- 1Department of Cardiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University, Ningbo, China
- 2Health Science Center, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Precision Medicine for Atherosclerotic Diseases of Zhejiang Province, Department of Cardiology, Ningbo, China
- 4Clinical Medicine Research Centre for Cardiovascular Disease of Ningbo, Ningbo, China
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain a leading cause of global morbidity and mortality, largely driven by the progression of atherosclerotic plaques. In atherosclerosis (AS), transcription factors and epigenetic mechanisms play pivotal roles in regulating gene expression. Interferon regulatory factors (IRFs), a family of transcription factors initially identified for their role in coordinating interferon (IFN) responses, are now recognized as critical modulators of innate and adaptive immunity. Emerging evidences highlights their involvement in inflammation, lipid metabolism, cell differentiation, cell proliferation, and programmed cell death during AS pathogenesis. This review synthesizes current knowledge on the roles and regulatory mechanisms of IRFs in AS, offering novel insights and potential therapeutic targets for AS management.
1 Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain a leading cause of global morbidity and mortality, which projected to account for 23.6 million annual deaths by 2030 (1). Atherosclerosis (AS) serves as the primary pathological basis for most CVD-related fatalities. It is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by endothelial dysfunction, lipid accumulation, and immune cell infiltration. During early atherogenesis, specific plasma lipoproteins, including low-density lipoprotein (LDL), lipoprotein(a), and triglyceride-rich lipoprotein remnants may undergo modifications within the arterial intima. This process initiates an inflammatory cascade that drives monocyte recruitment and their subsequent differentiation into macrophages. Within this microenvironment, macrophages phagocytose modified lipoprotein particles, forming foam cells that progressively accumulate lipids, cholesterol esters, and cellular debris. Concurrently, vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) migrate to the intima, proliferate, and contribute to plaque calcification (2). These events are tightly regulated by transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms, with transcription factors such as Interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) emerging as key players in AS progression (3).
The IRFs are a family of transcription factors that are highly conserved across species. Originally identified as regulators of IFN signaling, IRFs (IRF1–IRF9) have expanded roles in immune responses, lipid metabolism, and cellular stress. They are extensively involved in diverse biological processes, including cytokine signaling, pathogen response, cell cycle regulation, cell differentiation, apoptosis, and hematopoietic development (4–9). Emerging evidence highlights their role in AS-related processes, including endothelial activation, macrophage polarization, and VSMC dysfunction (3, 10–12). However, the specific roles and mechanisms haven't yet to be fully elucidated. This review comprehensively examines the contributions of IRF family members to AS pathogenesis, emphasizing their potential as therapeutic targets.
2 Interferon regulatory factors: structure and function
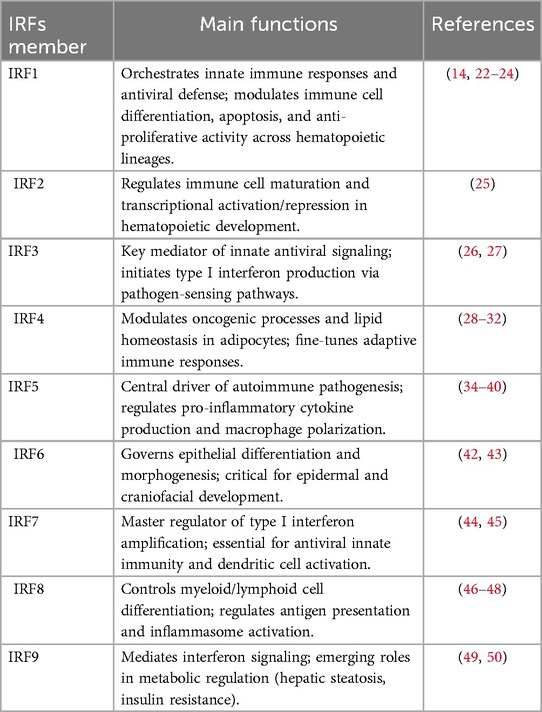
The mammalian IRF family comprises nine members (IRF1- IRF9), each containing a conserved N-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD) and a C-terminal IRF-association domain (IAD) (Figure 1) (13, 14). While the DBD facilitates recognition of IFN-stimulated response elements (ISREs), the IAD mediates interactions with cofactors, enabling diverse regulatory functions (Table 1) (15, 16). Key signaling pathways, such as Toll-like receptor (TLR) and cytosolic DNA-sensing cascades (e.g., cGAS-STING), converge on IRFs to modulate inflammatory and metabolic responses (17).
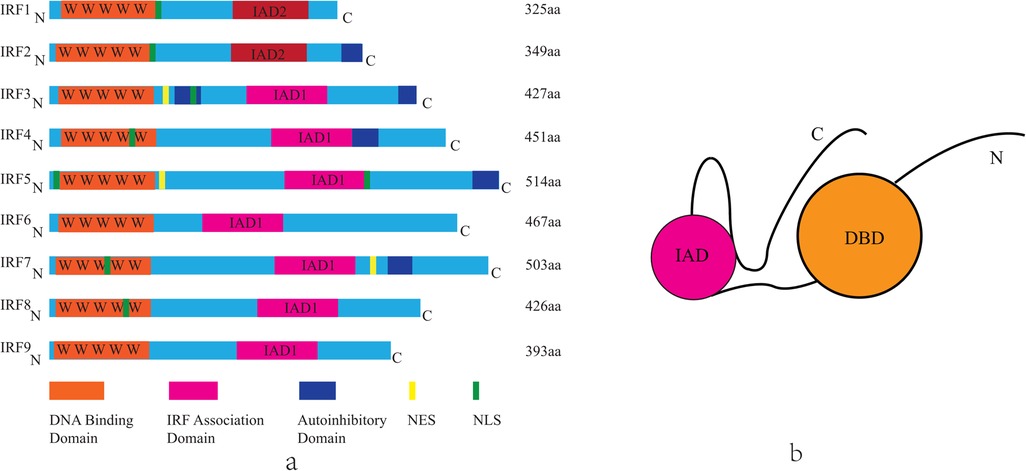
Figure 1. The structure of mammalian IRF family members. (a) Each IRF contains a highly conserved N-terminal DNA-binding domain composed of five tryptophan repeat sequences(DBD, orange). In the C-terminal region, IRF1 and IRF2 share the IRF association domain 2 (IAD2, pink), while the other IRFs share the IRF association domain 1 (IAD1, pink). Other domains include the nuclear localization signal (NLS, green), the nuclear export signal (NES, yellow), the autoinhibitory domain (blue). The length of each IRF is represented by the number of amino acids (aa), found in Uniprot. IRF, interferon regulatory factor; C, carboxy terminus; N, amino terminus. (b) Schematic illustration of the structure of the IRFs.
IRF activation progresses through five core phases: (1) signal perception, (2) post-translational modifications (PTMs), (3) dimerization, (4) nuclear translocation, and (5) transcriptional regulation. Crucially, PTMs serve as the initiating molecular switch, with phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, and SUMOylation being principal modifications that dynamically regulate IRF functional states (17). Subsequently, homo- or hetero-dimerization constitutes an essential activation prerequisite, enabling conformational changes required for nuclear trafficking (18). Latent cytoplasmic IRFs undergo stimulus-dependent nuclear translocation upon PRR activation. These receptors—including TLRs, NLRs, RLRs, and DNA sensors—detect PAMPs/DAMPs to trigger IRF-mediated IFN/pro-inflammatory responses, demonstrating dual roles in AS pathogenesis (protective vs. pathogenic) (19–21). The TLR pathway bifurcates into TRIF- and MyD88-dependent arms, with IRF members exhibiting selective or combinatorial pathway activation to drive context-specific transcriptional programs (17).
