Abstract
Background:
Observational studies have indicated a potential association between ankylosing spondylitis and elevated cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk. However, it remains uncertain whether this association reflects a causal association. Therefore, we conducted this Mendelian randomization to investigate the causal relationship between ankylosing spondylitis and CVD.
Methods:
We performed a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis to establish a causal relationship between ankylosing spondylitis and the risk of six prevalent CVDs: hypertension, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, and peripheral artery disease. Furthermore, multivariate Mendelian randomization was employed to determine the influence of confounding factors.
Results:
Genetically predicted ankylosing spondylitis increased the risk of heart failure according to the Mendelian randomization analysis (OR = 1.02; 95% CI = 1.00–1.04; p = 0.030). Multivariate analysis results indicated that the causal relationship between ankylosing spondylitis and heart failure risk remained significant after adjusting for hypertension, diabetes, smoking, body mass index, and pulse wave reflection index. The associations diminished and lost significance after adjusting for pulse wave peak-to-peak time and pulse wave arterial stiffness index.
Conclusion:
Genetically predicted ankylosing spondylitis increased the risk of heart failure, and the causality may partly be mediated by increased arterial stiffness.
Introduction
Ankylosing spondylitis is an emerging interdisciplinary subject, with cardio-rheumatology aiming to explore the relationship between rheumatic diseases and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) (1). It is generally recognized that patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases have a higher incidence of cardiovascular complications (2). Meta-analyses have indicated that people with rheumatoid arthritis have a 48% increased cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk (3). In addition, patients with ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis may be associated with increased CVD risk (4, 5). The role of chronic systemic inflammation and autoimmunity in this process is significant, although the precise pathophysiological mechanisms remain incompletely elucidated. Furthermore, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, including smoking, obesity, and others, along with medications, may also contribute to this phenomenon. Therefore, clarifying the causal relationship between rheumatic diseases and CVDs and exploring their mediating factors stands as highly significant and has great potential to improve the prognosis for patients with rheumatic disease.
Ankylosing spondylitis is an inflammatory arthritis that is distinguished by inflammation and excessive bone growth in the axial skeleton, resulting in limited mobility and potential lifelong disability (6). Furthermore, ankylosing spondylitis frequently presents with extra-articular manifestations, including anterior uveitis, inflammatory bowel disease, aortic valve insufficiency, and cardiac conduction disorder (7). The involvement of cardiovascular complications significantly influences the progression of ankylosing spondylitis. Cardiac complications, such as aortitis, valvular heart diseases, and cardiac conduction abnormalities, are observed in 10%–30% of individuals with ankylosing spondylitis (8). Ankylosing spondylitis patients face a higher risk of mortality due to cardiovascular diseases (9). However, it is important to note that the vast majority of the existing research is derived from observational studies, which are susceptible to confounding factors and reverse causality (10).
Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis is a novel epidemiological tool to avoid potential unmeasured confounders and to confirm whether a trait is causally associated with an outcome by incorporating single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) as a diagnostic tool (11, 12). Therefore, Mendelian randomization analysis has been widely used to investigate the causality of disease. Nevertheless, few Mendelian randomization studies have focused on the association between ankylosing spondylitis and cardiovascular outcomes. Therefore, we performed univariate analysis to clarify the causality between ankylosing spondylitis and six common CVDs, including hypertension, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, and peripheral artery disease. For the positive outcome in the univariate analysis, we further performed multivariate analysis to assess the influence of confounders or mediators.
