Abstract
Introduction:
Transcatheter device closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defect (PmVSD) using the Lifetech KONAR-MF ventricular septal defect occluder (MFO) presents a promising and effective alternative to surgical repair.
Objectives:
This study aims to evaluate the 6-month safety and efficacy of the MFO device for PmVSD closure.
Materials and methods:
We conducted a retrospective analysis of clinical data from patients who underwent percutaneous PmVSD closure using the MFO device at our institution between December 2021 and June 2024. Safety, procedural and 6-month outcomes were systematically assessed.
Results:
A total of 115 patients (52.2% male) underwent transcatheter PmVSD closure. The median age was 7.6 years [interquartile range (IQR), 4.0–27.2] and weight 25.6 kg (IQR, 14.2–62.6). Median defect size by angiography was 5.7 mm (IQR, 3.8–8.3) on the left ventricle side and 3.3 mm (IQR, 2.3–4.4) on the right ventricle side. Aortic valve prolapse (AVP) was noted in 114 patients (99.1%), with pre-procedural aortic regurgitation (AR) in 36 (31.3%). Median pulmonary artery pressure was 17 mmHg (IQR, 14–20); 48 (41.7%) had Qp/Qs >1.5. All procedures were successful; 33 (28.7%) used a retrograde approach. Median fluoroscopy time was 22 min (IQR, 15–33). Complete closure was achieved in 51.3% at 1 day, 62.6% at 1 month, 69.6% at 3 months, and 83.5% at 6 months. Transient conduction disturbances (n = 4), hypotension (n = 1), and femoral hematoma (n = 1) were observed. No cases of endocarditis, valve injury, or complete atrioventricular block occurred.
Conclusion:
Transcatheter closure of PmVSD with the MFO demonstrated safety and efficacy during the 6-month follow-up period. Notably, the majority of defects in this cohort were small in size.
Introduction
Perimembranous ventricular septal defect (PmVSD) is the most common congenital heart disease (1). Since Lock et al. first achieved a successful percutaneous ventricular septal defect (VSD) closure in 1988, transcatheter approaches have been recognized as a viable treatment option in selected patients. Progress in device design and procedural methods has allowed this intervention to be performed regularly in many healthcare institutions (2, 3). Early approaches primarily utilized double-disc devices, which required sufficient septal and aortic rims, making them unsuitable for many defects (4, 5). The Amplatzer asymmetrical membranous VSD occluder (St. Jude Medical, St. Paul, MN, USA) was specifically engineered for PmVSD and demonstrated generally favorable outcomes with widespread use (6, 7). However, its association with a significant risk of complete atrioventricular (AV) block led to its discontinuation (3, 8). Currently, devices such as the Nit-Occlud® Lê VSD-Coil (PFM Medical, Germany) (9), Cera VSD devices (Lifetech, Shenzhen, China), and other device occluders from Amplatzer (Abbott, USA) are being utilized (8, 10). In a meta-analysis comparing percutaneous and surgical closure of PmVSD, both approaches demonstrated comparable procedural success, major complications, and valvular outcomes, though percutaneous closure offered advantages in terms of shorter hospital stay and lower transfusion requirements (11). Despite ongoing debates and limited regulatory approval in several countries, transcatheter closure of PmVSD continues, including in Taiwan, where various adapted devices, initially intended for different conditions, are used off-label. PmVSD closure remains challenging due to anatomical complexities, such as proximity to the aortic and tricuspid valves, right coronary cusp (RCC) prolapses, and the risk of complete heart block. An optimal device for this procedure has yet to be developed. The Lifetech KONAR-MF ventricular septal defect occluder (MFO), a CE-approved for VSD closure, flexible device with single- and double- disc features, that allows antegrade and retrograde delivery, minimizing structural damage and complications; The MFO has been increasingly adopted in recent years for PmVSD closure due to its smart features, and data on its safety and efficacy in this population is accumulating (12, 13). Despite its growing use worldwide, clinical data, particularly from East Asia, remain scarce. This study provides short-term real-world data on the MFO device for PmVSD closure in Taiwan, focusing on procedural safety, efficacy, and anatomical considerations.
Methods
Study design and population
We conducted a retrospective analysis of clinical data from patients who underwent percutaneous PmVSD closure using the MFO device at our institution between December 2021 and June 2024. Safety, procedural and 6-month outcomes were systematically assessed. Each case was approved by a multidisciplinary team, and patients were informed of all treatment options, including surgery. The study complied with local regulations and institutional requirements, with protocol approval from the institutional review board [IRB TCVGH No. CG16272B]. Written informed consent was obtained from participants' legal guardians or next of kin.
Inclusion criteria: Patients with clinically symptoms and hemodynamically relevant PmVSD were included in this study. Hemodynamically significant VSDs were identified in patients with left heart chamber enlargement, evidence of pulmonary hypertension, a pulmonary-to-systemic flow ratio (Qp/Qs) exceeding 1.5, cardiomegaly on chest radiography, or clinical manifestations such as frequent respiratory infections, failure to thrive, or weight loss. Patients with PmVSD and mild RCC prolapse were eligible only if aortic regurgitation (AR) was assessed as trivial or mild.
