- Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
The pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is complex, involving multiple cell types and biological processes. Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) are small, cell-derived particles increasingly recognized for their role in cardiovascular diseases. EVs are believed to play key roles in this context by promoting inflammation, regulating intercellular communication, and influencing lipid metabolism. As a crucial mediators of cell communication, EVs contribute to both the progression of atherosclerosis (AS) and plaques stability. Although research on the role of EVs in AS and the role of biomarkers or drug carriers in clinical practice has been expanding, several challenges remain for clinical applications, including the lack of specific therapeutic targets for EVs, flaws in the separation and purification processes, and limited clinical trial data on their safety. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the function of EVs in AS and recent advances in their diagnostic and therapeutic potential, aiming to inform future clinical applications.
1 Introduction
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide, which both incidence and mortality continuing to rise (1). ASCVD can also lead to severe complications such as heart failure, arrhythmias, and renal failure (2), affecting the patients' quality of life and imposing a substantial burden on healthcare systems. Currently, lowering LDL-C levels remains the cornerstone of ASCVD prevention and treatment. However, in clinical practice, many patients remain at high risk of cardiovascular events despite achieving optimal LDL-C control (3). Even with a combination of pharmacotherapy, lifestyle interventions, and surgical interventions, some patients continue to exhibit residual cardiovascular risk (4).
Extracellular Vesicles (EVs), as important mediators of intercellular communication, have garnered increasing interest in biomedical research. While early studies mainly focused on their biological characteristics (5), more recent investigations have highlighted their emerging potential in clinical diagnosis and therapy (6, 7). EVs derived from endothelial cells, platelets, vascular smooth muscle cells, monocytes, and macrophages are implicated in various mechanisms involved in atherosclerosis (AS), including modulation of endothelial cell function, promotion of inflammatory responses, platelet activation and vascular remodeling (8–10). Moreover, specific molecules carried by EVs not only reflect the status of their cell of origin but can also serve as biomarkers for the early diagnosis and monitoring of ASCVD (11, 12). From a therapeutic perspective, EVs are considered ideal drug delivery vehicles due to their inherent biocompatibility and targeting capabilities (13, 14), enabling efficient delivery of therapeutic agents to diseased sites. Engineered EVs, derived from natural ones, may further enhance targeting capability and therapeutic efficacy (15), offering innovative strategies for ASCVD treatment.
This review aims to elucidate the role of EVs in ASCVD pathogenesis and progression, providing new insights for their clinical application and laying the foundation for future targeted therapies.
2 Classification and characterization of extracellular vesicles
EVs are small, membrane-bound vesicles secreted by cells that play a crucial role in intercellular communication and material exchange. Based on their origin, size, and biological characteristics, EVs are classified into the exosomes, the microvesicles, and the apoptotic bodies (16).
2.1 Exosome
Exosomes are small EVs, typically ranging from 30 to 150 nanometers in diameter, surrounded by a lipid bilayer. They contain various bioactive substances such as proteins, lipids, and RNA (including miRNA and mRNA) (17). Surface proteins such as cluster of differentiation 9 (CD9), cluster of differentiation (CD63), and cluster of differentiation (CD81) are often present, facilitating their formation, release, and recognition (18). Additionally, exosomes lipid composition can influence their binding to target cells and uptake efficiency (19), making them valuable as drug delivery vehicles.
The biosynthesis and release process of exosomes is complex. Exosome biogenesis involves the invagination of the cell membrane to form endosomes, which mature into multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Within MVBs, intraluminal vesicles form through inward budding and are release as exosomes when MVBs fuse with the plasma membrane (20). Exosomes play a vital role in intercellular communication by transporting signaling molecules, miRNA, mRNA, and proteins, and protein to neighboring or distant cells, influencing various cellular processes such as cell growth, differentiation, movement, and death (21).
2.2 Microvesicles
Microvesicles (MVs) are EVs secreted by cells, typically ranging from 100 to 1,000 nanometers in diameter. They contents mRNA, miRNA, proteins, and lipids, which can influence target cells function (22). MVs form through the budding of the cell membrane in response to specific stimuli, with calcium influx, cytoskeletal changes, and membrane movement regulating the process (23).
MVs are efficient in cell-to-cell communication, primarily by transporting bioactive substances and binding on target cells, activating downstream signaling pathways (22). In immune responses, MVs play a dual role, promoting immune responses while potentially leading to immune suppression. MVs can promote immuity by carrying tumor-specific antigens that activat dendritic cells and enhance anti-tumor responses (24), but they can also suppress immunity (25). MVs from tumor cells can carry immunosuppressive factors that inhibit T cell function, contributing to immune evasion in the tumor's microenvironment (17). Additionally, some MVs influence macrophages differentiation, carrying cytokine that promote an anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype (26), aiding tissue repair and regeneration (27).
2.3 Apoptotic bodies
Apoptotic bodies are membrane-bound vesicles formed during apoptosis, typically measuring 5–10 micrometers in diameter. They arise from the breakdown of the cell membrane during the final stages of programmed cell death (28). These vehicles contain a complex mix of components, including membrane proteins, cytoplasmic contents, and organelles fragments (28). The membrane may carry proteins such as adhesion and transport proteins (29), while the cytoplasmic components include enzymes, RNA, and small molecules (30). Upon release, these components can influence neighboring cells, potentially promoting either apoptosis or proliferation (30). Additionally, residual organelles like mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum can release pro-inflammatory factors during apoptosis, further affecting surrounding cells (31).
The formation of apoptotic bodies involves distinct morphological changes, such as cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, and membrane blebbing (32, 33). Besides facilitating the clearance of cellular debris, apoptosis bodies may also modulate autophagy and apoptosis of adjacent cells through their contents, forming a feedback regulation mechanism (34). In the immune responses, apoptotic bodies enhance the phagocytic activity of macrophages and dendritic cells by exposing signals like phosphatidylserine, promoting the clearance of dying cells and preventing autoimmune responses triggered by self-antigens (35).
3 The role of EVs in the pathogenesis of ASCVD
3.1 Evs in endothelial cell activation and dysfunction
EVs can adhere to and interact with endothelial cells through various ligands like P-selectin (36), αvβ3, and α4β1 integrins (37). Upon recognition and binding, endothelial cells internalize EVs through mechanisms including endocytosis, membrane fusion, and phagocytosis (38). This uptake contributes to the progress and exacerbation of AS by promoting inflammation, apoptosis, and endothelial dysfunction (Figure 1).
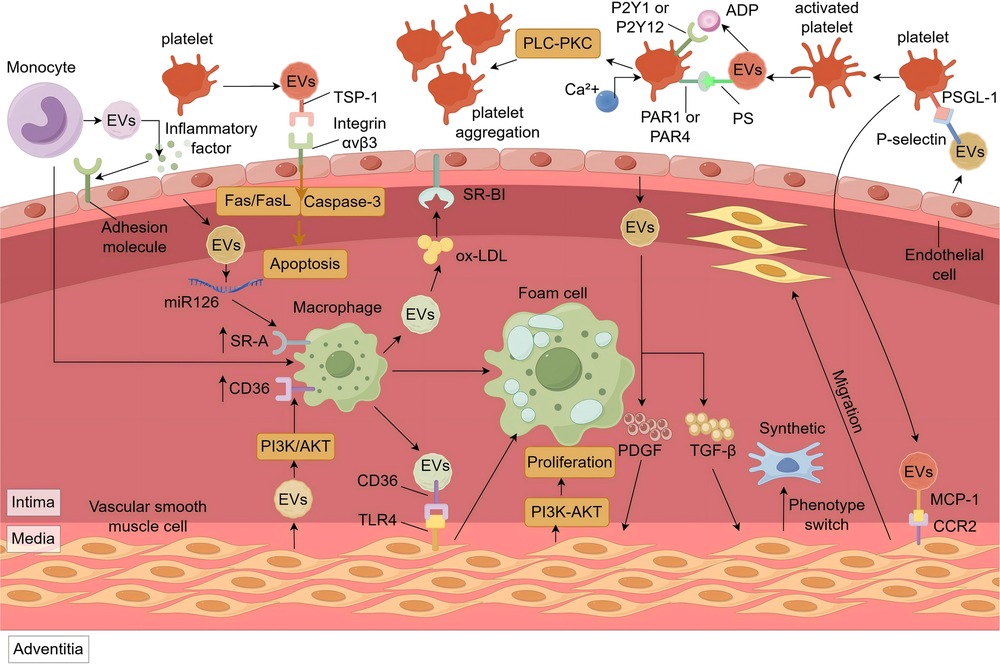
Figure 1. The role of EVs in the pathogenesis of ASCVD. M-EVs promote endothelial adhesion molecule expression via inflammatory ligands. P-EVs induce endothelial apoptosis through TSP-1/αvβ3-mediated Fas/FasL signaling and ROS/caspase-3 activation. Cholesterol-rich EVs from macrophages enter endothelial cells via SR-BI or stimulate ox-LDL uptake in SMCs via CD36/TLR4. Endothelial EVs with miR-126 and SMC-EVs with α-SMA/miR-21 upregulate SR-A and CD36 in macrophages, promoting foam cell formation. PDGF and TGF-β in endothelial EVs drive SMC proliferation (PI3K-Akt) and phenotype switching. MCP-1 in P-EVs promotes SMC migration via CCR2. P-EVs activate platelets via PS-receptor interaction, thrombin/PAR1/4, and ADP/P2Y1/12 signaling, increasing Ca2+ and promoting aggregation. EVs, Extracellular Vesicles; SR-A, scavenger receptor class A; CD-36, cluster of differentiation 14; Fas/FasL, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6/tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 6; TSP-1, thrombus proteins like thrombospondin-1; PI3K/Akt, phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/protein kinase B; SR-BI, scavenger receptor class B type I; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; PLC-PKC, phospholipase C-protein kinase C; P2Y1, P2Y purinoceptor 1; P2Y12, P2Y purinoceptor 12; PAR1, protease activated receptor 1; PAR4, protease activated receptor 4; PS, phosphatidylserine; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; PSGL-1, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; CCR2, C-C motif chemokine receptor 2.
Monocyte- and macrophage-derived EVs can carry pro-inflammatory molecules such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), and IL-6 (39–42). Under inflammatory conditions or upon ox-LDL stimulation, these EVs transfer their cargo to endothelial cells, where ligands such as lipopolysaccharides engage toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), activating the NF-κB signaling pathway (43, 44). Once activated, NF-κB translocates to the nucleus, inducing the expression of cell adhesion molecules, chemokines, and additional cytokines (42, 45). This persistent signaling forms a self-amplifying loop that facilitates leukocyte adhesion, exacerbates vascular inflammation, and accelerates the progression of atherosclerotic plaques.
EVs can contribute to endothelial apoptosis (Figure 1), thereby compromising vascular endothelium. Studies have shown that platelet-derived EVs (P-EVs) are significantly elevated in patients with acute coronary syndrome (46). These P-EVs can induce endothelial apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway (47). On the one hand, surface proteins on P-EVs, such as thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1), can bind to integrin αvβ3 on endothelial cells, triggering the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6/tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 6(Fas/FasL) signaling cascade and mitochondrial damage (48). On the other hand, P-EVs can increase intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels (47, 49), leading to reduced mitochondrial membrane potential (50), release of cytochrome c, activation of caspase-9, and ultimately caspase-3 activation, initiating apoptosis (51). Apoptosis endothelial cells compromised the vascular barrier, facilitating the infiltration of lipids and inflammatory cells into the subendothelial space, thereby promoting plaque instability and rupture. However, EVs derived from pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells have been found to enhance the integrity of the endothelial barrier by transferring miR-125b-5p and inhibiting cell apoptosis (52), providing a direction for the treatment of ASCVD.
