- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan university Chengdu, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases and National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases and Engineering Research Center of Oral Translational Medicine, Ministry of Education and National Engineering Laboratory for Oral Regenerative Medicine, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 3Chengdu Shiliankangjian Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Chengdu, Sichuan, China
Due to their accessibility, wide range of sources and unique biological characteristics, dental stem cells have broad application prospects in regenerative medicine. This cell population mainly includes dental pulp stem cells, periodontal ligament stem cells, stem cells from deciduous teeth, and dental follicle stem cells. In addition, dental stem cells have good microenvironment-specific immunomodulatory functions, including inhibiting T cell activation, promoting the polarization of regulatory T cells and regulating the phenotype of macrophages, thereby promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation. These advantages are complemented by its strong osteogenic differentiation ability, providing a new strategy for oral tissue regeneration, and providing broad prospects for the treatment of nervous system related diseases due to its ectodermal homology with neural crest. This review systematically summarizes the major advantages of dental stem cells in the field of regenerative medicine, outlines current progress in clinical translation, and discusses future research directions, while critically comparing their therapeutic potential and challenges with other mesenchymal stem cells sources to guide seed cell selection and clinical applications.
1 Introduction
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are adult stem cells that are widely distributed in various organs of vertebrates, such as adipose, teeth, bone marrow, and umbilical cord and placenta of newborns (Zhao et al., 2025) (Figure 1). Due to their superior self-renewal, differentiation potential, immunomodulation and other abilities, they are now regarded as an important tool for various types of tissue regeneration and treatment of immune and inflammatory diseases (Peishan et al., 2023).
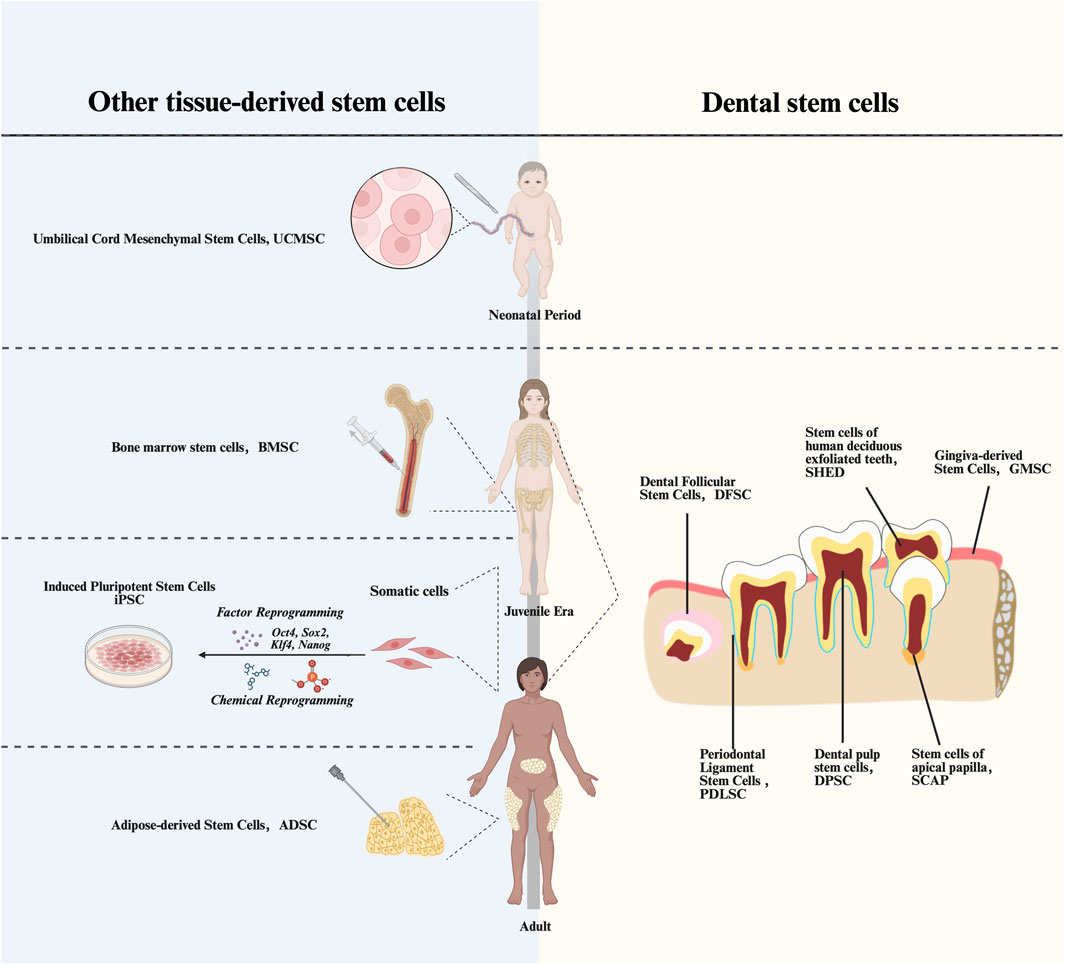
Figure 1. Timeline of acquisition of various types of MScs. UCMSCs, Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells; BMSCs, Bone Marrow Stem Cells; iPSCs, Induced pluripotent stem cells; ADSCs, Adipose-derived Stem Cells; DPSCs, Dental Pulp Stem Cells; PDLSCs, Periodontal Ligament stem Cells; DFSCs, Dental Follicle Stem Cells; SCAPs, Stem Cells from Apical Papilla; GMSCs, Gingiva-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells; SCAPs, Stem Cells from Apical Papilla.
As the most extensively studied MSCs, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) demonstrate remarkable differentiation potential, showing therapeutic promise for osteoporosis and bone defects (Song et al., 2025). However, their clinical application is constrained by the invasive bone marrow aspiration procedure required for isolation, which may cause secondary trauma to patients (Rossi et al., 2023). While adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) offer wider tissue accessibility, their weak chondrogenic differentiation ability limits their application in bone tissue engineering (Lee et al., 2012). The immunomodulatory effects of Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UCMSCs) diminish, with their aging in vivo, which may affect their clinical applications (Paladino et al., 2017).
In contrast, dental stem cells (DSCs) can address these limitations while exhibiting unique immunological and sourcing advantages. Their low immunogenicity enhances allogeneic transplantation efficacy, and their availability from clinical waste materials (e.g., exfoliated deciduous teeth and extracted wisdom teeth) eliminates invasive procedures and ethical concerns (Pires et al., 2025). DSCs primarily include dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs), stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHEDs), periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs), and dental follicle stem cells (DFSCs) (Umapathy et al., 2025). These ectoderm-derived stem cells not only exhibit regenerative potential in oral tissue regeneration, but also show promising preclinical results that may indicate advantages for nerve regeneration compared to other MSCs (Gopalarethinam et al., 2023). These characteristics endow dental stem cells with broader prospects for therapeutic applications.
Through systematic comparison of DSCs with other stem cell sources in terms of accessibility and biological properties, coupled with an in-depth exploration of their therapeutic potential across multiple pathological conditions, this review aims to provide valuable insights for future research and clinical translation.
2 Methodology of literature review
This review was designed as a methods-informed narrative review to provide a transparent overview of DSCs and their comparison with MSCs. Relevant studies were retrieved from PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, Web of Science, and Scopus, covering the period January 2000–September 2025. Keywords combined terms related to DSC subtypes (DPSCs, SHEDs, PDLSCs, SCAPs, DFSCs, GMSCs) and their biological functions (immunomodulation, osteogenesis, neurogenesis, regeneration, clinical trials) using Boolean operators.
We included peer-reviewed English-language original studies (in vitro, animal, or early-phase clinical) that characterized DSC identity, differentiation, or immunomodulatory properties, or directly compared DSCs with other MSCs. Editorials, conference abstracts, and studies lacking primary data were excluded.
Two authors independently screened titles and abstracts, followed by full-text assessment. Disagreements were resolved by discussion. The final evidence was grouped thematically—cell identity, immunomodulation, osteogenic/neurogenic differentiation, and clinical applications—and summarized qualitatively, highlighting comparative findings and limitations of current data.
3 Types and properties of dental stem cells
Originating from the ectomesenchyme, DSCs are a class of mesenchymal-stem-cell-like with self-renewal ability and multi-lineage differentiation potential. DSCs share not only the common of features and expression markers, but also their unique characteristics.
3.1 DPSCs
Dental pulp tissue is differentiated from the dental papilla, which performs functions such as repair, nutrition, and dentin formation within the dental tissues. Gronthos et al. first isolated DPSCs from pulp tissues of third molar obstruction in 2000 and described their basic properties (Gronthos et al., 2000). The application of DPSCs in tooth restoration and regeneration has been widely studied. Some scholars injected DPSCs into a small porcine periodontitis model and showed that they have a lower cellular senescence rate, higher proliferation rate, and stronger osteogenic maintenance ability, and can promote periodontal regeneration (Ma et al., 2019). In addition to this, DPSCs have lower immunogenicity, low levels of major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) expression, and negative MHC class II expression (MHC-II) (Uccelli et al., 2007). Furthermore, several studies have shown that DPSCs retain their stem cell properties after cryopreservation (Wang et al., 2024), DPSCs culture can be established from extracted human molar teeth with high efficiency even when whole teeth are cryopreserved for up to a month (Perry et al., 2008), demonstrating the potential of DPSCs for facile preservation and cell banking. These advantages have facilitated the rapid clinical translation of DPSCs. A recent multicenter randomized clinical trial conducted in China demonstrated that human DPSCs injection exhibited a favorable safety profile and significantly improved clinical outcomes in the treatment of stage III periodontitis (Liu et al., 2025). This milestone study marks a pivotal step forward in the clinical application of DPSCs.
3.2 PDLSCs
The periodontal membrane is derived from the dental follicle of the dental embryo, which is an important structure connecting the alveolar bone to the dentin and helps protect the health of the teeth and alveolar bone by evenly distributing the pressure on the teeth during mastication (Seo et al., 2004). The periodontium undergoes lifelong regeneration and remodeling. It harbors periodontal stem cells expressing MSCs markers STRO-1 and CD146/MUC18 (Wang et al., 2022). These cells are capable of regenerating functional periodontal complexes comprising both ligamentous and osseous structures (Inchingolo et al., 2024). Liu et al. demonstrated successful periodontal defect repair and alveolar bone regeneration through autologous PDLSCs transplantation in a miniature swine model (Liu et al., 2008). A clinical study conducted in Japan demonstrated that autologous PDLSC sheets were effective in treating chronic periodontitis, as evidenced by reductions in probing depth, improvements in clinical attachment levels, and increases in radiographic bone height, with confirmed safety and stability over mid-to long-term follow-up (Iwata et al., 2018). Meanwhile, PDLSCs exhibit neurogenic differentiation potential (Mohebichamkhorami et al., 2022), generating neuronal precursors with morphological and phenotypic characteristics of neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes, suggesting therapeutic applicability for neurological disorders.
3.3 DFSCs
DFSCs are the only type of dental stem cell derived from the dental follicle of the developing tooth germ. Distinct from other types originating from mature dental tissues (e.g., PDLSCs, DPSCs, SHED), their earlier developmental origin confers greater differentiation capacity and broader application potential. These cells exhibit accelerated proliferation under inflammatory conditions and can effectively regenerate functional periodontal complexes in various animal defect models, recapitulating the native sandwich-like multilayered architecture of periodontal tissues (Chen et al., 2025a). Experimental evidence indicates that DFSCs significantly upregulate periostin expression under inflammatory conditions and exhibit superior periodontal tissue regenerative capacity compared to PDLSCs in beagle dog defect repair models (Guo et al., 2017). Furthermore, DFSCs possess particularly remarkable osteogenic potential, which effectively enhances alveolar bone regeneration efficiency (Morsczeck et al., 2023). According to publicly available information, the Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) of the National Medical Products Administration of China has recently approved a human DFSCs injection developed in Chengdu for clinical trials targeting periodontitis treatment, marking a significant step toward the clinical application of DFSCs. In addition, owing to their neural crest origin, DFSCs have recently attracted attention for their potential in spinal cord injury therapy (Wen et al., 2024). Moreover, studies have demonstrated their capacity to differentiate into retinal precursors and neurons (Lee et al., 2025), suggesting possible applications in the treatment of diverse neurological disorders.
3.4 SHEDs
SHEDs are isolated from physiologically shed primary teeth. In vitro analyses demonstrate that beyond the conventional trilineage differentiation potential (osteogenic, adipogenic, and chondrogenic) (Miura et al., 2003), SHEDs additionally possess neurogenic and myogenic differentiation capacities (Zeng et al., 2020), suggesting their potential applicability in the treatment of cartilage-related diseases and muscle tissue injuries. SHEDs exhibit superior proliferative kinetics compared to DPSCs, characterized by accelerated population doublings, spontaneous spheroid formation, and upregulated endogenous bone morphogenic protein-2 (BMP-2) expression that enhances osteogenic differentiation and matrix mineralization capacity (Kunimatsu et al., 2018). SHEDs mediate osteogenesis through paracrine mechanisms rather than direct differentiation, establishing osteoinductive niches that recruit murine host osteoprogenitors for de novo bone formation. Xenotransplantation studies in immunodeficient murine models reveal SHED’s capacity to generate ectopic dentinoid structures, though complete dentin-pulp complex regeneration remains unachieved (Mohd et al., 2023). SHEDs and DFSCs have similar ability to regenerate periodontal tissue in vivo, but SHEDs is more conducive to vascularization and neuralization (Yang et al., 2019). Meanwhile, SHEDs have also been investigated in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease (Chen et al., 2024), corneal repair (Sato et al., 2025) and other conditions, and are increasingly recognized as important seed cells for therapeutic applications in nervous system disorders (Mi et al., 2023), as well as skin and cardiovascular injuries (Qin et al., 2024).
3.5 Gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells (GMSCs)
Zhang et al. first isolated gingival MSCs from discarded gingival tissues in good health, which showed clonogenicity, self-renewal ability and multiple differentiation capabilities. Lineage tracing studies by Xu et al. revealed dual embryonic origins of GMSCs: 90% originating from neural crest derivatives and 10% from mesodermal precursors. Neural crest-originating GMSCs exhibit enhanced neurogenic differentiation capacity and superior immunomodulatory properties compared to their mesoderm-derived counterparts (Zhang et al., 2009). More surprisingly, unlike BMSCs that exhibit age-related functional decline in migratory capacity and anti-inflammatory responses, human GMSCs maintain phenotypic stability and immunomodulatory competence through extended in vitro passaging. In addition, longitudinal culture analyses confirm GMSCs preserve genomic integrity through maintained telomerase activity and stable karyotypic profiles, with no observed tumorigenic potential (Bustos et al., 2014). A previous study obtained GMSCs from 13 to 80-year-old sources for assay, respectively, and found that the expression of cell surface markers did not change with increasing donor age and number of passages. Moreover, GMSCs derived from donors across this age spectrum were found to effectively attenuate inflammatory conditions and contribute to the regeneration of injured lung tissue (Dave et al., 2022). In addition, In vitro tumor suppression assays revealed GMSCs significantly inhibit oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation through direct cell-contact mechanisms (Ji et al., 2016). These collective properties position GMSCs as promising candidates for developing novel cell-based therapies targeting inflammatory, degenerative, and neoplastic pathologies (Shetty et al., 2025).
