- 1Department of Orthopedics, National Taiwan University Hospital Yunlin Branch, Yunlin, Taiwan
- 2Department of Post-Baccalaureate Medicine, College of Medicine, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan
- 3Department of Orthopedics, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan
- 4Technology Translation Center for Medical Device, Chung Yuan Christian University, Taoyuan, Taiwan
- 5Department of Orthopedics, Show Chwan Memorial Hospital, Changhua, Taiwan
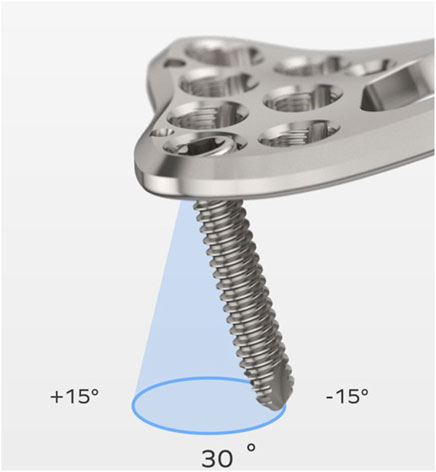
Introduction: Variable-angle locking systems offer increased surgical flexibility by permitting off-axis screw insertion, with some designs allowing angulation up to 15°. However, clinical challenges such as screw loosening and insufficient mechanical stability data persist. This study aims to evaluate the impact of different plate hole design parameters on the locking strength of plate-screw head interface under various screw insertion angles, providing insights to optimize VALS performance in fracture fixation.
Methods: Variable-angle locking system with Point-Loading Thread-In mechanism was designed for investigation. Variations in locking hole design were evaluated based on slot size (1.3 mm vs. 1.5 mm), number of thread columns (three vs. four), and cone angle (20° vs. 22°). A total of eight distinct design groups were included for analysis. The screws, inserted at different inclinations (0°–15°), and locked at 0.8 Nm were subjected to a cantilever load-to-failure test. Ultimate bending moment at the screw-head interface and failure mode of the locking mechanism were determined.
Results: The results exhibited a decrease in bending strength with increasing screw angulation in both three- and four-thread designs, with all groups exceeding 1 Nm at 0° but falling below 1 Nm at 15°. The highest bending moment was 1.46 Nm in the three-thread-column design at 0°, compared with 1.32 Nm in the four-thread-column design. At 15° screw angulation, the highest moments were 0.92 Nm and 0.90 Nm for the three-thread and four-thread designs, respectively. The plate hole with 1.3 mm slot, three thread column and 22° cone design showed higher bending moment than all other designs at each insertion angles.
Discussion: Plate hole design—specifically slot size, thread number, and cone angle—significantly influences locking strength. The optimal design (3 slots, 1.3 mm, 22°) offers superior mechanical stability, guiding device optimization.
1 Introduction
The introduction of fixed-angle locking screws in the early 2000s (e.g., PC-FIX; Synthes) revolutionized fracture fixation by enabling constructs that maintain relative stability where absolute stability is difficult to achieve (Borgeaud et al., 2000). Traditional locking plates derive their strength from forming a single-beam construct through fixed-angle screw fixation. However, one major limitation of this system is the inability to adjust screw trajectory based on individual fracture patterns or anatomical variations (Konstantinidis et al., 2010). To overcome this, variable-angle locking plate systems (VALS) were developed, allowing variable screw angulation while maintaining angular stability. These designs aimed to offer the potential to optimize plate placement and screw orientation according to fracture anatomy without compromising mechanical rigidity.
Despite their theoretical advantages, the clinical adoption of variable-angle locking screws has been limited due to several technical and biomechanical concerns. Studies have demonstrated that variable-angle constructs may exhibit reduced load to failure, particularly when screws are inserted at extreme angles or depending on the implant design (Hebert-Davies et al., 2013; Mehling et al., 2013; Tidwell et al., 2016). Furthermore, clinical reports have documented cases of variable-angle locking screw loosening, even in low-load regions such as the distal radius (Foo et al., 2013; Fowler and Ilyas, 2013; Nishiwaki et al., 2021; Tank et al., 2016; Collinge et al., 2023; Schmidt et al., 2024). Fowler and Ilyas (Fowler and Ilyas, 2013) reported one case of screw loosening among 39 distal radius fractures treated with variable-angle volar locking plates, whereas two mechanical failures were observed in a cohort of 55 patients (Nishiwaki et al., 2021). In two retrospective cohort analyses (Tank et al., 2016; Collinge et al., 2023), higher failure rates of variable-angle locking screws were seen in 22% and 36% of cases, respectively. Given the increased cost and potential for reduced mechanical integrity, further investigation into the biomechanical performance of these implants is warranted.
