- 1Shandong Technology Innovation Center of Molecular Targeting and Intelligent Diagnosis and Treatment, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai, Shandong, China
- 2Pharmacology and Toxicology Department, Yantai Food and Drug Inspection Center, Yantai, Shandong, China
- 3Department of Stomach and Intestine, Yantai Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Yantai, Shandong, China
Aim: The dysregulation of hepatic lipid metabolism is closely associated with dyslipidemia. Previous research suggested that Hepatic Morc4 may play a role in regulating lipid metabolism. This research aims to elucidate the function of MORC4 in hepatic lipid metabolism, thereby improving the understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying lipid metabolism disorders.
Methods: Data regarding circulating lipid traits and hepatic Morc4 expression in BXD mice were obtained from GeneNetwork. An Expression-Based Phenome-wide Association Study (ePheWAS), correlation analysis, and gene enrichment analysis were conducted to explore the relationship between Morc4 expression and hepatic lipid metabolism. in vitro, the levels of total cholesterol (TC) and triglycerides (TG), lipid accumulation, and the expression of lipid metabolism-related genes were assessed subsequent to MORC4 knockdown/overexpression in hepatocytes. in vivo, the impact of Morc4 knockout on lipid metabolism-related traits in mice was examined using the IMPC database.
Results: Hepatic Morc4 level was found to be negatively correlated with plasma free fatty acids and triglycerides in BXD mice. Further analysis indicated that genes associated with Morc4 were enriched in the cholesterol metabolic pathway. In hepatocytes, MORC4 knockdown significantly elevated total TC/TG levels, as well as enhanced lipid accumulation. Whereas MORC4 overexpression restored total TC/TG levels, along with lipid accumulation in knockdown cell lines. Furthermore, MORC4 knockdown led to an increased expression of genes associated with cholesterol synthesis (HMGCR), varying levels of genes implicated in the uptake of fatty acids and cholesterol (PCSK9, PLTP, CD36), and a decrease in the levels of genes involved in triglyceride hydrolysis (APOC2, APOA4, LIPG, LIPA). MORC4 overexpression reversed the observed alterations in the expression levels of these genes. According on the IMPC database, Morc4 knockout in mice resulted in increased fat mass, fat/body weight ratio, and elevated cholesterol level and ratio.
Conclusion: This study identifies MORC4 as a crucial regulator of hepatic lipid metabolism and underscores its potential as a therapeutic target for disorders related to lipid.
1 Introduction
The liver is the principal site for maintaining lipid and cholesterol homeostasis, facilitating processes such as lipid oxidation, packaging, and secretion of excess lipids to peripheral tissues, while also serving as a key provider of lipid substrates for the body (1–3). Disruptions in hepatic lipid metabolism can contribute to the development of various metabolic syndrome including hyperlipidemia. Importantly, hepatic lipid metabolism is influenced by a complex interplay of environmental factors and genetic predispositions (4–6).
The BXD recombinant inbred strains derived from the interbreeding of C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice is a significant genetic reference population (7, 8). Compared to single-generation genetic mapping, the BXD strains demonstrate an approximate fourfold increase in recombination frequency, thereby improving the resolution of genetic mapping (9, 10). Furthermore, BXD mice exhibit considerable variability in lipid metabolism, rendering them an optimal genetic model for the exploration of lipid metabolic processes (11, 12). These mice are extensively employed in the analysis of genetic variations linked to the etiology of human diseases, highlighting significant differences in lipid metabolism and thus providing a foundational genetic framework for the investigation of lipid metabolic mechanisms.
In our prior research, Morc4 was identified as a pivotal hub gene significantly linked to lipid metabolism in BXD mice (13). MORC4 is a highly conserved member of the MORC family, which comprises four members (MORC1-4) that exhibit a shared an N-terminal ATPase-like ATP-binding domain and a CW-type cysteine-rich zinc finger domain (14). As nucleolar-associated nuclear proteins, MORC members are considered important transcriptional regulators involved in various biological processes. In the prior research, the differentially expressed genes in livers from normal-fed mice and high-fat diet-fed mice were analyzed and enriched in various biological processes. A gene module, which includes Cd36 and Mogat1, was enriched in lipid metabolic processes. CD36 functions as a critical sensor of fatty acids and serves as a regulatory element in lipid metabolism (15). MOGAT1 is a lipogenic enzyme involved in the regulation of the lipolytic process (16). Evidence supports the identification of CD36 as a pharmacological target for the modulation of fatty acid uptake (17). Additionally, compounds that target MOGAT1 may represent promising therapeutic options for the prevention of hepatic steatosis (18). Morc4 was identified as a pivotal hub gene of this gene module. A recent proteome-Wide Mendelian Randomization analysis identifies MORC4 as a genetic risk locus associated with acute pancreatitis (19). These suggest MOCR4 may play a critical role in lipid metabolism. However, the mechanism by which MOCR4 regulates lipid metabolism remains unclear.
This study aimed to elucidate the role of MORC4 in regulating lipid metabolism through the integration of systems genetics analysis in BXD mice and subsequent in vitro experimental validation. The results revealed that MORC4 knockdown led to elevated levels of hepatocytic triglycerides and cholesterol, primarily through the modulation of gene expression associated with cholesterol metabolic pathways. These findings establish a significant relationship between MORC4 and lipid metabolism in the liver, suggesting potential new therapeutic target for metabolic liver disorders.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 BXD liver transcriptomic data Set
The BXD liver transcriptome dataset was sourced from GeneNetwork website (https://gn1.genenetwork.org/webqtl/main.py) (20). The parameters were set as follows: Species, Mouse (mm10); Group, BXD Family; Type, Liver mRNA; Data Set, EPFL/LISP BXD CD Liver Affy Mouse Gene 1.0 ST (Aug18) RMA; Get Any, Morc4. The transcriptome dataset with ID10606948 was obtained. GraphPad Prism 8.0 was used for data visualization to display the changes in Morc4 gene expression levels in BXD mice.
2.2 Expression-based phenome-wide association study (ePheWAS)
The ePheWAS data were obtained from the GeneNetwork system genetics platform (https://systems-genetics.org/ephewas) (21). The data were downloaded from this website for the experiment [Tissues: GN432, EPFL/LISP BXD CD Liver Affy Mouse Gene 1.0 ST (Apr13) RMA, Gene: Morc4], which included Free Fatty Acids (FFA) in plasma (ID: 17813) and Triglycerides in plasma (ID: 17809). The data were ultimately visualized using GraphPad Prism 8.0.
2.3 Gene correlation analysis
The Top 2,000 genes associated with Morc4 in the BXD mouse liver were obtained from GeneNetwork (in conjunction with BXD liver transcriptome data). Subsequently, gene correlation analysis was performed under the “Compute Correlation” option to identify the Top 2,000 genes associated with Morc4.