3.2 Evs are involved in foam cell formation
EVs are not only important mediators of intercellular communication but also regulate multiple aspects of lipid metabolism through various mechanisms, thereby promoting foam cells formation and influencing the initiation and progresses of AS (Figure 1).
The promotion of cholesterol synthesis by EVs primarily involves the sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP-2) pathway. EVs derived from cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells (53, 54) containing miR-9-5p and oxidized lipids, such as 7-ketocholesterol, can activate this pathway. Specifically, miR-9-5p inhibits Insig1 (55), thereby relieving its suppression of SREBP cleavage-activating protein and allowing for the activation and nuclear translocation of SREBP-2 (56); oxidized lipids can also induce endoplasmic reticulum stress, promoting the cleavage of SREBP-2 into its active forms (57). As a key transcription factor, SREBP-2 enhances the expression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase and squalene epoxidase upon nuclear entry (58), thereby boosting cholesterol synthesis (59). Simultaneously, it upregulates LDL-R expression (60), promoting uptake. Moreover, SREBP-2 increases proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9(PCSK9) expression, accelerating LDLR degradation and leading to elevated LDL-C levels, thereby increasing intracellular cholesterol concentrations.
Regarding cholesterol uptake, EVs exert influence via two primary mechanisms: directly cholesterol uptake and modulation of cell surface receptors involved in uptake. Firstly, EVs can directly transport cholesterol; macrophages under cholesterol overload conditions encapsulate cholesterol into EVs via transporters such as ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 1 (ABCA1) and scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) (61). These EVs can taken up by endothelial cells specific receptors (like SR-BI), or interact with cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36) carried on the EVs surface (62), which in turn binds to TLR4 on the smooth muscle cells, enhancing ox-LDL uptake (63, 64). This promotes droplet accumulation in endothelial cells (65) and activates the NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in smooth muscle cells (66), accelerating their transformation into foam cells. Secondly, EVs can modulate ox-LDL receptor expression. Endothelial cell-derived EVs, once taken up by macrophages, can release miR-126, which inhibits sprouty-related EVH1 domain-containing protein 1 (Spred-1) expression (67), thereby activating the rat sarcoma/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (RAS-ERK) signaling pathway (68). The activation enhances scavenger receptor class A (SR-A) and CD36 expression (69), promoting ox-LDL uptake by macrophage (70). Meanwhile, smooth muscle cell-derived EVs can upregulate SR-A and CD36 in macrophages via activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K-Akt) signaling pathway (71), further promoting foam cell formation (72).
EVs also inhibit intracellular cholesterol efflux mainly by suppressing cholesterol transporters proteins, ABCA1 and ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 1 (ABCG1), and by inhibiting macrophage autophagy. Under pathological conditions such as obesity, adipocyte-derived EVs enriched wirh fatty acid binding protein 4 inhibit the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma signaling pathway upon uptake by macrophages, resulting in downregulation of liver X receptor alpha(LXRα) (73, 74). Consequently, LXRα-mediated transcription of ABCA1 and ABCG1 is reduced, impairing cholesterol efflux (75). Furthermore, EVs enriched in miR-155-released by macrophages upon TNF-αstimulation (76), can suppress LXRαexpression, and directly inhibit translation of autophagy-related protein 5 and autophagy-related protein 7 mRNA (77). This impairs macrophage autophagy (78), reducing the degradation of ox-LDL and promoting foam cell formation.
Furthermore, EVs can promote foam cell formation by influencing macrophages polarization. M1 macrophages, characterized by high expression of scavenger receptors such as SR-A and CD36 (79), exhibit reduced expression of ABCA1 and ABCG1, leading to enhance lipid uptake and impair efflux, thereby promoting cholesterol accumulation and foam cells transformation. EVs from different sources influence this polarization through specific mechanisms. Under oxLDL stimulation, endothelial cells secrete EVs rich in miR-126, which, after being taken by macrophages, upregulate M1 polarization-related genes such as inducible nitric oxide synthase(NOS2) and interleukin-12(IL-12) (80) through pathways involving phosphatase and tensin homolog(PTEN), PI3K/AKT, and NF-κB (81). The NO produced by NOS2 (82), not only promotes inflammation response but also reacts with ROS to generate peroxynitrite (83), exacerbating local tissue damage and creating a vicious cycle. In addition, platelet-derived EVs containing platelet-derived growth factor(PDGF) can activate the RAS/ERK pathway by binding to PDGF receptors on macrophages (84), regulatin transcription factors such as activator protein 1(AP-1) and cAMP response element-binding protein (85), thereby enhancing the expression of pro-inflammatory genes such as TNF-α and IL-12 (86). PDGF can also promotes macrophage proliferation and migration (87), further amplifying the local inflammatory response.
3.3 EVs affect plaque stability
EVs not only participate in lipid metabolism but also influence plaque stability by mediating inflammatory responses, regulating vascular smooth muscle cell(VSMC) proliferation, migration, and phenotypic transformation, and promoting AS plaque calcification (Figure 1).
During AS progression, inflammatory cells such as macrophages and T lymphocytes accumulate within plaques and release EVs enriched with specific cytokines (88). T lymphocyte-derived EVs carry pro-inflammatory factors like interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) (89), which inhibit cholesterol efflux, promote foam cell formation, and contribute to lipid core expansion (90). In advanced plaques, inflammatory cell-derived EVs are rich in matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) (91), such as MMP-2 and MMP-9, which degrade extracellular matrix components like collagen and elastin (92), thinning the fibrous cap and increasing the risk of rupture.
EVs from endothelial cells and platelets influence plaque structure by regulating VSMC behavior. Endothelial cell-derived EVs contain platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), which act via distinct pathways. PDGF activates the PI3K-Akt pathway to upregulate Cyclin D1 expression (93, 94), promoting G1/S phase transition and VSMC proliferation (95). TGF-β activates the Smad pathway, inducing phenotypic switching of VSMCs from contractile to synthetic states (96, 97). These synthetic VSMCs secrete more type I collagen, reduce elastin content, and upregulate MMP-9 (98), thereby weakening the fibrous cap (99). Platelet-derived EVs carry chemokines such as monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) (100), which bind to C-C motif chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) on VSMCs and activate G protein-coupled signaling to promote migration (101).
EVs also contribute to plaque calcification via bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and miR-221/222. BMP-2 binds to BMP receptors on VSMCs and activates Smad signaling (102), inducing osteogenic transcription factors such as runt-related transcription factor 2 and Osterix (103), leading to calcium deposition (104). EVs enriched in miR-221/222 enhance VSMC proliferation, migration, and phenotypic switching (105), and may regulate phosphate metabolism by modulating ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 and phosphate transporter 1 (106), thereby promoting calcification (107).
Endothelial-VSMC communication also relies on EVs. Damaged or inflamed endothelial cells release EVs containing PDGF (108), which bind to receptors on VSMCs and activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. ERK1/2 translocates into the nucleus, phosphorylates transcription factors such as Ets-like transcription factor 1 (Elk-1), and enhances the expression of FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog (c-Fos) and Jun proto-oncogene (c-Jun), forming the AP-1 complex (109, 110). This complex promotes transcription of genes such as Cyclin D1 (111) and MMPs (112), facilitating VSMC proliferation, extracellular matrix degradation, and plaque progression. In addition, miR-21 from endothelial-derived EVs (113) suppresses programmed cell death protein 4 (114), reducing MMP inhibition and further impairing plaque stability.
Macrophage-VSMC communication is another critical axis. Macrophages exposed to ox-LDL secrete EVs containing chemokines such as MCP-1 (115), which activate the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway upon uptake by VSMCs (116). This enhances pseudopodia formation and promotes VSMC migration (117). Meanwhile, the PI3K-Akt pathway also upregulates MMP-9, facilitating elastin degradation, VSMC infiltration into the intima, and AS plaque development (118, 119).
3.4 The role of EVs in thrombosis
EVs play an important role in thrombosis by promoting platelet activation and aggregation, and regulating coagulation cascade (Figure 1). In inflammatory or thrombotic micro-environments, P-selectin on endothelial cell-derived EVs bind to P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1) on platelets, triggering their transformation from a resting discoid shape to an activated state with pseudopod (120). Activated platelets and erythrocytes (121) release EVs enriched in phosphatidylserine (PS) (122), which, along with thrombin carried by EVs, can activate platelets (123) via protease-activated receptors protease-activated receptor 1(PAR1) and protease-activated receptor 4(PAR4), initiating the phospholipase C (PLC) pathway (124, 125). PLC promotes inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate(IP3), leading to calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum and increasing intracellular ca2+ levels, enhancing platelet activation (126).
EVs also deliver pro-aggregatory factors. ADP within P-EVs (127) bind to P2Y purinoceptor 1 (P2Y1) and P2Y purinoceptor 12 (P2Y12) receptors (128) on the platelets, activating the PLC-protein kinase C (PKC) signaling pathway. This cascade further elevates intracellular ca2+, induces shape changes and activates fibrinogen receptors (glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex), promoting platelet aggregation (129).
TF (Tissue factor)-positive EVs are central to initiating the coagulation During vascular inflammation (130, 131), activated monocytes release a large number of TF-rich MDEVs (40, 132). In circulation, TF on MDEVs (133) binds to factor VII, forming a TF-VIIa complex (134) that activates coagulation factor X,which can promote the release of endothelial cell-derived TF + EVs (135), and triggers the extrinsic coagulation pathway (136). However, activated coagulation factor VII can also play a protective role by inducing endothelial cells to secrete EVs rich in miR-10a through the activated Factor VII-endothelial protein C receptor-protease activated receptor 1(FVIIa-EPCR-PAR1) axis (137). After being taken up by monocytes, these EVs can downregulate the transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1 pro-inflammatory signaling pathway, creating an anti-inflammatory environment (138). In addition, tumor cell-derived TF + EVs can also promote thrombosis (139). Concurrently, PS exposure on the EV surface facilitates the assembly of the prothrombinase complex, which effectively converts prothrombin to thrombin (140, 141), promoting the release of EVs rich in pro-coagulation proteins and adhesion proteins from platelets (142) and amplying coagulation.On the contrary, EVs derived from endothelial cells and leukocytes carry plasmin and plasminogen activators, playing a comprehensive role in regulating thrombus balance (143).
4 Evs in ASCVD diagnosis and treatment
4.1 EVs as biomarkers
In recent years, EVs have shown increasing value in the early diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases like ASCVD, as well as in monitoring disease progression, evaluating prognosis, and assessing treatment response (Figure 2; Table 1).
