- 1Department of Plastic Surgery, Ningbo NO. 2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Ningbo NO. 2 Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
Introduction: Abnormal wound healing impairs bodily functions and burdens healthcare systems. Adipose mesenchymal stem cells (AMSCs)-derived exosomes promote wound healing, with exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) playing pivotal roles. This study investigated the roles and mechanisms of miR-26a-5p (delivered by AMSCs-derived exosomes) in wound healing.
Methods: The GSE55661 dataset was analyzed to screen a crucial miRNA (miR-26a-5p) and its target gene (MAP2K4), and their interaction was further validated by dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. Exosomes were isolated from miR-26a-5p-overexpressing AMSCs, and a mouse skin defect model was used to evaluate their effects on wound healing.
Results: Bioinformatics identified 13 differentially expressed miRNAs, and a miRNA-mRNA regulatory network composed of 12 DEmiRNAs and 143 regulated target genes was built. In this network, miR-26a served as the hub node, and the target genes were enriched in the MAPK cascade, as well as cAMP, relaxin, Hippo, Apelin, Wnt, and cGMP-PKG signaling pathways. Thereafter, MAP2K4 was identified as the target of miR-26a-5p, and exosomes were successfully isolated from AMSCs overexpressing miR-26a-5p. Exosomes from miR-26a-5p overexpressed AMSCs (like miR-26a-5p agomir) could facilitate wound healing, and down-regulated MAP2K4, Il6, Il1β, and Tnf-α, whereas up-regulated Col1a1, Cd31, Col2a1, α-Sma, and Col3a1.
Discussion: AMSCs-derived exosomes delivering miR-26a-5p may expedite wound healing by targeting MAP2K4, inhibiting inflammation, and enhancing angiogenesis and ECM synthesis.
1 Introduction
Wound healing, a complex and dynamic physiological process, begins immediately after injury and continues for months or years after wound closure, involving multiple stages such as the inflammatory response, cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling (Hassanshahi et al., 2022; Sorg and Sorg, 2023). During the inflammatory phase, it lays the foundation for subsequent repair by clearing pathogens and necrotic tissues (Hassanshahi et al., 2022). During the proliferation phase, granulation tissues and neovascularization are formed to provide support for wound filling and nutrient supply (Sharifiaghdam et al., 2022). During the remodeling period, the newly formed tissues are refined to resemble normal tissues in both structure and function (Al-Masawa et al., 2022). Generally, wounds are classified into acute and chronic wounds. Acute wounds typically heal at a predictable and expected rate, whereas wounds that fail to heal within 6 weeks and exhibit inefficient cellular and molecular function are classified as chronic wounds (Dai et al., 2020). If not properly treated, they may increase the incidence rate and medical care costs of patients, and even lead to amputation in serious cases (Cioce et al., 2024). At present, the methods used in clinical practice to promote wound healing include various types of wound dressings, drug therapy (such as antibiotics, growth factors), physical therapy (such as negative pressure wound therapy, laser therapy), and skin transplantation (Wilkinson and Hardman, 2020; Freedman et al., 2023). However, although these approaches may exhibit some benefits, their widespread use is limited by the emergence of drug resistance and immune rejection reactions, complex administration methods, and high costs (Kolimi et al., 2022). Therefore, an in-depth understanding of the underlying mechanisms of wound healing, along with the development of more effective new therapeutic strategies to promote wound healing, is essential in the field of regenerative medicine.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), including adipose mesenchymal stem cells (AMSCs), are multipotent stem cells with self-renewal ability, multipotent differentiation potential, and paracrine regulation (Zhou et al., 2023). Due to their ease of isolation, in vitro expansion, and multipotency, AMSCs have been recognized as a crucial source of stem cells in the field of regenerative medicine, including tissue repair and regeneration (Guillamat-Prats, 2021). Notably, the therapeutic utilization of stem cells in wound healing is also limited by storage challenges, mutation-related tumorigenicity, optimal cell activity, immune rejection, and ethical factors (Margiana et al., 2022). Previous research has reported that AMSCs can activate a series of bioactive factors through autocrine and paracrine pathways, thereby participating in the healing process of skin injuries (Mazini et al., 2020). Exosomes, with a size of approximately 30–150 nm, can be secreted by almost all cells and absorbed by cells through autocrine or paracrine pathways, which are the primary contributors to stem cell efficacy (Tan et al., 2024). Zhou et al. (2022) demonstrated that hydrogel Pluronic F-127 (PF-127) loaded in the AMSCs-derived exosomes could improve the efficiency of exosome delivery, and keep the bioactivity of AMSCs-derived exosomes; as well as have a better effect on promoting wound healing and regeneration than AMSCs-derived exosomes administered alone. Another study prepared a biological scaffold of AMSCs-derived exosomes modified gelatin sponge/polydopamine scaffold (GS-PDA-Exos), and found that AMSCs-derived exosomes could be released slowly from GS-PDA-Exos. The study also showed that GS-PDA-Exos had significant potential in the treatment of bone defects (Li et al., 2023). Furthermore, AMSCs-derived exosomes can promote skin wound healing by influencing all stages of wound healing, including regulating inflammatory responses, promoting the proliferation and migration of fibroblasts and keratinocytes, promoting angiogenesis, and regulating extracellular matrix remodeling (Weiliang and Lili, 2021). These investigations further confirmed that AMSCs-derived exosomes are a very promising and novel factor in wound repair and regeneration.
Exosomes are rich in proteins, lipids, microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and mRNAs; they are considered a communication tool between cells and a promising biological gene delivery system. Exosomes can endow miRNAs with considerable stability and resistance to RNA enzyme degradation, thereby exerting post-transcriptional gene regulation through their miRNA content. MiRNAs, a small endogenous RNA molecule with a length of approximately 22 nucleotides (nt), have been shown to play a crucial role in health and disease, including various types of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and wound healing. Wang et al. (2021) used high-throughput sequencing to demonstrate that upregulated miR-126-5p, miR-21-3p, and miR-31-5p, while downregulated miR-99b and miR-146a, were associated with wound healing. Additionally, hypoxic AMSCs-derived exosomes were found to promote diabetic wound healing and inhibit inflammation through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Another investigation revealed that the level of miR-488-3p was significantly decreased in the wound tissues of diabetic patients with skin defects compared to the control group, and miR-488-3p overexpression could accelerate wound healing by targeting the MeCP2 and CYP1B1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (Zuo et al., 2024). Therefore, miRNAs play crucial roles in regulating various biological processes, including wound healing. Additionally, the roles of miR-26a-5p have been reported in many cancers (Cai et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2023); however, its potential roles and underlying mechanisms, particularly with AMSCs-derived exosomes as carriers in wound healing, need to be further explored.
In our study, miRNA profiles associated with wound injury were downloaded from NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), and a series of bioinformatics analyses were performed to identify the crucial miRNAs. Based on the regulatory network, miR-26a-5p served as the hub node, and its target gene, MAP2K4, participated in the MAPK cascade, relaxin signaling pathway, and growth hormone synthesis, secretion, and action. Therefore, the interaction between miR-26a-5p and MAP2K4 was further validated, and the roles and related potential mechanisms of AMSCs-derived exosomal miR-26a-5p in wound healing were investigated in vivo. Notably, while miR-26a-5p has been reported to exert regenerative effects in other tissues, such as inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in lung fibrosis via human umbilical cord MSC (hUCMSC)-derived exosomes (Zhao et al., 2023) and alleviating inflammation in diabetic retinopathy through the USP14/NF-κB pathway (Bian et al., 2024), but its role in cutaneous wound healing remains unaddressed. Two critical gaps distinguish our work from these prior studies: first, the tissue-specific regulatory mechanisms of miR-26a-5p differ across organs—lung fibrosis and retinal inflammation involve distinct cell types (e.g., alveolar epithelial cells, retinal Müller cells) and pathways (e.g., EMT, NF-κB) that are not the core drivers of skin wound healing (which relies on inflammation resolution, angiogenesis, and extracellular matrix (ECM) synthesis). Second, prior studies have utilized non-adipose MSC sources (e.g., hUCMSCs) or administered miRNA directly. In contrast, we focus on AMSCs-derived exosomes, a carrier with unique advantages for skin repair, including easier isolation from adipose tissue, stronger paracrine potential for activating cutaneous cells, and better biocompatibility with the skin microenvironment. Moreover, our bioinformatics analysis identifies MAP2K4 (a key upstream regulator of the MAPK cascade) as a novel target of miR-26a-5p in wound healing, which is not reported in lung or retinal studies. This tissue-specific target and carrier system combination fills the gap in understanding miR-26a-5p′s role in skin repair and provides a more translational strategy for wound therapy.
2 Methods
2.1 Bioinformatics analysis
The expression profile of GSE55661 was downloaded from NCBI GEO (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) (Edgar et al., 2002), which contained miRNA expression profile data from 18 mouse skin tissue samples. The tested platform was GPL18386 Luminex Multi-species miRNA array (miRBase 8.0). Then, we selected 6 samples, 2 days after the injury, including 3 samples from the damaged area and 3 normal control skin samples. The limma package version 3.34.7 in R4.3.1 (https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/limma.html) (Ritchie et al., 2015) was used to identify the differentially expressed miRNAs (DEmiRNAs) between the damaged samples and normal control samples based on the thresholds of false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 using the Benjamini and Hochberg method and |log2 fold change (FC)| > 1.
Thereafter, the identified DEmiRNAs were submitted for the search of target genes using the miRWalk 3.0 database (http://mirwalk.umm.uni-heidelberg.de/) (Hemmat et al., 2020). The linkage pairs (miRNA-mRNA pairs) labeled with “validated” (i.e., regulatory linkage confirmed by experiments) were retained and visualized using Cytoscape version 3.6.1 (http://www.cytoscape.org/) (Shannon et al., 2003). After that, the target genes in the network were subjected to the functional analyses based on DAVID version 6.8 (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/), including biological process (BP) of gene ontology (GO) terms and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways; as well as FDR <0.05 with the Benjamini and Hochberg method was selected as the threshold of enrichment significance.
