Abstract
Objective:
The purpose of this study was to investigate the correlation between plasma homocysteine (Hcy) levels and cardiovascular disease (CVD) in United States adults based on the National Health and Examination Survey (NHANES) database of the United States.
Methods:
Data from two survey periods (2003–2006) in the NHANES database were used as the research data set. Plasma Hcy levels are considered an independent variable, while CVD is a dependent variable. Weighted logistic regression, linear trend analysis, subgroup analysis and limiting cubic spline plots were used for analysis. A total of 4,418 samples were included.
Results:
In the weighted logistic regression model, a significant positive correlation between Hcy level and CVD risk was observed (P for trend = 0.007).The subgroup analysis revealed that various characteristics such as age, race, education level, obesity, alcohol use, diabetes, and hypertension did not affect this positive correlation (P for interaction ≥0.05). The nonlinear association between Hcy level and CVD risk was explored by limiting cubic spline plots, revealing the overall significant trend (P for overall <0.0001) and the significant nonlinear trend (P for nonlinear <0.01).
Conclusion:
In this large cross-sectional study, an increase in Hcy levels leads to an increased risk of CVD. There is a nonlinearly positive correlation between Hcy levels and the risk of CVD.
1 Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) remain a major cause of death and disability globally, posing a significant threat to global health (1). According to the findings of the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) studies, the global incidence of cardiovascular diseases has grown by 93% over the past three decades, reaching an astonishing 523 million cases by 2019, which has imposed a heavy economic burden on global healthcare systems and communities (2).
In recent years, an increasing number of studies have shown that elevated levels of serum homocysteine (Hcy) are associated with atherosclerosis, and it is an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis (3). Additional research confirms that: Elevated serum homocysteine (Hcy) levels are an independent risk factor for the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. This factor is equally important as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, and other risk factors, and can lead to an increase in the incidence and mortality of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases (4).
Therefore, reducing Hcy levels may lower the risk of CVD, with significant preventive implications. However, there is currently a lack of large-scale population studies specifically focused on the association between Hcy and CVD risk.
We comprehensively analyzed the relationship between Hcy levels and CVD in American adults using data from two cycles of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2003 to 2006. This analysis also aimed to uncover whether the potential relationship between Hcy and CVD is more pronounced in specific populations. These findings provide strong support for further investigations into the pathogenesis of CVD and the relevance of Hcy levels as a molecular marker in CVD patients.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population
The data source for this study is based on the NHANES database (http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.htm), which originates from a stratified, multi-stage study that combines interviews, physical examinations, and laboratory tests to assess the health and nutritional status of the US population, conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics. This freely accessible database has been approved by the Institutional Review Board of the National Center for Health Statistics and has obtained informed consent from all participants. The procedures follow the principles of the Helsinki Declaration. The NHANES data used in this study is publicly available; therefore, this study is considered not to require ethical or administrative approval.
2.2 Selection criteria
In this study, information was collected from 20,470 participants across two consecutive cycles (2003–2006) of the NHANES database. Given that CVD primarily affects adults, and with a lower prevalence in the under-20 age group, 10,450 participants under 20 years of age were excluded. Participants lacking CVD diagnostic data, based on the CVD questionnaire, were also excluded, amounting to 4,980 individuals. Furthermore, 532 participants without plasma Hcy data and 90 participants lacking relevant covariate information were excluded. Ultimately, 4,418 participants met the criteria and were included in the study. The detailed process of participant selection is illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1
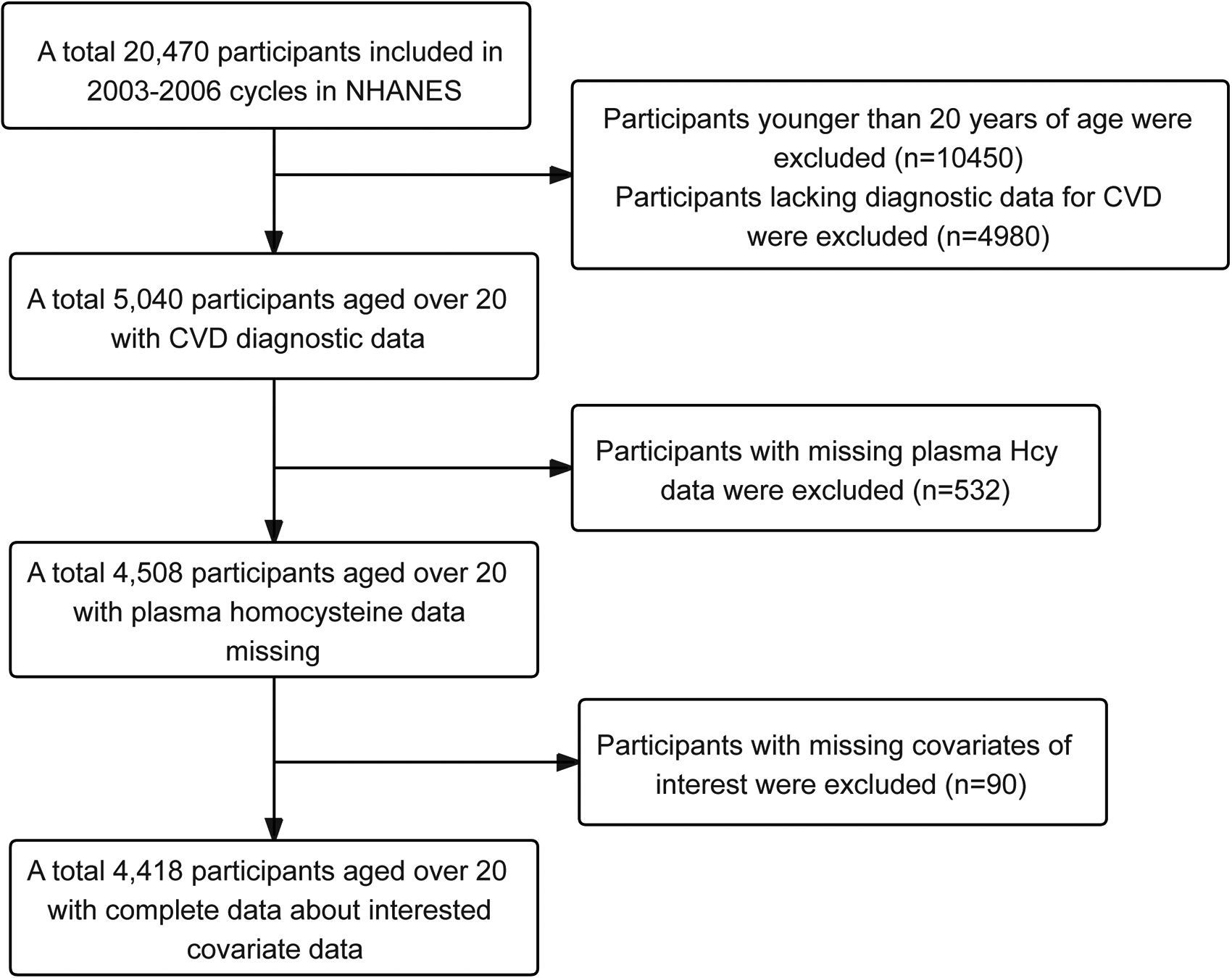
Flowchart illustrating the sample selection process for NHANES 2003 to 2006.