Methods
Study design
We performed univariate analysis to assess the potential causal association between ankylosing spondylitis and CVDs (including hypertension, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, and peripheral artery disease). For the positive outcomes, multivariate analysis was used to search for confounders or mediators. The flowchart of our study design is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1
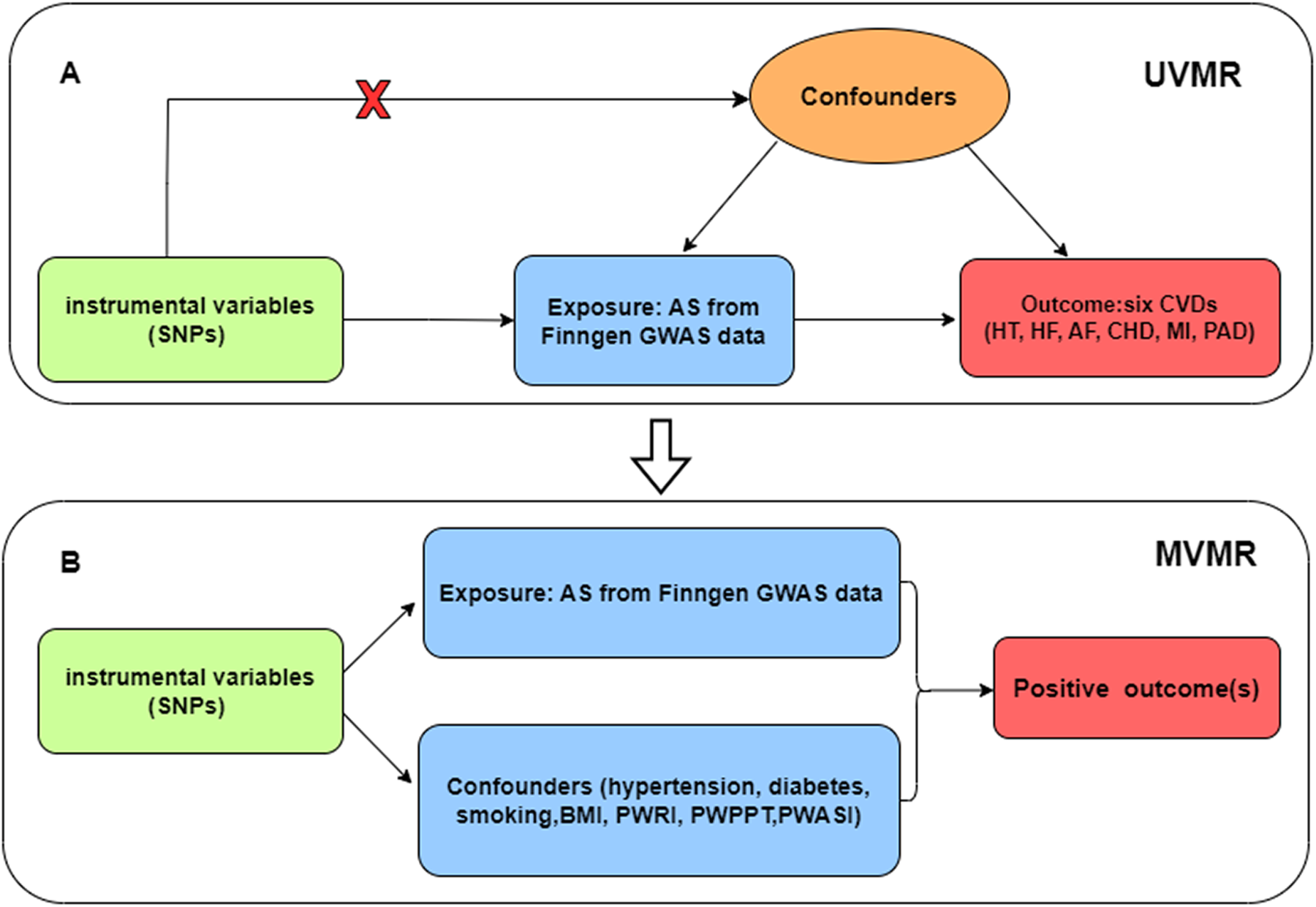
(A) Univariate Mendelian randomization; (B) Multivariate Mendelian randomization. Three main assumptions of Mendelian randomization analysis need to be followed: (1) Genetic instrumental variables (IVs) were strongly correlated with exposure (AS); (2) IVs were independent of any confounding factors; (3) IVs had effects on the outcomes (CVD) only via exposure (AS). SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; UVMR, univariate Mendelian randomization; MVMR, multivariate Mendelian randomization; AS, ankylosing spondylitis; HT, hypertension; HF, heart failure; AF, atrial fibrillation; CHD, coronary heart disease; MI, myocardial infarction; PAD, peripheral artery disease; BMI, body mass index; PWRI, pulse wave reflection index; PWPPT, pulse wave peak -to-peak time; PWASI, pulse wave arterial stiffness index.
Selection of instrumental variables
Firstly, we extracted the genetic instruments of exposure at a strict threshold (p < 5 × 10−8). To remove linkage disequilibrium (LD), we chose the clumping window of r2 = 0.01 and a genetic distance of 10,000 kb. Secondly, we harmonized the filtered data to exclude palindromic SNPs. We examined the association between selected SNPs and potential confounders by PhenoScanner (13). Finally, to ensure that the SNPs selected have sufficient statistical strength, we used the following formula: F = R2 × (N–k–1)/[(1–R2) × k], where R2 = 2 × β2 × (1–EAF) × EAF to calculate the F statistics for each SNP (N = sample size, k = the number of SNPs). Instrumental variables (IVs) with low statistical power (F < 10) were removed from Mendelian randomization analysis (14). Detailed information on selected SNPs is presented in Supplementary Table 1.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was carried out using R software (version 4.3.0) and TwoSampleMR (version 0.5.7).
