Abstract
Background:
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) poses a critical challenge to global public health, especially in individuals with Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) syndrome. The association between the triglyceride glucose-waist-to-height ratio index (TyG-WHtR) and CVD among middle-aged and older Chinese adults with CKM stages 0–3 is not well understood.
Methods:
Data were obtained from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS), a nationally representative longitudinal study of individuals aged 45 years and older. Cox proportional hazards models were constructed to evaluate the association between TyG-WHtR and CVD risk. Subgroup analyses were conducted among different groups to evaluate consistency of findings and explore potential interactions. Restricted cubic spline regression was employed to evaluate the dose-response relationship.
Results:
During a mean follow-up period of 7.77 ± 2.13 years, 1,595 participants (23.58%) developed CVD. After adjusting for covariates, TyG-WHtR was significantly associated with CVD risk (HR: 1.09, 95% CI: 1.01–1.18). Notably, this relationship was independent of other variables and displayed a nonlinear pattern, with an inflection point identified at 3.57. Beyond this threshold, the adjusted HR increased to 1.17 (95%CI: 1.08–1.71).
Conclusion:
TyG-WHtR demonstrates a nonlinear relationship with CVD among middle-aged and older Chinese adults with CKM stages 0–3.
1 Introduction
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the foremost contributor to global mortality, accounting for 32% of fatalities in 2019 (1). Although the global CVD mortality rate declined by 14.5% from 2000 to 2019, the absolute burden of the disease continues to rise, particularly in Asia (2). In China, CVD-related disability-adjusted life years increased by 58.5% between 1990 and 2019, highlighting the urgent need for improved risk assessment and prevention strategies tailored to the Chinese population (3).
The pathophysiological relationship between metabolic disorders and CVD has been extensively investigated, with obesity and insulin resistance emerging as critical modifiable risk factors. Body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC) have shown limited effectiveness in accurately representing metabolic risks associated with central adiposity (4). The waist-to-height ratio (WHtR) demonstrates a more robust correlation with CVD (5). The WHtR is more effective than alternative body measurement methods in predicting cardiovascular outcomes, significantly exceeding both BMI and WC (6). At the same time, triglyceride-glucose (TyG) has emerged as a trustworthy indicator of insulin resistance (7, 8). Numerous studies across diverse Asian populations, including those from China, Thailand, and South Korea, have consistently demonstrated an independent association between TyG and CVD (9–11). These results highlight the necessity of incorporating both lipid metabolism and glycemic control in the evaluation of cardiovascular risk.
Recently, a composite marker that combines TyG and WHtR, known as TyG-WHtR, has been introduced to encapsulate glucose and lipid metabolism disorders along with central obesity into a unified measurement. A study from the US, UK, and China indicates that among hypertensive populations, TyG and its related indices are associated with CVD in a U-shaped pattern (12). In populations with metabolic abnormalities, the advantages of TyG-WHtR remain evident (13, 14). In 2013, the American Heart Association first conceptualized Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) syndrome, integrating the complex interconnections among metabolic risk factors, chronic kidney disease (CKD), and cardiovascular disease (15, 16). A 2024 study established a linear relationship between TyG-BMI and CVD specifically within the CKM stages 0–3 population (17). Therefore, we hypothesized that TyG-WHtR exhibits a dose-response relationship with CVD incidence in this cohort and aimed to identify potential inflection points.
In this study, we utilized a substantial longitudinal cohort derived from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) to analyze the dose-response correlation between TyG-WHtR and CVD among middle-aged and older Chinese adults with CKM stages 0–3.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design and population
CHARLS is a prominent nationally representative longitudinal survey targeting individuals aged 45 years and older. The initial assessment (2011–2012) employed stratified sampling methodology spanning 28 provinces, encompassing 150 counties and 450 communities across mainland China. Additional surveys were completed in 2013, 2015, 2018, and 2020 to document evolving health, social, and economic metrics. This research received approval from Peking University's Biomedical Ethics Committee (IRB00001052-11015) and secured informed consent from participants.
We used data from the first wave (2011–2012) for this analysis, focusing on participants for whom blood sample data were available. The data analysis excluded cases under the following criteria: those lacking BMI data (n = 4,078), participants without CVD follow-up information (n = 647), participants missing baseline CVD details (n = 1,816), those without WC data (n = 27), participants lacking FBG data (n = 3,852), tumor patients or participants with missing tumor information (n = 74), participants lacking a history of diabetes and hypertension data (n = 158), and instances missing baseline variable data (n = 74). Finally, participants without CKM data and those in CKM stage 4 were excluded (n = 218). 6,764 participants were included in this study for analysis (Figure 1).