3.6 Stem cells from Apical Papilla (SCAPs)
During odontogenesis, the dental papilla differentiates into pulp-dentin complexes. These undifferentiated mesenchymal cells regulate tooth morphogenesis and demonstrate odontogenic induction capacity in non-dental epithelium. SCAPs, possessing self-renewal capacity and fibroblastic morphology, are isolatable from developing root apices (Sonoyama et al., 2006). SCAPs exhibit superior proliferative kinetics compared to DPSCs, with constitutive expression of MSCs markers (STRO-1/CD146) and putative SCAPs-specific antigen CD24 (Liang et al., 2022). Zhang et al. established immortalized SCAP lines (iSCAPs) from murine models, demonstrating Wnt3A-mediated upregulation of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) expression and enhanced osteogenic commitment. Moreover, in vitro analyses revealed SCAPs’ tripartite regenerative competence: enhanced migratory capacity, matrix mineralization potential, and neo-tissue formation ability, positioning them as prime candidates for craniofacial tissue engineering applications (Bakopoulo et al., 2011). In addition, under hypoxic conditions, SCAPs demonstrate enhanced neurogenic differentiation through upregulation of neuron-specific enolase (NSE), vascular endothelial growth factor-B (VEGF-B), and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), accompanied by increased expression of neuronal lineage markers. GDNF overexpression coupled with neuronal marker activation potentiates neurodifferentiation capacity of SCAPs (Vanacker et al., 2014). These neurogenic properties suggest therapeutic potential for SCAPs in neurodegenerative disorder management.
In summary, DPSCs, PDLSCs, and DFSCs have either entered or are approaching the stage of large-scale clinical trials or application. Compared to other dental-derived stem cells, this progress primarily stems from their superior tissue accessibility and well-defined therapeutic indications—particularly in the treatment of periodontitis. With further expansion of application scope and in-depth investigation into their mechanisms of action, other types of dental-derived stem cells also hold promise for future clinical translation.
4 Comparison of the properties of dental stem cells with other sources of stem cells
4.1 Comparison of sources and access
Mesenchymal cells derived from different germ layers show different characteristics. In addition to DSCs, a wide range of MSCs sources have been extensively explored for regenerative medicine. These provide useful reference points for evaluating the potential of DSCs.
BMSCs are the most established and historically applied stem cell type, serving as a benchmark for osteogenesis and immunomodulation (Isobe et al., 2016). However, bone marrow aspiration is invasive, and cell quality declines with donor age (Brunello et al., 2022; Derubeis and Cancedda, 2004), which may affect their application in clinical translation. Compared with DSCs, BMSCs retain robust osteogenic ability but show weaker neurogenic and angiogenic potential (Arthur et al., 2008).
ADSCs can be easily harvested in large quantities with minimal invasiveness. They secrete abundant trophic and angiogenic factors, supporting soft tissue repair (Hutchings et al., 2020). Nevertheless, the performance of ADSCs in angiogenic gene expression, late osteogenesis, proliferation and migration is not as good as some DSCs, such as DPSCs (D’Alimonte et al., 2017; Jin et al., 2019).
UCMSCs are widely utilized allogeneic stem cells with robust differentiation potential (McElreavey et al., 1991). The abundance of these cells in umbilical cord tissue allows for relatively easy collection without harm to neonates. UCMSCs are considered more primitive than BMSCs and exhibit stem cell properties closer to embryonic stem cells (Yoon et al., 2013; Salehinejad et al., 2012). However, their immunomodulatory capacity declines with in vivo aging, which may limit their clinical application (Paladino et al., 2017).
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) possess unlimited proliferative and differentiation capacity (Takahashi et al., 2007). Dental-derived iPSCs have been successfully generated from DPSCs (El Ayachi et al., 2018), SHEDs, SCAPs (Yan et al., 2010), oral mucosal fibroblasts (Miyoshi et al., 2010), and gingival fibroblasts (Egusa et al., 2010). Notably, oral tissue-derived cells exhibit higher reprogramming efficiency than conventional human dermal fibroblasts (Yan et al., 2010). However, the reconstruction of periodontal supporting tissues using iPSCs remains challenging. In addition, concerns regarding tumorigenicity, genetic instability, and high production costs continue to hinder clinical translation (Takahashi et al., 2007; Nakagawa et al., 2014).
Overall, BMSCs, ADSCs, UCMSCs, and iPSCs each provide valuable insights and benchmarks for regenerative medicine, supported by varying levels of preclinical and clinical evidence. DSCs combine several practical advantages, including relatively non-invasive harvest and promising neurogenic and immunomodulatory properties. A clearer contrast is shown in Table 1. However, the characteristics and functions of various MSCs may be different due to donor age, site and other factors. Meanwhile, their long-term safety, scalability, and comparative efficacy remain to be established in large, well-designed clinical trials, especially for DSCs, which are almost only in early clinical research. Future research should therefore aim to directly compare DSCs with established stem cell sources across different disease models, to clarify whether DSCs can become broadly adopted in clinical practice.
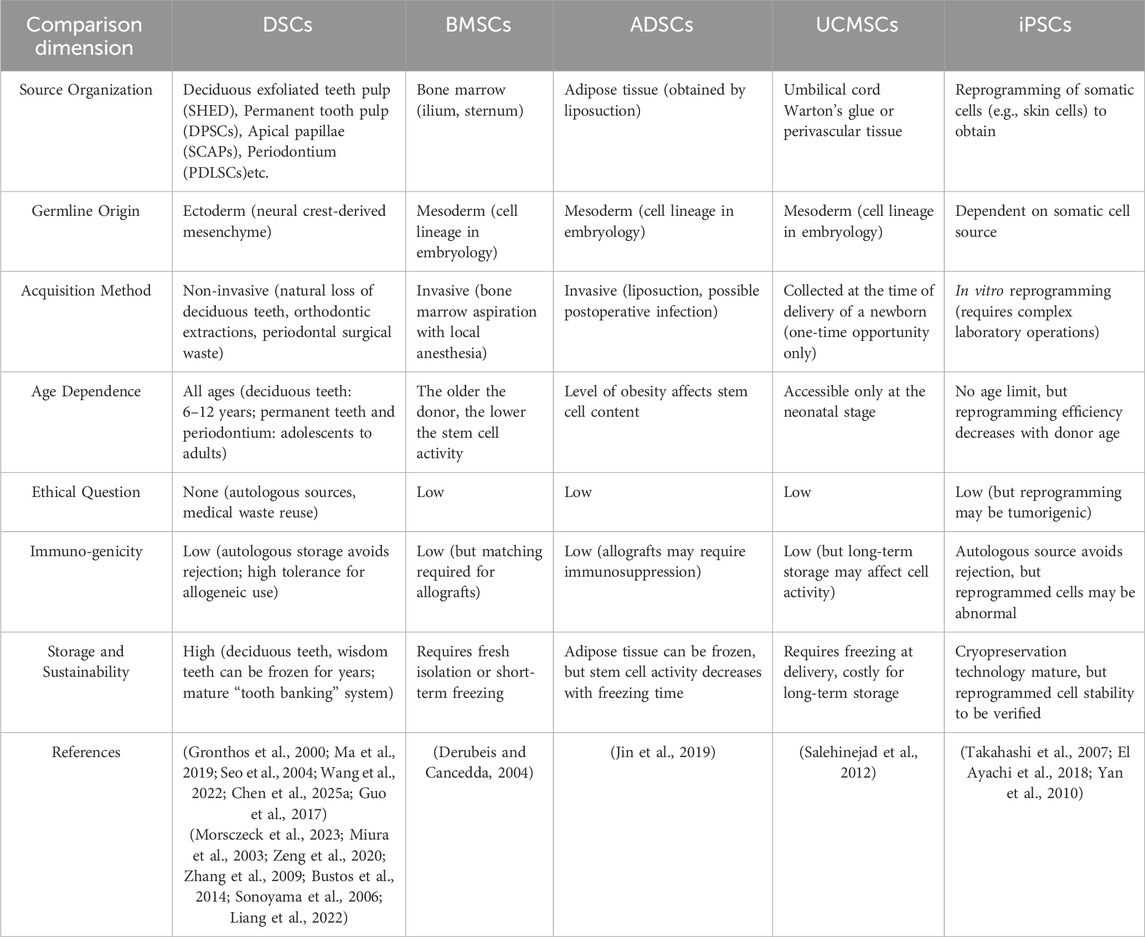
Table 1. Comparison of the origin and characteristics of stem cells from different tissues and germ layers.
4.2 Comparison of proliferation characteristics
Compared with other sources of stem cells, DSCs demonstrate enhanced self-renewal potential and maintain more stable proliferative properties under diverse microenvironmental conditions. First, DSCs exhibit better basal proliferative capacity, with their proliferative activity exceeding that of traditional MSCs in some studies. For example, GMSCs demonstrate greater expansion potential, with significantly higher proliferation rates and population expansion numbers compared to BMSCs (Zhang et al., 2009). Studies have shown that SCAPs possess shortened cell cycles and elevated expression of proliferation-related markers, such as proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and proliferation marker protein Ki-67 (Qu et al., 2021). The capacity of SHED to proliferate and migrate is greater than that of human UCMSCs (Yang et al., 2020). Nakamura et al. observed similar results by comparing SHEDs, DPSCs and BMSCs’ proliferation rates and gene expression profiles, it was found that SHEDs exhibited significantly higher proliferation efficiency than the other two (p < 0.05). This enhanced proliferation may be associated with upregulated expression of genes related to cell proliferation pathways in SHEDs, including various cytokines such as fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) (Nakamura et al., 2009). Comparing DPSCs and BMSCs from the same source, DPSCs had higher proliferation rates, mineralization potential, and clone formation. In addition, they had a higher number of stem/progenitor cells compared to the total cell population (Alge et al., 2010). In contrast to BMSCs that undergo proliferation decay after successive passages, DSCs maintain long-term proliferative stability. For example, both SHEDs and DPSCs retain stable expansion capacity at passage 15 (mean population doubling time [PDT]: 25–30 h), whereas BMSCs lose this capacity by passage 8. Beyond passage 8, BMSCs exhibit prolonged PDT (>40 h), flattened morphology, and significantly reduced Ki-67 expression (Shi et al., 2020).
Overall, DSCs performed better than BMSCs and UCMSCs in long-term passage and high proliferation efficiency, and this stability gives them an advantage in regenerative medicine where long-term cell expansion is required. However, the current study still has the effect of donor differences and heterogeneity of culture conditions, and further standardization is needed.
4.3 Comparison of immunomodulatory properties
DSCs have low immunogenicity, and existing studies have confirmed that DSCs used in rats did not show immune rejection, and can significantly improve tissue regeneration and repair capacity (Peishan et al., 2023). Moreover, due to their strong immunomodulatory properties, DSCs can inhibit allogeneic transplantation-associated T lymphocytes through direct cell-to-cell contact or through secretion of cytokines or soluble factors such as immunoreceptors or extracellular vesicles (Liu et al., 2015) (Figure 2). This excellent property may be related to the various bacterial flora in the oral cavity and the frequent exposure to inflammatory responses (Wada et al., 2009; Paganelli et al., 2021).
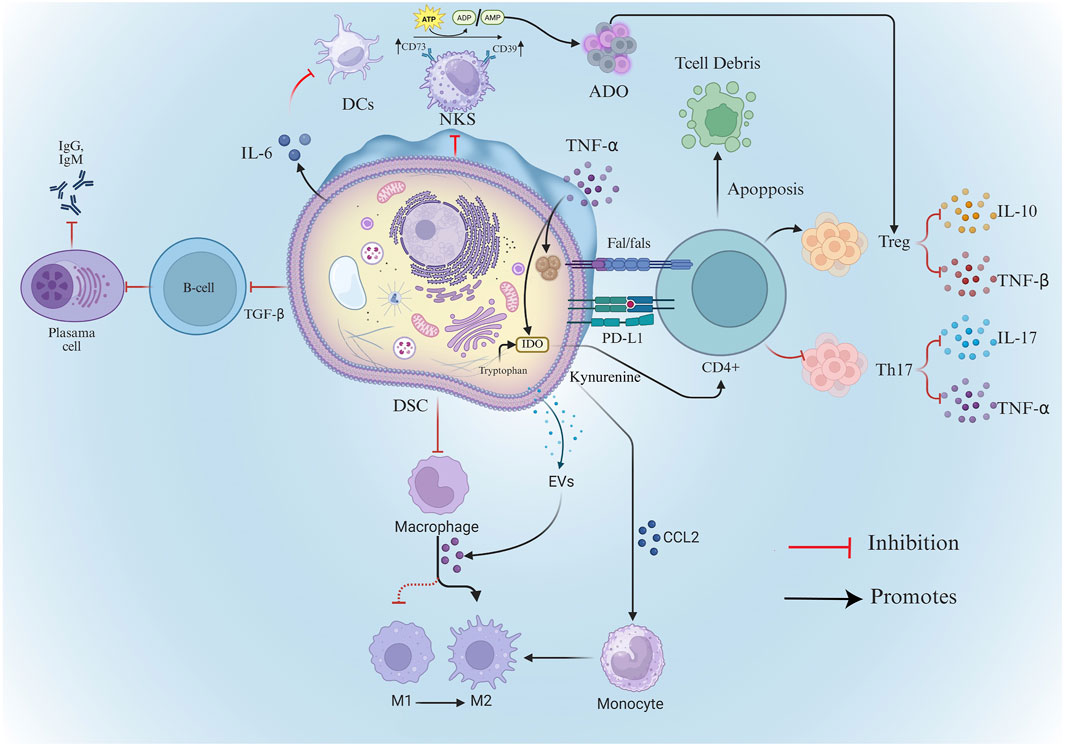
Figure 2. Mechanisms of DSC’s immunomodulatory capacity. DSCs, Dental Stem Cells; Treg, Regulatory T Cells; TGF-β, Transforming Growth Factor-beta; TNF-α, Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha; DCs, Dendritic Cells; ADO, Adenosin; ATP, Adenosine Triphosphate; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; AMP, Adenosine monophosphate; Evs, extracellular vesicles; NKs, Natural Killer Cell; IDO-Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase.
Similar to MSCs from other tissue sources, DSCs secrete immunomodulatory factors including prostaglandin E2 (PGE-2), indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) and TGF-β. These factors regulate innate/adaptive immunity and complement systems, enabling DSCs to suppress excessive inflammation and maintain tissue homeostasis (Lee et al., 2016; Magalhães et al., 2021). For instance, GMSCs upregulate immunosuppressive factors (e.g., IDO, iNOS [inducible nitric oxide synthase], COX-2 [cyclooxygenase-2]) and specifically inhibit peripheral blood lymphocyte proliferation in response to inflammatory cytokines (Zhang et al., 2009; Ding et al., 2010a).
However, in contrast to MSCs from other sources, DSCs exhibit distinct expression patterns of immunomodulatory factors. For instance, SCAPs secrete higher levels of chemotactic and metabolic regulatory proteins than BMSCs (Yu et al., 2016). Similarly, compared with BMSCs, DPSCs can secrete more immunosuppressive factors (e.g., TGF-β1, HGF, IL-10, and IL-13), and have a stronger inhibitory ability against activated T cells (Matsumura-Kawashima et al., 2021). Separately, the conditioned medium from stem cells of human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHEDs-CM) was found to contain a higher level of the ectodomain of sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin-9 (ED-Siglec-9) than BMSC-CM. This specific factor demonstrated significant therapeutic efficacy in a mouse model of autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inducing anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages (Shimojima et al., 2016). And compared with BMSCs-CM and ADSCs-CM, SHEDs-CM had higher levels of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) expression, which plays an important role in SHEDs-CM treatment of myocardial infarction after ischemia-reperfusion, especially in terms of improvement of infarct size and inhibition of cardiomyocyte apoptosis (Yamaguchi et al., 2015).