The inverse variance weighted (IVW) method was used to perform the Mendelian randomization analysis since it is conventionally the most reliable when the total IVs are available (10). The random-effects IVW technique was applied to obtain a more accurate estimation when heterogeneity is present (12). As a part of the reliability assessment, MR-Egger regression (15) and weighted median (16) were also conducted. To confirm that the results were valid and robust, we applied multiple methods for sensitivity analysis. A Cochrane's Q test was used to evaluate heterogeneity, and if heterogeneity was detected (p < 0.05), we used the random-effects IVW model to ensure a conservative outcome (17). Our MR-Egger regression was used to assess whether there was pleiotropy on the horizontal scale, with the intercept term showing how pleiotropy was distributed across the IVs (15). Outliers in IVW linear regression were identified using MR pleiotropy residual sum and outlier (MR-PRESSO), which corrects estimates by removing outliers when they are present (18). Furthermore, the results of Mendelian randomization analysis were examined for robustness and reliability using the leave-one-out method.
As the univariate analysis we conducted may be confounded or mediated by common cardiovascular risks, we performed multivariate analysis, adjusting for hypertension, diabetes, body mass index, smoking, and arteriosclerosis-related characteristics (pulse wave reflection index, pulse wave peak-to-peak time, pulse wave arterial stiffness index). Based on the same criteria, we obtained instrumented variables for possible risk factors and conducted multivariate analysis with the exposure data of ankylosing spondylitis to assess the impact on outcomes.
Results
Data source
Genome-wide association study (GWAS) data on ankylosing spondylitis were derived from the FinnGen database, which contains 166,144 individuals of European ancestry (1,462 cases and 164,682 controls). All ankylosing spondylitis cases followed the definition of M13 code in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 10. We derived the data on heart failure from the Heart Failure Molecular Therapeutic Target Epidemiology (HERMES) Consortium, containing 977,323 European individuals (47,309 cases and 930,014 controls) (19). The GWAS summary data on hypertension were from the UK Biobank, including 91,033 cases and 245,650 controls. The data source of atrial fibrillation was accessed from a summary GWAS meta-analysis by Roselli et al (20), incorporating 537,409 individuals of European ancestry (55,114 cases and 482,295 controls). We derived the summary data on coronary heart disease from the Coronary Artery Disease Genetics Consortium, which consisted of 60,801 patients and 123,504 controls (21). The genetic data on myocardial infarction were obtained from a large-scale GWAS analysis, including 395,795 individuals of European ancestry (14,825 cases and 380,970 controls) (22). The data source of peripheral artery disease was accessed from the UK Biobank, containing 1,230 cases and 359,964 controls. All summary statistics for ankylosing spondylitis and six CVDs were accessed from the IEU OpenGWAS database. Table 1 shows the details of the datasets used in this study.
Table 1
| Phenotypes | Data source | Phenotypic code | Cases/controls | Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure | ||||
| AS | FinnGen | finn-b-M13_ANKYLOSPON | 1,462/164,682 | European |
| Outcome | ||||
| HT | UK Biobank | ukb-a-437 | 91,033/245,650 | European |
| HF | Shah S | ebi-a-GCST009541 | 47,309/930,014 | European |
| AF | Roselli C | ebi-a-GCST006061 | 55,114/482,295 | European |
| CHD | CARDIoGRAMplusC4D | ieu-a-7 | 60,801/123,504 | Mixed (77% European) |
| MI | Hartiala JA | ebi-a-GCST011365 | 14,825/ 380,970 | European |
| PAD | UK Biobank | ukb-d-I9_PAD | 1,230/359,964 | European |
| Confounder | ||||
| HT | MRC-IEU | ukb-b-14177 | 124,227/337,653 | European |
| Diabetes | MRC-IEU | ukb-b-10753 | 22,340/439,238 | European |
| Smoking | MRC-IEU | ukb-b-20261 | 280,508/180,558 | European |
| BMI | MRC-IEU | ukb-b-19953 | 461,460 | European |
| PWRI | MRC-IEU | ukb-b-11598 | 151,546 | European |
| PWPPT | MRC-IEU | ukb-b-8778 | 151,466 | European |
| PWASI | MRC-IEU | ukb-b-11971 | 151,053 | European |
Data source.