Figure 1
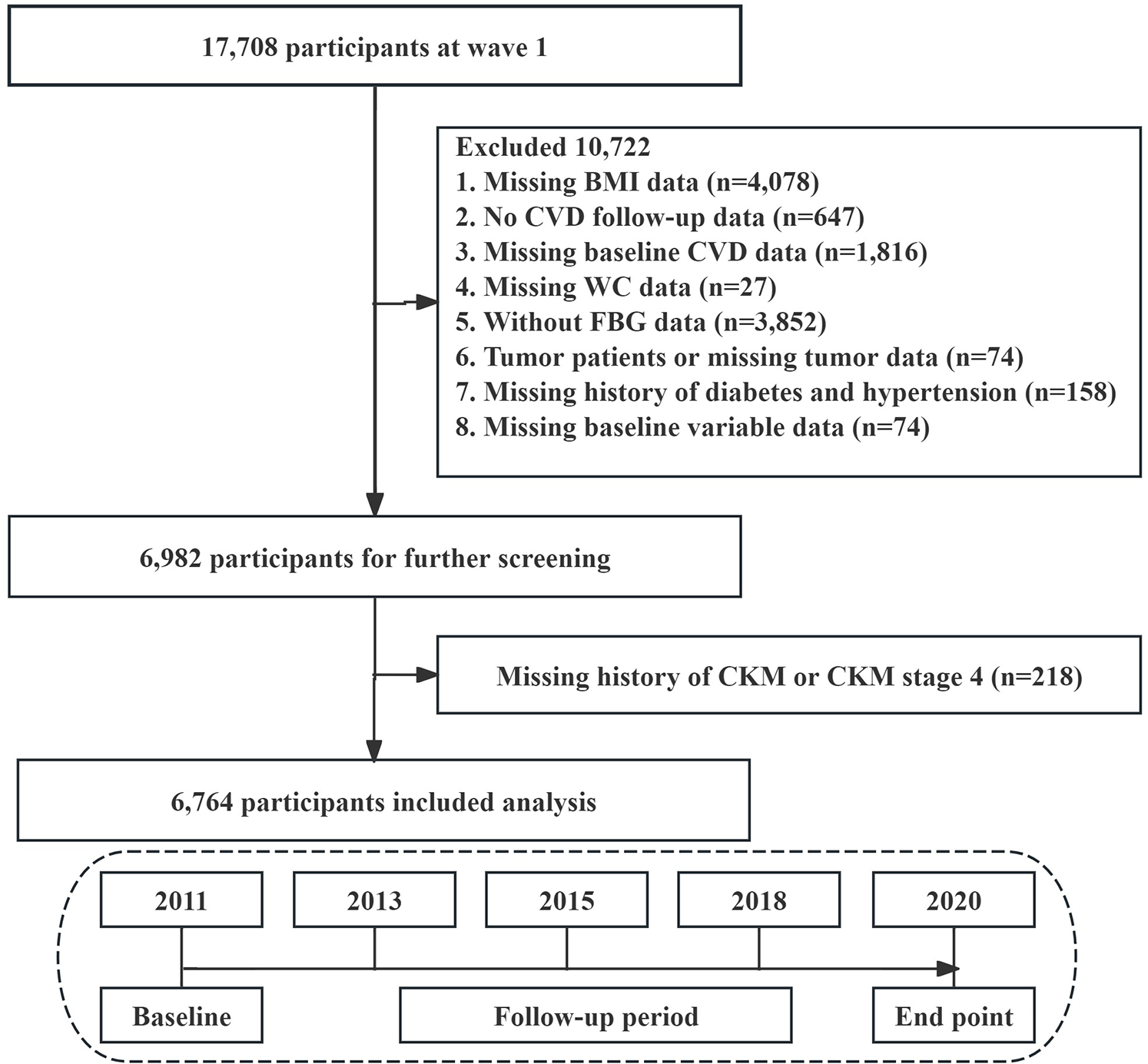
Flowchart of the selection process of study subjects.
2.2 Determination of CVD and calculation of TyG-WHtR
In this study, CVD constituted the principal outcome of interest. CVD status was determined based on participants' self-reported medical histories, elicited through a structured health questionnaire during face-to-face interviews. Study subjects reported whether a healthcare professional had diagnosed them with heart failure, myocardial infarction, angina, coronary heart disease, or stroke (18). A positive response to any of these conditions led to the participant's classification as having CVD.
TyG-WHtR = Ln[TG (mg/dl) × glucose (mg/dl)/2] × [WC (cm)/height (cm)] (19).
2.3 Definition of CKM syndrome stages 0 to 4
The staging framework for Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) syndrome classifies disease progression across five distinct phases (0–4):
Stage 0: Absence of recognized CKM risk factors;
Stage 1: Characterized by excess adiposity (abdominal obesity) and/or impaired glucose regulation (prediabetes);
Stage 2: Manifestation of confirmed metabolic dysfunction (including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia) or renal impairment;
Stage 3: Presence of asymptomatic cardiovascular pathology within the CKM context
Stage 4: Established clinical cardiovascular disease (encompassing coronary artery disease, heart failure, cerebrovascular events, peripheral arterial disease, or atrial fibrillation) with underlying CKM pathophysiology (20).
2.4 Ascertainment of covariates
Our investigation utilized the CHARLS dataset, which provides extensive health-related variables for participants aged 45 and above. Professional interviewers conducted standardized data collection procedures. Comprehensive data collection encompassed multiple domains. Demographic characteristics included age, gender, educational attainment, marital status (married/unmarried), medication history (yes/no), and residential environment (rural/urban). Current lifestyle behaviors, particularly smoking status and alcohol consumption patterns, were systematically documented. Anthropometric measurements were conducted under standardized conditions, with participants instructed to remove shoes and heavy clothing before assessment of height, weight, and blood pressure parameters.
Blood specimen collection followed a mandatory minimum 8 h fasting period. Laboratory analyses employed standardized enzymatic methodologies to quantify multiple biochemical parameters: fasting blood glucose (FBG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), uric acid (UA), HbA1c, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and C-reactive protein (CRP). All research procedures strictly adhered to established ethical guidelines and protocols throughout the study duration. The covariates included in this study were carefully selected, building on the methodologies and analytical frameworks utilized in previously published research that also analyzed data from the CHARLS database (21). Additionally, cardiovascular-related indicators, such as UA, CRP, and BUN, were included in the analysis (22–24).
2.5 Statistical analysis
Summary statistics included means ± standard deviations or medians (interquartile ranges) for continuous variables, and frequencies (percentages) for categorical data. Between-group differences were assessed using one-way ANOVA or Kruskal–Wallis tests for continuous variables, and Chi-square tests for categorical variables. We evaluated multicollinearity through Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) calculations, excluding variables with VIF values exceeding 5 from subsequent analyses (Supplementary Table S1). Our statistical framework employed multiple approaches to examine metabolic parameters and diabetes relationships. The investigation began with univariate Cox regression, followed by comprehensive multivariate analysis. Three models were established: Model I (unadjusted), Model II (adjusted for demographic and clinical factors such as marital status, rural residence, hypertension, drinking status, smoking status, medication history, CKM, SBP, DBP, age, and education), and Model III (further adjusted for biochemical markers, including HDL-C, LDL-C, CRP, BUN, UA, and HbA1c). To evaluate result consistency, we conducted stratified analyses across various population subsets: age groups (<60 vs. ≥60 years), gender categories, BMI classifications (<24 kg/m2 vs. ≥24 kg/m2), smoking and alcohol consumption patterns, and presence of metabolic conditions including diabetes and dyslipidemia. Potential interactions between subgroup variables were also assessed. Dose-response relationships underwent examination through restricted cubic spline analysis with four knots, utilizing two-segment logistic regression to identify critical threshold points. Statistical analyses utilized EmpowerStats and R software, with significance determined by a two-tailed p-value threshold of 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics of participants
This study included 6,764 participants, comprising 3,620 females and 3,144 males, with an average age of 58.47 ± 9.50 years. Over a follow-up period of 7.77 ± 2.13 years, 1,595 individuals (23.58%) developed CVD. Participants in the highest TyG-WHtR quartile (Q4) exhibited markedly worse metabolic parameters and higher CVD prevalence compared to lower quartiles (Table 1). Notably, cardiometabolic comorbidities increased progressively across quartiles, with hypertension prevalence rising from 30.51% (Q1) to 61.92% (Q4), diabetes from 5.38% to 28.86%, and dyslipidemia from 3.14% to 12.90%. An incremental trend was observed between TyG-WHtR levels and CVD risk (Figure 2). CVD prevalence nearly doubled from Q1 (18.10%) to Q4 (30.46%).