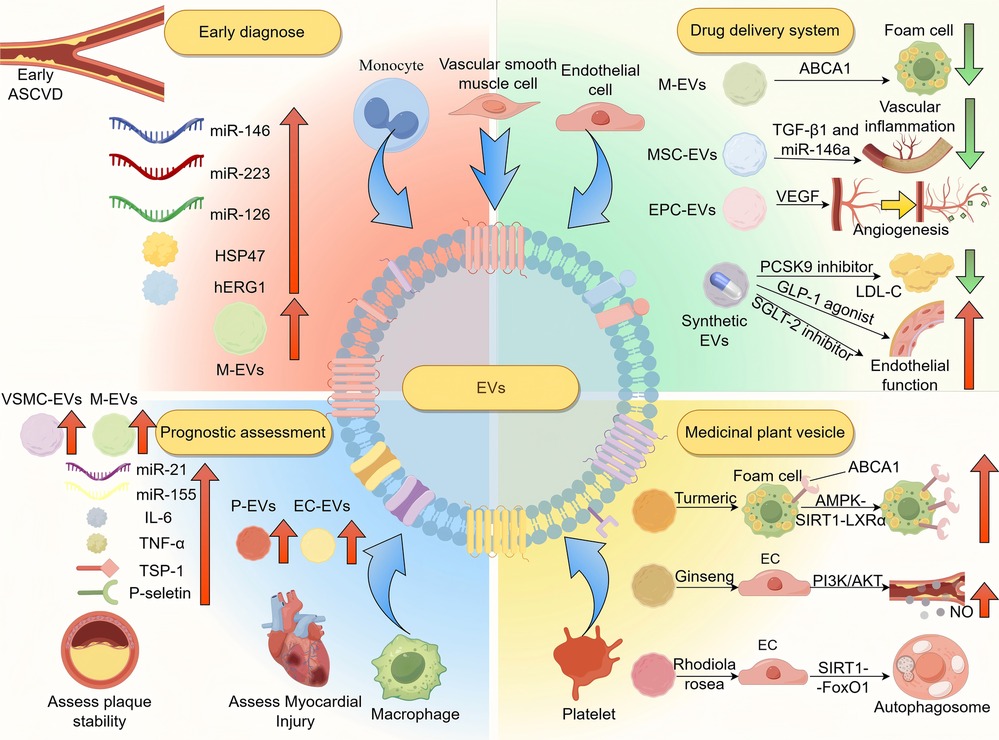
Figure 2. The application of EVs in the diagnosis and treatment of ASCVD. EVs serve as diagnostic markers in ASCVD. M-EVs and EVs enriched with miR-146a, miR-223, and miR-126 are elevated in early atherosclerosis. Hsp47 and hERG1-related changes reflect cardiac stress and arrhythmia risk. EV quantity and origin vary by stage: SMC- and macrophage-derived EVs increase during plaque formation, while platelet- and endothelial-derived EVs rise in ACS. EVs from severe cases show elevated IL-6, TNF-α, TSP-1, P-selectin, miR-21, and miR-155. Therapeutically, EVs can deliver ABCA1, miR-146a, TGF-β1, VEGF, PCSK9 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists to reduce inflammation, promote angiogenesis, and improve endothelial function. Plant-derived EVs activate AMPK-SIRT1-LXRα, PI3K/Akt, and SIRT1-FoxO1 pathways to enhance endothelial repair and autophagy. ASCVD, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; Hsp47, heat shock protein 47; hERG1, human ether-à-go-go-related gene 1; M-EVs, macrophage-EVs; VSMC-EVs, vascular smooth muscle cell-EVs; IL-6, interleukin-1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TSP-1, thrombus proteins like thrombospondin-1; P-EVs, platelet-EVs; EC-EVs, endothelial-derived EVs; MSC-EVs, mesenchymal stem cell-EVs; EPC-EVs, endothelial progenitor cell-EVs; ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor beta 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; AMPK-SIRT1-LXRα, AMP-activated protein kinase-sirtuin 1-liver X receptor alpha; PI3K/Akt, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B; SIRT1-FoxO1, sirtuin 1-forkhead box protein O1.
Studies indicates that specific EVs subpopulations and their bioactive components could be potential early diagnostic markers or indicators of disease progression (144). For example, monocytes-derived EVs are significantly elevated in the blood of patients with early AS (145), which may contribute to endothelial dysfunction. This plays a role in ASCVD initiation and progression (12). IL-33 can induce a significant increase in TF + EVs derived from monocytes, promoting thrombosis, suggesting that IL-33 may serve as a biomarker for predicting ASCVD (146). The expression levels of miR-146a, miR-223, and miR-126 in EVs change significantly in AS patients (147). miR-126, which is abundant in endothelial-derived EVs (148), plays a protective role. Reduced miR-126 increases Spred-1, blocks VEGF signaling, and impairs endothelial function, promoting ASCVD (149). miR-146a-5p derived from cardiomyocyte-derived EVs can inhibit M1 macrophage activation and reduce inflammatory responses by targeting CD80 (150) and TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (151). Therefore, the expression of miR-146a-5p in cardiomyocyte-derived EVs from ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients is significantly reduced (152). miR-223 is highly expressed in monocyte-derived EVs and can alleviate myocardial inflammation by targeting semaphorin 3A and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (153). Therefore, miR-223 is significantly reduced in EVs from patients with heart failure due to inflammation-induced myocardial fibrosis (154). EV proteins like heat shock protein 47 (Hsp47) and human ether-à-go-go-related gene 1 (hERG1) also aid early diagnosis—Hsp47 reflects cardiac stress and fibrosis (155), while hERG1 dysfunction may cause arrhythmias (156).
EVs are also valuable for prognostic assessment. During early plaque formation, levels of EVs derived from VSMCs and macrophages significantly increases (157), potentially reflecting plaque stability. Meanwhile, in acute coronary syndrome, EVs from platelets and endothelial cells increase sharply, correlating with myocardial injury and the risk of cardiovascular events (158). Moreover, EVs composition Reflects disease severity: inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α, TSP-1 and P-selectin (159), and miRNAs such as miR-21, miR-155 (160) and miR-133 (161), are evaluated in patients with severe ASCVD. miR-21 and miR-155 in EVs enhance inflammation in AS plaques and worsen prognosis, making them potential biomarkers for disease progression and outcome prediction.In the MINERVA study, researchers conducted a retrospective case-control analysis of 269 patients with acute chest pain and found that low levels of the plasma EVs protein Cystatin C in patients with low levels of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin were associated with unstable angina (162, 163). This suggests that EVs may be useful in the risk stratification of cardiovascular events. Data analysis from the Athero-Express biobank showed that among 864 patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy, preoperative levels of EV-related proteins (such as CD14 and Cystatin C) were significantly associated with the risk of major cardiovascular events within three years after surgery (164, 165). This indicates that EV-derived proteins could serve as biomarkers for assessing remaining cardiovascular risk and may help identify high-risk patients for more tailored secondary prevention.
EVs also have potential in motoring treatment responses. In patients with AMI receiving statin therapy, levels of monocyte-derived CD14+ EVs and platelet-derived CD41+ EVs significantly decreased post-treatment (166), reflecting the anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic effects of statins and serving as markers of therapeutic efficacy (167). In patients with AMI after PCI who were treated with the P2Y12 antagonist ticagrelor, the concentrations of plasma platelet-derived EVs, endothelial cell-derived EVs, leukocyte-derived EVs, fibrinogen-exposed EVs, and PS-exposed EVs all significantly decreased (168), indicating that this regimen has good anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic effects (169). Furthermore, Changes in inflammatory-related EVs content may indicate treatment tolerance (170), helping guide timely therapeutic adjustments and improving clinical decision-making.
4.2 EVs as drug delivery systems
The therapeutic value of EVs lies in their role as intervention targets and drug delivery vehicles (Figure 2; Table 1). During AS progression, EVs affect the disease progression in several ways, such as regulating lipid metabolism, inflammation and endothelial function (12). Therefore, regulating their production or altering their cargo offers new approaches for ASCVD treatment.
Recent researches indicates that natural IgM antibodies may inhibit thrombosis by competing with coagulation factor X/Xa for binding to coagulation-related EVs (171). Exosomes derived from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells can significantly reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6 (172). This anti-inflammatory effect is mainly attributed to the transfer of miR-21 and miR-146a, which inhibit TLR4/NF-κB signaling in macrophages, thereby suppressing M1 polarization and reducing the production of pro-inflammatory mediators. These exosomes also significantly improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction by modulating macrophage phenotypes and reducing myocardial fibrosis and inflammatory cell infiltration (173). Exosomes derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are rich in miR-29a-3p, which can activate the VEGF signaling pathway (174), thereby enhancing the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells and promoting angiogenesis (175). Mechanistically, miR-29a-3p targets PTEN and upregulates the PI3K/Akt/eNOS axis, increasing NO production and supporting vascular homeostasis.
As drug carriers, EVs have distinct advantages: they exhibit good biocompatibility and low immunogenicity (176), enabling them to evade immune clearance. Their surface molecules can mediate targeted delivery to specific cells (177), and their lipid bilayer protects encapsulated drugs from degradation (178, 179), allowing efficient release via membrane fusion (167).
Therapeutically, EVs are involved in key ASCVD processes. Macrophage-derived EVs carrying ABCA1 promote cholesterol efflux from foam cells by enhancing reverse cholesterol transport pathways (180, 181). This process helps stabilize plaques and prevent necrotic core expansion. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived EVs loaded with miR-146a and TGF-β1 (182) can target atherosclerotic plaques, suppress NF-κB signaling (183), reduce vascular inflammation, and regulate VSMC phenotype by inhibiting osteogenic transition and promoting contractile markers (184). Furthermore, EPC-derived EVs enriched with VEGF promote angiogenesis and improve tissue perfusion in ischemic myocardium (185). These EVs activate VEGFR2 on endothelial cells and downstream PI3K/Akt signaling, which enhances endothelial proliferation, migration, and capillary network formation (186).
4.3 Application of synthetic EVs
Artificially synthesized EVs can mimic natural EVs by carrying therapeutic molecules and targeting specific tissues (Figure 2 and Table 1). Compared with natural EVs, synthetic EVs allow for improved surface modification to enhance targeting and drug-loading capacity and their profucing yields higher purity with reduced batch variability (187), addressing limitations in the clinical applications of natural EVs (188). Moreover, emerging light-responsive EVs have been developed, which enable spatiotemporal control of drug release upon specific light stimulation, thus improving delivery precision and minimizing off-target toxicity (189, 190).
In the treatment of ASCVD, synthetic EVs show broad potential across multiple pathological mechanisms. To regulate lipid metabolism, synthetic EVs can deliver PCSK9 inhibitors, which increase hepatic LDL receptor levels and promote LDL-C clearance (191). By encapsulating these agents in EV-mimetic nanocarriers, hepatic uptake is enhanced and systemic side effects reduced. To improve vascular homeostasis, synthetic EVs have been designed to release nitric oxide (NO), which activates the soluble guanylate cyclase pathway and promotes vasodilation (192).
Furthermore, synthetic EVs can encapsulate SGLT2 inhibitors or GLP-1 receptor agonists to improve endothelial function and glycemic control in patients with metabolic syndrome (193). Their surface can be functionalized with endothelial-targeting peptides (e.g., RGD motifs) to enhance specificity and accumulation in vascular lesions. Synthetic EVs can also carry VEGF to stimulate angiogenesis through VEGFR2-mediated PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling (194), or transport anti–PD-L1 antibodies to block the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, thus enhancing T-cell activation and restoring immune balance within the plaque microenvironment (195, 196).
In terms of inflammation regulation, artificially synthesized EVs loaded with miR-146a can significantly reduce inflammatory factors and inhibit the polarization of M1 macrophages (197) by intervening in the TLR4/NF-κB pathway (198). In maintaining plaque stability, artificially synthesized EVs can deliver tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 3 mRNA, suppress the expression of MMPs, and reduce collagen degradation (199).
However, synthetic EVs may still be cleared by the immune system or bind to non-target cells during circulation. To improve targeting accuracy, it may be necessary to develop multi- ligand surface modifications that recognize several key targets, reducing off-target effects and enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
4.4 Applications of medicinal plant vesicles
Medicinal plant vesicles, due to their natural origin, show unique therapeutic potential in treating ASCVD by regulating lipid metabolism, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, and promoting angiogenesis (200) (Figure 2 and Table 1). They offer strong targeting ability (201) and excellent biocompatibility (202), making them less likely to trigger immune responses compared to synthetic carriers. Recent studies have also found that microsphere systems using poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) as a carrier can achieve sustained release in vivo, prolonging the duration of drug action and reducing the frequency of administration for patients (203). In the future, it may be considered to apply PLGA to load medicinal plant vesicles, extending the in vivo circulation time of the plant vesicles through the sustained release characteristics of PLGA.
