Abstract
Panic Disorder (PD) is a prevalent psychiatric condition characterized by recurrent episodes of acute severe anxiety. These episodes frequently present with symptoms that overlap with those of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), such as elevated blood pressure and chest pain. Despite the prevalence and impact of this comorbidity, the underlying mechanisms are not well understood and remain underexplored. This review synthesizes current understanding and recent findings on the role of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in the intersection of PD and vascular dysfunction. 5-HT, a critical inhibitory neurotransmitter, has been implicated in the etiology of PD and linked to panic symptoms. This review underscores the importance of 5-HT in modulating vascular tone through its action on 5-HT1B and 5-HT2A receptors, influencing the production of nitric oxide (NO) and the subsequent vasomotor response. Furthermore, the impact of 5-HT system on platelet activation and aggregation adds another layer to the complex relationship between PD and CVD. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) have shown promise in improving vascular endothelial function. However, the influence of SSRIs on CVD outcomes remains a controversial issue with conflicting findings from various studies. The review also highlights the role of the PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling pathway in 5-HT's influence on vascular endothelial function. In conclusion, the intricate relationship between PD, 5-HT, and vascular endothelial function warrants further investigation. A deeper understanding of these mechanisms could lead to more effective treatments for PD and related CVD, ultimately improving patients’ mental health and cardiovascular outcomes.
1 Introduction
Panic Disorder (PD) is a prevalent psychiatric condition characterized by recurrent episodes of acute, severe anxiety, known as panic attacks. These episodes can emerge independently or coexist with other mental health disorders, such as agoraphobia and depression. Panic attacks (PAs) frequently present with symptoms that overlap with those of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), such as elevated blood pressure, palpitations, and chest pain. Individuals experiencing a panic attack may be scared of dying from a heart attack during the episode. Studies have revealed that over 20% of patients undergoing cardiac emergency treatment do not have heart disease but are suffering from PD (1–3). Typically, these patients maintain a level of skepticism even after cardiac examinations yield negative results.
A wealth of epidemiological evidence has demonstrated a robust association between PD and CVD caused by vascular endothelial dysfunction. This includes conditions such as coronary heart disease (e.g., myocardial infarction and angina) and hypertension (2, 4–6). However, the precise mechanisms underlying this association remain unclear. This article will focus on the relationship between PD and endothelial dysfunction, as well as explore the potential mechanisms involved.
2 Panic disorder and its biological markers
The definition of PD has undergone several revisions in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) in the United States. The fifth edition, DSM-5, classifies PD as a subtype of anxiety disorder (7).
2.1 Clinical features of PD
PD is characterized by recurrent, unexpected PAs, which may be accompanied by symptoms such as fear of subsequent PAs, worry about the potential impact or consequences of these attacks, and significant behavioral changes related to the attacks. It is important to note that fear and panic behaviors are considered protective states, and PAs are automatic responses to protect individuals from life-threatening situations (8). The primary symptoms of PAs include cardiovascular symptoms (e.g., chest pain, increased blood pressure), autonomic nervous system responses (e.g., accelerated heartbeat, sweating), respiratory difficulties (e.g., dyspnea, chest tightness, a sensation of suffocation), and cognitive symptoms (e.g., depersonalization, fear of losing control, fear of death) (9). Among these, cardiac-related symptoms are most frequently reported (8).
2.2 5-HT as a biomarker for PD
Biomarkers are measurable indicators of normal biological processes, pathological processes, or responses to an intervention. Numerous studies have identified various biomarkers that reflect PD, including 5-HT and cortisol levels, and heart rate variability. The structural changes of the amygdala or hippocampus and cerebral blood flow in the left occipital cortex are considered to be potential markers for PD (10–14).
Serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is an endogenous monoamine and a critical inhibitory neurotransmitter widely distributed in the central and peripheral nervous systems. It plays a vital role in regulating emotions, cognition, anxiety, learning, memory, and sleep (15).
The hypothesis of serotonin system imbalance is widely recognized in the etiology of PD. Carbon dioxide inhalation-induced panic attacks and neuroimaging studies have shown that the serotonin system is closely related to panic symptoms (16). The mechanism may be that serotonin inhibits anxiety-specific adaptive behavior, has the effect of maintaining alertness, and controls anxiety, and serotonin can inhibit the dorsal periaqueductal gray (PAG) structure related to fear response behavior in PD (17, 18). Consequently, PD patients often exhibit reduced 5-HT levels in the brain (11). Abnormally increased serotonin turnover rates have been observed in PD patients (19), and the serotonin transporter (SERT) encoding gene SLC6A4 was demonstrated as a promising diagnostic gene for PD (20). Peripherally, studies have confirmed lower serum serotonin levels in PD patients compared to controls (21), and other studies have shown increased 5-HT uptake by platelets in these patients (22, 23). The cause of this change in peripheral 5-HT levels, whether due to reduced synthesis or increased reuptake or degradation, remains unclear. Clinically, selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as fluoxetine, paroxetine, and sertraline, are first-line treatments for PD (24). They work by inhibiting the 5-HT transporter (SERT) to reduce 5-HT reuptake, thereby increasing the concentrations in the synaptic cleft and restoring 5-HT balance in the brain.
3 The impact of Pd on vascular endothelial function
3.1 Physiological structure and function of vascular endothelial cells
Vascular endothelial cells (ECs) form a single layer lining the interior walls of arteries, veins, and capillaries. The primary function of ECs is their barrier role, forming an inner lamina of blood vessels that restricts the passage of large molecules into the vessel wall (25). ECs also regulate vascular tone by sensing changes in blood flow dynamics (blood shear stress) and releasing endothelium-dependent vasodilatory and vasoconstrictive factors. Nitric oxide (NO) is the principal vasodilatory factor released by ECs (26), and they also produce prostacyclin (PGI2) to relax vascular smooth muscle (25). Conversely, ECs can release vasoconstrictive factors such as endothelin-1 (ET-1), angiotensin II (AngII), thromboxane A2, prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) (27, 28). Under normal conditions, the balance of vasoactive factors released by ECs maintains vascular tone and vascular homeostasis (29).
Vascular endothelial dysfunction can occur due to various unhealthy lifestyles and physicochemical factors, such as oxidative stress and inflammation. This dysfunction is characterized by a decrease of NO production and impaired endothelial barrier function. Reduced NO can impair vasodilation, and the disruption of endothelial barrier function can lead to the influx of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) into the arterial wall, the adhesion of monocytes and platelets, and the localized release of cytokines and growth factors. This can cause the migration, proliferation, and phenotypic transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), resulting in the development of atherosclerosis (30). Vascular endothelial dysfunction is thus a contributing factor in the progression of various cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, atherosclerosis, and acute coronary syndrome (31, 32).