AS, ankylosing spondylitis; HT, hypertension; HF, heart failure; AF, atrial fibrillation; CHD, coronary heart disease; MI, myocardial infarction; PAD, peripheral artery disease; BMI, body mass index; PWRI, pulse wave reflection index; PWPPT, pulse wave peak-to-peak time; PWASI, pulse wave arterial stiffness index.
Causal estimates of genetic susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis and CVD risk
According to the IVW model, there is evidence to suggest that genetically predicted ankylosing spondylitis has a significant causal impact on heart failure. Patients with ankylosing spondylitis have an increased risk of heart failure compared with those without ankylosing spondylitis (OR = 1.02; 95% CI = 1.00–1.04; p = 0.030). The effect estimates obtained from the weighted median and MR-Egger models also generally align with the findings of the IVW model. Nevertheless, we did not find a significant causal relationship between ankylosing spondylitis and other cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension (OR = 1.00; 95% Cl = 0.99–1.01; p = 0.864), atrial fibrillation (OR = 1.02, 95% Cl = 0.99–1.05; p = 0.224), and myocardial infarction (OR = 1.02; 95% Cl = 0.99–1.04; p = 0.186). All the univariate results between ankylosing spondylitis and six CVDs are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2
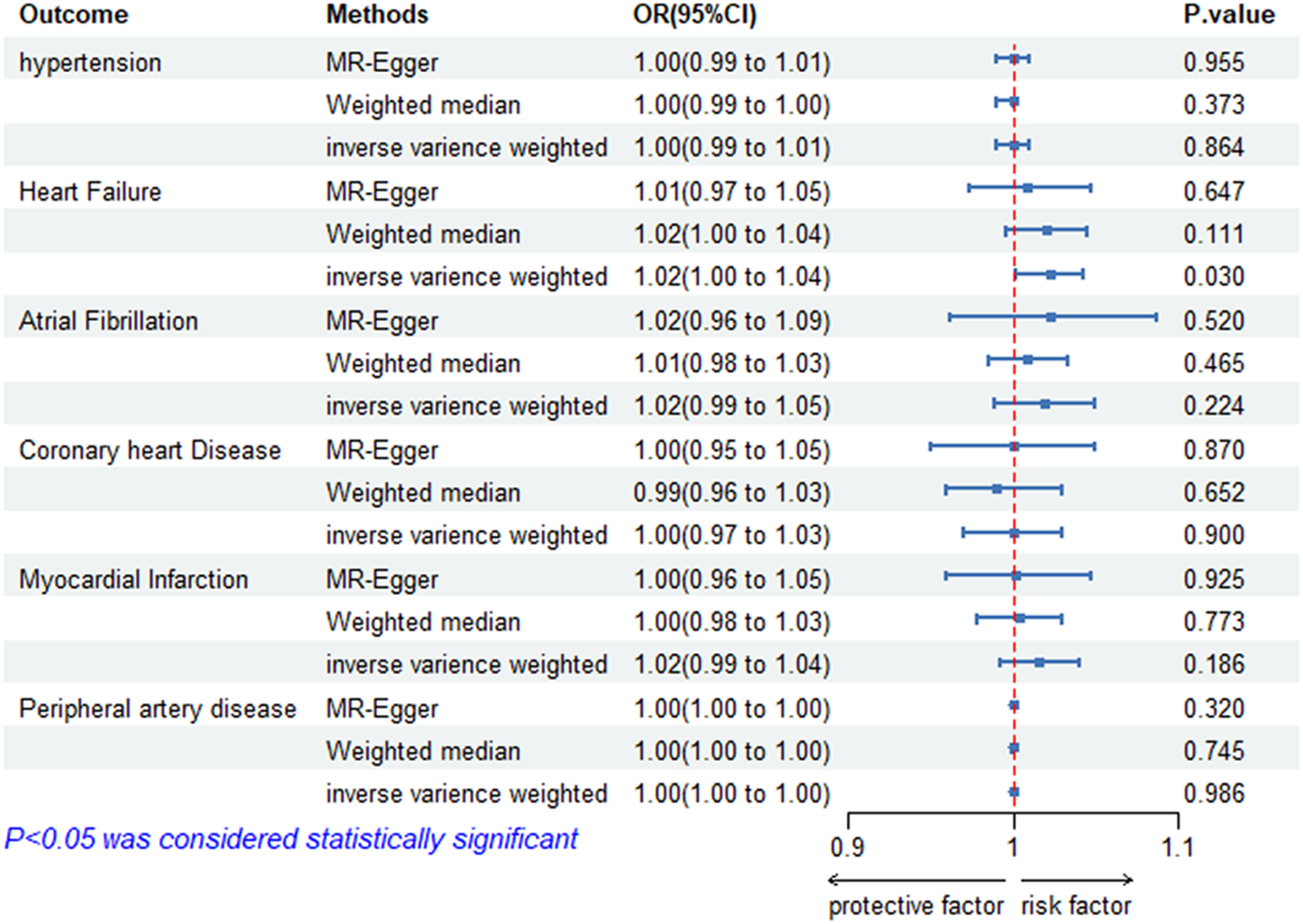
Risk of CVDs for individuals with genetically predicted ankylosing spondylitis. OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; HT, hypertension; HF, heart failure; AF, atrial fibrillation; CHD, coronary heart disease; MI, myocardial infarction; PAD, peripheral artery disease; AS, ankylosing spondylitis.