Curcumin-derived EVs (204), for instance, activate the AMPK-SIRT1-LXRα pathway in foam cells, upregulating ABCA1 and enhancing cholesterol efflux (205). They also directly bind and inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome, thereby attenuating the downstream release of IL-1β and suppressing vascular inflammation associated with atherosclerosis progression (206). Ginseng-derived EVs, enriched in ginsenosides, promote eNOS phosphorylation and NO production through PI3K/Akt pathway activation while inhibiting NF-κB–mediated inflammatory gene transcription via SIRT1 modulation (207). Rhodiola-derived EVs, containing salidroside (208), activate the sirtuin 1-forkhead box O1(SIRT1-FoxO1) to induce autophagy and reduce oxidative damage in endothelial cells, while also promoting ABCA1 and inhibiting ox-LDL receptor expression to reduce foam cell formation. Despite their promise and good biocompatibility (209), further studies are needed to assess their safety and potential side effects.
5 Limitations of EVs in the clinical application of ASCVD
Although EVs have shown great promise in ASCVD, their clinical application still faces considerable challenges. As biomarkers, their utility is hindered by technical limitations in isolation and purification. EVs are typically present in low abundance in body fluids (210), and conventional isolation methods such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, and immunocapture often suffer from drawbacks including prolonged processing time, high cost, sample loss, and compromised EV integrity (211, 212). Moreover, these methods frequently co-isolate contaminants from other cellular components, which can reduce the specificity of EV detection and introduce false-positive or false-negative results in biomarker analysis (213, 214).
It is important to note that the impact of purity varies depending on the intended application of EVs. When EVs are studied as mediators of intercellular communication or therapeutic agents, the presence of non-vesicular contaminants may significantly distort functional interpretations. However, in the context of EVs as biomarkers, minor contamination may not critically impair their diagnostic value, provided that marker-specific signatures are preserved.
To address purification challenges, newer methods such as size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) have gained attention. SEC allows for the gentle separation of EVs from complex biofluids by physical exclusion, avoiding the use of harsh mechanical or chemical conditions that could damage vesicle integrity or surface proteins (215, 216). This approach improves EV purity while maintaining their biological functionality, which is crucial for downstream diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Nonetheless, SEC also has limitations. It is not very effective in removing certain high-density protein aggregates or lipoproteins, which may still interfere with subsequent analyses (217).
In terms of therapeutic applications, long-term efficacy and safety data on EV-based treatments remain limited. Challenges such as low yield, suboptimal purity, and potential functional degradation of EVs during processing continue to hinder their clinical translation (218). Therefore, overcoming these barriers will require the development of innovative isolation techniques, standardized quality control frameworks, and rigorous preclinical and clinical studies to fully realize the diagnostic and therapeutic potential of EVs in ASCVD.
6 Summary and outlook
As important mediators of intercellular communication, EVs play multifaceted roles in the development of ASCVD. This review summarizes the biological characteristics of EVs and their involvement in the initiation and progression of ASCVD. Clinically, EVs act as emerging biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis assessment. Their natural targeting ability and biocompatibility also make them promising drug delivery vehicles, with engineered and plant-based EVs offering new personalized therapy.
Future research should integrate multi-omics technologies to track dynamic changes in EV components, establish standardized isolation and identification protocals, and validate therapeutic strategies in preclinical models. Further exploration of EVs interactions with metabolic and immune system, along with AI-based prediction models, may open new ideas for precision medicine.
Author contributions
HD: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WQ: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Validation. YZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JH: Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (No.2021FSYYZZ12) (JH), Quzhou Science and Technology Bureau (No.2023K158) (JH), Quzhou Science and Technology Bureau (No.2022K114) (JH) and Zhejiang Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No.2022ZZ018) (JH).
Acknowledgments
We thank Figgraw (https://www.figdraw.com) for their help with the figures.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Nedkoff L, Briffa T, Zemedikun D, Herrington S, Wright FL. Global trends in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Clin Ther. (2023) 45(11):1087–91. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2023.09.020
2. Libby P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature. (2021) 592(7855):524–33. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03392-8
3. Reyes-Soffer G. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk: current status and treatments. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. (2021) 28(2):85–9. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000619
4. Brockmeyer M, Wies E, Joerges J, Sommer J, Borgmann SO, Chernyak N, et al. Knowledge of HbA1c and LDL-C treatment goals, subjective level of disease-related information and information needs in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Clin Cardiol. (2023) 46(2):223–31. doi: 10.1002/clc.23948
5. Théry C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol. (2002) 2(8):569–79. doi: 10.1038/nri855
6. Hoshino A, Kim HS, Bojmar L, Gyan KE, Cioffi M, Hernandez J, et al. Extracellular vesicle and particle biomarkers define multiple human cancers. Cell. (2020) 182(4):1044–61.e1018. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.009
7. Yoshida M, Satoh A, Lin JB, Mills KF, Sasaki Y, Rensing N, et al. Extracellular vesicle-contained eNAMPT delays aging and extends lifespan in mice. Cell Metab. (2019) 30(2):329–42.e325. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.05.015
8. Deregibus MC, Cantaluppi V, Calogero R, Lo Iacono M, Tetta C, Biancone L, et al. Endothelial progenitor cell derived microvesicles activate an angiogenic program in endothelial cells by a horizontal transfer of mRNA. Blood. (2007) 110(7):2440–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-03-078709
9. Taraboletti G, D'Ascenzo S, Borsotti P, Giavazzi R, Pavan A, Dolo V. Shedding of the matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2, MMP-9, and MT1-MMP as membrane vesicle-associated components by endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. (2002) 160(2):673–80. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64887-0
10. Del Conde I, Shrimpton CN, Thiagarajan P, López JA. Tissue-factor-bearing microvesicles arise from lipid rafts and fuse with activated platelets to initiate coagulation. Blood. (2005) 106(5):1604–11. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-03-1095
11. Boulanger CM, Loyer X, Rautou PE, Amabile N. Extracellular vesicles in coronary artery disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2017) 14(5):259–72. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2017.7
12. Deng W, Tang T, Hou Y, Zeng Q, Wang Y, Fan W, et al. Extracellular vesicles in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. (2019) 495:109–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.04.051
13. Zhang M, Zang X, Wang M, Li Z, Qiao M, Hu H, et al. Exosome-based nanocarriers as bio-inspired and versatile vehicles for drug delivery: recent advances and challenges. J Mater Chem B. (2019) 7(15):2421–33. doi: 10.1039/C9TB00170K
14. Liu X, Lou K, Zhang Y, Li C, Wei S, Feng S. Unlocking the medicinal potential of plant-derived extracellular vesicles: current progress and future perspectives. Int J Nanomedicine. (2024) 19:4877–92. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S463145
15. Mazahir F, Yadav AK. Recent progress in engineered extracellular vesicles and their biomedical applications. Life Sci. (2024) 350:122747. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122747
16. Welsh JA, Goberdhan DCI, O'Driscoll L, Buzas EI, Blenkiron C, Bussolati B, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): from basic to advanced approaches. J Extracell Vesicles. (2024) 13(2):e12404. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12404
17. Papakonstantinou E, Dragoumani K, Mitsis T, Chrousos GP, Vlachakis D. Milk exosomes and a new way of communication between mother and child. EMBnet J. (2024) 29:e1050. doi: 10.14806/ej.29.0.1050
18. Fang Z, Ding Y, Xue Z, Li P, Li J, Li F. Roles of exosomes as drug delivery systems in cancer immunotherapy: a mini-review. Discov Oncol. (2022) 13(1):74. doi: 10.1007/s12672-022-00539-5
19. Erdoğan H, Yılmaz Ö, Çevik PK, Doğan M, Özen R. Synthesis of schiff bases and secondary amines with indane skeleton; evaluation of their antioxidant, antibiotic, and antifungal activities. Chem Biodivers. (2023) 20(9):e202300684. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202300684
20. Wang Y, Xiao T, Zhao C, Li G. The regulation of exosome generation and function in physiological and pathological processes. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 25(1):255. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010255
21. Zhou XJ, Xu HM, Huang GS, Lin BR. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma derived exosomes regulate the proliferation and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by mediating the miR-99a-5p BAZ2A axis. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. (2024) 90(1):101343. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2023.101343
22. Zhang W, Zhuang X, Wu C, Jin Y, Xing J, Hou M, et al. Apigenin inhibits tumor angiogenesis by hindering microvesicle biogenesis via ARHGEF1. Cancer Lett. (2024) 596:216961. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216961
23. Piening LM, Wachs RA. Matrix-bound nanovesicles: what are they and what do they do? Cells Tissues Organs. (2023) 212(1):111–23. doi: 10.1159/000522575
24. Wortzel I, Dror S, Kenific CM, Lyden D. Exosome-mediated metastasis: communication from a distance. Dev Cell. (2019) 49(3):347–60. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.04.011
25. Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. Exosomes/microvesicles: mediators of cancer-associated immunosuppressive microenvironments. Semin Immunopathol. (2011) 33(5):441–54. doi: 10.1007/s00281-010-0234-8
26. Mahmoudi M, Taghavi-Farahabadi M, Hashemi SM, Mousavizadeh K, Rezaei N, Mojtabavi N. Reprogramming tumor-associated macrophages using exosomes from M1 macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2024) 733:150697. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150697
27. Souza NHC, Mesquita-Ferrari RA, Rodrigues M, da Silva DFT, Ribeiro BG, Alves AN, et al. Photobiomodulation and different macrophages phenotypes during muscle tissue repair. J Cell Mol Med. (2018) 22(10):4922–34. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13757
28. Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. (1972) 26(4):239–57. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.33
29. Caruso S, Atkin-Smith GK, Baxter AA, Tixeira R, Jiang L, Ozkocak DC, et al. Defining the role of cytoskeletal components in the formation of apoptopodia and apoptotic bodies during apoptosis. Apoptosis. (2019) 24(11-12):862–77. doi: 10.1007/s10495-019-01565-5
30. Sorkou KN, Theotokis P, Deftereou TE, Maria L, Meditskou S, Manthou ME. Detecting apoptotic human lens epithelial cells with transmission electron microscopy. Cureus. (2023) 15(9):e45916. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45916
31. Kakarla R, Hur J, Kim YJ, Kim J, Chwae YJ. Apoptotic cell-derived exosomes: messages from dying cells. Exp Mol Med. (2020) 52(1):1–6. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0362-8
32. Pich K, Respekta N, Dawid M, Mlyczynska E, Kurowska P, Rak A. New insights into cell apoptosis and proliferation: the potential role of vaspin. J Physiol Pharmacol. (2021) 72(6). doi: 10.26402/jpp.2021.6.02
