- Department of Cardiology, The Second Hospital of Jiaxing, Jiaxing, Zhejiang, China
Background: The treatment focus for patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) remains on acute resuscitation and maintenance during the stabilization phase. Despite significant advances in CHF management, treatment outcomes and disease control remain suboptimal. This study investigates the impact of a refined nursing model incorporating risk assessment strategies, combined with early exercise rehabilitation, on patients with CHF.
Method: Ninety cases of patients with CHF admitted to our hospital between February 2024 and November 2024 were selected and divided into the control group and the study group according to the randomized numerical table method, with 45 cases in each group. The control group carried out routine nursing care under a traditional model, and the study group applied a refined nursing model under a risk assessment strategy, combined with early exercise rehabilitation for nursing care, on the basis of the traditional model.
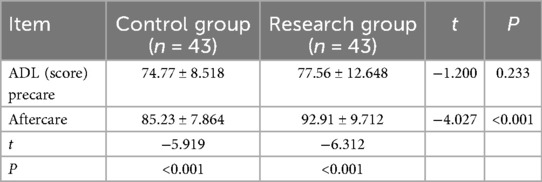
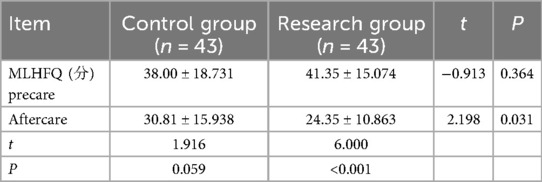
Result: The left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEFs) of CHF patients in the study group were significantly higher after cardiac ultrasound care compared with the control group, B-type natriuretic peptide was significantly lower, and 6-minute walk distance (6-MWD) was significantly longer. Walk distance (6-MWD) was significantly prolonged. The difference between the two groups was statistically significant (t = 2.172, P = 0.033; t = 2.097, P = 0.039; t = −4.594, P < 0.001). After care, patients in the study group had significantly higher scores on the activity of daily living scale and significantly lower scores on the Minnesota living with heart failure questionnaire than those in the control group. The difference between the two groups was statistically significant (t = −4.027, P < 0.001; t = 2.198, P = 0.031).
Conclusion: A refined nursing model under a risk assessment strategy, combined with early exercise rehabilitation nursing, can significantly improve the cardiac function of patients with chronic heart failure and also the quality of life of such patients.
1 Introduction
Chronic heart failure (CHF) is a complex group of clinical syndromes characterized by impaired ventricular filling or ejection capacity due to any structural or functional cardiac abnormality, mainly manifested by dyspnea, weakness (limited activity tolerance), and fluid retention (pulmonary stasis and peripheral edema), and it is an end-stage manifestation of cardiovascular disease and the most prominent cause of death (1). Patients with CHF are becoming increasingly younger, and their susceptibility to recurrent episodes, high morbidity, mortality, and rehospitalization, coupled with symptoms such as dyspnea, and the economic pressure of high medical bills, lead to a decline in their quality of life (2–6). Despite significant advances in the treatment of CHF, outcomes and disease control are still not optimal because the focus of treatment for patients with CHF remains on resuscitation in the acute phase and maintenance in the stable phase. Gu (7) and others showed that the rehabilitation exercise of early cardiac function can adjust the patient's body movement, which can repair the autonomic nerve function, thus promoting the patient's cardiac rehabilitation. However, in recent years, in the exercise rehabilitation treatment carried out in China, it has been found that there are still problems such as the lack of medical rehabilitation professional support, the lack of personalization of the existing exercise treatment program, and the fear of exercise expressed by patients (8–10); therefore, difficulties persist in the effective implementation of exercise rehabilitation treatment in patients with CHF (11, 12). Wang et al. (13) pointed out that although conventional exercise rehabilitation training can improve the cardiac function of patients to a certain extent, adverse events are prone to occur. Therefore, a safe and personalized nursing rehabilitation model that can comprehensively assess the early exercise rehabilitation of patients with CHF and meet their actual needs is needed in clinical nursing. To this end, the present study aims to explore the impact on patients with CHF using a refined nursing model, combined with early exercise rehabilitation, under a risk assessment strategy, which is reported as follows.
