- 1Department of Pharmacy, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Second Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Nursing, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shangha, China
- 4Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 5Department of Pharmacy, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University (Xiamen Branch), Xiamen, Fujian, China
Objective: This study aims to investigate the prognostic value of integrating inflammatory biomarkers with the established Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) risk score for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with myocardial infarction (MI).
Methods: This prospective, single-center study enrolled adult MI patients admitted to the coronary care unit at Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University. Blood samples were collected to measure inflammatory markers (IL-1β, sIL-2R, IL-6, IL-8) and myocardial biomarkers. The Gensini score and GRACE score were calculated for each patient. The primary endpoint was the post-MI occurrence of a composite of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), including cardiovascular death, non-fatal MI, and non-fatal ischemic stroke. Predictive performance of biomarkers was evaluated using Kaplan–Meier survival curves, Cox regression analysis, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
Results: A total of 724 patients (median age 64 years, 85.0% male) were included with a median follow-up of 1.7 years. During follow-up, 81 patients (11.1%) experienced MACE, including 45 cardiovascular deaths, 23 MIs, and 13 strokes. Multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that sIL-2R and IL-8 were independent predictors of MACE. Elevated levels of sIL-2R (HR = 9.123, 95% CI: 5.883–14.147, p < 0.001) and IL-8 (HR = 4.443, 95% CI: 2.769–7.131, p < 0.001) were significantly associated with an increased risk of MACE. After adjustment for cardiovascular risk factors, elevated sIL-2R (adjusted HR: 3.761, 95% CI: 2.269–6.233, p < 0.001) and IL-8 (adjusted HR: 2.294, 95% CI: 1.375–3.825, p = 0.001) levels remained significantly associated with an increased risk of MACE. The combination of sIL-2R, IL-8, and GRACE score displayed effective predictive performance for long-term MACE, as evidenced by ROC curve analysis (AUC = 0.824, 95% CI: 0.775–0.873, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Elevated levels of sIL-2R and IL-8 independently predict increased risk of MACE in MI patients. Integrating biomarkers such as sIL-2R and IL-8 with the GRACE score can significantly improve predictive performance, offering a robust approach for risk stratification in MI patients.
1 Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain the leading cause of premature morbidity and mortality worldwide, accounting for over 40% of all deaths in China (1). A significant subset of these deaths is attributed to severe acute myocardial infarction (AMI) (2). The burden of myocardial infarction (MI) is rising rapidly as China faces an aging population and increasing metabolic risk factors (3).
Despite optimal therapy and secondary prevention measures targeting low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), blood pressure, and glycemia, residual risks of recurrent major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) post-MI persist. Extensive evidence supports the role of inflammation in the progression of atherosclerosis, formation of unstable plaques, and plaque erosion and rupture (4, 5).
Several inflammatory biomarkers have gained prominence for their role in predicting MACE, such as high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP), Interleukin-6 (IL-6), and IL-1β (6, 7). Interleukins (ILs) are a group of proteins secreted by various cells, such as monocytes, macrophages, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to proinflammatory stimuli (8). Numerous studies have investigated the relationship between ILs and MI (6). In mouse models of MI, IL-1α is released by dying cardiomyocytes (9), and IL-1β synthesis is significantly upregulated post-infarction (10). IL-6 is assumed to be produced by cardiomyocytes during ischemia and reperfusion. In recent studies, IL-6R-targeting monoclonal antibodies improved myocardial salvage in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI) patients, though adverse events were similar between the treatment and placebo groups (11). Elevated baseline IL-8 levels have been associated with long-term all-cause mortality in male post-MI patients, but there are few reports on other cardiovascular outcomes (12). Moreover, although sIL-2R is recognized for its role in immune response and inflammation, studies directly linking it to MI prognosis in humans remain relatively limited (13).
