- 1Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China
- 3Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and outcomes of embolo/sclerotherapy in treating Schobinger Stage IV peripheral arteriovenous malformations (pAVMs) associated with high-output cardiac failure (HOCF).
Methods: Between January 2017 and December 2024, 12 patients with Schobinger Stage IV pAVMs and associated HOCF were treated with embolization using coils and sclerosing agents, including bleomycin polidocanol foam (BPF) and anhydrous ethanol. Procedural outcomes, complications, devascularization and improvements in cardiac function were evaluated during follow-up.
Results: A total of 24 embolo/sclerotherapy sessions were performed on the 12 patients. Complete or over 80% devascularization of the vascular malformations was achieved in 9 patients. Echocardiographic follow-up revealed significant improvements in cardiac ejection fraction and ventricular dilatation. Additionally, 8 patients showed improvement in heart valve regurgitation. For all patients, the symptom of dyspnea disappeared after embolization and no serious complications occurred. LVEF improvement showed a significant positive correlation with a decrease in venous drainage pressure of the nidus after surgery (P < 0.001) in 11 patients, while one patient was excluded due to an increase in venous drainage post-surgery.
Conclusion: This study provides evidence that embolo/sclerotherapy effectively treats pAVMs with associated HOCF by reducing abnormal blood flow and significantly improving symptoms. The results also reveal a linear relationship between the decrease in venous drainage pressure and improvement in LVEF in patients with HOCF caused by pAVMs after embolo/sclerotherapy.
Introduction
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are congenital vascular abnormalities caused by a birth defect, resulting in direct connections between primitive reticular networks of dysplastic vessels which referred to “nidus” (1). As aggressive congenital high-flow vascular lesions, AVMs are characterized by shunting of high velocity, low resistance flow from the arterial vasculature into the venous system (2), necessitating early intervention. Delayed treatment can lead to chronic vascular “steal phenomenon”, this condition can result in ventricular remodeling and myocardial dysfunction, and eventually progress to high-output cardiac failure (HOCF) (3, 4). AVMs are prone to complications such as pain, pulsations, swelling, and ulcerations. Clinical staging is typically based on the Schobinger classification, with Stage IV indicating systemic symptoms, including cardiac failure. Schobinger Stage IV AVMs usually appear in early adulthood, with symptoms often developing between the ages of 10 and 40, according to the Mayo Clinic and the Cleveland Clinic. While some individuals may have symptoms present at birth or develop them later in childhood, the peak incidence of symptomatic AVMs, including those classified as Schobinger Stage IV, generally occurs within this early adulthood range.
In HOCF, the predominant phenotype is characterized by enlarged cardiac chambers, typically caused by arteriovenous shunts (5). HOCF can cause further morbidity and mortality due to its impact on various complications, including structural heart changes, pulmonary hypertension, and dysfunction of other organs. Effective treatment to reduce the cardiac burden can significantly improve patients' quality of life and survival rates. Conventional heart failure medications offer limited symptomatic relief, whereas treatment aimed at correcting the abnormal arteriovenous shunting results in substantial improvement in heart failure symptoms.
The primary goal in treating pAVMs associated with HOCF is to unload the heart, thereby aiding recovery from cardiac volume overload. Embolization and sclerotherapy have proven clinically effective in managing these patients. Embolization is considered the main endovascular therapy and typically involves the use of various coils. Sclerotherapy, on the other hand, is a widely used, low-risk, and highly successful option for treating malformation. Our previous research has demonstrated the effectiveness of bleomycin-polidocanol foam (BPF) as a sclerosing agent in the treatment of AVMs (6). Polidocanol helps alleviate pain and enhances the ability to better fill the lesion area in foam form (7). Bleomycin further strengthens the sclerosing effect (8). When combined with anhydrous ethanol, which completely destroys vascular endothelial cells and blocks vascular reperfusion, BPF improves treatment outcomes and reduces recurrence rates (2, 9). Therefore, BPF combined with anhydrous ethanol was chosen as the sclerosing agent for this study.
