Abstract
Mitochondrial depletion syndrome (MTDPS) is a heterogeneous group of genetic disorders characterized by a significant reduction in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number, leading to the impaired mitochondrial function. The pathogenesis of MTDPS includes impaired mtDNA replication, damaged nucleotide metabolism and dysregulated mitochondrial dynamics. Due to its high energy demands, the heart is sensitive to the mitochondrial dysfunction. And the energy deficiency caused by the MTDPS contributes to the development of the mitochondrial cardiomyopathy. In this review, we summarize the cardiac phenotypes in the MTDPS, and the role of the mitochondrial injury in the myocardial damage. In specific, the association of the MTDPS-causing genes and their cardiac phenotypes are detailed. Moreover, the current treatment strategies for MTDPS are summarized. This review aims to integrate the current knowledge on the MTDPS and its cardiac phenotypes in order to provide insights for the further research and the clinic management.
1 Introduction
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) depletion syndrome (MTDPS), a disorder caused by defects in the mtDNA maintenance, arises from disrupted nuclear genes that affect proteins crucial for the mtDNA synthesis and replication (1). This leads to the reduced mtDNA, the impaired respiratory chain and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, which causes the specific tissue and organ dysfunction.
Animal mtDNA has average about 16,000 base pairs in length, and human mtDNA has 16,569 base pairs and encodes 13 proteins (2). The mitochondrial genome consists of a noncoding region (NCR) that includes promoters, origins of the replication of the heavy strand and the light strand, three conserved repeats, and a termination sequence. It encodes 37 genes essential for the oxidative phosphorylation, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The cut-off level of the mtDNA amount for the MTDPS diagnosis has been set to 35%–40% of the amount in age-matched controls (3).
Mitochondrial diseases exhibit a wide phenotypic diversity because of the heteroplasmy and the threshold effect (1–3). The MTDPS also encompasses a wide range of autosomal dominant or recessive disorders and is typically classified into four forms: myopathic, encephalomyopathic, hepatocerebral, and neurogastrointestinal. The myopathic MTDPS is characterized by its impact on the muscle, mostly stemming from mutations in the TK2 gene. The encephalomyopathic MTDPS primarily involves the brain and muscles. The hepatopathic MTDPS affects the brain and liver, associated with mutations in genes such as DGUOK, POLG, or TWNK. Lastly, the neurogastrointestinal MTDPS is notable for its effects on the brain and gastrointestinal tract, also known as the mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy (MNGIE) and mainly caused by the mutations of the TYMP gene. To be noticed, studies have found that MTDPS could affect the heart and some mitochondrial cardiomyopathies could be fatal (4–13). The cardiac involvement most commonly occurs in myopathic and encephalomyopathic MTDPS, which we will elaborate separately in each section.
2 Cardiac involvements of the MTDPS
Mitochondria compose 30%–40% of cardiomyocyte volume and supply energy through oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) (14, 15). As the heart is sensitive to mitochondrial dysfunction due to its high energy demands, the energy deficiency caused by the mtDNA depletion contributes to the development of the mitochondrial cardiomyopathy, characterized by the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) or the dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) (16, 17). Currently, pathogenic mutants of MTDPS-causing genes have also been identified in families with the idiopathic cardiomyopathy. However, the incidence of cardiac phenotypes varies among different mutants of MTDPS-causing genes (Table 1). For example, no cardiac manifestations have been reported in mutants of DGUOK (18, 19), based on searches in public databases including the OMIM, the InterVar, and the PubMed. The tissue-specific expression pattern of DGUOK may explain the phenomenon of the predominant hepatic and neurological involvement, but no cardiac phenotype. Other mutants, like POLG, were only reported in family cases. The following reasons may contribute to the scarce presentation of cardiac manifestations in these types of the MTDPS. First, the embryonic lethality observed in homozygous MTDPS mouse models could potentially explain the low incidence of cardiac phenotypes observed in human MTDPS patients, as affected embryos might not survive. This phenomenon was observed in homozygous knockout mouse embryos including POLG−/− (20) and TFAM−/− (21). This pattern of the embryonic death increases the difficulty of studying the pathogenic mechanisms of these specific types of MTDPS, especially in the embryonic period. The impact of MTDPS related pathogenic genes in embryos has also been reported in human. Recently, there have been reports of prenatal-onset cases of MTDPS13 in the population, accompanied by ventriculomegaly, cardiac anomalies, and etc. (22). Secondly, the cardiac involvement in MTDPS patients may also be underdiagnosed due to early mortality from neurologic or hepatic failure. Additionally, the propensity in some existing MTDPS animal models to develop cardiac phenotypes, which were less commonly reported in corresponding human cohorts may arise from interspecies differences in species as well (23).
Table 1
| Gene | Protein | Protein Function/Pathway | Type of MTDPS | Clinical Features | Type of Inheritance | Type of mtDNA Aberration | Cardiac involvements in human | Cardiac involvements in mice | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | Animal | |||||||||
| mtDNA replication | ||||||||||
| POLG | DNA polymerase gamma | Polymerase | Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome 4A/Hepatopathic form | Alpers–Huttenlocher syndrome/ataxia/PEO | AR/AD | D/MD/PM | ACM | Cardiac hypertrophy, cardiomegaly, biventricular dilation, and bradycardia | (62) | (57–60) |
| TWNK | Twinkle | Helicase | Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome 7 | Perrault syndrome/PEO/ataxia/encephalopathy/IOSCA | AD/AR | D/MD/PM | In 24% (8/33) of the patients, cardiac abnormalities were reported including sinus bradycardia, DCM and atrial arrhythmias. Other cases: CAVB/idiopathic left ventricular hypertrophy/LBBB | In tissue-specific (heart and skeletal muscle) Twinkle knockout mice, generated by crossing Twinkle+/loxP mice with Ckmm-cre mice, progressive heart enlargement consistent with mitochondrial cardiomyopathy was presented from 8 weeks. Homozygous knockout mouse embryos (TWNK−/−) die at ∼E8.5 due to severe mtDNA depletion. | (54–56) | (53) |
| TOP1MT | mitochondrial type IB topoisomerase | Topoisomerase | Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome 15 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 33 | AR | defective mtDNA regeneration following mtDNA depletion induced by ethidium bromide | HCM | TOP1MT knockout (KO) mice were susceptible to doxorubicin—induced cardiotoxicity. | (70) | (69) |
| TOP3A | DNA topoisomerase 3 alpha | Topoisomerase | / | PEO/Bloom syndrome-like disorder | AR | MD/D | rapidly progressed DCM/HCM | / | (67) | / |
| Nucleotide metabolism | ||||||||||
| TK2 | Thymidine kinase 2 | dNTP anabolism | Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome 2/Myopathic form | Myopathy/PEO | AR | D/MD | One-third of early-onset patients (age ≤1 year) have extraskeletal muscle manifestations including cardiomyopathy, while less than 20% of the childhood-onset (age > 1 through 12 years) show prolonged QT and arrhythmia. | Tk2 − / − animals showed mtDNA depletion. Depletion of mtDNA was most prominent in brain, less in heart (20% of controls). | (77–79) | (75, 76) |
| Mitochondrial dynamics | ||||||||||
| OPA1 | Dynamin-like 120 kDa protein, mitochondrial | GTPase/mitochondrial fusion | Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome 14 | Optic atrophy/Behr Syndrome | AD | MD | Family reports: HCM/Early-onset myocardial infarction/Symptomatic tachycardia | DCM and heart failure | (46, 47, 85) | (86) |
| AGK | Acylglycerol kinase | Lipid metabolism | Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome 10 | Congenital cataract/HCM/skeletal myopathy and lactic acidosis/Sengers syndrome | AD | D | Ten cases with AGK mutants identified in 12 cases of Sengers syndrome, characterized by HCM. Terminal heart failure is universally inevitable. Other case reports: DCM/LVNC | / | (87, 89, 90) | / |
| Other pathways | ||||||||||
| FBXL4 | F-box/LRR-repeat protein 4 | Protein homeostasis | Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome 13 | Encephalo-myopathy | AR | D | Cardiac involvements observed in 54% of cases include cardiomyopathy, congenital heart malformations, arrhythmia, and pulmonary hypertension. | Transfection of FBXL4 rescued the cardiac geometry and the mitochondrial integrity with altered mitochondrial dynamics in the adult mice model of the heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. | (95–97) | (94) |
| SLC25A4 | Adenine nucleotide translocator | ADP/ATP carrier | Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome 12 | PEO/cardiomyopathy/myopathy | AD/AR | MD | The cardiomyopathy was observed in 77% of cases (17/22), though most types were not differentiated. | SLC25A4 −/− mice develop cardiomyopathy and myopathy. | (48, 109) | (105, 108) |
| CHCHD10 | coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain-containing protein 10 | local and global stress responses | / | IMMD,ALS, FTD, SMAJ | AD | MD | Family report: Cardiomyopathy | Mitochondrial cardiomyopathy | (101) | (98–104) |
Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome and its related cardiac involvements.