2.1 Key IRF family members
IRF1: a pleiotropic transcription factor predominantly localized within the nuclear compartment. Its expression undergoes significant upregulation following viral infection or immune stimulation, mediated through critical signaling pathways IFN(Interferon), NF-κB(Nuclear Factor kappa B), TBK-1(TANK-Binding Kinase 1), and IKK-ɛ(Inhibitor of Nuclear Factor Kappa-B Kinase Subunit ɛ). This transcription factor plays a pivotal role in orchestrating the development, differentiation, and functional regulation of key immune cell populations, particularly B lymphocytes, T helper 1 (Th1) cells, and dendritic cells (DCs). Additionally, IRF1 exerts critical cytostatic and pro-apoptotic effects across diverse mammalian cell types. Mechanistically, these activities involve modulation of oxidative stress responses and participation in regulated cell death pathways, including ferroptosis (14, 22–24).
IRF2: a competing factor engages in cis-regulatory element occupation, directly antagonizing IRF1-mediated transcriptional activity by binding to shared DNA recognition motifs. This molecular interference suppresses the expression of IRF1-dependent pro-inflammatory genes, while simultaneously fine-tuning transcriptional programs critical for immune cell ontogeny and functional maturation including lineage commitment, antigen presentation capacity, and effector molecule production. Such competitive regulation establishes a dynamic equilibrium between inflammatory activation and homeostatic restraint, ensuring balanced immune responses while preventing pathological hyperinflammation (25).
IRF3: primarily resides in the cytoplasm in an inactive state, serving as an essential component of the innate immune defense system. This transcription factor demonstrates remarkable sensitivity in detecting viral components and plays a pivotal role in initiating antiviral responses to prevent pathogenic infections. Furthermore, recent studies have revealed IRF3's significant involvement in cardiovascular pathophysiology, where it functions as a negative regulator of pathological cardiac remodeling. Mechanistically, IRF3 binds to Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase(ERK) 2 through protein-protein interaction, leading to subsequent suppression of ERK 1/2 signaling activity (26, 27). This regulatory mechanism not only highlights IRF3's dual functionality in both immune regulation and cardiac homeostasis but also provides potential therapeutic targets for CVDs.
IRF4: initially characterized as a lymphocyte-specific nuclear factor and discovered to exhibit conserved cardiac expression in both human and animal models (28). Distinct from other IRF family members, IRF4 demonstrates unique activation mechanisms, primarily responding to mitogenic stimuli such as antigen receptor signaling, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation, and CD40 receptor engagement rather than canonical interferon-mediated pathways (29, 30). Beyond its established role as an oncogenic transcription factor that modulates upstream signaling cascades and protein-DNA interactions, IRF4 paradoxically serves dual functions in metabolic regulation. It acts as a master transcriptional regulator of lipid homeostasis in adipocytes and functions as an anti-inflammatory mediator in diet-induced obesity, positioning it at the intersection of metabolic inflammation and energy balance (31, 32).
IRF5: predominantly expressed in immune cells such as monocytes, macrophages, B lymphocytes, and DCs. Its dysregulation is strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (33). his transcription factor plays a pivotal role in inflammatory responses through its synergistic interaction with the NF-κB p65 subunit RelA, co-activating inflammatory gene networks and driving the production of key pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-12, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) (34–36). Emerging genetic evidence further underscores the clinical significance of IRF5 polymorphisms, which have been associated with both susceptibility to and protection against AS. Notably, the high degree of genetic variation in IRF5 correlates with pathological changes in carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) and demonstrates a strong association with coronary artery disease (CAD) development in SLE patients (37–40).
IRF6: critically regulates epidermal development and differentiation (41). Emerging evidence further suggests its potential involvement in the pathogenesis and metabolic reprogramming of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and gliomas (42, 43).
IRF7: a key regulatory component in type I/III IFN-mediated signaling cascades. It shares significant structural homology with IRF3 while exhibiting distinct functional specialization. Notably, it serves multifaceted roles in antiviral defense mechanisms and innate immune responses (44). Emerging evidence implicates IRF7 in modulating obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation (45).
IRF8: originally characterized as being selectively expressed in immune system lineages (lymphoid and myeloid cells). It serves as a master regulator of immune cell development and maturation (14). Additionally, IRF8 acts as a potent inducer of macrophage differentiation from bone marrow progenitor cells. Genome-wide association studies have revealed significant correlations between IRF8 genetic variants and CAD manifestations, particularly through three key phenotypic markers: carotid plaque formation, augmented carotid intima-media thickness, and systemic leukocytosis. These clinical observations collectively establish its potential role as a biomarker for subclinical AS risk (46–48).
IRF9: a critical downstream effector of type I IFN signaling through its integration into the STAT1-STAT2 heterotrimeric complex, collectively forming the interferon-stimulated gene factor 3 (ISGF3) transcriptional machinery. While its canonical role in IFN response pathways is well-established, its specific regulatory mechanisms governing immune cell ontogeny remain underexplored (49). Notably, IRF9 interacts with peroxisome proliferator activating receptor alpha (PPARα) and forms a metabolic-regulatory axis that co-activates PPARα-responsive genes. This interaction manifests therapeutic potential by ameliorating pathological processes including inflammatory responses, hepatic lipid accumulation, and insulin resistance (50).
3 IRFs and as
Current observations highlight a significant role for IRFs in murine models of atherosclerosis AS. In apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE−/−) mice, IRF1 promotes a proinflammatory M1 macrophage phenotype, exacerbates atherosclerotic burden (51), facilitates foam cell formation and increases plaque instability (3). Conversely, ablation of IRF3 expression enhances plaque stability, characterized by thicker fibrous caps, increased collagen deposition and smooth muscle cell (SMC) content, alongside reduced macrophage infiltration (10, 52). Similar to IRF1, IRF5 can also promotes macrophage polarization towards a pro-atherogenic state and foam cell formation (53–55). Notably, IRF7 plays a non-redundant role in AS pathogenesis specifically in diabetic mouse models (56). Furthermore, in chronic myelogenous leukemia-prone mice, IRF8 is implicated in regulating phagocytic function of macrophages (57). Whether these specific roles of IRFs translate identically to humans, beyond in vitro and animal studies, remains to be elucidated. The mechanisms by which IRFs contribute to AS are summarized below.
3.1 Inflammatory regulation
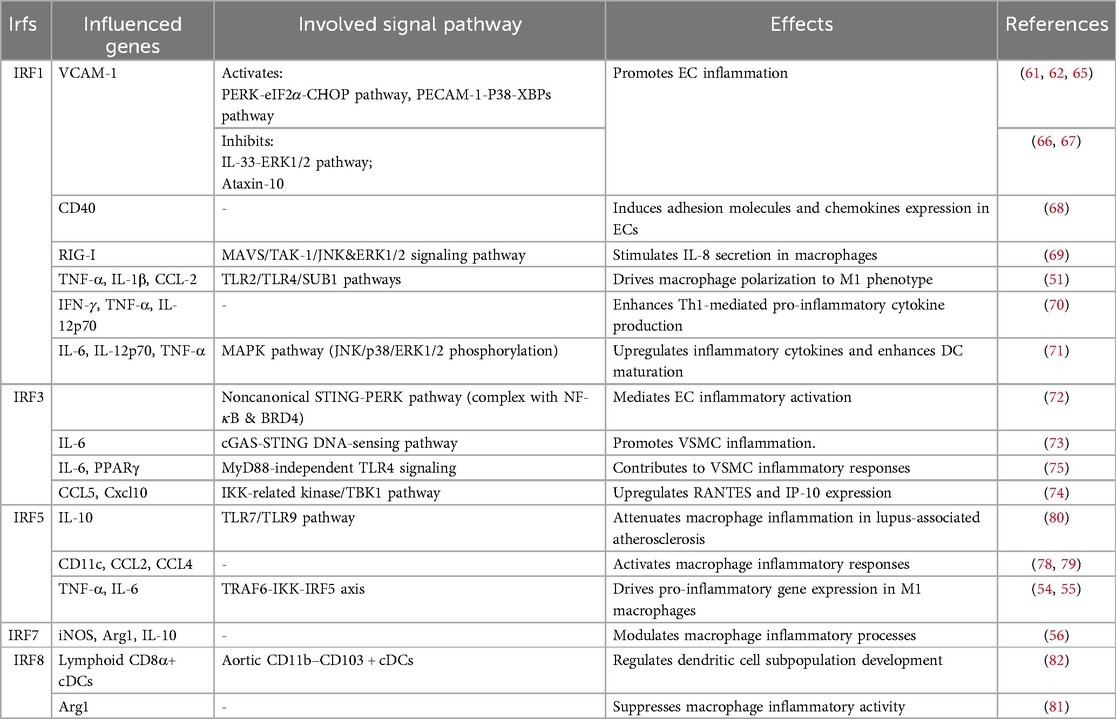
The inflammatory cascade permeates all stages of AS, with endothelial cells (ECs) and immune cells coordinating vascular inflammation through IRF-mediated mechanisms. Key IRF members demonstrate cell-type specific pro-atherogenic effects: IRF1/IRF3 modulate cytokine production in ECs and T cells, IRF5/IRF8 drive macrophage polarization, while IRF7 exhibits context-dependent anti-inflammatory properties (Table 2).