Currently, due to the rarity of clinical cases of HOCF caused by pAVMs, no consensus exists on a standardized treatment strategy. This study aims to retrospectively analyze the effectiveness of coil embolization combined with sclerotherapy in treating patients with Schobinger Stage IV.
Materials and methods
Patients
This study was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of China-Japan Friendship Hospital (2024-KY-246-1), and informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to data collection. In this retrospective study, all patients with HOCF caused by pAVMs who underwent embolo/sclerotherapy between May 2017 and December 2024 were included. The average age of the cohort was 42 years (range: 13–65 years), with all patients primarily receiving coil embolization combined with sclerosing agents.
Inclusion criteria were: 1. echocardiographic evidence of cardiac failure; 2. symptoms, signs, angiography, and physical examination consistent with Schobinger Stage IV; 3. lesions located in the head, neck, or limbs. Exclusion criteria included patients with congenital heart disease (right-to-left-shunt), or contraindications to polidocanol or anhydrous ethanol.
All 12 patients experienced limb edema, pain, and exertional dyspnea (100%). Echocardiography revealed varying degrees of cardiac enlargement in all 12 patients, 8 of whom had atrioventricular valve regurgitation. According to the New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification of heart failure, 6 patients were classified as NYHA IV. Other indications included hyperpigmentation (n = 5, 41.7%), vascular murmurs (n = 4, 33.3%), pulsations (n = 3, 25%), and ulcerations (n = 2, 16.7%). All patients presented with some degree of psychosocial burden at the time of presentation.
Among the 12 patients, 4 (33.3%) had undergone unsuccessful treatments at other hospitals before admission to our institution. Of these 4 patients, 1 (8.3%) had undergone stent placement, 1 (8.3%) had undergone arterial ligation, sclerotherapy, stent placement, radiofrequency ablation, and venous ligation, and 1 (8.3%) had undergone unsuccessful sclerotherapy. All 12 patients reported the presence of pAVMs at birth, and 1 (8.3%) noted recognizable expansion of the lesion during pregnancy. Baseline demographic data are presented in Table 1.
The treatment strategy was determined through a multidisciplinary approach. The decision regarding the proposed treatment method was made following a collaborative discussion among interventional adiologists, anesthesiologists, cardiologists, respiratory specialists, and vascular surgeons.
Technique
All procedures were performed under general anesthesia. Continuous pulmonary artery monitoring was performed if the expected total ethanol dosage exceeded 0.5 ml/kg (10).
Baseline angiography was conducted to assess the extent and hemodynamic characteristics of AVMs. The angiographic findings determined the appropriate treatment approach. The angiographic classification was based on the consensus of two interventional radiologists, in accordance with the Yakes classification system (11).
The markedly dilated dominant drainage vein (RDDOV) was identified on the angiogram (Figure 1A). A guidewire and catheter system (Cordis, Florida, USA) were introduced through the needle and advanced into the dilated venous sac. The catheter tip was positioned as close as possible to the outlet of the RDDOV. Coils (Cook, Bloomington, IN, USA) and interlock detachable coils (IDCs) (Boston Scientific, Marlborough, Massachusetts) were deployed to embolize the RDDOV (Figure 1B). After the confirmation of slow flow in the AVM lesions, the sclerosing agent was initiated through a transvenous approach (Figure 1C). If venous embolization failed, a direct puncture approach was considered as an alternative. Postoperative angiography demonstrated the extent of devascularization achieved (Figure 1D). The technique for treating pAVMs with HOCF is summarized in Figure 1.