Secondly, DSCs and BMSCs exhibit divergent abilities in regulating T cell differentiation (Demircan et al., 2011). For example, DSCs can mediate immunoregulatory responses through T cell death. Similar to BMSCs, DPSCs can activate the caspase cascade through the binding of Fas and FasL. This activation leads to T cell apoptosis, which subsequently stimulates macrophages to produce high levels of TGF-β. The increased secretion of TGF-β enhances immune tolerance (Akiyama et al., 2012) and mitigates inflammation-associated tissue damage. Notably, this mechanism has been shown to improve therapeutic efficacy in a mouse model of colitis (Zhao et al., 2012).
DSCs can promote T cell differentiation. DPSCs can induce immune tolerance by increasing the number of local regulatory T cells (Treg) in vitro and in a mouse allogeneic skin graft model also (Hong et al., 2019). In addition to promoting Treg differentiation, DPSCs also influence the polarization of CD4+ T cells through paracrine mechanisms. Exosomes—small extracellular vesicles (EVs) secreted by stem cells—have emerged as key mediators of this process. These nanosized vesicles carry bioactive molecules such as proteins, lipids, and RNAs, enabling targeted immunoregulatory effects. Notably, exosomes derived from DPSCs (DPSCs-Exo) exhibit stronger immunomodulatory capacity compared to those from BMSCs. They suppress the differentiation of CD4+ T cells into pro-inflammatory Th17 cells, reduce the secretion of IL-17 and TNF-α, and simultaneously promote the polarization of CD4+ T cells toward the Treg phenotype. This exosome-mediated pathway contributes significantly to establishing immune tolerance and controlling inflammation (Lujun et al., 2019).
Finally, DSCs demonstrate notable distinctions in their immunomodulatory mechanisms compared to MSCs from other sources. DSCs expressed more CD39 than BMSCs and were able to produce more adenosine (ADO) from adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which inhibited the proliferation of CD3+ T cells and promoted the generation of CD4+CD25+FoxP3+CD39+CD73+ Tregs. This study demonstrated that DSCs were able to utilize the adenopurinergic pathway as an immunomodulatory mechanism, which was more effective than BMSCs (Poblano-Pérez et al., 2023). PGE-2 was found to play an important role in PDLSC-mediated immunomodulation and periodontal tissue regeneration in a small porcine model of periodontitis (Ding et al., 2010b). Similar to them, GMSCs can significantly inhibit contact hypersensitivity (CHS) by suppressing mast cell pro-inflammatory cytokine expression at source through PGE2 (Su et al., 2011). TGF-β eliminates IgM and IgG production through allogeneic activation of responder B lymphocytes. TGF-β secreted by DPSCs has been shown to be a major factor in inducing immunosuppression in acute allogeneic immune responses (Kwack et al., 2017) and can increase CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Hong et al., 2019) and inhibit the proliferation of allogeneic lymphocytes (Hossein-Khannazer et al., 2019). Furthermore, PDLSCs suppress B cell activation via PD-1/PD-L1 ligand-receptor interactions during cell-cell contact. When co-cultured with normal B cells, it can inhibit their proliferation, differentiation, and migration, and reduce the secretion of IgM and IgG (Liu et al., 2013). GMSCs additionally reduce dendritic cell (DC) and mast cell (MC) infiltration, consequently suppressing production of multiple inflammatory cytokine (Su et al., 2011).
In contrast, the immunomodulatory mechanisms of BMSCs and ADSCs are more dependent on IDO and PGE-2, while DSCs also show special adaptability derived from the oral microenvironment (Table 2). This suggests that MSCs from different sources may have differential applicability in specific disease models.
However, these experiments based on simplified or static conditions may not fully replicate the complexity of the in vivo immune microenvironment. Moreover, the heterogeneity among different types of DSCs suggests that their immunomodulatory capabilities may be inconsistent, and the molecular basis for these differences remains unclear. In addition, although paracrine signaling through EVs is considered an important mechanism of immune regulation, few studies have systematically compared EVs composition or activity of DSCs from the same individual or from different sources. Therefore, future studies should focus on standardising in vitro experimental conditions and elucidating the signaling pathways responsible for DSCs-mediated immune regulation to more accurately characterize the immune properties of DSCs.
4.4 Comparison of osteogenic capacity
Multiple studies demonstrate the osteoregenerative capacity of DSCs (Omori et al., 2015; Ge et al., 2012a). This is dependent on its promotion of osteogenesis, inhibition of osteoclastogenesis, and regulation of inflammation during bone healing.
Firstly, the excellent osteogenic ability of DSCs is due to the high expression of osteogenic genes. ALP is well-known critically involved in osteogenesis. Alge et al. compared matched donor-derived DPSCs and BMSCs, revealing significantly higher ALP activity in DPSCs (Alge et al., 2010). SHEDs-CM induces BMSCs and osteoblast precursor cells (MC3T3-E1 cells) osteogenic differentiation with higher levels of mRNA expression of osteogenic differentiation markers (ALP, OCN, Runx2) (Kunimatsu et al., 2022). Furthermore, DSCs can secrete higher levels of VEGF (Kushiro et al., 2021). VEGF modulates osteogenic signaling, stimulates osteoblast chemotaxis/differentiation, and promotes angiogenesis in bone defects, thereby facilitating osteogenesis (Tarkka et al., 2003). SCAPs maintain proliferative stability under hypoxia while upregulating osteogenic/angiogenic genes. Notably, SCAPs enhance sustained VEGF-A production (Vanacker et al., 2014). Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)-mobilized DPSCs express higher VEGF-A than BMSCs and ADSCs (Murakami et al., 2015).
Secondly, DSCs help to reduce bone mass loss by inhibiting osteoclast activity. OPG is a well-established inhibitor of osteoclast differentiation. Kanji et al. demonstrated that DPSCs suppress osteoclastogenesis through OPG secretion and AKT signaling inactivation in myeloid cells (Kanji et al., 2021). SHEDs-CM contains 2.8-fold higher OPG levels than BMSCs-CM. Additionally, ED-Siglec-9—a characteristic component—more potently inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Combined with anti-inflammatory properties, ED-Siglec-9 demonstrates significant therapeutic efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) mouse models (Ishikawa et al., 2016). Furthermore, Lu et al. (Lu et al., 2023) revealed that PDLSCs-derived exosomes suppress osteoclastogenesis via the miR-31–5p/eNOS signaling pathway in vitro. According to previous studies, GMSCs-derived EVs significantly attenuate inflammatory bone loss and reduce TRAP-positive osteoclasts in periodontitis models. This effect is mediated by exosomal miR-1260b, which inhibits RANKL signaling via Wnt5a suppression, thereby blocking osteoclastogenesis (Nakao et al., 2021).
Finally, relying on the powerful immunomodulatory ability of DSCs mentioned earlier, it helps them to better repair bone defects. In addition to the immunological properties already mentioned earlier, in terms of osteogenesis, DPSCs-CM contains elevated levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines—including IL-10, IL-13, and TGF-β1—compared to BMSCs-CM (Ogata et al., 2021; Bousnaki et al., 2022). Moreover, SHEDs rescue dysfunctional BMSCs by suppressing IL-17 in recipient bone marrow, restoring osteoblast-osteoclast equilibrium. In addition, Ge et al. demonstrated that GMSCs maintain stable proliferation and trilineage differentiation capacity under inflammatory conditions (Ge et al., 2012b). Similarly, TNF-α exposure minimally inhibited the osteogenic potential of GMSCs compared to other DSCs (Tian et al., 2022). But meanwhile, DSC properties exhibit microenvironment-dependent heterogeneity (Zhou et al., 2020). Comparison of the properties of PDLSCs from healthy and “inflamed” patients revealed that the latter showed greater migratory potential and higher proliferative capacity, but a reduced capacity for osteogenic differentiation (Tang et al., 2016). It has been suggested that this may be related to the upregulation of Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1) in inflamed periodontal tissues, which activates the negative feedback regulation of the BMP2/Smad signaling pathway, consequently impairs the osteogenic capacity of PDLSCs, and accelerates bone resorption in alveolar bone (Lin L. et al., 2023).
DSCs, particularly DPSCs and PDLSCs, exhibit robust osteogenic differentiation potential, generally comparable to BMSCs (Zhao et al., 2023). ADSCs also display osteogenic ability but often generate less mineralized tissue (Truchan et al., 2025), while UCMSCs contribute to bone repair primarily via paracrine effects rather than direct osteogenesis (Yang X. et al., 2024). Overall, BMSCs remain the benchmark for osteogenic studies, yet DSCs offer unique tissue-specific compatibility in craniofacial contexts, which may facilitate improved integration and regeneration. In several studies, DSCs exhibit comparable or even superior mineralization capacity to BMSCs, yet these observations are not always consistent across research groups, suggesting potential methodological bias or variation in osteoinductive stimuli. Moreover, the intrinsic mechanisms governing osteogenic differentiation in DSCs remain incompletely understood. For example, signaling pathways such as BMP/Smad, Wnt/β-catenin, and MAPK have been implicated, but the relative contribution of each pathway may differ among DSCs types. Additionally, most in vitro assays rely on short-term mineral deposition as the endpoint, which may not accurately reflect long-term matrix maturation and biomechanical stability. To strengthen the evidence base, future studies should actively explore the relevant osteogenic regulators that determine the lineage-specific differentiation of DSCs.
4.5 Comparison of neurological capacity
DSCs derive from the neural crest—an ectodermal progenitor population that generates peripheral nervous system cells (Martens et al., 2013). Because of its homology with nerve cells, DSCs exhibit neural characteristics including neural marker expression, neurotrophic factor secretion, and differentiation into functional neurons (Arthur et al., 2009; Király et al., 2011). Naive DPSCs express neural markers including nestin, neurofilaments, vimentin, S100, and βIII-tubulin (Karaöz et al., 2010; Kerkis et al., 2006). Increased expression of class III b microtubulin (TUBB3) and microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) in RT-PCR compared to BMSCs confirms that DPSCs and SHEDs exhibit neurogenic potential (Isobe et al., 2016). Meanwhile, the synergistic immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties of DSCs (Cooper et al., 2019) enhance their suitability for neural tissue engineering over other MSCs.
DSCs promote neuronal growth, survival, and protect neuronal cells through higher levels of neurotrophic factors, primarily comprising brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), nerve growth factor (NGF), and neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) (Qiu et al., 2025). G-CSF-mobilized DPSCs exhibit elevated neurotrophic factor expression and enhanced trophic effects on cell migration/apoptosis versus BMSCs or ADSCs (Murakami et al., 2015). Apical complex-derived DPSCs express higher NT-3 and NT-4 in conditioned media than dental apical complex cells (DACC) during odontogenic differentiation (Joo et al., 2018). In particular, DPSCs-CM was able to induce greater neurite growth in neuroblastoma. Comparative analysis revealed DPSCs secrete 3- to 10-fold higher neurotrophic factors (e.g., NGF, BDNF) than BMSCs or ADSCs in co-culture systems, as quantified by RT-qPCR, microarray, and ELISA (Mead et al., 2014). In other study, SHEDs exhibit better neural process outgrowth promotion compared to UCMSCs (Yang et al., 2020). Sakai et al. demonstrated therapeutic efficacy of DPSCs and SHEDs transplantation in rat spinal cord injury models (Sakai et al., 2012). Additionally, Tomokiyo et al. revealed that hPDLSC-derived neural crest cells (NCCs) exhibit greater pluripotency than NCCs differentiated from foreskin fibroblast-iPSCs (Tomokiyo et al., 2017).
To sum up, SHEDs and DPSCs demonstrate better neurogenic potential compared with other MSC sources, reflecting their neural crest origin. They express neuronal markers, promote neurite outgrowth, and support angiogenic processes, which collectively favor neurovascular regeneration. In contrast, BMSCs and ADSCs show more limited neurogenic differentiation (Isobe et al., 2016), and UCMSCs mainly exert neuroprotective roles through trophic and immunomodulatory factors (Yang et al., 2020). Thus, DSCs provide a distinct advantage for neuroregenerative applications within dental and craniofacial tissues. However, as most studies on the neurogenic potential of DSCs rely on various animal models, significant gaps remain in our understanding of the underlying mechanisms. For instance, although DPSCs and SHEDs have been shown to differentiate into neural-like cells in vitro, their ability to integrate into existing neural networks in vivo is still uncertain, highlighting the need for further research.
Figure 3 shows the radar map of the characteristics of MSCS from each source.
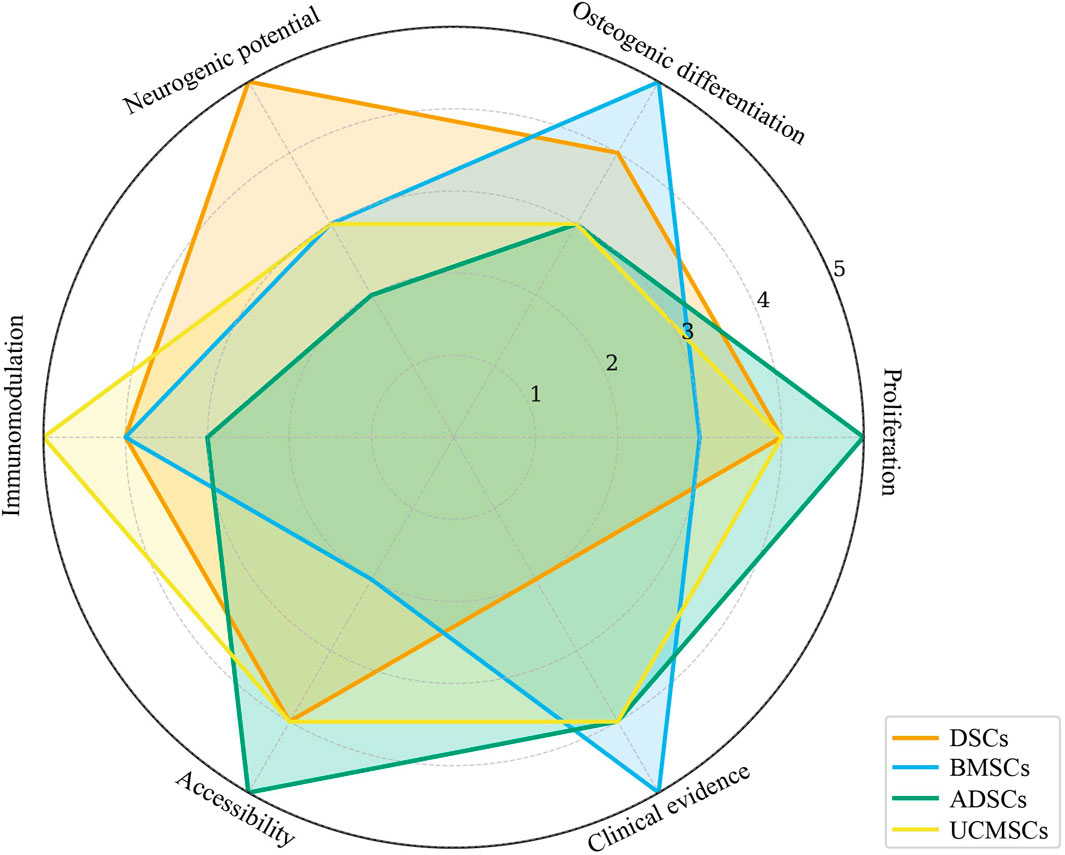
Figure 3. Radar chart summarizing key biological properties of MSCs from different sources. DSCs, Dental Stem Cells; BMSCs, Bone Marrow Stem Cells; ADSCs, Adipose-derived Stem Cells; UCMSCs, Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells.
