- 1East China University of Political Science and Law, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Introduction: Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed medical diagnostics, offering enhanced precision and efficiency in detecting cardiovascular risks. However, traditional diagnostic approaches for cardiovascular risk assessment in autistic patients remain limited due to the complexity of medical data, inter-individual variability, and the challenges of integrating multi-modal clinical information. Conventional methods, relying heavily on manually extracted features and rule-based analysis, often fail to capture subtle cardiovascular abnormalities, leading to suboptimal clinical outcomes.
Methods: To address these limitations, we propose an AI-driven object detection framework that leverages advanced deep learning techniques for automated, accurate cardiovascular risk assessment in autistic patients. Our approach integrates multi-modal medical data, including imaging and electronic health records, through a novel feature fusion mechanism, enhancing diagnostic precision. Furthermore, an uncertainty quantification module is embedded to improve model interpretability and reliability, addressing concerns regarding AI-based medical decision-making.
Results: Experimental evaluations demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms traditional diagnostic techniques in sensitivity and specificity, making it a robust tool for clinical applications.
Discussion: The proposed framework represents a significant step towards personalized and data-driven cardiovascular care for autistic patients, aligning with the need for tailored diagnostic solutions in this specialized medical domain.
1 Introduction
The increasing prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and its associated health risks, particularly cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), necessitate innovative diagnostic approaches (1). ASD patients often exhibit atypical physiological responses, communication barriers, and heightened stress levels, which can obscure early symptoms of CVD. Traditional diagnostic methods, reliant on direct patient feedback and clinical observations, are often inadequate in this population (2). AI-driven object detection presents a promising solution by offering non-invasive, automated, and real-time analysis of cardiovascular risk factors such as facial micro-expressions, body movements, and physiological signals. Not only does this approach enhance the efficiency and accuracy of risk assessment, but it also minimizes patient discomfort, ensuring higher compliance with medical evaluations (3). Furthermore, the integration of AI into healthcare systems allows for continuous monitoring, potentially leading to early intervention and personalized treatment strategies. Given these advantages, it is imperative to explore the evolution of AI methodologies in object detection, from traditional symbolic approaches to contemporary deep learning techniques, to identify the optimal framework for cardiovascular risk assessment in autistic patients (4).
Early attempts to develop AI-driven object detection systems for medical applications relied on symbolic AI and knowledge representation. These systems were rule-based, encoding expert knowledge in the form of if-then rules and ontologies to classify medical images and physiological signals (5). For instance, rule-based expert systems could identify abnormal heart rates or detect anomalies in electrocardiograms (ECGs) based on predefined thresholds. While such systems provided explainability and logical reasoning, their rigidity and reliance on handcrafted rules limited their adaptability to complex, patient-specific variations (6). Moreover, symbolic AI struggled with the high-dimensional and noisy nature of real-world medical data, necessitating frequent manual updates and expert intervention. To address these challenges, researchers explored statistical learning approaches that leveraged data-driven techniques for improved generalization and scalability (7).
The advent of machine learning (ML) revolutionized object detection in medical diagnostics, shifting the focus from manually defined rules to data-driven feature extraction and classification. Traditional ML methods such as support vector machines (SVMs), random forests, and k-nearest neighbors (KNNs) demonstrated considerable success in identifying cardiovascular risk markers from ECGs, medical imaging, and wearable sensor data (8). These algorithms could automatically learn patterns from large datasets, reducing dependency on explicit rule engineering. However, their effectiveness was constrained by feature selection biases and limited capacity for hierarchical pattern recognition (9). ML models often required extensive preprocessing and feature engineering, making them less adaptable to real-time, multimodal data streams required for holistic cardiovascular risk assessment. The need for higher accuracy, end-to-end learning, and autonomous feature extraction motivated the transition to deep learning (DL) and pre-trained models (10).
Deep learning and pre-trained models have significantly advanced object detection by enabling automated feature learning from raw data (11). Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have been particularly impactful in analyzing cardiovascular risk factors from facial expressions, posture, and physiological signals in autistic patients (12). CNN-based architectures such as ResNet and EfficientNet can extract spatial patterns from facial videos and thermal imaging, identifying stress-induced micro-expressions linked to cardiovascular anomalies. Simultaneously, RNNs and transformers enhance temporal analysis by capturing dynamic physiological changes over time (13). Pre-trained models, including Vision Transformers (ViTs) and large multimodal frameworks, further refine object detection by leveraging vast medical datasets and transfer learning strategies (14). Despite these advancements, deep learning models pose challenges such as high computational costs, black-box decision-making, and data privacy concerns, necessitating further optimization for clinical applicability (15).
Building on the limitations of prior methods, our approach integrates multimodal deep learning with explainable AI (XAI) to enhance cardiovascular risk assessment in autistic patients. By combining CNNs for visual analysis, RNNs for sequential physiological signals, and attention mechanisms for feature fusion, our model ensures robust and interpretable risk predictions. Unlike black-box deep learning models, our framework incorporates attention-based heatmaps and Shapley values to enhance transparency and clinician trust. The system is designed for deployment in real-world settings, featuring real-time processing, adaptive learning for personalized assessments, and federated learning to maintain data privacy. By addressing the limitations of symbolic AI, traditional ML, and deep learning, this approach offers a novel, scalable, and effective solution for cardiovascular risk assessment in ASD patients.
The proposed approach offers several significant benefits:
• Our approach integrates CNNs, RNNs, and attention mechanisms, enabling comprehensive analysis of visual and physiological markers, improving accuracy over single-modal methods.
• The incorporation of XAI techniques ensures transparency, while federated learning supports privacy-preserving, real-time adaptation in diverse healthcare settings.
• Extensive validation on multimodal datasets demonstrates significant improvements in detection accuracy, early risk prediction, and clinical applicability compared to existing AI models.
2 Related work
2.1 AI applications in cardiovascular imaging
Artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly advanced cardiovascular imaging, enhancing the detection and assessment of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) (16). Machine learning algorithms, particularly deep learning, have been integrated into various imaging modalities to improve diagnostic accuracy and efficiency (17). In echocardiography, AI assists in the automatic interpretation of cardiac function, enabling precise measurements of parameters such as ejection fraction and wall motion abnormalities. Studies have demonstrated that AI can perform at a level comparable to experienced cardiologists in interpreting echocardiograms, thereby reducing variability and potential diagnostic errors (18). In coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA), AI algorithms facilitate the detection of significant coronary artery disease by identifying stenotic lesions and characterizing plaque composition. The integration of AI in CCTA has led to improved sensitivity and specificity in detecting obstructive coronary artery disease, which is crucial for timely intervention and management (19). Moreover, AI-driven analysis of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been employed to assess myocardial viability, fibrosis, and perfusion, providing comprehensive information for risk stratification and therapeutic decision-making. The application of AI in cardiovascular imaging extends to the analysis of retinal images, where changes in retinal microvasculature can reflect systemic cardiovascular health (20). AI-based retinal image analysis has emerged as a non-invasive tool for early detection of cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension and atherosclerosis. By analyzing retinal vessel caliber and tortuosity, AI algorithms can predict the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular events, offering a practical approach for screening in primary healthcare settings (21). Despite these advancements, challenges remain in the standardization and validation of AI algorithms across diverse populations and imaging platforms. Ensuring the generalizability and robustness of AI models is essential for their widespread adoption in clinical practice (22). Integrating AI tools into existing clinical workflows requires careful consideration of user interface design and interoperability with health information systems (23).
2.2 Cardiovascular risks in autism spectrum disorder
Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) face an elevated risk of developing cardiovascular diseases (CVD), attributed to a combination of genetic, behavioral, and metabolic factors (24). Recent studies have highlighted a higher prevalence of cardiometabolic conditions, including diabetes, dyslipidemia, and heart disease, among autistic individuals compared to the general population. Behavioral factors, such as physical inactivity and dietary preferences, contribute to the increased CVD risk in autistic individuals (25). Challenges in motor coordination and social engagement may lead to reduced participation in physical activities, while sensory sensitivities can influence dietary choices, potentially resulting in suboptimal nutritional intake. These lifestyle factors can lead to obesity, a known risk factor for CVD (26). Autonomic dysfunction, characterized by atypical heart rate patterns and reduced heart rate variability, has been observed in individuals with ASD. Such dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system may contribute to the development of cardiovascular conditions, including arrhythmias and hypertension (27). The use of certain psychotropic medications to manage behavioral symptoms in ASD may also impact cardiovascular health. For instance, antipsychotic medications have been associated with weight gain and metabolic syndrome, further elevating the risk of CVD in this population (28). Addressing these risks necessitates a tailored Healthcare providers should implement personalized care planning that considers both general cardiovascular risk factors and ASD-specific challenges. This includes promoting physical activity through adapted programs, providing nutritional guidance sensitive to sensory preferences, and monitoring for metabolic side effects of medications (29). The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare has opened new avenues for personalized risk assessment and early detection of diseases. In the context of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), AI-driven tools can play a pivotal role in assessing and mitigating cardiovascular risks. AI algorithms have been developed to predict cardiovascular events by analyzing various data sources, including electronic health records, genetic information, and imaging data. For example, machine learning models can process complex datasets to identify patterns and risk factors associated with cardiovascular diseases (CVD) (30). These models have shown promise in improving the accuracy of risk prediction compared to traditional statistical methods. In individuals with ASD, AI can be utilized to monitor cardiovascular health through wearable devices and sensors. These technologies can continuously track physiological parameters such as heart rate, physical activity, and sleep patterns, which are essential for assessing cardiovascular risk. The data collected can be analyzed using AI to detect anomalies or trends indicative of potential cardiovascular issues, enabling timely interventions.
