- 1Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a critical condition characterized by rapid-onset lung inflammation, often resulting in respiratory distress. Current treatments are mainly based on glucocorticoids, but side effects and variable efficacy limit their effectiveness. This has prompted research into novel treatments, focusing on natural-product-based nanomaterials (NP-NMs), which offer a promising alternative. NP-NMs, synthesized from biological sources such as plants and microorganisms, have shown potential in therapy of ALI by enhancing drug delivery, reducing systemic side effects, and modulating inflammation. This review summarizes the latest research on NP-NMs, highlights their advantages in terms of biocompatibility, targeted delivery, and overcoming biologic barriers, and explores the challenges of developing NP-NMs in terms of standardized synthesis methods, comprehensive toxicological evaluation, and optimization for clinical translation. The significance of this review is to provide ideas for the development of more effective treatments for ALI, supporting further investigation into their clinical applicability.
1 Introduction
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a respiratory disease characterized by severe hypoxemia and diffuse alveolar damage (He et al., 2021). The primary clinical symptoms include shortness of breath, respiratory distress, and hypoxemia. A chest X-ray reveals diffuse infiltrative shadows in both lungs. ALI can deteriorate into a severe condition, known as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) (Bein et al., 2018; Cheng et al., 2021; Sasidharan et al., 2019). Globally, ARDS has been reported to account for 10.4% of all admissions to intensive care units and 23.4% of cases requiring mechanical ventilation, and it has a high in-hospital mortality rate of 35%. It is therefore a serious threat to public health (Bellani et al., 2016). Currently, the most effective treatments for ALI involve medical interventions that target the reduction of pulmonary and systemic inflammation, combined with supportive care in the form of mechanical ventilation (Fan et al., 2018; Zhang J. et al., 2024). Nevertheless, these therapeutic approaches are subject to several constraints, including strategies of low tidal volume ventilation, which may result in carbon dioxide retention or inadequate blood oxygenation, the absence of specific medications, and the lack of safer or more efficacious treatment options.
The limitations of the abovementioned clinical therapies have necessitated the development of more promising drugs for treating ALI. In recent years, an increasing number of natural products and their derivatives have been shown to have therapeutic potential for treating ALI. Increasingly compelling evidence suggests that natural products, derived from a diverse array of sources such as plants, animals, microorganisms, and marine life, which have been subjected to natural selection and evolution within their unique environments, exhibit significant bioactivity and adaptability (Chopra and Dhingra, 2021; Luo et al., 2024). They play an important role in multiple pathological stages of ALI due to their structural diversity and multiple biological activities, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immune regulation. In contrast, most compounds may have limited therapeutic effects due to their single target design. In addition, natural products often have low toxicity and good metabolism in the body, making them safer for the treatment of ALI. However, owing to their unique physicochemical properties, these products have shortcomings such as low solubility and limited bioavailability. Therefore, it is necessary to identify appropriate drug delivery methods to improve their utilization rates and thereby achieve the desired therapeutic effects (Xu et al., 2015; Cao et al., 2020; Cao et al., 2022).
Nanotechnology involves methods of manipulating and controlling matter on the nanoscale (Cao et al., 2022; de Alcantara Lemos et al., 2021). Research on nanomaterials is rapidly developing, and these materials are widely applied in areas including medicine, electronics, and materials science. Many studies have shown that nanomaterials greatly facilitate the treatment of respiratory diseases in ways such as improving drug solubility, increasing drug bioavailability, and achieving targeted drug delivery (Peng et al., 2024). Consequently, by integrating nanomaterials with natural substances may holds the potential to enhance the bioavailability of medications.
In this review, we summarize recent progress in the use of natural product-based nanomaterials (NP-NMs) for the treatment of ALI, and we analyze the underlying principles of their therapeutic action. Additionally, we examine recent studies on the use of nanocarriers for treating ALI, drawing upon an original overview, and provide a concise summary of their mechanisms in addressing ALI. Lastly, we discuss the challenges associated with the development of NP-NMs, aiming to facilitate their advancement toward becoming a viable therapeutic option for ALI in the future (Figure 1).
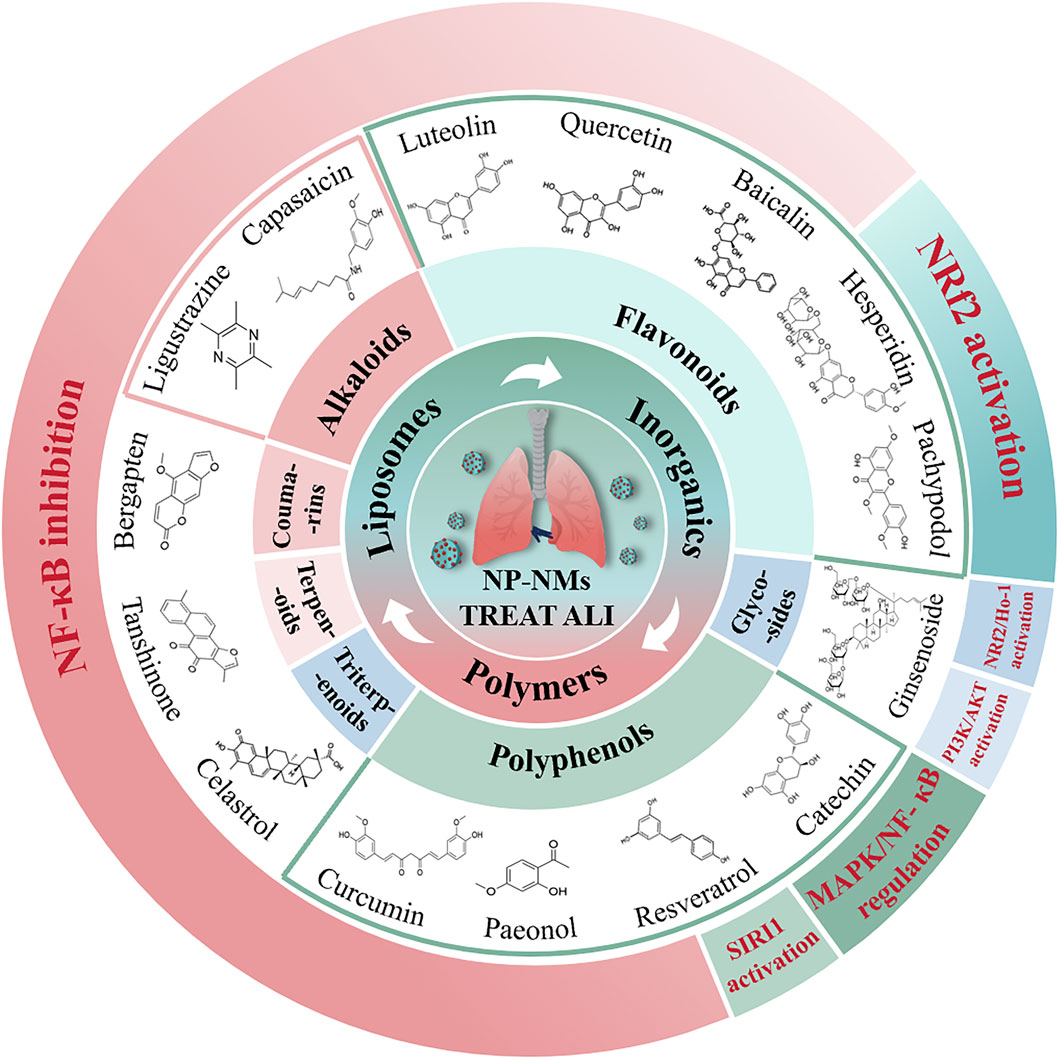
Figure 1. The illustration of the potential therapeutic role of natural product-based nanomedicines for ALI is presented. These are mainly categorized into alkaloids, flavonoids, polyphenols, triterpenoids, glycosides, terpenoids, and coumarins.
2 Pathogenesis and current treatment of ALI
It is widely recognized that uncontrolled inflammation in the lungs or throughout the body is the primary cause of the pathogenesis of ALI and ARDS (Dechert et al.). Inflammation caused by infectious agents, poisons, or trauma is thus an important factor in the development of ALI. Macrophages represent the first line of defense and play a major role in inflammation (Aggarwal et al., 2014; Bian et al., 2021a). When exposed to inflammatory stimuli, resting macrophages (M0) become activated and differentiate into either a proinflammatory phenotype (M1) or an anti-inflammatory phenotype (M2). This causes the release of proinflammatory substances such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6 (Bian et al., 2021a; Huang et al., 2018; Sica and Mantovani, 2012).
Moreover, neutrophils, epithelial cells, and endothelial cells are also involved in the inflammatory response (Silva and Rocco, 2017). Under the influence of chemotaxis, neutrophils are the first cells to disrupt the epithelial–endothelial barrier. They release cytotoxic mediators such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) in this process, which contributes to the inflammatory response. Nanomedicines have the potential to alleviate lung injury by inhibiting the production of proinflammatory cytokines and reducing neutrophil aggregation (Potey et al., 2019). Furthermore, lung injury can result in the dissociation of intercellular junctions within the lung epithelium, trigger cell death, and induce apoptosis of endothelial cells, which further leads to impaired lung function. Nanomedicines may help to preserve the integrity of the epithelial–endothelial barrier by reducing cell death (Lucas et al., 2009; Jiang et al., 2020; Short et al., 2016; Lin et al., 2013). Neutrophils, alveolar macrophages, endothelial cells, epithelial cells, etc., are activated in lung injury, and their release of large amounts of ROS leads to the development of oxidative stress. The release of ROS creates a feedback loop that further activates inflammatory cells and perpetuates the cytokine storm (Potey et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2020). Numerous inflammatory signaling pathways, such as the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), toll-like receptor (TLR), and Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathways, are activated when ROS are produced (Yeung et al., 2018). Therefore, nanomedicines can be used as therapeutic agents for ALI and reduce oxidative damage to lung tissue by inhibiting various inflammatory pathways and suppressing ROS-induced oxidative stress.
In 2019, the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) emerged as a major global health crisis, significantly impacting human health and social development. COVID-19 is caused by infection with the enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 infection exhibits a broad tendency across various tissues; however, most severe SARS-CoV-2 infections are typically associated with extensive lung damage, which can lead to pneumonia, acute respiratory failure, and death. Research has found that natural products exert pre- and post-infection inhibition, multi-stage inhibition, immune regulation, and combined targeted therapy effects, which have a positive effect on lung damage caused by COVID-19 (Low et al., 2023; Singh and Sodhi, 2023).
In addition, pulmonary endothelial cells and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) have important roles in ALI. VEGF induces lung endothelial cells to synthesize and release prostacyclin, nitric oxide (NO), and inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-8 (Chicione et al., 2011; Gill et al., 2015). In addition, VEGF can enhance angiogenesis and increase microvascular permeability by binding to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and can thereby alleviate structural lung injury. This provides a rationale for the possible utilization of nanomedicine-delivered endothelial growth factor for the treatment of ALI (Cahill and Redmond, 2016).
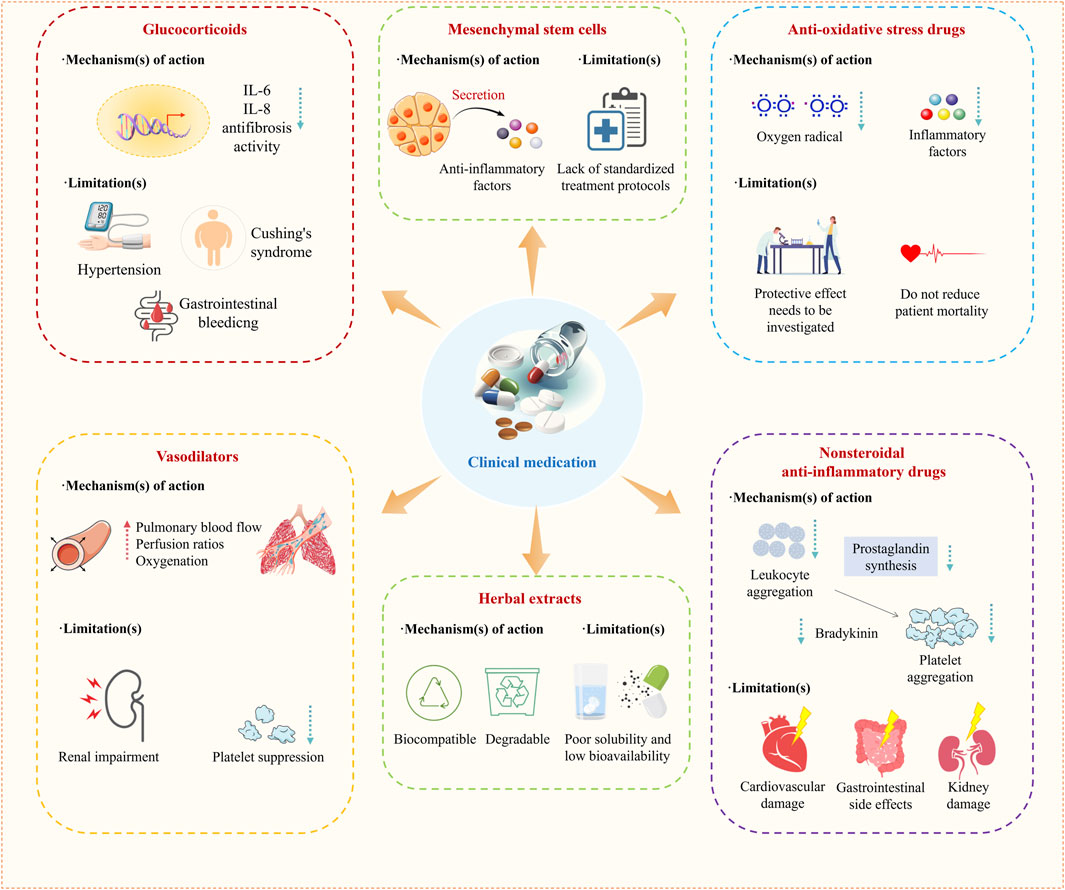
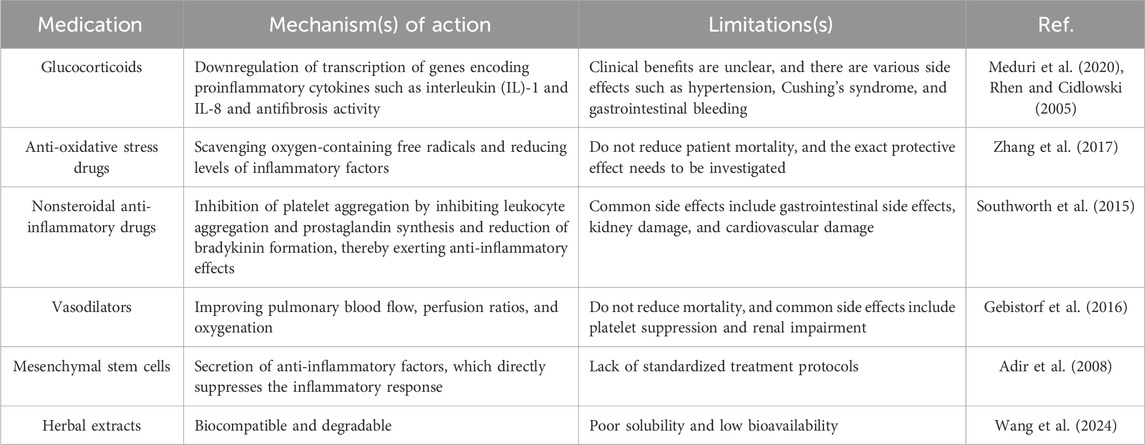
Treatments of ALI are mainly categorized into nonpharmacological mechanical ventilation and pharmacological treatments (Zhang J. et al., 2024; Guo et al., 2016). For the purpose of respiratory support and improving the patient’s oxygenation levels, it is appropriate to adopt a strategy of lung protective ventilation using a low tidal volume (less than 6 mL/kg predicted body weight) combined with a limited inspiratory plateau pressure, thus preventing lung hyperinflation (Zhang J. et al., 2024). In drug therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly used in clinical practice. Among them, glucocorticoids are the most widely used (Figure 2). In addition, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (Bian et al., 2021a; Matthay et al., 2019; Hamid et al., 2017), N-acetylcysteine (NAC) (Hecker, 2018; Sarma and Ward, 2011), Vasodilators are also commonly used drugs in the clinical treatment of ALI (Searcy et al., 2015) (Figure 2). In recent years, mesenchymal stem cells, herbal extracts, and intestinal flora have also emerged as new options for treating ALI (Figure 2) (Table 1) (Qu et al., 2024; Fernández-Francos et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2022).