5 Advantages of dental stem cells in the treatment of related diseases
Due to their excellent properties, DSCs can be used to treat a variety of diseases, including immune-related diseases, osteogenesis diseases, nervous system diseases and oral diseases (Figure 4).
Figure 4. DSCs have been used in the treatment of a variety of diseases SLE, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
5.1 Immunomodulation and immune-related diseases
Most immune disorders result from dysregulated immune responses causing imbalance and chronic inflammation. These include Sjögren’s syndrome, SLE, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and diabetes mellitus (Shoda et al., 2023). Current treatments for these diseases rely on the use of non-antigen specific, broad-spectrum immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory compounds, but these drugs can also impair the normal immune response and even increase the risk of infection and malignancy (Montaño et al., 2021). DSCs exhibit low immunogenicity and potent immunomodulatory capacity, enabling therapy for diverse immune-mediated diseases. DPSCs-CM ameliorates Sjögren’s syndrome by suppressing Th17 differentiation and enhancing Treg generation in splenic tissue. Compared to BMSCs, DPSCs demonstrate better T cell inhibition and anti-apoptotic effects, improving salivary secretion in Sjögren’s syndrome (Matsumura-Kawashima et al., 2021). The pioneering clinical study demonstrated that stem cells from SHEDs transplantation improves glucose metabolism and islet function in type 2 diabetes patients (Li W. et al., 2021). On the one hand, stem cells can be induced to differentiate into insulin-like cells, and on the other hand, stem cells can be used to modulate the immune response against pancreatic antigen tolerance (Xu et al., 2020). GMSCs inhibit allergic responses and enhance tissue regeneration/wound healing, offering novel therapies for autoimmune diseases including RA and IBD (Tian et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2019).
In addition, BMSCs from SLE patients exhibit impaired proliferation, increased senescence/apoptosis, and reduced immunosuppressive capacity (Sun et al., 2007). Conversely, Yamaza et al. demonstrated successful application of SHEDs in SLE mouse models. SHEDs reduced peripheral Th17 cells, restored bone trabecular structure, and inhibited osteoclast activity, collectively ameliorating SLE pathology (Yamaza et al., 2010). Therefore, SHEDs may serve as new seed cells for the treatment of SLE patients. Meanwhile, DPSCs demonstrate enhanced efficacy against severe COVID-19 pneumonia compared to other stem cell sources (Zayed and Iohara, 2020).
Although DSCs exhibit strong immunomodulatory properties, and in vitro studies have shown promising results, the reported therapeutic effects vary. Additionally, most studies have been conducted on small animal models, which may limit the generalizability of these findings to human clinical settings. For example, some studies focus on inflammatory conditions in rodents, but the results may not fully reflect the complexity of the human immune system. Future research should aim to use animal models that more closely resemble human lineage, larger sample sizes, and attempt to include multicenter clinical trials to better assess the immunomodulatory potential of DSCs.Although in vitro studies have shown promising results, most evidence remains at the animal level. Most of the existing clinical trials are phase I/II, and the sample size is limited, which is not enough to support widespread use.
5.2 Treatment of bone defects
Alveolar and cranial bone defects typically arise from congenital malformations, trauma, or tumor resection (Lin et al., 2024). Current treatments mainly include the use of autologous bone grafts (Mahardawi et al., 2023) and allogeneic bone and synthetic material grafts, but their usual limitations such as insufficient autologous bone volume, allogeneic rejection, or suboptimal osteoinductive capacity (Ashfaq et al., 2024). Stem cell advancements offer novel strategies for bone regeneration therapies.
As mentioned previously, DSCs have good osteogenic properties. Compared with ADSCs, UCMSCs, and amniotic membrane mesenchymal stem cells (AMSCs), DPSCs have the best therapeutic effect on postmenopausal osteoporosis, and can preserving bone mass, This advantage may stem from DPSCs’ unique capacity to modulate Th17/Treg balance and macrophage M1/M2 polarization (Li et al., 2024). In addition, Yu et al. compared the treatment of critical-size cranial defects in immunodeficient rats with BMSCs and PDLSCs and found that the PDLSCs had a stronger bone regeneration ability (Yu et al., 2014). Besides, in a study in 2009, DPSCs isolated from the patient’s maxillary third molar then co-cultured with collagen scaffolds, and a significant increase in the amount of bone repair in the extraction sockets was observed at 3 months postoperatively compared with that in the control group (d’Aquino et al., 2009). Three-year follow-up revealed denser, more homogeneous vascularized bone regeneration in DPSC-collagen scaffold treated sites, confirming the long-term efficacy of DPSCs-mediated osteoinduction (Giuliani et al., 2013).
In preclinical and clinical studies, BMSCs have consistently shown efficacy in bone defect repair and remain widely applied in alveolar cleft and craniofacial bone augmentation (Bajestan et al., 2017; Luo et al., 2022). DSCs have demonstrated comparable outcomes in periodontal and alveolar regeneration, with additional benefits in microenvironmental matching. ADSCs have been explored for periodontal bone repair but generally yield fewer stable outcomes than BMSCs or DSCs (Truchan et al., 2025). UCMSCs-based therapies show promise through immunomodulation and angiogenesis but require further validation. Together, these findings suggest DSCs hold a context-specific advantage for oral and maxillofacial bone regeneration, complementing the broader clinical experience of BMSCs.
5.3 Diseases of the nervous system
In recent years, various types of neurological diseases are highly prevalent, such as: Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, spinal cord injury and peripheral nerve injury. Advances in stem cell therapy have increased the potential for treating neurological diseases with stem cells (Ibarretxe et al., 2012). Although neural stem cells (NSCs) can be differentiated into neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes and help to delay neuronal or other neural cell damage by using self-renewal and neural differentiation (Stenu et al., 2015), their procurement from human brain tissue remains challenging and invasive. Consequently, DSCs—owing to their homology with NSCs—have emerged as promising candidates for neurodegenerative disease research.
Several animal studies demonstrate the reparative potential of DSCs in peripheral and central nerve injuries. For example, DPSCs, SHEDs, and SCAPs show therapeutic efficacy in spinal cord injury (Zhou et al., 2023), Alzheimer’s disease (Howlader et al., 2024), Parkinson’s disease (Chen et al., 2024), stroke (Miao et al., 2024), etc. Sharma et al. report that DPSCs may have a better therapeutic potential for Parkinson’s disease than BMSCs due to their better propensity for neural differentiation and neuronal regeneration capacity (Sharma et al., 2022). And because it may be able to transform into dopaminergic neuronal cells under hypoxic conditions in vitro, it showed better behavioral improvement in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease (Greene, 2009).
Compared with BMSCs, intravenous transplantation of DPSCs resulted in a similar state of functional repair but reduced infarct volumes observed in a rat stroke model (Song et al., 2017). DPSCs overexpressing stem cell growth factor can modulate the inflammatory response and blood-brain barrier permeability during the acute phase of stroke, increasing their neuroprotective effects and preventing brain injury after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) (Sowa et al., 2018). Wu et al. compared the therapeutic effects of DPSCs and PDLSCs on stroke by using PKH26 staining to tracer the migration of stem cells, and found that the latter showed a more pronounced PKH26 fluorescence labeling signal and more significant efficacy in promoting neurological recovery (Wu et al., 2020). DPSCs-Exo attenuated cerebral edema, cerebral infarction and neurological impairment in cerebral I/R mice, and it significantly inhibited I/R-mediated expression of TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB expression and increased anti-inflammatory levels by inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway (Li S. et al., 2021). In addition, because of the higher expression level of neurotrophic factors in DPSCs, their co-culture with retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) significantly promoted RGCs survival and neurite regeneration, and the transplantation of DPSCs induced a more pronounced promotion of axon regeneration and neuroprotective effects compared with BMSCs (Mead et al., 2017).
DSCs-based therapies, particularly those employing SHEDs and DPSCs, have shown favorable results in models of nerve regeneration, demonstrating restoration of vascularized and innervated tissues. BMSCs and ADSCs have also been tested in neurodegenerative disease models but with limited differentiation capacity, relying more on trophic support. UCMSCs exhibit indirect benefits through secretion of neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory mediators. While current clinical evidence remains preliminary, DSCs emerge as an attractive candidate for future neuroregenerative therapies in dental and broader neurological contexts. But the neurorepair efficacy observed in animal models may not fully reflect outcomes in humans. The complexity of the nervous system, along with variations in experimental conditions, such as the use of different neurotrophic factors and scaffold materials, further complicates the translation of these results. Therefore, more reliable studies, particularly clinical trials involving human patients, are needed to evaluate the true neurogenic potential of DSCs in humans.
6 Unique benefits of oral disease treatment
Owing to their inherent homology and microenvironmental niche compatibility with oral tissues, DSCs have been the most extensively studied for the treatment of oral diseases. This section will focus on their specific potential and clinical progress in oral tissue regeneration. There have been many animal experiments using MSCs to treat oral diseases, and representative ones in recent years are shown in Table 3.
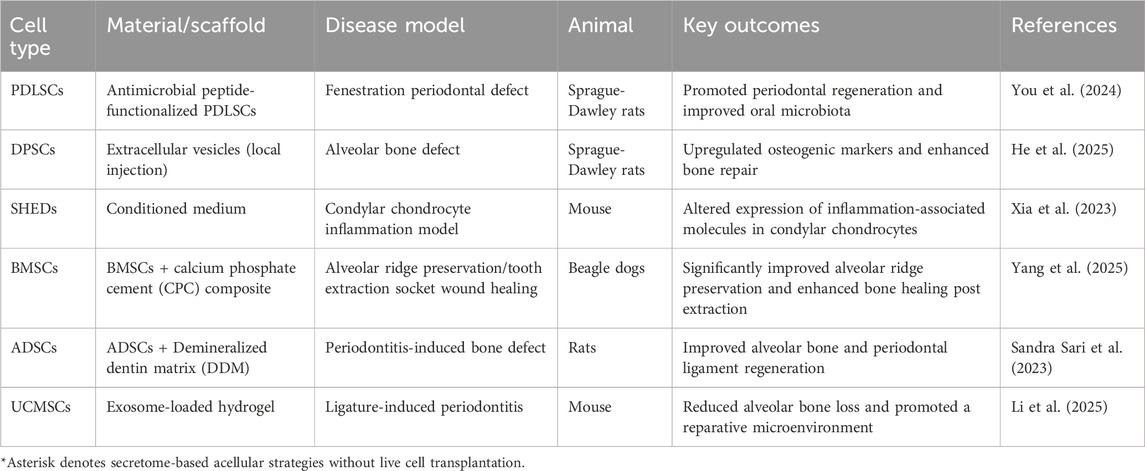
Table 3. Summary of recent animal studies using MSCs in oral and maxillofacial disease models (2023–2025).
6.1 Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a disease of the oral cavity that has become prevalent in recent years. When treating periodontitis, in addition to the mentioned previously regeneration of alveolar bone, it is necessary to focus on the specific microenvironmental factors within the patient’s mouth. When inflammation is caused by pathologic factors, the pH value in the oral cavity may decrease, leading to a decrease in the osteogenic capacity of BMSCs and DPSCs (Massa et al., 2017). And the regenerative capacity of stem cells will be reduced in the case of localized inflammation. Some researchers tried to insert recombinant human IGFBP5 protein (rhIGFBP5) into PDLSCs to enhance their regenerative ability, which can improve higher osteogenic differentiation ability in an animal model of inbred male minipigs (Han et al., 2017). Meanwhile, the osteogenic capacity of stem cells can be enhanced by co-culturing different stem cells, such as co-culturing BMSCs with PDLSCs to mimic 3D bone tissues in vitro, which has stronger performance than a single species of stem cells (Zhang et al., 2016). BMSCs derived from the maxilla can also enhance the osteogenic capacity of PDLSCs in vitro (Jin et al., 2016).
In addition, the local inflammatory state can also be regulated by appropriate scaffold design, for example, using calcium alginate hydrogel, into which PDLSCs and BMSCs were incorporated, and both types of stem cells showed good osteogenic differentiation and reduced the degree of inflammation of local tissues in New Zealand rabbits in vivo (Chen et al., 2017). Chen et al. conducted the first study of DSCs in clinical trials, a randomized trial using autologous PDLSCs to treat periodontal intraosseous defects, which validated the safety of PDLSCs in clinical applications (Chen et al., 2016). In addition, the phase III clinical trials of DPSCs injection (Liu et al., 2025) and the recently approved human clinical trials of DFSCs injection in the targeted treatment of periodontitis further demonstrated the promising efficacy of DSCs in the treatment of periodontitis.
6.2 Gingival recession
Gingival recession is a common oral disease with a high prevalence. It may be caused by several factors, including aggressive brushing, smoking, concentrated occlusal stress, and orthodontic treatment in older adults. GMSCs exhibit therapeutic advantages for gingival recession owing to tissue homology. GMSCs produce and secrete higher amounts of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA)–expressing small EVs than skin MSCs. These sEVs accelerate the healing of gingival wounds (Kou et al., 2018). Sanchez et al. combined the treatment of localized gingival recession with the addition of stem cells by inoculation of autologous GMSCs into an allogenic collagen matrix with a coronal late-stage flap inoculated, and found that wound healing was better with the addition of stem cells, and that inflammation and postoperative complications associated with gingival surgery were greatly reduced (Sanchez et al., 2022).
6.3 Pulp regeneration
When a tooth has irreversible pulpal inflammation due to dental caries or when the pulp is exposed due to trauma, pulpotomy or endodontic treatment is required, but these treatments result in inactivation of the pulp that supplies nutrients to the tooth, which tends to lead to darkening of the color of the tooth in later stages as well as to increased brittleness of the tooth and the risk of fracture (Xie et al., 2021). Therefore, there is an urgent need to find a way to help reestablish active and functional pulp regeneration.
SHEDs and DPSCs have strong angiogenic capacity and neurogenicity, and are for pulp regeneration excellent seed cells due to their homology with pulp tissue (Yang N. et al., 2024; Chen et al., 2021). Xuan et al. implanted ex vivo-expanded autologous SHEDs into pulp necrosis patients, observing regeneration of three-dimensional pulp structures containing odontoblasts, vasculature, and neural networks (Xuan et al., 2018). However, the survival time of DSCs in the root canal is limited. In recent years, advances in biomaterials enable stem cell delivery via scaffold systems for enhanced pulp regeneration. For instance, DPSCs seeded in thermoresponsive hydrogels and implanted into human root canals subcutaneously transplanted in immunodeficient mice formed vascularized pulp-like tissues within 6 weeks. Odontogenic differentiation occurred at dentin-contact sites, with mineralized centers containing CD31+ endothelial cells (Itoh et al., 2018). Prescott et al. implanted DPSCs with gelatin scaffolds containing dentin matrix protein-1 (DMP-1) into dentinal cavities of veneers in nude mice, demonstrating pulp-like tissue formation in cavities after 6 weeks (Prescott et al., 2008). Lu et al. cultured SHEDs in odontogenic medium (OM) within photocrosslinkable gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels, observing odontogenesis in subcutaneously grafted root sections. After 8 weeks, mineralized tissue showed elevated dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP) and DMP-1 levels versus controls (Lu et al., 2024).
A clinical trial study on the feasibility of using DPSCs to replace infected pulp tissue has been conducted in Japan in 2014, which utilized autologous DPSCs to treat irreducible pulpitis in autogenous teeth, and patients had no adverse effects and there was restoration of pulp vitality after 25 weeks (Nakashima and Iohara, 2014). There is also a study in the United States using autologous SHEDs to treat pulp and apical tissues in patients with pulp necrosis in young permanent teeth, focusing on evaluating its efficacy and safety.