2.3 Measurement of plasma Hcy
Total homocysteine (Hcy) in plasma is measured using the “Abbott HCY assay”, an automated fluorescence polarization immunoassay (FPIA) from Abbott Diagnostics (5).
2.4 Main outcomes
The outcome of this study was considered to the incident of CVD. The definition of CVD is based on self-reported issues: Ever told you had congestive heart failure, coronary heart disease, angina/angina pectoris, heart attack or stroke. Respondents who answer “yes” to these questions are defined as having CVD (6, 7).
2.5 Covariates
Age is divided into three groups: 20–39, 40–59, and ≥60 years. Gender is divided into male and female. Race is divided into Mexican Americans, non-Hispanic whites, non-Hispanic blacks, and other. Marital status is divided into married (married or living with a partner) or unmarried (other). Poverty status is divided into poor and not poor: The poverty income ratio (PIR) ≥ 1 is defined as the non-poor, and PIR < 1 is defined as the poor. Education level is divided into below high school and high school or above. obesity is divided into Yes and No: obesity is defined as BMI ≥ 30, and non-obesity as BMI < 30 (8) [Body Mass Index (BMI): BMI is calculated as weight (kg) divided by height squared (m2)].
Smoking is categorized as Yes or No: smoking are those who answer “every day” or “some days” to the question “Do you smoke now?” and also answer “yes” to the question “Have you smoked at least 100 cigarettes in your life?”; the rest are classified as not smoking. Alcohol use was determined after the response to the question “Had at least 12 alcohol drinks/1yr?” with “Yes”or “No” (1 drink refers to 12 ounces of beer, 4 ounces of wine, or 1 ounce of liquor) (9).
Hypertension is defined as meeting any of the following criteria: (1) an average systolic/diastolic blood pressure of ≥140/90 mmHg, (2) a previous diagnosis by a doctor or healthcare professional, or (3) currently taking antihypertensive medication (10, 11). Diabetes is defined as meeting any of the following criteria: (1) being told by a doctor they have diabetes, (2) taking antidiabetic medication, (3) having glycated hemoglobin >6.5%, or (4) fasting blood glucose >126 mg/100 ml (12).
2.6 Statistical analysis
In this study, the “tableone” package was used to generate baseline tables. Participants were grouped according to whether they had CVD or not, and based on this, sample size and proportion of categorical variables were calculated, as well as mean and standard deviation. The sample size (n) was unweighted, whereas proportions [n (%)], means, and SD were adjusted according to weights. One-way ANOVA and chi-square tests were used to compare continuous and categorical variables, respectively.
Divide the plasma Hcy levels into quartiles. If the P < 0.05 in univariate analysis, input the variable into a multivariate logistic regression model. Weighted multivariate logistic regression analysis is used to estimate the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) for the association between CVD and Hcy, and a linear trend analysis is performed further, with P < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
The models in this study include Model 1 (Adjusted for gender, age, race, marital status, education level, and poverty status.); Model 2 (Adjusted for gender, age, race, marital status, education level, poverty status, obesity, smoking, and alcohol use.); and Model 3 (Adjusted for gender, age, race, marital status, education level, poverty status, obesity, smoking, alcohol use, hypertension, and DM.). Restricted cubic splines (RCS) are used in the three models to explore the association between Hcy levels and the prevalence of CVD. Subgroup analyses are conducted on the relationship between Hcy and CVD, stratified by age, race, education level, obesity, alcohol use, hypertension, and DM, to assess potential modifying factors. The data are weighted using complex survey sampling analysis methods to ensure they are representative of the US population. A two-sided p-value of <0.05 is considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using R (version 4.4.1).
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of the study population
Table 1 provides a brief summary of the baseline characteristics distribution of the study population. The study included a total of 4,418 people, of which 582 were patients with CVD, and 3,836 were non-CVD patients. The sample population comprised 48.3% men and 51.7% women. The proportions of young patients (20–40 years), middle-aged patients (40–59 years) and older adults (≥60 years) were 38.6%, 38.8% and 22.6%, respectively. Of the participants, 36.9% had hypertension and 10.3% had a history of diabetes.