Sensitivity analysis
The sensitivity analysis results are presented in Table 2. Based on IVW Cochran's Q test, none of the causal effects analyses showed heterogeneity among the used SNPs, except for ankylosing spondylitis—hypertension (Cochrane's Q = 11.329, p = 0.023) and ankylosing spondylitis—atrial fibrillation (Cochrane's Q = 9.57, p = 0.048). In Egger regression analysis, there was no horizontal pleiotropy detected since all Egger intercepts exceeded 0.05. According to the MR-PRESSO test, there were no outliers in the causal analysis, indicating that the estimated causal relationships in this study are reliable. In addition, the funnel plots, scatter plots, and leave-one-out analysis for each association pair can be found in the Supplementary Material.
Table 2
| MR analysis | Heterogeneity test | Pleiotropy | se | pval | MR-PRESSO | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q_pval | Q_df | Q | Egger_intercept | Global test p-value | |||
| AS-HT | 0.023 | 4 | 11.329 | 7.65 × 10−5 | 0.003 | 0.98 | 0.086 |
| AS-HF | 0.95 | 5 | 1.139 | 0.0086 | 0.01 | 0.455 | 0.9593 |
| AS-AF | 0.048 | 4 | 9.57 | −0.0026 | 0.017 | 0.89 | 0.1098 |
| AS-CHD | 0.6287 | 4 | 2.589 | −0.004 | 0.013 | 0.78 | 0.6282 |
| AS-MI | 0.268 | 4 | 5.193 | 0.00897 | 0.0123 | 0.519 | 0.3441 |
| AS-PAD | 0.242 | 4 | 5.47 | 0.00027 | 0.0001 | 0.24 | 0.2754 |
Sensitivity analysis.
MR, Mendelian randomization; AS, ankylosing spondylitis; HT, hypertension; HF, heart failure; AF, atrial fibrillation; CHD, coronary heart disease; MI, myocardial infarction; PAD, peripheral artery disease.
Multivariate Mendelian randomization
We found the causal relationship between ankylosing spondylitis and heart failure in the univariate analysis. Given that potential confounders may interfere with the causal inference, we conducted a multivariate analysis to explore the direct effect of ankylosing spondylitis on heart failure risk (Table 3).
Table 3
| Exposure | Model | Outcome | OR (95% Cl) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS | MVMR (adjusted for hypertension) | HF | 1.015 (1.005–1.024) | 0.00113 |
| MVMR (adjusted for diabetes) | 1.017 (1.002–1.032) | 0.028 | ||
| MVMR (adjusted for smoking) | 1.016 (1.008–1.023) | 7.54 × 10−5 | ||
| MVMR (adjusted for BMI) | 1.014 (1.006–1.021) | 4.18 × 10−4 | ||
| MVMR (adjusted for PWRI | 1.015 (1.003–1.026) | 0.013 | ||
| MVMR (adjusted for PWPPT) | 1.016 (0.999–1.032) | 0.052 | ||
| MVMR (adjusted for PWASI | 1.017 (0.998–1.035) | 0.067 |
Results from multivariate Mendelian randomization.
AS, ankylosing spondylitis; HF, heart failure; BMI, body mass index; PWRI, pulse wave reflection index; PWPPT, pulse wave peak-to-peak time; PWASI, pulse wave arterial stiffness index; MVMR, multivariate Mendelian randomization.