D, depletion; MD, multiple deletions; PM, point mutations; ACM, arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy; CAVB, complete atrioventricular block; DM, dilated cardiomyopathy; HM, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; AD, autosomal dominant; AR, autosomal recessive; dNTP, deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate; IOSCA, infantile onset spinocerebellar ataxia; MNGIE, mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy; PEO, progressive external ophthalmoplegia; PM, mtDNA somatic point mutations; IMMD, autosomal dominant mitochondrial myopathy; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; FTD, frontotemporal dementia; SMAJ, late-onset spinal muscular atrophy.
3 Role of mitochondria in cardiac development and homeostasis
Mitochondrial function is essential for cardiomyocytes. The distribution and metabolic function of these organelles varies depending on the developmental stage of the myocardium (24). In neonatal cardiomyocytes, the heart preferentially obtains its energy from glycolysis and glucose oxidation. During this period, mitochondria manifest a characteristic reticular distribution in the cytosol that allows them to move freely. As cardiomyocytes reach the state of the terminal differentiation, fatty acid beta-oxidation becomes a primary energy source. In adult cardiomyocytes, energy derives mainly from the oxidation of fatty acids, and the motility of mitochondria is restricted (25). To be noticed, in the cardiac hypertrophy and the heart failure, the cardiac energy metabolism undergoes a shift towards a phenotype similar to the fetal state (26, 27). This transformation is characterized by a reduction in mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation and an elevation in glycolysis.
Apart from the mitochondrial related metabolism, mitochondrial morphology has been found acting as a mechanism for bioenergetic adaptation during cardiac pathological remodeling. Mitofusins, namely Mfn-1 and Mfn-2, are regulators of mitochondrial network. Double-knockout (DKO) mice of Mfn-1 and Mfn-2 develop DCM with reduced mitochondria biogenesis genes and mtDNA (28).
Mitochondrial abnormalities could activate inflammatory pathways as well. Pathological conditions of the unregulated and elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production result in oxidative stress through the oxidative damage to DNA and the cell death (29, 30). Dysregulated ROS production and oxidative stress have been implicated in a host of cardiac diseases (31). ROS has been found as a signaling molecule to activate signaling pathways associated with inflammation, such as the NF-κB pathway, to further promote the generation of inflammatory mediators. The mtDNA has been found to be released through minority mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (miMOMP) (32–34). The oxidized mitochondrial DNA, which escapes from mitochondria, could ignite the NLRP3 and the cGAS-STING signaling (35). In heart failure, the cGAS-STING signaling is progressively activated, leading to the pathological cardiac remodeling and left ventricular dysfunction (36). These results suggest that the cytosolic release of mtDNA harms the cardiac function by activating inflammatory pathways. The cGAS-STING signaling has also been identified in the mutants of TFAM and TOP1MT related MTDPS, separately (37, 38). Moreover, TFAM +/− mice exposed to ionizing radiation exhibit enhanced nDNA repair responses in spleen (39). It can be inferred that subsequent release of mtDNA elicits a protective signaling response that enhances nDNA repair in cells and tissues, suggesting mtDNA is a genotoxic stress sentinel (39). In general, the effect of the release of mtDNA on the nDNA repair remains further study. Whether the activation of the cGAS-STING plays a part in the cardiac involvements of the MTDPS needs further elucidation.
4 Genes involved in the etiology of MTDPS with cardiac phenotypes
The MTDPS is one of the subgroups of the mtDNA maintenance disorder (MMD) and the other subgroup is the mtDNA multiple deletion syndrome (40). More deleterious and often recessive variants usually cause the mtDNA depletion, leading to early-onset, severe, multisystemic, and potentially fatal conditions. On the other hand, less severe and often dominant variants result in more slowly progressive, adult-onset myopathic diseases characterized by the accumulation of multiple mtDNA deletions (41). However, recent research showed that both depletion and multiple deletions could appear in the one patient at the same time, indicating they may stem from the same genetic defect (42, 43).
The pathogenesis of MTDPS can be classified into four categories according to the biological process:(1) mtDNA replication; (2) deoxyribonucleotide metabolism; (3) mitochondrial dynamics; and (4) other functions (44–48) (Table 1) (Figure 1).
Figure 1
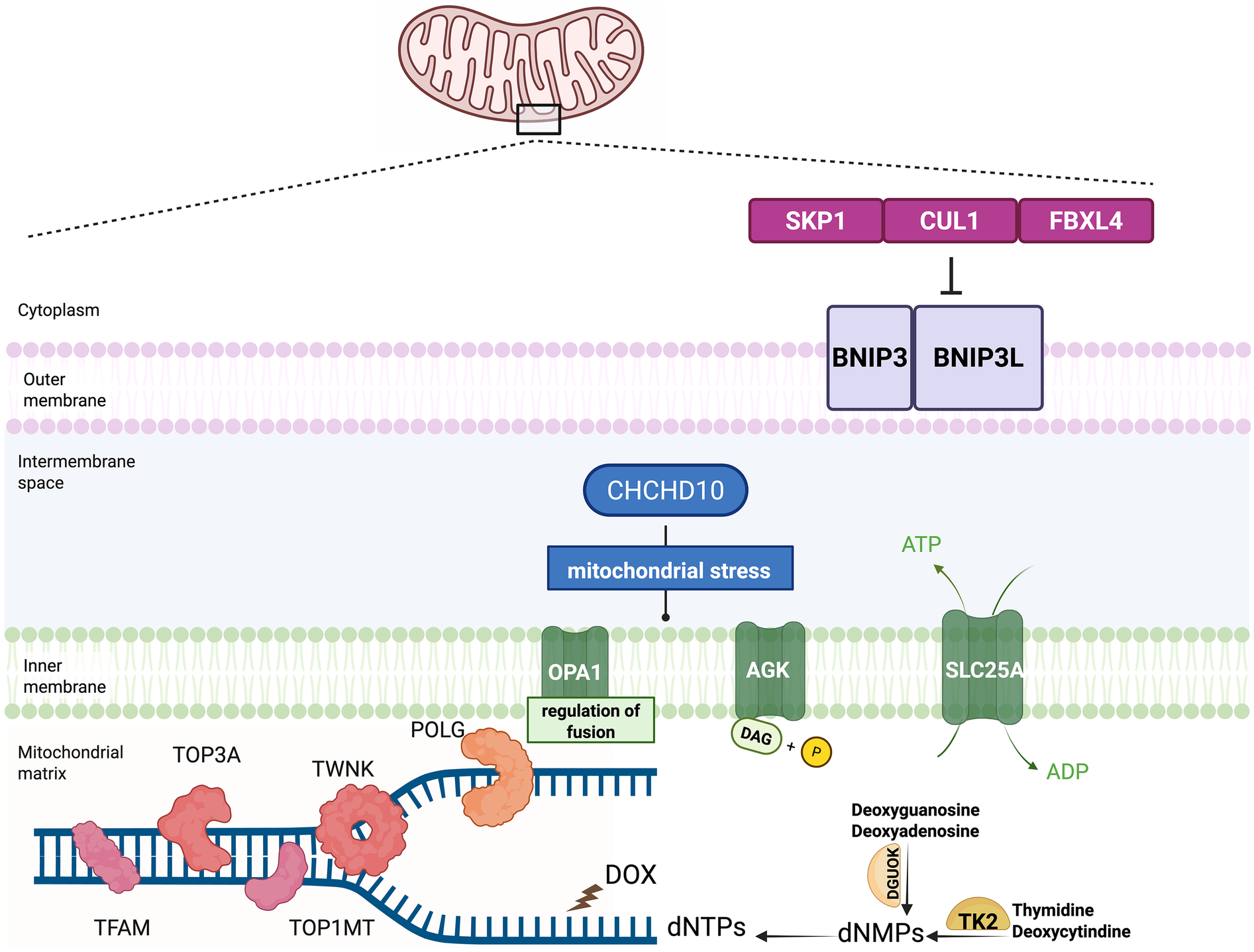
Model of pathogenesis involved in the mitochondrial depletion syndrome and the circumstance of doxorubicin mimicking the mitochondrial depletion syndrome. Dysfunctional mtDNA maintenance, nucleotide imbalance, and mitochondrial dynamics contribute to the mitochondrial depletion syndrome. The crucial proteins participating in the mitochondrial DNA maintenance include POLG, TWNK, TFAM, TOP3A and TOP1MT. Nucleotide metabolism plays a crucial role in the development of the MTDPS as well. Two key enzymes in the nucleotide salvage pathway, TK2 and DGUOK, are responsible for maintaining the mitochondrial dNTP pools. Mitochondrial dynamics are essential for maintaining the mitochondrial function. The proteins participating in the mitochondrial fusion, fission, and transport include OPA1 and AGK. FBXL4 serves as a component of E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes, called SKP1-CUL1-F-box (SCF) complexes. The SCF-FBXL4 E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes function as the suppressor of the mitophagy by mediating the degradation of BNIP3 and BNIP3l mitophagy receptors. FBXL4 functions to protect mitochondria from the depletion by inhibiting the mitophagy. Doxorubicin (DOX), widely used in oncology, could disrupt mitochondrial homeostasis by depleting mtDNA mimicking MTDPS.