33. Barman J, Kumar R, Saha G, Tiwari K, Dubey VK. Apoptosis: mediator molecules, interplay with other cell death processes and therapeutic potentials. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. (2018) 19(8):644–63. doi: 10.2174/1389201019666180821093239
34. Bernardo-Bermejo S, Fernández-Martínez AB, Lucio-Cazaña FJ, Castro-Puyana M, Marina ML. Quantification of relevant metabolites in apoptotic bodies from HK-2 cells by targeted metabolomics based on liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. (2024) 1329:343190. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2024.343190
35. Arienti S, Barth ND, Dorward DA, Rossi AG, Dransfield I. Regulation of apoptotic cell clearance during resolution of inflammation. Front Pharmacol. (2019) 10:891. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00891
36. Khandagale A, Åberg M, Wikström G, Bergström Lind S, Shevchenko G, Björklund E, et al. Role of extracellular vesicles in pulmonary arterial hypertension: modulation of pulmonary endothelial function and angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2020) 40(9):2293–309. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314152
37. Nakakura T, Suzuki T, Tanaka H, Arisawa K, Miyashita T, Nekooki-Machida Y, et al. Fibronectin is essential for formation of fenestrae in endothelial cells of the fenestrated capillary. Cell Tissue Res. (2021) 383(2):823–33. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03273-y
38. Mulcahy LA, Pink RC, Carter DR. Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J Extracell Vesicles. (2014) 3. doi: 10.3402/jev.v3.24641
39. Adamczyk AM, Leicaj ML, Fabiano MP, Cabrerizo G, Bannoud N, Croci DO, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human plasma dampen inflammation and promote tissue repair functions in macrophages. J Extracell Vesicles. (2023) 12(6):e12331. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12331
40. Aharon A, Tamari T, Brenner B. Monocyte-derived microparticles and exosomes induce procoagulant and apoptotic effects on endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. (2008) 100(5):878–85. doi: 10.1160/TH07-11-0691
41. Yang Y, Luo H, Zhou C, Zhang R, Liu S, Zhu X, et al. Regulation of capillary tubules and lipid formation in vascular endothelial cells and macrophages via extracellular vesicle-mediated microRNA-4306 transfer. J Int Med Res. (2019) 47(1):453–69. doi: 10.1177/0300060518809255
42. Gao Z, Zhang J, Henagan TM, Lee JH, Ye X, Wang H, et al. P65 inactivation in adipocytes and macrophages attenuates adipose inflammatory response in lean but not in obese mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2015) 308(6):E496–505. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00532.2014
43. Roshan MH, Tambo A, Pace NP. The role of TLR2, TLR4, and TLR9 in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Int J Inflam. (2016) 2016:1532832. doi: 10.1155/2016/1532832
44. Giusti L, Gabriele M, Penno G, Garofolo M, Longo V, Del Prato S, et al. A fermented whole grain prevents lipopolysaccharides-induced dysfunction in human endothelial progenitor cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:1026268. doi: 10.1155/2017/1026268
45. Singh S, Singh TG. Role of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signalling in neurodegenerative diseases: an mechanistic approach. Curr Neuropharmacol. (2020) 18(10):918–35. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200207120949
46. Vilella-Figuerola A, Cordero A, Mirabet S, Muñoz-García N, Suades R, Padró T, et al. Platelet-released extracellular vesicle characteristics differ in chronic and in acute heart disease. Thromb Haemost. (2023) 123(9):892–903. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-57017
47. Kong L, Li K, Gao L, Yin A, Zhou L, Teng G, et al. Mediating effects of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles on PM2.5-induced vascular endothelial injury. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2020) 198:110652. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110652
48. Lin S, Liu X, Yin R, Kong D, Qu Y, Zhang Y. Inhibitory effects of short hairpin RNA against caspase-8 on apoptosis of murine hepatoma Hepa1-6 cells. Biosci Trends. (2009) 3(2):53–7.20103947
49. Coly PM, Chatterjee S, Mezine F, Jekmek CE, Devue C, Nipoti T, et al. Low fluid shear stress stimulates the uptake of noxious endothelial extracellular vesicles via MCAM and PECAM-1 cell adhesion molecules. J Extracell Vesicles. (2024) 13(10):e12414. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12414
50. Dominiak K, Galganski L, Budzinska A, Jarmuszkiewicz W. Coenzyme Q deficiency in endothelial mitochondria caused by hypoxia; remodeling of the respiratory chain and sensitivity to anoxia/reoxygenation. Free Radic Biol Med. (2024) 214:158–70. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.02.005
51. Liu X, Lei J, Wang K, Ma L, Liu D, Du Y, et al. Mitochondrial omi/HtrA2 promotes caspase activation through cleavage of HAX-1 in aging heart. Rejuvenation Res. (2017) 20(3):183–92. doi: 10.1089/rej.2016.1861
52. Gu Z, Sun M, Liu J, Huang Q, Wang Y, Liao J, et al. Endothelium-derived engineered extracellular vesicles protect the pulmonary endothelial barrier in acute lung injury. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2024) 11(6):e2306156. doi: 10.1002/advs.202306156
53. Zhang Y, Li X, Dai Y, Han Y, Wei X, Wei G, et al. Neutrophil N1 polarization induced by cardiomyocyte-derived extracellular vesicle miR-9-5p aggravates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22(1):632. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02902-w
54. Yuan X, Bhat OM, Samidurai A, Das A, Zhang Y, Li PL. Reversal of endothelial extracellular vesicle-induced smooth muscle phenotype transition by hypercholesterolemia stimulation: role of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:597423. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.597423
55. Li MX, Hu S, Lei HH, Yuan M, Li X, Hou WK, et al. Tumor-derived miR-9-5p-loaded EVs regulate cholesterol homeostasis to promote breast cancer liver metastasis in mice. Nat Commun. (2024) 15(1):10539. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54706-z
56. Nakanishi T, Tanaka R, Tonai S, Lee JY, Yamaoka M, Kawai T, et al. LH Induces de novo cholesterol biosynthesis via SREBP activation in granulosa cells during ovulation in female mice. Endocrinology. (2021) 162(11):bqab166. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab166
57. Xiaoping Z, Fajun Y. Regulation of SREBP-mediated gene expression. Sheng Wu Wu Li Hsueh Bao. (2012) 28(4):287–94. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1260.2012.20034
58. Howe V, Sharpe LJ, Prabhu AV, Brown AJ. New insights into cellular cholesterol acquisition: promoter analysis of human HMGCR and SQLE, two key control enzymes in cholesterol synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. (2017) 1862(7):647–57. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.03.009
59. Geng C, Dong T, Jin W, Yu B, Yin F, Peng F, et al. MicroRNA-98 regulates hepatic cholesterol metabolism via targeting sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2018) 504(2):422–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.205
60. Xia XD, Peng ZS, Gu HM, Wang M, Wang GQ, Zhang DW. Regulation of PCSK9 expression and function: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:764038. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.764038
61. Stamatikos A, Knight E, Vojtech L, Bi L, Wacker BK, Tang C, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of anti-mir-33a-5p from transduced endothelial cells enhances macrophage and vascular smooth muscle cell cholesterol efflux. Hum Gene Ther. (2020) 31(3-4):219–32. doi: 10.1089/hum.2019.245
62. Ramakrishnan DP, Hajj-Ali RA, Chen Y, Silverstein RL. Extracellular vesicles activate a CD36-dependent signaling pathway to inhibit microvascular endothelial cell migration and tube formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2016) 36(3):534–44. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.307085
63. Sun Z, Yuan W, Li L, Cai H, Mao X, Zhang L, et al. Macrophage CD36 and TLR4 cooperation promotes foam cell formation and VSMC migration and proliferation under circadian oscillations. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. (2022) 15(5):985–97. doi: 10.1007/s12265-022-10225-0
64. Gui Y, Zheng H, Cao RY. Foam cells in atherosclerosis: novel insights into its origins, consequences, and molecular mechanisms. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:845942. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.845942
65. Comariţa IK, Vîlcu A, Constantin A, Procopciuc A, Safciuc F, Alexandru N, et al. Therapeutic potential of stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles on atherosclerosis-induced vascular dysfunction and its key molecular players. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2022) 10:817180. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.817180
66. Schwarz N, Fernando S, Chen YC, Salagaras T, Rao SR, Liyanage S, et al. Colchicine exerts anti-atherosclerotic and -plaque-stabilizing effects targeting foam cell formation. Faseb J. (2023) 37(4):e22846. doi: 10.1096/fj.202201469R
67. Potus F, Ruffenach G, Dahou A, Thebault C, Breuils-Bonnet S, Tremblay È, et al. Downregulation of MicroRNA-126 contributes to the failing right ventricle in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation. (2015) 132(10):932–43. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.016382
68. Inoue H, Fukuyama S, Matsumoto K, Kubo M, Yoshimura A. Role of endogenous inhibitors of cytokine signaling in allergic asthma. Curr Med Chem. (2007) 14(2):181–9. doi: 10.2174/092986707779313327
69. Lin CS, Lin FY, Ho LJ, Tsai CS, Cheng SM, Wu WL, et al. PKCδ signalling regulates SR-A and CD36 expression and foam cell formation. Cardiovasc Res. (2012) 95(3):346–55. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs189
70. Dong N, Yang G, Liu Y, Wu K. Hydrogen sulfide inhibits early development of atherosclerosis by modulating macrophage uptake of oxidized lipoproteins. J Investig Med. (2024) 72(8):947–55. doi: 10.1177/10815589241279599
71. Zhang Y, Shang Z, Liu A. Angiotensin-(3-7) alleviates isoprenaline-induced cardiac remodeling via attenuating cAMP-PKA and PI3K/akt signaling pathways. Amino Acids. (2021) 53(10):1533–43. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03074-9
72. Hemmings BA, Restuccia DF. The PI3K-PKB/akt pathway. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2015) 7(4):a026609. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a026609
73. Hui X, Li H, Zhou Z, Lam KS, Xiao Y, Wu D, et al. Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein modulates inflammatory responses in macrophages through a positive feedback loop involving c-jun NH2-terminal kinases and activator protein-1. J Biol Chem. (2010) 285(14):10273–80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.097907
74. Makowski L, Brittingham KC, Reynolds JM, Suttles J, Hotamisligil GS. The fatty acid-binding protein, aP2, coordinates macrophage cholesterol trafficking and inflammatory activity. Macrophage expression of aP2 impacts peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and IkappaB kinase activities. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280(13):12888–95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413788200
75. Chen X, Chen S, Pang J, Huang R, You Y, Zhang H, et al. Hepatic steatosis aggravates atherosclerosis via small extracellular vesicle-mediated inhibition of cellular cholesterol efflux. J Hepatol. (2023) 79(6):1491–501. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.08.023
76. Jiang K, Yang J, Guo S, Zhao G, Wu H, Deng G. Peripheral circulating exosome-mediated delivery of miR-155 as a novel mechanism for acute lung inflammation. Mol Ther. (2019) 27(10):1758–71. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.07.003
77. Witucki Ł, Jakubowski H. Homocysteine metabolites inhibit autophagy by upregulating miR-21-5p, miR-155-5p, miR-216-5p, and miR-320c-3p in human vascular endothelial cells. Sci Rep. (2024) 14(1):7151. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57750-3
78. Huang Y, Wang Y, Meng S, Chen Z, Kong H, Pan T, et al. Autophagy contributes to host immunity and protection against Zika virus infection via type I IFN signaling. Mediators Inflamm. (2020) 2020:9527147. doi: 10.1155/2020/9527147
79. Shirsath K, Joshi A, Vohra A, Devkar R. HSP60 Knockdown exerts differential response in endothelial cells and monocyte derived macrophages during atherogenic transformation. Sci Rep. (2021) 11(1):1086. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79927-2
