Abstract
Objective:
Sepsis is a common and life-threatening syndrome in intensive care units, frequently accompanied by myocardial dysfunction, which significantly worsens patient outcomes. S100A12, a calcium-binding protein associated with inflammation, is upregulated in various inflammatory conditions. However, its role in sepsis and related cardiac injury remains unclear.
Methods:
This study performed differential expression analysis using datasets from GEO to evaluate changes in S100A12 expression in sepsis and sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction (SIMD), followed by GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses. Patients diagnosed with sepsis were assigned into SIMD and non-SIMD groups, along with healthy controls. Serum S100A12 expression was evaluated by ELISA and RT-qPCR. Correlations with cardiac enzymes, inflammatory markers, and cardiac function indicators were assessed.
Results:
Bioinformatics analysis showed upregulation of S100A12 in sepsis and SIMD, enriched in multiple inflammation-related pathways. Clinically, S100A12 mRNA and protein levels were higher in the SIMD group. There was a positive association between S100A12 concentrations and cTnI, CK-MB, PCT, and IL-6, whereas MAP and LVEF exhibited a negative correlation. Logistic regression identified S100A12 as an independent risk factor for SIMD.
Conclusion:
As an inflammatory biomarker, S100A12 has independent predictive value, and its combination with cardiac enzymes enables the development of an efficient clinical warning model. The study highlights a potential new biomarker and treatment focus that could aid in early detection and management of sepsis-related cardiac injury.
1 Introduction
Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory syndrome triggered by infection, characterized by rapid onset, fast progression, and high mortality. It remains one of the leading causes of death in intensive care units worldwide (1). Approximately 30%–60% of sepsis patients develop varying degrees of sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction (SIMD) during the disease course. This complication severely impairs organ perfusion and worsens clinical outcomes, serving as an independent risk factor for sepsis-related mortality (2). Currently, early identification of SIMD relies primarily on echocardiography (3), sometimes in combination with conventional cardiac biomarkers such as cardiac troponin I (cTnI) (4, 5), and creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) (6). However, these methods lack sufficient sensitivity and specificity and often fail to reflect pathological changes in real time, highlighting the urgent need for novel molecular biomarkers to improve diagnostic and prognostic capabilities.
Scientific interest has recently shifted toward understanding the impact of inflammation-related markers in organ damage caused by sepsis (7, 8). Notably, therapeutic inhibition of S100A8/A9 has been shown to attenuate both myocardial and systemic inflammation, thereby alleviating sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction (9). Interestingly, S100A12, another key member of the S100 calcium-binding protein family, is primarily secreted by activated neutrophils and monocytes. It is markedly upregulated in various pathological states including infection (10), inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction (11–13). Through activation of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE), S100A12 stimulates nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling and the release of multiple pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby exacerbating systemic inflammation (14, 15). Existing studies have linked S100A12 levels to mortality of sepsis (16) and organ dysfunction in sepsis (17, 18). However, its specific involvement in the pathogenesis and clinical diagnosis of SIMD remains largely unexplored.
With the advent of high-throughput sequencing and the availability of public databases, bioinformatics tools such as those provided by Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) offer valuable opportunities to identify novel molecular mechanisms and targets related to sepsis and its complications. Nevertheless, studies integrating bioinformatics screening with clinical validation remain scarce, which limits the translational potential of candidate biomarkers.
Therefore, this study aims to investigate the diagnostic value of S100A12 in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. We identified upregulation of S100A12 in SIMD through GEO database analysis and further validated these findings in clinical serum samples. By employing RT-qPCR combined with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), we quantified S100A12 mRNA and protein levels, assessed their correlations with cardiac enzymes, inflammatory cytokines, and echocardiographic parameters, and explored their diagnostic potential via logistic regression and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve modeling. This study not only reveals a possible mechanistic link between S100A12 and septic cardiac injury but also supports its utility as an early diagnostic biomarker, potentially offering a new strategy for timely management of SIMD. Although S100A12 has been extensively investigated in other cardiac conditions such as heart failure, Kawasaki disease, and myocardial infarction, studies specifically addressing its role in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction (SIMD) are scarce. This gap highlights the novelty and clinical relevance of our investigation.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Dataset acquisition and bioinformatics analysis
Based on publicly available datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, specifically GSE65682 and GSE79962, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) associated with sepsis and SIMD were identified. Differential gene expression analysis was performed using the “limma” package in R software. DEGs meeting the cutoff criteria (absolute log₂ fold change >2 and adjusted p-value <0.05) were analyzed using GO term and KEGG pathway enrichment to investigate their functional characteristics and pathway involvement. These analyses were conducted using the “clusterProfiler” package in R, with a significance threshold of adjusted p-value < 0.05.
2.2 Study population and grouping
From March 2020 to December 2023, two hundred seventeen sepsis patients treated in the intensive care unit of the First People's Hospital of Guiyang participated in the study. Patients were classified into two groups based on the presence of myocardial dysfunction: the SIMD group (n = 106) and the non-SIMD group (n = 111). Sixty healthy volunteers completing routine medical examinations during the parallel period were selected as the control. Sepsis was diagnosed according to the Sepsis-3 criteria (19). Diagnosis of myocardial dysfunction was based on clinical symptoms, transthoracic echocardiography, and laboratory findings, including reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and elevated myocardial enzymes. Exclusion criteria included: history of severe cardiovascular disease, malignancy, autoimmune disorders, or recent major surgery. The study has been approved by the ethics committee of the First People's Hospital of Guiyang (No. 2025-S082), and the signed informed consent forms have been obtained from the direct relatives of all the study subjects involved. SIMD was defined according to established diagnostic criteria, combining echocardiographic findings—such as reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and abnormal wall motion—with elevated cardiac biomarkers including cTnI and CK-MB, in the absence of alternative causes for myocardial depression. All transthoracic echocardiographic examinations were performed within 24 h of ICU admission by two senior cardiologists who were blinded to patient group allocation. A standardized imaging protocol was applied to minimize inter-operator variability, and discrepant results were resolved by consensus review.
2.3 Sample size estimation
Prior to the study, a power analysis was performed based on preliminary experimental data showing differences in S100A12 protein levels between the SIMD and non-SIMD groups. Using PASS software or G*Power 3.1, and assuming a two-sided test with α = 0.05 and power (1-β) = 0.90, the minimum sample size per group was calculated. Based on pretest means (SIMD: 19.6 ± 3.4 ng/ml; non-SIMD: 14.8 ± 2.9 ng/ml), at least 52 subjects were needed per group. Considering potential bias, loss to follow-up, and the demand for statistical analyses, more than 100 subjects were ultimately included in each group.
2.4 Sample collection and detection
Peripheral venous blood (5 ml) was collected from each subject within 24 h of ICU admission. Serum was isolated by centrifugation and stored at −80°C until analysis.
For quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR), total RNA was extracted from serum samples, and complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized via reverse transcription. qRT-PCR was performed using the SYBR Green method on an ABI 7500 Real-Time PCR System. As an internal control, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was utilized, and gene expression was analyzed using the comparative Ct method.
For enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), S100A12 protein levels in serum were measured using a commercial S100A12 ELISA kit (abcam, Lot No.ab213822). Optical density was read at 450 nm, and protein concentrations (ng/ml) were calculated accordingly.
Within detection of other clinical indicators, standardized procedures were used to assess cTnI, CK-MB, procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), lactate, mean arterial pressure (MAP), LVEF, and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score.
2.5 Correlation and regression analyses
Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated to assess the relationships between S100A12 expression and clinical indicators, including myocardial enzymes (cTnI, CK-MB), inflammatory markers (PCT, CRP, IL-6), and cardiac function parameters (MAP, LVEF).
Subsequently, to determine independent risk factors for SIMD, we performed multivariate logistic regression modeling. Variables included in the model were S100A12 mRNA and protein levels, myocardial enzymes, lactate, and SOFA score. Variables were retained if p < 0.1 and excluded if p > 0.05. Stepwise regression was used for model construction.
2.6 Model evaluation
Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted to assess the diagnostic performance of individual and combined models. Diagnostic efficacy was evaluated by calculating the area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity. The model's calibration was evaluated through the Hosmer-Lemeshow (HL) goodness-of-fit test, with p > 0.05 indicating good calibration. Decision Curve Analysis (DCA) was further performed to evaluate the net clinical benefit across different threshold probabilities and compare the clinical utility of different models.
2.7 Data analysis
Statistical processing was conducted with SPSS 26.0, GraphPad Prism 9.0, and R version 4.2.2. Continuous measures followed either parametric (mean ± standard deviation, independent t-test) or non-parametric [median (IQR), Mann–Whitney test] approaches based on distributional assumptions. Count data were presented as n (%) and analyzed via chi-square tests. For multiple group comparisons, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) or Kruskal–Wallis H test was used, with Bonferroni correction for post hoc analyses. A two-sided p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Bioinformatics analysis reveals significant upregulation of S100A12 in sepsis and myocardial dysfunction
To explore the potential role of S100A12 in sepsis and SIMD, differential expression analysis was conducted using GSE65682 and GSE79962 databases. The results showed that S100A12 expression was significantly upregulated in patients with sepsis and SIMD (|log₂ FC| > 2, adjusted p < 0.05) (Figure 1).
Figure 1
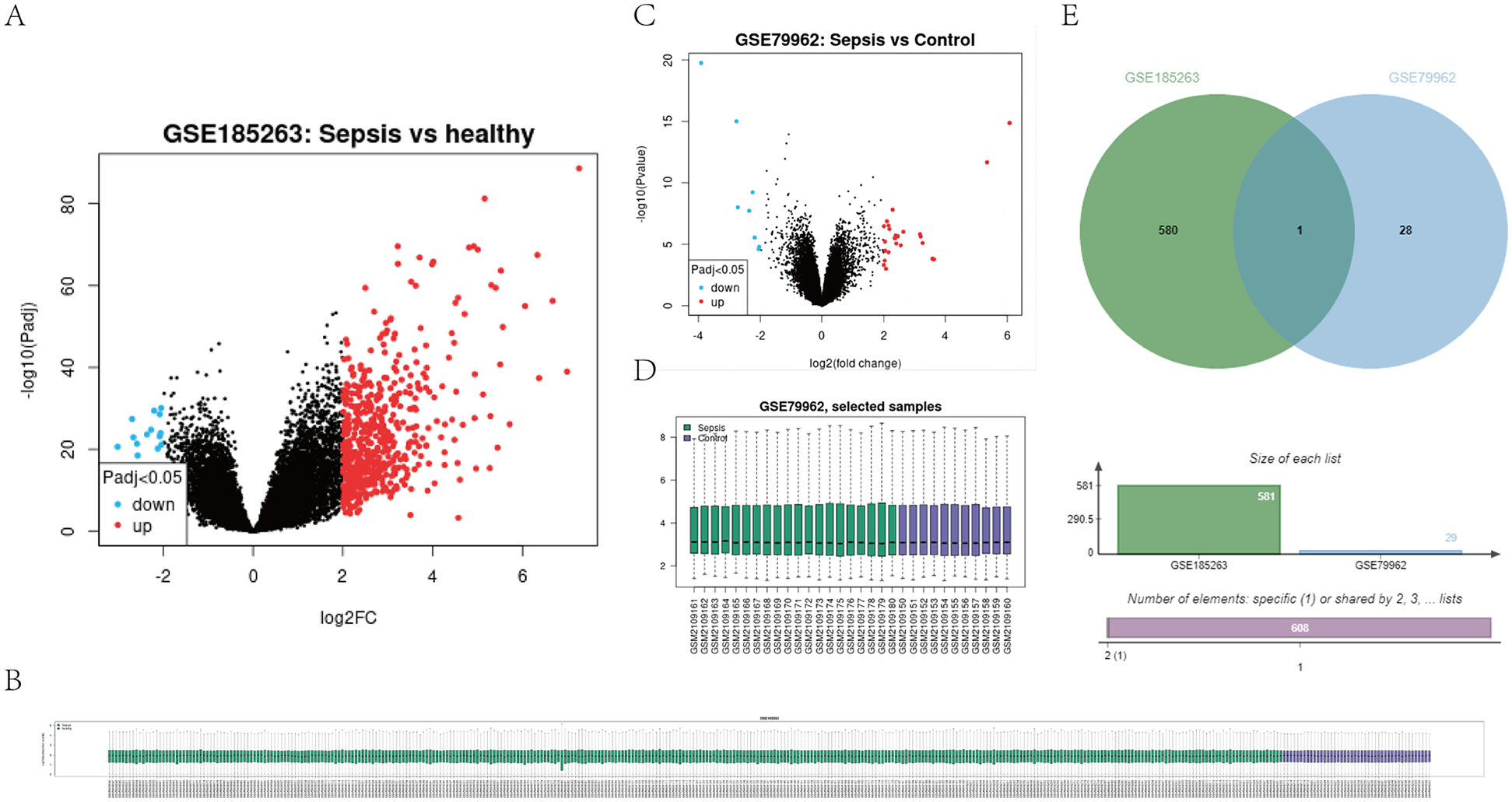
Expression profile of S100A12 in sepsis and SIMD based on GEO datasets (e.g., GSE65682, GSE79962). (A) Shows a volcano plot for GSE185263, indicating gene expression differences between sepsis and healthy samples. (B) Displays a sample clustering heatmap for GSE185263. (C) Presents a volcano plot for GSE79962, comparing sepsis and control samples. (D) Shows a box plot of selected samples from GSE79962. (E) Features a Venn diagram comparing datasets GSE185263 and GSE79962, indicating one shared element and specific numbers of unique elements in each set. (|log2FC| > 2, adjusted P < 0.05). Differential expression analysis was performed using the “limma” package in R.
Further GO and KEGG enrichment analyses displayed that upregulated genes coordinately expressed with S100A12 were particularly abundant in biological processes related to inflammation, including positive regulation of MAPK activity, NF-κB signaling pathway, inflammatory response regulation, and RAGE receptor binding (all adjusted p < 0.05) (Table 1). These findings suggest that S100A12 may play a key role in the inflammatory mechanisms underlying SIMD.
