- 1Department of Cardiology, Qingpu Branch of Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Hospital Infection Management, Qingpu Branch of Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Background: Acute myocardial infarction in the elderly often leads to significant left ventricular structural remodeling, which adversely affects prognosis. This study aims to evaluate the effects of intensive rosuvastatin therapy on markers of ventricular remodeling and cardiac function following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in elderly patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
Methods: This study enrolled 100 patients aged ≥60 years with STEMI who underwent emergency PCI. The patients were randomly assigned to either an intensive therapy group (n = 50), receiving rosuvastatin 20 mg/day, or a control group (n = 50), receiving 10 mg/day. Differences in lipid profiles, serum inflammatory markers, fibrosis indicators, and echocardiographic parameters were compared between the two groups before treatment and after 8 weeks of therapy.
Results: After 8 weeks of treatment, the intensive group showed significantly reduced serum inflammatory levels compared to the control group, including C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) (P < 0.05). Markers of ventricular remodeling also improved in the intensive group, with lower levels of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), galectin-3, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) compared to the control group (P < 0.05), while levels of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-4 (TIMP-4) were significantly higher (P < 0.05). Additionally, after treatment, the intensive group demonstrated significantly higher levels of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), stroke volume, and peak systolic velocity at the lateral mitral annulus (TDI s′-l) compared to the control group (P < 0.05). Conversely, the left ventricular end-systolic diameter (LVESD) and left ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV) were significantly lower in the intensive group than in the control group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: In elderly patients with STEMI, high-dose rosuvastatin demonstrates superior therapeutic efficacy compared to conventional-dose therapy in alleviating inflammatory responses, improving ventricular remodeling, and enhancing cardiac function.
Clinical Trial Registration: [www.chictr.org.cn], identifier [ChiCTR2200066956].
1 Introduction
ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is the most severe form of acute coronary syndrome (ACS). It is typically caused by thrombus formation following the rupture or erosion of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to acute and complete occlusion of a coronary artery, which results in sustained myocardial ischemia and necrosis (1). As a critical and life-threatening condition, STEMI has a sudden onset and rapid progression. Without timely and appropriate treatment, it often leads to extensive myocardial cell necrosis, which can subsequently result in ventricular remodeling and cardiac dysfunction, among other serious complications (2). Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is currently a key therapeutic approach for STEMI, capable of rapidly reopening the infarct-related artery, restoring blood perfusion, and salvaging jeopardized myocardium. Although the implementation of chest pain centers has significantly shortened the door-to-wire (D-to-W) and symptom-onset to first medical contact (S-to-FMC) times for STEMI patients undergoing PCI, thereby effectively reducing mortality and disability rates, a considerable number of patients still experience ventricular remodeling and develop heart failure after PCI, particularly among elderly individuals (3). With population aging and lifestyle changes, the proportion of elderly patients with STEMI has been gradually increasing (4). This subset of patients is more susceptible to ventricular remodeling due to multiple comorbidities, poor vascular conditions, and reduced myocardial reserve, resulting in generally poorer prognoses (5). Previous studies have shown that intensive rosuvastatin therapy can significantly improve clinical outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease without increasing adverse events (6–8). However, robust evidence is still lacking regarding whether intensive statin therapy can improve ventricular remodeling and cardiac function in elderly patients undergoing emergency PCI.
The pathophysiological process of left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction is complex. Previous studies have demonstrated that systemic inflammation, as well as extracellular matrix remodeling and fibrosis, play critical roles in the initiation and progression of left ventricular remodeling (9). C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) reflect the level of systemic inflammation (10), while Galectin-3, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-4 (TIMP-4), and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) are associated with extracellular matrix remodeling and fibrosis (11). Therefore, the combined assessment of inflammatory markers and fibrosis-related factors may provide a more comprehensive evaluation of ventricular remodeling and the progression of heart failure following myocardial infarction.
As a guideline-recommended routine medication after STEMI, statins competitively inhibit endogenous enzymes involved in total cholesterol (TC) synthesis, thereby reducing serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels (12). Studies have shown that statins may exert multiple beneficial effects beyond lipid-lowering, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant actions, improvement of endothelial function, plaque stabilization, inhibition of myocardial fibrosis, and promotion of angiogenesis (13, 14). These pleiotropic effects are thought to be mediated through mechanisms such as inhibition of isoprenylation of small G-proteins, enhancement of nitric oxide production, and modulation of various signaling pathways (15). Such pleiotropic effects may contribute to reducing ischemia-reperfusion injury, enhancing microvascular perfusion, and inhibiting ventricular remodeling in patients with STEMI. Rosuvastatin, a hydrophilic statin widely used in clinical practice, has been shown to significantly reduce the incidence and mortality of cardiovascular diseases (16). Compared to lipophilic statins such as simvastatin and atorvastatin, rosuvastatin has higher bioavailability, a lower incidence of muscle-related adverse events, and a reduced risk of drug–drug interactions (17). However, direct comparative studies between intensive and conventional statin therapy regarding their effects on ventricular remodeling and left ventricular function in elderly patients undergoing emergency PCI for STEMI remain scarce. Therefore, the primary aim of this study is to investigate the effects of intensive rosuvastatin therapy on lipid profiles, myocardial fibrosis, serum inflammatory markers, and left ventricular function in elderly patients with STEMI, in order to provide a clinical basis for optimizing treatment strategies.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design
This study was a randomized, parallel-controlled, open-label trial conducted at Qingpu Branch of Zhongshan Hospital affiliated to Fudan University. The final outcome assessment was performed in a blinded manner. Laboratory testing personnel, echocardiography evaluators, and data analysts were all blinded to the treatment allocation of the patients. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Qingpu Branch of Zhongshan Hospital. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to enrollment. All procedures were conducted in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki by the World Medical Association. The study was registered on the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (www.chictr.org.cn) under the registration number ChiCTR2200066956.