Despite their predictive value, inflammatory biomarkers face challenges in clinical application. For instance, their specificity is limited, as levels can be influenced by infections, autoimmune diseases, or other non-cardiovascular conditions. Thus, integrating these biomarkers with traditional risk scores and clinical parameters to develop more accurate predictive models remains a key research priority. To bridge this gap, the present study utilizes the Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) score and incorporates interleukin-based biomarkers to predict long-term adverse cardiovascular events in a large cohort of MI patients. This approach is contextualized within a framework of well-established covariates associated with poor clinical outcomes, including congestive heart failure, hypertension, impaired renal function, advanced age, and validated myocardial markers.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population
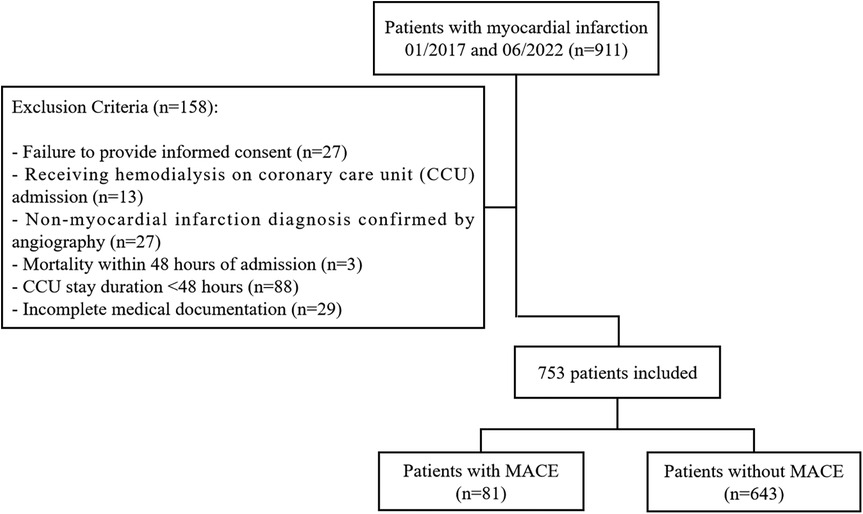
Patients diagnosed with MI and admitted to the coronary care unit (CCU) of Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, between January 2017 and June 2022 were prospectively enrolled (14) (Figure 1). Treatment and management were following guideline recommendations (15, 16). Patients were followed up for a minimum of one year with regular evaluations. Exclusion criteria included incomplete follow-up, inability to provide informed consent, unavailable clinical data, and coronary angiography findings inconsistent with MI diagnosis. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University (approval number: B2022-375R), and all participants provided written informed consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2 Biomarker measurements
Blood samples were obtained after 12 h of overnight fasting on the second day of admission to the CCU. All biomarkers were analyzed at the Department of Laboratory Medicine, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University. Samples were aliquoted and stored at −70°C until analysis. Interleukin levels (IL-1β, sIL-2R, IL-6, and IL-8) were measured using chemiluminescence on the IMMULITE 1000 automated chemiluminescence immune analyzer (Siemens, Germany), with predefined detection limits. Cardiac troponin T (cTnT) and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels were measured using electrochemiluminescence on the Cobas e 801 (Roche Diagnostics, Germany), while hs-CRP levels were measured using immunoturbidimetry on the Cobas c 702 (Roche Diagnostics, Germany). Routine biochemical analyses were performed using standard laboratory methods. Values below detection limits were recorded as the lowest detectable value.
2.3 Follow-up and clinical outcomes
Patients were followed up post-discharge through outpatient visits or telephone interviews at 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months, and quarterly thereafter. The follow-up duration ranged from 1 to 7.6 years, with a median of 1.7 years, calculated using the median follow-up time among surviving patients at the study's conclusion.
The primary endpoint was a composite of MACE, defined as a composite of cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and non-fatal ischemic stroke. Deaths of unknown cause were also classified as MACE.
2.4 Calculation of risk scores
The severity of coronary artery stenosis was evaluated using the Gensini scoring system, which assigns a weighted score based on the degree of luminal narrowing: <25% = 1 point, 25%–50% = 2 points, 51%–75% = 4 points, 76%–90% = 8 points, 91%–99% = 16 points, and total occlusion = 32 points. These scores were further adjusted by multiplying with segment-specific coefficients, such as the left main trunk (×5), proximal left anterior descending artery (×2.5), and other segments with coefficients ranging from 0.5 to 2.5, as described in established protocols (17).
The GRACE score, a validated tool for predicting in-hospital and long-term mortality and recurrent MI risk (18), was calculated for each patient upon admission using an online calculator (http://www.outcomes-umassmed.org/grace). The GRACE score incorporates eight clinical variables: age, heart rate, systolic blood pressure, serum creatinine, Killip class, cardiac arrest, presence of ST-segment deviation, and elevated cardiac enzymes or markers.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS (version 26.0, IBM Inc., Armonk, NY, USA) and R (version 4.2.1; R Core Team). The normality of continuous variables was evaluated using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Continuous variables were summarized as mean ± standard deviation or median (interquartile range, IQR) and compared using the independent samples t-test or Mann–Whitney U test, as appropriate. Categorical variables were presented as frequencies (percentages) and analyzed using the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test.
Univariate Cox regression analysis was used to explore the relationships between ILs and clinical variables and outcomes. Variables with p < 0.1 in univariate analysis, along with clinically relevant factors, were incorporated into multivariate Cox regression models using a stepwise backward elimination approach. Renal insufficiency was defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 60 ml/min, calculated using the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation.