3.2 PD and vascular endothelial dysfunction
PD or PAs are often associated with symptoms like chest pain and increased blood pressure. Given the role of endothelium in regulating vascular tension, it is hypothesized that there may be a close relationship between PD and vascular endothelial dysfunction.
Flow-mediated dilatation (FMD) is the clinical standard for evaluating vascular endothelial function. Clinical studies found that psychosocial stress could reduce FMD response in healthy men (33), and anxiety disorders are significantly associated with coronary endothelial dysfunction (CED) in women presenting with chest pain and nonobstructive coronary artery disease by using invasive coronary reactivity testing (34).
Additionally, PD patients exhibit changes in inflammatory factor concentrations (35) and platelet activation (36), which may contribute to the development of CVD. A large-scale study demonstrated a positive correlation between PD and the incidence and mortality of CVD (37). Furthermore, the prevalence of PD is higher among patients with coronary heart disease, chronic heart failure, and hypertension compared to the general population (4, 38). PD is also linked to increased arterial stiffness (39), which can adversely affect cardiovascular health and endothelial function. A meta-analysis of 12 studies involving 58,111 cases of sudden cardiac events indicated that PD is independently correlated with the incidence of coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction (MI), and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) (40).
As mentioned above, apart from serotonergic mechanisms, PD is linked to increased sympathetic nervous system activity, systemic inflammation, and elevated levels of stress hormones like cortisol and catecholamines (19, 35). These factors can promote endothelial dysfunction through mechanisms including oxidative stress, reduced nitric oxide bioavailability, and vascular inflammation (34). Therefore, vascular changes in PD likely involve several interacting pathways.
4 The role of 5-HT in vascular endothelial function
As previously discussed, the role of 5-HT as a biomarker for PD has been widely confirmed. However, research on the role of 5-HT in the impact of PD on vascular endothelial function is currently limited.
4.1 Synthesis and metabolism of 5-HT
Due to the presence of the blood-brain barrier, the synthesis of 5-HT is typically divided into central and peripheral systems. Once tryptophan enters the body, it can be converted into 5-HT by tryptophan hydroxylase (Tph), with over 90% of 5-HT being synthesized by Tph1 in enterochromaffin cells of the intestine, and the remainder by Tph2 in the serotonergic neurons of the brainstem's raphe nuclei. Excess tryptophan is metabolized in the liver and excreted into the bloodstream (Figure 1).
Figure 1
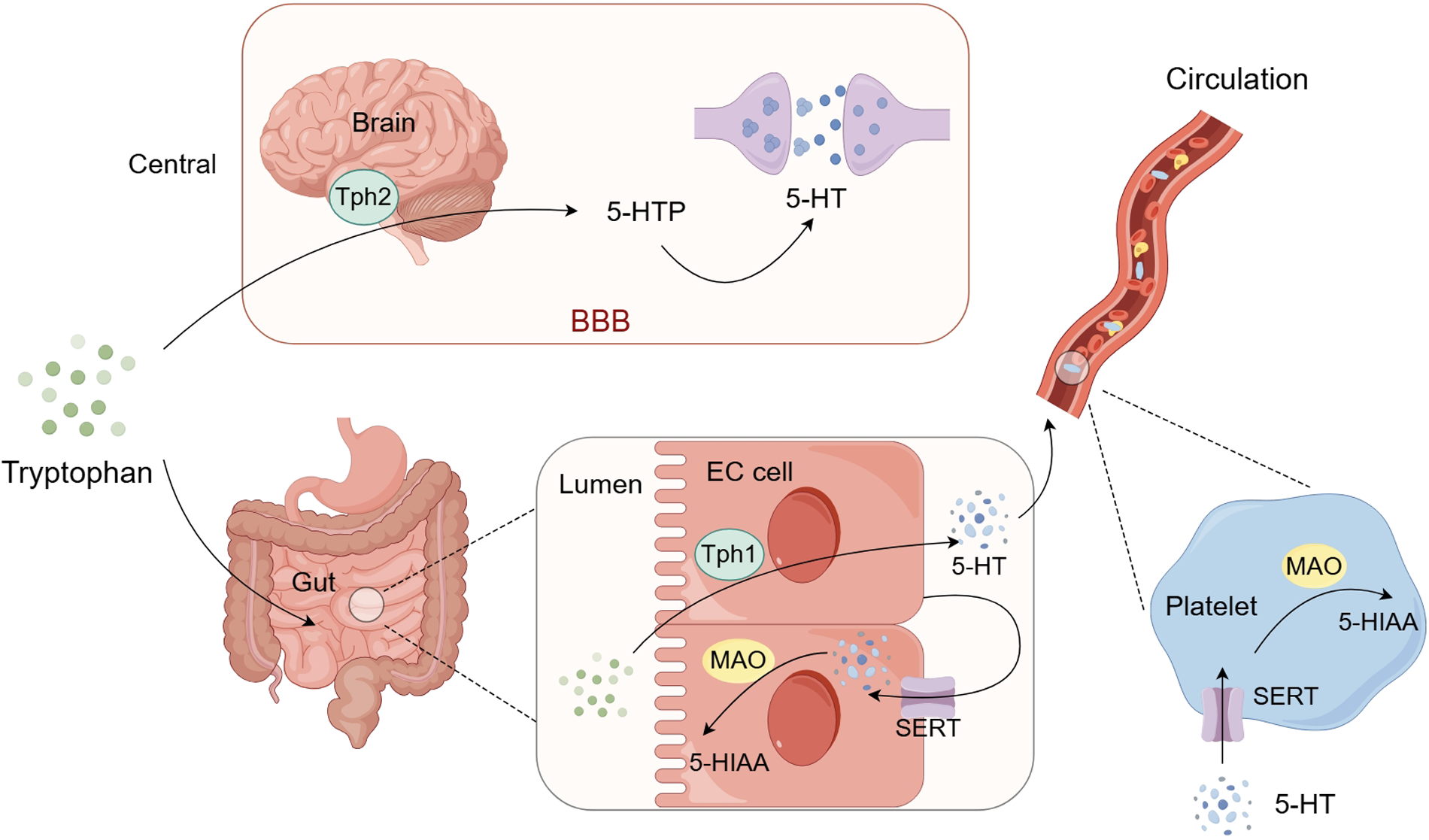
Schematic representation of 5-HT synthesis and metabolism. Tryptophan that enters the brain is synthesized into 5-HT by Tph2 and released into the synaptic cleft to exert its effects. Tryptophan that enters the gut lumen is synthesized into 5-HTby Tph1 in enterochromaffin cells. A small portion of this peripheral 5-HT is reuptaked back into the cells by the SERT of the enterochromaffin cells while the majority enters the blood circulation and is stored in platelets. When platelets are activated, 5-HT can be released and then exert its effects. Intracellular 5-HT can be metabolized by monoamine oxidase (MAO) into 5-HIAA and excreted in the urine. BBB: blood-brain barrier; Tph1: tryptophan hydroxylase 1; Tph2: tryptophan hydroxylase 2; SERT: 5-HT transporter; MAO: monoamine oxidase; 5-HTP: 5-hydroxytryptophan; 5-HIAA: 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid. (By Figdraw.)
