- 1Department of Cardiosurgery Intensive Care Unit, Ningbo Medical Centre Lihuili Hospital, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China
- 2Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Ningbo Medical Centre Lihuili Hospital, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China
Objective: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are involved in various Cardiovascular diseases; however, the circRNA expression profiles and the circRNA-microRNA(miRNA)-messenger RNA (mRNA) regulatory network in rheumatic heart disease (RHD) remain poorly understood. This study aimed to investigate the expression profiles of circRNAs and construct a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA interaction network to reveal new diagnostic biomarkers and potential pathogenesis of RHD.
Methods: Clinical data and plasma samples from 46 patients with RHD and 46 non-RHD patients were collected between January 2021 and December 2023. Arraystar Human CircRNA microarray was used to profile differentially expressed circRNAs in 3 paired samples (RHD vs. non-RHD). Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) validated four candidate circRNAs in all 92 samples. The diagnostic value of differentially expressed circRNAs was analyzed by the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve. Bioinformatics analysis was used to predict the target miRNA and analyze the co-expressed mRNA to construct a circRNA–miRNA-mRNA regulatory network. The Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses were conducted to predict the potential functions of the differentially expressed genes and RHD-related pathways.
Results: Four circRNAs were selected from circRNA microarray data. qRT-PCR confirmed that hsa_circ_0001490 and hsa_circ_0001296 were significantly upregulated in RHD plasma (4.28-fold, P < 0.001; 5.24-fold, P < 0.001, respectively). ROC analysis revealed hsa_circ_0001490 had an AUC of 0.792 (95% CI: 0.69–0.89; sensitivity: 93.5%; specificity: 67.4%), while hsa_circ_0001296 showed superior accuracy (AUC = 0.896; 95% CI: 0.83–0.96; sensitivity: 69.6%; specificity: 95.7%). A predicted hsa_circ_0001490-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network included 11 miRNAs and 1,973 mRNAs, and hsa_the circ_0001296-miRNA-mRNA interaction network included 9 miRNAs and 1,404 mRNAs. Moreover, the top 10 hub genes were screened within the two networks, respectively. The significantly enriched GO terms associated with hsa_circ_0001490 downstream genes were Smad binding and regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway. The significantly involved KEGG pathways included the Wnt signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway and TGF-beta signaling pathway. For hsa_circ_0001296, the significantly enriched GO terms were transforming growth factor beta receptor activity(type I) and Smad binding. The Autophagy pathway and MAPK signaling pathway were significantly involved in KEGG pathways.
Conclusion: This study provides the first evidence of significant upregulation of hsa_circ_0001490 and hsa_circ_0001296 in RHD patients, suggesting their potential as diagnostic biomarkers for RHD. The constructed circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network reveals potential molecular mechanisms underlying RHD pathogenesis. Future studies should investigate these circRNAs' functional roles to fully elucidate their contribution to RHD development.
Introduction
Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is a post-infectious sequelae of acute rheumatic fever resulting from an abnormal immune response to streptococcal pharyngitis that triggers valvular damage, including stenosis and insufficiency and eventually develops into heart failure (1–3). Recent estimates suggest RHD affects approximately 40.5 million people worldwide (4, 5). Rheumatic heart disease represents a major global health burden, predominantly affecting young populations and causing significant cardiovascular morbidity and mortality (6). The current standard for rheumatic heart disease diagnosis remains based on clinical examination, the Jones criteria, and echocardiographic findings. However, the diagnosis criteria overly depend on clinicians' technical skills and judgment, resulting in poor sensitivity and specificity (7, 8). Novel biomarkers could significantly improve RHD diagnostic accuracy. CircRNAs show promise as potential diagnostic biomarkers that could establish new standards for RHD diagnosis (9).
Recent studies indicate that circRNA plays a crucial role in the occurrence and progression of cardiovascular diseases (10). Because circRNA is not easily degraded by exonuclease, its half-life is significantly longer than that of linear RNA. Its high abundance, relative stability, and evolutionary conservation in the peripheral blood distinguish it from traditional linear RNAs. Certain circRNAs show potential as biomarkers for their diagnosis (9). Currently, there are limited studies on the role and mechanisms of circRNA in RHD. This study aims to identify RHD-specific circRNAs and construct their regulatory networks, which may provide new insights into circRNA functions as potential diagnostic biomarkers and reveal underlying disease mechanisms.
Materials and methods
CircRNA microarray assays
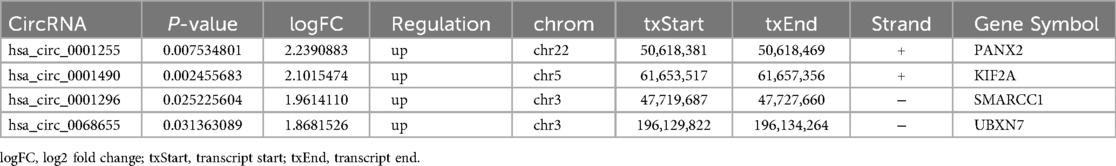
In the present study, the expression profile of circRNA in the plasma of three RHD patients and three non-RHD patients was analyzed using the Arraystar Human CircRNA microarray. Differentially expressed circRNAs were identified and had been uploaded to the GEO database (GSE168932, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE168932). Candidate circRNAs with fold-change >1.5 and p < 0.05 were selected. We conducted a literature search on circRNAs that had not been previously studied in RHD. Ultimately, we chose four circRNAs as our research subjects (Table 1).
Study population
Ninety-two plasma samples were obtained from the inpatients in the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery at Ningbo Medical Centre Lihuili Hospital from January 2021 to December 2023. All patients were diagnosed with clinical symptoms, physical examination, electrocardiograph (ECG), chest x-ray, and TTE. The RHD group met the following criteria: (1) age ≥18 years old. (2) meeting the RHD diagnostic criteria (7), (3) at least one of the heart valves is damaged. The non-RHD group was recruited during the same period from the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery at Ningbo Medical Centre Lihuili Hospital. They were diagnosed with non-rheumatic heart valve disease. All patients meeting the exclusion criteria were: (1) patients with valvular heart disease combined with coronary heart disease or acute myocardial infarction. (2) patients with infective endocarditis. A propensity score match was used to pair patients between the RHD and non-RHD groups. This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Ningbo Medical Center Li Huili Hospital (Approval No. 2023310). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Collection and storage of plasma samples
Peripheral blood samples were collected into EDTA-containing anticoagulation tubes, and plasma was separated within a maximum of 3 h of blood withdrawal by centrifugation of the tubes at 3,000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C. The upper plasma layer was then removed into 2 ml RNase-free Eppendorf tubes and stored at −80°C.
