- 1Department of Cardiology, Shenzhen Nanshan People’s Hospital, Shenzhen, China
- 2Department of Intensive Care, Shenzhen Nanshan People’s Hospital, Shenzhen, China
Background: Coronary artery spasm (CAS), one of the etiologies for MINOCA, is an uncommon cause of acute chest pain. Toripalimab, a recombinant monoclonal antibody targeting programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1), exhibits a wide range of anti-tumor activities. Nevertheless, instances of toripalimab-induced cardiotoxicity have been seldom reported.
Methods: We present the case of a 60-year-old male patient diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma who experienced MINOCA subsequent to the administration of toripalimab. Based on the patient's symptoms, electrocardiogram (ECG) findings, and coronary angiography, transient occurrence CAS was established. The patient was prescribed diltiazem sustained-release capsules. During his follow-up on an outpatient basis, he did not experience a recurrence of the previously reported chest discomfort or any other symptoms. We used the CARE checklist when writing our report.
Conclusion: This is the first case report of MINOCA induced by toripalimab, mediated through coronary artery spasm. This case report emphasizes the awareness regarding the potential for severe cardiovascular complications associated with the administration of toripalimab.
Introduction
Myocardial Infarction with No Obstructive Coronary Artery disease (MINOCA) refers to patients who meet the criteria for a fourth myocardial infarction but do not have any obstructive coronary artery disease (≥50% stenosis) on coronary angiography (1–3). MINOCA can be caused by various factors, including coronary artery spasm (CAS) syndrome, coronary dissection, in situ thrombosis, tachycardia, and coronary embolism (4). Toripalimab, a humanized IgG4K monoclonal antibody specifically targeting human PD-1, is the first domestically marketed anti-tumor PD-1 antibody in China (5). It has demonstrated a wide spectrum of anti-tumor activity, including melanoma, lung cancer, and gastrointestinal tumors (6–8). However, it is uncommon for toripalimab to cause acute coronary vasoconstriction. This case report documents an instance of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction caused by severe coronary vasospasm following the administration of toripalimab in a 60-year-old man.
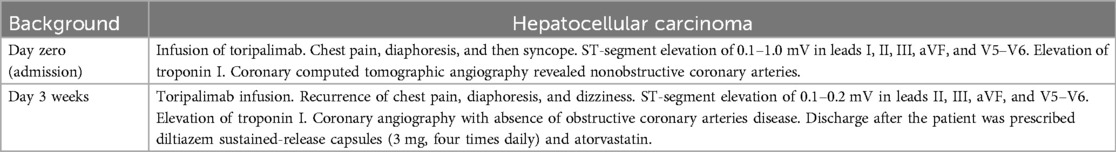
Case presentation