The majority of mechanical studies focused either on comparing the locking strength of various variable-angle technologies (Hebert-Davies et al., 2013; Mehling et al., 2013; Tidwell et al., 2016; Foo et al., 2013) or on assessing the influence of multiple screw insertions on the failure load of a specific system (Glowacki et al., 2023a). However, comprehensive mechanical stability data for contemporary VALS remain unavailable, and the variety of currently VALS technology influence the biomechanical performance. Among FDA-cleared variable-angle designs, point-loading thread-in mechanisms—where screws engage lightly threaded tabs within the plate—are most frequently used clinically (Figure 1). By using multiple thread columns (formed by several slots), this technology achieves several locking points between the conical plate hole and the spherical screw head, enabling a fixed-angle construct with unrestricted screw trajectories (Chan and Fernandez, 2013). From a mechanical perspective, slot size, number of thread columns, and cone angle influence thread engagement, thereby affecting locking strength. This study aims to investigate the effect of design parameters of variable-angle locking plate holes on plate/screw locking strength at different screw angulations.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Design parameters of the variable-angle locking hole
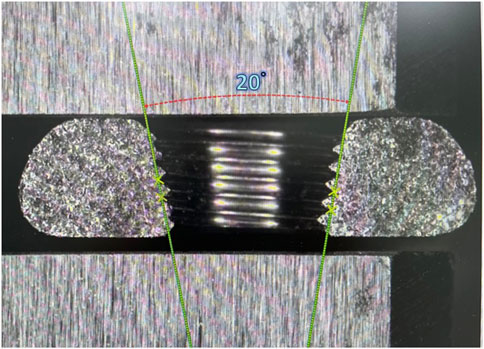
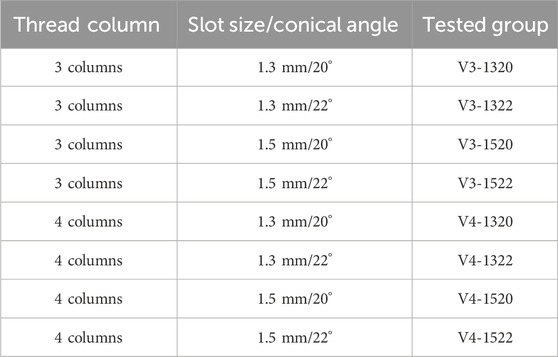
Three or four slots, forming corresponding thread columns (Figure 2), were proposed for the VALS hole design in this study. Mechanically, these slots are intended to facilitate cross-thread engagement between the screw head and the plate hole, thereby accommodating multidirectional screw insertion. Consequently, the performance of the variable-angle locking system is closely associated with both the slot size and the conical angle of the threaded hole. In most of commercialized bone plates, the conical angle of the threaded hole is 20° to accommodate both fixed-angle locking screw and variable-angle locking screw (Figure 3). For the feasibility of head thread fabrication of the variable-angle locking screw, the longitudinal axis of thread cutting bit is set perpendicular to longitudinal axis of the screw shaft, thus representing a manner that head thread profile lines is parallel to each other (Figure 4). Therefore, thread engagement between the plate hole and the screw head and the thread-to-thread contact area of the locking interface varies with the conical thread profile of the plate hole. Theoretically, a greater inclination of the hole profile results in more thread engagement (Figure 5). We proposed a 22° conical hole to be included in this study. Further, slot size of 1.3 and 1.5 mm was designed VALS hole for comparison. Therefore, 8 VALS hole features were applied in the custom-made plates for investigation (Table 1). 2.4 mm variable angle locking screws of 20 mm length and made of titanium (Depuy Synthes, Oberdorf, Switzerland) (Young’s modulus = 110 GPa; Poisson ratio = 0.3) were inserted into the VALS hole of titanium custom-made plates (Young’s modulus = 105 GPa; Poisson ratio = 0.37) (Figure 6). The holes of the custom-made plates were machined with the eight VALS design features. The thread pitch of the plate hole was designed at 0.3 mm to correspond to the head thread of the 2.4 mm variable angle locking screw. A guiding block was used to ensure the exact angle for the screw insertion into the VALS plate hole. Screws were inserted at different angles (0°, 5°, 10°, 15°) covering the full range of possible angulations of the VALS mechanism. All screws were tightened by 0.8 Nm torque.