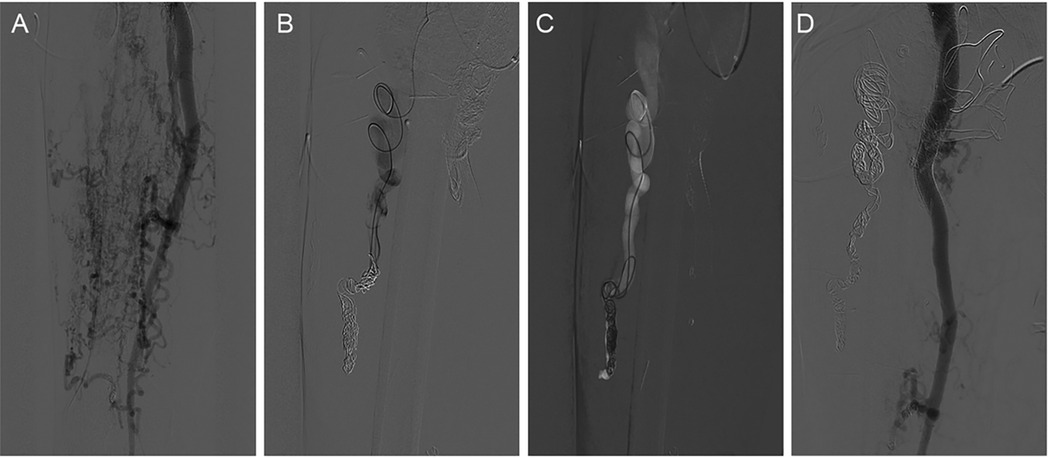
Figure 1. Case1 with the complaint of progressive dyspnea for 2year. A HOCF patient with right lower extremity arteriovenous malformations. (A) Preoperative baseline angiography shows Yakes IIIB type. (B) A total of 16 interlock detachable coils (IDCs) and 22 coils were used. (C) A total of 20 ml of 3% BPF and 5 ml of ethanol were injected. (D) Follow-up angiography via the right common iliac artery showed a devascularization degree of 60%.
During the interventional embolization procedure, the injection volume and rate of the sclerosing agents were carefully controlled to ensure adequate filling of the nidus. Careful attention was given to avoiding over-injection of the sclerosing agent, as over-injection could lead to reflux, ectopic embolism and severe complications.
Follow-up
Follow-up was completed in the outpatient clinic at 3-month intervals—specifically at 3, 6, and 12 months—including physical examinations and echocardiography. If symptoms were not relieved or recurred during the follow-up period, additional treatment was recommended.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS software version 26.0. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Changes in vascular and venous pressure, as well as echocardiographic indices between baseline and the final treatment session, were assessed using a paired t-test. Pearson correlation analysis was conducted to examine the relationship between a reduction in venous drainage pressure and LVEF. A two-sided p-value of <0.05 was regarded as statistically significant.
Results
Degree of devascularization and improvement in symptoms
Super-selective angiography revealed that AVMs were located in the left lower limb (n = 7, 58.3%), right lower limb (n = 4, 33.3%), and right upper limb (n = 1, 8.3%) in the 12 patients. According to the Yakes classification, all 12 patients were classified as Type III B (n = 4, 33.3%), Type II B (n = 4, 33.3%), Type IV (n = 2, 18.3%), III A (n = 1, 8.3%), and Type II A (n = 1, 8.3%).
A total of 24 embolo/sclerotherapy sessions were performed (mean 2; range 1–3). The results demonstrated substantial efficacy, with 5 patients (41.7%) achieving >90% devascularization, 4 patients (33.3%) achieving 80%, and 3 (25.0%) patients achieving >60%, as shown in Table 2.
All the 12 patients initially classified as Schobinger stage IV were downgraded to stage I (n = 10, 83.3%) and stage II (n = 2, 16.7%) following the procedure. Dyspnea was the primary reason for seeking intervention in all 12 patients. Postoperatively, 2 (16.7%) had complete relief, and 10 (83.3%) experienced major improvement in dyspnea. No significant complications were encountered during the hospitalization of the 12 patients as shown in Table 3.
Postoperatively, the patients' previously high pressure in venous drainage (P = 0.049) due to nidus decreased significantly, but not in vascular drainage (P = 0.395), Table 4.
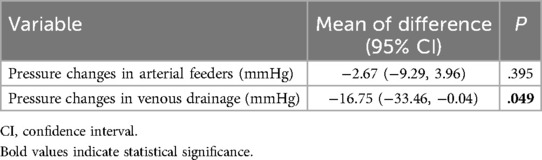
Table 4. Comparison between pre- and post-operative pressure in arterial feeders and venous drainage of nidus.