A 60-year-old man was found to have a liver-occupying lesion during a medical checkup. He underwent laparoscopic liver resection of segment 7 and was diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) via liver biopsy in May 2022. Subsequently, he was initiated on a combination therapy involving tislelizumab (200 mg q3w) and lenvatinib (8 mg qd) from June 2022. Throughout the tislelizumab and lenvatinib combination therapy, no significant complications were observed. An MR scan of the upper abdomen conducted three months earlier showed a rounded signal in the S6 segment of the liver, along with adjacent multiple abnormal signal nodules. On May 4, 2023, the patient was admitted to the hepatobiliary surgery department. No chest discomfort was reported, and his troponin level was negative. His temperature was 36.4°C, pulse rate 81 bpm, respiratory rate 20 breaths per min, and blood pressure 124/79 mmHg. Cardiac and pulmonary examinations revealed normal heart sounds without murmurs, as well as clear lung sounds. Abdominal examination indicated a soft and nontender abdomen without rebound tenderness. A treatment plan was established for anti-tumor therapy, involving toripalimab and lenvatinib/oxaliplatin/gemcitabine. However, shortly after the infusion of toripalimab, the patient experienced sudden chest pain, diaphoresis, and then syncope. Upon physical examination, his heart rate dropped to 50 beats per min, respiratory rate remained at 20 breaths per minute, and blood pressure decreased to 85/60 mmHg. Auscultation indicated normal heart sounds and no murmurs. The patient's face appeared pale, with no rash. The electrocardiogram (ECG) displayed ST-segment elevation of 0.1–1.0 mV in dynamic leads I, II, III, aVF, and V5–V6 (Figure 1A). Toripalimab was promptly discontinued, leading to the spontaneous resolution of symptoms after 10 min and a return of the ECG to baseline. Cardiac troponin I enzyme levels peaked at 0.080 ng/ml (0–0.034) around 18 h after symptom onset. The patient did not agree to undergo coronary angiography (CAG) due to the symptom relief. Coronary computed tomographic angiography revealed nonobstructive coronary arteries with mild stenosis, 11% stenosis in the left main artery (LM), 11% stenosis in the proximal-left anterior descending artery (pLAD), myocardial bridge-mural coronary artery in the proximal-left anterior descending artery and the distal-left anterior descending artery (dLAD), without stenosis in the left circumflex artery (LCX), 10% stenosis in the middle right coronary artery (mRCA), and 10% stenosis in the distal right coronary artery (dRCA). A transthoracic echocardiogram confirmed normal