Abstract
Background:
Left ventricular aneurysm (LVA) often occurs as a complication following an acute myocardial infarction. This research focused on assessing the ability of the fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index to predict LVA formation in individuals with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) who underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Methods:
We included 1,384 consecutive patients diagnosed with STEMI and compared their clinical and laboratory data between the LVA group and the non-LVA group. To determine the independent risk factors for LVA formation, multivariable logistic regression analysis was employed. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis was conducted to evaluate the nonlinear relationship between FIB-4 index and LVA formation. The ROC curve was used to determine the predictive capability of the FIB-4 index and composite variable for LVA formation.
Results:
LVA occurred in 12.7% of the population. An elevated FIB-4 index correlated with a higher occurrence of LVA (19% vs. 9.3%, P < 0.001). In the LVA group, the FIB-4 index was higher than in the non-LVA group [1.8 (1.1–4.6) vs. 3.5 (1.4–8.1), P < 0.001]. Analysis using multivariable logistic regression showed that the FIB-4 index independently correlated with LVA risk (OR = 1.73, P = 0.004). The analysis using RCS uncovered a nonlinear correlation between a higher FIB-4 index and a heightened risk of LVA (Nonlinear P = 0.009). Additionally, the area under the ROC curve for the FIB-4 index in predicting LVA was 0.617. The composite variable comprising the FIB-4 index, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and left anterior descending artery (LAD) as culprit vessel significantly improved the predictive power (C statistic = 0.722).
Conclusion:
An increased FIB-4 index was positively associated with LVA formation in patients with acute STEMI who underwent primary PCI.
Introduction
Left ventricular aneurysm (LVA) is characterized by an abnormal protrusion of the left ventricular wall, which occurs during both systole and diastole as a result of localized myocardial necrosis and fibrosis following myocardial infarction (1). This is a typical complication associated with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), with an incidence ranging from 5% to 15% (2). Patients with LVA formation are more likely to experience arrhythmias (3), thromboembolic events (4), cardiac rupture, and potentially fatal outcomes (5). A previous study has demonstrated that the risk of cardiovascular death was doubled in AMI patients with LVA compared to those without (6). Therefore, predicting LVA formation early is vital for prompt diagnosis and treatment, with the goal of lowering the mortality rate in AMI patients.
The fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index, derived from age, platelet count, and the levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), serves as an easy and non-invasive marker for liver fibrosis (7). A substantial body of clinical research has demonstrated a robust relationship between the FIB-4 index and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). A retrospective cohort study of 81,108 participants with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease identified the FIB-4 index as a key independent predictor of major adverse cardiovascular events (8). A study by Takae et al. indicated that the FIB-4 index is an effective predictor of total cardiovascular events in patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (9). A higher FIB-4 index has been linked to a greater risk of ischemic heart disease in a general population followed up for 10 years (7). Additionally, individuals with a higher FIB-4 index exhibited an increased risk of all-cause mortality among patients with AMI (10). To date, no studies have focused on the FIB-4 index's ability to predict LVA formation in patients suffering from AMI. The objective of this study is to investigate the relationship between the FIB-4 index and the risk of LVA formation in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
Methods
Study subjects
This investigation complied with the Declaration of Helsinki principles and was approved by the Central China Fuwai Hospital's Review Board, with all patients giving informed consent before taking part. For this prospective study, we recruited 1,832 consecutive acute STEMI patients who underwent primary PCI at Central China Fuwai Hospital from 2018 to 2024. Acute STEMI was determined by the criteria outlined in the fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (11), which encompasses the following criteria: typical chest pain persisting for over 30 minutes, with new ST-segment elevation at the J point in at least two contiguous leads of >2 mm (0.2 mV) in men or >1.5 mm (0.15 mV) in women on admission electrocardiogram, and an increase in cardiac enzyme levels above the 99th percentile cut-off point for cardiac troponin I (cTnI). Individuals were excluded if they had congenital heart disease, non-ischemic cardiomyopathy (such as hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy), failure of the kidneys or liver, active infection, malignant tumors, or a life expectancy of less than one year, or if they had received thrombolytic therapy prior to admission, or loss to follow-up. Finally, the analysis involved a total of 1,384 patients (Figure 1).
Figure 1
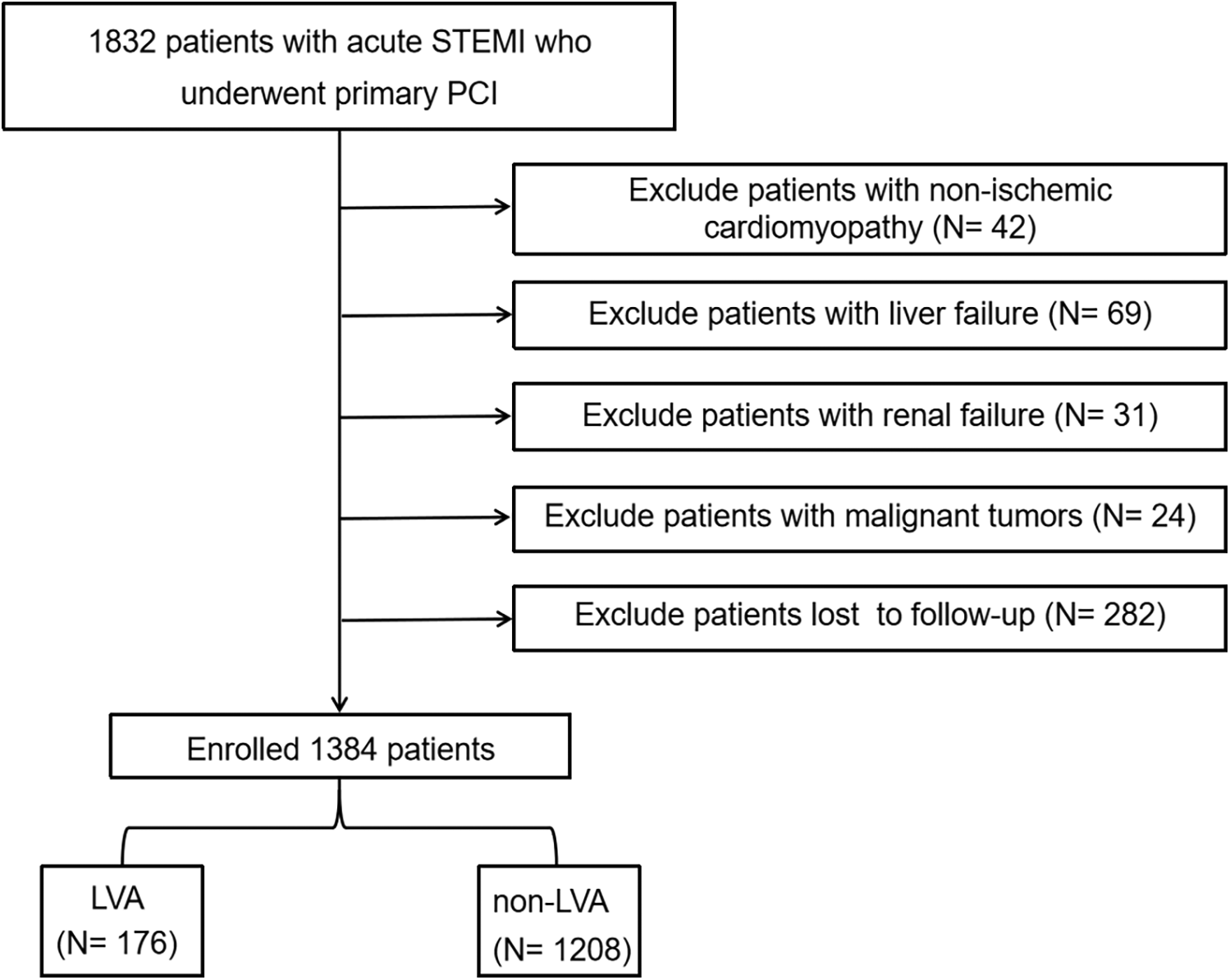
Flow diagram of the study participants. STEMI, acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; LVA, left ventricular aneurysm.