2.2 Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay
The wild-type and mutant sequences of MAP2K4 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) were synthesized, and the pGL3-basic vector (Yanzai Biotechnology, Shanghai, China) was employed to construct the 3′-UTR MAP2K4 report plasmids (pGL3-MAP2K4-WT and pGL3-MAP2K4-MUT). Thereafter, the pGL3-basic vector (500 ng), pGL3-MAP2K4-WT (500 ng) and pGL3-MAP2K4-MUT (500 ng) were co-transfected with 293T cells (Cell Bank. Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai, China) with miR-26a-5p mimics (100 nM) or negative control (NC) mimics (100 nM) using Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States) in line with the manufacturer’s protocols. After transfection for 6 h, the medium was changed to complete medium, and the cells were cultured for another 48 h. After that, the cells were harvested to determine the relative luciferase activity using a dual luciferase reporter system (Promega, WI, United States) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
2.3 Cell culture and transfection
Mouse AMSCs were purchased from Cyagen Biosciences Inc. (Guangzhou, China) and were maintained in α-MEM medium (Servicebio, Wuhan, China) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The construction of AMSCs with miR-26a-5p overexpression was performed using Lipofectamine 200 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) based on the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, the mouse AMSCs were seeded into a 24-well plate at a density of 4 × 104, and cultured overnight. The next day, the cell medium was changed to serum-free medium, and the cells were transfected with 15 pmol miR-26a-5p agomir (GeneRay, Shanghai, China) or NC (GeneRay) using Lipofectamine 200. After 6 h of transfection, the medium was replaced with complete medium. After culturing for an additional 48 h, total RNA was extracted from the different cells, and the miR-26a-5p level was determined using real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) to assess the cell transfection efficiency.
2.4 Isolation and characterization of AMSCs-derived exosomes
The supernatants of mouse AMSCs and AMSCs transfected with miR-26a-5p agomir were harvested for exosome isolation, and the isolation was performed at 4 °C. The harvested cell supernatants were centrifuged at 500 × g for 5 min, and then the supernatants were transferred to a new tube. After centrifugation at 2000 × g for 30 min, followed by 10,000 × g for 60 min, the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm sterile filter and collected into an ultra-high-speed centrifuge tube. After centrifugation at 120,000 × g for 70 min, the supernatants were removed, and the sediments were resuspended in sterile PBS (200 μL), which contained the exosomes, and were stored at −80 °C.
The concentrations of the isolated exosomes were determined using a BCA assay kit (Beyotime Biotechnology, Shanghai, China) according to the manufacturer’s protocols. Then, a Nanosight NS300 particle size analyzer (NTA; Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, United Kingdom) was used to determine the exosome size distribution based on the method of Yang et al. (2021). The morphology and ultrastructure of isolated exosomes were visualized using a transmission electron microscope (TEM, JEOL LTD, Peabody, MA, United States) as previously reported (Lin et al., 2024). Additionally, the expression of exosome-specific proteins, including CD63, CD81, and HSP70, and a negative control protein (calnexin), was detected by Western blot using their corresponding antibodies.
2.5 Animal experiments
A total of 24 specific pathogen-free (SPF) male C57BL/6 mice weighing 20 ± 2 g were purchased from Shanghai SLAC Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). All the mice were kept under controlled temperature (24 °C ± 2 °C) and humidity (50% ± 5%), with a 12 h light/dark cycle. All the mice had free access to standard laboratory food and filtered water during the experiments. Our animal experiments were conducted in strict accordance with the guidelines and regulations of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Guoke Ningbo Life Science and Health Industry Research Institute (approval no. GX-2025-XM-0004). The committee reviewed and approved the experimental protocol to ensure the ethical treatment of animals.
After 7 days of acclimatization, all the mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 6 for each group): control, model, AMSCs-agomir-Exo, and miR-26a-5p agomir groups. The mice in the model, AMSCs-agomir-Exo and miR-26a-5p agomir groups, were first used to establish a skin defect mouse model as previously reported (Liu et al., 2023). Briefly, the mice were deeply anesthetized using 4% isoflurane, and then fixed in a prone position. Thereafter, the back hair of the mice was removed, and the area was disinfected with 75% alcohol. A circular full-thickness skin defect with a diameter of 2 cm was then created. On the first day after injury, the mice in the model, AMSCs-agomir-Exo, and agomir groups were injected with PBS, exosomes isolated from AMSCs with miR-26a-5p overexpression (AMSCs-agomir-Exo, 200 μg/mice), and miR-26a-5p agomir (20 nmol/mice), respectively. The mice in the control group did not receive any treatment. Additionally, 12 C57BL/6 mice were obtained and randomly divided into two groups (n = 6 for each group): the si-NC and si-MAP2K4 groups. Firstly, all the mice were used to construct a skin defect mouse model. The mice in the si-NC and si-MAP2K4 groups were injected with si-NC (20 nmol/mouse) and si-MAP2K4 (20 nmol/mouse), respectively, on the first day after injury. After treatment for 0, 4, 8, and 12 days, the wounds of each mouse in the different groups were photographed and compared. Using a 2 cm × 2 cm unified field of view, image analysis software IPP 6.0 was used to analyze the change of wound area. Additionally, on the 12th day after treatment, all mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and the wounds and surrounding skin tissues were collected. A portion of the tissue was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for subsequent histopathological analysis, and the other part was used for further RT-qPCR and Western blot analysis.
2.6 Histopathological analysis
The fixed tissue samples were dehydrated, embedded in paraffin, and cut into 4-μm slices. After baking at 60 °C for 30 min, the slices were dewaxed and rehydrated. For hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining, the processed slices were stained with hematoxylin for 10 min, and re-stained with eosin for 90 s. After dehydration, transparentization, and sealing, the slices were scanned and photographed under an optical microscope (Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
For Masson staining, the slices were treated with potassium dichromate mordant for 12 h, and after washing, they were stained with Weigert iron hematoxylin for 10 min. After washing and differentiation with 1% hydrochloric acid alcohol, the slices were stained with Lichun red acid fuchsin dye for 10 min. After washing and being treated with phosphomolybdic acid for 150 s, the slices were re-stained with aniline blue dye for 5 min. After being treated with 1% glacial acetic acid for 1 min and dehydrated with ethanol, the slices were sealed with neutral gum, and the images were observed using an optical microscope (Olympus Corporation).
2.7 Real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
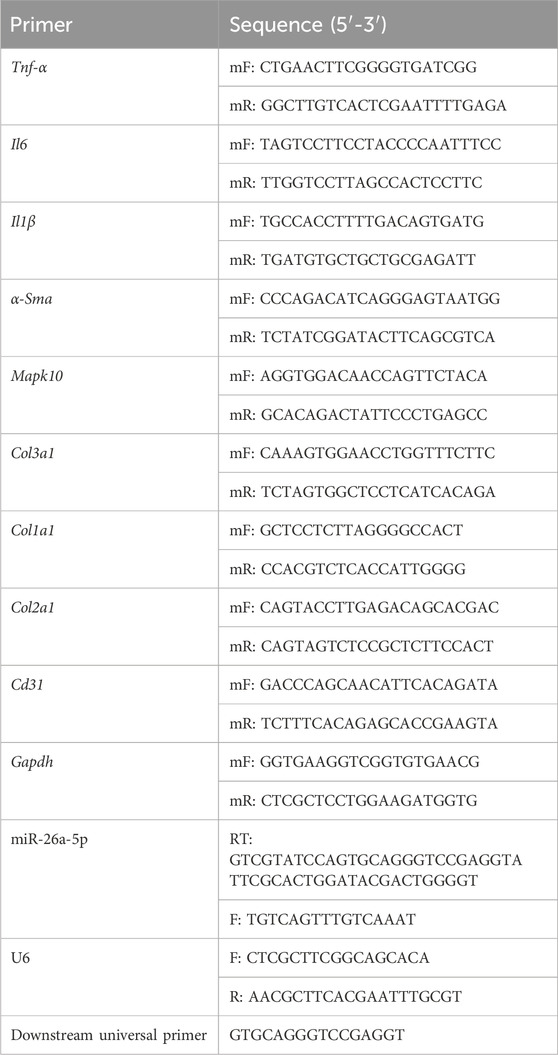
Total RNA was isolated using an RNA extraction solution (Servicebio) according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and then qualified and quantified using a microplate reader. Afterward, total RNA (1 μg) was reverse transcribed into cDNA using the PrimeScriptTM II 1st Strand cDNA synthesis kit (TaKaRa, Osaka, Japan), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The sequences of all primers are displayed in Table 1.
For the miR-26a-5p level, the stem loop RT-PCR method was employed with U6 as the endogenous reference gene. First, a 10 μL denaturation mixture was prepared for miR-26a-5p reverse transcription. The subsequent reverse transcription reaction was carried out in a 20 μL total volume, containing 10 μL of denaturation solution, 4 μL of 5X PrimeScript II buffer, 0.5 μL of RNase inhibitor (40 U/μL), 1 μL of PrimeScript II reverse transcriptase (200 U/μL), and 4.5 μL of RNase-free distilled water. The reverse transcription procedure consisted of incubation at 42 °C for 60 min, followed by a 5-min incubation at 95 °C to inactivate the enzyme. For qPCR, the thermal profile began with an initial denaturation step at 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s and 60 °C for 30 s.
For the expression levels of related genes, Gapdh served as a housekeeping gene. The thermal cycling protocol used for the associated genes reserve transcription involved incubation of the reverse transcription mix at 37 °C for 60 min and 85 °C for 5 s. The RT-qPCR reaction was initiated at 95 °C for 30 s, followed by a total of 40 cycles at 95 °C for 5 s and 60 °C for 30 s, and then a melting step at 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 60 s, and 95 °C for 15 s. Finally, the miR-26a-5p level and the expression of Map2k4, Col1a1, Col2a1, Col3a1, α-Sma, Tnf-α, Il1β, Il6, and Cd31 were analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCT method (Xu et al., 2019).