2 Information and methods
2.1 Clinical information
This study is experimental in nature, employing the formula for comparing the means of two independent samples in experimental research. The formula is , where n₁ denotes the sample size of the control group, n₂ denotes the sample size of the study group, σ denotes the population standard deviation, δ denotes the difference between the two population means, and Zα and Zβ denote the critical values of the standard normal distribution corresponding to α and β, respectively. This study selected α = 0.05 and β = 0.10. Preliminary trial results yielded σ = 6.10 and δ = 3.80. Consulted tables provided Zα = 1.645 and Zβ = 1.282. Integrating all values into the formula determined a final sample size of 90 cases. This study enrolled 90 patients with CHF admitted to two wards of the Cardiovascular Department at our hospital between February 2024 and November 2024. The patients were randomly assigned using a random number table to either a control group or a study group, and were placed in two separate wards: one ward exclusively for the control group and the other exclusively for the study group. The study employed a blinded design; all enrolled patients remained unaware of their group assignment, and the researchers responsible for data collection, collation, and statistical analysis were also completely uninformed of the allocation scheme. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) meet the diagnostic criteria of chronic heart failure in China Heart Failure Diagnostic and Treatment Guidelines 2018 (4); (2) cardiac function grading II to III (New York Heart Association, NYHA grading); (3) no serious dysfunction of important organs (brain, liver, lungs, kidneys); (4) sound limb function; (5) clear consciousness and smooth communication; (6) low or medium risk of exercise; and (7) informed and voluntary participation in this study. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) patients with contraindications to exercise testing and training; (2) patients with end-stage disease or no voluntary activity; (3) those with cognitive dysfunction, communication disorders, and psychiatric disorders; (4) those who are currently participating in other interventional studies. Additional exclusion criteria: (1) patients or family members requesting to withdraw themselves; and (2) sudden illness, unable to continue to participate in the study. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Jiaxing Second Hospital (approval number 2024-089-01).
2.2 Methods
A comprehensive assessment of patients with CHF in the control group and the study group includes the following: (1) general data collection: through the questioning of patients with CHF and combined with the review of the patients' historical cases, fully understanding and recording the patients' complaints, disease history, other medical history, family history, lifestyle (smoking, alcohol consumption), compliance with the standardized use of heart failure medications and adverse drug reactions, and nutritional assessment, risk factors, etc. (2) Physical examination, vital signs monitoring, auscultation of heart sounds and lung rales, observation of jugular venous filling, hepatic jugular signs, and peripheral edema. (3) Assessment of cardiac function: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), and 6-min walk distance (6-MWD). (4) Assessment of patients' ability to carry on their routine tasks by performing activities of daily living (ADLs), and assessment of patients' quality of life using the Minnesota living with heart failure questionnaire (MLHFQ).
The CHF patients in the control group underwent routine nursing care in the traditional mode. The following are the forms of oral teaching and distribution of teaching manuals and other teaching methods, including general care: dietary principles of low-salt diet, small and frequent meals, limiting sodium and water intake, remembering the amount of intake and output; rest and activities: reasonable arrangements for rest time, limiting physical activity, moderate exercise, avoiding exertion, avoiding colds; medication care: taking medication as prescribed, observing the role of medication and side effects; psychological care: ensuring adequate sleep, providing disease knowledge–related education, eliminating patients' concerns; quitting smoking and limiting alcohol, etc.