Data collection and definitions
Physicians who were unaware of the study's objectives gathered patient demographic and clinical data from the electronic medical records, such as age, gender, hypertension, diabetes, and medication prescribed upon discharge. The diagnosis of hypertension and diabetes have been previously described (1). Between 7:00 and 9:00 a.m., blood samples were taken from the elbow vein of every patient admitted to the emergency room. The FIB-4 index was calculated using the following formula: FIB-4 index = age (years) × AST (U/L)/[ALT (U/L)1/2 × platelet count (109/L)] (12).
Echocardiography and PCI procedure
For all patients, two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) was carried out within three days of admission and at the end of the first and sixth months during follow-up. Diagnosis of LVA was established using the criteria from the Coronary Artery Surgery Study (CASS) (13). Criteria for LVA diagnosis were: (I) bulging of the left ventricular wall during diastole and systole with either akinesia or dyskinesia; (II) a distinct boundary of the infarcted segment; and (III) no trabeculation present in the affected segment. The procedural details of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) have been documented in prior studies (1).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed utilizing SPSS version 13.0 (SPSS, Inc, Chicago, Illinois) for the Windows operating system (Microsoft Corp, Redmond,Washington). In terms of data presentation, categorical variables were summarized as counts accompanied by their respective percentages. For continuous variables, the presentation varied based on the distribution of the data; these variables were represented either as the mean ± standard deviation or the median with interquartile range, depending on whether the data adhered to a normal distribution. Through ROC curve analysis, the optimal FIB-4 index cut-off for dividing patients into two groups was set at 3.25. Group differences were evaluated using the chi-squared test for categorical data, the independent-sample t-test for normally distributed continuous data, and the Mann–Whitney U-test for continuous data with a skewed distribution. Univariate logistic regression analysis was performed to explore the relationship between different variables and the risk of LVA formation. The multivariate logistic regression analysis incorporated variables that demonstrated a significance level of P < 0.05 during the univariate analysis. All comparisons conducted within this analysis were two-sided. Statistical significance was firmly established at a threshold of p < 0.05.
Results
Patient characteristics
Our research comprised 1,384 individuals diagnosed with acute STEMI who received primary PC. The average age of the participants in this study was 60.4 ± 12.6, with males making up 75.9% of the cohort. Throughout the follow-up period involving TTE, we observed 176 instances (12.7%) of LVA.
Participants were categorized into two groups: the LVA group (N = 176) and the no-LVA group (N = 1,208). As presented in Table 1, individuals in the LVA group were generally older and exhibited elevated levels of left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD), white blood cell count, platelet count, as well as higher values for AST, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), and the FIB-4 index. Additionally, they demonstrated a greater prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and LAD as culprit vessel (P < 0.05). In contrast, the LVA group displayed reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) when compared to those without LVA (P < 0.05).
Table 1
| Variables | Whole cohort (N = 1,384) | Non-LVA patients (N = 1,208) | LVA patients (N = 176) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||||
| Age, years | 60.4 ± 12.6 | 60.0 ± 12.6 | 63.4 ± 12.3 | <0.001 |
| Male, n (%) | 1,050 (75.9) | 921 (76.2) | 129 (73.3) | 0.39 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 673 (48.6) | 567 (46.9) | 106 (60.2) | 0.001 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 403 (29.1) | 332 (27.5) | 71 (40.3) | <0.001 |
| LVEF, % | 48.1 ± 11.7 | 49.1 ± 11.7 | 41.6 ± 9.8 | <0.001 |
| LVEDD, mm | 49.8 ± 6.5 | 49.5 ± 6.3 | 51.8 ± 7.2 | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.4 ± 3.3 | 25.4 ± 3.3 | 25.2 ± 3.4 | 0.532 |
| Laboratory parameters | ||||
| White blood cell count, × 109/L | 8.5 (6.5-11.3) | 8.4 (6.5-11.0) | 9.2 (6.7-12.8) | 0.02 |
| Platelet count, × 109/L | 235.2 ± 73.7 | 233.1 ± 70.6 | 249.6 ± 90.9 | 0.005 |
| ALT, U/L | 27.7 (11.4-76.4) | 28.5 (11.6-77.4) | 24.2 (10.6-66.5) | 0.262 |
| AST, U/L | 42.1 (22.6-114.3) | 40.25 (22.00, 99.00) | 66.20 (29.95, 177.65) | <0.001 |
| ALB, g/L | 41.3 ± 8.4 | 41.4 ± 8.2 | 40.9 ± 9.3 | 0.54 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.8 (5.5-7.0) | 5.8 (5.5-7.0) | 5.9 (5.6-7.1) | 0.019 |
| TC, mmol/L | 4.8 ± 1.2 | 4.8 ± 1.3 | 4.8 ± 1.0 | 0.647 |
| TG, mmol/L | 1.4 (1.0-1.9) | 1.4 (1.0-1.9) | 1.4 (1.1-1.9) | 0.848 |
| HDL, mmol/L | 1.0 ± 2.2 | 1.1 ± 2.3 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.488 |
| LDL, mmol/L | 3.2 ± 0.9 | 3.2 ± 0.9 | 3.2 ± 0.9 | 0.764 |
| LDH, U/L | 325 (212-658) | 316 (210-623) | 393 (236-822) | 0.017 |
| eGFR, ml/min/1.73m2 | 82.6 ± 21.6 | 83.9 ± 20.9 | 73.4 ± 23.8 | <0.001 |
| NTproBNP, pg/ml | 1,435 (537-3,321) | 1,282 (486-2,921) | 2,580 (1,387-5,000) | <0.001 |
| FIB-4 | 1.9 (1.1-5.0) | 1.8 (1.1-4.6) | 3.5 (1.4-8.1) | <0.001 |
| Medication at hospital discharge | ||||
| Statin, n (%) | 1,317 (95.2) | 1,154 (95.5) | 163 (92.6) | 0.092 |
| β-blockers, n (%) | 1,295 (93.6) | 1,133 (93.8) | 162 (92.0) | 0.378 |
| ACE inhibitors or ARB, n (%) | 943 (68.1) | 824 (68.2) | 119 (67.6) | 0.874 |
| Coronary artery injure | ||||
| LAD as Culprit vessel, (%) | 1,114 (80.5) | 959 (79.4) | 155 (88.1) | 0.007 |
| Multiple vessel disease, (%) | 866 (62.6) | 759 (62.8) | 107 (60.8) | 0.602 |
Baseline characteristics of patients stratified by the presence of left ventricular aneurysm.
LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; LVEDD, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter; BMI, body mass index; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALB, albumin; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; LDH, Lactate dehydrogenase; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; ACE, Angiotensin converting enzym; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; LAD, Left anterior descending artery.