Biomarker levels were stratified using optimal cut-off values determined by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. Kaplan–Meier curves were plotted based on follow-up time (years), and the cumulative survival rates between high and low IL level groups were estimated using the log-rank test. The predictive performance of IL-based models, both independently and in combination with established risk scores, was quantified using area under the ROC curve (AUC) analysis. All data were analyzed using two-sided tests, with p < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Patient characteristics according to MACE
A cohort of 724 patients (85% male, with a median age of 64 years) was followed for a median duration of 1.7 years. During follow-up, 81 patients (11.1%) reached the primary endpoint, comprising 45 cardiovascular deaths, 23 MIs, and 13 strokes. Patients with MACE were older and had a higher prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors, including HR > 100 b.p.m., diabetes, coronary artery disease, heart failure, history of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), renal insufficiency, and anemia (Table 1). These patients had significantly higher GRACE scores and elevated levels of cTnT, hs-CRP, NT-proBNP, sIL-2R, IL-6, and IL-8. However, there were no significant differences in creatine kinase (CK), CK-MB, and Gensini scores between groups. Medication analysis revealed that patients without MACE were more frequently prescribed aspirin, ticagrelor, beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB), and statins compared to those with MACE.
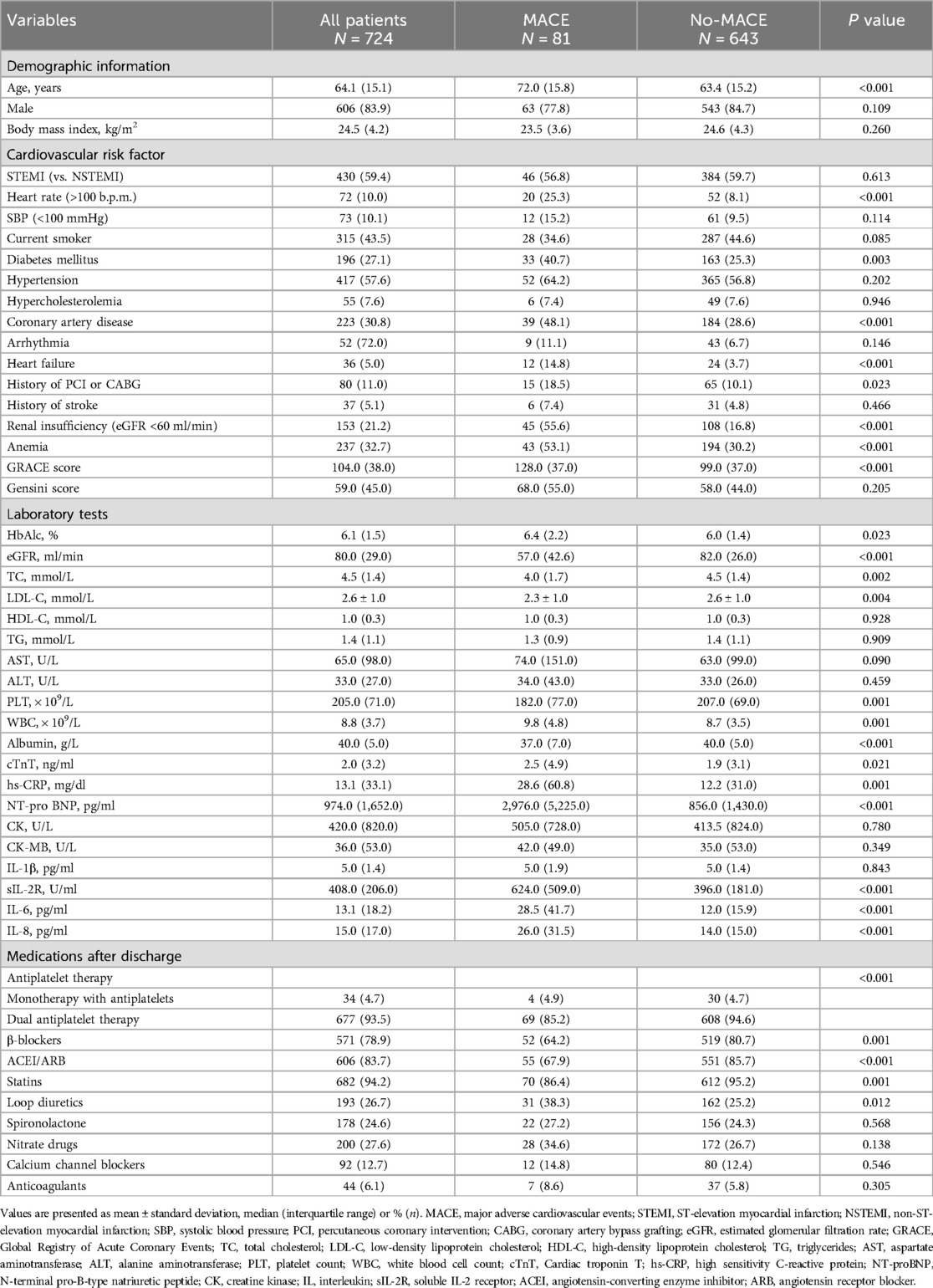
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of study participants stratified by major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) status during 1.7-year follow-up.
