- 1Hubei Key Laboratory of Wudang Local Chinese Medicine Research, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, China
- 2Department of Drug Quality Inspection, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, China
- 3Department of Preventive Medicine, School of Public Health, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, China
- 4Department of Hepatobiliary Pancreatic Surgery, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, China
- 5Health Management Center, Shiyan Renmin Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, China
Atherosclerosis is a chronic vascular disorder characterized by the pathological accumulation of lipids, inflammatory cells, and extracellular matrix within arterial walls. With the escalating global incidence of atherosclerosis, the development of more effective therapeutic interventions has emerged as a critical priority in biomedical research. Conventional treatment modalities, encompassing pharmacological agents and, endovascular interventions, have demonstrated partial efficacy in disease management. However, their clinical utility remains constrained by suboptimal therapeutic outcomes, treatment-related adverse effects, and instances of therapeutic failure. In response to these limitations, contemporary research has shifted focus toward novel therapeutic strategies targeting molecular pathways and immunomodulatory mechanisms, aiming to achieve enhanced precision and efficacy. This review synthesizes recent innovations in atherosclerosis therapeutics. Notable advancements include PCSK9 inhibitors and next-generation lipid-modulating agents, which have shown significant promise in clinical trials by achieving substantial reductions in atherogenic lipoprotein levels. Gene-editing technologies, particularly CRISPR-based approaches, exhibit potential for halting disease progression through targeted modulation of pro-atherogenic genes. Furthermore, emerging insights into the regulatory role of microRNAs in atherosclerotic plaque formation and instability have positioned miRNA-based therapeutics as a compelling frontier in precision medicine for cardiovascular diseases.
1 Introduction
Atherosclerosis is a chronic cardiovascular disease characterized by the convergence of endothelial injury, lipid deposition, and chronic inflammatory response, manifesting as multifocal changes that predominantly affect large and medium-sized arteries (1). The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that atherosclerosis contributes to approximately 1.7 million annual fatalities globally, representing nearly one-third of all-cause mortality worldwide (2). As a leading contributor to cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, atherosclerosis has emerged as a paradigmatic disease entity within the spectrum of cardiovascular pathologies (3).
The hallmark pathological manifestations of atherosclerosis encompass lipid deposition within the arterial intima, focal fibrotic proliferation, plaque formation, vascular wall stiffening, and luminal stenosis, collectively resulting in end-organ ischemic injury (4, 5). These pathophysiological processes are mediated through dynamic interactions among low-density lipoprotein (LDL), oxidized LDL (ox-LDL), endothelial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), and associated molecular mediators.
LDL and its oxidized derivatives constitute principal drivers of atherosclerotic progression. Under pathological conditions, ApoB-containing lipoproteins infiltrate compromised vascular endothelium into the subendothelial space, where reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediate their oxidative modification (6, 7). This transformation generates ox-LDL, which accumulates within the arterial wall and initiates monocyte recruitment to the intimal layer. These monocytes subsequently differentiate into macrophages, perpetuating inflammatory cascades (8). Crucially, ox-LDL exhibits high affinity for macrophage scavenger receptors (e.g., CD36, LOX-1), enabling receptor-mediated internalization (9). Progressive phagocytosis of ox-LDL drives macrophage foam cell transformation, thereby facilitating necrotic core formation and atherosclerotic plaque expansion (10, 11).
Endothelial cells maintain vascular homeostasis through dual regulatory functions: (i) secretion of anti-angiogenic factors (e.g., nitric oxide) to suppress cellular proliferation, and (ii) production of vasoconstrictive mediators (e.g., endothelin-1) to modulate vascular tone (12–14). Concurrently, VSMCs and their synthesized collagen-rich extracellular matrix confer structural stability to advanced plaques, mitigating risks of plaque rupture and thrombotic complications (15). These mechanistic insights have directly informed current therapeutic paradigms targeting vascular remodeling.
Statins, as competitive inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme. It is a (HMG-CoA) reductase, remain the cornerstone of pharmacological management for atherosclerosis in clinical practice. While the emergence of monoclonal antibody-based PCSK9 inhibitors has introduced a paradigm-shifting therapeutic strategy (16), contemporary pharmacological interventions continue to face significant clinical constraints.