2.8 Western blotting
Total proteins were extracted from tissue samples or exosome samples using RIPA (Beyotime Biotechnology) and were quantified by a BCA assay kit (Beyotime Biotechnology). Subsequently, the total protein samples were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE (stacking gel: 60 V for 30 min; and running gel: 110 V for 120 min), and then transferred to PVDF membranes (100 V for 50 min on ice). After blocking with 5% skim milk at 37 °C for 2 h, the membranes were incubated the primary antibodies, including anti-CD63 antibody (1: 1,000, Abclonal, Wuhan, China), anti-CD81 antibody (1: 1,000, Abclonal), anti-HSP70 antibody (1: 1,000, Proteintech, Wuhan, China), anti-calnexin antibody (1: 1,000, Proteintech), anti-MAP2K4 antibody (1: 1,000, Proteintech), anti-COL1A1 antibody (1: 1,000, NOVUS, St. Louis, MO, United States), anti-α-SMA antibody (1: 1,000, Cell Signaling Technology, Boston, MA, United States), anti-TNF-α antibody (1: 1,000, Cell Signaling Technology), and anti-GAPDH antibody (1: 10,000, Proteintech). After incubation overnight at 4 °C, the membranes were incubated with the secondary antibodies ((H + L)-HRP goat anti-rabbit/anti-mouse IgG) at 37 °C for 2 h. After washing, the protein bands were visualized using a Millipore ECL kit (Beyotime Biotechnology) and photographed using a system (Shanghai Tanon Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China).
2.9 Statistical analysis
Each experiment was repeated three times, and data were reported as mean ± standard deviation. The statistical analyses were conducted using the SPSS software, and all figures were plotted in GraphPad Prism 9 (GraphPad software, San Diego, CA, United States). Before the analyses, a homogeneity of variance test was performed on all data, and the P values were obtained. For comparisons between two independent groups, the independent-samples t-test was used. For comparisons among more than two groups, if the P value > 0.05, a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Least-Significant Difference (LSD) was applied for multiple comparisons; if the P value ≤0.05, ANOVA followed by Dunnett T3 was employed. Statistical significances were set at a P-value of less than 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Identification of DEmiRNAs and their functional analyses
Based on FDR <0.05 and |log2FC| > 1, 13 DEmiRNAs were screened between the damaged tissue samples and normal control samples, including miR-424, miR-20b, miR-101b, miR-30c, miR-185, miR-30d, miR-26a, miR-133a, miR-26b, miR-1, miR-29a, miR-223, and miR-202 (Table 2). Then, these DEmiRNAs were submitted for the search of target genes. We identified 149 miRNA-mRNA regulatory pairs labeled as “validated,” and a miRNA-mRNA regulatory network composed of 12 DEmiRNAs and 143 regulated target genes was constructed (Figure 1A). In this network, miR-26a, which was downregulated in the damaged tissues, served as the hub node and was chosen for further experiments.
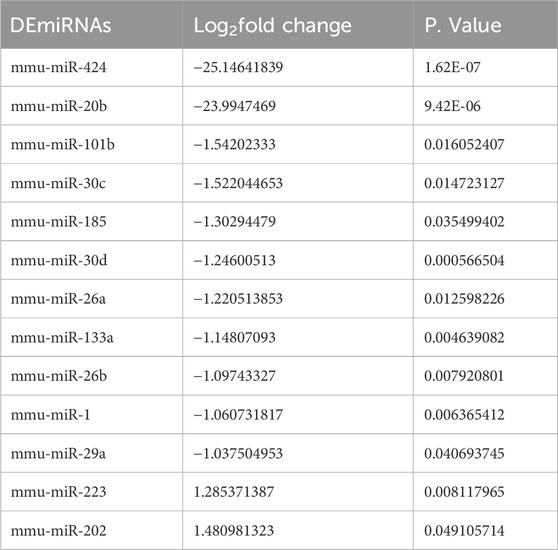
Table 2. Identification of differentially expressed miRNAs (DEmiRNAs) between the damaged samples and normal control samples.
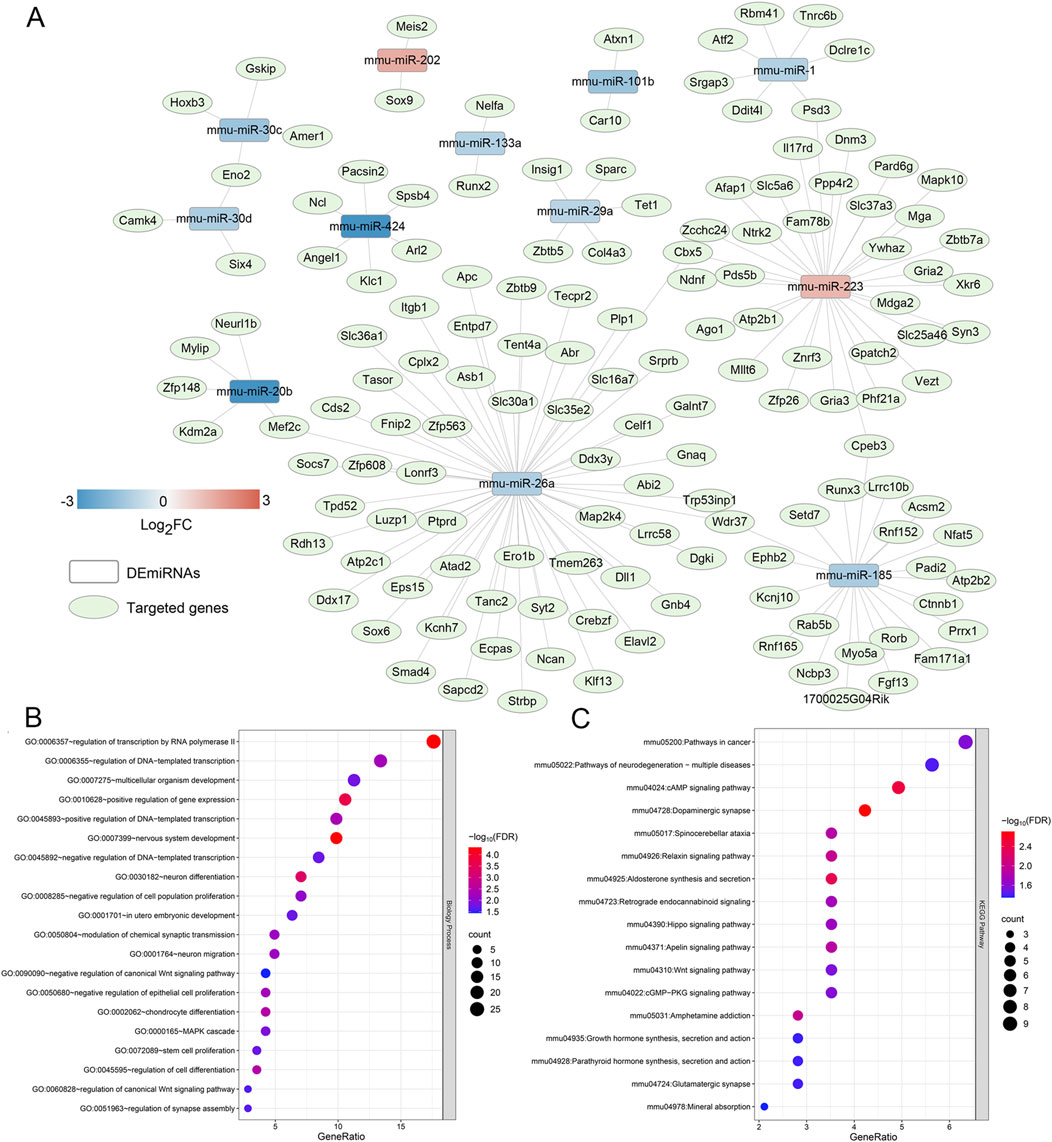
Figure 1. Construction of a miRNA-mRNA regulatory network, and functional analysis of the genes in the network. (A) The miRNA-mRNA regulatory network composed of 12 differentially expressed miRNAs and 143 regulated target genes, and miR-26a, which was down-regulated in the damaged tissues, was the hub node. (B) The significant gene ontology terms of biological process enriched by the genes in the network. (C) The significant Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways enriched by the target genes in the network.
After that, the genes in the built network were used for BP of GO terms and KEGG analyses. It was found that these genes were significantly enriched in 21 GO terms of BP, and 17 KEGG pathways. The significantly GO terms of BP contained “MAPK cascade”, “regulation of transcription nu RNA polymerase II”, “multicellular organism development”, “neuron differentiation”, “negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway”, “chondrocyte differentiation”, and “stem cell proliferation” (Figure 1B). Additionally, these genes were also closely associated with “cAMP signaling pathway”, “relaxin signaling pathway”, “Hippo signaling pathway”, “Apelin signaling pathway”, “Wnt signaling pathway”, “cGMP-PKG signaling pathway”, and “glutamatergic synapse” (Figure 1C).
3.2 MAP2K4 as a target of miR-26a-5p
Based on the proposed miRNA-mRNA regulatory network, we observed that miR-26a interacted with MAP2K4, and MAP2K4 was significantly involved in the MAPK cascade, relaxin signaling pathway, and growth hormone synthesis, secretion, and action. Therefore, a dual luciferase reporter gene assay was conducted to confirm the relationship between miR-26a-5p and MAP2K4. In the pGL3-basic plasmids, there was no significant difference in relative luciferase activity between the NC mimics and miR-26a-5p mimics (P > 0.05, Figure 2A). In the pGL3-MAP2K4-WT plasmids, the relative luciferase activity after transfection with miR-26a-5p mimics was evidently lower than that after transfection with NC mimics (P < 0.05, Figure 2A). However, when MAP2K4 was mutated (pGL3-MAP2K4-MUT plasmids), the relative luciferase activity after being transfected with miR-26a-5p mimics was markedly increased in comparison with the pGL3-MAP2K4-WT plasmids transfected with miR-26a-5p mimics (P < 0.05, Figure 2A). These outcomes suggested that MAP2K4 was the target of miR-26a-5p.