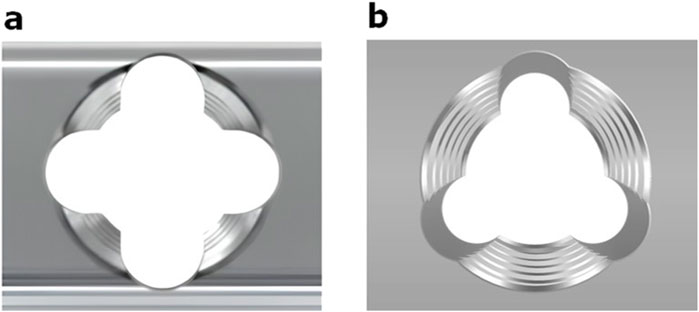
Figure 2. (a) Schematic of a variable-angle locking hole with four slots forming four columns of threads (DePuy Synthes). (b) Variable-angle locking hole with three slots (three thread columns).
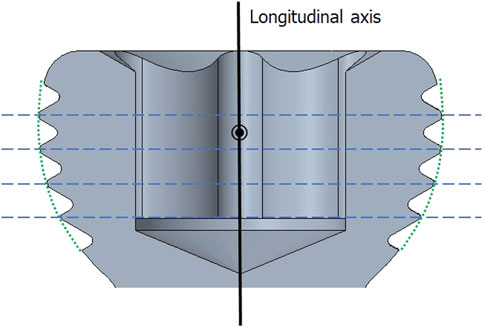
Figure 4. Schematic view of the screw head of the variable angle locking screw. Green dotted curve outlining the thread peaks represents a spherical-shaped screw head. Thread profile lines (blue dotted lines) are parallel to each other and perpendicular to central axis.
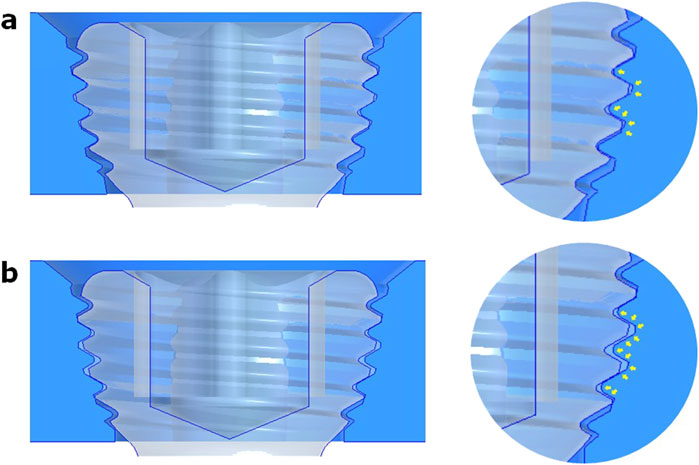
Figure 5. Schematic view illustrating the variable-angle locking screw (in grey) engaging with threaded holes (in blue) designed with (a) 20° and (b) 22° cone shapes. A magnified view shows the portions of cross-thread engagement (yellow arrows). The 22° conical hole has obviously more thread engagement than the 20° conical hole.
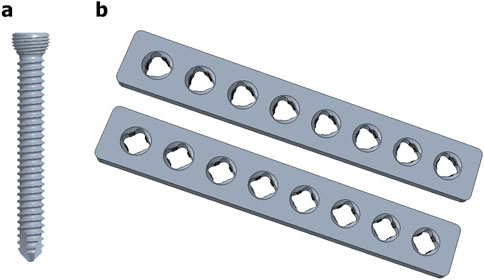
Figure 6. 3D models of (a) the variable-angle locking screw and (b) the custom-made plates featuring three (upper) and four (lower) thread columns.