2.2 Patients and drug intervention
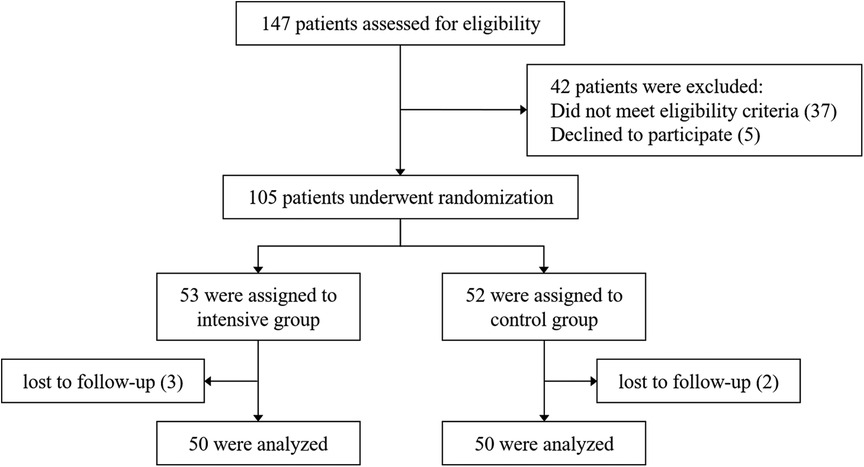
From March 2023 to March 2024, a total of 147 patients admitted to our hospital for acute STEMI were assessed, of whom 105 met the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Using a computer-generated randomization system, patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to either the intensive group (rosuvastatin, 20 mg/d) or the control group (rosuvastatin, 10 mg/d). The first dose of rosuvastatin was administered prior to emergency PCI. Both groups received treatment for 8 weeks. In the end, 100 patients completed the follow-up. A detailed flowchart is shown in Figure 1. The diagnosis of STEMI was confirmed according to the 2018 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines (18). In accordance with the 2023 ESC guidelines for the management of ACS (19), all patients received guideline-directed medical therapy in addition to statin treatment, including dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin combined with either ticagrelor or clopidogrel), β-blockers, and renin–angiotensin system inhibitors, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI), angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARB), or angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitors (ARNI). To ensure patient compliance, monitor adverse events, and record cardiovascular events, researchers conducted telephone follow-ups every two weeks. At week 8, patients were scheduled for an outpatient visit. Medication adherence was assessed using the pill count method.
2.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria were as follows: age ≥60 years; electrocardiographic ST-segment elevation meeting the diagnostic criteria for STEMI; first occurrence of myocardial infarction; successful emergency PCI performed within 12 h of symptom onset. Exclusion criteria were as follows: severe heart failure (Killip class IV); hepatic dysfunction [alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels persistently elevated to more than three times the upper limit of normal]; renal dysfunction [estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <30 ml/min/1.73 m2]; use of antioxidant agents (including coenzyme Q10 and trimetazidine) or lipid-lowering drugs (including statins, fibrates, PCSK9 inhibitors, ezetimibe, niacin and its derivatives) within 2 weeks prior to hospitalization; familial hypercholesterolemia; autoimmune diseases; malignant tumors; acute infections; severe hematologic disorders; cognitive impairment; allergy to rosuvastatin.
2.4 Blood index testing
Venous blood samples were collected from all patients at hospital admission and after 8 weeks of rosuvastatin treatment. Lipid profiles were assessed, including triglycerides (TG), TC, LDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), apolipoprotein AI (ApoAI), apolipoprotein B (ApoB), and lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)]. Liver function was evaluated by measuring ALT and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels. Additional laboratory parameters included creatine kinase (CK), high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP), IL-6, TNF-α, N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT). The levels of ICAM-1, galectin-3, TIMP-4, and MMP-9 were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits (MEIMIAN, Jiangsu, China).
2.5 Echocardiographic assessment
Transthoracic echocardiography was performed at baseline and after 8 weeks of treatment by an experienced sonographer who was blinded to both treatment allocation and the timing of the assessments (baseline and post-treatment). For each parameter, the average value of three consecutive cardiac cycles was recorded. Left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV), left ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV), and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) were measured using the Simpson's biplane method. M-mode echocardiography in the parasternal long-axis view was used to assess left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD), left ventricular end-systolic diameter (LVESD), and interventricular septal thickness (IVST). In the apical four-chamber view, tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) was employed to measure the peak systolic velocity at the septal (s′-s) and lateral (s′-l) mitral annulus, and the average of these two values (s′-av) was calculated.
2.6 Study endpoints
The primary endpoints of this study were the changes in inflammatory markers, ventricular remodeling indicators, and LVEF after 8 weeks of treatment.
2.7 Sample size calculation
Based on relevant literature and previous studies (20), the expected difference in mean LVEF between the two groups was set at 3.5%, with a standard deviation of 6%. Using a two-sided test with a significance level (α) of 0.05 and a power (1 − β) of 0.80, the required sample size was calculated to be 45 patients per group. Considering an approximate dropout rate of 10%, a minimum of 50 patients was required in each group.