3.1.1 IRF 1
Inflammation of damaged ECs leads to endothelial dysfunction, a critical initiating event in atherosclerotic plaque development and progression (58). IRF1 orchestrates endothelial dysfunction through multiple mechanosensitive pathways, though its role in the atherosclerotic microenvironment remains controversial. Previous studies have reported conflicting IRF1-dependent regulation of TNF-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) expression (59, 60). Emerging evidence clarifies that IRF1 mediates triglyceride-rich lipoprotein (TGRL)-induced VCAM-1 via the PERK/eIF2α/CHOP signaling axis, with polyunsaturated fatty acids counteracting this pro-inflammatory pathway in human aortic endothelial cells(HAECs) (61, 62). Shear stress (SS), the frictional force exerted by blood flow on ECs, modulates IRF1 activity through distinct mechanisms (63). Fluid SS regulates IRF1 nuclear translocation via platelet EC adhesion molecule 1 (PECAM-1)-mediated mechanotransduction, involving p38/x-box binding protein 1 (XBP1s) interactions and Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3 K)/MAPK phosphatase 1 (MKP-1) modulation (64, 65). Conversely, interleukin 33 (IL-33) inhibits VCAM-1 expression through IRF1- ERK 1/2 pathway cross-talk in HAECs (66). Additionally, Ataxin-10 binds cytoplasmic IRF1 to suppress its nuclear translocation and downstream cytokine/chemokine transcription (67). Moreover, IRF1 drives CD40(TNFR5) expression in ECs, promoting adhesion molecules and chemokines essential for leukocyte recruitment (68). By constructing a mouse atherosclerotic model, Wang et al. found in human and mouse primary cells that the IRF1/RIG-I axis mediates 25-hydroxycholesterol-induced IL-8 production in AS, activating NF-κB, AP-1, and NF-IL-6 through MAVS/TAK-1/JNK/ERK1/2 signaling (69). In ApoE−/− mice, IRF1 promotes M1 polarization via TLR2/4-casein kinase 2 (CK2)- RNA polymerase II transcriptional coactivator p15 (SUB1/Sub1, PC4) signaling, enhancing TNF-α/IL-1β production (51). This pro-inflammatory shift exacerbates plaque vulnerability. IRF1-driven IFN-γ/TNF-α production contributes to plaque rupture and acute coronary syndromes (ACS) (70). In rat VSMCs, IRF1 amplifies DC inflammatory responses through MAPK pathway activation (JNK/p38/ERK1/2 phosphorylation), accelerating plaque destabilization (71).
3.1.2 IRF 3
IRF3 demonstrates paradoxical regulatory effects in vascular inflammation through distinct molecular mechanisms (72). Knockdown of EC-specific IRF3 significantly attenuates plaque formation in Western diet-fed ApoE−/− mice, while bone marrow-derived macrophage IRF3 shows no such effect. Mechanistic studies demonstrate that IRF3 specifically binds to the ISRE within the ICAM-1 promoter(P1 site), predominantly suppressing ICAM-1 transcription and moderately inhibiting VCAM-1 expression (10, 52). Paradoxically, while suppressing ICAM-1 transcription through ISRE binding, IRF3 simultaneously promotes inflammatory signaling through four distinct axes.
3.1.2.1 Axis 1: cGAS-STING-PERK activation via oxidized mtDNA
Oxidized mitochondrial DNA triggers cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of IFN genes (STING) signaling, leading to the formation of a transcriptional complex comprising IRF3, NF-κB, and bromodomain protein 4 (BRD4). This complex drives pro-inflammatory genes expression including ICAM-1, through PERK pathway activation in both human and mouse ECs (72).
3.1.2.2 Axis 2: cGAS-STING-IRF3-Il6 activation via DNA double-strand breaks
In ApoE−/− mice, DNA damage-induced double-strand breaks (DSBs) activate this axis to amplify pro-inflammatory responses in AS, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target (73).
3.1.2.3 Axis 3: TBK1/IRF3/CCL5-CXCL10 activation in HCMV-infected VSMCs
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection in human VSMCs activates a novel IκB kinase (IKK)-related pathway involving TBK1, IRF3, and chemokines CCL5/RANTES and CXCL10/IP-10. This axis contributes to atherosclerotic lesion progression by modulating inflammatory chemokine production (74).
3.1.2.4 Axis 4: TLR4-TRIF-Ip10 pathway modulation
IRF3 mediates C-reactive protein (CRP)-induced NF-κB activation in rat VSMCs via the MyD88-independent TLR4 pathway. This mechanism suppresses peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) expression, a key anti-inflammatory regulator while enhancing IL-6 production. Notably, the PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone reverses PPARγ downregulation and demonstrates novel anti-inflammatory effects through modulation of the TLR4/TRIF/IRF3/IP-10 signaling axis (75, 76).
Recent work by Zeyu Xing et al. reveals that karyopherin subunit alpha 2 (KPNA2) facilitates nuclear translocation of IRF3 and NF-κB p65,.a process regulated by the E3 ubiquitin ligase F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 (FBXW7) (77). This discovery expands our understanding of post-translational regulation in IRF3-mediated inflammatory responses.
3.1.3 IRF5/7/8
IRF5 is well-established as a driver of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophage polarization. Emerging evidence highlights its paradoxical role in inflammatory regulation. Julia Leipner et al. demonstrated that IRF5 deficiency reduces M1 marker expression in vitro and enhances atherosclerotic plaque stability, suggesting its critical role in sustaining vascular inflammation (53). Mechanistically, in ApoE−/− mice, IRF5 promotes M1 polarization via TRAF6-IKK and miR-22-dependent pathways, positioning it as a promising therapeutic target for AS management (54, 55). IRF5 further induces the differentiation of macrophages into the pro-inflammatory CD11c + subset by directly targeting the CD11c gene, thereby amplifying chemokine release (CCL2 and CCL4) to fuel inflammatory cascades (78, 79). Notably, IRF5 exhibits disease-specific functionality. TLR7/9-activated IRF5 elevates IL-10 in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) models, contrasting with its pro-inflammatory role in TLR2/4-mediated pathways (80).
In diabetic contexts of mice, IRF7 disrupts macrophage homeostasis by suppressing the anti-inflammatory M2 marker arginase-1 (Arg1) and IL-10 via RAGE signaling, while enhancing pro-inflammatory TNF-α and CCL2 production (56). Conversely, IRF8 cooperates with the Ets family transcription factor PU.1, a downstream effector of liver X receptors (LXRs), to regulate Arg1 expression, highlighting its role in balancing macrophage functional states (81).