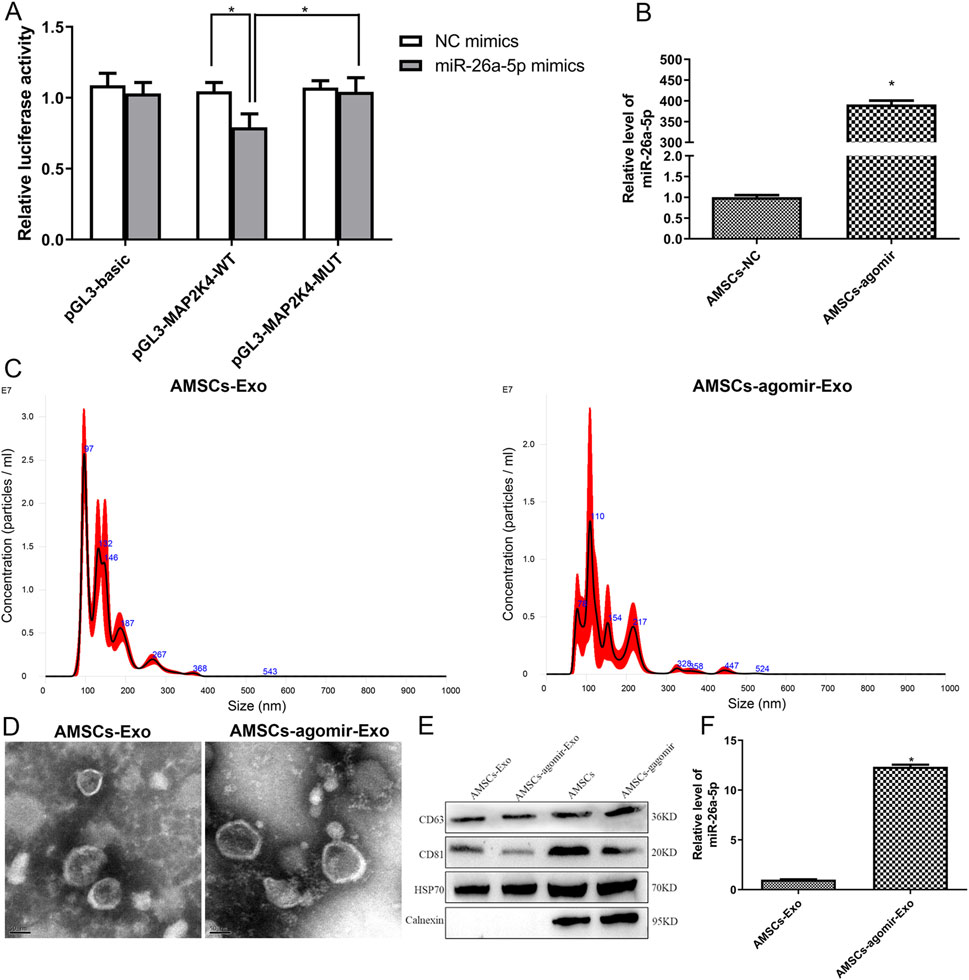
Figure 2. Interaction between miR-26a-5p and MAP2K4, as well as cell transfection efficiency and characterization of the isolated exosomes. (A) MAP2K4 was the target of miR-26a-5p by dual luciferase reporter gene assay. N = 3. *: P < 0.05. (B) The miR-26a-5p level in the AMSCs with miR-26a-5p overexpression to verify the cell transfection efficiency. N = 3. *: P < 0.05, vs. AMSCs-NC. (C) Particle size distribution of AMSCs-derived exosomes and miR-26a-5p overexpressed AMSCs-derived exosomes determined by Nanosight. (D) The morphology of AMSCs-derived exosomes and miR-26a-5p overexpressed AMSCs-derived exosomes, visualized by transmission electron microscopy. (E) The expression of exosomes-specific markers (CD63, CD81, and HSP70) and negative control protein (calnexin) in exosomes and cells, detected by Western blot. (F) The level of miR-26a-5p in the AMSCs-derived exosomes and miR-26a-5p overexpressed AMSCs-derived exosomes. N = 3. *: P < 0.05, vs. AMSCs-Exo.
3.3 Cell transfection efficiency and exosomes characterization
To investigate the effects of AMSCs-derived exosomal miR-26a-5p on wound healing, AMSCs with miR-26a-5p overexpression were constructed with miR-26a-5p agomir, and exosomes were isolated. It was obvious that the levels of miR-26a-5p in the AMSCs and AMSCs transfected with miR-26a-5p agomir were, respectively, 1.00 ± 0.09 and 391.51 ± 16.22, which displayed that the miR-26a-5p level in the AMSCs transfected with miR-26a-5p agomir was significantly higher than that in the AMSCs (P < 0.05, Figure 2B). These results revealed that the AMSCs with miR-26a-5p overexpression were successfully constructed and could be employed for subsequent exosome isolation.
Then, the exosomes were isolated from AMSCs and AMSCs with miR-26a-5p overexpression, and were identified by NTA, TEM, and Western blot. Our NTA results showed that the main peaks of the isolated substances from AMSCs and AMSCs with miR-26a-5p overexpression were respectively 96.5 nm and 109 nm, as well as the mean particle sizes of the isolated substances from AMSCs and AMSCs with miR-26a-5p overexpression were 147.4 nm and 151.5 nm, respectively (Figure 2C). The results were in line with the size distribution of exosomes (Krylova and Feng, 2023). Thereafter, the TEM images showed that the isolated substances from AMSCs and AMSCs with miR-26a-5p overexpression exhibited nearly round or cup-shaped morphology with a diameter of approximately 100 nm (Figure 2D). Additionally, Western blot analysis showed that the exosome-specific markers CD63, CD81, and HSP70 were expressed in both the exosomes (AMSCs-derived exosomes and miR-26a-5p overexpressed AMSCs-derived exosomes) and the cells (AMSCs and miR-26a-5p overexpressed AMSCs). However, the expression of negative control protein calnexin was only observed in the cells (Figure 2E). Finally, the level of miR-26a-5p was determined in the AMSC-derived exosomes and in miR-26a-5p-overexpressing AMSC-derived exosomes. Compared with the AMSCs-derived exosomes, the miR-26a-5p level in the miR-26a-5p overexpressed AMSCs-derived exosomes was significantly increased (P < 0.05, Figure 2F). These findings indicated that the exosomes were successfully isolated from the miR-26a-5p-overexpressed AMSCs and could be employed in subsequent animal experiments.
3.4 Effects of miR-26a-5p overexpressed AMSCs-derived exosomes on wound healing in mice
Further to explore the effects of miR-26a-5p overexpressed AMSCs-derived exosomes on wound healing in vivo, a circular full-thickness skin defect with a diameter of 2 cm was created on the back of mice, which were randomized to be administered with miR-26a-5p overexpressed AMSCs-derived exosomes and miR-26a-5p agomir. Wound images were obtained at days 0, 4, 8, and 12. As shown in Figure 3A, the wounds of the mice healed gradually with the gradual increase of the days, as well as the wounds of the mice in the AMSCs-agomir-Exo and miR-26a-5p agomir healed well on day 12 after injury. At day 12, the wound healing rates were significantly elevated in the AMSCs-agomir-Exo and miR-26a-5p agomir groups compared to the model group (P < 0.05), and were evidently increased in the AMSCs-agomir-Exo group in comparison with the miR-26a-5p agomir group (P < 0.05, Figure 3A). After that, the morphology of the injured skin in the different groups was observed by HE staining and Masson staining. It was found that the tissues in the control mice were normal, whereas the tissues in the model group were damaged with infiltration of inflammatory cells and deposition of collagen (Figure 3B). However, after treatment with miR-26a-5p overexpressed AMSCs-derived exosomes or miR-26a-5p agomir, wound healing was faster with lower infiltration of inflammatory cells, collagen deposition was less, and collagen structure arrangement was thinner and more orderly (Figure 3B). Furthermore, when the miR-26a-5p level was measured, we found that it was significantly reduced in the model mice compared to the control mice (P < 0.05). However, miR-26a-5p was overexpressed in AMSCs-derived exosomes, and miR-26a-5p agomir significantly elevated the miR-26a-5p level caused by damage (P < 0.05, Figure 3C). Our in vivo experiments confirmed that the AMSCs-derived exosomal miR-26a-5p could facilitate wound healing.
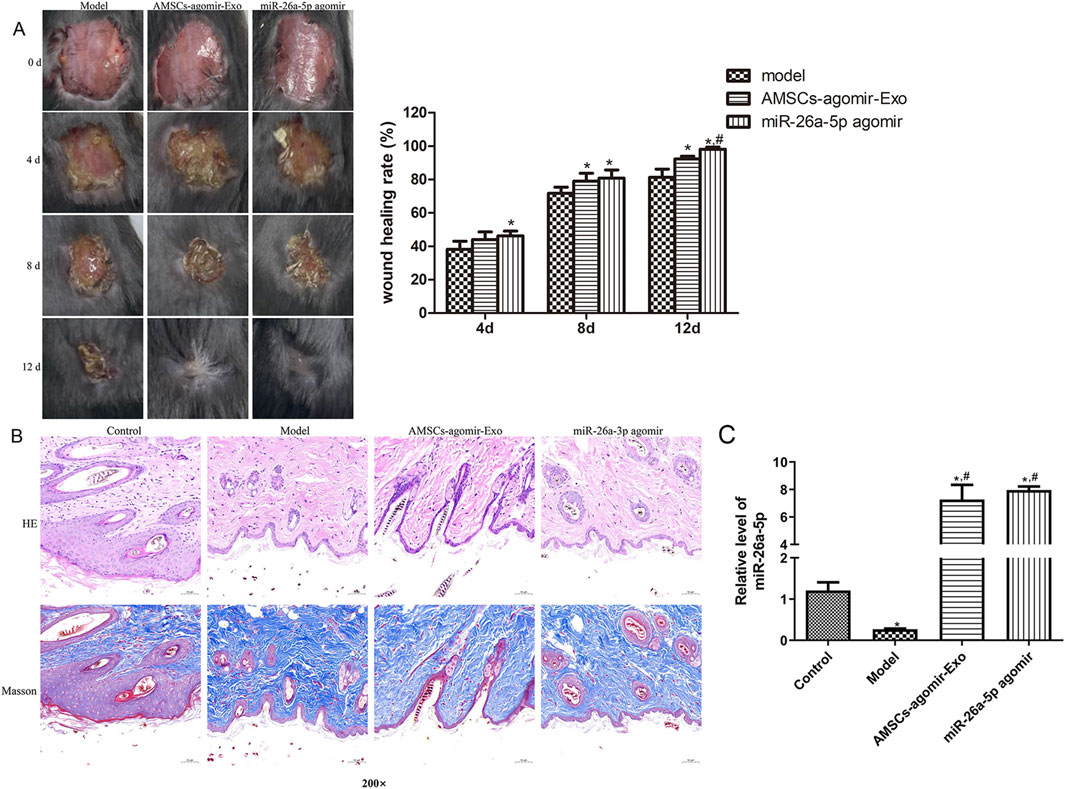
Figure 3. Effects of miR-26a-5p overexpressed AMSCs-derived exosomes on wound healing in mice. (A) The wound healing process in the different groups of mice at days 0, 4, 8, and 12. N = 6. *: P < 0.05, vs. model; #: P < 0.05, vs. AMSCs-agomir-Exo. (B) The morphology of the injured skin in the different groups, observed by Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) staining and Masson staining. N = 6. (C) The level of miR-26a-5p in the skin tissues of different mice. N = 3. *: P < 0.05, vs. control; #: P < 0.05, vs. model.