Total RNA extraction and quantitative real-time PCR
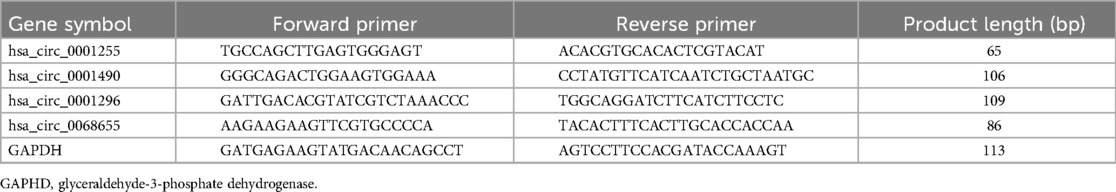
According to the manufacturer's instructions, total RNA was extracted from plasma using TRIzol LS reagent (Invitrogen). RNA purity was assessed by measuring A260/A280 ratios. The integrity of the RNA was assessed by denaturing agarose gel electrophoresis. cDNA was synthesized using the GoScript Reverse Transcription System (Promega, USA) with gene-specific primers. We used the Applied Biosystems 7,500 Realtime PCR system (ThermoFisher Scientific, USA) to amplify four circRNAs using GoTaq qPCR Master Mix (Promega, USA) according to the kit instructions. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) mRNA served as the endogenous control for relative quantification. The primer sequences were designed in the laboratory and synthesized by Genepharma Biotech (Genepharma, China) based on the mRNA sequences obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology Information database. BLAST was used to verify the specificity of the PCR primers. The specific convergent primer sequences of four circRNAs and GAPDH primer sequences are shown in Table 2. Amplification curve and melting curve analysis were performed to validate the specific generation of the expected PCR product. The expression fold change of the circRNAs was then calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method.
Prediction of target miRNAs for circRNAs and target mRNAs for miRNAs
To predict the interactions between circular circRNAs and miRNAs, we utilized several online databases, including circAtlas 3.0 (http://circatlas.biols.ac.cn), Circular RNA Interactome (https://circinteractome.nia.nih.gov/mirna_target_sites.html), and circBank (https://www.circbank.cn/#/home). The miRNAs predicted simultaneously by the circAtlas, the Circular RNA Interactome, and circBank were considered target miRNAs of the circRNAs. For identifying the downstream target mRNAs of these miRNAs, we employed the online databases TargetScanHuman 8.0 (http://www.targetscan.org/), DIANA-microT (http://diana.imis.athena-innovation.gr/DianaTools/index.php), and miRDB (https://mirdb.org/index.html). Similarly, the mRNAs predicted by TargetScan, DIANA-microT, and miRDB were classified as candidate downstream target mRNAs simultaneously. A Venn diagram was used to improve predictive accuracies (via intersection) (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/). Using the information from circRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs, we constructed a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network.
GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses
The GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses were applied to investigate the potential functions of differentially expressed circRNAs. The GO and KEGG analyses were performed to identify the downstream target genes of miRNAs, which were completed using the Metascape online software (https://metascape.org/gp/index.html). GO analysis was applied to annotate the genes with terms under the biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF) categories. KEGG pathway analysis was performed to identify the significant pathways associated with the differentially expressed genes.
Construct the protein-protein interaction network of target genes
The protein interactions for the target genes were obtained from the STRING database (https://string-db.org/), using a minimum required interaction score ≥0.9 as the threshold. A protein-protein interaction network(PPI) was then constructed using Cytoscape version 3.10.3 software. The top ten genes were identified as hub genes through the MCC algorithm in the CytoHubba plugin.
Construction of the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network
The top 10 hub genes screened were further constructed by the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network, which was visualized using Cytoscape software (version 3.10.3).
Statistical analysis
For numerical variables, a normal distribution was assessed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Numerical variables with a normal distribution are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and compared using Student's t-test; otherwise, they are expressed as median (Q25, Q75) and compared using the Mann–Whitney U test. Categorical data are shown as numbers (%) and analyzed using the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test as appropriate. The diagnostic value of circRNAs was analyzed by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and the area under the ROC curve (AUC). A two-tailed p-value < 0.05 was considered to indicate a significant difference. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics 26.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY) and GraphPad Prism 9.0 (GraphPad Software, USA) software.
Results
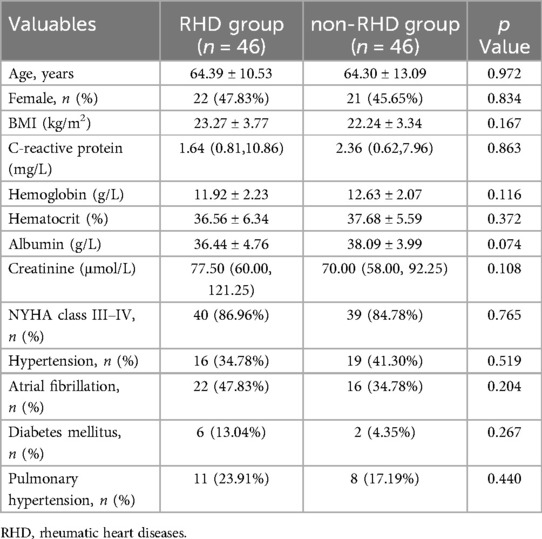
Clinical characteristics comparison between the RHD group and the non-RHD group
In the 92 patients, there were no significant differences in clinical characteristics between the RHD and control groups (P > 0.05) (Table 3).
Plasma circRNA relative expression
Four candidate circRNAs were validated in a large sample using qRT-PCR, and the results were confirmed through agarose gel electrophoresis. Hsa_circ_0001490, hsa_circ_0001296, hsa_circ_0001255, and hsa_circ_0068566 expression fold change in plasma samples of patients with RHD calculated relative to non-RHD patients is shown in Figure 1. Plasma hsa_circ_0001490 and hsa_circ_0001296 relative expression were significantly elevated in patients with RHD (3.94 ± 3.50) (P < 0.001) and (2.70 ± 1.99) (P < 0.001), respectively (Figures 1A,B). However, there were no significant differences in the relative expression of plasma hsa_circ_0001255 (P = 0.051) and hsa_circ_0068655 (P = 0.073) between the two patient groups (Figures 1C,D).