Utilizing the criterion of the Maximum Youden Index, we determined the optimal cut-off value for the FIB-4 index to be 3.25, which allows for the stratification of patients into two categories: FIB-4 < 3.25 and FIB-4 ≥ 3.25. Table 2 illustrates that individuals in the FIB-4 ≥ 3.25 group were generally older and exhibited elevated levels of white blood cell count, ALT, AST, albumin (ALB), HbA1c, LDH, and NT-proBNP, alongside a greater prevalence of diabetes and left ventricular aneurysm (LVA) formation. Conversely, patients with FIB-4 ≥ 3.25 demonstrated reduced levels of LVEF, platelet count, and eGFR, and were also less inclined to be prescribed angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) when compared to those with FIB-4 < 3.25.
Table 2
| Variables | FIB-4 < 3.25 (N = 895) | FIB-4 ≥ 3.25 (N = 489) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||
| Age, years | 59.1 ± 12.7 | 62.8 ± 12.1 | <0.001 |
| Male, n (%) | 677 (75.6) | 373 (76.3) | 0.792 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 430 (48.0) | 243 (49.7) | 0.558 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 232 (25.9) | 171 (35.0) | <0.001 |
| LVEF, % | 50.5 ± 11.2 | 43.8 ± 11.5 | <0.001 |
| LVEDD, mm | 49.7 ± 6.3 | 49.9 ± 6.7 | 0.698 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.5 ± 3.4 | 25.2 ± 3.1 | 0.097 |
| Laboratory parameters | |||
| White blood cell count, × 109/L | 7.6 (6.1-9.6) | 10.8 (8.3-14.1) | <0.001 |
| Platelet count, × 109/L | 238.9 ± 67.6 | 228.3 ± 83.4 | <0.001 |
| ALT, U/L | 29 (18–50) | 46.2 (31–83.7) | <0.001 |
| AST, U/L | 25.0 (16.0–42.4) | 144.4 (89.8–219.3) | <0.001 |
| ALB, g/L | 42.6 ± 8.4 | 38.9 ± 7.9 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.8 (5.4–6.7) | 6.0 (5.5–7.5) | <0.001 |
| TC, mmol/L | 4.8 ± 1.3 | 4.8 ± 1.0 | 0.935 |
| TG, mmol/L | 1.4 (1.0–1.9) | 1.4 (1.0–1.8) | 0.177 |
| HDL, mmol/L | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 0.135 |
| LDL, mmol/L | 3.2 ± 0.9 | 3.2 ± 0.8 | 0.781 |
| LDH, U/L | 256 (188–409) | 610 (340–1,113) | <0.001 |
| eGFR, ml/min/1.73m2 | 85.4 ± 19.7 | 77.3 ± 23.8 | <0.001 |
| NT-proBNP, pg/ml | 1,038 (384.2–2,430) | 2,460 (1,240–5,029.5) | <0.001 |
| FIB-4 | 1.3 (0.9–1.9) | 7.0 (4.7–11.4) | <0.001 |
| Medication at hospital discharge | |||
| Statin, n (%) | 851 (95.1) | 466 (95.3) | 0.86 |
| β-blockers, n (%) | 839 (93.7) | 456 (93.3) | 0.722 |
| ACE inhibitors or ARB, n (%) | 635 (70.9) | 308 (63.0) | 0.002 |
| Coronary artery injure | |||
| LAD as Culprit vessel, (%) | 708 (79.1) | 406 (83.0) | 0.079 |
| Multiple vessel disease, (%) | 547 (61.1) | 319 (65.2) | 0.13 |
| LVA, n (%) | 83 (9.3) | 93 (19.0) | <0.001 |
Baseline characteristics of patients stratified by FIB-4 level.
LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; LVEDD, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter; BMI, Body Mass Index; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALB, albumin; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; LDH, Lactate dehydrogenase; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; ACE, Angiotensin converting enzym; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; LAD, left anterior descending artery; LVA, left ventricular aneurysm.
FIB-4 index and the incidence of LVA
The data illustrated in Figures 2A,B indicate that the formation of LVA occurred more frequently as the FIB-4 index increased (9.3% vs. 19%, P < 0.001). Additionally, the group with LVA showed a considerably elevated FIB-4 index in comparison to the group without LVA [3.5 (1.4–8.1) vs. 1.8 (1.1–4.6), P < 0.001].
Figure 2
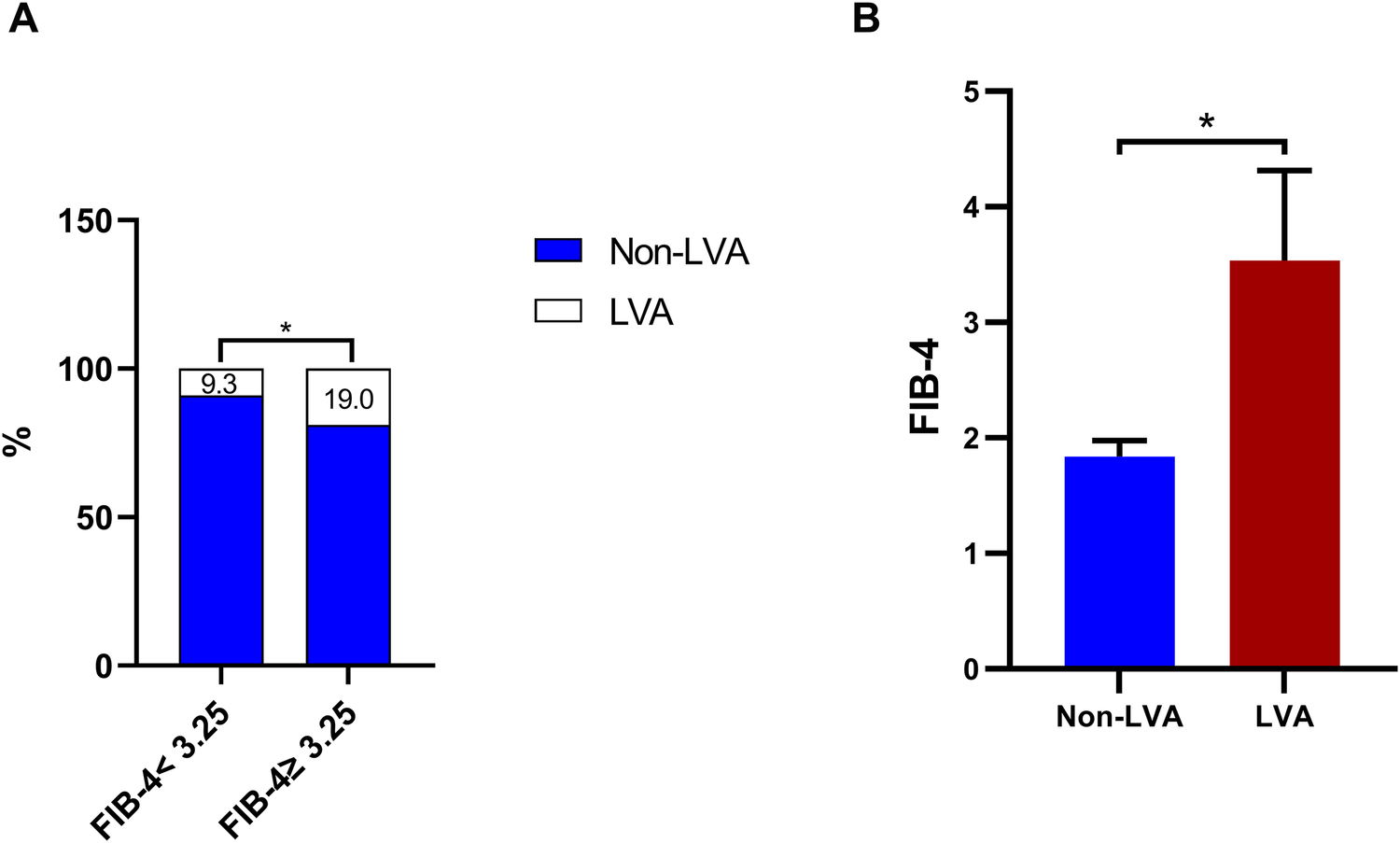
The effect of the FIB-4 index on the prevalence of LVA (A) and comparison of the FIB-4 index level between the LVA and non-LVA groups (B) FIB-4, fibrosis-4; LVA, left ventricular aneurysm; * P < 0.05.