3.5 RT-qPCR and Western blot analyses
In addition, to unearth the underlying molecular mechanisms of AMSCs-derived exosomal miR-26a-5p promoting wound healing, the expression of some related genes/proteins was detected using RT-qPCR and Western blot. In comparison with the control mice, the target of miR-26a-5p (Map2k4) was significantly upregulated in the model mice (P < 0.05). However, it was evidently downregulated after treatment with miR-26a-5p-overexpressing AMSCs-derived exosomes and miR-26a-5p agomir compared with the model mice (P < 0.05, Figure 4). For Col1a1, Col2a1, and Col3a1, the expression of Col1a1 and Col3a1 was evidently downregulated, while Col2a1 was markedly upregulated in the model mice than the control mice (P < 0.05). However, miR-26a-5p-overexpressing AMSCs-derived exosomes and miR-26a-5p agomir significantly upregulated the expression levels of Col1a1, Col2a1, and Col3a1 than the model mice (P < 0.05, Figure 4). For Cd31 and α-Sma, their expression was significantly lower in the model mice than in the control mice (P < 0.05); however, it was evidently upregulated in the AMSCs-agomir-Exo and miR-26a-5p agomir groups induced by injury (P < 0.05, Figure 4). Afterward, we also measured the expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) in the mice with different treatments. The results showed that, compared with the control mice, the expression of Tnf-α, Il1β, and Il6 was significantly upregulated in the model mice (P < 0.05). However, it was evidently downregulated after treatment with miR-26a-5p-overexpressing AMSCs-derived exosomes and miR-26a-5p agomir (P < 0.05, Figure 4). Additionally, a Western blot was applied to test the protein expression of MAP2K4, COL1A1, α-SMA, and TNF-α in the different groups. It was evident that the trend of MAP2K4, COL1A1, α-SMA, and TNF-α protein expression in different mice, as determined by Western blot, was consistent with their mRNA expression levels examined by RT-qPCR (Figure 5).
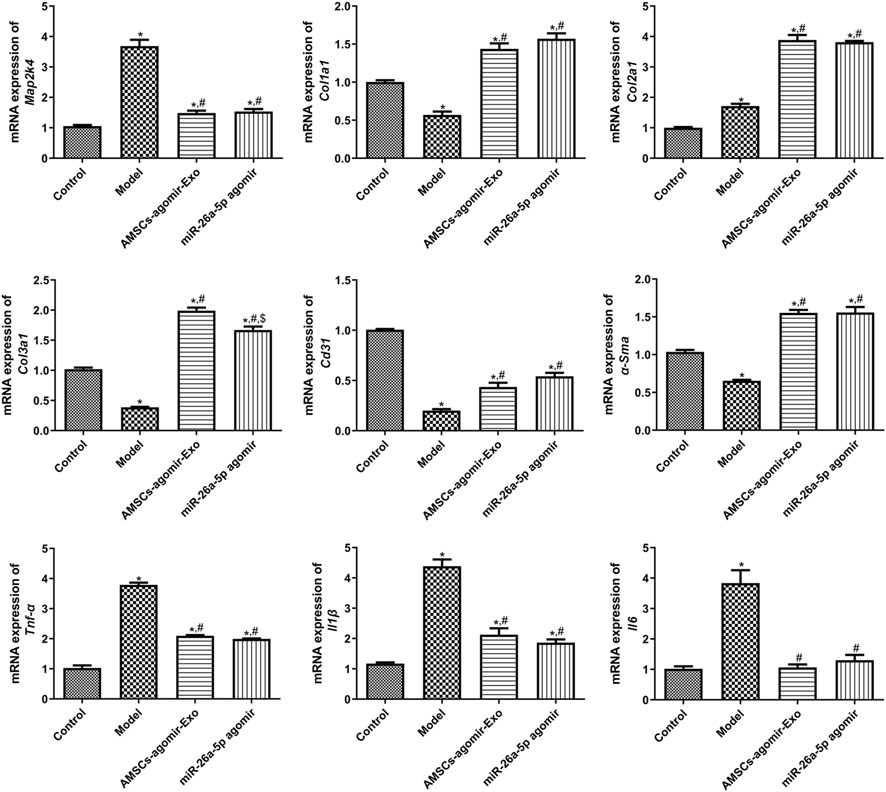
Figure 4. The mRNA expression of related genes, including Map2k4, Col1a1, Col2a1, Col3a1, α-Sma, Tnf-α, Il1β, Il6, and Cd31 in the different groups measured by RT-qPCR. N = 3. *: P < 0.05, vs. control; #: P < 0.05, vs. model; $: vs. AMSCs-agomir-Exo.
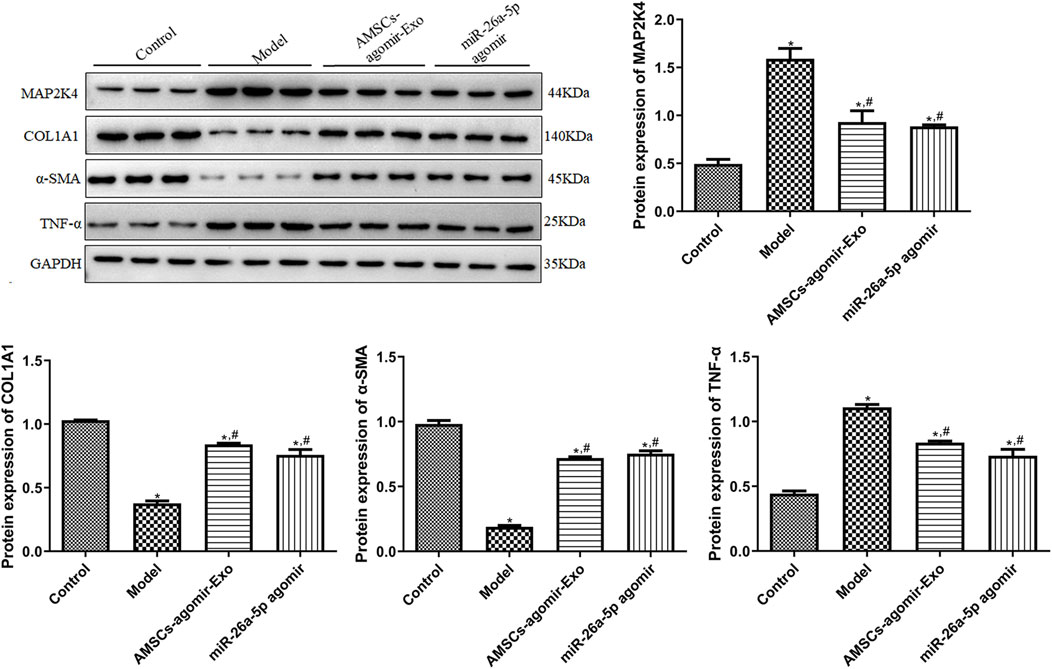
Figure 5. The protein expression of MAP2K4, COL1A1, α-SMA, and TNF-α in the different groups, determined by Western blot. N = 3. *: P < 0.05, vs. control; #: P < 0.05, vs. model; $: vs. AMSCs-agomir-Exo.
3.6 Roles and potential mechanisms of MAP2K4 in wound healing in mice
Additionally, the roles and potential mechanisms of MAP2K4 in wound healing were investigated. As shown in Figure 6A, with the gradual increase in days, the wounds in the mouse gradually healed in the si-NC and si-MAP2K4 groups. Quantification analysis displayed that at day 4, there was no significant difference in wound healing rate between the si-NC and si-MAP2K4 groups (P > 0.05); but at day 8 and 12, the wound healing rate in the si-MAP2K4 group was significantly higher than that in the si-NC group (P < 0.05), with the best wound healing rate of the si-MAP2K4 treatment at day 12 (Figure 6B). Then, RT-qPCR showed that compared to the si-NC group, the mRNA expression of Map2k4 and Tnf-α was significantly downregulated in the si-MAP2K4 group (P < 0.05); while the mRNA expression of Col1a1 and α-Sma was evidently upregulated (P < 0.05, Figure 6C). For miR-26a-5p, its level in the si-MAP2K4 group was significantly elevated compared with the si-NC group (P < 0.05, Figure 6D). Finally, the tendency of MAP2K4, COL1A1, α-SMA, and TNF-α protein expression in the different mice, as detected by Western blot, was similar to that determined by RT-qPCR (Figure 6E). These results indicated that MAP2K4 knockdown could promote wound healing, increase the miR-26a-5p level, and upregulate COL1A1 and α-SMA, while downregulating MAP2K4 and TNF-α.