6.4 Dental reconstruction
Tooth regeneration presents a multifaceted challenge, primarily requiring coordinated regeneration of the alveolar bone-periodontium complex and functional restoration of the pulp-dentin unit. Some studies have seeded on PDLSCs and DFSCs on material scaffolds and applied them to tooth regeneration models in animals, and found that root-periodontal-like tissues were formed (Lu et al., 2024; Guo et al., 2012). Similarly, iPSCs and PDLSCs transplanted into periodontal defect models regenerate periodontal ligament, odontoblasts, and alveolar bone (Chen et al., 2025b). This approach effectively repairs periodontal tissue defects (Seo et al., 2004). And the regenerative aspects of the first two have been described previously.
In addition to this, the utilization of DSCs to regenerate the non-regenerable enamel after abrasion is of great research significance. Kim et al. developed a method in which direct co-culture of hESCs/hiPSCs with Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath/epithelial rests of Malassez successfully generated dental epithelial-like stem cells. Additionally, the iPSC line co-cultured with DPSCs showed increased expression of amelogenic and odontogenic genes. (Kim et al., 2020). CD24a+ SCAP can regenerate functional dentin and neurovascular-like structures in the tooth roots (Chen et al., 2020). In addition to this, iPSCs can be used for the reconstruction of enamel that is theoretically non-regenerative after abrasion, and the ability to differentiate iPSCs into enamel-forming cells was first reported by Arakaki et al. (Arakaki et al., 2012). Subsequent studies show that iPSCs cultured in ameloblast serum-free conditioned medium with BMP-4 differentiate into ameloblast- and odontoblast-like cells (Liu et al., 2016). Thus, iPSCs offer a viable pathway for enamel regeneration.
In general, different sources of stem cells have their own advantages in the treatment of diseases. DSCs have shown unique potential in neurological, immune and oral diseases, while BMSCs and ADSCs have accumulated more clinical experience in bone defect repair. Future studies need cross-source systematic comparison and long-term follow-up to promote the precise and individualized application of stem cell therapy.
7 Conclusion and prospects
DSCs have many advantages in addition to the various types of excellent properties mentioned previously. DSCs can be stored for long periods of time. With the invention of storage solution for isolated teeth, treated isolated teeth can be stored at 4 °C for 120 h and can be isolated and cultured to produce active and proliferative DPSCs (Perry et al., 2008). And with the development of cryoprotective solution, to a certain extent, it provides a basis for the long-distance transportation of isolated teeth. Moreover, with the establishment of “tooth banks” in developed countries such as Japan, the United States and Norway, cell sources can be provided for basic research and clinical application of tooth-derived stem cells. More surprisingly, Arora et al. (Arora et al., 2009) showed that the storage cost of SHEDs bank is about 1/3 of that of umbilical cord blood cell bank, which is an important advantage of tooth-derived stem cell bank over other sources of stem cell bank. Though, comparative evidence indicates that while DSCs display strong neurogenic, angiogenic, and immunomodulatory capacities, other MSC sources retain established advantages, particularly in osteogenesis and systemic immune disorders. Accordingly, no single MSC source can be regarded as universally optimal, and their use should be tailored to specific clinical contexts.
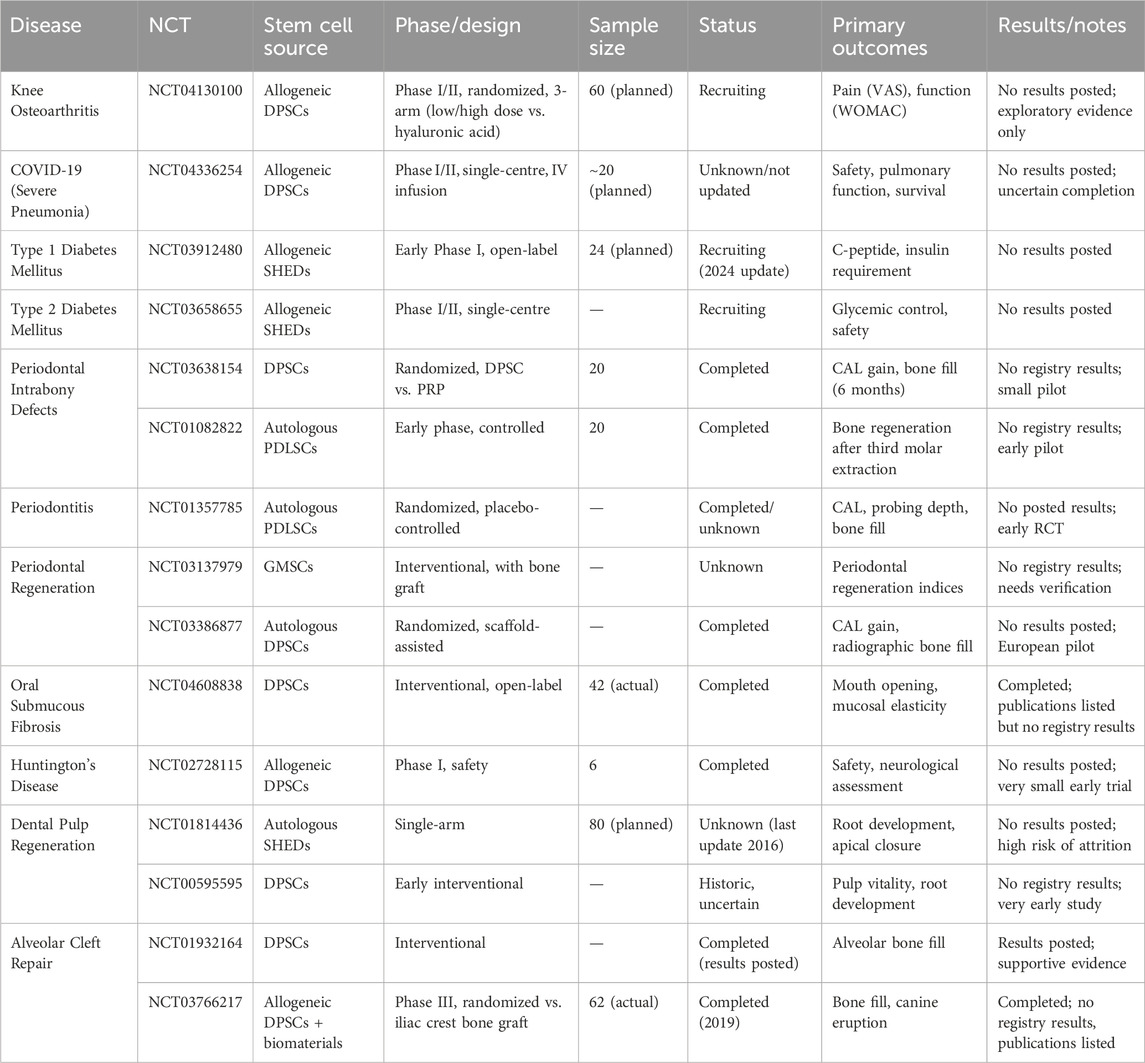
Despite encouraging findings, the translation of MSC-based therapies remains constrained by donor heterogeneity, lack of standardized isolation and expansion protocols, and limited long-term safety and efficacy data. As several clinical trials have been registered on www.clinicaltrials.gov. (Table 4), but most clinical studies remain at early phases (I/II) with small cohorts and non-uniform outcome measures. And simultaneously, regulatory divergence across countries further complicates clinical adoption. In the long run, we still need some reliable industry norms to ensure the institutional standardization and standardization of the process of obtaining, producing, and using DSCs (Miguita et al., 2017).
Meanwhile, there is increasing evidence that DSCs have functional differences in osteogenic differentiation, proliferation rate and angiogenic potential (Okić-Đorđević et al., 2021). Therefore, for DSCs we need to further explore the function of different types of DSCs and perform tissue-specific labeling. Based on this, there are no definitive studies on how to determine the standard process of DSCs therapy, how to clarify the optimal transplantation time, quantity, and form of injection, as well as whether there is a postoperative response and long-term efficacy, which all need to be further explored. Advances in single-cell lineage tracing technology hold great promise for elucidating the heterogeneity and specific functions among different types of DSCs and may hold the key to solving this problem.
To sum up, future progress will require international collaboration to harmonize research and clinical practices. Establishing unified Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) protocols for MSCs processing and quality control, as well as building an international stem cell consortium or alliance, could provide shared resources, standardize endpoints, and facilitate large-scale multicenter trials. Moreover, integrating omics technologies to clarify mechanisms and advancing acellular strategies such as exosome- or secretome-based therapies may help overcome current barriers. By addressing these challenges, MSCs-based therapies—including DSCs and other sources—may ultimately evolve into reliable, safe, and personalized approaches for regenerative medicine. But that is still a long way to go.
Author contributions
KY: Conceptualization, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SY: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. YW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. AL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. FH: Visualization, Writing – review and editing. ZJ: Visualization, Writing – review and editing. CY: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. WT: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFA1104400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U21A20369).
Acknowledgments
AcknowledgementsWe would like to express their gratitude for the support from the the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFA1104400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U21A20369). The figures were created using BioRender.com.
Conflict of interest
Author CY was employed by Chengdu Shiliankangjian Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Akiyama, K., Chen, C., Wang, D., Xu, X., Qu, C., Yamaza, T., et al. (2012). Mesenchymal-stem-cell-induced immunoregulation involves FAS-ligand-/FAS-mediated T cell apoptosis. Cell Stem Cell 10 (5), 544–555. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2012.03.007
Alge, D. L., Zhou, D., Adams, L. L., Wyss, B. K., Shadday, M. D., Woods, E. J., et al. (2010). Donor-matched comparison of dental pulp stem cells and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 4 (1), 73–81. doi:10.1002/term.220
Arakaki, M., Ishikawa, M., Nakamura, T., Iwamoto, T., Yamada, A., Fukumoto, E., et al. (2012). Role of epithelial-stem cell interactions during dental cell differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 287 (13), 10590–10601. doi:10.1074/jbc.m111.285874
Arora, V., Arora, P., and Munshi, A. K. (2009). Banking stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHED): saving for the future. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 33 (4), 289–294. doi:10.17796/jcpd.33.4.y887672r0j703654
Arthur, A., Rychkov, G., Shi, S., Koblar, S. A., and Gronthos, S. (2008). Adult human dental pulp stem cells differentiate toward functionally active neurons under appropriate environmental cues. Stem Cells 26 (7), 1787–1795. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2007-0979
Arthur, A., Shi, S., Zannettino, A. C. W., Fujii, N., Gronthos, S., and Koblar, S. A. (2009). Implanted adult human dental pulp stem cells induce endogenous axon guidance. Stem Cells 27 (9), 2229–2237. doi:10.1002/stem.138
Ashfaq, R., Kovács, A., Berkó, S., and Budai-Szűcs, M. (2024). Developments in alloplastic bone grafts and barrier membrane biomaterials for periodontal guided tissue and bone regeneration therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (14), 7746. doi:10.3390/ijms25147746
Bajestan, M. N., Rajan, A., Edwards, S. P., Aronovich, S., Cevidanes, L. H. S., Polymeri, A., et al. (2017). Stem cell therapy for reconstruction of alveolar cleft and trauma defects in adults: a randomized controlled, clinical trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 19 (5), 793–801. doi:10.1111/cid.12506
Bakopoulou, A., Leyhausen, G., Volk, J., Tsiftsoglou, A., Garefis, P., Koidis, P., et al. (2011). Comparative analysis of in vitro osteo/odontogenic differentiation potential of human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) and stem cells from the apical papilla (SCAP). Arch. Oral Biol. 56 (7), 709–721. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2010.12.008
Bousnaki, M., Bakopoulou, A., Pich, A., Papachristou, E., Kritis, A., and Koidis, P. (2022). Mapping the secretome of dental pulp stem cells under variable microenvironmental conditions. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 18 (4), 1372–1407. doi:10.1007/s12015-021-10255-2
Brunello, G., Zanotti, F., Trentini, M., Zanolla, I., Pishavar, E., Favero, V., et al. (2022). Exosomes derived from dental pulp stem cells show different angiogenic and osteogenic properties in relation to the age of the donor. Pharmaceutics 14 (5), 908. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14050908
Bustos, M. L., Huleihel, L., Kapetanaki, M. G., Lino-Cardenas, C. L., Mroz, L., Ellis, B. M., et al. (2014). Aging mesenchymal stem cells fail to protect because of impaired migration and antiinflammatory response. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 189 (7), 787–798. doi:10.1164/rccm.201306-1043oc
Chen, F. M., Gao, L. N., Tian, B. M., Zhang, X. Y., Zhang, Y. J., Dong, G. Y., et al. (2016). Treatment of periodontal intrabony defects using autologous periodontal ligament stem cells: a randomized clinical trial. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 7, 33. doi:10.1186/s13287-016-0288-1
Chen, L., Shen, R., Komasa, S., Xue, Y., Jin, B., Hou, Y., et al. (2017). Drug-Loadable calcium alginate Hydrogel System for use in oral bone tissue repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18 (5), 989. doi:10.3390/ijms18050989
Chen, H., Fu, H., Wu, X., Duan, Y., Zhang, S., Hu, H., et al. (2020). Regeneration of pulpo-dentinal-like complex by a group of unique multipotent CD24a+ stem cells. Sci. Adv. 6 (15), eaay1514. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aay1514
Chen, J., Xu, H., Xia, K., Cheng, S., and Zhang, Q. (2021). Resolvin E1 accelerates pulp repair by regulating inflammation and stimulating dentin regeneration in dental pulp stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 12 (1), 75. doi:10.1186/s13287-021-02141-y
Chen, Y. R., Wong, C. C., Chen, Y. N., Yang, B. H., Lee, P. H., Shiau, C. Y., et al. (2024). Factors derived from human exfoliated deciduous teeth stem cells reverse neurological deficits in a zebrafish model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Dent. Sci. 19 (4), 2035–2044. doi:10.1016/j.jds.2024.06.004
Chen, L., Zhang, J., Yu, J., Guo, S., and Tian, W. (2025a). LPS pretreated dental follicle stem cell derived exosomes promote periodontal tissue regeneration via miR-184 and PPARα-Akt-JNK signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 16 (1), 347. doi:10.1186/s13287-025-04462-8
Chen, L., Liu, Y., Yu, C., Cao, P., Ma, Y., Geng, Y., et al. (2025b). Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells (iMSCs) inhibit M1 macrophage polarization and reduce alveolar bone loss associated with periodontitis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 16 (1), 223. doi:10.1186/s13287-025-04327-0
Cooper, L. F., Ravindran, S., Huang, C. C., and Kang, M. (2019). A role for exosomes in craniofacial tissue engineering and regeneration. Front. Physiol. 10, 1569. doi:10.3389/fphys.2019.01569
Dave, J. R., Chandekar, S. S., Behera, S., Desai, K. U., Salve, P. M., Sapkal, N. B., et al. (2022). Human gingival mesenchymal stem cells retain their growth and immunomodulatory characteristics independent of donor age. Sci. Adv. 8 (25), eabm6504. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abm6504
Demircan, P. C., Sariboyaci, A. E., Unal, Z. S., Gacar, G., Subasi, C., and Karaoz, E. (2011). Immunoregulatory effects of human dental pulp-derived stem cells on T cells: comparison of transwell co-culture and mixed lymphocyte reaction systems. Cytotherapy 13 (10), 1205–1220. doi:10.3109/14653249.2011.605351
Derubeis, A. R., and Cancedda, R. (2004). Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) in bone engineering: limitations and recent advances. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 32 (1), 160–165. doi:10.1023/b:abme.0000007800.89194.95
Ding, G., Liu, Y., An, Y., Zhang, C., Shi, S., Wang, W., et al. (2010a). Suppression of T cell proliferation by root apical papilla stem cells in vitro. Cells Tissues Organs 191 (5), 357–364. doi:10.1159/000276589
Ding, G., Liu, Y., Wang, W., Wei, F., Liu, D., Fan, Z., et al. (2010b). Allogeneic periodontal ligament stem cell therapy for periodontitis in swine. Stem Cells 28 (10), 1829–1838. doi:10.1002/stem.512
D’Alimonte, I., Mastrangelo, F., Giuliani, P., Pierdomenico, L., Marchisio, M., Zuccarini, M., et al. (2017). Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells: a comparative analysis between human subcutaneous adipose tissue and dental pulp. Stem Cells Dev. 26 (11), 843–855. doi:10.1089/scd.2016.0190
d’Aquino, R., De Rosa, A., Lanza, V., Tirino, V., Laino, L., Graziano, A., et al. (2009). Human mandible bone defect repair by the grafting of dental pulp stem/progenitor cells and collagen sponge biocomplexes. Eur. Cell Mater. 18, 75–83. doi:10.22203/ecm.v018a07
Egusa, H., Okita, K., Kayashima, H., Yu, G., Fukuyasu, S., Saeki, M., et al. (2010). Gingival fibroblasts as a promising source of induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS One 5 (9), e12743. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012743
El Ayachi, I., Zhang, J., Zou, X. Y., Li, D., Yu, Z., Wei, W., et al. (2018). Human dental stem cell derived transgene-free iPSCs generate functional neurons via embryoid body-mediated and direct induction methods. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 12 (4), e1836–e1851. doi:10.1002/term.2615