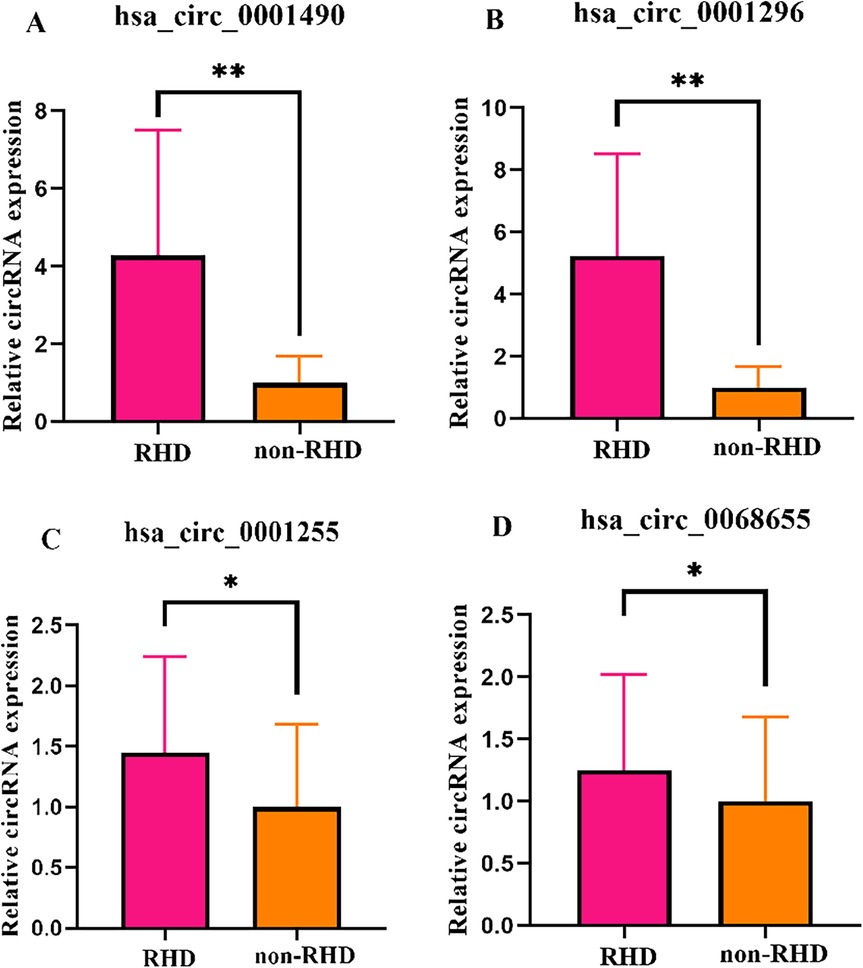
Figure 1. The expression levels of circRNAs were validated in both the RHD and non-RHD groups using qRT-PCR. Relative plasma expression (fold change) of hsa_circ_0001490 (A), hsa_circ_0001296 (B), hsa_circ_0001255 (C) and hsa_circ_0068655 (D) in patients with RHD compared to non-RHD patients. *p > 0.05; **p < 0.01.
Diagnostic efficacy of hsa_circ_0001490 and hsa_circ_0001296 for RHD
The diagnostic potential of plasma hsa_circ_0001490 and hsa_circ_0001296 expression fold change was assessed by plotting ROC curves for RHD status (Figures 2A,B). The area under the curve (AUC) for hsa_circ_0001490 was 0.792 (95% CI, 0.69–0.89, P < 0.001), and the cutoff value for hsa_circ_0001490 fold change for predicting RHD was 1.47 (sensitivity = 93.5%, specificity = 67.4%). Similarly, the AUC for hsa_circ_0001296 was 0.896 (95% CI, 0.83–0.96, P < 0.001) for RHD, and the threshold for the hsa_circ_0001296 fold change in predicting RHD was 1.69 (sensitivity, 69.6%; specificity, 95.7%).
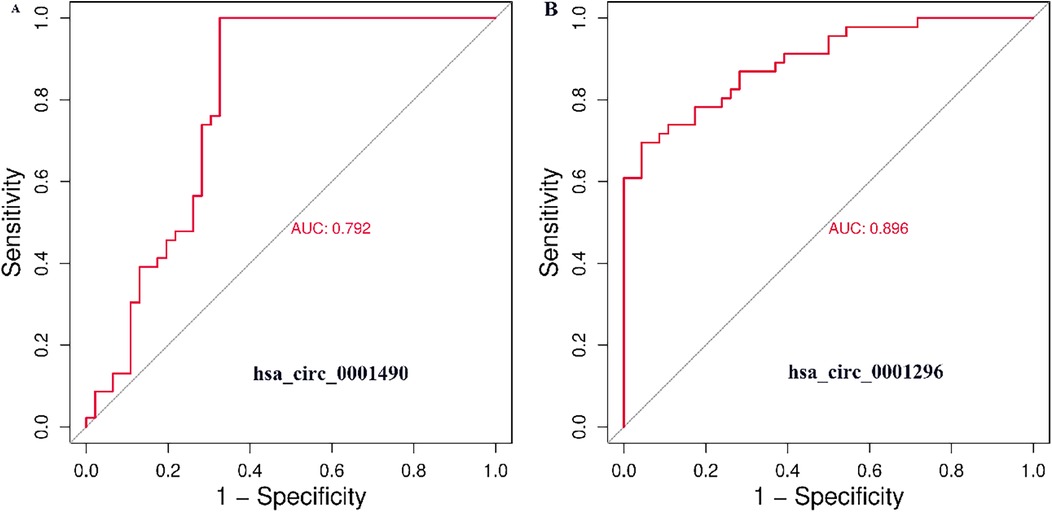
Figure 2. ROC curve analysis of plasma hsa_circ_0001490 (AUC = 0.792, cutoff point = 1.47, P < 0.001, sensitivity = 93.5% and specificity = 67.4%) (A) and hsa_circ_00011296 (AUC = 0.896, cutoff point = 1.69, P < 0.001, sensitivity = 69.6% and specificity = 95.7%) (B) were performed to predict RHD.