Exclusion criteria: Patients with PmVSD were excluded if they had more than mild aortic valve regurgitation or prolapse, severe pulmonary hypertension [mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) ≥ 35 mmHg], other congenital heart defects requiring surgery, or large VSDs [right ventricle [RV]-side diameter > 14 mm or left ventricle [LV]-side diameter > 18 mm] requiring an MFO device size > 14/12. Additionally, patients with a body weight < 7 kg, active bacterial infections (e.g., endocarditis or sepsis), or malaligned VSDs were excluded.
AR assessment
AR was evaluated in all patients using transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) by experienced pediatric cardiologists. The severity of regurgitation was graded according to the guidelines of the American Society of Echocardiography (ASE), using an integrative approach based on multiple parameters, including jet width, vena contracta width, and the presence of holodiastolic flow reversal in the descending aorta.
Study device and device selection protocol
The MFO is a self-expanding, double-disc device made of 144 nitinol wires connected by a cone-shaped waist. It comes in eight sizes (5/3 to 14/12 mm); larger sizes (≥9/7 mm) are reinforced with a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane to improve occlusion, while smaller ones are not. The device is delivered via the SteerEase™ introducer (Lifetech, Shenzhen, China), using 5F to 7F sheaths depending on the device size. Device selection followed previously published recommendations (14). Conical defects (RV/LV ratio ≤ 0.5) were closed with waist diameters 1–2 mm larger than the LV size, while tubular defects (RV/LV > 0.5) were oversized by 2–3 mm. For subaortic rims ≥ 2 mm, the right disc (D2) was chosen 1–2 mm larger than the LV opening; for deficient rims (<2 mm), D2 matched the LV size.
Study procedure
The procedure was performed under local anesthesia or conscious sedation with TTE guidance. Femoral vein and artery access were obtained, and patients received heparin (75–100 IU/kg) and antibiotics prior to the intervention. Left ventriculography was performed to assess the defect size, morphology, and relationships to surrounding structures. Device size was selected based on measurements at the narrowest right-side diameter of the defect, with adjustments for aneurysms or deficient aortic rims. The approach, retrograde or antegrade, was chosen based on the patient's anatomy and procedural requirements. All procedures were performed under conscious sedation via femoral access. An arteriovenous loop (AVL) was routinely established at the beginning of each procedure to enable antegrade delivery of the device. This approach was preferred due to the ability of the femoral vein to accommodate larger sheath sizes and was especially suitable in younger or smaller patients, as well as in cases where the defect was located close to the tricuspid valve or exhibited a complex aneurysmal morphology. The retrograde approach was utilized selectively when advancement of the AVL was unsuccessful, most commonly due to entanglement with the tricuspid valve or difficulty navigating through elongated aneurysmal tissue. In such cases, direct retrograde delivery from the femoral artery allowed for a more favorable trajectory and simplified device positioning. Deployment of the device involved careful positioning of the left and right discs to ensure no interference with valve function. TTE and angiography confirmed proper placement and closure before release. Post-procedure, patients received aspirin (3–5 mg/kg daily for 3 months) if there was no residual shunt and were followed up with echocardiography at regular intervals to monitor outcomes and assess residual shunts or valve complications.
Post-operative care and follow-up
Postprocedural anticoagulation with a 24 h Heparin infusion was deemed unnecessary in all patients. In the absence of a residual shunt, patients received oral aspirin (3–5 mg/kg daily) for 3 months. Follow-up assessments, including physical examination, TTE, and electrocardiography (ECG), were performed at 1 day, 1, 3, and 6 months. Residual shunts were categorized by Doppler jet width: trivial (<1 mm), small (1–2 mm), moderate (3–4 mm), and large (≥4 mm). Valve regurgitation and rhythm disturbances were evaluated based on new or persistent complications requiring intervention.
Statistical analysis
Categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages, while continuous variables were reported as mean ± standard deviation or median with interquartile range (IQR), based on data distribution assessed by the Shapiro–Wilk test. Group comparisons were conducted using the chi- squared test for categorical variables and Student's t-test for continuous variables, with statistical significance set at two-sided p-value < 0.05.
Results
Patients
Transcatheter closure of PmVSD using the MFO device was attempted in 115 patients. Sixty (52.2%) were male. The median age was 7.6 years (IQR, 4–27.2), and the median body weight was 25.6 kg (IQR, 14.2–62.6) (Table 1).
