10.3390/ijms21207533
Assuncao-Silva, R. C., Gomes, E. D., Sousa, N., Silva, N. A., and Salgado, A. J. (2015). Hydrogels and cell based therapies in spinal cord injury regeneration. Stem cells Int. 2015, 1–24. doi:10.1155/2015/948040
Blagovic, K., Gong, E. S., Milano, D. F., Natividad, R. J., and Asthagiri, A. R. (2013). Engineering cell-cell signaling. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 24, 940–947. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2013.05.007
Bose, A., Roy Burman, D., Sikdar, B., and Patra, P. (2021). Nanomicelles: types, properties and applications in drug delivery. IET nanobiotechnology 15, 19–27. doi:10.1049/nbt2.12018
Chay, W., and Kirshblum, S. (2020). Predicting outcomes after spinal cord injury. Phys. Med. rehabilitation Clin. N. Am. 31, 331–343. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2020.03.003
Chen, J., Cheng, X., Yu, Z., Deng, R., Cui, R., Zhou, J., et al. (2024). Sustained delivery of NT-3 and curcumin augments microenvironment modulation effects of decellularized spinal cord matrix hydrogel for spinal cord injury repair. Regen. Biomater. 11, rbae039. doi:10.1093/rb/rbae039
Chomoucka, J., Drbohlavova, J., Huska, D., Adam, V., Kizek, R., and Hubalek, J. (2010). Magnetic nanoparticles and targeted drug delivering. Pharmacol. Res. 62, 144–149. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2010.01.014
Cui, Y., Liu, J., Lei, X., Liu, S., Chen, H., Wei, Z., et al. (2024). Dual-directional regulation of spinal cord injury and the gut microbiota. Neural Regen. Res. 19, 548–556. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.380881
Dadfar, S. M., Roemhild, K., Drude, N. I., von Stillfried, S., Knuchel, R., Kiessling, F., et al. (2019). Iron oxide nanoparticles: diagnostic, therapeutic and theranostic applications. Adv. drug Deliv. Rev. 138, 302–325. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2019.01.005
Dams-O'Connor, K., Juengst, S. B., Bogner, J., Chiaravalloti, N. D., Corrigan, J. D., Giacino, J. T., et al. (2023). Traumatic brain injury as a chronic disease: insights from the United States traumatic brain injury model systems research program. Lancet. Neurology 22, 517–528. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(23)00065-0
De Jong, W. H., and Borm, P. J. A. (2008). Drug delivery and nanoparticles:applications and hazards. Int. J. nanomedicine 3, 133–149. doi:10.2147/ijn.s596
Duarte, D., Correia, C., Reis, R. L., Pashkuleva, I., Peixoto, D., and Alves, N. M. (2024). Bioadhesive hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels for spinal cord injury. Biomacromolecules 25, 1592–1601. doi:10.1021/acs.biomac.3c01186
Dutt, Y., Pandey, R. P., Dutt, M., Gupta, A., Vibhuti, A., Vidic, J., et al. (2023). Therapeutic applications of nanobiotechnology. J. nanobiotechnology 21, 148. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-01909-z
Eckert, M. J., and Martin, M. J. (2017). Trauma: spinal cord injury. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 97, 1031–1045. doi:10.1016/j.suc.2017.06.008
Feng, F., Song, X., Tan, Z., Tu, Y., Xiao, L., Xie, P., et al. (2023). Cooperative assembly of a designer peptide and silk fibroin into hybrid nanofiber gels for neural regeneration after spinal cord injury. Sci. Adv. 9, eadg0234. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adg0234
Fan, L., Liu, C., Chen, X., Zheng, L., Zou, Y., Wen, H., et al. (2022). Exosomes-loaded electroconductive hydrogel synergistically promotes tissue repair after spinal cord injury via immunoregulation and Enhancement of myelinated axon growth. Adv. Sci. Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Ger. 9, e2105586. doi:10.1002/advs.202105586