3 Research on the mechanisms of nanomaterials used for the treatment of ALI
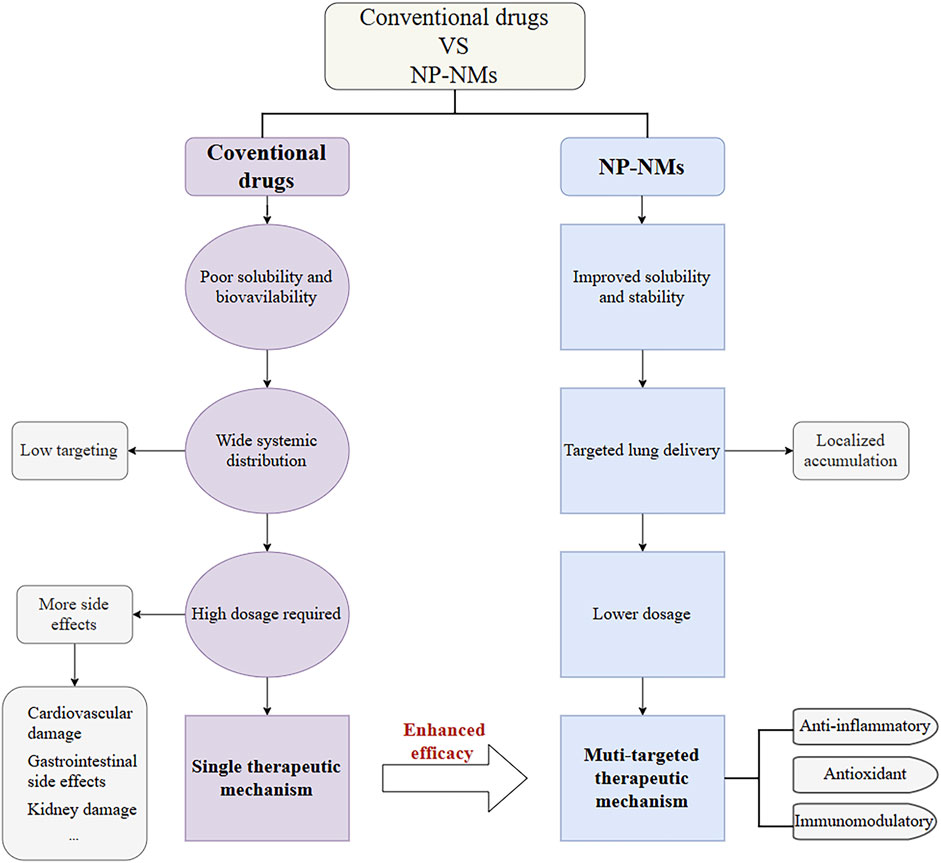
The pathogenesis of ALI is complex and multifactorial, involving an imbalance in the inflammatory response, dysregulation of endothelial cell function, and the effects of vasoactive substances. Investigation of the mechanisms of nanomedicines used in the treatment of ALI is beneficial for more effectively exploring their potential. Compared to conventional drugs, natural product-based nanomaterials (NP-NMs) exhibit significantly optimized pharmacological properties. Conventional drugs often suffer from poor solubility and bioavailability, leading to wide systemic distribution and low targeting efficiency. As a result, high doses are required to achieve effective therapeutic outcomes, which increases the burden on the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and renal systems. Additionally, traditional drugs typically act through a single therapeutic mechanism, limiting their clinical efficacy. In contrast, NP-NMs enhance drug solubility and stability, enabling targeted delivery to the lungs and promoting local drug accumulation. This targeted delivery allows for reduced doses while maintaining therapeutic efficacy, thereby minimizing systemic side effects. NP-NMs often exhibit multi-targeted therapeutic effects, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory activities, which collectively contribute to their superior efficacy. By summarizing a large number of studies, it has been found that nanomaterials mainly treat ALI via the following mechanisms (Figure 3).
3.1 Anti-inflammatory mechanisms
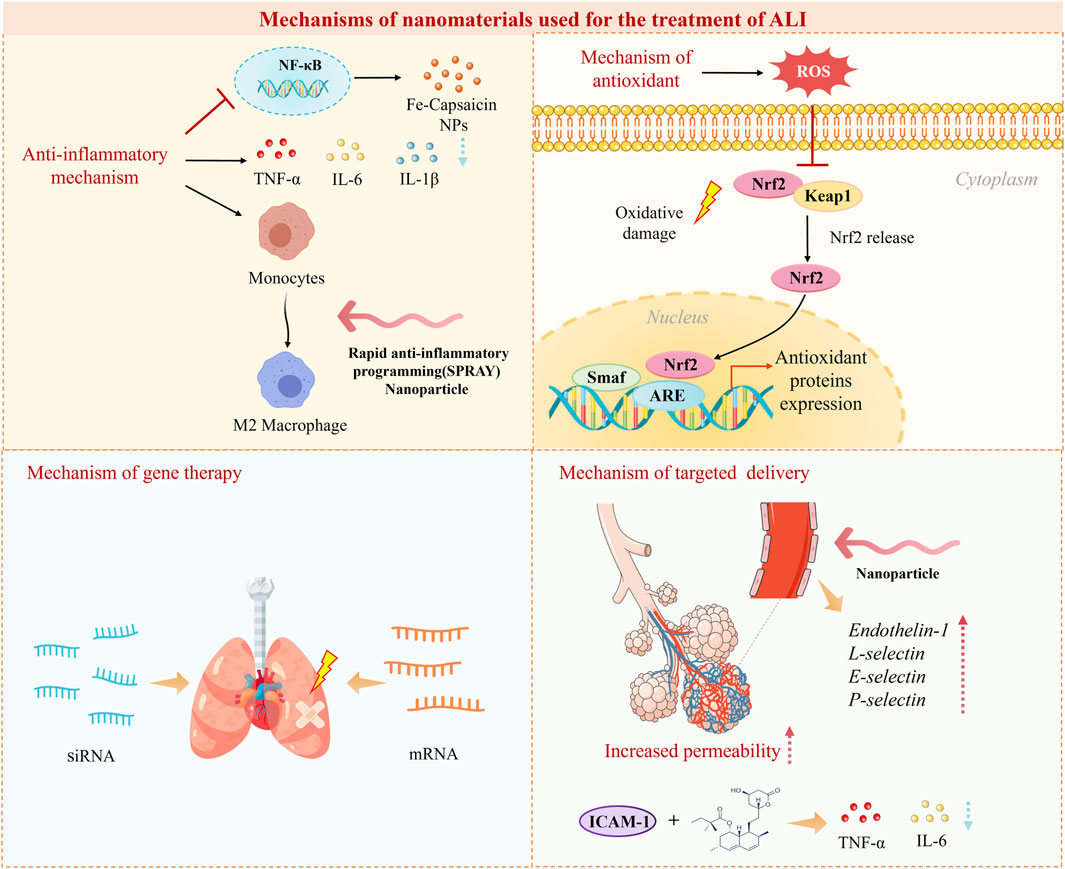
The cellular inflammatory storm is one of the main causes of severe inflammation in ALI and leads to the release of various inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β (Figure 4). A promising approach is to exert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. For example, ROS-responsive polythione nanoparticles (NPs) loaded with dexamethasone (DEX) have been shown to significantly reduce the levels of the pro-inflammatory factors IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β. This reduction exerts an inhibitory effect on inflammation and helps alleviate acute lung injury (Zhai et al., 2022). Nanomaterials can exert anti-inflammatory effects by modulating macrophage polarization (Figure 4). One research team constructed novel NPs comprising self-assembling peptides for rapid anti-inflammatory programming (SPRAY), which self-assemble to form NPs, by screening to identify the best SPRAY candidate, namely, the peptide BLKR (Chen D. et al., 2024). These NPs were experimentally found to specifically target alveolar macrophages to promote M2 polarization and inhibit M1-related signaling. Inhibition of signaling pathways is also one of the ways in which nanomaterials exert anti-inflammatory effects, with the NF-κB signaling pathway being a central regulator of the inflammatory response (Figure 4) (Jing et al., 2015). NF-κB is the main regulatory pathway of the inflammatory response. The expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines depends on NF-κB, and the expression of these factors activates neutrophils, leading to increased alveolar capillary permeability, manifested as pulmonary edema and oxygenation disorders. When ALI occurs, NF-κB can be activated by multiple factors, and its sustained activation can lead to an inflammatory storm, thereby exacerbating ALI (Zhou et al., 2023). It has been found that iron-capsaicin nanozymes are able to alleviate sepsis-induced ALI via the NF-κB signaling pathway (Wang R. et al., 2024).
3.2 Antioxidant mechanisms of action
Oxidative stress plays an important role in the development of ALI due to endothelial damage and capillary leakage. Nanomaterials can mitigate lung damage resulting from excessive oxidative stress by increasing antioxidant capacity and reducing the production of oxygen-containing free radicals (Laforge et al., 2020). Strategies have been developed to modulate the oxidative microenvironment in ALI using ROS-responsive nanoparticles (NPs). For instance, Muhammad et al. prepared DEX-loaded polyurethane (PFTU@DEX) NPs by a modified emulsification method and investigated their effects by using an ROS-specific bioluminescent probe (L012) to assess ROS levels in different groups in a mouse model. They concluded that the PFTU@DEX NPs significantly reduced the local expression of ROS and thus alleviated ALI (Muhammad et al., 2022). In addition, some nanomaterials possess endogenous antioxidant mechanisms. The Nrf2/antioxidant response element (ARE) signaling pathway plays an important role in the activity of endogenous antioxidants, as Nrf2 induces the action of ARE genes to prevent the production of excessive ROS (Figure 4). Recent studies have shown that various metal-based NPs (e.g., Au, TiO2, and Ag NPs) can stimulate the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway to achieve an antioxidant effect by increasing the levels of ROS and malondialdehyde (Xiong et al., 2022).
3.3 Mechanisms of gene therapy
Gene therapy is a new type of treatment that replaces abnormal genes with normal genes, introduces new genes, or edits existing genes to combat specific diseases (Verma and Somia, 1997). Nanomaterials can be used as carriers for targeted delivery of gene drugs, retarding their degradation, extending their half-life, and improving the efficiency of their action (Salameh et al., 2020; Xin et al., 2017; Miyazawa et al., 2017; Alex et al., 2013). The delivery of specific siRNAs is a new strategy with potential for the treatment of ALI in clinical practice. Nanomaterials can deliver specific siRNAs to inhibit the expression of inflammatory genes (Figure 4). Chen et al. constructed a selenium nanozyme therapeutic system (cationic water-soluble pillar arene [CWP]-Se@mannose [Man]) loaded with C-C chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2)-siRNA. This system exhibited electroneutrality and targeting properties for lung macrophages. It was observed that the mucus permeability of CWP-Se@Man was increased by a factor of about 15. CWP-Se@Man was able to effectively penetrate the mucus layer of the lungs to deliver CCR2-siRNA into macrophages. Moreover, in an inflammatory situation, the CWP-Se@Man nanotherapeutic system loaded with CCR2-siRNA could exert an inhibitory effect on chemotaxis and was able to scavenge ROS, which could alleviate ALI (Chen X. et al., 2024). LNPs have great potential for the delivery of mRNA, and studies of LNP-mRNA complexes for the treatment of ALI are becoming increasingly widespread. Research on the inhalation delivery of mRNA also shows great potential (Jiang et al., 2024). However, LNP-mRNA complexes have the disadvantage of a low in vivo degradation rate, which limits their applicability in ALI. Another research team used the azide-acetal linkage as a platform for generating rapidly hydrolyzed (RD)-LNPs to overcome this shortcoming. It was experimentally demonstrated that RD-LNPs designed for the delivery of mRNA to the lungs could rescue mice from ALI by delivering IL-22 mRNA (Zhao et al., 2024).