Additionally, we examined the relationship between the FIB-4 index and the prevalence of LVA across various subgroups. The data presented in Figures 3A–F demonstrate a correlation between increased FIB-4 index and higher incidence of LVA in both males (8.7% vs. 18.8%, P < 0.001) and females (11% vs. 19.8%, P = 0.027), individuals aged ≤ 60 (8.4% vs. 16.6%, P = 0.001) and those >60 (10.2% vs. 21.1%, P < 0.001), non-hypertensive (7.7% vs. 13.8%, P = 0.01) and hypertensive (11.2% vs. 24.3%, P < 0.001), non-diabetics (7.2% vs. 16.4%, P < 0.001) and diabetics (15.1% vs. 23.2%, P = 0.034), individuals with LVEF < 50% (17.3% vs. 24.2%, P = 0.024) and LVEF ≥ 50% (3.6% vs. 8.2%, P = 0.017), those BMI < 25 (9.4% vs. 19.8%, P < 0.001) and BMI ≥ 25 (9.2% vs. 18.3%, P < 0.001).
Figure 3
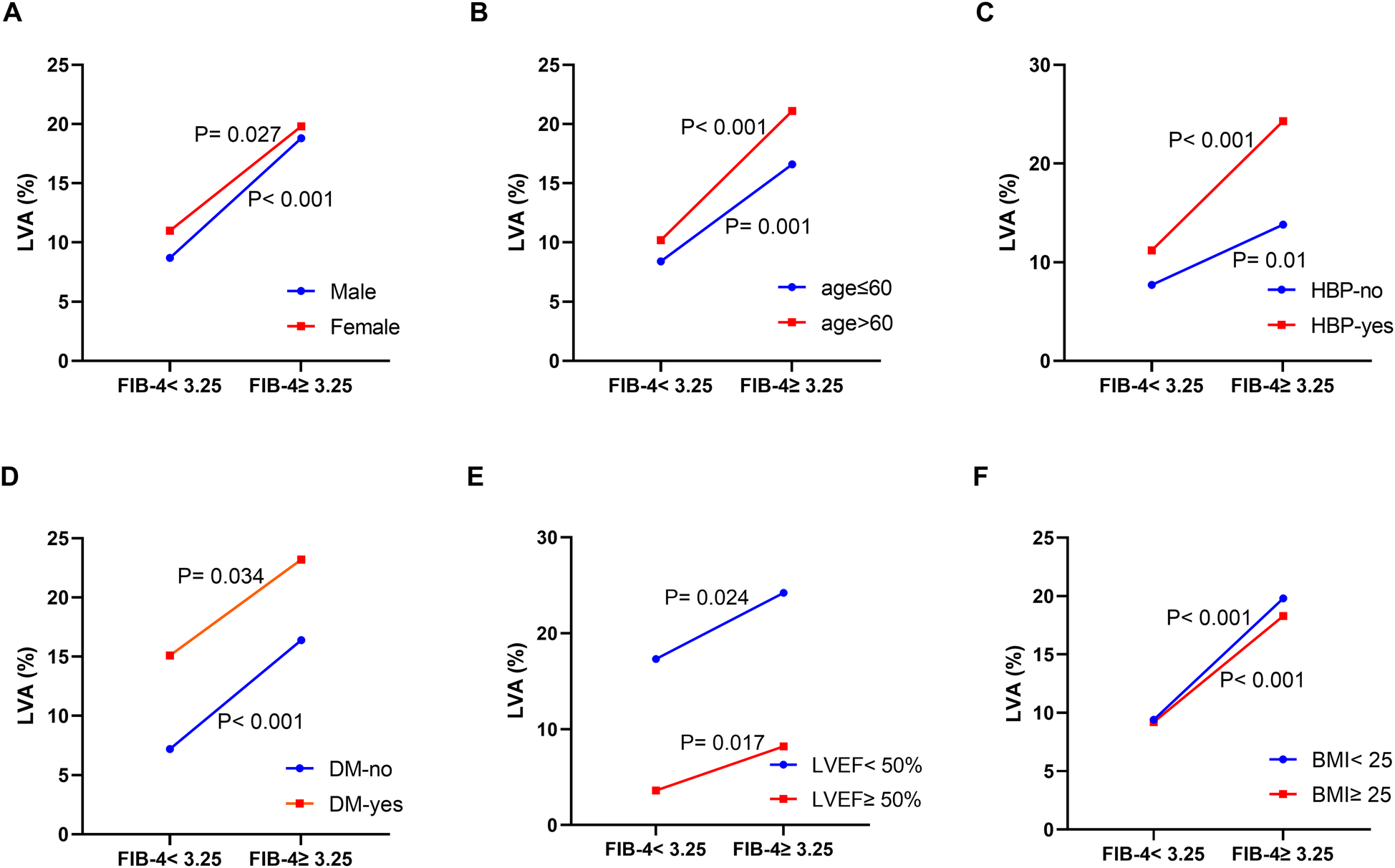
The impact of the FIB-4 index on the prevalence of LVA across subgroups of gender (A), age (B), HBP status (C), DM status (D), LVEF (E), and BMI (F) FIB-4, fibrosis-4; LVA, left ventricular aneurysm; HBP, hypertension; DM, diabetes mellitus; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; BMI, body mass Index.
Logistic regression analyses
We performed logistic regression analysis to evaluate the potential risk factors linked to the development of LVA. In the univariate logistic regression, a noteworthy association was identified between LVA and various parameters such as age, hypertension, diabetes, LVEF, LVEDD, white blood cell count, platelet count, HDL, eGFR, NT-proBNP, LAD as the culprit vessel, and the FIB-4 index (Table 3). Following this, a multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed, incorporating these 12 variables, which indicated that only LVEF (OR = 0.961, 95% CI = 0.944–0.978, P < 0.001), eGFR (OR = 0.989, 95% CI = 0.981–0.998, P = 0.012), LAD as the culprit vessel (OR = 1.837, 95% CI = 1.118–3.019, P = 0.016), and FIB-4 index (OR = 1.776, 95% CI = 1.225–2.575, P = 0.002) showed a significant correlation with the risk of developing LVA (Table 3).
Table 3
| Variables | Univariate logistic regression analysis | Multivariate logistic regression analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | P-value | OR | 95% CI | P-value | |
| Age | 1.023 | 1.009–1.036 | <0.001 | |||
| Hypertension | 1.712 | 1.24–2.363 | 0.001 | |||
| Diabetes | 1.784 | 1.287–2.473 | <0.001 | |||
| LVEF | 0.948 | 0.935–0.961 | <0.001 | 0.961 | 0.944–0.978 | <0.001 |
| LVEDD | 1.051 | 1.027–1.075 | <0.001 | |||
| White blood cell count | 1.054 | 1.018–1.092 | 0.003 | |||
| Platelet count | 1.003 | 1.001–1.005 | 0.006 | |||
| HDL | 0.45 | 0.236–0.859 | 0.015 | |||
| eGFR | 0.979 | 0.973–0.986 | <0.001 | 0.989 | 0.981–0.998 | 0.012 |
| NTproBNP | 1 | 1.000–1.000 | 0.003 | |||
| LAD as Culprit vessel | 1.916 | 1.19–3.087 | 0.007 | 1.837 | 1.118–3.019 | 0.016 |
| FIB-4 (<3.25/≥3.25) | 2.3 | 1.67–3.16 | <0.001 | 1.776 | 1.225–2.575 | 0.002 |
Logistic regression analysis.
LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; LVEDD, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; LAD, Left anterior descending artery; FIB-4, fibrosis-4; OR, odds ratio.
Additionally, RCS was performed to model and visually represent the connection between the FIB-4 index and the risk of LVA. As illustrated in Figure 4, the findings reveal a positive nonlinear correlation between the FIB-4 index and the formation of LVA. This correlation persists even after adjusting for other potential risk factors such as age, hypertension, and diabetes (Nonlinear P = 0.009).
Figure 4
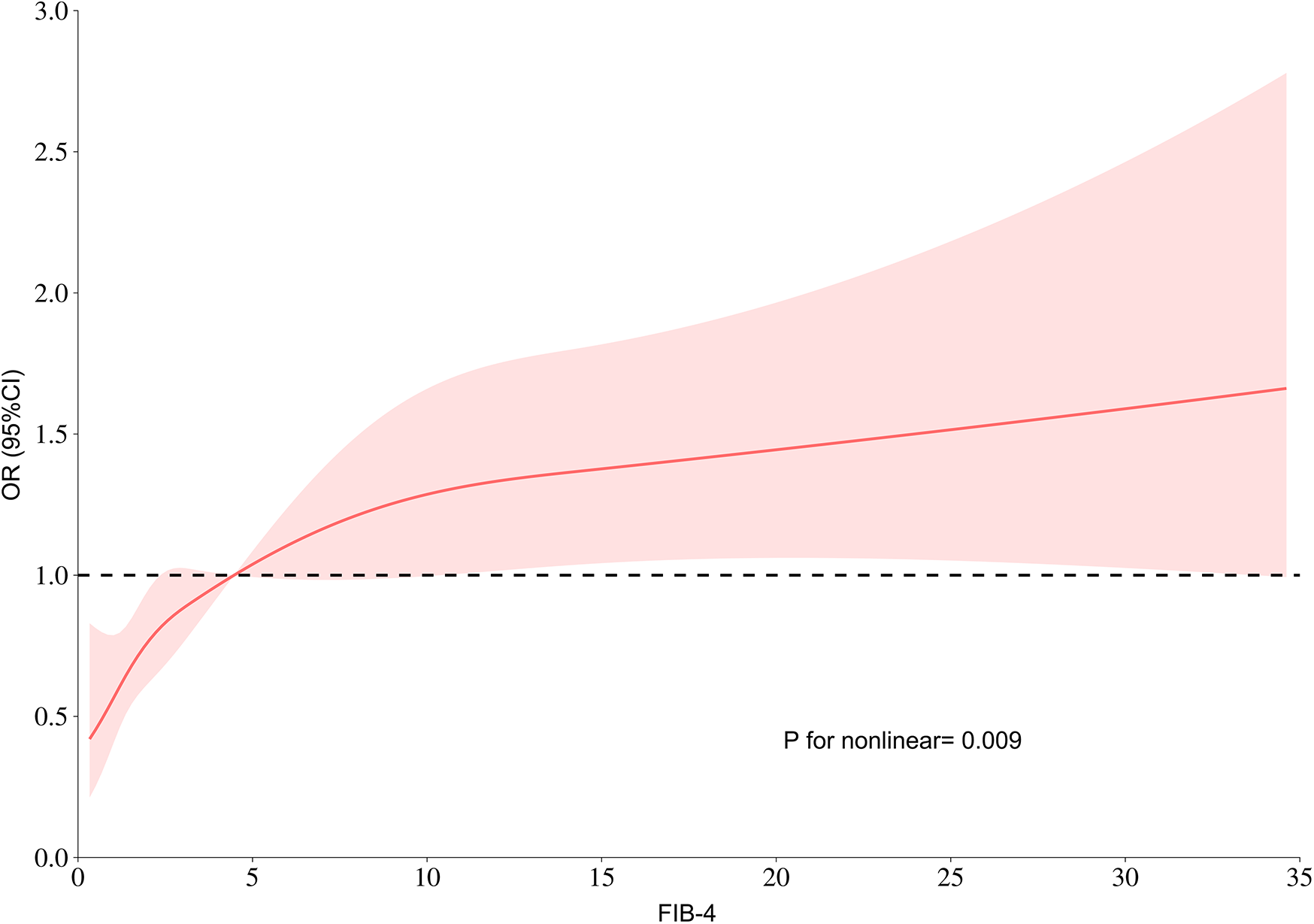
RCS model showing the links between the FIB-4 index and the risk of LVA. FIB-4, fibrosis-4; LVA, left ventricular aneurysm; OR, odds ratio.
Subgroup analysis
We evaluated the independent relationship between the FIB-4 index and LVA formation in different clinically relevant subgroups (Figure 5). The FIB-4 index was significantly associated with the risk of LVA formation in the subgroups of males and females, individuals with age ≤ 60 and >65 years, with and without hypertension, without diabetes, individuals with BMI < 25 kg/m2 and ≥25 kg/m2, with LVEF < 50% and LVEF ≥ 50%, as well as individuals with NT-proBNP < 1,435 pg/ml and ≥1,435 pg/ml. Besides, no notable interactions were identified between the FIB-4 index and these subgroups with regard to the risk of LVA (P for interaction > 0.05).