Conventional dendritic cells (cDCs) in atherosclerotic plaques, characterized by the CD11b− CD103+ IRF8hi phenotype, originate from DNGR1-expressing precursors. Conditional deletion of IRF8 in CD11c+ cells ablates lymphoid-like CD8α+ cDCs and CD11b-CD103 + cDCs, significantly attenuating AS progression despite hypercholesterolemia. This effect correlates with suppressed T/B cell activation and differentiation under high-fat diet (HFD) conditions, underscoring IRF8's non-redundant role in bridging innate and adaptive immune responses in AS pathogenesis (82).
3.2 Dysregulation of lipid homeostasis
Under physiological conditions, macrophages maintain lipid homeostasis through balanced uptake, efflux, and degradation. Foam cell formation, a hallmark of early AS, is tightly linked to dysregulated lipid metabolism in macrophages (83). Emerging evidence implicates IRF1, IRF3, IRF5, and IRF7 as critical regulators of lipid handling in macrophages, with distinct roles in modulating scavenger receptors, cholesterol transporters, and nuclear receptor signaling (Figure 2).
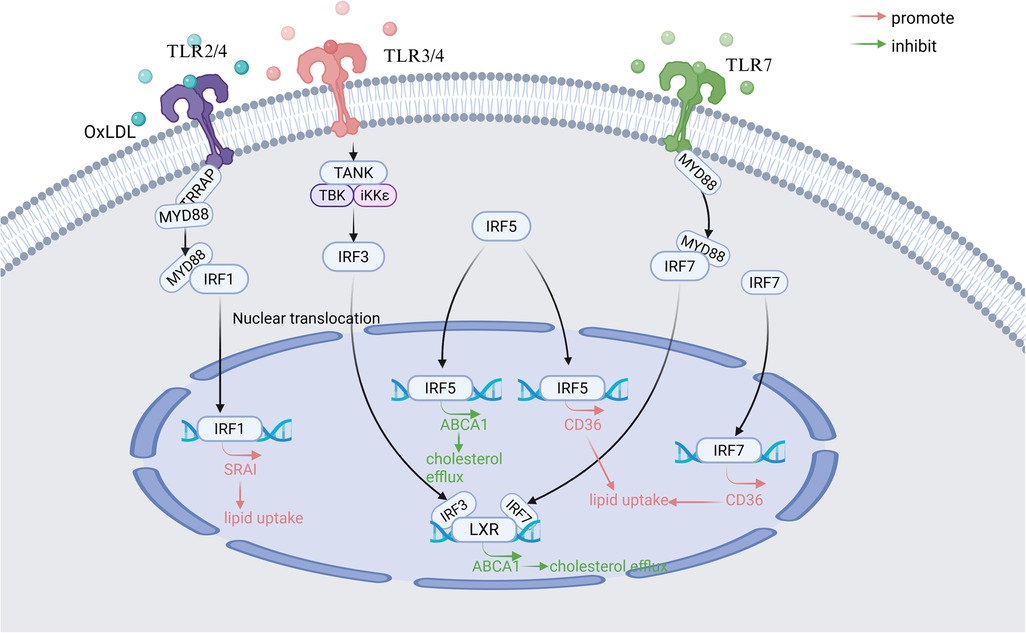
Figure 2. Main signaling pathways of IRFs involved in regulating macrophage lipid metabolism in atherosclerosis. TLR, Toll-like receptor; MyD88, Myeloid differentiation primary response 88; TANK, TRAF family member-associated NF-kappa-B activator; TBK-1, TANK-binding kinase 1; LXR, Liver X Receptor; IKK-ε, Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit epsilon; SR-AI, scavenger receptor AI; ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; CD36, Cluster of Differentiation 36. Created in BioRender. Wang, Y. (2025) https://BioRender.com/zmlx50r.
3.2.1 IRF1
Elevated IRF1 expression correlates with atherosclerotic lesion progression and oxidized LDL (oxLDL)-induced foam cell formation (84). Scavenger receptor AI (SR-AI), which is a direct downstream gene target of IRF1, is primarily responsible for the recognition and uptake of oxLDL (85). Mechanistically, in a mouse atherosclerotic model, IRF1 amplifies lipid uptake in macrophages by upregulating scavenger receptor AI (SR-AI) through the TLR2/4-MyD88 pathway, while IRF1 silencing reverses this opposite effect (3). OxLDL receptor-1 (LOX-1), a transmembrane glycoprotein, is also famous for binding to and internalizing oxLDL (71). In DCs in acute coronary syndrome(ACS) patients, IRF1 overexpression enhances lectin-like LOX-1 expression, promoting oxLDL binding and internalization (71).
3.2.2 IRF3
IRF3 exerts dual regulatory effects on lipid metabolism. ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) is a key transporter protein for cholesterol efflux in macrophages (86). IRF3 suppresses the transcriptional activity of Liver × Receptor (LXR) at the ABCA1 promoter through TLR3/4 signaling in aortic tissue in vivo. This process could reduce cholesterol efflux and favor lipid accumulation (87). Concurrently, IRF3 synergizes with Chlamydia pneumoniae-activated TLR2/4 signaling via MyD88 and TRIF-dependent pathways to drive foam cell formation. Intriguingly, crosstalk between IRF3 and LXR pathways suggests therapeutic potential for LXR agonists in mitigating AS progression (88).
3.2.3 IRF5
Cluster of Differentiation 36 (CD36) is a class B scavenger receptor primarily responsible for lipid uptake (89). Demonstrated in vivo and in vitro models, IRF5 promotes foam cells formation by skewing the ABCA1/CD36 ratio toward lipid uptake. This means IRF5 can reduce the expression of ABCA1 and increase the expression of CD36 in macrophages (53). Paradoxically, in SLE, IRF5 improves systemic lipid profiles by lowering very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and elevating high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels, highlighting its context-dependent functionality (80).
3.2.4 IRF7
IRF7 disrupts cholesterol homeostasis through the TLR7-MyD88-ABCA1 axis, suppressing cholesterol efflux in murine macrophages (90). In diabetic mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs), IRF7 downregulation increases cholesterol transporter expression while reducing CD36 levels, implicating that IRF7 is a negative regulator of reverse cholesterol transport (56).
3.3 Regulation of programmed cell death in atherosclerosis
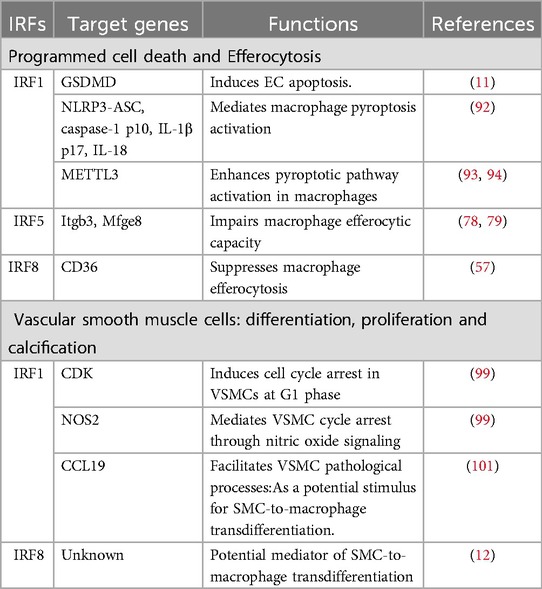
Programmed cell death (e.g., pyroptosis, apoptosis) and efferocytosis, the phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells, are critical determinants of atherosclerotic plaque stability. Emerging evidence highlights that exacerbated programmed cell death coupled with impaired efferocytosis drives atherosclerotic progression. Key IRF family members regulate these processes through distinct mechanisms (Table 3).