Regarding the metabolism of 5-HT, a small portion of centrally synthesized 5-HT is released into the synaptic cleft to act on various regions of the brain, while the surplus is reabsorbed by the 5-HT transporter (SERT) on the presynaptic membrane and metabolized by monoamine oxidase (MAO) into 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), which are then excreted in urine. The 5-HT synthesized in enterochromaffin cells has two main fates: 1. a significant portion is released into the intestinal lamina propria, where some are reabsorbed by SERT on the enterochromaffin cell membrane and metabolized by MAO on the outer mitochondrial membrane of intestinal epithelial cells into 5-HIAA; the rest enters the blood circulation through the capillary bed of the intestinal mucosa, where most is reabsorbed by SERT on platelets and stored in dense granules. Ultimately, a large amount of 5-HT stored in platelets can be transported throughout the bloodstream, and when platelets are activated, they can release their granule contents, including 5-HT, binding to various receptors and exerting effects such as regulating vascular tone, permeability and inducing platelet activation and aggregation (41, 42); 2. a small portion of 5-HT is released into the intestinal lumen through the apical membrane, mixed with chyme, and eventually excreted with feces (Figure 1).
Under normal conditions, only about 2% of peripheral 5-HT is free in the bloodstream, while approximately 98% is stored in platelets. The freely circulating fraction determines immediate bioavailability (43). Free 5-HT produces various effects by binding to 5-HT receptors on the surface of various cell membranes. Platelets can release stored 5-HT rapidly upon activation triggered by vascular injury, thrombin, collagen, or shear stress (44). SERT is not only distributed on the presynaptic membrane of nerve terminals, but also expressed in platelets, gastrointestinal chromaffin cell membranes, vascular endothelial cells, myocardium, and kidneys. As a clearance tool for 5-HT, SERT can terminate its action by absorbing 5-HT.
4.2 Regulation of vascular tone by 5-HT
Peripherally distributed 5-HT can have complex and even biphasic effects (vasoconstriction/vasodilation) on peripheral blood vessels. The complex biological functions of 5-HT are related to its multiple receptor subtypes. To date, seven major classes of 5-HT receptors have been identified, namely 5-HT1-7 receptors, with a total of 14 receptor subtypes (45).
5-HT acts on several receptor types in the vasculature. The 5-HT1B receptor is expressed on ECs, is linked to Gi/o proteins, and mediates vasodilation through NO production via the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. In contrast, the 5-HT2A receptor on VSMCs causes vasoconstriction through phospholipase C activation and calcium signaling. These receptors couple to Gq proteins, activating phospholipase C (PLC). PLC hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol trisphosphate (IP3). IP3 then triggers calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, raising intracellular calcium levels and promoting smooth muscle contraction (43, 45). Therefore, selectively blocking the 5-HT2A receptor and selectively activating the 5-HT1B receptor are considered potential mechanisms for vascular protection (46, 47). Other receptors, such as 5-HT2B and 5-HT7, may also influence vascular tone in specific regions. These receptors activate downstream signaling cascades that regulate vascular tone and endothelial function (43). Sapogrelate, an antagonist of the 5-HT2A receptor, can indirectly enhance the function of the 5-HT1B receptor on ECs by inhibiting the 5-HT2A receptor on VSMCs, thereby increasing NO production and vasodilatory response (48–50).
Meanwhile, the vasoactive effects of 5-HT on blood vessels also depend on the integrity of the endothelium. When the endothelium is intact, 5-HT acts on receptors of ECs to induce vasodilation, whereas when the endothelium is injured, 5-HT may directly act on receptors of VSMCs to induce vasoconstriction (51). In addition to vascular ECs, the 5-HT1B receptor is also distributed on VSMCs, and contrary to its EC-derived vasodilatory effect, it mediates vasoconstriction in VSMCs. The function mediated by the 5-HT1B receptor was analyzed using arteries with intact endothelium and with denuded endothelium. It was found that the presence of intact endothelium hinders the 5-HT1B receptor-mediated contraction of VSMCs (52). Rat-based experiments have confirmed that when the endothelium is impaired, 5-HT can directly act on the 5-HT1B receptor of VSMCs, inducing vasospasm (53). The findings underscore the critical role of intact endothelium in maintaining the equilibrium of 5-HT's vasomotor effects.
4.3 5-HT promotes platelet activation and aggregation
Platelets, lacking tryptophan hydroxylase (Tph), do not have the capability to synthesize 5-HTserotonin. Under physiological conditions, platelets act as carriers of 5-HTserotonin, storing it in their dense granules. Upon activation by stimuli such as thrombin, collagen, or shear stress, platelets release 5-HT into the local environment (44). During platelet activation, 5-HTserotonin is secreted from these granules and acts on the 5-HT2A receptors on the platelet surface, accelerating platelet activation and aggregation (54). This receptor activation increases intracellular calcium levels, leading to shape change, granule secretion, and activation of integrin αIIbβ3, which is essential for fibrinogen binding and platelet-platelet interactions. 5-HT can thereby act as a positive feedback mediator in thrombosis (54). Moreover, studies on serotonylation have suggested that serotonylation of small GTPases can trigger the release of platelet α-granules (55). Ultrastructural analysis has also observed that 5-HT serotonin can induce the formation of pseudopodia in platelets (56). Activated platelets can further secrete other pro-coagulant substances through exocytoses, such as fibrinogen, platelet-derived growth factor, and platelet factor 4 from α-granules (57), which are released into the bloodstream, leading to secondary platelet aggregation and an increased risk of thrombosis.
Additionally, when platelets are activated, they can induce the production of vasoconstrictors such as thromboxane A2 (TXA2), which may also be part of the reason why 5-HT can promote vasoconstriction. Elevated platelet activation in PD may contribute to a higher risk of endothelial dysfunction and vascular events.
5 PD modulates vascular endothelial function via 5-HT mechanisms
Although central 5-HT plays a primary role in the pathophysiology of PD, peripheral free 5-HT, despite its low concentration, can exert significant biological effects, particularly in the regulation of vascular tone. As the majority of peripheral 5-HT is stored in platelets, platelet aggregation and activation under conditions such as endothelial injury or inflammation can rapidly alter circulating 5-HT levels, enabling it to act through high-affinity receptor binding (43, 58, 59). As mentioned above, PD is characterized by decreased peripheral 5-HT levels. It is supposed that during PAs, 5-HT predominantly targets the 5-HT1B receptors on ECs, and its diminished levels result in attenuated NO synthesis via the 5-HT1B receptor pathway, consequently lessening the extent of vasodilation. Moreover, patients with PD often exhibit platelet activation and endothelial dysfunction, which may lead to increased release of serotonin from platelets and further enhance the role of peripheral 5-HT in regulating vascular tone in this disorder.
