- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Tongde Hospital of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Intensive Care Unit, Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the clinical efficacy, safety, and impact on outcomes of levosimendan compared with dobutamine in patients with septic cardiomyopathy.
Methods: A randomized clinical trial was conducted in patients with septic cardiomyopathy between December 2022 and March 2024. Eligible patients received either levosimendan or dobutamine in addition to standard sepsis treatments. Baseline characteristics, laboratory parameters, pulse index continuous cardiac output, clinical outcomes, and adverse reactions were recorded and compared between the two groups.
Results: A total of 50 patients were analyzed, with 25 patients in each group. The mean age was 76.4 (±12.3) years, and 28 patients (56%) were male. Baseline characteristics were comparable between groups. Following treatment, improvements were observed in both groups in left ventricular ejection fracture and levels of cardiac troponin I, B-type natriuretic peptide, cardiac index (CI), lactate, and norepinephrine infusion rate(all P < 0.05), with significantly greater improvements in the levosimendan group (P < 0.05). Additionally, the CI was higher in the levosimendan group compared to the dobutamine group (P < 0.05). No statistically significant differences were observed between groups in other pulse index continuous cardiac output variables, laboratory tests, clinical outcomes, or adverse reactions.
Conclusions: In patients with septic cardiomyopathy, levosimendan treatment resulted in greater improvements in cardiac function, hemodynamic stability, and tissue perfusion compared with dobutamine, without an increase in adverse reactions. Further studies are needed to evaluate the long-term effects of levosimendan on clinical outcomes in this patient population.
Registration number: ChiCTR2500101261.
Introduction
Sepsis is a life-threatening multi-organ dysfunction resulting from a dysregulated host response to infection (1). Septic cardiomyopathy refers to acute cardiac dysfunction unrelated to myocardial ischemia that occurs in sepsis patients. Its prevalence in septic patients was estimated at up to 70% (2), with a mortality rate as high as 70%–90% (3). Currently, the treatment for septic cardiomyopathy is to improve the cardiac function. In clinical practice, the most commonly applied positive inotropic drug in septic shock patients is dobutamine (4). Dobutamine can increase myocardial contractility by directly activating cardiac β1 receptors and augment cardiac output, reducing peripheral vascular resistance and ventricular filling pressures, and promoting atrioventricular node conduction. However, dobutamine can increase heart rate and myocardial oxygen consumption, with potential negative impacts on patient outcomes (5). There is no consensus on the selection of inotropic drugs for septic cardiomyopathy.
As a novel cardiotonic drug, levosimendan binds to cardiac troponin C in a calcium-dependent manner. Levosimendan can enhance the calcium sensitivity of contractile proteins and produce positive inotropic effects. In addition, levosimendan can induce diastole in coronary resistance vessels and dilate systemic venous volume vessels by opening adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels in vascular smooth muscle (6). Theoretically, levosimendan has the advantages of maintaining systemic and pulmonary circulation without elevating intracellular calcium ion concentration, accelerating ventricular rate, and increasing myocardial oxygen consumption. However, the potential benefits or limitations of levosimendan have not been confirmed in the clinic. Gordan et al. reported that the addition of levosimendan in patients with septic shock failed to improve the morbidity and mortality but led to supraventricular tachycardia and difficulty in weaning from mechanical ventilation (7). Subsequent subgroup analyses also suggested that the addition of levosimendan to standard sepsis treatment was not associated with improved organ dysfunction and reduced mortality in patients with cardiac insufficiency (8). However, a meta-analysis, including 192 patients with sepsis-associated cardiac insufficiency, found that levosimendan improved cardiac function and reduced extravascular lung fluid and lactic acid better than dobutamine (9).
In this study, we compared the clinical efficacy, safety, and outcomes of levosimendan vs. dobutamine treatments in patients with septic cardiomyopathy to provide evidence-based clinical application of levosimendan in this patient population.
Materials and methods
Study design and participant selection
A randomized clinical trial was conducted in patients with septic cardiomyopathy admitted to the Department of Intensive Care Medicine at the Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University, China, between December 2022 and March 2024. The study protocol was approved by the university's ethics committee and registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (registration number: ChiCTR2500101261). Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants.
The inclusion criteria were (10) as follows: (1) diagnosis of sepsis or septic shock based on the Sepsis-3.0 criteria (2) left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <45%, or > a decrease of 10% from baseline; (3) cardiac troponin I (cTnI) >0.06 ng/ml and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) >100 pg/ml; and 4) age ≥18 years.