Ge, S., Zhao, N., Wang, L., Yu, M., Liu, H., Song, A., et al. (2012a). Bone repair by periodontal ligament stem cellseeded nanohydroxyapatite-chitosan scaffold. Int. J. Nanomedicine 7, 5405–5414. doi:10.2147/ijn.s36714
Ge, S., Mrozik, K. M., Menicanin, D., Gronthos, S., and Bartold, P. M. (2012b). Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stem cell-like cells from healthy and inflamed gingival tissue: potential use for clinical therapy. Regen. Med. 7 (6), 819–832. doi:10.2217/rme.12.61
Giuliani, A., Manescu, A., Langer, M., Rustichelli, F., Desiderio, V., Paino, F., et al. (2013). Three years after transplants in human mandibles, histological and in-line holotomography revealed that stem cells regenerated a compact rather than a spongy bone: biological and clinical implications. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2 (4), 316–324. doi:10.5966/sctm.2012-0136
Gopalarethinam, J., Nair, A. P., Iyer, M., Vellingiri, B., and Subramaniam, M. D. (2023). Advantages of mesenchymal stem cell over the other stem cells. Acta histochem. 125 (4), 152041. doi:10.1016/j.acthis.2023.152041
Greene, P. (2009). Cell-based therapies in Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 9 (4), 292–297. doi:10.1007/s11910-009-0044-3
Gronthos, S., Mankani, M., Brahim, J., Robey, P. G., and Shi, S. (2000). Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97 (25), 13625–13630. doi:10.1073/pnas.240309797
Guo, W., Gong, K., Shi, H., Zhu, G., He, Y., Ding, B., et al. (2012). Dental follicle cells and treated dentin matrix scaffold for tissue engineering the tooth root. Biomaterials 33 (5), 1291–1302. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.09.068
Guo, S., Kang, J., Ji, B., Guo, W., Ding, Y., Wu, Y., et al. (2017). Periodontal-Derived mesenchymal cell sheets promote periodontal regeneration in inflammatory microenvironment. Tissue Eng. Part A 23 (13–14), 585–596. doi:10.1089/ten.tea.2016.0334
Han, N., Zhang, F., Li, G., Zhang, X., Lin, X., Yang, H., et al. (2017). Local application of IGFBP5 protein enhanced periodontal tissue regeneration via increasing the migration, cell proliferation and osteo/dentinogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in an inflammatory niche. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 8 (1), 210. doi:10.1186/s13287-017-0663-6
He, X., Chu, X. Y., Chen, X., Xiang, Y. L., Li, Z. L., Gao, C. Y., et al. (2025). Dental pulp stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles loaded with hydrogels promote osteogenesis in rats with alveolar bone defects. Mol. Med. Rep. 31 (1), 29. doi:10.3892/mmr.2024.13393
Hong, J. W., Lim, J. H., Chung, C. J., Kang, T. J., Kim, T. Y., Kim, Y. S., et al. (2019). Immune tolerance of human dental pulp-derived mesenchymal stem cells mediated by CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T-Cells and induced by TGF-β1 and IL-10. Yonsei Med. J. 58 (5), 1031–1039. doi:10.3349/ymj.2017.58.5.1031
Hossein-Khannazer, N., Hashemi, S. M., Namaki, S., Ghanbarian, H., Sattari, M., and Khojasteh, A. (2019). Study of the immunomodulatory effects of osteogenic differentiated human dental pulp stem cells. Life Sci. 216, 111–118. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2018.11.040
Howlader, M. S. I., Prateeksha, P., Hansda, S., Naidu, P., Das, M., Barthels, D., et al. (2024). Secretory products of DPSC mitigate inflammatory effects in microglial cells by targeting MAPK pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 170, 115971. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115971
Hussien, N., Khalil, M., Schagerl, M., and Ali, S. (2025). Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles as a promising nanomedicine approach for anticancer, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory therapies. Int. J. Nanomedicine 20, 4299–4317. doi:10.2147/ijn.s507214
Hutchings, G., Janowicz, K., Moncrieff, L., Dompe, C., Strauss, E., Kocherova, I., et al. (2020). The proliferation and differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells in neovascularization and angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (11), 3790. doi:10.3390/ijms21113790
Ibarretxe, G., Crende, O., Aurrekoetxea, M., García-Murga, V., Etxaniz, J., and Unda, F. (2012). Neural crest stem cells from dental tissues: a new hope for dental and neural regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2012, 1–12. doi:10.1155/2012/103503
Inchingolo, A. M., Inchingolo, A. D., Nardelli, P., Latini, G., Trilli, I., Ferrante, L., et al. (2024). Stem cells: present understanding and prospects for regenerative dentistry. J. Funct. Biomater. 15 (10), 308. doi:10.3390/jfb15100308
Ishikawa, J., Takahashi, N., Matsumoto, T., Yoshioka, Y., Yamamoto, N., Nishikawa, M., et al. (2016). Factors secreted from dental pulp stem cells show multifaceted benefits for treating experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Bone 83, 210–219. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2015.11.012
Isobe, Y., Koyama, N., Nakao, K., Osawa, K., Ikeno, M., Yamanaka, S., et al. (2016). Comparison of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, synovial fluid, adult dental pulp, and exfoliated deciduous tooth pulp. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 45 (1), 124–131. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2015.06.022
Itoh, Y., Sasaki, J. I., Hashimoto, M., Katata, C., Hayashi, M., and Imazato, S. (2018). Pulp regeneration by 3-dimensional dental pulp stem cell constructs. J. Dent. Res. 97 (10), 1137–1143. doi:10.1177/0022034518772260
Iwata, T., Yamato, M., Washio, K., Yoshida, T., Tsumanuma, Y., Yamada, A., et al. (2018). Periodontal regeneration with autologous periodontal ligament-derived cell sheets - a safety and efficacy study in ten patients. Regen. Ther. 9, 38–44. doi:10.1016/j.reth.2018.07.002
Ji, X., Zhang, Z., Han, Y., Song, J., Xu, X., Jin, J., et al. (2016). Mesenchymal stem cells derived from normal gingival tissue inhibit the proliferation of oral cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 49 (5), 2011–2022. doi:10.3892/ijo.2016.3715
Jin, Z., Feng, Y., and Liu, H. (2016). Conditioned media from differentiating craniofacial bone marrow stromal cells influence mineralization and proliferation in periodontal ligament stem cells. Hum. Cell 29 (4), 162–175. doi:10.1007/s13577-016-0144-8
Jin, Q., Yuan, K., Lin, W., Niu, C., Ma, R., and Huang, Z. (2019). Comparative characterization of mesenchymal stem cells from human dental pulp and adipose tissue for bone regeneration potential. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47 (1), 1577–1584. doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1594861
Joo, K. H., Song, J. S., Kim, S., Lee, H. S., Jeon, M., Kim, S. O., et al. (2018). Cytokine expression of stem cells originating from the apical complex and coronal pulp of immature teeth. J. Endod. 44 (1), 87–92.e1. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2017.08.018
Kanji, S., Sarkar, R., Pramanik, A., Kshirsagar, S., Greene, C. J., and Das, H. (2021). Dental pulp-derived stem cells inhibit osteoclast differentiation by secreting osteoprotegerin and deactivating AKT signalling in myeloid cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 25 (5), 2390–2403. doi:10.1111/jcmm.16071
Karaöz, E., Doğan, B. N., Aksoy, A., Gacar, G., Akyüz, S., Ayhan, S., et al. (2010). Isolation and in vitro characterisation of dental pulp stem cells from natal teeth. Histochem Cell Biol. 133 (1), 95–112. doi:10.1007/s00418-009-0646-5
Kerkis, I., Kerkis, A., Dozortsev, D., Stukart-Parsons, G. C., Gomes Massironi, S. M., Pereira, L. V., et al. (2006). Isolation and characterization of a population of immature dental pulp stem cells expressing OCT-4 and other embryonic stem cell markers. Cells Tissues Organs 184 (3–4), 105–116. doi:10.1159/000099617
Kim, G. H., Yang, J., Jeon, D. H., Kim, J. H., Chae, G. Y., Jang, M., et al. (2020). Differentiation and establishment of dental epithelial-like stem cells derived from human ESCs and iPSCs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (12), 4384. doi:10.3390/ijms21124384
Király, M., Kádár, K., Horváthy, D. B., Nardai, P., Rácz, G. Z., Lacza, Z., et al. (2011). Integration of neuronally predifferentiated human dental pulp stem cells into rat brain in vivo. Neurochem. Int. 59 (3), 371–381. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2011.01.006
Kou, X., Xu, X., Chen, C., Sanmillan, M. L., Cai, T., Zhou, Y., et al. (2018). The Fas/Fap-1/Cav-1 complex regulates IL-1RA secretion in mesenchymal stem cells to accelerate wound healing. Sci. Transl. Med. 10 (432), eaai8524. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aai8524
Kunimatsu, R., Nakajima, K., Awada, T., Tsuka, Y., Abe, T., Ando, K., et al. (2018). Comparative characterization of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth, dental pulp, and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 501 (1), 193–198. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.213
Kunimatsu, R., Hiraki, T., Rikitake, K., Nakajima, K., Putranti, N. A. R., Abe, T., et al. (2022). Effects of human deciduous dental pulp-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived conditioned medium on the metabolism of HUVECs, osteoblasts, and BMSCs. Cells 11 (20), 3222. doi:10.3390/cells11203222
Kushiro, H., Takahashi, H., and Tanaka, A. (2021). Effects of the prevention of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw by local administration of a dental pulp stem cell-conditioned medium to the rat tooth extraction socket. Odontology 109 (4), 836–844. doi:10.1007/s10266-021-00607-2
Kwack, K. H., Lee, J. M., Park, S. H., and Lee, H. W. (2017). Human dental pulp stem cells suppress alloantigen-induced immunity by stimulating T cells to release transforming growth factor beta. J. Endod. 43 (1), 100–108. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2016.09.005
Lujun, J., Liuliu, B., Zhifeng, G., Qiao, Z., Yi, L., Ya, Z., et al. (2019). Comparison of immunomodulatory properties of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and dental pulp stem cells. Immunol. Res. 67 (4–5), 432–442. doi:10.1007/s12026-019-09088-6
Lee, C. S., Burnsed, O. A., Raghuram, V., Kalisvaart, J., Boyan, B. D., and Schwartz, Z. (2012). Adipose stem cells can secrete angiogenic factors that inhibit hyaline cartilage regeneration. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 3 (4), 35. doi:10.1186/scrt126
Lee, S., Zhang, Q. Z., Karabucak, B., and Le, A. D. (2016). DPSCs from inflamed pulp modulate macrophage function via the TNF-α/IDO axis. J. Dent. Res. 95 (11), 1274–1281. doi:10.1177/0022034516657817
Lee, T. P., Ho, M. H., Chen, Y. R., Lin, K. M., and Li, C. H. (2025). Induction of retinal progenitors and neurons from dental follicle stem cell under defined conditions. J. Dent. Sci. 20 (3), 1629–1638. doi:10.1016/j.jds.2025.03.008
Li, W., Jiao, X., Song, J., Sui, B., Guo, Z., Zhao, Y., et al. (2021a). Therapeutic potential of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth infusion into patients with type 2 diabetes depends on basal lipid levels and islet function. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 10 (7), 956–967. doi:10.1002/sctm.20-0303
Li, S., Luo, L., He, Y., Li, R., Xiang, Y., Xing, Z., et al. (2021b). Dental pulp stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury through suppressing inflammatory response. Cell Prolif. 54 (8), e13093. doi:10.1111/cpr.13093
Li, C., Liu, Y., Deng, M., Li, J., Li, S., Li, X., et al. (2024). Comparison of the therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human dental pulp (DP), adipose tissue (AD), placental amniotic membrane (PM), and umbilical cord (UC) on postmenopausal osteoporosis. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1349199. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1349199
Li, K., Gu, X., Zhu, Y., Guan, N., Wang, J., and Wang, L. (2025). Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes attenuates experimental periodontitis in mice partly by delivering miRNAs. Int. J. Nanomedicine 20, 2879–2899. doi:10.2147/ijn.s502192
Liang, J., Zhao, Y. J., Li, J. Q., Lan, L., Tao, W. J., and Wu, J. Y. (2022). A pilot study on biological characteristics of human CD24(+) stem cells from the apical papilla. J. Dent. Sci. 17 (1), 264–275. doi:10.1016/j.jds.2021.01.012
Lin, X., Wang, Y., Guo, X., Li, C., Wu, K., Wang, S., et al. (2023a). Shikonin promotes rat periodontal bone defect repair and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by p38 MAPK pathway. Odontology 111 (3), 649–657. doi:10.1007/s10266-022-00774-w
Lin, L., Li, S., Hu, S., Yu, W., Jiang, B., Mao, C., et al. (2023b). UCHL1 impairs periodontal ligament stem cell osteogenesis in periodontitis. J. Dent. Res. 102 (1), 61–71. doi:10.1177/00220345221116031
Lin, C., Yang, Y. S., Ma, H., Chen, Z., Chen, D., John, A. A., et al. (2024). Engineering a targeted and safe bone anabolic gene therapy to treat osteoporosis in alveolar bone loss. Mol. Ther. 32 (9), 3080–3100. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.06.036
Liu, Y., Zheng, Y., Ding, G., Fang, D., Zhang, C., Bartold, P. M., et al. (2008). Periodontal ligament stem cell-mediated treatment for periodontitis in miniature swine. Stem Cells 26 (4), 1065–1073. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2007-0734
Liu, O., Xu, J., Ding, G., Liu, D., Fan, Z., Zhang, C., et al. (2013). Periodontal ligament stem cells regulate B lymphocyte function via programmed cell death protein 1. Stem Cells 31 (7), 1371–1382. doi:10.1002/stem.1387
Liu, J., Yu, F., Sun, Y., Jiang, B., Zhang, W., Yang, J., et al. (2015). Concise reviews: characteristics and potential applications of human dental tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 33 (3), 627–638. doi:10.1002/stem.1909
Liu, L., Liu, Y. F., Zhang, J., Duan, Y. Z., and Jin, Y. (2016). Ameloblasts serum-free conditioned medium: bone morphogenic protein 4-induced odontogenic differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 10 (6), 466–474. doi:10.1002/term.1742
Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Hu, J., Han, J., Song, L., Liu, X., et al. (2025). Impact of allogeneic dental pulp stem cell injection on tissue regeneration in periodontitis: a multicenter randomized clinical trial. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 10 (1), 239. doi:10.1038/s41392-025-02320-w
Lu, Y., Xu, Y., Zhang, S., Gao, J., Gan, X., Zheng, J., et al. (2019). Human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate inflammatory bowel disease via IL-10 signalling-dependent modulation of immune cells. Scand. J. Immunol. 90 (3), e12751. doi:10.1111/sji.12751
Lu, J., Yu, N., Liu, Q., Xie, Y., and Zhen, L. (2023). Periodontal ligament stem cell exosomes key to regulate periodontal regeneration by miR-31-5p in mice model. Int. J. Nanomedicine 18, 5327–5342. doi:10.2147/ijn.s409664
Lu, H., Mu, Q., Ku, W., Zheng, Y., Yi, P., Lin, L., et al. (2024). Functional extracellular vesicles from SHEDs combined with gelatin methacryloyl promote the odontogenic differentiation of DPSCs for pulp regeneration. J. Nanobiotechnology 22 (1), 265. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02542-0