5.1 The influence of SSRIs on vascular endothelial function
The SERT is mainly distributed on the presynaptic membrane and various types of non-neuronal cells, including platelets, ECs, and myocardial cells. The levels of 5-HT and the timing of its transmission in the synaptic cleft and peripheral bloodstream are meticulously regulated by the reuptake of free 5-HT through the SERT. The development of selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) is centered on targeting this SERT mechanism, representing the first-line therapeutic approach for PD.
Regarding the influence of SSRIs on vascular endothelial function, some studies have found that during treatment with escitalopram, the levels of biomarkers of vascular endothelial dysfunction, such as soluble von Willebrand factor (sVWF) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1(VCAM-1), gradually decrease in patients with major depression (60). A study has confirmed the impact of psychological stress on the activation of pathways related to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which affects endothelial cells, and impairs neovascularization following ischemia, and fluoxetine may offer a potential therapeutic benefit (61). A recent meta-analysis has demonstrated that treatment with SSRIs can lead to a significant improvement in FMD, suggesting that SSRIs may have a beneficial impact on vascular endothelial function beyond their effects on mood and anxiety disorders (62).
The influence of SSRIs on CVD, particularly thrombosis, is a subject of debate with two divergent perspectives. Some researchers have found that SSRIs can have a protective effect against MI through cohort studies and meta-analysis (63, 64), which may be related to SSRIs reducing the storage of 5-HT in platelets, thereby reducing platelet activation. Kim et al. followed up 300 patients with acute coronary syndrome and depression for 8 years and found that the incidence of MI in patients taking escitalopram was significantly lower than in those taking a placebo (65). However, some other studies suggested that SSRIs may exacerbate the deterioration of CVD. In an experiment with atherosclerotic mice, it was found that intake of fluoxetine can deplete 5-HT in platelets, induce a significant reduction in serum 5-HT, and promote the formation of atherosclerotic plaques by enhancing the activation of adhesion molecules (66). A recent study also found that escitalopram treatment can increase the degree of myocardial fibrosis in mice with MI combined with chronic mild stress (67). The findings indicate that a cautious approach is warranted when prescribing SSRIs to patients with concurrent cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions.
5.2 The modulation of vascular endothelium function by 5-HT via the Pi3k/Akt/eNOS signaling pathway
Extensive clinical researched have substantiated the correlation between CVD and mental health disorders, with 5-HT potentially serving as a common pathological mechanism. However, a comprehensive understanding of the serotonergic pathway—from its origins to its terminal effects—and its precise role in modulating vascular endothelial function remains elusive. Thus, meticulously exploring the complex interplay among 5-HT, its signaling pathways, and CVD is a promising frontier for progress in psycho-cardiology.
Studies have confirmed that 5-HT can stimulate angiogenesis by activating Protein Kinase B (Akt) in ECs (68), and fluoxetine can increase the expression of Akt, protecting vascular endothelium in a mouse model of psychological stress (61). It was discovered that the physiological levels of 5-HT are capable of inducing the phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt via the 5-HT1B receptor in cultured primary ECs (69). Activation of 5-HT1B receptors on ECs is linked to Gi/o proteins, which inhibit adenylate cyclase and activate the PI3K/Akt pathway. PI3K phosphorylates PIP2 to generate PIP3, which attracts PDK1 to the membrane. PDK1 then phosphorylates Akt. This leads to phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), increasing nitric oxide (NO) production (Figure 2) (70–72). Based on previous research, the PI3K/Akt signaling cascade may predominantly influence three critical aspects within endothelial cells, i.e., cellular survival and apoptosis, the inflammatory response, and oxidative stress. Activation of the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway can induce the release of NO from ECs, which induces vasodilation and exhibits vascular protection and is key to maintaining vascular homeostasis (73). NO diffuses into adjacent VSMCs, stimulates soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC), elevates cyclic GMP levels, and promotes smooth muscle relaxation, contributing to vasodilation (74). Conversely, the inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway can diminish the phosphorylation of eNOS, consequently leading to a decrease in NO synthesis (75). Furthermore, NO possesses the ability to inhibit reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby mitigating the oxidative stress associated with vascular endothelial dysfunction (76).
Figure 2
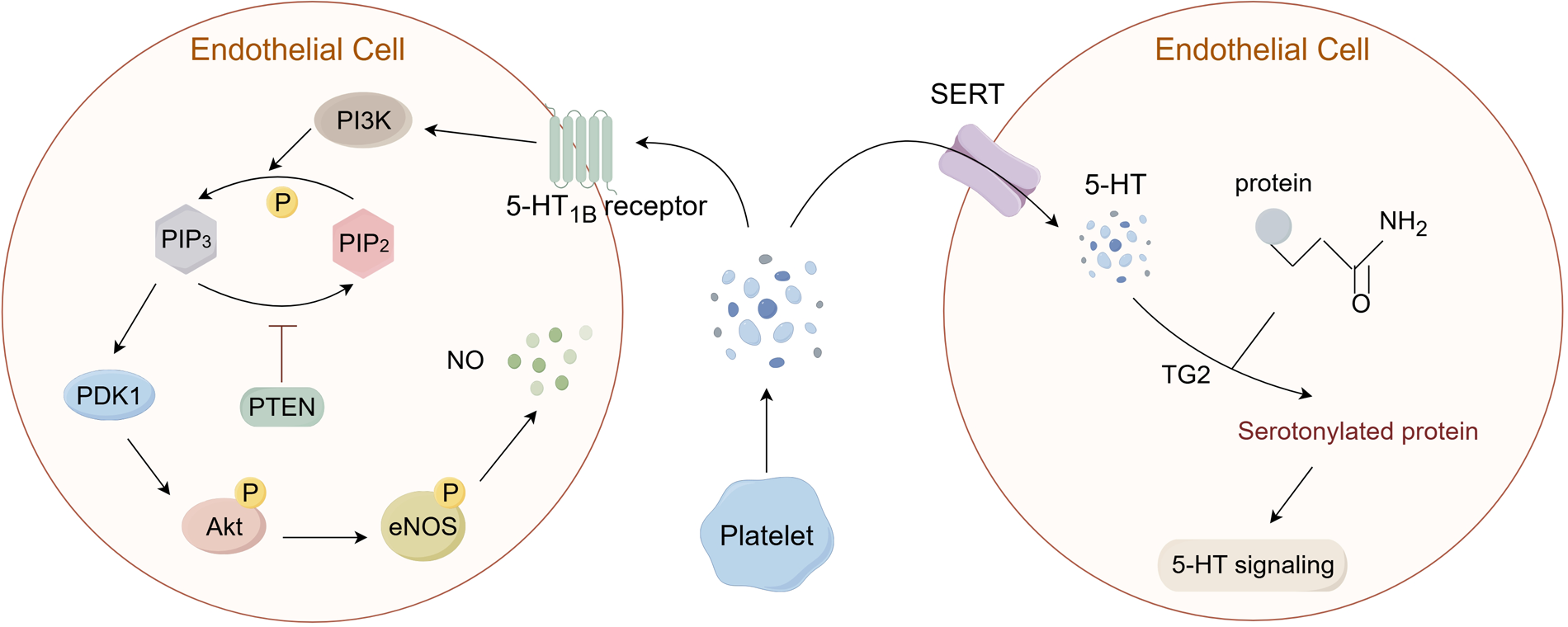
5-HT can transmit signals through two pathways: G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and serotonylation. (1) In ECs, 5-HT can bind to the 5-HT1B receptor, leading to the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and the phosphorylation of eNOS, which mediates the generation of NO. (2) In addition, 5-HT that is reuptaked into the cell via SERT can combine with protein substrates containing glutamine residues under the catalysis of TG2, causing serotonylation of the substrates and the activation of related signaling pathways. PI3K: phosphoinositol-3 kinase; PIP2: phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3: phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate; PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog; PDK1: 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1; Akt: Protein Kinase B; eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase; NO: nitric oxide; TG2: transglutaminases 2. (By Figdraw.).