Table 1
| Total (n = 115) | |
|---|---|
| Variable | Number (%) or median [IQR] |
| Age (Months) | 7.6 (4.0–27.2) |
| Body weight (kg) | 25.6 (14.2–62.6) |
| Sex (Male) | 60 (52.2%) |
| With septal aneurysm | 107 (93.0%) |
| Size of VSD (mm) | |
| LV side (TTE), mm | 5.5 (4.6–6.7) |
| RV side (TTE), mm | 4.1 (2.9–4.8) |
| LV side (Angiography), mm | 5.7 (3.8–8.3) |
| RV side (Angiography), mm | 3.3 (2.3–4.4) |
| Size distribution of VSD, LV side (mm) | |
| <4 | 33 (28.7%) |
| 4–8 mm | 49 (42.6%) |
| >8 | 33 (28.7%) |
| Mild aortic valve prolapse | 114 (99.1%) |
| Mitral valve insufficiency | |
| Absent | 56 (48.7%) |
| Trivial | 19 (16.5%) |
| Mild | 40 (34.8%) |
| Moderate | 0 |
| Tricuspid valve insufficiency | |
| Absent | 76 (66.1%) |
| Trivial | 16 (13.9%) |
| Mild | 15 (13.0%) |
| Moderate | 8 (7.0%) |
| Aortic valve insufficiency | |
| Absent | 79 (68.7%) |
| Trivial | 21 (18.3%) |
| Mild | 15 (13.0%) |
| Moderate | 0 |
Demographic characteristics of the patients.
VSD, ventricular septal defect; LV, left ventricle; RV, right ventricle; TTE, transthoracic echocardiography.
[Data are presented as number (%) or as median [interquartile range, IQR].
Defects
On TTE, the median diameter of the VSD on the LV side was 5.5 mm (IQR, 4.6–6.7), and 4.1 mm (IQR, 2.9–4.8) on the RV side. On angiography, the median LV-side diameter was 5.7 mm (IQR, 3.8–8.3), and the RV-side diameter was 3.3 mm (IQR, 2.3–4.4). Aneurysmal tissue of the membranous septum was identified in 107 (93.0%) patients. Mild AVP was present in 114 (99.1%) patients—111 RCC and 3 non-coronary cusp (NCC) prolapse—with pre-procedural AR in 36 patients (21 trivial, 15 mild) (Table 1).
Procedure
Closure indications included abundant shunting with Qp/Qs >1.5 (n = 48, 41.7%), mild AVP (n = 114), and failure to thrive (n = 71, 61.7%). Some had multiple indications. The median Qp/Qs ratio was 1.36 (IQR, 1.2–1.7), and the median mPAP was 17 mmHg (IQR, 14–20). Angiographic assessment before device implantation demonstrated PmVSD frequently accompanied by aneurysmal transformation of the membranous septum (Figure 1A) and, in most cases, mild AVP (Figure 1C). The median device size was 8 × 6 mm (range, 5 × 3 to 14 × 12 mm). The antegrade approach was initially attempted in 82 (71.3%) procedures and the retrograde approach in 33 (28.7%), with crossover in 11 procedures. The median procedure time was 62 min (IQR, 52–84), and the median fluoroscopy time was 22 min (IQR, 15–33) (Table 2). Post-deployment angiography confirmed successful device placement without interference with aortic valve function (Figure 1D), and no residual shunt was observed in the majority of cases (Figure 1B).