4.1 Pathogenesis involved in the mtDNA replication
The crucial proteins participating in the mitochondrial DNA maintenance comprise mitochondrial single-strand binding protein (MTSSB), which stabilizes unwound DNA, and the Twinkle protein (TWNK), which unwinds the double helix before replication at the origin of replication (OriH). Mitochondrial DNA-directed RNA polymerase (POLRMT) initiates RNA primer synthesis, while DNA polymerase gamma (POLG) extends DNA polymerization (1). These mtDNA replication and maintenance proteins play critical roles in the pathogenesis of MTDPS.
4.1.1 TWNK
TWNK, located at the 10q24.31, encodes the mitochondrial helicase Twinkle in the mitochondrial nucleoids, and is crucial for the mtDNA replication and maintenance. TWNK unwinds the double helix of the DNA to initiate the replication (49, 50).
TWNK consists of a 5-primase domain, a linker region, and a helicase domain. Most pathogenic mutations are related to the linker region and the helicase domain. Dominant TWNK mutations cause the adult-onset progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO) and the proximal weakness (51). Recessive TWNK mutations lead to the MTDPS 7, manifesting as severe neurological disorders, the liver disease, the epilepsy, and the infant death (52).
Homozygous knockout mouse embryos (TWNK−/−) died at ∼E8.5 due to severe mtDNA depletion. In tissue-specific (heart and skeletal muscle) TWNK knockout mice, generated by crossing TWNK+/loxP mice with Ckmm-cre mice, progressive heart enlargement consistent with mitochondrial cardiomyopathy was presented from 8 weeks. Severe mtDNA depletion and profound respiratory chain deficiency were observed in these mice (53).
In human, approximately 24% (8/33) of the patients harboring TWNK mutations, manifest cardiac abnormalities, including sinus bradycardia, cardiomyopathy and atrial arrhythmias (54, 55). Recently, the c.1485-1 G > A(p.T496_R531del) TWNK variant, resulting in a truncated mutant with part of the helicase domain, was identified in an autopsy case, aged 79-year-old, with complete atrioventricular block and idiopathic left ventricular hypertrophy (56).
4.1.2 POLG
POLG, located at the 15q25, is a nuclear gene coding for the catalytic subunit of mitochondrial DNA polymerase, which exhibit a DNA polymerase activity, a 3′-5′ exonuclease activity that proofreads mis-incorporated nucleotides, and a 5′ deoxyribose phosphate lyase activity required for base excision repair.
In animal models, the POLG mutator mice carrying a proofreading-deficient form POLG-D257A point mutation results in reduced mitochondrial DNA integrity. These POLG-D257A mice exhibited a premature aging phenotype, though the degree of the cardiac dysfunction varied across studies (57–59). To figure out the influence on the heart, a cardiac targeted mouse model with POLG-Y955C was made and the cardiomegaly, biventricular dilation, and bradycardia were observed (60). The mechanism linking the premature aging and the cardiac involvement is not yet clear.
In human, POLG disease has been reported to be the most common single gene mitochondrial disease (10%) in the Australian adult population (61). Dominant POLG mutations manifest as slow progressive diseases in adults, typically PEO, ptosis, and myopathy (61). Recessive POLG mutations lead to MTDPS 4, manifested in the early life as multisystem and rapidly progressing neurodegenerative diseases, often accompanied by refractory epilepsy and end-stage liver failure (61). It was reported that a specific POLG mutation (c.2492A > G, p.Tyr831Cys) lead to the arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy in a South African family (62). It seems POLG mutations play a role in the development of cardiomyopathy, although the precise pathogenesis requires further elucidation.
4.1.3 TOP3A
The type IA topoisomerase 3α (TOP3A) removes the negative supercoiling and decatenate interlinked molecules (63). This decatenation activity of TOP3A is essential for separating replicated mtDNA molecules (63). Knockdown of TOP3A with siRNA could stall the replication fork, increase the mtDNA catenation and decrease the mtDNA copy number (64). To be noticed, TOP3A localizes in both the mitochondria and the nucleus. The function of TOP3A is complicated by the dual presence of mitochondrial and nuclear isoforms. The mitochondrial isoform of TOP3A has been found involved not only in the mtDNA segregation, but also the progression of the replication fork (64).
Recessive TOP3A variants can cause either mtDNA depletion and severe multisystemic neonatal disease, or adult-onset PEO, ptosis, and proximal myopathy, accompanied by peripheral neuropathy and cardiac disease (65). More severe variants result in a Bloom syndrome-like disorder (66).
Case-reports have demonstrated the involvement of TOP3A in both the DCM and the HCM, suggesting a complicated pathogenesis (67). Diverse manifestations of patients may be related with the phenomenon that TOP3A variants have different levels of impact on its functions. For example, the p.Leu37Val and p.Met575Val variants of TOP3A exhibited a significant loss of DNA-binding activity. While the p.Ser810* truncating variant showed a comparable level of DNA-binding activity (68). Another hypothesis of variable clinical presentations and different onset ages with similar genotypes is the influence of unidentified modifying variants.
4.1.4 TOP1MT
Mitochondrial topoisomerase type IB (TOP1MT) is important for mtDNA regulation and is involved in mitochondrial replication, transcription, and translation. The susceptibility of TOP1MT knockout (KO) mice to doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity also underscores the role of TOP1MT in maintaining cardiac function (69). In human, two TOP1MT variants (R198C and V338l) at a highly conserved site in the core domain located within the DNA binding barrel were identified in a newborn with HCM, which implied the role of the mitochondrial topoisomerase in the cardiac phenotype (70). These two variants contributed to the mitochondrial dysfunction, including the impaired topoisomerase activity, altered mtDNA replication, and reduced mitochondrial translation.
4.1.5 TFAM
Mitochondrial transcription factor A, abbreviated as TFAM, is the major protein constituent of the mammalian nucleoid. TFAM belongs to the high-mobility group domain proteins and induces a dramatic U-turn with an overall bend of 180° when bound to promoters or unspecific DNA (71, 72). In mouse models, heterozygous mice demonstrated a decrease in mtDNA copy number and a deficiency in the respiratory chain within the heart (21, 73). Furthermore, a potential pathogenic link between the TFAM dysfunction and the doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity was found (74). The embryonic lethality was reported in mouse model with TFAM−/− (21). In human, homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations in the TFAM gene cause MTDPS 15, characterized by the onset of severe progressive liver disease soon after birth. Cardiac phenotypes associated with TFAM mutations have not yet been identified.
4.2 Pathogenesis involved in the nucleotide metabolism
Nucleotide metabolism plays a crucial role in the development of the MTDPS. Two key enzymes in the nucleotide salvage pathway, thymidine kinase 2 (TK2) and deoxyguanosine kinase (DGUOK), are responsible for maintaining the mitochondrial deoxynucleotide triphosphate (dNTP) pools.
The TK2 regulates the first and the rate limiting step in the phosphorylation of deoxypyrimidine nucleosides in the mitochondria. Mutations in TK2 manifests in a range of clinical symptoms, with myopathy being the most frequently observed. Specifically, skeletal muscle contains TK2 levels that are 5- to 14-fold lower than those in the liver, heart, and fibroblasts. This relative deficiency may render skeletal muscle more vulnerable to TK2 dysfunction (75).
The currently available TK2 animal models cannot definitively establish a link between TK2 and the cardiac phenotype because the homozygous TK2 mutant mice developed the progressive weakness and the tremor shortly after birth and died at the early age of 2–3 weeks before the possible appearance of the cardiac phenotype (76). In order to figure out the impact of TK2 on the cardiac phenotype, the cardiomyocyte or the heart-specific Cre mouse models are needed to further elucidate the mechanisms underlying cardiomyopathy caused by TK2 mutations.
It was reported that one-third of early-onset patients with the TK2 mutation(age ≤1 year) had extraskeletal muscle manifestations including cardiomyopathy, while less than 20% of the childhood-onset (age > 1 through 12 years) patients showed prolonged QT and arrhythmia (77). Three cases with cardiac manifestations were reported, including cardiac arrest caused by the ventricular fibrillation (78). The other cases with fatal mitochondrial HCM were observed, combined with the leucoencephalopathy and the hepatic steatosis at the age of 18 months (79).