2.4 Gene function enrichment analysis
Gene function enrichment analysis of Top 2,000 genes was conducted utilizing the hypergeometric test provided by the WebGestalt platform (https://www.webgestalt.org/) (22). The objective of this analysis was to identify biological terms that are significantly overrepresented, including KEGG pathways and Gene Ontology (GO) categories.
2.5 International mouse phenotyping
The lipid metabolism-related phenotype data in Morc4 knockout mice were obtained from the International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium (IMPC) (https://www.mousephenotype.org/). IMPC employs high-throughput workflows to phenotype gene knockout mouse strains. For each gene, a homologous gene knockout mouse strain is generated, consisting of seven males and seven females. Wild-type (WT) control mice are analyzed in batches over an extended time period (23). The data obtained from IMPC, which have been analyzed using the PhenStat R package developed by IMPC (24), were ultimately visualized using GraphPad Prism 8.0.
2.6 Cell lines and cell culture
In this research, THLE-2 cells, which are immortalized adult liver epithelial cells, and HepG2 cells, which represent human hepatocellular carcinoma, serve as models for investigating lipid metabolism. HepG2 and THLE cells were purchased from Wuhan Pricella Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The cells were cultured under standard conditions using two types of media: RPMI 1640 for THLE-2 (Qidu, China) and DMEM for HepG2 (Qidu, China). The media were supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Vazyme, China) and 10% penicillin-streptomycin (Solarbio, China). Cells were maintained in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 5% CO₂. To induce lipid dysregulation, a 0.5 mmol/L oleic acid (OA) solution (Sangon Biotech, China) was used to incubate the cells for 24 h.
2.7 MORC4 knockdown and overexpression
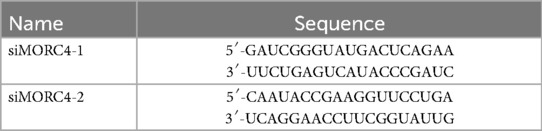
Two small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) designed for the knockdown of Morc4 were synthesized by Tsingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (China). The specific sequences of the siRNAs are provided in Table 1. The Flag-MORC4 plasmid, utilized for the overexpression of Morc4, was obtained from Hunan Fenghui Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (China). In knockdown and overexpression experiments, siRNA and Flag-MOCR4 were transfected into cells separately for a duration of 48 h, followed by treatment with 0.5 mmol/L oleic acid (OA) for 24 h. For the rescue experiments, cells were first transfected with siRNA for 24 h. Subsequently, Flag- MOCR4 was transfected into the cells for another 24 h, followed by OA treatment for an additional 24 h. The control groups, which did not receive OA treatment, adhered to the same protocols, with the exception of the OA exposure.
2.8 Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
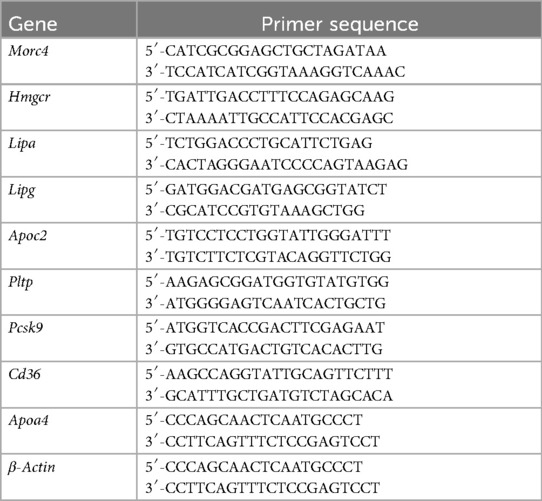
THLE-2 and HepG2 cells were washed with PBS. Total RNA was extracted using Trizol reagent, following the manufacturer's protocol (Vazyme, China). Reverse transcription was conducted utilizing the HiScript III cDNA Synthesis Kit (Vazyme, China), following the protocol to remove genomic DNA contamination. qRT-PCR was conducted on the Applied Biosystems (Thermo Fisher, USA) as follows: initial denaturation at 95°C for 10 min, 36 cycles of 95°C for 25 s, 60°C for 1 min, and 72°C for 30 s. The mRNA expression levels were quantified employing 2−ΔΔCt method, with β-actin serving as the internal control. The results were presented as relative expression changes in comparison to the control. The primers were synthesized by Tsingke Biotechnology Co. (China), Ltd., and their sequences are detailed in Table 2.
2.9 Total cholesterol and triglyceride assays
After 24 h of siRNA transfection in THLE-2 and HepG2 cells, cultures were washed with PBS and detached utilizing 0.25% trypsin-EDTA (Gibco, USA). Cells were lysed for 30 min in WB-IP lysis buffer (Beyotime, China) to obtain homogenates. Protein concentrations were determined using a Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA) Protein Assay Kit (Beyotime, China) to ensure uniformity across samples. The levels of total cholesterol (TC) and triglycerides (TG) were assessed employing assay kits from Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (China), according to the manufacturer's instructions. Absorbance readings at 500 nm was measured using a BioTek microplate reader (BioTek, USA), and lipid concentrations were calculated based on standard curves to ensure accurate data assessment.
2.10 Oil red O staining
THLE-2 and HepG2 cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min to maintain cellular morphology. Following fixation, the cells were dehydrated through treatment with 60% isopropanol for 10 min to facilitate optimal dye uptake. Subsequently, the cells were stained with Oil Red O working solution (Meilunbio, China) for an hour to visualize lipid content effectively. After staining, excess dye was removed by washing the cells three times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (Qidu, China), ensuring clear visualization of lipid droplets. The stained cells were then examined and documented using a Zeiss microscope (Germany), allowing for a detailed assessment of lipid accumulation within the cells.
2.11 Statistical analyses
The experimental data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 8.0. Statistical evaluations between two groups were carried out using Student's t test (Un-paired, two-tailed), and for comparison between multiple groups, one-way ANOVA was used. Pearson correlation analysis was employed for comparisons involving correlations. Statistical significance was set at *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.
3 Results
3.1 Significant correlation between Morc4 expression and lipid metabolism in BXD mice
The expression levels of Morc4 in the liver from 41 BXD mouse strains were assessed. An average expression level of 6.99 ± 0.20 SD was observed with the lowest expression at 6.635 in BXD84 and the highest at 7.841 in BXD44 (Figure 1A). Further ePheWAS of Morc4 in BXD mice delineated associations between hepatic Morc4 expression and lipid metabolism-related phenotypes (Figure 1B). These phenotypes encompass plasma free fatty acids [ID: 17813, -log10(p) = 5.05] and plasma triglycerides [ID: 17809, -log10(p) = 2.69]. Furthermore, a negative correlation was observed between Morc4 expression and levels of plasma free fatty acids (ID: 17811, P = 0.0151, r = 0.3771 Figure 1C) and plasma triglycerides (ID: 17809, P = 0.0053, r = 0.4273 Figure 1D).