Figure 1
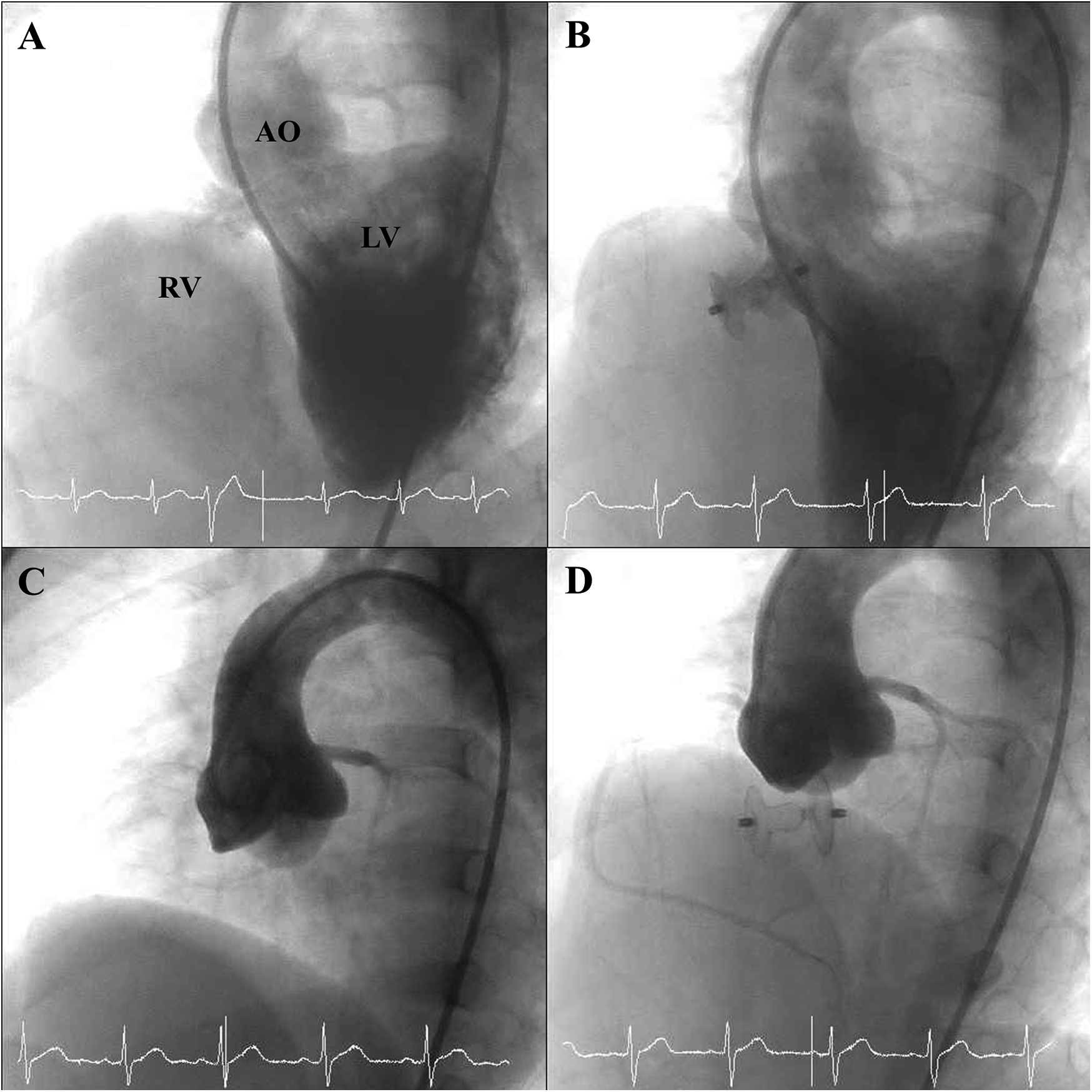
Angiographic findings before and after device deployment. (A) Pre-deployment angiographic image illustrating aneurysmal tissue of the membranous septum associated with the PmVSD. (B) Post-deployment angiographic view showing successful closure of the PmVSD without residual shunt. (C) Pre-deployment angiographic view demonstrating AVP associated with a PmVSD. (D) Post-deployment angiographic view showing persistent AVP in relation to the PmVSD, without interference from the occluder device.
Table 2
| Total (n = 115) | |
|---|---|
| Variable | Number (%) or median [IQR] |
| Pulmonary arterial hypertension | |
| No | 87 (75.7%) |
| Mild (21–30 mmHg) | 24 (20.9%) |
| Moderate (31–45 mmHg) | 4 (3.5%) |
| PAm (mmHg) | 17 (14–20) |
| Qp/Qs | 1.36 (1.2–1.7) |
| Approach used for device closure | |
| Antegrade | 82 (71.3%) |
| Retrograde | 33 (28.7%) |
| Implanted device size (mm) | |
| 5 × 3 | 6 (5.2%) |
| 6 × 4 | 32 (27.8%) |
| 7 × 5 | 6 (5.2%) |
| 8 × 6 | 40 (34.8%) |
| 9 × 7 | 5 (4.3%) |
| 10 × 8 | 20 (17.4%) |
| 12 × 10 | 3 (2.6%) |
| 14 × 12 | 3 (2.6%) |
| Device characteristic | |
| Without PTFE membrane | 84 (73%) |
| With PTFE membrane | 31 (27%) |
| Duration of procedure (min) | 62 (52–84) |
| Fluoroscopy time (min) | 22 (15–33) |
Procedural features.
Pam, mean pulmonary arterial pressure; PTFE, polytetrafluoroethylene; Qp, pulmonary blood; Qs, systemic blood flow.
[Data are presented as number (%) or as median [interquartile range, IQR].
Post-operative care and complications
Percutaneous device closure was successful in all patients. No major vascular complications, mortality, device embolization, infective endocarditis, erosion, or thromboembolic events occurred. Four patients experienced transient arrhythmias (1 s-degree AV block, 2 right bundle branch block, 1 left bundle branch block), all of which resolved after steroid therapy. One patient had transient hypotension, and another developed a femoral hematoma. During the 6-month follow-up, no additional complications, including arrhythmias, valve dysfunction, or device-related issues, were noted (Table 3).