In the multivariate analysis, the results of our study indicate that the causal association between ankylosing spondylitis and the risk of heart failure remained statistically significant even after controlling for hypertension (OR = 1.015; 95% CI = 1.006–1.024; p = 1.13 × 10−3), diabetes (OR = 1.017; 95% CI = 1.002–1.032; p = 0.028), smoking (OR = 1.016; 95% CI = 1.008–1.024; p = 7.54 × 10−5), body mass index (OR = 1.014; 95% CI = 1.006–1.022; p = 4.18 × 10−4), and pulse wave reflection index (OR = 1.015; 95% CI = 1.003–1.026; p = 0.013). However, after adjusting for pulse wave peak-to-peak time (OR = 1.016; 95% CI = 0.999–1.032; p = 0.052) and pulse wave arterial stiffness index (OR = 1.017; 95% CI = 0.998–1.036; p = 0.067), the causal association between ankylosing spondylitis and heart failure became less significant.
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this study represents the investigation into the causal association between ankylosing spondylitis and multiple CVDs utilizing Mendelian randomization analysis. Our findings suggest that ankylosing spondylitis might serve as a risk factor for heart failure, and no analogous significant relationship was observed with other cardiovascular outcomes. Moreover, upon adjusting for arterial stiffness-related characteristics, the previously observed significant causal impact of ankylosing spondylitis on heart failure became non-significant.
Previous studies have documented the correlation between ankylosing spondylitis and susceptibility to CVDs. An observational study including 14,129 patients newly diagnosed with ankylosing spondylitis has posited that ankylosing spondylitis is an independent risk factor for atrial fibrillation (23). Additionally, patients with ankylosing spondylitis had more enhanced monocyte–endothelial interactions, which can accelerate atherogenesis (24). Nevertheless, it is important to acknowledge that these observational studies are prone to confounding variables and reverse causation, and our Mendelian randomization analysis did not yield significant causal associations. Regarding heart failure, prior observational studies have reported the association between ankylosing spondylitis and heart failure. A cohort study including 12,988 ankylosing spondylitis cases suggested that patients with ankylosing spondylitis are at a heightened risk of developing congestive heart failure, consistent with our findings (25). Nevertheless, the precise mechanism underlying the increased occurrence of heart failure in ankylosing spondylitis patients remains unclear.
Studies have demonstrated a higher incidence of aortic valve disease and heart failure among ankylosing spondylitis patients when compared with the general population (26). Damage to the aortic valve is a frequently observed complication of ankylosing spondylitis (8). This damage often manifests as valve thickening, insufficiency, and regurgitation (27). The impaired function of the valve has a significant impact on the hemodynamics, potentially leading to an increased burden on the heart and the development of heart failure. Additionally, aortitis, primarily affecting the aortic ring and ascending aorta, is a common occurrence in ankylosing spondylitis patients (28). Furthermore, individuals with ankylosing spondylitis have an elevated prevalence of heart conduction disorders, particularly atrioventricular block, with the conduction abnormality potentially being linked to the presence of human leukocyte antigen B27 (27). Conduction disorders affect the rhythm and ejection of the heart, increasing the risk of heart failure.
In our multivariate analysis, it was found that the causal effect of ankylosing spondylitis on heart failure lost significance upon adjustment for pulse wave peak-to-peak time and pulse wave arterial stiffness index, which serve as measurements of arterial stiffness. This finding suggested that increased arterial stiffness may play a partial mediating role in the process from ankylosing spondylitis to heart failure. Prior systemic review had demonstrated that an elevation in arterial stiffness among individuals with chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, including ankylosing spondylitis (29). Furthermore, a case–control study indicated a strong association between disease activity and arterial stiffness levels in ankylosing spondylitis patients (30). Increased arterial stiffness in chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases is a leading cause of diastolic dysfunction, which serves as one of the primary mechanisms for the development of heart failure (29). Consequently, early screening and intervention measures for atherosclerosis can mitigate the incidence of cardiovascular events in ankylosing spondylitis patients, including heart failure.
A previous Mendelian study by Zhong et al. (32) pointed out that there is no causal relationship between ankylosing spondylitis and cardiovascular diseases. They used the genetic data of the GWAS study on ankylosing spondylitis published by Crotes et al. (31) in 2013, which included a total of 22,647 European participants (9,069 cases and 13,578 controls) (31). In our research, the genetic data for ankylosing spondylitis were derived from the 2021 FinnGen dataset, which contains 166,144 individuals of European ancestry (1,462 cases and 164,682 controls). Compared with the study by Zhong et al. (32), our exposure data were obtained from a different cohort, and the data were more recent with a larger sample size. We found a significant genetic association between ankylosing spondylitis and heart failure. We applied multivariate analysis to further demonstrate the reliability of our result for the first time, which had not been implemented in previous similar Mendelian randomization studies.
