- 1Department of Coronary Artery Disease and Heart Failure, St. John Paul II Hospital, Kraków, Poland
- 2Department of Emergency Medical Services, Jagiellonian University Medical College, Kraków, Poland
- 3Department of Thromboembolic Disorders, Institute of Cardiology, Jagiellonian University Medical College, Kraków, Poland
- 4"Club 30”, Polish Cardiac Society, Warsaw, Poland
- 5Student Research Group at Department of Coronary Artery Disease and Heart Failure, Jagiellonian University Medical College, Kraków, Poland
- 6Department of Coronary Artery Disease and Heart Failure, Institute of Cardiology, Jagiellonian University Medical College, Kraków, Poland
Background: The mortality rate in decompensated heart failure (HF) with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) remains high. In recent years the prognostic role of CHA2DS2-VASc score, initially formulated for embolic risk prediction in atrial fibrillation, has been shown in other diseases including HF. We sought to analyze a long-term mortality in decompensated HFpEF patients depending on CHA2DS2-VASc score.
Methods: 261 (22.74%) out of 1,148 patients included in the single-center Lesser Poland Cracovian Heart Failure (LECRA-HF) Registry between 2009 and 2022 were diagnosed with decompensated HFpEF. We identified 213 (81.61%) subjects with CHA₂DS₂-VASc score ≥4 points and 48 (18.39%) < 4 points.
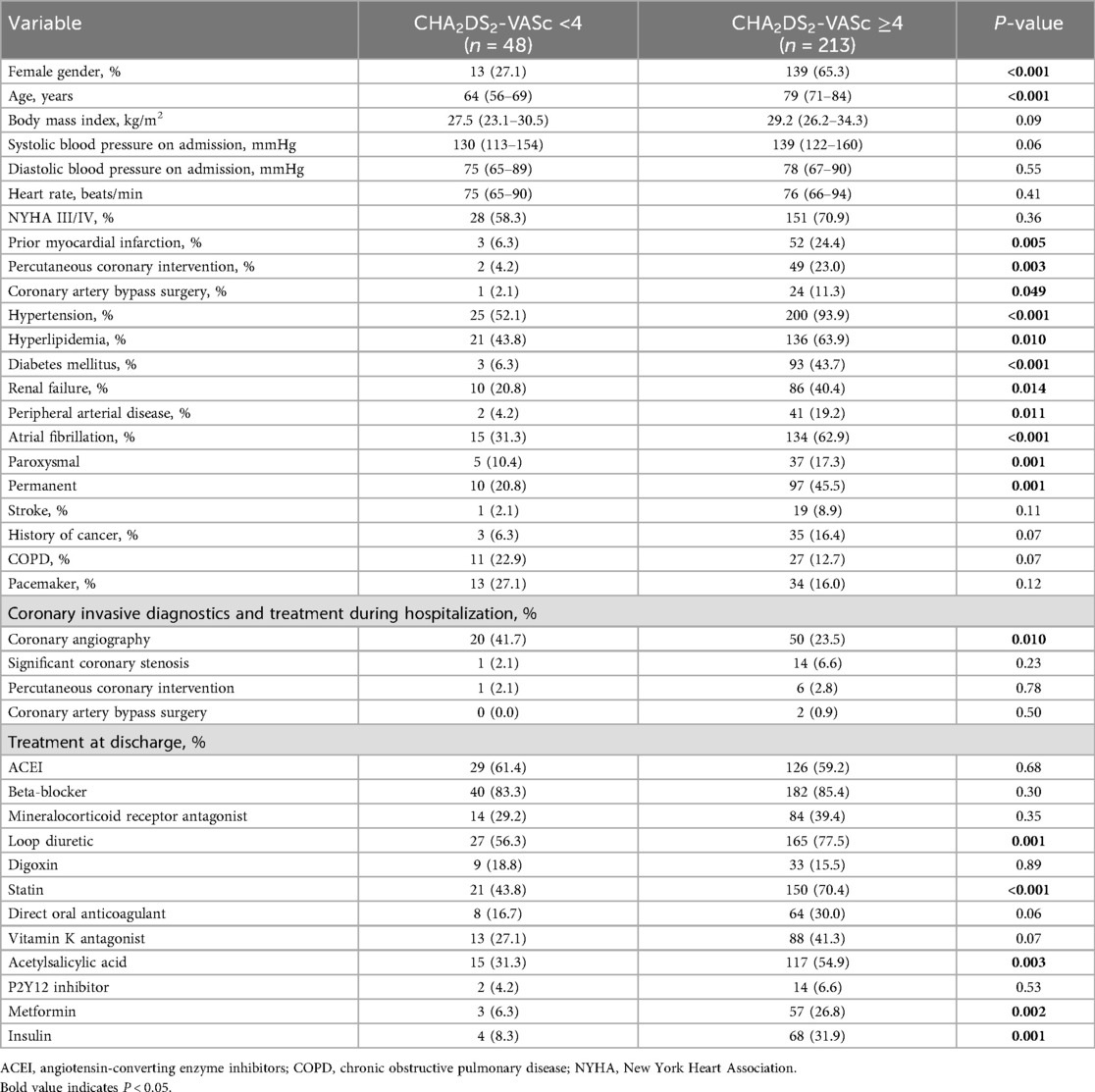
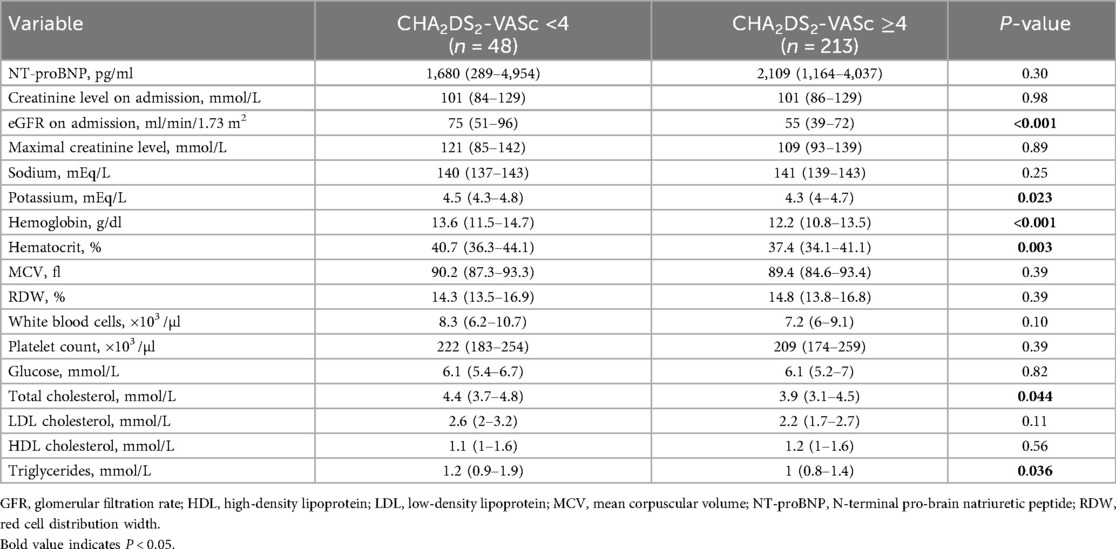
Results: Patients with CHA₂DS₂-VASc ≥4 were older (79 vs. 64 years, P < 0.001), mostly females (65.3% vs. 27.1%, P < 0.001), and were characterized by atrial fibrillation (62.9% vs. 31.3%, P < 0.001), prior myocardial infarction (24.4% vs. 6.3%, P = 0.005), percutaneous coronary intervention (23.0% vs. 4.2%, P = 0.003) and coronary artery bypass surgery (11.3% vs. 2.1%, P = 0.049) compared to CHA2DS2-VASc <4 cohort. Lower baseline GFR (by 26.7%, P < 0.001), potassium (by 4.4%, P = 0.02), hemoglobin (by 10.3%, P < 0.001), as well as hematocrit (by 8.1%, P = 0.003) were noted in CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 patients. In a long-term follow-up (median 4.3 years), overall mortality was significantly higher in CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 group (P = 0.005) and CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 was its independent predictor (HR 3.54, 95% confidence interval 1.68–7.49). In a multivariable Cox regression analysis, each one-point increase in CHA2DS2-VASc score raised all-cause mortality risk by 32%.
Conclusions: As has been shown for the first time CHA2DS2-VASc score was an independent prognostic parameter in decompensated HFpEF.
1 Introduction
In accordance with the current data heart failure (HF) affects more than 64 million people worldwide (1). Approximately 50% of them suffer from HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) (2–5). The prevalence of HFpEF still increases due to better diagnostic methods, aging of the population, multimorbidity and improved survival with co-morbidities leading to HFpEF in individual patients (4, 6–9). The approximate annual all-cause mortality in general HF population was of 8.1%. This number can widely change depending on left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) phenotype and is 8.8% in patients with LVEF < 50%, 7.6% in patients with LVEF 40%–50% and is lowest in patients with LVEF > 50%–6.3% (10). Other study showed that the annual all-cause mortality in HFpEF reached 15% or even more in elderly patients (6). In contrast, patients with acute decompensated HF had worse clinical outcomes, reaching 35%–45% compared to 10%–20% in chronic HF (11).