Luo, D., Chen, B., and Chen, Y. (2022). Stem cells-loaded 3D-Printed scaffolds for the reconstruction of alveolar cleft. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 939199. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.939199
Ma, L., Hu, J., Cao, Y., Xie, Y., Wang, H., Fan, Z., et al. (2019). Maintained properties of aged dental pulp stem cells for superior periodontal tissue regeneration. Aging Dis. 10 (4), 793–806. doi:10.14336/ad.2018.0729
Magalhães, F. D., Sarra, G., Carvalho, G. L., Pedroni, A. C. F., Marques, M. M., Chambrone, L., et al. (2021). Dental tissue-derived stem cell sheet biotechnology for periodontal tissue regeneration: a systematic review. Arch. Oral Biol. 129, 105182. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2021.105182
Mahardawi, B., Rochanavibhata, S., Jiaranuchart, S., Arunjaroensuk, S., Mattheos, N., and Pimkhaokham, A. (2023). Autogenous tooth bone graft material prepared chairside and its clinical applications: a systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 52 (1), 132–141. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2022.04.018
Martens, W., Bronckaers, A., Politis, C., Jacobs, R., and Lambrichts, I. (2013). Dental stem cells and their promising role in neural regeneration: an update. Clin. Oral Investig. 17 (9), 1969–1983. doi:10.1007/s00784-013-1030-3
Massa, A., Perut, F., Chano, T., Woloszyk, A., Mitsiadis, T. A., Avnet, S., et al. (2017). The effect of extracellular acidosis on the behaviour of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Eur. Cell Mater 33, 252–267. doi:10.22203/ecm.v033a19
Matsumura-Kawashima, M., Ogata, K., Moriyama, M., Murakami, Y., Kawado, T., and Nakamura, S. (2021). Secreted factors from dental pulp stem cells improve Sjögren’s syndrome via regulatory T cell-mediated immunosuppression. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 12 (1), 182. doi:10.1186/s13287-021-02236-6
McElreavey, K. D., Irvine, A. I., Ennis, K. T., and McLean, W. H. (1991). Isolation, culture and characterisation of fibroblast-like cells derived from the Wharton’s jelly portion of human umbilical cord. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 19 (1), 29S. doi:10.1042/bst019029s
Mead, B., Logan, A., Berry, M., Leadbeater, W., and Scheven, B. A. (2014). Paracrine-mediated neuroprotection and neuritogenesis of axotomised retinal ganglion cells by human dental pulp stem cells: comparison with human bone marrow and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One 9 (10), e109305. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109305
Mead, B., Logan, A., Berry, M., Leadbeater, W., and Scheven, B. A. (2017). Concise review: dental pulp stem cells: a novel cell therapy for retinal and central nervous System repair. Stem Cells 35 (1), 61–67. doi:10.1002/stem.2398
Mi, S., Wang, X., Gao, J., Liu, Y., and Qi, Z. (2023). Implantation with SHED sheet induced with homogenate protein of spinal cord promotes functional recovery from spinal cord injury in rats. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1119639. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1119639
Miao, Y., Liang, X., Chen, J., Liu, H., He, Z., Qin, Y., et al. (2024). Transfer of miR-877-3p via extracellular vesicles derived from dental pulp stem cells attenuates neuronal apoptosis and facilitates early neurological functional recovery after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through the Bclaf1/P53 signaling pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 206, 107266. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107266
Miguita, L., Mantesso, A., Pannuti, C. M., and Deboni, M. C. Z. (2017). Can stem cells enhance bone formation in the human edentulous alveolar ridge? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cell Tissue Bank. 18 (2), 217–228. doi:10.1007/s10561-017-9612-y
Miura, M., Gronthos, S., Zhao, M., Lu, B., Fisher, L. W., Robey, P. G., et al. (2003). SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100 (10), 5807–5812. doi:10.1073/pnas.0937635100
Miyoshi, K., Tsuji, D., Kudoh, K., Satomura, K., Muto, T., Itoh, K., et al. (2010). Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells from oral mucosa. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 110 (3), 345–350. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2010.03.004
Mohan Kumar, P., and Thakkar, R. (2024). Periodontal ligament and bone marrow derived stem cells in periodontal regeneration – a systematic review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Med. Pathol. 36 (5), 665–671. doi:10.1016/j.ajoms.2024.02.009
Mohd, N. N. H., Mansor, N. I., Mohd Kashim, M. I. A., Mokhtar, M. H., and Mohd Hatta, F. A. (2023). From teeth to therapy: a review of therapeutic potential within the secretome of stem cells from Human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (14), 11763. doi:10.3390/ijms241411763
Mohebichamkhorami, F., Fattahi, R., Niknam, Z., Aliashrafi, M., Khakpour Naeimi, S., Gilanchi, S., et al. (2022). Periodontal ligament stem cells as a promising therapeutic target for neural damage. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 13 (1), 273. doi:10.1186/s13287-022-02942-9
Montaño, J., Garnica, J., and Santamaria, P. (2021). Immunomodulatory and immunoregulatory nanomedicines for autoimmunity. Semin. Immunol. 56, 101535. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2021.101535
Morsczeck, C., De Pellegrin, M., Reck, A., and Reichert, T. E. (2023). Evaluation of Current studies to elucidate processes in dental follicle cells driving osteogenic differentiation. Biomedicines 11 (10), 2787. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11102787
Murakami, M., Hayashi, Y., Iohara, K., Osako, Y., Hirose, Y., and Nakashima, M. (2015). Trophic effects and regenerative potential of mobilized mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue as alternative cell sources for Pulp/Dentin regeneration. Cell Transpl. 24 (9), 1753–1765. doi:10.3727/096368914x683502
Nakagawa, M., Taniguchi, Y., Senda, S., Takizawa, N., Ichisaka, T., Asano, K., et al. (2014). A novel efficient feeder-free culture system for the derivation of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci. Rep. 4, 3594. doi:10.1038/srep03594
Nakamura, S., Yamada, Y., Katagiri, W., Sugito, T., Ito, K., and Ueda, M. (2009). Stem cell proliferation pathways comparison between human exfoliated deciduous teeth and dental pulp stem cells by gene expression profile from promising dental pulp. J. Endod. 35 (11), 1536–1542. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2009.07.024
Nakao, Y., Fukuda, T., Zhang, Q., Sanui, T., Shinjo, T., Kou, X., et al. (2021). Exosomes from TNF-α-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs enhance M2 macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss. Acta Biomater. 122, 306–324. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2020.12.046
Nakashima, M., and Iohara, K. (2014). Mobilized dental pulp stem cells for pulp regeneration: initiation of clinical trial. J. Endod. 40 (4 Suppl. l), S26–S32. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2014.01.020
Ogata, K., Matsumura-Kawashima, M., Moriyama, M., Kawado, T., and Nakamura, S. (2021). Dental pulp-derived stem cell-conditioned media attenuates secondary Sjögren's syndrome via suppression of inflammatory cytokines in the submandibular glands. Regen. Ther. 16, 73–80. doi:10.1016/j.reth.2021.01.006
Okić-Đorđević, I., Obradović, H., Kukolj, T., Petrović, A., Mojsilović, S., Bugarski, D., et al. (2021). Dental mesenchymal stromal/stem cells in different microenvironments-implications in regenerative therapy. World J. Stem Cells 13 (12), 1863–1880. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v13.i12.1863
Omori, M., Tsuchiya, S., Hara, K., Kuroda, K., Hibi, H., Okido, M., et al. (2015). A new application of cell-free bone regeneration: immobilizing stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth-conditioned medium onto titanium implants using atmospheric pressure plasma treatment. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 6 (1), 124. doi:10.1186/s13287-015-0114-1
Peishan, L., Qianmin, O., Songtao, S., and Changshun, S. (2023). Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells/dental stem cells and their therapeutic applications. Cell. & Mol. Immunol. 20 (6), 558–569. doi:10.1038/s41423-023-00998-y
Paganelli, A., Trubiani, O., Diomede, F., Pisciotta, A., and Paganelli, R. (2021). Immunomodulating profile of dental mesenchymal stromal cells: a comprehensive overview. Front. Oral Health 2, 635055. doi:10.3389/froh.2021.635055
Paladino, F. V., Sardinha, L. R., Piccinato, C. A., and Goldberg, A. C. (2017). Intrinsic variability present in Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells and T cell responses May impact cell therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 1–12. doi:10.1155/2017/8492797
Perry, B. C., Zhou, D., Wu, X., Yang, F. C., Byers, M. A., Chu, T. M. G., et al. (2008). Collection, cryopreservation, and characterization of human dental pulp-derived mesenchymal stem cells for banking and clinical use. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 14 (2), 149–156. doi:10.1089/ten.tec.2008.0031
Pires, R. S., Santos, M. S., Miguel, F., da Silva, C. L., and Silva, J. C. (2025). Electrical stimulation of oral tissue-derived stem cells: unlocking new potential for dental and periodontal regeneration. Cells 14 (11), 840. doi:10.3390/cells14110840
Poblano-Pérez, L. I., Monroy-García, A., Fragoso-González, G., Mora-García, M. de L., Castell-Rodríguez, A., Mayani, H., et al. (2023). Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal cells derived from dental tissues mediate the immunoregulation of T cells through the purinergic pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024 Sept. 25 (17), 9578. doi:10.3390/ijms25179578
Prescott, R. S., Alsanea, R., Fayad, M. I., Johnson, B. R., Wenckus, C. S., Hao, J., et al. (2008). In vivo generation of dental pulp-like tissue by using dental pulp stem cells, a collagen scaffold, and dentin matrix protein 1 after subcutaneous transplantation in mice. J. Endod. 34 (4), 421–426. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2008.02.005
Qin, D., Wang, X., Pu, J., and Hu, H. (2024). Cardiac cells and mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles: a potential therapeutic strategy for myocardial infarction. Front. Cardiovasc Med. 11, 1493290. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2024.1493290
Qiu, W., Zhou, B., Luo, Y., Chen, Y., Chen, Z., Wu, K., et al. (2025). An optimized decellularized extracellular matrix from dental pulp stem cell sheets promotes axonal regeneration by multiple modes in spinal cord injury rats. Adv. Healthc. Mater 14 (1), e2402312. doi:10.1002/adhm.202402312
Qu, G., Li, Y., Chen, L., Chen, Q., Zou, D., Yang, C., et al. (2021). Comparison of Osteogenic Differentiation Potential of Human Dental-Derived stem cells isolated from Dental pulp, periodontal ligament, Dental follicle, and alveolar bone. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 1–12. doi:10.1155/2021/6631905
Rossi, N., Hadad, H., Bejar-Chapa, M., Peretti, G. M., Randolph, M. A., Redmond, R. W., et al. (2023). Bone marrow stem cells with tissue-engineered scaffolds for large bone segmental defects: a systematic review. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 29 (5), 457–472. doi:10.1089/ten.teb.2022.0213
Sakai, K., Yamamoto, A., Matsubara, K., Nakamura, S., Naruse, M., Yamagata, M., et al. (2012). Human dental pulp-derived stem cells promote locomotor recovery after complete transection of the rat spinal cord by multiple neuro-regenerative mechanisms. J. Clin. Invest 122 (1), 80–90. doi:10.1172/JCI59251
Salehinejad, P., Alitheen, N. B., Ali, A. M., Omar, A. R., Mohit, M., Janzamin, E., et al. (2012). Comparison of different methods for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord Wharton’s jelly. Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 48 (2), 75–83. doi:10.1007/s11626-011-9480-x
Sanchez, N., Vignoletti, F., Sanz-Martin, I., Coca, A., Nuñez, J., Maldonado, E., et al. (2022). Cell therapy based on Gingiva-Derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded in a xenogeneic collagen matrix for root coverage of RT1 gingival lesions: an in vivo experimental Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (6), 3248. doi:10.3390/ijms23063248
Sandra Sari, D., Martin, M., Maduratna, E., Basuki Notobroto, H., Mahyudin, F., Sudiana, K., et al. (2023). Combination adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-demineralized dentin matrix increase bone marker expression in periodontitis rats. Saudi Dent. J. 35 (8), 960–968. doi:10.1016/j.sdentj.2023.07.019
Sato, S., Teramura, Y., Ogawa, Y., Shimizu, E., Otake, M., Hori, K., et al. (2025). Conditioned media of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth contain factors related to extracellular matrix organization and promotes corneal epithelial wound healing. Regen. Ther. 29, 148–161. doi:10.1016/j.reth.2025.03.002
Seo, B. M., Miura, M., Gronthos, S., Bartold, P. M., Batouli, S., Brahim, J., et al. (2004). Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet 364 (9429), 149–155. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(04)16627-0
Sharma, Y., Shobha, K., Sundeep, M., Pinnelli, V. B., Parveen, S., and Dhanushkodi, A. (2022). Neural basis of dental pulp stem cells and its potential application in parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 21 (1), 62–76. doi:10.2174/1871527320666210311122921
Shetty, S. S., Sowmya, S., Pradeep, A., and Jayakumar, R. (2025). Gingival mesenchymal stem cells: a periodontal regenerative substitute. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 22 (1), 1–21. doi:10.1007/s13770-024-00676-8
Shi, X., Mao, J., and Liu, Y. (2020). Pulp stem cells derived from human permanent and deciduous teeth: biological characteristics and therapeutic applications. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 9 (4), 445–464. doi:10.1002/sctm.19-0398
Shimojima, C., Takeuchi, H., Jin, S., Parajuli, B., Hattori, H., Suzumura, A., et al. (2016). Conditioned Medium from the stem cells of Human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 196 (10), 4164–4171. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1501457
Shoda, H., Natsumoto, B., and Fujio, K. (2023). Investigation of immune-related diseases using patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. Inflamm. Regen. 43 (1), 51. doi:10.1186/s41232-023-00303-4
Song, M., Lee, J. H., Bae, J., Bu, Y., and Kim, E. C. (2017). Human dental pulp stem cells are more effective than human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in cerebral ischemic injury. Cell Transpl. 26 (6), 1001–1016. doi:10.3727/096368916x694391
Song, D., He, C., Ocansey, D. K. W., Wang, B., Wu, Y., and Mao, F. (2025). Mesenchymal stem cell in immunomodulation of dendritic cells: implications for inflammatory bowel disease therapy. Autoimmun. Rev. 24 (9), 103861. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2025.103861