Table 1
| Ontology | ID | Description | P-value | p. adjust |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP | GO:0043406 | Positive regulation of map kinase activity | 0.006170213 | 0.020921986 |
| BP | GO:0050729 | Positive regulation of inflammatory response | 0.007712766 | 0.020921986 |
| BP | GO:0051092 | Positive regulation of NF-kappab transcription factor activity | 0.008191489 | 0.020921986 |
| BP | GO:0043405 | Regulation of MAP kinase activity | 0.009734043 | 0.020921986 |
| BP | GO:0043123 | Positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | 0.01 | 0.020921986 |
| BP | GO:0071902 | Positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity | 0.01106383 | 0.020921986 |
| BP | GO:0043122 | Regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | 0.013510638 | 0.021617021 |
| BP | GO:0051091 | Positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity | 0.014095745 | 0.021685761 |
| BP | GO:0007249 | I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | 0.015319149 | 0.021960486 |
| BP | GO:0071900 | Regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity | 0.019787234 | 0.024072948 |
| BP | GO:0050727 | Regulation of inflammatory response | 0.020957447 | 0.024072948 |
| BP | GO:0045860 | Positive regulation of protein kinase activity | 0.02106383 | 0.024072948 |
| BP | GO:0051090 | Regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity | 0.024042553 | 0.025307951 |
| BP | GO:0033674 | Positive regulation of kinase activity | 0.025319149 | 0.025968358 |
| BP | GO:0043410 | Positive regulation of MAPK cascade | 0.026117021 | 0.026117021 |
| MF | GO:0050786 | RAGE receptor binding | 0.000543183 | 0.001629549 |
Go enrichment results of DEGs associated with S100A12 upregulation.
Significantly enriched BP and MF are listed. Multiple testing was corrected using the Benjamini-Hochberg method, with a significance threshold set at adjusted P-value < 0.05.
3.2 S100A12 levels are elevated in the serum of SIMD patients
Two hundred seventeen confirmed sepsis cases were included in our analysis, and classified into SIMD group (n = 106) and the non-SIMD group (n = 111). In addition, 60 healthy volunteers served as the control group. No significant variations were found between the groups regarding demographic characteristics including gender, age, BMI, or comorbidities (e.g., hypertension, diabetes) (all p > 0.05, Table 2), indicating good comparability.
Table 2
| Parameters | Healthy (n = 60) | Non-SIMD (n = 111) | SIMD (n = 106) | X 2/F | P (3 groups) | X 2/t (2 groups) | P (2 groups) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 43.47 ± 9.103 | 46.38 ± 10.292 | 47.2 ± 11.496 | 2.487 | 0.085 | 0.554 | 0.58 | |
| Sex | Male | 22 (36.67%) | 57 (51.35%) | 47 (44.34%) | 3.478 | 0.176 | 1.068 | 0.301 |
| Female | 38 (63.33%) | 54 (48.65%) | 59 (55.66%) | |||||
| BMI | 22.1 (20,23.475) | 22.1 (20.7,23.7) | 21.55 (20.4,22.925) | 3.057 | 0.217 | −1.799 | 0.072 | |
| Hypertension | Yes | 21 (35.0%) | 37 (33.33%) | 38 (35.85%) | 0.156 | 0.925 | 0.152 | 0.697 |
| No | 39 (65.0%) | 74 (66.67%) | 68 (64.15%) | |||||
| Yes | 11 (18.33%) | 15 (13.51%) | 11 (10.38%) | 2.099 | 0.350 | 0.506 | 0.477 | |
| No | 49 (81.67%) | 96 (86.49%) | 95 (89.62%) | |||||
| S100A12 mRNA | 1.03 ± 0.31 | 1.79 ± 0.41 | 2.58 ± 0.48 | 272.35 | 0 | 13.113 | 0 | |
| S100A12 Protein | 10.33 ± 1.97 | 14.79 ± 2.92 | 19.60 ± 3.36 | 200.815 | 0 | 11.293 | 0 | |
Baseline characteristics and S100A12 expression levels among three study groups.
At the molecular level, serum S100A12 mRNA expression was higher in the SIMD group (2.58 ± 0.48) than in the non-SIMD group (1.79 ± 0.41) and the healthy control group (1.03 ± 0.31) (all p < 0.001) (Figure 2A). Additionally, the non-SIMD group exhibited higher S100A12 expression (p < 0.001).
Figure 2
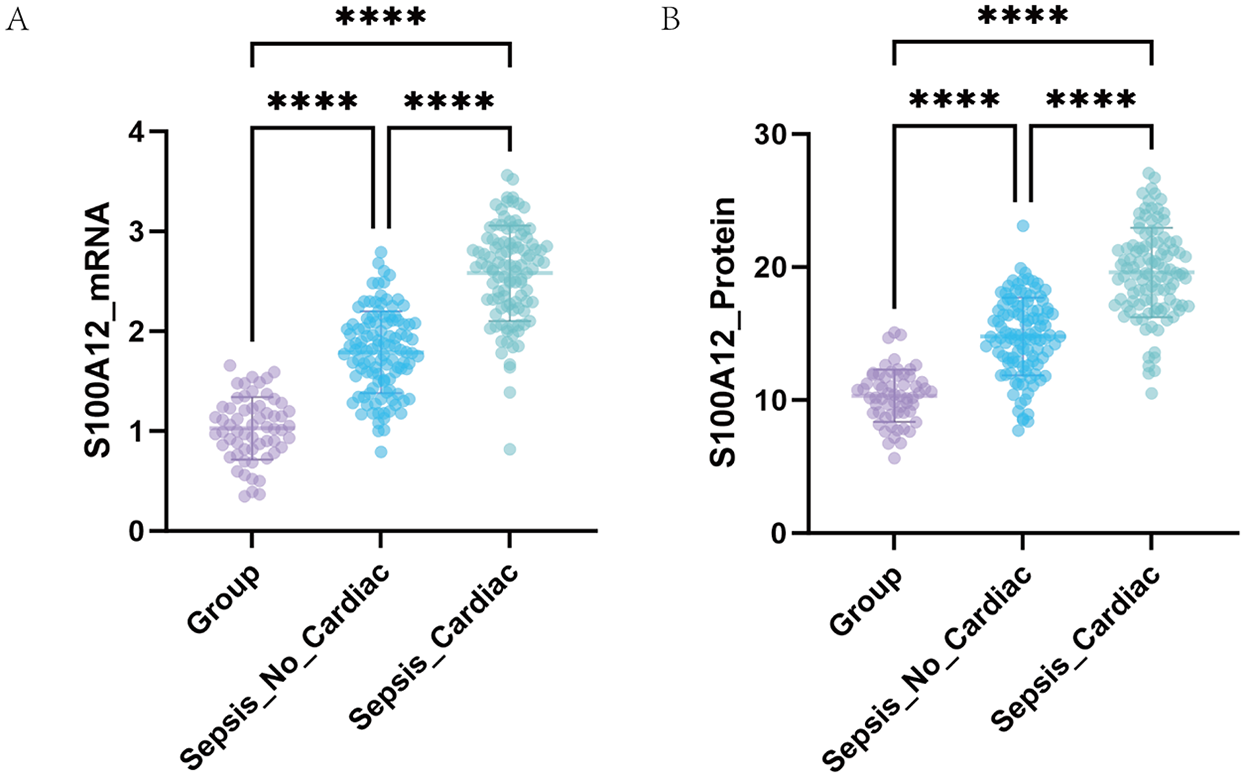
Expression of S100A12 detected by qRT-PCR and ELISA. (A) Comparison of serum S100A12 mRNA levels among different groups. (B) Comparison of serum S100A12 protein levels among different groups.