Exclusion criteria included: (1) confirmed diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome within two weeks before or after sepsis diagnosis; (2) history of chronic heart failure; (3) history of cardiac surgery or pacemaker implantation; (4) malignant arrhythmias; (5) hypertrophic or restrictive cardiomyopathy, or severe valvular stenosis or regurgitation; (6) severe hepatic or renal dysfunction; and (7) use of positive inotropic agents within one week prior to the trial. Additionally, patients who underwent cardiopulmonary resuscitation, electrical defibrillation, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or intra-aortic balloon pump after trial initiation were excluded from the analysis.
Study protocol
The participants were randomly assigned to either the levosimendan group or dobutamine group. All of them were treated following the standard sepsis guidelines, including antibiotics, fluid resuscitation, and supportive care, and were monitored by the pulse index continuous cardiac output (PiCCO). In the levosimendan group, levosimendan was initiated at 0.1 μg/kg/min and titrated to a range of 0.05–0.2 μg/kg/min to maintain the mean arterial pressure above 65 mmHg. The treatment was continued for 24 h. In the dobutamine group, dobutamine was initiated at 5 μg/kg/min and titrated within a range of 2.5–20 μg/kg/min to maintain mean arterial pressure (MAP) above 65 mmHg. Treatment was continued for 72 h.
If adverse reactions related to the study drugs occurred, symptomatic management was implemented. This included maintaining adequate volume status, adjusting doses of vasoactive and sedative–analgesic agents, replenishing electrolytes, correcting acid–base imbalances, and optimizing respiratory parameters. If symptoms persisted after 2 h of such interventions, the dose of levosimendan or dobutamine was appropriately reduced. The observation was continued for an additional two hours. If symptoms resolved, the drug dose was re-adjusted to the original level. If symptoms remained unresolved, the study drug was discontinued, the trial was terminated for that patient, and further symptomatic treatment was provided to ensure patient safety.
If there was suspected excessive fluid infusion prior to the admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), restricted fluid intake would be applied. Patients with two or more of the following characteristics would receive intravenous diuretics, (1) clinical symptoms or signs of increased heart rate, shortness of breath, edema, or pink frothy sputum, (2) chest imaging showing hilar butterfly shadow, pleural effusion, (3) negative passive leg-lifting test, (4) significant increase in BNP, (5) ultrasound demonstrating right heart or inferior vena cava dilation.
If a patient's daily urine output remained <800 ml after a daily dose of 80 mg furosemide, with significantly elevated serum creatinine level, continuous renal replacement therapy would be initiated and the patient would be excluded from this trial.
Data collection
Baseline information, including sex, age, height, weight, the primary site of infection, sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score, and acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE) II score were recorded. Clinical and laboratory parameters, including heart rate (HR), MAP, norepinephrine dosage (NED), lactate, left ventricular ejection fracture (LVEF), cTnI, BNP, cardiac index (CI), central venous pressure (CVP), global end-diastolic volume index (GEDVI), extravascular lung water index (EVLWI), systemic vascular resistance index (SVRI), white blood cell (WBC) count, C-reactive protein (CRP), and procalcitonin (PCT) were measured at baseline and 24, 48, and 72 h after treatment initiation. Additionally, the length of ICU stay, duration of mechanical ventilation, 28-day mortality, SOFA score at 72 h post-treatment and APACHE II score at 72 h post-treatment were recorded. Adverse reactions during treatment were also documented.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed in SPSS (version 27.0, IBM, New York, USA). The continuous data were presented as mean ± standard deviation or median with interquartile range and were compared by either t-test, ANOVA, Mann–Whitney, or Kruskal–Wallis test, depending on the normality test results. The categorical data were presented as numbers with percentages and compared using the Chi-square test. A P < 0.05 was considered statistically significantly different.