To date, few well-validated scales have been developed to assess the mortality risk in HFpEF. As has been shown the MAGGIC, MEESSI-AHF, EHMRG scores could be useful to assess the risk of various clinical endpoints in HFpEF population (12–15). The CHA2DS2-VASc is a recognized worldwide, and widely recommended practical scale originally formulated for the annual thromboembolic event risk estimation and decision-making for anticoagulant treatment initiation in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF) (15–18). However, there are plenty of studies demonstrating its usefulness of this score in assessing the risk of other clinical endpoints regardless of the AF presence. This score was also evaluated in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (19), chronic kidney disease (17). Recently, the CHA2DS2-VASc score has also been investigated in the setting of acute coronary syndromes. In a cohort of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention, a score greater than two points independently predicted new-onset atrial fibrillation and hemodynamic complications such as cardiogenic shock or asystole (20, 21). In another study, patients with STEMI and a CHA2DS2-VASc ≥ 4 exhibited significantly higher in-hospital, 12-month and long-term mortality, with areas under the ROC curve of 0.88, 0.82 and 0.79, respectively (22). These findings highlight that the CHA₂DS₂-VASc score may aid risk stratification across a broad spectrum of cardiovascular conditions beyond its original thromboembolic focus.
There are also promising data regarding the use of this scale in HF, especially HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) (18, 23). Noteworthy, hypertension, older age, diabetes mellitus (DM) and coronary artery disease included in CHA2DS2-VASc score are also the significant risk factors for HFpEF (3, 4, 6, 8, 16, 24). However, the current data regarding the application of this scale in HFpEF are scarce (12, 25, 26), HFpEF remains an under-recognized entity with increasing prevalence and few evidence-based therapeutic options. Its heterogeneity and frequent comorbidities make diagnosis challenging and only limited treatments are currently available (27). This context underscores the importance of simple, inexpensive and non-invasive risk scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc, which could facilitate closer follow-up and early intervention in HFpEF patients.
To the best of our knowledge, no studies have evaluated the CHA2DS2-VASc score for risk stratification of long-term all-cause mortality among patients hospitalized with acute decompensated HFpEF. Therefore, based on data from the Lesser Poland Cracovian Heart Failure (LECRA-HF) Registry, we investigated the prognostic utility of the CHA₂DS₂-VASc score for long-term all-cause mortality in patients with HFpEF.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 LECRA-HF registry
The LECRA-HF Registry (NCT05746923) is a constantly updated database of patients admitted to the Department of Coronary Artery Disease and Heart Failure in St. John Paul II Hospital in Kraków, Poland, between 2009 and 2022 hospitalized due to the acute decompensation of HF (28). We obtained all-cause mortality follow-up from the Polish National Death Registry, censored April 7, 2024. The study protocol is compliant with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the local Ethics Committee (Consent No. 1072.6120.349.2022). Each patient included in LECRA-HF gave the informed consent. The data in LECRA-HF will be continuously collected until 2026. The LECRA-HF Registry contains data of consecutive 1148 adult (aged 18 years or older) patients treated in tertiary clinic due to its acute decompensation (28, 29). The detailed characteristics included demographic and anthropometric data, as well as cardiovascular risk factors, comorbidities, pharmacological treatment, transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) parameters, laboratory results, all collected during the index hospitalization. Based on LECRA-HF, 261 (22.74%) were diagnosed with decompensated HFpEF.