Table 1
| Characteristics | Overall (n = 4,418) | Non-CVD (n = 3,836) | CVD (n = 582) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <0.001 | |||
| 20–39 | 1538 (38.6%) | 1521 (42.2%) | 17 (4.8%) | |
| 40–59 | 1256 (38.8%) | 1156 (39.8%) | 100 (30.0%) | |
| ≥60 | 1624 (22.6%) | 1159 (18.0%) | 465 (65.2%) | |
| Gender | 0.677 | |||
| Male | 2137 (48.3%) | 1827 (48.2%) | 310 (49.3%) | |
| Female | 2281 (51.7%) | 2009 (51.8%) | 272 (50.7%) | |
| Race | 0.04 | |||
| Mexican American | 884 (7.7%) | 795 (8.2%) | 89 (3.4%) | |
| Non-Hispanic White | 2363 (72.6%) | 1983 (71.8%) | 380 (80.2%) | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 846 (10.8%) | 767 (11.0%) | 79 (8.9%) | |
| Other | 325 (8.9%) | 291 (9.1%) | 34 (7.5%) | |
| Marital status | 0.055 | |||
| Married | 2694 (64.6%) | 2357 (65.0%) | 337 (60.3%) | |
| Unmarried | 1724 (35.4%) | 1479 (35.0%) | 245 (39.7%) | |
| Education level | <0.001 | |||
| Below high school | 1279 (17.8%) | 1042 (16.5%) | 237 (30.0%) | |
| High School or above | 3139 (82.2%) | 2794 (83.5%) | 345 (70.0%) | |
| Poverty status | 0.352 | |||
| Poor | 763 (11.9%) | 662 (11.8%) | 101 (13.2%) | |
| Not poor | 3655 (88.1%) | 3174 (88.2%) | 481 (86.8%) | |
| Obesity | 0.005 | |||
| Yes | 1458 (32.2%) | 1233 (31.3%) | 225 (40.1%) | |
| No | 2960 (67.8%) | 2603 (68.7%) | 357 (59.9%) | |
| Smoking | 0.072 | |||
| Yes | 992 (25.3%) | 898 (25.7%) | 94 (20.8%) | |
| No | 3426 (74.7%) | 2938 (74.3%) | 488 (79.2%) | |
| Alcohol use | 0.003 | |||
| Yes | 2827 (66.7%) | 2489 (67.8%) | 338 (57.0%) | |
| No | 1591 (33.3%) | 1347 (32.2%) | 244 (43.0%) | |
| Hypertension | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 1900 (36.9%) | 1453 (32.9%) | 447 (74.2%) | |
| No | 2518 (63.1%) | 2383 (67.1%) | 135 (25.8%) | |
| DM | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 603 (10.3%) | 416 (8.2%) | 187 (30.1%) | |
| No | 3815 (89.7%) | 3420 (91.8%) | 395(69.9%) | |
| Hcy (μmol/L) | 9.13 (4.28) | 8.86 (3.98) | 11.61 (5.89) | <0.001 |
Characteristics distribution of CVD patients and non-CVD patients.
Categorical variables are presented as n (%), while continuous variables are presented as mean (sd); n is unweighted, n (%), mean, and sd are weighted.
DM, diabetes; Hcy, homocysteine.
Divide participants into two groups based on whether they have CVD. There were statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) between the two groups in terms of age, race, education level, obesity, alcohol use, hypertension, diabetes, and homocysteine levels. However, there were no statistically significant differences in terms of gender, marital status, poverty status and smoking (P > 0.05).
Compared to those without CVD, participants with CVD were more likely to be older, non-Hispanic White, less educated, obesity and not alcohol use. Furthermore, they were more likely to have a history of hypertension and diabetes. There was no difference in smoking distribution, but CVD patients were more likely to have higher levels of homocysteine.
3.2 Association between Hcy and CVD
As shown in Table 2, three models were constructed in the population. Taking Hcy level as a continuous variable, the risk of CVD increased with every 1SD increase in Hcy level in all three models (P < 0.05). In models 1, 2, and 3, the corresponding OR (95% CI) for each 1SD increase in Hcy levels was 1.25 (1.11, 1.40), 1.25 (1.11, 1.42), and 1.19 (1.05, 1.35), respectively. If the Hcy level is categorized into quartile variables, with the first quartile (Q1) as the reference, weighted logistic regression analysis and linear trend analysis were performed. According to the results of the linear trend analysis, there is a significant positive correlation between Hcy level and the risk of CVD in all three models (P < 0.05). Further analysis of the impact of Hcy levels on the occurrence of CVD showed that compared to the first quartile (Q1), the fourth quartile (Q4) of Hcy levels significantly increased the risk of CVD in models 1 and 2 (P < 0.05), while there was no significant relationship in model 3 (P > 0.05).
Table 2
| Variable | Model 1 OR (95% CI) | P | Model 2 OR (95% CI) | P | Model 3 OR (95% CI) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hcy continuous | 1.25 (1.11, 1.40) | 0.002 | 1.25 (1.11, 1.42) | 0.004 | 1.19 (1.05, 1.35) | 0.017 |
| Hcy quartiles | ||||||
| Q1 (<6.92) | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | |||
| Q2 (6.92–8.32) | 1.34 (0.74, 2.44) | 0.274 | 1.32 (0.66, 2.62) | 0.326 | 1.30 (0.43, 3.90) | 0.415 |
| Q3 (8.32–10.24) | 1.48 (0.92, 2.36) | 0.088 | 1.46 (0.85, 2.52) | 0.126 | 1.44 (0.61, 3.43) | 0.209 |
| Q4 (≥10.24) | 2.66 (1.59, 4.46) | 0.003 | 2.60 (1.46, 4.66) | 0.01 | 2.28 (0.96, 5.38) | 0.054 |
| P for trend | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.007 | |||
Relationship model between serum Hcy levels and CVD risk adjusted for different confounding factors.