2.8 Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 26. Variables with a normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Between-group comparisons were performed using the independent samples t-test, and within-group comparisons before and after treatment were analyzed using the paired t-test. Non-normally distributed data were expressed as median with interquartile ranges (Q1, Q3), with between-group comparisons conducted using the Mann–Whitney U test and within-group comparisons using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Categorical variables were presented as counts and percentages. Comparisons between the two groups were performed using the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test. A P-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant for all analyses.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics of the study population
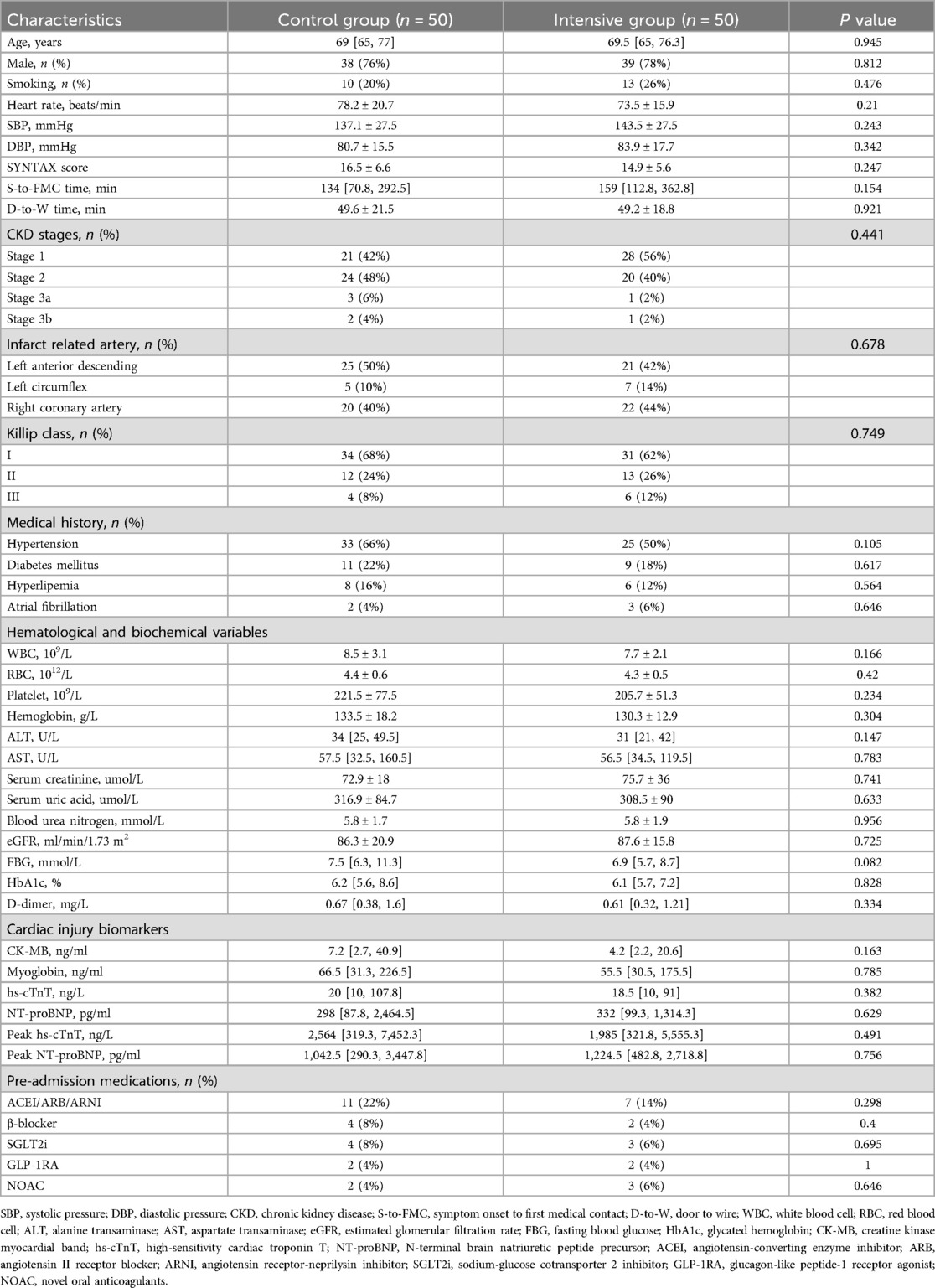
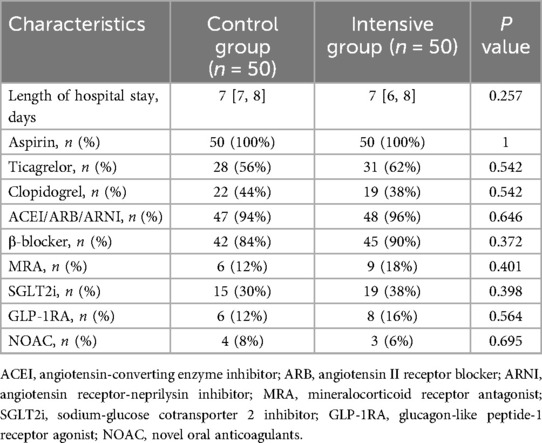
A total of 147 STEMI patients aged ≥60 years were initially screened. Forty-two patients either did not meet the inclusion criteria or declined to participate. The remaining 105 patients were randomly assigned to the intensive group (n = 53) and the control group (n = 52). During the follow-up period, 3 patients in the intensive group and 2 patients in the control group were lost to follow-up. Ultimately, 50 patients in each group completed the entire study protocol and were included in the final analysis. The baseline and clinical characteristics of the participants are summarized in Table 1. The control group included 38 male and 12 female patients, with a median age of 69 [65, 77] years. The intensive group included 39 male and 11 female patients, with a median age of 69.5 [65, 76.3] years. There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in terms of age, sex, smoking history, heart rate, blood pressure at admission, comorbidities, laboratory biochemical tests, cardiac injury and necrosis markers, or pre-admission medication use (P > 0.05). Additionally, no significant differences were observed in S-to-FMC time, D-to-W time, or SYNTAX scores between the two groups (P > 0.05). As shown in Table 2, the length of hospital stay and discharge medication regimens also did not differ significantly between the groups (P > 0.05).