Prediction of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network
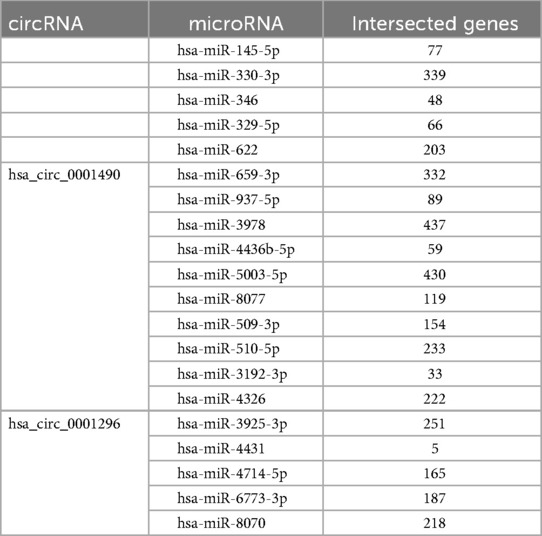
Bioinformatic predictions were performed for two significantly differentially expressed circRNAs to construct their circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Regulatory networks. For hsa_circ_0001490, potential miRNA binding sites were predicted using three databases (circAtlas, the Circular RNA Interactome, and circBank). This analysis identified 11 high-confidence miRNAs with conserved binding sites across all three databases. Downstream targets of these miRNAs were predicted using TargetScan, DIANA-microT, and miRDB. Initial screening yielded 2,199 target mRNAs, which were refined to 1,973 non-redundant mRNAs after intersection analysis (Table 4 and Supplementary Figure S1). Similarly, for hsa_circ_0001296, the analysis identified 9 high-confidence miRNAs with conserved binding sites, and the initial screening yielded 1,468 target mRNAs, which were refined to 1,404 non-redundant mRNAs after intersection analysis (Table 4 and Supplementary Figure S2).
GO and KEGG pathway analysis of circRNAs downstream genes
We conducted the GO and KEGG pathway analyses to predict the potential functions of circRNAs. The predicted functional terms with p-value < 0.05 were selected and ranked by enrichment score [−log10 (p-value)]. For hsa_circ_0001490 targets, the top 20 enriched GO terms spanned biological processes (BP), cellular components (CC), and molecular functions (MF) (Figure 3A). KEGG analysis revealed the top 20 potentially relevant pathways for RHD pathogenesis (Figure 3B). Similarly, hsa_circ_0001296 targets showed enrichment in 20 top GO terms across BP, CC, and MF categories (Figure 3C). Corresponding KEGG analysis identified 20 top pathways potentially associated with RHD (Figure 3D).
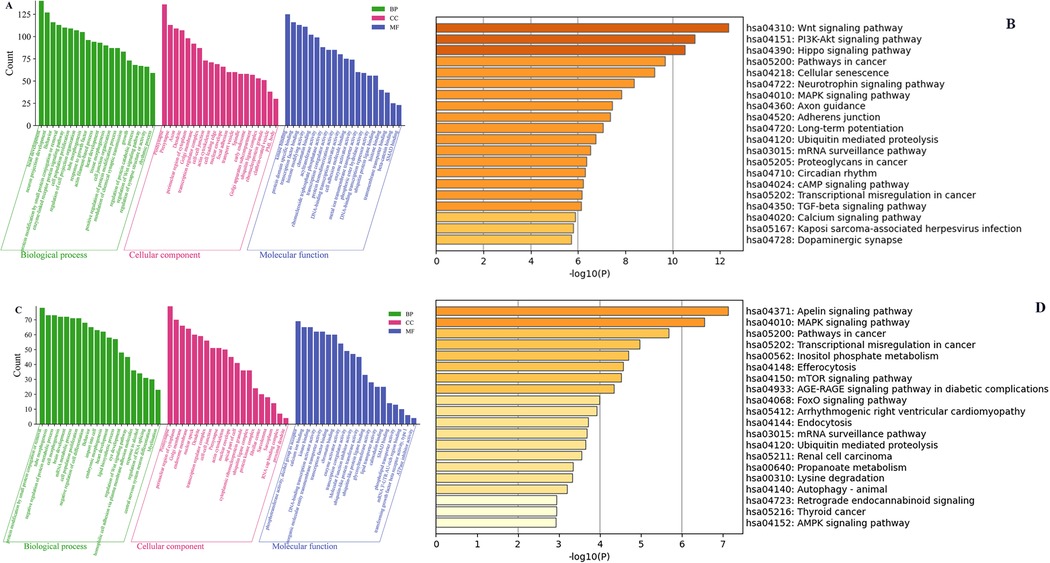
Figure 3. The GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses of the downstream target genes for differentially expressed circRNAs. The top 20 significantly enriched BP, CC, and MF terms by GO analysis (A) and the top 20 significantly enriched pathways by KEGG analysis (B) of the downstream genes of hsa_circ_0001490. The top 20 significantly enriched BP, CC, and MF terms by GO analysis (C) and the top 20 significantly enriched pathways by KEGG analysis (D) of the downstream genes of hsa_circ_0001296. GO, Gene Ontology; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; BP, biological process; CC, cellular component; MF, molecular function. Column length represents enrichment score (−log10[P-value]), with longer bars indicating greater statistical significance.
Protein-protein interaction network analysis and hub genes screening
The target genes of miRNAs associated with hsa_circ_0001490 and hsa_circ_0001296 were analyzed for functional interactions using the STRING database. The resulting interaction networks were visualized and analyzed using Cytoscape (Figures 4A,C). The significant hub genes were identified using the CytoHubba plugin with the Molecular Complex Detection (MCC) method. The top ten hub genes for each circRNA were as follows: For the hsacirc0001490 network, these were MED17, MED22, MED6, MED29, CDK8, MED8, CDK19, PPARGC1B, MED20, and THRAP3. For the hsa_circ_0001296 network: SNRPD1, SF3B3, SNW1, SNIP1, PLRG1, SF3B4, CT47A10, CT47A5, CT47A3, and CT47A8 (Figures 4B,D).