Model 1: Adjusted for gender, age, race, marital status, education level, and poverty status.
Model 2: Adjusted for gender, age, race, marital status, education level, poverty status, obesity, smoking, and alcohol use.
Model 3: Adjusted for gender, age, race, marital status, education level, poverty status, obesity, smoking, alcohol use, hypertension, and DM.
DM, diabetes; Hcy, homocysteine.
Figure 2 illustrates the non-linear association between Hcy levels and CVD risk. The results of the RCS curves in all three models indicate a significant overall trend between Hcy levels and CVD risk (P for overall <0.0001). A significant non-linear association was observed in all three models (P for nonlinear <0.01). Risk of CVD continuously increased with higher Hcy levels.The RCS curves show a consistent overall trend between Hcy levels and CVD risk across all three models, indication a stable association between the two.
Figure 2
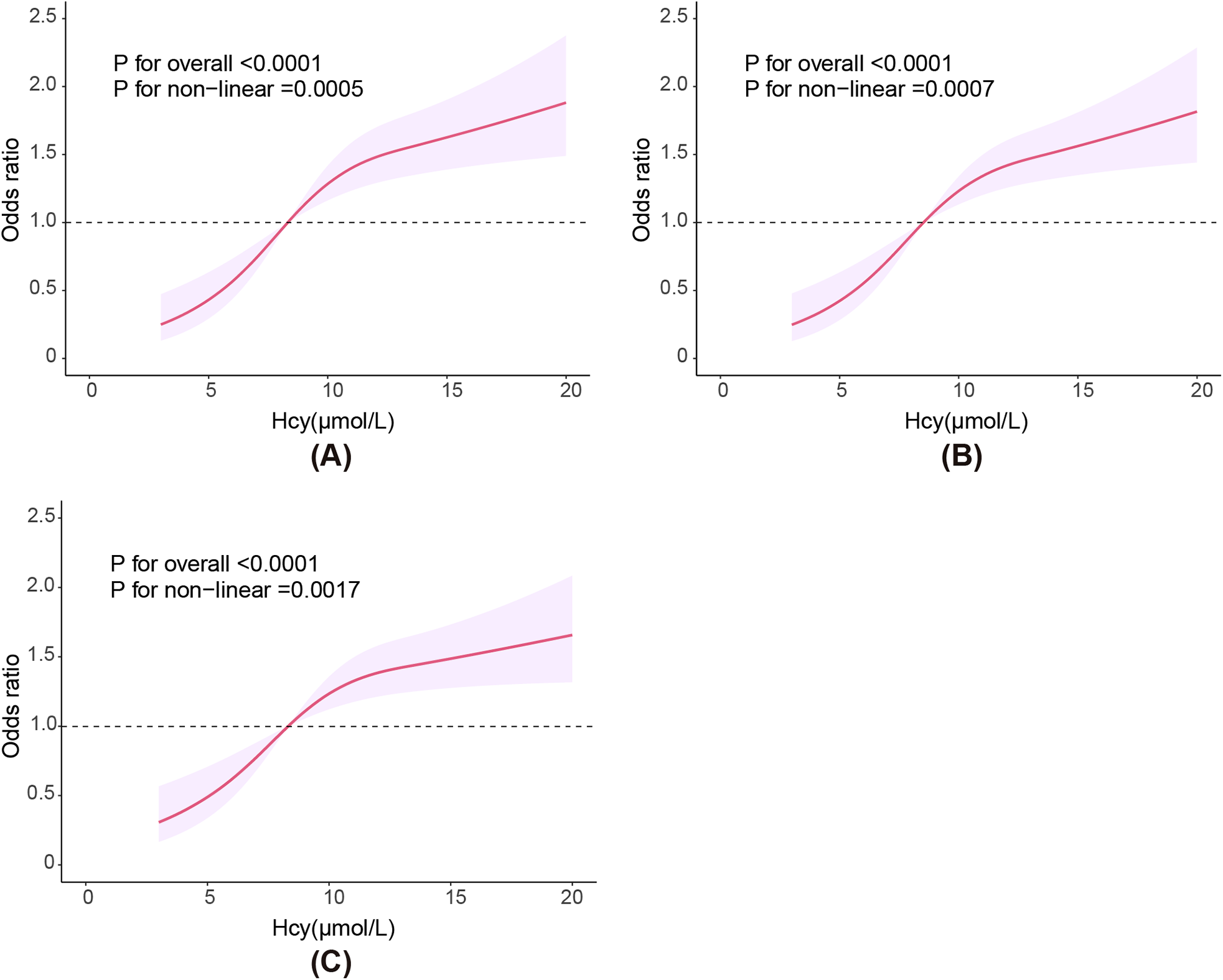
RCS plot showing the association between plasma Hcy level and risk of CVD. (A) Model 1, (B) Model 2, (C) Model 3. Model 1: Adjusted for gender, age, race, marital status, education level, and poverty status. Model 2: Adjusted for gender, age, race, marital status, education level, poverty status, obesity, smoking, and alcohol use. Model 3: Adjusted for gender, age, race, marital status, education level, poverty status, obesity, smoking, alcohol use, hypertension, and DM. DM, diabetes; Hcy, homocysteine.
