- 1National Laboratory Astana, Nazarbayev University, Astana, Kazakhstan
- 2CF “University Medical Center”, Heart Center, Astana, Kazakhstan
Background: Heart failure (HF) represents a global health burden with distinct phenotypes characterized by varying left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Despite shared endothelial dysfunction, heart failure with reduced (HFrEF) and preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) exhibit fundamentally different pathophysiological mechanisms, comorbidity profiles, and treatment responses.
Methods: This systematic review and meta-analysis examine inflammatory, cardiac remodelling and congestion, and myocardial injury biomarkers across HF phenotypes, integrating data from 78 studies encompassing 58,076 subjects.
Results: Our analysis reveals a significant elevation of IL-6, TNF-alpha, and hs-CRP in HF compared to controls, with distinct biomarker profiles emerging between phenotypes. While inflammatory markers universally increase with disease severity, their utility in phenotypic differentiation remains limited due to substantial overlap. Comorbidity burden significantly influences inflammatory profiles, creating diagnostic challenges that multi-biomarker approaches may address. NT-proBNP, sST2, GDF-15, and cardiac troponins demonstrate complementary value when combined with inflammatory markers, potentially enabling more precise phenotypic classification.
Conclusion: Our findings highlight the central role of inflammation in HF pathophysiology while identifying critical knowledge gaps, particularly regarding HFpEF-specific inflammatory signatures. This comprehensive analysis provides a foundation for developing targeted immunomodulatory therapies and personalized diagnostic approaches in heart failure management.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42025639405, PROSPERO CRD42025639405.
1 Introduction
Heart failure (HF) represents a global health crisis, significantly contributing to mortality, disability, and morbidity worldwide (1). Recent advances in our understanding of HF have revealed its complex nature, with three distinct phenotypes based on Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF): Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF, LVEF ≤40%), Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF, LVEF ≥50%), and the intermediary Heart Failure with mildly reduced Ejection Fraction (HFmrEF, LVEF 41%–49%) (2). This phenotypic variation is crucial, as it reflects differences in etiology, demographics, comorbidities, and therapeutic responses (3–5). While HFrEF and HFpEF share risk factors and comorbidities (6), they exhibit distinct gender predispositions and underlying mechanisms. HFpEF often results from chronic inflammation associated with conditions like obesity and diabetes, leading to microvascular dysfunction and oxidative stress (7). In contrast, HFrEF stems from various etiologies including ischemic cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic factors, and direct cardiac insults (7–9). Regardless of the distinct phenotypic differences of HFmrEF, its treatment strategy usually considered alike with that of HFpEF (10).
The use of biomarkers in diagnosis and management of HF patients under thoroughly investigation. Among them NT-proBNP is the most promising biomarker, which is currently the most used one aiding to make diagnosis and prognosis of HF development (11). However, debates arise across usage of NT-proBNP and other biomarkers in HF, as individually they are not specific for HF pathogenesis (12). Therefore, there is need in construction of multibiomarkeral approach, targeting novel therapeutical strategy to diagnosis and management of CHF and its distinct phenotypes (13).
Biomarkers describing HF have no strict classification, and individually can fall into more than one category. To address this complexity and to facilitate a clearer comprehension, we have categorized them based on their primary association with pathogenetic processes, namely: biomarkers of inflammation, biomarkers of cardiac remodeling and congestion, and biomarkers of myocardial injury (Figure 1).
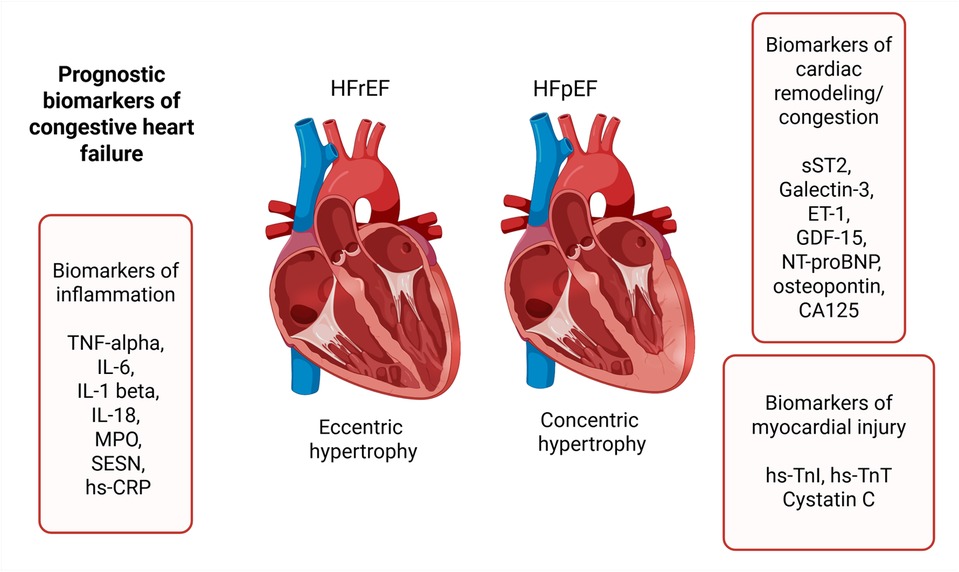
Figure 1. Prognostic biomarkers of heart failure. TNF-alpha, tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-1 beta, interleukin-1 beta; IL-18, interleukin-18; MPO, myeloperoxidase; SESN, sestrin proteins; hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; sST2, soluble suppression of tumorigenesis-2; ET-1, endothelin-1; GDF-15, growth differentiation factor-15; NT-proBNP, N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide; hs-TnI, high-sensitivity troponin I; hs-TnT, high-sensitivity troponin T.
This systematic review is going to emphasize diagnostic capability of HF biomarkers individually and from multibiomarkeral perspective. This review synthesizes current understanding of biomarkers in HF, highlighting their potential as diagnostic tools and therapeutic targets. By elucidating the complex interplay between inflammation, cardiac remodeling, congestion, myocardial injury and heart failure, we pave the way for personalized medicine approaches in HF management, potentially revolutionizing patient care and outcomes in this devastating disease.