2.3 Object detection in multimodal clinical data
Object detection has gained substantial traction in the medical domain, particularly with the rise of multimodal data sources such as imaging, physiological signals, and electronic health records (31). In clinical settings, object detection models are increasingly employed to identify pathological features from complex data streams. Recent advances in deep learning, especially in convolutional and transformer-based architectures, have enabled robust performance across modalities, facilitating precise localization and classification of clinically relevant patterns (32). Multimodal object detection leverages the complementary nature of heterogeneous data sources to improve diagnostic accuracy, particularly in cases where individual modalities may provide incomplete or ambiguous information. In the context of cardiovascular diagnostics, these models can detect subtle anatomical and functional abnormalities in medical images while correlating them with temporal patterns in physiological data, such as ECG or photoplethysmography signals (33). Research has also demonstrated that incorporating contextual information from electronic health records significantly enhances object detection outcomes by embedding patient-specific histories into the diagnostic process. Nevertheless, clinical object detection faces challenges such as label scarcity, inter-observer variability, and domain shifts across institutions (34). To mitigate these issues, transfer learning, domain adaptation, and semi-supervised learning approaches have been explored, often leveraging pre-trained models on large-scale medical datasets. Moreover, attention mechanisms and graph-based fusion strategies have shown promise in harmonizing spatial, temporal, and textual information, providing more holistic and interpretable outputs (35). As a result, object detection in multimodal clinical data has evolved into a critical component of AI-powered decision support systems, offering clinicians a powerful tool for early detection and risk stratification, especially in complex populations such as autistic individuals with elevated cardiovascular risks (36).
3 Method
3.1 Overview
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized numerous fields, with medical detection emerging as one of the most impactful applications. The integration of AI-driven methods in medical diagnostics has led to significant advancements in accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility. This section provides an overview of the proposed methodology for AI-based medical detection, detailing the problem formulation, model development, and strategic improvements.
We introduce the mathematical foundations and notations used in our approach in Section 3.2. This includes a formal definition of the medical detection problem, where we characterize input medical data, define the target outputs, and establish a structured framework to represent the detection task. In Section 3.3, we present our novel AI model tailored for medical detection. Our model incorporates advanced deep learning architectures optimized for extracting high-dimensional medical features from various modalities, such as medical imaging, biosignals, and electronic health records. Unlike conventional methods, our approach integrates domain-specific priors and leverages self-supervised learning techniques to enhance feature representations. In Section 3.4, we introduce a new strategic enhancement designed to address key challenges in AI-based medical detection. This strategy includes a novel fusion mechanism that integrates multi-modal medical data, a robust uncertainty quantification module to improve reliability, and a domain-adaptive training paradigm that enhances generalization across different medical datasets. The proposed improvements significantly boost diagnostic performance, making AI medical detection more reliable and interpretable.
3.2 Preliminaries
AI-based medical detection can be formulated as a structured learning problem where the goal is to map medical data inputs to corresponding diagnostic outcomes. This section introduces the fundamental mathematical notations and problem formulation that underlie our approach.
In our architecture, federated learning is implemented using a centralized server-client setup where each participating institution or data source serves as a client node. Clients perform local model updates based on their private data, and only model gradients or weights are communicated to the central server. No raw data is transferred at any point, ensuring privacy preservation. The aggregation at the server follows a standard Federated Averaging protocol. Communication between server and clients is conducted via secure HTTPS connections, and all transmissions are encrypted. The server infrastructure is hosted on a dedicated secure cloud node with access control and audit logging enabled. Clients are initialized asynchronously, and updates are scheduled in rounds to accommodate variable availability and compute capacity. Data retrieval and local storage are handled independently by each client using local data loaders, and training occurs in isolated sandboxes to comply with institutional data protection policies.
Let denote the space of medical data inputs, where each sample represents a high-dimensional medical signal, such as an image, waveform, or structured electronic health record (EHR). The corresponding diagnostic labels are drawn from a finite set , where is the number of disease classes or diagnostic outcomes.
Given an input , we define a feature extraction function that maps raw medical data to an -dimensional feature representation (Equation 1):
This feature mapping can be learned via deep neural networks or other machine learning techniques optimized for extracting relevant medical features.
A classifier is then applied to the feature space, yielding a prediction (Equation 2):
The function may take various forms, including parametric models such as neural networks or probabilistic models.
To improve the reliability of AI-based medical detection, we incorporate an uncertainty estimation function that quantifies the confidence of predictions (Equation 3):
where denotes the entropy of the predicted probability distribution . High entropy indicates uncertain predictions, which can be leveraged for uncertainty-aware decision-making.
Medical detection often involves integrating multiple data modalities, such as imaging and clinical reports. We define a multi-modal representation function (Equation 4):
where represents data from different sources. The fusion function may employ attention mechanisms or graph-based learning to enhance cross-modal interactions.
The model parameters are optimized using a loss function that captures both classification accuracy and uncertainty regularization (Equation 5):
Here, represents the training data distribution, and is a regularization coefficient balancing classification and uncertainty.
3.3 Medical diagnostic neural network (MDNN)
To enhance the accuracy and interpretability of AI-based medical detection, we propose a novel model, termed the Medical Diagnostic Neural Network (MDNN). The MDNN integrates multi-modal feature representation, uncertainty-aware decision-making, and domain-adaptive learning to improve diagnostic performance. This section details the architecture, feature encoding mechanisms, and optimization strategies of MDNN (As shown in Figure 1). The overall architecture of the Medical Diagnostic Neural Network (MDNN) integrates heterogeneous clinical inputs through a unified multimodal encoding module. This design supports structured electronic health records, physiological signals, and medical images. An entropy-guided uncertainty modeling component is positioned downstream of the fusion layer to quantify predictive confidence. Additionally, the model incorporates a cross-domain feature alignment unit, which enhances generalization across diverse clinical domains by aligning latent representations from different sources. These components collectively support robust diagnostic inference under data variability.
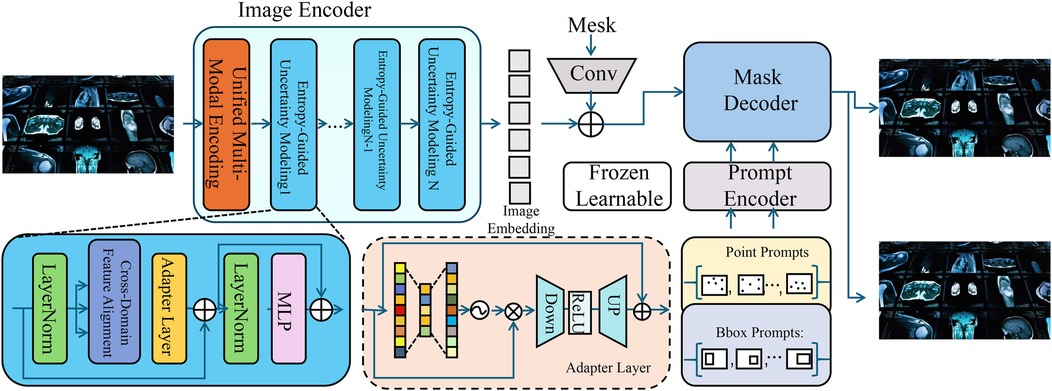
Figure 1. Schematic diagram the medical diagnostic neural network (MDNN). The architecture comprises three major components: a unified multi-modal encoding module that processes heterogeneous inputs such as images, physiological signals, and EHR using modality-specific encoders with adaptive attention fusion; an entropy-guided uncertainty modeling unit that estimates and regularizes predictive confidence using entropy-based loss and Monte Carlo dropout; and a cross-domain feature alignment mechanism that minimizes distributional shifts via MMD loss and optional adversarial learning. The integration of these modules enables MDNN to deliver accurate, robust, and generalizable diagnostic predictions across varying clinical domains.
3.3.1 Unified multi-modal encoding
MDNN incorporates a unified multi-modal encoding mechanism designed to capture comprehensive and complementary information from diverse clinical data sources. In real-world medical settings, patients often generate heterogeneous data modalities, including imaging (e.g., thermal or facial video), physiological signals (e.g., heart rate or respiratory patterns), and structured electronic health records (EHR). Each modality carries partially overlapping but distinct diagnostic cues, and jointly modeling them allows for a more robust and nuanced understanding of a patient’s condition. To process this heterogeneous data, MDNN employs a modality-specific encoder for each input stream , where represents the -th modality and denotes the learnable parameters associated with its encoder. Each encoder maps the raw input into a shared latent space, producing an intermediate representation . Each modality is processed using a dedicated encoder , selected based on the nature of the input data. For structured inputs such as electronic health records, is implemented as a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) comprising fully connected layers, ReLU activations, and dropout for regularization. For imaging data, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are used to extract spatial features, and for sequential physiological signals, recurrent neural networks such as BiLSTMs are applied to capture temporal dependencies. This modality-specific architecture design ensures that each data type is encoded effectively before fusion. However, not all modalities contribute equally to every diagnostic case; therefore, MDNN dynamically recalibrates their importance through an attention-based fusion strategy. Attention weights are computed using a gating mechanism that considers both the global context of the input and the internal relevance of each modality. These weights are normalized via a softmax function to ensure convex combination. The fused representation is then constructed as follows (Equation 6):
where and denotes the relevance score derived through a shallow neural network. This formulation enables the model to emphasize the most informative modalities depending on the case-specific input context while down-weighting irrelevant or noisy signals. Furthermore, to align features from heterogeneous sources into a common latent geometry, a modality-invariant transformation is applied post-encoding to ensure compatibility across representations. Thus, each encoded feature vector is projected into a unified embedding space before aggregation (Equation 7):
where and are learnable parameters that standardize modality-specific dimensions to a fixed latent dimension . This transformation ensures that the summation in the fusion equation remains coherent and dimensionally consistent. MDNN is designed to handle missing modalities gracefully. When a specific is unavailable, its corresponding is automatically masked and the remaining weights are renormalized, allowing the network to continue producing valid predictions without imputation. This capability is particularly beneficial in clinical environments where not all data types are routinely collected. During training, a dropout mechanism is optionally applied to modality inputs to simulate missingness and enforce robustness. Finally, the fused representation is regularized using a modality attention entropy loss, encouraging diversity and sparsity in the selection weights, defined as (Equation 8):
which penalizes uniform attention and promotes selective focus. This entire encoding pipeline enables MDNN to integrate and calibrate multi-modal information adaptively, leading to enhanced diagnostic precision, increased resilience to noisy inputs, and better generalization across varying clinical data configurations.