Table 3
| Total (n = 115) | |
|---|---|
| Variable | Number (%) or median [IQR] |
| Procedural success | |
| Successful closure | 115 (100%) |
| Complete occlusion of shunt | |
| 1-day follow-up | 59 (51.3%) |
| 1-month follow-up | 72 (62.6%) |
| 3-month follow-up | 80 (69.6%) |
| 6-month follow-up | 96 (83.5%) |
| Complications | |
| Major | |
| Device embolization | 0 |
| Increase in aortic regurgitation | 0 |
| Minor | |
| Transient hypotension | 1 (0.9%) |
| Hematoma | 1 (0.9%) |
| Heart block/AV block | |
| RBBB/LBBB | 2 (1.7%) |
| RBBB/LBBB | 1 (0.9%) |
| Second-degree AV block | 1 (0.9%) |
Outcomes, follow up, complications related to procedure.
MFO, lifetech konar-MF VSD occluder; RBBB, right bundle branch block; LBBB, left bundle branch block; AV, atrioventricular.
[Data are presented as number (%) or as median [interquartile range, IQR].
Follow-up
Residual shunts were detected in 57 (49.6%) patients after device deployment—17 trivial, 32 mild, and 8 moderate. Complete closure rates improved progressively over time: 51.3% the next day, 62.6% at 1 month, 69.6% at 3 months, and 83.5% at 6 months. No patient developed progressive AR during follow-up. TTE further illustrated the structural changes before and after intervention. Pre-procedural TTE revealed aneurysmal tissue in the short-axis view (Figure 2A) and mild AR in several cases (Figure 2C). At 6-month follow-up, TTE confirmed complete closure of the defect without residual shunting (Figure 2B), and the degree of AR remained stable in all patients, with no evidence of progression (Figure 2D).
Figure 2
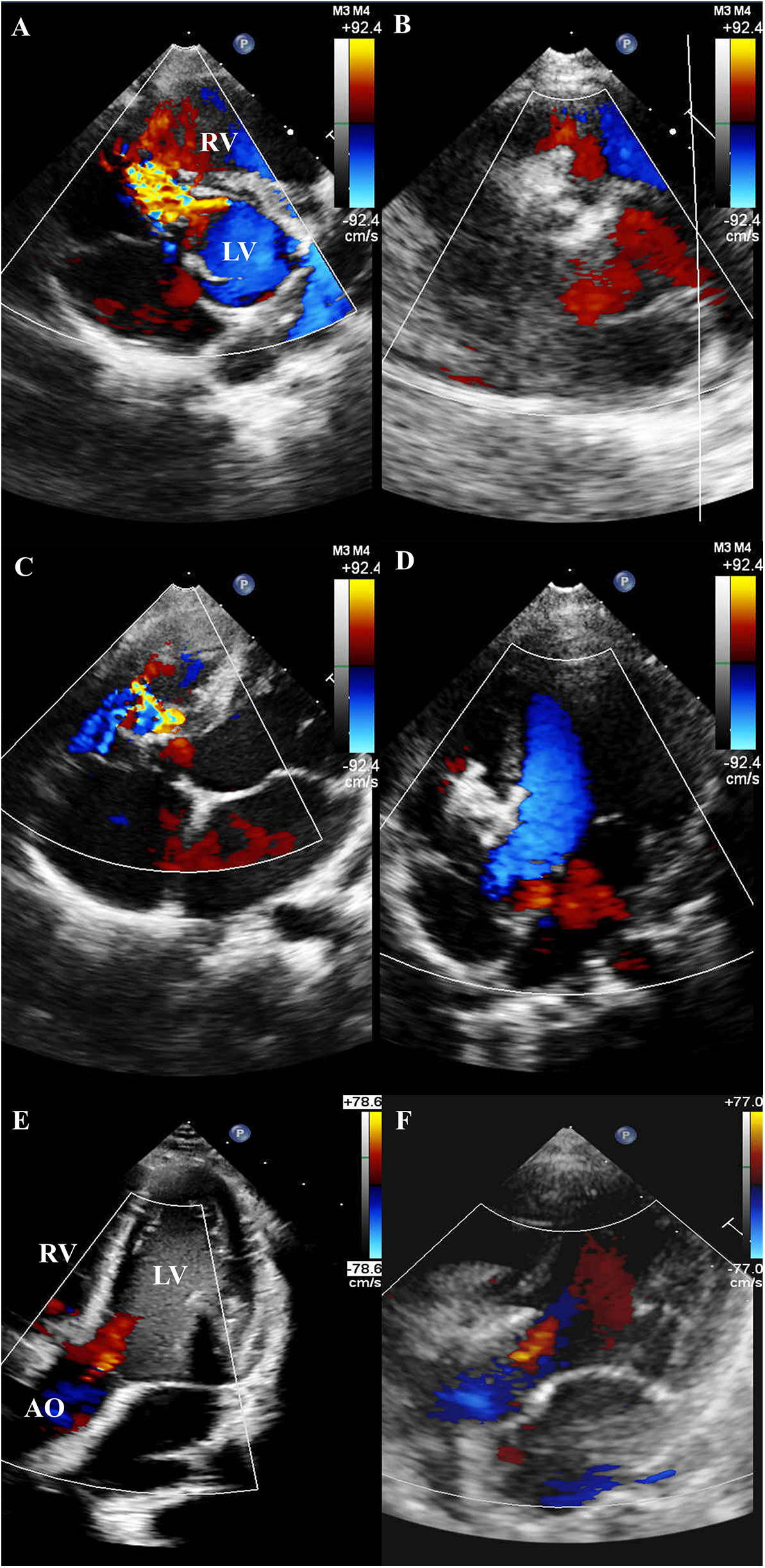
TTE findings before and after device implantation. (A) Pre-procedural TTE (short-axis view) revealing a PmVSD with associated aneurysmal tissue. (B) Follow-up TTE at 6 months (short-axis view) demonstrating complete closure of the PmVSD without residual shunt. (C) Pre-procedural TTE revealing a PmVSD with associated aneurysmal tissue. (D) Follow-up TTE at 6 months demonstrating complete closure of the PmVSD without residual shunt. (E) Pre-procedural TTE demonstrating mild AR. (F) Follow-up TTE at 6 months showing persistent mild AR, with no evidence of progression following device implantation.
