- 1Department of Critical Care Medicine, the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of School of Medicine, and International School of Medicine, International Institutes of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Yiwu, China
- 2Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Center for Oncology Medicine, the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of School of Medicine and International School of Medicine, International Institutes of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Yiwu, China
Correction on
By Qiu F, Song B, Chen L and Hong J (2025). Front Cardiovasc Med. 12:1578970. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1578970
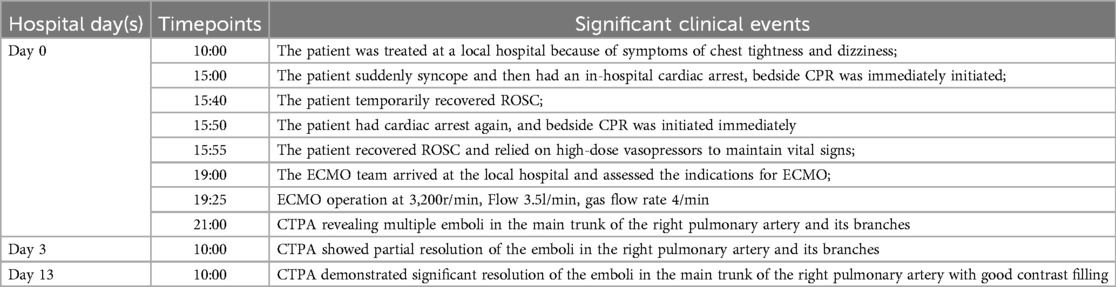
There was an error in Table 1 and its caption as published. The author mistakenly identified Table 2 as Table 1 which resulted in both table contents being similar. The corrected Table 1 and its caption appear below.
The original version of this article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: pulmonary embolism-diagnosis, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), thrombolysis, cardiac arrest (CA), disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Citation: Qiu F, Song B, Chen L and Hong J (2025) Correction: Case report: Does extracorporeal membrane oxygenation treatment for acute pulmonary embolism-induced respiratory and cardiac arrest still require thrombolysis?. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1634497. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1634497
Received: 24 May 2025; Accepted: 5 June 2025;
Published: 20 June 2025.
Approved by: Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, Switzerland
Copyright: © 2025 Qiu, Song, Chen and Hong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fangfang Qiu, enlzeWljdTE5OTFAemp1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Fangfang Qiu
Fangfang Qiu Bingxin Song2
Bingxin Song2 Jiayi Hong
Jiayi Hong