Table 1
| Characteristic | Q1 (<4.09) | Q2 (4.09 to 4.58) | Q3 (4.59 to 5.13) | Q4 (>5.13) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subjects, n | 1,691 | 1,691 | 1,691 | 1,691 | |
| Age, years | 58.35 ± 9.60 | 57.93 ± 9.50 | 58.27 ± 9.43 | 59.34 ± 9.44 | <0.001 |
| Gender | <0.001 | ||||
| Female | 602 (35.60%) | 831 (49.14%) | 977 (57.78%) | 1,210 (71.56%) | |
| Male | 1,089 (64.40%) | 860 (50.86%) | 714 (42.22%) | 481 (28.44%) | |
| Married, n (%) | 1,504 (88.94%) | 1,519 (89.83%) | 1,514 (89.53%) | 1,487 (87.94%) | 0.304 |
| Rural, n (%) | 1,221 (72.21%) | 1,172 (69.31%) | 1,062 (62.80%) | 992 (58.66%) | <0.001 |
| SBP, mmHg | 123.71 ± 19.88 | 126.69 ± 20.09 | 130.75 ± 20.52 | 136.90 ± 21.70 | <0.001 |
| DBP, mmHg | 72.28 ± 11.59 | 74.09 ± 11.82 | 76.28 ± 11.86 | 79.01 ± 11.80 | <0.001 |
| BUN, mg/dl | 16.24 ± 4.62 | 15.61 ± 4.50 | 15.61 ± 4.52 | 15.27 ± 4.26 | <0.001 |
| FBG, mg/dl | 99.22 ± 17.96 | 103.12 ± 22.54 | 107.93 ± 29.03 | 124.05 ± 47.15 | <0.001 |
| TC, mg/dl | 182.75 ± 35.79 | 189.39 ± 34.90 | 197.26 ± 36.50 | 205.31 ± 40.22 | <0.001 |
| TG, mg/dl | 78.28 ± 39.60 | 100.58 ± 47.10 | 125.76 ± 59.03 | 202.23 ± 134.06 | <0.001 |
| HDL-C, mg/dl | 59.49 ± 15.60 | 54.51 ± 14.61 | 50.01 ± 13.28 | 43.14 ± 11.93 | <0.001 |
| LDL-C, mg/dl | 109.62 ± 31.57 | 116.21 ± 31.33 | 123.06 ± 33.30 | 119.22 ± 40.39 | <0.001 |
| CRP, mg/dl | 2.35 ± 7.52 | 2.75 ± 9.42 | 2.49 ± 6.89 | 2.78 ± 4.63 | 0.261 |
| HbA1c % | 5.08 ± 0.50 | 5.15 ± 0.59 | 5.25 ± 0.71 | 5.57 ± 1.12 | <0.001 |
| UA, mg/dl | 4.29 ± 1.16 | 4.32 ± 1.19 | 4.41 ± 1.28 | 4.61 ± 1.27 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 516 (30.51%) | 628 (37.14%) | 816 (48.26%) | 1,047 (61.92%) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 91 (5.38%) | 144 (8.52%) | 239 (14.13%) | 488 (28.86%) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 51 (3.02%) | 74 (4.38%) | 127 (7.51%) | 242 (14.31%) | <0.001 |
| Drinking, n (%) | 814 (48.14%) | 692 (40.92%) | 650 (38.44%) | 511 (30.22%) | <0.001 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 911 (53.87%) | 695 (41.10%) | 582 (34.42%) | 417 (24.66%) | <0.001 |
| Education | 0.158 | ||||
| Lower level | 1,169 (69.13%) | 1,169 (69.13%) | 1,167 (69.01%) | 1,218 (72.03%) | |
| Higher level | 522 (30.87%) | 522 (30.87%) | 524 (30.99%) | 473 (27.97%) | |
| Medication history | <0.001 | ||||
| No | 1,217 (71.97%) | 1,177 (69.60%) | 1,107 (65.46%) | 931 (55.06%) | |
| Yes | 474 (28.03%) | 514 (30.40%) | 584 (34.54%) | 760 (44.94%) | |
| CKM | <0.001 | ||||
| 0 | 216 (12.77%) | 75 (4.44%) | 3 (0.18%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| 1 | 173 (10.23%) | 294 (17.39%) | 252 (14.90%) | 64 (3.78%) | |
| 2 | 220 (13.01%) | 408 (24.13%) | 565 (33.41%) | 682 (40.33%) | |
| 3 | 1,082 (63.99%) | 914 (54.05%) | 871 (51.51%) | 945 (55.88%) |
Baseline characteristics of study population.
BUN, blood urea nitrogen; FBG, fasting blood glucose; TC, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; CRP, C-reactive protein; UA, uric acid.