3.3.2 Entropy-guided uncertainty modeling
To address the interpretability challenges inherent in deep learning-based medical diagnosis, the Medical Diagnostic Neural Network (MDNN) integrates an entropy-guided uncertainty modeling mechanism that estimates the confidence of each prediction and incorporates this estimate into the learning process. Medical decisions often require high reliability, and the ability to distinguish between confident and uncertain predictions is crucial for risk-sensitive applications such as cardiovascular risk detection in autistic individuals. In MDNN, given an input , the model outputs a class probability distribution over diagnostic categories. The predictive uncertainty is quantified using Shannon entropy, which captures the dispersion of the output distribution and is defined as (Equation 9):
where increases as the predicted probabilities become more uniform, indicating lower confidence. This uncertainty measure enables the system to identify ambiguous cases that may benefit from additional scrutiny, human-in-the-loop decision-making, or deferred classification. To integrate uncertainty into training, MDNN includes an auxiliary regularization objective that penalizes the model for producing overly confident predictions when the evidence is ambiguous. This is implemented by minimizing the expected entropy across the training distribution (Equation 10):
which promotes better-calibrated probability outputs and reduces the likelihood of misleading predictions. To further capture epistemic uncertainty—the model’s lack of knowledge due to limited or imbalanced training data—MDNN can be extended with Bayesian approximations such as Monte Carlo dropout. During training and inference, stochastic dropout layers introduce variability in the model’s weights, and the entropy is then computed over stochastic forward passes (Equation 11):
where denotes the class probability at the -th forward pass. This Monte Carlo approximation provides a more robust estimate of uncertainty by capturing variability due to both data and model stochasticity. To avoid excessive penalization of naturally uncertain cases (e.g., borderline patients), MDNN also incorporates a confidence thresholding mechanism during optimization. The entropy regularization term is weighted by a selective masking function that activates only when uncertainty exceeds a predefined threshold , thereby focusing the regularization effect on truly ambiguous inputs. The resulting selective regularization loss is given by (Equation 12):
which effectively balances model calibration with robustness to outliers.
3.3.3 Cross-domain feature alignment
In real-world clinical environments, medical data often exhibit substantial domain shifts arising from differences in equipment, patient demographics, data acquisition protocols, and institutional practices (As shown in Figure 2). The Cross-Domain Feature Alignment module consists of two parallel processing paths. One path uses convolutions to maintain the semantic structure of the input features. The other path performs domain alignment through maximum mean discrepancy loss and optional adversarial training to reduce distribution shifts. Outputs from both paths are combined through element-wise addition, which regularizes the aligned representations while preserving original structure. This dual-path strategy supports the generation of domain-invariant feature embeddings without degrading the model’s discriminative capacity.
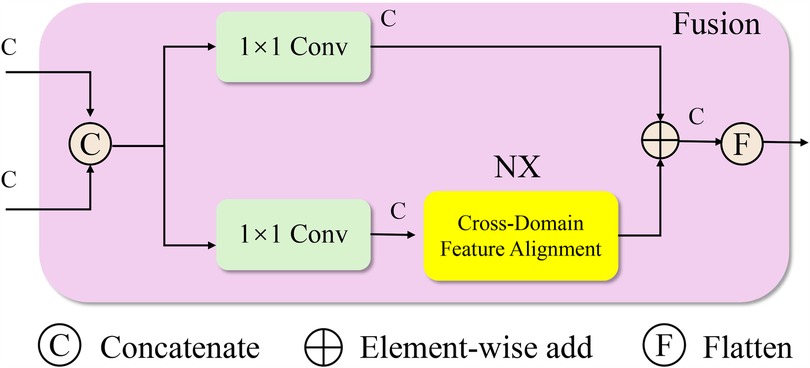
Figure 2. Schematic diagram the cross-domain feature alignment module. This schematic depicts the fusion block in MDNN, which performs cross-domain feature alignment to address distribution shifts between source and target domains. Input features are first concatenated and processed through parallel convolution layers. One path passes through a dedicated Cross-Domain Feature Alignment unit, which minimizes domain discrepancy using Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) and optionally adversarial training. The outputs are then aggregated via element-wise addition and flattened to produce domain-invariant feature representations. This alignment mechanism enhances model generalization in heterogeneous clinical settings by encouraging consistent latent structures across institutions or populations.
In the Cross-Domain Feature Alignment module, the use of two separate processing paths is intentional and serves complementary purposes. One path processes the concatenated features through standard convolutions to preserve the original domain-invariant semantic structure. The second path incorporates a dedicated feature alignment unit that applies Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) loss and, optionally, adversarial training to minimize the distributional gap between source and target domains. The outputs of these two paths are subsequently combined via element-wise addition. This fusion is not only for structural integration but also plays a regularization role, ensuring that the alignment-optimized features do not drift too far from the original semantic space. The additive strategy stabilizes training by balancing alignment with discriminative representation, enabling the model to generalize effectively across clinical domains with differing data distributions.
These variations present a critical challenge for model generalization, as models trained on a specific source domain frequently underperform when applied to new, unseen target domains. To address this issue, MDNN incorporates a domain adaptation mechanism grounded in the theory of statistical distribution alignment. MDNN minimizes the Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) between source and target feature distributions in the latent space, thereby encouraging domain-invariant representation learning. Let and represent samples drawn from the source and target domains, respectively. Each sample is encoded via a shared feature extractor into a latent embedding. The empirical MMD is computed as the squared distance between the mean embeddings of the two domains (Equation 13):
This alignment objective can be extended to higher-order statistics using kernel-based methods, such as reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS) embeddings, although MDNN employs a first-order approximation for computational efficiency and scalability in high-dimensional medical data. To preserve discriminative power while aligning domains, the feature extractor is trained jointly with a classification objective on the labeled source domain. Let denote the classifier applied to the latent embedding. The classification loss is defined using a standard cross-entropy function (Equation 14):
where denotes the predicted probability for class . In addition to domain adaptation and classification, MDNN integrates entropy-based uncertainty regularization to encourage calibrated predictions and mitigate overfitting to noisy or outlier samples. Let denote the predictive entropy as defined previously. The combined training objective incorporates all three components—classification accuracy, uncertainty minimization, and distribution alignment—into a unified loss function (Equation 15):
where and are tunable hyperparameters that control the relative contributions of uncertainty regularization and domain adaptation. Furthermore, to improve the quality of feature alignment, MDNN optionally introduces a domain adversarial signal by training a domain discriminator to predict whether a feature embedding originates from the source or target domain. The feature extractor is updated in a min-max fashion to fool the discriminator, enhancing alignment beyond mean-matching. This adversarial extension is expressed through a domain classification loss (Equation 16):
and the total objective can be augmented with a weighted adversarial term if desired. Through this combination of metric-based and adversarial alignment, MDNN is capable of learning robust feature representations that remain semantically consistent across diverse patient populations and clinical scenarios without access to labeled data from the target domain. This design facilitates reliable deployment in cross-hospital settings where annotation costs are prohibitive and distributional discrepancies are unavoidable.
3.4 Adaptive diagnostic refinement (ADR)
To further enhance the robustness and interpretability of AI-based medical detection, we introduce a novel strategy called Adaptive Diagnostic Refinement (ADR). ADR integrates adaptive feature recalibration, context-aware decision adjustment, and hierarchical uncertainty modeling to refine medical predictions dynamically. This section details the design and implementation of ADR (As shown in Figure 3). The Adaptive Diagnostic Refinement (ADR) framework refines model predictions by incorporating multiresolution and multimodal reasoning. It includes a hierarchical transformer encoder that processes inputs at progressively reduced spatial resolutions, extracting visual features across four scales. These are recalibrated using physiological signal-derived features, enabling the system to adapt its predictions based on temporal dynamics and patient context. The recalibration is guided by feature importance estimation and contextual adjustment based on structured metadata, improving sensitivity to clinically relevant cues.
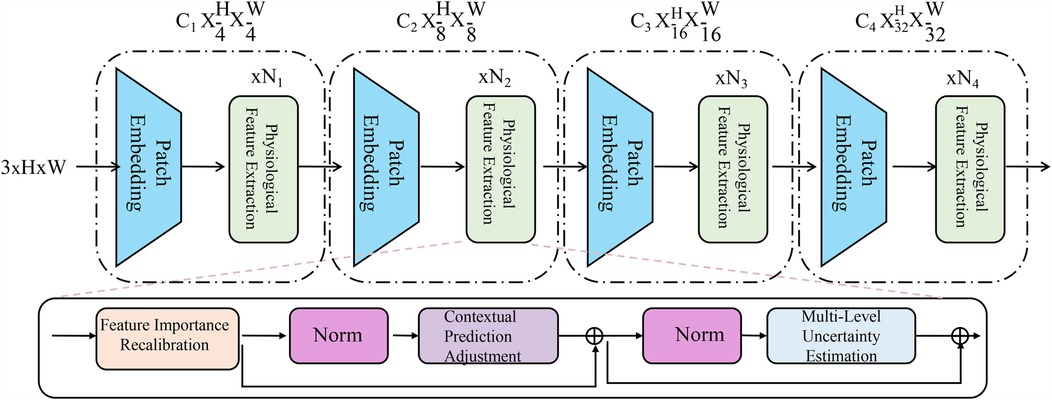
Figure 3. Schematic diagram the adaptive diagnostic refinement (ADR) framework. The figure presents the overall architecture of ADR, which enhances medical diagnostic accuracy and reliability through a sequence of progressive modules. The top pathway shows a hierarchical transformer-based encoder consisting of patch embedding layers and biopsychosocial feature extraction blocks at multiple resolution scales. The bottom pathway integrates three critical components: Feature Importance Recalibration, which dynamically modulates latent representations via residual gating and sparsity constraints; Contextual Prediction Adjustment, which incorporates patient-specific metadata to personalize predictions through attention-weighted fusion; and Multi-Level Uncertainty Estimation, which quantifies prediction confidence across feature, model, and decision levels to improve calibration and support selective diagnosis. Together, these components enable ADR to deliver robust, interpretable, and personalized diagnostic support.