Statin therapy is frequently complicated by dose-dependent musculoskeletal toxicity, encompassing a spectrum from mild myalgia (60%–70% of cases) to life-threatening rhabdomyolysis (<0.1% incidence). Severe manifestations may precipitate acute kidney injury, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and mortality, with statin discontinuation representing the sole definitive management approach for statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS) (17). Although PCSK9 inhibitors demonstrate favorable safety profiles in clinical trials, their therapeutic application is associated with transient adverse effects including nasopharyngitis (10%–15%), injection-site reactions (5%–7%), and upper respiratory infections (18–20). Furthermore, the cost of PCSK9 inhibitors remains prohibitively high. Therefore, the aforementioned deficiencies have largely restricted its wide application in clinical practice. At present, the comprehensive analysis systematically evaluates of intervention and therapy for atherosclerosis: (1) Optimization protocols for conventional pharmacotherapies; (2) Structural refinement strategies for next-generation inhibitors; (3) Emerging therapeutic modalities currently under preclinical/clinical investigation. Therefore, through this tripartite evaluation, we aim to delineate actionable strategies for overcoming current therapeutic limitations and inform future translational research directions in atherosclerosis management.
2 Therapeutic challenges of traditional therapies
Atherosclerosis is characterized by the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. Targeting this pathologically character, current clinical management primarily involves lifestyle modifications and pharmacological interventions, including statins, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors, anti-inflammatory agents, and antiplatelet medications.
As a commonly used traditional medicine for atherosclerosis, statins demonstrates therapeutic efficacy through significant reduction of serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) concentrations, thereby attenuating plaque development (21). However, current pharmacotherapeutic approaches present several clinical limitations: restricted cellular permeability, suboptimal aqueous solubility, and diminished bioavailability significantly compromise treatment outcomes (22). Furthermore, high-dose statin regimens are associated with adverse effects including drug intolerance, fatigue manifestations, and statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS), while alternative non-statin therapies frequently prove inadequate in halting disease progression (23).
These therapeutic challenges underscore the critical need for developing novel strategies to enhance statin pharmacokinetic profiles and optimize therapeutic outcomes in atherosclerotic management.
3 Application of nanotechnology in the optimization of traditional interventions
3.1 The optimization of traditional statin drugs by nanotechnology
The progressive evolution of nanotechnology has established engineered nanoparticles as a promising platform in cardiovascular therapeutics, leveraging their enhanced delivery efficiency, precise target selectivity, and reduced off-target effects (24). To augment the anti-atherosclerotic performance of statins, specialized nanocarrier systems engineered for atherosclerotic microenvironments have demonstrated superior therapeutic outcomes compared to conventional free drug formulations (25, 26) (Figure 1).
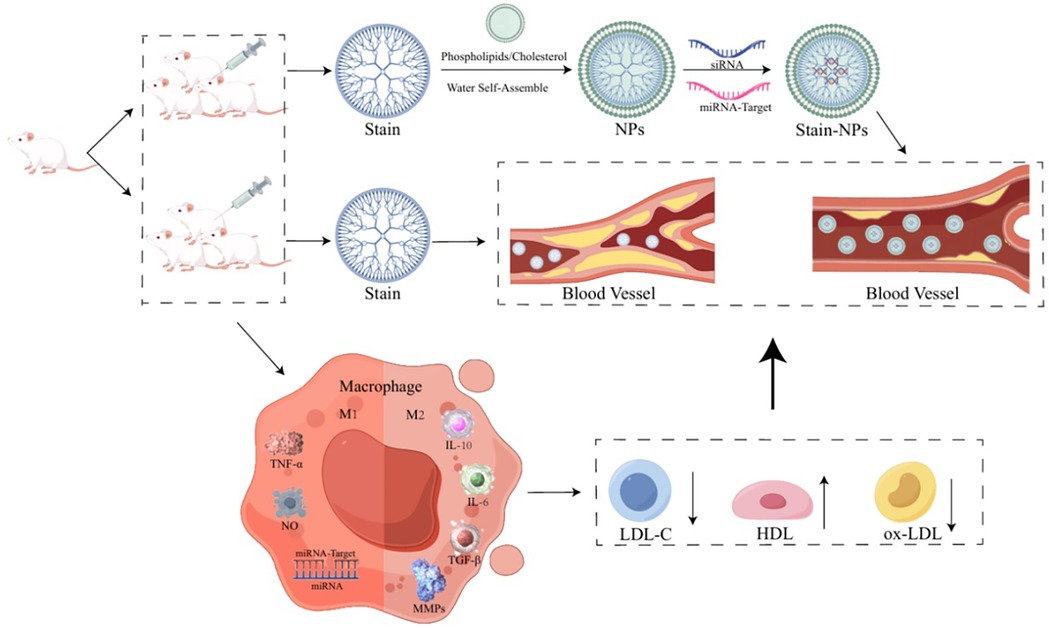
Figure 1. The anti-atherosclerotic performance of statins, specialized nanocarrier systems engineered for atherosclerotic microenvironments. Created using Figdraw.