Echocardiography result
Echocardiographic examination revealed that, postoperative regurgitation was reduced in all 8 (66.7%) patients who had valvular regurgitation as shown in Table 5. The preoperative dilation of left ventricular end-diastolic dimension (LVDd) (P < 0.001), left ventricular end-systolic dimension (LVDs) (P = 0.016), right atrial diameter (RAD) (P = 0.002), and right ventricular basal diameter (RVD1) (P = 0.002) all decreased with statistical significance, as well as the elevated pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP) (P = 0.034). Also, the LVEF improved after surgery (P < 0.01) as shown in Table 6.
Correlation between decreased pressure in venous drainage and LEVF in patients with HOCF caused by pAVMs after embolo/sclerotherapy
Excluding one case of elevated venous drainage pressure following surgery, further analysis of the linear relationships between reductions in venous drainage pressure, devascularization, and the improvement of LVEF in 11 patients with HOCF caused by pAVMs as shown in Table 7, indicated that LVEF improvement (P < 0.001) was significantly positively correlated with decrease in venous drainage pressure of nidus (r = 0.923) through surgery, and the scatter plots of correlation were plotted in Figure 2.

Table 7. The correlation between pressure in venous drainage, devascularization and left ventricular ejection fraction in patients before and after embolo/sclerotherapy.

Figure 2. Scatter plots of correlation between changes in venous drainage pressure and LVEF improvement of patients with HOCF caused by pAVMs after embolo/sclerotherapy.
Discussion
AVMs are the second leading cause of HOCF (12). HOCF resulting from pAVMs remains a challenging clinical issue. Severe pAVMs may result in systemic arterial hypotension and neurohormonal activation. However, the use of conventional heart failure medications may reduce systemic vascular resistance, potentially exacerbating the condition (13). Historically, treatment options for AVMs included resection and ligation, which, while effective, were associated with significant complications, such as increased intraoperative bleeding risk and limited impact on recurrence rates (14).
The advancement of endovascular techniques and novel embolic agents has made embolization and sclerotherapy the primary treatments for AVMs. These methods significantly improve outcomes by reducing the flow rate in major draining veins and addressing the underlying causes of high-output states (15–17). The primary treatment goal for pAVMs with HOCF is to eliminate abnormal pathways and reduce cardiac volume overload, thereby improving patients' quality of life.
Endovascular embolization for pAVMs includes transarterial, transvenous, and direct puncture approaches. Compared with the transarterial route, the transvenous approach may achieve curative embolization of pAVMs more effectively (18). Studies have shown that transvenous pAVM embolization is associated with higher complete occlusion rates and relatively lower complication and recurrence rates (19). Although veins are generally thinner than arteries, the arterialized venous walls found in AVMs are thicker (20). Additionally, advances in microcatheter and microwire technologies have improved the accuracy and safety of transvenous catheterization in recent years. Furthermore, the direct puncture approach enables more precise delivery of embolic agents to the nidus.
In this study, a treatment strategy combining transvenous embolization and direct puncture approaches was chosen for the 12 patients. To mitigate potential complications from percutaneous puncture, such as hematoma or embolic agent leakage at the puncture site, manual compression time at the puncture site was extended post-procedure. Consequently, no complications were observed in this study.
In embolo/sclerotherapy, the use of coils offers advantages in limiting the spread of embolic agents, reducing complications, and minimizing intraoperative bleeding (21). This approach helps control the reflux of embolization materials, facilitating complete occlusion of fistulous areas and potential abnormal shunts (16, 22). The choice of coil length and stiffness depends on the location and morphology of the malformation. High coil density within the vessel is essential for effectively reducing flow velocity (23, 24). Surgeons must measure and operate precisely to prevent complications, such as ectopic embolization. Additionally, the use of conventional coils in combination with IDC coils improves localization and release accuracy, allowing for easier adjustments (25). After transvenous embolization, some patients received ethanol injections into the feeding artery of AVMs, followed by transarterial embolization. This approach significantly improved the efficacy of transvenous embolization and reduced recurrence rates when compared to pure arterial embolization.