2.2 HFpEF definition
HFpEF was diagnosed according to the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines in force at the time of the index hospitalization (30–33). To harmonize case ascertainment across 2009–2022, we required: (1) signs and/or symptoms of heart failure; (2) left-ventricular ejection fraction ≥50% measured by the biplane Simpson method (34); and (3) evidence of elevated filling pressures documented by natriuretic peptides and/or echocardiography, as available. Consistent with ESC guidance for the acute setting, an admission NT-proBNP ≥ 300 pg/ml was considered biochemical evidence of elevated filling pressures (32, 33). When both natriuretic peptides and echocardiography were available, both were expected to support the diagnosis; when NT-proBNP did not meet the threshold defined above or was not measured, echocardiographic evidence of structural heart disease and/or diastolic dysfunction was required in accordance with ESC criteria current at the time of the index hospitalization (30–34).
2.3 Assessments and variable definitions
HF symptoms were classified by the New York Heart Association class (NYHA), while laboratory tests and TTE were performed by a qualified medical staff according to the current standards (34). N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) level was measured using standard methods (35). Renal function was established based on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) < 30 ml/min using the Cockroft-Gault formula (35). LVEF and left atrial volume were measured using the biplane Simpson method (34). COPD was diagnosed accordingly to the current criteria based on the GOLD guidelines (36). DM was defined as treatment with oral hypoglycemic drugs, insulin or both equally, as well as fasting blood glucose level >125 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) (16).
2.4 CHA2Ds2-VASc score
CHA2DS2-VASc score was calculated for all patients as validated for anticoagulant initiation in AF, giving 1 point for each category: congestive HF, hypertension, age 65–74 years, DM, vascular disease and sex category (female), while 2 points for age ≥75 years and for previous stroke/transient ischemic attack/thromboembolism incident (16).
2.5 Statistical analysis
Categorical variables were reported as numbers and percentages. Continuous variables were presented as median (first and third quartile, Q1-Q3). Shapiro–Wilk test was used to assess the normal distribution of variables. The continuous variables were compared between two groups using Student's or U-Mann Whitney tests. Categorical variables were analyzed using the χ2 test or the Fisher exact test. The associations between numerical variables were assessed by Pearson's or Spearman's rank correlation coefficient. Kaplan–Meier curves of all-cause mortality in the studied groups were prepared and compared with the log-rank test. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and the area under the curve (AUC) were computed for CHA₂DS₂-VASc, MAGGIC, EHMRG, and MEESSI-AHF using nonparametric methods. Pairwise comparisons of AUCs were performed using DeLong's test with two-sided P-values.
The multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression analysis was performed to investigate the relationships of CHA2DS2-VASc with mortality. Two sets of models were conducted: CHA2DS2-VASc as numerical variable and as dichotomized variable (CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4). The final models were adjusted for NYHA, COPD, renal failure, hemoglobin and maximal aortic gradient. The selection of variables for the multivariable model was based on the results in univariable models, literature and to avoid collinearity. Moreover, to avoid overfitting given the relatively small number of events, we limited the number of covariates in the multivariable model. Established prognostic markers such as NT-proBNP are highly correlated with NYHA class and renal function. Including them introduced multicollinearity and did not materially change the hazard ratios of the variables retained in the model. Therefore, for statistical and practical reasons we chose to exclude NT-proBNP and detailed LVEF categorizations from the final models. The results of Cox regression were presented as hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). The f goodness-of-fit of preformed model were assessed using Harrell's C-index. A two-sided P-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using STATISTICA software Version 13.3 (StatSoft, Krakow, Poland) or R Core Team (2013, Vienna, Austria).
3 Results
We analysed 261 patients hospitalized for decompensated HFpEF with a median follow-up of 4.3 years. Of these, 213 patients (81.6%) had a CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥ 4 and 48 (18.4 %) had a score <4 (Table 1; Figure 1).
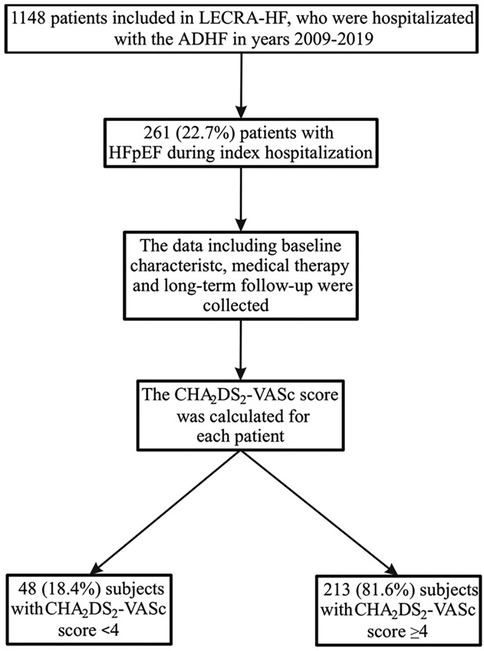
Figure 1. Study flowchart. ADHF, acute decompensated heart failure; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
3.1 Baseline characteristics of the studied patients
Patients with CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 were more often female (P < 0.001), older (P < 0.001) and more frequently had hypertension (P < 0.001), hyperlipidemia (P = 0.01), DM (P < 0.001), renal failure (P = 0.01) and peripheral arterial disease (P = 0.01) (Table 1). They were also more often diagnosed with atrial fibrillation, both paroxysmal (P = 0.001) and permanent (P = 0.001). Prior myocardial infarction (P = 0.005), percutaneous coronary intervention (P = 0.003) and coronary artery bypass grafting (P = 0.049) were more common, whereas coronary angiography during the index hospitalization was performed less frequently (P = 0.01) (Table 1). Moreover, acetylsalicylic acid, statins, loop diuretics, metformin and insulin were prescribed more often in patients with CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 (Table 1).
3.2 Laboratory parameters
Patients with CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 had lower baseline glomerular filtration rate (P < 0.001), potassium (P = 0.02), hemoglobin (P < 0.001) and hematocrit (P = 0.003) compared with those scoring < 4 (Table 2). Total cholesterol and triglycerides were also lower in the CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 group (P = 0.04 and P = 0.03, respectively) (Table 2).