Inevitably, certain limitations should be acknowledged. For the outcomes, we did not find data on specific subtypes, such as the types of heart failure classified by ejection fraction. The study population consisted mostly of individuals with European ancestry, and we do not know if we can get similar results in other populations. Lastly, the relatively low values of ORs in this study indicate that the results should be interpreted with caution.
Conclusion
Our study revealed that genetically predicted ankylosing spondylitis increases the risk of heart failure. Nevertheless, ankylosing spondylitis and other cardiovascular outcomes did not show a causal relationship in our investigation. The connection between ankylosing spondylitis and heart failure may be mediated by increased arterial stiffness, implying that early screening and intervention for atherosclerosis might mitigate the occurrence of heart failure and enhance the quality of life of individuals with ankylosing spondylitis.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
CL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft. LW: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft. ML: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. JY: Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft. XZ: Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft. AW: Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YL: Writing – original draft. FP: Writing – review & editing. DH: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Joint Funds for the Innovation of Science and Technology, Fujian Province (Grant Number: 2021Y9121) and Joint Funds for the Innovation of Science and Technology, Fujian province (Grant Number: 2023Y9436).
Acknowledgments
We thank the participants and researchers who provided us with GWAS data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1415263/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Manolis AS Tzioufas AG . Cardio-rheumatology: two collaborating disciplines to deal with the enhanced cardiovascular risk in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. (2020) 18:533–7. 10.2174/1570161118666200721145718
2.
Buleu F Sirbu E Caraba A Dragan S . Heart involvement in inflammatory rheumatic diseases: a systematic literature review. Medicina (Kaunas). (2019) 55:249. 10.3390/medicina55060249
3.
Avina-Zubieta JA Thomas J Sadatsafavi M Lehman AJ Lacaille D . Risk of incident cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann Rheum Dis. (2012) 71:1524–9. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200726
4.
Peters MJ van der Horst-Bruinsma IE Dijkmans BA Nurmohamed MT . Cardiovascular risk profile of patients with spondylarthropathies, particularly ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. (2004) 34:585–92. 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2004.07.010
5.
Papagoras C Voulgari PV Drosos AA . Atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease in the spondyloarthritides, particularly ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2013) 31:612–20.
6.
Braun J Sieper J . Ankylosing spondylitis. Lancet. (2007) 369:1379–90. 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60635-7
7.
Elewaut D Matucci-Cerinic M . Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis and extra-articular manifestations in everyday rheumatology practice. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2009) 48:1029–35. 10.1093/rheumatology/kep146
8.
El Maghraoui A . Extra-articular manifestations of ankylosing spondylitis: prevalence, characteristics and therapeutic implications. Eur J Intern Med. (2011) 22:554–60. 10.1016/j.ejim.2011.06.006
9.
Escárcega RO Lipinski MJ García-Carrasco M Mendoza-Pinto C Galvez-Romero JL Cervera R . Inflammation and atherosclerosis: cardiovascular evaluation in patients with autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. (2018) 17:703–8. 10.1016/j.autrev.2018.01.021
10.
Lawlor DA Harbord RM Sterne JAC Timpson N Davey Smith G . Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat Med. (2008) 27:1133–63. 10.1002/sim.3034
11.
Smith GD Ebrahim S . ‘Mendelian randomization’: can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease?Int J Epidemiol. (2003) 32:1–22. 10.1093/ije/dyg070
12.
Hemani G Zheng J Elsworth B Wade KH Haberland V Baird D et al The MR-base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife. (2018) 7:e34408. 10.7554/eLife.34408
13.
Kamat MA Blackshaw JA Young R Surendran P Burgess S Danesh J et al Phenoscanner V2: an expanded tool for searching human genotype-phenotype associations. Bioinformatics. (2019) 35:4851–3. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz469
14.
Burgess S Thompson SG , CRP CHD Genetics Collaboration. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. Int J Epidemiol. (2011) 40:755–64. 10.1093/ije/dyr036
15.
Bowden J Davey Smith G Burgess S . Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. (2015) 44:512–25. 10.1093/ije/dyv080
16.
Bowden J Davey Smith G Haycock PC Burgess S . Consistent estimation in Mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol. (2016) 40:304–14. 10.1002/gepi.21965
17.