Results
Patient enrollment and baseline characteristic comparisons
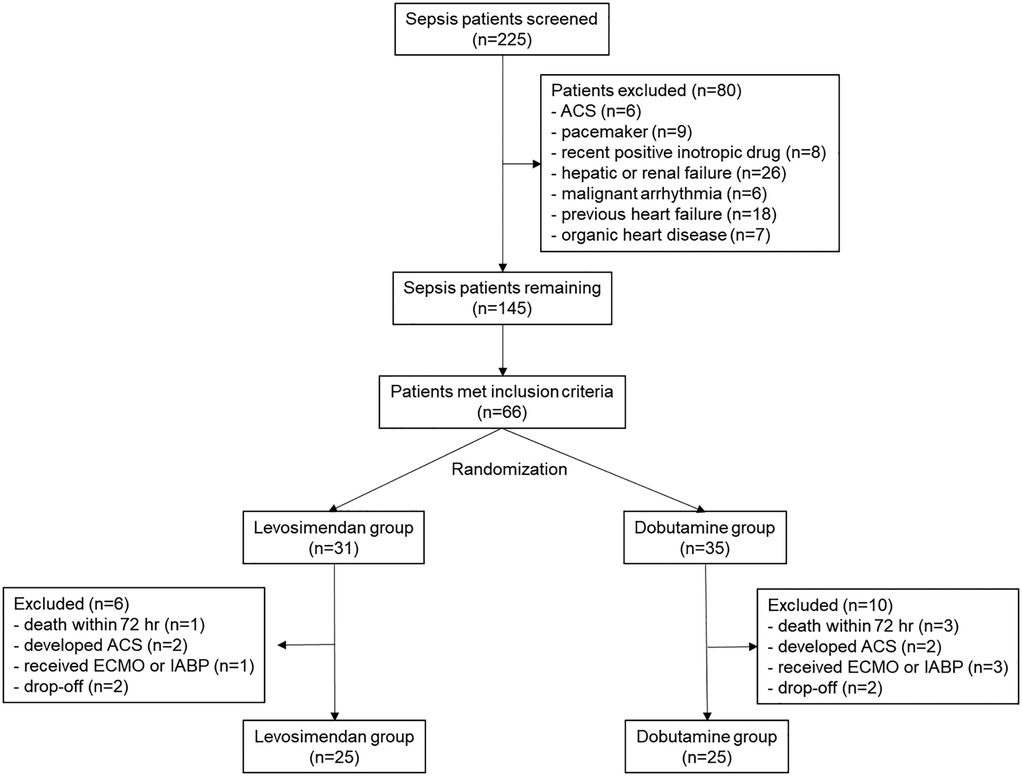
A total of 225 sepsis or septic shock patients were screened. Finally, 50 patients were analyzed, with 25 in both the levosimendan and the dobutamine groups. The CONSORT flowchart is shown in Figure 1. Their mean age was 76.4 (±12.3), with 28 (56%) male patients.
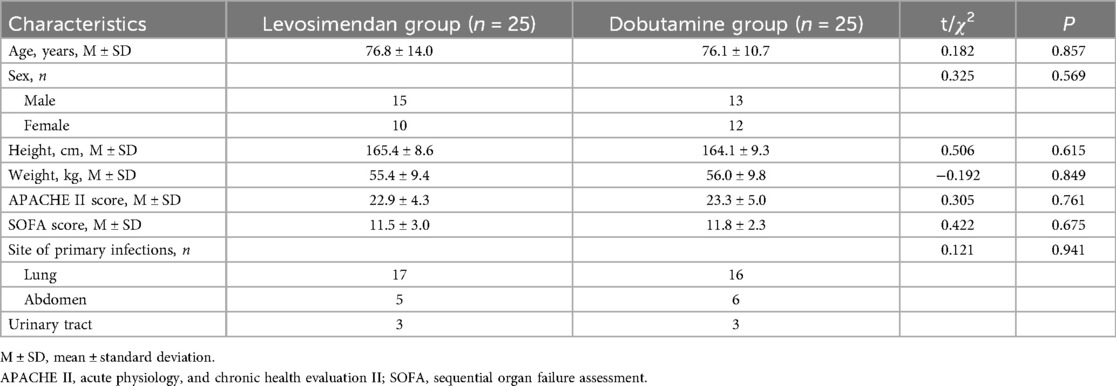
The baseline clinical characteristic comparisons showed no statistically significant differences between the two groups (Table 1). The baseline cardiac function measurements, blood pressure, laboratory test results, and PiCCO examinations were comparable between the two groups (Table 2).

Table 2. Baseline mean arterial pressure, lactate, doses of norepinephrine, cardiac function measurements, laboratory test results, and pulse index continuous cardiac output examination comparisons between two groups.
Comparisons of cardiac function measurements, MAP, doses of norepinephrine, and lactate level after treatments between two groups
As shown in Figure 2; Table 3, following treatment initiation, the LVEF level in the levosimendan group was significantly higher than in the dobutamine group (P < 0.05). In contrast, levels of cTnI, BNP, lactate, and NED were significantly lower in the levosimendan group compared with the dobutamine group (all P < 0.05). However, the two groups had no significant difference in MAP (P > 0.05).