Fan, P., Li, S., Yang, J., Yang, K., Wu, P., Dong, Q., et al. (2024). Injectable, self-healing hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels for spinal cord injury repair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 263, 130333. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130333
Feliu, N., and Parak, W. J. (2024). Developing future nanomedicines. Sci. (New York, N.Y.) 384, 385–386. doi:10.1126/science.abq3711
Gal, L., Bellak, T., Marton, A., Fekecs, Z., Weissman, D., Torok, D., et al. (2023). Restoration of motor function through delayed intraspinal delivery of human IL-10-encoding nucleoside-modified mRNA after spinal cord injury. Research 6, 0056. doi:10.34133/research.0056
Gao, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Q., and Zhang, L. (2016). Nanoparticle-hydrogel: a hybrid biomaterial system for localized drug delivery. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 44, 2049–2061. doi:10.1007/s10439-016-1583-9
Gao, W., Wang, X., Zhou, Y., Wang, X., and Yu, Y. (2022). Autophagy, ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis in tumor immunotherapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7, 196. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01046-3
Gao, X., Han, Z., Huang, C., Lei, H., Li, G., Chen, L., et al. (2022). An anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective biomimetic nanoplatform for repairing spinal cord injury. Bioact. Mater. 18, 569–582. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.05.026
Ghezzi, M., Pescina, S., Padula, C., Santi, P., Del Favero, E., Cantu, L., et al. (2021). Polymeric micelles in drug delivery: an insight of the techniques for their characterization and assessment in biorelevant conditions. J. Control. release official J. Control. Release Soc. 332, 312–336. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.02.031
Gill, K. K., Kaddoumi, A., and Nazzal, S. (2015). PEG-lipid micelles as drug carriers: physiochemical attributes, formulation principles and biological implication. J. drug Target. 23, 222–231. doi:10.3109/1061186x.2014.997735
Grijalvo, S., Nieto-Diaz, M., Maza, R. M., Eritja, R., and Diaz, D. D. (2019). Alginate hydrogels as scaffolds and delivery systems to repair the damaged spinal cord. Biotechnol. J. 14, e1900275. doi:10.1002/biot.201900275
Guan, P., Fan, L., Zhu, Z., Yang, Q., Kang, X., Li, J., et al. (2024). M2 microglia-derived exosome-loaded electroconductive hydrogel for enhancing neurological recovery after spinal cord injury. J. nanobiotechnology 22, 8. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-02255-w
Guo, S., Redenski, I., and Levenberg, S. (2021). Spinal cord repair: from cells and tissue engineering to extracellular vesicles. Cells 10, 1872. doi:10.3390/cells10081872
Hallaj-Nezhadi, S., and Hassan, M. (2015). Nanoliposome-based antibacterial drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 22, 581–589. doi:10.3109/10717544.2013.863409
Han, M., Yang, H., Lu, X., Li, Y., Liu, Z., Li, F., et al. (2022). Three-dimensional-cultured MSC-derived exosome-hydrogel hybrid microneedle array patch for spinal cord repair. Nano Lett. 22, 6391–6401. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c02259
Hopf, A., Schaefer, D. J., Kalbermatten, D. F., Guzman, R., and Madduri, S. (2020). Schwann cell-like cells: origin and usability for repair and regeneration of the peripheral and central nervous system. Cells 9, 1990. doi:10.3390/cells9091990
Hossen, S., Hossain, M. K., Basher, M. K., Mia, M. N. H., Rahman, M. T., and Uddin, M. J. (2019). Smart nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy and toxicity studies: a review. J. Adv. Res. 15, 1–18. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2018.06.005
Jendelova, P. (2018). Therapeutic strategies for spinal cord injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 3200. doi:10.3390/ijms19103200