4.3 Pathogenesis involved in the mitochondrial dynamics
Mitochondrial dynamics refers to the continuous processes of mitochondrial fusion, fission, and transport that are essential for maintaining the mitochondrial function and the cellular homeostasis. Disruptions in these processes can significantly contribute to diseases.
4.3.1 OPA1
Optic atrophy 1 (OPA1) encodes a dynamin-like GTPase protein in the inner mitochondrial membrane (80). It involves in the regulation of the mitochondrial fusion, the cristae structure, the stability of the respiratory chain, and the mtDNA maintenance (81). The mitochondrial peptidases YME1l and OMA1 process OPA1 (69). In mouse models, cardiac-specific ablation of YME1l activated OMA1, accelerating OPA1 proteolysis, which induced mitochondrial fragmentation and altered cardiac metabolism, leading to DCM and heart failure (69). In return, the deletion of OMA1 prevented OPA1 cleavage, rescuing cardiac function and restoring mitochondrial morphology. Additionally, interventions of a high-fat diet or skeletal muscle-specific YME1l ablation were shown to restore cardiac metabolism and preserve heart function, independent of mitochondrial fragmentation suppression. Thus, OPA1 plays a critical role in sustaining cardiomyocyte survival. Intriguingly, cardiac metabolism and mitochondrial morphology are closely interconnected. Recent research has further revealed that mitochondria can be divided into two distinct functional subpopulations based on their reliance on OXPHOS-dependent ATP production (82). This discovery not only enriches but also complicates the understanding of mitochondrial morphology and metabolic regulation.
In human, mutations in the catalytic GTPase domain of OPA1 were linked to dominant optic atrophy (83). OPA1 also plays a pivotal role in the formation and function of cardiomyocytes (84). A homozygous missense mutation in the OPA1 gene (c.1601T > G, p.Leu534Arg) was identified in siblings from a consanguineous family. This mutation resulted in severe clinical manifestations, including lethal infantile-onset encephalopathy, optic atrophy, and HCM (85). In these siblings, a significant reduction in OPA1 protein levels was observed, attributed to the structural disturbances of the GTPase domain. Muscle biopsies revealed the mtDNA depletion (85), consistent with findings in OPA1-mutated mouse models (86). Other reports of cardiac manifestations in families with heterozygous OPA1 mutations include early-onset myocardial infarction (46) and symptomatic tachycardia (47). These observed symptomatic and even fatal cardiac manifestations extend the phenotype associated with pathogenic OPA1 mutations. Although cardiac manifestations are currently documented only in familial cases, cardiac monitoring is still warranted for patients with dominant optic atrophy.
4.3.2 AGK
Acylglycerol kinase (AGK) plays a role in mitochondrial lipid metabolism and dynamics. AGK catalyzes the phosphorylation of diacylglycerol (DAG) using ATP and acylglycerol as substrates, producing ADP and acylsn-glycerol 3-phosphate as byproducts. Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane, AGK functions as a multisubstrate lipid kinase, and its activity triggers ROS signaling through a pathway involving protein kinase D1 (87).
The underlying pathogenic mechanisms of these cardiac phenotypes are intricate. Besides its role as a lipid kinase, AGK is an integral component of the mitochondrial translocase of the inner membrane 22 (TIM22) complex. This complex is essential for the translocation of transmembrane proteins into the mitochondrial matrix. Mutations in AGK that disrupt this function can compromise mitochondrial membrane integrity and impair energy production. Studies using AGK knockout cells have revealed downregulation of mitochondrial carrier proteins, OXPHOS components, and enzymes involved in mitochondrial one-carbon (1C) metabolism (88). As a result, cardiac energy metabolism is severely impaired, ultimately resulting in the cardiomyopathy and the heart failure. These observations highlight the critical role of AGK in the mitochondrial function and its related cardiac phenotypes.
In human, autosomal recessive mutations in AGK are associated with Sengers syndrome (10 cases with AGK mutants identified in 12 cases of Sengers syndrome) (87), which was characterized by congenital cataracts, HCM, skeletal myopathy, and lactic acidosis. Terminal heart failure secondary to HCM is universally inevitable and leads to death (89). There were also cases of DCM and a single instance of left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy(LVNC) (90).
4.4 Pathogenesis involved in other pathways
4.4.1 FBXL4: mitophagy related
F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 4 (FBXL4) encodes a member of the F-box protein family characterized by the F-box motif, which serves as a component of E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes, called SKP1-CUL1-F-box (SCF) complexes. The SCF-FBXL4 E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes at the mitochondrial outer membrane function as the suppressor of the mitophagy by mediating the degradation of the BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa interacting protein 3(BNIP3) and NIP3-like protein X(Nix)/BNIP3l mitophagy receptors (91). FBXL4's role in controlling mitophagy levels were observed in patient cells and animal models (92). It has been found that FBXL4 mutations impair the SCF-FBXL4 complex formation, and thus cause the excessive mitophagy (93). Transfection of FBXL4 rescued the cardiac geometry and the mitochondrial integrity with altered mitochondrial dynamics in the adult mice model of the heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (94).
In the FBXL4-related encephalomyopathy, also known as the MTDPS13, increased mitophagy and mitochondrial DNA depletion were identified in patient's fibroblasts (95). Among the MTDPS13, the cardiac involvement was observed in 54% of cases (20/37), with specific manifestations including cardiomyopathy (27%, 10/37), congenital heart malformations (19%, 7/37), arrhythmia (15%, 6/41), and pulmonary hypertension (11%, 4/37) (96). The typical cardiomyopathy is HCM (96). LVNC was also reported (97).
4.4.2 CHCHD10: metabolic and stress sensor
Coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain containing protein 10(CHCHD10) enriches at cristae junctions within the mitochondrial intermembrane space. CHCHD10 restrains the initiation of the mitochondrial integrated response stress, and suppresses the processing of OPA1 for mitochondrial fusion by interacting with OMA1 and suppressing its enzyme activity (98). A recent study on adipocytes and adipose tissue-specific CHCHD10 overexpressing mice has found that CHCHD10 is involved in cellular metabolic homeostasis as a metabolic sensor (99). Knock in mouse models bearing CHCHD10 variants were made and could present the symptoms of the CHCHD10-related disease including mitochondrial myopathy, cardiomyopathy, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (98–102). Specifically, in the CHCHD10-G58R knockin mice(C10G58R), complex I and complex IV activities were diminished, and multiple mtDNA deletions and decreased mtDNA copy numbers were observed in the heart (99–101). To be noticed, an extensive cardiac metabolic rewiring triggered by the proteotoxic mitochondrial stress response was identified in the C10G58R mice. The stress response began before the overt OXPHOS dysfunction (98). Specifically, the metabolic imbalance from the oxidative to the glycolytic metabolism and the activation of the 1C metabolism were triggered to provide increased 1C units for the methionine biosynthesis and transsulfuration. Meanwhile, increased NADPH oxidases elicit antioxidant responses. The metabolic stress response was believed to prolong the survival of C10G58R mice, though the fatal cardiomyopathy was inevitable as the disease progresses (103). Further studies were needed to elucidate the role of the mitochondrial stress response in the pathogenesis of MTDPS related cardiac phenotypes (104).
In human, due to the limited number of affected individuals reported so far and its recent discovery, the natural history of CHCHD10-related diseases is unclear (102). An autosomal dominant p.G58R mutation of CHCHD10 was reported in a family, presenting characteristics of mitochondrial myopathy and cardiomyopathy (101). The proband received a heart transplant due to the heart failure caused by his cardiomyopathy at the age of 20 (101).
4.4.3 SLC25A4: mitochondrial carrier family
The Solute Carrier Family 25 Member 4 (SLC25A4) gene, which is responsible for encoding the heart- and muscle- specific isoform 1 of the adenine nucleotide transporter (ANT) located in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM), also known as ANT1, plays a critical role in transporting ADP into the mitochondrial matrix and ATP from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space. SLC25A4 also participated in the components of mitochondrial permeability transition pore governing in vivo cell death (105). Recently, SLC25A4 was identified as a direct target of S-nitrosoglutathione reductase, functioning to maintain mitochondrial homeostasis in hearts (106). The expression of SLC25A4 was found increased in hearts of the myocardial infarction and SLC25A4 was identified as a biomarker of the apoptosis-associated cardiomyocyte subcluster with single-cell data of from Gene Expression Omnibus database (107). These current findings demonstrated that SLC25A4 could be a potential novel therapeutic target for the heart failure. SLC25A4 knockout (SLC25A4−/−) mice develop cardiomyopathy and myopathy as well (108).