3.3 Echocardiographic parameters
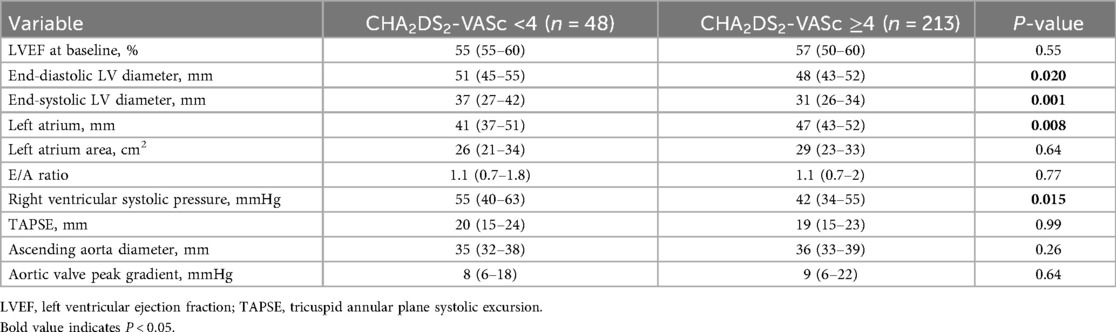
Echocardiography showed that patients with CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 had smaller left-ventricular end-diastolic and end-systolic diameters, larger left-atrial diameter, and lower right-ventricular systolic pressure than those with scores <4 (Table 3). As expected, left-ventricular ejection fraction did not differ significantly between the groups (P = 0.55) (Table 3).
3.4 Correlation analysis
Exploratory correlation analyses revealed that the CHA2DS2-VASc score correlated positively with age (r = 0.64, P < 0.001) and negatively with GFR (r = –0.35, P < 0.001). Age and GFR were inversely related (r = –0.52, P < 0.001), whereas left-ventricular end-diastolic and end-systolic diameters were positively correlated (r = 0.58, P < 0.001).
3.5 Long-term mortality
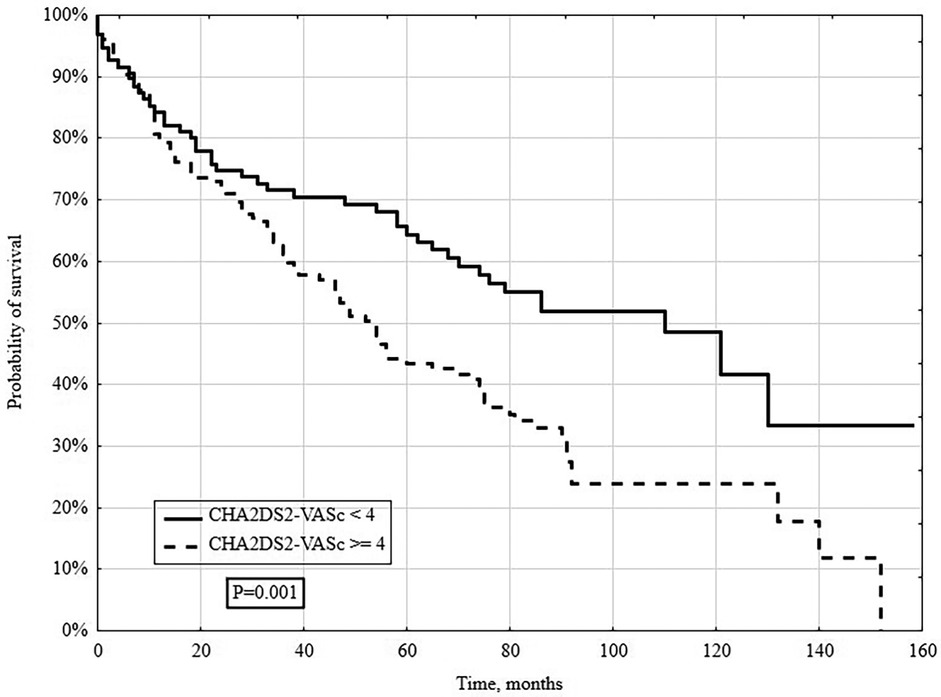
In a long-term follow-up (median 4.3 years), 148/261 (56.7%) patients died. Deaths occurred in 131/213 (61.5%) patients with CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 and 17/48 (35.4%) with CHA2DS2-VASc <4 (P = 0.005; Figure 2). When stratified by individual CHA2DS2-VASc categories (1–3, 4, 5, 6, ≥7), survival declined stepwise with higher scores (log-rank P = 0.005; Figure 2). Kaplan–Meier analysis showed significantly lower survival in the CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 group (log-rank P = 0.001; Figure 3).
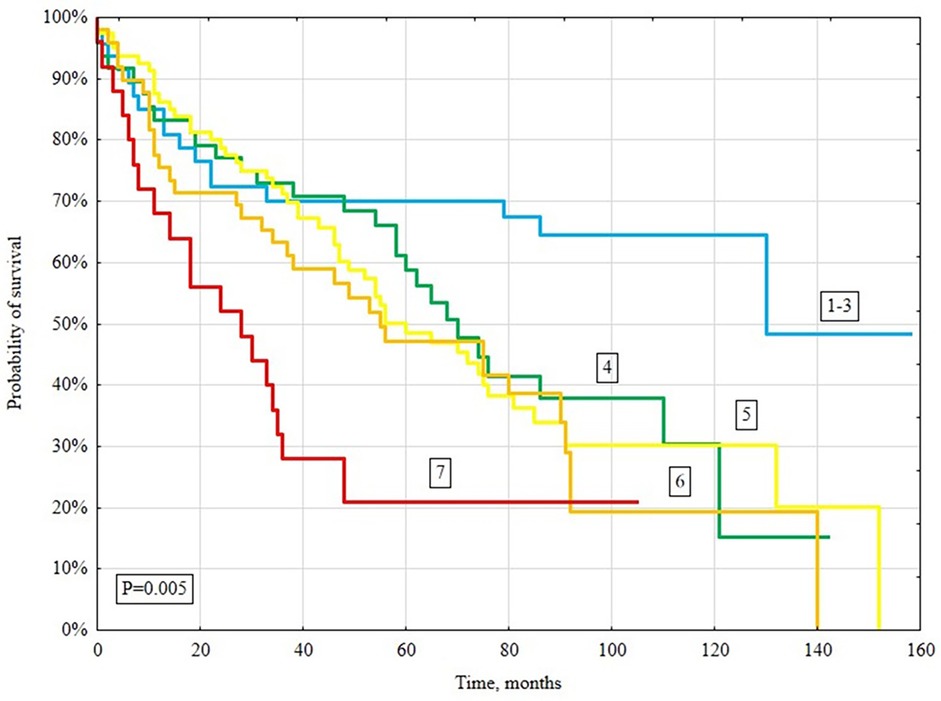
Figure 2. Kaplan–Meier survival curves for all-cause mortality based on the CHA2DS2-VASc score (1–3, 4, 5, 6, ≥7).