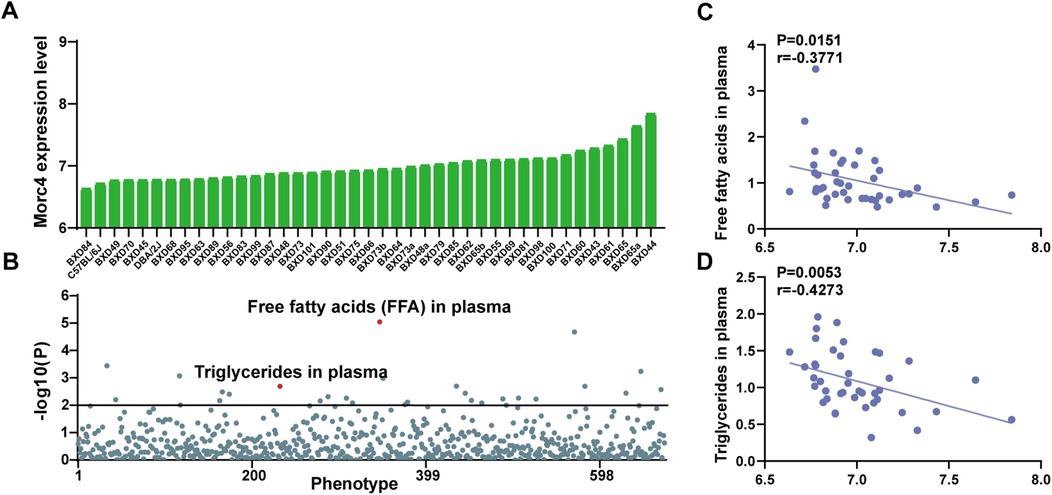
Figure 1. The expression levels of the hepatic Morc4 associated with hepatic lipid metabolism phenotypes. (A) hepatic Morc4 expression levels across 41 BXD mouse strains. (B) Manhattan plots from ePWAS emphasizing the metabolic phenotypes associated with Morc4 expression in BXD mice. Each point represents a distinct metabolic phenotype, with the red horizontal line denoting the threshold for statistical significance (log10 p > 2). (C,D) Scatterplots depicting the correlation between Morc4 expression and plasma lipid metabolism levels in the liver of BXD mice. Each point corresponds to an individual BXD strain. Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated to evaluate the relationship.
3.2 MORC4 affects hepatic lipid metabolism in vitro
To further elucidate the role of MORC4 in hepatic lipid metabolism, MORC4 expression was knocked down in the THLE-2 and HepG2 cell lines using two different siRNAs (siMORC4#1 and siMORC4#2) and siMORC4#2 presents better knockdown efficiency. Moreover, the knockdown of MORC4 expression were rescued by the transfection of Flag-MORC4 (Figures 2A,B; Supplementary Figure S1). THLE-2 and HepG2 cells were exposed to oleic acid (OA) to induce lipid metabolism dysregulation (25, 26). The total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) levels within the cells were quantified using assay kits. Notably, MORC4 knockdown led to a significant increase in TC and TG levels in both normal and OA-treated cells, while MORC4 overexpression significantly downregulated TC and TG levels in both normal and OA-treated cells. Additionally, MORC4 overexpression in siRNA-transfected cell lines restored the TC and TG levels Figures 2B,D). Similarly, Oil Red O staining revealed that MORC4 knockdown exacerbated the accumulation of lipid (droplets in both normal and OA-treated cells, which could be mitigated by the overexpression of MORC4 (Figures 2E–H). Furthermore, a marked elevation of MORC4 level was observed in THLE-2 and HepG2 cells following OA treatment (Figures 2A,C; Supplementary Figure S1). These results indicate that MORC4 plays a critical role in the accumulation of cholesterol, triglycerides, and lipid droplets, thereby highlighting its significant involvement in hepatic lipid metabolism.
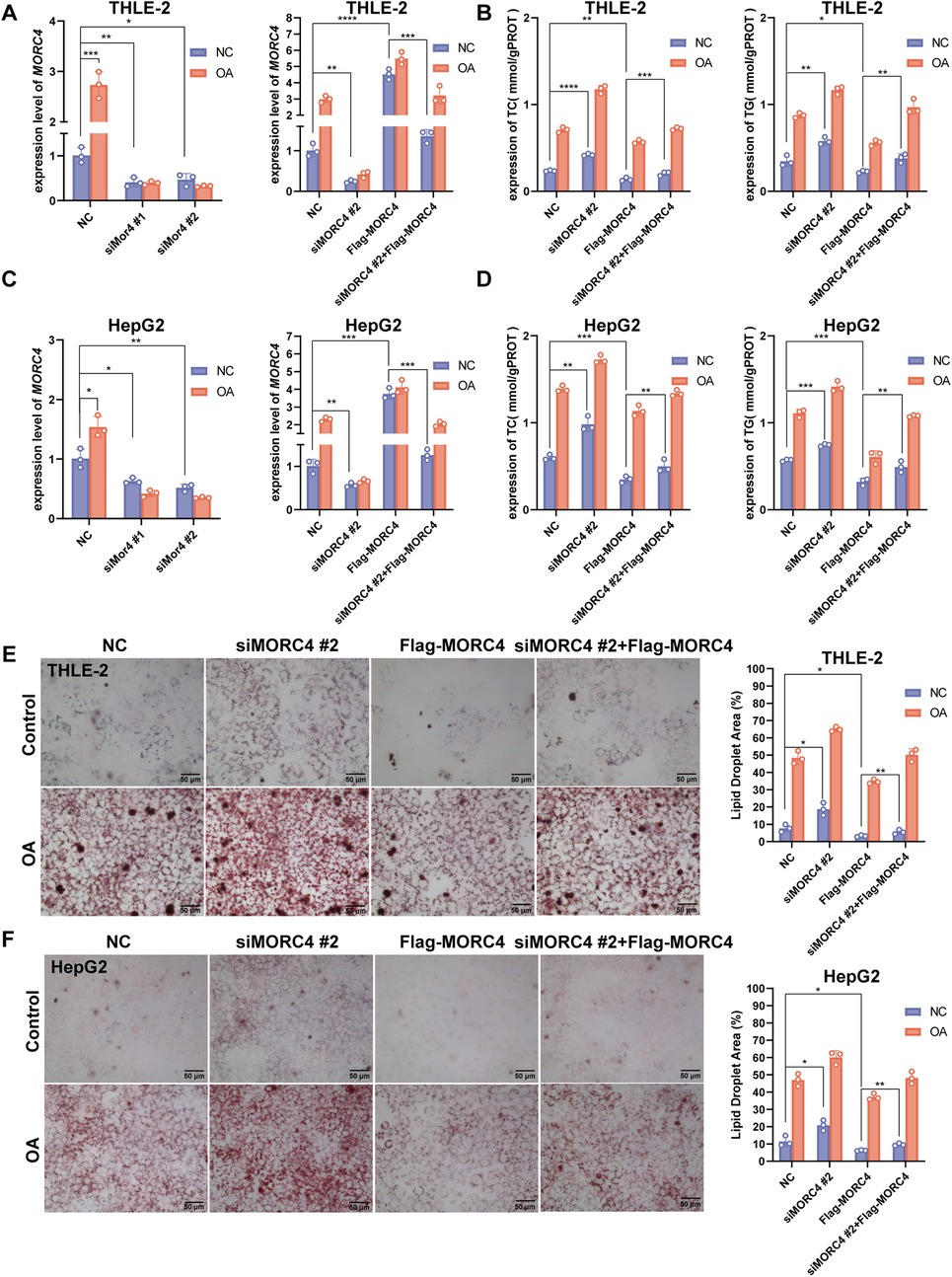
Figure 2. The role of MORC4 on lipid metabolism in THLE-2 and HepG2 cells. The knockdown and overexpression of MORC4 in THLE-2 cells (A) and HepG2 cells (C) were analyzed using qPCR experiment. The total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) levels following MOCR4 knockdown and overexpression in THLE-2 cells (B) and HepG2 cells (D) were measured by assay kits. The accumulation of lipid droplets in THLE-2 cells (E) and HepG2 cells (F) after MOCR4 knockdown and overexpression were detected with Oil Red O staining. OA, oleic acid; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; n = 3.