2 Methods
Medline, Scopus and Embase databases were used in order to collect all eligible data for our study. Search strategy included our study population (using both terms “congestive heart failure” and “heart failure” to capture all relevant publications) and biomarkers with previous evidence (hs-CRP, TNF-alpha, soluble TNF receptors, IL-1, IL-6, IL-18, MPO, Sestrin proteins, sST2, GDF-15, Galectin-3, ET-1, NT-proBNP, osteopontin, cTnT, cTnI, Cystatin C). In addition, only English and human subject type articles were included (Supplementary Table S1). CRP is secreted during most of the inflammation responses that can be triggered by infection, tissue damage (14). Because CRP secretion is not specific and gives poor clinical information, articles that included only non-specific CRP were excluded. Inclusion criteria was having high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), which was recognized as inflammation marker that predicts reverse cardiovascular events (15). Search was conducted on 27 December 2024 and managed by EndNote. Following PRISMA guideline inclusion and exclusion criteria was conducted and illustrated in Figure 2 (16). 885 articles were collected using Medline, Scopus and Embase databases. Twenty-three duplicates were removed using EndNote (n = 23), after those 16 articles were excluded during abstracts screening, 13 were duplicates, two written not in English language and one was animal study. Full text assessment for eligibility excluded 768 studies due to various reasons including studies lacking inflammatory biomarkers from our search strategy (n = 93), review articles (n = 45), studies not included congestive heart failure patients (n = 242), therapeutical studies without healthy control group were also excluded due to inability to assess diagnostic role of biomarkers following drag intervention (n = 386), duplicated cohort (n = 2). 78 studies were included after screening and assessment for eligibility. The protocol was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42025639405).
Risk of bias assessment was performed for all included studies by risk of bias tool (RoB 2). Risk of bias graph and summary were designed by Review Manager 5 software (Supplementary Figures S1, S2).
The following study characteristics were extracted independently by two reviewers into Microsoft Excel 2021 (version 2108): First author, publication year, title, study design, number of subjects, age, HF type, comorbidities, inflammation biomarkers, evaluated results. Subgroup meta-analysis was done by Review Manager 5 (version 5.4) software to compare sST2, GDF-15, NT-proBNP, IL-6, hs-TnT, hs-TnI concentrations between HF phenotypes and IL-6, TNF-alpha, hs-CRP concentrations between HF and healthy control cohorts. Meta-analysis was performed using standard deviation mean difference (IV, Random effects, 95% CI). Studies reporting concentrations with interquartile ranges were recalculated using method of Wan et al. (17).
3 Results
A total of 58,076 subjects from 78 studies were included in this systematic review, with a mean patient age of over 65 years. Study characteristics of included studies are presented in Supplementary Tables S2–S4.
3.1 Inflammatory biomarkers
Only seven studies included HF patients with preserved ejection fraction. The remaining studies included only HFrEF patients or had a mixed cohort with predominantly HFrEF patients compared to HFpEF. Only few articles studied IL-1 beta, showing IL-1beta concentration being lower than detection limit in Almasood's study and significantly elevated in congestive heart failure (CHF) cohort compared to control group in Stanciu's study (18, 19). Despite the theoretical basis suggesting that IL-18 and sestrin proteins play a role in the inflammation associated with heart failure (20–22), the search did not find articles measuring IL-18 and sestrin protein concentrations.
3.1.1 IL-6
Abernethy found that IL-6 levels were higher in the acute decompensated heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (AD-HFpEF) compared to stable HFpEF (S-HFpEF) (23). Pandhi found that IL-6 was significantly elevated in patients with severe congestion HF (24). Almasood's study showed that IL-6 levels correlates with NYHA class, indicating severity. Aulin suggested that IL-6, along with other biomarkers, could improve the identification of the risk of developing or worsening HF (25). However, Niebauer's study found no association between IL-6 and CHF worsening (26). Based on a median follow-up duration of 1.9 years, IL-6 demonstrated a stronger association with mortality in the healthy control (HC) group compared to the HF groups (25). Susa reported that IL-6 level do not change between chronic HF patients with and without cardiac events (27), but Davarzani's results of 19-month follow-up of congestive HF patients concluded that the event group had higher IL-6 levels compared to no-event group (28). Boulogne reported that IL-6, among other biomarkers, showed no difference between acute and chronic HF cohorts (29).
Meta-analysis comparing IL-6 concentration (ng/L) between HFrEF and HFpEF groups included three studies, as illustrated in Figure 3. The total SMD was 0.14 (95% CI: −0.22 to 0.50) with p = 0.45, indicating no statistically significant difference in IL-6 levels between HFrEF and HFpEF. The heterogeneity of the analysis is high (I2 = 88%), showing that the results vary substantially across studies.
3.1.2 TNF-alpha
Tromp reported that TNF-alpha levels don't differ significantly between HFrEF and HFpEF phenotypes (30). According to Almasood's and Nakamura's work, TNF-alpha levels correlated with NYHA class severity (18, 31). Fedacko indicated that TNF-alpha can be related to CHF cause and severity, while Richter showed that TNF-alpha can predict all-cause mortality in the HF population (32, 33). On the other hand, Susa and Niebauer reported that TNF-alpha is not associated with adverse outcomes in HF (26, 27).
3.1.3 hs-CRP
Cakmak found a positive correlation between novel HF biomarkers, microRNAs, and hs-CRP levels (34). Dubrock reported that a high hs-CRP levels were associated with a greater comorbidity burden, younger age, higher NT-proBNP levels, right ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (35). However, 40% of HFpEF patients had hs-CRP levels within the normal range, and no correlation with NYHA functional class was observed (35).
3.2 Cardiac remodeling and congestion biomarkers
Andersson revealed that during heart failure, endothelin A receptor mediated vasodilation is primarily diminished, despite the fact that endothelin-1 level is high (36). Pandhi reported that congestion elevates endothelin-1 levels (24). Mohebi's study indicates that endothelin-1 can be considered as reliable predictor of adverse outcomes in HF (37), while Galindo-Fraga reported that endothelin is associated with poor prognosis in HF severity (38).
According to Tromp and Boulogne, Galectin-3 levels weren't significantly different between phenotypes or between the acute and chronic forms of HF (29, 30). Mohebi reported that Galectin-3 is a significant predictor of hospitalization and cardiovascular death (37). Gocer proposed Galectin-3 concentration ranges according to HF severity: “100–460 pg/ml” for mild, “460–1,170 pg/ml” for moderate and “>1,170 pg/ml” for severe HF (39). Galectin-3 levels were significantly correlated with diabetes mellitus, but not with COPD (40, 41).