3.4 Mechanism of targeted delivery
The permeability of the alveolar–capillary barrier increases during ALI, leading to an increase in the width of the vascular–endothelial cell gap. Nanomaterials are therefore able to passively accumulate in the alveolar region of this highly permeable area and thus achieve a passive targeting effect via the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect (Figure 4) (Zhang S. et al., 2024). Wang et al. prepared a drug delivery platform based on triangular DNA origami modified with R9 peptide and demonstrated the ability of this nanomaterial to exert an enhanced passive macrophage-targeting effect in a mouse model of ALI (Wang H. et al., 2024). At the onset of ALI, various biomarkers can be more highly expressed on the surface of endothelial cells, including endothelin-1, L-selectin, E-selectin, and P-selectin (Mokra and Kosutova, 2015; Vassiliou et al., 2020). Nanomaterials are capable of targeting these biomarkers that exhibit increased expression and can thus achieve active targeting by ligand-receptor interactions. Li et al. developed a lung-targeted drug delivery system that targeted intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 and delivered simvastatin for the treatment of ALI (Figure 4). This system exhibited good lung-targeting properties in mice with lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI and was effective in inhibiting the expression of TNF-α and IL-6 and the infiltration of inflammatory cells. This nano-delivery system was shown to significantly improve the histological condition by hematoxylin-eosin staining, which demonstrated that the nanomaterial can treat ALI via this active targeting mechanism mediated by ICAM-1 recognition (Li et al., 2017). A team designed lung-targeted DEX-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers with the same target. These nanocarriers, which were modified with anti-ICAM-1 antibody, were demonstrated to significantly reduce the infiltration of inflammatory cells in the lung and the production of the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6. They also improved the histological condition in a mouse model of LPS-induced ALI (Li et al., 2018). Furthermore, biomimetic strategies have emerged, such as Cell-derived biomimetic nanoparticle. They have characteristics such as low immunogenicity, long circulation time, and strong targeting. Gao et al. conducted a detailed analysis of the current research progress on cell membrane-based biomimetic technology and extracellular vesicle (EV)-based biomimetic nanotechnology in acute lung injury (ALI), and explored their clinical feasibility. Clinical trials involving EVs are currently underway, indicating that biomimetic nanoparticles offer a promising platform for the treatment of ALI (Gao et al., 2024). Another innovative approach utilizes mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes as nanoparticles that can convey most of the biological effects and therapeutic benefits of their source cells, demonstrating high compatibility with damaged lung tissue and targeted accumulation (Zhu et al., 2013). Moreover, responsive targeting systems, including ROS-responsive polymers and pH-sensitive micelles, have allowed for drug release to be selectively triggered in the inflammatory microenvironment. Zhai et al. developed ROS-responsive polysulfone nanoparticles loaded with dexamethasone (PTKNPs@Dex), demonstrating that PTKNPs@Dex can accumulate at sites of pulmonary inflammation and rapidly release the encapsulated payloads, exerting a responsive targeted effect in the treatment of ALI (Zhai et al., 2022).
4 Progress of research on nanocarriers for the treatment of ALI
An excessive inflammatory response and lung tissue damage are important features of ALI, and oxidative stress is a principal cause of ALI. An increasing number of studies have shown that nanocarriers have important roles in anti-inflammatory and antioxidant therapies (Lang et al., 2020). Owing to the limited availability of clinical drugs for the treatment of ALI, research on the use of nanocarriers for the treatment of ALI is gradually intensifying. Common types of nanocarriers include LNPs, polymer NPs, and inorganic nanomaterials. Next, new findings with regard to the use of nanocarriers in the treatment of ALI are introduced.
4.1 Liposomes
Lipid nanocarriers are mainly amphiphilic or hydrophobic molecules composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, fat-soluble drugs, and other auxiliary lipids (Figure 1) (Gordillo-Galeano and Mora-Huertas, 2018). Owing to their simple processing, high biocompatibility, high bioavailability, etc. (Sercombe et al., 2015; Fonseca-Santos et al., 2015; Mitchell et al., 2020), they make efficient drug delivery systems available. The main types of Lipid nanoparticle (LNPs) include liposomes, solid lipid carriers, nanostructured lipid carriers, and nanoemulsions. Bian et al. summarized the characteristics of various lipid nanomaterials used for the treatment of ALI. These included 1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC) used for the preparation of drug formulations containing DEX and α-tocopherol/glutathione and other lipid components used for the preparation of different medications, e.g., cholesterol, soybean lecithin, and distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol (PEG) (Figure 5A) (Suntres and Shek, 2000; Suntres and Shek, 1996; Hettiarachchi et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2013). The efficacy of LNPs in the treatment of ALI was demonstrated by determining their effects on lung weight, the lung index, and levels of proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6), neutrophil elastase, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) and assessing their therapeutic effects in different mouse models (Bian et al., 2021b). Ravivi et al. similarly developed liposomes with DPPC as the main lipid and with sizes of 100 nm for pulmonary drug delivery for the treatment of ARDS. The loading efficiency of drugs in these liposomes reached 98% for methylprednisolone (a steroid) and 92% for NAC (a mucolytic agent). In cell experiments, a reduction in secretion of TNF-α and NO was observed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages treated with the liposomes. In C57BL/6 mice used as a model of LPS-induced lung inflammation, the therapeutic efficacy of the liposomes in reducing inflammation and secretion of the cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β was observed to be better than that of the free drug administered by the intravenous and endotracheal routes (Figure 5B) (Arber Raviv et al., 2022). Inhalable nanomedicine delivery systems encapsulate drugs within nanoscale carriers and deliver them via inhalation to specific regions or areas of the lungs, particularly those with affected or diseased cells (Kuzmov and Minko, 2015). Compared to traditional treatment methods, inhalable nanomedicine delivery systems can penetrate the mucus barrier, deposit precisely at lung lesion sites, prolong drug retention time, and reduce administration efficiency. Currently, this delivery system is widely used in the treatment of lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, and other diseases (Jin Z. et al., 2023; Gupta et al., 2022; Anderson et al., 2020; Goswami et al., 2025). Liu et al. developed an inhalable nanoplatform for sequential drug release referred to as D-SEL. This was formed by attachment of a peptide cleavable by matrix metalloproteinase-9 to serum exosomes and liposomes and subsequent encapsulation of methylprednisolone sodium succinate (MPS) (Figure 5C). It was found that treatment with MPS/D-SEL significantly inhibited activation of neutrophils and macrophages, reduced the number of neutrophils, and promoted the polarization of M2-type macrophages in a mouse model of LPS-induced ALI. It also effectively inhibited the expression of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6), increased the level of production of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4 and IL-10), and alleviated pathological disorders in the lungs (Figure 5D) (Liu et al., 2023).
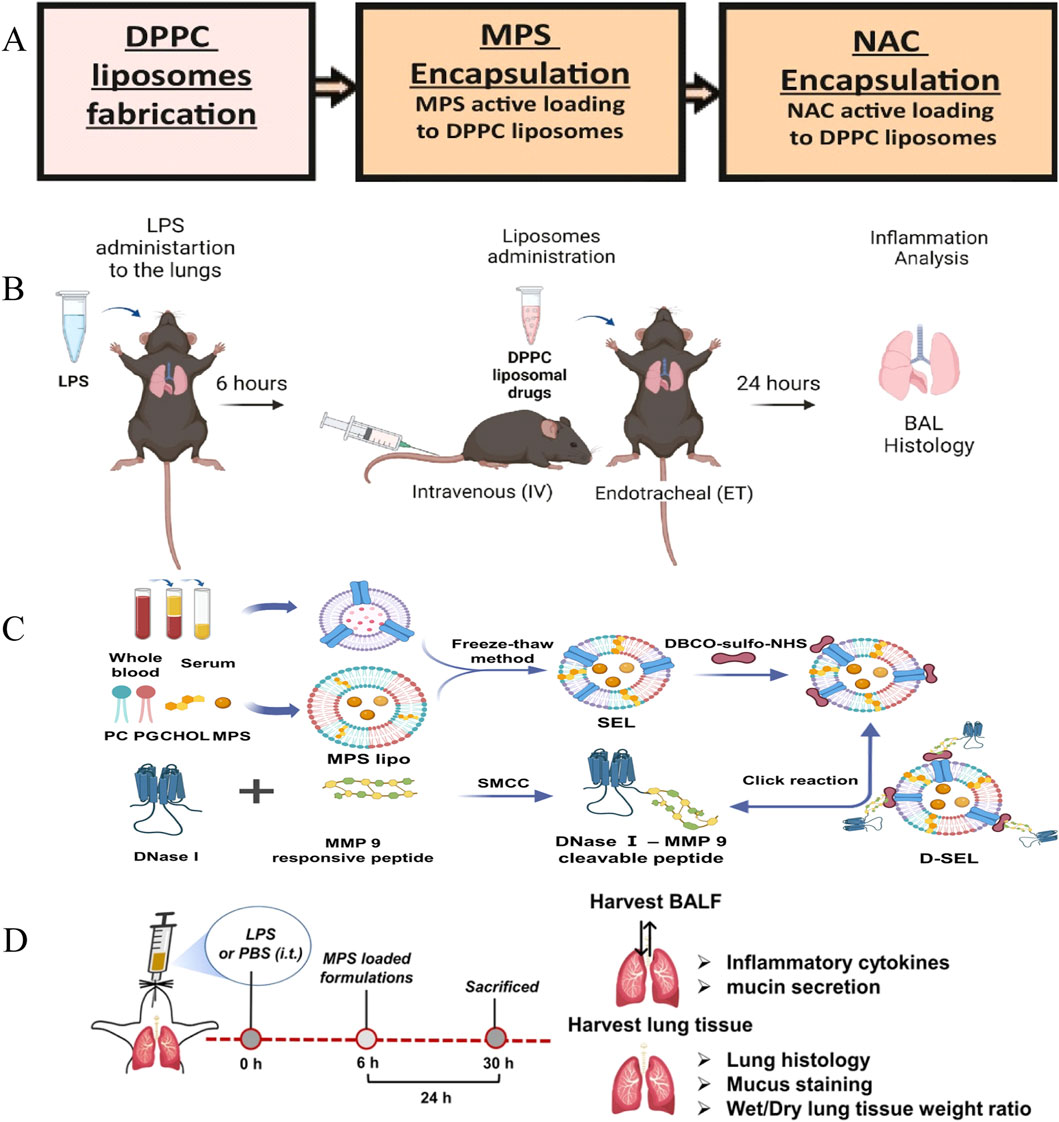
Figure 5. Liposomes therapy for ALI. (A) MPS and NAC preparation. (B) Flow chart of DPPC lipid drug experiment (Arber Raviv et al., 2022) Copyright (2022), with permission from Elsevier. (C) D-SEL design, preparation process (Liu et al., 2023) Copyright (2023) American Chemical Society. (D) D-SEL in vivo procedure.
4.2 Polymers
Polymeric nanocarrier systems are constructed from natural or synthetic polymers formed from either monomeric units or pre-existing polymers (Figure 1). Various synthesis techniques are available for creating polymeric nanomaterials, including emulsification (via solvent displacement or diffusion), nanoprecipitation, ionic gelation, and microfluidic methods (Kurd et al., 2019; Sawasdee et al., 2018). Polymeric nanomaterials can efficiently carry hydrophobic and hydrophilic drug molecules as a result of their flexible drug delivery capabilities. Consequently, they are extensively employed in domains such as pharmaceutical delivery and genetic delivery. Among these nanomaterials, poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA)-based polymer NPs have been proven to exhibit good drug release tunability, which is a popular area for polymer NPs in terms of research and applications (Jha and Mayanovic, 2023). Recent studies have found that PLGA-mediated stimulation of aging signaling triggers precise macrophage-mediated clearance of inflammatory neutrophils, which can ultimately have the effect of reducing inflammation. Chen et al. developed PC@PLGA polymeric nanoparticles by encapsulating PLGA with platelet-derived vesicle membranes (P) and calmodulin-expressing membranes (C), enabling specific targeting of activated neutrophils and deceiving macrophages into recognizing them as “aging” neutrophils. In an LPS-induced ALI mouse model, these nanoparticles effectively targeted activated neutrophils promoted macrophage-mediated programmed cell removal, and reduced inflammation and tissue damage (Chen et al., 2023). In addition, dendritic macromolecules, with their large internal cavities and dense surface active functional groups, are able to improve bioavailability and biocompatibility and have been studied extensively in ALI (Nikzamir et al., 2021; Albr et al., 2008). Polyamide-amine (PAMAM) dendrimer is one of the most intensively studied dendrimers. Fifth-generation (G5) PAMAM dendrimer was used as the basic platform, which was modified with DEX and PEG on its surface, and gold nanoparticles (GNPs) were encapsulated in the internal cavity to form a nanocarrier with the composition (Au0)25-G5NH2-(PEG-DEX) (denoted by V2). The nanocarrier was then electrostatically bound to a microRNA-155 inhibitor of an anti-inflammatory gene (miR-155i) to form a nanocomplex (V2/miR-155i) (Figure 6A). In vitro studies with mouse alveolar macrophages showed that the nanocomplex exhibited low cytotoxicity and efficiently co-delivered miR-155i and DEX, suppressing TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 mRNA expression (Figure 6C). In an LPS-induced ALI mouse model, airway nebulization of the nanocomplex significantly inhibited proinflammatory factors and improved lung repair, outperforming single-modality chemotherapy and gene therapy, as confirmed by histopathological analysis (Figure 6B) (Li et al., 2021).
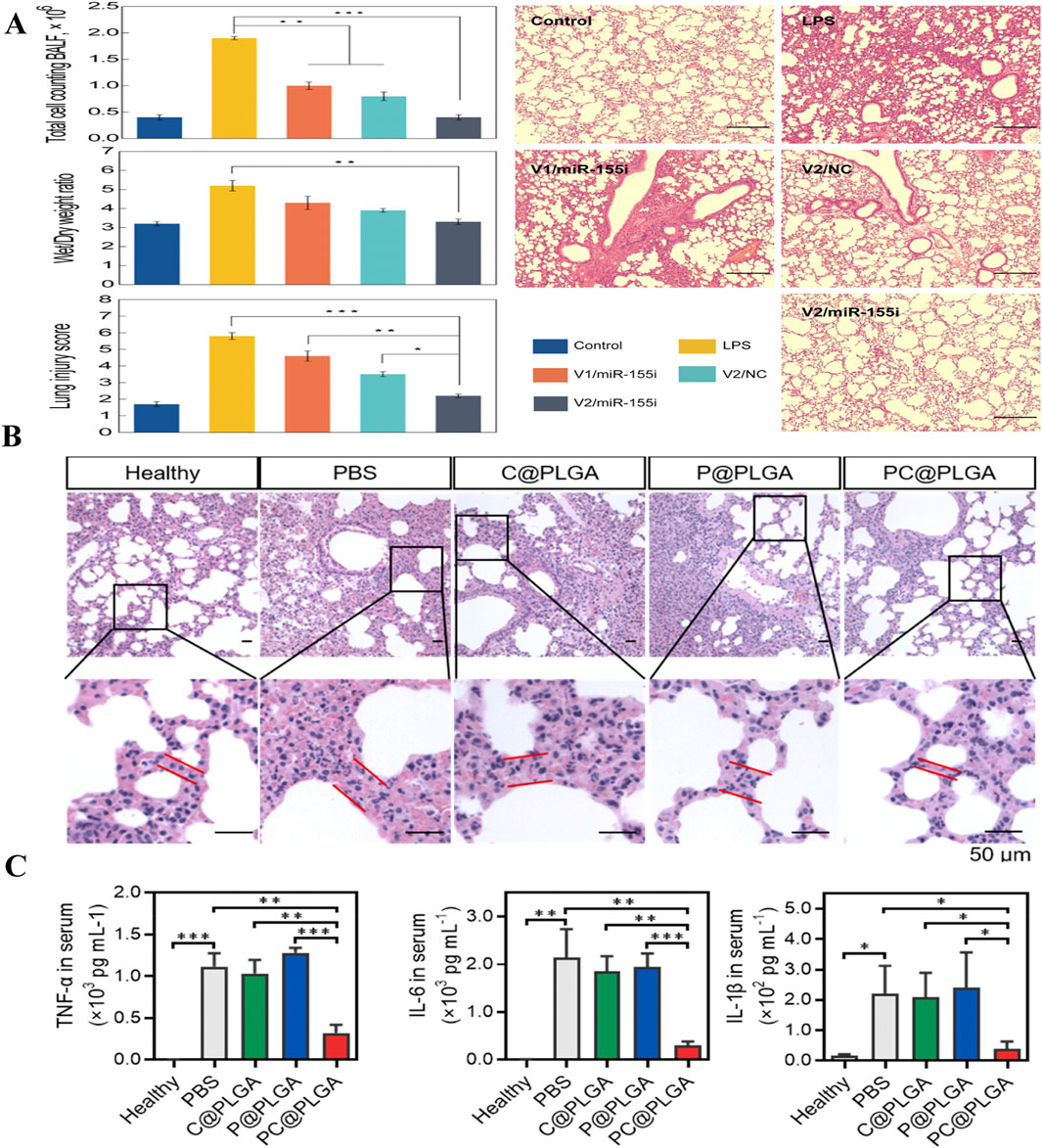
Figure 6. Polymer therapy for ALI. (A) Comparison of the effects of different treatments on lung injury (Li et al., 2021) Copyright (2021) American Chemical Society. (B) Histopathological observations of PC@PLGA in an inflammatory model of lung injury. (C) Analysis of PC@PLGA levels of inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β) in an inflammatory model of lung injury (Chen et al., 2023) Copyright (2023) American Chemical Society.