3.3.1 IRF1
Pyroptosis, a caspase-dependent inflammatory cell death mechanism, is critically regulated by IRF1 (91). In HAECs, IRF1 binds promoter regions of Gasdermin D (GSDMD) and CASP1, enhancing their expression to drive NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. This progress is initiated by RelB/p52-mediated NF-κB activation (11). Similarly, in macrophages, IRF1 modulates Cysteine-aspartic proteases 1 (caspase-1) activation, GSDMD-N cleavage, and IL-1β/IL-18 maturation via ROS-dependent NLRP3-ASC inflammasome. IRF1 overexpression amplifies pyroptotic signaling, whereas its inhibition attenuates inflammatory cell death (92).
Notably, IRF1 further promotes macrophage from patients with CAD pyroptosis by regulating Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)-mediated m6A modification of circular RNA circ_0029589. This interaction suppresses circ_0029589 expression, which normally inhibits caspase-1 p10, GSDMD-N, IL-1β p17, and IL-18 production (93, 94). IRF1 also facilitates NLRP3-ASC recruitment to enhance caspase-1 activation, establishing a feedforward loop of inflammation (93, 94).
3.3.2 IRF5
In human carotid artery and mouse models, IRF5 impairs macrophage efferocytosis by downregulating integrin-β3 (Itgb3) and milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8 (Mfge8), the key mediators of apoptotic cells, in pro-inflammatory CD11c + macrophages. This defect enlarges the necrotic core and increases plaque rupture susceptibility, underscoring IRF5's role in destabilizing advanced lesions (78, 79).
3.3.3 IRF8
IRF8-deficient macrophages from chronic myelogenous leukemia-prone mice exhibit reduced CD36 expression, impairing efferocytosis of apoptotic polymorphonuclear neutrophilic leukocytes (PMNs) (57). This finding positions IRF8 as a regulator of phagocytic function in inflammatory contexts.
3.4 VSMC plasticity and phenotypic switching in atherosclerosis
VSMCs undergo dynamic phenotypic changes during AS, migrating from the medial layer to the intima, proliferating, and depositing extracellular matrix to shape plaque architecture (95). Emerging evidence highlights the regulatory roles of IRFs in VSMC plasticity, which governs their transition into distinct functional subtypes with divergent roles in AS progression (96) (Table 3).
3.4.1 IRF1
IRF1 exerts antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects across vascular cell types (3). In murine neointimal hyperplasia models, IRF1 suppresses coronary artery smooth muscle cell (CASMC) proliferation and migration while inhibiting neointima formation. Mechanistically, IRF1 induces G1-phase cell cycle arrest via two complementary pathways: (1)P21-Dependent CDK Inhibition: IRF1 upregulates the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor p21, directly or indirectly blocking CDK activity (97, 98); (2)Nitric Oxide (NO)-Mediated Arrest: IRF1 enhances NO production, a known inducer of cell cycle arrest and endothelial function modulator (99).The p21 pathway also inhibits CASMC migration, potentially through interactions with CDK inhibitory proteins (CKIs) of the Cip/Kip family (100). These dual mechanisms provide novel insights into IRF1's role in mitigating VSMC-driven AS pathophysiology.Paradoxically, IRF1 promotes AS progression by upregulating CCL19, a chemokine elevated in AS patient serum. CCL19 enhances VSMC proliferation, migration, inflammatory factor secretion (IL-1α/β, TNF-α, IL-6), and extracellular matrix deposition (collagen III, osteopontin), positioning it as a potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target (101).
3.4.2 IRF8
Single-cell transcriptomic analyses reveal five VSMC subtypes in AS: contractile, fibroblast-like, osteogenic, synthetic, and macrophage-like. Notably, Xue Gong et al. identified IRF8 as a master regulator SMC-to-macrophage transdifferentiation via NF-κB signaling activation in human carotid plaque laden with atherosclerotic core (12). The macrophage-like SMC subtype exhibits a hybrid phenotype co-expressing inflammatory mediators(CCL2, CXCL1-3), matrix-remodeling enzymes(MMP3, MMP9, MMP19) and osteogenic markers(LGALS3, KLF4) (102–105). This transdifferentiation process amplifies plaque instability by promoting matrix degradation, inflammation, and calcification, underscoring IRF8's pathogenic role in advanced AS.
4 Conclusions
IRFs are multifaceted regulators of AS, influencing inflammation, lipid handling, cell death, and VSMC plasticity. While IRF1, IRF3, IRF5, and IRF8 predominantly exacerbate AS, context-dependent roles (e.g., IRF5 in lupus-associated AS) highlight their therapeutic complexity. Future studies must clarify unresolved questions, including functional redundancies among IRFs, tissue-specific effects, and translational potential. Targeting IRF signaling pathways may offer novel strategies for stabilizing atherosclerotic plaques and reducing CVD burden.
Author contributions
YW: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. TF: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. NH: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (ZCLMS25H0201), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82200489), Ningbo Young Scientific and Technological Innovation Leading Talent Program (2024QL027), Key Laboratory of Precision Medicine for Atherosclerotic Diseases of Zhejiang Province, China (2022E10026).
Acknowledgments
Figure 2 was created with BioRender.com.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Anderson CAM, Arora P, Avery CL, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2023 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2023) 147(8):e93–e621. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001123
2. Libby P, Buring JE, Badimon L, Hansson GK, Deanfield J, Bittencourt MS, et al. Atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2019) 5(1):56. doi: 10.1038/s41572-019-0106-z
3. Du M, Wang X, Mao X, Yang L, Huang K, Zhang F, et al. Absence of interferon regulatory factor 1 protects against atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Theranostics. (2019) 9(16):4688–703. doi: 10.7150/thno.36862
4. Stoy N. Involvement of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 and interferon regulatory factor 5 in the immunopathogenesis of sars-cov-2 infection: implications for the treatment of COVID-19. Front Immunol. (2021) 12(1664-3224):638446. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.638446
5. Luo WW, Tong Z, Cao P, Wang FB, Liu Y, Zheng ZQ, et al. Transcription-independent regulation of sting activation and innate immune responses by Irf8 in monocytes. Nat Commun. (2022) 13(1):4822. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32401-1
6. Vaughan PS, Aziz F, van Wijnen AJ, Wu S, Harada H, Taniguchi T, et al. Activation of a cell-cycle-regulated histone gene by the oncogenic transcription factor irf-2. Nature. (1995) 377(6547):362–5. doi: 10.1038/377362a0
7. Sun C, Sun H, Wei J, Fan X, Simon SI, Passerini AG. Irf-1 regulates mitochondrial respiration and intrinsic apoptosis under metabolic stress through atp synthase ancillary factor Tmem70. Inflammation. (2024) 48(4):2548–62. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02209-w
8. Alfarano G, Audano M, Di Chiaro P, Balestrieri C, Milan M, Polletti S, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 1 (Irf1) controls the metabolic programmes of low-grade pancreatic cancer cells. Gut. (2023) 72(1):109–28. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325811
9. Lien C, Fang CM, Huso D, Livak F, Lu R, Pitha PM. Critical role of irf-5 in regulation of B-cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2010) 107(10):4664–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911193107
10. Okon I, Ding Y, Zou MH. Ablation of interferon regulatory factor 3 promotes the stability of atherosclerotic plaques. Hypertension. (2017) 69(3):407–8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08486
11. Fan X, Li Q, Wang Y, Zhang DM, Zhou J, Chen Q, et al. Non-canonical nf-kappab contributes to endothelial pyroptosis and atherogenesis dependent on irf-1. Transl Res. (2023) 255(1878-1810):1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2022.11.001