In the previous study, we evaluated the safety and efficacy of BPF as a sclerosing agent (26). Both polidocanol and bleomycin are widely used as clinical sclerosants. Polidocanol exhibits concentration-dependent efficacy in occluding blood vessels, while bleomycin promotes vascular endothelial damage and fibrosis (27, 28). To enhance drug contact with the vasculature and reduce washout rates in the lesion area, BPF is typically prepared as foam for clinical use. Our previous study confirmed that BPF achieves greater lesion volume reduction in AVM treatment than polidocanol foam alone (29). Anhydrous ethanol, while highly effective in symptom improvement or resolution in AVM patients (30), is associated with significant toxicity (31), particularly cardiotoxicity, such as arrhythmias and right heart failure (32, 33). Given that all patients in this study presented with HOCF, a combination of anhydrous ethanol and the milder BPF was chosen to balance efficacy and safety (8, 34, 35).
HOCF, although rare, represents a severe complication in pAVM patients. Our approach aimed to improve cardiac function through devascularization. While previous studies primarily assessed cardiac improvement using NYHA functional class and clinical indicators, this study also analyzed echocardiographic results. Comparisons of pre- and post-operative echocardiograms revealed significant cardiac remodeling, with statistically significant improvements in LVDd, LVEF, and PASP, among other parameters. These findings provide strong evidence of improvement in cardiac function. While some studies classify this type of cardiac failure as preserved ejection fraction heart failure, delayed diagnosis and treatment may have resulted in reduced ejection fraction.
This study demonstrated a linear relationship between the reduction in venous pressure in the nidus drainage and the improvement of LEVF in patients with HOCF caused by pAVMs through embolo/sclerotherapy. Previously, postoperative devascularisation was considered a factor contributing to improvements in cardiac failure associated with pAVMs; however, our study found no statistical significance related to this.
All 12 patients in this study experienced significant psychosocial stress due to their malformations. The psychological burden was exacerbated by the chronicity and progression of the condition, as many patients had lived with their malformations for extended periods before seeking treatment. All patients noted significant improvement in the appearance of the affected limb and expressed satisfaction with the cosmetic outcomes post-surgery. These findings underscore the importance of addressing both physical and psychological aspects of pAVMs to enhance patients' quality of life.
This study has limitations. High-flow AVMs require timely and early treatment, but late presentation with severe heart failure symptoms and the high cost of treatment presented challenges. The small sample size and loss to follow-up due to prolonged staged treatment limited the study. As a retrospective study, future research should incorporate prospective designs with larger patient cohorts for more accurate evaluation and enhanced follow-up protocols.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Clinical Research Ethics Committee of China-Japan Friendship Hospital (2024-KY-246-1). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
XG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. QN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. KZ: Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. BN: Data curation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YY: Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. ZY: Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft. PL: Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XF: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding (2024-NHLHCRF-PY II-04).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Lee BB, Baumgartner I, Berlien HP, Bianchini G, Burrows P, Do YS, et al. Consensus document of the international union of angiology (IUA)-2013. Current concept on the management of arterio-venous malformations. Int Angiol. (2013) 32(1):9–36.23435389
2. Zhou J, Hua C, Yang X, Jia H, Yu W, Jin Y, et al. Ethanol embolotherapy for cutaneous erythema of high-flow vascular malformations in the head and neck. Dermatol Surg. (2023) 49(11):1017–22. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000003923