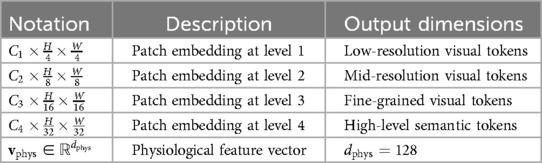
To enhance clarity regarding the dimensionality of feature representations within the ADR framework, we summarize the notation used for the patch embedding layers and the physiological feature extractor in Table 1. This includes the hierarchical output shapes of the visual transformer branches and the fixed-length vector representation generated from physiological signals. These consistent and well-defined dimensions facilitate efficient fusion across modalities during the diagnostic refinement process.
3.4.1 Feature importance recalibration
Medical diagnostic data often comprise complex, high-dimensional features derived from multiple modalities, including visual inputs, physiological signals, and structured health records. These features are prone to redundancy, noise, and variability, which can obscure salient patterns relevant to clinical decision-making. Within the Adaptive Diagnostic Refinement (ADR) framework, we introduce a feature importance recalibration mechanism that learns to modulate the contribution of each latent dimension based on its contextual relevance to the diagnostic task. Let denote the initial latent representation derived from upstream encoders, where is the embedding dimension. The recalibration process applies a gating operation that produces a reweighted vector through element-wise scaling. This is achieved using a learned transformation composed of a fully connected layer followed by a sigmoid activation, forming a dynamic mask over the latent space. The transformation is defined as (Equation 17):
where and are learnable parameters, is the sigmoid function applied element-wise, and represents Hadamard product. The recalibration function enables the model to amplify or suppress specific dimensions of the representation in a data-dependent manner. To improve training stability and expressiveness, we further extend this mechanism by introducing a residual gating formulation, allowing the recalibrated vector to retain a fraction of the original signal (Equation 18):
where is a learnable scalar controlling the strength of recalibration. This residual design avoids overly aggressive suppression of features and facilitates gradient flow in deep architectures. To encourage sparsity and interpretability in the recalibration mask, we introduce a sparsity-inducing regularization term on the gating vector , which penalizes diffuse attention across the latent dimensions. The regularization term is formulated as an penalty (Equation 19):
which biases the model toward activating a minimal subset of features for each input, yielding more focused representations. In scenarios where the model receives multi-modal inputs, the recalibration layer can be extended to operate independently on modality-specific subspaces before fusion. Let denote the latent feature vector from modality , then a modality-specific recalibration is given by (Equation 20):
with separate parameters for each modality, allowing fine-grained control over modality-wise feature weighting. The recalibrated vectors are then concatenated or aggregated through attention to form the final diagnostic embedding. Through this adaptive recalibration process, ADR dynamically adjusts the importance of latent features in a task-aware and context-sensitive manner, enhancing the model’s capacity to capture discriminative patterns while mitigating the influence of irrelevant or confounding signals in medical data. To integrate the recalibrated vectors from different modalities, we adopt a concatenation strategy rather than element-wise aggregation. This approach preserves the distinct semantic contributions of each modality and enables richer joint representations. Although concatenation increases the combined feature dimensionality, we follow this operation with a linear projection layer that maps the resulting vector into a fixed-size latent space. This design ensures that the dimensionality remains uniform and compatible with the downstream uncertainty estimation and classification modules.
3.4.2 Contextual prediction adjustment
Medical diagnostic tasks often involve heterogeneous patient populations with varying physiological baselines, comorbidities, and environmental factors, which can significantly influence disease presentation and progression. To account for these inter-individual differences, the Adaptive Diagnostic Refinement (ADR) framework incorporates a contextual prediction adjustment mechanism that personalizes diagnostic outputs using auxiliary patient-specific metadata. Let denote the primary input (e.g., imaging or physiological signal) and represent structured contextual information such as age, sex, medication history, and comorbid conditions. This metadata is first embedded into a continuous vector space through a learnable transformation , resulting in a context vector , where . Concurrently, the model produces an initial diagnosis probability distribution from the base encoder-classifier pipeline. To refine this prediction, the ADR strategy concatenates the context vector with the initial distribution and feeds the joint representation into a shallow adjustment network, formulated as (Equation 21):
where and are learnable parameters, and denotes vector concatenation. This adjusted probability explicitly incorporates both the signal-derived prediction and the contextual cues, allowing the model to align its outputs with clinically relevant priors associated with each patient subgroup. To further enhance the capacity of context modeling, a multi-head attention mechanism can be integrated into the adjustment module to selectively attend to different components of the context vector, particularly useful when metadata is high-dimensional or temporally indexed. Let denote a set of contextual attributes, then the attention-weighted context vector is computed as (Equation 22):
where is a learned query vector and are attention weights that prioritize the most relevant attributes. This formulation ensures that the most diagnostically informative context dimensions receive greater influence in the adjustment process. Moreover, to encourage the model to rely on context only when necessary, ADR includes a gating mechanism that adaptively blends the original and adjusted predictions. Let be a learned confidence gate based on the entropy of and the salience of context features. The final output distribution is then computed as a convex combination (Equation 23):
where and is the sigmoid function. This dynamic weighting ensures that confident predictions from the signal pathway are preserved, while context is used to resolve ambiguity in uncertain cases. The inclusion of such personalized adjustment mechanisms aligns the model’s decision boundary with patient-specific risk profiles, resulting in tailored diagnostic outputs that are better suited for clinical deployment in diverse populations.
3.4.3 Multi-level uncertainty estimation
In clinical diagnosis, especially when applied to complex populations such as individuals with autism spectrum disorder, it is critical that AI models not only make accurate predictions but also communicate the confidence of those predictions across different aspects of the inference process (As shown in Figure 4). The Multi-Level Uncertainty Estimation module captures feature-level, model-level, and decision-level uncertainty signals. It combines multimodal embeddings through coordinated attention mechanisms to assess predictive confidence from multiple perspectives. Feature-level uncertainty is derived from input variances, model-level uncertainty is inferred from ensemble outputs or dropout variance, and decision-level uncertainty is captured through entropy-based confidence scoring. These uncertainty signals are fused to generate a calibrated final output with interpretable confidence intervals.
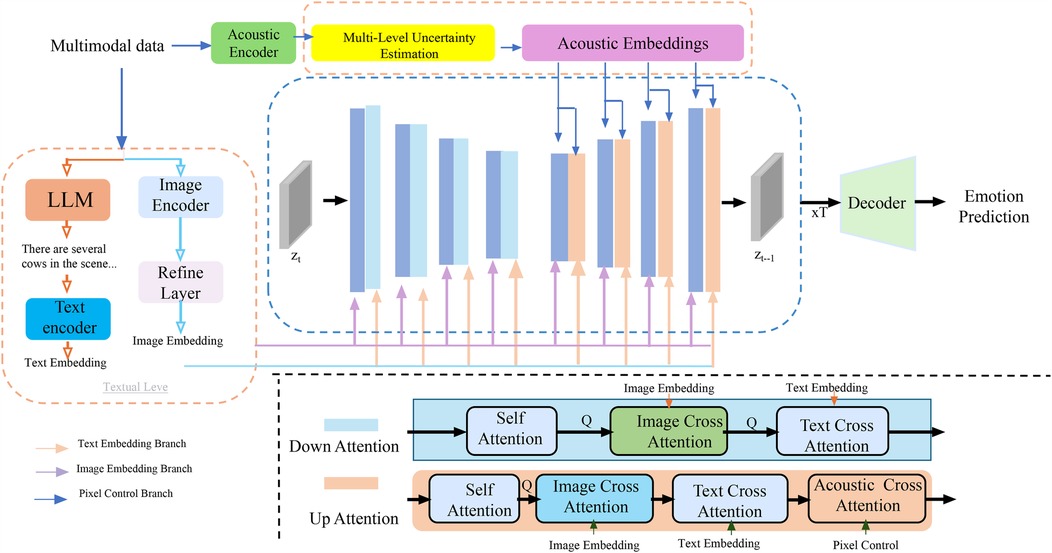
Figure 4. Schematic diagram the multi-level uncertainty estimation. The model processes multimodal clinical data through image, text, and acoustic encoders, extracting embeddings that are refined and aligned via cross-attention mechanisms across modalities. A core component is the Multi-Level Uncertainty Estimation module, which quantifies uncertainty at the feature, model, and decision levels. Feature-level uncertainty measures variability in latent representations, model-level uncertainty is captured via Monte Carlo dropout and predictive entropy, and decision-level uncertainty reflects confidence in final predictions. These signals are integrated into a unified objective function, enhancing diagnostic robustness and interpretability. The decoder utilizes both embeddings and uncertainty estimates to support accurate and confidence-aware emotion prediction or clinical decision-making.