Discussion
Our study achieved a 100% procedural success rate and an 83.5% complete closure rate. There were no cases of hemolysis, permanent heart block, endocarditis, or other valvar complications during short-term follow-up, and no fatalities were reported, further supporting the MFO device's safety profile. Compared to the MIOS-MFO multicenter study (n = 333) (15), our cohort (n = 115) showed a lower 6-month complete closure rate (83.5% vs. 97.1%) but no cases of device embolization (0% vs. 2.4%). This may be attributed to our strict inclusion policy favoring small defects, which are potentially less prone to complications such as device embolization. However, proper case selection, careful consideration of identified risk factors, and appropriate device matching are crucial, as embolization may occur, immediately and during early follow-up (16). Smaller cohort studies in the literature also reported low embolization rates with the MFO device: Tanıdır et al. (13) reported a 2%, and Haddad et al. (12) described one case occurring 24 h post-procedure. In our series, device migration into the RV occurred intra-procedurally in two patients (4.1%), both of whom presented with high-risk anatomical features (e.g., defect location or an aortic rim <2 mm). Contributing factors likely included underestimation of defect size, suboptimal device selection, or technical challenges during deployment. Moreover, the MFO's dual delivery design enhances procedural flexibility, allowing both antegrade and retrograde approaches (17). However, in our study, the retrograde route was used in only 28.4% of cases, primarily due to sheath size limitations in smaller children.
Importantly, the markedly higher prevalence of mild AVP in our cohort (99.1% vs. 10.5%) likely reflects differences in clinical presentation, timing of diagnosis, and intervention, as well as broader case selection criteria driven by national health insurance reimbursement policies. However, prior studies have also demonstrated successful pmVSD closure in patients with AVP and less than mild aortic regurgitation using various devices, including the MFO (7, 15, 18).
Residual shunt
Residual shunting rates reported in the literature vary. In a comprehensive study by Haddad et al. (12), complete closure rate of 40% (8/20) at the end of the procedure, which increased to 57.9% (11/19) at discharge and 84.2% (16/19) after six months of follow-up. In our study, immediate post- procedural closure was relatively lower, with fewer than 25% of patients exhibiting small, smoky residual shunts. This may reflect a delayed closure process, as the smaller MFO sizes (first four models) lack a PTFE membrane that would otherwise promote thrombosis. These residual flows were not hemodynamically significant and were thus considered acceptable. Nevertheless, both prior studies and our current investigation confirm that residual shunts tend to decrease over time (12, 13).
Heart block
Complete AV block after transcatheter pmVSD closure is typically observed either early in the procedure or later during short-term follow-up, which has limited the widespread adoption of this method in several countries (3, 6, 7, 19). Oversized devices may cause early-onset heart block due to clamping force and mechanical trauma during deployment, while late-onset heart block can result from fibrosis, compression, or inflammation of the conduction system (20). Smaller infants are also considered at higher risk of developing heart block following percutaneous pmVSD closure (19). Unlike some conventional pmVSD occluders that require large-profile delivery systems, the MFO can be deployed using a smaller 4–7 Fr sheath or guiding catheter (21). In comparison with published data, Tanıdır et al. (13) reported transient AV block in two patients, both of which resolved after sheath withdrawal without the need for pacemaker implantation. Haddad et al. (12), as well as the MIOS-MFO multicenter study (15), reported no rhythm disturbances in their respective small patient cohorts. Nevertheless, heart block may still occur in rare cases, particularly in anatomically challenging defects or suboptimal device selection (13, 22), underscoring the importance of long-term rhythm monitoring until this risk is fully mitigated. In our study, despite a younger and lower-weight cohort, only one case of transient AV block was observed, which was resolved with medical therapy. Notably, most defects in our series were small and associated with membranous septal aneurysms—an anatomic feature previously suggested to be protective against conduction disturbances.