3.2 Changes in lipid profiles, liver function, and CK levels
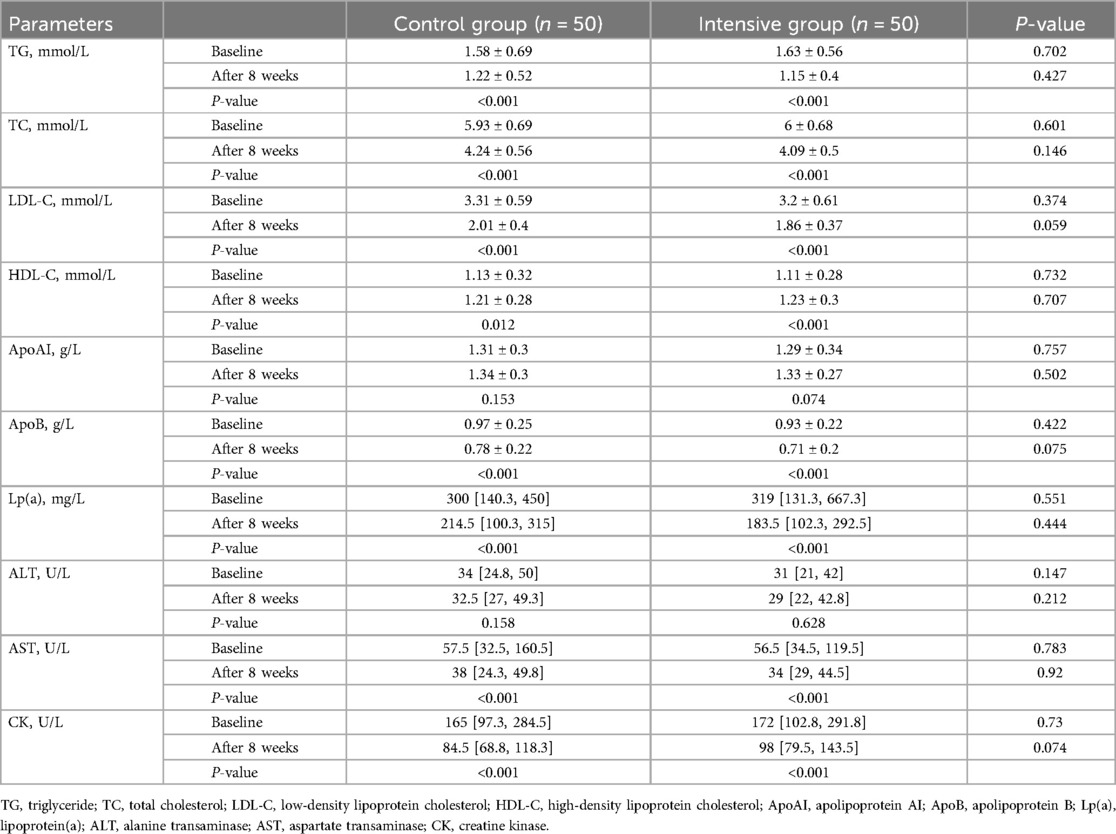
Before treatment, there were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in lipid parameters, including TG, TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, ApoAI, ApoB, and Lp(a) (P > 0.05). After 8 weeks of rosuvastatin therapy, both groups showed significant reductions in TG, TC, LDL-C, ApoB, and Lp(a) levels (P < 0.05), as well as significant increases in HDL-C levels (P < 0.05), while ApoAI levels remained unchanged (P > 0.05). After treatment, the levels of TG, TC, and LDL-C were lower in the intensive group compared to the control group, but the differences were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). There were no significant differences in HDL-C, ApoAI, ApoB, and Lp(a) levels between the two groups after treatment (Table 3).
Before treatment, no statistically significant differences were observed between the two groups in liver function markers (ALT, AST) or CK levels (P > 0.05). Compared with baseline, both groups exhibited significant decreases in AST and CK levels after treatment (P < 0.05), while ALT levels showed no significant change (P > 0.05). After treatment, there were no significant differences in ALT and AST levels between the intensive and control groups (P > 0.05). Although CK levels were higher in the intensive group than in the control group, the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05) (Table 3). In addition, two patients in the intensive group and one patient in the control group experienced myalgia after treatment, with no significant difference between the groups (P > 0.05). No major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), such as repeat PCI, hospitalization for heart failure, or cardiac death, were observed in either group.
3.3 Changes in serum inflammatory factors
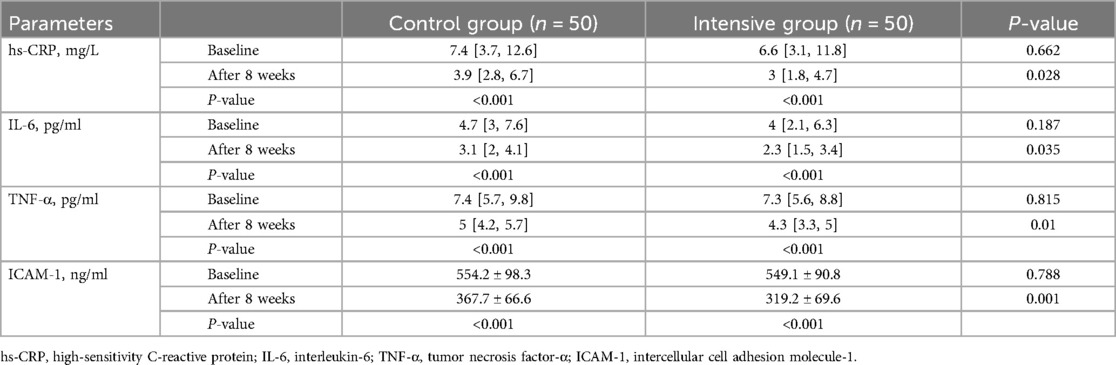
Before treatment, there were no significant differences in the concentrations of hs-CRP, IL-6, TNF-α, and ICAM-1 between the two groups (P > 0.05). After treatment, serum levels of hs-CRP, IL-6, TNF-α, and ICAM-1 decreased in both groups (P < 0.05), with the reductions being more pronounced in the intensive group compared to the control group (P < 0.05) (Table 4).
3.4 Changes in indicators of ventricular remodeling and myocardial fibrosis
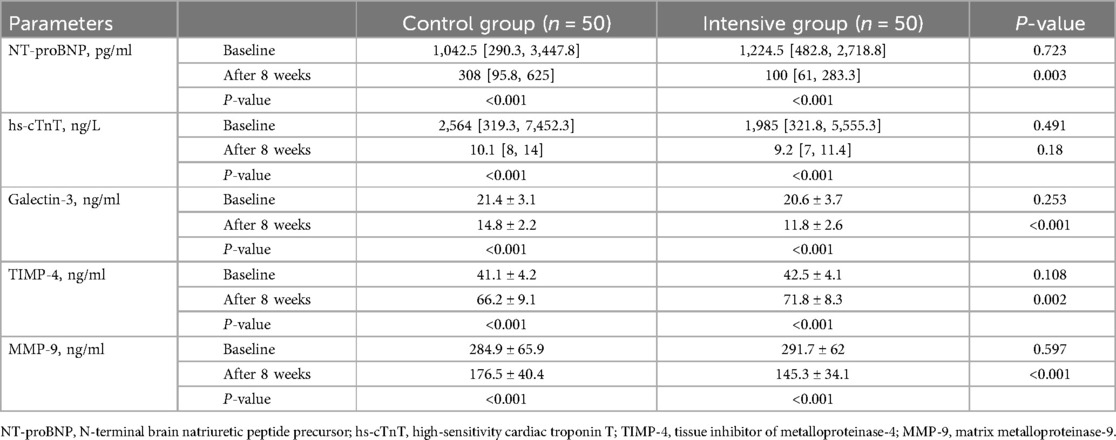
Before treatment, there were no significant differences in NT-proBNP, hs-cTnT, galectin-3, TIMP-4, and MMP-9 levels between the two groups (P > 0.05). After treatment, levels of NT-proBNP, hs-cTnT, Galectin-3, and MMP-9 in both groups significantly decreased (P < 0.05), while TIMP-4 levels significantly increased (P < 0.05). Post-treatment comparisons between groups showed that the intensive group had significantly lower levels of NT-proBNP, Galectin-3, and MMP-9 compared to the control group (P < 0.05), and significantly higher TIMP-4 levels (P < 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in hs-cTnT levels between the two groups (P > 0.05) (Table 5).