left ventricular size and function. Lipid-regulating drugs atorvastatin (20 mg/day) was prescribed, and the patient remained symptom-free in the subsequent days. Thus, he was planned to continue to implement a anti-tumor therapy course. However, on May 25, 2023, during toripalimab infusion, the patient experienced a recurrence of chest pain, diaphoresis, and dizziness. Physical examination indicated a heart rate of 68 bpm, respiratory rate of 26 breaths per min, and blood pressure of 63/40 mmHg. Auscultation indicated normal heart sounds and no murmurs. The ECG revealed dynamic ST-segment elevation of 0.1–0.2 mV in leads II, III, aVF, and V5–V6 (Figure 1B). Toripalimab was immediately discontinued, leading to symptom resolution within 30 min, and the ECG returned to baseline (Figure 1C). Cardiac troponin I enzyme levels were measured at 0.138 ng/ml. A transthoracic echocardiogram revealed an ejection fraction of 60%, with normal left ventricle's size and no significant regional wall motion abnormalities. Following the doctor's advice, he had CAG examination. Subsequent CAG confirmed patent coronaries, without any substantial flow-limiting lesions (Figure 2). The patient did not agree to undergo coronary vasospasm provocation testing due to possible serious adverse event risk, and refused further examination to further confirm the cause. However, based on the patient's symptoms, ECG findings, and coronary angiography, a diagnosis of CAS was established. The patient was prescribed diltiazem sustained-release capsules (30 mg, four times daily) and atorvastatin (20 mg/day).
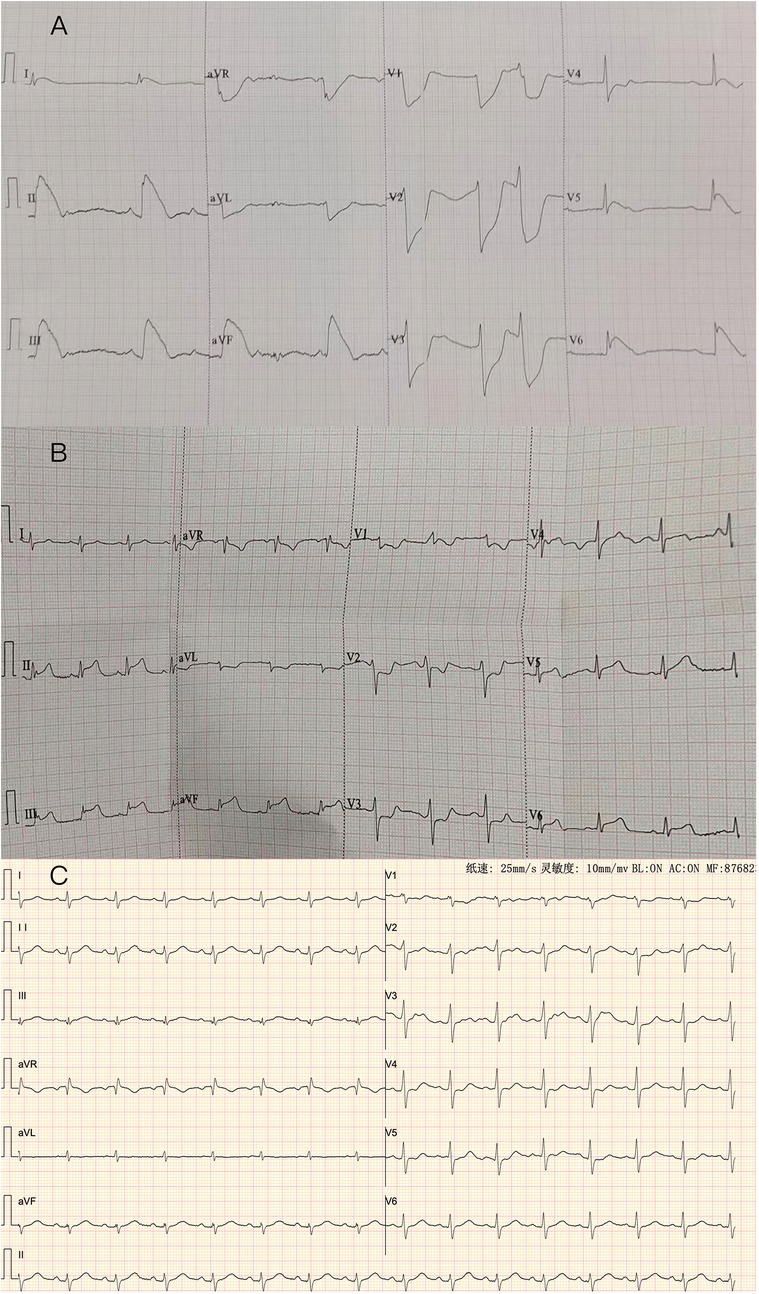
Figure 1. (A) ECG: the ECG shows a 0.1–1.0 mv ST elevation at leads DI, II, III, aVF, V5, V6, with reciprocal depression in DaVL, V1, V2, V3 and V4. (B) ECG: The ECG shows a 0.1–0.2 mv ST elevation at leads DII, III, aVF, V5, V6, with reciprocal depression in DI, aVL, V1, V2, and V3. (C): Repeated ECG revealed normal sinus rhythm with no significant ST-T changes in all leads.
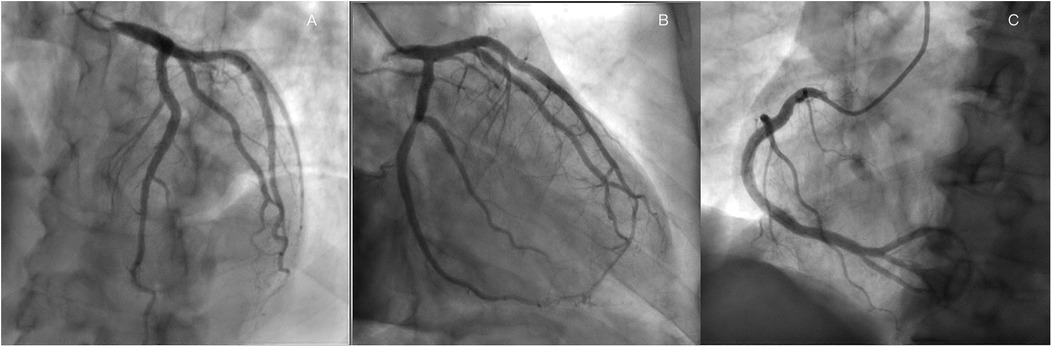
Figure 2. Coronary angiography revealed nonobstructive coronary arteries in the LAD, (A), LCX, (B) RCA (C).
He was transferred back to the former department to complete the anti-tumor therapy after being stable. Throughout the subsequent anti-tumor treatment, the patient did not experience any chest pain or discomfort. Moreover, during his follow-up on an outpatient basis, he did not experience a recurrence of the previously reported chest discomfort or any other symptoms. Patient's timeline is shown in Table 1.