Patients carrying a SLC25A4 mutation manifest with encephalo-myo-cardiomyopathy. The cardiomyopathy was observed in 77% of cases (17/22), though the majority of the studies did not differentiate the types and not mention whether these patients combined with the arrhythmia (48). For example, a de novo dominant SLC25A4 mutant (c.239G > A, p.Arg80His) was reported in a female infant, who presented with HCM, hypotonia, elevated lactate levels. She eventually passed away at 14 days. Severe mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies, and the mitochondrial DNA depletion in skeletal muscle, caused by the impairment of SLC25A4 were found in this patient (109). In addition, the severity of SLC25A4 mutants was related with the mtDNA haplogroup (110). It was found that the mtDNA haplogroup U, which was defined by the mutations of A11467G, A12308G and G12372A, was linked to a more severe and rapidly progressive cardiomyopathy (110).
4.5 Cardiotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents inducing mtDNA depletion
Emerging evidence highlights a critical intersection between mitochondrial genome integrity and chemotherapeutic toxicity. Anthracyclines (e.g., doxorubicin), widely used in oncology, exhibit dual roles. While inducing tumor cell death via nuclear DNA damage, they concurrently disrupt mitochondrial homeostasis by depleting mtDNA via the BAX/BAK-mediated mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and the cGAS-STING hyperactivation (111–113). This collateral mitochondrial toxicity poses heightened risks of myocardial dysfunction for patients whose mtDNA maintenance machinery were compromised. In detail, a negative correlation between the mitochondrial copy number and the heart failure biomarkers was observed in cancer patients' peripheral blood mononuclear cells after the anthracycline chemotherapy (113). Human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived cardiomyocytes with the pre-existing mtDNA depletion(mimicking MTDPS) showed the amplified doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity compared to controls, as mitochondrial insufficiency impairs the detoxification of ROS and augments the mtDNA leakage. It was reported that over expression of mitochondrial tagged DNase1 in mice could partially rescue doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction (113). These insights offer new co-administration strategies for cancer patients with the compromised mitochondrial amount.
5 Treatment of mtDNA depletion syndrome
There are no efficacious treatments for MTDPS, so the management is mainly directed toward the symptomatic relief. For those MTDPS with cardiac involvements, heart failure in the MTDPS should be treated in the similar way as the heart failure triggered by other causes.
Administration of beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, neprilysin inhibitors, angiotensin-II receptor blockers, and diuretics may be given to restore the systolic and diastolic dysfunction. For patients with severe cardiac involvements, the heart transplantation is inevitable.
Recently, preclinical studies and clinical trials were involved including the nucleoside bypass therapy, stem cells and organ transplantation (114). Early recognition and immediate therapy to restore mitochondrial function might potentially improve clinical course.
5.1 Nucleoside bypass therapy
Clinical trials studies and in vitro/in vivo research studies showed that the enhancement of the salvage pathway by increasing the availability of deoxyribonucleosides needed for each specific genetic defect may prevent mtDNA depletion (115). Deoxycytidine and deoxythymidine (dC/dT) has been regarded as a treatment option for patients with POLG-related disorders with the evidence of the improved Newcastle Mitochondrial Disease Scale (NMDS) score and electroencephalography after the 6 months of treatment (116). Patients with TK2 deficiency, who treated with a similar compound, reported the improvement on the life quality as well (117). In a phase II Trial (NCT04802707), a mix of dC/dT will be used as the early treatment of MTDPS, including the mutations of following genes: POLG, TWNK, RRM2B, MPV17, SUCLA2, SUCLG1, and FBXL4. These trials demonstrate that dC/dT may have broader therapeutic potential for a range of different mitochondrial disorders. Long time follow-up studies are expected in the future.
5.2 Others
Unlike approaches for most mitochondrial diseases, potentially disease modifying therapies are available for MNGIE. Therapeutic options include the direct removal of metabolites by peritoneal dialysis, the substitution of the missing enzyme and the enzyme replacement by the allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (118). Nevertheless, no cases of heart involvements have been reported in the patients of the MNGIE so far, so whether the options for the MNGIE could be used in the other MTDPS patients with heart involvements still depends. Although some approaches could have a more general benefit, others may only treat specific mitochondrial disease.
6 Conclusion
MTDPS represents a significant challenge due to its impact on multiple organ systems, with cardiomyopathy being a critical and often life-threatening component. Understanding the genetic basis and pathophysiological mechanisms underlying MTDPS can help developing better diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in order to ultimately improve outcomes for affected individuals. Ongoing research into mitochondrial biology and genetics holds promise for future advancements in the management of these complex disorders.
Statements
Author contributions
SB: Writing – original draft. JY: Data curation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Software, Writing – review & editing. YX: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision. SC: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. No. 82270311/National Natural Science Foundation of China(NSFC), No. 82470316/National Natural Science Foundation of China(NSFC), No. 82271740/National Natural Science Foundation of China(NSFC), No. 21Y31900303/Project of Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission, No. BJKJ2024002/2024 Shanghai Leading Talent Program of Eastern Talent Plan (leading talent program).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Sen R Jetto CT Manjithaya R . Decoding the mitochondria without a code: mechanistic insights into mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes. J Biosci. (2024) 49:32. 10.1007/s12038-024-00428-9
2.
Boore JL . Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. (1999) 27:1767–80. 10.1093/nar/27.8.1767
3.
Suomalainen A Isohanni P . Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes–many genes, common mechanisms. Neuromuscul Disord. (2010) 20:429–37. 10.1016/j.nmd.2010.03.017
4.
Ravindran S Rau CD . The multifaceted role of mitochondria in cardiac function: insights and approaches. Cell Commun Signal. (2024) 22(1):525. 10.1186/s12964-024-01899-x
5.
Fan P Yang KQ Han B Kong D Yin WH Li JH et al A novel AGK splicing mutation in a patient with Sengers syndrome and left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy. Pediatr Res. (2023) 94(2):683–90. 10.1038/s41390-023-02515-3
6.
Lim AZ Jones DM Bates MGD Schaefer AM Sullivan J Feeney C et al Risk of cardiac manifestations in adult mitochondrial disease caused by nuclear genetic defects. Open Heart. (2021) 8:e001510. 10.1136/openhrt-2020-001510
7.
Jiang W Jia N Guo C Wen J Wu L Ogi T et al Predominant cellular mitochondrial dysfunction in the TOP3A gene-caused bloom syndrome-like disorder. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2021) 1867:166106. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166106
8.
Saha LK Pommier Y . TOP3A coupling with replication forks and repair of TOP3A cleavage complexes. Cell Cycle. (2024) 23(2):115–30. 10.1080/15384101.2024.2314440
9.
Keshavan N Rahman S . Natural history of deoxyguanosine kinase deficiency. Mol Genet Metab. (2024) 143:108554. 10.1016/j.ymgme.2024.108554
10.
Ravizzoni Dartora D Flahault A Pontes CNR He Y Deprez A Cloutier A et al Cardiac left ventricle mitochondrial dysfunction after neonatal exposure to hyperoxia: relevance for cardiomyopathy after preterm birth. Hypertension. (2022) 79:575–87. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.17979
11.
Weiner JG Lambert AN Thurm C Hall M Soslow JH Reimschisel TE et al Heart transplantation in children with mitochondrial disease. J Pediatr. (2020) 217:46–51.e4. 10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.10.016
12.
Barbosa-Gouveia S Vázquez-Mosquera ME Gonzalez-Vioque E Hermida-Ameijeiras Á Valverde LL Armstrong-Moron J et al Characterization of a novel splicing variant in acylglycerol kinase (AGK) associated with fatal sengers syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:13484. 10.3390/ijms222413484
13.
Zhao Q Zhou X Kuiper R Curbo S Karlsson A . Mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with lipid metabolism disorder and upregulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. PLoS One. (2022) 17(6):e0270418. 10.1371/journal.pone.0270418
14.
Piquereau J Caffin F Novotova M Lemaire C Veksler V Garnier A et al Mitochondrial dynamics in the adult cardiomyocytes: which roles for a highly specialized cell? Front Physiol. (2013) 4:102. 10.3389/fphys.2013.00102
15.
Dorn GW 2nd . Neurohormonal connections with mitochondria in cardiomyopathy and other diseases. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2022) 323:C461–c477. 10.1152/ajpcell.00167.2022
16.
Wang H Han Y Li S Chen Y Chen Y Wang J et al Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome and its associated cardiac disease. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 8:808115. 10.3389/fcvm.2021.808115
17.
Campbell T Slone J Huang T . Mitochondrial genome variants as a cause of mitochondrial cardiomyopathy. Cells. (2022) 11(18):2835. 10.3390/cells11182835
18.