3.5 Changes in echocardiographic parameters
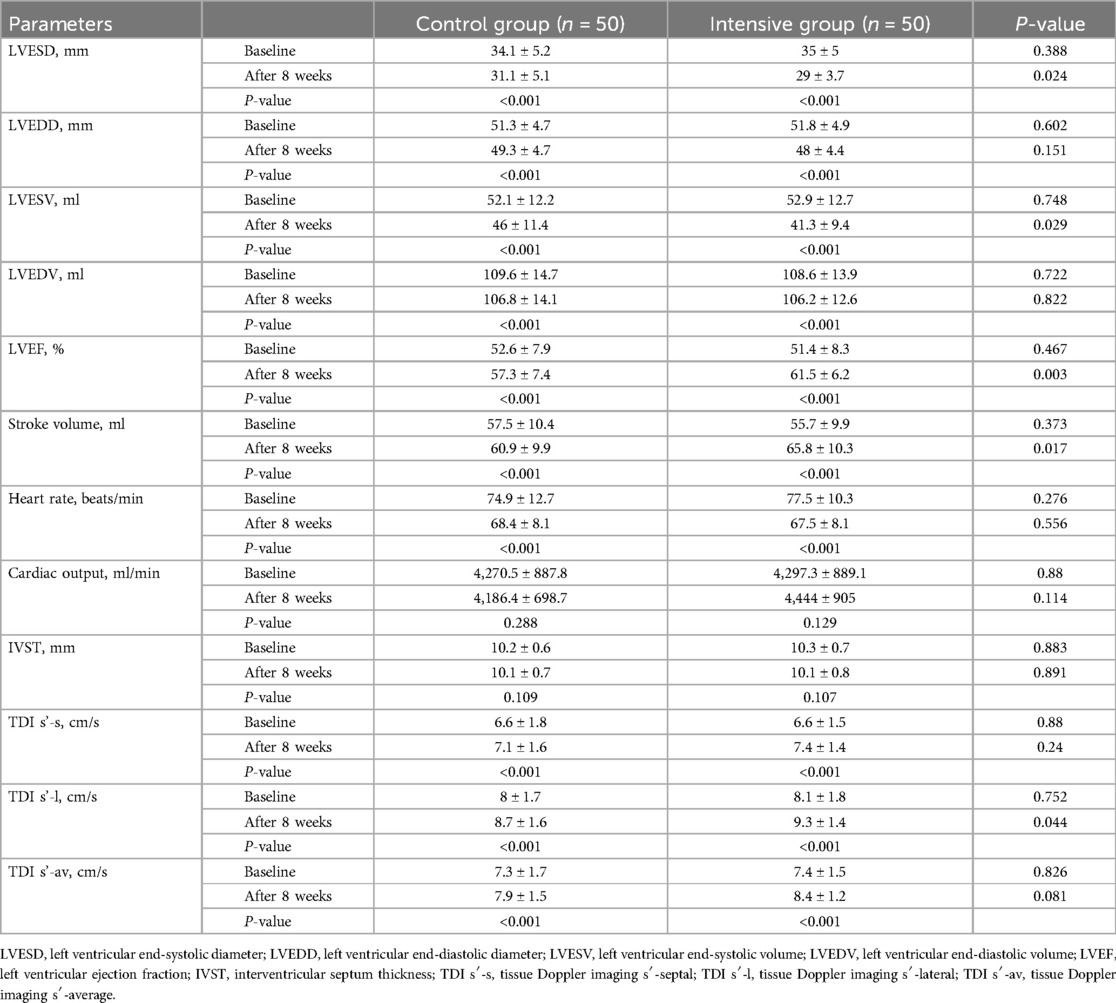
At baseline, there were no significant differences in all measured parameters between the two groups (P > 0.05). After 8 weeks of treatment, both groups showed a downward trend in LVESD, LVEDD, LVESV, and LVEDV compared to baseline (P < 0.05), while LVEF, stroke volume, and TDI parameters (TDI s′-s, TDI s′-l, and TDI s′-av) improved (P < 0.05). Intergroup comparisons after treatment revealed that the intensive group had significantly lower LVESD and LVESV values (P < 0.05), and significantly higher LVEF and stroke volume compared to the control group (P < 0.05). Furthermore, improvement in TDI s′-l was greater in the intensive group than in the control group (P < 0.05). Although heart rate decreased significantly from baseline in both groups (P < 0.05), there was no significant difference between the two groups after treatment (P > 0.05). After 8 weeks, no significant differences were observed between the two groups in cardiac output or IVST (P > 0.05) (Table 6).
4 Discussion
Patients with STEMI are prone to ventricular remodeling and heart failure due to acute myocardial ischemic injury. Studies have shown that rosuvastatin may improve left ventricular remodeling through its anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects (20). According to the recommendations of the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the ESC, high-intensity rosuvastatin (20 mg/d) offers superior lipid-lowering efficacy and cardiovascular protection for STEMI patients (21, 22). The results of this study indicate that, compared with moderate-intensity rosuvastatin (10 mg/d), a dosage of 20 mg/d is more effective in attenuating the postoperative inflammatory response, suppressing ventricular remodeling, and improving cardiac function in elderly patients undergoing PCI, without causing significant adverse effects on liver function.