Discussion
Roughly 6% of patients presenting with acute myocardial infarction are identified as having non-obstructive coronary arteries through coronary angiography. The initial diagnosis of MINOCA requires the presence of ischemic signs/symptoms, an elevation and subsequent decline in cardiac troponin levels, with at least one value exceeding or equaling the 99th percentile upper limit of normal, and the identification of non-obstructive coronary artery disease through imaging techniques (9). Coronary vasospasm is characterized by a significant constriction of the coronary arteries, leading to a notable imbalance between oxygen demand and supply. This phenomenon can potentially induce substantial myocardial ischemia, acute myocardial infarction, or even sudden cardiac death (10). The primary treatment approach, calcium channel blockade, aims to diminish intracellular calcium levels in order to restrict contraction and spasm of coronary smooth muscle. Several pathological mechanisms have been proposed, including the direct impact of catecholamines, inflammation, endothelial cell dysfunction, hypercontractility of smooth muscle cells, or heightened oxidative stress (10). In contrast to typical angina arising from atherosclerotic artery disease, vasospastic angina resulting from coronary vasospasm frequently occurs in patients without notable cardiovascular risk factors (11). Furthermore, common triggers for this condition lncluede cold exposure, mental stress, stimulants, and medications (10, 11).
The advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has brought about a transformative shift in cancer therapy. Among these ICIs, PD-1 plays a critical role in facilitating tumor immune evasion and modulating the immune response to identify and combat cancer cells (12). Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are a result of the immune system being abnormally stimulated in normal tissues. Compared to irAEs in other organs, cardiac irAEs are relatively uncommon, but they have a significant mortality rate. Cardiac irAEs include myocarditis, pericarditis, heart failure, and myocardial infarction (13–16). Toripalimab, a relatively new ICIs developed in China, was usually well tolerated in clinical studies in Chinese patients with advanced malignancies.
Rare instances of toripalimab-related fatal cardiac irAEs have been reported. In this context, we present a case of a patient with HCC who experienced fatal cardiac irAEs subsequent to toripalimab therapy. To date, there have been only three case reports describing coronary spasm after administration of PD-L1 inhibitor (17–19). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to describe a patient who developed MINOCA due to coronary artery spasm induced by toripalimab.
A case of coronary artery spasm was caused by nivolumab (17). In a separate case, a patient undergoing pembrolizumab treatment, a PD-L1 inhibitor, experienced coronary artery spasm (18). It was attributed to a systemic inflammatory reaction, and the patient's condition rapidly improved following anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory treatments. In the third case, thyrotoxicosis-associated coronary artery spasm and ventricular tachycardia were prompted by camrelizumab, a PD-1 inhibitor (19). Mechanisms behind thyroid hormone-induced coronary spasm encompass an imbalance between blood supply and oxygen demand during thyrotoxic states, coupled with augmented vascular reactivity (20). In contrast, our patient's coronary artery spasm was neither a consequence of ICIs-associated vasculitis nor thyrotoxicosis, given the absence of hyperthyroidism, the lack of administration of immunosuppressive or anti-inflammatory medications and calcium channel blockers were efficacive.
Kounis syndrome, also known as hypersensitivity acute coronary syndrome, is a rare disorder in which an allergic or hypersensitivity reaction triggers an acute coronary syndrome. Type I Kounis syndrome is usually associated with MINOCA, in which the coronary arteries are normal or nearly normal (21).
The exact cause of coronary artery spasm induced by ICIs remains not fully elucidated. One mechanisms suggests that immunotherapy could directly exert toxicity on cardiac cells through PD-1 inhibition. Both cardiomyocytes and vascular endothelial cells might express programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). When ICIs prevent the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1, endothelial cells become susceptible to attack by CD8+ T lymphocytes, which execute endothelial cell destruction through perforin-mediated cytolysis. This intensified cytolytic activity of CD8+ T lymphocytes further compromises vascular integrity, leading to vascular injury (22). Additionally, a number of studies employing human and animal models have demonstrated that a deficiency in PD-1/PD-L1 exacerbates the progression of atherosclerotic plaques and raises levels of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and anti-PD-1 antibodies thave a propensity to heighten inflammation (23–25). These mechanisms can contribute to vascular spasms (10).