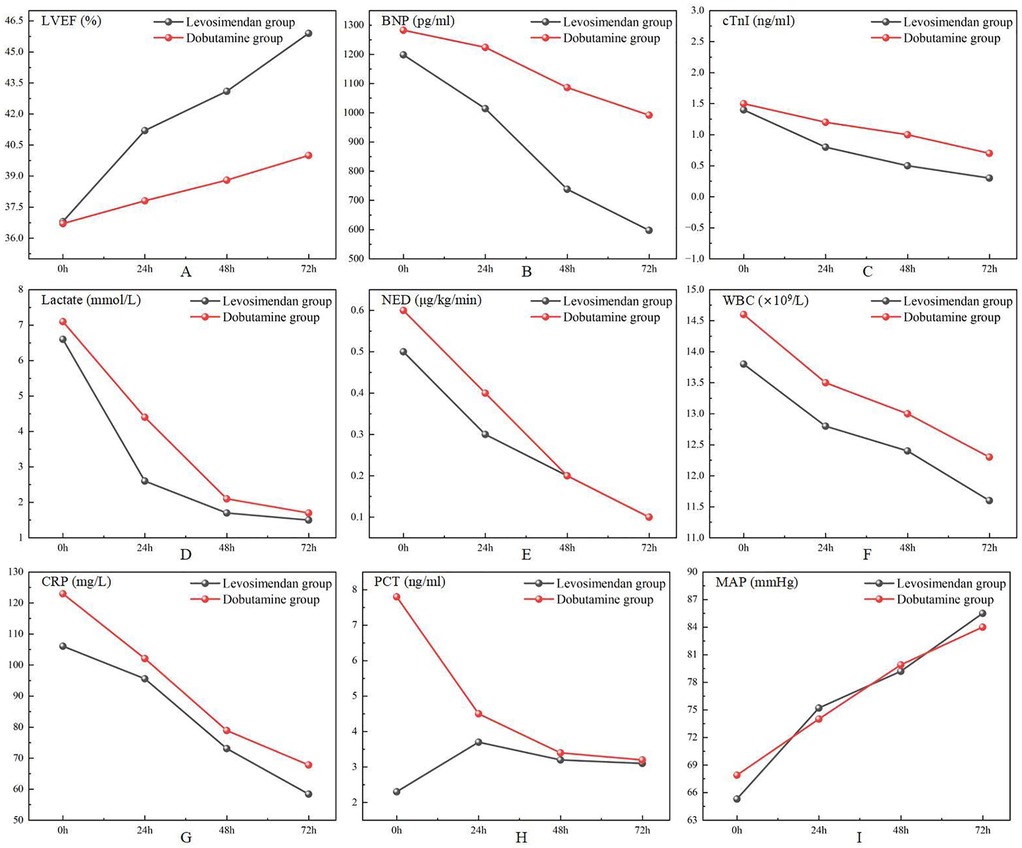
Figure 2. Comparison of cardiac function measurements, doses of norepinephrine, lactate, laboratory test results, and mean arterial pressure after treatments between two groups.
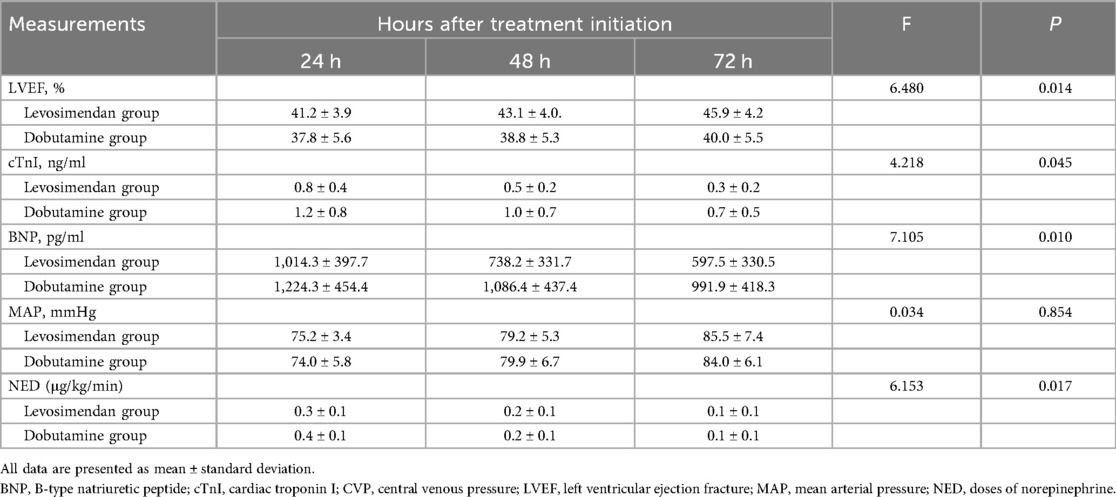
Table 3. Comparison of cardiac function measurements, mean arterial pressure, lactate, and doses of norepinephrine after treatments between two groups.