3.6 Multivariable cox regression analysis
In multivariable Cox regression, CHA2DS2-VASc dichotomised as ≥4 vs. <4 independently predicted all-cause mortality (P = 0.001), alongside NYHA class ≥III, COPD, lower hemoglobin and higher peak aortic-valve gradient (Table 4). When modeled as a continuous variable, each one-point increase in CHA2DS2-VASc was associated with a 32% higher risk of all-cause mortality (P = 0.001) (Table 5).
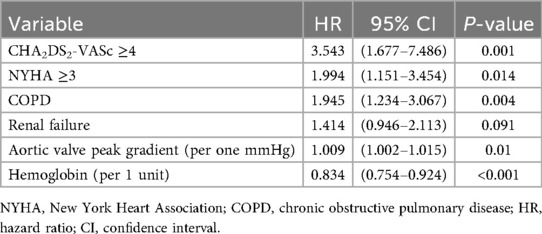
Table 4. Cox regression analysis of all-cause mortality prediction with CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 (C-index 0.690; 95%: 0.639–0.741).
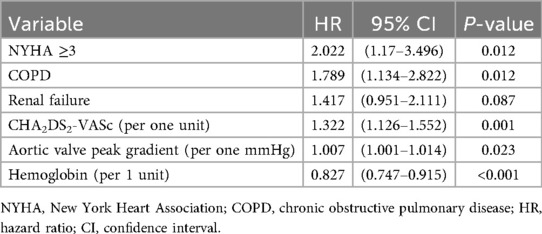
Table 5. Cox regression analysis of all-cause mortality prediction with CHA2DS2-VASc score expressed per one unit (C-index 0.691; 95% CI: 0.642–0.740).
3.7 Comparison with other scales–ROC analyses
In head-to-head ROC analyses for all-cause mortality, the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.629 (95% CI 0.559–0.699) for CHA2DS2-VASc, 0.697 (95% CI 0.631–0.763) for MAGGIC, 0.618 (95% CI 0.548–0.688) for EHMRG, and 0.682 (95% CI 0.616–0.748) for MEESSI-AHF. In pairwise AUC comparisons there was no statistically significant difference between the scores (all P > 0.05) and each score discriminated mortality significantly above chance (AUC > 0.5; all P < 0.01). The corresponding overlaid ROC curve is shown in Figure 4; individual curves are provided in Supplementary Figures S1a–d.
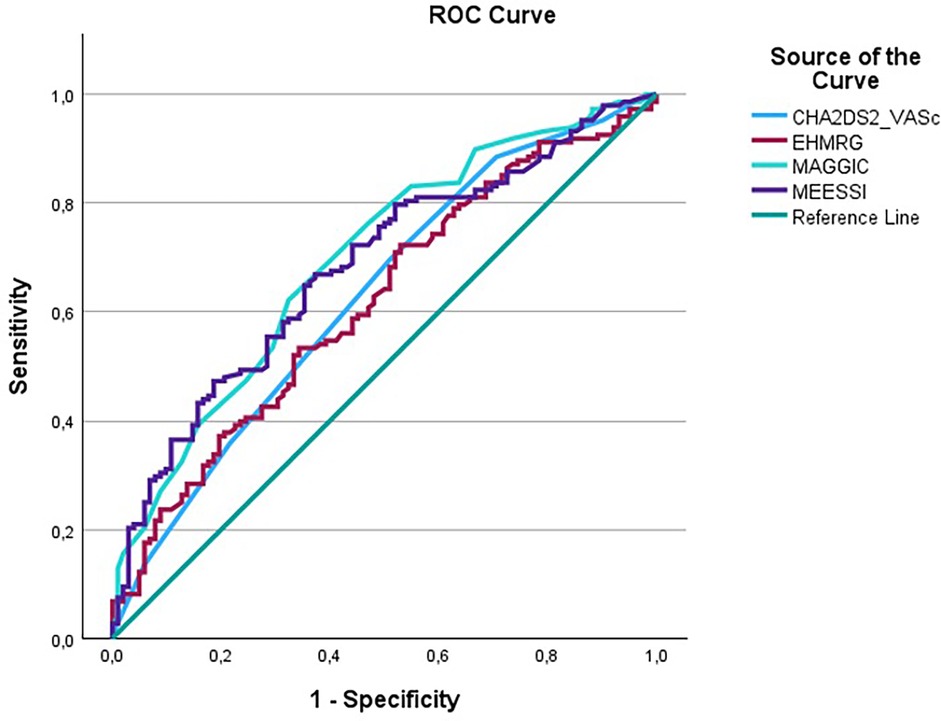
Figure 4. Overlaid ROC curves comparing discrimination across CHA2DS2-VASc, MAGGIC, EHMRG and MEESSI-AHF for all-cause mortality.
4 Discussion
4.1 Principal findings
To our knowledge, this study is the first to demonstrate that the CHA2DS2-VASc score independently predicts long-term mortality in patients hospitalized for acute decompensated HFpEF, irrespective of atrial fibrillation. Each one-point increase in the score was associated with a 32% higher risk of death.
These data suggest that a score originally devised for thromboembolic risk in atrial fibrillation can capture global vulnerability in HFpEF, where multimorbidity and systemic dysfunction drive outcomes.
4.2 Context within existing risk tools
Risk stratification in HFpEF remains challenging. Although tools like MAGGIC, EHMRG and MEESSI-AHF are validated, they require numerous inputs and often focus on short-term horizons (7–30 days), which limits bedside uptake in routine wards and at discharge planning in HFpEF patients (13, 14, 37). In contrast, CHA2DS2-VASc uses information universally collected on admission and clinic visits (age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, vascular disease, stroke history, HF), enabling immediate calculation without calculators or laboratory dependencies (16). The simplicity of a single integer that stratifies long-term risk is especially attractive in HFpEF, a syndrome with high readmission and mortality risk but limited disease-modifying therapies compared with HFrEF (10, 11, 27).