3.3 Stratification analysis
Subgroup analysis was performed based on age, race, education level, obesity, alcohol use, diabetes, and hypertension (Figure 3). Hcy was significantly associated with CVD in all subgroups. No interaction effects were observed between plasma Hcy concentration and age (P for interaction = 0.05), race (P for interaction = 0.546), education level (P for interaction = 0.527), obesity (P for interaction = 0.911), alcohol use (P for interaction = 0.576), diabetes (P for interaction = 0.067), and hypertension (P for interaction = 0.486); therefore, these variables did not significantly alter the association between Hcy and CVD. Although there was no significant association between Hcy and CVD in the 40–59 age group, non-Hispanic black population, and diabetes group, there was no interaction effect (all P for interaction ≥ 0.05).
Figure 3
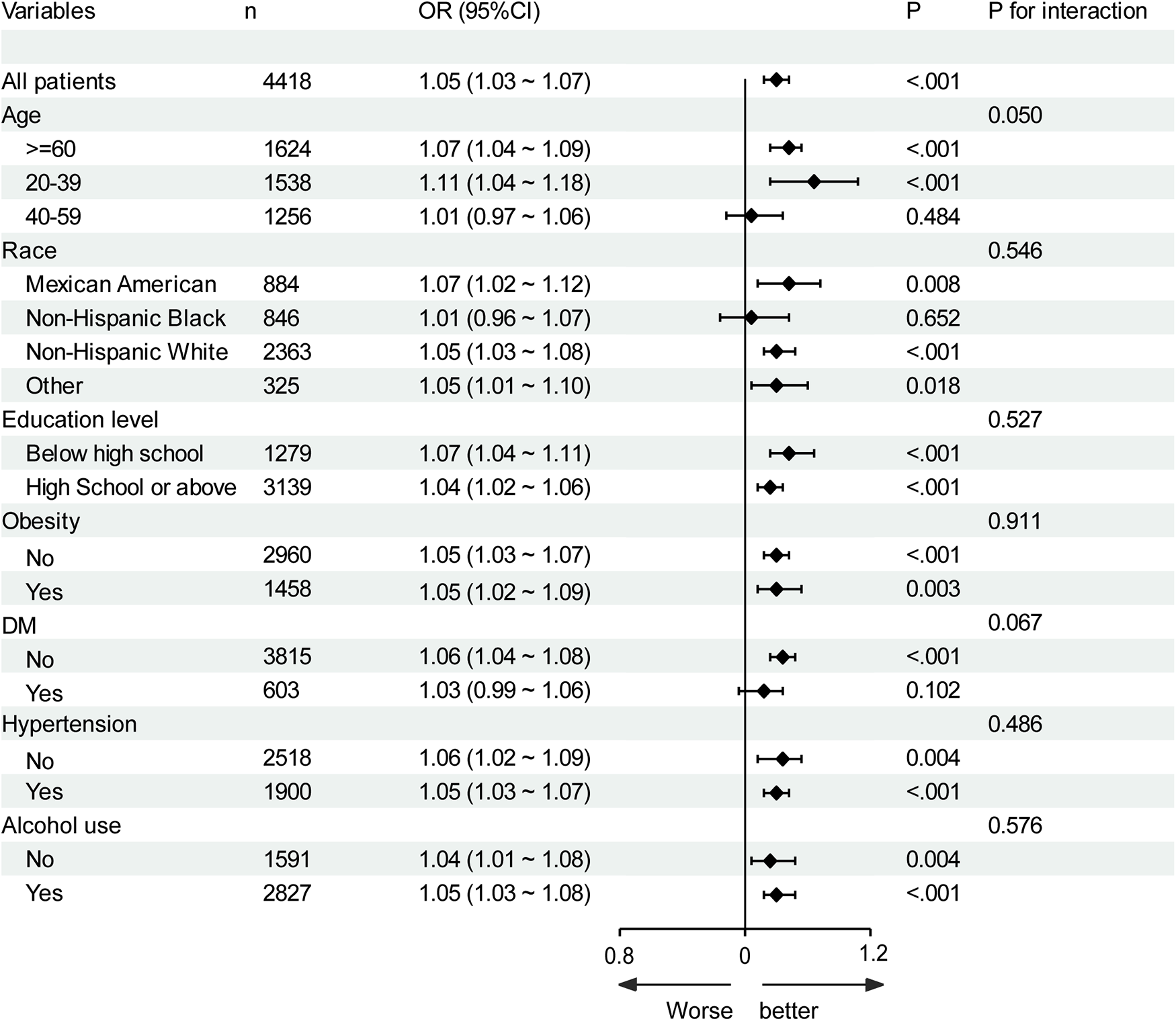
Subgroup analysis of the association of homocysteine with CVD. Results were adjusted for all covariates except the corresponding stratification variable. DM, diabetes.
4 Discussion
We selected data from the nationally representative NHANES database (2003–2006) to assess the association between Hcy levels and the risk of CVD. Our study found that higher Hcy levels are associated with an increased risk of CVD, showing a significant positive correlation between Hcy levels and CVD risk. Further analysis showed that there was a significant nonlinear positive correlation between Hcy level and CVD risk. This discovery may play a certain role in the diagnosis and prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Hcy can lead to dysfunction and even apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells, which is one of the important initiating factors in the development of artery atherosclerosis. High levels of Hcy reduce the expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), leading to a decrease in endogenous nitric oxide (NO) and an increase in the production of malonaldehyde (MDA) (13). This results in a reduction, and potentially a complete loss, of vasodilatory function, accelerating the progression of atherosclerotic lesions (14). Moreover, Hcy can also induce endothelial cell apoptosis through activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) (15, 16).
High concentration of Hcy can lead to the migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) through multiple pathways. These pathways include enhancing the expression of caveolin to inhibit the action of eNOS and NO (17), enhancing the expression of key proteins and molecules in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) signaling pathway (18), and inducing VSMCs to secrete matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2), affecting the dynamic balance of extracellular matrix in and around cells (19). These mechanisms collectively promote the migration and proliferation of VSMCs, thereby intensifying the process of atherosclerosis in coronary arteries.