Figure 2
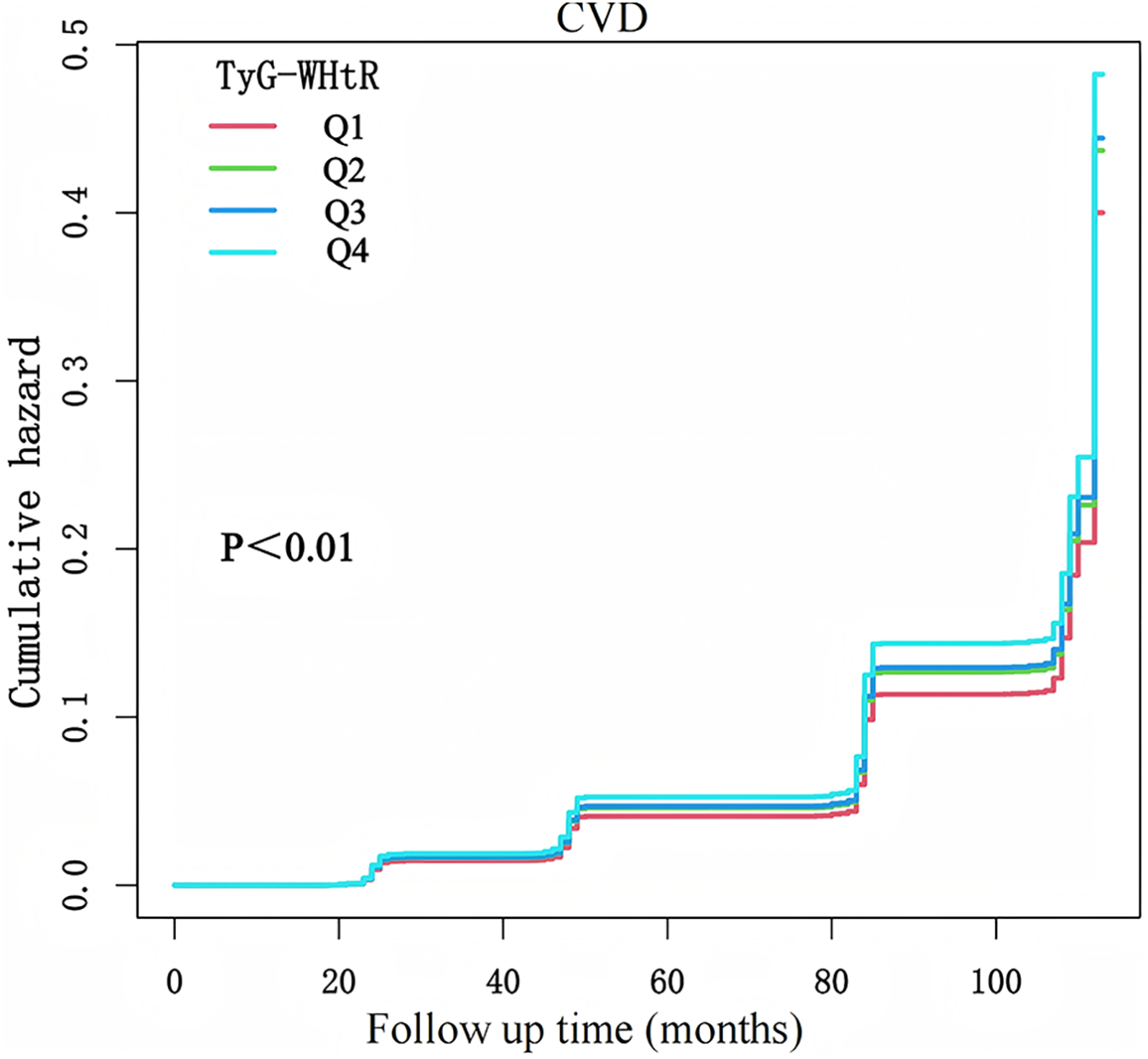
K-M plot of CVD incidence by TyG-WHtR.
3.2 Association between TyG-WHtR and CVD
Multivariate Cox regression analysis was employed to evaluate the association between TyG-WHtR and CVD (Table 2). Following the multicollinearity analysis, all variables exhibited VIF below 5. In Model 1, without adjusting for covariates, each one standard deviation increase in TyG-WHtR was associated with a 29% increased risk of CVD (HR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.22–1.37). After sequential adjustment for sociodemographic factors, blood pressure, lipid profiles, and inflammation-related indicators in Models 2 and 3, the association remained significant, with the HR decreasing slightly to 1.10 (95% CI: 1.03–1.17) in Model 2 and 1.09 (95% CI: 1.01–1.18) in Model 3. A trend test within the multivariate Cox regression analysis indicated a statistically significant relationship. Moreover, within CKM stages 0–4, we also arrived at similar conclusions (Supplementary Table S2). To prevent reverse causality, we excluded participants whose follow-up time was under 2 years. The findings from this subgroup were consistent with the main results (Supplementary Table S3). Subgroup analysis showed no significant interactions that modified the association between TyG-WHtR and CVD (Figure 3).
Table 2
| HR (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |
| TyG-WHtR | 1.29 (1.22, 1.37) | 1.10 (1.03, 1.17) | 1.09 (1.01, 1.18) |
| TyG-WHtR quartile | |||
| Q1 | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Q2 | 1.19 (1.02, 1.38) | 1.14 (0.97, 1.33) | 1.12 (0.96, 1.31) |
| Q3 | 1.37 (1.18, 1.59) | 1.17 (1.00, 1.37) | 1.15 (0.98, 1.35) |
| Q4 | 1.80 (1.56, 2.08) | 1.31 (1.11, 1.54) | 1.28 (1.07, 1.54) |
| P-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Multivariate Cox regression analyses for the association between TyG-WHtR and CVD across CKM stages 0–3.
Model 1: No covariates were adjusted. Model 2: Age, sex, marital status, rural, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, drinking status, smoking status, CKM, medication history, SBP, DBP were adjusted. Model 3: HDL-C, LDL-C, TC, UA, BUN, HbA1c and CRP were further adjusted based on model 2.