There is a limited number of studies with measuring osteopontin levels. According to Tromp's study, its levels do not differ between phenotypic groups (30). Osteopontin is a good predictor of adverse outcomes. According to Behnes, its predicting value is higher compared to NT-proBNP (42).
3.2.1 sST2
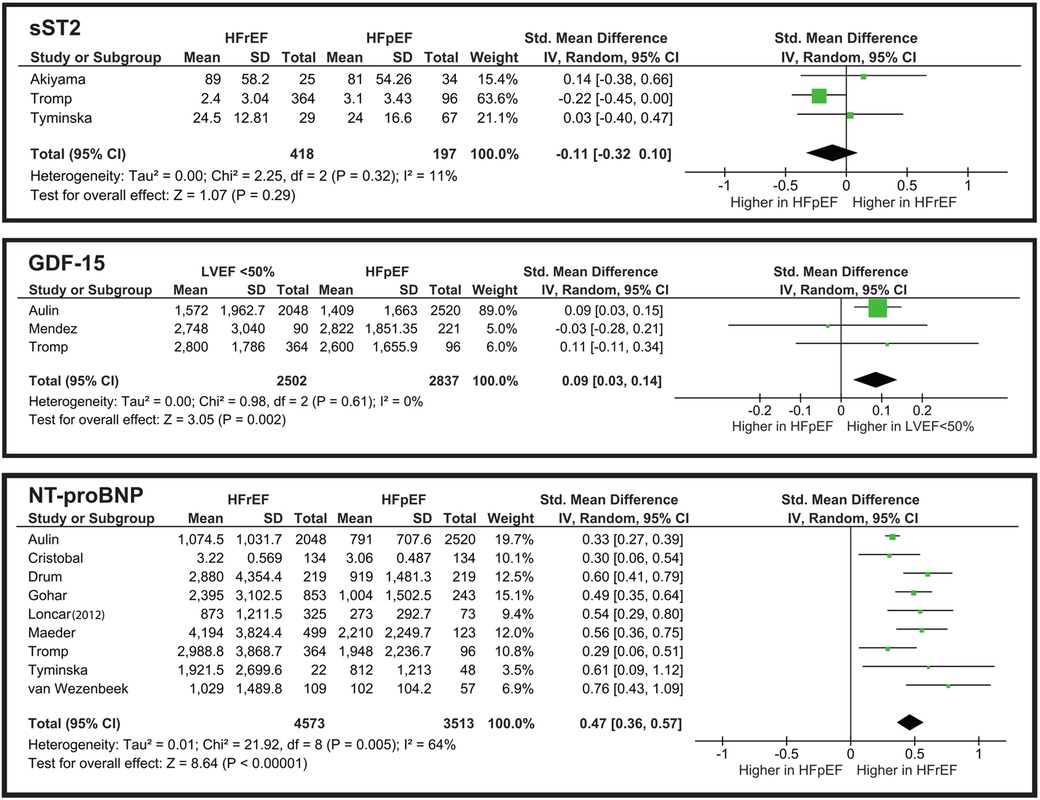
According to Mohebi, sST2 is a reliable biomarker for predicting adverse outcomes in advanced HF patients (37). The same conclusion was made by Davarzani and Bahuleyan, who found association of sST2 with adverse outcomes and cardiac events (28, 43). However, Boulogne reported opposite results, additionally indicating that sST2 levels do not differ between the acute and chronic forms of HF (29). Crnko made an important observation, indicating that sST2 levels fluctuate during the day, with the highest concentration in the afternoon, and the lowest at night (44). This finding suggests considering blood sample collection time to improve the prognostic potential of sST2. Menghoum's study showed a significant elevation of sST2 in HFpEF compared to control subjects (45). On the contrary, Firouzabadi reported no significant difference in sST2 concentrations between HF and control groups (46). According to the included studies, sST2 does not correlate with the comorbid conditions of diabetes mellitus and COPD, but it showed significance in predicting HF patients with cachexia (40, 41, 47).
From the meta-analysis illustrated in Figure 4, the overall SMD is −0.11, indicating that sST2 levels are slightly higher in the HFpEF group. However, the still do not show a significant difference. The overall effect is Z = 1.07 (P = 0.29), and all three studies cross the line of no effect. Heterogeneity is low (I2 = 11%), showing that the studies are consistent and do not vary drastically.
3.2.2 GDF-15
Mendez-Fernandez observed that GDF-15 is an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in HF patients with LVEF “>40%” (48). Similarly, Teramoto reported that GDF-15 predicts cardiovascular endpoints, but specifically in elderly patients (49). Davarzani's study shows that GDF-15 is associated with cardiac events in CHF patients (28). When comparing CHF with comorbidities, Ehteshami-Afshar reported significant elevation of GDF-15 in CHF patients with COPD (41).
From the meta-analysis illustrated in Figure 4, we evaluated that while it reaches statistical significance Z = 3.05 (P = 0.002), its clinical implementation for distinguishing HFpEF from LVEF “<50%” is poor. The heterogeneity is significantly low (I2 = 0%), which may suggest the need for further studies to establish whether GDF-15 truly aids in phenotype differentiation in clinical practice.
3.2.3 NT-proBNP
The meta-analysis illustrated in Figure 4 shows that NT-proBNP has a statistically significant difference when comparing HFrEF and HFpEF groups. However, in clinical terms this difference is limited. The SMD of 0.47 corresponds to a small-to-moderate effect size. Nonetheless, in combination with other biomarkers NT-proBNP can be a valid diagnostic tool.