In this cohort, discrimination across CHA2DS2-VASc, MAGGIC, EHMRG, and MEESSI-AHF was broadly similar, with no statistically significant differences in AUC on pairwise testing. Accordingly, the practical advantage of CHA₂DS₂-VASc is its simplicity and universal availability at admission, rather than superior discrimination.
4.3 Alignment and divergence from prior literature
Our findings extend prior observations showing that CHA₂DS₂-VASc predicts adverse outcomes beyond AF. The score has shown prognostic value across chronic kidney disease, COPD, and acute myocardial infarction cohorts, indicating it functions as a marker of aggregated cardiovascular risk rather than a purely embolic tool (17, 19, 20). In heart failure specifically, the score predicted mortality across LVEF phenotypes in large cohorts and registries, including HFrEF and mixed HF populations, supporting its generalisability (23, 25, 26). By contrast, a post-hoc analysis of TOPCAT did not demonstrate independent associations between CHA2DS2-VASc and outcomes in a mixed acute/chronic HFpEF cohort with LVEF ≥ 45%, a difference likely related to population composition, event rates, and endpoint structure (12). Importantly, our cohort comprised exclusively acutely decompensated HFpEF—patients in whom pragmatic, fast triage tools are most needed at the point of care (10, 14, 37).
4.4 Clinical differences by CHA2Ds2-VASc category
In the present cohort, patients with CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 differed substantially from those with CHA2DS2-VASc <4. Multimorbidity clustered within the higher-score group and, as expected, was associated with increasing CHA2DS2-VASc values. A cut-off of 4 points has been commonly used in previous studies and effectively identifies patients at higher risk of ischaemic stroke and other thromboembolic events compared with lower scores (38). Moreover, higher CHA2DS2-VASc values have been associated with increased mortality and adverse cardiovascular outcomes in populations with atrial fibrillation and heart failure, supporting its broader prognostic signal beyond embolic risk alone (39).
4.5 Medication patterns and procedural context
In our population, increasing CHA2DS2-VASc scores were accompanied by more frequent use of loop diuretics, which likely reflects greater clinical severity at decompensation. Consistent with a higher comorbidity burden, patients with CHA2DS2-VASc ≥4 also more often received statins, acetylsalicylic acid, metformin and insulin, aligning with prior observations that polypharmacy in heart-failure care tracks with cardiometabolic multimorbidity (40, 41). Interestingly, coronary angiography during the index hospitalization was performed less often in the high-score group. This may reflect prior angiographic evaluation and previous percutaneous coronary interventions, as well as clinical judgement that prioritized medical management in patients with advanced age and comorbidity.
4.6 Echocardiographic phenotype and structural remodelling
We observed that end-diastolic and end-systolic LV diameters were larger in patients with CHA2DS2-VASc <4 than in those with scores ≥4, whereas left-atrial size was greater in the higher-score group. This pattern is compatible with a phenotype of long-standing hypertension and concentric remodelling in patients with higher CHA2DS2-VASc values, who frequently accumulate vascular risk factors over time (42, 43). Given that components of the CHA2DS2-VASc score are established risk factors for composite cardiovascular outcomes, this likely explains why the score stratifies all-cause mortality in HFpEF irrespective of atrial fibrillation (44, 45).
4.7 Thromboembolic risk across heart-failure phenotypes
It is worth taking into account that thromboembolic complications are associated with all subtypes of HF (46–48). The reasons for this phenomenon might be due to increased concentrations of prothrombotic molecules, systemic inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and disruption of the Virchow triad regardless of AF (46–48). Notably, patients with HFpEF are more often characterized by comorbidities indirectly increasing thromboembolic risk than in other HF subtypes, especially with coexisting AF (46–48). Given that comorbidities included in the CHA2DS2-VASc scale increase thromboembolic complications it might be useful to estimate the thromboembolic risk in HF and sinus rhythm (46–48).
4.8 Strengths and limitations in interpretation
Strengths include a consecutive real-world cohort, linkage to a national death registry, and consistent HFpEF definition according to contemporaneous ESC guidance across the study window (30–33). This study has some limitations. First, it is a single-centre registry with a relatively small HFpEF cohort and a limited number of patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score <4 (n = 48). This modest sample size reflects the low incidence of HFpEF admissions to a tertiary centre that mainly treats advanced HFrEF. However, it reduces the statistical power of subgroup analyses and leads to wide confidence intervals in the multivariable models, so our estimates should be viewed as exploratory. Second, as we focused on all-cause mortality, future studies should assess other cardiovascular endpoints and the impact of evolving pharmacotherapies over longer follow-up. Third, because recruitment spanned 2009–2022, we could not evaluate the influence of sodium–glucose co-transport-2 inhibitors or other recent guideline-directed therapies on HFpEF outcomes. Taken together, these factors warrant cautious interpretation of our findings and highlight the need for validation in larger, multicentre cohorts.
5 Conclusions
In the current study we indicated that patients with acute decompensated HFpEF are characterized by a higher all-cause mortality risk with each incremental point in the CHA2DS2-VASc score, regardless of the presence of AF. Given its predictive value for mortality, the CHA2DS2-VASc score may serve as a simple and practical tool for risk stratification in patients with HFpEF, identifying those at higher risk who may benefit from more aggressive monitoring and therapeutic strategies in a syndrome that remains heterogeneous and difficult to treat. Future multicenter studies are required to confirm our observations.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee in Krakow, Poland. (Consent No. 1072.6120.349.2022). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
OK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. Ad: Writing – review & editing. MK: Writing – review & editing. NK: Writing – review & editing. AK: Writing – review & editing. MP: Writing – review & editing. ZW: Writing – review & editing. KN: Writing – review & editing. AS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JN: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The Article Processing Charge was covered by Jagiellonian University Medical College.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1611825/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure S1 | Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for prediction of all-cause mortality: (a) CHA2DS2-VASc; (b) MAGGIC; (c) EHMRG; (d) MEESSI-AHF.