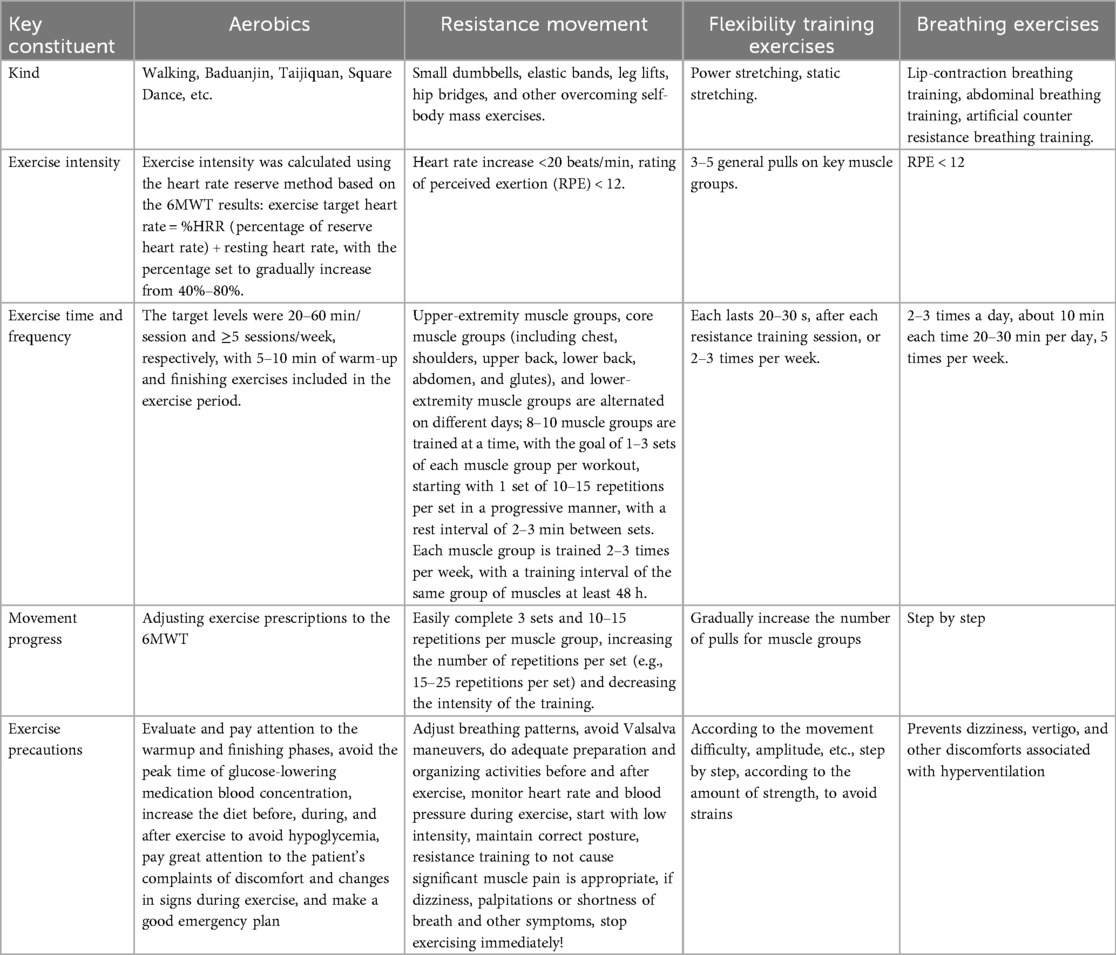
The patients with CHF in the study group applied the refined nursing model, combined with early exercise rehabilitation, under the risk assessment strategy on the basis of the control group: (1) formation of the CHF study group: (a) It consisted of the researcher herself, a cardiac rehabilitation doctor of the Department of Cardiology, a head nurse, a cardiac rehabilitation therapist, a cardiac rehabilitation nurse, two cardiovascular nurses, two data collection tools and recorders, and a data collation tool and statistician. (b) All members of the study group received learning and training on risk assessment, the refined nursing model, and theoretical knowledge related to early exercise rehabilitation in patients with CHF. Statisticians. (b) All members of the research team received study and training in risk assessment, the refined nursing model, and theoretical knowledge related to early exercise rehabilitation for patients with CHF. After training, team members selected patients for enrollment according to the nativity criteria, conducted assessments, and formulated plans and implemented interventions. The patients signed an informed consent form at the time of enrollment. (2) Implementation and application of the refined nursing model in early exercise rehabilitation of patients with CHF based on the risk assessment strategy: Phase 1: Standardized Assessment and Admission Screening (within 24 h) to identify patients suitable for early rehabilitation, ensure safety, and establish baseline data. The standardized assessment primarily encompasses the following: Collection of general patient details—physical examination—vital signs monitoring—cardiac function evaluation—assessment of ADLs and quality of life—evaluation of exercise habits and willingness to exercise—selection of the 6-min walk test (6MWT) as the exercise stress protocol (14)—Assessment of exercise risk in patients with CHF [low risk: 6MWD (15) >450 m, moderate risk: 6MWD 300–450 m; high risk: 6MWD <300 m; very high risk: 6MWD <150 m]. This study selected CHF patients classified as moderate or low risk for exercise. Phase 2: Refined early exercise rehabilitation nursing program development (refer to Chronic Heart Failure Cardiac Rehabilitation Expert Consensus 2020 Edition) (16): the general principles followed in the development of exercise prescription, including six elements: type of exercise, intensity, frequency, time, progress, and precautions, the specific content includes aerobic exercise, resistance exercise, flexibility training, and respiratory training (see Table 1 for details). Phase 3: Program Implementation and Safety Monitoring. Early exercise rehabilitation for CHF patients must adhere to the principle of “safety first, conservative progression.” Patients must comfortably complete the current intensity level (Borg RPE 11-13) in two consecutive training sessions without discomfort, while key physiological indicators remain stable: exercise heart rate increment <20 bpm, oxygen saturation >88%, blood pressure fluctuations within safe ranges, and rapid recovery of heart rate/shortness of breath within 5 min postexercise. Upon meeting these criteria, the rehabilitation program should progress sequentially: first extending duration, then increasing frequency, and finally elevating intensity. The exercise rehabilitation program must be conducted under “one-to-one supervision with continuous monitoring.” A cardiac rehabilitation therapist provides close guidance, continuously observing the patient's condition. An electrocardiogram monitor tracks the heart rate and blood oxygen levels in