3.3 Genes associated with Morc4 involved in lipid metabolism functions and pathways
In order to elucidate the role of MORC4 in the regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism, Pearson correlation analysis of Morc4 against the other transcripts using the BXD mice liver transcriptome was employed on GeneNetwork. The top 2,000 genes exhibiting strong correlation with Morc4 were identified (r > 0.3, P < 0.05) and analyzed with gene enrichment analyses. GO analysis demonstrated significant enrichment in biological processes (BP) associated with cholesterol metabolism (P < 0.0001) and fatty acid metabolism (P < 0.0001), cellular components (CC) linked to lipid droplets (P < 0.0001) and the endoplasmic reticulum (P < 0.0001), and molecular functions (MF) related to lipid transporter activity (P < 0.0001) and fatty acid binding (P = 0.0036) (Figure 3A). Pathway enrichment analysis was performed by KEGG analysis which highlighted enrichment in pathways associated with metabolic pathways (P < 0.0001), (Figure 3B). Particularly, 14 genes were significantly enriched in the cholesterol metabolism pathway (P < 0.05), (Supplementary Table S1). The protein-protein interaction network for these 14 genes is illustrated in Figure 3C. Among these, seven key genes were identified as being closely related to cholesterol and fatty acid endocytosis, as well as triglyceride degradation. Six of these genes demonstrated significant positive correlations with Morc4 expression, including Lipa (r = 0.5168, P = 0.0005), Lipg (r = 0.3189, P = 0.0119), Pltp (r = 0.6081, P < 0.0001), Apoc2 (r = 0.5534, P = 0.0002), Cd36 (r = 0.6733, P < 0.0001), and Apoa4 (r = 0.6471, P < 0.0001), (Figures 3D,G–L). In contrast, Pcsk9 exhibited a significant negative correlation with Morc4 expression (r = −0.5167, P = 0.0005), (Figures 3D,F). Furthermore, a strong negative correlation was observed between Morc4 and Hmgcr (r = −0.4030, P = 0.0090), (Figures 3D,E),which is recognized as a critical rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis (27).
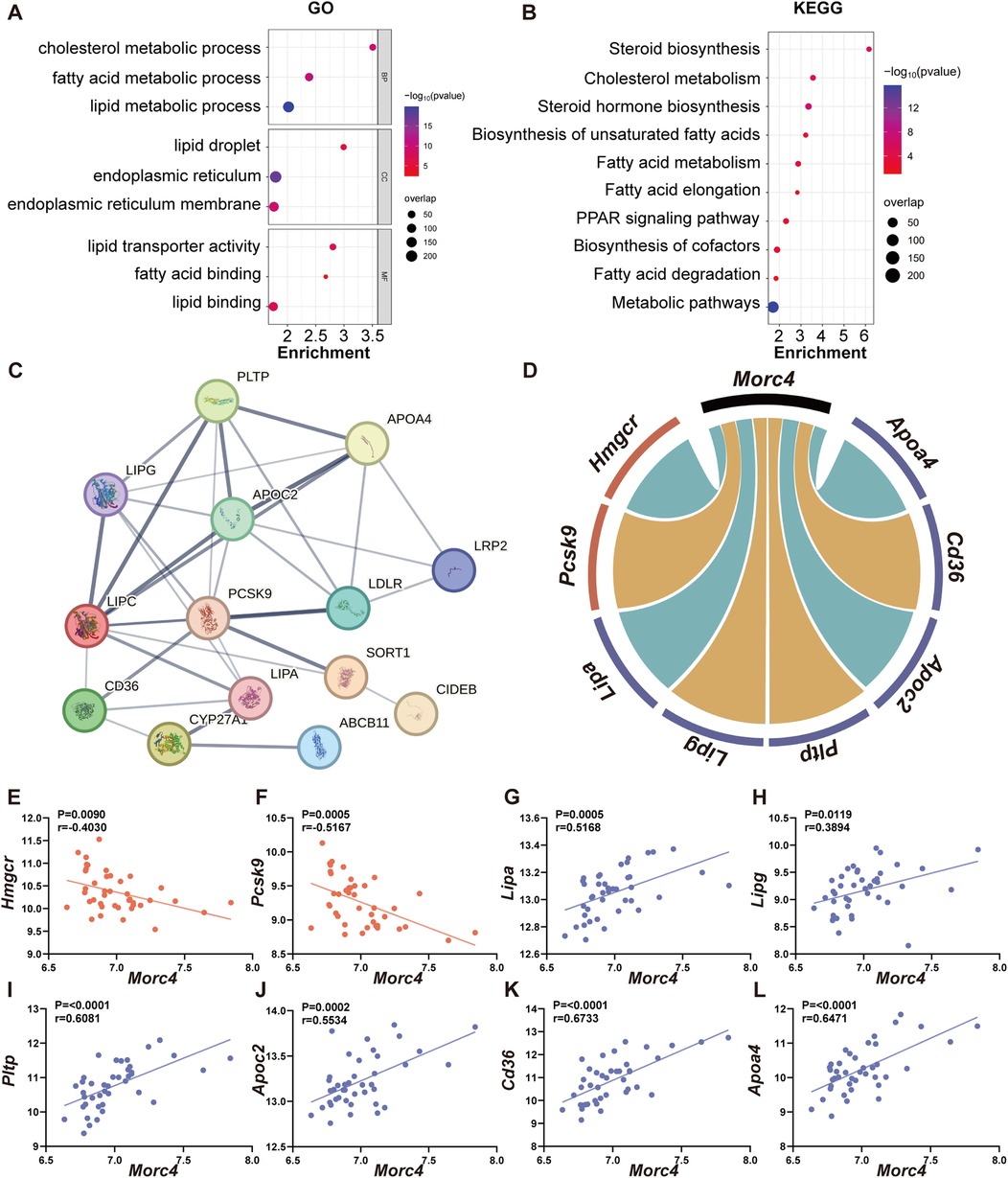
Figure 3. The relationship between Morc4 and cholesterol metabolism pathways. The GO enrichment bubble plot (A) and KEGG enrichment bubble plot (B) of the top 2,000 genes related to Morc4.The x-axis represents the enrichment ratio, the y-axis lists the GO terms, the bubble size reflects the gene count, and the color indicates the FDR value. (C) The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network related to the cholesterol metabolism pathway highlights genes with an interaction score greater than 0.4 (indicating moderate confidence), (D) sourced from the STRING database (https://www.string-db.org/). In the cholesterol metabolism pathway, Morc4 shows significant correlations with eight key lipid metabolism genes, with negative correlations shown in blue and positive correlations shown in red. (E–L) A scatter plot of the correlation between these eight genes and MORC4 is provided, along with the correlation coefficient (r) and corresponding p-values for each plot.