4.3 Inorganics
Inorganic nanomaterials have been widely studied due to their stable structures, high drug loading rates, and easy surface modification (Figure 1) (Cho et al., 2010). Studies have shown that these materials hold significant potential in the treatment of ALI (Bian et al., 2021b). GNPs, which are a popular subject of research, have been shown to alleviate ALI by inhibiting inflammatory signaling pathways and scavenging ROS (dos Santos Haupenthal et al., 2020). The cumulative toxicity exhibited in vivo, stemming from their prolonged retention within the liver and spleen, coupled with their inherently poor biocompatibility, presents challenges that necessitate further research. Consequently, inorganic peptides have been employed for the modification of GNPs, which has enhanced their biocompatibility and alleviated their associated toxic side effects (Singh et al., 2018). Gao et al. designed a unique class of peptide-GNP hybrids that act as potent nano-inhibitors of TLR4 signaling by modulating the endosomal acidification process. It was found that the size of the NPs was a significant factor in their inhibitory effect on TLR4 (Figure 7B). In particular, a peptide-GNP hybrid with a 20 nm GNP core (P12 (G20)) exhibited the strongest inhibitory activity in THP-1 cell-derived macrophages (Figure 7A). In a mouse model of LPS-induced ALI, P12 (G20) was more effective than P12 (G13) (with a 13 nm GNP core) in prolonging survival time, reducing lung inflammation, and alleviating alveolar injury (Gao et al., 2019). Molybdenum NPs are also promising for scavenging ROS, according to new research findings. Yan et al. developed a functional nanomaterial, namely, molybdenum nanodots (MNDs), with a size of approximately 5 nm by ultrasonic stripping. Their ability to scavenge ROS was assessed by assaying cellular activity in RAW 264.7 cells (a mouse macrophage cell line) and MLE-12 cells (a mouse lung epithelial cell line). It was found that MNDs were able to induce a significant increase in the activity of RAW 264.7 and MLE-12 cells. Intracellular ROS levels were found to be significantly reduced after fluorescence staining. This demonstrated that MNDs were able to limit oxidative-stress-induced damage to RAW 264.7 and MLE-12 cells by scavenging ROS. In a mouse model of LPS-induced ALI, after injection by tracheal drip of different doses of MNDs, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and lung tissues were taken. The levels of ROS in the lung tissues of the mice were determined by dihydroethidium staining, which revealed that the levels of ROS in the lung tissues of mice treated with MNDs were significantly reduced. In addition, it was found that MNDs reduced MPO levels in BALF and decreased the numbers of monocytes/macrophages and neutrophils in lung tissue. Lung histopathological examination showed that MNDs were able to reduce lung tissue injury, which proved that MNDs can exert anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects and thus reduce ALI (Yan et al., 2023).
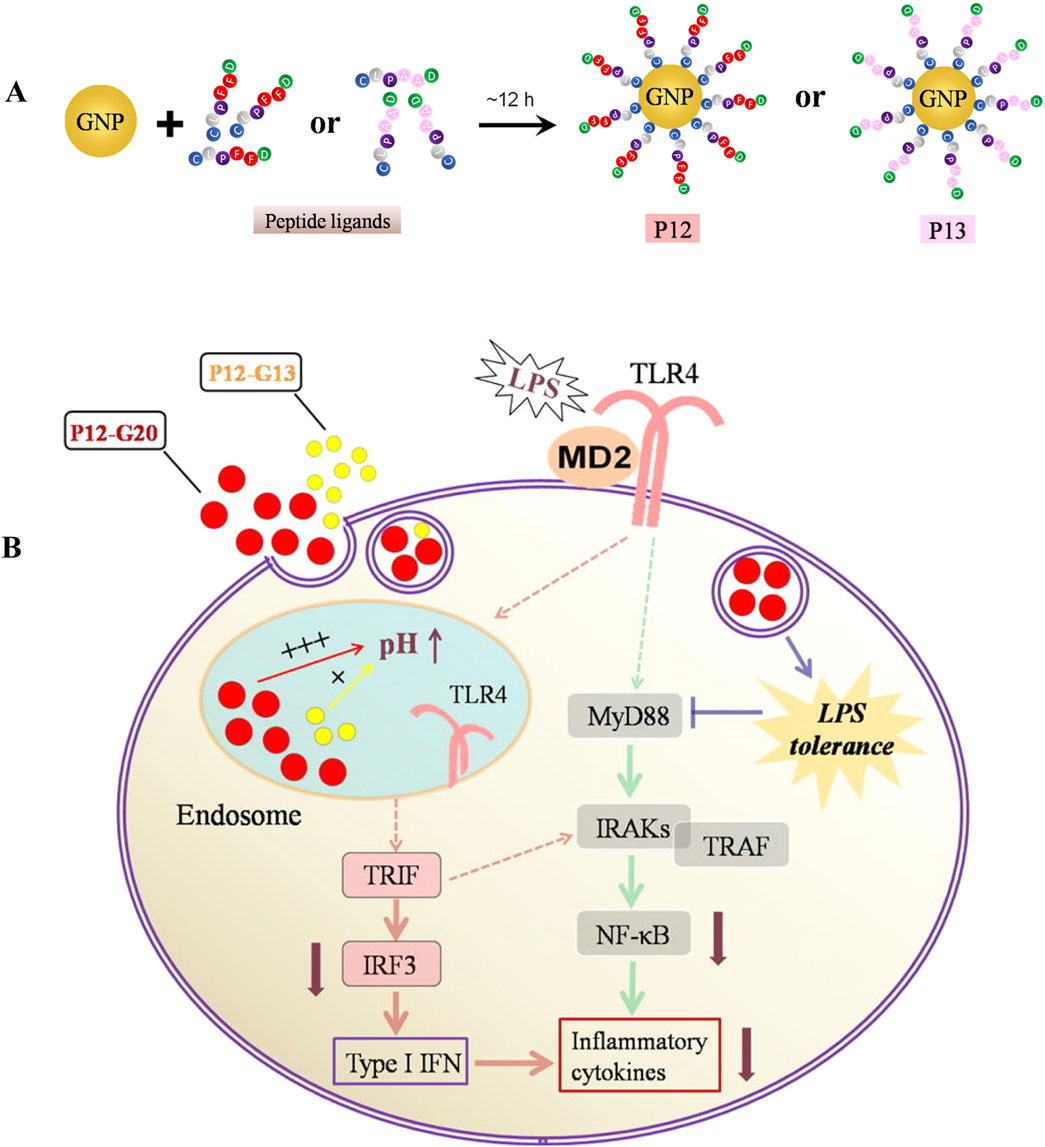
Figure 7. Inorganic nanomedicine. (A) Fabrication and characterization of bare GNPs and peptide-GNP hybrids with different sizes. (B) Mechanism of enhanced inhibitory activity of hybrid P12 (G20) on TLR4 activation (Gao et al., 2019) Copyright (2019), with permission from Elsevier.
5 Recent developments in NP-NMs for treating ALI
Natural products, predominantly sourced from herbs, inherently possess biocompatibility, thereby significantly reducing adverse effects when incorporated into nanomedicines. Their biodegradable nature ensures they decompose within the body, thus diminishing their potential for toxicity (Wang et al.). Owing to their complex and diverse chemical structures, natural products can interact with nanomedicines to target multiple pathways and injury sites with precision, which improves the accuracy and effectiveness of treatment (Wang et al.; Atanasov et al., 2021). In addition, natural products can be integrated with nanocarriers to enable controlled release in response to specific stimuli, such as temperature, enzymes, or pH (Xu et al., 2015). Natural products also possess inherent therapeutic properties, including anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anticancer activities (Fernandes et al., 2023; Guo et al., 2024; Akbari et al., 2022; Hashem et al., 2022). However, their unique structures and poor solubility limit their therapeutic potential and bioavailability. By combining natural products with nanocarriers, their solubility and bioavailability can be enhanced, which can maximize their efficacy. This approach offers a promising strategy for the treatment of ALI. The following sections discuss the use of various nanocarrier-based natural products for treating ALI.
5.1 Polyphenols
Polyphenols are a class of plant-derived antioxidants that are structurally based on the benzene ring and are found in everyday human foods in the form of glycosides or glycosidic elements.
5.1.1 Curcumin
Curcumin, a hydrophobic polyphenol derived from the roots of turmeric (Curcuma longa), exerts anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiapoptotic effects by modulating molecular targets through multiple signaling pathways (Huang et al., 2018; Gupta et al., 2013; Shakeri and Boskabady, 2017; Hu et al., 2017; Xu and Zhu, 2017). Leng et al. developed an amphiphilic multifunctional poly (citric acid-polyethylene glycol-curcumin) (PCGC) nano-oligomer using citric acid, curcumin, and PEG via a one-pot thermal polymerization synthesis strategy. PCGC was found to inhibit the expression of TNF-α, IL-6, NF-κB, and IL-1β. The incorporation of curcumin enhanced the ability of PCGC to inhibit the expression of proinflammatory factors. PCGC can also effectively inhibit pulmonary edema and reduce infiltration of bronchial cells and can thereby alleviate ALI (Leng et al., 2024). Additional studies have shown that curcumin-loaded tyramine-bearing sodium dimethylphosphonate-modified amphiphilic phosphorus dendron (C11G3-TBP@Cur) nanomicelles have good biosafety and stable loading capacity. In addition, C11G3-TBP@Cur inhibited the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and MPO while promoting the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines (arginase-1, IL-10, and CD206). This indicated that C11G3-TBP@Cur could promote the repolarization of alveolar macrophages from the M1 type to the anti-inflammatory M2 type. Histopathological findings indicated that C11G3-TBP@Cur was able to promote the repair of lung tissue injury (Li et al., 2022). In addition, inorganic NPs have been used in combination with curcumin. Yuan et al. synthesized iron-curcumin nanoparticles (Fe-Cur NPs) and demonstrated that Fe-Cur NPs significantly reduced the levels of the proinflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in both in vivo and ex vivo experiments. In addition, Fe-Cur was shown to inhibit NLR family pyrin-domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) and NF-κB and thereby exert anti-inflammatory effects. This suggests that Fe-Cur NPs may exert anti-inflammatory effects via multiple pathways. In a mouse model, Fe-Cur NPs exhibited higher distribution levels in lung tissues than in the heart, liver, and kidneys, which suggested precise targeting of affected areas. Moreover, Fe-Cur NPs possess ROS-scavenging abilities, which contribute to the treatment of ALI. Furthermore, Fe-Cur NPs also reduced the numbers of macrophages and CD3+CD45+ T cells, which served to inhibit inflammatory cytokine storms (Yuan et al., 2021). Piao et al. prepared curcumin-loaded glycyrrhetinic acid nanoparticles (GA-Cur) to address the low bioavailability of curcumin due to its hydrophobicity. They observed that GA-Cur inhibited hemolysis of monocytes and lung infiltration more efficiently and reduced the levels of proinflammatory cytokines in comparison with other treatments (Piao et al., 2022). Sun et al. prepared curcumin-loaded ROS-responsive bovine serum albumin-coated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles (Cur@HMSN-BSA), which provide a new therapeutic option for PM2.5-induced ALI (Sun et al., 2023). Inhalable arginine-modified chitosan nanocrystals containing curcumin (Arg-CS-Cur) were prepared by Wu et al. Arg-CS-Cur was found to exhibit higher uptake by M1 macrophages in vitro and to inhibit TNF-α and IL-6 effectively. In a rat model of ALI, lung tissue damage was reduced after treatment with the nanocrystals (Wu et al., 2024a). Su et al. developed a highly crosslinked curcumin-containing polyphosphazene nanodrug (PHCH) for the targeted delivery and inflammation-responsive release of curcumin for the treatment of ALI. It was experimentally demonstrated that this nanomedicine was able to downregulate the expression of key proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-8) and inhibit the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB signaling pathway and thus exert anti-inflammatory activity. In a mouse model of ALI, PHCH exhibited effective ROS-scavenging ability, which is beneficial for the treatment of ALI (Su et al., 2023).
5.1.2 Resveratrol
Resveratrol (RSV), naturally occurring in various foods like blueberries, mulberries, and grapes, has been proven to possess significant biological functions in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Oliveira et al. prepared resveratrol-containing polymer nanocapsules (RSV-LNCs) using interfacial polymer deposition and demonstrated their ability to inhibit leukocytes and reduce the expression of transcription factors related to the inflammatory response. By evaluating the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of RSV-LNCs 6 h after exposure to LPS in a mouse model of ALI, they confirmed the potential of RSV-LNCs to reduce lung inflammation and improve lung function to treat ALI. RSV levels in mouse tissues were also found to be higher than after the administration of the free form of RSV, which demonstrated the enhanced bioavailability of RSV in the RSV-LNC form (de Oliveira et al., 2019). In another study, PLGA NPs were combined with platelet membrane vesicles (PMs) to prepare a new type of biomimetic NPs referred to as PM@Cur-RV NPs, which could deliver curcumin and RSV in a highly targeted manner. In a mouse model of ALI, inhalation of PM@Cur-RV NPs reduced pulmonary vascular permeability and the proinflammatory cytokine load and thereby effectively inhibited pulmonary vascular injury. In addition, it reduced the level of histone acetylation in macrophages and promoted polarization of macrophages toward the M2 phenotype, thereby alleviating ALI (Jin et al., 2022). Wang et al. prepared an inhalable RSV formulation (referred to as RES-β-CD) consisting of an inclusion complex formed by RSV and β-cyclodextrin for preventing ALI induced by zinc chloride smoke. RES-β-CD exhibited low cytotoxicity and, in a mouse model of ALI, it was able to inhibit the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, STAT3, and GATA3 and upregulate T-box transcription factor and forkhead box P3 to achieve alleviation of inflammation and apoptosis. It thus provides a new idea for the treatment of smoke-induced ALI (Wang et al., 2022).