Building on these developments, researchers pioneered a co-delivery system integrating statins with nucleic acid therapeutics, and revealed that anti-miR-33 exhibits dual functionality as both an atheroprotective nucleic acid and a modulator of macrophage phenotypic polarization (27, 28). Through covalent conjugation of hydrophobic atorvastatin with synthetic tri-glucosyl-methyl chitosan (TMC) via amide and ester linkages, the team achieved spontaneous self-assembly of cationic nanoparticles (GTANPs) in aqueous media. Subsequent electrostatic complexation enabled efficient encapsulation of anionic nucleic acid payloads (siBaf60a and anti-miR-33 pDNA), yielding GTANPs/siBaf60a and GTANPs/pAnti-miR-33 nanocomposites (29).
This innovative methodology provides valuable mechanistic insights for advancing statin-based therapeutic strategies in atherosclerosis through nanotechnology-enabled drug optimization.
3.2 Nanotechnology and atherosclerosis imaging diagnosis
Molecular imaging technology enables high spatiotemporal resolution visualization of rupture-prone or erosion-susceptible atherosclerotic plaques, serving as a critical tool for both disease discovery and diagnostic evaluation (30). Beyond their established delivery efficiency, engineered nanoparticles exhibit nanoscale dimensions and enhanced tissue penetrability (31). These intrinsic properties empower nanoparticle-modified therapeutics to exploit the unique vascular permeability of atherosclerotic lesions, facilitating passive or ligand-directed active transport across endothelial barriers for targeted accumulation at pathological sites (31). Integration of these platforms synergistically enhances diagnostic precision in atherosclerosis management.
Current clinical imaging modalities for atherosclerosis primarily encompass two paradigms: structural imaging (e.g., MRI, CT) and functional imaging (e.g., PET, SPECT) utilizing radiotracer-based techniques. However, these approaches exhibit persistent limitations in differentiating vulnerable plaques from stable lesions, particularly in early-stage disease (32–34). Emerging strategies focusing on molecular engineering of contrast agents and enhancing their plaque-specific accumulation demonstrate potential for achieving superior diagnostic specificity.
Iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs), characterized by their superparamagnetic properties, align their magnetic domains under external fields and serve as potent MRI contrast enhancers. Recent advancements confirm that surface functionalization of IONPs with inorganic coatings significantly enhances biocompatibility profiles while maintaining imaging efficacy (35). Such optimized nanocomposites exhibit exceptional performance as theranostic agents when integrated with MRI for atherosclerotic plaque detection. Notably, ferumoxytol, currently the sole FDA-approved nanoparticle for clinical imaging applications, has demonstrated remarkable translational potential in this domain (36).
4 Therapeutic integration and future perspectives of PCSK9 inhibitors in atherosclerosis management
Since the beginning of the 21st century, scientific research on atherosclerosis treatment has faced persistent challenges in developing novel therapeutic interventions that combine enhanced efficacy with improved safety profiles and cost-effectiveness (37, 38) (Table 1). Notably, the pandemic era has accelerated interest in nucleic acid-based therapies, with emerging research focusing on diverse non-coding RNA species, including microRNAs, lncRNAs, circular RNAs, si-RNAs, and tRNA-derived fragments, as promising therapeutic targets (39).