Valvar disturbances
Aortic and tricuspid regurgitation are potential complications that are often closely monitored during the procedure. Haddad et al. (12) emphasized the continuous assessment of the right disk position via echocardiography. Their study found no instances of tricuspid regurgitation either at the conclusion of the procedure or during follow-up. Similarly, Tanıdır et al. (13) reported only one patient of moderate tricuspid insufficiency (1%) in their series.
New-onset AR following transcatheter closure of PmVSD has been reported in up to 16% of patients with ductal occluders (23), and up to 17% with the Amplatzer membranous occluder (3, 6, 12, 19). The incidence of new-onset AR is lower with the ADO II (24) and the modified Chinese occluder (25, 26).
Regarding aortic valve insufficiency, only one patient experienced it in the study by Haddad et al. (12), and mild AR was noted in one patient in the research by Tanıdır et al. (13). In our study, only two cases of trivial AR occurred, without progression during follow-up. Notably, all AVP cases in this study were mild, with no progression to moderate or severe AR during follow-up, suggesting that transcatheter closure with the MFO device is safe and feasible in carefully selected patients. These findings also support that mild AVP should not be an absolute contraindication to device closure, though prior research highlights valve prolapse and subaortic rim deficiency as risk factors for post-procedural valve dysfunction (15, 27). However, we believe the device's soft, flexible design with a nitinol wire mesh layer allows it to conform to the plane of the aortic valve without disrupting leaflet coaptation.
Study limitations
This study has several limitations. In addition to its single-center, retrospective design, the six-month follow-up may be insufficient to detect delayed complications such as progressive aortic regurgitation or conduction abnormalities. The predominance of small defects in our cohort further limits the generalizability of these findings to larger or more complex anatomies. Moreover, selection bias may have contributed to the high prevalence of AVP, as Taiwan's National Health Insurance reimburses pmVSD closure only for patients with clinically significant defects—such as cardiomegaly, heart failure symptoms, or AVP without severe aortic regurgitation—excluding those with small, asymptomatic shunts.
Conclusion
Based on our short-term results, transcatheter closure of PmVSD using the MFO device is both feasible and safe. Most defects in this cohort were relatively small, which should be taken into account when interpreting the outcomes.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans because the study was based on existing data. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
L-CL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Y-CF: Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. P-CL: Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. S-LJ: Investigation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. M-CL: Formal analysis, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. C-MC: Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. H-CH: Data curation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Hoffman JI Kaplan S . The incidence of congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2002) 39(12):1890–900. 10.1016/s0735-1097(02)01886-7
2.
Lock JE Block PC McKay RG Baim DS Keane JF . Transcatheter closure of ventricular septal defects. Circulation. (1988) 78(2):361–8. 10.1161/01.cir.78.2.361
3.
Predescu D Chaturvedi RR Friedberg MK Benson LN Ozawa A Lee KJ . Complete heart block associated with device closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2008) 136(5):1223–8. 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2008.02.037
4.
Sideris EB Walsh KP Haddad JL Chen CR Ren SG Kulkarni H . Occlusion of congenital ventricular septal defects by the buttoned device. “Buttoned device” clinical trials international register. Heart. (1997) 77(3):276–9. 10.1136/hrt.77.3.276
5.
Knauth AL Lock JE Perry SB McElhinney DB Gauvreau K Landzberg MJ et al Transcatheter device closure of congenital and postoperative residual ventricular septal defects. Circulation. (2004) 110(5):501–7. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000137116.12176.A6
6.
Carminati M Butera G Chessa M De Giovanni J Fisher G Gewillig M et al Transcatheter closure of congenital ventricular septal defects: results of the European registry. Eur Heart J. (2007) 28(19):2361–8. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm314
7.
Santhanam H Yang L Chen Z Tai BC Rajgor DD Quek SC . A meta-analysis of transcatheter device closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defect. Int J Cardiol. (2018) 254:75–83. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.12.011
8.
Yang R Kong XQ Sheng YH Zhou L Xu D Yong YH et al Risk factors and outcomes of post-procedure heart blocks after transcatheter device closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defect. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2012) 5(4):422–7. 10.1016/j.jcin.2012.01.015
9.
Kozlik-Feldmann R Lorber A Sievert H Ewert P Jux C Müller GC et al Long-term outcome of perimembranous VSD closure using the Nit-Occlud(R) Le VSD coil system. Clin Res Cardiol. (2021) 110(3):382–90. 10.1007/s00392-020-01750-6
10.
Esteves CA Solarewicz LA Cassar R Neves JR Esteves V Arrieta R . Occlusion of the perimembranous ventricular septal defect using CERA(R) devices. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2012) 80(2):182–7. 10.1002/ccd.24371
11.
Saurav A Kaushik M Mahesh Alla V White MD Satpathy R Lanspa T et al Comparison of percutaneous device closure versus surgical closure of peri-membranous ventricular septal defects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2015) 86(6):1048–56. 10.1002/ccd.26097
12.