3.3 Biomarkers of myocardial injury
3.3.1 hs-TnT
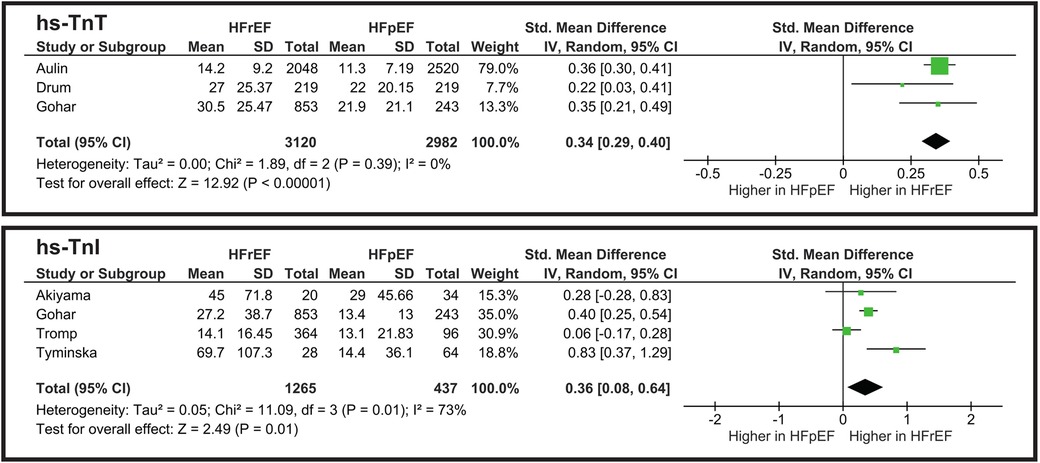
The meta-analysis illustrated in Figure 5 shows a statistically significant difference between HFpEF and HFrEF. However, an SMD of 0.34 indicates that hs-TnT levels highly overlap between the two groups, thus limiting its clinical utility for phenotype differentiation. Heterogeneity is low (I2 = 0%), showing the consistency of the studies.
3.3.2 hs-TnI
The pooled standardized mean difference (SMD) for hs-TnI is approximately 0.36 (p = 0.01), favoring slightly higher levels in HFpEF (Figure 5). This is a small-to-moderate effect size, suggesting a partial overlap between the two HF subtypes. Heterogeneity is I2 = 73%, indicating moderate variability among studies. While hs-TnI levels differ statistically between HFrEF and HFpEF, the difference is not large enough to serve as a strong phenotypic discriminator on its own.
3.3.3 Cystatin C
According to Mohebi's study Cystatin C levels significantly increase with HF severity (37). Aulin reported that cystatin C is associated with HF hospitalization and death (25). Both Aulin and Akiyama indicated that Cystatin C does not show a significant difference between phenotypic groups and cannot be used to clinically differentiate them (25, 50).
4 Discussion
This systematic review represents the most up-to-date analysis on biomarkers related to HF. Everett's study showed a promising future for anti-cytokine treatments, a monoclonal antibody against IL-1 beta significantly decreased hospitalization and mortality, which reveals importance of chronic inflammation in CHF pathogenesis (51). Additionally, the concentration of inflammatory biomarkers is positively correlated with the number of comorbid conditions, complicating the differentiation between HFpEF and HFrEF (35). Aulin's research demonstrated the biomechanical stress prevalence in HFrEF, showing higher NT-proBNP levels in HFrEF (1,074 ng/L) compared to HfpEF (791 ng/L) (25). The plasma NT-proBNP threshold for inclusion criteria in heart failure patients varies greatly. In Pandhi's study, the threshold was NT-proBNP “>2,000 pg/ml”, whereas in Dubrock's study, it was NT-proBNP “>400 pg/ml” (24, 35). In Stanciu's study both coronary sinus (CS) and peripheral venous (PV) NT-proBNP concentration correlated to CS IL-6, IL1-beta and TNF-alpha levels (19). According to the results of the CORONA clinical trials, NT-proBNP was the strongest predictor of death from worsening heart failure during the 3-month follow-up period (52, 53).
Normal biomarker values, according to Boulogne's and Dubrock's research are the following: hs-CRP “<3 mg/L”, TNF-alpha “<6 pg/ml”, IL-6 “<7 pg/ml”, MPO “<50 pg/ml”, ST2 “<35 ng/ml”, GDF-15 “<1,200 ng/L”, Gal-3 “<10 ng/ml” (29, 35). The threshold levels of biomarkers for detecting cachectic HF are “>5 mg/L” for hs-CRP and “>4 pg/ml” for IL-6 (54). According to Nakamura's study, the normal value for hs-CRP was 0.02 mg/dl, and for TNF-alpha, it was 3.8 pg/ml (31). In Everett's study, patients with hs-CRP levels “<2 mg/L” were considered to have achieved treatment success, indicating the treatment threshold as established in the CANTOS clinical trial (51). Thibodeau reported elevated threshold levels of NT-proBNP and hs-TnT as 1,000 pg/ml and 52 ng/L, respectively (55). NT-proBNP level standards are age-dependent, and increase with older age (56). Chenevier-Gobeaux reported NT-proBNP threshold values as 1,700 pg/ml for patients “<85 years old” and 2,800 pg/ml for those “>85 years old” with CHF. Maeder's treatment strategy focused on reducing NT-proBNP below the inclusion criteria: “<400 ng/L” in patients “<75 years old”, “<800 ng/L” in those “≥75 years old” (57). According to the literature, NT-proBNP-guided therapy improves disease management and shows a trend toward cost reduction, with the highest cost-effectiveness in HF patients aged 60–75 years with two or fewer comorbidities (58, 59).
While some biomarkers, such as NT-proBNP and hs-TnT, remain central to diagnosis and prognosis, others, including ET-1, sST2, and GDF-15, show potential but require further validation. Multi-biomarker approaches may enhance predictive accuracy, though clinical implementation remains challenging due to biomarker overlap and variability. The multi-biomarker approach has demonstrated superior predictive value compared to single-biomarker assessments in heart failure prognosis. Richter reported that a combination of NT-proBNP, hs-TnT, TIMP-1, GDF-15, and IBP-4 provided more accurate predictions than relying solely on NT-proBNP (33). Similarly, Wright observed that combining NT-proBNP with urocortin levels enhanced the ability to predict heart failure outcomes more effectively than using either marker alone (60). Lupón's findings further support this approach, indicating that hs-cTnT and hs-ST2 together offer better prognostic accuracy than when combined with NT-proBNP (61). The meta-analysis illustrated in Figure 4 underscores that while NT-proBNP alone shows a statistically significant difference between HFrEF and HFpEF, its clinical utility is limited. However, when integrated into a multimarker panel, NT-proBNP significantly enhances the diagnostic and prognostic capabilities, emphasizing the potential of a comprehensive biomarker strategy in heart failure management. Standardizing sampling protocols, particularly for time-sensitive biomarkers like sST2, may improve diagnostic precision (44). In addition, recent evidence from Menghoum's study suggests that CA125 represents a promising biomarker of congestion, particularly in HFpEF, further highlighting the need to expand future multi-biomarker strategies (45). Future research should focus on refining biomarker thresholds and establishing their utility in distinguishing HF phenotypes, ultimately enhancing individualized HF management strategies.