Oxidative stress is one of the important pathogenic mechanisms in the development of artery atherosclerosis. The metabolism of Hcy produces thiols that can auto-oxidize into active oxygen clusters such as hydrogen peroxide, leading to an increase in the content of oxidants in the body (20). At the same time, Hcy inhibits the expression and secretion of extracellular superoxide dismutase (SOD), further triggering oxidative stress. This state of oxidative stress disrupts the balance of the oxidation-antioxidation system within the body, causing lipid peroxidation, structural and functional changes in proteins, and DNA damage, thus promoting the development of atherosclerosis (21–23).
Inflammatory factors play a crucial role in the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis. Hcy can enhance the oxidative stress of vascular endothelial cells, leading to the production of a series of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the body. An excess of ROS can oxidize low-density lipoprotein (LDL) into oxidized LDL, which is cytotoxic and can cause the destruction of fibroblast-actin microfilaments, leading to a disordered distribution. This results in an increase in the permeability of endothelial cells (24). Consequently, this causes a large expression of inflammatory factors such as vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and P-selectin, making mononuclear macrophages more prone to enter the endothelial cells through adhesion molecules, exacerbating cellular damage and further promoting the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis (25).
The levels of Hcy show a clear relationship with the development of atherosclerosis, suggesting that Hcy may exert its effect on CVD through the aforementioned mechanisms.
Some research indicates that Hcy is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, with elevated serum Hcy levels being associated with CVD events (26–29).
In a prospective study by Esteghamati et al. over an 8.5-year follow-up on two sub-cohorts, it was shown that Hcy is associated with the development of metabolic syndrome, and both Hcy and metabolic syndrome are independent risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) (30). A cross-sectional study by Mohamed et al. involving 972 non-diabetic patients showed significant associations between high homocysteine levels (P = 0.01) and smoking (P = 0.004) and an increase in the carotid total plaque area (TPA) (31). TPA is a strong predictor of cardiovascular risk, measured through carotid ultrasound (32).
A meta-analysis found that after adjusting for other known risk factors, a 25% increase in total homocysteine (Hcy) in the serum (approximately 3 μmol/L) was associated with a 10% increase in the risk of cardiovascular events and a 20% increase in the risk of stroke (33). Another systematic review and meta-analysis, based on 26 articles, found that after adjusting for traditional CHD risk factors, for every 5 μmol/L increase in Hcy levels, the risk of CHD events increased by about 20% (34).
A systematic review and meta-analysis incorporating 35 studies that met the design criteria showed that in most of the studies, an increase in carotid intima-media thickness was observed when homocysteine levels were above normal. It was concluded that homocysteine is highly associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in young and overweight patients. This meta-analysis focused on the role of homocysteine in the formation of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in young and pediatric patients (35).
In addition, several studies have explored the association between Hcy and CVD events. Veeranna et al. conducted a multi-ethnic study on atherosclerosis and found that in the NHANES III database, Hcy level (>15 μmol/L) significantly predicted CVD (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR]: 1.79, 95% confidence intervals [CI]: 1.19–1.95; P = 0.006) and CHD events (aHR: 2.22, 95% CI: 1.20–4.09; P = 0.01) in the MESA trial and CVD (aHR: 2.72, 95% CI: 2.01–3.68; P < 0.001) and CHD mortality (aHR: 2.61, 95% CI: 1.83–3.73; P < 0.001) in the NHANES III (36). Drewes et al. concluded from a prospective study on pravastatin in high-risk elderly individuals (a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with a follow-up of 3.2 years) that patients with higher Hcy levels had a higher risk of fatal and non-fatal CHD compared to those with lower Hcy levels (adjusted OR: 1.8, 95% CI: 1.2–2.5, P = 0.001) (37).
In this study, Hcy levels were significantly positively correlated with the risk of CVD in all three models. In model 3, which adjusted for all confounding factors, this correlation remained stable (P for trend = 0.007). Moreover, in model 3, a clear non-linear positive correlation was also observed (P for overall < 0.0001, P for nonlinear = 0.0017), similar to the above results.
Despite the significant results obtained in our research, it is important to acknowledge some limitations. Firstly, NHANES was designed as a cross-sectional study, inherently observational; thus, it does not allow for the establishment of causality and cannot fully rule out residual confounding. Future longitudinal studies are needed to ascertain the predictive value of Hcy for CVD risk. Secondly, self-reporting of CVD in the questionnaire may introduce bias. However, the questionnaires administered in this study have been widely used in previous studies to assess cardiovascular disease (6, 7). Thirdly, dietary habits, particularly nutraceutical intake (e.g., folate, vitamin B6/B12, and omega-3 fatty acids), may confound or modify the Hcy-CVD relationship by altering Hcy levels or lipid metabolism (38). This study did not include detailed dietary intake and nutraceutical usage records, limiting our ability to analyze interactions between these factors and Hcy/CVD risk. Future studies should incorporate dietary metrics, such as Mediterranean Diet scores and supplement use, to clarify these interactions.
Fourth, our analysis relied on a single Hcy measurement, which may not fully capture intra-individual variability over time. Longitudinal studies with repeated Hcy assessments are warranted to validate our findings. Fifth, the use of older NHANES data (2003–2006) limits generalizability to modern populations. Future research should use new cohorts to validate the results. Sixth, the absence of detailed pharmacological and dietary data hinders exploration of drug-diet-Hcy interactions.