5.1.3 Paeonol
Paeonol (PAE), a naturally occurring active compound derived from the root bark of the peony plant, exhibits diverse pharmacological activities and is a quintessential member of the anti-inflammatory class of active ingredients (Wang et al., 2020). Li et al. used incubation to load PAE into a γ-cyclodextrin metal-organic framework (CD-MOF) with a respirable particle size and mix it with lactose to prepare a dry powder inhaler (DPI). The physicochemical properties of PAE-CD-MOF were observed using scanning electron microscopy, powder X-ray diffraction analysis, thermal analysis, and hot-stage microscopy. The in vitro release behavior of PAE from CD-MOF was observed, and it was found that the release of PAE was significantly accelerated in simulated lung fluid. Moreover, via in vitro cell experiments, CD-MOF was found to increase the cellular permeability of PAE in A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells, which suggested that CD-MOF may promote the uptake of PAE in the lung. A healthy rat model was established, and it was demonstrated that administration by inhalation significantly increased the bioavailability of PAE in comparison with oral administration. In a rat model of ALI, histopathological examination and measurement of serum levels of proinflammatory factors confirmed that the PAE-CD-MOF DPI reduced lung inflammation and thereby alleviated lung injury (Li et al., 2020).
5.1.4 Catechin
Catechin belongs to a class of flavanols found in tea and is an important secondary metabolite. Jin et al. prepared a novel nanomicellar complex (Ac/Pc) by binding catechin to a cationic lipid polymer (polyethyleneimine-cholesterol, Pc) and serum albumin (Ac). The nanomicelles were evaluated for their capacity to selectively induce apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells at low concentrations. The nanomicelles induced a rise in ROS levels and stimulated the activity of caspase-3 in lung cancer cells, thus promoting apoptosis. In in vivo real-time fluorescence imaging using cyanine 5-labeled nanomicelles injected into mice, the cationic polymeric liposomes (Pc) were demonstrated to have lung-targeting efficacy, while albumin (Ac) contributed to prolonged retention of the complex in vivo. These results suggest that the nanomicellar complex possesses lung-targeting capability and can effectively deliver drugs, which provides a promising strategy for treating ALI (Jin M. et al., 2023).
5.2 Flavonoids
Flavonoids are a class of natural substances widely found in nature, with 2-phenylchromone as the parent structure, usually in the form of free glycosides or combined with sugar to form glycosides, with a wide range of biological activities and pharmacological effects.
5.2.1 Quercetin
Quercetin is a flavonol widely found in the bark, flowers, leaves, seeds, and fruits of a wide variety of plants. Quercetin has been demonstrated to have various biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory activities (Chen J. et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2020). Chen et al. prepared an inhalable quercetin-alginate nanogel (QU-Nanogel) using emulsion polymerization. The “substance-drug” complex formed between the two components was stabilized via intermolecular hydrogen bonds, forming a synergistically developed water-soluble nanogel system. Experiments on A549 cells examined the toxicity of QU-Nanogel and revealed its inhibitory effect on ROS. In a rat model of ALI, histological analysis after administration by ultrasonic nebulization showed strong fluorescence intensity in the rat lung tissues, which indicated good lung targeting and renal excretion and confirmed the safety of QU-Nanogel. Levels of three proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β) in lung tissues were measured, and the expression of these cytokines was significantly reduced following treatment with QU-Nanogel. These findings suggest that QU-Nanogel can downregulate the mRNA and protein expression of proinflammatory factors via ultrasonic nebulization and inhalation and thereby alleviate lung inflammation (Chen Y.-B. et al., 2022). Zhang et al. prepared coordination polymer nanoparticles (MCQ/R NPs) using D-mannitol, cerium ions, quercetin, and rutin. In a mouse model of LPS-induced ALI, treatment with MCQ/R NPs significantly reduced the lung wet weight/dry weight ratio and the total cell count and number of inflammatory cells (neutrophils and macrophages) in BALF. Serum levels of IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α and the mRNA expression of TLR4 and NLRP3 were also reduced. Histopathological examination demonstrated that MCQ/R NPs reduced the extent of inflammatory infiltration and interstitial edema in mice, which provides an idea for the treatment of ALI (Zhang Y. et al., 2024).
5.2.2 Pachypodol
Pachypodol is a significant secondary metabolite that is widely present in nature and is classified as a plant flavonoid. Sun et al. encapsulated the hydrophobic flavonol pachypodol in a liposome (Pac-lipo) and demonstrated that in vitro Pac-lipo exhibited anti-inflammatory and protective effects on the endothelial and epithelial barriers of macrophages and endothelial cells exposed to LPS. In addition, in a mouse model of LPS-induced ALI, Pac-lipo inhibited the expression of cytokines including TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in lung tissues. It also repaired the lung epithelial barrier and vascular endothelial barrier and inhibited the activation of the TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway, and it thereby reduced lung injury (Sun et al., 2024).
5.2.3 Hesperidin
Hesperidin, a natural flavonoid found in citrus fruits and vegetables, has demonstrated the ability to treat Acute Lung Injury (ALI) in an experimental mouse model (Dong et al., 2020; de Souza et al., 2024). Jin et al. prepared chitosan NPs loaded with hesperidin (HPD/NPs) for nasal delivery to inflamed lungs. In a mouse model of LPS-induced ALI, IL-1β and IL-6 levels in peripheral blood, together with TNF-α, IL-17, and NO levels in BALF, were measured to assess the inflammatory response. The results confirmed that HPD/NPs reduced the levels of the proinflammatory cytokines and alleviated lung injury more effectively than free hesperidin. Pulmonary vascular permeability was assessed using the Evans blue-albumin extravasation assay, and expression levels of IL-1β and caspase-1 were determined by immunohistochemical staining of lung tissues. The findings showed that HPD/NPs were effective in reducing pulmonary vascular permeability and inhibiting cellular sepsis, which suggested that they hold potential for the treatment of ALI (Jin et al., 2021).
5.2.4 Luteolin
Luteolin is a flavonoid commonly found in fruits, vegetables, flowers, and herbs. Luteolin has exhibited superior therapeutic efficacy in experimental models of ALI (Xie et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021). Gu et al. synthesized cerium ion-luteolin protein nanocomplexes (CeLutNCs) by coordinating cerium ions with luteolin. In vitro experiments demonstrated that CeLutNCs effectively scavenged various ROS, including H2O2, O2−, ·OH, DPPH·, and ABTS+, and exhibited favorable cytoprotective effects in RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages. In a mouse model of ALI, CeLutNCs also exhibited therapeutic effects, reducing inflammatory responses and histopathological alterations (Gu et al., 2024).
5.2.5 Baicalin
Baicalin is one of the main active ingredients extracted from the Chinese medicine baical skullcap root, which has anti-inflammatory properties (Hu et al., 2021; Fu et al., 2021). Yu et al. prepared a new drug delivery system, namely, baicalin liposome (BA-LP), which overcame the defect of the low solubility of baicalin. In a mouse model of LPS-induced ALI, BA-LP was found to reduce the lung wet weight/dry weight ratio, reduce the lung injury score, and inhibit the expression of proinflammatory factors (TNF-α and IL-1β) in BALF. It also exerted an anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the TLR4-NF-κBp65 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways. BA-LP thus provides a new option for the treatment of ALI (Long et al., 2020).
5.3 Alkaloids
Alkaloids are a class of nitrogen-containing alkaline organic compounds that are widely found in plants and have a variety of biological activities such as antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, immunomodulatory and analgesic.
5.3.1 Ligustrazine
Ligustrazine is an alkaloid extracted from the traditional Chinese medicinal herb chuanxiong. He et al. synthesized a novel reactive oxygen-sensitive carrier in the form of a covalent cyclodextrin framework (OC-COF), which was based on a CD-MOF, using oxalyl chloride as a crosslinking agent. A reactive oxygen-sensitive DPI referred to as LIG@OC-COF was developed by loading ligustrazine onto OC-COF. LIG@OC-COF exhibited anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects at the cellular level in vitro and in an animal model of ALI. In addition, combining ligustrazine with nanomaterials enhanced its bioavailability (H et al., 2022).
5.3.2 Capsaicin
Capsaicin is an active compound derived from chili peppers. It has been shown to have great potential in pain, high blood pressure, inflammation, and other conditions (Ferreira et al., 2020; Richards et al., 2012; Singh and Bernstein, 2014). Dynamic development of capsaicin’s anti-inflammatory ability is an effective way to treat ALI. Wang et al. prepared NPs referred to as Fe-CAP NPs containing capsaicin and iron. The anti-inflammatory ability of Fe-CAP NPs was confirmed by cell experiments, which revealed that the expression of TNF-α and iNOS was reduced in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells treated with Fe-CAP NPs and that these NPs could regulate the NF-κB signaling pathway. In a mouse model of ALI, Fe-CAP NPs inhibited the expression of IL-6 and iNOS. Via histopathological studies, it was observed that Fe-CAP NPs reduced the leakage of Evans blue in the lung and alleviated lung histopathology in rats and thus exhibited good anti-inflammatory ability, which holds significance for the treatment of ALI (Wang R. et al., 2024).
5.4 Terpenoids
Terpenoids are a class of organic compounds formed by the polymerization of isoprene units (C5H8) that are rich in chemical and biological activities such as anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and neuroprotective effects (Zhao et al., 2022).
5.4.1 Tanshinones
Tanshinones are a class of fat-soluble bioactive compounds extracted from the traditional Chinese medicinal herb Danshen. El-Moslemany et al. prepared a nanoemulsion using a biosurfactant (rhamnolipid) and tea tree oil loaded with tanshinone IIA (TSIIA) via ultrasonication. In a model of LPS-induced ALI, animals treated with the TSIIA nanoemulsion (TSIIA-NE) exhibited significant increases in tidal volume and respiratory rate, a reduction in the lung wet weight/dry weight ratio, and an improvement in arterial blood gas levels. In addition, histopathological examination of the lung and biochemical analysis of various biomarkers suggested that TSIIA-NE exhibited antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects and thereby alleviated symptoms of LPS-induced ALI (El-Moslemany et al., 2022).
5.5 Glycosides
Glycosides are natural products synthesized from a variety of natural plants, with anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, antioxidant and other effects.
5.5.1 Ginsenoside
Ginsenoside Rb1 is a principal bioactive component of ginseng (Zhang et al., 2023). Wu et al. prepared novel bionanoparticles (R@ZQC NPs) loaded with ginsenoside Rb1, utilizing a metal-organic framework (zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 NPs) as a carrier. These particles encapsulated ginsenoside Rb1 internally and were coated externally with a quaternary chitosan layer and a macrophage membrane. Experimental results indicated that R@ZQC NPs enhanced mitochondrial function and reduced oxidative stress by activating or directly binding to AMP-activated protein kinase, inhibited apoptosis in alveolar macrophages, and thus mitigated ALI. In a mouse model of ALI, tail vein administration of R@ZQC NPs increased the survival rate of mice with sepsis-induced ALI and alleviated histopathological damage to the structure of the lungs. These results suggest a promising therapeutic approach for addressing ALI caused by sepsis (Wu et al., 2024b).
5.6 Triterpenoids
Triterpenoids are terpenoids with a basic nucleus consisting of 30 carbon atoms that have a wide range of biological activities including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumor and antifibrotic.
5.6.1 Celastrol
Celastrol is derived from the root bark of the traditional Chinese medicine Common Threewingnut Root and is a natural product with a variety of biological activities. Yao et al. developed a mannose-modified drug delivery system for targeted delivery of celastrol to alveolar macrophages. Celastrol nanoparticles (Cel-NPs) were synthesized using emulsification and evaporation techniques. In vitro studies demonstrated that mannose-modified Cel-NPs significantly enhanced the delivery of celastrol to inflammatory macrophages and exhibited strong biocompatibility. In a mouse model of ALI, Cel-NPs effectively inhibited infiltration of inflammatory cells, reduced lung edema, and suppressed LPS-induced lung inflammation and cytokine storms, which suggested that they hold promise for treating ALI (Yao et al., 2024).
5.7 Coumarins
Coumarins are a group of secondary metabolites widely found in plants with different biological activities such as anti-inflammatory, antiviral and bacteriostatic effects using phenanthrene α-pyrone as the parent nucleus.
5.7.1 Bergapten
Bergamot lactone (bergapten) is a coumarin analog widely found in medicinal plants such as Buddha’s hand and Dahurian angelica root (B et al., 2016; Li et al., 2011; Murray and Wynn, 2011). It has various pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and antioxidative effects (Luo et al., 2023; Adakudugu et al., 2020). Liao et al. integrated bergapten and DPPC liposomes to develop a biologically active lung-targeted lipid nanomedicine named Ber-lipo. Ber-lipo was found to exhibit good biocompatibility, low cytotoxicity, and lung-targeting properties and repaired the epithelial and endothelial barriers. Immunofluorescence analysis showed that Ber-lipo decreased the proportion of M1-type macrophages and increased the proportion of M2-type macrophages in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells, thereby maintaining the M1/M2 balance. In a mouse model of LPS-induced ALI, Ber-lipo significantly reduced body weight loss and the lung index and alleviated pulmonary edema. In addition, it was found that Ber-lipo could effectively inhibit the activation of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB proinflammatory pathway and thereby alleviate ALI (Liao et al., 2025) (Table 2).
6 Challenges faced in the development of NP-NMs
Firstly, in terms of their preparation process, different types of NPs have different preparation methods. There is a lack of unified safety management, and unintentional release of NPs during production and processing is difficult to measure and track. This results in poor controllability and thus can be a great challenge for clinical conversion (Ramanathan, 2019). Secondly, in terms of drug delivery, the delivery of NPs faces multiple challenges, including shear, protein adsorption, and rapid clearance. These biological barriers become even more difficult to overcome in pathological states and thus limit the proportion of NPs that reach their targets (Mitchell et al., 2020; Blanco et al., 2015; Ensign et al., 2012). Furthermore, some NPs, such as liposomes, may be difficult to bind to the released drug in a controlled manner, which limits the controlled release effect (Cao et al., 2022). The mechanisms of the biocompatibility and toxicity of NPs are not yet fully understood (Mitchell et al., 2020; Ciganė et al., 2021). Unfortunately, although NPs have an important role in biomedicine, there is still very little information on studies of their long-term toxicity and analyses of their animal tolerance, which are necessary steps prior to human clinical trials (Mohammed-Sadhakathullah et al., 2023).