Sonoyama, W., Liu, Y., Fang, D., Yamaza, T., Seo, B. M., Zhang, C., et al. (2006). Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated functional tooth regeneration in swine. PLoS One 1 (1), e79. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000079
Sowa, K., Nito, C., Nakajima, M., Suda, S., Nishiyama, Y., Sakamoto, Y., et al. (2018). Impact of dental pulp stem cells overexpressing hepatocyte growth factor after cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion in rats. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 10, 281–290. doi:10.1016/j.omtm.2018.07.009
Stenudd, M., Sabelström, H., and Frisén, J. (2015). Role of endogenous neural stem cells in spinal cord injury and repair. JAMA Neurol. 72 (2), 235–237. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.2927
Su, W. R., Zhang, Q. Z., Shi, S. H., Nguyen, A. L., and Le, A. D. (2011). Human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate contact hypersensitivity via prostaglandin E2-dependent mechanisms. Stem Cells 29 (11), 1849–1860. doi:10.1002/stem.738
Sun, L. Y., Zhang, H. Y., Feng, X. B., Hou, Y. Y., Lu, L. W., and Fan, L. M. (2007). Abnormality of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 16 (2), 121–128. doi:10.1177/0961203306075793
Takahashi, K., Tanabe, K., Ohnuki, M., Narita, M., Ichisaka, T., Tomoda, K., et al. (2007). Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131 (5), 861–872. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.019
Tang, H. N., Xia, Y., Yu, Y., Wu, R. X., Gao, L. N., and Chen, F. M. (2016). Stem cells derived from “inflamed” and healthy periodontal ligament tissues and their sheet functionalities: a patient-matched comparison. J. Clin. Periodontol. 43 (1), 72–84. doi:10.1111/jcpe.12501
Tarkka, T., Sipola, A., Jämsä, T., Soini, Y., Ylä-Herttuala, S., Tuukkanen, J., et al. (2003). Adenoviral VEGF-A gene transfer induces angiogenesis and promotes bone formation in healing osseous tissues. J. Gene Med. 5 (7), 560–566. doi:10.1002/jgm.392
Tian, X., Wei, W., Cao, Y., Ao, T., Huang, F., Javed, R., et al. (2022). Gingival mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes are immunosuppressive in preventing collagen-induced arthritis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 26 (3), 693–708. doi:10.1111/jcmm.17086
Tomokiyo, A., Hynes, K., Ng, J., Menicanin, D., Camp, E., Arthur, A., et al. (2017). Generation of neural crest-like cells from human periodontal ligament cell-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Cell Physiol. 232 (2), 402–416. doi:10.1002/jcp.25437
Truchan, K., Zagrajczuk, B., Cholewa-Kowalska, K., and Osyczka, A. M. (2025). Rapid osteoinduction of human adipose-derived stem cells grown on bioactive surfaces and stimulated by chemically modified media flow. J. Biol. Eng. 19 (1), 23. doi:10.1186/s13036-025-00491-2
Uccelli, A., Pistoia, V., and Moretta, L. (2007). Mesenchymal stem cells: a new strategy for immunosuppression? Trends Immunol. 28 (5), 219–226. doi:10.1016/j.it.2007.03.001
Umapathy, V. R., Natarajan, P. M., and Swamikannu, B. (2025). Regenerative strategies in dentistry: harnessing stem cells, biomaterials and bioactive materials for tissue repair. Biomolecules 15 (4), 546. doi:10.3390/biom15040546
Vanacker, J., Viswanath, A., De Berdt, P., Everard, A., Cani, P. D., Bouzin, C., et al. (2014). Hypoxia modulates the differentiation potential of stem cells of the apical papilla. J. Endod. 40 (9), 1410–1418. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2014.04.008
Wada, N., Menicanin, D., Shi, S., Bartold, P. M., and Gronthos, S. (2009). Immunomodulatory properties of human periodontal ligament stem cells. J. Cell Physiol. 219 (3), 667–676. doi:10.1002/jcp.21710
Wang, L. H., Gao, S. Z., Bai, X. L., Chen, Z. L., and Yang, F. (2022). An up-to-date overview of dental tissue regeneration using dental origin mesenchymal stem cells: challenges and road ahead. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 855396. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.855396
Wang, X., Li, F., Wu, S., Xing, W., Fu, J., Wang, R., et al. (2024). Research progress on optimization of in vitro isolation, cultivation and preservation methods of dental pulp stem cells for clinical application. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 12, 1305614. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2024.1305614
Wen, X., Jiang, W., Li, X., Liu, Q., Kang, Y., and Song, B. (2024). Advancements in spinal cord injury repair: insights from dental-derived stem cells. Biomedicines 12 (3), 683. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12030683
Wu, T., Xu, W., Chen, H., Li, S., Dou, R., Shen, H., et al. (2020). Comparison of the differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and periodontal ligament stem cells into neuron-like cells and their effects on focal cerebral ischemia. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 52 (9), 1016–1029. doi:10.1093/abbs/gmaa082
Xia, L., Kano, F., Hashimoto, N., Ding, C., Xu, Y., Hibi, H., et al. (2023). Conditioned Medium from stem cells of Human exfoliated deciduous teeth partially alters the expression of inflammation-associated molecules of mouse condylar chondrocytes via secreted frizzled-related protein 1. J. Oral Health Biosci. 35 (2), 52–60. doi:10.20738/johb.35.2_52
Xie, Z., Shen, Z., Zhan, P., Yang, J., Huang, Q., Huang, S., et al. (2021). Functional dental pulp regeneration: basic research and clinical translation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (16), 8991. doi:10.3390/ijms22168991
Xu, Y., Chen, J., Zhou, H., Wang, J., Song, J., Xie, J., et al. (2020). Effects and mechanism of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth combined with hyperbaric oxygen therapy in type 2 diabetic rats. Clin. (Sao Paulo) 75, e1656. doi:10.6061/clinics/2020/e1656
Xuan, K., Li, B., Guo, H., Sun, W., Kou, X., He, X., et al. (2018). Deciduous autologous tooth stem cells regenerate dental pulp after implantation into injured teeth. Sci. Transl. Med. 10 (455), eaaf3227. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf3227
Yamaguchi, S., Shibata, R., Yamamoto, N., Nishikawa, M., Hibi, H., Tanigawa, T., et al. (2015). Dental pulp-derived stem cell conditioned medium reduces cardiac injury following ischemia-reperfusion. Sci. Rep. 5, 16295. doi:10.1038/srep16295
Yamaza, T., Kentaro, A., Chen, C., Liu, Y., Shi, Y., Gronthos, S., et al. (2010). Immunomodulatory properties of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 1 (1), 5. doi:10.1186/scrt5
Yan, X., Qin, H., Qu, C., Tuan, R. S., Shi, S., and Huang, G. T. J. (2010). iPS cells reprogrammed from human mesenchymal-like stem/progenitor cells of dental tissue origin. Stem Cells Dev. 19 (4), 469–480. doi:10.1089/scd.2009.0314
Yang, X., Ma, Y., Guo, W., Yang, B., and Tian, W. (2019). Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth as an alternative cell source in bio-root regeneration. Theranostics 9 (9), 2694–2711. doi:10.7150/thno.31801
Yang, C., Chen, Y., Zhong, L., You, M., Yan, Z., Luo, M., et al. (2020). Homogeneity and heterogeneity of biological characteristics in mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cords and exfoliated deciduous teeth. Biochem. Cell Biol. 98 (3), 415–425. doi:10.1139/bcb-2019-0253
Yang, X., Zhang, S., Lu, J., Chen, X., Zheng, T., He, R., et al. (2024a). Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in skeletal diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 11, 1268019. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2024.1268019
Yang, N., Shen, R., Yang, W., Zhang, S., Gong, T., and Liu, Y. (2024b). Biomimetic pulp scaffolds prepared from extracellular matrix derived from stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth promote pulp-dentine complex regeneration. Int. Endod. J. 57 (9), 1279–1292. doi:10.1111/iej.14099
Yang, X., Sun, P., Yu, D., Liang, X., and Zhang, X. (2025). Evaluation of the osteogenic effect of Naringin-enhanced bmscs/cpc composite for alveolar ridge preservation and tooth extraction wound healing in beagle dogs. BMC Oral Health 25 (1), 1202. doi:10.1186/s12903-025-06545-7
Yoon, J. H., Roh, E. Y., Shin, S., Jung, N. H., Song, E. Y., Chang, J. Y., et al. (2013). Comparison of explant-derived and enzymatic digestion-derived MSCs and the growth factors from Wharton’s jelly. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 1–8. doi:10.1155/2013/428726
You, J., Zhang, Q., Qian, L., Shi, Z., Wang, X., Jia, L., et al. (2024). Antibacterial periodontal ligament stem cells enhance periodontal regeneration and regulate the oral microbiome. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 15 (1), 334. doi:10.1186/s13287-024-03939-2
Yu, B. H., Zhou, Q., and Wang, Z. L. (2014). Periodontal ligament versus bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in combination with Bio-Oss scaffolds for ectopic and in situ bone formation: a comparative study in the rat. J. Biomater. Appl. 29 (2), 243–253. doi:10.1177/0885328214521846
Yu, S., Zhao, Y., Ma, Y., and Ge, L. (2016). Profiling the secretome of human stem cells from dental apical papilla. Stem Cells Dev. 25 (6), 499–508. doi:10.1089/scd.2015.0298
Zayed, M., and Iohara, K. (2020). Immunomodulation and regeneration properties of dental pulp stem cells: a potential therapy to treat coronavirus disease 2019. Cell Transpl. 29. doi:10.1177/0963689720952089
Zeng, S., Zhao, X., Zhang, L., Pathak, J. L., Huang, W., Li, Y., et al. (2020). Effect of ciliary neurotrophic factor on neural differentiation of stem cells of human exfoliated deciduous teeth. J. Biol. Eng. 14 (1), 29. doi:10.1186/s13036-020-00251-4
Zhang, Q., Shi, S., Liu, Y., Uyanne, J., Shi, Y., Shi, S., et al. (2009). Mesenchymal stem cells derived from human gingiva are capable of immunomodulatory functions and ameliorate inflammation-related tissue destruction in experimental colitis. J. Immunol. 183 (12), 7787–7798. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0902318
Zhang, H., Liu, S., Zhu, B., Xu, Q., Ding, Y., and Jin, Y. (2016). Composite cell sheet for periodontal regeneration: crosstalk between different types of MSCs in cell sheet facilitates complex periodontal-like tissue regeneration. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 7 (1), 168. doi:10.1186/s13287-016-0417-x
Zhao, Y., Wang, L., Jin, Y., and Shi, S. (2012). Fas ligand regulates the immunomodulatory properties of dental pulp stem cells. J. Dent. Res. 91 (10), 948–954. doi:10.1177/0022034512458690
Zhao, J., Zhou, Y. H., Zhao, Y. Q., Gao, Z. R., Ouyang, Z. Y., Ye, Q., et al. (2023). Oral cavity-derived stem cells and preclinical models of jaw-bone defects for bone tissue engineering. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 14 (1), 39. doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03265-z
Zhao, D. Z., Wei, H. X., Yang, Y. B., Yang, K., Chen, F., Zhang, Q., et al. (2025). Advances in the research of mesenchymal stromal cells in the treatment of maxillofacial neurological disorders and the promotion of facial nerve regeneration. Mol. Neurobiol. 28. doi:10.1007/s12035-025-04981-8
Zhou, L. L., Liu, W., Wu, Y. M., Sun, W. L., Dörfer, C. E., and Fawzy El-Sayed, K. M. (2020). Oral mesenchymal Stem/Progenitor cells: the immunomodulatory masters. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 1–16. doi:10.1155/2020/1327405
Zhou, H., Jing, S., Xiong, W., Zhu, Y., Duan, X., Li, R., et al. (2023). Metal-organic framework materials promote neural differentiation of dental pulp stem cells in spinal cord injury. J. Nanobiotechnology 21 (1), 316. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-02001-2
Glossary
DSCs Dental Stem Cells
DPSCs Dental Pulp Stem Cells
PDLSCs Periodontal Ligament stem Cells
SHEDs Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth
DFSCs Dental Follicle Stem Cells
BMSCs Bone Marrow Stem Cells
UCMSCs Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells
ADSCs Adipose-derived Stem Cells
MSCs Mesenchymal stem cells
MHC-I Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I
MHC-II Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II
CDE Center for Drug Evaluation
BMP-2 Bone Morphogenic Protein-2
GMSCs Gingiva-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
SCAPs Stem Cells from Apical Papilla
iSCAPs Immortalized Stem Cells from Apical Papilla Lines
ALP Alkaline Phosphatase
NSE Neuron-specific Enolase
VEGF-B Vascular Endothelial Frowth Factor-B
GDNF Glial Cell Line-derived Neurotrophic Factor
iPSCs Induced pluripotent stem cells
PCNA Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen
FGF Fibroblast Growth Factor
PDT Population Doubling Time
PGE-2 Prostaglandin E2
IDO Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase
iNOS Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase
TGF-β Transforming Growth Factor-beta
COX-2 Cyclooxygenase-2
SHEDs-CM Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Conditioned Medium
ED Siglec-9-Ectodomain of Sialic Acid-binding Ig-like Lectin-9
HGF Hepatocyte Growth Factor
Treg Regulatory T Cells
EVs Extracellular Vesicles
DPSCs-Exo exosomes derived from DPSCs
TNF-α Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
ADO Adenosine
ATP Adenosine Triphosphate
CHS contact hypersensitivity
DC Dendritic Cell
MC Mast Cell
G-CSF Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor
RA Rheumatoid Arthritis
SLE Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
UCHL1 Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1
TUBB3 Class III b Microtubulin
MAP2 Microtubule-associated Protein 2
BDNF Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor
NGF Nerve Growth Factor
NT-3 Neurotrophin-3
DACC Dental Apical Complex Cells
NCCs Neural Crest Cells
IBD Inflammatory Bowel Disease
AMSCs Amniotic Membrane Mesenchymal Stem Cells
NSCs Neural Stem Cells
I/R Ischemia-Reperfusion
RGCs Retinal Ganglion Cells
rhIGFBP5 Recombinant Human IGFBP5 Protein
IL 1RA-Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist
DMP-1 Dentin Matrix Protein-1
OM Odontogenic Medium
GelMA Gelatin Methacryloyl
DSPP Dentin Sialophosphoprotein
GMP Good Manufacturing Practice
CAL clinical attachment level
VAS visual analogue scale
WOMAC Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index
Keywords: mesenchymal stem cells, dental stem cells, cell therapy, tissue regeneration, regenerative medicine
Citation: Yang K, Yuan S, Wang Y, Lin A, Huo F, Jin Z, Yang C and Tian W (2025) Comparative analysis of dental-derived stem cells and alternative stem cell sources: properties and regenerative functions. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1717849. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1717849
Received: 02 October 2025; Accepted: 31 October 2025;
Published: 18 November 2025.
Edited by:
Karim Boumédiene, Université de Caen Normandie, FranceReviewed by:
Alessandra Pisciotta, University of Modena and, ItalyChafik Ghayor, University of Zurich, Switzerland
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Yuan, Wang, Lin, Huo, Jin, Yang and Tian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chao Yang, eWFuZ2NoYW8xMjA3QHFxLmNvbQ==; Weidong Tian, ZHJ0d2RAc2luYS5jb20=
 Kexin Yang
Kexin Yang Shengmeng Yuan1,2
Shengmeng Yuan1,2 Chao Yang
Chao Yang