5.3 Intracellular 5-HT can mediate the serotonylation of substrates
The peripheral 5-HT exerts its effects by binding to 5-HTR on the cell membrane, which has been widely recognized. However, 5-HT can also exert intracellular effects through a process known as serotonylation. Although these pathways operate via distinct processes, they collectively influence vascular tone and endothelial behavior (Figure 2). In recent years, it has been discovered that the 5-HT taken up into the cell by SERT can also exert its effects (77). Over 60 years ago, researchers discovered that 5-HT could covalently bind to certain proteins under the action of transglutaminases (TG), which is a new type of post-translational modification (PTM) known as serotonylation. However, it was only in recent years that the mechanisms related to serotonylation have gradually been elucidated (78–80). TG is a multifunctional enzyme composed of eight isoenzymes, known as factor XIII and TG1-7. Among them, TG2 is widely expressed in almost all tissues and participates in a variety of biological processes. TG2 has GTP-binding activity and Ca2+-dependent transglutaminase activity (81). Under the action of Ca2+, TG2 is activated and acts on its common substrates, including small GTPases such as RhoA, histones, and other proteins like SERCA2a, Akt (79, 82, 83). Catalyzing the binding of substrates with 5-HT, thereby causing constitutive activation of the substrate and degradation through an enhanced proteasome pathway (Figure 2) (84).
The Rho protein family, as substrates of TG2, often undergo serotonylation, which leads to the activation of related signaling pathways. Studies have found that in ECs, the RhoA/ROCK pathway can affect vascular endothelial function and the synthesis of nitric oxide (NO) (85, 86). The ROCK inhibitor fasudil can reduce the expression levels of endothelin-1(ET-1) and endothelin receptors (ETR), inhibit the proliferation of pulmonary arterial endothelial cells, and promote the generation of NO (87). Moreover, inhibiting the RhoA/ROCK pathway can also activate the PI3K/Akt pathway, leading to the phosphorylation of eNOS, playing a protective role in vascular spasm and endothelial dysfunction (88–90).
6 Conclusions
In the rapidly evolving modern society, individuals frequently confront substantial psychological pressures. PD, a prevalent mental health condition, is intricately linked to the onset and poor prognosis of CVD. Therefore, a thorough understanding of the interplay between PD and CVD, along with the underlying mechanisms, is crucial for the effective management of psycho-cardiac conditions. Such understanding is pivotal not only for reducing the prevalence and mortality rates of CVD but also for enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals living with PD.
Statements
Author contributions
YF: Writing – original draft. XL: Writing – original draft. ZL: Writing – review & editing. XH: Writing – review & editing. YT: Writing – review & editing. WT: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Shenyang Science and Technology Project (2024)—Special Project for Public Health Research and Development (24-214-3-10) and the Applied Fundamental Research Program of Liaoning Province (2023JH2/101300031).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge all people with personal experience of mental illness; their contributions are essential to progress in this area. We thank all participants and staff involved in the studies cited here. The authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Soares-Filho GL Arias-Carrión O Santulli G Silva AC Machado S Valenca AM et al Chest pain, panic disorder and coronary artery disease: a systematic review. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. (2014) 13(6):992–1001. 10.2174/1871527313666140612141500
2.
McDevitt-Petrovic O Kirby K Shevlin M . The prevalence of non-cardiac chest pain (nccp) using emergency department (ed) data: a northern Ireland based study. BMC Health Serv Res. (2017) 17(1):549. 10.1186/s12913-017-2493-8
3.
Sung SC Rush AJ Earnest A Lim LEC Pek MPP Choi JMF et al A brief interview to detect panic attacks and panic disorder in emergency department patients with cardiopulmonary complaints. J Psychiatr Pract. (2018) 24(1):32–44. 10.1097/pra.0000000000000283
4.
Shahimi NH Lim R Mat S Goh CH Tan MP Lim E . Association between mental illness and blood pressure variability: a systematic review. Biomed Eng Online. (2022) 21(1):19. 10.1186/s12938-022-00985-w
5.
Irfan S McCarthy M Miner S . Association between panic attack and coronary ischemia due to reduction in coronary blood flow. Can J Cardiol. (2023) 39(1):71–2. 10.1016/j.cjca.2022.09.005
6.
Lim PO . Do panic attacks causes coronary microvascular spasm?Can J Cardiol. (2023) 39(7):970. 10.1016/j.cjca.2023.02.019
7.
Craske MG Kircanski K Epstein A Wittchen HU Pine DS Lewis-Fernández R et al Panic disorder: a review of dsm-iv panic disorder and proposals for dsm-V. Depress Anxiety. (2010) 27(2):93–112. 10.1002/da.20654
8.
Meuret AE Kroll J Ritz T . Panic disorder comorbidity with medical conditions and treatment implications. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. (2017) 13:209–40. 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-021815-093044
9.
Meuret AE Tunnell N Roque A . Anxiety disorders and medical comorbidity: treatment implications. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2020) 1191:237–61. 10.1007/978-981-32-9705-0_15
10.
Zou Z Xiang M Zhang Y Huang Y Wang J He Y et al Associations of DNA methylation of hpa axis-related genes and neuroendocrine abnormalities in panic disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2022) 142:105777. 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2022.105777
11.