3.4 MORC4 influences the expression of genes associated with lipid metabolism in vitro
To assess the interaction between MORC4 and eight identified genes, the expression levels of the identified genes in normal and OA-treated THLE-2 and HepG2 cell lines were quantified by qPCR analysis following MORC4 knockdown and overexpression. Consistent with the results of Pearson correlation analysis, MORC4 knockdown led to a decrease in the expression of LIPA, LIPG, PLTP, APOC2, CD36 and APOA4, while simultaneously increasing the expression of HMGCR and PCSK9. However, MORC4 overexpression rescued the alteration in these genes’ expression levels caused by MORC4 knockdown (Figure 4). Moreover, OA treatment significantly increased the expression of APOC2, LIPA, LIPG, and APOA4, similar to the effects of MORC4. These results suggest that MORC4 may regulate lipid metabolism by modulating the expression of genes involved in cholesterol metabolism and biosynthetic pathways.
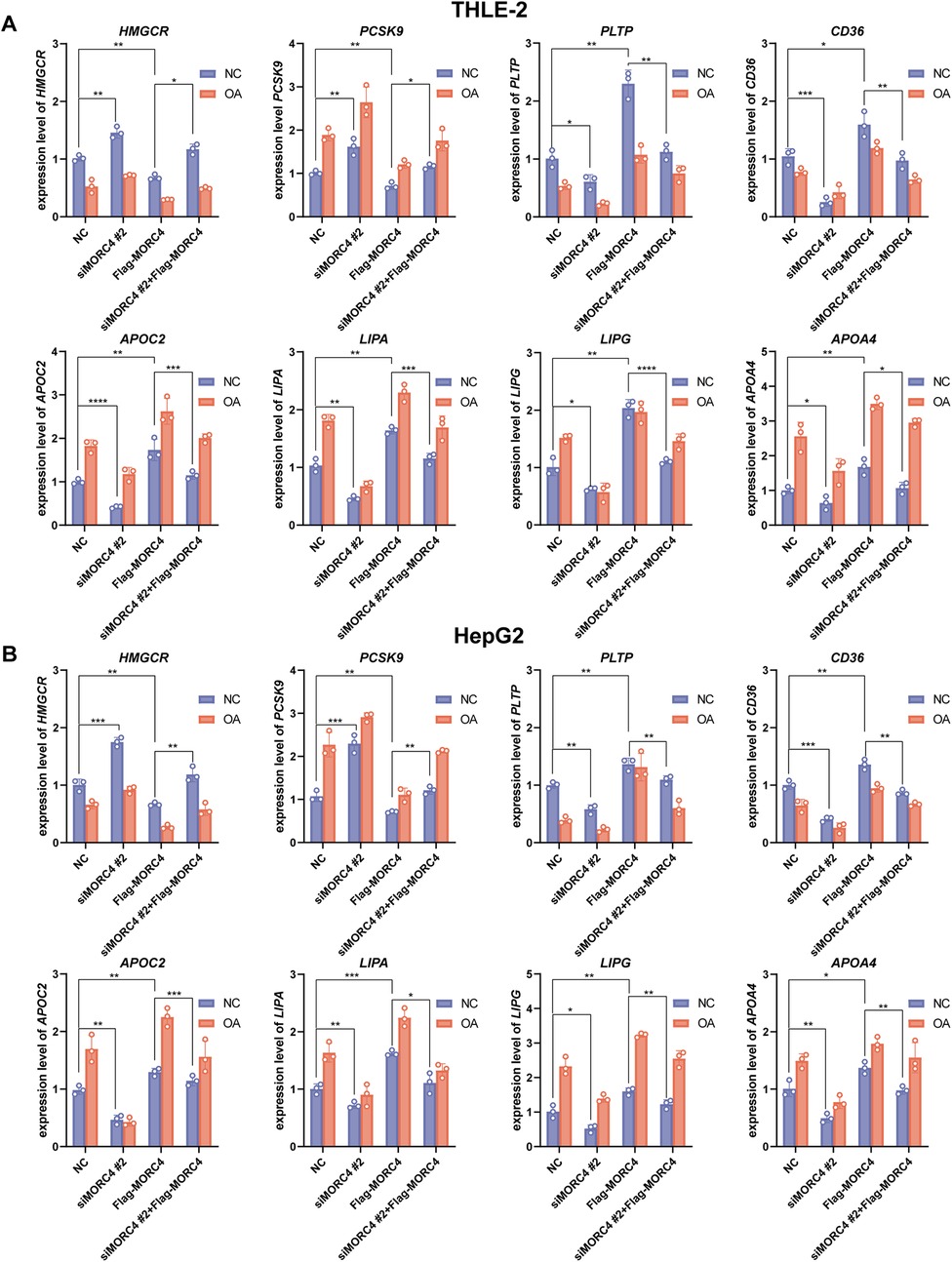
Figure 4. The role of MORC4 in regulating the expression levels of lipid metabolism-related genes. After changes in MORC4 expression levels, alterations in the expression of lipid metabolism-related genes in THLE-2 cells (A) and HepG2 cells (B) were observed. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; n = 3.
3.5 Impact of Morc4 knockout on lipid metabolism-related phenotypes in mice
The association between Morc4 and lipid metabolism-related phenotypes in mice was examined utilizing the International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium (IMPC) database. Compared to wild-type mice, Morc4 knockout mice demonstrated a reduction in body weight (Figure 5A), an increase in the fat mass and fat/body weight ratio (Figures 5B,C), a decrease in the lean/body weight ratio (Figure 5D), as well as elevated total cholesterol levels (Figure 5E) and cholesterol ratios (Figure 5F). In summary, these results suggest that the silence of Morc4 disrupts cholesterol metabolism and contributes to abnormal weight distribution in mice.

Figure 5. Alterations in lipid metabolism phenotypes following Morc4 knockout in IMPC database. The residuals of whole-body lipid metabolism-related traits were adjusted for genotype and sex in mice that are heterozygous for a Morc4 gene-trap allele. (A) Body weight, (B) Fat mass, (C) Fat/body weight ratio, (D) Lean/body weight ratio, (E) Total cholesterol, (F) Cholesterol ratio, (G) Proposed model illustrating that MORC4 regulates hepatic lipid metabolism. The downregulation of Morc4 expression leads to reduced uptake of free fatty acids/cholesterol, as well as a decrease in triglyceride hydrolysis, while concurrently enhancing cholesterol synthesis. This interplay contributes to the dysfunction of lipid metabolism.