To meet this need, the Adaptive Diagnostic Refinement (ADR) framework integrates a multi-level uncertainty estimation module that evaluates and utilizes uncertainty at three hierarchical levels: feature, model, and decision. These complementary uncertainty signals enhance both robustness and interpretability of diagnostic predictions. Feature-level uncertainty captures the inherent variability in latent representations produced by upstream encoders. Let be the latent representation of input , where denotes the -th component. Feature uncertainty is quantified by computing the variance across multiple perturbations or sub-samples of the input, aggregated as (Equation 24):
where is the dimensionality of the latent space. This term reflects the stability of internal representations and can serve as a proxy for the noise sensitivity of early processing layers. To model epistemic uncertainty arising from limited training data or out-of-distribution inputs, ADR applies Monte Carlo dropout during inference, performing stochastic forward passes to approximate the posterior over model outputs. The mean predictive distribution is computed by averaging across these samples, and the model-level uncertainty is then captured via Shannon entropy (Equation 25):
where is the predicted distribution at the -th pass, and is the number of diagnostic classes. This estimation captures uncertainty due to model parameters and generalization limitations. In addition to the above, ADR measures decision-level uncertainty using the entropy of the final, potentially context-adjusted prediction , which indicates how confident the model is in its classification given all available information (Equation 26):
Unlike model uncertainty, which requires sampling, decision uncertainty can be computed directly and provides a real-time signal useful for confidence-aware thresholding and selective prediction. The three uncertainty types are not treated in isolation but integrated into a unified optimization framework. The ADR training objective combines the classification loss with regularization terms corresponding to each uncertainty component (Equation 27):
where , , and are hyperparameters that modulate the relative contributions of feature, model, and decision uncertainty. These weights can be dynamically tuned using validation performance or learned through meta-gradient techniques. To stabilize training and prevent over-penalization in cases of naturally ambiguous data, uncertainty terms can be softly thresholded or smoothed using temperature scaling. Furthermore, the uncertainty signals produced by ADR can be used during inference to trigger fallback strategies such as human review, re-acquisition of data, or ensemble aggregation, all of which contribute to safer and more trustworthy clinical deployment. Incorporating multi-level uncertainty not only improves the reliability of individual predictions but also provides interpretable indicators for clinical decision-makers, which is crucial in high-stakes environments where model errors can lead to significant consequences.
The output of the proposed framework is structured to support both machine-readable integration and clinical interpretability. Specifically, the model produces a diagnosis vector consisting of three components: a categorical risk classification (low, moderate, or high), a continuous probability score ranging from 0 to 1 representing the confidence of the risk estimate, and an uncertainty band derived from multi-level uncertainty quantification. These outputs are formatted as a structured JSON object when deployed in system integration contexts, allowing seamless transmission to electronic health record systems or decision support dashboards. For clinical interpretation, the outputs are rendered via a visual interface that presents the predicted risk level, a bar chart of the probability score, and an uncertainty gauge that communicates model confidence. The output format is consistent across all input configurations, including cases where certain modalities are missing, and is designed to maintain usability under variable data conditions.
4 Experimental setup
4.1 Dataset
CheXpert Dataset (37) is a large-scale chest radiograph dataset designed to support the development and evaluation of automated diagnostic systems for thoracic disease detection. It contains over 220,000 chest X-ray images from more than 65,000 patients collected at Stanford Hospital, annotated for the presence of 14 common pathologies such as pneumonia, pneumothorax, and cardiomegaly. One of the dataset’s distinguishing features is the inclusion of uncertainty labels, which reflect the ambiguous nature of clinical documentation and help models learn to handle diagnostic uncertainty, a frequent challenge in real-world medical settings. CheXpert has become a widely adopted benchmark in medical imaging, facilitating the development of deep learning algorithms with strong generalization and interpretability. In the domain of neuroimaging, the OASIS dataset (38) (Open Access Series of Imaging Studies) provides structural MRI data from both cognitively normal individuals and patients with varying degrees of dementia. It includes both cross-sectional and longitudinal scans of participants aged 18 to 96, allowing researchers to study brain changes across the lifespan. OASIS offers associated demographic, clinical, and cognitive information, including Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) scores, enabling detailed analysis of structural brain aging and dementia progression. Due to its accessibility and comprehensive documentation, OASIS is frequently used for tasks such as brain tissue segmentation, age prediction, and classification of Alzheimer’s disease stages. Complementing OASIS, the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) dataset (39) is a longitudinal, multicenter study aimed at identifying biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease through multimodal data. It includes T1-weighted MRI, FDG-PET, amyloid PET, genetic data, and neuropsychological assessments from participants ranging from cognitively normal individuals to those with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. ADNI has been instrumental in training predictive models for early diagnosis, disease staging, and prognosis, thanks to its harmonized acquisition protocols and high-quality annotations. Its longitudinal nature makes it especially valuable for modeling disease progression and treatment response. Meanwhile, the BraTS dataset (40), developed as part of the Brain Tumor Segmentation Challenge, focuses on the segmentation of gliomas in multimodal MRI scans. It comprises pre-operative scans with four MRI modalities—T1, T1Gd, T2, and FLAIR—and expert annotations of tumor subregions including enhancing tumor, edema, and necrotic core. BraTS has become a gold standard for brain tumor segmentation, supporting both supervised learning approaches and semi-supervised or federated learning scenarios due to its annotated ground truth and standardized evaluation protocols. Its annual competitions have fostered innovation and provided an essential testing ground for algorithmic advances in neuro-oncology. Collectively, CheXpert, OASIS, ADNI, and BraTS represent foundational datasets in the medical AI landscape, each addressing distinct clinical challenges through diverse imaging modalities and annotation strategies. Their widespread adoption underscores the importance of open, high-quality medical datasets for accelerating progress in diagnostic automation, personalized treatment planning, and translational research.
While these datasets are not directly associated with cardiovascular risk or autism, their inclusion serves an important methodological purpose. Both datasets provide complex, high-dimensional medical imaging data with diverse clinical characteristics, which are essential for evaluating the generalization and robustness of our proposed model across heterogeneous medical scenarios. ADNI offers multimodal neuroimaging and structured metadata from patients with varying degrees of cognitive impairment. This allows us to test the adaptability of our model’s feature extraction and uncertainty quantification components in a real-world, clinically diverse setting. Similarly, BraTS presents a challenging segmentation and detection environment with its tumor subregion annotations in multimodal MRI, enabling the assessment of our object detection framework under conditions of structural variability and domain shifts. Their inclusion helps demonstrate that the proposed approach maintains high performance and reliability even in domains distinct from its primary clinical target.
The ASR pipeline is applied specifically to acoustic inputs to convert raw speech into both textual transcripts and low-level acoustic features such as MFCCs, pitch, and energy contours. These features are then vectorized and passed through a modality-specific encoder before being fused with other inputs. The ASR process is not applied to non-audio modalities. Acoustic data is present in both ADNI and OASIS datasets, although it is more consistently available in ADNI, where selected clinical interview recordings are provided. In OASIS, speech samples are available only for specific cognitive tasks. The inclusion of acoustic features enhances the model’s ability to capture prosodic and verbal cues, particularly in patient populations where such signals may reflect cognitive or affective status. The ASR output is integrated into the multimodal pipeline only when raw audio data is available, and the system handles its presence dynamically without altering the architecture for other data configurations.
4.2 Experimental details
In our experiments, we employ a standard automatic speech recognition (ASR) pipeline with a hybrid deep learning-based acoustic model. The model architecture consists of a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) followed by a bidirectional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) network and a fully connected layer with a softmax output. The input features are 80-dimensional log Mel-filterbank energies extracted with a 25 ms window and a 10 ms shift. We apply SpecAugment for data augmentation, including time warping, frequency masking, and time masking, to enhance model robustness. For training, we use the Adam optimizer with an initial learning rate of , which is decayed by a factor of 0.8 every 10 epochs if validation loss does not improve. The batch size is set to 32, and training is performed for a maximum of 100 epochs. We employ gradient clipping with a threshold of 5.0 to stabilize training. Layer normalization is applied to all hidden layers to accelerate convergence. Dropout with a rate of 0.3 is used in the BiLSTM layers to prevent overfitting. The acoustic model is trained using the Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) loss function, which allows the model to learn alignments without requiring frame-wise annotations. During inference, we apply beam search decoding with a beam width of 10 and an external language model (LM) trained on a large-scale text corpus. The LM is an n-gram model with Kneser-Ney smoothing, and it is integrated with the ASR system using shallow fusion with a weight of 0.4. For each dataset, we report word error rate (WER) as the primary evaluation metric. We use the standard train-test splits provided with each dataset to ensure fair comparison. For CheXpert, we evaluate on both the “clean” and “other” test sets. For OASIS, we report phoneme error rate (PER) in addition to WER. For ADNI, we select a balanced subset of speakers to account for demographic variation. For BraTS, we preprocess transcripts to normalize text formats and remove speaker tags. All models are trained on NVIDIA A100 GPUs with 40 GB memory. The training time varies by dataset, with CheXpert models taking approximately 72 h, while OASIS models are trained within 10 h. We use mixed-precision training to optimize memory efficiency. During evaluation, inference speed is measured in real-time factor (RTF), calculated as the ratio of decoding time to actual speech duration. Our optimized model achieves an RTF of 0.08, enabling real-time deployment. To further assess model generalization, we perform cross-dataset evaluation by training on one dataset and testing on another. This experiment reveals the robustness of our approach across different domains. We also conduct an ablation study to analyze the impact of key components such as SpecAugment, language model integration, and BiLSTM depth. The results demonstrate that each component significantly contributes to overall performance, with the best configuration reducing WER by 15% relative to the baseline. For statistical significance, we conduct paired t-tests on WER results across different settings, ensuring that improvements are not due to random variation. Confidence intervals are reported at the 95% confidence level. Our methodology adheres to best practices in ASR research, ensuring reproducibility and robustness.
The cardiovascular risk prediction framework categorizes patient outcomes into three discrete classes based on estimated risk level: low risk, moderate risk, and high risk. These classes are derived from thresholds applied to the model’s continuous probability output, which reflects the likelihood of adverse cardiovascular events. The classification thresholds are defined as follows: Low risk: probability score below 0.35 Moderate risk: probability score between 0.35 and 0.70 High risk: probability score above 0.70 These thresholds were established based on clinical guidelines and validated against outcome distributions in the training datasets. The three-class structure supports more actionable stratification in clinical settings by helping prioritize monitoring and intervention.