12. Gong X, Liu Y, Liu H, Cao N, Zeng L, Tian M, et al. Re-analysis of single-cell transcriptomics reveals a critical role of macrophage-like smooth muscle cells in advanced atherosclerotic plaque. Theranostics. (2024) 14(4):1450–63. doi: 10.7150/thno.87201
13. Thompson CD, Matta B, Barnes BJ. Therapeutic targeting of irfs: pathway-dependence or structure-based? Front Immunol. (2018) 9(1664-3224):2622. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02622
14. Tamura T, Yanai H, Savitsky D, Taniguchi T. The irf family transcription factors in immunity and oncogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol. (2008) 26(0732-0582):535–84. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090400
15. Ning S, Pagano JS, Barber GN. Irf7: activation, regulation, modification and function. Genes Immun. (2011) 12(6):399–414. doi: 10.1038/gene.2011.21
16. Qin BY, Liu C, Lam SS, Srinath H, Delston R, Correia JJ, et al. Crystal structure of irf-3 reveals mechanism of autoinhibition and virus-induced phosphoactivation. Nat Struct Biol. (2003) 10(11):913–21. doi: 10.1038/nsb1002
17. Matta B, Song S, Li D, Barnes BJ. Interferon regulatory factor signaling in autoimmune disease. Cytokine. (2017) 98(1096-0023):15–26. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.02.006
18. Chen W, Royer WE Jr. Structural insights into interferon regulatory factor activation. Cell Signal. (2010) 22(6):883–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.12.005
19. O'Neill LA, Bowie AG. Sensing and signaling in antiviral innate immunity. Curr Biol. (2010) 20(7):R328–33. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.01.044
20. Santana-de Anda K, Gomez-Martin D, Diaz-Zamudio M, Alcocer-Varela J. Interferon regulatory factors: beyond the antiviral response and their link to the development of autoimmune pathology. Autoimmun Rev. (2011) 11(2):98–103. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2011.08.006
21. Taniguchi T, Ogasawara K, Takaoka A, Tanaka N. Irf family of transcription factors as regulators of host defense. Annu Rev Immunol. (2001) 19(0732-0582):623–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.623
22. Kong P, Yang M, Wang Y, Yu KN, Wu L, Han W. Ferroptosis triggered by Stat1- Irf1-Acsl4 pathway was involved in radiation-induced intestinal injury. Redox Biol. (2023) 66(2213-2317):102857. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102857
23. Rundberg Nilsson AJS, Xian H, Shalapour S, Cammenga J, Karin M. Irf1 regulates self-renewal and stress responsiveness to support hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. Sci Adv. (2023) 9(43):eadg5391. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg5391
24. Li H, Chen X, Xu J, Zhu L, Li C, Sun X, et al. Grp/grpr enhances alcohol-associated liver injury through the Irf1-mediated caspase-1 inflammasome and Nox2-dependent ros pathway. Hepatology. (2024) 79(2):392–408. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000531
25. Klune JR, Dhupar R, Kimura S, Ueki S, Cardinal J, Nakao A, et al. Interferon regulatory factor-2 is protective against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2012) 303(5):G666–73. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00050.2012
26. Lu J, Bian ZY, Zhang R, Zhang Y, Liu C, Yan L, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 3 is a negative regulator of pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Basic Res Cardiol. (2013) 108(2):326. doi: 10.1007/s00395-012-0326-9
27. Wang J, Li H, Xue B, Deng R, Huang X, Xu Y, et al. Irf1 promotes the innate immune response to viral infection by enhancing the activation of Irf3. J Virol. (2020) 94(22):e01231–20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01231-20
28. Huber M, Lohoff M. Irf4 at the crossroads of effector T-cell fate decision. Eur J Immunol. (2014) 44(7):1886–95. doi: 10.1002/eji.201344279
29. Guo S, Li ZZ, Jiang DS, Lu YY, Liu Y, Gao L, et al. Irf4 is a novel mediator for neuronal survival in ischaemic stroke. Cell Death Differ. (2014) 21(6):888–903. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.9
30. Gupta S, Jiang M, Anthony A, Pernis AB. Lineage-Specific modulation of interleukin 4 signaling by interferon regulatory factor 4. J Exp Med. (1999) 190(12):1837–48. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.12.1837
31. Eguchi J, Kong X, Tenta M, Wang X, Kang S, Rosen ED. Interferon regulatory factor 4 regulates obesity-induced inflammation through regulation of adipose tissue macrophage polarization. Diabetes. (2013) 62(10):3394–403. doi: 10.2337/db12-1327
32. Wong RWJ, Ong JZL, Theardy MS, Sanda T. Irf4 as an oncogenic master transcription factor. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14(17):4314. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174314
33. Xu WD, Pan HF, Xu Y, Ye DQ. Interferon regulatory factor 5 and autoimmune lupus. Expert Rev Mol Med. (2013) 15(1462-3994):e6. doi: 10.1017/erm.2013.7
34. Saliba DG, Heger A, Eames HL, Oikonomopoulos S, Teixeira A, Blazek K, et al. Irf5:rela interaction targets inflammatory genes in macrophages. Cell Rep. (2014) 8(5):1308–17. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.034
35. Krausgruber T, Blazek K, Smallie T, Alzabin S, Lockstone H, Sahgal N, et al. Irf5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and Th1-Th17 responses. Nat Immunol. (2011) 12(3):231–8. doi: 10.1038/ni.1990
36. Takaoka A, Yanai H, Kondo S, Duncan G, Negishi H, Mizutani T, et al. Integral role of irf-5 in the gene induction programme activated by toll-like receptors. Nature. (2005) 434(7030):243–9. doi: 10.1038/nature03308
37. Garcia-Bermudez M, Lopez-Mejias R, Genre F, Castaneda S, Llorca J, Gonzalez-Juanatey C, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 5 genetic variants are associated with cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2014) 16(4):R146. doi: 10.1186/ar4608
38. Agca R, van Sijl AM, Vosslamber S, Voskuyl AE, Verweij CL, Nurmohamed MT. Interferon regulatory factor 5 gene variants Rs2004640 and Rs4728142 are associated with carotid intima media thickness but not with cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2022) 40(1):64–8. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/pf511x
39. Chung CP, Solus JF, Oeser A, Li C, Raggi P, Smith JR, et al. Genetic variation and coronary atherosclerosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2014) 23(9):876–80. doi: 10.1177/0961203314530019
40. Posadas-Sanchez R, Cardoso-Saldana G, Fragoso JM, Vargas-Alarcon G. Interferon regulatory factor 5 (Irf5) gene haplotypes are associated with premature coronary artery disease. Association of the Irf5 polymorphisms with cardiometabolic parameters. The genetics of atherosclerotic disease (gea) Mexican study. Biomolecules. (2021) 11(3):443. doi: 10.3390/biom11030443
41. Oberbeck N, Pham VC, Webster JD, Reja R, Huang CS, Zhang Y, et al. The Ripk4-Irf6 signalling axis safeguards epidermal differentiation and barrier function. Nature. (2019) 574(7777):249–53. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1615-3
42. Kim IK, Diamond MS, Yuan S, Kemp SB, Kahn BM, Li Q, et al. Plasticity-induced repression of Irf6 underlies acquired resistance to cancer immunotherapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat Commun. (2024) 15(1):1532. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46048-7
43. Lu J, Liu X, Zheng J, Song J, Liu Y, Ruan X, et al. Lin28a promotes Irf6-regulated aerobic glycolysis in glioma cells by stabilizing Snhg14. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11(6):447. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2650-6
44. Ma W, Huang G, Wang Z, Wang L, Gao Q. Irf7: role and regulation in immunity and autoimmunity. Front Immunol. (2023) 14(1664-3224):1236923. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1236923
45. Mummidi S, Kuroda M, Nishiguchi M, Ugawa N, Ishikawa E, Kawabata Y, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 7 mediates obesity-associated mcp-1 transcription. PLoS One. (2020) 15(5):e0233390. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233390
46. Nezos A, Evangelopoulos ME, Mavragani CP. Genetic contributors and soluble mediators in prediction of autoimmune comorbidity. J Autoimmun. (2019) 104(1095-9157):102317. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.102317