Figure 5
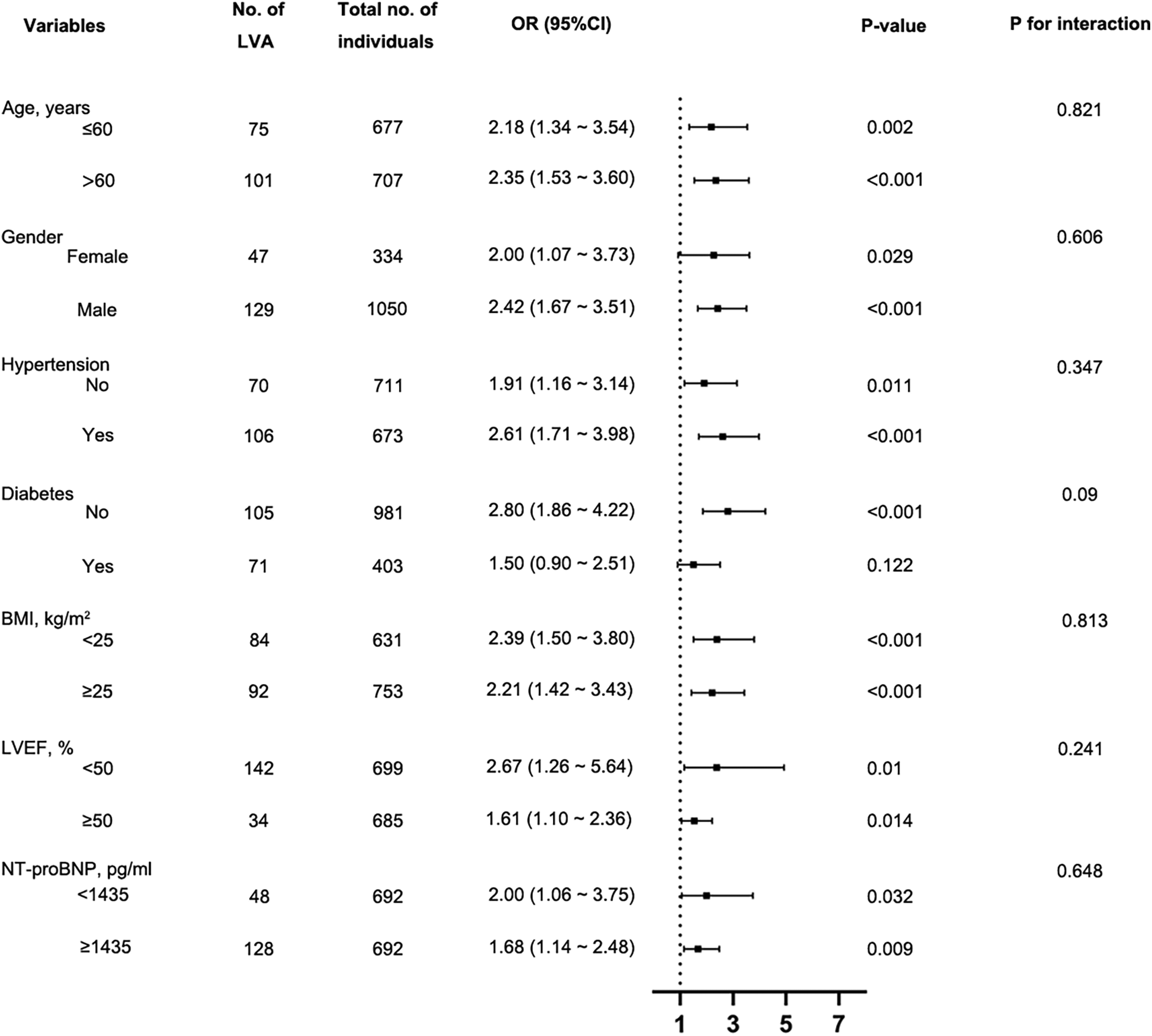
Subgroup analysis using forest plots to assess the connection between the FIB-4 index and the likelihood of LVA formation. FIB-4, fibrosis-4; LVA, left ventricular aneurysm; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; BMI, Body Mass Index; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; OR, Odds Ratio.
Association between FIB-4 index and echocardiography parameters of LVA
Based on echocardiographic findings, we conducted a comparison of LVA dimensions between patients categorized as FIB-4 < 3.25 and those with FIB-4 ≥ 3.25. As illustrated in Figures 6A–C, patients with FIB-4 ≥ 3.25 demonstrated a notable increase in maximal length, maximal width, and area (calculated as the product of length and width) in contrast to patients with FIB-4 < 3.25 (29.5 ± 8.1 vs. 32.5 ± 8.8 for maximal length, 17.7 ± 5.4 vs. 19.9 ± 6.4 for maximal width, and 549.8 ± 293.3 vs. 696.3 ± 400.3 for the area).
Figure 6
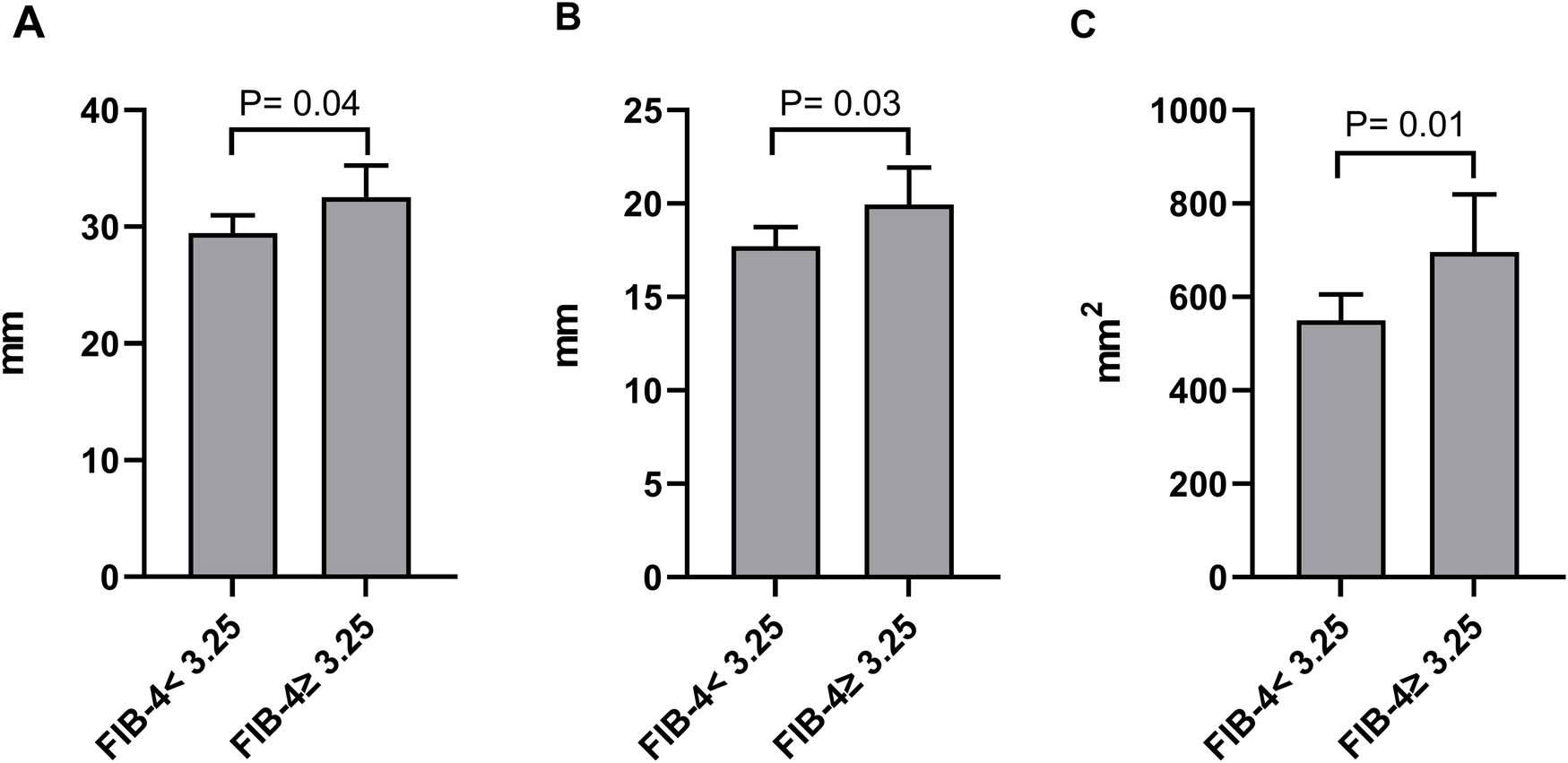
Comparison of the maximal length (A), maximal width (B), and product of length and width (C) of LVA between patients grouped by FIB-4 index.
ROC analysis
We performed ROC analysis to evaluate the discriminative capability of the FIB-4 index and composite variable (FIB-4 combined with LVEF, eGFR, and LAD as culprit vessel) in predicting the risk of LVA formation. As shown in Figure 7 and Table 4, the average AUCs for FIB-4 index and the composite variable were 0.617 (95% CI = 0.591–0.642) and 0.722 (95% CI = 0.698–0.746), respectively. The discrepancy between FIB-4 index and the composite variable was statistically significant (P < 0.001), indicating that combining FIB-4 index with LVEF, eGFR, and LAD as culprit vessel notably improved the predictive accuracy.