References
1. Savarese G, Becher PM, Lund LH, Seferovic P, Rosano GMC, Coats AJS. Global burden of heart failure: a comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc Res. (2023) 118:3272–87. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvac013
2. Roger VL. Epidemiology of heart failure. Circ Res. (2021) 128:1421–34. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318172
3. Dunlay SM, Roger VL, Redfield MM. Epidemiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2017) 14:591–602. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2017.65
4. Lelonek M, Pawlak A, Straburzyńska-Migaj E, Nessler J, Rubiś P. Identification and therapy for patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: an expert opinion of the heart failure association of the Polish cardiac society. Kardiol Pol. (2024) 82:247–54. doi: 10.33963/v.phj.98878
5. Lewkowicz J, Tankiewicz-Kwedlo A, Pawlak D, Kiluk M, Lagoda K, Kowalska I. Kynurenines in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: an influence of type 2 diabetes. Pol Arch Intern Med. (2024) 134(9):16837. doi: 10.20452/pamw.16837
6. Redfield MM, Borlaug BA. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a review. JAMA. (2023) 329:827. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.2020
7. Nowak K, Stępień K, Furczyńska P, Owsianka I, Włodarczyk A, Zalewski J, et al. Awareness and knowledge about heart failure in Poland-lessons from Heart Failure Awareness Day and internet surveys. Folia Med Cracov. (2019) 59(2):93–109. doi: 10.24425/fmc.2019.128458
8. Rywik TM, Doryńska A, Wiśniewska A, Cegłowska U, Drohomirecka A, Topór-Mądry R, et al. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of hospitalized patients with heart failure with reduced, mildly reduced, and preserved ejection fraction. Pol Arch Intern Med. (2022) 132:16227. doi: 10.20452/pamw.16227
9. Niedziela JT, Rozentryt P, Nowak J, Szyguła-Jurkiewicz B, Pyka Ł, Cieśla D, et al. Characteristics and outcomes for patients with heart failure diagnosed according to the universal definition and classification of heart failure. Data from a single-center registry. Pol Heart J Kardiologia Pol. (2024) 82:391–7. doi: 10.33963/v.phj.99549
10. Chioncel O, Lainscak M, Seferovic PM, Anker SD, Crespo-Leiro MG, Harjola V-P, et al. Epidemiology and one-year outcomes in patients with chronic heart failure and preserved, mid-range and reduced ejection fraction: an analysis of the ESC heart failure long-term registry. Eur J Heart Fail. (2017) 19:1574–85. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.813
11. Jones NR, Roalfe AK, Adoki I, Hobbs FDR, Taylor CJ. Survival of patients with chronic heart failure in the community: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Heart Fail. (2019) 21:1306–25. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1594
12. Zhu W, Wu Y, Zhou Y, Liang W, Xue R, Wu Z, et al. CHA2DS2-VASc and ATRIA scores and clinical outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. (2020) 34:763–72. doi: 10.1007/s10557-020-07011-y
13. Rich JD, Burns J, Freed BH, Maurer MS, Burkhoff D, Shah SJ. Meta-analysis global group in chronic (MAGGIC) heart failure risk score: validation of a simple tool for the prediction of morbidity and mortality in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. J Am Heart Assoc. (2018) 7:e009594. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.009594
14. Lee DS, Stitt A, Austin PC, Stukel TA, Schull MJ, Chong A, et al. Prediction of heart failure mortality in emergent care. Ann Intern Med. (2012) 156:767–75. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-156-11-201206050-00003
15. Procyk G, Grabowski M, Gąsecka A. The role of lipoprotein(a) in atrial fibrillation: a systematic review. Pol Arch Intern Med. (2025) 135(2):16924. doi: 10.20452/pamw.16924
16. Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, et al. 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European association for cardio-thoracic surgery (EACTS). Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:373–498. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa612
17. Goudis C, Daios S, Korantzopoulos P, Liu T. Does CHA2DS2-VASc score predict mortality in chronic kidney disease? Intern Emerg Med. (2021) 16:1737–42. doi: 10.1007/s11739-021-02799-5
18. Kuczaj A, Nowalany-Kozielska E, Skrzypek M, Opolski G, Ociessa A, Jankowska E, et al. Relationship between the CHA2DS2-VASc score and atrial fibrillation in patients hospitalised due to heart failure. Pol Heart J Kardiologia Pol. (2019) 77:380–5. doi: 10.5603/KP.a2019.0034
19. Hu W-S, Lin C-L. CHA2DS2-VASc score for ischaemic stroke risk stratification in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with and without atrial fibrillation: a nationwide cohort study. EP Eur. (2018) 20:575–81. doi: 10.1093/europace/eux065
20. Li C-Y, Chang C-J, Chung W-J, Lin C-J, Hsueh S-K, Lee C-H, et al. Assessment of CHA2DS2-VASc score for predicting cardiovascular and cerebrovascular outcomes in acute myocardial infarction patients. Medicine (Baltimore). (2018) 97:e11230. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011230
21. Cozac DA, Lakatos EK, Demjen Z, Ceamburu A, Fișcă PC, Șuș I, et al. The CHA2DS2-VASc score predicts new-onset atrial fibrillation and hemodynamic complications in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction treated by primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Diagn Basel Switz. (2022) 12:2396. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12102396
22. Keskin K, Sezai Yıldız S, Çetinkal G, Aksan G, Kilci H, Çetin Ş, et al. The value of CHA2DS2VASC score in predicting all-cause mortality in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction who have undergone primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Acta Cardiol Sin. (2017) 33:598–604. doi: 10.6515/ACS20170723A
23. Chen Y-L, Cheng C-L, Huang J-L, Yang N-I, Chang H-C, Chang K-C, et al. Mortality prediction using CHADS2/CHA2DS2-VASc/R2CHADS2 scores in systolic heart failure patients with or without atrial fibrillation. Medicine (Baltimore). (2017) 96:e8338. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008338
24. Stepien K, Nowak K, Skorek P, Baravik V, Kozynacka A. Baseline indicators of coronary artery disease burden in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. Minerva Cardioangiol. (2019) 67(3):181–90. doi: 10.23736/S0026-4725.19.04838-2
25. Melgaard L, Gorst-Rasmussen A, Lane DA, Rasmussen LH, Larsen TB, Lip GYH. Assessment of the CHA2DS2-VASc score in predicting ischemic stroke, thromboembolism, and death in patients with heart failure with and without atrial fibrillation. JAMA. (2015) 314:1030–8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.10725
26. Shuvy M, Zwas DR, Keren A, Gotsman I. Value of the CHA2DS2-VASc score for predicting outcome in patients with heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. (2020) 7:2553–60. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12831
27. Gioia G, Kresoja K-P, Rosch S, Schöber A, Harnisch E, von Roeder M, et al. Clinical trajectory and risk stratification for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in a real-world cohort of patients with suspected coronary artery disease. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:2092. doi: 10.3390/jcm13072092