2.2 Biomechanical testing
Mechanical property investigation was conducted using a material testing machine (HT-2402, Hung-Ta Instrument Co., Taiwan) equipped with a 1000 N load cell, with the test setup illustrated in Figure 7. The VALS plate was securely fixed within a vise to allow for the application of axial compressive load. The screw shaft was inserted into the hole of a ball joint, which also functioned as a protective device. This is necessary to minimize point stress on the screw. As the screw specimen was loaded and displaced, the ball joint was able to rotate accordingly as the section moved downward (Collinge et al., 2023). The ball joint was connected via a linear slide to the actuator of the testing machine, which operated in displacement control mode at a speed of 1 mm/min. An axial load was applied at a distance of 4 mm from the undersurface of the plate. The test was continued until screw failure occurred, defined as (1) breakage, (2) a rapid force drop exceeding 50%, or (3) a displacement reaching 2 mm (Hebert-Davies et al., 2013). The axial displacement (mm) and load (N) were recorded from the actuator. The maximum load was determined from the load-displacement curve. Ultimate bending moment at the VALS interface was derived from multiplying the maximum load with the lever arm.
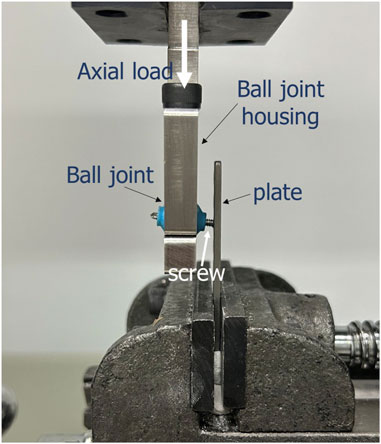
Figure 7. Diagram of biomechanical test setup. The custom plate was clamped by a vice. A vertical compression load was applied to the screw shaft at a distance of 4 mm from the plate.
2.3 Statistical analysis
SPSS 21.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, United States) was used for statistical analysis. Any significant differences between the four VALS groups were assessed using one-way analyses of variance. Post hoc analysis was conducted using Tukey multiple comparison test. The statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Five tests were conducted per group for each angle.
3 Results
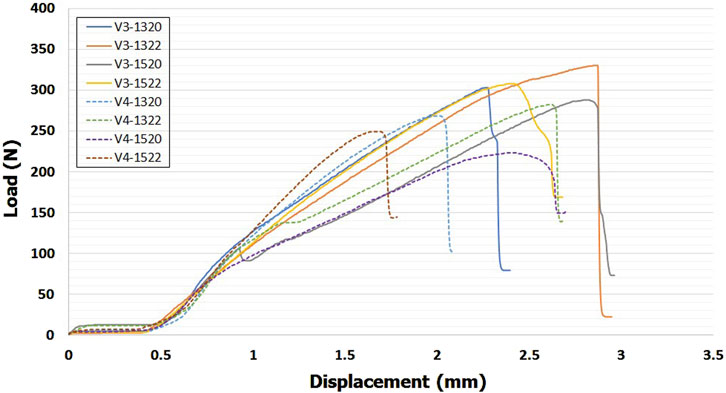
Typical force–displacement curves was shown in Figure 8. Mean ultimate bending moments for eight VALS holes at the different screw angulation is presented in Table 2 and a bar chart with statistical comparison results is shown in Figure 9. For all eight VALS groups, comparable bending moments were seen between off-axis insertions ranging from 0° to 10° though it slight decreased at both 5° and 10°. Ultimate bending moments decreased at a 15° inclination, with all 15° angulated VALS groups showing statistically significant differences compared to the 0° groups and all other off-axis VALS groups. The V3-1322 design showed higher bending moment than 7 other VALS designs at each insertion angles. Significant differences were seen at 0°–15°, with V3-1322 design being mechanically superior than V4-1320 (p < 0.05) and V4-1520 (p < 0.01) designs. The V3-1322 design also showed significantly higher moment at 5° and 10° off-axis compared to V4-1322 (p < 0.05) and V4-1522 (p < 0.01) designs. At 0°–10° inclination, all VALS locking screws failed due to breakage or plastic deformation at the neck region, while the screw heads remained fixed to the plate (Figure 10a). All screws showed macroscopic damage on the head thread (Figure 10b).