In conclusion, this case analysis suggests that ICIS use is associated with MINOCA, although we do not yet have conclusive evidence to elucidate the mechanism. Future studies should investigate the mechanisms by which ICIs lead to myocardial infarction. This case report emphasizes the awareness regarding the potential for severe cardiovascular complications associated with the administration of toripalimab.
Conclusion
To our understanding, this is the first case report of a toripalimab-induced MINOCA due to acute coronary vasospasm. Monitoring is required during therapy to guarantee patient safety. Given the common exclusion of cancer patients from randomized controlled trials, the management experience for this population was also limited to observational research. Therefore, we urgently require additional clinical experience and research data to aid in the development of treatment strategies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Shenzhen Nanshan People's Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
BH: Project administration, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. SC: Writing – original draft, Investigation. HZ: Writing – original draft. XH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Municipal Financial Subsidy of Nanshan District Medical Key Discipline Construction, the Natural Science Foundation of Shenzhen (grant number JCYJ20220530141815035), the Health Science and Technology Program of Nanshan District (grant number NS2022062), the Health Science and Technology Program of Nanshan District (grant number NS2024023), and the Scientific Research Projects of Huazhong University of Science and Technology Union Shenzhen Hospital (grant number YN2022025).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
CAS, coronary artery spasm; PD-1, programmed death receptor 1; ECG, electrocardiogram; MINOCA, myocardial infarction with nonobstructive coronary arteries; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; LM, left main artery; pLAD, proximal-left anterior descending artery; dLAD, distal-left anterior descending artery; LCX, left circumflex artery; mRCA, middle right coronary artery; dRCA, distal right coronary artery; ICIs, immune checkpoint inhibitors; irAEs, immune-related adverse events; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1.
References
1. Prinzmetal M. A variant form of angina pectoris: preliminary report. Am J Med. (1959) 27:375–88. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90003-8
2. Bakhshi H, Gibson CM. MINOCA: myocardial infarction no obstructive coronary artery disease. Am Heart J Plus. (2023) 33:100312. doi: 10.1016/j.ahjo.2023.100312
3. Ceasovschih A, Mantzouranis E, Dimitriadis K, Sorodoc V, Vlachakis PK, Karanikola AE, et al. Coronary artery thromboembolism as a cause of myocardial infarction with non-obstructive coronary arteries (MINOCA). Hellenic J Cardiol. (2024) 79:70–83. doi: 10.1016/j.hjc.2024.05.001
4. Tamis-Holland JE, Jneid H, Reynolds HR, Agewall S, Brilakis ES, Brown TM, et al. Contemporary diagnosis and management of patients with myocardial infarction in the absence of obstructive coronary artery disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2019) 139(18):e891–908. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000670
5. Zhang L, Hao B, Geng Z, Geng Q. Toripalimab: the first domestic anti-tumor PD-1 antibody in China. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:730666. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.73066
6. Wang FH, Wei XL, Feng J, Li Q, Xu N, Hu XC, et al. Efficacy, safety, and correlative biomarkers of toripalimab in previously treated recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a phase II clinical trial (POLARIS-02). J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39(7):704. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.02712
7. Wang ZX, Cui C, Yao J, Zhang Y, Li M, Feng J, et al. Toripalimab plus chemotherapy in treatment-naïve, advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (JUPITER-06): a multi-center phase 3 trial. Cancer Cell. (2022) 40(3):277–88. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.02.007
8. Mai HQ, Chen QY, Chen D, Hu C, Yang K, Wen J, et al. Toripalimab or placebo plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a multicenter randomized phase 3 trial. Nat Med. (2021) 27(9):1536–43. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01444-0
9. Pasupathy S, Air T, Dreyer RP, Tavella R, Beltrame JF. Systematic review of patients presenting with suspected myocardial infarction and nonobstructive coronary arteries. Circulation. (2015) 131(10):861–70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.011201