There is a deficit in systematic reviews related to the diagnostic role of inflammatory biomarkers in heart failure. A previous meta-analysis that studied CRP, IL-6 and TNF receptor-1 in HFrEF and HFpEF concluded that HFpEF can be differentiated from HFrEF by a higher concentration of IL-6 and lower level of NO (62). However, in our study there is no difference between HFrEF and HFpEF based on inflammatory biomarkers. The results from the meta-analyses of IL-6, hs-CRP, and TNF-alpha levels in heart failure patients compared to healthy controls consistently demonstrate that systemic inflammation is significantly elevated in heart failure, with inflammatory markers showing a strong association with disease severity. However, the high heterogeneity observed in these meta-analyses suggests that further research is needed to clarify the relationship between IL-6, TNF-alpha, and hs-CRP in relation to heart failure subtypes, and to assess whether IL-6, TNF-alpha, and hs-CRP could serve as a reliable biomarkers for disease severity or treatment response.
Studies show that high-sensitivity cardiac troponin and cystatin C are strong predictors of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality (63–65). The importance of multiple biomarker monitoring was described in a recent systematic review, but the inclusion criteria was focused mainly on the acute form of heart failure (66). Rabkin conducted a systematic review with meta-analysis focused on GDF-15, Galectin-3, sST2 and NT-proBNP (67). They came to similar conclusions when compared NT-proBNP levels between HFrEF and HFpEF. However, the meta-analysis of sST2 and GDF-15 yielded slightly differed results. Rabkin reported that sST2 levels were slightly higher in HFrEF, with higher heterogeneity in the studies (I2 = 55.8%). On the contrary, our meta-analysis found elevated sST2 levels in the HFpEF phenotype, with low heterogeneity (I2 = 11%). The GDF-15 meta-analysis also differed significantly from Rabkin's observations. Our results demonstrated a statistically significant elevation of GDF-15 in HFrEF, and Rabkin showed no statistical significance, with slightly higher concentration in HFpEF. Further studies are needed to assess sST2 and GDF-15 levels between HF phenotypes, as the small number of studies and limited population sizes may not accurately represent HF phenotypes' nature.
A strength of our study is that our articles include a larger population than previous systematic reviews, making it more statistically reliable. A limitation of our study is that the number of included studies with phenotypically diversified data is not enough to conduct a meta-analysis comparing HF phenotypes for some biomarkers of interest, such as ET-1, Galectin-3, hs-CRP, TNF-alpha, and cystatin C. The varying classifications of heart failure make it challenging to focus only on congestive heart failure cohorts. Some included studies classify patients under general heart failure, resulting in mixed groups that include both congestive and acute heart failure patients.
In conclusion, our comprehensive review reveals the complex role of inflammatory biomarkers (IL-6, TNF-alpha, hs-CRP) in heart failure, demonstrating their variable associations with disease subtypes, comorbidities, and outcomes. These biomarkers show potential as indicators of severity, progression, and treatment response, paving the way for personalized management. Notably, comorbidities significantly influence biomarker concentrations, necessitating a nuanced interpretation, especially when differentiating HFrEF from HFpEF. The lack of HFpEF-specific data highlights an urgent research need. Beyond inflammation, cardiac remodeling and congestion biomarkers such as sST2, Galectin-3, GDF-15, osteopontin, and ET-1 provide valuable prognostic insights, reflecting fibrosis, extracellular matrix degradation, and adverse ventricular remodeling. These markers have demonstrated predictive potential for heart failure progression, hospitalization, and mortality, although their clinical implementation remains limited by variability across studies. Additionally, myocardial injury biomarkers, including hs-TnT, hs-TnI, and Cystatin C, are crucial for assessing myocardial injury and distinguishing between ischemic and non-ischemic heart failure etiologies. Their elevated levels in HFrEF suggests a direct link to cardiomyocyte damage and necrosis, further reinforcing their diagnostic and prognostic relevance. Given the multifaceted pathophysiology of heart failure, a multi-biomarker approach integrating inflammatory biomarkers, biomarkers of cardiac remodeling and congestion, and biomarkers of myocardial injury may enhance diagnostic precision and risk stratification. Future research should focus on refining biomarker panels, establishing optimal cutoff values, and exploring their role in personalized heart failure management. Standardized sampling protocols and longitudinal studies are necessary to validate these findings and optimize clinical application.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
AK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. ZM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. MB: Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Science Committee of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan [AP23488818 and BR21882152 to A. Kushugulova].
Acknowledgments
Figure 1 was created in BioRender. Nurgaziyev, M. (2025) https://BioRender.com/xipitcc.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1633164/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure S1 | Risk of bias graph.
Supplementary Figure S2 | Risk of bias summary.
References
1. Schocken DD, Benjamin EJ, Fonarow GC, Krumholz HM, Levy D, Mensah GA, et al. Prevention of heart failure: a scientific statement from the American heart association councils on epidemiology and prevention, clinical cardiology, cardiovascular nursing, and high blood pressure research; quality of care and outcomes research interdisciplinary working group; and functional genomics and translational biology interdisciplinary working group. Circulation. (2008) 117(19):2544–65. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.188965
2. McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, et al. 2023 focused update of the 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44(37):3627–39. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad195
3. Ho JE, Lyass A, Lee DS, Vasan RS, Kannel WB, Larson MG, et al. Predictors of new-onset heart failure: differences in preserved versus reduced ejection fraction. Circ Heart Fail. (2013) 6(2):279–86. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.112.972828
4. Mishra S, Kass DA. Cellular and molecular pathobiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2021) 18(6):400–23. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-00480-6
5. Krumholz HM, Larson M, Levy D. Sex differences in cardiac adaptation to isolated systolic hypertension. Am J Cardiol. (1993) 72(3):310–3. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(93)90678-6
6. Jeong EM, Dudley SC Jr. Diastolic dysfunction. Circ J. (2015) 79(3):470–7. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-15-0064
7. Paulus WJ, Tschöpe C. A novel paradigm for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: comorbidities drive myocardial dysfunction and remodeling through coronary microvascular endothelial inflammation. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2013) 62(4):263–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.02.092
8. Van Linthout S, Tschöpe C. Inflammation—cause or consequence of heart failure or both? Curr Heart Fail Rep. (2017) 14(4):251–65. doi: 10.1007/s11897-017-0337-9
9. Golla MSG, Hajouli S, Ludhwani D. Heart failure and ejection fraction. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing (2024). Copyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC.