Bowden J Del Greco MF Minelli C Davey Smith G Sheehan N Thompson J . A framework for the investigation of pleiotropy in two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization. Stat Med. (2017) 36:1783–802. 10.1002/sim.7221
18.
Verbanck M Chen C-Y Neale B Do R . Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. (2018) 50:693–8. 10.1038/s41588-018-0099-7
19.
Shah S Henry A Roselli C Lin H Sveinbjörnsson G Fatemifar G et al Genome-wide association and Mendelian randomisation analysis provide insights into the pathogenesis of heart failure. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:163. 10.1038/s41467-019-13690-5
20.
Roselli C Chaffin MD Weng L-C Aeschbacher S Ahlberg G Albert CM et al Multi-ethnic genome-wide association study for atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet. (2018) 50:1225–33. 10.1038/s41588-018-0133-9
21.
Nikpay M Goel A Won H-H Hall LM Willenborg C Kanoni S et al A comprehensive 1,000 genomes-based genome-wide association meta-analysis of coronary artery disease. Nat Genet. (2015) 47:1121–30. 10.1038/ng.3396
22.
Hartiala JA Han Y Jia Q Hilser JR Huang P Gukasyan J et al Genome-wide analysis identifies novel susceptibility loci for myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:919–33. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa1040
23.
Moon I Choi E-K Jung J-H Han K-D Choi Y-J Park J et al Ankylosing spondylitis: a novel risk factor for atrial fibrillation - a nationwide population-based study. Int J Cardiol. (2019) 275:77–82. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.10.024
24.
Surdacki A Sulicka J Korkosz M Mikolajczyk T Telesinska-Jasiówka D Klimek E et al Blood monocyte heterogeneity and markers of endothelial activation in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. (2014) 41:481–9. 10.3899/jrheum.130803
25.
Bae KH Hong JB Choi YJ Jung JH Han I-B Choi JM et al Association of congestive heart failure and death with ankylosing spondylitis : a nationwide longitudinal cohort study in Korea. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. (2019) 62:217–24. 10.3340/jkns.2018.0110
26.
Szabo SM Levy AR Rao SR Kirbach SE Lacaille D Cifaldi M et al Increased risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in individuals with ankylosing spondylitis: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum. (2011) 63:3294–304. 10.1002/art.30581
27.
Braun J Krüger K Manger B Schneider M Specker C Trappe HJ . Cardiovascular comorbidity in inflammatory rheumatological conditions. Dtsch Arztebl Int. (2017) 114:197–203. 10.3238/arztebl.2017.0197
28.
Chetrit M Khan MA Kapadia S . State of the art management of aortic valve disease in ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2020) 22:23. 10.1007/s11926-020-00898-4
29.
Berger M Fesler P Roubille C . Arterial stiffness, the hidden face of cardiovascular risk in autoimmune and chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Autoimmun Rev. (2021) 20:102891. 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102891
30.
Avram C Drăgoi RG Popoviciu H Drăgoi M Avram A Amaricăi E . Association between arterial stiffness, disease activity and functional impairment in ankylosing spondylitis patients: a cross-sectional study. Clin Rheumatol. (2016) 35:2017–22. 10.1007/s10067-016-3297-7
31.
International Genetics of Ankylosing Spondylitis Consortium (IGAS); CortesAHadlerJPointonJPRobinsonPCKaraderiTLeoPet alIdentification of multiple risk variants for ankylosing spondylitis through high-density genotyping of immune-related loci. Nat Genet. (2013) 45:730–8. 10.1038/ng.2667
32.
Zhong Y Chen Y Zhang X Cai W Zhao C Zhao W . No evidence of a causal relationship between ankylosing spondylitis and cardiovascular disease: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 10:1243867. 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1243867
Summary
Keywords
ankylosing spondylitis, Mendelian randomization, cardiovascular disease, heart failure, the causal link
Citation
Liu C, Wang L, Lin M, You J, Zheng X, Wang A, Lin Y, Peng F and Hu D (2025) Genetically predicted ankylosing spondylitis increases the risk of heart failure: a Mendelian randomization study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1415263. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1415263
Received
26 April 2024
Accepted
07 July 2025
Published
22 July 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Dexter Canoy, Newcastle University, United Kingdom
Reviewed by
Yi-Chiao Bai, Chung Shan Medical University, Taiwan
Wun Zhih Siao, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taiwan
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Liu, Wang, Lin, You, Zheng, Wang, Lin, Peng and Hu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Feng Peng pengfeng@fjmu.edu.cn Dan Hu hudan@fjmu.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.