80. Feng K, Di Y, Han M, Yan W, Wang Y. SORBS1 Inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) of breast cancer cells by regulating PI3K/AKT signaling and macrophage phenotypic polarization. Aging (Albany NY). (2024) 16(5):4789–810. doi: 10.18632/aging.205632
81. Zha L, Chen J, Sun S, Mao L, Chu X, Deng H, et al. Soyasaponins can blunt inflammation by inhibiting the reactive oxygen species-mediated activation of PI3K/akt/NF-kB pathway. PLoS One. (2014) 9(9):e107655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107655
82. Weinberg JB. Nitric oxide synthase 2 and cyclooxygenase 2 interactions in inflammation. Immunol Res. (2000) 22(2-3):319–41. doi: 10.1385/IR:22:2-3:319
83. Yuste JE, Tarragon E, Campuzano CM, Ros-Bernal F. Implications of glial nitric oxide in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Neurosci. (2015) 9:322. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00322
84. Song Y, Bi Z, Liu Y, Qin F, Wei Y, Wei X. Targeting RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signaling pathway in human cancer: current status in clinical trials. Genes Dis. (2023) 10(1):76–88. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.05.006
85. Yaniv SP, Lucki A, Klein E, Ben-Shachar D. Dexamethasone enhances the norepinephrine-induced ERK/MAPK intracellular pathway possibly via dysregulation of the alpha2-adrenergic receptor: implications for antidepressant drug mechanism of action. Eur J Cell Biol. (2010) 89(9):712–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.05.002
86. Zhu L, Yang T, Li L, Sun L, Hou Y, Hu X, et al. TSC1 Controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disease. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:4696. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5696
87. Yamamura A, Fujiwara M, Kawade A, Amano T, Hossain A, Nayeem MJ, et al. Corosolic acid attenuates platelet-derived growth factor signaling in macrophages and smooth muscle cells of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur J Pharmacol. (2024) 973:176564. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176564
88. Bullenkamp J, Dinkla S, Kaski JC, Dumitriu IE. Targeting T cells to treat atherosclerosis: odyssey from bench to bedside. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. (2016) 2(3):194–9. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvw001
89. Xu J, Yu Y, Zhang Y, Dai H, Yang Q, Wang B, et al. Oral administration of garlic-derived nanoparticles improves cancer immunotherapy by inducing intestinal IFNγ-producing γδ T cells. Nat Nanotechnol. (2024) 19(10):1569–78. doi: 10.1038/s41565-024-01722-1
90. Yu XH, Jiang HL, Chen WJ, Yin K, Zhao GJ, Mo ZC, et al. Interleukin-18 and interleukin-12 together downregulate ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 expression through the interleukin-18R/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. Circ J. (2012) 76(7):1780–91. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-11-1338
91. Nawaz M, Shah N, Zanetti BR, Maugeri M, Silvestre RN, Fatima F, et al. Extracellular vesicles and matrix remodeling enzymes: the emerging roles in extracellular matrix remodeling, progression of diseases and tissue repair. Cells. (2018) 7(10):167. doi: 10.3390/cells7100167
92. Van Doren SR. Matrix metalloproteinase interactions with collagen and elastin. Matrix Biol. (2015) 44-46:224–31. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2015.01.005
93. Zhu Y, Wu F, Hu J, Xu Y, Zhang J, Li Y, et al. LDHA Deficiency inhibits trophoblast proliferation via the PI3K/AKT/FOXO1/CyclinD1 signaling pathway in unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. Faseb J. (2023) 37(2):e22744. doi: 10.1096/fj.202201219RR
94. Long ZW, Wu JH, Cai H, Wang YN, Zhou Y. MiR-374b promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of human GIST cells by inhibiting PTEN through activation of the PI3K/akt pathway. Mol Cells. (2018) 41(6):532–44. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2018.2211
95. Gao J, Wang R, Yang Q, Chen C, Wu Q. Effect of oxaliplatin on cell cycle of hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. (2013) 42(4):437–42. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2013.04.011
96. Song T, Zhao S, Luo S, Chen C, Liu X, Wu X, et al. SLC44A2 Regulates vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching and aortic aneurysm. J Clin Invest. (2024) 134(16):e173690. doi: 10.1172/JCI173690
97. Liu J, Yu W, Liu Y, Chen S, Huang Y, Li X, et al. Mechanical stretching stimulates collagen synthesis via down-regulating SO2/AAT1 pathway. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:21112. doi: 10.1038/srep21112
98. Olejarz W, Łacheta D, Kubiak-Tomaszewska G. Matrix metalloproteinases as biomarkers of atherosclerotic plaque instability. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(11):3946. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113946
99. Petsophonsakul P, Furmanik M, Forsythe R, Dweck M, Schurink GW, Natour E, et al. Role of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching and calcification in aortic aneurysm formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2019) 39(7):1351–68. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312787
100. Jiang M, Wu W, Xia Y, Wang X, Liang J. Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles promote endothelial dysfunction in sepsis by enhancing neutrophil extracellular traps. BMC Immunol. (2023) 24(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12865-023-00560-5
101. Huang Z, Li Y, Niu L, Xiao Y, Pu X, Zheng H, et al. Dynamic expressions of monocyte chemo attractant protein-1 and CC chamomile receptor 2 after balloon injury and their effects in intimal proliferation. Biomed Eng Online. (2015) 14:55. doi: 10.1186/s12938-015-0030-8
102. Hruska KA, Mathew S, Saab G. Bone morphogenetic proteins in vascular calcification. Circ Res. (2005) 97(2):105–14. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.00000175571.53833.6c
103. Li X, Yang HY, Giachelli CM. BMP-2 promotes phosphate uptake, phenotypic modulation, and calcification of human vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. (2008) 199(2):271–7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2007.11.031
104. Yang P, Troncone L, Augur ZM, Kim SSJ, McNeil ME, Yu PB. The role of bone morphogenetic protein signaling in vascular calcification. Bone. (2020) 141:115542. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115542
105. Liu X, Cheng Y, Yang J, Xu L, Zhang C. Cell-specific effects of miR-221/222 in vessels: molecular mechanism and therapeutic application. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2012) 52(1):245–55. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.11.008
106. Mackenzie NC, Staines KA, Zhu D, Genever P, Macrae VE. miRNA-221 and miRNA-222 synergistically function to promote vascular calcification. Cell Biochem Funct. (2014) 32(2):209–16. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3005
107. Chistiakov DA, Sobenin IA, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV. Human miR-221/222 in physiological and atherosclerotic vascular remodeling. Biomed Res Int. (2015) 2015:354517. doi: 10.1155/2015/354517
108. Togliatto G, Dentelli P, Rosso A, Lombardo G, Gili M, Gallo S, et al. PDGF-BB carried by endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles reduces vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis in diabetes. Diabetes. (2018) 67(4):704–16. doi: 10.2337/db17-0371
109. Frödin M, Gammeltoft S. Role and regulation of 90kDa ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) in signal transduction. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (1999) 151(1-2):65–77. doi: 10.1016/S0303-7207(99)00061-1
110. Hao D, Gao P, Liu P, Zhao J, Wang Y, Yang W, et al. AC3-33, A novel secretory protein, inhibits Elk1 transcriptional activity via ERK pathway. Mol Biol Rep. (2011) 38(2):1375–82. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0240-x
111. Li L, Dang Y, Zhang J, Yan W, Zhai W, Chen H, et al. REGγ is critical for skin carcinogenesis by modulating the wnt/β-catenin pathway. Nat Commun. (2015) 6:6875. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7875
112. Muller A, Gasch J, Albring KF, Aberger F, Nivarthi H, Khemeri M, et al. Interplay of transcription factors STAT3, STAT1 and AP-1 mediates activity of the matrix metallo-proteinase-1 promoter in colorectal carcinoma cells. Neoplasma. (2019) 66(3):357–66. doi: 10.4149/neo_2018_180731N560
113. Yamamoto K, Chiba M. MicroRNA-21-5p expression in extracellular vesicles is increased in the blood of aging mice and in vascular endothelial cells induced by ionizing radiation. Exp Ther Med. (2025) 29(2):22. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12772
114. Fan B, Jin Y, Zhang H, Zhao R, Sun M, Sun M, et al. MicroRNA-21 contributes to renal cell carcinoma cell invasiveness and angiogenesis via the PDCD4/c-jun (AP-1) signalling pathway. Int J Oncol. (2020) 56(1):178–92. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4928
115. Su J, Zhou H, Liu X, Nilsson J, Fredrikson GN, Zhao M. oxLDL antibody inhibits MCP-1 release in monocytes/macrophages by regulating Ca2+/K+ channel flow. J Cell Mol Med. (2017) 21(5):929–40. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13033
116. Fougerat A, Smirnova NF, Gayral S, Malet N, Hirsch E, Wymann MP, et al. Key role of PI3Kγ in monocyte chemotactic protein-1-mediated amplification of PDGF-induced aortic smooth muscle cell migration. Br J Pharmacol. (2012) 166(5):1643–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01866.x
117. Dou L, Yan Y, Lu E, Li F, Tian D, Deng L, et al. Composition analysis and mechanism of guizhi fuling capsule in anti-cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer. Transl Oncol. (2025) 52:102244. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102244
118. Chen JS, Wang Q, Fu XH, Huang XH, Chen XL, Cao LQ, et al. Involvement of PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway in invasion and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma: association with MMP-9. Hepatol Res. (2009) 39(2):177–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2008.00449.x
119. Seidl SE, Pessolano LG Jr, Bishop CA, Best M, Rich CB, Stone PJ, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 activation and serum amyloid A regulate smooth muscle cell extracellular matrix. PLoS One. (2017) 12(3):e0171711. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171711
120. Stivala S, Gobbato S, Bonetti N, Camici GG, Lüscher TF, Beer JH. Dietary alpha-linolenic acid reduces platelet activation and collagen-mediated cell adhesion in sickle cell disease mice. J Thromb Haemost. (2022) 20(2):375–86. doi: 10.1111/jth.15581
121. Van Der Meijden PE, Van Schilfgaarde M, Van Oerle R, Renné T, ten Cate H, Spronk HM. Platelet- and erythrocyte-derived microparticles trigger thrombin generation via factor XIIa. J Thromb Haemost. (2012) 10(7):1355–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04758.x
122. Razmara M, Hu H, Masquelier M, Li N. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa blockade inhibits platelet aminophospholipid exposure by potentiating translocase and attenuating scramblase activity. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2007) 64(7-8):999–1008. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-6546-8
123. Schiavello M, Vizio B, Bosco O, Pivetta E, Mariano F, Montrucchio G, et al. Extracellular vesicles: new players in the mechanisms of sepsis-and COVID-19-related thromboinflammation. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(3):1920. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031920
124. Reséndiz JC, Kroll MH, Lassila R. Protease-activated receptor-induced akt activation–regulation and possible function. J Thromb Haemost. (2007) 5(12):2484–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02769.x
125. Marjoram RJ, Voss B, Pan Y, Dickeson SK, Zutter MM, Hamm HE, et al. Suboptimal activation of protease-activated receptors enhances alpha2beta1 integrin-mediated platelet adhesion to collagen. J Biol Chem. (2009) 284(50):34640–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.020990
126. Prole DL, Taylor CW. Structure and function of IP3 receptors. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2019) 11(4):a035063. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a035063
127. Suades R, Padró T, Vilahur G, Badimon L. Circulating and platelet-derived microparticles in human blood enhance thrombosis on atherosclerotic plaques. Thromb Haemost. (2012) 108(6):1208–19. doi: 10.1160/TH12-07-0486
128. Gutmann C, Mayr M. Differential effects of physiological agonists on the proteome of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles. Proteomics. (2024) 24(16):e2400090. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202400090