10. Li P, Zhao H, Zhang J, Ning Y, Tu Y, Xu D, et al. Similarities and differences between HFmrEF and HFpEF. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:678614. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.678614
11. Castiglione V, Aimo A, Vergaro G, Saccaro L, Passino C, Emdin M. Biomarkers for the diagnosis and management of heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. (2022) 27(2):625–43. doi: 10.1007/s10741-021-10105-w
12. Daniels LB, Maisel AS. Natriuretic peptides. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2007) 50(25):2357–68. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.09.021
13. Topf A, Mirna M, Ohnewein B, Jirak P, Kopp K, Fejzic D, et al. The diagnostic and therapeutic value of multimarker analysis in heart failure. An approach to biomarker-targeted therapy. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2020) 7:579567. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.579567
14. Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM. C-reactive protein: a critical update. J Clin Invest. (2003) 111(12):1805–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI200318921
15. Bassuk SS, Rifai N, Ridker PM. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein: clinical importance. Curr Probl Cardiol. (2004) 29(8):439–93.15258556
16. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Br Med J. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
17. Wan X, Wang W, Liu J, Tong T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2014) 14(1):135. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-135
18. Almasood A, Sheshgiri R, Joseph JM, Rao V, Kamali M, Tumiati L, et al. Human leukocyte antigen-G is upregulated in heart failure patients: a potential novel biomarker. Hum Immunol. (2011) 72(11):1064–7. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2011.08.016
19. Stanciu AE, Stanciu MM, Vatasescu RG. NT-proBNP and CA 125 levels are associated with increased pro-inflammatory cytokines in coronary sinus serum of patients with chronic heart failure. Cytokine. (2018) 111:13–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.07.037
20. Xiao H, Li H, Wang JJ, Zhang JS, Shen J, An XB, et al. IL-18 cleavage triggers cardiac inflammation and fibrosis upon β-adrenergic insult. Eur Heart J. (2018) 39(1):60–9. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx261
21. Yamaoka-Tojo M, Tojo T, Inomata T, Machida Y, Osada K, Izumi T. Circulating levels of interleukin 18 reflect etiologies of heart failure: th1/Th2 cytokine imbalance exaggerates the pathophysiology of advanced heart failure. J Card Fail. (2002) 8(1):21–7. doi: 10.1054/jcaf.2002.31628
22. Sun Y, Wu Y, Tang S, Liu H, Jiang Y. Sestrin proteins in cardiovascular disease. Clin Chim Acta. (2020) 508:43–6. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.05.013
23. Abernethy A, Raza S, Sun JL, Anstrom KJ, Tracy R, Steiner J, et al. Pro-inflammatory biomarkers in stable versus acutely decompensated heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. J Am Heart Assoc. (2018) 7(8). doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007385
24. Pandhi P, ter Maaten JM, Anker SD, Ng LL, Metra M, Samani NJ, et al. Pathophysiologic processes and novel biomarkers associated with congestion in heart failure. JACC Heart Fail. (2022) 10(9):623–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2022.05.013
25. Aulin J, Hijazi Z, Lindbäck J, Alexander JH, Gersh BJ, Granger CB, et al. Biomarkers and heart failure events in patients with atrial fibrillation in the ARISTOTLE trial evaluated by a multi-state model. Am Heart J. (2022) 251:13–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2022.03.009
26. Niebauer J, Clark AL, Webb-Peploe KM, Coats AJ. Exercise training in chronic heart failure: effects on pro-inflammatory markers. Eur J Heart Fail. (2005) 7(2):189–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2004.07.012
27. Susa T, Kobayashi S, Tanaka T, Murakami W, Akashi S, Kunitsugu I, et al. Urinary 8-hydroxy-2ʹ-deoxyguanosine as a novel biomarker for predicting cardiac events and evaluating the effectiveness of carvedilol treatment in patients with chronic systolic heart failure. Circ J. (2012) 76(1):117–26. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-11-0537
28. Davarzani N, Sanders-van Wijk S, Maeder MT, Rickenbacher P, Smirnov E, Karel J, et al. Novel concept to guide systolic heart failure medication by repeated biomarker testing—results from TIME-CHF in context of predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine. EPMA J. (2018) 9(2):161–73. doi: 10.1007/s13167-018-0137-7
29. Boulogne M, Sadoune M, Launay JM, Baudet M, Cohen-Solal A, Logeart D. Inflammation versus mechanical stretch biomarkers over time in acutely decompensated heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Int J Cardiol. (2017) 226:53–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.10.038
30. Tromp J, Khan MAF, Klip IT, Meyer S, de Boer RA, Jaarsma T, et al. Biomarker profiles in heart failure patients with preserved and reduced ejection fraction. J Am Heart Assoc. (2017) 6(4). doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003989
31. Nakamura T, Funayama H, Kubo N, Yasu T, Kawakami M, Momomura S, et al. Elevation of plasma placental growth factor in the patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol. (2009) 131(2):186–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.10.050
32. Fedacko J, Singh RB, Gupta A, Hristova K, Toda E, Kumar A, et al. Inflammatory mediators in chronic heart failure in north India. Acta Cardiol. (2014) 69(4):391–8. doi: 10.1080/AC.69.4.3036655
33. Richter B, Koller L, Hohensinner PJ, Zorn G, Brekalo M, Berger R, et al. A multi-biomarker risk score improves prediction of long-term mortality in patients with advanced heart failure. Int J Cardiol. (2013) 168(2):1251–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.11.052