4.1 Gene structure and functional mechanisms of PCSK9
4.1.1 Gene structure of PCSK9
As a member of the proprotein convertase family, PCSK9 plays a pivotal role in protein hydrolysis activation, post-translational modification, and regulation of secreted protein degradation (40). Its structural architecture comprises three distinct domains: an N-terminal signal peptide (SP, residues 1–30), a propeptide domain (PD, residues 31–152), and a catalytic domain (CD, residues 153–426) (41).
The propeptide domain facilitates PCSK9 synthesis and secretion through autocleavage-mediated maturation, while maintaining post-secretion autoinhibition via non-covalent binding to the catalytic domain. Functionally, the catalytic domain features a conserved serine protease fold housing the catalytic triad (His226, Asp374, Ser386), which is essential for low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) binding (42).
4.1.2 Low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) biology and pathogenic significance
The LDL-R, a transmembrane glycoprotein, is critically involved in lipoprotein metabolism, with its genetic mutations recognized as the principal etiology of familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) (43). Structurally, it consists of an extracellular ligand-binding domain, an epidermal growth factor precursor homology domain, and an O-linked glycosylation region proximal to the transmembrane helix.
The transcriptional regulation of the LDL-R gene relies on two TATA-like sequences and three conserved 16-bp direct repeats within its promoter region (44). Mechanistically, LDL-R mediates circulatory lipoprotein clearance through clathrin-coated pit endocytosis. At physiological pH, its extracellular domain adopts an extended conformation to capture apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins (45).
4.1.3 PCSK9-LDL-R interaction dynamics on atherosclerosis management
Predominantly expressed in hepatic, intestinal, renal, and neural tissues (46), PCSK9 exerts its primary lipid-modulating effects by regulating LDL-R expression on hepatocyte membranes (47). Upon secretion, circulating PCSK9 engages LDL-R at the hepatocyte surface through pH-dependent interactions (48). Under neutral plasma membrane conditions, the catalytic domain of PCSK9 binds the EGF-A domain of LDL-R with moderate affinity (Kd = 170–750 nM), forming a 1:1 stoichiometric complex (49, 50).
Following internalization, acidic endosomal conditions enhance binding avidity by 150-fold through electrostatic interactions between the positively charged C-terminal histidine-rich domain (CHRD) of PCSK9 and the negatively charged LDL-R ligand-binding domain (51). This pH-driven conformational shift disrupts receptor recycling, diverting the PCSK9-LDL-R complex to lysosomal degradation (40, 52).
Recent advances in PCSK9 inhibitor development, particularly through integration with emerging biotechnologies, have substantially expanded therapeutic strategies for atherosclerosis management (Figure 2).
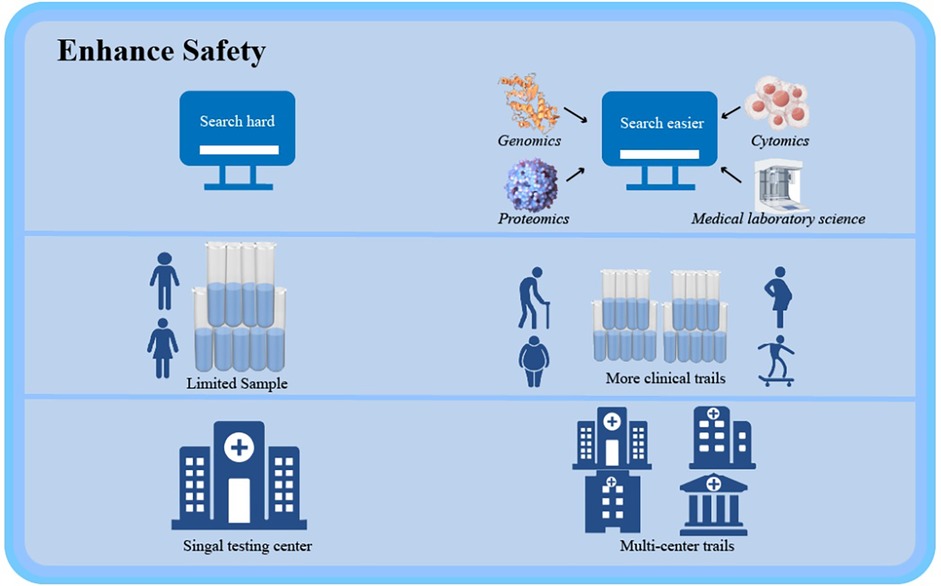
Figure 2. Recent advances in PCSK9 inhibitor development, particularly through integration with emerging biotechnologies, have substantially expanded therapeutic strategies for atherosclerosis management. Created using Figdraw.