Jiang, D., Gong, F., Ge, X., Lv, C., Huang, C., Feng, S., et al. (2020). Neuron-derived exosomes-transmitted miR-124-3p protect traumatically injured spinal cord by suppressing the activation of neurotoxic microglia and astrocytes. J. nanobiotechnology 18, 105. doi:10.1186/s12951-020-00665-8
Jiang, X., Liu, X., Yu, Q., Shen, W., Mei, X., Tian, H., et al. (2022). Functional resveratrol-biodegradable manganese doped silica nanoparticles for the spinal cord injury treatment. Mater. today. Bio 13, 100177. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100177
Kim, S., Fan, J., Lee, C., Chen, C., and Lee, M. (2021). Sulfonate hydrogel-siRNA conjugate facilitates osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by controlled gene silencing and activation of BMP signaling. ACS Appl. bio Mater. 4, 5189–5200. doi:10.1021/acsabm.1c00369
Koffler, J., Zhu, W., Qu, X., Platoshyn, O., Dulin, J. N., Brock, J., et al. (2019). Biomimetic 3D-printed scaffolds for spinal cord injury repair. Nat. Med. 25, 263–269. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0296-z
Koli, V. B., Delekar, S. D., and Pawar, S. H. (2016). Photoinactivation of bacteria by using Fe-doped TiO(2)-MWCNTs nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 27, 177. doi:10.1007/s10856-016-5788-0
Kong, G., Liu, J., Wang, J., Yu, X., Li, C., Deng, M., et al. (2025). Engineered extracellular vesicles modified by angiopep-2 peptide promote targeted repair of spinal cord injury and brain inflammation. ACS nano 19, 4582–4600. doi:10.1021/acsnano.4c14675
Li, L., Xiao, B., Mu, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., Cao, H., et al. (2019). A MnO(2) nanoparticle-dotted hydrogel promotes spinal cord repair via regulating reactive oxygen species microenvironment and synergizing with mesenchymal stem cells. ACS nano 13, 14283–14293. doi:10.1021/acsnano.9b07598
Liang, G., Cao, W., Tang, D., Zhang, H., Yu, Y., Ding, J., et al. (2024). Nanomedomics. ACS nano 18, 10979–11024. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c11154
Liu, W., Gu, R., Zhu, Q., Xiao, C., Huang, L., Zhuang, X., et al. (2017). Rapid fluorescence imaging of spinal cord following epidural administration of a nerve-highlighting fluorophore. Theranostics 7, 1863–1874. doi:10.7150/thno.18962
Liu, Y., Yang, G., Jin, S., Xu, L., and Zhao, C. (2020). Development of high-drug-loading nanoparticles. ChemPlusChem 85, 2143–2157. doi:10.1002/cplu.202000496
Liu, K., Dong, X., Wang, Y., Wu, X., and Dai, H. (2022). Dopamine-modified chitosan hydrogel for spinal cord injury. Carbohydr. Polym. 298, 120047. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120047
Liu, D., Lu, G., Shi, B., Ni, H., Wang, J., Qiu, Y., et al. (2023). ROS-scavenging hydrogels synergize with neural stem cells to enhance spinal cord injury repair via regulating microenvironment and facilitating nerve regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 12, e2300123. doi:10.1002/adhm.202300123
Luo, J., Shi, X., Li, L., Tan, Z., Feng, F., Li, J., et al. (2021). An injectable and self-healing hydrogel with controlled release of curcumin to repair spinal cord injury. Bioact. Mater. 6, 4816–4829. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.05.022
Malekzadeh, H., Golpayegani, M., Ghodsi, Z., Sadeghi-Naini, M., Asgardoon, M., Baigi, V., et al. (2022). Direct cost of illness for spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Glob. spine J. 12, 1267–1281. doi:10.1177/21925682211031190
Matson, K. J. E., Russ, D. E., Kathe, C., Hua, I., Maric, D., Ding, Y., et al. (2022). Single cell atlas of spinal cord injury in mice reveals a pro-regenerative signature in spinocerebellar neurons. Nat. Commun. 13, 5628. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-33184-1