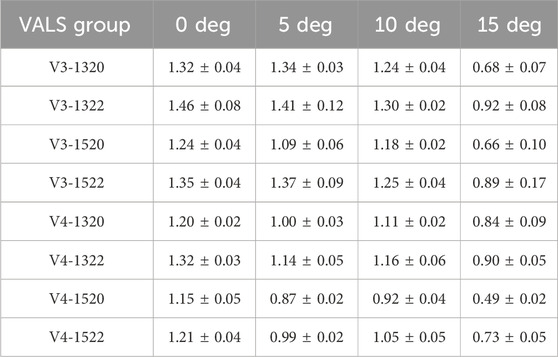
Table 2. Mean bending strength (Mean ± SD, Nm) in eight VALS hole designs at different screw insertion angles.
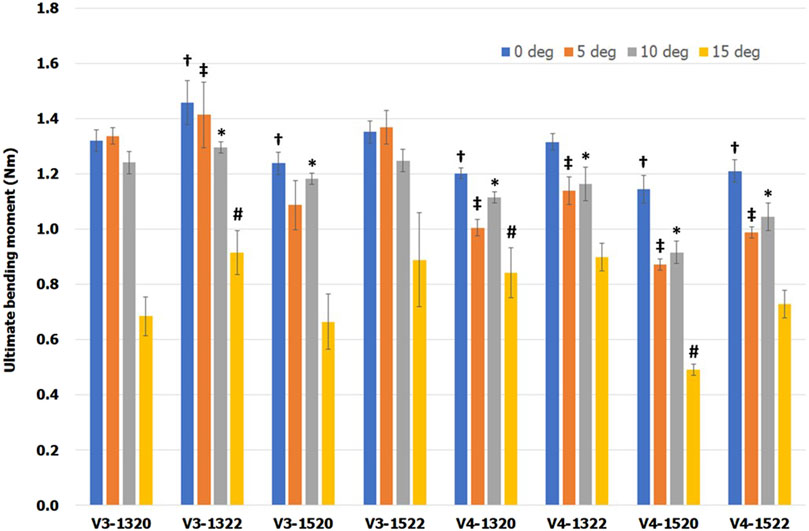
Figure 9. Mean ultimate bending moment with one standard error. Special markers (†, ‡, ✱ and #) indicate significant differences between VALS groups with the same insertion angle.
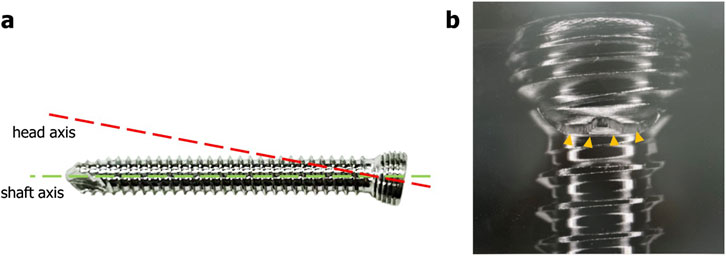
Figure 10. (a) Screw with catastrophic deformation at head-neck junction. (b) Screw breakage at head-neck junction indicated by arrows.
In design models with identical thread columns and slot diameter, 22° conical hole exhibited greater strength than 20° cone design. Similarly, models with a smaller slot size (1.3 mm) or three thread columns (V3), with other features held constant, demonstrated higher load resistance compared to those with a larger slot size (1.5 mm) or thread columns (V4).
4 Discussion
Variable angle locking screws have been developed to overcome specific limitations associated with conventional fixed-angle locking systems, particularly in scenarios requiring more surgical flexibility. These screws enable enhanced freedom in screw trajectory by incorporating design mechanisms that facilitate secure locking in a non-perpendicular fashion, thereby accommodating complex anatomical structures and variable fracture patterns. Several studies on variable-angle plating systems have employed biomechanical testing using fracture models or full constructs with multiple screws to replicate clinical applications (Mehling et al., 2013; Hart et al., 2015; Nourbakhsh et al., 2019; Martínez-Fortún et al., 2024; Hoffmeier et al., 2009; Adler et al., 2017). Others have focused on the single screw–plate interface to isolate mechanical behavior (Hebert-Davies et al., 2013; Glowacki et al., 2023a; Lenz et al., 2015; Glowacki et al., 2023b). However, direct comparisons of bending moments across systems must be approached with caution, as differences in testing methods, plate designs, and locking mechanisms can significantly influence outcomes. Little is known how the variable angle hole profiles impact the capacity of the locking strength under different screw insertion directions. This study investigated the biomechanical performance of three distinct plate hole features under off-axis screw insertion conditions.