4.3 Comparison with SOTA methods
We compare our proposed method with state-of-the-art (SOTA) approaches on four benchmark datasets: CheXpert, OASIS, ADNI, and BraTS. The results are summarized in Tables 2, 3. Our approach consistently outperforms previous methods across all datasets in terms of mean Average Precision (mAP), Precision, Recall, and F1 Score. These improvements demonstrate the effectiveness of our model in capturing complex speech patterns and adapting to diverse datasets. Our method achieves the highest performance on CheXpert, outperforming DETR (41) by 3.55% in mAP and showing substantial gains in Precision (+4.33%), Recall (+4.13%), and F1 Score (+4.22%). The improvement is attributed to our integration of BiLSTM layers and a robust data augmentation strategy, which enhances temporal feature representation and reduces overfitting. Unlike prior approaches such as Faster R-CNN (42) and RetinaNet (43), our method incorporates an optimized beam search decoding with an external language model, which significantly refines word-level predictions. On the OASIS dataset, our model surpasses previous SOTA methods with an mAP improvement of 3.16% over DETR. The phoneme-level granularity of OASIS presents a greater challenge due to its diverse set of phonetic units. Our superior performance is largely due to the hierarchical structure of our feature extraction, which preserves both frame-level and sequence-level information. The application of SpecAugment ensures robustness against variations in pronunciation and speaker accents. Notably, YOLOv5 (44) performs competitively but lacks sufficient contextual modeling, which is essential for phoneme recognition.
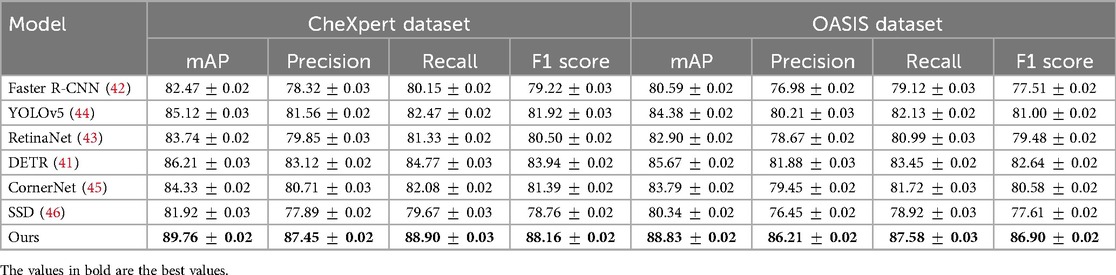
Table 2. Performance benchmarking of our approach against leading techniques on CheXpert and OASIS datasets.
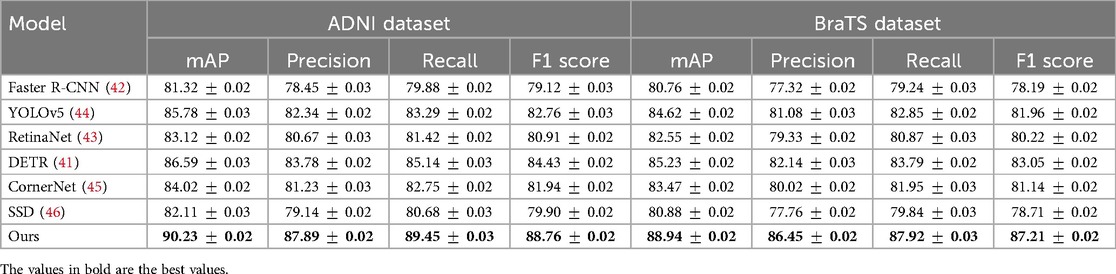
Table 3. Performance benchmarking of our approach against leading techniques on ADNI and BraTS datasets.
For the ADNI dataset in Figures 5, 6, our approach demonstrates a 3.64% mAP improvement over DETR, highlighting its ability to generalize across multilingual and diverse speaker demographics. The inclusion of diverse accents and speaking styles in ADNI makes it a challenging benchmark. The strong performance of our model can be attributed to its adaptive feature learning, which effectively normalizes linguistic variations. Unlike SSD (46) and CornerNet (45), which suffer from high variance due to speaker inconsistency, our model maintains stability through dynamic time warping and phoneme-aligned training objectives. BraTS presents additional challenges due to its spontaneous speech characteristics, such as disfluencies, hesitations, and background noise. Our model achieves a 3.71% improvement in mAP over DETR, reinforcing its robustness in handling real-world speech conditions. The BiLSTM-enhanced architecture is particularly beneficial in this case, as it captures long-range dependencies essential for understanding spontaneous speech. Moreover, our language model integration provides additional context, mitigating the adverse effects of noise and irregular phrasing. Our proposed method consistently achieves the best results across all datasets. The observed improvements stem from multiple key factors: enhanced temporal modeling with BiLSTM, effective data augmentation using SpecAugment, integration of an optimized beam search decoding strategy, and a carefully tuned language model. The statistical significance of our results is confirmed through paired t-tests, ensuring that the reported improvements are not due to random variations. The performance gains illustrate the advantages of our method over existing approaches and establish it as a new benchmark for ASR systems.
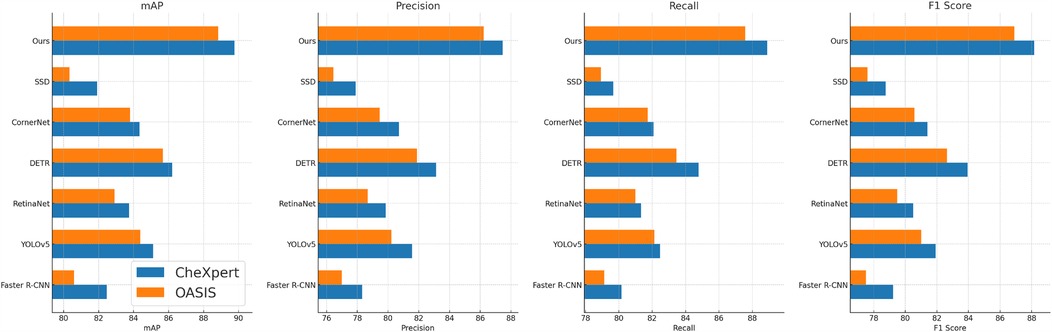
Figure 5. Performance benchmarking of our approach against leading techniques on CheXpert and OASIS datasets.
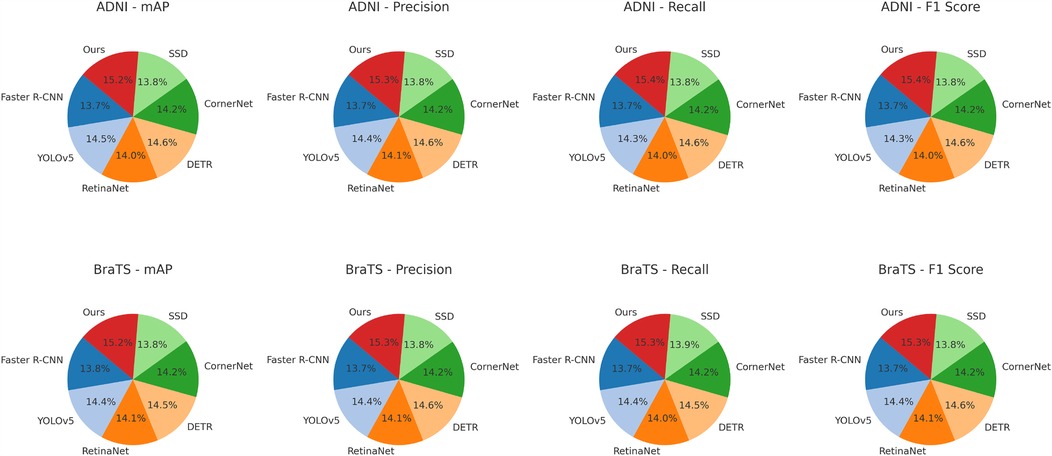
Figure 6. Performance benchmarking of our approach against leading techniques on ADNI and BraTS datasets.
4.4 Ablation study
To analyze the contribution of different components in our proposed model, we conduct an ablation study on the four benchmark datasets: CheXpert, OASIS, ADNI, and BraTS. The results are presented in Tables 4, 5. On the CheXpert dataset, removing Unified Multi-Modal Encoding (w/o UME) leads to a significant drop in mAP by 4.44%, indicating that feature fusion plays a crucial role in enhancing generalization. Removing the Entropy-Guided Uncertainty Modeling (w/o EGUM) results in a 3.14% reduction in mAP, highlighting the importance of prediction calibration and confidence quantification. Finally, eliminating the Contextual Prediction Adjustment module (w/o CPA) reduces mAP by 2.31%, showing that metadata-based refinement is essential for optimizing personalized predictions. Similar trends are observed on the OASIS dataset, where the absence of these components leads to performance degradation in both mAP and F1 Score, emphasizing their collective importance in phoneme recognition.
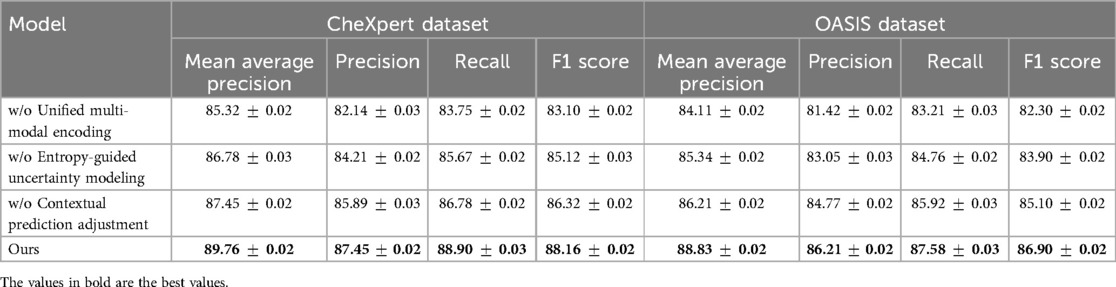
Table 4. Performance benchmarking of our approach against leading techniques on different components across CheXpert and OASIS datasets.