McDonald, J. W., and Sadowsky, C. (2002). Spinal-cord injury. Lancet London, Engl. 359, 417–425. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(02)07603-1
Meyer, R. A., Sunshine, J. C., and Green, J. J. (2015). Biomimetic particles as therapeutics. Trends Biotechnol. 33, 514–524. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.07.001
Mousavi, S. M., Zarei, M., Hashemi, S. A., Ramakrishna, S., Chiang, W., Lai, C. W., et al. (2020). Gold nanostars-diagnosis, bioimaging and biomedical applications. Drug metab. Rev. 52, 299–318. doi:10.1080/03602532.2020.1734021
Movassaghian, S., Merkel, O. M., and Torchilin, V. P. (2015). Applications of polymer micelles for imaging and drug delivery. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomedicine nanobiotechnology 7, 691–707. doi:10.1002/wnan.1332
Mozafari, M. R. (2010). Nanoliposomes: preparation and analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. Clift. N.J. 605, 29–50. doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-360-2_2
Paleos, C. M., Tsiourvas, D., and Sideratou, Z. (2007). Molecular engineering of dendritic polymers and their application as drug and gene delivery systems. Mol. Pharm. 4, 169–188. doi:10.1021/mp060076n
Park, J., Lim, E., Back, S., Na, H., Park, Y., and Sun, K. (2010). Nerve regeneration following spinal cord injury using matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive, hyaluronic acid-based biomimetic hydrogel scaffold containing brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 93, 1091–1099. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.32519
Prakash, S. (2023). Nano-based drug delivery system for therapeutics: a comprehensive review. Biomed. Phys. and Eng. express 9, 052002. doi:10.1088/2057-1976/acedb2
Qian, J., Guo, Y., Xu, Y., Wang, X., Chen, J., and Wu, X. (2023). Combination of micelles and liposomes as a promising drug delivery system: a review. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 13, 2767–2789. doi:10.1007/s13346-023-01368-x
Qin, B., Hu, X., Huang, Y., Yang, R., and Xiong, K. (2024). A new paradigm in spinal cord injury therapy: from cell-free treatment to engineering modifications. CNS and neurological Disord. drug targets 23, 656–673. doi:10.2174/1871527322666230418090857
Qiu, C., Sun, Y., Li, J., Zhou, J., Xu, Y., Qiu, C., et al. (2023). A 3D-printed dual driving forces scaffold with self-promoted cell absorption for spinal cord injury repair. Adv. Sci. Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Ger. 10, e2301639. doi:10.1002/advs.202301639
Radhakrishna, M., Makriyianni, I., Marcoux, J., and Zhang, X. (2014). Effects of injury level and severity on direct costs of care for acute spinal cord injury. Int. J. rehabilitation Res. Int. Zeitschrift fur Rehabilitationsforschung. Revue Int. de recherches de readaptation 37, 349–353. doi:10.1097/mrr.0000000000000081
Rasoulianboroujeni, M., Repp, L., Lee, H. J., and Kwon, G. S. (2022). Production of paclitaxel-loaded PEG-b-PLA micelles using PEG for drug loading and freeze-drying. J. Control. release official J. Control. Release Soc. 350, 350–359. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.08.032
Roh, E. J., Kim, D., Kim, J. H., Lim, C. S., Choi, H., Kwon, S. Y., et al. (2023). Multimodal therapy strategy based on a bioactive hydrogel for repair of spinal cord injury. Biomaterials 299, 122160. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122160
Rossi, F., Perale, G., Papa, S., Forloni, G., and Veglianese, P. (2013). Current options for drug delivery to the spinal cord. Expert Opin. drug Deliv. 10, 385–396. doi:10.1517/17425247.2013.751372
Rust, R., Yin, H., Achon Buil, B., Sagare, A. P., and Kisler, K. (2025). The blood-brain barrier: a help and a hindrance. Brain a J. neurology 148, 2262–2282. doi:10.1093/brain/awaf068