3. Reddy YNV, Obokata M, Dean PG, Melenovsky V, Nath KA, Borlaug BA. Long-term cardiovascular changes following creation of arteriovenous fistula in patients with end stage renal disease. Eur Heart J. (2017) 38(24):1913–23. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx045
4. McCullough PA, Rios A, Smith B. Dialysis fistulas and heart failure. Eur Heart J. (2017) 38(24):1924–5. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx114
5. de Ávila DX, Villacorta H, de Andrade Martins W, Mesquita ET. High-output cardiac failure: a forgotten phenotype in clinical practice. Curr Cardiol Rev. (2022) 18(1):e050821195319. doi: 10.2174/1573403X17666210805142010
6. Liu JW, Ni B, Gao XX, He B, Fan XQ, Nie QQ, et al. Comparison of bleomycin polidocanol foam vs electrochemotherapy combined with polidocanol foam for treatment of venous malformations. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. (2024) 12(5):101911. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2024.101911
7. Zhang W, Chen G, Ren JG, Zhao YF. Bleomycin induces endothelial mesenchymal transition through activation of mTOR pathway: a possible mechanism contributing to the sclerotherapy of venous malformations. Br J Pharmacol. (2013) 170(6):1210–20. doi: 10.1111/bph.12355
8. Sun LM, Ni XD, Yuan SM. The efficacy of absolute ethanol and polidocanol in the treatment of venous malformations. J Craniofac Surg. (2020) 31(3):e272–5. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000006268
9. Lee BB, Kim DI, Huh S, Kim HH, Choo IW, Byun HS, et al. New experiences with absolute ethanol sclerotherapy in the management of a complex form of congenital venous malformation. J Vasc Surg. (2001) 33(4):764–72. doi: 10.1067/mva.2001.112209
10. Jo JY, Chin JH, Park PH, Ku SW. Cardiovascular collapse due to right heart failure following ethanol sclerotherapy: a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. (2014) 66(5):388–91. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2014.66.5.388
11. Frey S, Haine A, Kammer R, von Tengg-Kobligk H, Obrist D, Baumgartner I. Hemodynamic characterization of peripheral arterio-venous malformations. Ann Biomed Eng. (2017) 45(6):1449–61. doi: 10.1007/s10439-017-1821-9
12. Reddy YNV, Melenovsky V, Redfield MM, Nishimura RA, Borlaug BA. High-output heart failure: a 15-year experience. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2016) 68(5):473–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.05.043
13. Mehta PA, Dubrey SW. High output heart failure. QJM. (2009) 102(4):235–41. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcn147
14. Kim R, Do YS, Park KB. How to treat peripheral arteriovenous malformations. Korean J Radiol. (2021) 22(4):568–76. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0981
15. Chen Y, Han H, Jin H, Zhang H, Wang Y, Liu X, et al. Association of embolization with long-term outcomes in brain arteriovenous malformations: a propensity score-matched analysis using nationwide multicenter prospective registry data. Int J Surg. (2023) 109:1900–9. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000341
16. Carqueja IM, Sousa J, Mansilha A. Vascular malformations: classification, diagnosis and treatment. Int Angiol. (2018) 37(2):127–42. doi: 10.23736/S0392-9590.18.03961-5
17. Hwang JH, Do YS, Park KB, Chung HH, Park HS, Hyun D. Embolization of congenital renal arteriovenous malformations using ethanol and coil depending on angiographic types. J Vasc Interv Radiol. (2017) 28(5):64. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2016.09.004
18. Chen C-J, Norat P, Ding D, Mendes GAC, Tvrdik P, Park MS, et al. Transvenous embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations: a review of techniques, indications, and outcomes. Neurosurg Focus. (2018) 45(1):E13. doi: 10.3171/2018.3.FOCUS18113
19. Pollak JS, Egglin TK, Rosenblatt MM, Dickey KW, White RI Jr. Clinical results of transvenous systemic embolotherapy with a neuroradiologic detachable balloon. Radiology. (1994) 191(2):477–82. doi: 10.1148/radiology.191.2.8153325
20. Scherschinski L, Rahmani R, Srinivasan VM, Catapano JS, Oh SP, Lawton MT. Genetics and emerging therapies for brain arteriovenous malformations. World Neurosurg. (2022) 159:327–37. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.10.127
21. Parizadeh D, Vasconcelos AHC, Miller DA, Fermo OP, Huynh TJ. Dual microcatheter and coil/balloon pressure cooker technique for transvenous embolization of cerebrospinal fluid-venous fistulas. J Neurointerv Surg. (2023) 15(6):614. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2022-019005