4.1.4 Nucleic acid drugs and gene editing drugs
Inclisiran, a first-in-class siRNA-based inhibitor, targets PCSK9 mRNA for degradation, thereby mimicking natural PCSK9 loss-of-function (LOF) and reducing PCSK9 levels (53). Approved by the FDA in December 2021, inclisiran's impact on major adverse cardiovascular events is currently being evaluated in the ORION-9, ORION-10, and ORION-11 clinical trials involving individuals with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), with primary completion anticipated in July 2026. Meanwhile, Verve-101, the first PCSK9-targeted gene-editing drug developed by Verve Therapeutics, is in Phase I clinical trials. In the FOURIER trial, over three-quarters of enrolled patients had a history of myocardial infarction (with the indicator event occurring a median of 3.4 years prior), 19% had a history of non-hemorrhagic stroke, and 13% had peripheral artery disease (PAD). In contrast, the ODYSSEY OUTCOMES trial targeted a more acute population, enrolling patients who had recently experienced acute coronary syndrome. Despite this difference in patient acuity, the average baseline LDL-C levels were similar between the two trials: 92 mg/dl in FOURIER and 87 mg/dl in ODYSSEY OUTCOMES (54–56). This single-course treatment permanently silences the PCSK9 gene in the liver using a CRISPR-Cas9-derived editing tool that introduces A-to-G base edits at specific PCSK9 loci to disable gene function (57).
4.2 mRNA-based therapeutic strategies targeting PCSK9
As an emerging therapeutic modality, mRNA technology has demonstrated revolutionary potential across diverse disease domains (58). The rapid clinical translation of highly efficacious mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines during the pandemic era has particularly highlighted its therapeutic versatility.
Of particular interest in atherosclerosis management is interleukin-10 (IL-10), a potent immunomodulator predominantly secreted by macrophages. This cytokine exerts critical regulatory effects on inflammatory responses and promotes tissue repair within atherosclerotic plaques (59, 60). Capitalizing on these properties, predecessors pioneered a macrophage-targeted nanoparticle delivery system for anti-inflammatory mRNA therapeutics. Their innovative approach utilizes pH-responsive, charge-switching polymeric nanoparticles capable of precise delivery of IL-10-encoding mRNA to plaque-associated macrophages.
Through comprehensive evaluation in a HFD model, this platform addressed two key pharmacological challenges: (1) overcoming the inherent instability and rapid systemic clearance of naked mRNA, and (2) achieving sustained therapeutic effects within the complex plaque microenvironment. These findings hold dual significance—they not only establish a robust methodology for mRNA-based modulation of local inflammatory processes but also provide a strategic framework for combining anti-inflammatory therapies with conventional LDL-C-lowering interventions (61).
4.3 Efficacy and safety considerations of optimizing long-term outcomes of PCSK9 inhibitors
The development of extended-action PCSK9 inhibitor formulations aims to improve therapeutic adherence by minimizing dosing frequency. Clinical surveillance data reveal characteristic adverse event profiles, with musculoskeletal pain (27.2%), nasopharyngitis (9.3%), transaminase elevation (6%), and influenza-like symptoms (7.5%) representing the most frequently reported complications (62–64). These findings underscore the imperative for optimizing both pharmacological durability and safety parameters in PCSK9-targeted therapies.
4.3.1 Precision medicine approaches
Advancements in mechanistic understanding enable tailored therapeutic strategies to bridge guideline-practice disparities. Integrative multi-omics platforms, spanning genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, facilitate comprehensive biomarker discovery and systems-level analysis of drug response heterogeneity (65). Such approaches empower: (1) Identification of phenotype-specific therapeutic targets; (2) Prediction of protein-drug interactions and off-target effects; (3) Stratification of patients for personalized dosing regimens (66–68).