At protein level, serum S100A12 protein concentration was highest in the SIMD group (19.60 ± 3.36 ng/ml), followed by the non-SIMD group (14.79 ± 2.92 ng/ml), and lowest in the control group (10.33 ± 1.97 ng/ml), with highly significant differences between groups (all p < 0.001) (Figure 2B). These findings indicate a stepwise increase in S100A12 expression in sepsis patients, closely associated with the presence of myocardial dysfunction.
3.3 S100A12 expression correlates with cardiac function-related parameters
To further investigate the clinical significance of S100A12 in SIMD, Pearson correlation analysis was performed between S100A12 levels and myocardial enzymes, inflammatory markers, and cardiac function parameters (Table 3; Figure 3). S100A12 mRNA expression showed a moderate positive correlation with cTnI and CK-MB levels (r = 0.4065 and 0.6696, respectively; both p < 0.001). S100A12 protein levels were strongly positively correlated with these myocardial enzymes, particularly CK-MB (r = 0.7069, p < 0.001). Regarding inflammation, both mRNA and protein levels of S100A12 showed significant positive correlations with CRP, PCT, and IL-6, with the strongest correlation observed between S100A12 protein and PCT (r = 0.7182). Additionally, S100A12 expression was negatively correlated with cardiac function indicators. Specifically, S100A12 mRNA was negatively correlated with LVEF and MAP (r = −0.408 and −0.6762, respectively; both p < 0.001), while the protein expression of S100A12 showed a strong negative correlation with MAP (r = −0.7735, p < 0.001). These results suggest that S100A12 may be involved in the pathogenesis of SIMD.
Table 3
| Parameters | S100A12 mRNA | S100A12 protein | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | |
| cTnI (ng/ml) | 0.4065 | <0.0001 | 0.6322 | <0.0001 |
| CK_MB (U/L) | 0.6696 | <0.0001 | 0.7069 | <0.0001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 0.5067 | <0.0001 | 0.6604 | <0.0001 |
| PCT (ng/ml) | 0.6602 | <0.0001 | 0.7182 | <0.0001 |
| IL-6 (pg/ml) | 0.385 | <0.0001 | 0.4971 | <0.0001 |
| LVEF (%) | −0.408 | <0.0001 | −0.6479 | <0.0001 |
| MAP (mmHg) | −0.6762 | <0.0001 | −0.7735 | <0.0001 |
Correlation analysis between S100A12 expression and clinical indicators of myocardial injury, inflammation, and cardiac function.
Pearson correlation analysis was performed to report the correlation coefficients (r) and corresponding P-values for S100A12 mRNA and protein expression. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Figure 3
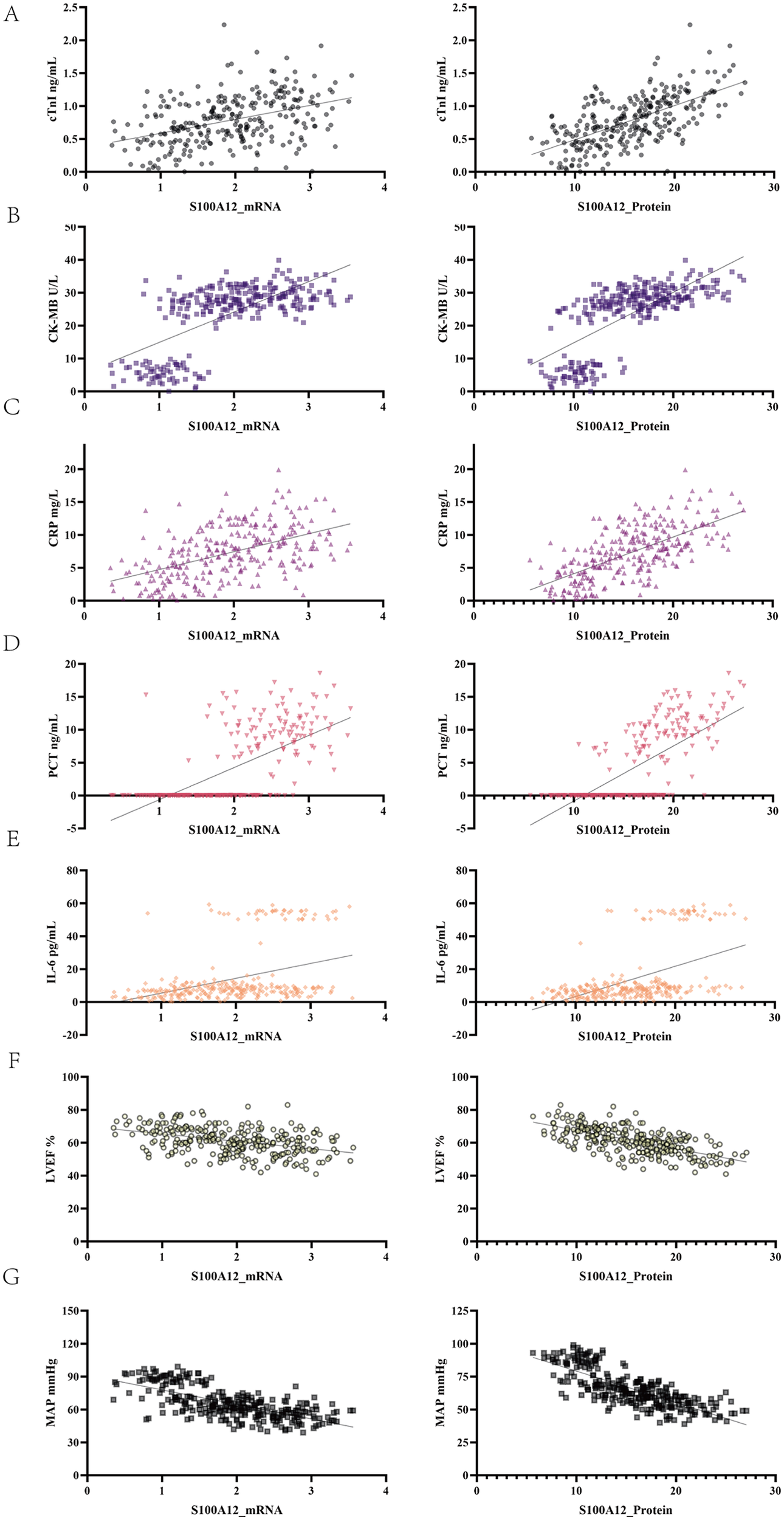
Correlation between S100A12 expression and indicators of myocardial injury, inflammation, and cardiac function. The left column shows scatter plots of Pearson correlations between S100A12 mRNA and each indicator, while the right column shows those for S100A12 protein expression. (A) cTnI. (B) CK-MB. (C) CRP. (D) PCT. (E) IL-6. (F) LVEF. (G) MAP.