Figure 7
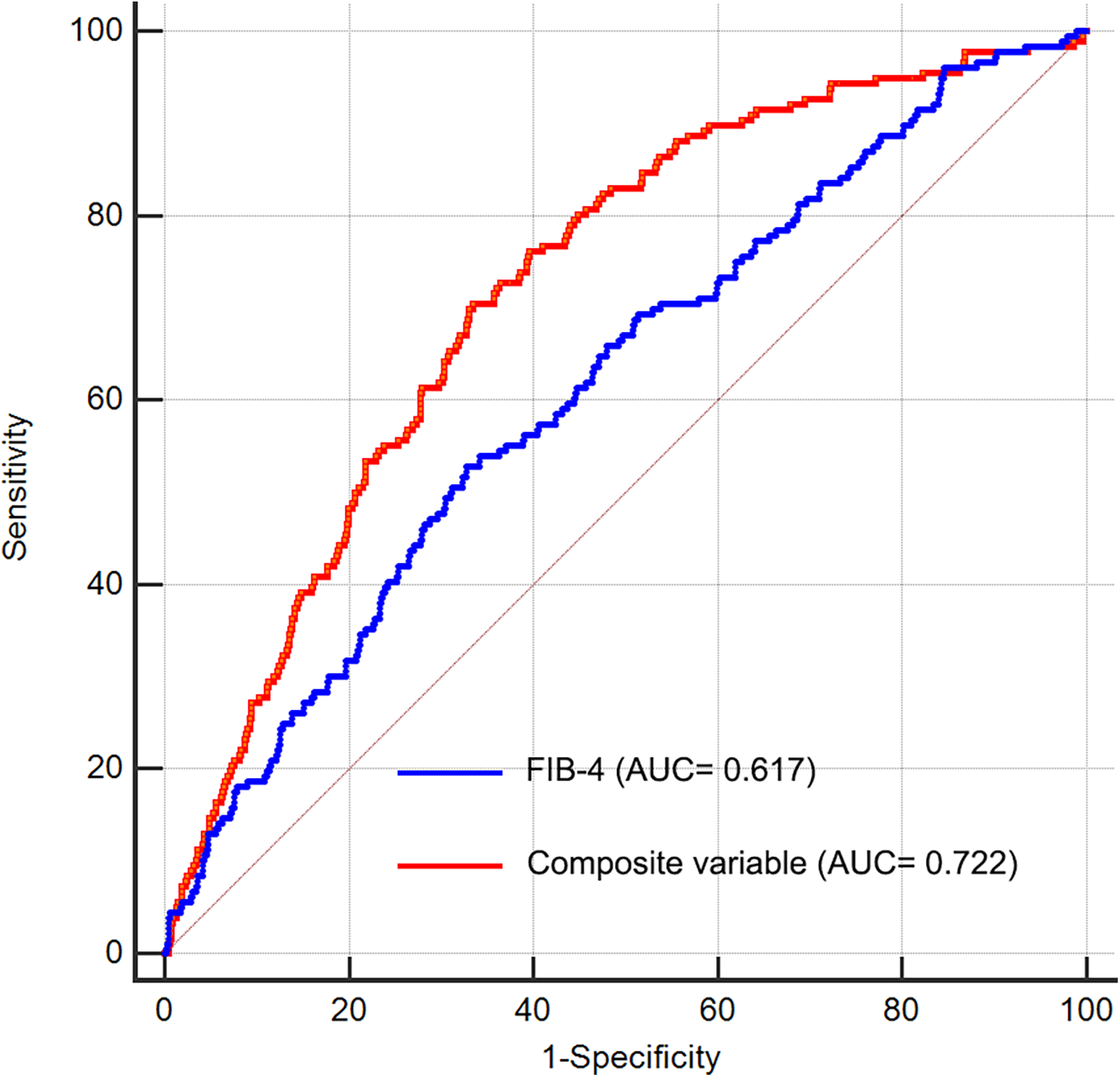
Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of the FIB-4 index to predict LVA formation. AUC, area under the curve; FIB-4, fibrosis-4.
Table 4
| Variables | AUC | SE | Sensitivity | Specificity | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIB-4 | 0.617 | 0.0226 | 0.54 | 0.68 | 0.591–0.642 |
| Composite variable | 0.722 | 0.0195 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 0.698–0.746 |
ROC curve analysis.
ROC, receiver operating characteristic; FIB-4, Fibrosis-4; AUC, area under curve; SE, standard error; CI, confidence interval.
Discussion
In this study of 1,384 patients hospitalized due to acute STEMI and who underwent primary PCI, we discovered that a greater FIB-4 index correlated with a heightened risk of LVA formation. The statistical significance persisted following a multivariate logistic regression analysis. In our stratified analysis, the influence of other covariates—aside from diabetes—on the association between FIB-4 and LVA risk was minimal. Among patients identified with LVA, individuals with a FIB-4 index of 3.25 or greater displayed significantly larger maximal length, maximal width, and area of LVA when compared to those with a FIB-4 index below 3.25. The combination of FIB-4 index, LVEF, eGFR, and LAD as culprit vessel could substantially improve the ability to distinguish LVA formation.
LVA often occurs as a complication following an acute myocardial infarction, with morbidity rates ranging from 5% to 15% (6). In the context of our research, we found that the incidence of LVA was 12.7%. This finding aligns with previously published data (6, 14). FIB-4, a highly-sensitive biomarker for advanced liver fibrosis, has been linked to various cardiovascular diseases. A study comprising 12,380 patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrated that a FIB-4 score of ≥2.67 correlated with a heightened risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) and increased cardiovascular mortality (15). Another study by Nakashima et al. revealed that an elevated FIB-4 index was linked to right ventricular dysfunction, as well as a greater likelihood of subsequent MACE in individuals diagnosed with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) (12). A prospective, single-center analysis involving 414 patients who suffered from ischemic strokes indicated that the FIB-4 score was independently linked to atrial fibrillation (16). Furthermore, elevated FIB-4 values were connected to higher all-cause mortality risks in patients with acute myocardial infarction (10). Similar to the previous studies, our research indicated that the FIB-4 index was significantly elevated in the LVA group compared to the non-LVA group. Specifically, individuals with FIB-4 ≥ 3.25 had a higher prevalence of LVA than those with FIB-4 < 3.25. Additionally, our analysis using univariate and multivariate logistic regression demonstrated a notably link between the FIB-4 index and the risk of LVA development. RCS analysis also presented a nonlinear association between FIB-4 index and LVA formation after adjusting for possible confounders.
Numerous predictors have been recognized for assessing the risk of LVA development in individuals suffering from AMI. Ran et al. pinpointed the monocyte to HDL cholesterol ratio as a significant predictor of LVA formation in patients experiencing STEMI (2). A case-control study involving 193 patients revealed that abnormalities in the glomerular filtration rate and serum ferritin level served as independent risk factors for LVA after AMI (3). In a retrospectively cohort study comprising 1,823 STEMI patients, factors such as female gender, peak levels of NT-pro BNP, the duration from the onset of pain to balloon intervention, the presence of QS-waves on the initial electrocardiogram, and regional wall motion abnormalities (RWMA) in the left ventricular anterior wall and apex emerged as independent predictors for early LVA (17). Research conducted by Celebi et al. indicated that plasma levels of N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide at the time of admission offered significant predictive insights concerning the onset of LVA following acute STEMI (18). Nevertheless, inconsistencies are present concerning these risk factors due to variations in population data. In this research, we introduced the FIB-4 index as a novel predictor of LVA formation in patients experiencing acute STEMI, with FIB-4 ≥ 3.25 increasing the risk of LVA by 73%. In addition, our study found that LVEF and eGFR also showed significant correlations with LVA formation, aligning with earlier reports in the literature (3, 5). Furthermore, the maximal length, maximal width and area of LVA in patients with FIB-4 ≥ 3.25 were significantly increased compared to those with FIB-4 < 3.25, highlighting the crucial role of the FIB-4 index in predicting the severity of LVA. Combining the FIB-4 index with LVEF, eGFR, and LAD as culprit vessel could substantially improve the predictive accuracy for LVA formation.