47. Leonard D, Svenungsson E, Sandling JK, Berggren O, Jonsen A, Bengtsson C, et al. Coronary heart disease in systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with interferon regulatory factor-8 gene variants. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. (2013) 6(3):255–63. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.113.000044
48. Crosslin DR, McDavid A, Weston N, Zheng X, Hart E, de Andrade M, et al. Genetic variation associated with circulating monocyte count in the emerge network. Hum Mol Genet. (2013) 22(10):2119–27. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt010
49. Zhang Q, Kisand K, Feng Y, Rinchai D, Jouanguy E, Cobat A, et al. In search of a function for human type iii interferons: insights from inherited and acquired deficits. Curr Opin Immunol. (2024) 87(1879-0372):102427. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2024.102427
50. Wang XA, Zhang R, Jiang D, Deng W, Zhang S, Deng S, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 9 protects against hepatic insulin resistance and steatosis in male mice. Hepatology. (2013) 58(2):603–16. doi: 10.1002/hep.26368
51. Huang R, Hu Z, Chen X, Cao Y, Li H, Zhang H, et al. The transcription factor Sub1 is a master regulator of the macrophage tlr response in atherosclerosis. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2021) 8(19):e2004162. doi: 10.1002/advs.202004162
52. Liu H, Cheng WL, Jiang X, Wang PX, Fang C, Zhu XY, et al. Ablation of interferon regulatory factor 3 protects against atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Hypertension. (2017) 69(3):510–20. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08395
53. Leipner J, Dederichs TS, von Ehr A, Rauterberg S, Ehlert C, Merz J, et al. Myeloid cell-specific Irf5 deficiency stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques in apoe(-/-) mice. Mol Metab. (2021) 53(2212-8778):101250. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101250
54. Lv JJ, Wang H, Zhang C, Zhang TJ, Wei HL, Liu ZK, et al. Cd147 sparks atherosclerosis by driving M1 phenotype and impairing efferocytosis. Circ Res. (2024) 134(2):165–85. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.323223
55. Wu Z, Geng J, Bai Y, Qi Y, Chang C, Jiao Y, et al. Microrna-22 inhibition promotes the development of atherosclerosis via targeting interferon regulator factor 5. Exp Cell Res. (2021) 409(2):112922. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112922
56. Senatus L, Lopez-Diez R, Egana-Gorrono L, Liu J, Hu J, Daffu G, et al. Rage impairs murine diabetic atherosclerosis regression and implicates Irf7 in macrophage inflammation and cholesterol metabolism. JCI Insight. (2020) 5(13):e137289. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.137289
57. Doring Y, Soehnlein O, Drechsler M, Shagdarsuren E, Chaudhari SM, Meiler S, et al. Hematopoietic interferon regulatory factor 8-deficiency accelerates atherosclerosis in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2012) 32(7):1613–23. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.236539
58. Gimbrone MA Jr, Garcia-Cardena G. Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2016) 118(4):620–36. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306301
59. Dagia NM, Harii N, Meli AE, Sun X, Lewis CJ, Kohn LD, et al. Phenyl methimazole inhibits tnf-alpha-induced vcam-1 expression in an ifn regulatory factor-1-dependent manner and reduces monocytic cell adhesion to endothelial cells. J Immunol. (2004) 173(3):2041–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.3.2041
60. Neish AS, Read MA, Thanos D, Pine R, Maniatis T, Collins T. Endothelial interferon regulatory factor 1 cooperates with nf-kappa B as a transcriptional activator of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1. Mol Cell Biol. (1995) 15(5):2558–69. doi: 10.1128/MCB.15.5.2558
61. Sun C, Alkhoury K, Wang YI, Foster GA, Radecke CE, Tam K, et al. Irf-1 and Mirna126 modulate vcam-1 expression in response to a high-fat meal. Circ Res. (2012) 111(8):1054–64. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.270314
62. Wang YI, Bettaieb A, Sun C, DeVerse JS, Radecke CE, Mathew S, et al. Triglyceride-rich lipoprotein modulates endothelial vascular cell adhesion molecule (vcam)-1 expression via differential regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress. PLoS One. (2013) 8(10):e78322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078322
63. Tamargo IA, Baek KI, Kim Y, Park C, Jo H. Flow-induced reprogramming of endothelial cells in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2023) 20(11):738–53. doi: 10.1038/s41569-023-00883-1
64. DeVerse JS, Sandhu AS, Mendoza N, Edwards CM, Sun C, Simon SI, et al. Shear stress modulates vcam-1 expression in response to tnf-alpha and dietary lipids via interferon regulatory factor-1 in cultured endothelium. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2013) 305(8):H1149–57. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00311.2013
65. Bailey KA, Moreno E, Haj FG, Simon SI, Passerini AG. Mechanoregulation of P38 activity enhances endoplasmic Reticulum stress-mediated inflammation by arterial endothelium. FASEB J. (2019) 33(11):12888–99. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900236R
66. Qian Z, Shaofang F, Chen C, Chunhua S, Nan W, Chao L. Il-33 suppresses the progression of atherosclerosis via the Erk1/2-Irf1-vcam-1 pathway. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. (2024) 38(3):569–80. doi: 10.1007/s10557-023-07523-3
67. Li Y, Zhang Q, Li N, Ding L, Yi J, Xiao Y, et al. Ataxin-10 inhibits tnf-alpha-induced endothelial inflammation via suppressing interferon regulatory factor-1. Mediators Inflamm. (2021) 2021(1466-1861):7042148. doi: 10.1155/2021/7042148
68. Wagner AH, Gebauer M, Pollok-Kopp B, Hecker M. Cytokine-inducible Cd40 expression in human endothelial cells is mediated by interferon regulatory factor-1. Blood. (2002) 99(2):520–5. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.2.520
69. Wang F, Xia W, Liu F, Li J, Wang G, Gu J. Interferon regulator factor 1/retinoic inducible gene I (Irf1/rig-I) axis mediates 25-hydroxycholesterol-induced interleukin-8 production in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res. (2012) 93(1):190–9. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr260
70. Guo M, Mao X, Ji Q, Lang M, Li S, Peng Y, et al. Inhibition of ifn regulatory factor-1 down-regulate Th1 cell function in patients with acute coronary syndrome. J Clin Immunol. (2010) 30(2):241–52. doi: 10.1007/s10875-010-9367-8
71. Guo M, Yan R, Wang C, Shi H, Sun M, Guo S, et al. Ifn regulatory factor-1 modulates the function of dendritic cells in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2015) 36(2):599–610. doi: 10.1159/000430123
72. Li X, Chen X, Zheng L, Chen M, Zhang Y, Zhu R, et al. Non-canonical sting-perk pathway dependent epigenetic regulation of vascular endothelial dysfunction via integrating Irf3 and nf-kappab in inflammatory response. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2023) 13(12):4765–84. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.08.015
73. Sakai C, Ueda K, Goda K, Fujita R, Maeda J, Nakayama S, et al. A possible role for proinflammatory activation via cgas-sting pathway in atherosclerosis induced by accumulation of DNA double-strand breaks. Sci Rep. (2023) 13(1):16470. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43848-7
74. Gravel S-P, Servant MJ. Roles of an iκb kinase-related pathway in human cytomegalovirus-infected vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280(9):7477–86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410392200
75. Liu N, Liu JT, Ji YY, Lu PP. C-reactive protein triggers inflammatory responses partly via Tlr4/Irf3/nf-kappab signaling pathway in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Life Sci. (2010) 87(11-12):367–74. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2010.07.012
76. Ji Y, Liu J, Wang Z, Li Z. Ppargamma agonist rosiglitazone ameliorates lps-induced inflammation in vascular smooth muscle cells via the Tlr4/trif/Irf3/ip-10 signaling pathway. Cytokine. (2011) 55(3):409–19. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.05.020