3.4 S100A12 is an independent risk factor for SIMD
To further clarify the clinical role of S100A12, a comparative analysis of serum lactate concentrations and SOFA scores was performed between the two sepsis cohorts. The SIMD group had higher lactate levels (3.09 ± 1.23 vs. 2.70 ± 1.16, p = 0.016) and SOFA scores (median 8 vs. 7, p = 0.002) (Table 4).
Table 4
| Index | Non-SIMD (n = 111) | SIMD (n = 106) | Z/t | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lactate level | 2.6997 ± 1.16491 | 3.0927 ± 1.22679 | 2.421 | 0.016 |
| SOFA score | 7 (5, 9) | 8 (6, 9) | 3.063 | 0.002 |
Comparison of lactate levels and SOFA scores between two patient groups.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed including S100A12 mRNA and protein levels, lactate, SOFA score, cTnI, and CK-MB. As shown in Table 5; Figure 4, S100A12 remained an independent risk factor for SIMD. Specifically, the OR for S100A12 mRNA was 63.364 (95% CI: 17.026–235.812, p < 0.001), and for S100A12 protein it was 1.808 (95% CI: 1.432–2.283, p < 0.001). In contrast, lactate, SOFA score, cTnI, and CK-MB did not reach statistical significance in the multivariate model (p > 0.05 for all). These findings suggest that S100A12 has independent predictive value for early risk identification of SIMD.
Table 5
| Variable | β | SE | Wald | p-value | OR | 95% CI (lower limit, superior limit) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S100A12_mRNA | 4.149 | 0.67 | 38.289 | 0 | 63.364 | 17.026–235.812 |
| S100A12_Protein | 0.592 | 0.119 | 24.766 | 0 | 1.808 | 1.432-2.283 |
| Lactate level | 0.029 | 0.2 | 0.022 | 0.883 | 1.03 | 0.695–1.525 |
| SOFA score | 0.142 | 0.108 | 1.739 | 0.187 | 1.152 | 0.933–1.423 |
| cTnI | 0.27 | 0.763 | 0.125 | 0.723 | 1.31 | 0.294–5.845 |
| CK_MB | −0.163 | 0.09 | 3.248 | 0.072 | 0.85 | 0.711–1.014 |
| Constant | −15.9 | 2.809 | 32.034 | 0 | 0 |
Multivariate logistic regression analysis of S100A12 as an independent predictor in SIMD.
Included variables: S100A12 mRNA, protein expression, lactate, SOFA score, cTnI, CK-MB. P < 0.05 indicates statistical significance.
Figure 4
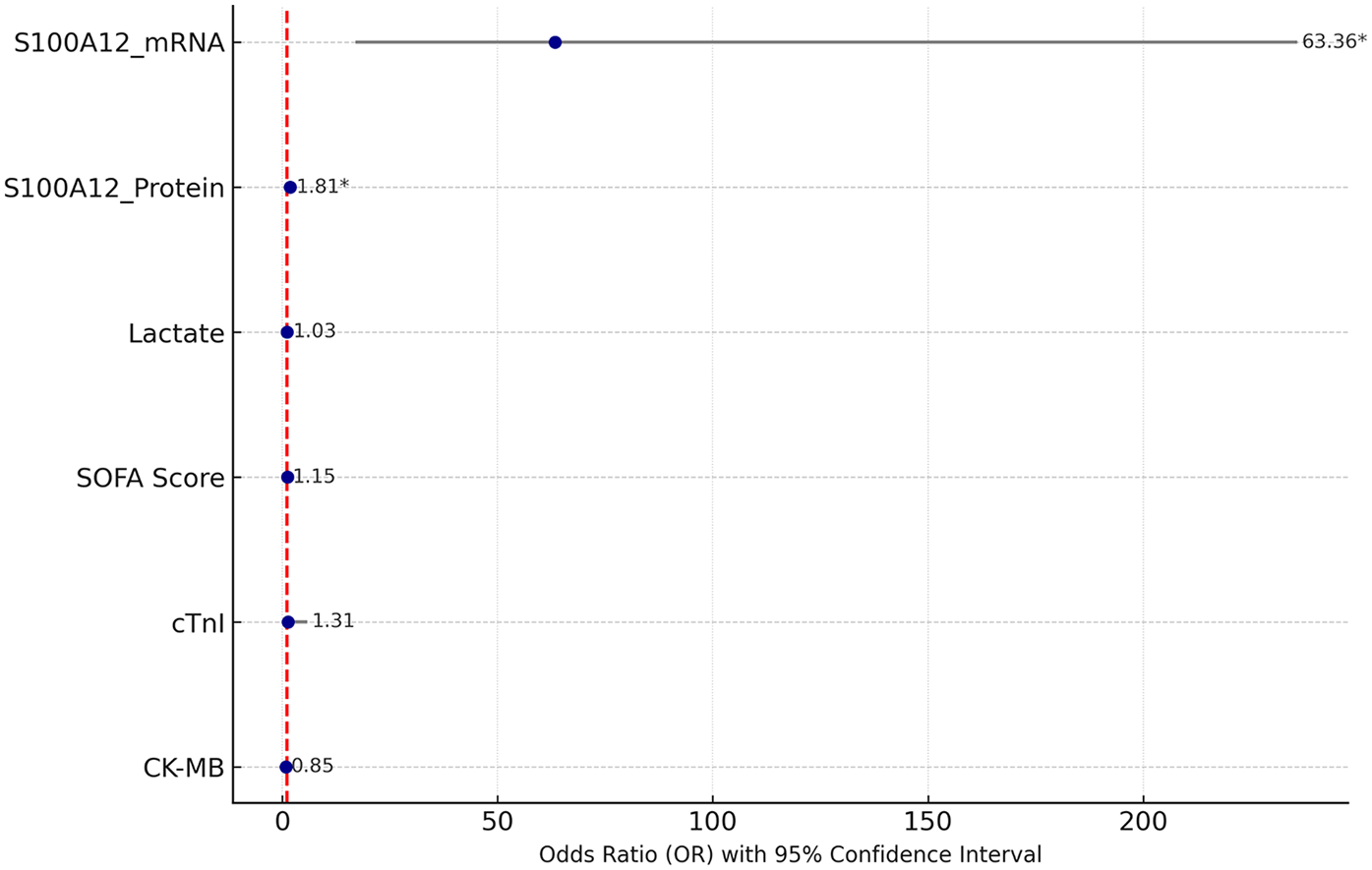
Forest plot of multivariate logistic regression analysis. The figure shows the OR values of each variable and their 95% CI, with significant variables marked by an asterisk (*).
3.5 Diagnostic performance of S100A12-based predictive models for SIMD
To assess the diagnostic value of S100A12 for sepsis-associated myocardial dysfunction, we performed ROC curve evaluation. ROC curve analysis indicated excellent discriminative capacity for S100A12 mRNA (AUC 0.895, 95% CI 0.853–0.937; sensitivity 81.1%, specificity 83.8%). The protein counterpart maintained good diagnostic value (AUC 0.865, 95% CI 0.817–0.914; sensitivity 82.1%, specificity 74.8%). In comparison, the AUCs for cTnI and CK-MB were 0.6997 and 0.6491, respectively, with significantly lower diagnostic accuracy. Lactate and SOFA scores also demonstrated limited diagnostic value. The standalone diagnostic performance of S100A12 mRNA and protein is superior to that of traditional markers cTnI and CK-MB (Table 6; Figure 5).