129. Chou J, Mackman N, Merrill-Skoloff G, Pedersen B, Furie BC, Furie B. Hematopoietic cell-derived microparticle tissue factor contributes to fibrin formation during thrombus propagation. Blood. (2004) 104(10):3190–7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-03-0935
130. Müller I, Klocke A, Alex M, Kotzsch M, Luther T, Morgenstern E, et al. Intravascular tissue factor initiates coagulation via circulating microvesicles and platelets. Faseb J. (2003) 17(3):476–8. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0574fje
131. Hisada Y, Sachetto ATA, Mackman N. Circulating tissue factor-positive extracellular vesicles and their association with thrombosis in different diseases. Immunol Rev. (2022) 312(1):61–75. doi: 10.1111/imr.13106
132. Weiss R, Mostageer M, Eichhorn T, Huber S, Egger D, Spittler A, et al. The fluorochrome-to-protein ratio is crucial for the flow cytometric detection of tissue factor on extracellular vesicles. Sci Rep. (2024) 14(1):6419. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56841-5
133. Biró E, Sturk-Maquelin KN, Vogel GM, Meuleman DG, Smit MJ, Hack CE, et al. Human cell-derived microparticles promote thrombus formation in vivo in a tissue factor-dependent manner. J Thromb Haemost. (2003) 1(12):2561–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00456.x
134. Steppich B, Mattisek C, Sobczyk D, Kastrati A, Schömig A, Ott I. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor on circulating microparticles in acute myocardial infarction. Thromb Haemost. (2005) 93(1):35–9. doi: 10.1160/TH04-06-0393
135. Rothmeier AS, Versteeg HH, Ruf W. Factor VIIa-induced interaction with integrin controls the release of tissue factor on extracellular vesicles from endothelial cells. J Thromb Haemost. (2019) 17(4):627–34. doi: 10.1111/jth.14406
136. Lee JH, Gu J, Kim HK. Factor VIIa-AT complex is an independent prognostic marker of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Ann Clin Lab Sci. (2021) 51(4):546–51.34452894
137. Das K, Keshava S, Pendurthi UR, Rao LVM. Factor VIIa suppresses inflammation and barrier disruption through the release of EEVs and transfer of microRNA 10a. Blood. (2022) 139(1):118–33. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021012358
138. Ding H, Li J, Li Y, Yang M, Nie S, Zhou M, et al. MicroRNA-10 negatively regulates inflammation in diabetic kidney via targeting activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Mol Ther. (2021) 29(7):2308–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.03.012
139. Geddings JE, Hisada Y, Boulaftali Y, Getz TM, Whelihan M, Fuentes R, et al. Tissue factor-positive tumor microvesicles activate platelets and enhance thrombosis in mice. J Thromb Haemost. (2016) 14(1):153–66. doi: 10.1111/jth.13181
140. Carman CV, Nikova DN, Sakurai Y, Shi J, Novakovic VA, Rasmussen JT, et al. Membrane curvature and PS localize coagulation proteins to filopodia and retraction fibers of endothelial cells. Blood Adv. (2023) 7(1):60–72. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006870
141. Tripisciano C, Weiss R, Eichhorn T, Spittler A, Heuser T, Fischer MB, et al. Different potential of extracellular vesicles to support thrombin generation: contributions of phosphatidylserine, tissue factor, and cellular origin. Sci Rep. (2017) 7(1):6522. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03262-2
142. Suades R, Padró T, Vilahur G, Badimon L. Platelet-released extracellular vesicles: the effects of thrombin activation. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2022) 79(3):190. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04222-4
143. Lacroix R, Plawinski L, Robert S, Doeuvre L, Sabatier F, Martinez de Lizarrondo S, et al. Leukocyte- and endothelial-derived microparticles: a circulating source for fibrinolysis. Haematologica. (2012) 97(12):1864–72. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.066167
144. Chen W, Li L, Wang J, Li Q, Zhang R, Wang S, et al. Extracellular vesicle YRNA in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. (2021) 517:15–22. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2021.02.003
145. Wang C, Liu C, Shi J, Li H, Jiang S, Zhao P, et al. Nicotine exacerbates endothelial dysfunction and drives atherosclerosis via extracellular vesicle-miRNA. Cardiovasc Res. (2023) 119(3):729–42. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvac140
146. Stojkovic S, Thulin Å, Hell L, Thaler B, Rauscher S, Baumgartner J, et al. IL-33 stimulates the release of procoagulant microvesicles from human monocytes and differentially increases tissue factor in human monocyte subsets. Thromb Haemost. (2017) 117(7):1379–90. doi: 10.1160/TH16-10-0784
147. Letonja J, Petrovič D. A review of MicroRNAs and lncRNAs in atherosclerosis as well as some major inflammatory conditions affecting atherosclerosis. Biomedicines. (2024) 12(6):1322. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061322
148. Choi YY, Kim A, Lee Y, Lee YH, Park M, Shin E, et al. The miR-126-5p and miR-212-3p in the extracellular vesicles activate monocytes in the early stage of radiation-induced vascular inflammation implicated in atherosclerosis. J Extracell Vesicles. (2023) 12(5):e12325. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12325
149. Wang Y, Wang M, Yu P, Zuo L, Zhou Q, Zhou X, et al. MicroRNA-126 modulates palmitate-induced migration in HUVECs by downregulating myosin light chain kinase via the ERK/MAPK pathway. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2020) 8:913. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00913
150. Zhang H, Wang Y, Feng K, Niu Q, Xin Y, Xuan S, et al. MiR-146a-5p-enriched exosomes inhibit M1 macrophage activation and inflammatory response by targeting CD80. Mol Biol Rep. (2024) 51(1):1133. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10088-5
151. Chen C, Cai S, Wu M, Wang R, Liu M, Cao G, et al. Role of cardiomyocyte-derived exosomal MicroRNA-146a-5p in macrophage polarization and activation. Dis Markers. (2022) 2022:2948578. doi: 10.1155/2022/2948578
152. Bukauskas T, Mickus R, Cereskevicius D, Macas A. Value of Serum miR-23a, miR-30d, and miR-146a biomarkers in ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Med Sci Monit. (2019) 25:3925–32. doi: 10.12659/MSM.913743
153. Ismail N, Wang Y, Dakhlallah D, Moldovan L, Agarwal K, Batte K, et al. Macrophage microvesicles induce macrophage differentiation and miR-223 transfer. Blood. (2013) 121(6):984–95. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-08-374793
154. Wang X, Gu H, Qin D, Yang L, Huang W, Essandoh K, et al. Exosomal miR-223 contributes to mesenchymal stem cell-elicited cardioprotection in polymicrobial sepsis. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:13721. doi: 10.1038/srep13721
155. Xie S, Xing Y, Shi W, Zhang M, Chen M, Fang W, et al. Cardiac fibroblast heat shock protein 47 aggravates cardiac fibrosis post myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by encouraging ubiquitin specific peptidase 10 dependent Smad4 deubiquitination. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2022) 12(11):4138–53. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.07.022
156. Kudaibergenova M, Guo J, Khan HM, Zahid F, Lees-Miller J, Noskov SY, et al. Allosteric coupling between drug binding and the aromatic cassette in the pore domain of the hERG1 channel: implications for a state-dependent blockade. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:914. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00914
157. Li T, Wang B, Ding H, Chen S, Cheng W, Li Y, et al. Effect of extracellular vesicles from multiple cells on vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:857331. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.857331
158. Vagida M, Arakelyan A, Lebedeva A, Grivel JC, Shpektor A, Vasilieva E, et al. Flow analysis of individual blood extracellular vesicles in acute coronary syndrome. Platelets. (2017) 28(2):165–73. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2016.1212002
159. Sharma P, Dhamija RK, Nag TC, Roy A, Inampudi KK. Different biofluids, small extracellular vesicles or exosomes: structural analysis in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease using electron microscopy techniques. Microsc Microanal. (2023) 29(3):1168–77. doi: 10.1093/micmic/ozad025
160. Alidadi M, Hjazi A, Ahmad I, Mahmoudi R, Sarrafha M, Reza Hosseini-Fard S, et al. Exosomal non-coding RNAs: emerging therapeutic targets in atherosclerosis. Biochem Pharmacol. (2023) 212:115572. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115572
161. Wang F, Long G, Zhao C, Li H, Chaugai S, Wang Y, et al. Plasma microRNA-133a is a new marker for both acute myocardial infarction and underlying coronary artery stenosis. J Transl Med. (2013) 11:222. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-222
162. Dekker M, Waissi F, van Bennekom J, Silvis MJM, Timmerman N, Schoneveld AH, et al. Extracellular vesicle cystatin c is associated with unstable angina in troponin negative patients with acute chest pain. PLoS One. (2020) 15(8):e0237036. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237036
163. Costamagna G, Navi BB, Beyeler M, Hottinger AF, Alberio L, Michel P. Ischemic stroke in cancer: mechanisms, biomarkers, and implications for treatment. Semin Thromb Hemost. (2024) 50(3):342–59. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1771270
164. Timmerman N, Waissi F, Dekker M, van de Pol QY, van Bennekom J, Schoneveld A, et al. Pre-operative plasma extracellular vesicle proteins are associated with a high risk of long term secondary major cardiovascular events in patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. (2021) 62(5):705–15. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2021.06.039
165. Kanhai DA, Visseren FL, van der Graaf Y, Schoneveld AH, Catanzariti LM, Timmers L, et al. Microvesicle protein levels are associated with increased risk for future vascular events and mortality in patients with clinically manifest vascular disease. Int J Cardiol. (2013) 168(3):2358–63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.01.231
166. Oggero S, Godec T, van Gorp R, Pinto AL, Schurgers LJ, Reutelingsperger C, et al. Role of plasma extracellular vesicles in prediction of cardiovascular risk and alterations in response to statin therapy in hypertensive patients. J Hypertens. (2022) 40(8):1522–9. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003178
167. Páramo JA, Cenarro A, Civeira F, Roncal C. Extracellular vesicles in atherosclerosis: current and forthcoming impact. Clin Investig Arterioscler. (2025) 37(2):100718. doi: 10.1016/j.arteri.2024.03.006
168. Gasecka A, Nieuwland R, Budnik M, Dignat-George F, Eyileten C, Harrison P, et al. Randomized controlled trial protocol to investigate the antiplatelet therapy effect on extracellular vesicles (AFFECT EV) in acute myocardial infarction. Platelets. (2020) 31(1):26–32. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2018.1557616
169. Cheow ES, Cheng WC, Lee CN, de Kleijn D, Sorokin V, Sze SK. Plasma-derived extracellular vesicles contain predictive biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for myocardial ischemic (MI) injury. Mol Cell Proteomics. (2016) 15(8):2628–40. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M115.055731
170. Da Fonseca Ferreira A, Wei J, Zhang L, Macon CJ, Degnan B, Jayaweera D, et al. HIV Promotes atherosclerosis via circulating extracellular vesicle MicroRNAs. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(8):7567. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087567
171. Obermayer G, Afonyushkin T, Göderle L, Puhm F, Schrottmaier W, Taqi S, et al. Natural IgM antibodies inhibit microvesicle-driven coagulation and thrombosis. Blood. (2021) 137(10):1406–15. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020007155
172. Lee JS, Jeong YH, Kim YH, Yun JH, Ahn JO, Chung JY, et al. Analyzing small RNA sequences from canine stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles primed with TNF-α and IFN-γ and exploring their potential in lung repair. Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1411886. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1411886
173. Mori D, Miyagawa S, Kawamura T, Yoshioka D, Hata H, Ueno T, et al. Mitochondrial transfer induced by adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation improves cardiac function in rat models of ischemic cardiomyopathy. Cell Transplant. (2023) 32:9636897221148457. doi: 10.1177/09636897221148457
174. Wu X, Yuan P, Wei N, Ma C, Fu M, Wu W. Extracellular vesicles derived from “serum and glucose” deprived HUCMSCs promoted skin wound healing through enhanced angiogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem. (2025) 480(2):1255–73. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05058-1