3.2 Determination of risk factors for MACE
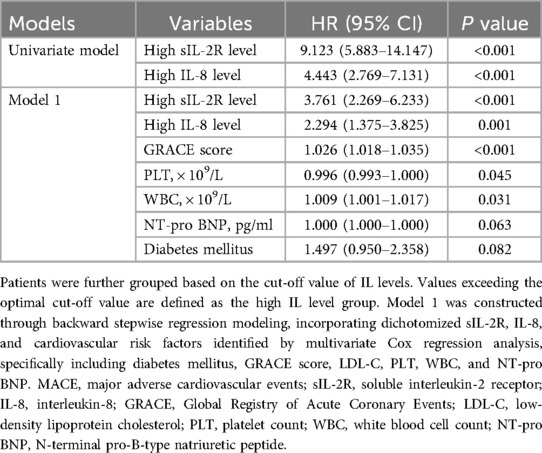
Univariate Cox analysis identified several parameters associated with increased risk of MACE, including age, HR > 100 b.p.m., diabetes, coronary artery disease, heart failure, history of PCI or CABG, renal insufficiency, anemia, GRACE score, lower levels of serum total cholesterol (TC), LDL-C, and platelet (PLT), as well as elevated levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), white blood cell (WBC), cTnT, hs-CRP, NT-proBNP, CK, CK-MB, sIL-2R, IL-6, and IL-8 (Supplementary Table S1). Subsequent multivariate Cox regression analyses using backward stepwise regression models demonstrated that diabetes mellitus, higher GRACE scores, and indicators of inflammatory-immune activation (sIL-2R, IL-8, and WBC) were significantly associated with an elevated risk of MACE (Supplementary Table S2).
3.3 sIL-2R and IL-8 as predictive biomarkers for MACE
ROC analysis demonstrated that both sIL-2R and IL-8 effectively discriminated between patients with and without MACE. The optimal cut-off values were 611 U/ml for sIL-2R (sensitivity 53.1%; specificity 90.4%) and 18.5 pg/ml for IL-8 (sensitivity 69.1%; specificity 66.9%). Patients were further grouped based on the cut-off value of each variable. As shown in Figure 2, patients were stratified into high-level and low-level groups for sIL-2R and IL-8. The analysis demonstrated that both high-level sIL-2R and high-level IL-8 were significantly associated with inferior MACE-free survival compared to their respective low-level groups (log-rank test, p < 0.0001 for both). Specifically, patients with elevated levels of sIL-2R had a significantly higher risk of MACE during follow-up (HR = 9.123, 95% CI: 5.883–14.147, p < 0.001), which remained significant after adjusting for cardiovascular risk factors identified in this study (adjusted HR = 3.761, 95% CI: 2.269–6.233, p < 0.001) (Supplementary Table S2). Similarly, elevated IL-8 levels were associated with a higher risk of MACE (HR = 4.443, 95% CI: 2.769–7.131, p < 0.001), with the association persisting after adjustment for relevant cardiovascular risk factors (adjusted HR = 2.294, 95% CI: 1.375–3.825, p = 0.001) (Table 2).
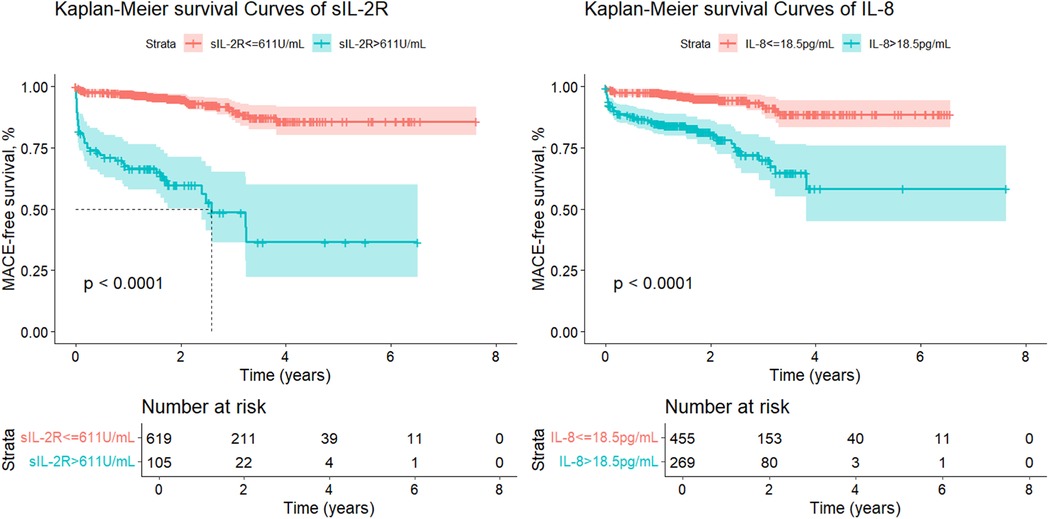
Figure 2. Kaplan–Meier curves for MACE according to sIL-2R and IL-8. MACE, major adverse cardiovascular events; sIL-2R, soluble interleukin-2 receptor; IL-8, interleukin-8.