28. Stępień K, Nowak K, Kachnic N, Karcińska A, Del Carmen Yika A, Furczyński J, et al. Clinical characteristics and long-term outcomes of patients with heart failure with improved ejection fraction. First Polish experience from LECRA-HF registry. Adv Med Sci. (2024) 69:132–8. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2024.02.009
29. Stepien K, Furczynska P, Zalewska M, Nowak K, Wlodarczyk A. Dementia screening in elderly high-risk patients following heart failure decompensation may predict unfavorable long-term clinical outcomes. Minerva Cardiol Angiol. (2021) 69(3):251–60. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5683.20.05157-9
30. Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G, McMurray JJV, Ponikowski P, Poole-Wilson PA, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the heart failure association of the ESC (HFA) and endorsed by the European society of intensive care medicine (ESICM). Eur J Heart Fail. (2008) 10:933–89. doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2008.08.005
31. McMurray JJV, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Böhm M, Dickstein K, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the heart failure association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. (2012) 33:1787–847. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs104
32. Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, et al. 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)developed with the special contribution of the heart failure association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. (2016) 37:2129–200. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128
33. McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, et al. 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: developed by the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) with the special contribution of the heart failure association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:3599–726. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab368
34. Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American society of echocardiography and the European association of cardiovascular imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2015) 16:233–71. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jev014
35. Stepien K, Nowak K, Szlosarczyk B, Nessler J, Zalewski J. Clinical characteristics and long-term outcomes of MINOCA accompanied by active cancer: a retrospective insight into a cardio-oncology center registry. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:785246. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.785246
36. Agusti A, Böhm M, Celli B, Criner GJ, Garcia-Alvarez A, Martinez F, et al. GOLD COPD DOCUMENT 2023: a brief update for practicing cardiologists. Clin Res Cardiol. (2024) 113:195–204. doi: 10.1007/s00392-023-02217-0
37. Miró Ò, Rossello X, Gil V, Martín-Sánchez FJ, Llorens P, Herrero-Puente P, et al. Predicting 30-day mortality for patients with acute heart failure in the emergency department: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. (2017) 167:698. doi: 10.7326/M16-2726
38. Johnson LS, Benz AP, Shoamanesh A, Eikelboom JW, Ezekowitz M, Giugliano RP, et al. Residual stroke risk among patients with atrial fibrillation prescribed oral anticoagulants: a patient-level meta-analysis from COMBINE AF. J Am Heart Assoc. (2024) 13:e034758. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.034758
39. Abouzid MR, Kamel I, Saleh A, Vidal Margenat A, Hariharan R. Assessing stroke and mortality risk in heart failure: the CHA2DS2-VASc score’s prognostic value in patients with and without atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. Cardiol Rev. (2024). doi: 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000749
40. Stępień K, Siudut J, Konieczyńska M, Nowak K, Zalewski J, Undas A. Effect of high-dose statin therapy on coagulation factors: lowering of factor XI as a modifier of fibrin clot properties in coronary artery disease. Vascul Pharmacol. (2023) 149:107153. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2023.107153
41. Stępień K, Żółciński M, Ząbczyk M, Zalewski J, Undas A. Effect of three-day atorvastatin administration on coagulation factors in patients with prior venous thromboembolism and healthy subjects: a preliminary study. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2024) 83:289. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001529
42. Gaasch WH, Zile MR. Left ventricular structural remodeling in health and disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2011) 58:1733–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.07.022
43. Hasiec A, Kruk M, Kępka C, Warmiński G, Kowalik I, Bilińska M, et al. Evaluating the effect of coronary atherosclerosis on the occurrence of atrial fibrillation through coronary computed tomography angiography. Pol Heart J Kardiologia Pol. (2025) 83:43–51. doi: 10.33963/v.phj.102554
44. Lin S, Yang Z, Liu Y, Bi Y, Liu Y, Zhang Z, et al. Risk prediction models and novel prognostic factors for heart failure withPreserved ejection fraction: a systematic and comprehensive review. Curr Pharm Des. (2023) 29:1992–2008. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666230830105740
45. Zhu W, Cao Y, Ye M, Huang H, Wu Y, Ma J, et al. Essen stroke risk score predicts clinical outcomes in heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction: evidence from the TOPCAT trial. Thromb Haemost. (2023) 123:85–96. doi: 10.1055/a-1932-8854
46. Siniarski A, Gąsecka A, Borovac JA, Papakonstantinou PE, Bongiovanni D, Ehrlinder H, et al. Blood coagulation disorders in heart failure: from basic science to clinical perspectives. J Card Fail. (2023) 29:517–26. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2022.12.012
47. Siniarski A, Stępień K, Golińska-Grzybała K, Trębacz J, Stąpór M, Szlósarczyk B, et al. Thrombin generation, fibrin clot permeation and lysis in patients with severe mitral regurgitation undergoing transcatheter edge-to-edge mitral valve repair: mitral fibrin study. Pol Arch Intern Med. (2024) 134(7–8):16755. doi: 10.20452/pamw.16755
Keywords: CHA₂DS₂-VASc, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, risk stratification, mortality, acute decompensated heart failure, registry, prognosis
Citation: Kądzioła O, Stępień K, del Carmen Yika A, Kurek M, Kachnic N, Karcińska A, Platschek M, Wyleciał Z, Nowak K, Siniarski A and Nessler J (2025) CHA2DS2-VASc score as a mortality predictor in acute heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1611825. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1611825
Received: 14 April 2025; Accepted: 13 October 2025;
Published: 3 November 2025.
Edited by:
Tomasz Zieliński, National Institute of Cardiology, PolandReviewed by:
Mohamed Aboel-Kassem F. Abdelmegid, Assiut University Hospital, EgyptDan-Alexandru Cozac, George Emil Palade University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Sciences and Technology of Târgu Mureş, Romania
Copyright: © 2025 Kądzioła, Stępień, del Carmen Yika, Kurek, Kachnic, Karcińska, Platschek, Wyleciał, Nowak, Siniarski and Nessler. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Konrad Stępień, a29uc3RlQGludGVyaWEuZXU=
 Olaf Kądzioła
Olaf Kądzioła Konrad Stępień
Konrad Stępień Alicia del Carmen Yika5
Alicia del Carmen Yika5 Karol Nowak
Karol Nowak Aleksander Siniarski
Aleksander Siniarski Jadwiga Nessler
Jadwiga Nessler