175. Wei Q, Wang Y, Ma K, Li Q, Li B, Hu W, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells facilitate diabetic wound healing through MiR-17-5p-mediated enhancement of angiogenesis. Stem Cell Rev Rep. (2022) 18(3):1025–40. doi: 10.1007/s12015-021-10176-0
176. Wang J, Yin B, Lian J, Wang X. Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery system for cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics. (2024) 16(8):1029. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081029
177. Ivanova A, Badertscher L, O'Driscoll G, Bergman J, Gordon E, Gunnarsson A, et al. Creating designer engineered extracellular vesicles for diverse ligand display, target recognition, and controlled protein loading and delivery. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10(34):e2304389. doi: 10.1002/advs.202304389
178. Gebeyehu A, Kommineni N, Meckes DG Jr, Sachdeva MS. Role of exosomes for delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. (2021) 38(5):53–97. doi: 10.1615/CritRevTherDrugCarrierSyst.2021036301
179. Zhang Y, Dou Y, Liu Y, Di M, Bian H, Sun X, et al. Advances in therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles. Int J Nanomedicine. (2023) 18:3285–307. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S409588
180. Chen W, Zhou M, Guan B, Xie B, Liu Y, He J, et al. Tumour-associated macrophage-derived DOCK7-enriched extracellular vesicles drive tumour metastasis in colorectal cancer via the RAC1/ABCA1 axis. Clin Transl Med. (2024) 14(2):e1591. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1591
181. Dracheva KV, Pobozheva IA, Anisimova KA, Panteleeva AA, Garaeva LA, Balandov SG, et al. Extracellular vesicles secreted by adipose tissue during obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus influence reverse cholesterol transport-related gene expression in human macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25(12):6457. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126457
182. Kaur G, Bae EH, Zhang Y, Ciacciofera N, Jung KM, Barreda H, et al. Biopotency and surrogate assays to validate the immunomodulatory potency of extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells for the treatment of experimental autoimmune uveitis. J Extracell Vesicles. (2024) 13(8):e12497. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12497
183. Zhang J, Li P, Zhao G, He S, Xu D, Jiang W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles protect retina in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa by anti-inflammation through miR-146a-Nr4a3 axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 13(1):394. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03100-x
184. Martin-Garrido A, Brown DI, Lyle NA, Dikalova A, Griendling KK. Abstract 5473: tGFβ induction of vascular smooth muscle differentiation markers is mediated by Nox4 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Circulation. (2009) 120(suppl_18):S1098. doi: 10.1161/circ.120.suppl_18.S1098-a
185. Ngo NH, Chang YH, Vuong CK, Yamashita T, Obata-Yasuoka M, Hamada H, et al. Transformed extracellular vesicles with high angiogenic ability as therapeutics of distal ischemic tissues. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2022) 10:869850. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.869850
186. Cheng M, Yang J, Zhao X, Zhang E, Zeng Q, Yu Y, et al. Circulating myocardial microRNAs from infarcted hearts are carried in exosomes and mobilise bone marrow progenitor cells. Nat Commun. (2019) 10(1):959. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08895-7
187. Torabi C, Choi SE, Pisanic TR, Paulaitis M, Hur SC. Streamlined miRNA loading of surface protein-specific extracellular vesicle subpopulations through electroporation. Biomed Eng Online. (2024) 23(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12938-024-01311-2
188. Ormazabal V, Nair S, Carrión F, McIntyre HD, Salomon C. The link between gestational diabetes and cardiovascular diseases: potential role of extracellular vesicles. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01597-3
189. Zhu X, Yang Q, Zhao Y, Sheng X, Zhang L. The effect of strain effect on WS2 monolayer as a potential delivery carrier for anti-myocardial infarction drug: first-principles study. J Mol Model. (2024) 30(9):313. doi: 10.1007/s00894-024-06111-y
190. Aubertin K, Silva AK, Luciani N, Espinosa A, Djemat A, Charue D, et al. Massive release of extracellular vesicles from cancer cells after photodynamic treatment or chemotherapy. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:35376. doi: 10.1038/srep35376
191. Motta-Mejia C, Kandzija N, Zhang W, Mhlomi V, Cerdeira AS, Burdujan A, et al. Placental vesicles carry active endothelial nitric oxide synthase and their activity is reduced in preeclampsia. Hypertension. (2017) 70(2):372–81. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.09321
192. Chen Q, Che C, Yang S, Ding P, Si M, Yang G. Anti-inflammatory effects of extracellular vesicles from morchella on LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells via the ROS-mediated p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. (2023) 478(2):317–27. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04508-y
193. Wang T, Ding J, Cheng X, Yang Q, Hu P. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: new strategies and therapeutic targets to treat atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1396656. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1396656
194. Bozkurt AS, Kaplan DS, Çeribaşi AO, Orkmez M, Çanak A, Tarakçioğlu M. An investigation of the effect of extracellular vesicles isolated from mouse embryonic fibroblasts on wound healing in an experimental diabetic mouse model. An Acad Bras Cienc. (2022) 94(1):e20201562. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765202120201562
195. Chen Y, Wang L, Zheng M, Zhu C, Wang G, Xia Y, et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles for concurrent anti-PDL1 immunotherapy and chemotherapy. Bioact Mater. (2022) 9:251–65. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.07.012
196. Choe EJ, Lee CH, Bae JH, Park JM, Park SS, Baek MC. Atorvastatin enhances the efficacy of immune checkpoint therapy and suppresses the cellular and extracellular vesicle PD-L1. Pharmaceutics. (2022) 14(8):1660. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081660
197. Akhmerov A, Parimon T. Extracellular vesicles, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Cells. (2022) 11(14):2229. doi: 10.3390/cells11142229
198. Ohayon L, Zhang X, Dutta P. The role of extracellular vesicles in regulating local and systemic inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol Res. (2021) 170:105692. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105692
199. Giannasi C, Niada S, Magagnotti C, Ragni E, Andolfo A, Brini AT. Comparison of two ASC-derived therapeutics in an in vitro OA model: secretome versus extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 11(1):521. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-02035-5
200. Yuan Y, Cao K, Gao P, Wang Y, An W, Dong Y. Extracellular vesicles and bioactive peptides for regenerative medicine in cosmetology. Ageing Res Rev. (2025) 107:102712. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2025.102712
201. Dutta S, Ghosh S, Rahaman M, Chowdhury SR. Plant-derived exosomes: pioneering breakthroughs in therapeutics, targeted drug delivery, and regenerative medicine. Pharm Nanotechnol. (2024). doi: 10.2174/0122117385305245240424093014
202. An Y, Sun JX, Ma SY, Xu MY, Xu JZ, Liu CQ, et al. From plant based therapy to plant-derived vesicle-like nanoparticles for cancer treatment: past, present and future. Int J Nanomedicine. (2025) 20:3471–91. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S499893
203. Hao L, Jiang Y, Zhang R, Zhang N, Yang Y, Gao Y, et al. Preparation and in vivo/in vitro characterization of ticagrelor PLGA sustained-release microspheres for injection. Des Monomers Polym. (2021) 24(1):305–19. doi: 10.1080/15685551.2021.1984008
204. Kazsoki A, Németh K, Visnovitz T, Lenzinger D, Buzás EI, Zelkó R. Formulation and characterization of nanofibrous scaffolds incorporating extracellular vesicles loaded with curcumin. Sci Rep. (2024) 14(1):27574. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79277-3
205. Lin XL, Liu MH, Hu HJ, Feng HR, Fan XJ, Zou WW, et al. Curcumin enhanced cholesterol efflux by upregulating ABCA1 expression through AMPK-SIRT1-LXRα signaling in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. DNA Cell Biol. (2015) 34(9):561–72. doi: 10.1089/dna.2015.2866
206. Du X, Amin N, Xu L, Botchway BOA, Zhang B, Fang M. Pharmacological intervention of curcumin via the NLRP3 inflammasome in ischemic stroke. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1249644. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1249644
207. Cho EG, Choi SY, Kim H, Choi EJ, Lee EJ, Park PJ, et al. Panax ginseng-derived extracellular vesicles facilitate anti-senescence effects in human skin cells: an eco-friendly and sustainable way to use ginseng substances. Cells. (2021) 10(3):486. doi: 10.3390/cells10030486
208. You L, Zhang D, Geng H, Sun F, Lei M. Salidroside protects endothelial cells against LPS-induced inflammatory injury by inhibiting NLRP3 and enhancing autophagy. BMC Complement Med Ther. (2021) 21(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03307-0
209. Jung D, Kim NE, Kim S, Bae JH, Jung IY, Doh KW, et al. Plant-derived nanovesicles and therapeutic application. Pharmacol Ther. (2025) 269:108832. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2025.108832
210. Yim KHW, Krzyzaniak O, Al Hrout A, Peacock B, Chahwan R. Assessing extracellular vesicles in human biofluids using flow-based analyzers. Adv Healthc Mater. (2023) 12(32):e2301706. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202301706
211. Wan M, Amrollahi P, Sun D, Lyon C, Hu TY. Using nanoplasmon-enhanced scattering and low-magnification microscope imaging to quantify tumor-derived exosomes. J Vis Exp. (2019) 147:10.3791/59177. doi: 10.3791/59177
212. Cao F, Gao Y, Chu Q, Wu Q, Zhao L, Lan T, et al. Proteomics comparison of exosomes from serum and plasma between ultracentrifugation and polymer-based precipitation kit methods. Electrophoresis. (2019) 40(23-24):3092–8. doi: 10.1002/elps.201900295
213. Jimenez L, Barman B, Jung YJ, Cocozza L, Krystofiak E, Saffold C, et al. Culture conditions greatly impact the levels of vesicular and extravesicular Ago2 and RNA in extracellular vesicle preparations. J Extracell Vesicles. (2023) 12(11):e12366. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12366
214. Peng M, Liu X, Xu G. Extracellular vesicles as messengers in atherosclerosis. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. (2020) 13(2):121–30. doi: 10.1007/s12265-019-09923-z
215. Vanderboom PM, Dasari S, Ruegsegger GN, Pataky MW, Lucien F, Heppelmann CJ, et al. A size-exclusion-based approach for purifying extracellular vesicles from human plasma. Cell Rep Methods. (2021) 1(3):100055. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2021.100055
216. Liu Z, Pang B, Wang Y, Zheng J, Li Y, Jiang J. Advances of new extracellular vesicle isolation and detection technologies in cancer diagnosis. Small. (2024):e2405872. doi: 10.1002/smll.202405872
217. Esmaeili A, Alini M, Baghaban Eslaminejad M, Hosseini S. Engineering strategies for customizing extracellular vesicle uptake in a therapeutic context. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 13(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02806-2
Keywords: extracellular vesicles, atherosclerosis, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory response, intercellular communication
Citation: Deng H, Qiu W, Zhang Y and Hua J (2025) Extracellular vesicles in atherosclerosis cardiovascular disease: emerging roles and mechanisms. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1611557. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1611557
Received: 14 April 2025; Accepted: 9 June 2025;
Published: 24 June 2025.
Edited by:
Adriana Georgescu, Institute of Cellular Biology and Pathology (ICBP), RomaniaReviewed by:
Rosa Suades, Sant Pau Institute for Biomedical Research, SpainMartina Schiavello, University of Turin, Italy
Khaled Al-Massri, University of Palestine, Palestine
Arezoo Mohammadipoor, United States Army Institute of Surgical Research, United States
Copyright: © 2025 Deng, Qiu, Zhang and Hua. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Junyi Hua, MTM3MDY1MTMyNjRAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Haoxuan Deng
Haoxuan Deng Wei Qiu
Wei Qiu Junyi Hua
Junyi Hua