Patients with acute myocardial infarction often exhibit lipid metabolism disorders, characterized by elevated levels of LDL-C, TG, TC, and Lp(a), along with reduced HDL-C levels (23). LDL-C is an independent risk factor for acute myocardial infarction, and patients with elevated LDL-C levels have a higher risk of recurrent myocardial infarction during long-term follow-up (24, 25). ApoB is the core protein of atherogenic lipoproteins such as LDL. In this study, after 8 weeks of rosuvastatin treatment, both groups showed significant improvements in lipid profiles. Although the differences between the two groups were not statistically significant, the reductions in LDL-C and ApoB were slightly greater in the intensive group, suggesting a potential advantage for secondary prevention of cardiovascular events. A previous study on elderly Chinese patients with coronary heart disease compared the effects of 10 mg and 20 mg rosuvastatin. After four months of treatment, there were no significant differences in lipid parameters (including LDL-C, TG, TC, and HDL-C) between the two groups, and the incidence of adverse events was similar (26). These findings are consistent with our results. It should be noted that acute myocardial infarction can lead to significant elevations in AST and CK levels. Our study demonstrated that high-dose rosuvastatin had no adverse effect on liver function and did not lead to increased ALT or AST levels. There was also no significant difference in CK levels between the two groups. These findings are supported by a study conducted by Taherkhani et al., in which 110 elderly patients received 40 mg/d rosuvastatin for 6 weeks. The safety assessment showed that only two patients experienced myalgia, 12 had muscle cramps, no cases of jaundice were observed, and no patients discontinued treatment due to adverse events (6). Therefore, high-dose rosuvastatin appears to be well tolerated in elderly patients with STEMI.
Inflammatory factors are closely associated with coronary artery disease, and changes in serum inflammatory markers can help predict the prognosis of patients with cardiovascular disease. TNF-α and IL-6 are key pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the pathophysiological response following myocardial infarction. Studies have shown that their levels increase significantly after myocardial infarction and contribute to the expansion of myocardial injury through direct cytotoxic effects or by inducing inflammatory responses (27). Hs-CRP is an acute-phase protein synthesized by the liver in response to IL-6 stimulation. It participates in the pathological process following myocardial infarction by promoting inflammatory cell infiltration and affecting endothelial function (28). Elevated hs-CRP levels after myocardial infarction are associated with left ventricular remodeling, the development of heart failure, and an increased risk of mortality (29, 30). A meta-analysis involving 18,715 patients with acute myocardial infarction who underwent PCI demonstrated that elevated CRP levels were associated with an increased risk of in-hospital and short-term all-cause mortality, as well as significantly higher rates of cardiovascular mortality and MACE (31). The potential mechanisms may include CRP-mediated inflammatory responses that exacerbate plaque instability, microvascular dysfunction, and myocardial remodeling. One study evaluated the effect of a single preoperative 40 mg dose of rosuvastatin on the acute inflammatory response after PCI in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Compared with patients who did not receive pretreatment, those receiving high-dose rosuvastatin had significantly reduced serum levels of IL-6 and hs-CRP (32). In addition, serum ICAM-1 levels are significantly elevated in patients with acute myocardial infarction (33). ICAM-1 mediates the adhesion of neutrophils to cardiomyocytes, facilitating the release of proteases, reactive oxygen species, and other cytotoxic substances that exacerbate myocardial injury and promote adverse remodeling (34). The results of this study showed that, compared with the control group, the intensive group achieved significantly greater reductions in serum hs-CRP, IL-6, TNF-α, and ICAM-1 levels, indicating a more effective suppression of the postoperative inflammatory response.
Galectin-3 is a β-galactoside-binding lectin that plays a key role in myocardial fibrosis and inflammatory processes. Researches have shown that galectin-3 can activate macrophages, promote the proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts, and stimulate collagen synthesis (35). Furthermore, elevated levels of galectin-3 are associated with the severity of heart failure and poor clinical outcomes (36). A randomized controlled trial compared the effects of high-dose atorvastatin (80 mg/d) and rosuvastatin (40 mg/d) on serum galectin-3 levels in patients with acute myocardial infarction. The results showed that patients in the rosuvastatin group experienced a significant reduction in galectin-3 levels after 4 weeks of treatment, whereas no significant change was observed in the atorvastatin group (37), suggesting that rosuvastatin may have a stronger effect in modulating biomarkers related to myocardial fibrosis. MMP-9 and TIMP-4 belong to the matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) protein families, respectively. MMPs are primarily responsible for extracellular matrix degradation, and their increased activity has been linked to ventricular dilation and cardiac dysfunction (38). TIMPs are natural antagonists of MMPs, capable of inhibiting MMPs activity and maintaining the structural integrity of the myocardium (39). In the present study, after 8 weeks of treatment, the intensive group had significantly higher TIMP-4 levels and significantly lower levels of MMP-9 and galectin-3 compared to the control group. NT-proBNP is a key biomarker for evaluating cardiac function and ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. In this study, high-dose rosuvastatin produced a more pronounced reduction in NT-proBNP levels. Therefore, rosuvastatin at 20 mg/d may be more effective than 10 mg/d in reducing myocardial fibrosis and improving cardiac function.
Heart failure is one of the most common complications in patients with STEMI and has a significant impact on prognosis. Previous studies have shown that high-intensity statin therapy may improve clinical outcomes through its anti-inflammatory effects. Gavazzoni et al. compared the efficacy of high-dose vs. moderate-dose atorvastatin in patients with STEMI (40). The results indicated that high-dose treatment led to more significant reductions in inflammatory markers (such as hs-CRP and IL-6) and greater improvements in endothelial function. These findings suggest that intensive statin therapy may exert stronger anti-inflammatory and vascular protective effects in the early phase of myocardial infarction, supporting its role in delaying ventricular remodeling and preventing heart failure. In a meta-analysis conducted by Sun et al., three cohort studies and four randomized controlled trials were evaluated to compare the effects of rosuvastatin combined with ticagrelor vs. ticagrelor alone in patients undergoing PCI (41). The findings indicated that the combination of rosuvastatin and ticagrelor not only significantly reduced the incidence of MACE compared to ticagrelor monotherapy, but also improved left ventricular structure and function (including LVESD, LVEDD, and LVEF) and lowered NT-proBNP levels. These findings highlight the potential of rosuvastatin in myocardial protection and heart failure prevention. Notably, improvement in ventricular function carries clear clinical significance. Breathett et al. demonstrated that even a modest increase in LVEF can predict a lower risk of all-cause mortality and is associated with a reduced risk of hospitalization for heart failure (42). In our study, echocardiographic results showed that LVEF, TDI s′-l, and stroke volume were significantly higher in the intensive group than in the control group after treatment, indicating improved cardiac systolic function. This suggests that high-dose rosuvastatin may be more effective than conventional doses in improving ventricular remodeling and cardiac function. Given that there were no significant differences in lipid levels between the two groups after treatment, rosuvastatin may exert cardioprotective effects independent of its lipid-lowering properties.