Our data revealed that small slotted design is advantageous for the locking strength of the variable-angle mechanism. This is reasonable because the plate hole with small slot size provides more thread-to-thread contact area at the locking interface. In the aspect of mechanics, better thread engagement would ensure better resistance against external load. Also, three slotted design groups represented superior bending strength than four slotted groups owing to the same rationale as mentioned above. Recently, Glowacki et al. used a micro-CT to examined the contact area between the variable angle locking interfaces (Glowacki et al., 2023b). The results demonstrated a strong correlation between bending strength and the thread engagement, which can support our finding.
Furthermore, the conical design of the plate hole affected the VALS strength as well. As our hypothesis, 22° conical hole design has larger thread contact area than 20° conical hole design (Figure 11). Our results revealed that the 22° cone-shaped plate hole has higher bending moment than that of 20° conical hole. This was attributed to the conical geometry of the plate hole and the thread profile of screw head.
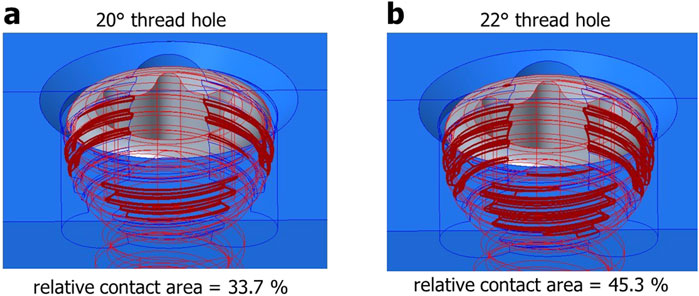
Figure 11. Visualization of the thread contact area in the variable-angle locking interface: (a) 20° conical hole; (b) 22° conical hole.
From a manufacturing perspective, the proposed slot size, cone angle, and thread configuration are technically feasible with modern machining but may increase production complexity and cost compared with conventional designs. These practical challenges should be considered alongside the biomechanical advantages when evaluating the clinical translation of the design.
Overall, our results showed that bending strength decreased as screw insertion angle increased, either in three-thread-column groups or in four-thread-column groups. The highest bending moment was 1.46 Nm among three-thread-column designs at 0° inclination while it was 1.32 Nm among four-thread-column designs. At 15° screw angulation, the highest moments were 0.92 Nm and 0.90 Nm for the three-thread and four-thread designs, respectively. In comparison, Lenz et al. simulated a variable angle locking hole design with four thread columns and 2.4 mm variable angle locking screws (Ti6Al7Nb alloy) (Lenz et al., 2015). They reported a statistically significant reduction at 15° compared to 2°–10°. Specifically, the bending moments were 1.67 Nm and 1.33 Nm at 0° and 15°, respectively. While the overall trend in bending moment was comparable, the magnitudes differed between our study and that of Lenz et al. These differences may be attributed to variations in experimental jigs, setup and the custom manufacturing of plates (such as the slot size and thread). Additionally, the material properties differed: our plates were pure titanium (yield strength = 483 MPa; tensile strength = 550 MPa), whereas Lenz et al. used Ti6Al7Nb alloy (yield strength = 800 MPa; tensile strength = 900 MPa). The higher mechanical strength of Ti6Al7Nb likely enhanced thread engagement at the screw–plate interface, which may partly explain the higher bending moments observed in their study.
Inserted at 15° inclination, all screws revealed a lower bending moment in the current study. Numerous studies also concluded similar finding (Hebert-Davies et al., 2013; Lenz et al., 2015; Glowacki et al., 2023b). In a cantilever load study, Hebert-Davies et al. (2013) comparing three commercialized VALS devices, found significant reduction of failure load of up to 45%. Lenz et al. (2015) revealed that difference in ultimate failure moment was statistically significant between the 15° angulated group and other off-axis groups. Recently, Glowacki et al. (2023b) tested the mechanical performance of three variable angle locking systems. They described a reduction of bending force of up to 57% with 15° of angulation. Accordingly, we suggested extreme off-axis of 15° should be used with caution and should not be exceeded.