Table 6
| Variable | AUC | Youden | S.E. | 95% CI | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S100A12 mRNA | 0.8952 | 0.6491 | 0.02133 | 0.8534–0.9370 | 81.13 | 83.78 |
| S100A12 protein | 0.8652 | 0.5685 | 0.02466 | 0.8168–0.9135 | 82.08 | 74.77 |
| cTnI | 0.6997 | 0.2901 | 0.03531 | 0.6305–0.7689 | 64.15 | 64.86 |
| CK-MB | 0.6491 | 0.2678 | 0.03720 | 0.5762–0.7220 | 74.53 | 52.25 |
| Lactate level | 0.5917 | 0.1714 | 0.03855 | 0.5162–0.6673 | 60.38 | 56.76 |
| SOFA score | 0.6193 | 0.1907 | 0.03778 | 0.5452–0.6933 | 63.21 | 55.86 |
| Constant (Combined) | 0.9576 | 0.7902 | 0.01182 | 0.9344–0.9808 | 94.34 | 84.68 |
ROC analysis results of S100A12 and conventional indicators in diagnosing septic myocardial dysfunction.
Metrics such as AUC, standard error, Youden index, sensitivity, and specificity were included. The combined prediction model is a logistic model constructed based on S100A12, cTnI, and CK-MB. The closeness of AUC to 1 indicates better predictive performance.
Figure 5
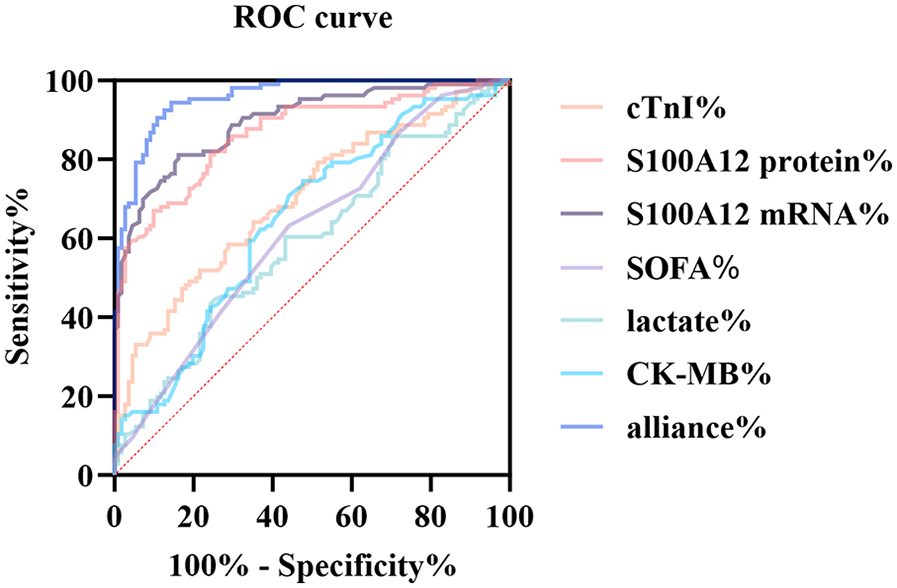
ROC curve comparison of multiple biomarkers for diagnosing SIMD. The figure displays the ROC curves of S100A12 mRNA, S100A12 protein, cTnI, CK-MB, lactate, SOFA score, and the combined prediction model (alliance) for identifying sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction.
3.6 Combined model incorporating S100A12 and cardiac function indicators demonstrates high clinical applicability
A final logistic regression model was developed incorporating S100A12 mRNA, protein levels, and cardiac function indicators (LVEF, MAP). This model demonstrated excellent discrimination ability, with an AUC of 0.960 (Figure 6A). Model calibration was assessed using the HL test, yielding an HL statistic of 7.39 and P = 0.495 (Figure 6B), indicating good agreement between predicted and observed values. DCA was utilized to determine the threshold-dependent clinical value of the predictive model. As shown in Figure 6C, the blue curve representing the model was consistently above the “treat all” and “treat none” curves across most probability thresholds, demonstrating its strong clinical benefit and potential to support decision-making in practice.
Figure 6
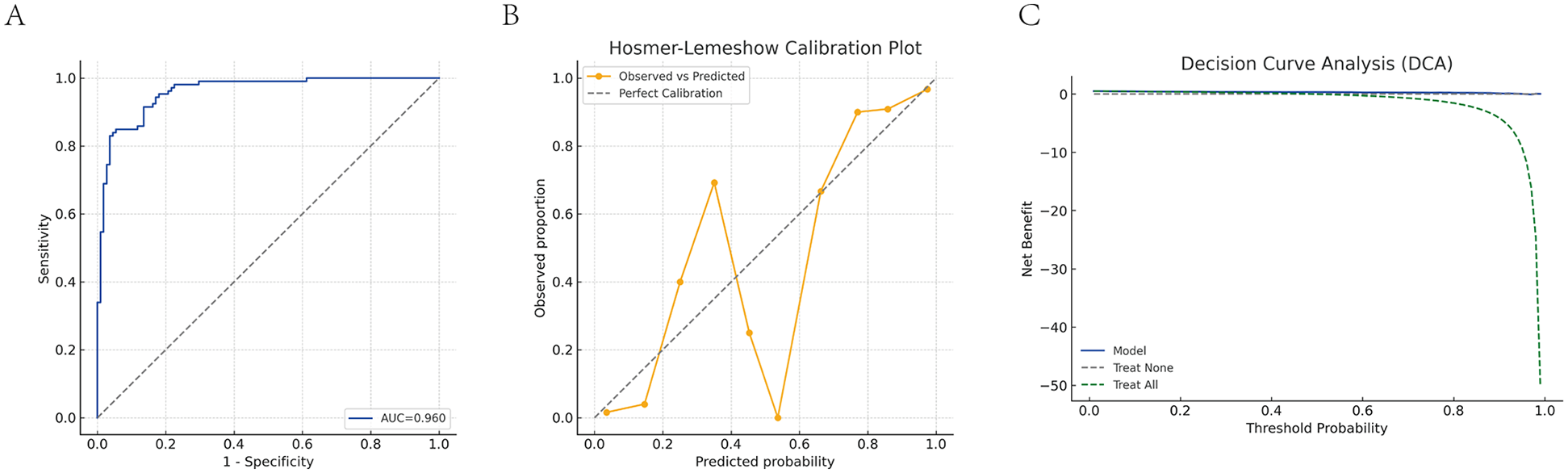
Diagnostic performance evaluation of the combined predictive model. (A) ROC curve analysis of the combined model. (B) HL calibration plot. (C) DCA of the combined model. The blue solid line represents the net benefit of the combined prediction model (S100A12 mRNA + S100A12 protein + LVEF + MAP) across different threshold probabilities; the green dashed line represents the “treat all” strategy (intervene on all patients); the gray dashed line represents the “treat none” strategy (no intervention for anyone). When the model curve is above these two dashed lines, it indicates a positive clinical net benefit.