3.4 Superior predictive performance of combined sIL-2R, IL-8, and GRACE model
The GRACE score demonstrated the highest individual predictive value, with an AUC of 0.785 (95% CI: 0.734–0.837, p < 0.001). Among the biomarkers, sIL-2R and IL-8 showed significant predictive performance, with AUCs of 0.749 (95% CI: 0.687–0.811, p < 0.001) and 0.703 (95% CI: 0.643–0.764, p < 0.001), respectively. The combination of multiple indicators is significantly superior to single-variable prediction. The synergistic effect of inflammatory factors (sIL-2R/IL-8) and GRACE score can improve the prediction accuracy. Notably, the combination of sIL-2R, IL-8, and GRACE score displayed effective predictive performance for long-term MACE, as evidenced by ROC curve analysis (AUC = 0.824, 95% CI: 0.775–0.873, p < 0.001). Model 1 was constructed via backward stepwise regression modeling using dichotomized sIL-2R, IL-8, and cardiovascular risk factors identified by multivariate Cox regression. Model 1 was identified as the optimal combination, with an AUC of 0.853 (95% CI: 0.805–0.902, p < 0.001) (Figure 3).
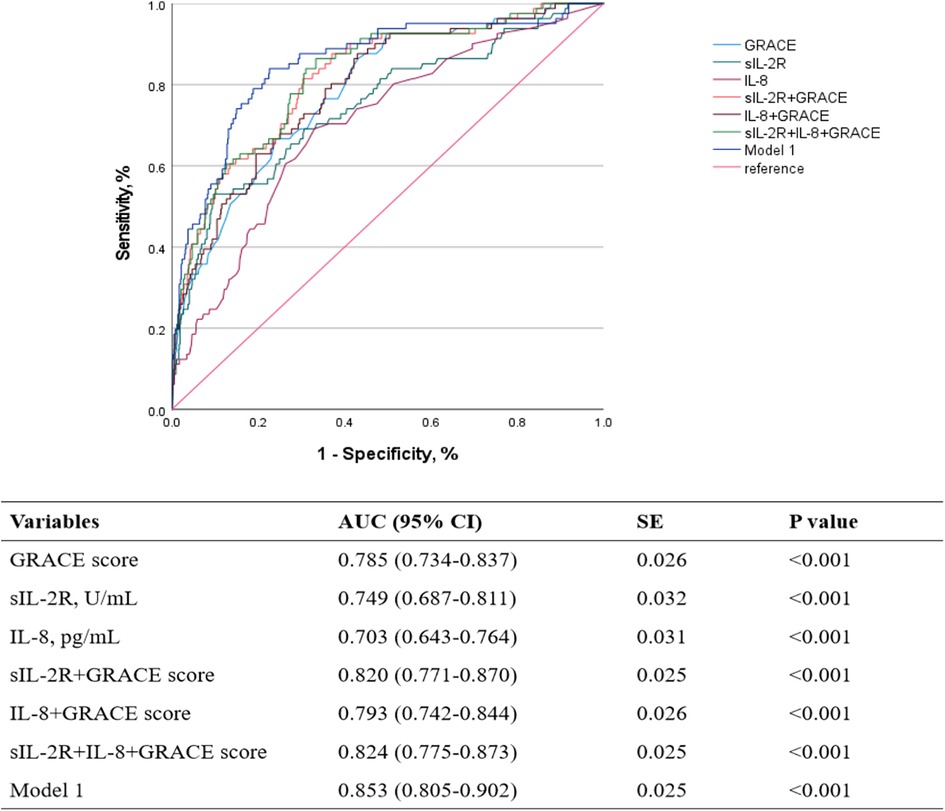
Figure 3. ROC curves for the predictive model discriminating MACE based on different indicators. ROC, receiver operating characteristic; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular events; AUC, area under curve; SE, standard error; sIL-2R, soluble interleukin-2 receptor; IL-8, interleukin-8; GRACE, Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events.
4 Discussion
Our study indicated that higher levels of sIL-2R (>611 U/ml) and IL-8 (>18.5 pg/ml) were significantly associated with increased long-term post-MI risk of MACE, even after adjusting for cardiovascular risk factors. ROC analysis showed that sIL-2R had the best predictive performance for MACE, and the combination of sIL-2R, IL-8, and GRACE score was the most predictive.
Inflammation is a pivotal factor in the progression of atherosclerosis, plaque formation, and rupture, particularly in patients with MI (4, 19). The process is driven by cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, and IL-8, which activate monocyte-macrophages, leading to the release of additional cytokines, including IL-2 (8, 20–22). IL-2 promotes T cell activation, leading to the proteolytic cleavage of the IL-2 receptor α-chain (CD25) and the release of sIL-2R, a 45-kDa glycoprotein that serves as a marker of immune activation (23–25). Elevated sIL-2R levels reflect heightened immune activation, contributing to endothelial dysfunction, atherosclerotic plaque instability, and adverse cardiovascular outcomes in MI patients (13). Our previous work demonstrated that elevated baseline sIL-2R levels were associated with poor outcomes in MI patients (26). A recent study further identified sIL-2R as an independent predictor of acute kidney injury and in-hospital all-cause mortality in MI patients, with ROC cut-off values of 423 U/ml and 615 U/ml, respectively (27). In this study, the sIL-2R cut-off value for predicting MACE was 611 U/ml, consistent with previous findings, supporting the external validity of our results.