4 Discussion
The liver serves as a central organ for the synthesis of fatty acids and the circulation of lipids, thereby playing a crucial role in the regulation of lipid metabolism homeostasis. Within the liver, fatty acids (FAs) derived from various sources are utilized for the synthesis of triglycerides, which may subsequently undergo oxidation, storage, or secretion into the systemic circulation. Disruptions in these metabolic processes can lead to the accumulation of intrahepatic triglycerides, potentially contributing to the development of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, such as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) (28). In our previous study, Morc4 has been identified as a central hub gene within the network of lipid metabolism co-expression genes (13). This study elucidates the significant correlation between Morc4 expression and lipid metabolism, utilizing BXD recombinant inbred strains and the IMPC database, and further explores the associated mechanisms through in vitro experiments.
A systematic genetic analysis reveals a significant negative correlation between hepatic Morc4 expression and the levels of plasma free fatty acids and triglycerides. in vitro experiments, MORC4 gene silencing elevated TC and TG levels, with lipid droplet accumulation observed in both normal and OA-treated cells, whereas MORC4 overexpression restored total TC and TG levels, along with lipid accumulation in these cell models. Similar phenotypes are also observed in IMPC database. Compared with wild-type mice, Morc4 knockout mice exhibit elevated total cholesterol levels and cholesterol ratios, as well as an increase in fat mass and fat/body weight ratios. Collectively, these findings underscore the critical role of MORC4 in maintaining hepatic lipid metabolism homeostasis. To further investigate the potential influence of MORC4 on lipid metabolism signaling pathways, 2,000 genes that were co-expressed with Morc4 expression in the liver were identified and analyzed. Notably, many of these genes are involved in cholesterol metabolism including Pcsk9, Lipa, Lipg, Pltp, Apoc2, Cd36, and Apoa4.
Our findings reveal a significant negative correlation between Morc4 and Pcsk9 expression, while a significant positive correlation exists between Morc4 expression and that of Pltp and Cd36. PCSK9 is a hepatic protease that facilitates the degradation of low-density lipoprotein receptors (LDLRs) (29, 30). LDLRs are responsible for the uptake of LDLs from the bloodstream, subsequently transporting them to the liver for degradation, which releases cholesterol (31). Gain-of-function mutations in Pcsk9 are linked to familial hypercholesterolemia and the inhibition of PCSK9 is emerging as a novel strategy for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia (32, 33). PLTP plays a crucial role in the transport of cholesterol to the liver for its degradation and excretion (34, 35). CD36 functions as a fatty acid transporter, contributing to the cellular uptake of fatty acids (36, 37). A reduction or loss of function in both PLTP and CD36 may lead to lipid accumulation and metabolic dysfunction (36, 38). MORC4 knockdown results in an upregulation of PCSK9 level and a downregulation of PLTP and CD36 levels. Furthermore, MORC4 overexpression restored the expression changes of these genes induced by MORC4 knockdown. These results suggest that MORC4 may play a regulatory role in lipid metabolism by influencing the uptake of free fatty acids and cholesterol.
Our research indicates a significant positive correlation between Morc4 expression and the levels of Apoc2, Apoa4, Lipg and Lipa, all of which play essential roles in triglyceride metabolism. APOC2 could activates lipoprotein lipase for the hydrolysis of hydrolysis of triglyceride-rich plasma lipoproteins, a process that is critically supported by APOA4 (39, 40). Apoc2 deficiency elicits severe hypertriglyceridemia (41). Additionally, LIPG and LIPA are involved in the hydrolysis of triglycerides (42, 43). Moreover, our findings imply a significant negative correlation between Morc4 and Hmgcr expression. HMGCR serves as a key rate-limiting enzyme in de novo cholesterol synthesis (44, 45). An increase in HMGCR expression enhances cholesterol synthesis, while its inhibition leads to a reduction in serum cholesterol levels (46, 47). in vitro experiments, MORC4 knockdown is associated with a reduction in the expression of APOC2, APOA4, LIPG and LIPA, alongside an increase in HMGCR expression. Whereas, MORC4 overexpression in cells with MORC4 knockdown reinstates the expression levels of these genes. These results suggest the critical role of MORC4 in the regulation of cholesterol synthesis and metabolism.
Research on the regulatory mechanisms of MORC4 remains limited. A Study in HEK293 T cells shows that MORC4 mediates nuclear body formation and inhibits binding of transcription factors (48). In Arabidopsis, MORC4 was implicated in DNA methylation establishment (49). These findings suggest MORC4 may suppress PCSK9 and HMGCR expression by enhancing promoter methylation. However, the mechanisms through which MORC4 upregulates genes such as LIPA still remain to be investigated. Furthermore, targeting PCSK9 to enhance its methylation has been proposed as a therapeutic strategy for hypercholesterolemia (50). Consequently, MORC4 may also represent as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia.
In addition, an elevated expression of PCSK9, LIPA, LIPG, PLTP and APCO2 was noted in OA-treated THLE-2 and HepG2 cells. Conversely, Hmgcr expression was found to be downregulated in these OA-treated cells. These findings suggest that cholesterol synthesis is inhibited while cholesterol uptake and triglyceride hydrolysis are activated, thereby contributing to the maintenance of intrahepatic lipid homeostasis in hyperlipidemic milieu. The expression of MORC4 was also increased in OA-treated cells. It aligns with its role in negatively regulating cellular triglyceride and cholesterol levels, as indicated by our results. However, the expression of PLTP and CD36 was downregulated in OA-treated cells, potentially due to their primary function in lipid absorption within the vascular compartment (51, 52). Notably, the levels of PLTP have been reported to be elevated in the liver of mice fed a high-fat high-cholesterol (HFHC) diet, as well as in the plasma of patients with NAFLD (53, 54).