Lastly, CVD has many potential influencing factors, and although we included as many relevant covariates as possible in our model, we cannot completely exclude the effects of unmeasured or other confounding factors, such as dietary patterns, physical activity, genetic predisposition, and environmental exposures that may influence both Hcy levels and CVD risk. Future studies incorporating these variables are warranted to refine the association between Hcy and CVD. Despite these limitations, our research still demonstrates a positive correlation between Hcy levels and CVD risk.
Future research should prioritize prospective cohorts with serial Hcy and B-vitamins measurements, stratified analyses by demographic and metabolic subgroups, and randomized clinical trials testing Hcy-lowering therapies to confirm causality and identify high-risk populations.
5 Conclusion
In this large cross-sectional study, an increase in Hcy levels leads to an increased risk of CVD. There is a positive correlation between Hcy levels and the risk of CVD. Further analysis revealed that the relationship between Hcy levels and CVD risk is nonlinearly positive.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
ZH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. RZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YH: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Validation. DX: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was sponsored (supported) by Xiamen City Key Medical and Health Project (3502Z20234018), Incubation Project of Zhongshan Hospital (Xiamen), Fudan University (2020ZSXMGL01).
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the efforts of the US National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) for the creation of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data and thank all the researchers for their efforts in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1528540/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Masaebi F Salehi M Kazemi M Vahabi N Azizmohammad Looha M Zayeri F . Trend analysis of disability adjusted life years due to cardiovascular diseases: results from the global burden of disease study 2019. BMC Public Health. (2021) 21(1):1268. 10.1186/s12889-021-11348-w
2.
Roth GA Mensah GA Johnson CO Addolorato G Ammirati E Baddour LM et al Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 76(25):2982–3021. 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010
3.
Wu DF Yin RX Deng JL . Homocysteine, hyperhomocysteinemia, and H-type hypertension. Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2024) 31(9):1092–103. 10.1093/eurjpc/zwae022
4.
Go AS Mozaffarian D Roger VL Benjamin EJ Berry JD Borden WB et al Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics–2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2013) 127(1):143–52. 10.1161/CIR.0b013e318282ab8f
5.
Boushey CJ Beresford SA Omenn GS Motulsky AG . A quantitative assessment of plasma homocysteine as a risk factor for vascular disease. Probable benefits of increasing folic acid intakes. JAMA. (1995) 274(13):1049–57. 10.1001/jama.1995.03530130055028
6.
Xie Z Wang L Sun M Wang R Li J Wang X et al Mediation of 10-year cardiovascular disease risk between inflammatory diet and handgrip strength: base on NHANES 2011–2014. Nutrients. (2023) 15(4):918. 10.3390/nu15040918
7.
Zhan Y Yang Z Liu Y Zhan F Lin S . Interaction between rheumatoid arthritis and Mediterranean diet on the risk of cardiovascular disease for the middle aged and elderly from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). BMC Public Health. (2023) 23(1):620. 10.1186/s12889-023-15478-1
8.
Ogden CL Carroll MD Fryar CD Flegal KM . Prevalence of obesity among adults and youth: United States, 2011–2014. NCHS Data Brief. (2015) (219):1–8.
9.
Tian X Xue B Wang B Lei R Shan X Niu J et al Physical activity reduces the role of blood cadmium on depression: a cross-sectional analysis with NHANES data. Environ Pollut. (2022) 304:119211. 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119211
10.
Lee C Kim H . Machine learning-based predictive modeling of depression in hypertensive populations. PLoS One. (2022) 17(7):e0272330. 10.1371/journal.pone.0272330
11.
Miao H Liu Y Tsai TC Schwartz J Ji JS . Association between blood lead level and uncontrolled hypertension in the US population (NHANES 1999–2016). J Am Heart Assoc. (2020) 9(13):e015533. 10.1161/JAHA.119.015533
12.
Liu Y Geng T Wan Z Lu Q Zhang X Qiu Z et al Associations of serum folate and vitamin B12 levels with cardiovascular disease mortality among patients with type 2 diabetes. JAMA Netw Open. (2022) 5(1):e2146124. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.46124
13.
Meye C Schumann J Wagner A Gross P . Effects of homocysteine on the levels of caveolin-1 and eNOS in caveolae of human coronary artery endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. (2007) 190(2):256–63. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.03.009
14.
Ma Y Li L Shang XM Tan Z Geng X-B Zhao B-Q et al Analysis of factors related to short-term prognosis in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction. Exp Ther Med. (2013) 5(4):1206–10. 10.3892/etm.2013.927
15.
Dong F Zhang X Li SY Zhang Z Ren Q Culver B et al Possible involvement of NADPH oxidase and JNK in homocysteine-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Toxicol. (2005) 5(1):9–20. 10.1385/ct:5:1:009
16.
Zhang C Kawauchi J Adachi MT Hashimoto Y Oshiro S Aso T et al Activation of JNK and transcriptional repressor ATF3/LRF1 through the IRE1/TRAF2 pathway is implicated in human vascular endothelial cell death by homocysteine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2001) 289(3):718–24. 10.1006/bbrc.2001.6044
17.
Lan TH Xu ZW Wang Z Wu YL Wu WK Tan HM . Ginsenoside Rb1 prevents homocysteine-induced endothelial dysfunction via PI3K/Akt activation and PKC inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol. (2011) 82(2):148–55. 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.04.001
18.
Li H Peng W Zhuang J Lu Y Jian W Wei Y et al Vaspin attenuates high glucose-induced vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and chemokinesis by inhibiting the MAPK, PI3K/Akt, and NF-κB signaling pathways. Atherosclerosis. (2013) 228(1):61–8. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.02.013
19.
Bennett MR Sinha S Owens GK . Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2016) 118(4):692–702. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306361
20.