This study has several limitations. Firstly, as a single-center study with a relatively small sample size, the statistical power and generalizability of the findings may be limited. Secondly, although efforts were made to ensure the completeness of data collection, some data were missing—for example, a few patients did not complete follow-up—which may have introduced bias in the analysis of certain parameters. In addition, the follow-up period was relatively short, and the primary endpoints focused mainly on inflammatory markers, indicators of ventricular remodeling, and cardiac function parameters, without including long-term clinical outcomes such as cardiac death, heart failure hospitalization, or MACE. Therefore, the assessment of clinical benefits requires further validation. Since this study only evaluated the differences between high-dose and standard-dose rosuvastatin, without considering a comparison with other high-intensity statins (such as atorvastatin), the comprehensiveness of the results may be limited. Future studies with multicenter designs, larger sample sizes, comparisons across different statins, and longer follow-up durations are needed to confirm these findings.
5 Conclusion
In elderly patients with STEMI undergoing PCI, high-dose rosuvastatin demonstrated superior efficacy compared to the conventional dose in reducing inflammation, attenuating myocardial fibrosis, and improving ventricular remodeling and cardiac function. Its cardioprotective effects may be independent of lipid-lowering mechanisms.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Qingpu Branch of Zhongshan Hospital affiliated to Fudan University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YQ: Writing – original draft. SJ: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. XS: Writing – review & editing. RL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. HL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Foundation of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (202140237 and 202240156) and Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (23ZR1411600).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Galli M, Niccoli G, De Maria G, Brugaletta S, Montone RA, Vergallo R, et al. Coronary microvascular obstruction and dysfunction in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2024) 21:283–98. doi: 10.1038/s41569-023-00953-4
2. Frantz S, Hundertmark MJ, Schulz-Menger J, Bengel FM, Bauersachs J. Left ventricular remodelling post-myocardial infarction: pathophysiology, imaging, and novel therapies. Eur Heart J. (2022) 43:2549–61. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac223
3. Arnautu D, Andor M, Buz B, Tomescu M, Vacarescu C, Crisan S, et al. Left ventricular remodeling and heart failure predictors in acute myocardial infarction patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction after successful percutaneous intervention in western Romania. Life (Basel). (2022) 12:1636. doi: 10.3390/life12101636
4. Qin Y, Qin H, Yang B, Chen L, Chen C, Xu J, et al. Impact of multimorbidity on risk stratification and prognosis in elderly patients after acute myocardial infarction. J Thorac Dis. (2024) 16:6677–87. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-772
5. Sagris M, Antonopoulos AS, Theofilis P, Oikonomou E, Siasos G, Tsalamandris S, et al. Risk factors profile of young and older patients with myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. (2022) 118:2281–92. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab264
6. Taherkhani M, Khanifar Z, Taherkhani A, Hajishah H, Tavasol A. Assessing the effect of high-dose rosuvastatin in elderly patients over 75 with acute coronary syndrome. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2024) 24:474. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04142-0
7. Kim DY, Kim SH, Kim E, Han S, Park J, Youn J, et al. ROsulord(R) sAfety for patients with dyslipidemia study: a non-interventional, multicenter, prospective, observational study in South Korea. Cardiol Ther. (2025) 14:17–29. doi: 10.1007/s40119-024-00391-4
8. He W, Cao M, Li Z. Effects of different doses of atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin on elderly patients with ST-elevation acute myocardial infarction (AMI) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Drug Dev Res. (2020) 81:551–56. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21651
9. Wegiel M, Rakowski T. Circulating biomarkers as predictors of left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. (2021) 17:21–32. doi: 10.5114/aic.2021.104764
10. Patoulias D, Stavropoulos K, Imprialos K, Athyros V, Grassos H, Doumas M, et al. Inflammatory markers in cardiovascular disease; lessons learned and future perspectives. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. (2021) 19:323–42. doi: 10.2174/1570161118666200318104434
11. Maruyama K, Imanaka-Yoshida K. The pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis: a review of recent progress. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:2617. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052617
12. Preiss D, Tobert JA, Hovingh GK, Reith C. Lipid-modifying agents, from statins to PCSK9 inhibitors: JACC focus seminar. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 75:1945–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.11.072
13. Oesterle A, Laufs U, Liao JK. Pleiotropic effects of statins on the cardiovascular system. Circ Res. (2017) 120:229–43. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308537
14. Ovchinnikov A, Potekhina A, Arefieva T, Filatova A, Ageev F, Belyavskiy E. Use of statins in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: current evidence and perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:4958. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094958
15. German CA, Liao JK. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of statin pleiotropic effects. Arch Toxicol. (2023) 97:1529–45. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03492-6
16. Paparodis RD, Bantouna D, Livadas S, Angelopoulos N. Statin therapy in primary and secondary cardiovascular disease prevention. Curr Atheroscler Rep. (2024) 27:21. doi: 10.1007/s11883-024-01265-9
17. Jaam M, Al-Naimi HN, Haddad MM, Abushanab D, Al-Badriyeh D. Comparative efficacy and safety among high-intensity statins. Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Comp Eff Res. (2023) 12:e220163. doi: 10.57264/cer-2022-0163
18. Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Chaitman BR, Bax JJ, Morrow DA, et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). Eur Heart J. (2019) 40:237–69. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy462
19. Byrne RA, Rossello X, Coughlan JJ, Barbato E, Berry C, Chieffo A, et al. 2023 ESC guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44:3720–826. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad191