77. Xing Z, Zhen Y, Chen J, Du M, Li D, Liu R, et al. Kpna2 silencing, regulated by E3 ubiquitin ligase Fbxw7, alleviates endothelial dysfunction and inflammation through inhibiting the nuclear translocation of P65 and Irf3: a possible therapeutic approach for atherosclerosis. Inflammation. (2023) 46(6):2071–88. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01863-w
78. Seneviratne AN, Edsfeldt A, Cole JE, Kassiteridi C, Swart M, Park I, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 5 controls necrotic core formation in atherosclerotic lesions by impairing efferocytosis. Circulation. (2017) 136(12):1140–54. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027844
79. Edsfeldt A, Swart M, Singh P, Dib L, Sun J, Cole JE, et al. Interferon regulatory factor-5-dependent Cd11c+ macrophages contribute to the formation of rupture-prone atherosclerotic plaques. Eur Heart J. (2022) 43(19):1864–77. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab920
80. Watkins AA, Yasuda K, Wilson GE, Aprahamian T, Xie Y, Maganto-Garcia E, et al. Irf5 deficiency ameliorates lupus but promotes atherosclerosis and metabolic dysfunction in a mouse model of lupus-associated atherosclerosis. J Immunol. (2015) 194(4):1467–79. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402807
81. Pourcet B, Feig JE, Vengrenyuk Y, Hobbs AJ, Kepka-Lenhart D, Garabedian MJ, et al. Lxralpha regulates macrophage arginase 1 through pu.1 and interferon regulatory factor 8. Circ Res. (2011) 109(5):492–501. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.241810
82. Clement M, Haddad Y, Raffort J, Lareyre F, Newland SA, Master L, et al. Deletion of Irf8 (interferon regulatory factor 8)-dependent dendritic cells abrogates proatherogenic adaptive immunity. Circ Res. (2018) 122(6):813–20. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312713
83. Yan J, Horng T. Lipid metabolism in regulation of macrophage functions. Trends Cell Biol. (2020) 30(12):979–89. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.09.006
84. Holvoet P, Davey PC, De Keyzer D, Doukoure M, Deridder E, Bochaton-Piallat ML, et al. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein correlates positively with toll-like receptor 2 and interferon regulatory factor-1 and inversely with superoxide dismutase-1 expression: studies in hypercholesterolemic swine and thp-1 cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2006) 26(7):1558–65. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000226553.01555.02
85. Zhu Y, Xu Y, Han D, Zhang X, Qin C, Liu J, et al. Scavenger receptor-ai targeted theranostic nanoparticles for regression of atherosclerotic plaques via Abca1 modulation. Nanomedicine. (2023) 50(1549-9642):102672. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2023.102672
86. Wang J, Xiao Q, Wang L, Wang Y, Wang D, Ding H. Role of Abca1 in cardiovascular disease. J Pers Med. (2022) 12(6):1010. doi: 10.3390/jpm12061010
87. Castrillo A, Joseph SB, Vaidya SA, Haberland M, Fogelman AM, Cheng G, et al. Crosstalk between lxr and toll-like receptor signaling mediates bacterial and viral antagonism of cholesterol metabolism. Mol Cell. (2003) 12(4):805–16. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00384-8
88. Chen S, Sorrentino R, Shimada K, Bulut Y, Doherty TM, Crother TR, et al. Chlamydia pneumoniae-induced foam cell formation requires Myd88-dependent and -independent signaling and is reciprocally modulated by liver X receptor activation. J Immunol. (2008) 181(10):7186–93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.7186
89. Shu H, Peng Y, Hang W, Nie J, Zhou N, Wang DW. The role of Cd36 in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Res. (2022) 118(1):115–29. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa319
90. Sorrentino R, Morello S, Chen S, Bonavita E, Pinto A. The activation of liver X receptors inhibits toll-like receptor-9-induced foam cell formation. J Cell Physiol. (2010) 223(1):158–67. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22022
91. Wei Y, Lan B, Zheng T, Yang L, Zhang X, Cheng L, et al. Gsdme-mediated pyroptosis promotes the progression and associated inflammation of atherosclerosis. Nat Commun. (2023) 14(1):929. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36614-w
92. Guo M, Yan R, Yao H, Duan L, Sun M, Xue Z, et al. Ifn regulatory factor 1 mediates macrophage pyroptosis induced by oxidized low-density lipoprotein in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Mediators Inflamm. (2019) 2019(1466-1861):2917128. doi: 10.1155/2019/2917128
93. Franchi L, Eigenbrod T, Munoz-Planillo R, Nunez G. The inflammasome: a caspase-1-activation platform that regulates immune responses and disease pathogenesis. Nat Immunol. (2009) 10(3):241–7. doi: 10.1038/ni.1703
94. Guo M, Yan R, Ji Q, Yao H, Sun M, Duan L, et al. Ifn regulatory factor-1 induced macrophage pyroptosis by modulating M6a modification of circ_0029589 in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 86(1529-2916):106800. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106800
95. Grootaert MOJ, Bennett MR. Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis: time for a re-assessment. Cardiovasc Res. (2021) 117(11):2326–39. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab046
96. Zhang F, Guo X, Xia Y, Mao L. An update on the phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2021) 79(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04079-z
97. Tanner FC, Meier P, Greutert H, Champion C, Nabel EG, Luscher TF. Nitric oxide modulates expression of cell cycle regulatory proteins: a cytostatic strategy for inhibition of human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation. (2000) 101(16):1982–9. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.101.16.1982
98. Quyyumi AA, Dakak N, Andrews NP, Gilligan DM, Panza JA, Cannon RO 3rd. Contribution of nitric oxide to metabolic coronary vasodilation in the human heart. Circulation. (1995) 92(3):320–6. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.92.3.320
99. Poon M, Marx SO, Gallo R, Badimon JJ, Taubman MB, Marks AR. Rapamycin inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell migration. J Clin Invest. (1996) 98(10):2277–83. doi: 10.1172/JCI119038
100. Wessely R, Hengst L, Jaschke B, Wegener F, Richter T, Lupetti R, et al. A central role of interferon regulatory factor-1 for the limitation of neointimal hyperplasia. Hum Mol Genet. (2003) 12(2):177–87. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg018
101. Shen Y, Sun Z, Mao S, Zhang Y, Jiang W, Wang H. Irf-1 contributes to the pathological phenotype of vsmcs during atherogenesis by increasing Ccl19 transcription. Aging (Albany NY. (2020) 13(1):933–43. doi: 10.18632/aging.202204
102. Mittal B, Mishra A, Srivastava A, Kumar S, Garg N. Matrix metalloproteinases in coronary artery disease. Adv Clin Chem. (2014) 64(0065-2423):1–72. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-800263-6.00001-x
103. Newby AC. Metalloproteinases and vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques. Trends Cardiovasc Med. (2007) 17(8):253–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2007.09.001
104. Pugliese G, Iacobini C, Fantauzzi CB, Menini S. The dark and bright Side of atherosclerotic calcification. Atherosclerosis. (2015) 238(2):220–30. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.12.011
Keywords: interferon regulatory factors, atherosclerosis, inflammation, lipid metabolism, cell death
Citation: Wang Y, Fang T, Zheng X and Huangfu N (2025) The role of interferon regulatory factors in atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1606034. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1606034
Received: 4 April 2025; Accepted: 14 August 2025;
Published: 4 September 2025.
Edited by:
Olivier M. Vanakker, Ghent University, BelgiumReviewed by:
Valery Bochkov, University of Graz, AustriaMartina B. Lorey, Wihuri Research Institute, Finland
Copyright: © 2025 Wang, Fang, Zheng and Huangfu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ning Huangfu, bmluZ2h1YW5nZnVAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Yingsong Wang
Yingsong Wang Tianxiang Fang
Tianxiang Fang Xiaoya Zheng1,2
Xiaoya Zheng1,2 Ning Huangfu
Ning Huangfu