Comparisons of PiCCO measurements after treatments between two groups
As shown in Figure 3; Table 4, the CI was significantly higher in the levosimendan group compared to the dobutamine group after treatment (P < 0.05). No significant differences were observed between groups in GEDVI, EVLWI, SVRI, HR, or CVP (P > 0.05).

Figure 3. Comparison of measurements on the pulse index continuous cardiac output measurements after treatments between two groups.
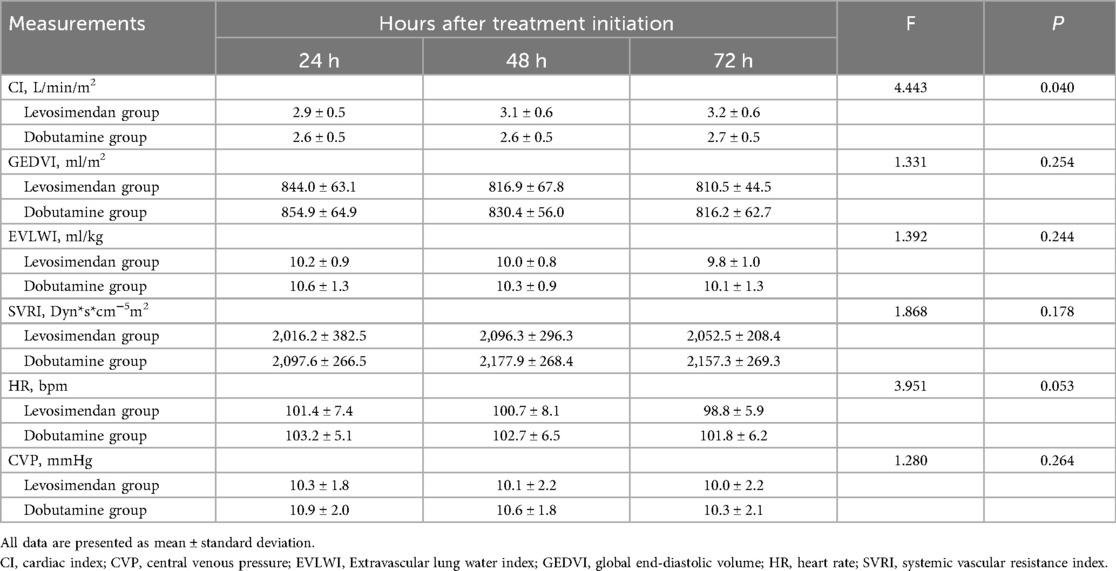
Table 4. Comparison of measurements on the pulse index continuous cardiac output measurements after treatments between two groups.
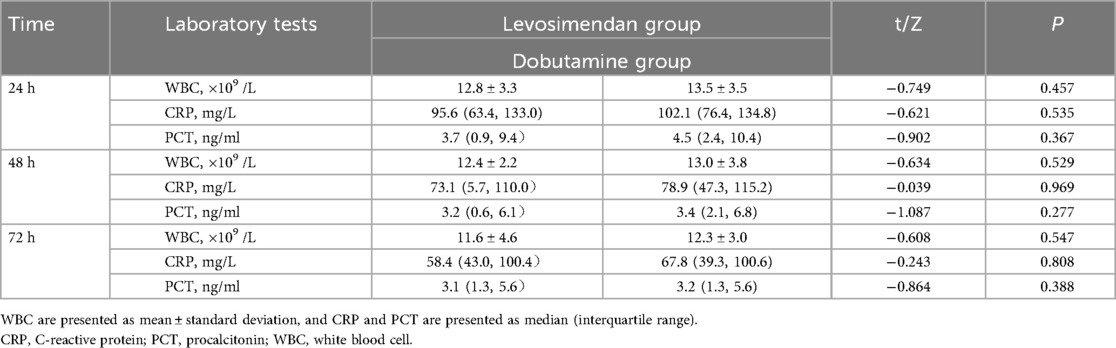
Comparison of laboratory test results after treatments between two groups
As shown in Figure 2; Table 5, post-treatment levels of WBC, CRP, and PCT did not differ significantly between the levosimendan and dobutamine groups (P > 0.05).