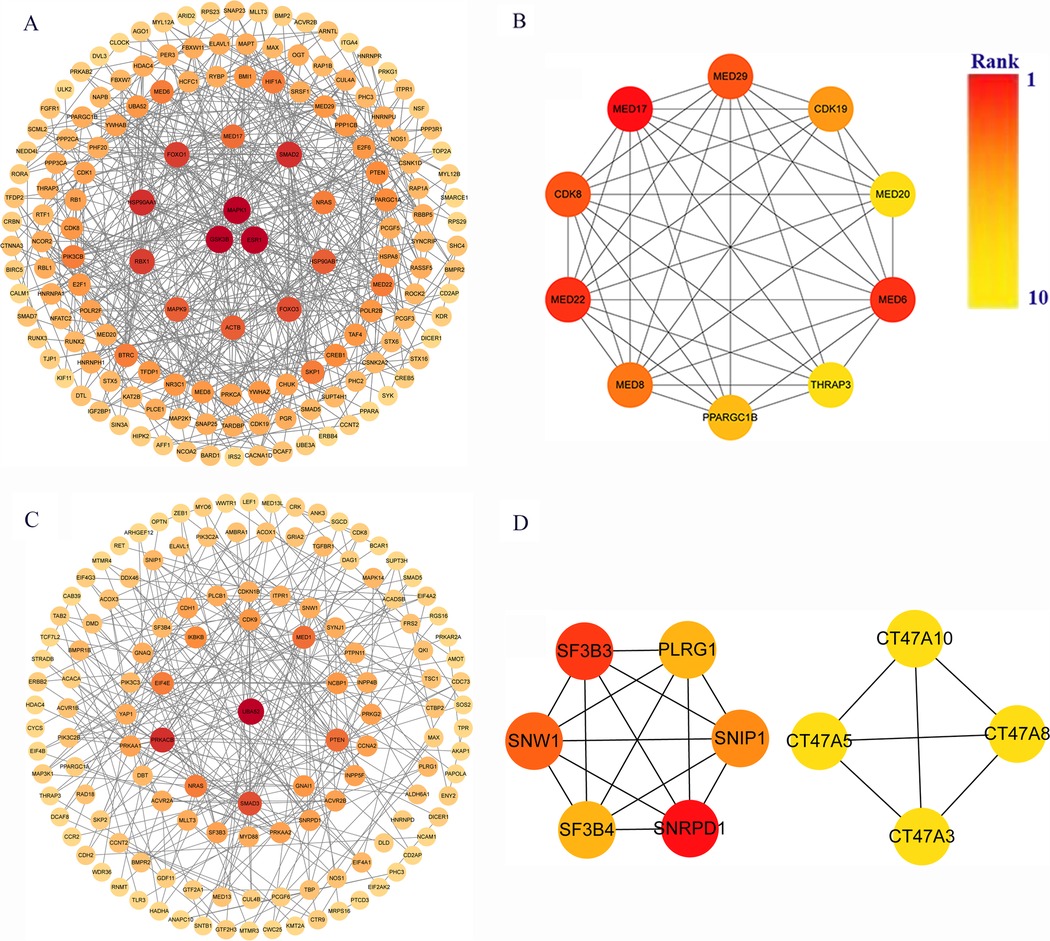
Figure 4. Identification of key genes in rheumatic heart disease pathogenesis. (A) Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of 1,973 hsa_circ_0001490 downstream targets in the ceRNA network. (B) Top 10 hub genes from hsa_circ_0001490's PPI network. (C) PPI network of 1,404 hsa_circ_0001296 downstream targets in the ceRNA network. (D) Top 10 hub genes from hsa_circ_0001296's PPI network. PPI, Protein-protein interaction. Circular nodes represent genes; node darkness corresponds to degree score, reflecting interaction strength.
Construction of the circRNA–miRNA-hub gene network
Based on bioinformatic predictions, hsa_circ_0001490 interacted with six miRNAs (hsa-miR-5003-5p, hsa-miR-659-3p, hsa-miR-330-3p, hsa-miR-8077, hsa-miR-622, and hsa-miR-329-5p) and ten hub genes, while hsa_circ_0001296 was associated with five miRNAs (hsa-miR-510-5p, hsa-miR-3925-3p, hsa-miR-6773-3p, hsa-miR-4326, and hsa-miR-509-3p) and an additional ten hub genes. These interactions formed a comprehensive circRNA–miRNA–hub gene regulatory network, suggesting a potential competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) mechanism in RHD (Figures 5A,B).
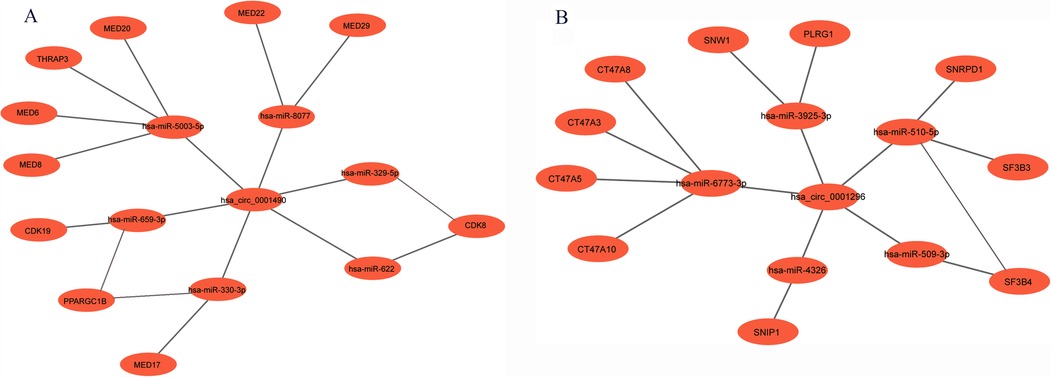
Figure 5. The circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network. (A) The hsa_circ_0001490-miRNA-hub gene regulatory network: In this network, hsa_circ_0001490 could affect functions of 6 miRNAs and then regulate the 10 downstream hub genes. (B) The hsa_circ_0001296-miRNA-hub gene regulatory network: In this network, hsa_circ_0001296 affects the functions of 5 miRNAs, leading to the regulation of 10 downstream hub genes.
Discussion
Rheumatic heart disease is responsible for nearly 250,000 deaths annually and poses a significant health threat in developing areas. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying RHD remains poorly understood, and there is a lack of specific diagnostic methods (7, 11). Although valvular surgery serves as the primary treatment, its high costs and requirement for long-term postoperative medication create substantial socioeconomic burdens for patients in developing areas (12, 13). These limitations highlight the urgent need for novel diagnostic biomarkers and improved therapeutic strategies to enable early detection and targeted interventions. CircRNA is highly conservative, and increasing studies show that it plays an important role in the diagnosis and pathogenesis of Cardiovascular diseases (14). Previous studies assessed circRNA as a potential biomarker for coronary heart disease (15), acute myocardial infarction (16), and heart failure (17). For instance, Xiong et al. elucidated the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in sepsis-induced cardiovascular dysfunction (18). However, there are relatively few studies on circRNA in RHD.