34. Cakmak HA, Coskunpinar E, Ikitimur B, Barman HA, Karadag B, Tiryakioglu NO, et al. The prognostic value of circulating microRNAs in heart failure: preliminary results from a genome-wide expression study. J Cardiovasc Med. (2015) 16(6):431–7. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0000000000000233
35. DuBrock HM, AbouEzzeddine OF, Redfield MM. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. PLoS One. (2018) 13(8):e0201836. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201836
36. Andersson SE, Edvinsson ML, Alving K, Edvinsson L. Vasodilator effect of endothelin in cutaneous microcirculation of heart failure patients. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. (2005) 97(2):80–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto_84.x
37. Mohebi R, Murphy S, Jackson L, McCarthy C, Abboud A, Murtagh G, et al. Biomarker prognostication across universal definition of heart failure stages. ESC Heart Fail. (2022) 9(6):3876–87. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14071
38. Galindo-Fraga A, Arrieta O, Castillo-Martínez L, Narváez R, Oseguera-Moguel J, Orea-Tejeda A. Elevation of plasmatic endothelin in patients with heart failure. Arch Med Res. (2003) 34(5):367–72. doi: 10.1016/S0188-4409(03)00071-7
39. Gocer H, Günday M, Ünal M. Plasma galectin-3 as a biomarker for clinical staging of heart failure: a cross-sectional evaluation of 100 cases. Clin Ter. (2019) 170(4):e267–e71. doi: 10.7417/CT.2019.2146
40. De Marco C, Claggett BL, de Denus S, Zile MR, Huynh T, Desai AS, et al. Impact of diabetes on serum biomarkers in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: insights from the TOPCAT trial. ESC Heart Fail. (2021) 8(2):1130–8. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13153
41. Ehteshami-Afshar S, Mooney L, Dewan P, Desai AS, Lang NN, Lefkowitz MP, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: insights from PARADIGM-HF. J Am Heart Assoc. (2021) 10(4):e019238. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019238
42. Behnes M, Brueckmann M, Lang S, Espeter F, Weiss C, Neumaier M, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of osteopontin in patients with acute congestive heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. (2013) 15(12):1390–400. doi: 10.1093/eurjhf/hft112
43. Bahuleyan CG, Alummoottil GK, Abdullakutty J, Lordson AJ, Babu S, Krishnakumar VV, et al. Prognostic value of soluble ST2 biomarker in heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction—a multicenter study. Indian Heart J. (2018) 70:S79–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2017.09.010
44. Crnko S, Printezi MI, Jansen TPJ, Leiteris L, van der Meer MG, Schutte H, et al. Prognostic biomarker soluble ST2 exhibits diurnal variation in chronic heart failure patients. ESC Heart Fail. (2020) 7(3):1224–33. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12673
45. Menghoum N, Badii MC, Deltombe M, Lejeune S, Roy C, Vancraeynest D, et al. Carbohydrate antigen 125: a useful marker of congestion, fibrosis, and prognosis in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail. (2024) 11(3):1493–505. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14699
46. Firouzabadi N, Dashti M, Dehshahri A, Bahramali E. Biomarkers of IL-33 and SST2 and lack of association with carvedilol therapy in heart failure. Clin Pharm. (2020) 12:53–8. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S256290
47. Gaggin HK, Belcher AM, Gandhi PU, Ibrahim NE, Januzzi JL Jr. Serial echocardiographic characteristics, novel biomarkers and cachexia development in patients with stable chronic heart failure. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. (2016) 9:429–31. doi: 10.1007/s12265-016-9710-4
48. Mendez Fernandez AB, Ferrero-Gregori A, Garcia-Osuna A, Mirabet-Perez S, Pirla-Buxo MJ, Cinca-Cuscullola J, et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 as mortality predictor in heart failure patients with non-reduced ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail. (2020) 7(5):2223–9. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12621
49. Teramoto K, Nochioka K, Sakata Y, Nishimura K, Shimokawa H, Yasuda S. Prognostic significance of growth differentiation factor-15 across age in chronic heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. (2024) 11(3):1666–76. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14738
50. Akiyama E, Cinotti R, Čerlinskaitė K, Van Aelst LNL, Arrigo M, Placido R, et al. Improved cardiac and venous pressures during hospital stay in patients with acute heart failure: an echocardiography and biomarkers study. ESC Heart Fail. (2020) 7(3):996–1006. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12645
51. Everett BM, Cornel JH, Lainscak M, Anker SD, Abbate A, Thuren T, et al. Anti-inflammatory therapy with canakinumab for the prevention of hospitalization for heart failure. Circulation. (2019) 139(10):1289–99. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.038010
52. Cleland JG, McMurray JJ, Kjekshus J, Cornel JH, Dunselman P, Fonseca C, et al. Plasma concentration of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in chronic heart failure: prediction of cardiovascular events and interaction with the effects of rosuvastatin: a report from CORONA (controlled rosuvastatin multinational trial in heart failure). J Am Coll Cardiol. (2009) 54(20):1850–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.06.041
53. Gravning J, Askevold ET, Nymo SH, Ueland T, Wikstrand J, McMurray JJ, et al. Prognostic effect of high-sensitive troponin T assessment in elderly patients with chronic heart failure: results from the CORONA trial. Circ Heart Fail. (2014) 7(1):96–103. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.000450