20. Luo R, Sun X, Shen F, Hong B, Wang Z. Effects of high-dose rosuvastatin on ventricular remodelling and cardiac function in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2020) 14:3891–98. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S254948
21. Rao SV, O'Donoghue ML, Ruel M, Rab T, Tamis-Holland JE, Alexander JH, et al. 2025 ACC/AHA/ACEP/NAEMSP/SCAI guideline for the management of patients with acute coronary syndromes: a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association joint committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. (2025) 151:e771–862. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001309
22. Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, Koskinas KC, Casula M, Badimon L, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41:111–88. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz455
23. Khan HA, Alhomida AS, Sobki SH. Lipid profile of patients with acute myocardial infarction and its correlation with systemic inflammation. Biomark Insights. (2013) 8:1–07. doi: 10.4137/BMI.S11015
24. Kim A, Han JY, Kim M, Lee H, Baek Y, Ahn I, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes of early LDL-C goal achievement in patients with very-high-risk ASCVD. Cardiol Ther. (2025) 14:101–15. doi: 10.1007/s40119-025-00397-6
25. Abdullah SM, Defina LF, Leonard D, Barlow CE, Radford NB, Willis BL, et al. Long-term association of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol with cardiovascular mortality in individuals at low 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Circulation. (2018) 138:2315–25. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.034273
26. Zhang J, Gong Y, Peng J, Han J, Li F, Song L, et al. Dose study of rosuvastatin calcium in the treatment of coronary heart disease and hyperlipidemia. Am J Transl Res. (2023) 15:3403–09.37303665
27. Nian M, Lee P, Khaper N, Liu P. Inflammatory cytokines and postmyocardial infarction remodeling. Circ Res. (2004) 94:1543–53. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000130526.20854.fa
28. Polyakova EA, Mikhaylov EN. The prognostic role of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Geriatr Cardiol. (2020) 17:379–83. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2020.07.007
29. Carrero JJ, Andersson Franko M, Obergfell A, Gabrielsen A, Jernberg T. hsCRP level and the risk of death or recurrent cardiovascular events in patients with myocardial infarction: a healthcare-based study. J Am Heart Assoc. (2019) 8:e012638. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012638
30. Vanhaverbeke M, Veltman D, Pattyn N, De Crem N, Gillijns H, Cornelissen V, et al. C-reactive protein during and after myocardial infarction in relation to cardiac injury and left ventricular function at follow-up. Clin Cardiol. (2018) 41:1201–06. doi: 10.1002/clc.23017
31. Liu S, Jiang H, Dhuromsingh M, Dai L, Jiang Y, Zeng H. Evaluation of C-reactive protein as predictor of adverse prognosis in acute myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention: a systematic review and meta-analysis from 18,715 individuals. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:1013501. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1013501
32. Slhessarenko JR, Hirata M, Sousa A, Bastos GM, Higa EMS, Mouro MG, et al. Effect of preloading with high dose of rosuvastatin on Serum levels of inflammatory markers after percutaneous coronary intervention. J Invasive Cardiol. (2020) 32:335–41. doi: 10.25270/jic/20.00064
33. Yu J, Liu Y, Peng W, Xu Z. Serum VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 measurement assists for MACE risk estimation in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients. J Clin Lab Anal. (2022) 36:e24685. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24685
34. Singh V, Kaur R, Kumari P, Pasricha C, Singh R. ICAM-1 and VCAM-1: gatekeepers in various inflammatory and cardiovascular disorders. Clin Chim Acta. (2023) 548:117487. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2023.117487
35. Seropian IM, Cassaglia P, Miksztowicz V, Gonzalez GE. Unraveling the role of galectin-3 in cardiac pathology and physiology. Front Physiol. (2023) 14:1304735. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1304735
36. Wu C, Lv Z, Li X, Zhou X, Mao W, Zhu M. Galectin-3 in predicting mortality of heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Surg Forum. (2021) 24:E327–32. doi: 10.1532/hsf.3547
37. Tuncez A, Altunkeser BB, Ozturk B, Ates MS, Tezcan H, Aydogan C, et al. Comparative effects of atorvastatin 80 mg and rosuvastatin 40 mg on the levels of serum endocan, chemerin, and galectin-3 in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Anatol J Cardiol. (2019) 22:240–49. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2019.64249
38. Tanase DM, Valasciuc E, Anton I, Gosav EM, Dima N, Cucu AI, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases: pathophysiologic implications and potential therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. Biomolecules. (2025) 15:598. doi: 10.3390/biom15040598
39. Cabral-Pacheco GA, Garza-Veloz I, Castruita-De La Rosa C, Ramirez-Acuna JM, Perez-Romero BA, Guerrero-Rodriguez JF, et al. The roles of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in human diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:9739. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249739
40. Gavazzoni M, Gorga E, Derosa G, Maffioli P, Metra M, Raddino R. High-dose atorvastatin versus moderate dose on early vascular protection after ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2017) 11:3425–34. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S135173
41. Sun J, Jin X, Zhang L, Shen H, Yu H. Rosuvastatin plus ticagrelor decreases the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events and elevates cardiac function compared with ticagrelor alone in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis. Exp Ther Med. (2023) 26:525. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12224
Keywords: rosuvastatin, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, inflammatory cytokines, ventricular remodeling, cardiac function
Citation: Qin Y, Jin S, Sun X, Luo R and Liu H (2025) Effects of intensive rosuvastatin on ventricular remodeling and cardiac function in elderly patients with STEMI undergoing PCI. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1638967. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1638967
Received: 31 May 2025; Accepted: 6 August 2025;
Published: 22 August 2025.
Edited by:
Alessandro Sticchi, University of Pisa, ItalyReviewed by:
Cesar Jimenez-Mendez, Hospital Universitario Puerta del Mar, SpainAnna Van Veelen, Amsterdam UMC, Netherlands
Copyright: © 2025 Qin, Jin, Sun, Luo and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rong Luo, Mzk1NjMwM0BxcS5jb20=; Haibo Liu, aGFpYm9saXUxM0BmdWRhbi5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yiran Qin
Yiran Qin Siyi Jin2,†
Siyi Jin2,† Xusen Sun
Xusen Sun Haibo Liu
Haibo Liu