This study focused on the investigation of design variable in point-loading thread-in mechanism. Several biomechanical evaluations have demonstrated this mechanism provides higher locking strength than the cut-in mechanism which utilizes a harder screw head to cut a track into a softer plate thread (Mehling et al., 2013; Hoffmeier et al., 2009; Adler et al., 2017). Consistent with related work (Lenz et al., 2015; Glowacki et al., 2023b; Adler et al., 2017), our results revealed a significant reduction in locking strength at screw inclination of 10°–15°. In contrast, Mehling et al. presented that the cut-in mechanism had the highest ultimate strength at large screw angulation (10°–15°) (Mehling et al., 2013). Similarly, Herbert-Davies et al. found that the locking cap mechanism tended to sustain higher loading at both 10° and 15° (Hebert-Davies et al., 2013). These differences may be attributed to the distinct contact mechanisms at the screw–plate interface.
This study contains several limitations:
1. The plate-screw head locking interfaces were tested under a cantilever load scenario which cannot reflect the physiological conditions.
2. We only focused on the locking interface rather than the whole plate-screw construct. While this mechanical study shows that all screws lose force when angulated, the clinical impact is uncertain. Further tests that apply the superior VALS design in the bone plate is necessary to evaluate the biomechanical properties in different simulated fracture patterns.
3. Screw loosening is a continuous process driven by cyclic loading. Although static loading tests in this study can serve as predictors of cyclic performance, fatigue testing is essential to further evaluate the biomechanical behavior of the better combination of plate hole design variables prior to clinical application.
4. A formal a priori power analysis was not conducted due to the limited availability of specimens and the large number of experimental groups. As a result, certain subgroup comparisons may be underpowered. Nevertheless, the primary objective of this study was to explore overall trends in plate hole design, rather than to establish definitive conclusions for each subgroup.
5. This study was limited to experimental testing. Future work employing finite element modeling or digital image correlation could provide more detailed validation of the contact mechanics.
5 Conclusion
This study demonstrated that the slot diameter, number of slots, and conical angle of the plate hole significantly influence the mechanical performance of the variable-angle locking interface under different screw angulations. A plate hole design variables—specifically a three slots, a 1.3 mm slot diameter, and a 22° conical angle—may provide improved mechanical performance under static loading conditions. Further efforts must be taken to find out the fatigue performance and clinical practice of a variable-angle locking plate system designed with these parameters.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
C-CL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review and editing. S-PW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review and editing. K-JL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft. M-HH: Data curation, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adler, T., Schaefer, T., and Yates, P. (2017). Mechanical testing of two different variable angle locking systems for treatment of distal radius fractures. Clin. Surg. 2 (1), 1313. doi:10.25107/2474-1647.1313
Borgeaud, M., Cordey, J., Leyvraz, P. E., and Perren, S. M. (2000). Mechanical analysis of the bone to plate interface of the LC-DCP and of the PC-FIX on human femora. Injury 31 (Suppl. 3), C29–C92. doi:10.1016/s0020-1383(00)80029-7
Chan, J. S., and Fernandez, A. A. (2013). Highly-versatile variable-angle bone plate system, 574,268 B2. U.S. Patent No. Dresher, PA (US): Alberto Angel Fernandez, Montevideo (UY).
Collinge, C. A., Reeb, A. F., Rodriguez-Buitrago, A. F., Archdeacon, M. T., Beltran, M. J., Gardner, M. J., et al. (2023). Analysis of 101 mechanical failures in distal femur fractures treated with 3 generations of precontoured locking plates. J. Orthop. Trauma 37 (1), 8–13. doi:10.1097/BOT.0000000000002460
Foo, T. L., Gan, A. W., Soh, T., and Chew, W. Y. (2013). Mechanical failure of the distal radius volar locking plate. J. Orthop. Surg. Hong. Kong 21 (3), 332–336. doi:10.1177/230949901302100314
Fowler, J. R., and Ilyas, A. M. (2013). Prospective evaluation of distal radius fractures treated with variable-angle volar locking plates. J. Hand Surg. Am. 38 (11), 2198–2203. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2013.08.116