4.3.2 Robust clinical validation frameworks
Large-scale multicenter trials are critical for validating therapeutic outcomes across diverse populations. Key implementation strategies include: (1) Population diversification: Expanding enrollment to understudied cohorts (geriatric, gestational, high-comorbidity patients) to characterize long-term safety profiles; (2) Geographic generalizability: Incorporating multi-regional clinical practice data to ensure therapeutic consistency across ethnicities and healthcare systems. This dual focus on molecular precision and epidemiological rigor establishes a sustainable paradigm for next-generation PCSK9 inhibitor development (Figure 3).
Figure 3. The development of molecular biology and the rigor of epidemiology provide sustainable development for the safety and long-term efficacy of PCSK9 inhibitors. Created using Figdraw.
4.3.3 Clinical promise for lipid management of PCSK9 inhibitor MK-0616
The current clinical strategy encompasses FDA-approved monoclonal antibodies (evolocumab, alirocumab, bococizumab) and liver-targeted PCSK9 synthesis inhibitors (69). Among emerging therapies, MK-0616, a potent oral macrocyclic peptide PCSK9 inhibitor, demonstrates dual efficacy in reducing LDL-cholesterol, non-HDL-cholesterol, apoB, and Lp(a), while offering potential advantages over injectable alternatives through simplified dosing, enhanced patient adherence, and cost efficiency (70). Preclinically, MK-0616 exhibited high PCSK9-binding affinity (Ki = 5 pM), favorable safety, and sufficient oral bioavailability to support clinical translation. Phase 1 trials in healthy adults revealed that single oral doses achieved >93% geometric mean reduction (95% CI: 84–103) in free plasma PCSK9; notably, statin-treated participants receiving 20 mg MK-0616 daily for 14 days showed a maximal 61% geometric mean reduction (95% CI: 43–85) in LDL-cholesterol from baseline (71).
4.4 Pharmacological research on trodusquemine
Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) have been extensively studied as the primary cellular component implicated in the vulnerability of carotid atherosclerotic plaques (72). The platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) family comprises two principal isoforms, PDGFR-α and PDGFR-β, with studies indicating that both PDGF ligands and their corresponding receptors demonstrate significantly higher expression levels in atherosclerotic vessels compared to normal controls (73–75).
4.4.1 PTP1B mediates dual pathogenic roles in vascular pathophysiology
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), a key regulatory enzyme in tyrosine phosphorylation processes, has been shown to critically modulate PDGF receptor signaling pathways. Mechanistic studies reveal that PTP1B mediates PDGF/PDGFR signal regulation in VSMCs through endocytic processing, thereby suppressing PDGF-induced hyperactivation of VSMC biological functions (76–78).
The elevated systemic PTP1B activity promotes macrophage uptake of oxidized cholesterol through scavenger receptors, facilitating their transformation into lipid-laden foam cells. This cellular transformation accelerates arterial lipid accumulation and potentiates pro-inflammatory responses within vascular tissues.
4.4.2 PTP1B targeting from molecular inhibition to clinical atherosclerosis therapy
Experimental investigations using animal models, researchers demonstrated that PTP1B upregulation induces cellular apoptosis and suppresses smooth muscle cell migratory capacity in carotid arteries. Notably, KY266-treated mice (a selective PTP1B inhibitor) exhibited significant reductions in pathology-associated protein expression levels, correlating with attenuated atherosclerotic progression. These findings collectively indicate PTP1B's critical regulatory role in atherogenesis and its potential as a molecular target for therapeutic intervention (79, 80).
Structural analyses reveal that trodusquemine binds specifically to the primary binding site formed by α-helices 7 and 9 of PTP1B. This interaction triggers structural reorganization of α-helices 7, 3, and 6, generating a secondary pocket with partial overlap to the exosite. The resultant allosteric inhibition stabilizes the WPD loop in an open conformation, effectively locking PTP1B in an inactive state through dynamic domain rearrangements (80).
Recent translational research demonstrated trodusquemine's therapeutic efficacy. The compound is systematically evaluated using peripheral blood leukocytes from 30 atherosclerotic patients with confirmed coronary artery disease and 30 age-matched healthy controls, showing consistent pharmacological activity across disease states.