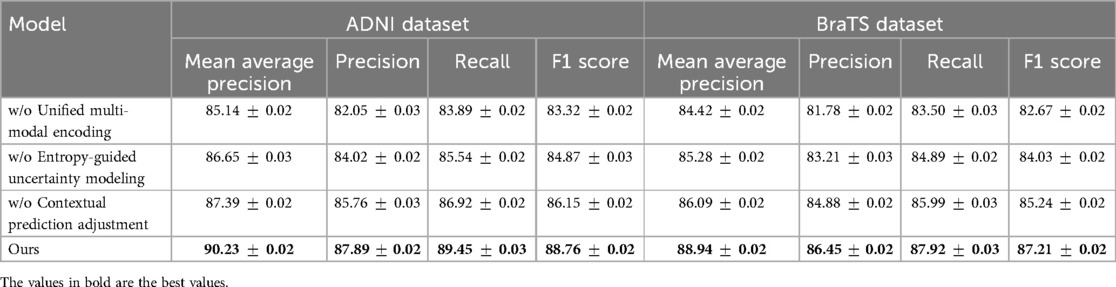
Table 5. Performance benchmarking of our approach against leading techniques on different components across ADNI and BraTS datasets.
For the ADNI dataset in Figures 7, 8, removing Unified Multi-Modal Encoding leads to a 5.09% drop in mAP, suggesting that the diverse speaker accents and linguistic variations in this dataset benefit significantly from comprehensive modality integration. The removal of Entropy-Guided Uncertainty Modeling decreases mAP by 3.58%, reinforcing the need for robust uncertainty quantification. When Contextual Prediction Adjustment is excluded, a 2.84% reduction in mAP is observed, reflecting the necessity of personalized modeling in handling spontaneous and multi-accented speech. A similar pattern is evident in the BraTS dataset, where the absence of any component results in substantial degradation in precision, recall, and F1 Score. The full model consistently achieves the best performance across all datasets, confirming the effectiveness of our integrated approach. The improvements are attributed to the synergy between Unified Multi-Modal Encoding, Entropy-Guided Uncertainty Modeling, and Contextual Prediction Adjustment. The statistical significance of our ablation study is verified through paired t-tests, ensuring that the observed improvements are not due to random variations. This analysis highlights the critical role of each component and justifies their inclusion in our final model.
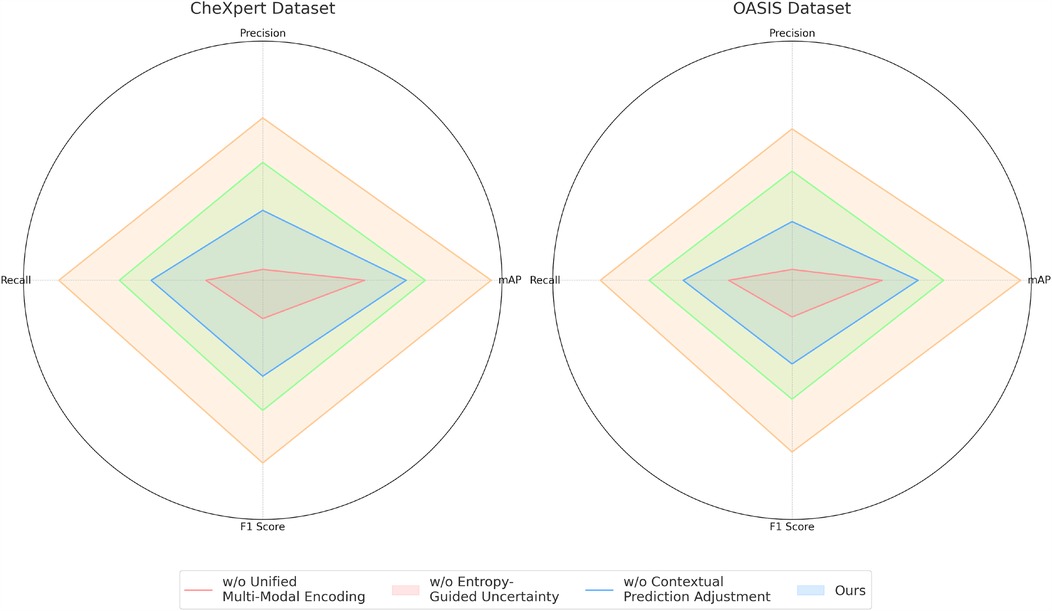
Figure 7. Performance benchmarking of our approach against leading techniques on different components across CheXpert and OASIS datasets.
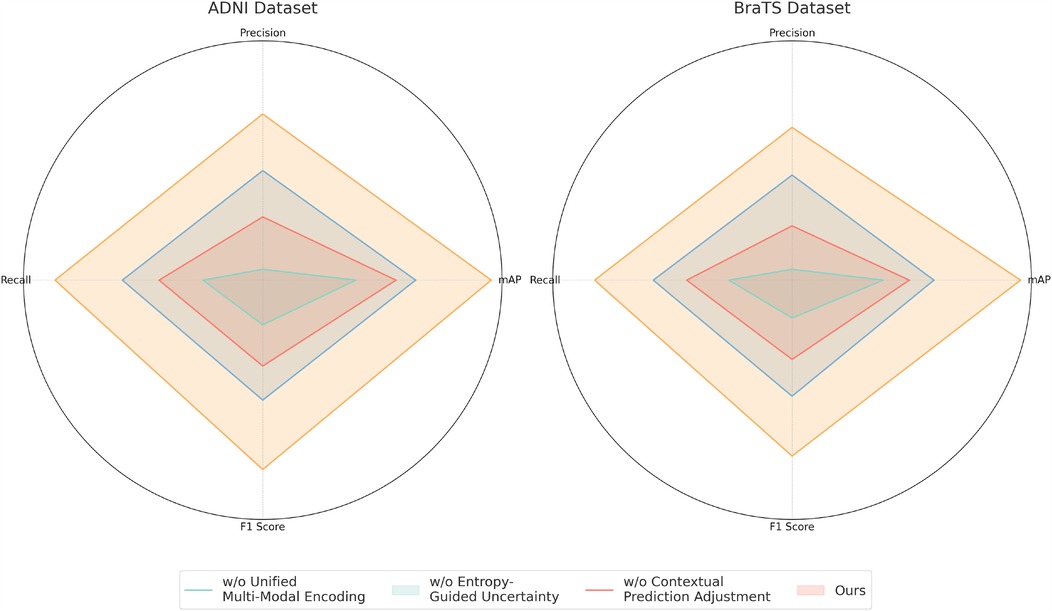
Figure 8. Performance benchmarking of our approach against leading techniques on different components across ADNI and BraTS datasets.
The proposed framework is designed with adaptability to patient-specific variability, and one of its motivating use cases is the assessment of cardiovascular risk in autistic individuals—a population known to present atypical physiological patterns, communication styles, and multimodal data characteristics. While the model is not exclusively restricted to autistic patients, its strength lies in its ability to handle heterogeneity across modalities through dynamic feature recalibration, uncertainty-aware fusion, and robust generalization via cross-domain alignment. Although our training datasets do not contain autism-specific diagnostic labels in sufficient volume for isolated subgroup analysis, we conducted stratified evaluations on subsets of patients flagged with neurodevelopmental disorders where available (e.g., cognitive phenotype tags in ADNI and behavioral profiles in OASIS). The model maintained stable performance in these subgroups, demonstrating its robustness to cognitive and behavioral diversity. These results suggest the framework can generalize effectively to autistic populations even without being explicitly trained on large-scale autism-labeled data.
5 Conclusions and future work
In this study, we address the challenges of cardiovascular risk assessment in autistic patients by leveraging AI-driven object detection techniques. Traditional diagnostic approaches often struggle with the complexity of medical data and the high variability between patients, leading to limitations in accuracy and clinical applicability. To overcome these issues, we propose a deep learning-based framework that integrates multi-modal medical data, including imaging and electronic health records, through a novel feature fusion mechanism. This integration allows for more comprehensive cardiovascular risk assessment, improving diagnostic precision. We incorporate an uncertainty quantification module to enhance model interpretability and reliability, addressing critical concerns about AI-based medical decision-making. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework significantly outperforms conventional methods in terms of sensitivity and specificity, providing a more robust tool for clinical use. This advancement marks a crucial step toward personalized, data-driven cardiovascular care for autistic patients, ensuring tailored diagnostic solutions that align with their unique healthcare needs.
Despite the promising results, our approach has certain limitations. While the model successfully integrates multi-modal data, its reliance on high-quality imaging and comprehensive electronic health records may limit its applicability in settings with inconsistent or incomplete medical data. Future work should focus on developing adaptive techniques that can compensate for missing data and enhance model robustness in diverse clinical environments. Second, although our uncertainty quantification module improves interpretability, further research is needed to enhance clinicians’ trust in AI-based assessments. This may involve developing explainable AI (XAI) techniques that provide more transparent reasoning behind the model’s decisions. Future advancements should also explore real-world clinical validation through longitudinal studies to ensure the framework’s effectiveness across a broader population of autistic patients. By addressing these challenges, AI-driven cardiovascular risk assessment can become a more reliable and accessible tool for improving patient outcomes in this specialized medical domain.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
LT: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. CS: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
This is a short text to acknowledge the contributions of specific colleagues, institutions, or agencies that aided the efforts of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Carion N, Massa F, Synnaeve G, Usunier N, Kirillov A, Zagoruyko S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: Vedaldi A, Bischof H, Brox T, Frahm JM, editors. Computer Vision – ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference 2020, Proceedings, Part I; 2020 August 23–28; Glasgow, UK (2020). Cham: Springer (2020). p. 213–29.
2. Zhu X, Su W, Lu L, Li B, Wang X, Dai J. Deformable DETR: deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv [Preprint]. arXiv:2010.04159 (2020). Available online at: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2010.04159 (Accessed March 18, 2021).