Our study revealed significant upregulation of hsa_circ_0001490 and hsa_circ_0001296 in RHD patients' plasma, with ROC analysis supporting their potential as diagnostic biomarkers (AUC = 0.792 and 0.896, respectively). In our previous studies, the researchers selected 42 patients RHD who had severe valvular lesions necessitating valve surgery, alongside 42 non-RHD patients and 42 healthy individuals. The findings indicated that hsa_circ_0000437 was elevated in surgical RHD cases compared to controls (19). However, that study's cohort was limited to severe valvular lesions, whereas our current study included all RHD patients meeting clinical criteria (7), enhancing generalizability. Comparatively, Hu et al. (20) conducted a study on nine samples of atrial tissue from patients with atrial fibrillation combined with RHD. The researchers identified six dysregulated circRNAs ((circRNA_20118, circRNA_17558, circRNA_16688, circRNA_11109, circRNA_11017, and circRNA_11058) in atrial tissue from RHD patients with atrial fibrillation. However, they focused only on patients with RHD combined with atrial fibrillation, collecting atrial tissue samples proved difficult, and a small sample size limited clinical applicability. In contrast, our use of peripheral blood offers practical advantages for broader diagnostic implementation.
Rheumatic heart disease mainly manifests as valvular damage caused by recurrent rheumatic fever, such as valve fibrosis, stenosis and calcification (21). hsa_circ_0001490 is a circular RNA located on chromosome 5(chr5: 61653517-61657356), which is transcribed and reverse-spliced from the KIF2A gene. We predicted the potential functions of the differentially expressed hsa_circ_0001490 using the GO and KEGG pathway analyses in patients with RHD. GO analysis revealed that hsa_circ_0001490's downstream target genes regulate multiple biological processes, such as Smad binding, regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway, transcription factor binding, and response to growth factor. The endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) plays a key role in several diseases, including cardiac fibrosis. Smads are key regulators of EndMT, as their phosphorylation (Smad2/3) modulates EndMT-related transcription factors, suggesting EndMT involvement in RHD (22). KEGG analysis indicated that the target genes were involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, TGF-beta signaling pathway, and MAPK signaling pathway. Guo and colleagues demonstrated that the Wnt signaling pathway may be involved in the increased expression of Snail1 and atrial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and RHD. These findings suggested the Wnt signaling pathway promoted EndMT development, potentially enhancing Snail1 levels and atrial fibrosis in AF and RHD patients (23). The transforming growth factor-beta(TGF-β) signaling pathway is a major regulator of EndMT, with key factors such as activin, Smad2, and Smad3 (24). Xiao et al. demonstrated that the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway is involved in the RHD-mediated atrial fibrosis (25). Cardiac fibrosis is promoted through the activation of MAPK and their downstream signaling, including their interaction with TGF-β and Smad proteins. Cardiac fibrosis further causes calcification and stiffening of the heart valves in RHD (26).
CircRNAs primarily function as potent miRNA sponges, modulating the biological activity of downstream miRNAs and their target mRNAs in cardiovascular diseases (27, 28). We predicted a potential hsa_circ_0001490-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network that may be involved in the pathogenesis of RHD using bioinformatics tools. We further constructed a protein-protein interaction network for the target genes and identified the top 10 hub genes: MED17, MED22, MED6, MED29, CDK8, MED8, CDK19, PPARGC1B, MED20, and THRAP3. The Mediator complex (MED) is a vital multiprotein transcriptional co-regulator that plays a crucial role in activating the transcription machinery during the initial stages of RNA polymerase II recruitment, as well as the subsequent processing and termination steps of transcription. Increasing evidence suggests that MED is involved in major cardiovascular diseases (29). Cyclin-dependent kinases 8 (CDK8) and 19 assemble with cyclin C, Med12, and Med13 to form the Mediator kinase module, which is reversibly associated with MED, controlling gene transcription both positively and negatively. The researchers found that pharmacological inhibition of CDK8 and CDK19, which were reversibly associated with MED and mainly control the function of transcription factors positively and negatively, was able to induce the transcription factor forkhead box protein 3(Foxp3) expression in naïve and effector/memory T cells, thereby suppressing harmful immune responses (30). The abnormally expressed hsa_circ_0001490 in RHD patients may affect the occurrence and development of RHD by regulating the expression of related downstream target genes.
Hsa_circ_0001296 is formed by the reverse splicing of exons 14, 15, and 16 of the gene SMARCC1 located on chromosome 3 (chr3: 47719687-47727660). Its expression was significantly upregulated in RHD patients, suggesting its potential as a diagnostic biomarker for RHD. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying its role in RHD pathogenesis remain unclear. Using GO and KEGG pathway analyses, we predicted the functional roles of hsa_circ_0001296 in RHD. GO analysis revealed that its downstream target genes regulate multiple biological processes, including transforming growth factor beta receptor activity (type I), transcription factor binding, regulation of Wnt signaling pathway, and Smad binding. TGF-β1, a key member of the TGF-β family and a major secretory cytokine of regulatory T cells (Tregs), induces phosphorylation of membrane-bound receptors to mediate nuclear signaling. Zhou et al. suggested that overexpressed TGF-β1 in valvular tissues had a potential role in the myofibroblast proliferation, valvular fibrosis, inflammatory cell infiltration and valve calcification, which might cause the scarring sequelae of RHD (31). KEGG analysis revealed that the Autophagy pathway and MAPK signaling pathway were closely associated with the downstream target genes of hsa_circ_0001296. Autophagy is a self-degradative pathway by which subcellular elements are broken down intracellularly to maintain cellular homeostasis (32). The PTEN-induced putative kinase protein 1 (PINK1)/Parkin pathway is a well-known autophagic pathway (33). Excessive autophagy has been linked to valve diseases, resulting in the recruitment of inflammatory cells and calcification (32, 34). Bai et al. revealed that IL-17 plays a crucial role in EndMT in RHD via the PINK1/Parkin autophagic pathway and macrophage polarization, providing a potential therapeutic target (21). Zhou, et al. preliminarily explored the mechanism of CD4+ T cells and the TGF-β1/MAPK pathway involved in the pathological process of valvular hyperplasia and fibrosis of RHD (31).