As a result of these challenges, we are therefore required to: 1) Aim to establish methods for the assessment of health risk during the preparation of NPs and prepare new exposure models that can track particles in the environment. 2) Continuously explore new options, such as intelligent nanoparticle design and responsive nanomaterials, so as to improve the targeting and controlled release of NPs. 3) Optimize the selection of nanomaterials–for example, by aiming to select materials that have been proved by existing studies to be highly biocompatible and have low toxicity–and continue to study the intrinsic mechanisms of the biocompatibility and toxicity of nanomaterials. 4) Develop a standardized manufacturing process to meet the requirements of drug regulatory agencies and more effectively facilitate the clinical conversion of NPs. Currently, a relatively large number of natural product nanomedicines have entered the clinical trial stage. Among them, curcumin-loaded nanoparticles represent the most extensively investigated formulations, having progressed through multiple phases of clinical evaluation. In addition, nanoparticle systems derived from other natural compounds have also been explored. For instance, clove extract-based nanoparticles have been evaluated for the treatment of dental caries, while quercetin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles have demonstrated promising activity in in vitro studies using oral cancer cell lines (Sanjai et al., 2024; Hassan et al., 2023). Nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel), which is a nanoparticle derived from the natural product paclitaxel and bound to human serum protein. Owing to its favorable clinical efficacy and safety profile, nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel) has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and other malignancies. In addition, the combination of nab-paclitaxel with gemcitabine has become a standard first-line therapy for metastatic pancreatic cancer (MPC), as demonstrated by the positive outcomes of the global phase III MPACT trial (Kim, 2017). Moreover, emerging clinical evidence supports the potential utility of nab-paclitaxel, either as monotherapy or in combination with other agents, in the management of metastatic esophageal, gastric, colorectal, and biliary tract cancers (Hassan et al., 2023).
7 Conclusion and perspective
Natural products are widely used in biomedicine, genetic engineering, and other fields because of their natural biocompatibility, biodegradability, and other intrinsic properties, but their poor bioavailability limits their exploitation. By combining natural products with nanomaterials, new strategies are provided for natural products to utilize their unique advantages, improve their bioavailability, expand the scope of targeted therapies, and take advantage of controlled release. These provide new ideas for the treatment of ALI. In addition, compared with traditional treatment methods, the initial development and preparation costs of NP-NMs are relatively high. However, from the perspective of long-term treatment efficacy, NP-NMs, with their excellent targeting properties, can reduce the number of doses required and shorten the treatment cycle, thereby lowering costs. This is particularly advantageous in the management of chronic diseases, where they offer significant economic benefits.
However, promoting the translation of NP-NMs to clinical practice is an arduous process that requires a large number of basic experiments and clinical trials to advance the widespread clinical application of NP-NMs. We will vigorously promote standardized preparation processes for NP-NMs, long-term toxicology research, and research on multi-mechanism coordinated release control combined with AI development (Joyce et al., 2024). With the continuous development of nanotechnology and the exploration of the mechanisms of natural products, there is no doubt that NP-NMs hold promise and will become important drugs for the treatment of ALI and other diseases in the future.
Author contributions
JY: Writing – original draft. YH: Writing – original draft. RL: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. DC: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. ZZ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. JZ: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. PX: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. LZ: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study is jointly supported by funding from (1) the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52102340); (2) Xinglin Talent Program of Chengdu University of TCM (330023085); (3) Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Project (2023MS300).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adakudugu, E. A., Ameyaw, E. O., Obese, E., Biney, R. P., Henneh, I. T., Aidoo, D. B., et al. (2020). Protective effect of bergapten in acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Heliyon 6, e04710. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04710
Adir, Y., Welch, L. C., Dumasius, V., Factor, P., Sznajder, J. I., Ridge, K. M. J. A. J. o.P.-L. C., et al. (2008). Overexpression of the Na-K-ATPase alpha2-subunit improves lung liquid clearance during ventilation-induced lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 294, L1233–L1237. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00076.2007
Aggarwal, N. R., King, L. S., and D'Alessio, F. R. (2014). Diverse macrophage populations mediate acute lung inflammation and resolution. Am. J. Physiology-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiology 306, L709–L725. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00341.2013
Akbari, B., Baghaei-Yazdi, N., Bahmaie, M., and Mahdavi Abhari, F. (2022). The role of plant-derived natural antioxidants in reduction of oxidative stress. BioFactors 48, 611–633. doi:10.1002/biof.1831
Albrecht, K., Kasai, Y., and Yamamoto, K. (2008). The fluorescence and electroluminescence properties of the carbazole–phenylazomethine double layer-type dendrimer. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 19, 118–123. doi:10.1007/s10904-008-9239-3
Alex, S. M., Sharma, C. P. J. D. d., and research, t. (2013). Nanomedicine for gene therapy. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 3, 437–445. doi:10.1007/s13346-012-0120-0
Anderson, C. F., Grimmett, M. E., Domalewski, C. J., and Cui, H. (2020). Inhalable nanotherapeutics to improve treatment efficacy for common lung diseases. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomedicine nanobiotechnology 12, e1586. doi:10.1002/wnan.1586
Arber Raviv, S., Alyan, M., Egorov, E., Zano, A., Harush, M. Y., Pieters, C., et al. (2022). Lung targeted liposomes for treating ARDS. J. Control. Release 346, 421–433. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.03.028
Atanasov, A. G., Zotchev, S. B., Dirsch, V. M., and Supuran, C. T. (2021). Natural products in drug discovery: advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 20, 200–216. doi:10.1038/s41573-020-00114-z
Broz, P., and Dixit, V. M. J. N. R. I. (2016). Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 407–420. doi:10.1038/nri.2016.58
Bein, T., Weber-Carstens, S., and Apfelbacher, C. J. C. o.i.c.c. (2018). Long-term outcome after the acute respiratory distress syndrome: different from general critical illness? Curr. Opin. Crit. care 24, 35–40. doi:10.1097/MCC.0000000000000476
Bellani, G., Laffey, J. G., Pham, T., Fan, E., Brochard, L., Esteban, A., et al. (2016). Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries. Jama 315. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.0291
Bian, S., Cai, H., Cui, Y., Liu, W., and Xiao, C. (2021a). Nanomedicine-based therapeutics to combat acute lung injury. Int. J. Nanomedicine 16, 2247–2269. doi:10.2147/ijn.S300594
Bian, S., Cai, H., Cui, Y., Liu, W., and Xiao, C. J. I. J. o.N. (2021b). Nanomedicine-based therapeutics to combat acute lung injury. N. T. J. Nanomedicine, 2247–2269. doi:10.2147/IJN.S300594
Blanco, E., Shen, H., and Ferrari, M. (2015). Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 941–951. doi:10.1038/nbt.3330
Cahill, P. A., and Redmond, E. M. J. A. (2016). Vascular endothelium–gatekeeper of vessel health. Atherosclerosis 248, 97–109. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.03.007
Cao, F., Cheng, M.-H., Hu, L.-Q., Shen, H.-H., Tao, J.-H., Li, X.-M., et al. (2020). Natural products action on pathogenic cues in autoimmunity: efficacy in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis as compared to classical treatments. Pharmacol. Res. 160, 105054. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105054
Cao, F., Gui, S.-Y., Gao, X., Zhang, W., Fu, Z.-Y., Tao, L.-M., et al. (2022). Research progress of natural product-based nanomaterials for the treatment of inflammation-related diseases. Mater. and Des. 218. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2022.110686
Chen, X.-Y., Wang, S.-M., Li, N., Hu, Y., Zhang, Y., Xu, J.-F., et al. (2013). Creation of lung-targeted dexamethasone immunoliposome and its therapeutic effect on bleomycin-induced lung injury in rats. PLoS One 8, e58275. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058275
Chen, J., Li, G., Sun, C., Peng, F., Yu, L., Chen, Y., et al. (2022a). Chemistry, pharmacokinetics, pharmacological activities, and toxicity of Quercitrin. Phytother. Res. 36, 1545–1575. doi:10.1002/ptr.7397
Chen, Y.-B., Zhang, Y.-B., Wang, Y.-L., Kaur, P., Yang, B.-G., Zhu, Y., et al. (2022b). A novel inhalable quercetin-alginate nanogel as a promising therapy for acute lung injury. J. Nanobiotechnology 20. doi:10.1186/s12951-022-01452-3
Chen, K., Zhang, Z., Fang, Z., Zhang, J., Liu, Q., Dong, W., et al. (2023). Aged-Signal-Eliciting nanoparticles stimulated macrophage-mediated programmed removal of inflammatory neutrophils. ACS Nano 17, 13903–13916. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c03815
Chen, D., Zhou, Z., Kong, N., Xu, T., Liang, J., Xu, P., et al. (2024a). Inhalable SPRAY nanoparticles by modular peptide assemblies reverse alveolar inflammation in lethal Gram-negative bacteria infection. Sci. Adv. 10, eado1749. doi:10.1126/sciadv.ado1749
Chen, X., Yang, Y., Mai, Q., Ye, G., Liu, Y., and Liu, J. J. B. (2024b). Pillar arene Se nanozyme therapeutic systems with dual drive power effectively penetrated mucus layer combined therapy acute lung injury. Biomaterials 304, 122384. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122384
Cheng, P., Li, S., and Chen, H. J. C. (2021). Macrophages in lung injury, repair, and fibrosis. Cells 10, 436. doi:10.3390/cells10020436
Chicione, L. G., Stenger, M. R., Cui, H., Calvert, A., Evans, R. J., English, B. K., et al. (2011). Nitric oxide suppression of cellular proliferation depends on cationic amino acid transporter activity in cytokine-stimulated pulmonary endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 300, L596–L604. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00029.2010
Cho, E. C., Glaus, C., Chen, J., Welch, M. J., and Xia, Y. J. T. i.m.m. (2010). Inorganic nanoparticle-based contrast agents for molecular imaging. Trends Mol. Med. 16, 561–573. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2010.09.004
Chopra, B., and Dhingra, A. K. (2021). Natural products: a lead for drug discovery and development. Phytotherapy Res. 35, 4660–4702. doi:10.1002/ptr.7099
Ciganė, U., Palevičius, A., and Janušas, G. (2021). Review of nanomembranes: materials, fabrications and applications in tissue engineering (bone and skin) and drug delivery systems. J. Mater. Sci. 56, 13479–13498. doi:10.1007/s10853-021-06164-x
de Alcantara Lemos, J., Oliveira, A. E. M. F. M., Araujo, R. S., Townsend, D. M., Ferreira, L. A. M., and de Barros, A. L. B. (2021). Recent progress in micro and nano-encapsulation of bioactive derivatives of the Brazilian genus Pterodon. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 143. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112137
de Oliveira, M. T. P., de Sa Coutinho, D., Tenorio de Souza, E., Staniscuaski Guterres, S., Pohlmann, A. R., Silva, P. M. R., et al. (2019). Orally delivered resveratrol-loaded lipid-core nanocapsules ameliorate LPS-induced acute lung injury via the ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Int. J. Nanomedicine 14, 5215–5228. doi:10.2147/IJN.S200666
de Souza, A. B. F., de Matos, N. A., de Freitas Castro, T., de Paula Costa, G., Talvani, A., Nagato, A. C., et al. (2024). Neurobiology. Preventive effects of hesperidin in an experimental model ofs acute lung inflammation. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 323, 104240. doi:10.1016/j.resp.2024.104240
Dechert, R. E., Haas, C. F., and Ostwani, W. (2012). Current knowledge of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 24, 377–401. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2012.06.006
Dong, J., Zhou, H., Zhao, H., Zhao, Y., Chang, C. J. J. o.B., and Toxicology, M. (2020). Hesperetin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via the miR-410/SOX18 axis. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 34, e22588. doi:10.1002/jbt.22588
dos Santos Haupenthal, D. P., Mendes, C., de Bem Silveira, G., Zaccaron, R. P., Corrêa, M. E. A. B., Nesi, R. T., et al. (2020). Effects of treatment with gold nanoparticles in a model of acute pulmonary inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide. J. Biomed. Mater Res. A 108, 103–115. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.36796
El-Moslemany, R. M., El-Kamel, A. H., Allam, E. A., Khalifa, H. M., Hussein, A., and Ashour, A. A. (2022). Tanshinone IIA loaded bioactive nanoemulsion for alleviation of lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury via inhibition of endothelial glycocalyx shedding. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 155. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113666
Ensign, L. M., Cone, R., and Hanes, J. (2012). Oral drug delivery with polymeric nanoparticles: the gastrointestinal mucus barriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 64, 557–570. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2011.12.009
Fan, E., Brodie, D., and Slutsky, A. S. (2018). Acute respiratory distress syndrome: advances in diagnosis and treatment. Jama 319, 698–710. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.21907
Fernandes, E. S., da Silva Figueiredo, I. F., Monteiro, C. R. A. V., and Monteiro-Neto, V. (2023). Antimicrobial and anti-infective activity of natural Products—Gaining knowledge from novel studies. Antibiotics 12. doi:10.3390/antibiotics12061051
Fernández-Francos, S., Eiro, N., González-Galiano, N., and Vizoso, F. J. (2021). Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy as an alternative to the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome: current evidence and future perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22. doi:10.3390/ijms22157850
Ferreira, L. G. B., Faria, J. V., Dos Santos, J. P. S., and Capsaicin, R. X. J. E. J. o.P. (2020). Capsaicin: TRPV1-independent mechanisms and novel therapeutic possibilities. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 887. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173356
Fonseca-Santos, B., Gremiao, M. P., and Chorilli, M. (2015). Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Int. J. Nanomedicine 10, 4981–5003. doi:10.2147/IJN.S87148
Fu, Y.-j., Xu, B., Huang, S.-w., Luo, X., Deng, X.-l., Luo, S., et al. (2021). Baicalin prevents LPS-induced activation of TLR4/NF-κB p65 pathway and inflammation in mice via inhibiting the expression of CD14. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 42, 88–96. doi:10.1038/s41401-020-0411-9