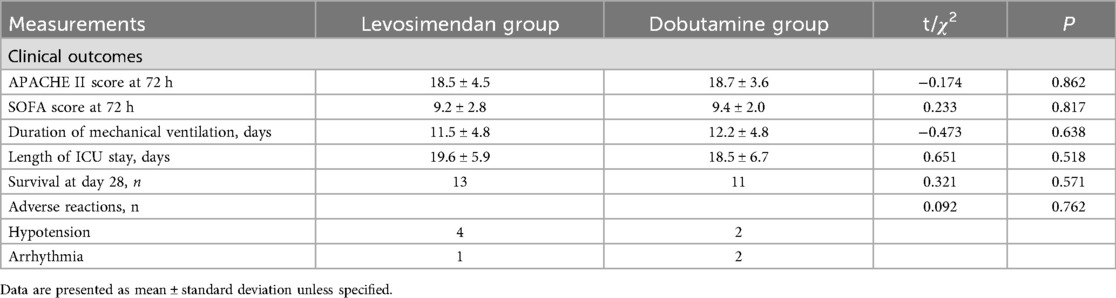
Comparisons of clinical outcomes and adverse reactions between two groups
There were no significant differences in the length of ICU days, duration of mechanical ventilation, death at 28 days, SOFA scores after 72 h of treatments, and APACHE II scores after 72 h of treatments, as well as the incidence of adverse reactions, between the two groups (P > 0.05) (Table 6).
Discussion
Septic cardiomyopathy is a common complication of severe sepsis and septic shock and is a reversible myocardial dysfunction. Its pathogenesis is not fully understood and can result from myocardial damage from bacterial toxins and various cytokines (11). The optimal management strategy is unclear. In the present study, we showed that levosimendan treatment could provide better cardiac function, hemodynamic stability, and tissue perfusion than dobutamine treatment without increasing the incidences of adverse reactions. Levosimendan could be a treatment option in this patient population.
There are no universally accepted diagnostic criteria for septic cardiomyopathy; however, most researchers agree on the following defining features (10): (1) acute and reversible myocardial dysfunction, with gradual recovery of cardiac function within 7–10 days after disease onset; (2) left ventricular dilatation; (3) bilateral systolic and/or diastolic dysfunction; (4) poor responsiveness to fluid resuscitation and catecholamines; and (5) exclusion of acute myocardial ischemia resulting from coronary artery stenosis.
The primary therapeutic goal in septic cardiomyopathy is to improve cardiac function. In patients who have completed initial volume resuscitation but continue to exhibit MAP below 65 mmHg despite high-dose vasopressor therapy, positive inotropic agents are required to enhance myocardial contractility, increase cardiac output, and improve tissue perfusion. Dobutamine is currently the first-line inotropic agent recommended for patients with septic shock and concurrent cardiac dysfunction (12). However, several subsequent studies have failed to demonstrate that dobutamine improves microcirculatory function or long-term prognosis in patients with septic shock (13, 14).
The results of our study suggested that the addition of levosimendan to the standard treatment of patients with septic cardiomyopathy improved cardiac function and reduced myocardial injury better than dobutamine. Our results were similar to previous reports from Sun et al. (15) and Tsolaki et al. (16), as well as a meta-analysis of clinical trials of levosimendan vs. dobutamine in sepsis-associated cardiac insufficiency conducted by Liu et al. (9). The benefits of levosimendan might be related to the following mechanisms: (1) in sepsis/septic shock, β-adrenergic responsiveness is reduced, and catecholamines increase the risk of arrhythmias and myocardial oxygen consumption (17); (2) levosimendan increases the sensitivity of cardiomyocytes to calcium ions by altering the conformation of troponin C, which increases the calcium load and cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels in the absence of an increase in intracellular calcium loading and myocardial contractility and does not cause severe ventricular arrhythmias at therapeutic doses (18, 19); (3) levosimendan improves diastolic function of the heart by improving the diastolic flow velocity ratio, shortening the diastolic phase, and improving diastolic filling (20). In contrast, dobutamine improves only the systolic function, with insignificant improvement in diastolic function (21); (4) levosimendan has antioxidant activity, which can inhibit the release of oxygen free radicals through neutrophils and attenuate the damage of oxygen free radicals to mitochondria, thus reducing myocardial injury (22). Meanwhile, levosimendan can also inhibit the release of various cytokines and minimize their inhibitory effects on the myocardium (20).
The present study showed that, after treatments, hemodynamic measurements improved to varying degrees in both groups. In particular, levosimendan decreased lactate levels more rapidly within the first 24 h and reduced the norepinephrine dose faster than dobutamine. Similar results have been reported in previous studies. Hajjej et al. found that levosimendan could clear lactate better than dobutamine (23). Morelli et al. found that levosimendan improved sublingual microcirculation in patients with septic shock (24). Meng et al. found that levosimendan reduced extravascular lung water and lactate levels and improved tissue perfusion better than dobutamine (25).