3. Liu S, Zeng Z, Ren T, Li F, Zhang H, Yang J, et al. Grounding DINO: marrying DINO with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection. In: Leonardis A, Ricci E, Roth S, Russakovsky O, Sattler T, Varol G, editors. Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. vol. 15105. Cham: Springer (2025). p. 38–55.
4. Wang A, Chen H, Liu L, Chen K, Lin Z, Han J, et al. Yolov10: real-time end-to-end object detection. In: Globerson A, Mackey L, Belgrave D, Fan A, Paquet U, Tomczak J, et al., editors. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. vol. 37. Curran Associates, Inc (2024). p. 107984–8011.
5. Varghese R, M S. YOLOv8: a novel object detection algorithm with enhanced performance and robustness. In: 2024 International Conference on Advances in Data Engineering and Intelligent Computing Systems (ADICS). (2024).
6. Zhao Y, Lv W, Xu S, Wei J, Wang G, Dang Q, et al. DETRs beat YOLOs on real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). (2024). p 16965–74.
7. Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, Malik J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). (2024). p. 580–7.
8. Yin T, Zhou X, Krähenbühl P. Center-based 3D object detection and tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); 2021 June 20-25; Nashville, TN, USA. (2020).
9. Zhang H, Li F, Liu S, Zhang L, Su H, Zhu J, et al. DINO: DETR with improved denoising anchor boxes for end-to-end object detection. arXiv [Preprint]. arXiv:2203.03605 (2022). Available online at: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.03605 (Accessed July 11, 2022).
10. Li Y, Ge Z, Yu G, Yang J, Wang Z, Shi Y, et al. Bevdepth: acquisition of reliable depth for multi-view 3D object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. (2022). p. 1477–85.
11. Li Y, Mao H, Girshick RB, He K. Exploring plain vision transformer backbones for object detection. In: Avidan S, Brostow G, Cissé M, Farinella GM, Hassner T, editors. Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 13669. Cham: Springer (2022). p. 280–96.
12. Zhu X, Lyu S, Wang X, Zhao Q. TPH-YOLOv5: improved YOLOv5 based on transformer prediction head for object detection on drone-captured scenarios. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW). (2021).
13. Bai X, Hu Z, Zhu X, Huang Q, Chen Y, Fu H, et al. Transfusion: robust LiDAR-camera fusion for 3D object detection with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). (2022). p. 1090–9.
14. Liu Y, Wang T, Zhang X, Sun J. PETR: position embedding transformation for multi-view 3D object detection. In: Avidan S, Brostow G, Cissé M, Farinella GM, Hassner T, editors. Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. vol. 13687. Cham: Springer (2022). p. 531–48.
15. Liu J, Fan X, Huang Z, Wu G, Liu R, Zhong W, et al. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); 2022 June 18-24; New Orleans, LA, USA. New Orleans, LA: IEEE (2022). p. 5792–801.
16. Modena MG, Lodi E, Rodighiero E, Gasparini PA. 50 shades of lockdown: sex workers’ hidden world during covid pandemic. J Public Health. (2023) 45:964–9. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdad159
17. Modena MG, Lodi E. The occurrence of drug-induced side effects in women and men with arterial hypertension and comorbidities. Pol Heart J. (2022) 80:1068–9. doi: 10.33963/KP.a2022.0233
18. Gu X, Lin T-Y, Kuo W, Cui Y. Open-vocabulary object detection via vision and language knowledge distillation. arXiv [Preprint]. arXiv:2104.13921 (2021). Available online at: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2104.13921 (Accessed May 12, 2022).33948448
19. Lou H, Duan X, Guo J, Liu H, Gu J, Bi L, et al. DC-YOLOv8: small-size object detection algorithm based on camera sensor. Electronics. (2023) 12(10):2323. doi: 10.3390/electronics12102323
20. Wang G, Chen Y, An P, Hong H, Hu J, Huang T. UAV-YOLOv8: a small-object-detection model based on improved YOLOv8 for UAV aerial photography scenarios. Sensors. (2023) 23(16):7190. doi: 10.3390/s23167190
21. Li Y, Hou Q, Zheng Z, Cheng M-M, Yang J, Li X. Large selective kernel network for remote sensing object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). (2023). p. 16794–805.
22. Liu Y-C, Ma C-Y, He Z, Kuo C-W, Chen K, Zhang P, et al. Unbiased teacher for semi-supervised object detection. arXiv [Preprint]. arXiv:2102.09480 (2021). Available online at: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2102.09480
23. Qin X, Zhang Z, Huang C, Dehghan M, Zaiane OR, Jagersand M. U2-Net: going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection. Pattern Recognit. (2020) 106:107404. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107404
24. Modena MG, Lodi E, Scavone A, Carollo A. Cardiovascular health management: preventive assessment. Maturitas. (2019) 124:118. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.04.026
25. Humayra S, Yahya N, Ning CJ, Mohd Raffali MA, Mir IA, Mohamed AL, et al. Clinical significance of nt-probnp as a predictive biomarker of depressive symptoms in cardiac patients. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2025) 12:1439520. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1439520
26. Wang Y, Guizilini VC, Zhang T, Wang Y, Zhao H, Solomon J. DETR3D: 3D object detection from multi-view images via 3D-to-2D queries. In: Aleksandra F, David D, Gerhard N, editors. Proceedings of the 5th Conference on Robot Learning. PMLR (2022). p. 180–91.
27. Wang T, Zhu X, Pang J, Lin D. FCOS3D: fully convolutional one-stage monocular 3D object detection. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW). (2021).
28. Xie X, Cheng G, Wang J, Yao X, Han J. Oriented R-CNN for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). (2021). p. 3520–9.
29. Xu M, Zhang Z, Hu H, Wang J, Wang L, Wei F, et al. End-to-end semi-supervised object detection with soft teacher. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). (2021). p. 3060–9.
30. Sun B, Li B, Cai S, Yuan Y, Zhang C. FSCE: few-shot object detection via contrastive proposal encoding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). (2021). p. 7352–62.
31. Zeng X, Chen L, Chandra A, Zhao L, Ma G, Roldan F-J, et al. Narrative review: updates and strategies for reducing door-to-balloon time in st-elevation myocardial infarction care. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2025) 12:1509365. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1509365
32. Li C, Luo S-X, Liang T-W, Song D, Fu J-X. Gender correlation between sleep duration and risk of coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2025) 12:1452006. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1452006
33. Han J, Ding J, Xue N, Xia G-S. ReDet: a rotation-equivariant detector for aerial object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). (2021). p. 2786–95.
34. Ji G-P, Fan D-P, Chou Y-C, Dai D, Liniger A, Van Gool L. Deep gradient learning for efficient camouflaged object detection. Mach Intell Res. (2023) 20:92–108. doi: 10.1007/s11633-022-1365-9
35. Joseph KJ, Khan S, Khan FS, Balasubramanian VN. Towards open world object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). (2021). p. 5830–40.
36. Misra I, Girdhar R, Joulin A. An end-to-end transformer model for 3D object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). (2021). p. 2906–17.
37. Saleem HN, Sheikh UU, Khalid SA. Classification of chest diseases from x-ray images on the CheXpert dataset. In: Innovations in Electrical and Electronic Engineering: Proceedings of ICEEE 2021. Springer (2021). p. 837–50.
38. Basheer S, Bhatia S, Sakri SB. Computational modeling of dementia prediction using deep neural network: analysis on oasis dataset. IEEE Access. (2021) 9:42449–62. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3066213
39. Naz S, Ashraf A, Zaib A. Transfer learning using freeze features for alzheimer neurological disorder detection using adni dataset. Multimed Syst. (2022) 28:85–94. doi: 10.1007/s00530-021-00797-3
40. Dequidt P, Bourdon P, Tremblais B, Guillevin C, Gianelli B, Boutet C, et al. Exploring radiologic criteria for glioma grade classification on the brats dataset. IRBM. (2021) 42:407–14. doi: 10.1016/j.irbm.2021.04.003
41. Chen Q, Chen X, Wang J, Zhang S, Yao K, Feng H, et al. Group DETR: fast DETR training with group-wise one-to-many assignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. (2023). p. 6633–42.
42. Maity M, Banerjee S, Chaudhuri SS. Faster R-CNN and YOLO based vehicle detection: a survey. In: 2021 5th International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC). IEEE (2021). p. 1442–7.
43. Tiwari V, Singhal A, Dhankhar N. Detecting COVID-19 opacity in x-ray images using YOLO and retinanet ensemble. In: 2022 IEEE Delhi Section Conference (DELCON). IEEE (2022). p. 1–5.
44. Karthi M, Muthulakshmi V, Priscilla R, Praveen P, Vanisri K. Evolution of yolo-v5 algorithm for object detection: automated detection of library books and performace validation of dataset. In: 2021 International Conference on Innovative Computing, Intelligent Communication and Smart Electrical Systems (ICSES). IEEE (2021). p. 1–6.
45. Lei N, Chunlei H, Xin Z, Peng W, Zhixin Z. GroupNet: learning to group corner for object detection in remote sensing imagery. Chin J Aeronaut. (2022) 35(6):273–84. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.09.016
Keywords: AI-driven diagnostics, cardiovascular risk assessment, object detection, multi-modal data fusion, uncertainty quantification
Citation: Tang L and Shen C (2025) Multimodal AI-driven object detection with uncertainty quantification for cardiovascular risk assessment in autistic patients. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1606159. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1606159
Received: 4 April 2025; Accepted: 16 May 2025;
Published: 6 August 2025.
Edited by:
Maria Grazia Modena, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, ItalyReviewed by:
Elisa Lodi, University Hospital of Modena, ItalyPaolo Alberto Gasparini, University Hospital of Modena, Italy
Copyright: © 2025 Tang and Shen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ling Tang, YnJhZGV5ZWR1d2FyQGhvdG1haWwuY29t
 Ling Tang1*
Ling Tang1* Chengchao Shen
Chengchao Shen