real time, with blood pressure measured every 5–10 min. Active questioning and communication ensure that the patient can engage in a brief conversation without any discomfort during exercise, enabling real-time assessment of their status. Clear indications for “immediate cessation of exercise” include the following: chest pain, severe arrhythmia, acute blood pressure abnormalities (systolic >220 mmHg or drop >10 mmHg with symptoms), SpO₂ plunge >5% or below 88%, and dizziness/syncope. Upon occurrence, exercise must be halted immediately, emergency services summoned, and the patient positioned for rest with oxygen administered. Subsequent documentation, analysis, and program reassessment are mandatory. Phase 4: Discharge Preparation and Long-Term Planning. Ensure patients transition smoothly to home or community-based rehabilitation, while maintaining long-term adherence. Conduct standardized assessments prior to discharge, such as 6MWD, LVEF, and MLHFQ, to quantify improvements in cardiac function and quality of life. Develop a discharge plan, provide written discharge instructions, and formulate a personalized home exercise program: recommend accessible, preferred activities (e.g., walking in local parks, practicing Tai Chi at home). Refer patients requiring ongoing rehabilitation to community cardiac rehabilitation centers; offer home-based rehabilitation services for those with mobility limitations. Conduct telephone follow-up within 24–72 h postdischarge.
2.3 Evaluation indicators
1. The evaluation of cardiac function in patients with CHF includes LVEF, BNP, and 6MWD. LVEF: data collected according to the report of cardiac ultrasound, with a normal range of 50%–70%; the lower the value, the lower the myocardial contractility and the worse the heart's contractile function. BNP: according to the report of laboratory examination, with a normal value of 0–100 ng/mL, the higher the value, the more serious the heart failure. 6MWD reference Standard (14): <150 m severe cardiac insufficiency, 150–425 m moderate cardiac insufficiency, 426–550 m mild cardiac insufficiency, the larger the value, the better the patient's cardiac function.
2. Assessment of daily life self-care ability (17) was assessed using the ADL scale with a full score of 100 points. A total score of ≤40 was classified as severe dependence, all of which required care by others; a total score of 41–60 was classified as severe dependence, most of which required care by others; a total score of 61–99 was classified as mild dependence, a small portion of which required care by others; and a total score of 100 was classified as no need for dependence and no need for care by others. The higher the score of ADL, the better the ability of the patient's daily living activities.
3. Quality of life assessment: assessed by MLHFQ (18) using a 6-point Likert scale from 0 to 5: 21 specification items, 0—none, 1—very slight, 2—slightly, 3—slightly obvious, 4—obviously, and 5—very obvious, with a range of scores from 0 to 105 points on three dimensions: symptomatic, physical activity, and affective, with higher scores implying a poorer quality of life for the patient.
2.4 Statistical methods
SPSS 24.0 statistical software was applied to analyze the data. Measurement data conforming to normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s), an independent sample t-test was used for intergroup comparison, and a paired sample t-test was used for intragroup comparison; counting data were expressed as the frequency and constitutive ratio, and a χ2 test was used for comparison. A value of P < 0.05 was considered as the difference was statistically significant.