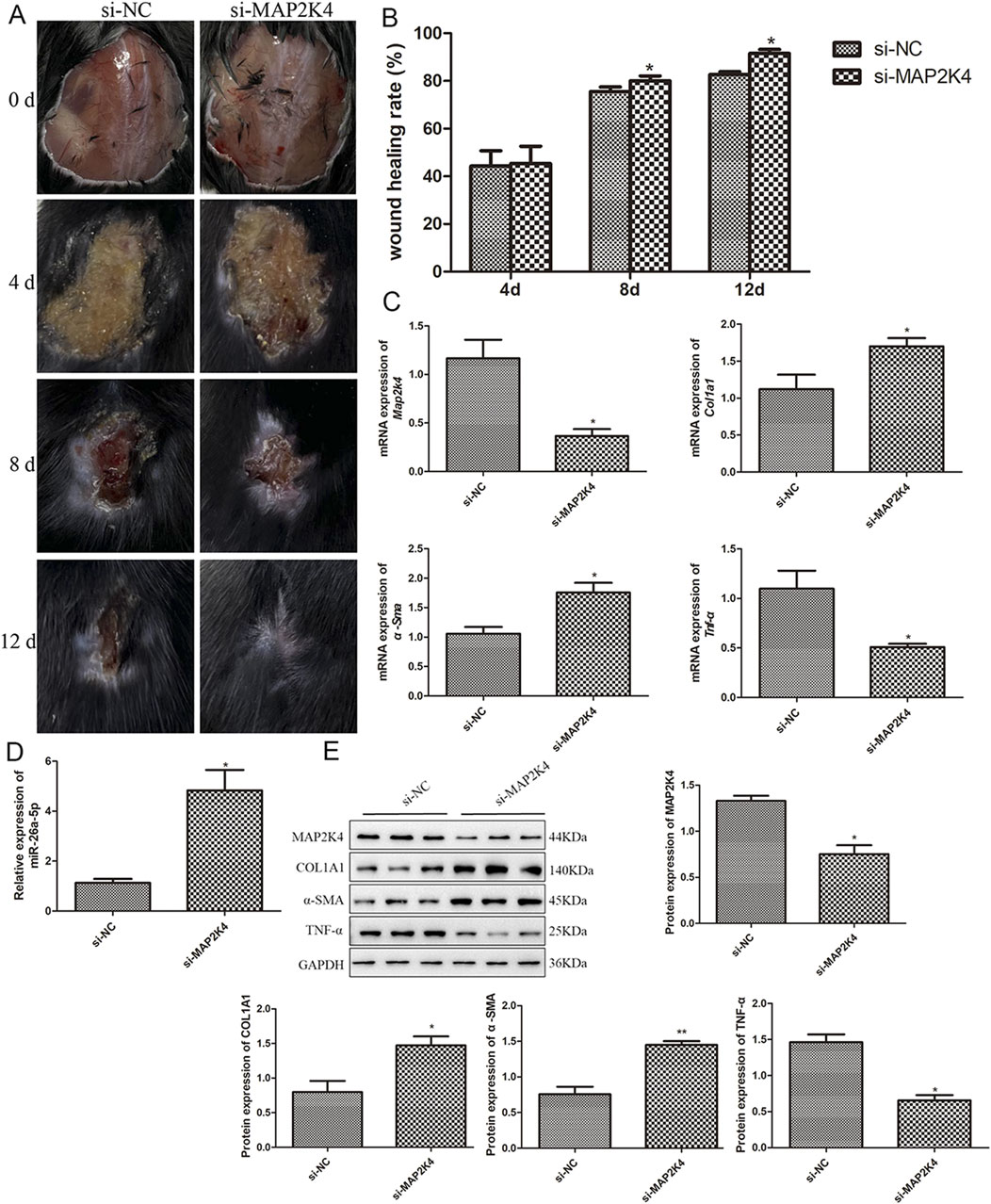
Figure 6. Roles and potential mechanisms of MAP2K4 in wound healing in mice. (A) The wound healing process in the skin defect mice treated with si-NC and si-MAP2K4 at days 0, 4, 8, and 12. N = 6. (B) Quantification analysis of wound healing rate in the skin defect mice treated with si-NC and si-MAP2K4 at days 4, 8, and 12. N = 6. *: P < 0.05, vs. si-NC. (C) The mRNA expression of Map2k4, Col1a1, α-Sma, and Tnf-α in the skin defect mice treated with si-NC and si-MAP2K4, measured by RT-qPCR. N = 3. *: P < 0.05, vs. si-NC. (D) The level of miR-26a-5p in the skin tissues of different mice. N = 3. *: P < 0.05, vs. si-NC. (E) The protein expression of MAP2K4, COL1A1, α-SMA, and TNF-α in the skin defect mice treated with si-NC and si-MAP2K4, detected by Western blot. N = 3. *: P < 0.05, vs. si-NC.
4 Discussion
Abnormal wound healing, including chronic wounds (ulcers), scar hyperplasia, and wound dehiscence, can damage normal bodily functions and consume significant resources of the healthcare system (Adebayo et al., 2023). MSCs-derived exosomes are observed to expedite diabetic wound healing by promoting angiogenesis, migration, proliferation, collagen deposition, and ECM remodeling, as well as activating the PI3K/AKT/eNOS pathway (Hu et al., 2021). It has been reported that exosomal miRNAs play pivotal roles in the wound healing process, but the exact mechanisms underlying this are unclear. Therefore, we first analyzed the miRNA profiles 2 days after the injury (in normal control and damaged samples) and identified 13 DEmiRNAs. Their corresponding target genes were enriched in the MAPK cascade, as well as in cAMP, relaxin, Hippo, Apelin, Wnt, and cGMP-PKG signaling pathways.
MAPK is an important intracellular signal that plays a key role in cell response to external stimuli (such as growth factors, cytokines, stress, etc.), and regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, apoptosis, and other physiological processes through phosphorylation of a series of downstream target proteins (Aubé et al., 2024). A previous study demonstrated that NED416, a novel synthetic Sirt1 activator, can accelerate wound closure, macrophage infiltration, and the formation of epithelial and collagen through the MAPK/Rho pathway, thereby promoting wound healing (Wahedi et al., 2020). CAMP is one of the important small molecules present at high concentrations in wound sites, mediating various signaling pathways in stem cell cytoskeleton dynamics, cell adhesion, and migration. This indicates that cAMP is a novel biological factor in tissue repair and regeneration (Peddibhotla et al., 2023). Sang et al. (2024) demonstrated that the loss of lncRNA NEAT1 could facilitate epithelial repair during corneal wound healing by activating the cAMP signaling pathway. Relaxin, a pleiotropic hormone in the insulin family, plays a role not only in promoting cervical softening to facilitate labor but also in regulating collagen renewal, angiogenesis, connective tissue metabolism, and tumor metastasis (Aragón-Herrera et al., 2022). Notably, relaxin could promote bone regeneration through BMP-2-loaded hydroxyapatite microspheres, thereby decreasing the dose of BMP-2 and reducing adverse physiological effects (Injamuri et al., 2020). The Hippo pathway is primarily mediated by YAP and TAZ, and their roles in controlling basal stem cells are evident in epidermal development and skin wound repair (Dey et al., 2020). Nuclear YAP and TAZ localization were observed in the basal layer of the skin, and these nuclear levels were elevated during wound healing (Dey et al., 2020). The Apelin pathway is reported to be involved in alleviating oxidative stress, restoring antioxidant enzyme levels, and reducing cardiovascular, renal, and neurological complications associated with diabetes (Guo et al., 2024). Elabela, a ligand of the apelin receptor, was observed to promote diabetic foot ulcer wound healing by inhibiting TRAF1/NF-κB-mediated inflammation and reducing oxidative DNA damage (Hong et al., 2023). The functions of Wnt pathways have been extensively studied. It is not only involved in the cellular processes (such as proliferation, apoptosis, and cycle), but also in multiple stages of wound healing (Yoon et al., 2023). The cGMP-PKG signaling pathway has been found to enhance keratinocyte migration, as well as play a crucial part in bone remodeling (Kim et al., 2021). Taken together, we speculate that the function of the MAPK cascade and the signaling pathways of cAMP, relaxin, Hippo, Apelin, Wnt, and cGMP-PKG may participate in the process of wound healing; however, their exact roles and underlying mechanisms in wound healing should be further elucidated.
Next, miR-26a-5p was identified as the hub node in the proposed miRNA-mRNA regulatory network, and its target gene, MAP2K4, significantly participated in the MAPK cascade, relaxin signaling pathway, and growth hormone synthesis, secretion, and action, all of which are closely associated with wound healing. Bian et al. (2024) manifested that miR-26a-5p level was lower in diabetic retinopathy (DR) tissues and high glucose-induced Müller cells, and overexpression of miR-26a-5p could improve retinal histopathological injury, and reduce the concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress-related markers in the retina of DR mice by down-regulating USP14 and inhibiting the activation of NF-κB. Another study revealed that low levels of miR-26a-5p and high levels of RNABP9 were detected in intracerebral hemorrhage tissues and cells. Furthermore, miR-26a-5p overexpression was found to alleviate neuronal apoptosis and brain damage by targeting RANBP9 (Zhang et al., 2020). MAP2K4 is an upstream member of the MAPK signaling pathway, activating p38 MAPK and JNK, thereby participating in various cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, transcriptional regulation, and development (Liu et al., 2019). Our dual luciferase reporter gene assay demonstrated that MAP2K4 was a target of miR-26a-5p. A previous study also employed a dual luciferase reporter gene assay to demonstrate that miR-26a-5p could directly bind to CTGF, and showed that miR-26a-5p could mitigate lung inflammation and apoptosis in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by targeting CTGF (Li et al., 2021). Therefore, miR-26a-5p/MAP2K4 were selected as the dominating objectives in the follow-up experiments.
Previous research has suggested that human umbilical cord MSCs-derived exosomes can deliver miR-26a-5p to MLE-12 cells, thereby promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transformation in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by targeting ADM17 (Zhao et al., 2023). In addition, AMSCs-derived exosomes have been reported to promote wound healing; however, whether the exosomal miR-26a-5p plays an essential role remains unknown. Therefore, in the current study, exosomes were successfully isolated for the first time from AMSCs with miR-26a-5p overexpression. Thereafter, a skin defect mouse model was established and then administered with exosomes derived from AMSCs with miR-26a-5p overexpression and miR-26a-5p agomir. Based on our results, miR-26a-5p-overexpressing AMSCs-derived exosomes, similar to treatment with miR-26a-5p agomir, could facilitate wound healing, suggesting that AMSCs-derived exosomes may deliver miR-26a-5p to the wound site. Compared with the model mice, AMSCs-derived exosomes delivered miR-26a-5p could downregulate MAP2K4, Il6, Il1β, and TNF-α, whereas up-regulate COL1A1, Cd31, Col2a1, α-SMA, and Col3a1. Our results have confirmed that MAP2K4 was the target of miR-26a-5p. Liu et al. (2023) indicated that AMSCs-derived exosomal miR-223-3p could target MAPK to regulate the pathways of PI3K-Akt, cAMP, neurotrophin, and cGMP-PKG, thus promoting wound healing. In addition, our results also showed that MAP2K4 knockdown could facilitate wound healing, increase miR-26a-5p levels, and upregulate COL1A1 and α-SMA, while downregulating TNF-α.