22. Ihn YK, Kim BM, Suh SH, Kim DJ, Kim DI. Coil-protected embolization technique for a branch-incorporated aneurysm. Korean J Radiol. (2013) 14(2):329–36. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.329
23. Fujimura S, Takao H, Suzuki T, Dahmani C, Ishibashi T, Mamori H, et al. Hemodynamics and coil distribution with changing coil stiffness and length in intracranial aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg. (2018) 10(8):797–801. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2017-013457
24. Lamano JB, Bushnell GG, Chen H, Badrinathan A, El Tecle NE, Bendok BR, et al. Force characterization of intracranial endovascular embolization: coil type, microcatheter placement, and insertion rate. Neurosurgery. (2014) 75(6):707–16. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000000525
25. Chen Y, Qin W, Zhu Z, Wang X, Yu W, Li F, et al. Interlocking detachable coil embolization for giant tandem bronchial aneurysms: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). (2021) 100(51):e28416. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028416
26. Ni B, Liu J-w, Fan X-q, He B, Nie Q-q, Ye Z-d, et al. Clinical outcomes and predictors of bleomycin polidocanol foam sclerotherapy treatment response in venous malformations. J Int Med Res. (2024) 52(1):3000605231223441. doi: 10.1177/03000605231223441
27. Parsi K. Interaction of detergent sclerosants with cell membranes. Phlebology. (2015) 30(5):306–15. doi: 10.1177/0268355514534648
28. Heit JJ, Do HM, Prestigiacomo CJ, Delgado-Almandoz JA, English J, Gandhi CD, et al. Guidelines and parameters: percutaneous sclerotherapy for the treatment of head and neck venous and lymphatic malformations. J Neurointerv Surg. (2017) 9(6):611–7. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2015-012255
29. He B, Yang B, Nie Q-q, Zhang J-b, Chen J, Liu P, et al. Comparison of polidocanol foam versus bleomycin polidocanol foam for treatment of venous malformations. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. (2023) 11(1):143–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2022.06.005
30. van der Vleuten CJ, Kater A, Wijnen MH, Schultze Kool LJ, Rovers MM. Effectiveness of sclerotherapy, surgery, and laser therapy in patients with venous malformations: a systematic review. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. (2014) 37(4):977–89. doi: 10.1007/s00270-013-0764-2
31. Odeyinde SO, Kangesu L, Badran M. Sclerotherapy for vascular malformations: complications and a review of techniques to avoid them. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. (2013) 66(2):215–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2012.09.002
32. Mustroph J, Lebek S, Maier LS, Neef S. Mechanisms of cardiac ethanol toxicity and novel treatment options. Pharmacol Ther. (2019) 197:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.12.006
33. Wong GA, Armstrong DC, Robertson JM. Cardiovascular collapse during ethanol sclerotherapy in a pediatric patient. Paediatr Anaesth. (2006) 16(3):343–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2005.01710.x
34. Wijnands TF, Schoenemeier B, Potthoff A, Gevers TJ, Groenewoud H, Gebel MJ, et al. Ethanol sclerotherapy or polidocanol sclerotherapy for symptomatic hepatic cysts. United European Gastroenterol J. (2018) 6(6):919–25. doi: 10.1177/2050640618764940
Keywords: peripheral arteriovenous malformations, high-output cardiac failure, embolo/sclerotherapy, devascularization, pressure of venous drainage
Citation: Guo X, Nie Q, Zheng K, Ni B, Yang Y, Ye Z, Liu P and Fan X (2025) Efficacy of embolo/sclerotherapy in the treatment of high-output cardiac failure caused by peripheral arteriovenous malformations. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1592077. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1592077
Received: 27 March 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 1 September 2025.
Edited by:
Salah D. Qanadli, Université de Lausanne, SwitzerlandReviewed by:
Robert Ruemmler, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, GermanyEdit Dósa, Semmelweis University, Hungary
Rodolfo Arantes, University of Ribeirão Preto, Brazil
Copyright: © 2025 Guo, Nie, Zheng, Ni, Yang, Ye, Liu and Fan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Peng Liu, bGl1cGVuZzU0MTdAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Xueqiang Fan, ZmFueHVlcWlhbmc3OEBmb3htYWlsLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xixi Guo
Xixi Guo Qiangqiang Nie
Qiangqiang Nie Kai Zheng
Kai Zheng Bin Ni
Bin Ni Yuguang Yang2
Yuguang Yang2 Peng Liu
Peng Liu