Antoniades C Shirodaria C Warrick N Cai S de Bono J Lee J et al 5-methyltetrahydrofolate Rapidly improves endothelial function and decreases superoxide production in human vessels: effects on vascular tetrahydrobiopterin availability and endothelial nitric oxide synthase coupling. Circulation. (2006) 114(11):1193–201. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.612325
21.
Vesentini N Kusmic C Battaglia D Taddei MC Barsanti L Parodi O et al Modulation of erythrocyte sensitivity to oxidative stress by transient hyperhomocysteinemia in healthy subjects and in patients with coronary artery disease. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2008) 18(6):402–7. 10.1016/j.numecd.2007.03.009
22.
Makino J Nii M Kamiya T Hara H Adachi T . Oxidized low-density lipoprotein accelerates the destabilization of extracellular-superoxide dismutase mRNA during foam cell formation. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2015) 575:54–60. 10.1016/j.abb.2015.04.001
23.
Nihei S Tasaki H Yamashita K Ozumi K Morishita T Tsutsui M et al Hyperhomocysteinemia is associated with human coronary atherosclerosis through the reduction of the ratio of endothelium-bound to basal extracellular superoxide dismutase. Circ J. (2004) 68(9):822–8. 10.1253/circj.68.822
24.
Vacek TP Rehman S Neamtu D Yu S Givimani S Tyagi SC . Matrix metalloproteinases in atherosclerosis: role of nitric oxide, hydrogen sulfide, homocysteine, and polymorphisms. Vasc Health Risk Manag. (2015) 11:173–83. 10.2147/VHRM.S68415
25.
Peng HY Man CF Xu J Fan Y . Elevated homocysteine levels and risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. (2015) 16(1):78–86. 10.1631/jzus.B1400183
26.
Akyürek Ö Akbal E Güneş F . Increase in the risk of ST elevation myocardial infarction is associated with homocysteine level. Arch Med Res. (2014) 45(6):501–6. 10.1016/j.arcmed.2014.08.003
27.
Wu Y Huang Y Hu Y Zhong J He Z Li W et al Hyperhomocysteinemia is an independent risk factor in young patients with coronary artery disease in southern China. Herz. (2013) 38(7):779–84. 10.1007/s00059-013-3761-y
28.
Alam N Khan HI Chowdhury AW Haque MS Ali MS Sabah KMN et al Elevated serum homocysteine level has a positive correlation with serum cardiac troponin I in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull. (2012) 38(1):9–13. 10.3329/bmrcb.v38i1.10445
29.
Balogh E Bereczky Z Katona E Kőszegi Z Édes I Muszbek L et al Interaction between homocysteine and lipoprotein(a) increases the prevalence of coronary artery disease/myocardial infarction in women: a case-control study. Thromb Res. (2012) 129(2):133–8. 10.1016/j.thromres.2011.07.001
30.
Esteghamati A Hafezi-Nejad N Zandieh A Sheikhbahaei S Ebadi M Nakhjavani M . Homocysteine and metabolic syndrome: from clustering to additional utility in prediction of coronary heart disease. J Cardiol. (2014) 64(4):290–6. 10.1016/j.jjcc.2014.02.001
31.
Azarpazhooh MR Andalibi MSS Hackam DG Spence JD . Interaction of smoking, hyperhomocysteinemia, and metabolic syndrome with carotid atherosclerosis: a cross-sectional study in 972 non-diabetic patients. Nutrition. (2020) 79-80:110874. 10.1016/j.nut.2020.110874
32.
Spence JD . Determinants of carotid plaque burden. Atherosclerosis. (2016) 255:122–3. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.10.045
33.
Homocysteine Studies Collaboration. Homocysteine and risk of ischemic heart disease and stroke: a meta-analysis. JAMA. (2002) 288(16):2015–22. 10.1001/jama.288.16.2015
34.
Humphrey LL Fu R Rogers K Freeman M Helfand M . Homocysteine level and coronary heart disease incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clin Proc. (2008) 83(11):1203–12. 10.4065/83.11.1203
35.
Habib SS Al-Khlaiwi T Almushawah A Alsomali A Habib SA . Homocysteine as a predictor and prognostic marker of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2023) 27(18):8598–608. 10.26355/eurrev_202309_33784
36.
Veeranna V Zalawadiya SK Niraj A Pradhan J Ference B Burack RC et al Homocysteine and reclassification of cardiovascular disease risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2011) 58(10):1025–33. 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.05.028
37.
Drewes YM Poortvliet RK Blom JW de Ruijter W Westendorp RGJ Stott DJ et al Homocysteine levels and treatment effect in the PROspective study of pravastatin in the elderly at risk. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2014) 62(2):213–21. 10.1111/jgs.12660
38.
Scicchitano P Cameli M Maiello M Modesti PA Muiesan ML Novo S et al Nutraceuticals and dyslipidaemia: beyond the common therapeutics. J Funct Foods. (2014) 6(1):11–32. 10.1016/j.jff.2013.12.006
Summary
Keywords
cardiovascular disease, homocysteine, logistic regression, linear trend analysis, National Health and Examination Survey
Citation
Huang Z, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Zhang R, Huang Y and Xu D (2025) Association of plasma homocysteine with cardiovascular disease in American adults: a study based on the national health and nutrition examination survey database. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1528540. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1528540
Received
15 November 2024
Accepted
28 May 2025
Published
09 June 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Krishna Misra, Indian Institute of Information Technology, India
Reviewed by
Pietro Scicchitano, ASLBari - Azienda Sanitaria Localedella provincia di Bari (ASL BA), Italy
Dheeraj Chitara, JECRC University, India
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Huang, Zhang, Zhang, Zhang, Huang and Xu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Demin Xu xudemin0829@126.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.