In summary, utilizing the BXD genetic reference population, alongside integrative approaches from systems genetics and molecular biology, we identified MORC4 as a critical determinant of hepatic lipid metabolism. MORC4 exerts its influence on lipid metabolism via three distinct pathways (Figure 5G). First, MORC4 influences hepatic uptake of free fatty acids and cholesterol from plasma through PCSK9, CD36 and PLTP. Second, it regulates the hydrolysis of triglycerides through APOC2, APOA4, LIPG, and LIPA. Lastly, Morc4 plays a role in the modulation of cholesterol synthesis through HMGCR. Our research reveals the regulator function of MOCR4 in lipid metabolism homeostasis. Dysregulation of liver metabolism can lead to liver diseases such as fatty liver and hepatitis, hepatocyte damage and abnormal liver function. It may also induce metabolic syndromes like obesity, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Consequently, MORC4 may represent a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of metabolic syndromes. Take together, our results enhance understanding of the regulatory networks governing lipid metabolism but also offer novel perspectives for the personalized treatment of metabolic diseases.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
Author contributions
ZY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JX: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. XY: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PY: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Investigation. JR: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YW: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. GT: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. FX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JM: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. HL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China [32170989], Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province [ZR2021MH141, ZR2021MH148, ZR2023MH373], Major Basic Research Project of Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation [ZR2019ZD27], Key R&D Program of Shandong Province, China [2023CXPT012], and Taishan Scholars Construction Engineering.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1570729/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Jones JG. Hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetologia. (2016) 59:1098–103. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-3940-5
2. Machado MV, Diehl AM. Pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. (2016) 150:1769–77. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.066
3. Rosenfeld B, Lang JM. Redistribution of lipid in rat liver homogenates. Nature. (1962) 193:64–5. doi: 10.1038/193064b0
4. Liu W, Baker RD, Bhatia T, Zhu L, Baker SS. Pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2016) 73:1969–87. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2161-x
5. Jensen T, Abdelmalek MF, Sullivan S, Nadeau KJ, Green M, Roncal C, et al. Fructose and sugar: a major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. (2018) 68:1063–75. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.01.019
6. Hodson L, Gunn PJ. The regulation of hepatic fatty acid synthesis and partitioning: the effect of nutritional state. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2019) 15:689–700. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0256-9
7. Martins AC, López-Granero C, Ferrer B, Tinkov AA, Skalny AV, Paoliello MMB, et al. BXD recombinant inbred mice as a model to study neurotoxicity. Biomolecules. (2021) 11:1762. doi: 10.3390/biom11121762
8. Smith ML, Mignogna KM, Rokita JL, MacLeod L, Damaj MI, Miles MF. Identification of candidate genes for nicotine withdrawal in C57BL/6J×DBA/2J recombinant inbred mice. Genes Brain Behav. (2023) 22:e12844. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12844
9. Peirce JL, Lu L, Gu J, Silver LM, Williams RW. A new set of BXD recombinant inbred lines from advanced intercross populations in mice. BMC Genet. (2004) 5:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-5-7
10. Andreux PA, Williams EG, Koutnikova H, Houtkooper RH, Champy M-F, Henry H, et al. Systems genetics of metabolism: the use of the BXD murine reference panel for multiscalar integration of traits. Cell. (2012) 150:1287–99. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.012
11. Jha P, McDevitt MT, Gupta R, Quiros PM, Williams EG, Gariani K, et al. Systems analyses reveal physiological roles and genetic regulators of liver lipid Species. Cell Syst. (2018) 6:722–733.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2018.05.016
12. Jha P, McDevitt MT, Halilbasic E, Williams EG, Quiros PM, Gariani K, et al. Genetic regulation of plasma lipid Species and their association with metabolic phenotypes. Cell Syst. (2018) 6:709–721.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2018.05.009
13. Xu F, Ziebarth JD, Goeminne LJE, Gao J, Williams EG, Quarles LD, et al. Gene network based analysis identifies a coexpression module involved in regulating plasma lipids with high-fat diet response. J Nutr Biochem. (2023) 119:109398. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109398
14. Liu Y, Tempel W, Zhang Q, Liang X, Loppnau P, Qin S, et al. Family-wide characterization of histone binding abilities of human CW domain-containing proteins. J Biol Chem. (2016) 291:9000–13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.718973
15. Glatz JFC, Heather LC, Luiken J. CD36 as a gatekeeper of myocardial lipid metabolism and therapeutic target for metabolic disease. Physiol Rev. (2024) 104:727–64. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00011.2023
16. Singer JM, Shew TM, Ferguson D, Renkemeyer MK, Pietka TA, Hall AM, et al. Monoacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 lowers adipocyte differentiation capacity in vitro but does not affect adiposity in mice. Obesity (Silver Spring). (2022) 30:2122–33. doi: 10.1002/oby.23538
17. Åbacka H, Masoni S, Poli G, Huang P, Gusso F, Granchi C, et al. SMS121, a new inhibitor of CD36, impairs fatty acid uptake and viability of acute myeloid leukemia. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:9104. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58689-1
18. Okuma C, Ohta T, Tadaki H, Ishigure T, Sakata S, Taniuchi H, et al. JTP-103237, a monoacylglycerol acyltransferase inhibitor, prevents fatty liver and suppresses both triglyceride synthesis and de novo lipogenesis. J Pharmacol Sci. (2015) 128:150–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2015.06.007
19. Bourgault J, Abner E, Manikpurage HD, Pujol-Gualdo N, Laisk T, Gobeil É, et al. Proteome-wide Mendelian randomization identifies causal links between blood proteins and acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. (2023) 164:953–965.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.01.028
20. Mulligan MK, Mozhui K, Prins P, Williams RW. Genenetwork: a toolbox for systems genetics. Syst Genet. (2017) 1488:75–120. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6427-7_4
21. Li H, Wang X, Rukina D, Huang Q, Lin T, Sorrentino V, et al. An integrated systems genetics and omics toolkit to probe gene function. Cell Syst. (2018) 6:90–102.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2017.10.016
22. Elizarraras JM, Liao Y, Shi Z, Zhu Q, Pico AR, Zhang B. Webgestalt 2024: faster gene set analysis and new support for metabolomics and multi-omics. Nucleic Acids Res. (2024) 52:W415–21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae456
23. Groza T, Gomez FL, Mashhadi HH, Muñoz-Fuentes V, Gunes O, Wilson R, et al. The international mouse phenotyping consortium: comprehensive knockout phenotyping underpinning the study of human disease. Nucleic Acids Res. (2023) 51:D1038–45. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac972
24. Haselimashhadi H, Mason JC, Mallon AM, Smedley D, Meehan TF, Parkinson H. Openstats: a robust and scalable software package for reproducible analysis of high-throughput phenotypic data. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0242933. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242933
25. Song H, Yang R, Zhang J, Sun P, Xing X, Wang L, et al. Oleic acid-induced steatosis model establishment in LMH cells and its effect on lipid metabolism. Poult Sci. (2023) 102:102297. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102297