Labarthe F Dobbelaere D Devisme L De Muret A Jardel C Taanman JW et al Clinical, biochemical and morphological features of hepatocerebral syndrome with mitochondrial DNA depletion due to deoxyguanosine kinase deficiency. J Hepatol. (2005) 43:333–41. 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.03.023
19.
Bennett B Helbling D Meng H Jarzembowski J Geurts AM Friederich MW et al Potentially diagnostic electron paramagnetic resonance spectra elucidate the underlying mechanism of mitochondrial dysfunction in the deoxyguanosine kinase deficient rat model of a genetic mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome. Free Radic Biol Med. (2016) 92:141–51. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.01.001
20.
Hance N Ekstrand MI Trifunovic A . Mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma is essential for mammalian embryogenesis. Hum Mol Genet. (2005) 14:1775–83. 10.1093/hmg/ddi184
21.
Larsson NG Wang J Wilhelmsson H Oldfors A Rustin P Lewandoski M et al Mitochondrial transcription factor A is necessary for mtDNA maintenance and embryogenesis in mice. Nat Genet. (1998) 18:231–6. 10.1038/ng0398-231
22.
Ros A Hurtado I Vázquez-Méndez É Monlleó-Neila L Pauta M Rovira-Remisa MM et al Prenatal FBXL4-associated mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome-13: a new case and review of the literature. Prenat Diagn. (2025). 10.1002/pd.6794
23.
Morotti S Liu C Hegyi B Ni H Fogli Iseppe A Wang L et al Quantitative cross-species translators of cardiac myocyte electrophysiology: model training, experimental validation, and applications. Sci Adv. (2021) 7:eabg0927. 10.1126/sciadv.abg0927
24.
Lopaschuk GD Jaswal JS . Energy metabolic phenotype of the cardiomyocyte during development, differentiation, and postnatal maturation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2010) 56:130–40. 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181e74a14
25.
Stanley WC Recchia FA Lopaschuk GD . Myocardial substrate metabolism in the normal and failing heart. Physiol Rev. (2005) 85:1093–129. 10.1152/physrev.00006.2004
26.
Razeghi P Young ME Alcorn JL Moravec CS Frazier OH Taegtmeyer H . Metabolic gene expression in fetal and failing human heart. Circulation. (2001) 104:2923–31. 10.1161/hc4901.100526
27.
Planavila A Laguna JC Vázquez-Carrera M . Nuclear factor-kappaB activation leads to down-regulation of fatty acid oxidation during cardiac hypertrophy. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280:17464–71. 10.1074/jbc.M414220200
28.
Papanicolaou KN Kikuchi R Ngoh GA Coughlan KA Dominguez I Stanley WC et al Mitofusins 1 and 2 are essential for postnatal metabolic remodeling in heart. Circ Res. (2012) 111:1012–26. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.274142
29.
Zorov DB Juhaszova M Sollott SJ . Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol Rev. (2014) 94:909–50. 10.1152/physrev.00026.2013
30.
Sies H Belousov VV Chandel NS Davies MJ Jones DP Mann GE et al Defining roles of specific reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cell biology and physiology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2022) 23:499–515. 10.1038/s41580-022-00456-z
31.
Peoples JN Saraf A Ghazal N Pham TT Kwong JQ . Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in heart disease. Exp Mol Med. (2019) 51:1–13. 10.1038/s12276-019-0355-7
32.
Victorelli S Salmonowicz H Chapman J Martini H Vizioli MG Riley JS et al Apoptotic stress causes mtDNA release during senescence and drives the SASP. Nature. (2023) 622:627–36. 10.1038/s41586-023-06621-4
33.
Vizioli MG Liu T Miller KN Robertson NA Gilroy K Lagnado AB et al Mitochondria-to-nucleus retrograde signaling drives formation of cytoplasmic chromatin and inflammation in senescence. Genes Dev. (2020) 34:428–45. 10.1101/gad.331272.119
34.
Zlotorynski E . Defective mitochondria ignite the SASP. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2020) 21:179. 10.1038/s41580-020-0228-x
35.
Xian H Watari K Sanchez-Lopez E Offenberger J Onyuru J Sampath H et al Oxidized DNA fragments exit mitochondria via mPTP- and VDAC-dependent channels to activate NLRP3 inflammasome and interferon signaling. Immunity. (2022) 55:1370–1385.e8. 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.06.007
36.
Oduro PK Zheng X Wei J Yang Y Wang Y Zhang H et al The cGAS-STING signaling in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: future novel target option for pharmacotherapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2022) 12:50–75. 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.011
37.
West AP Khoury-Hanold W Staron M Tal MC Pineda CM Lang SM et al Mitochondrial DNA stress primes the antiviral innate immune response. Nature. (2015) 520:553–7. 10.1038/nature14156
38.
Al Khatib I Deng J Lei Y Torres-Odio S Rojas GR Newman LE et al Activation of the cGAS-STING innate immune response in cells with deficient mitochondrial topoisomerase TOP1MT. Hum Mol Genet. (2023) 32:2422–40. 10.1093/hmg/ddad062
39.
Wu Z Oeck S West AP Mangalhara KC Sainz AG Newman LE et al Mitochondrial DNA stress signalling protects the nuclear genome. Nat Metab. (2019) 1:1209–18. 10.1038/s42255-019-0150-8
40.
El-Hattab AW Craigen WJ Scaglia F . Mitochondrial DNA maintenance defects. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2017) 1863(6):1539–55. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.02.017
41.
El-Hattab AW Scaglia F . Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes: review and updates of genetic basis, manifestations, and therapeutic options. Neurotherapeutics. (2013) 10:186–98. 10.1007/s13311-013-0177-6
42.
Hirano M Carelli V De Giorgio R Pironi L Accarino A Cenacchi G et al Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy (MNGIE): position paper on diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment by the MNGIE international network. J Inherit Metab Dis. (2021) 44:376–87. 10.1002/jimd.12300
43.
Ramón J Vila-Julià F Molina-Granada D Molina-Berenguer M Melià MJ García-Arumí E et al Therapy prospects for mitochondrial DNA maintenance disorders. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:6447. 10.3390/ijms22126447
44.
Basel D . Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes. Clin Perinatol. (2020) 47:123–41. 10.1016/j.clp.2019.10.008
45.
López-Gómez C Cámara Y Hirano M Martí R . 232nd ENMC international workshop: recommendations for treatment of mitochondrial DNA maintenance disorders. 16–18 June 2017, Heemskerk, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul Disord. (2022) 32:609–20. 10.1016/j.nmd.2022.05.008
46.
Liguori M La Russa A Manna I Andreoli V Caracciolo M Spadafora P et al A phenotypic variation of dominant optic atrophy and deafness (ADOAD) due to a novel OPA1 mutation. J Neurol. (2008) 255:127–9. 10.1007/s00415-008-0571-x
47.
Liskova P Ulmanova O Tesina P Melsova H Diblik P Hansikova H et al Novel OPA1 missense mutation in a family with optic atrophy and severe widespread neurological disorder. Acta Ophthalmol. (2013) 91:e225–31. 10.1111/aos.12038
48.
Finsterer J Zarrouk-Mahjoub S . Phenotypic spectrum of SLC25A4 mutations. Biomed Rep. (2018) 9:119–22. 10.3892/br.2018.1115
49.
Gorman GS Schaefer AM Ng Y Gomez N Blakely EL Alston CL et al Prevalence of nuclear and mitochondrial DNA mutations related to adult mitochondrial disease. Ann Neurol. (2015) 77:753–9. 10.1002/ana.24362
50.
Tyynismaa H Sembongi H Bokori-Brown M Granycome C Ashley N Poulton J et al Twinkle helicase is essential for mtDNA maintenance and regulates mtDNA copy number. Hum Mol Genet. (2004) 13:3219–27. 10.1093/hmg/ddh342
51.
Goffart S Cooper HM Tyynismaa H Wanrooij S Suomalainen A Spelbrink JN . Twinkle mutations associated with autosomal dominant progressive external ophthalmoplegia lead to impaired helicase function and in vivo mtDNA replication stalling. Hum Mol Genet. (2009) 18:328–40. 10.1093/hmg/ddn359
52.
Bernardino Gomes TM Vincent AE Menger KE Stewart JB Nicholls TJ . Mechanisms and pathologies of human mitochondrial DNA replication and deletion formation. Biochem J. (2024) 481:683–715. 10.1042/BCJ20230262
53.
Milenkovic D Matic S Kühl I Ruzzenente B Freyer C Jemt E et al TWINKLE is an essential mitochondrial helicase required for synthesis of nascent D-loop strands and complete mtDNA replication. Hum Mol Genet. (2013) 22:1983–93. 10.1093/hmg/ddt051
54.