Bandelow B Baldwin D Abelli M Altamura C Dell'Osso B Domschke K et al Biological markers for anxiety disorders, ocd and ptsd—a consensus statement. Part I: neuroimaging and genetics. World J Biol Psychiatry. (2016) 17(5):321–65. 10.1080/15622975.2016.1181783
12.
Bandelow B Baldwin D Abelli M Bolea-Alamanac B Bourin M Chamberlain SR et al Biological markers for anxiety disorders, ocd and ptsd: a consensus statement. Part ii: neurochemistry, neurophysiology and neurocognition. World J Biol Psychiatry. (2017) 18(3):162–214. 10.1080/15622975.2016.1190867
13.
Zhang Y Zhou B Qiu J Zhang L Zou Z . Heart rate variability changes in patients with panic disorder. J Affect Disord. (2020) 267:297–306. 10.1016/j.jad.2020.01.132
14.
Immanuel S Teferra MN Baumert M Bidargaddi N . Heart rate variability for evaluating psychological stress changes in healthy adults: a scoping review. Neuropsychobiology. (2023) 82(4):187–202. 10.1159/000530376
15.
Pourhamzeh M Moravej FG Arabi M Shahriari E Mehrabi S Ward R et al The roles of serotonin in neuropsychiatric disorders. Cell Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 42(6):1671–92. 10.1007/s10571-021-01064-9
16.
Šilhán P Jelínková M Walter U Pavlov Praško J Herzig R Langová K et al Transcranial sonography of brainstem structures in panic disorder. Psychiatry Res. (2015) 234(1):137–43. 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2015.09.010
17.
Vilela-Costa HH Spiacci A Jr Bissolli IG Zangrossi H Jr . A shift in the activation of serotonergic and non-serotonergic neurons in the dorsal raphe lateral wings subnucleus underlies the panicolytic-like effect of fluoxetine in rats. Mol Neurobiol. (2019) 56(9):6487–500. 10.1007/s12035-019-1536-z
18.
Batistela MF Vilela-Costa HH Frias AT Hernandes PM Lovick TA Zangrossi H Jr . Enhanced responsiveness to hypoxic panicogenic challenge in female rats in late diestrus is suppressed by short-term, low-dose fluoxetine: involvement of the dorsal raphe nucleus and the dorsal periaqueductal gray. J Psychopharmacol (Oxford, England) (2021) 35(12):1523–35. 10.1177/02698811211058986
19.
Esler M Alvarenga M Barton D Jennings G Kaye D Guo L et al Measurement of noradrenaline and serotonin metabolites with internal jugular vein sampling: an indicator of brain monoamine turnover in depressive illness and panic disorder. Front Psychiatry. (2022) 13:818012. 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.818012
20.
Tretiakov A Malakhova A Naumova E Rudko O Klimov E . Genetic biomarkers of panic disorder: a systematic review. Genes (Basel). (2020) 11(11):1310. 10.3390/genes11111310
21.
Vismara M Girone N Cirnigliaro G Fasciana F Vanzetto S Ferrara L et al Peripheral biomarkers in dsm-5 anxiety disorders: an updated overview. Brain Sci. (2020) 10(8):564. 10.3390/brainsci10080564
22.
Norman TR Judd FK Gregory M James RH Kimber NM McIntyre IM et al Platelet serotonin uptake in panic disorder. J Affect Disord. (1986) 11(1):69–72. 10.1016/0165-0327(86)90062-5
23.
Norman TR Sartor DM Judd FK Burrows GD Gregory MS McIntyre IM . Platelet serotonin uptake and 3h-imipramine binding in panic disorder. J Affect Disord. (1989) 17(1):77–81. 10.1016/0165-0327(89)90026-8
24.
Bandelow B Allgulander C Baldwin DS Costa D Denys D Dilbaz N et al World federation of societies of biological psychiatry (wfsbp) guidelines for treatment of anxiety, obsessive-compulsive and posttraumatic stress disorders—version 3. Part I: anxiety disorders. World J Biol Psychiatry. (2023) 24(2):79–117. 10.1080/15622975.2022.2086295
25.
Xu S Ilyas I Little PJ Li H Kamato D Zheng X et al Endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases and beyond: from mechanism to pharmacotherapies. Pharmacol Rev. (2021) 73(3):924–67. 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000096
26.
Sluiter TJ van Buul JD Huveneers S Quax PHA de Vries MR . Endothelial barrier function and leukocyte transmigration in atherosclerosis. Biomedicines. (2021) 9(4):328. 10.3390/biomedicines9040328
27.
Vanhoutte PM Shimokawa H Feletou M Tang EH . Endothelial dysfunction and vascular disease—a 30th anniversary update. Acta Physiol (Oxford, England). (2017) 219(1):22–96. 10.1111/apha.12646
28.
Krüger-Genge A Blocki A Franke RP Jung F . Vascular endothelial cell biology: an update. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(18):4411. 10.3390/ijms20184411
29.
Peng Z Shu B Zhang Y Wang M . Endothelial response to pathophysiological stress. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2019) 39(11):e233–43. 10.1161/atvbaha.119.312580
30.
Francis GA . The greatly under-represented role of smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. (2023) 25(10):741–9. 10.1007/s11883-023-01145-8
31.
Bloom SI Islam MT Lesniewski LA Donato AJ . Mechanisms and consequences of endothelial cell senescence. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2023) 20(1):38–51. 10.1038/s41569-022-00739-0
32.
Sun HJ Wu ZY Nie XW Bian JS . Role of endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: the link between inflammation and hydrogen sulfide. Front Pharmacol. (2019) 10:1568. 10.3389/fphar.2019.01568
33.
Ghiadoni L Donald AE Cropley M Mullen MJ Oakley G Taylor M et al Mental stress induces transient endothelial dysfunction in humans. Circulation. (2000) 102(20):2473–8. 10.1161/01.cir.102.20.2473
34.
Sara JDS Ahmad A Toya T Suarez Pardo L Lerman LO Lerman A . Anxiety disorders are associated with coronary endothelial dysfunction in women with chest pain and nonobstructive coronary artery disease. J Am Heart Assoc. (2021) 10(17):e021722. 10.1161/jaha.121.021722
35.
Petrowski K Wichmann S Kirschbaum C . Stress-Induced pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine concentrations in panic disorder patients. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2018) 94:31–7. 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.05.005
36.
Ransing RS Patil B Grigo O . Mean platelet volume and platelet distribution width level in patients with panic disorder. J Neurosci Rural Pract. (2017) 8(2):174–8. 10.4103/jnrp.jnrp_445_16
37.
Smoller JW Pollack MH Wassertheil-Smoller S Jackson RD Oberman A Wong ND et al Panic attacks and risk of incident cardiovascular events among postmenopausal women in the women’s health initiative observational study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (2007) 64(10):1153–60. 10.1001/archpsyc.64.10.1153
38.