26. Cao P, Huang G, Yang Q, Guo J, Su Z. The effect of chitooligosaccharides on oleic acid-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. Saudi Pharm J. (2016) 24:292–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2016.04.023
27. Engelking LJ. Schoenheimer effect explained—feedback regulation of cholesterol synthesis in mice mediated by insig proteins. J Clin Invest. (2005) 115:2489–98. doi: 10.1172/JCI25614
28. Smith K, Dennis K, Hodson L. The ins and outs of liver fat metabolism: the effect of phenotype and diet on risk of intrahepatic triglyceride accumulation. Exp Physiol. (2025):1–13. doi: 10.1113/EP092001
29. Seidah NG, Prat A. The multifaceted biology of PCSK9. Endocr Rev. (2022) 43:558–82. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnab035
30. Tavori H, Giunzioni I, Predazzi IM, Plubell D, Shivinsky A, Miles J, et al. Human PCSK9 promotes hepatic lipogenesis and atherosclerosis development via apoE- and LDLR-mediated mechanisms. Cardiovasc Res. (2016) 110:268–78. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw053
31. Riad A, Zeng C, Weng CC, Winters H, Xu K, Makvandi M, et al. Sigma-2 receptor/TMEM97 and PGRMC-1 increase the rate of internalization of LDL by LDL receptor through the formation of a ternary Complex. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:16845. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35430-3
32. Chen Z, Shao W, Li Y, Zhang X, Geng Y, Ma X, et al. Inhibition of PCSK9 prevents and alleviates cholesterol gallstones through PPARα-mediated CYP7A1 activation. Metab Clin Exp. (2024) 152:155774. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155774
33. Noguchi T, Katsuda S, Kawashiri MA, Tada H, Nohara A, Inazu A, et al. The E32K variant of PCSK9 exacerbates the phenotype of familial hypercholesterolaemia by increasing PCSK9 function and concentration in the circulation. Atherosclerosis. (2010) 210:166–72. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.11.018
34. Sponton CH, Hosono T, Taura J, Jedrychowski MP, Yoneshiro T, Wang Q, et al. The regulation of glucose and lipid homeostasis via PLTP as a mediator of BAT-liver communication. EMBO Rep. (2020) 21:e49828. doi: 10.15252/embr.201949828
35. Huuskonen J, Olkkonen VM, Jauhiainen M, Ehnholm C. The impact of phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP) on HDL metabolism. Atherosclerosis. (2001) 155:269–81. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9150(01)00447-6
36. Li Y, Huang X, Yang G, Xu K, Yin Y, Brecchia G, et al. CD36 favours fat sensing and transport to govern lipid metabolism. Prog Lipid Res. (2022) 88:101193. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2022.101193
37. Hao JW, Wang J, Guo H, Zhao YY, Sun HH, Li YF, et al. CD36 facilitates fatty acid uptake by dynamic palmitoylation-regulated endocytosis. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:4765. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18565-8
38. Ajoolabady A, Pratico D, Mazidi M, Davies IG, Lip GYH, Seidah N, et al. PCSK9 in metabolism and diseases. Metab Clin Exp. (2025) 163:156064. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2024.156064
39. Cao Y, Araki M, Nakagawa Y, Deisen L, Lundsgaard A, Kanta JM, et al. Dietary medium-chain fatty acids reduce hepatic fat accumulation via activation of a CREBH-FGF21 axis. Mol Metab. (2024) 87:101991. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.101991
40. Mehta A, Shapiro MD. Apolipoproteins in vascular biology and atherosclerotic disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2022) 19:168–79. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00613-5
41. Gao M, Yang C, Wang X, Guo M, Yang L, Gao S, et al. Apoc2 deficiency elicits severe hypertriglyceridemia and spontaneous atherosclerosis: a rodent model rescued from neonatal death. Metab Clin Exp. (2020) 109:154296. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154296
42. Khetarpal SA, Vitali C, Levin MG, Klarin D, Park J, Pampana A, et al. Endothelial lipase mediates efficient lipolysis of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. PLoS Genet. (2021) 17:e1009802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009802
43. Hollak CE, Hovingh GK. Dyslipidaemia: lysosomal acid lipase deficiency-a cautious leap forward. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2015) 11:696–7. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.182
44. Lu XY, Shi XJ, Hu A, Wang JQ, Ding Y, Jiang W, et al. Feeding induces cholesterol biosynthesis via the mTORC1-USP20-HMGCR axis. Nature. (2020) 588:479–84. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2928-y
45. Goedeke L, Fernández-Hernando C. Regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2012) 69:915–30. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0857-5
46. Yogev Y, Shorer Z, Koifman A, Wormser O, Drabkin M, Halperin D, et al. Limb girdle muscular disease caused by HMGCR mutation and statin myopathy treatable with mevalonolactone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2023) 120:e2217831120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2217831120
47. Cuccioloni M, Mozzicafreddo M, Spina M, Tran CN, Falconi M, Eleuteri AM, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate potently inhibits the in vitro activity of hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase. J Lipid Res. (2011) 52:897–907. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M011817
48. Tencer AH, Cox KL, Wright GM, Zhang Y, Petell CJ, Klein BJ, et al. Molecular mechanism of the MORC4 ATPase activation. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:5466. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19278-8
49. Xue Y, Zhong Z, Harris CJ, Gallego-Bartolomé J, Wang M, Picard C, et al. Arabidopsis MORC proteins function in the efficient establishment of RNA directed DNA methylation. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:4292. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24553-3
50. Tremblay F, Xiong Q, Shah SS, Ko CW, Kelly K, Morrison MS, et al. A potent epigenetic editor targeting human PCSK9 for durable reduction of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Nat Med. (2025) 31:1329–38. doi: 10.1038/s41591-025-03508-x
51. Son NH, Basu D, Samovski D, Pietka TA, Peche VS, Willecke F, et al. Endothelial cell CD36 optimizes tissue fatty acid uptake. J Clin Invest. (2018) 128:4329–42. doi: 10.1172/JCI99315
52. Jiang XC. Phospholipid transfer protein: its impact on lipoprotein homeostasis and atherosclerosis. J Lipid Res. (2018) 59:764–71. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R082503
53. Shelly L, Royer L, Sand T, Jensen H, Luo Y. Phospholipid transfer protein deficiency ameliorates diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and inflammation in mice. J Lipid Res. (2008) 49:773–81. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M700336-JLR200
54. Dullaart RP, de Vries R, Dallinga-Thie GM, Sluiter WJ, van Tol A. Phospholipid transfer protein activity is determined by type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome, and is positively associated with serum transaminases. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). (2008) 68:375–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.03049.x
Keywords: BXD mice, lipid metabolism, MORC4, TC, TG
Citation: Yang Z, Xu J, Yang X, Yi P, Ruan J, Wu Y, Li Y, Tian G, Xu F, Mi J, Li H and Yang C (2025) Morc4 is a novel functional gene associated with lipid metabolism in BXD recombinant inbred population. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1570729. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1570729
Received: 12 February 2025; Accepted: 2 June 2025;
Published: 18 June 2025.
Edited by:
Sasha A. Singh, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, United StatesCopyright: © 2025 Yang, Xu, Yang, Yi, Ruan, Wu, Li, Tian, Xu, Mi, Li and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: He Li, bGloZWRvY0AxNjMuY29t; Chunhua Yang, eWFuZ2NodW5odWFAYnptYy5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
‡ORCID:
Chunhua Yang
orcid.org/0009-0007-0434-2867
 Zhanyi Yang
Zhanyi Yang Jiaai Xu1,†
Jiaai Xu1,† Xiaoyu Yang
Xiaoyu Yang Geng Tian
Geng Tian Fuyi Xu
Fuyi Xu Jia Mi
Jia Mi He Li
He Li Chunhua Yang
Chunhua Yang