54. Sobieszek G, Powrózek T, Mazurek M, Skwarek-Dziekanowska A, Małecka-Massalska T. Electrical and hormonal biomarkers in cachectic elderly women with chronic heart failure. J Clin Med. (2020) 9(4). doi: 10.3390/jcm9041021
55. Thibodeau JT, Pham DD, Kelly SA, Ayers CR, Garg S, Grodin JL, et al. Subclinical myocardial injury and the phenotype of clinical congestion in patients with heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. J Card Fail. (2022) 28(3):422–30. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2021.09.002
56. Hildebrandt P, Collinson PO, Doughty RN, Fuat A, Gaze DC, Gustafsson F, et al. Age-dependent values of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide are superior to a single cut-point for ruling out suspected systolic dysfunction in primary care. Eur Heart J. (2010) 31(15):1881–9. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq163
57. Maeder MT, Rickenbacher P, Rickli H, Abbühl H, Gutmann M, Erne P, et al. N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide-guided management in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: findings from the trial of intensified versus standard medical therapy in elderly patients with congestive heart failure (TIME-CHF). Eur J Heart Fail. (2013) 15(10):1148–56. doi: 10.1093/eurjhf/hft076
58. Moertl D, Steiner S, Coyle D, Berger R. Cost-utility analysis of nt-probnp-guided multidisciplinary care in chronic heart failure. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. (2013) 29(1):3–11. doi: 10.1017/S0266462312000712
59. Sanders-van Wijk S, van Asselt AD, Rickli H, Estlinbaum W, Erne P, Rickenbacher P, et al. Cost-effectiveness of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic-guided therapy in elderly heart failure patients: results from TIME-CHF (trial of intensified versus standard medical therapy in elderly patients with congestive heart failure). JACC Heart Fail. (2013) 1(1):64–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2012.08.002
60. Wright SP, Doughty RN, Frampton CM, Gamble GD, Yandle TG, Richards AM. Plasma urocortin 1 in human heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. (2009) 2(5):465–71. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.108.840207
61. Lupón J, de Antonio M, Galán A, Vila J, Zamora E, Urrutia A, et al. Combined use of the novel biomarkers high-sensitivity troponin T and ST2 for heart failure risk stratification vs conventional assessment. Mayo Clin Proc. (2013) 88(3):234–43. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.09.016
62. Gui XY, Rabkin SW. C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, trimethylamine-N-oxide, syndecan-1, nitric oxide, and tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 in heart failure with preserved versus reduced ejection fraction: a meta-analysis. Curr Heart Fail Rep. (2023) 20(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/s11897-022-00584-9
63. Aimo A, Januzzi JL Jr, Vergaro G, Ripoli A, Latini R, Masson S, et al. Prognostic value of high-sensitivity troponin T in chronic heart failure: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Circulation. (2018) 137(3):286–97. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031560
64. Yousufuddin M, Abdalrhim AD, Wang Z, Murad MH. Cardiac troponin in patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hosp Med. (2016) 11(6):446–54. doi: 10.1002/jhm.2558
65. Chen S, Tang Y, Zhou X. Cystatin C for predicting all-cause mortality and rehospitalization in patients with heart failure: a meta-analysis. Biosci Rep. (2019) 39(2). doi: 10.1042/BSR20181761
66. Singh G, Bamba H, Inban P, Chandrasekaran SH, Priyatha V, John J, et al. The role of biomarkers in the prognosis and risk stratification in heart failure: a systematic review. Dis Mon. (2024) 70(10):101782. doi: 10.1016/j.disamonth.2024.101782
67. Rabkin SW, Tang JKK. The utility of growth differentiation factor-15, galectin-3, and sST2 as biomarkers for the diagnosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and compared to heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a systematic review. Heart Fail Rev. (2021) 26(4):799–812.32472523
Keywords: heart failure, biomarker, meta-analysis, inflammation, comorbidities
Citation: Kovenskiy A, Mukhatayev Z, Sailybayeva A, Bekbossynova M and Kushugulova A (2025) Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating biomarkers in heart failure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1633164. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1633164
Received: 26 May 2025; Accepted: 8 September 2025;
Published: 24 September 2025.
Edited by:
Erberto Carluccio, Heart Failure Unit, ItalyReviewed by:
Stefano Coiro, Hospital of Santa Maria della Misericordia in Perugia, ItalyJuan Rico-Mesa, Johns Hopkins University, United States
Copyright: © 2025 Kovenskiy, Mukhatayev, Sailybayeva, Bekbossynova and Kushugulova. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Artur Kovenskiy, YXJ0dXIua292ZW5za2l5QG51LmVkdS5reg==
 Artur Kovenskiy
Artur Kovenskiy Zhussipbek Mukhatayev
Zhussipbek Mukhatayev Aliya Sailybayeva2
Aliya Sailybayeva2 Almagul Kushugulova
Almagul Kushugulova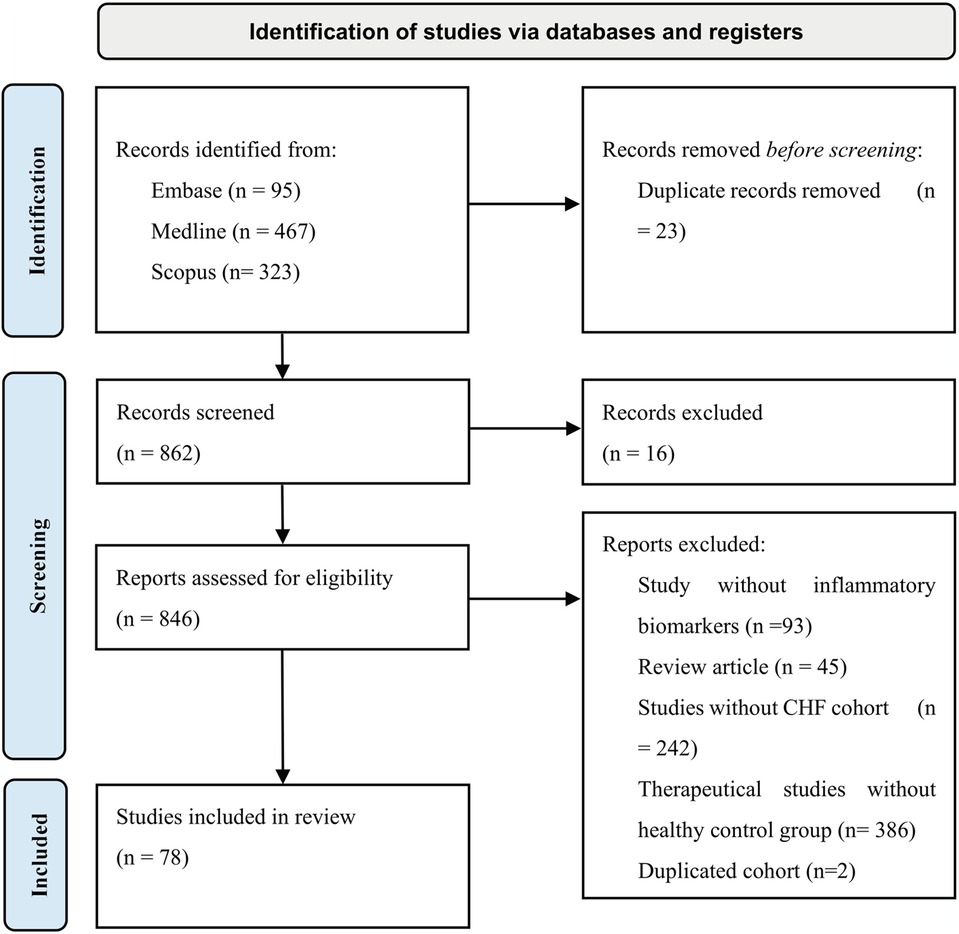
![Forest plot comparing IL-6 levels in heart failure patients with reduced (HFrEF) and preserved (HFpEF) ejection fraction. Studies listed are Aulin, Fedacko, and Tromp. Mean differences range from -0.25 to 0.67. Overall standardized mean difference is 0.14 with a confidence interval of [-0.22, 0.50]. Heterogeneity is significant at 88%. The plot shows effects on either side of zero, indicating variability in study results.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1633164/fcvm-12-1633164-HTML/image_m/fcvm-12-1633164-g003.jpg)