Shi, C., Wang, B., Zhai, T., Zhang, C., Ma, J., Guo, Y., et al. (2025). Exploring ubiquitination in spinal cord injury therapy: multifaceted targets and promising strategies. Neurochem. Res. 50, 82. doi:10.1007/s11064-025-04332-y
Somredngan, S., Theerakittayakorn, K., Nguyen, H. T., Ngernsoungnern, A., Ngernsoungnern, P., Sritangos, P., et al. (2023). The efficiency of neurospheres derived from human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells for spinal cord injury regeneration in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 3846. doi:10.3390/ijms24043846
Sterner, R. C., and Sterner, R. M. (2022). Immune response following traumatic spinal cord injury: pathophysiology and therapies. Front. Immunol. 13, 1084101. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1084101
Sun, Z., Zhu, D., Zhao, H., Liu, J., He, P., Luan, X., et al. (2023). Recent advance in bioactive hydrogels for repairing spinal cord injury: material design, biofunctional regulation, and applications. J. nanobiotechnology 21, 238. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-01996-y
Talens-Visconti, R., Diez-Sales, O., de Julian-Ortiz, J. V., and Nacher, A. (2022). Nanoliposomes in cancer therapy: marketed products and current clinical trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 4249. doi:10.3390/ijms23084249
Tereshkina, Y. A., Torkhovskaya, T. I., Tikhonova, E. G., Kostryukova, L. V., Sanzhakov, M. A., Korotkevich, E. I., et al. (2022). Nanoliposomes as drug delivery systems: safety concerns. J. drug Target. 30, 313–325. doi:10.1080/1061186x.2021.1992630
Wang, R., and Bai, J. (2024). Pharmacological interventions targeting the microcirculation following traumatic spinal cord injury. Neural Regen. Res. 19, 35–42. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.375304
Wang, X., Peng, C., Zhang, S., Xu, X., Shu, G., Qi, J., et al. (2021). Correction to “polysialic-acid-based micelles promote neural regeneration in spinal cord injury therapy”. Nano Lett. 21, 10146–10147. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c04394
Wang, S., Wang, R., Chen, J., Yang, B., Shu, J., Cheng, F., et al. (2023). Controlled extracellular vesicles release from aminoguanidine nanoparticle-loaded polylysine hydrogel for synergistic treatment of spinal cord injury. J. Control. release official J. Control. Release Soc. 363, 27–42. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.09.026
Wang, X., Shen, J., Xu, C., Wan, C., Yang, H., Qiu, Y., et al. (2023). Proteomic profile of Trichinella spiralis infected mice with acute spinal cord injury: a 4D label-free quantitative analysis. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 97, 101994. doi:10.1016/j.cimid.2023.101994
Wang, W., Yong, J., Marciano, P., O'Hare Doig, R., Mao, G., and Clark, J. (2024). The translation of nanomedicines in the contexts of spinal cord injury and repair. Cells 13, 569. doi:10.3390/cells13070569
Woerly, S., Doan, V. D., Evans-Martin, F., Paramore, C. G., and Peduzzi, J. D. (2001). Spinal cord reconstruction using NeuroGel implants and functional recovery after chronic injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 66, 1187–1197. doi:10.1002/jnr.1255
Xiong, M., Feng, Y., Luo, C., Guo, J., Zeng, J., Deng, L., et al. (2024). Teriparatide: an innovative and promising strategy for protecting the blood-spinal cord barrier following spinal cord injury. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1386565. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1386565
Xu, L., Mu, J., Ma, Z., Lin, P., Xia, F., Hu, X., et al. (2023). Nanozyme-integrated thermoresponsive in situ forming hydrogel enhances mesenchymal stem cell viability and paracrine effect for efficient spinal cord repair. ACS Appl. Mater. and interfaces 15, 37193–37204. doi:10.1021/acsami.3c06189