3 Results
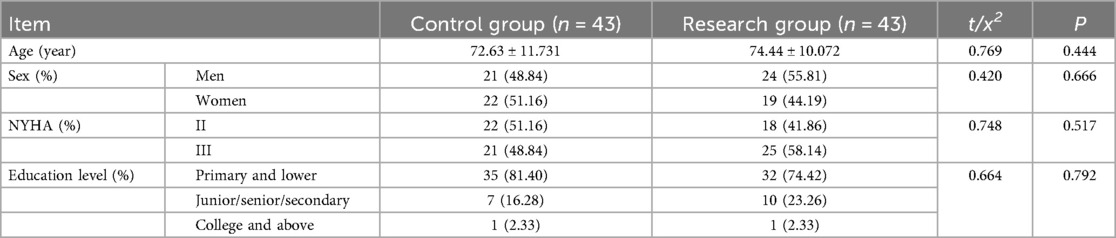
A total of 90 cases of research subjects were initially included in this study, due to changes in condition during treatment, two patients in each of the control group and the research group withdrew from the study prematurely, and finally a total of 86 patients completed the study, 43 patients each in the control group and the research group. The general information of the two groups was compared, and the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05), and was comparable, see Table 2.
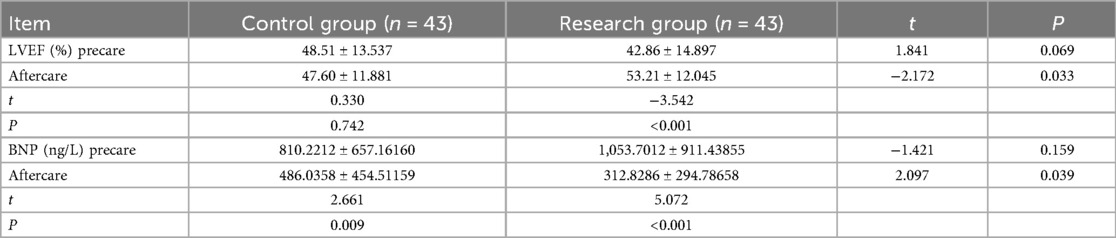
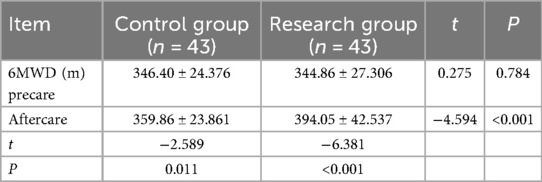
The LVEF and BNP of the two groups, and the 6MWD of the study group were compared () and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05), as given in Tables 3, 4.
A comparison of ADL between the two groups () showed that the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05), see Table 5.
The MLHFQ of the two groups was compared (), and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05), see Table 6.
4 Discussion
4.1 Refined care model under the risk assessment strategy, combined with early exercise rehabilitation, improves cardiac function in patients with CHF
In this study, the percentage of LVEF in the study group increased significantly compared with that in the control group, the BNP value decreased significantly compared with that in the control group, and the 6MWD in the study group increased significantly after care compared with before care (P < 0.05), all of which was statistically significant, suggesting that the refined care model under the risk assessment strategy, in conjunction with early exercise rehabilitation, improves the cardiac function of patients with CHF, which may be related to the implementation of early exercise rehabilitation in these patients. The Heidenreich et al. (19) study, which deals with exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation for the improvement of cardiac function in patients with heart failure, is recommended as Class I evidence level A. Early exercise rehabilitation can effectively promote limb muscle contraction and skeletal muscle blood flow velocity, speed up the reversal of the symptoms of myocardial damage, and accelerate the rate of cardiac function recovery, and risk assessment is a prerequisite for and a guarantee of patients' cardiac rehabilitation, as it involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's condition to identify potential risks, followed by the implementation of appropriate measures to mitigate or eliminate these risks, thereby ensuring the safety of the rehabilitation process. The results of one study (20) showed that impaired HRR1 (1-min postexercise heart rate decline value) increased the risk of all-cause mortality by 70% (HR = 1.70), highlighting the central role of dynamic risk assessment in rehabilitation. It is a scientific approach that can help people to better understand and manage all types of risk. In this study, the research group conducted a comprehensive risk assessment of early exercise rehabilitation for patients with CHF and applied 6MWT to select CHF patients with a low degree of exercise risk whose risk stratification was medium or low risk, which avoided the adverse events caused by early exercise rehabilitation The exercise rehabilitation could be implemented safely without any events, which is in line with the findings of scholars such as Sun et al. (21), Liu et al. (22), and so on. The use of the risk-assessed exercise rehabilitation nursing model can improve the cardiac function of patients with CHF, which is consistent with the findings of Rongmei (23) and Song et al. (24). Refined nursing, on the other hand, is based on the traditional nursing model to specify, detail, and standardize the nursing content, constantly summarize the clinical nursing experience, break down the nursing procedures in fine detail, and implement targeted and personalized quality nursing services, which can better improve the prognosis of patients. A number of studies (25, 26) have confirmed the application of refined nursing care in surgical patients and its facilitating effect on the recovery of postoperative patients, as well as an improvement in patients' psychological status. In this study, the research group formulated a personalized early exercise rehabilitation nursing program for patients with CHF according to their aerobic exercise, resistance exercise, flexibility training, and respiratory training exercise prescription, which refined the exercise rehabilitation nursing link, improved patient adherence, and could lead to a better implementation of the exercise rehabilitation and an improvement in the patients’ cardiac function. Therefore, the refined nursing care model under the risk assessment strategy, combined with early exercise rehabilitation, can improve the cardiac function of patients with CHF.