In previous animal experiments (26), levosimendan was demonstrated to have anti-inflammatory activity and could prevent sepsis-induced multi-organ dysfunction. However, in the present study, we did not find any significant differences when comparing the laboratory inflammatory measurements of the two groups of patients before and after treatments. During sepsis, the inflammatory cytokines could be affected by the patient's underlying disease, the source and severity of the infection, and treatments, including antibiotics or steroids. In addition, dobutamine treatment might alter cytokine levels, contributing to the non-significant difference between the two groups.
There has been ongoing controversy regarding whether levosimendan reduces mortality and improves prognosis in patients with sepsis. Gordan et al. reported no difference in morbidity or mortality when levosimendan was administered to septic patients compared to placebo (8). In contrast, Zangrillo et al. observed a reduction in mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock treated with levosimendan (27). A more recent meta-analysis concluded that levosimendan did not significantly affect mortality in this patient population (9).
In the present study, SOFA score at 72 h post-treatment, APACHE II score at 72 h post-treatment, duration of mechanical ventilation, length of ICU stay, and 28-day mortality had no statistically significant inter-group differences, suggesting that levosimendan did not reduce disease severity or improve short-term prognosis compared with dobutamine.
Additionally, there was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of adverse reactions between the two groups, indicating that levosimendan was safe for use in treating patients with septic cardiomyopathy.
This study has several limitations. It was a single-center investigation with a small sample size. Cardiac diastolic function was not assessed, and levosimendan and dobutamine were administered for a short duration. Therefore, large-scale, prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trials are needed to further evaluate the clinical efficacy of levosimendan in patients with septic cardiomyopathy.
In conclusion, adding levosimendan to standard treatment in patients with septic cardiomyopathy resulted in greater cardiac function, myocardial protection, hemodynamic stability, and tissue perfusion compared with dobutamine, without an increase in significant drug-related adverse reactions. Further studies are warranted to confirm these findings and to investigate the potential long-term effects of levosimendan on clinical outcomes in this patient population.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the study protocol was approved by the university's ethics committee and registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (registration number: ChiCTR2500101261). Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
FZ: Methodology, Writing – original draft. HWe: Formal analysis, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. LL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. HWa: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LG: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Zhejiang Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Program Project (NO.2020ZB200) and the Zhejiang Medical and Health Science and Technology Plan Project (2025KY1105).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA. (2016) 315(8):801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287
2. Beesley SJ, Weber G, Sarge T, Nikravan S, Grissom CK, Lanspa MJ, et al. Septic cardiomyopathy. Crit Care Med. (2018) 46(4):625–34. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002851
3. Ravikumar N, Sayed MA, Poonsuph CJ, Sehgal R, Shirke MM, Harky A. Septic cardiomyopathy: from basics to management choices. Curr Probl Cardiol. (2021) 46(4):100767. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2020.100767
4. Dubin A, Mugno M. The effects of dobutamine in septic shock: an updated narrative review of clinical and experimental studies. Medicina (Kaunas). (2024) 60(5):751. doi: 10.3390/medicina60050751
5. Annane D, Ouanes-Besbes L, de Backer D, Du B, Gordon AC, Hernández G, et al. A global perspective on vasoactive agents in shock. Intensive Care Med. (2018) 44(6):833–46. doi: 10.1007/s00134-018-5242-5
6. Antoniades C, Tousoulis D, Koumallos N, Marinou K, Stefanadis C. Levosimendan: beyond its simple inotropic effect in heart failure. Pharmacol Ther. (2007) 114(2):184–97. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.01.008
7. Gordon AC, Perkins GD, Singer M, McAuley DF, Orme RM, Santhakumaran S, et al. Levosimendan for the prevention of acute organ dysfunction in sepsis. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375(17):1638–48. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1609409
8. Antcliffe DB, Santhakumaran S, Orme RML, Ward JK, Al-Beidh F, O'Dea K, et al. Levosimendan in septic shock in patients with biochemical evidence of cardiac dysfunction: a subgroup analysis of the LeoPARDS randomised trial. Intensive Care Med. (2019) 45(10):1392–400. doi: 10.1007/s00134-019-05731-w
9. Liu DH, Ning YL, Lei YY, Chen J, Liu YY, Lin XF, et al. Levosimendan versus dobutamine for sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. (2021) 11(1):20333. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99716-9