Gao, W., Wang, Y., Xiong, Y., Sun, L., Wang, L., Wang, K., et al. (2019). Size-dependent anti-inflammatory activity of a peptide-gold nanoparticle hybrid in vitro and in a mouse model of acute lung injury. Acta Biomater. 85, 203–217. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2018.12.046
Gao, R., Lin, P., Fang, Z., Yang, W., Gao, W., Wang, F., et al. (2024). Cell-derived biomimetic nanoparticles for the targeted therapy of ALI/ARDS. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 14, 1432–1457. doi:10.1007/s13346-023-01494-6
Gebistorf, F., Karam, O., Wetterslev, J., and Afshari, A. J. C. d.o.s.r. (2016). Inhaled nitric oxide for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in children and adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev., CD002787. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002787.pub3
Gill, S. E., Rohan, M., and Mehta, S. J. R. r. (2015). Role of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis in murine sepsis-induced lung injury in vivo. Respir. Res. 16, 109–113. doi:10.1186/s12931-015-0266-7
Gordillo-Galeano, A., and Mora-Huertas, C. E. (2018). Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: a review emphasizing on particle structure and drug release. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 133, 285–308. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.10.017
Goswami, V., Sodhi, K. K., and Singh, C. K. (2025). Innovative approaches to asthma treatment: harnessing nanoparticle technology. Discov. Nano 20, 21. doi:10.1186/s11671-025-04211-z
Gu, J., Zhang, P., Li, H., Wang, Y., Huang, Y., Fan, L., et al. (2024). Cerium-Luteolin nanocomplexes in managing inflammation-related diseases by antioxidant and immunoregulation. ACS Nano 18, 6229–6242. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c09528
Guo, L., Wang, W., Zhao, N., Guo, L., Chi, C., Hou, W., et al. (2016). Mechanical ventilation strategies for intensive care unit patients without acute lung injury or acute respiratory distress syndrome: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Crit. Care 20, 226. doi:10.1186/s13054-016-1396-0
Guo, Y., Peng, X., Liu, F., Zhang, Q., Ding, L., Li, G., et al. (2024). Potential of natural products in inflammation: biological activities, structure–activity relationships, and mechanistic targets. Archives Pharmacal Res. 47, 377–409. doi:10.1007/s12272-024-01496-z
Gupta, S. C., Kismali, G., and Aggarwal, B. B. (2013). Curcumin, a component of turmeric: from farm to pharmacy. BioFactors 39, 2–13. doi:10.1002/biof.1079
Gupta, C., Jaipuria, A., and Gupta, N. (2022). Inhalable formulations to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): recent therapies and developments. Pharmaceutics 15. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15010139
He, S., Wu, L., Sun, H., Wu, D., Wang, C., Ren, X., et al. (2022). Antioxidant biodegradable covalent cyclodextrin frameworks as particulate carriers for inhalation therapy against Acute lung injury. ACS Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 14, 38421–38435. doi:10.1021/acsami.2c05220
Hamid, U., Krasnodembskaya, A., Fitzgerald, M., Shyamsundar, M., Kissenpfennig, A., Scott, C., et al. (2017). Aspirin reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation in human models of ARDS. Thorax 72, 971–980. doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-208571
Hashem, S., Ali, T. A., Akhtar, S., Nisar, S., Sageena, G., Ali, S., et al. (2022). Targeting cancer signaling pathways by natural products: exploring promising anti-cancer agents. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 150. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113054
Hassan, M. S., Awasthi, N., Ponna, S., and von Holzen, U. (2023). Nab-Paclitaxel in the treatment of gastrointestinal cancers-improvements in clinical efficacy and safety. Biomedicines 11. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11072000
He, Y.-Q., Zhou, C.-C., Yu, L.-Y., Wang, L., Deng, J.-l., Tao, Y.-L., et al. (2021). Natural product derived phytochemicals in managing acute lung injury by multiple mechanisms. Pharmacol. Res. 163, 105224. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105224
Hecker, L. (2018). Mechanisms and consequences of oxidative stress in lung disease: therapeutic implications for an aging populace. Am. J. Physiology-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiology 314, L642-L653–L653. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00275.2017
Hettiarachchi, S. D., Zhou, Y., Seven, E., Lakshmana, M. K., Kaushik, A. K., Chand, H. S., et al. (2019). Nanoparticle-mediated approaches for Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutics. J. Control Release 314, 125–140. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.10.034
Hu, A., Huang, J.-J., Zhang, J.-F., Dai, W.-J., Li, R.-L., Lu, Z.-Y., et al. (2017). Curcumin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo through ATM/Chk2/p53-dependent pathway. Oncotarget 8, 50747–50760. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.17096
Hu, Q., Zhang, W., Wu, Z., Tian, X., Xiang, J., Li, L., et al. (2021). Baicalin and the liver-gut system: pharmacological bases explaining its therapeutic effects. Pharmacol. Res. 165, 105444. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105444
Huang, X., Xiu, H., Zhang, S., and Zhang, G. (2018). The role of macrophages in the pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 1264913–1264918. doi:10.1155/2018/1264913
Jha, R., and Mayanovic, R. A. (2023). A review of the preparation, characterization, and applications of chitosan nanoparticles in nanomedicine. Nanomater. (Basel) 13. doi:10.3390/nano13081302
Jiang, J., Huang, K., Xu, S., Garcia, J. G. N., Wang, C., and Cai, H. (2020). Targeting NOX4 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via attenuation of redox-sensitive activation of CaMKII/ERK1/2/MLCK and endothelial cell barrier dysfunction. Redox Biol. 36, 101638. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101638
Jiang, A. Y., Witten, J., Raji, I. O., Eweje, F., MacIsaac, C., Meng, S., et al. (2024). Combinatorial development of nebulized mRNA delivery formulations for the lungs. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 364–375. doi:10.1038/s41565-023-01548-3
Jin, H., Zhao, Z., Lan, Q., Zhou, H., Mai, Z., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). Nasal delivery of Hesperidin/Chitosan nanoparticles suppresses cytokine storm syndrome in a mouse model of Acute lung injury. Front. Pharmacol. 11. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.592238
Jin, H., Luo, R., Li, J., Zhao, H., Ouyang, S., Yao, Y., et al. (2022). Inhaled platelet vesicle-decoyed biomimetic nanoparticles attenuate inflammatory lung injury. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1050224. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1050224
Jin, Z., Gao, Q., Wu, K., Ouyang, J., Guo, W., and Liang, X. J. (2023a). Harnessing inhaled nanoparticles to overcome the pulmonary barrier for respiratory disease therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 202, 115111. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2023.115111
Jin, M., Liu, B., Zhang, Z., Mu, Y., Ma, L., Yao, H., et al. (2023b). Catechin-Functionalized cationic lipopolymer based multicomponent nanomicelles for lung-targeting delivery. Adv. Mater. 36. doi:10.1002/adma.202302985
Jing, W., Chunhua, M., Shumin, W. J. T., and Pharmacology, A. (2015). Effects of acteoside on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in acute lung injury via regulation of NF-κB pathway in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 285, 128–135. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2015.04.004
Joyce, P., Allen, C. J., Alonso, M. J., Ashford, M., Bradbury, M. S., Germain, M., et al. (2024). A translational framework to DELIVER nanomedicines to the clinic. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 1597–1611. doi:10.1038/s41565-024-01754-7
Kim, G. (2017). nab-Paclitaxel for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 9, 85–96. doi:10.2147/cmar.S127840
Kurd, M., Sadegh Malvajerd, S., Rezaee, S., Hamidi, M., and Derakhshandeh, K. (2019). Oral delivery of indinavir using mPEG-PCL nanoparticles: preparation, optimization, cellular uptake, transport and pharmacokinetic evaluation. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47, 2123–2133. doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1616553
Kuzmov, A., and Minko, T. (2015). Nanotechnology approaches for inhalation treatment of lung diseases. J. Control. release official J. Control. Release Soc. 219, 500–518. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.07.024
Laforge, M., Elbim, C., Frère, C., Hémadi, M., Massaad, C., Nuss, P., et al. (2020). Tissue damage from neutrophil-induced oxidative stress in COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 20, 515–516. doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0407-1
Lang, F. M., Lee, K. M. C., Teijaro, J. R., Becher, B., and Hamilton, J. A. (2020). GM-CSF-based treatments in COVID-19: reconciling opposing therapeutic approaches. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 20, 507–514. doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0357-7
Leng, T., Zhang, L., Ma, J., Qu, X., and Lei, B. (2024). Intrinsically bioactive multifunctional Poly(citrate-curcumin) for rapid lung injury and MRSA infection therapy. Bioact. Mater. 41, 158–173. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.07.002
Li, C., Lin, G., Zuo, Z. J. B., and disposition, d. (2011). Pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetics properties of Radix Scutellariae and its bioactive flavones. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 32, 427–445. doi:10.1002/bdd.771
Li, S.-J., Wang, X.-J., Hu, J.-B., Kang, X.-Q., Chen, L., Xu, X.-L., et al. (2017). Targeting delivery of simvastatin using ICAM-1 antibody-conjugated nanostructured lipid carriers for acute lung injury therapy. Drug Deliv. 24, 402–413. doi:10.1080/10717544.2016.1259369
Li, S., Chen, L., Wang, G., Xu, L., Hou, S., Chen, Z., et al. (2018). Anti-ICAM-1 antibody-modified nanostructured lipid carriers: a pulmonary vascular endothelium-targeted device for acute lung injury therapy. J. Nanobiotechnology 16, 105–114. doi:10.1186/s12951-018-0431-5
Li, H., Zhu, J., Wang, C., Qin, W., Hu, X., Tong, J., et al. (2020). Paeonol loaded cyclodextrin metal-organic framework particles for treatment of acute lung injury via inhalation. Int. J. Pharm. 587, 119649. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119649
Li, C., Li, J., Fan, Y., Wang, D., Zhan, M., Shen, M., et al. (2021). Co-delivery of dexamethasone and a MicroRNA-155 inhibitor using dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles for acute lung injury therapy. Biomacromolecules 22, 5108–5117. doi:10.1021/acs.biomac.1c01081
Li, J., Chen, L., Li, C., Fan, Y., Zhan, M., Sun, H., et al. (2022). Phosphorus dendron nanomicelles as a platform for combination anti-inflammatory and antioxidative therapy of acute lung injury. Theranostics 12, 3407. doi:10.7150/thno.70701
Liao, R., Sun, Z.-C., Wang, L., Xian, C., Lin, R., Zhuo, G., et al. (2025). Inhalable and bioactive lipid-nanomedicine based on bergapten for targeted acute lung injury therapy via orchestrating macrophage polarization. Bioact. Mater. 43, 406–422. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.09.020
Lin, E.-H., Chang, H.-Y., Yeh, S.-D., Yang, K.-Y., Hu, H.-S., and Wu, C.-W. (2013). Polyethyleneimine and DNA nanoparticles-based gene therapy for acute lung injury. Nanomedicine Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 9, 1293–1303. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2013.05.004
Liu, C., Xiao, K., and Xie, L. J. F. i.I. (2022). Advances in the regulation of macrophage polarization by mesenchymal stem cells and implications for ALI/ARDS treatment. Front. Immunol. 13, 928134. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.928134
Liu, C., Xi, L., Liu, Y., Mak, J. C. W., Mao, S., Wang, Z., et al. (2023). An inhalable hybrid biomimetic nanoplatform for sequential drug release and remodeling lung immune homeostasis in acute lung injury treatment. ACS Nano 17, 11626–11644. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c02075
Long, Y., Xiang, Y., Liu, S., Zhang, Y., Wan, J., Yang, Q., et al. (2020). Baicalin liposome alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung injury in mice via inhibiting TLR4/JNK/ERK/NF-κB pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 8414062. doi:10.1155/2020/8414062
Low, Z., Lani, R., Tiong, V., Poh, C., AbuBakar, S., and Hassandarvish, P. (2023). COVID-19 therapeutic potential of natural products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24. doi:10.3390/ijms24119589
Lucas, R., Verin, A. D., Black, S. M., and Catravas, J. D. (2009). Regulators of endothelial and epithelial barrier integrity and function in acute lung injury. Biochem. Pharmacol. 77, 1763–1772. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.01.014
Luo, T., Jia, X., Feng, W.-d., Wang, J.-y., Xie, F., Kong, L.-d., et al. (2023). Bergapten inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis via promoting mitophagy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 44, 1867–1878. doi:10.1038/s41401-023-01094-7
Luo, Z., Yin, F., Wang, X., and Kong, L. (2024). Progress in approved drugs from natural product resources. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 22, 195–211. doi:10.1016/s1875-5364(24)60582-0
Matthay, M. A., Zemans, R. L., Zimmerman, G. A., Arabi, Y. M., Beitler, J. R., Mercat, A., et al. (2019). Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 5, 18. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0069-0
Meduri, G. U., Annane, D., Confalonieri, M., Chrousos, G. P., Rochwerg, B., Busby, A., et al. (2020). Pharmacological principles guiding prolonged glucocorticoid treatment in ARDS. Intensive Care Med. 46, 2284–2296. doi:10.1007/s00134-020-06289-8
Mitchell, M. J., Billingsley, M. M., Haley, R. M., Wechsler, M. E., Peppas, N. A., and Langer, R. (2020). Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 20, 101–124. doi:10.1038/s41573-020-0090-8
Miyazawa, H., Hirai, K., Ookawara, S., Ishibashi, K., and Morishita, Y. J. N. R. (2017). Nano-sized carriers in gene therapy for renal fibrosis in vivo. Nano Rev. Exp. 8, 1331099. doi:10.1080/20022727.2017.1331099
Mohammed-Sadhakathullah, A. H. M., Paulo-Mirasol, S., Torras, J., and Armelin, E. (2023). Advances in functionalization of bioresorbable nanomembranes and nanoparticles for their use in biomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24. doi:10.3390/ijms241210312
Mokra, D., and Kosutova, P. J. R. p. (2015). Biomarkers in acute lung injury. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol 209, 52–58. doi:10.1016/j.resp.2014.10.006
Muhammad, W., Zhu, J., Zhai, Z., Xie, J., Zhou, J., Feng, X., et al. (2022). ROS-responsive polymer nanoparticles with enhanced loading of dexamethasone effectively modulate the lung injury microenvironment. Acta Biomater. 148, 258–270. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2022.06.024
Murray, P. J., and Wynn, T. A. J. N. r.i (2011). Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 723–737. doi:10.1038/nri3073
Nikzamir, M., Hanifehpour, Y., Akbarzadeh, A., and Panahi, Y. (2021). Applications of dendrimers in nanomedicine and drug delivery: a review. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31, 2246–2261. doi:10.1007/s10904-021-01925-2