Figure 3
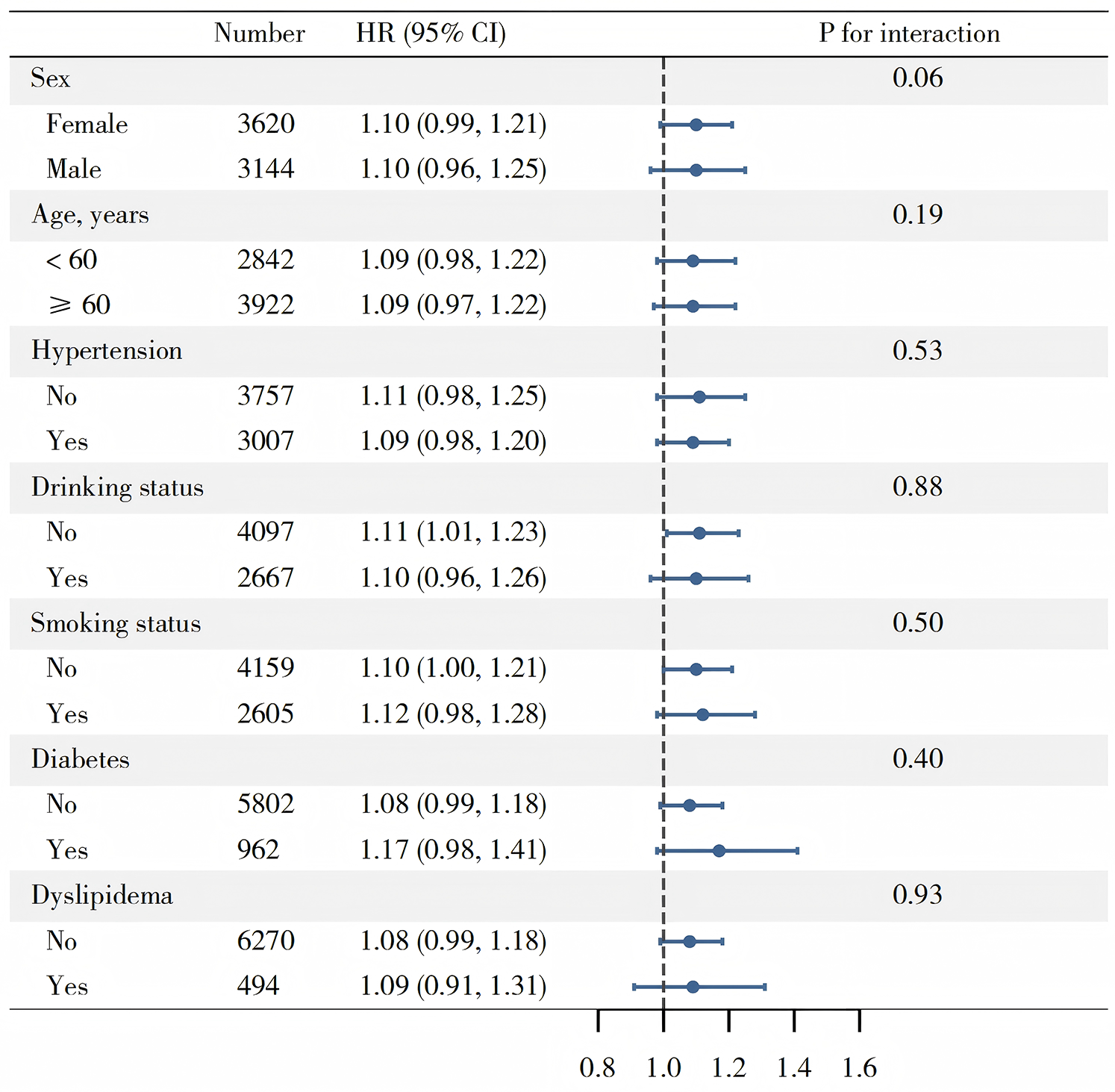
Subgroup analysis of associations between TyG-WHtR and CVD.
3.3 Nonlinear association between TyG-WHtR and CVD
A restricted cubic spline demonstrated a nonlinear association between TyG-WHtR and CVD (Figure 4). The inflection point, calculated using model 3, was determined to be 3.57. When TyG-WHtR was below the threshold of 3.57, HR was 0.90 (95% CI: 0.72–1.04). When TyG-WHtR exceeded 3.57, each standard deviation increase was associated with a 17% increase in the risk of CVD (HR: 1.17, 95% CI: 1.08–1.71).
Figure 4
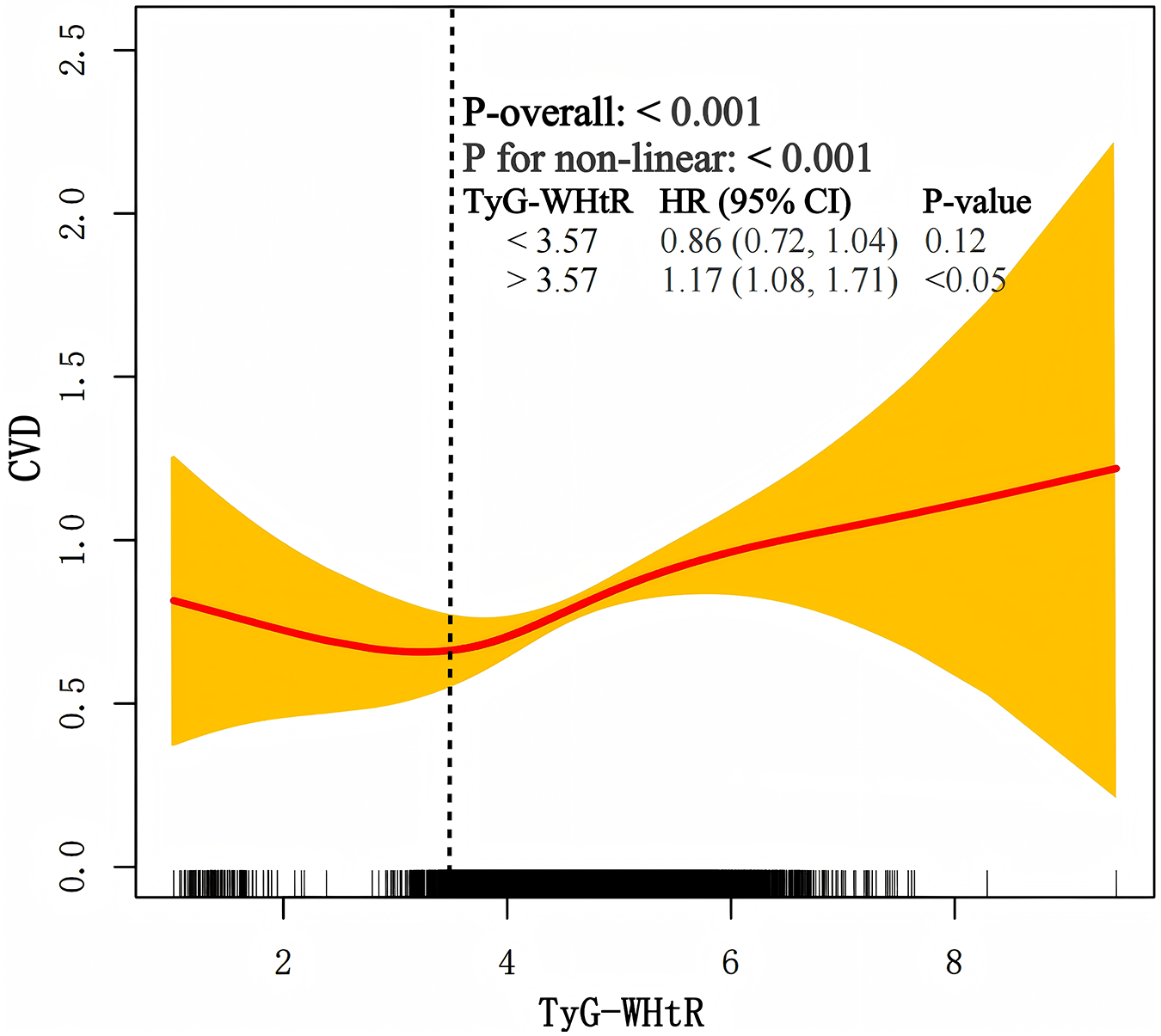
The nonlinear association between TyG-WHtR and CVD.