Furthermore, we predicted a potential hsa_circ_0001296-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network that may contribute to RHD pathogenesis. Protein-protein interaction network analysis identified the top 10 hub genes: SNRPD1, SF3B3, SNW1, SNIP1, PLRG1, SF3B4, CT47A10, CT47A5, CT47A3, and CT47A8. SNIP1 is a transcriptional repressor that inhibits the BMP signaling pathway by directly interacting with SMAD2/3 proteins, thereby limiting their effects. Furthermore, SNIP1 modulates TGF-β/BMP signaling by disrupting the association between SMAD2/3 and the histone acetyltransferases CBP/p300 (35). The nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) family of transcription factors is central to regulating gene expression involved in inflammation, immune responses, cell proliferation, and various other biological processes. SNW1 is a novel regulator of the NF-κB pathway activation in human macrophages (36). These findings suggest that dysregulated hsa_circ_0001296 expression in RHD patients may influence disease progression through modulation of this circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network.
This study has several limitations. First, the sample size of the circRNA microarray assays in this study is still limited, which may increase the false-positive rate and reduce statistical power. We plan to further validate these findings in future experiments. Second, in this study, we constructed a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network and analyzed hub genes through bioinformatics analysis of two circRNAs that exhibited significant expression differences in patients with RHD. However, these findings require further validation through in vivo and in vitro experiments. Third, we cannot exclude the possibility that hsa_circ_0001490 and hsa_circ_0001296 may be overexpressed in other types of cardiovascular diseases in our population, as we did not comprehensively include them in our study. Thus, the generalizability of these findings requires confirmation in larger, multicenter studies.
Conclusions
We are reporting for the first time that hsa_circ_0001490 and hsa_circ_0001296 are highly expressed in the plasma of patients with RHD. We further constructed a circRNA-miRNA-target gene ceRNA regulatory network that is related to the pathogenesis of RHD. This work lays the groundwork for further exploration of the molecular mechanisms underlying RHD and the identification of potential circRNA diagnostic biomarkers for the disease.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Ningbo Medical Center Li Huili Hospital (Approval No: 2023310). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
XC: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Methodology. LC: Data curation, Writing – original draft. LB: Validation, Writing – original draft. SZ: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. XH: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. NL: Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Data curation, Software, Writing – original draft. GS: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants from the Zhejiang Medical and Health Science and Technology Plan Project (no. 2024KY298), the Ningbo Top Medical and Health Research Program (no. 2022030107), the Ningbo Technology Innovation 2025 Major Special Project (no. 2022Z150), and the Ningbo Health Branding Subject Fund (no. PPXK2018-01).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1639767/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
circRNA, circularRNA; miRNA, microRNA; mRNA, messengerRNA; RHD, rheumatic heart diseases; GO, Gene Ontology; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; EndMT, endothelial-mesenchymal transition.
References
1. Coffey S, Roberts-Thomson R, Brown A, Carapetis J, Chen M, Enriquez-Sarano M, et al. Global epidemiology of valvular heart disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2021) 18(12):853–64. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00570-z
2. Dooley LM, Ahmad TB, Pandey M, Good MF, Kotiw M. Rheumatic heart disease: a review of the current status of global research activity. Autoimmun Rev. (2021) 20(2):102740. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102740
3. Watkins DA, Johnson CO, Colquhoun SM, Karthikeyan G, Beaton A, Bukhman G, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of rheumatic heart disease, 1990−2015. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377(8):713–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1603693
4. Santangelo G, Bursi F, Faggiano A, Moscardelli S, Simeoli PS, Guazzi M, et al. The global burden of valvular heart disease: from clinical epidemiology to management. J Clin Med. (2023) 12(6):2178. doi: 10.3390/jcm12062178
5. de Loizaga SR, Arthur L, Arya B, Beckman B, Belay W, Brokamp C, et al. Rheumatic heart disease in the United States: forgotten but not gone: results of a 10 year multicenter review. J Am Heart Assoc. (2021) 10(16):e020992. doi: 10.1161/jaha.120.020992
6. Milutinovic S, Petrovic M, Ziq A, Sanchez C, Hammami AS, Escarcega RO, et al. Rheumatic heart disease burden: a comparative analysis between the United States and the European union. JACC Adv. (2024) 3(12):101393. doi: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2024.101393
7. Dougherty S, Okello E, Mwangi J, Kumar RK. Rheumatic heart disease: JACC focus seminar 2/4. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2023) 81(1):81–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.09.050
8. Gewitz MH, Baltimore RS, Tani LY, Sable CA, Shulman ST, Carapetis J, et al. Revision of the jones criteria for the diagnosis of acute rheumatic fever in the era of doppler echocardiography: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2015) 131(20):1806–18. doi: 10.1161/cir.0000000000000205
9. Singh DD, Kim Y, Choi SA, Han I, Yadav DK. Clinical significance of MicroRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, and CircRNAs in cardiovascular diseases. Cells. (2023) 12(12):1629. doi: 10.3390/cells12121629
10. Zhu L, Li N, Sun L, Zheng D, Shao G. Non-coding RNAs: the key detectors and regulators in cardiovascular disease. Genomics. (2021) 113(1 Pt 2):1233–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.10.024
11. Xian S, Chen A, Wu Y, Wen H, Lu C, Huang F, et al. Interference with the expression of S1PR1 or STAT3 attenuates valvular damage due to rheumatic heart disease. Int J Mol Med. (2021) 48(3):179. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5012
12. Xian S, Zeng Z. Methods for establishing a rat model of rheumatic heart disease. Rev Cardiovasc Med. (2024) 25(9):346. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2509346
13. Ushioda R, Shirasaka T, Sakboon B, Cheewinmethasiri J, Yoongtong D, Hirofuji A, et al. Evaluating short-term postoperative outcomes in minimally invasive mitral valve surgery for patients with rheumatic disease. Heart Surg Forum. (2023) 26(2):E178–e82. doi: 10.1532/hsf.5391