4.2 Refined care model under the risk assessment strategy, combined with early exercise rehabilitation, improves the quality of life of patients with CHF
In this study, the ADL value of the study group increased significantly compared with that of the control group, and the MLHFQ value decreased significantly compared with that of the control group (P < 0.05), which are statistically significant, indicating that the refined nursing model under the risk assessment strategy, combined with early exercise rehabilitation, can improve the quality of life of patients with CHF. This may be related to the fact that the refined nursing model under the risk assessment strategy can improve the process of implementation of early exercise rehabilitation. This, in turn, may be related to the fact that early motor rehabilitation can improve the process of implementation of early motor rehabilitation. Through early motor rehabilitation, nerve excitation can be transmitted to the central nervous system, which can form a sensory stimulation of varying depths and shades, release a large number of nerve impulses, accelerate the reorganization of nerve cells, speed up the formation of collateral circulation, activate the neural pathways in the latent state, play its own role in plasticity, and improve the level of nerve growth factors in the intracranial cortex and hippocampus, which will ultimately promote the restoration of limb function (27). Relevant studies have shown (28) that exercise rehabilitation is conducive to increasing the level of secretion of doxylamine and other substances in the brain and improving the emotional and psychological states of patients, thereby accelerating the recovery of the condition and improving their overall physical and mental health. At the same time, cardiac rehabilitation can improve the clinical prognosis of patients with heart failure, reduce the readmission and mortality rates, and improve the quality of life of patients. The use of rehabilitation training can help change the patient's passive training regimen to an active one. Applying the refined nursing model under the risk assessment strategy will help to adjust the previous traditional training program, which is more targeted, increase the levels of the patient's acceptance and cooperation with exercise, reduce the patient's anxiety and fear, promote the recovery of the heart pump function, and decrease the number of adverse cardiovascular events (29), all of which will further enhance the patient's daily life activity, exercise endurance, and the psychological state, raising hopes for leading a better life in the future.(30, 31). Therefore, it can be concluded that the refined care model under the risk assessment strategy, combined with early exercise rehabilitation, can improve the quality of life of patients with CHF.
5 Conclusion
In summary, refined nursing care under the risk assessment strategy is a prospective nursing intervention method that assesses the possible risks of patients, determines the relevant nursing risk factors and the degree of risk, and then provides hierarchical nursing care for the patients to ensure that they can get the appropriate interventions, interventions that are more precise, scientific, and targeted. Such a refined nursing care will help effectively avoid the pitfalls of conventional nursing(32). The risk assessment strategy can predict the possible adverse events that may occur in the process of rehabilitation and exercise, and the refined nursing care can formulate personalized and practical nursing intervention plans for patients through a comprehensive and detailed assessment of patients. Therefore, guided by risk assessment strategies, the refined nursing model has standardized and personalized the implementation of early exercise rehabilitation measures. This has enhanced the acceptance, cooperation, and adherence to exercise among patients with CHF while simultaneously reducing the incidence of adverse events. This model effectively safeguards the safety and implementation outcomes of early exercise rehabilitation in patients with CHF. Modifying the physiological mechanisms (see Discussion sections 4.1 and 4.2) improves cardiac function and elevates patients' quality of life.