4 Discussion
This extensive cohort investigation, utilizing long-term follow-up data from CHARLS, uncovered three key findings. First, a significant association was established between TyG-WHtR and CVD. Secondly, the association between TyG-WHtR and CVD demonstrated a nonlinear pattern. Third, the RCS analysis indicated an inflection point at 3.57.
In 2016, Sánchez-Íñigo et al. (25) first introduced the concept of the TyG index, demonstrated a positive association between TyG and CVD. Given the strong connection between obesity and CVD, subsequent studies have increasingly examined TyG alongside obesity-related indicators to assess its association with CVD events. Currently, markers like TyG-BMI, TyG-WC, and TyG-WHtR are increasingly recognized as potential alternative indicators of insulin resistance (IR) (26, 27). Additionally, WHtR has been established as an effective measure for assessing central obesity and has shown a linear association with ischemic cardiovascular disease and ischemic stroke (28). A study conducted in the United States further confirmed that TyG-WHtR demonstrated a significant association with CVD-related mortality in NAFLD patients, with a HR of 2.22 (95% CI: 1.42–3.47) (14).
Our study also demonstrates a positive association between TyG-WHtR and CVD, aligning with results reported in earlier research (29). Earlier research using the CHARLS database also explored this relationship; however, it was limited to a cross-sectional design due to the absence of longitudinal data (21). A cohort study utilizing 12.5 years of UK Biobank data has shown that in patients with metabolic abnormalities, TyG-WHtR is significantly and linearly associated with CVD (30). Evidence regarding the association of baseline and modified TyG indices with incident CVD remains limited in CKM populations. A recent longitudinal study of individuals with CKM stages 0–3 demonstrated a linear relationship between triglyceride glucose-body mass index (TyG-BMI) and CVD risk (17). Furthermore, research utilizing the CHARLS database indicated correlations of cumulative TyG-WHtR with CVD outcomes; however, the cross-sectional design precludes causal inference (21). This study addressed this knowledge gap by incorporating four waves of longitudinal follow-up data and characterizing the dose-response relationship using restricted cubic splines. Notably, TyG-WHtR demonstrated a nonlinear relationship with CVD and identified a potential inflection point at 3.57 with CKM stages 0–3. To assess the robustness of our findings, we conducted sensitivity analyses by expanding the study population to include participants across all CKM stages 0–4. Furthermore, to reduce potential bias from short-term follow-up data, we performed additional analyses excluding participants with follow-up duration < 2 years. Despite these methodological refinements, the association between TyG-WHtR and CVD risk persisted with statistical significance. When TyG-WHtR exceeded 3.57, the risk of CVD increased significantly. Furthermore, given that CVD can change dynamically, the relationship may be influenced by factors such as sex and age (31). To investigate this, we performed additional subgroup analyses; however, no significant factors were identified that impact this relationship.
TyG-WHtR represents a novel marker significantly relevant to CVD. TyG is a well-established surrogate marker for insulin resistance and reflects associated metabolic consequences (32). Insulin resistance disrupts glucose metabolism, increases oxidative stress, induces systemic inflammation, promotes mitochondrial dysfunction, and contributes to dyslipidemia, endothelial dysfunction, and increased volume load, all of which influences the development of CVD (33). Additionally, triglycerides are known to accumulate within arterial walls, attracting inflammatory cells and further accelerating the development of atherosclerosis—the pathological foundation of many CVDs (34, 35). Additionally, insulin resistance and metabolic dysregulation induce endothelial dysfunction, characterized by decreased nitric oxide (NO) synthesis and bioavailability. This leads to vasoconstriction, platelet aggregation, and prothrombotic states, ultimately contributing to increased CVD risk (36). Additionally, WHtR is a more widely recognized marker of central obesity. Central obesity is strongly linked to various CVD risk factors, such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, and metabolic syndrome (21). Additionally, abdominal fat, known for its metabolic activity, secretes a variety of cytokines and inflammatory mediators, including adipokines. These substances contribute to chronic low-grade inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and elevated blood pressure, all of which are critical in the development of CVD (37). The biological mechanisms linking TyG-WHtR to CVD risk encompass insulin resistance, metabolic dysregulation, inflammatory pathways, vascular dysfunction, and prothrombotic processes. Therefore, TyG-WHtR combines markers of insulin resistance and central obesity, thereby capturing the synergistic effects of these two interrelated mechanisms on CVD risk (38).
Compared with traditional methods for assessing insulin resistance (IR), the TyG index is more convenient, cost-effective, and easier to promote and apply in clinical practice (39). By monitoring the TyG index, high-risk individuals can be identified, enabling proactive preventive measures such as lifestyle interventions and pharmacological treatments (40). Regarding the practical application of TyG-WHtR in clinical practice and public health interventions, current research remains exploratory, and no unified clinical guidelines or large-scale intervention strategies have been established.