Inflammation is the first stage of the wound healing process. It has been reported that inflammation delays wound healing and leads to increased scarring (Hassanshahi et al., 2022). The occurrence and regression of the inflammatory response are major conditions of wound healing, and one of the key factors determining wound quality and healing time (Matar et al., 2023). IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α are all pro-inflammatory cytokines that typically influence cell proliferation and migration, immune activation, and ECM remodeling during the wound healing process (Peña and Martin, 2024). Higher concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines in cells can lead to an increase in oxidative stress and the deactivation of endothelial and epidermal proliferation, eventually contributing to the formation of permanent wounds (Zhu et al., 2023). Ban et al. (2020) demonstrated that miR-497 overexpression could effectively accelerate diabetic wound closure and reduce the levels of IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α.
Fibroblasts are the main cells that synthesize ECM, and their proliferation is a key event in assessing the wound healing cycle (Talbott et al., 2022). COL1A1 and COL3A1 are widely presented in the ECM of various tissues, and COL2A1 is interwoven with other cartilage-specific molecules to build the ECM of cartilages. A previous investigation demonstrated that platelet-rich plasma lysate can protect chondrocytes from synovial-derived inflammatory mediators by upregulating COL1A1, COL2A1, and COL3A1, and downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and TNF-α) (Gilbertie et al., 2018). α-SMA is a marker of fibroblast activation, promoting tissue contraction, re-epithelialization, and wound healing (Shinde et al., 2017). The continuous expression of α-SMA in fibroblasts may result in ECM deposition, which is initially protective and plays key roles in wound repair and remodeling (Lee et al., 2019). A recent study by Yang et al. (2024) found that AMSCs-derived exosomes could not only accelerate the healing of diabetic wounds but also improve the healing quality by upregulating α-SMA, COL1A1, and COL3A1, while suppressing Bax/caspase-3. In addition, CD31 is primarily expressed on the surface of endothelial cells and participates in the migration, proliferation, and lumen formation of these cells, thereby promoting the construction of a neovascularization network. Experiments by Xiong et al. (2023) have shown that astragaloside IV-stimulated endothelial progenitor cells-derived exosomes can enhance the wound healing rate, collagen deposition, and increase the number of CD31 and α-SMA positive cells, thereby accelerating wound healing in type 1 diabetes. This literature, together with our findings, suggests that AMSCs-derived exosomes delivering miR-26a-5p may facilitate wound repair by directly down-regulating MAP2K4 and regulating the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α), ECM-related markers (α-SMA, COL1A1, Col2a1, and Col3a1), and an angiogenesis-related marker (Cd31).
Our findings on miR-26a-5p/AMSC-exosome-mediated wound healing extend beyond prior reports (Zhao et al., 2023; Bian et al., 2024) on miR-26a-5p′s regenerative functions by highlighting context-specific mechanisms and translational advantages for cutaneous repair. From a translational perspective, our use of AMSC-derived exosomes further differentiates this work from previous miR-26a-5p studies: compared to hUCMSCs (Zhao et al., 2023), AMSCs are more readily isolated from autologous adipose tissue (e.g., liposuction waste), lowering immune rejection risks for clinical use, and their exosomes inherently contain skin-repair-promoting factors (e.g., growth factors, lipids) that synergize with miR-26a-5p to enhance wound healing, advantages lacking in direct miR-26a-5p administration (Bian et al., 2024), which suffers from poor in vivo stability and no such synergism. Our animal experiments further confirm that AMSC-derived exosomal miR-26a-5p exhibits superior wound-healing efficacy compared to free miR-26a-5p agomir, underscoring the value of the carrier. Collectively, while miR-26a-5p′s broad regenerative potential is established, our study is the first to define its role in cutaneous wound healing via targeting MAP2K4, validate AMSCs-derived exosomes as an optimal carrier for miR-26a-5p delivery to skin wounds, and demonstrate its simultaneous regulation of inflammation, angiogenesis, and ECM synthesis, providing a novel mechanistic framework and a more clinically feasible strategy for wound therapy.
However, our study has some limitations. First, a scrambled miRNA-loaded exosome control or naive AMSC-derived exosomes should be included to more comprehensively and accurately demonstrate the specific regulatory role of miR-26a-5p in AMSC-derived exosome-mediated wound healing, and provide more solid experimental evidence for the potential application of AMSC-derived exosomes carrying miR-26a-5p in wound healing therapy. Additionally, the effects of the MAPK cascade and signaling pathways of cAMP, relaxin, Hippo, Apelin, Wnt, and cGMP-PKG in wound healing should be further explored. The roles and underlying mechanisms of other miRNAs in wound healing are also warranted for study in vitro and in vivo.
In conclusion, through bioinformatics analysis, we identified 13 DEmiRNAs and 143 regulatory target genes that are enriched in the MAPK cascade and signaling pathways of cAMP, relaxin, Hippo, Apelin, Wnt, and cGMP-PKG, which may be involved in the wound healing process. Additionally, in vivo experiments demonstrated that AMSCs-derived exosomes carrying miR-26a-5p may expedite the wound healing process by targeting MAP2K4, thereby inhibiting inflammation and promoting angiogenesis and ECM synthesis and deposition. Our findings lay the theoretical foundation for treating various wounds with AMSCs-derived exosomes as carriers, delivering miR-26a-5p and its target gene, MAP2K4, as promising therapeutic targets to promote wound healing.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Guoke Ningbo Life Science and Health Industry Research Institute. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
KC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft. WY: Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. LC: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. SX: Investigation, Project administration, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Zhu Xiu Shan Talent Project of Ningbo No. 2 Hospital (Project Number: 2023HMJQ05) and Ningbo Natural Science Foundation (Grant Number: 2024J392).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adebayo, O. E., Urcun, S., Rolin, G., Bordas, S. P. A., Trucu, D., and Eftimie, R. (2023). Mathematical investigation of normal and abnormal wound healing dynamics: local and non-local models. Math. Biosci. Eng. 20 (9), 17446–17498. doi:10.3934/mbe.2023776
Al-Masawa, M. E., Alshawsh, M. A., Ng, C. Y., Ng, A. M. H., Foo, J. B., Vijakumaran, U., et al. (2022). Efficacy and safety of small extracellular vesicle interventions in wound healing and skin regeneration: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Theranostics 12 (15), 6455–6508. doi:10.7150/thno.73436
Aragón-Herrera, A., Feijóo-Bandín, S., Anido-Varela, L., Moraña-Fernández, S., Roselló-Lletí, E., Portolés, M., et al. (2022). Relaxin-2 as a potential biomarker in cardiovascular diseases. J. Pers. Med. 12 (7), 1021. doi:10.3390/jpm12071021
Aubé, F., Fontrodona, N., Guiguettaz, L., Vallin, E., Fabbri, L., Lapendry, A., et al. (2024). Metabolism-dependent secondary effect of anti-MAPK cancer therapy on DNA repair. NAR Cancer 6 (2), zcae019. doi:10.1093/narcan/zcae019
Ban, E., Jeong, S., Park, M., Kwon, H., Park, J., Song, E. J., et al. (2020). Accelerated wound healing in diabetic mice by miRNA-497 and its anti-inflammatory activity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 121, 109613. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109613
Bian, J., Ge, W., and Jiang, Z. (2024). miR-26a-5p attenuates oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic retinopathy through the USP14/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 1–15. doi:10.1155/2024/1470898
Cai, B., Qu, X., Kan, D., and Luo, Y. (2022). miR-26a-5p suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by inhibiting PTGS2 expression. Cell Cycle 21 (6), 618–629. doi:10.1080/15384101.2022.2030168
Cioce, A., Cavani, A., Cattani, C., and Scopelliti, F. (2024). Role of the skin immune system in wound healing. Cells 13 (7), 624. doi:10.3390/cells13070624
Dai, C., Shih, S., and Khachemoune, A. (2020). Skin substitutes for acute and chronic wound healing: an updated review. J. Dermatol. Treat. 31 (6), 639–648. doi:10.1080/09546634.2018.1530443
Dey, A., Varelas, X., and Guan, K. L. (2020). Targeting the hippo pathway in cancer, fibrosis, wound healing and regenerative medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 19 (7), 480–494. doi:10.1038/s41573-020-0070-z
Edgar, R., Domrachev, M., and Lash, A. E. (2002). Gene expression omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 30 (1), 207–210. doi:10.1093/nar/30.1.207
Freedman, B. R., Hwang, C., Talbot, S., Hibler, B., Matoori, S., and Mooney, D. J. (2023). Breakthrough treatments for accelerated wound healing. Sci. Adv. 9 (20), eade7007. doi:10.1126/sciadv.ade7007
Gilbertie, J. M., Long, J. M., Schubert, A. G., Berglund, A. K., Schaer, T. P., and Schnabel, L. V. (2018). Pooled platelet-rich plasma lysate therapy increases synoviocyte proliferation and hyaluronic acid production while protecting chondrocytes from Synoviocyte-Derived inflammatory mediators. Front. Vet. Sci. 5, 150. doi:10.3389/fvets.2018.00150
Guillamat-Prats, R. (2021). The role of MSC in wound healing, scarring and regeneration. Cells 10 (7), 1729. doi:10.3390/cells10071729
Guo, Q., Liu, Q., Zhou, S., Lin, Y., Lv, A., Zhang, L., et al. (2024). Apelin regulates mitochondrial dynamics by inhibiting Mst1-JNK-Drp1 signaling pathway to reduce neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury. Neurochem. Int. 180, 105885. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105885
Hassanshahi, A., Moradzad, M., Ghalamkari, S., Fadaei, M., Cowin, A. J., and Hassanshahi, M. (2022). Macrophage-mediated inflammation in skin wound healing. Cells 11 (19), 2953. doi:10.3390/cells11192953
Hemmat, N., Mokhtarzadeh, A., Aghazadeh, M., Jadidi-Niaragh, F., Baradaran, B., and Bannazadeh Baghi, H. (2020). Role of microRNAs in epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway in cervical cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 47 (6), 4553–4568. doi:10.1007/s11033-020-05494-4