Fratter C Gorman GS Stewart JD Buddles M Smith C Evans J et al The clinical, histochemical, and molecular spectrum of PEO1 (Twinkle)-linked adPEO. Neurology. (2010) 74:1619–26. 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181df099f
55.
Kiechl S Horváth R Luoma P Kiechl-Kohlendorfer U Wallacher-Scholz B Stucka R et al Two families with autosomal dominant progressive external ophthalmoplegia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2004) 75:1125–8. 10.1136/jnnp.2003.025890
56.
Hata Y Ichimata S Hirono K Yamaguchi Y Oku Y Ichida F et al Pathological and comprehensive genetic investigation of autopsy cases of idiopathic bradyarrhythmia. Circ J. (2022) 87:111–9. 10.1253/circj.CJ-22-0397
57.
McLaughlin KL McClung JM Fisher-Wellman KH . Bioenergetic consequences of compromised mitochondrial DNA repair in the mouse heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2018) 504:742–8. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.022
58.
Gorr MW Francois A Marcho LM Saldana T McGrail E Sun N et al Molecular signature of cardiac remodeling associated with polymerase gamma mutation. Life Sci. (2022) 298:120469. 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120469
59.
Yu T Slone J Liu W Barnes R Opresko PL Wark L et al Premature aging is associated with higher levels of 8-oxoguanine and increased DNA damage in the Polg mutator mouse. Aging Cell. (2022) 21:e13669. 10.1111/acel.13669
60.
Lewis W Day BJ Kohler JJ Hosseini SH Chan SS Green EC et al Decreased mtDNA, oxidative stress, cardiomyopathy, and death from transgenic cardiac targeted human mutant polymerase gamma. Lab Invest. (2007) 87:326–35. 10.1038/labinvest.3700523
61.
Woodbridge P Liang C Davis RL Vandebona H Sue CM . POLG Mutations in Australian patients with mitochondrial disease. Intern Med J. (2013) 43:150–6. 10.1111/j.1445-5994.2012.02847.x
62.
Spracklen TF Kasher PR Kraus S Botha TL Page DJ Kamuli S et al Identification of a POLG variant in a family with arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy and left ventricular fibrosis. Circ Genom Precis Med. (2021) 14:e003138. 10.1161/CIRCGEN.120.003138
63.
Vidmar V Vayssières M Lamour V . What’s on the other side of the gate: a structural perspective on DNA gate opening of type IA and IIA DNA topoisomerases. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:3986. 10.3390/ijms24043986
64.
Hangas A Kekäläinen NJ Potter A Michell C Aho KJ Rutanen C et al Top3α is the replicative topoisomerase in mitochondrial DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. (2022) 50:8733–48. 10.1093/nar/gkac660
65.
Primiano G Torraco A Verrigni D Sabino A Bertini E Carrozzo R et al Novel TOP3A variant associated with mitochondrial disease: expanding the clinical spectrum of topoisomerase III alpha-related Diseases. Neurol Genet. (2022) 8:e200007. 10.1212/NXG.0000000000200007
66.
Wu L Davies SL North PS Goulaouic H Riou JF Turley H et al The bloom’s syndrome gene product interacts with topoisomerase III. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:9636–44. 10.1074/jbc.275.13.9636
67.
Martin CA Sarlós K Logan CV Thakur RS Parry DA Bizard AH et al Mutations in TOP3A cause a bloom syndrome-like disorder. Am J Hum Genet. (2018) 103:221–31. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.07.001
68.
Erdinc D Rodríguez-Luis A Fassad MR Mackenzie S Watson CM Valenzuela S et al Pathological variants in TOP3A cause distinct disorders of mitochondrial and nuclear genome stability. EMBO Mol Med. (2023) 15:e16775. 10.15252/emmm.202216775
69.
Khiati S Dalla Rosa I Sourbier C Ma X Rao VA Neckers LM et al Mitochondrial topoisomerase I (top1 mt) is a novel limiting factor of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Clin Cancer Res. (2014) 20:4873–81. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3373
70.
Al Khatib I Deng J Symes A Kerr M Zhang H Huang SN et al Functional characterization of two variants of mitochondrial topoisomerase TOP1MT that impact regulation of the mitochondrial genome. J Biol Chem. (2022) 298:102420. 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102420
71.
Bonekamp NA Larsson NG . Snapshot: mitochondrial nucleoid. Cell. (2018) 172:388–388.e1. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.039
72.
Wang J Wilhelmsson H Graff C Li H Oldfors A Rustin P et al Dilated cardiomyopathy and atrioventricular conduction blocks induced by heart-specific inactivation of mitochondrial DNA gene expression. Nat Genet. (1999) 21:133–7. 10.1038/5089
73.
Ghazal N Peoples JN Mohiuddin TA Kwong JQ . Mitochondrial functional resilience after TFAM ablation in the adult heart. Am J Physiology Cell Physiol. (2021) 320:C929–42. 10.1152/ajpcell.00508.2020
74.
Rawat PS Jaiswal A Khurana A Bhatti JS Navik U . Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: an update on the molecular mechanism and novel therapeutic strategies for effective management. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 139:111708. 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111708
75.
Saada A Shaag A Elpeleg O . mtDNA depletion myopathy: elucidation of the tissue specificity in the mitochondrial thymidine kinase (TK2) deficiency. Mol Genet Metab. (2003) 79:1–5. 10.1016/S1096-7192(03)00063-5
76.
Akman HO Dorado B López LC García-Cazorla A Vilà MR Tanabe LM et al Thymidine kinase 2 (H126N) knockin mice show the essential role of balanced deoxynucleotide pools for mitochondrial DNA maintenance. Hum Mol Genet. (2008) 17:2433–40. 10.1093/hmg/ddn143
77.
Berardo A Domínguez-González C Engelstad K Hirano M . Advances in thymidine kinase 2 deficiency: clinical aspects, translational progress, and emerging therapies. J Neuromuscul Dis. (2022) 9:225–35. 10.3233/JND-210786
78.
Chanprasert S Wang J Weng SW Enns GM Boué DR Wong BL et al Molecular and clinical characterization of the myopathic form of mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome caused by mutations in the thymidine kinase (TK2) gene. Mol Genet Metab. (2013) 110:153–61. 10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.07.009
79.
Mazurova S Magner M Kucerova-Vidrova V Vondrackova A Stranecky V Pristoupilova A et al Thymidine kinase 2 and alanyl-tRNA synthetase 2 deficiencies cause lethal mitochondrial cardiomyopathy: case reports and review of the literature. Cardiol Young. (2017) 27:936–44. 10.1017/S1047951116001876
80.
von der Malsburg A Sapp GM Zuccaro KE von Appen A Moss FR 3rd Kalia R et al Structural mechanism of mitochondrial membrane remodelling by human OPA1. Nature. (2023) 620:1101–8. 10.1038/s41586-023-06441-6
81.
Piquereau J Caffin F Novotova M Prola A Garnier A Mateo P et al Down-regulation of OPA1 alters mouse mitochondrial morphology, PTP function, and cardiac adaptation to pressure overload. Cardiovasc Res. (2012) 94:408–17. 10.1093/cvr/cvs117
82.
Ryu KW Fung TS Baker DC Saoi M Park J Febres-Aldana CA et al Cellular ATP demand creates metabolically distinct subpopulations of mitochondria. Nature. (2024) 635:746–54. 10.1038/s41586-024-08146-w
83.
Wang Y Dai X Li H Jiang H Zhou J Zhang S et al The role of mitochondrial dynamics in disease. MedComm. (2023) 4:e462. 10.1002/mco2.462
84.
Wai T García-Prieto J Baker MJ Merkwirth C Benit P Rustin P et al Imbalanced OPA1 processing and mitochondrial fragmentation cause heart failure in mice. Science. (2015) 350:aad0116. 10.1126/science.aad0116
85.
Spiegel R Saada A Flannery PJ Burté F Soiferman D Khayat M et al Fatal infantile mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and optic atrophy associated with a homozygous OPA1 mutation. J Med Genet. (2016) 53:127–31. 10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103361
86.
Chen L Liu T Tran A Lu X Tomilov AA Davies V et al OPA1 mutation and late-onset cardiomyopathy: mitochondrial dysfunction and mtDNA instability. J Am Heart Assoc. (2012) 1:e003012. 10.1161/JAHA.112.003012
87.
Mayr JA Haack TB Graf E Zimmermann FA Wieland T Haberberger B et al Lack of the mitochondrial protein acylglycerol kinase causes Sengers syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. (2012) 90(2):314–20. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.12.005
88.
Jackson TD Hock DH Fujihara KM Palmer CS Frazier AE Low YC et al The TIM22 complex mediates the import of sideroflexins and is required for efficient mitochondrial one-carbon metabolism. Mol Biol Cell. (2021) 32:475–91. 10.1091/mbc.E20-06-0390
89.