5 Strength and limitations of this study
This study includes a large sample size and a long-term follow-up cohort, with a nationally representative study population, ensuring its credibility. Notably, this is the first study to explore the longitudinal relationship between TyG-WHtR and CVD among middle-aged and older Chinese adults. However, certain methodological limitations warrant consideration: (1) CVD diagnoses were largely self-reported, which may introduce information bias due to misclassification. Although we supplemented with available treatment/medication data to improve specificity, some misclassification likely remains. This could bias effect estimates toward or away from the null and limit causal interpretation. Future work using clinically confirmed endpoints (medical records, registries, adjudicated outcomes) would help validate our findings. (2) Our sample comprises Chinese adults aged ≥45, limiting the generalizability of findings to younger individuals, other ethnicities, or different settings. The TyG-WHtR–CVD association may vary by age, genetics, culture, and healthcare context. We present our conclusions within the studied population and encourage replication in diverse, multiethnic cohorts. (3) Despite extensive adjustment, residual confounding from unmeasured factors (detailed dietary information, sedentary/activity patterns, family history, environmental exposures, psychosocial factors, broader medication use) may remain. Measurement error in covariates could further bias estimates. Future studies with richer lifestyle/genetic data and causal inference methods (IV, refined propensity scores, negative controls) are warranted to bolster causal interpretation.
6 Conclusion
This study confirms a positive association between TyG-WHtR and CVD in middle-aged and older Chinese adults with CKM stages 0–3. Evaluating the comparative predictive performance of TyG-WHtR vs. established and novel biomarkers across diverse age groups and racial/ethnic populations constitutes a critical area for future research.
Statements
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: The datasets analysed during the this study are available in the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study repository (http://charls.pku.edu.cn).
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Peking University's Biomedical Ethics Committee (IRB00001052-11015). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
CH: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JJ: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YH: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all the members of the CHARLS for their contributions and the participants who contributed their data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1604270/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Roth GA Mensah GA Johnson CO Addolorato G Ammirati E Baddour LM et al Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 76(25):2982–3021. 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010
2.
Li Z Lin L Wu H Yan L Wang H Yang H et al Global, regional, and national death, and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for cardiovascular disease in 2017 and trends and risk analysis from 1990 to 2017 using the global burden of disease study and implications for prevention. Front Public Health. (2021) 9:559751. 10.3389/fpubh.2021.559751
3.
Guo S Chen C Wang Y Cao Y Leng Z Zheng X . Differential impact of fertility on health-adjusted life expectancy of older adults across countries of various levels of socio-demographic index—worldwide, 1995–2019. China CDC Wkly. (2024) 6(39):991–5. 10.46234/ccdcw2024.207
4.
Moltrer M Pala L Cosentino C Mannucci E Rotella CM Cresci B . Body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), waist-to-height ratio (WHtR) e waist body mass index (wBMI): which is better?Endocrine. (2022) 76(3):578–83. 10.1007/s12020-022-03030-x
5.
Ashwell M Gunn P Gibson S . Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometabolic risk factors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. (2012) 13(3):275–86. 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2011.00952.x
6.
Browning LM Hsieh SD Ashwell M . A systematic review of waist-to-height ratio as a screening tool for the prediction of cardiovascular disease and diabetes: 0·5 could be a suitable global boundary value. Nutr Res Rev. (2010) 23(2):247–69. 10.1017/S0954422410000144
7.
Zhang Q Xiao S Jiao X Shen Y . The triglyceride-glucose index is a predictor for cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in CVD patients with diabetes or pre-diabetes: evidence from NHANES 2001–2018. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22(1):279. 10.1186/s12933-023-02030-z
8.
Tao L-C Xu J-N Wang T-T Hua F Li J-J . Triglyceride-glucose index as a marker in cardiovascular diseases: landscape and limitations. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21(1):68. 10.1186/s12933-022-01511-x
9.
Si Y Fan W Han C Liu J Sun L . Atherogenic index of plasma, triglyceride-glucose index and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio for predicting subclinical coronary artery disease. Am J Med Sci. (2021) 362(3):285–90. 10.1016/j.amjms.2021.05.001
10.
Park G-M Cho Y-R Won K-B Yang YJ Park S Ann SH et al Triglyceride glucose index is a useful marker for predicting subclinical coronary artery disease in the absence of traditional risk factors. Lipids Health Dis. (2020) 19(1):7. 10.1186/s12944-020-1187-0
11.
Thai PV Tien HA Van Minh H Valensi P . Triglyceride glucose index for the detection of asymptomatic coronary artery stenosis in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2020) 19(1):137. 10.1186/s12933-020-01108-2
12.
Huang Y Zhou Y Xu Y Wang X Zhou Z Wu K et al Inflammatory markers link triglyceride-glucose index and obesity indicators with adverse cardiovascular events in patients with hypertension: insights from three cohorts. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2025) 24(1):11. 10.1186/s12933-024-02571-x
13.
Zheng D Cai J Xu S Jiang S Li C Wang B . The association of triglyceride-glucose index and combined obesity indicators with chest pain and risk of cardiovascular disease in American population with pre-diabetes or diabetes. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1471535. 10.3389/fendo.2024.1471535
14.
Zhang Y Wang F Tang J Shen L He J Chen Y . Association of triglyceride glucose-related parameters with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease in NAFLD patients: NHANES 1999–2018. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23(1):262. 10.1186/s12933-024-02354-4
15.
Ndumele CE Rangaswami J Chow SL Neeland IJ Tuttle KR Khan SS et al Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic health: a presidential advisory from the American heart association. Circulation. (2023) 148(20):1606–35. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001184
16.
Ndumele CE Neeland IJ Tuttle KR Chow SL Mathew RO Khan SS et al A synopsis of the evidence for the science and clinical management of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome: a scientific statement from the American heart association. Circulation. (2023) 148(20):1636–64. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001186
17.
Li W Shen C Kong W Zhou X Fan H Zhang Y et al Association between the triglyceride glucose-body mass index and future cardiovascular disease risk in a population with cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome stage 0–3: a nationwide prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23(1):292. 10.1186/s12933-024-02352-6
18.
Cui C Liu L Zhang T Fang L Mo Z Qi Y et al Triglyceride-glucose index, renal function and cardiovascular disease: a national cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22(1):325. 10.1186/s12933-023-02055-4
19.
Tian N Chen S Han H Jin J Li Z . Association between triglyceride glucose index and total bone mineral density: a cross-sectional study from NHANES 2011–2018. Sci Rep. (2024) 14(1):4208. 10.1038/s41598-024-54192-9
20.