Müller-Tasch T Frankenstein L Holzapfel N Schellberg D Löwe B Nelles M et al Panic disorder in patients with chronic heart failure. J Psychosom Res. (2008) 64(3):299–303. 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2007.09.002
39.
Yanartas O Sunbul M Senkal Z Durmus E Kivrak T Subasi N et al Increased arterial stiffness parameters in panic disorder patients in long term treatment period. Ann Gen Psychiatry. (2016) 15:14. 10.1186/s12991-016-0102-6
40.
Tully PJ Turnbull DA Beltrame J Horowitz J Cosh S Baumeister H et al Panic disorder and incident coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-regression in 1131612 persons and 58111 cardiac events. Psychol Med. (2015) 45(14):2909–20. 10.1017/s0033291715000963
41.
Yabut JM Crane JD Green AE Keating DJ Khan WI Steinberg GR . Emerging roles for serotonin in regulating metabolism: new implications for an ancient molecule. Endocr Rev. (2019) 40(4):1092–107. 10.1210/er.2018-00283
42.
Liu N Sun S Wang P Sun Y Hu Q Wang X . The mechanism of secretion and metabolism of gut-derived 5-hydroxytryptamine. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(15):7931. 10.3390/ijms22157931
43.
Watts SW Morrison SF Davis RP Barman SM . Serotonin and blood pressure regulation. Pharmacol Rev. (2012) 64(2):359–88. 10.1124/pr.111.004697
44.
Ni W Watts SW . 5-Hydroxytryptamine In the cardiovascular system: focus on the serotonin transporter (sert). Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2006) 33(7):575–83. 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2006.04410.x
45.
Barnes NM Ahern GP Becamel C Bockaert J Camilleri M Chaumont-Dubel S et al International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. Cx. Classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine; pharmacology and function. Pharmacol Rev. (2021) 73(1):310–520. 10.1124/pr.118.015552
46.
García-Pedraza J Ferreira-Santos P Aparicio R Montero MJ Morán A . Blocking 5-Ht2 receptor restores cardiovascular disorders in type 1 experimental diabetes. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:33979. 10.1038/srep33979
47.
García-Pedraza JA García M Martín ML Rodríguez-Barbero A Morán A . 5-Ht2 Receptor blockade exhibits 5-ht vasodilator effects via nitric oxide, prostacyclin and atp-sensitive potassium channels in rat renal vasculature. Vasc Pharmacol. (2016) 79:51–9. 10.1016/j.vph.2015.11.039
48.
Wang H Gao XY Rao F Yang H Wang ZY Liu L et al Mechanism of Contractile dysfunction induced by serotonin in coronary artery in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. (2020) 393(11):2165–76. 10.1007/s00210-020-01813-5
49.
Shimizu K Sunagawa Y Funamoto M Honda H Katanasaka Y Murai N et al The selective serotonin 2a receptor antagonist sarpogrelate prevents cardiac hypertrophy and systolic dysfunction via inhibition of the Erk1/2-Gata4 signaling pathway. Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland). (2021) 14(12):1268. 10.3390/ph14121268
50.
Shuai J Gao Y Chen L Wang Z . Role of serotonin in regulation of pancreatic and mesenteric arterial function in diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. (2021) 901:174070. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174070
51.
Deng CY Yang H Kuang SJ Rao F Xue YM Zhou ZL et al Upregulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor signaling in coronary arteries after organ culture. PLoS One. (2014) 9(9):e107128. 10.1371/journal.pone.0107128
52.
Bhattacharya A Schenck KW Xu YC Nisenbaum L Galbreath E Cohen ML . 5-Hydroxytryptamine1b Receptor-Mediated contraction of rabbit saphenous vein and basilar artery: role of vascular endothelium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2004) 309(2):825–32. 10.1124/jpet.103.062653
53.
Datté JY Offoumou MA . Involvement of nitric oxide in fading of 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced vasocontraction in rat isolated vena Portae smooth muscle. J Pharm Pharm Sci. (2004) 7(1):1–7.
54.
Bampalis VG Dwivedi S Shai E Brandl R Varon D Siess W . Effect of 5-Ht2a receptor antagonists on human platelet activation in blood exposed to physiologic stimuli and atherosclerotic plaque. J Thromb Haemost. (2011) 9(10):2112–5. 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04476.x
55.
Walther DJ Peter JU Winter S Höltje M Paulmann N Grohmann M et al Serotonylation of small gtpases is a signal transduction pathway that triggers platelet alpha-granule release. Cell. (2003) 115(7):851–62. 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)01014-6
56.
Lopez-Vilchez I Diaz-Ricart M White JG Escolar G Galan AM . Serotonin enhances platelet procoagulant properties and their activation induced during platelet tissue factor uptake. Cardiovasc Res. (2009) 84(2):309–16. 10.1093/cvr/cvp205
57.
Smith CW . Release of Α-granule contents during platelet activation. Platelets. (2022) 33(4):491–502. 10.1080/09537104.2021.1913576
58.
Ni W Geddes TJ Priestley JR Szasz T Kuhn DM Watts SW . The existence of a local 5-hydroxytryptaminergic system in peripheral arteries. Br J Pharmacol. (2008) 154(3):663–74. 10.1038/bjp.2008.111
59.
Imamdin A van der Vorst EPC . Exploring the role of serotonin as an immune modulatory component in cardiovascular diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(2):1549. 10.3390/ijms24021549
60.
Lopez-Vilchez I Diaz-Ricart M Navarro V Torramade S Zamorano-Leon J Lopez-Farre A et al Endothelial damage in Major depression patients is modulated by ssri treatment, as demonstrated by circulating biomarkers and an in vitro cell model. Transl Psychiatry. (2016) 6(9):e886. 10.1038/tp.2016.156
61.
Maingrette F Dussault S Dhahri W Desjarlais M Mathieu R Turgeon J et al Psychological stress impairs ischemia-induced neovascularization: protective effect of fluoxetine. Atherosclerosis. (2015) 241(2):569–78. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.06.010
62.
Delialis D Mavraganis G Dimoula A Patras R Dimopoulou AM Sianis A et al A systematic review and meta-analysis on the effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on endothelial function. J Affect Disord. (2022) 316:71–5. 10.1016/j.jad.2022.08.007
63.
Coupland C Hill T Morriss R Moore M Arthur A Hippisley-Cox J . Antidepressant use and risk of cardiovascular outcomes in people aged 20 to 64: cohort study using primary care database. BMJ (Clin Res Ed). (2016) 352:i1350. 10.1136/bmj.i1350
64.
Kim Y Lee YS Kim MG Song YK Kim Y Jang H et al The effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on Major adverse cardiovascular events: a meta-analysis of randomized-controlled studies in depression. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. (2019) 34(1):9–17. 10.1097/yic.0000000000000238
65.