IL-8 is also implicated in atherosclerotic plaque destabilization and thrombosis (28), and inhibits cholesterol efflux, contributing to lipid accumulation and the progression of atherosclerosis (29). IL-8 concentrations are elevated in patients with ACS compared to those with chronic stable angina (30). Also, elevated baseline IL-8 levels are linked to an increased risk of long-term mortality, independent of various clinical, laboratory, and angiographic factors (12). Although the precise mechanisms remain unclear, IL-8's involvement in atherogenesis, plaque destabilization, and thrombosis likely underlies this association. Our study not only confirms the link between elevated IL-8 levels and post-MI mortality but also highlights its predictive value for composite endpoint events, underscoring its potential as a prognostic biomarker in MI.
Clinicians traditionally rely on risk scores and biomarkers to predict MACE (31). Widely used risk scores such as the GRACE score and Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) score are based on clinical parameters (32, 33). However, the TIMI score exhibits lower accuracy than the GRACE score in predicting long-term outcomes. This study found that the GRACE score had the highest individual predictive performance (AUC = 0.785), consistent with its established use in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients (18). However, these scores fail to effectively incorporate underlying pathophysiological mechanisms such as inflammation, and their predictive accuracy is lower in patients with complex comorbidities or atypical presentations in MI patients. In our study, sIL-2R and IL-8 demonstrated significant predictive value. By integrating biomarkers like sIL-2R and IL-8 with the GRACE score, we found that the predictive performance was significantly enhanced. This integration provides a robust method for risk stratification in myocardial infarction (MI) patients. Traditional biomarkers, such as troponin T/I and BNP/NT-proBNP, primarily reflect myocardial damage or cardiac stress, however, they fail to provide a comprehensive assessment of systemic risk, particularly the role of inflammation in cardiovascular events (34).
Platelets play a crucial role in thrombosis, making antiplatelet therapy essential for post-PCI MI patients (35). However, the association between baseline platelet levels and long-term MACE remains controversial. Yadav M et al. analyzed 10,603 Non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) or STEMI patients from the ACUITY and HORIZONS-AMI trials, finding that baseline thrombocytopenia significantly increased MACE rates (20.8% vs. 15.6%; p = 0.0002). Multivariate analysis confirmed thrombocytopenia as an independent MACE predictor (HR = 1.39, p = 0.009) (36). Conversely, Liu R et al.'s study of 16,957 STEMI patients from the CAMI registry showed higher MACE rates in thrombocytopenic patients (23.6% vs. 13.9%, p < 0.001), but this was not independent of other factors (HR = 1.18, p = 0.132) (37). These discrepancies may result from differences in controlling confounders, such as hemoglobin. Additionally, Brodsky MA et al. reported a high MACE incidence (28.6%) in immune-mediated thrombocytopenic purpura (iTTP) survivors over 7.6 years (38). Our study confirms a significant, independent link between baseline thrombocytopenia and long-term MACE, emphasizing the importance of monitoring platelet levels in clinical practice.