Wu CW Caha M Smoot L Harris DJ Roberts AE Sacharow S et al Sengers syndrome and AGK-related disorders—minireview of phenotypic variability and clinical outcomes in molecularly confirmed cases. Mol Genet Metab. (2023) 139(3):107626. 10.1016/j.ymgme.2023.107626
90.
Haghighi A Haack TB Atiq M Mottaghi H Haghighi-Kakhki H Bashir RA et al Sengers syndrome: six novel AGK mutations in seven new families and review of the phenotypic and mutational spectrum of 29 patients. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2014) 9:119. 10.1186/s13023-014-0119-3
91.
Saito T Sadoshima J . Molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial autophagy/mitophagy in the heart. Circ Res. (2015) 116:1477–90. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303790
92.
Nguyen-Dien GT Kozul KL Cui Y Townsend B Kulkarni PG Ooi SS et al FBXL4 suppresses mitophagy by restricting the accumulation of NIX and BNIP3 mitophagy receptors. Embo J. (2023) 42:e112767. 10.15252/embj.2022112767
93.
Liu K Zhao Q Sun H Liu L Wang C Li Z et al BNIP3 (BCL2 interacting protein 3) regulates pluripotency by modulating mitochondrial homeostasis via mitophagy. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:334. 10.1038/s41419-022-04795-9
94.
Abudureyimu M Luo X Jiang L Jin X Pan C Yu W et al FBXL4 protects against HFpEF through Drp1-mediated regulation of mitochondrial dynamics and the downstream SERCA2a. Redox Biol. (2024) 70:103081. 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103081
95.
Kulkarni P Nguyen-Dien GT Kozul KL Pagan JK . FBXL4: safeguarding against mitochondrial depletion through suppression of mitophagy. Autophagy. (2024) 20:1459–61. 10.1080/15548627.2024.2318077
96.
Almannai M Dai H El-Hattab AW Wong L-JC . FBXL4-Related Encephalomyopathic mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome. In: AdamMPFeldmanJMirzaaGMet al editors. GeneReviews®. Seattle (WA): University of Washington (2017). Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK425540/
97.
Huemer M Karall D Schossig A Abdenur JE Al Jasmi F Biagosch C et al Clinical, morphological, biochemical, imaging and outcome parameters in 21 individuals with mitochondrial maintenance defect related to FBXL4 mutations. J Inherit Metab Dis. (2015) 38:905–14. 10.1007/s10545-015-9836-6
98.
Shammas MK Nie Y Gilsrud A Huang X Narendra DP Chinnery PF . CHCHD10 Mutations induce tissue-specific mitochondrial DNA deletions with a distinct signature. Hum Mol Genet. (2023) 33(1):91–101. 10.1093/hmg/ddad161
99.
Southwell N Manzo O Bacman S Zhao D Sayles NM Dash J et al High fat diet ameliorates mitochondrial cardiomyopathy in CHCHD10 mutant mice. EMBO Mol Med. (2024) 16(6):1352–78. 10.1038/s44321-024-00067-5
100.
Genin EC di Borgo PP Lorivel T Hugues S Farinelli M Mauri-Crouzet A et al CHCHD10(S59l/+) Mouse model: behavioral and neuropathological features of frontotemporal dementia. Neurobiol Dis. (2024) 195:106498. 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106498
101.
Shammas MK Huang X Wu BP Fessler E Song IY Randolph NP et al OMA1 Mediates local and global stress responses against protein misfolding in CHCHD10 mitochondrial myopathy. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132:e157504. 10.1172/JCI157504
102.
Ait-El-Mkadem Saadi S Chaussenot A Bannwarth S Rouzier C Paquis-Flucklinger V . CHCHD10-Related disorders. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle (2015). Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26131548/
103.
Sayles NM Southwell N McAvoy K Kim K Pesini A Anderson CJ et al Mutant CHCHD10 causes an extensive metabolic rewiring that precedes OXPHOS dysfunction in a murine model of mitochondrial cardiomyopathy. Cell Rep. (2022) 38:110475. 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110475
104.
Lin HP Petersen JD Gilsrud AJ Madruga A D’Silva TM Huang X et al DELE1 promotes translation-associated homeostasis, growth, and survival in mitochondrial myopathy. EMBO J. (2024) 43(22):5548–85. 10.1038/s44318-024-00242-x
105.
Bround MJ Havens JR York AJ Sargent MA Karch J Molkentin JD . ANT-dependent MPTP underlies necrotic myofiber death in muscular dystrophy. Sci Adv. (2023) 9:eadi2767. 10.1126/sciadv.adi2767
106.
Tang X Zhao S Liu J Liu X Sha X Huang C et al Mitochondrial GSNOR alleviates cardiac dysfunction via ANT1 denitrosylation. Circ Res. (2023) 133:220–36. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.322654
107.
Zhou T Pan J Xu K Yan C Yuan J Song H et al Single-cell transcriptomics in MI identify Slc25a4 as a new modulator of mitochondrial malfunction and apoptosis-associated cardiomyocyte subcluster. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:9274. 10.1038/s41598-024-59975-8
108.
Graham BH Waymire KG Cottrell B Trounce IA MacGregor GR Wallace DC . A mouse model for mitochondrial myopathy and cardiomyopathy resulting from a deficiency in the heart/muscle isoform of the adenine nucleotide translocator. Nat Genet. (1997) 16:226–34. 10.1038/ng0797-226
109.
Thompson K Majd H Dallabona C Reinson K King MS Alston CL et al Recurrent de novo dominant mutations in SLC25A4 cause severe early-onset mitochondrial disease and loss of mitochondrial DNA copy number. Am J Hum Genet. (2016) 99:860–76. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.08.014
110.
Strauss KA DuBiner L Simon M Zaragoza M Sengupta PP Li P et al Severity of cardiomyopathy associated with adenine nucleotide translocator-1 deficiency correlates with mtDNA haplogroup. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2013) 110:3453–8. 10.1073/pnas.1300690110
111.
Wang C Zhang R He J Yu L Li X Zhang J et al Ultrasound-responsive low-dose doxorubicin liposomes trigger mitochondrial DNA release and activate cGAS-STING-mediated antitumour immunity. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:3877. 10.1038/s41467-023-39607-x
112.
Wang L Luo R Onyshchenko K Rao X Wang M Menz B et al Adding liposomal doxorubicin enhances the abscopal effect induced by radiation/αPD1 therapy depending on tumor cell mitochondrial DNA and cGAS/STING. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:e006235. 10.1136/jitc-2022-006235
113.
Xiong W Li B Pan J Li D Yuan H Wan X et al Mitochondrial amount determines doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in cardiomyocytes. Advanced Science. (2025) 12:e2412017. 10.1002/advs.202412017
114.
Almannai M El-Hattab AW Ali M Soler-Alfonso C Scaglia F . Clinical trials in mitochondrial disorders, an update. Mol Genet Metab. (2020) 131:1–13. 10.1016/j.ymgme.2020.10.002
115.
Dombi E Marinaki T Spingardi P Millar V Hadjichristou N Carver J et al Nucleoside supplements as treatments for mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 12:1260496. 10.3389/fcell.2024.1260496
116.
Pekeles H Berrahmoune S Dassi C Cheung ACT Gagnon T Waters PJ et al Safety and efficacy of deoxycytidine/deoxythymidine combination therapy in POLG-related disorders: 6-month interim results of an open-label, single arm, phase 2 trial. EClinicalMedicine. (2024) 74:102740. 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102740
117.
Amtmann D Gammaitoni AR Galer BS Salem R Jensen MP . The impact of TK2 deficiency syndrome and its treatment by nucleoside therapy on quality of life. Mitochondrion. (2023) 68:1–9. 10.1016/j.mito.2022.10.003
118.
Filosto M Cotti Piccinelli S Caria F Gallo Cassarino S Baldelli E Galvagni A et al Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy (MNGIE-MTDPS1). J Clin Med. (2018) 7:389. 10.3390/jcm7110389
Summary
Keywords
mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome, cardiomyopathy, mtDNA replication, nucleotide metabolism, mitochondrial dynamics, mitochondrial damage, mitochondrial dysfunction
Citation
Bao S, Ye J, Zhou J, Zheng C, Xu Y and Chen S (2025) Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome and its cardiac complication. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1582219. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1582219
Received
07 March 2025
Accepted
21 May 2025
Published
10 June 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Meijing Wang, Indiana University School of Medicine, United States
Reviewed by
Wenjun Zhang, Indiana University Bloomington, United States
Patrick Kang, Northeast Ohio Medical University, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Bao, Ye, Zhou, Zheng, Xu and Chen.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Yuejuan Xu xuyj1006@126.com Sun Chen chensun@xinhuamed.com.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.