10. Hung MJ, Hu P, Hung MY. Coronary artery spasm: review and update. Int J Med Sci. (2014) 11(11):1161. doi: 10.7150/ijms.9623
11. Slavich M, Patel RS. Coronary artery spasm: current knowledge and residual uncertainties. IJC Heart Vasc. (2016) 10:47–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2016.01.003
12. Ai L, Chen J, Yan H, He Q, Luo P, Xu Z, et al. Research status and outlook of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for cancer therapy. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2020) 14:3625–49. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S267433
13. Dolladille C, Akroun J, Morice PM, Dompmartin A, Ezine E, Sassier M, et al. Cardiovascular immunotoxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a safety meta-analysis. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42(48):4964–77. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab618
14. Stein-Merlob AF, Rothberg MV, Ribas A, Yang EH. Cardiotoxicities of novel cancer immunotherapies. Heart. (2021) 107(21):1694–703. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2020-318083
15. Sun JY, Qu Q, Lou YX, Hua Y, Sun GZ, Sun W, et al. Cardiotoxicity in cancer immune-checkpoint therapy: mechanisms, clinical evidence, and management strategies. Int J Cardiol. (2021) 344:170–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2021.09.041
16. Khunger A, Battel L, Wadhawan A, More A, Kapoor A, Agrawal N. New insights into mechanisms of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced cardiovascular toxicity. Curr Oncol Rep. (2020) 22:1–11. doi: 10.1007/s11912-020-00925-8
17. Ferreira M, Pichon E, Carmier D, Bouquet E, Pageot C, Bejan-Angoulvant T, et al. Coronary toxicities of anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 immunotherapies: a case report and review of the literature and international registries. Target Oncol. (2018) 13:509–15. doi: 10.1007/s11523-018-0579-9
18. Nykl R, Fischer O, Vykoupil K, Taborsky M. A unique reason for coronary spasm causing temporary ST elevation myocardial infarction (inferior STEMI)–systemic inflammatory response syndrome after use of pembrolizumab. Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis. (2017) 2(1):100–2. doi: 10.5114/amsad.2017.72531
19. Guo K, Chen M, Li J. PD-1 inhibitor-induced thyrotoxicosis associated with coronary artery spasm and ventricular tachycardia. Cardiovasc Toxicol. (2022) 22(10-11):892–7. doi: 10.1007/s12012-022-09756-4
20. Lanza GA, Careri G, Crea F. Mechanisms of coronary artery spasm. Circulation. (2011) 124(16):1774–82. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.037283
21. Abdelghany M, Subedi R, Shah S, Kozman H. Kounis syndrome: a review article on epidemiology, diagnostic findings, management and complications of allergic acute coronary syndrome. Int J Cardiol. (2017) 232:1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.01.124
22. Frebel H, Nindl V, Schuepbach RA, Braunschweiler T, Richter K, Vogel J, et al. Programmed death 1 protects from fatal circulatory failure during systemic virus infection of mice. J Exp Med. (2012) 209(13):2485–99. doi: 10.1084/jem.20121015
23. Gotsman I, Grabie N, Dacosta R, Sukhova G, Sharpe A, Lichtman AH. Proatherogenic immune responses are regulated by the PD-1/PD-L pathway in mice. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117(10):2974–82. doi: 10.1172/JCI31344
24. Koga N, Suzuki JI, Kosuge H, Haraguchi G, Onai Y, Futamatsu H, et al. Blockade of the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1 accelerates graft arterial disease in cardiac allografts. Arterioscler, Thromb, Vasc Biol. (2004) 24(11):2057–62. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000145015.23656.e4
Keywords: MINOCA, coronary artery spasm, acute myocardial infarction, PD-1, toripalimab
Citation: Huang B, Chen S, Zhang H and Han X (2025) Myocardial infarction with nonobstructive coronary arteries due to acute coronary vasospasm induced by toripalimab: a case report and review of literature. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1646968. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1646968
Received: 14 June 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 1 September 2025.
Edited by:
Tommaso Gori, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, GermanyReviewed by:
Alexandr Ceasovschih, Grigore T. Popa University of Medicine and Pharmacy, RomaniaManuel Flores-Sáenz, University of Alcalá, Spain
Copyright: © 2025 Huang, Chen, Zhang and Han. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bihan Huang, aHVhbmdiaDIwMjVAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Xueying Han, aGFueHlkZEAxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Bihan Huang
Bihan Huang Shaoyuan Chen
Shaoyuan Chen Haigang Zhang2
Haigang Zhang2