14. Zhao H, Tan Z, Zhou J, Wu Y, Hu Q, Ling Q, et al. The regulation of circRNA and lncRNAprotein binding in cardiovascular diseases: emerging therapeutic targets. Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 165:115067. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115067
15. Dinh P, Peng J, Tran T, Wu D, Tran C, Dinh T, et al. Identification of hsa_circ_0001445 of a novel circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network as potential biomarker for coronary heart disease. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 10:1104223. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1104223
16. Song Q, Fang L, Rong Z, Yan J, Wei J, Luan J. The role of circ_0050908 in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and its predictive value for AMI. J Cardiothorac Surg. (2025) 20(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s13019-025-03478-8
17. Boichenko V, Noakes VM, Reilly-O'Donnell B, Luciani GB, Emanueli C, Martelli F, et al. Circulating non-coding RNAs as indicators of fibrosis and heart failure severity. Cells. (2025) 14(7):553. doi: 10.3390/cells14070553
18. Xiong W, Feng S, Zhao Y, Liu X, Gong J. Revealing landscape of competing endogenous RNA networks in sepsis-induced cardiovascular diseases. Rev Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 24(7):214. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2407214
19. Zhu L, Wang Z, Sun L, Zheng D, Hu B, Li N, et al. Hsa_circ_0000437 upregulates and promotes disease progression in rheumatic valvular heart disease. J Clin Lab Anal. (2022) 36(2):e24197. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24197
20. Hu M, Wei X, Li M, Tao L, Wei L, Zhang M, et al. Circular RNA expression profiles of persistent atrial fibrillation in patients with rheumatic heart disease. Anatol J Cardiol. (2019) 21(1):2–10. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2018.35902
21. Bai L, Li Y, Lu C, Yang Y, Zhang J, Lu Z, et al. Anti-IL-17 inhibits PINK1/parkin autophagy and M1 macrophage polarization in rheumatic heart disease. Inflammation. (2025) 48(2):870–84. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02094-3
22. Xian S, Chen A, Wu X, Lu C, Wu Y, Huang F, et al. Activation of activin/Smad2 and 3 signaling pathway and the potential involvement of endothelial-mesenchymal transition in the valvular damage due to rheumatic heart disease. Mol Med Rep. (2021) 23(1):10. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11648
23. Guo F, Yi X, Li M, Fu J, Li S. Snail1 is positively correlated with atrial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and rheumatic heart disease. Exp Ther Med. (2017) 14(5):4231–7. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5084
24. Lu Z, Li Y, Lu C, Meng Z, Bai L, Huang F, et al. Inhibition of endothelial-mesenchymal transition mediated by activin receptor type IIA attenuates valvular injury induced by group A Streptococcus in Lewis rats. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). (2025) 30(1):26370. doi: 10.31083/fbl26370
25. Xiao M, Zhang M, Bie M, Wang X, Guo J, Xiao H. Galectin-3 induces atrial fibrosis by activating the TGF-β1/smad pathway in patients with atrial fibrillation. Cardiology. (2020) 145(7):446–55. doi: 10.1159/000506072
26. Ambari AM, Setianto B, Santoso A, Radi B, Dwiputra B, Susilowati E, et al. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) decrease the progression of cardiac fibrosis in rheumatic heart disease through the inhibition of IL-33/sST2. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2020) 7:115. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00115
27. Pan R, Koo C, Su W, You Q, Guo H, Liu B. Circular RNAs modulate cell death in cardiovascular diseases. Cell Death Discov. (2025) 11(1):214. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02504-x
28. Zhou WY, Cai ZR, Liu J, Wang DS, Ju HQ, Xu RH. Circular RNA: metabolism, functions and interactions with proteins. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01286-3
29. Schiano C, Infante T, Benincasa G, Burrello J, Ruocco A, Mauro C, et al. DNA hypermethylation of MED1 and MED23 as early diagnostic biomarkers for unsolved issues in atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol. (2025) 429:133179. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2025.133179
30. Akamatsu M, Mikami N, Ohkura N, Kawakami R, Kitagawa Y, Sugimoto A, et al. Conversion of antigen-specific effector/memory T cells into Foxp3-expressing T(reg) cells by inhibition of CDK8/19. Sci Immunol. (2019) 4(40):eaaw2707. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aaw2707
31. Zhao Z, He D, Ling F, Chu T, Huang D, Wu H, et al. CD4(+) T cells and TGFβ1/MAPK signal pathway involved in the valvular hyperblastosis and fibrosis in patients with rheumatic heart disease. Exp Mol Pathol. (2020) 114:104402. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104402
32. Fan Y, Shao J, Wei S, Song C, Li Y, Jiang S. Self-eating and heart: the emerging roles of autophagy in calcific aortic valve disease. Aging Dis. (2021) 12(5):1287–303. doi: 10.14336/ad.2021.0101
33. Zeng L, He J, Liu C, Zhang F, Zhang Z, Chen H, et al. Melatonin attenuates ropivacaine-induced apoptosis by inhibiting excessive mitophagy through the parkin/PINK1 pathway in PC12 and HT22 cells. Inflammation. (2022) 45(2):725–38. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01579-9
34. Liu X, Zheng Q, Wang K, Luo J, Wang Z, Li H, et al. Sam68 promotes osteogenic differentiation of aortic valvular interstitial cells by TNF-α/STAT3/autophagy axis. J Cell Commun Signal. (2023) 17(3):863–79. doi: 10.1007/s12079-023-00733-2
35. He D, Ma J, Zhou Z, Qi Y, Lian Y, Wang F, et al. TET2 suppresses vascular calcification by forming an inhibitory complex with HDAC1/2 and SNIP1 independent of demethylation. J Clin Invest. (2025) 135(9):e186673. doi: 10.1172/jci186673
Keywords: circular RNA, rheumatic heart diseases, regulatory network, diagnosis, biomarker
Citation: Chen X, Chen L, Bi L, Zhao S, Hu X, Li N, Zhu L and Shao G (2025) Expression profiles and bioinformatic analysis of circular RNA in rheumatic heart disease: potential hsa_circ_0001490 and hsa_circ_0001296 as a diagnostic biomarker. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1639767. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1639767
Received: 2 June 2025; Accepted: 22 July 2025;
Published: 1 August 2025.
Edited by:
Guo-wei Tu, Fudan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Qiancheng Luo, Shanghai Pudong New Area Gongli Hospital, ChinaJiehua Qiu, Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, China
Copyright: © 2025 Chen, Chen, Bi, Zhao, Hu, Li, Zhu and Shao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guofeng Shao, Y3hsMTk4NDAwQDE2My5jb20=
 Xiaoliang Chen
Xiaoliang Chen Lina Chen1
Lina Chen1