Peng, S., Wang, W., Zhang, R., Wu, C., Pan, X., and Huang, Z. (2024). Nano-Formulations for pulmonary delivery: past, present, and future perspectives. Pharmaceutics 16. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics16020161
Piao, C., Zhuang, C., Kang, M., Oh, J., and Lee, M. (2022). Pulmonary delivery of curcumin-loaded glycyrrhizic acid nanoparticles for anti-inflammatory therapy. Biomaterials Sci. 10, 6698–6706. doi:10.1039/d2bm00756h
Potey, P. M. D., Rossi, A. G., Lucas, C. D., and Dorward, D. A. (2019). Neutrophils in the initiation and resolution of acute pulmonary inflammation: understanding biological function and therapeutic potential. J. Pathology 247, 672–685. doi:10.1002/path.5221
Qu, Y., Wang, Z., Dong, L., Zhang, D., Shang, F., Li, A., et al. (2024). Natural small molecules synergize mesenchymal stem cells for injury repair in vital organs: a comprehensive review. Stem Cell Res. and Ther. 15. doi:10.1186/s13287-024-03856-4
Ramanathan, A. (2019). Toxicity of nanoparticles_ challenges and opportunities. Appl. Microsc. 49, 2. doi:10.1007/s42649-019-0004-6
Rhen, T., and Cidlowski, J. A. J. N. E. J. o.M. (2005). Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids—new mechanisms for old drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 353, 1711–1723. doi:10.1056/NEJMra050541
Richards, B. L., Whittle, S. L., and Buchbinder, R. J. C. D. o.S. R. (2012). Neuromodulators for pain management in rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 1, CD008921. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008921.pub2
Salameh, J. W., Zhou, L., Ward, S. M., Santa Chalarca, C. F., Emrick, T., and Figueiredo, M. L. J. W. I. R. N. (2020). Polymer-mediated gene therapy: recent advances and merging of delivery techniques. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 12, e1598. doi:10.1002/wnan.1598
Sanjai, C., Gaonkar, S. L., and Hakkimane, S. S. (2024). Harnessing nature's toolbox: naturally derived bioactive compounds in nanotechnology enhanced formulations. ACS omega 9, 43302–43318. doi:10.1021/acsomega.4c07756
Sarma, J. V., and Ward, P. A. (2011). Oxidants and redox signaling in Acute Lung Injury. Compr. Physiol. 1, 1365–1381. doi:10.1002/cphy.c100068
Sasidharan, R., Sreedharannair Leelabaiamma, M., Mohanan, R., Jose, S. P., Mathew, B., and Sukumaran, S. J. I. (2019). Anti-inflammatory effect of synthesized indole-based chalcone (2E)-3-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(1H-indol-3-yl) prop-2-en-1-one: an in vitro and in vivo studies. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 41, 568–576. doi:10.1080/08923973.2019.1672177
Sawasdee, K., Sucharitakul, J., Dhammaraj, T., Niamsiri, N., Chaiyen, P., and Prapainop, K. (2018). Encapsulation of the reductase component of p-hydroxyphenylacetate hydroxylase in poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles by three different emulsification techniques. IET Nanobiotechnol 12, 423–428. doi:10.1049/iet-nbt.2017.0189
Searcy, R. J., Morales, J. R., Ferreira, J. A., and Johnson, D. W. J. T. a.i.r.d. (2015). The role of inhaled prostacyclin in treating acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 9, 302–312. doi:10.1177/1753465815599345
Sercombe, L., Veerati, T., Moheimani, F., Wu, S. Y., Sood, A. K., and Hua, S. (2015). Advances and challenges of liposome assisted drug delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 6, 286. doi:10.3389/fphar.2015.00286
Shakeri, F., and Boskabady, M. H. J. B. (2017). Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects of curcumin in ovalbumin-sensitized rat. Biofactors 43, 567–576. doi:10.1002/biof.1364
Short, K. R., Kasper, J., van der Aa, S., Andeweg, A. C., Zaaraoui-Boutahar, F., Goeijenbier, M., et al. (2016). Influenza virus damages the alveolar barrier by disrupting epithelial cell tight junctions. Eur. Respir. J. 47, 954–966. doi:10.1183/13993003.01282-2015
Sica, A., and Mantovani, A. (2012). Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J. Clin. Investigation 122, 787–795. doi:10.1172/jci59643
Silva, P. L., and Rocco, P. R. M. (2017). “Pathophysiology of Acute respiratory distress syndrome,” in Acute respiratory distress syndrome, 15–27. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-41852-0_2
Singh, U., and Bernstein, J. A. J. C. a.a.T. M. (2014). Intranasal capsaicin in management of nonallergic (vasomotor) rhinitis. Prog. Drug Res. 68, 147–170. doi:10.1007/978-3-0348-0828-6_6
Singh, C. K., and Sodhi, K. K. (2023). The emerging significance of nanomedicine-based approaches to fighting COVID-19 variants of concern: a perspective on the nanotechnology’s role in COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment. Front. Nanotechnol. 4–2022. doi:10.3389/fnano.2022.1084033
Singh, A. V., Jahnke, T., Kishore, V., Park, B.-W., Batuwangala, M., Bill, J., et al. (2018). Cancer cells biomineralize ionic gold into nanoparticles-microplates via secreting defense proteins with specific gold-binding peptides. Acta Biomater. 71, 61–71. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2018.02.022
Southworth, S. R., Woodward, E. J., Peng, A., and Rock, A. D. J. J. o.p.r. (2015). An integrated safety analysis of intravenous ibuprofen (Caldolor®) in adults. J. Pain Res. 8, 753–765. doi:10.2147/JPR.S93547
Su, X., Jing, X., Jiang, W., Li, M., Liu, K., Teng, M., et al. (2023). Polyphosphazene nanodrugs for targeting delivery and inflammation responsive release of curcumin to treat acute lung injury by effectively inhibiting cytokine storms. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 229, 113446. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2023.113446
Sun, G., Wu, X., Zhu, H., Yuan, K., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., et al. (2023). Reactive oxygen species-triggered curcumin release from hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for PM(2.5)-Induced acute lung injury treatment. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 15, 33504–33513. doi:10.1021/acsami.3c07361
Sun, Z.-C., Liao, R., Xian, C., Lin, R., Wang, L., Fang, Y., et al. (2024). Natural pachypodol integrated, lung targeted and inhaled lipid nanomedicine ameliorates acute lung injury via anti-inflammation and repairing lung barrier. J. Control. Release 375, 300–315. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.09.013
Suntres, Z. E., and Shek, P. N. J. B. P. (1996). Alleviation of paraquat-induced lung injury by pretreatment with bifunctional liposomes containing α-tocopherol and glutathione. Biochem. Pharmacol. 52, 1515–1520. doi:10.1016/s0006-2952(96)89626-2
Suntres, Z. E., and Shek, P. N. J. B. p. (2000). Prophylaxis against lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injuries by liposome-entrapped dexamethasone in rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 59, 1155–1161. doi:10.1016/s0006-2952(99)00411-6
Vassiliou, A. G., Kotanidou, A., Dimopoulou, I., and Orfanos, S. E. J. I. j.o.m.s. (2020). Endothelial damage in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 8793. doi:10.3390/ijms21228793
Verma, I. M., and Somia, N. J. N. (1997). Gene therapy-promises, problems and prospects. Nature 389, 239–242. doi:10.1038/38410
Wang, B., Hu, S., Teng, Y., Chen, J., Wang, H., Xu, Y., et al. (2024). Current advance of nanotechnology in diagnosis and treatment for malignant tumors. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 9. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01889-y
Wang, J., Wu, G., Chu, H., Wu, Z., and Sun, J. J. M. r.i.m.c. (2020). Paeonol derivatives and pharmacological activities: a review of recent progress. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 20, 466–482. doi:10.2174/1389557519666191015204223
Wang, W., Liu, Y., Pan, P., Huang, Y., Chen, T., Yuan, T., et al. (2022). Pulmonary delivery of resveratrol-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes for the prevention of zinc chloride smoke-induced acute lung injury. Drug Deliv. 29, 1122–1131. doi:10.1080/10717544.2022.204813
Wang, R., Li, Q., Wu, P., Ren, K., Li, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2024a). Fe-Capsaicin nanozymes attenuate sepsis-induced acute lung injury via NF-κB signaling. Int. J. Nanomedicine, 73–90. doi:10.2147/IJN.S436271
Wang, H., Jiao, Y., Ma, S., Li, Z., Gong, J., Jiang, Q., et al. (2024b). Nebulized inhalation of peptide-modified DNA origami to alleviate Acute Lung injury. Nano Lett. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c01222
Wu, S., Guo, P., Zhou, Q., Yang, X., and Dai, J. (2024a). M1 macrophage-targeted curcumin nanocrystals with l-Arginine-Modified for acute lung injury by inhalation. J. Pharm. Sci. 113, 2492–2505. doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2024.05.011
Wu, S., Liu, H., Liu, X., Wang, Y., Song, X., and Hu, K. (2024b). Ginsenoside Rb1-loaded bionic nanoparticles alleviate sepsis-induced acute lung injury by reducing mitochondrial oxidative stress to inhibit macrophage PANoptosis. Mater. and Des. 245. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2024.113291
Xie, K., Chai, Y.-s., Lin, S.-h., Xu, F., and Wang, C.-j.J. J. o.i.r. (2021). Luteolin regulates the differentiation of regulatory T cells and activates IL-10-dependent macrophage polarization against acute lung injury. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 8883962. doi:10.1155/2021/8883962
Xin, Y., Huang, M., Guo, W. W., Huang, Q., Zhang, L. z., and Jiang, G. J. M. c. (2017). Nano-based delivery of RNAi in cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 16, 134–139. doi:10.1186/s12943-017-0683-y
Xiong, P., Huang, X., Ye, N., Lu, Q., Zhang, G., Peng, S., et al. (2022). Cytotoxicity of metal-based nanoparticles: from mechanisms and methods of evaluation to pathological manifestations. Adv. Sci. 9. doi:10.1002/advs.202106049
Xu, X., and Zhu, Y. J. A. j.o.t.r. (2017). Curcumin inhibits human non-small cell lung cancer xenografts by targeting STAT3 pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 9, 3633–3641.
Xu, B., Watkins, R., Wu, L., Zhang, C., and Davis, R. (2015). Natural product-based nanomedicine: recent advances and issues. Int. J. Nanomedicine 10, 6055–6074. doi:10.2147/ijn.S92162
Yan, J., Tang, Z., Li, Y., Wang, H., Hsu, J. C., Shi, M., et al. (2023). Molybdenum nanodots for acute lung injury therapy. ACS Nano 17, 23872–23888. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c08147
Yang, D., Wang, T., Long, M., Li, P. J. O. M., and Longevity, C. (2020). Quercetin: its main pharmacological activity and potential application in clinical medicine. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 8825387. doi:10.1155/2020/8825387
Yao, Y., Fan, S., Fan, Y., Shen, X., Chai, X., Shao, Y., et al. (2024). Intratracheal delivery of macrophage targeted Celastrol-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for enhanced anti-inflammatory efficacy in acute lung injury mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 114511. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2024.114511
Yeung, Y. T., Aziz, F., Guerrero-Castilla, A., and Arguelles, S. (2018). Signaling pathways in inflammation and anti-inflammatory therapies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 24, 1449–1484. doi:10.2174/1381612824666180327165604
Yuan, R., Li, Y., Han, S., Chen, X., Chen, J., He, J., et al. (2021). Fe-Curcumin nanozyme-mediated reactive oxygen species scavenging and anti-inflammation for Acute lung injury. ACS Central Sci. 8, 10–21. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.1c00866
Zhai, Z., Ouyang, W., Yao, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., Xu, F., et al. (2022). Dexamethasone-loaded ROS-responsive poly(thioketal) nanoparticles suppress inflammation and oxidative stress of acute lung injury. Bioact. Mater. 14, 430–442. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.01.047
Zhang, Y., Ding, S., Li, C., Wang, Y., Chen, Z., Wang, Z. J. E., et al. (2017). Effects of N-acetylcysteine treatment in acute respiratory distress syndrome: a meta-analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 14, 2863–2868. doi:10.3892/etm.2017.4891
Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Qiao, W., Zhang, J., and Qi, Z. (2020). Baricitinib, a drug with potential effect to prevent SARS-COV-2 from entering target cells and control cytokine storm induced by COVID-19. Int. Immunopharmacol. 86, 106749. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106749
Zhang, Z.-t., Zhang, D.-Y., Xie, K., Wang, C.-J., and Xu, F. J. I. I. (2021). Luteolin activates Tregs to promote IL-10 expression and alleviating caspase-11-dependent pyroptosis in sepsis-induced lung injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 99, 107914. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107914
Zhang, R., Li, X., Gao, Y., Tao, Q., Lang, Z., Zhan, Y., et al. (2023). Ginsenoside Rg1 epigenetically modulates Smad7 expression in liver fibrosis via MicroRNA-152. J. Ginseng Res. 47, 534–542. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2022.12.005
Zhang, J., Guo, Y., Mak, M., and Tao, Z. (2024a). Translational medicine for acute lung injury. J. Transl. Med. 22. doi:10.1186/s12967-023-04828-7
Zhang, S., Zhao, X., Xue, Y., Wang, X., and Chen, X.-L. J. J. o.N. (2024b). Advances in nanomaterial-targeted treatment of acute lung injury after burns. J. Nanobiotechnology 22, 342. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02615-0
Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Yang, R., Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Jiang, C., et al. (2024c). Synergistic therapeutic effects of D-Mannitol–Cerium–Quercetin (Rutin) coordination polymer nanoparticles on acute lung injury. Molecules 29, 2819. doi:10.3390/molecules29122819
Zhao, W.-Y., Yi, J., Chang, Y.-B., Sun, C.-P., and Ma, X.-C. J. P. (2022). Recent studies on terpenoids in Aspergillus fungi: chemical diversity, biosynthesis, and bioactivity. Phytochemistry 193, 113011. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.113011
Zhao, S., Gao, K., Han, H., Stenzel, M., Yin, B., Song, H., et al. (2024). Acid-degradable lipid nanoparticles enhance the delivery of mRNA. Nat. Nanotechnol., 1–10. doi:10.1038/s41565-024-01765-4
Zhou, A., Chen, K., Gao, Y., Zhou, X., Tian, Z., Chen, W., et al. (2023). Bioengineered neutrophil extinguisher targets Cascade immune pathways of macrophages for alleviating cytokine storm in pneumonia. ACS Nano 17, 16461–16477. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c00227
Keywords: acute lung injury, anti-inflammatory, nanomaterials, natural products, review
Citation: Yang J, Hsu Y, Liu R, Chen D, Zhou Z, Zou J, Xiong P and Zhou L (2025) Advances in natural-product-based nanomaterials for treatment of acute lung injury. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1663961. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1663961
Received: 11 July 2025; Accepted: 19 August 2025;
Published: 01 September 2025.
Edited by:
Maria Gazouli, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, GreeceReviewed by:
Rakesh A. Afre, Dr. D. Y. Patil Dnyan Prasad University, IndiaChandra Kant Singh, University of Delhi, India
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Hsu, Liu, Chen, Zhou, Zou, Xiong and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jingshan Zou, empzZmVuZzAyMTRAY2R1dGNtLmVkdS5jbg==; Peizheng Xiong, eGlvbmdwZWl6aGVuZ0BjZHV0Y20uZWR1LmNu; Li Zhou, MjAwNjEwNjNAY2R1dGNtLmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jiajing Yang1†
Jiajing Yang1† Peizheng Xiong
Peizheng Xiong