This study has several limitations. First, the cross-sectional design of biomarker assessment may introduce bias, as ILs' levels could fluctuate during disease progression, particularly before and after PCI, and variations in detection time points may affect result interpretation and limit causal inference. Second, the single-center design and absence of an external validation cohort restrict the generalizability of our findings. Future large-scale, multicenter prospective studies with extended follow-up periods are warranted to provide more robust evidence and validate these results.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, our findings indicate that elevated sIL-2R and IL-8 levels are independent predictors of long-term MACE in MI patients. The integration of biomarkers such as sIL-2R and IL-8 with the GRACE score can significantly improve predictive performance, offering a robust approach for risk stratification in MI patients.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
DT: Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. NY: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. TM: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. YL: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. RL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YX: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. DH: Writing – review & editing. QL: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. KP: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Shanghai Youth Medical Talents-Clinical Pharmacist Program [No. SHWSRS(2023)106], Shanghai Hospital Development Center Foundation (NO. SHDC12024632), China International Medical Foundation (No. Z-2021-46-2101), the Chinese Pharmaceutical Association (No.CPA-Z05-ZC-2023-003), Shanghai Pharmaceutical Association [No. (2023)04], and Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (No. shslczdzk06504).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Department of Biostatistics, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai China, for providing statistical advice. Also, I would like to thank the nurses from CCU for assisting with the blood collection.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1591578/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Vaduganathan M, Mensah GA, Turco JV, Fuster V, Roth GA. The global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk: a compass for future health. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2022) 80(25):2361–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.11.005
2. Writing Committee of the Report on Cardiovascular H, Diseases in C. Report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China 2021: an updated summary. Biomed Environ Sci. (2022) 35(7):573–603. doi: 10.3967/bes2022.079
3. Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, et al. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 76(25):2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010
4. Nakajima A, Sugiyama T, Araki M, Seegers LM, Dey D, McNulty I, et al. Plaque rupture, compared with plaque erosion, is associated with a higher level of pancoronary inflammation. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. (2022) 15(5):828–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2021.10.014
5. Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK, Leducq Transatlantic Network on A. Inflammation in atherosclerosis: from pathophysiology to practice. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2009) 54(23):2129–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.09.009
6. Batra G, Ghukasyan Lakic T, Lindback J, Held C, White HD, Stewart RAH, et al. Interleukin 6 and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease and chronic coronary syndrome. JAMA Cardiol. (2021) 6(12):1440–45. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2021.3079
7. Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Rifai N. C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women. N Engl J Med. (2000) 342(12):836–43. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200003233421202
8. Al-Qahtani AA, Alhamlan FS, Al-Qahtani AA. Pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory interleukins in infectious diseases: a comprehensive review. Trop Med Infect Dis. (2024) 9(1):13. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed9010013
9. Lugrin J, Parapanov R, Rosenblatt-Velin N, Rignault-Clerc S, Feihl F, Waeber B, et al. Cutting edge: iL-1alpha is a crucial danger signal triggering acute myocardial inflammation during myocardial infarction. J Immunol. (2015) 194(2):499–503. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401948
10. Dewald O, Ren G, Duerr GD, Zoerlein M, Klemm C, Gersch C, et al. Of mice and dogs: species-specific differences in the inflammatory response following myocardial infarction. Am J Pathol. (2004) 164(2):665–77. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63154-9
11. Broch K, Anstensrud AK, Woxholt S, Sharma K, Tollefsen IM, Bendz B, et al. Randomized trial of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2021) 77(15):1845–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.02.049
12. Cavusoglu E, Marmur JD, Yanamadala S, Chopra V, Hegde S, Nazli A, et al. Elevated baseline plasma IL-8 levels are an independent predictor of long-term all-cause mortality in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Atherosclerosis. (2015) 242(2):589–94. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.08.022
13. Gimbrone MA Jr, Garcia-Cardena G. Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2016) 118(4):620–36. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306301
14. Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Chaitman BR, Bax JJ, Morrow DA, et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). J Am Coll Cardiol. (2018) 72(18):2231–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.08.1038
15. Lawton JS, Tamis-Holland JE, Bangalore S, Bates ER, Beckie TM, Bischoff JM, et al. 2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI guideline for coronary artery revascularization: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. (2022) 145(3):e18–e114. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001038
16. Byrne RA, Rossello X, Coughlan JJ, Barbato E, Berry C, Chieffo A, et al. 2023 ESC guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. (2024) 13(1):55–161. doi: 10.1093/ehjacc/zuad107
17. Rampidis GP, Benetos G, Benz DC, Giannopoulos AA, Buechel RR. A guide for gensini score calculation. Atherosclerosis. (2019) 287:181–83. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.05.012