Zheng G Jin J Wang F Zheng Q Shao J Yao J et al Association between atherogenic index of plasma and future risk of cardiovascular disease in individuals with cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome stages 0–3: a nationwide prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2025) 24(1):22. 10.1186/s12933-025-02589-9
21.
Ren Q Huang Y Liu Q Chu T Li G Wu Z . Association between triglyceride glucose-waist height ratio index and cardiovascular disease in middle-aged and older Chinese individuals: a nationwide cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23(1):247. 10.1186/s12933-024-02336-6
22.
Yanai H Adachi H Hakoshima M Katsuyama H . Molecular biological and clinical understanding of the pathophysiology and treatments of hyperuricemia and its association with metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular diseases and chronic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(17):9221. 10.3390/ijms22179221
23.
Hong C Zhu H Zhou X Zhai X Li S Ma W et al Association of blood urea nitrogen with cardiovascular diseases and all-cause mortality in USA adults: results from NHANES 1999–2006. Nutrients. (2023) 15(2):461. 10.3390/nu15020461
24.
Kuppa A Tripathi H Al-Darraji A Tarhuni WM Abdel-Latif A . C-Reactive protein levels and risk of cardiovascular diseases: a two-sample bidirectional mendelian randomization study. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(11):9129. 10.3390/ijms24119129
25.
Sánchez-Íñigo L Navarro-González D Fernández-Montero A Pastrana-Delgado J Martínez JA . The TyG index may predict the development of cardiovascular events. Eur J Clin Invest. (2016) 46(2):189–97. 10.1111/eci.12583
26.
Zhai Y-J Lin C-Y Li J-B Qiu H-N Wu F Wang Y-L et al Mediating role of triglyceride-glucose index and its derivatives in the relationship between central obesity and Hashimoto thyroiditis in type 2 diabetes. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23(1):411. 10.1186/s12944-024-02402-8
27.
Zhang Z Zhao L Lu Y Meng X Zhou X . Association between non-insulin-based insulin resistance indices and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a retrospective study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22(1):161. 10.1186/s12933-023-01898-1
28.
Feng Q Bešević J Conroy M Omiyale W Woodward M Lacey B et al Waist-to-height ratio and body fat percentage as risk factors for ischemic cardiovascular disease: a prospective cohort study from UK Biobank. Am J Clin Nutr. (2024) 119(6):1386–96. 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2024.03.018
29.
Miao H Zhou Z Yang S Zhang Y . The association of triglyceride-glucose index and related parameters with hypertension and cardiovascular risk: a cross-sectional study. Hypertens Res. (2024) 47(4):877–86. 10.1038/s41440-023-01502-9
30.
Qiao Y Wang Y Chen C Huang Y Zhao C . Association between triglyceride-glucose (TyG) related indices and cardiovascular diseases and mortality among individuals with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: a cohort study of UK Biobank. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2025) 24(1):12. 10.1186/s12933-024-02572-w
31.
Liang W Ouyang H . The association between triglyceride-glucose index combined with obesity indicators and stroke risk: a longitudinal study based on CHARLS data. BMC Endocr Disord. (2024) 24(1):234. 10.1186/s12902-024-01729-8
32.
Son D-H Lee HS Lee Y-J Lee J-H Han J-H . Comparison of triglyceride-glucose index and HOMA-IR for predicting prevalence and incidence of metabolic syndrome. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2022) 32(3):596–604. 10.1016/j.numecd.2021.11.017
33.
Sun Y-H Hu N-Q Huang X-Y Liu Z-X Li Q-Y Li Q-L et al Central and peripheral blood pressures in relation to the triglyceride-glucose index in a Chinese population. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23(1):3. 10.1186/s12933-023-02068-z
34.
Ormazabal V Nair S Elfeky O Aguayo C Salomon C Zuñiga FA . Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2018) 17(1):122. 10.1186/s12933-018-0762-4
35.
Xu X Huang R Lin Y Guo Y Xiong Z Zhong X et al High triglyceride-glucose index in young adulthood is associated with incident cardiovascular disease and mortality in later life: insight from the CARDIA study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21(1):155. 10.1186/s12933-022-01593-7
36.
Hill MA Yang Y Zhang L Sun Z Jia G Parrish AR et al Insulin resistance, cardiovascular stiffening and cardiovascular disease. Metab Clin Exp. (2021) 119:154766. 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154766
37.
Lopez-Jimenez F Almahmeed W Bays H Cuevas A Angelantonio D le Roux E et al Obesity and cardiovascular disease: mechanistic insights and management strategies. A joint position paper by the world heart federation and world obesity federation. Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2022) 29(17):2218–37. 10.1093/eurjpc/zwac187
38.
Xu J Yin T Pan M Qin L Zhang L Wang X et al The mediating effect of TyG-related indicators between long-term exposure to particulate matter and cardiovascular disease: evidence from a national longitudinal cohort study. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23(1):319. 10.1186/s12944-024-02305-8
39.
Ramdas Nayak VK Satheesh P Shenoy MT Kalra S . Triglyceride glucose (TyG) index: a surrogate biomarker of insulin resistance. J Pak Med Assoc. (2022) 72(5):986–8. 10.47391/JPMA.22-63
40.
Zhang Y Liu Y Qiao H Ma Q Zhao B Wu Q et al Mediating role of triglyceride glucose-related index in the associations of composite dietary antioxidant index with cardiovascular disease and mortality in older adults with hypertension: a national cohort study. Front Nutr. (2025) 12:1574876. 10.3389/fnut.2025.1574876
Summary
Keywords
TyG-WHtR, cardiovascular disease, Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic syndrome, Chinese, CHARLS
Citation
Huang C, Jia J and He Y (2025) The nonlinear association between the triglyceride glucose-waist-to-height ratio index and cardiovascular disease among middle-aged and older adults in China with cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome stages 0–3. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1604270. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1604270
Received
01 April 2025
Accepted
18 August 2025
Published
29 August 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Serafino Fazio, Federico II University Hospital, Italy
Reviewed by
Adriyan Pramono, Diponegoro University, Indonesia
Zejiaxin Niu, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Huang, Jia and He.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Yuanyuan He yuanlotusyuan@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.