4 Discussion
SIMD is one of the most common and challenging complications in critical care, yet sensitive and reliable molecular markers for early identification remain lacking (20). This study combined bioinformatics analysis with clinical validation and found that S100A12 was persistently elevated in patients with sepsis and SIMD. Elevated S100A12 was significantly correlated with myocardial enzymes, inflammatory markers, and hemodynamic parameters, demonstrating independent predictive value. A diagnostic model incorporating S100A12 achieved an AUC of 0.9576, outperforming traditional indicators, suggesting strong potential for use in early clinical warning systems.
Compared with previous studies, this research is the first to systematically validate S100A12 within a clinical diagnostic framework for SIMD. Previous literature has identified S100A12 as a pro-inflammatory damage-associated molecular pattern, capable of binding to receptors such as RAGE (receptor for advanced glycation end-products) and TLR4, leading to downstream activation of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. These cascades result in increased transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β), endothelial dysfunction, and leukocyte recruitment, which together exacerbate tissue inflammation and injury (10, 11, 13, 21, 22). Our data not only reaffirmed these associations but also demonstrated that S100A12 levels correlated positively with cardiac injury markers (cTnI, CK-MB) and inflammatory mediators (IL-6, PCT), while showing negative correlation with LVEF and MAP, key indicators of cardiac function and hemodynamic stability. The GO and KEGG enrichment analyses further indicated significant involvement of S100A12-related genes in immune-inflammatory signaling, particularly MAPK, NF-κB, and Toll-like receptor pathways, all of which are known to be central in SIMD pathogenesis. Specifically, activation of NF-κB signaling has been shown to drive cardiomyocyte apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction under septic conditions, contributing to contractile impairment (23). MAPK signaling, especially through p38 and JNK sub-pathways, is implicated in the regulation of myocardial inflammation, calcium overload, and reactive oxygen species accumulation during systemic inflammatory responses (24).
S100A12, through its RAGE interaction, may serve as an upstream amplifier of these pro-death signals, forming a feed-forward loop that sustains and intensifies myocardial injury. Moreover, recent studies have highlighted that S100A12 can modulate endothelial permeability, exacerbate capillary leakage, and promote macrophage activation, all of which further contribute to the microcirculatory dysfunction and myocardial oxygen supply-demand mismatch observed in SIMD. This multifaceted role aligns with our observation that elevated S100A12 is associated with reduced MAP and LVEF, suggesting a direct link between systemic inflammation, vascular collapse, and myocardial depression. Collectively, these results indicate S100A12 may serve functions beyond a diagnostic biomarker, also an active pathogenic mediator in SIMD, contributing to myocardial damage via inflammatory injury, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction. The robust correlations observed in our clinical cohort provide translational relevance and support the incorporation of S100A12 into diagnostic or therapeutic frameworks for SIMD.
In terms of practical application, S100A12 has several advantages as a serum biomarker. Its expression is stable, sample collection is convenient, and it can be detected at both the mRNA level (via qRT-PCR) and the protein level (via ELISA). Compared with traditional cardiac enzymes such as cTnI and CK-MB, S100A12 demonstrated higher sensitivity and specificity in detecting SIMD, particularly in the early inflammatory phase when classical markers may still remain within normal ranges (25). This is likely because S100A12, as an alarmin of the S100/calgranulin family, is rapidly released by activated neutrophils and monocytes in response to systemic infection, serving as an early signal of innate immune activation and sterile inflammation (26). In contrast, cTnI and CK-MB primarily reflect structural myocardial injury, often representing a downstream consequence of prolonged inflammation or hypoperfusion, thus limiting their ability to detect subclinical or functional myocardial impairment. Previous studies have linked S100A12 to various cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure, ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), and coronary artery disease (CAD). Elevated S100A12 levels in these conditions have been associated with plaque instability, coronary calcification, and adverse clinical outcomes. Our findings in SIMD are consistent with these observations, suggesting that S100A12 may represent a shared inflammatory mediator across different cardiac pathologies, while also highlighting its potential as a specific biomarker for sepsis-related myocardial dysfunction.
The combined diagnostic model developed in this study incorporated S100A12 (mRNA and protein levels) together with inflammatory markers (such as IL-6 and PCT), cardiac function indicators (e.g., LVEF, MAP), and organ dysfunction scores (e.g., SOFA score). This multimodal approach significantly enhanced the discriminative power for SIMD, as evidenced by a high AUC in ROC curve analysis. From a mechanistic perspective, this combination model captures both upstream immune dysregulation (via S100A12 and IL-6), and downstream functional impairment (via LVEF and MAP), achieving temporal and pathophysiological complementarity. For instance, while S100A12 reflects early immune activation, IL-6 integrates the broader cytokine storm environment, and SOFA score quantifies multi-organ dysfunction severity. At the same time, LVEF offers a direct assessment of cardiac systolic performance, and MAP reflects hemodynamic stability and tissue perfusion. By integrating these heterogeneous but interrelated indicators, the combined model overcomes the limitations of single biomarkers and allows for more accurate identification of SIMD across its full clinical spectrum—from functional impairment without structural damage, to irreversible myocardial injury.
Such complementarity is particularly critical in the context of sepsis, where myocardial depression is often multifactorial, involving not only direct myocardial insult but also microcirculatory disturbance, cytokine-induced myocardial stunning, and oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction. In this framework, S100A12 acts not only as a surrogate of inflammation but also as a potential mediator of myocardial injury through RAGE-NF-κB signaling, thereby bridging the immune-inflammatory response and cardiac dysfunction. Taken together, these results suggest that S100A12-based multimarker strategies could serve as an effective early-warning system for SIMD, improving risk stratification, individualized monitoring, and potentially guiding targeted anti-inflammatory interventions in clinical practice. Decision curve analysis showed high net clinical benefit across a range of threshold probabilities, demonstrating its strong potential in clinical decision-making. This lays a foundation for future precision stratification and management of sepsis.
Despite the strengths in study design and data analysis, several limitations should be acknowledged, beginning with the retrospective nature and restricted sample size from a single institution, and further validation in multi-center, large-sample cohorts is necessary. Second, whether S100A12 acts as a pathogenic factor or is merely a reactive elevation in myocardial dysfunction remains unclear and requires further investigation using animal models and cell-based experiments. Third, this study did not include longitudinal samples, preventing an assessment of S100A12's dynamic changes over time and its relationship with patient outcomes. Future research should incorporate long-term follow-up and interventional studies to clarify its causal role and therapeutic potential. Several limitations warrant mention. First, although sample collection was standardized within 24 h of ICU admission, variability in disease onset prior to admission was not controlled and may have influenced biomarker levels. Second, while major cardiovascular diseases were excluded, data on medications such as vasopressors, corticosteroids, and the timing of antibiotic administration were not comprehensively recorded; these factors may confound biomarker interpretation and should be addressed in future prospective studies.
5 Conclusion
In summary, this study reveals the expression pattern of S100A12 in SIMD and its close association with inflammation and cardiac injury, confirming S100A12 as an independent predictive factor for SIMD. Beyond its superior diagnostic performance, S100A12 may also represent a potential target within the inflammation-cardiac dysfunction axis. These findings provide new insights and theoretical support for early identification and intervention in SIMD.