It is noteworthy that the odds ratio is higher in patients without diabetes compared to those with diabetes. As illustrated in Figure 5, the association between FIB-4 and LVA does not reach statistical significance among diabetic patients (P = 0.122), likely due to the small number of participants with diabetes (N = 403). This limitation may also explain the elevated odds ratio found in non-diabetic patients relative to those with diabetes. It is plausible that, with a sufficiently large sample size, the odds ratio for the diabetic population could surpass that of the non-diabetic group.
Our study has certain limitations that should be taken into account. Firstly, it is essential to highlight that the research was performed at a single center and involved a relatively small sample size. This limitation may restrict the applicability of our findings to a broader population and diminish the statistical power of our conclusions. To overcome this concern, it would be beneficial to conduct a multicenter prospective study that includes a larger cohort of participants. Secondly, the methodology for diagnosing LVA in our study was primarily based on ultrasonographic examination. While this technique is widely utilized in both clinical practice and epidemiological investigations due to its accessibility and non-invasive nature, it is crucial to acknowledge that it does not represent the gold standard for the detection of LVA. An alternative diagnostic approach may need to be considered in future studies to establish a more accurate assessment of LVA. Finally, the findings from our study raise questions regarding the causal relationship between an increased FIB-4 index and the formation of LVA. Although our results suggest a correlation, the evidence we gathered does not definitively support a causal link. Further research is necessary to explore this relationship comprehensively and clarify the mechanisms involved in the association between FIB-4 index levels and LVA development.
Conclusion
This study presents the first evidence that the FIB-4 index is a valuable predictor of LVA formation in patients with acute STEMI who underwent primary PCI. The combination of FIB-4 index, LVEF, eGFR, and LAD as culprit vessel could substantially improve the ability to distinguish LVA formation. These results may offer a novel reference point for the timely recognition of high-risk AMI patients, thereby aiding in the prevention of LVA formation.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Review Board of the Central China Fuwai Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
KZ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft. LY: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. YZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Zhang K Yang L Wu X Zheng X Zhao Y . Urea nitrogen-to-albumin ratio predicts ventricular aneurysm formation in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. ESC Heart Fail. (2024) 11:974–85. 10.1002/ehf2.14620
2.
Ran M Li S Lan J Chen F Wu D . Association of monocyte to HDL cholesterol ratio and a composite risk score with left ventricular aneurysm formation in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Coron Artery Dis. (2024) 35(6):490–7. 10.1097/MCA.0000000000001374
3.
Feng Y Wang Q Chen G Ye D Xu W . Impaired renal function and abnormal level of ferritin are independent risk factors of left ventricular aneurysm after acute myocardial infarction: a hospital-based case-control study. Medicine (Baltimore). (2018) 97:e12109. 10.1097/MD.0000000000012109
4.
Alenghat FJ Couper GS Givertz MM . Giant left ventricular aneurysm as a late complication of inferior myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. (2013) 34:344. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs357
5.
Wang Z Ren L Liu N Peng J . The relationship between post-procedural platelet count and left ventricular aneurysm in patients with acute anterior ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction following primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Kardiol Pol. (2018) 76:899–907. 10.5603/KP.2018.0008
6.
You J Gao L Shen Y Guo W Wang X Wan Q et al Predictors and long-term prognosis of left ventricular aneurysm in patients with acute anterior myocardial infarction treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention in the contemporary era. J Thorac Dis. (2021) 13:1706–16. 10.21037/jtd-20-3350
7.
Higashiura Y Tanaka M Mori K Mikami T Hosaka I Ohnishi H et al High fibrosis-4 index predicts the new onset of ischaemic heart disease during a 10-year period in a general population. European Heart Journal Open. (2022) 2:oeac030. 10.1093/ehjopen/oeac030
8.
Vieira Barbosa J Milligan S Frick A Broestl J Younossi Z Afdhal N et al Fibrosis-4 Index can independently predict Major adverse cardiovascular events in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. (2022) 117:453–61. 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001606
9.
Takae M Fujisue K Yamamoto E Egashira K Komorita T Oike F et al Prognostic significance of liver stiffness assessed by fibrosis-4 index in patients with heart failure. ESC heart Failure. (2021) 8:3809–21. 10.1002/ehf2.13351
10.
Cao M Li T Li Z Gong F Chen Z . A retrospective study on the relationship between fibrosis-4 index and all-cause mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Exp Ther Med. (2022) 24:643. 10.3892/etm.2022.11580
11.
Thygesen K Alpert JS Jaffe AS Chaitman BR Bax JJ Morrow DA et al Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). J Am Coll Cardiol. (2018) 72:2231–64. 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.08.1038
12.
Nakashima M Sakuragi S Miyoshi T Takayama S Kawaguchi T Kodera N et al Fibrosis-4 index reflects right ventricular function and prognosis in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail. (2021) 8:2240–7. 10.1002/ehf2.13317
13.
Bourassa MG Fisher LD Campeau L Gillespie MJ McConney M Lespérance J . Long-term fate of bypass grafts: the coronary artery surgery study (CASS) and Montreal heart institute experiences. Circulation. (1985) 72:V71–8.
14.
Yu P Xi P Tang Y Xu J Liu Y . Novel analysis of coronary angiography in predicting the formation of ventricular aneurysm in patients with acute myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:880289. 10.3389/fcvm.2022.880289
15.
Chew NW Ng CH Chan KE Chee D Syn N Tamaki N et al FIB-4 Predicts MACE and cardiovascular mortality in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Can J Cardiol. (2022) 38:1779–80. 10.1016/j.cjca.2022.07.016
16.
Fandler-Höfler S Kneihsl M Stauber RE Bisping E Mangge H Wünsch G et al Liver fibrosis-4 index indicates atrial fibrillation in acute ischemic stroke. Eur J Neurol. (2022) 29:2283–8. 10.1111/ene.15377
17.
Zhang Z Guo J . Predictive risk factors of early onset left ventricular aneurysm formation in patients with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Heart Lung. (2020) 49:80–5. 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2019.09.005
18.
Celebi S Celebi OO Cetin S Cetin HO Tek M Gokaslan S et al The usefulness of admission plasma NT-pro BNP level to predict left ventricular aneurysm formation after acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Arq Bras Cardiol. (2019) 113:1129–37. 10.5935/abc.20190226
Summary
Keywords
acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, primary percutaneous coronary intervention, left ventricular aneurysm, fibrosis-4 index, risk
Citation
Zhang K, Yang L and Zhao Y (2025) Association between the fibrosis-4 and the risk of left ventricular aneurysm formation in acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1477206. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1477206
Received
07 August 2024
Accepted
28 May 2025
Published
13 June 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Qiuwang Zhang, St Michael's Hospital, Canada
Reviewed by
DeLisa Fairweather, Mayo Clinic Florida, United States
Lorenzo Menicanti, IRCCS San Donato Polyclinic, Italy
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhang, Yang and Zhao.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Kai Zhang jlzhangkai000@163.com Yonghui Zhao zyh200000@126.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.