10. L'Heureux M, Sternberg M, Brath L, Turlington J, Kashiouris MG. Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: a comprehensive review. Curr Cardiol Rep. (2020) 22(5):35. doi: 10.1007/s11886-020-01277-2
11. Hollenberg SM, Singer M. Pathophysiology of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2021) 18(6):424–34. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-00492-2
12. Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli M, Coopersmith CM, French C, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. (2021) 47(11):1181–247. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06506-y
13. Hernandez G, Bruhn A, Luengo C, Regueira T, Kattan E, Fuentealba A, et al. Effects of dobutamine on systemic, regional and microcirculatory perfusion parameters in septic shock: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover study. Intensive Care Med. (2013) 39(8):1435–43. doi: 10.1007/s00134-013-2982-0
14. Gao F, Zhang Y. Inotrope use and intensive care unit mortality in patients with cardiogenic shock: an analysis of a large electronic intensive care unit database. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:696138. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.696138
15. Sun T, Zhang N, Cui N, Wang SH, Ding XX, Li N, et al. Efficacy of levosimendan in the treatment of patients with severe septic cardiomyopathy. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. (2023) 37(3):344–9. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2022.10.032
16. Tsolaki V, Zakynthinos GE, Papanikolaou J, Vazgiourakis V, Parisi K, Fotakopoulos G, et al. Levosimendan in the treatment of patients with severe septic cardiomyopathy. Life (Basel). (2023) 13(6):1346. doi: 10.3390/life13061346
17. Shahreyar M, Fahhoum R, Akinseye O, Bhandari S, Dang G, Khouzam RN. Severe sepsis and cardiac arrhythmias. Ann Transl Med. (2018) 6(1):6. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.12.26
18. Chang W, Xie JF, Xu JY, Yang Y. Effect of levosimendan on mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ Open. (2018) 8(3):e019338. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019338
19. Kolseth SM, Rolim NP, Salvesen Ø, Nordhaug DO, Wahba A, Høydal MA. Levosimendan improves contractility in vivo and in vitro in a rodent model of post-myocardial infarction heart failure. Acta Physiol (Oxf). (2014) 210(4):865–74. doi: 10.1111/apha.12248
20. Yang F, Zhao LN, Sun Y, Chen Z. Levosimendan as a new force in the treatment of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: mechanism and clinical application. J Int Med Res. (2019) 47(5):1817–28. doi: 10.1177/0300060519837103
21. Barraud D, Faivre V, Damy T, Welschbillig S, Gayat E, Heymes C, et al. Levosimendan restores both systolic and diastolic cardiac performance in lipopolysaccharide-treated rabbits: comparison with dobutamine and milrinone. Crit Care Med. (2007) 35(5):1376–82. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000261889.18102.84
22. Hasslacher J, Bijuklic K, Bertocchi C, Kountchev J, Bellmann R, Dunzendorfer S, et al. Levosimendan inhibits release of reactive oxygen species in polymorphonuclear leukocytes in vitro and in patients with acute heart failure and septic shock: a prospective observational study. Crit Care. (2011) 15(4):R166. doi: 10.1186/cc10307
23. Hajjej Z, Meddeb B, Sellami W, Labbene I, Morelli A, Ferjani M. Effects of levosimendan on cellular metabolic alterations in patients with septic shock: a randomized controlled pilot study. Shock. (2017) 48(3):307–12. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000851
24. Morelli A, Donati A, Ertmer C, Rehberg S, Lange M, Orecchioni A, et al. Levosimendan for resuscitating the microcirculation in patients with septic shock: a randomized controlled study. Crit Care. (2010) 14(6):R232. doi: 10.1186/cc9387
25. Meng JB, Hu MH, Lai ZZ, Ji CL, Xu XJ, Zhang G, et al. Levosimendan versus dobutamine in myocardial injury patients with septic shock: a randomized controlled trial. Med Sci Monit. (2016) 22:1486–96. doi: 10.12659/MSM.898457
26. Tsao CM, Li KY, Chen SJ, Ka SM, Liaw WJ, Huang HC, et al. Levosimendan attenuates multiple organ injury and improves survival in peritonitis-induced septic shock: studies in a rat model. Crit Care. (2014) 18(6):652. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0652-4
Keywords: sepsis, septic cardiomyopathy, levosimendan, dobutamine, cardiac function
Citation: Zhao F, Wei H, Lin L, Wang H, Zhang Z and Guo L (2025) Levosimendan versus dobutamine in septic cardiomyopathy: a randomized clinical trial on cardiac function and safety. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1641604. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1641604
Received: 5 June 2025; Accepted: 3 September 2025;
Published: 19 September 2025.
Edited by:
Paolo Trambaiolo, Sandro Pertini Hospital, ItalyReviewed by:
Alessandra D’Ambrosi, Sandro Pertini Hospital, ItalyCarmen Caira, Sandro Pertini Hospital, Italy
Copyright: © 2025 Zhao, Wei, Lin, Wang, Zhang and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liang Guo, emp4c2dsMTExMDJAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Feng Zhao1
Feng Zhao1 Leqing Lin
Leqing Lin Liang Guo
Liang Guo