Statements
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, accession numbers: GSE65682 and GSE79962.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the First People's Hospital of Guiyang (No. 2025-S082). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
FW: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Investigation. HH: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YT: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Data curation. XW: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Holmes CL Albin OR Mobley HLT Bachman MA . Bloodstream infections: mechanisms of pathogenesis and opportunities for intervention. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2025) 23:210–24. 10.1038/s41579-024-01105-2
2.
Yu X Gao J Zhang C . Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction: mitochondria and energy metabolism. Intensive Care Med Exp. (2025) 13:20. 10.1186/s40635-025-00728-w
3.
Kim JS Kim YJ Kim M Ryoo SM Kim WY . Association between right ventricle dysfunction and poor outcome in patients with septic shock. Heart. (2020) 106:1665–71. 10.1136/heartjnl-2020-316889
4.
Yang Y Leng J Tian X Wang H Hao C . Brain natriuretic peptide and cardiac troponin I for prediction of the prognosis in cancer patients with sepsis. BMC Anesthesiol. (2021) 21:159. 10.1186/s12871-021-01384-9
5.
Chen FC Xu YC Zhang ZC . Multi-biomarker strategy for prediction of myocardial dysfunction and mortality in sepsis. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. (2020) 21:537–48. 10.1631/jzus.B2000049
6.
Lin LQ Mao FK Lin J Guo L Yuan WR Wang BY . Ginsenoside Rg1 induces ferroptosis by regulating the focal adhesion kinase/protein kinase B-forkhead box O3A signaling pathway and alleviates sepsis-induced myocardial damage. J Physiol Pharmacol. (2024) 75(4):389–401. 10.26402/jpp.2024.4.04
7.
Shi X Yan Z Ding R Xia F Du Y Wang X et al Integrated bioinformatics and experiment validation reveal cuproptosis-related biomarkers and therapeutic targets in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. BMC Infect Dis. (2025) 25:445. 10.1186/s12879-025-10822-9
8.
Gong A Dai J Zhao Y Hu H Guan C Yu H et al Piezo1 activation protects against sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction in a pilot study. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:15975. 10.1038/s41598-025-00829-2
9.
Jakobsson G Papareddy P Andersson H Mulholland M Bhongir R Ljungcrantz I et al Therapeutic S100A8/A9 blockade inhibits myocardial and systemic inflammation and mitigates sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Crit Care. (2023) 27:374. 10.1186/s13054-023-04652-x
10.
Qin S Bie F Chen S Xu Y Chen L Shu B et al Targeting S100A12 to improve angiogenesis and accelerate diabetic wound healing. Inflammation. (2025) 48:633–48. 10.1007/s10753-024-02073-8
11.
Shen Y Ye X Jiang L Li H Zhang Y Wang W et al Inhibition of S100A12 attenuates LPS-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction in HPMECs through the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Curr Mol Med. (2025). 10.2174/0115665240338945250317082242
12.
Zhang X Song H Liu D Cai Y Liu Z Zhang X et al S100a12 triggers NETosis to aggravate myocardial infarction injury via the annexin A5-calcium axis. Nat Commun. (2025) 16:1746. 10.1038/s41467-025-56978-5
13.
Cai W He Y Li G Zhang D Chen Z Jin S et al Association between S100A12 and risk of peripheral arterial disease in patients with dyslipidemia: a cross-sectional study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2025) 25:313. 10.1186/s12872-025-04752-2
14.
Cao X Xu Z Zhang B Li Q Jiang Z Yuan X . Metabolic biomarkers mediate allergic conjunctivitis via circulating inflammatory proteins: evidence from a Mendelian randomization study. Transl Vis Sci Technol. (2025) 14:12. 10.1167/tvst.14.4.12
15.
Gkavogiannakis NA Tsoporis JN Drosatos IA Tsirebolos G Izhar S Sakadakis E et al Emergent inflammatory markers and echocardiographic indices in patients with bronchial asthma. Biomolecules. (2023) 13(6):955. 10.3390/biom13060955
16.
Zhang W . Critical roles of S100A12, MMP9, and PRTN3 in sepsis diagnosis: insights from multiple microarray data analyses. Comput Biol Med. (2024) 171:108222. 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108222
17.
Zhu J Lin X Yan C Yang S Xu Z . Tocilizumab attenuates acute lung injury in rats with sepsis by regulating S100A12/NLRP3. Am J Transl Res. (2023) 15:99–113. www.ajtr.org /ISSN:1943-8141/AJTR0147508
18.
You G Zhao X Liu J Yao K Yi X Chen H et al Machine learning-based identification of CYBB and FCAR as potential neutrophil extracellular trap-related treatment targets in sepsis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1253833. 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1253833
19.
Wu J Pei F Zhou L Li W Sun R Li Y et al The efficacy and safety of thymosin alpha1 for sepsis (TESTS): multicentre, double blinded, randomised, placebo controlled, phase 3 trial. Br Med J. (2025) 388:e082583. 10.1136/bmj-2024-082583
20.
Tong H Zhao Y Cui Y Yao J Zhang T . Multi-omic studies on the pathogenesis of sepsis. J Transl Med. (2025) 23:361. 10.1186/s12967-025-06366-w
21.
Oesterle A Bowman MA . S100A12 and the S100/calgranulins: emerging biomarkers for atherosclerosis and possibly therapeutic targets. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2015) 35:2496–507. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.302072
22.
Liu H Xu C Hu Q Wang Y . Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: understanding pathophysiology and clinical implications. Arch Toxicol. (2025) 99:467–80. 10.1007/s00204-024-03916-x
23.
Walley KR . Deeper understanding of mechanisms contributing to sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Crit Care. (2014) 18:137. 10.1186/cc13853
24.
Zhang Z Zhu L Wang Y Tian W Li H . CARD9 deficiency alleviates septic pulmonary embolism. Inhal Toxicol. (2025) 37:87–97. 10.1080/08958378.2025.2473432
25.
Yang H Feng L Jiang Z Wu X Zeng K . Amlexanox reduces new-onset atrial fibrillation risk in sepsis by downregulating S100A12: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2024) 11:1401314. 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1401314
26.
Nazari A Khorramdelazad H Hassanshahi G Day AS Sardoo AM Fard ET et al S100A12 in renal and cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci. (2017) 191:253–8. 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.10.036
Summary
Keywords
sepsis, myocardial dysfunction, S100A12, inflammatory biomarker, receiver operating characteristic curve, logistic regression, bioinformatics analysis
Citation
Wu F, Hong H, Tian Y and Wang X (2025) Serum S100A12 in the clinical diagnosis of sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction: an integrated bioinformatics and clinical data analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1640788. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1640788
Received
04 June 2025
Accepted
11 August 2025
Published
25 August 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
DeLisa Fairweather, Mayo Clinic Florida, United States
Reviewed by
Sianny Herawati, Udayana University, Indonesia
Esra Polat, Gaziantep City Hospital, Türkiye
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Wu, Hong, Tian and Wang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Xiaoyan Wang wang123456789wxy@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.