18. Fox KA, Dabbous OH, Goldberg RJ, Pieper KS, Eagle KA, Van de Werf F, et al. Prediction of risk of death and myocardial infarction in the six months after presentation with acute coronary syndrome: prospective multinational observational study (GRACE). Br Med J. (2006) 333(7578):1091. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38985.646481.55
19. Mahtta D, Sudhakar D, Koneru S, Silva GV, Alam M, Virani SS, et al. Targeting inflammation after myocardial infarction. Curr Cardiol Rep. (2020) 22(10):110. doi: 10.1007/s11886-020-01358-2
20. Libby P. Interleukin-1 beta as a target for atherosclerosis therapy: biological basis of CANTOS and beyond. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2017) 70(18):2278–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.09.028
21. De Gennaro L, Brunetti ND, Montrone D, De Rosa F, Cuculo A, Di Biase M. Subacute inflammatory activation in subjects with acute coronary syndrome and left ventricular dysfunction. Inflammation. (2012) 35(1):363–70. doi: 10.1007/s10753-011-9326-4
22. Beguin EP, van den Eshof BL, Hoogendijk AJ, Nota B, Mertens K, Meijer AB, et al. Integrated proteomic analysis of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1beta-induced endothelial inflammation. J Proteomics. (2019) 192:89–101. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2018.08.011
23. Authier FJ, Mhiri C, Chazaud B, Christov C, Cherin P, Barlovatz-Meimon G, et al. Interleukin-1 expression in inflammatory myopathies: evidence of marked immunoreactivity in sarcoid granulomas and muscle fibres showing ischaemic and regenerative changes. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. (1997) 23(2):132–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1997.tb01195.x
24. Vink A, Uyttenhove C, Wauters P, Van Snick J. Accessory factors involved in murine T cell activation. Distinct roles of interleukin 6, interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. Eur J Immunol. (1990) 20(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200102
25. Kumar A, Moreau JL, Gibert M, Theze J. Internalization of interleukin 2 (IL-2) by high affinity IL-2 receptors is required for the growth of IL-2-dependent T cell lines. J Immunol. (1987) 139(11):3680–4. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.139.11.3680
26. Pan K, Xu C, Chen C, Chen S, Zhang Y, Ding X, et al. Soluble interleukin-2 receptor combined with interleukin-8 is a powerful predictor of future adverse cardiovascular events in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 10:1110742. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1110742
27. Liao J, Zhang M, Xu R, Wu R, Shi H, Jin Q, et al. Soluble interleukin-2 receptor predicts acute kidney injury and in-hospital mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. (2023) 388:131156. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2023.131156
28. Li S, Sun Y, Zhong L, Xiao Z, Yang M, Chen M, et al. The suppression of ox-LDL-induced inflammatory cytokine release and apoptosis of HCAECs by long non-coding RNA-MALAT1 via regulating microRNA-155/SOCS1 pathway. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2018) 28(11):1175–87. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2018.06.017
29. Chen Y, Wang Z, Zhou L. Interleukin 8 inhibition enhanced cholesterol efflux in acetylated low-density lipoprotein-stimulated THP-1 macrophages. J Investig Med. (2014) 62(3):615–20. doi: 10.2310/JIM.0000000000000049
30. Tziakas DN, Chalikias GK, Tentes IK, Stakos D, Chatzikyriakou SV, Mitrousi K, et al. Interleukin-8 is increased in the membrane of circulating erythrocytes in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Eur Heart J. (2008) 29(22):2713–22. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehn382
31. Fox KA, Carruthers KF, Dunbar DR, Graham C, Manning JR, De Raedt H, et al. Underestimated and under-recognized: the late consequences of acute coronary syndrome (GRACE UK-Belgian study). Eur Heart J. (2010) 31(22):2755–64. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq326
32. Granger CB, Goldberg RJ, Dabbous O, Pieper KS, Eagle KA, Cannon CP, et al. Predictors of hospital mortality in the global registry of acute coronary events. Arch Intern Med. (2003) 163(19):2345–53. doi: 10.1001/archinte.163.19.2345
33. Antman EM, Cohen M, Bernink PJ, McCabe CH, Horacek T, Papuchis G, et al. The TIMI risk score for unstable angina/non-ST elevation MI: a method for prognostication and therapeutic decision making. JAMA. (2000) 284(7):835–42. doi: 10.1001/jama.284.7.835
34. Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Chaitman BR, Bax JJ, Morrow DA, et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). Circulation. (2018) 138(20):e618–e51. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000617
35. Byrne RA, Rossello X, Coughlan JJ, Barbato E, Berry C, Chieffo A, et al. 2023 ESC guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44(38):3720–826. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad191
36. Yadav M, Genereux P, Giustino G, Madhavan MV, Brener SJ, Mintz G, et al. Effect of baseline thrombocytopenia on ischemic outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes who undergo percutaneous coronary intervention. Can J Cardiol. (2016) 32(2):226–33. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2015.05.020
37. Liu R, Hu Y, Yang J, Wang Q, Yang H, Wang Z, et al. Effect of baseline thrombocytopenia on long-term outcomes in patients with acute ST-segment elevated myocardial infarction - a large propensity score-matching analysis from the China acute myocardial infarction (CAMI) registry. Circ J. (2021) 85(2):150–58. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-20-0781
Keywords: GRACE score, soluble interleukin-2 receptor, interleukin-8, major adverse cardiovascular events, myocardial infarction
Citation: Tian D, Yu N, Mao T, Li Y, Liu R, Xu Y, Huang D, Lv Q and Pan K (2025) Prediction of long-term major adverse cardiac events after myocardial infarction: value of combination of inflammatory biomarkers and GRACE score. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1591578. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1591578
Received: 11 March 2025; Accepted: 27 June 2025;
Published: 10 July 2025.
Edited by:
Istvan Szokodi, University of Pécs, HungaryReviewed by:
Alice Bonomi, Monzino Cardiology Center (IRCCS), ItalyZvonimir Ostojic, University Hospital Centre Zagreb, Croatia
Copyright: © 2025 Tian, Yu, Mao, Li, Liu, Xu, Huang, Lv and Pan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qianzhou Lv, MTM5MTYwODg5MzhAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Kunming Pan, cGFuLmt1bm1pbmdAenMtaG9zcGl0YWwuc2guY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Dan Tian
Dan Tian Nianxi Yu2,†
Nianxi Yu2,† Tianxiao Mao
Tianxiao Mao Dong Huang
Dong Huang Qianzhou Lv
Qianzhou Lv Kunming Pan
Kunming Pan