5.1 Limitations of this study
The sample size in this study was small, the intervention time was short, and none of the patients were involved in follow-up. In the future, the sample size can be expanded, and patients can be followed up regularly after discharge to prolong the intervention time and observe the long-term clinical effects to further confirm the findings of this study.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Hospital of Jiaxing. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
YS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. HJ: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Methodology. LW: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Data curation, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research work was supported by the Jiaxing Municipal Science and Technology Programme (2024AD30094) and the Jiaxing Municipal Institute-Level Programme (2023YJ005).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence, and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors, wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Haozhu C, Nanshan Z, Zaiying L. Internal Medicine. Beijing: People’s Health Publishing House (2018). p. 166.
2. Wang H, Chai K, Du M, Wang S, Cai JP, Li Y, et al. Prevalence and incidence of heart failure among urban patients in China: a national population-based analysis. Circ Heart Fail. (2021) 14(10):e008406. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.121.008406
3. Jones NR, Roalfe AK, Adoki I, Richard Hobbs FD, Taylor CJ. Survival of patients with chronic heart failure in the community: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol. Syst Rev. (2018) 7(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s13643-018-0810-x
4. Chinese Medical Association Cardiovascular Disease Branch Heart Failure Working Group, Chinese Medical Doctor Association Heart Failure Professional Committee, Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Cardiovascular Diseases. Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure 2018. Chin J Cardiovasc Dis. (2018) 46(10):760–89. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2018.10.004
5. Qingyan Z, Xiaomei X, Yan Y. Focusing on the effects of a nursing model combined with cardiac rehabilitation exercises on patients with chronic heart failure. J Qilu Nurs. (2022) 28(7):17–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7256.2022.07.005
6. Kitzman DW, Whellan DJ, Duncan P, Pastva AM, Mentz RJ, Reeves GR, et al. Physical rehabilitation for older patients hospitalized for heart failure. N Engl J Med. (2021) 385(3):203–16. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2026141
7. Yuqing G, Lili Z, Qingyin L, Dongyun Z, Yu H, Yuan W, et al. Development of an early cardiac rehabilitation nursing protocol for patients undergoing emergency percutaneous coronary intervention. Chin J Nurs. (2021) 56(4):7. doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2021.04.004
8. Li H, Liu Y, Liu Y, Xu Z, Pan P, Zeng L. Impact of exercise training on exercise tolerance, cardiac function and quality of life in individuals with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2025) 25(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04649-0
9. Chen L, Li JY, Ren ZQ, Wang LC, Huang PY, Jiang WJ, et al. Identifying factors contributing to kinesiophobia in patients post-percutaneous coronary intervention. BMC Nurs. (2025) 24(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-02810-w
10. Zihan W, Wenjing Y, Xiangyi Z, Xiaofeng K, Chunying H, Yue W. Meta-synthesis of qualitative studies on the formation and resolution of exercise phobia in cardiac rehabilitation patients. Chin J Nurs Manag. (2024) 24(5):725–30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2024.05.016
11. Isernia S, Pagliari C, Morici N, Toccafondi A, Banfi PI, Rossetto F, et al. Telerehabilitation approaches for people with chronic heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med. (2022) 12(1):64. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010064
12. Huiying G, Peixia C, Ningning Y, Suhua Y. Evidence synthesis for phase I exercise rehabilitation in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Evid Based Nurs. (2024) 10(19):3462–8. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.2095-8668.2024.19.007
13. Dan W, Jianmei J, Ke G. Research progress of early exercise training in cardiac rehabilitation of patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Nurs Rehabil. (2022) 21(8):85–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9875.2022.08.025
14. Chinese Society of Geriatrics, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Expert consensus on the clinical application of the 6-minute walk test in elderly patients. Chin J Geriatr. (2020) 39(11):1241–50. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2020.11.001
15. Jones PW, Quirk FH, Baveystock CM, Littlejohns P. A self-complete measure of health status for chronic airflow limitation. The St. George’s respiratory questionnaire. Am Rev Respir Dis. (1992) 145(6):1321–7. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.6.1321