Haddad RN Daou LS Saliba ZS . Percutaneous closure of restrictive-type perimembranous ventricular septal defect using the new KONAR multifunctional occluder: midterm outcomes of the first middle-eastern experience. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2020) 96(3):E295–302. 10.1002/ccd.28678
13.
Tanidir IC Baspinar O Saygi M Kervancioglu M Guzeltas A Odemis E . Use of Lifetech Konar-MF, a device for both perimembranous and muscular ventricular septal defects: a multicentre study. Int J Cardiol. (2020) 310:43–50. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.02.056
14.
Haddad RN Saliba ZS . Comparative outcomes of two competitive devices for retrograde closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 10:1215397. 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1215397
15.
Haddad RN Houeijeh A Odemis E Thambo JB Saritas T Ece I et al MIOS-MFO, a multicenter international observational study of the Lifetech KONAR-MF ventricular septal defect occluder in treating perimembranous ventricular septal defects. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). (2025):S1885-5857(25)00084-2. 10.1016/j.rec.2025.02.010
16.
Haddad RN Saliba Z . Word of caution: silent late device embolisation after perimembranous ventricular septal defect closure in a 6-Kg infant. Cardiol Young. (2024) 34(2):455–8. 10.1017/S104795112300433X
17.
Schubert S Kelm M Koneti NR Berger F . First European experience of percutaneous closure of ventricular septal defects using a new CE-marked VSD occluder. EuroIntervention. (2019) 15(3):e242–3. 10.4244/EIJ-D-18-00867
18.
Kuswiyanto RB Gunawijaya E Djer MM Noormanto Rahman MA Murni IK et al Transcatheter closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defect using the lifetech konar-multi functional occluder: early to midterm results of the Indonesian multicenter study. Glob Heart. (2022) 17(1):15. 10.5334/gh.1106
19.
Butera G Carminati M Chessa M Piazza L Micheletti A Negura DG et al Transcatheter closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects: early and long-term results. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2007) 50(12):1189–95. 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.03.068
20.
Callaghan MA Mannion D . No escape from a VSD device? Complete heart block and cardiac arrest associated with a ventricular septal defect occluder device. Paediatr Anaesth. (2012) 22(2):170–2. 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2011.03667.x
21.
Chungsomprasong P Durongpisitkul K Vijarnsorn C Soongswang J Le TP . The results of transcatheter closure of VSD using Amplatzer(R) device and Nit Occlud(R) Le coil. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2011) 78(7):1032–40. 10.1002/ccd.23084
22.
Leong MC Alwi M . Complete atrio-ventricular heart block, a not to be forgotten complication in transcatheter closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defect—a case report and review of literature. Cardiol Young. (2021) 31(12):2031–4. 10.1017/S1047951121001980
23.
Nguyen HL Phan QT Doan DD Dinh LH Tran HB Sharmin S et al Percutaneous closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defect using patent ductus arteriosus occluders. PLoS One. (2018) 13(11):e0206535. 10.1371/journal.pone.0206535
24.
Zhao LJ Han B Zhang JJ Yi YC Jiang DD Lyu JL . Transcatheter closure of congenital perimembranous ventricular septal defect using the Amplatzer duct occluder 2. Cardiol Young. (2018) 28(3):447–53. 10.1017/S1047951117002396
25.
Zhou D Pan W Guan L Ge J . Transcatheter closure of perimembranous and intracristal ventricular septal defects with the SHSMA occluder. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2012) 79(4):666–74. 10.1002/ccd.23344
26.
Mandal KD Su D Pang Y . Long-term outcome of transcatheter device closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects. Front Pediatr. (2018) 6:128. 10.3389/fped.2018.00128
27.
Haddad RN Sawan EB Saliba Z . Word of caution: severe aortic valve injury linked to retrograde closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects. J Card Surg. (2022) 37(6):1753–8. 10.1111/jocs.16441
Summary
Keywords
ventricular septal defect, occluder, transcatheter closure, KONAR-MF occluder, congenital heart defect
Citation
Liao L-C, Fu Y-C, Lee P-C, Jan S-L, Lin M-C, Chuang C-M and Hung H-C (2025) Short-term outcomes of transcatheter perimembranous ventricular septal defect closure using the konar-multifunctional occluder: the Taiwanese experience. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1572812. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1572812
Received
07 February 2025
Accepted
09 May 2025
Published
27 May 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Gianfranco Butera, Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital (IRCCS), Italy
Reviewed by
Mario Carminati, IRCCS San Donato Polyclinic, Italy
Raymond N. Haddad, Hôpital Universitaire Necker-Enfants Malades, France
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Liao, Fu, Lee, Jan, Lin, Chuang and Hung.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Yun-Ching Fu yunchingfu@gmail.com; Hui-Chih Hung hchung@dragon.nchu.edu.tw
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.