Glowacki, J., Bartkowiak, T., Paczos, P., Mietlinski, P., Zawadzki, P., and Lapaj, L. (2023a). Effect of screw angulation and multiple insertions on load-to-failure of polyaxial locking system. PLoS One 18 (12), e0295526. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0295526
Glowacki, J., Bartkowiak, T., Paczos, P., Gapinski, B., Mietlinski, P., Zawadzki, P., et al. (2023b). Effect of screw angulation on the bending performance of polyaxial locking interfaces: a micro-CT evaluation. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 21740. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-48791-1
Hart, A., Collins, M., Chhatwal, D., Steffen, T., Harvey, E. J., and Martineau, P. A. (2015). Can the use of variable-angle volar locking plates compensate for suboptimal plate positioning in unstable distal radius fractures? A biomechanical study. J. Orthop. Trauma 29 (1), e1–e6. doi:10.1097/BOT.0000000000000146
Hebert-Davies, J., Laflamme, G. Y., Rouleau, D., Canet, F., Sandman, E., Li, A., et al. (2013). A biomechanical study comparing polyaxial locking screw mechanisms. Injury 44 (10), 1358–1362. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2013.06.013
Hoffmeier, K. L., Hofmann, G. O., and Mückley, T. (2009). The strength of polyaxial locking interfaces of distal radius plates. Clin. Biomech. 24 (8), 637–641. doi:10.1016/J.CLINBIOMECH.2009.06.004
Konstantinidis, L., Hauschild, O., Beckmann, N. A., Hirschmüller, A., Südkamp, N. P., and Helwig, P. (2010). Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures with two different minimal invasive angle-stable plates: biomechanical comparison studies on cadaveric bones. Injury 41, 1256–1261. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2010.05.007
Lenz, M., Wahl, D., Gueorguiev, B., Jupiter, J. B., and Perren, S. M. (2015). Concept of variable angle locking-evolution and mechanical evaluation of a recent technology. J. Orthop. Res. 33, 988–992. doi:10.1002/jor.22851
Martínez-Fortún, G., Yánez, A., and Cuadrado, A. (2024). Influence of screw angulation on the mechanical properties on a polyaxial locking plate fixation. Bioeng. (Basel) 11 (10), 1024. doi:10.3390/bioengineering11101024
Mehling, I., Scheifl, R., Mehler, D., Klitscher, D., Hely, H., and Rommens, P. M. (2013). Are there any differences in various polyaxial locking systems? A mechanical study of different locking screws in multidirectional angular stable distal radius plates. Biomed. Tech(Berl). 58 (2), 187–194. doi:10.1515/bmt-2012-0105
Nishiwaki, M., Terasaka, Y., Kiyota, Y., Inaba, N., Koyanagi, T., and Horiuchi, Y. (2021). A prospective randomized comparison of variable-angle and fixed-angle volar locking plating for intra-articular distal radius fractures. J. Hand Surg. Am. 46 (7), 584–593. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2021.03.014
Nourbakhsh, A., Hirschfeld, A. G., Dhulipala, S., Hutton, W., Ganey, T., Lozada, L., et al. (2019). Biomechanical comparison of Fixed-versus variable-angle locking screws for distal humerus comminuted fractures. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 11 (3), 302–308. doi:10.4055/cios.2019.11.3.302
Schmidt, N. H., Birkelund, L., and Schønnemann, J. O. (2024). A retrospective cohort analysis of failure and potential causes after osteosynthesis of femoral fractures with VA-LCP condylar plate 4.5/5.0, depuy synthes. J. Orthop. 10 (55), 69–73. doi:10.1016/j.jor.2024.04.004
Tank, J. C., Schneider, P. S., Davis, E., Galpin, M., Prasarn, M. L., Choo, A. M., et al. (2016). Early mechanical failures of the synthes variable angle locking distal femur plate. J. Orthop. Trauma 30, e7–e11. doi:10.1097/BOT.0000000000000391
Keywords: variable angle locking, biomechanical study, angulation, bending moment, bone plate
Citation: Lin C-C, Wang S-P, Lin K-J and Hu M-H (2025) Mechanical optimization of plate-screw interfaces in variable-angle locking systems: a parametric study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1681460. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1681460
Received: 07 August 2025; Accepted: 21 October 2025;
Published: 30 October 2025.
Edited by:
Chuanxi Zheng, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, ChinaReviewed by:
Tomasz Bartkowiak, Poznań University of Technology, PolandUmesh Potdar, Pimpri Chinchwad College Of Engineering (PCCOE), India
Copyright © 2025 Lin, Wang, Lin and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ming-Hsien Hu, bWluZ2hzaWVuaHVAZ21haWwuY29t
 Chen-Chiang Lin1
Chen-Chiang Lin1 Shun-Ping Wang
Shun-Ping Wang Kun-Jhih Lin
Kun-Jhih Lin