Kim JM Stewart R Lee YS Lee HJ Kim MC Kim JW et al Effect of escitalopram vs placebo treatment for depression on long-term cardiac outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Jama. (2018) 320(4):350–8. 10.1001/jama.2018.9422
66.
Rami M Guillamat-Prats R Rinne P Salvermoser M Ring L Bianchini M et al Chronic intake of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor fluoxetine enhances atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2018) 38(5):1007–19. 10.1161/atvbaha.117.310536
67.
Zhang L Lu N Liu M . Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors regulate the interrelation between 5-ht and inflammation after myocardial infarction. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2023) 23(1):342. 10.1186/s12872-023-03378-6
68.
Iwabayashi M Taniyama Y Sanada F Azuma J Iekushi K Kusunoki H et al Role of serotonin in angiogenesis: induction of angiogenesis by sarpogrelate via endothelial 5-Ht1b/akt/enos pathway in diabetic mice. Atherosclerosis. (2012) 220(2):337–42. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.10.042
69.
Zamani A Qu Z . Serotonin activates angiogenic phosphorylation signaling in human endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. (2012) 586(16):2360–5. 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.05.047
70.
Zhao Y Qian Y Sun Z Shen X Cai Y Li L et al Role of Pi3k in the progression and regression of atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:632378. 10.3389/fphar.2021.632378
71.
Siragusa M Fleming I . The enos signalosome and its link to endothelial dysfunction. Pflugers Arch. (2016) 468(7):1125–37. 10.1007/s00424-016-1839-0
72.
Liu S Premont RT Rockey DC . Endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (enos) is activated through G-protein-coupled receptor kinase-interacting protein 1 (Git1) tyrosine phosphorylation and src protein. J Biol Chem. (2014) 289(26):18163–74. 10.1074/jbc.M113.521203
73.
Malekmohammad K Sewell RDE Rafieian-Kopaei M . Mechanisms of medicinal plant activity on nitric oxide (No) bioavailability as prospective treatments for atherosclerosis. Curr Pharm Des. (2020) 26(22):2591–601. 10.2174/1381612826666200318152049
74.
Förstermann U Sessa WC . Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. Eur Heart J. (2012) 33(7):829–37; 37a–37d. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304
75.
Zhu J Song W Xu S Ma Y Wei B Wang H et al Shenfu injection promotes vasodilation by enhancing enos activity through the Pi3k/akt signaling pathway in vitro. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:121. 10.3389/fphar.2020.00121
76.
Shaito A Aramouni K Assaf R Parenti A Orekhov A Yazbi AE et al Oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases. Front Biosci (Landmark Edition). (2022) 27(3):105. 10.31083/j.fbl2703105
77.
Bockaert J Bécamel C Chaumont-Dubel S Claeysen S Vandermoere F Marin P . Novel and atypical pathways for serotonin signaling. Fac Rev. (2021) 10:52. 10.12703/r/10-52
78.
Bader M . Serotonylation: serotonin signaling and epigenetics. Front Mol Neurosci. (2019) 12:288. 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00288
79.
Jiang SH Wang YH Hu LP Wang X Li J Zhang XL et al The physiology, pathology and potential therapeutic application of serotonylation. J Cell Sci. (2021) 134(11):jcs257337. 10.1242/jcs.257337
80.
Reddy AP Rawat P Rohr N Alvir R Bisht J Bushra MA et al Role of serotonylation and sert posttranslational modifications in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Aging Dis. (2024) 16(2):841. 10.14336/ad.2024.0328
81.
Rossin F Ciccosanti F D'Eletto M Occhigrossi L Fimia GM Piacentini M . Type 2 transglutaminase in the nucleus: the new epigenetic face of a cytoplasmic enzyme. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2023) 80(2):52. 10.1007/s00018-023-04698-8
82.
Lin J Wu SC . Implications of transglutaminase-mediated protein serotonylation in the epigenetic landscape, small cell lung cancer, and beyond. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15(4):1332. 10.3390/cancers15041332
83.
Liu B Wang D Luo E Hou J Qiao Y Yan G et al Role of Tg2-mediated Serca2 serotonylation on hypoxic pulmonary vein remodeling. Front Pharmacol. (2019) 10:1611. 10.3389/fphar.2019.01611
84.
Sheftel CM Hernandez LL . Serotonin stimulated parathyroid hormone related protein induction in the mammary epithelia by transglutaminase-dependent serotonylation. PLoS One. (2020) 15(10):e0241192. 10.1371/journal.pone.0241192
85.
Pillay LM Yano JJ Davis AE Butler MG Ezeude MO Park JS et al In vivo dissection of rhoa function in vascular development using zebrafish. Angiogenesis. (2022) 25(3):411–34. 10.1007/s10456-022-09834-9
86.
Hauke M Eckenstaler R Ripperger A Ender A Braun H Benndorf RA . Active rhoa exerts an inhibitory effect on the homeostasis and angiogenic capacity of human endothelial cells. J Am Heart Assoc. (2022) 11(12):e025119. 10.1161/jaha.121.025119
87.
Sun XZ Li SY Tian XY Hong Z Li JX . Effect of rho kinase inhibitor fasudil on the expression et-1 and No in rats with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. (2019) 71(1):3–8. 10.3233/ch-160232
88.
Palomo I Wehinger S Andrés V García-García FJ Fuentes E . Rhoa/rho kinase pathway activation in age-associated endothelial cell dysfunction and thrombosis. J Cell Mol Med. (2024) 28(8):e18153. 10.1111/jcmm.18153
89.
Basarici I Özen N Kilavuz E Kısak F Basrali F Yaras N et al Concealed role of red blood cells in pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension: decreased red blood cell nitric oxide generation and effect of rho-kinase inhibitor fasudil. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. (2020) 76(4):535–48. 10.3233/ch-200892
90.
Amin F Ahmed A Feroz A Khaki PSS Khan MS Tabrez S et al An update on the association of protein kinases with cardiovascular diseases. Curr Pharm Des. (2019) 25(2):174–83. 10.2174/1381612825666190312115140
Summary
Keywords
panic disorder, 5-HT, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, vascular endothelial function, signaling pathways, cardiovascular diseases
Citation
Feng Y, Li X, Li Z, He X, Tang Y and Tian W (2025) The effects of 5-HT on vascular endothelial dysfunction in patients with panic disorder. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1632070. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1632070
Received
20 May 2025
Accepted
05 August 2025
Published
20 August 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
DeLisa Fairweather, Mayo Clinic Florida, United States
Reviewed by
Jesus Alberto Olivares-Reyes, Center for Research and Advanced Studies (CINVESTAV), Mexico
Belinda H. McCully, Western University of Health Sciences, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Feng, Li, Li, He, Tang and Tian.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Wen Tian wtian56@cmu.edu.cn Yanqing Tang tangyanqing@cmu.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.