Hong, Y., Li, J., Zhong, Y., Yang, S., Pei, L., Huang, Z., et al. (2023). Elabela inhibits TRAF1/NF-κB induced oxidative DNA damage to promote diabetic foot ulcer wound healing. iScience 26 (9), 107601. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107601
Hu, Y., Tao, R., Chen, L., Xiong, Y., Xue, H., Hu, L., et al. (2021). Exosomes derived from pioglitazone-pretreated MSCs accelerate diabetic wound healing through enhancing angiogenesis. J. Nanobiotechnology 19 (1), 150. doi:10.1186/s12951-021-00894-5
Injamuri, S., Rahaman, M. N., Shen, Y., and Huang, Y. W. (2020). Relaxin enhances bone regeneration with BMP-2-loaded hydroxyapatite microspheres. J. Biomed. Mater Res. A 108 (5), 1231–1242. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.36897
Kim, S. M., Yuen, T., Iqbal, J., Rubin, M. R., and Zaidi, M. (2021). The NO-cGMP-PKG pathway in skeletal remodeling. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1487 (1), 21–30. doi:10.1111/nyas.14486
Kolimi, P., Narala, S., Nyavanandi, D., Youssef, A. a. A., and Dudhipala, N. (2022). Innovative treatment strategies to accelerate wound healing: trajectory and recent advancements. Cells 11 (15), 2439. doi:10.3390/cells11152439
Krylova, S. V., and Feng, D. (2023). The machinery of exosomes: biogenesis, release, and uptake. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (2), 1337. doi:10.3390/ijms24021337
Lee, Y. J., Baek, S. E., Lee, S., Cho, Y. W., Jeong, Y. J., Kim, K. J., et al. (2019). Wound-healing effect of adipose stem cell-derived extracellular matrix sheet on full-thickness skin defect rat model: histological and immunohistochemical study. Int. Wound J. 16 (1), 286–296. doi:10.1111/iwj.13030
Li, H., Yang, T., and Fei, Z. (2021). miR-26a-5p alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by targeting the connective tissue growth factor. Mol. Med. Rep. 23 (1), 1. doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11643
Li, G., Zhang, Y., Wu, J., Yang, R., Sun, Q., Xu, Y., et al. (2023). Adipose stem cells-derived exosomes modified gelatin sponge promotes bone regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1096390. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1096390
Lin, Z., Xu, G., Lu, X., Liu, S., Zou, F., Ma, X., et al. (2024). Chondrocyte-targeted exosome-mediated delivery of Nrf2 alleviates cartilaginous endplate degeneration by modulating mitochondrial fission. J. Nanobiotechnology 22 (1), 281. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02517-1
Liu, S., Huang, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Zuo, S., and Li, R. (2019). MAP2K4 interacts with vimentin to activate the PI3K/AKT pathway and promotes breast cancer pathogenesis. Aging (Albany NY) 11 (22), 10697–10710. doi:10.18632/aging.102485
Liu, X., Jin, S., Liu, J., and Xu, X. (2023). MiR-223-3p overexpressed adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote wound healing via targeting MAPK10. Acta Histochem. 125 (8), 152102. doi:10.1016/j.acthis.2023.152102
Margiana, R., Markov, A., Zekiy, A. O., Hamza, M. U., Al-Dabbagh, K. A., Al-Zubaidi, S. H., et al. (2022). Clinical application of mesenchymal stem cell in regenerative medicine: a narrative review. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 13 (1), 366. doi:10.1186/s13287-022-03054-0
Matar, D. Y., Ng, B., Darwish, O., Wu, M., Orgill, D. P., and Panayi, A. C. (2023). Skin inflammation with a focus on wound healing. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle) 12 (5), 269–287. doi:10.1089/wound.2021.0126
Mazini, L., Rochette, L., Admou, B., Amal, S., and Malka, G. (2020). Hopes and limits of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in wound healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (4), 1306. doi:10.3390/ijms21041306
Peddibhotla, S., Caples, K., Mehta, A., Chen, Q. Y., Hu, J., Idlett-Ali, S., et al. (2023). Triazolothiadiazine derivative positively modulates CXCR4 signaling and improves diabetic wound healing. Biochem. Pharmacol. 216, 115764. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115764
Peña, O. A., and Martin, P. (2024). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of skin wound healing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 25 (8), 599–616. doi:10.1038/s41580-024-00715-1
Ritchie, M. E., Phipson, B., Wu, D., Hu, Y., Law, C. W., Shi, W., et al. (2015). Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 43 (7), e47. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv007
Sang, T., Wang, Y., Wang, Z., Sun, D., Dou, S., Yu, Y., et al. (2024). NEAT1 deficiency promotes corneal epithelial wound healing by activating cAMP signaling pathway. Invest Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 65 (3), 10. doi:10.1167/iovs.65.3.10
Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., Baliga, N. S., Wang, J. T., Ramage, D., et al. (2003). Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13 (11), 2498–2504. doi:10.1101/gr.1239303
Sharifiaghdam, M., Shaabani, E., Faridi-Majidi, R., De Smedt, S. C., Braeckmans, K., and Fraire, J. C. (2022). Macrophages as a therapeutic target to promote diabetic wound healing. Mol. Ther. 30 (9), 2891–2908. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.07.016
Shinde, A. V., Humeres, C., and Frangogiannis, N. G. (2017). The role of α-smooth muscle actin in fibroblast-mediated matrix contraction and remodeling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1863 (1), 298–309. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.11.006
Sorg, H., and Sorg, C. G. G. (2023). Skin wound healing: of players, patterns, and processes. Eur. Surg. Res. 64 (2), 141–157. doi:10.1159/000528271
Talbott, H. E., Mascharak, S., Griffin, M., Wan, D. C., and Longaker, M. T. (2022). Wound healing, fibroblast heterogeneity, and fibrosis. Cell Stem Cell 29 (8), 1161–1180. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2022.07.006
Tan, F., Li, X., Wang, Z., Li, J., Shahzad, K., and Zheng, J. (2024). Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 9 (1), 17. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01704-0
Wahedi, H. M., Chae, J. K., Subedi, L., Kang, M. C., Cho, H., Kim, S., et al. (2020). NED416, a novel synthetic Sirt1 activator, promotes cutaneous wound healing via the MAPK/Rho pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 46 (1), 149–158. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4564
Wang, J., Wu, H., Peng, Y., Zhao, Y., Qin, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2021). Hypoxia adipose stem cell-derived exosomes promote high-quality healing of diabetic wound involves activation of PI3K/Akt pathways. J. Nanobiotechnology 19 (1), 202. doi:10.1186/s12951-021-00942-0
Weiliang, Z., and Lili, G. (2021). Research advances in the application of adipose-derived stem cells derived exosomes in cutaneous wound healing. Ann. Dermatol 33 (4), 309–317. doi:10.5021/ad.2021.33.4.309
Wilkinson, H. N., and Hardman, M. J. (2020). Wound healing: cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 10 (9), 200223. doi:10.1098/rsob.200223
Xiong, W., Bai, X., Zhang, X., Lei, H., Xiao, H., Zhang, L., et al. (2023). Endothelial progenitor-cell-derived exosomes induced by astragaloside IV accelerate type I diabetic-wound healing via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in rats. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 28 (11), 282. doi:10.31083/j.fbl2811282
Xu, G., Ao, R., Zhi, Z., Jia, J., and Yu, B. (2019). miR-21 and miR-19b delivered by hMSC-derived EVs regulate the apoptosis and differentiation of neurons in patients with spinal cord injury. J. Cell Physiol. 234 (7), 10205–10217. doi:10.1002/jcp.27690
Yang, H., Zhou, J., Wang, J., Zhang, L., Liu, Q., Luo, J., et al. (2021). Circulating exosomal MicroRNA profiles associated with acute soft tissue injury. Cell J. 23 (4), 474–484. doi:10.22074/cellj.2021.7275
Yang, C., Zhang, H., Zeng, C., Tian, C., Liu, W., Chen, Y., et al. (2024). Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells restore fibroblast function and accelerate diabetic wound healing. Heliyon 10 (1), e22802. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22802
Yoon, M., Kim, E., Seo, S. H., Kim, G. U., and Choi, K. Y. (2023). KY19382 accelerates cutaneous wound healing via activation of the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (14), 11742. doi:10.3390/ijms241411742
Zhang, H., Lu, X., Hao, Y., Tang, L., and He, Z. (2020). MicroRNA-26a-5p alleviates neuronal apoptosis and brain injury in intracerebral hemorrhage by targeting RAN binding protein 9. Acta Histochem. 122 (5), 151571. doi:10.1016/j.acthis.2020.151571
Zhang, Y., Lv, L., Zheng, R., Xie, R., Yu, Y., Liao, H., et al. (2023). Transcriptionally regulated miR-26a-5p may act as BRCAness in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 25 (1), 75. doi:10.1186/s13058-023-01663-y
Zhao, J., Jiang, Q., Xu, C., Jia, Q., Wang, H., Xue, W., et al. (2023). MiR-26a-5p from HucMSC-derived extracellular vesicles inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition by targeting Adam17 in silica-induced lung fibrosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 257, 114950. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114950
Zhou, Y., Zhang, X. L., Lu, S. T., Zhang, N. Y., Zhang, H. J., Zhang, J., et al. (2022). Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes encapsulated in pluronic F127 hydrogel promote wound healing and regeneration. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 13 (1), 407. doi:10.1186/s13287-022-02980-3
Zhou, C., Zhang, B., Yang, Y., Jiang, Q., Li, T., Gong, J., et al. (2023). Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 14 (1), 107. doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03345-0
Zhu, M., Cao, L., Melino, S., Candi, E., Wang, Y., Shao, C., et al. (2023). Orchestration of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and inflammation during wound healing. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 12 (9), 576–587. doi:10.1093/stcltm/szad043
Keywords: AMSCs-derived exosomes, miR-26a-5p, MAP2K4, angiogenesis, wound healing
Citation: Chen K, Ye W, Chi L and Xie S (2025) Exosomes derived from miR-26a-5p-modified adipose mesenchymal stem cells improve wound healing by targeting MAP2K4. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1662095. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1662095
Received: 08 July 2025; Accepted: 27 October 2025;
Published: 11 November 2025.
Edited by:
Fei Liu, Texas A and M University, United StatesReviewed by:
Li-Tzu Wang, National Taiwan University, TaiwanJuhi Jaiswal, Texas A and M University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Ye, Chi and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shujie Xie, c2lhYmM4M0AxNjMuY29t
 Kana Chen1
Kana Chen1 Shujie Xie
Shujie Xie