Yin, X., Lin, S., Xiong, Y., Zhang, P., and Mei, X. (2023). Biomimetic nanoplatform with anti-inflammation and neuroprotective effects for repairing spinal cord injury in mice. Mater. today. Bio 23, 100836. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100836
Yin, P., Liang, W., Han, B., Yang, Y., Sun, D., Qu, X., et al. (2024). Hydrogel and nanomedicine-based multimodal therapeutic strategies for spinal cord injury. Small methods 8, e2301173. doi:10.1002/smtd.202301173
You, Y., Jiang, J., Zheng, G., Chen, Z., Zhu, Y., Ma, H., et al. (2024). In situ piezoelectric-catalytic anti-inflammation promotes the rehabilitation of acute spinal cord injury in synergy. Adv. Mater. Deerf. Beach, Fla. 36, e2311429. doi:10.1002/adma.202311429
Yuan, T., Zhang, J., Yu, T., Wu, J., and Liu, Q. (2022). 3D bioprinting for spinal cord injury repair. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 847344. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.847344
Zafar, N., Uzair, B., Menaa, F., Khan, B. A., Niazi, M. B. K., Alaryani, F. S., et al. (2022). Moringa concanensis-mediated synthesis and characterizations of ciprofloxacin encapsulated into Ag/TiO(2)/Fe(2)O(3)/CS nanocomposite: a therapeutic solution against multidrug resistant E. coli strains of livestock infectious diseases. Pharmaceutics 14, 1719. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14081719
Zhang, B., Wang, W., Gao, P., Li, X., Chen, L., Lin, Z., et al. (2024). Injectable, electroconductive, free radical scavenging silk fibroin/black phosphorus/glycyrrhizic acid nanocomposite hydrogel for enhancing spinal cord repair. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13, e2304300. doi:10.1002/adhm.202304300
Zhang, X., Lu, Y., Yang, L., Sui, Y., Zhang, C., Zhang, W., et al. (2025). A dual-interaction supramolecular hydrogel system for siRNA delivery to enhance endometrial receptivity in stem cell therapy. Biomacromolecules 26, 3044–3058. doi:10.1021/acs.biomac.5c00132
Zheng, B., and Tuszynski, M. H. (2023). Regulation of axonal regeneration after mammalian spinal cord injury. Nat. Rev. Mol. cell Biol. 24, 396–413. doi:10.1038/s41580-022-00562-y
Zhu, B., Gu, G., Ren, J., Song, X., Li, J., Wang, C., et al. (2023). Schwann cell-derived exosomes and methylprednisolone composite patch for spinal cord injury repair. ACS nano 17, 22928–22943. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c08046
Zhu, S., Diao, S., Liu, X., Zhang, Z., Liu, F., Chen, W., et al. (2025). Biomaterial-based strategies: a new era in spinal cord injury treatment. Neural Regen. Res. 20, 3476–3500. doi:10.4103/nrr.nrr-d-24-00844
Zoghi, A., Khosravi-Darani, K., and Omri, A. (2018). Process variables and design of experiments in liposome and nanoliposome research. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 18, 324–344. doi:10.2174/1389557516666161031120752
Keywords: spinal cord injury, nanocarriers, drug delivery, targeted therapy, nanoparticles and nanomaterials
Citation: Cheng Y, Wang R, Zhou X, Jiang H, Li M and Wei X (2025) Nanocarrier-mediated drug delivery systems for spinal cord injury treatment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1660264. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1660264
Received: 09 July 2025; Accepted: 26 August 2025;
Published: 05 September 2025.
Edited by:
Maria Gazouli, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, GreeceReviewed by:
Kun Xiong, Central South University, ChinaRakesh A. Afre, Dr. D. Y. Patil Dnyan Prasad University, India
Copyright © 2025 Cheng, Wang, Zhou, Jiang, Li and Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ming Li, bGltaW5nc3BpbmVAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Xianzhao Wei, d2VpeGlhbnpoYW9AMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yajun Cheng1†
Yajun Cheng1† Rui Wang
Rui Wang Xiaoyi Zhou
Xiaoyi Zhou Xianzhao Wei
Xianzhao Wei