16. Specialized Committee on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Rehabilitation, Chinese Society of Rehabilitation Medicine. Chinese Expert consensus on cardiac rehabilitation for chronic heart failure. Chin J Intern Med. (2020) 59(12):942–52. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20200309-00210
17. Ling L, Jinghong L. Application of activities of daily living assessment in patients with advanced cancer. Gen Nurs. (2021) 19(13):1845–7. doi: 10.12104/j.issn.1674-4748.2021.13.036
18. Zu D, Zhang S, Wang N. Effect of collaborative rehabilitation nursing intervention on self-care ability and quality of life of chronic heart failure patients. Chin Fam Med. (2022) 20(1):169–71, 174. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002304
19. Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Joint Committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. (2022) 145(18):e895–1023. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063. Erratum in: Circulation. (2022) 145(18):e1033. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001073. Erratum in: Circulation. (2022) 146(13):e185. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001097. Erratum in: Circulation. (2023) 147(14):e674. doi: 10.1161/CIR.000000000000114235363499
20. Jou J, Zhou X, Lindow T, Brudin L, Hedman K, Ekström M, et al. Heart rate response and recovery in cycle exercise testing: normal values and association with mortality. Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2025) 32(1):32–42. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwae308
21. Li S, Haiyan G, Guanhua X, Zhiming C. Research progress on risk assessment tools for osteoporosis with sarcopenia in the elderly. Nurs Res. (2023) 37(4):650–4. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2023.04.016
22. Gui-juan L, Fan-li Z, Lu-yi W, Hua-hua Z. The impact of nursing interventions under risk assessment strategies on postoperative recovery in patients undergoing laparoscopic myomectomy. Jilin Med. (2023) 44(1):216–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0412.2023.01.069
23. Rongmei L. Effects of risk assessment-based rehabilitation nursing model on cardiac function and quality of life in heart failure patients. Mod J Integr Med. (2024) 33(6):858–860. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2024.06.026
24. Xiaopei S, Zhongping X, Zhengfang Z, Aihua Z. Effects of cardiac rehabilitation training based on rehabilitation risk assessment on cardiac function and cardiovascular event incidence in patients following percutaneous coronary intervention for acute coronary syndrome. J Bengbu Med Coll. (2023) 48(4):530–3. doi: 10.13898/j.cnki.issn.1000-2200.2023.04.026
25. He K, Li Q, Hou Y, He Y, Yue X. Effect of a refined nursing model based on nursing quality feedback on the postoperative mental state of patients with laryngeal cancer. Am J Transl Res. (2021) 13(6):6525–33.34306393
26. Pan J, Liu X, Chen D, Zhao W, Tao J, Wu S. Effect of refined management on the recovery of patients undergoing sinusitis surgery via nasal endoscopy. Am J Transl Res. (2023) 15(1):522–30.36777834
27. Yang Z. Efficacy of conventional treatment combined with early rehabilitation on elderly diabetic stroke patients and its effect on daily living ability. Clin Med. (2022) 42(9):72–4. doi: 10.19528/j.issn.1003-3548.2022.09.025
28. Qiuyun C. Analysis of the value of early targeted exercise rehabilitation nursing on cardiac function and quality of life in patients with chronic heart failure. Knowl Cardiovasc Dis Prev Treat. (2023) 13(33):87–88+93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3015(x).2023.33.029
29. Lijuan G, Lu C, Pingping C. The impact of early cardiac rehabilitation intervention on exercise phobia and exercise compliance in patients following percutaneous coronary intervention for coronary heart disease. Cardiovasc Dis Prev Treat Knowl. (2024) 14(8):56–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3015(x).2024.08.017
30. Lishang L. Effects of early systematic rehabilitation training on daily life activities of hemiplegic stroke patients. China Mod Drug Appl. (2024) 18(8):173–6. doi: 10.14164/j.cnki.cn11-5581/r.2024.08.047
31. Keifer J. Regulation of AMPAR trafficking in synaptic plasticity by BDNF and the impact of neurodegenerative disease. J Neurosci Res. (2022) 100(4):979–91. doi: 10.1002/jnr.25022
Keywords: risk assessment strategy, refined care, early exercise rehabilitation, chronic heart failure, cardiac function, quality of life
Citation: Sun Y, Jin H and Wu L (2025) Impact of a refined nursing model combined with early exercise rehabilitation on patients with chronic heart failure under a risk assessment strategy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1638025. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1638025
Received: 30 May 2025; Accepted: 15 September 2025;
Published: 8 October 2025.
Edited by:
Marilena Anastasaki, University of Crete, GreeceReviewed by:
Jiang Shijiu, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, ChinaOleksii Korzh, Kharkiv National Medical University, Ukraine
Copyright: © 2025 Sun, Jin and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haiqin Jin, MTA2NzY1ODgzOUBxcS5jb20=
 Yan Sun
Yan Sun Haiqin Jin*
Haiqin Jin* Lingsha Wu
Lingsha Wu