4.4.3 Phase status or translational challenges of PTP1B
In current research, numerous novel PTP1B inhibitors have emerged, including compounds such as BDB [3-bromo-4,5-bis(2,3-dibromo-4,5-dihydroxybenzyl)-1], derivatives of 2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazolidin-3-1,1-dioxide, MSI-1436 analogues like PMM-1001, and 5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazolidin-3-one. However, despite their potential as therapeutic agents, these inhibitors remain at the experimental stage, with no clinical trial data currently available (81–83).
However, a major limitation of PTP1B is its lack of specificity and cellular permeability, posing significant challenges to clinical translation (84). Most inhibitors target the catalytic active site, resulting in non-specific inhibition across all protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs). Consequently, developing novel strategies to overcome these limitations, such as designing inhibitors with enhanced membrane permeability and bioavailability, or optimizing administration routes, is critically important (85, 86). Future advances are expected to resolve these challenges, enabling safer and more effective therapeutic applications of PTP1B inhibitors in atherosclerosis treatment.
5 CRISPR-Cas systems as novel therapeutic platforms for atherosclerosis management
The CRISPR/Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) genome editing platform has revolutionized genetic engineering through its precision in manipulating mammalian genomes. This technology has enabled unprecedented capabilities in functional genomics research and therapeutic development for monogenic disorders, positioning it as a transformative modality in cardiovascular pathobiology (87, 88).
Although CRISPR/Cas9 technology demonstrates significant therapeutic promise for atherosclerosis, associated risks, including off-target effects, toxicity of delivery vectors, and limited editing efficiency, require further investigation (89).
Among various CRISPR-Cas variants, the Type II CRISPR-Cas system from Streptococcus pyogenes (SpCas9) remains the most extensively characterized and widely utilized in biomedical applications due to its high editing efficiency and programmable specificity (87, 90). In a mouse model receiving AAV-CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Ldlr gene correction, partial restoration of Ldlr expression effectively improved the atherosclerotic phenotype, resulting in reduced total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglyceride levels, diminished macrophage infiltration, and smaller plaques, with no significant off-target effects detected (91).
In the presence of iron, hepatic kupffer cells (KCs) have been shown to mediate critical metabolic processes under iron-replete conditions, particularly through ABCA1-dependent transfer of low-density lipoprotein-derived cholesterol to hepatocytes - a key pathway in systemic lipid homeostasis (92). Complementing these findings, mechanistic studies using the Huh7 human hepatocyte model revealed that MFGE8 overexpression, mediated through its conserved FV/FVIII domains, significantly correlates with enhanced coronary artery disease susceptibility and atherogenesis progression (93).
Of particular clinical relevance, VERVE-101 represents a breakthrough CRISPR-based therapeutic candidate utilizing adenine base-edited mRNA combined with PCSK9-targeting siRNA, delivered via an optimized lipid nanoparticle (LNP) system for single-dose intravenous administration. This innovative approach enables durable modulation of cholesterol metabolism through precision genome editing (57).
Building on these findings, predecessors developed an AAV-compatible dCas9 repressor system (dSaCas9KRAB) demonstrating efficient PCSK9 silencing in vivo, establishing proof-of-concept for CRISPR interference strategies in cardiovascular disease management (94). Further validation comes from ANGPTL3 gene silencing experiments in murine models, achieved significant reductions in atherogenic lipid parameters including LDL-C and triglycerides (95, 96). These collective advances underscore the transformative potential of CRISPR/Cas9 systems in developing targeted therapies for atherosclerosis (97).
6 MSC-based therapeutic strategies for atherosclerosis management
Inflammation, a fundamental host defense mechanism against pathogenic invasion, plays paradoxical roles in atherosclerosis progression by mediating both protective and pathological responses (88). Atherogenesis is intrinsically regulated through inflammatory cascades that orchestrate immune cell activation, endothelial dysfunction, and metabolic dysregulation across all disease stages (98). Central to this process is endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction, which manifests as impaired nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability due to eNOS (endothelial nitric oxide synthase) uncoupling - a hallmark mechanism linking hemodynamic stress and lipid metabolic disorders to atherosclerotic plaque development (13).
This pathophysiological continuum creates a self-perpetuating cycle where chronic endothelial inflammation promotes plaque vulnerability through matrix metalloproteinase activation and necrotic core expansion. Therapeutic interventions targeting this inflammatory-endothelial axis therefore represent critical strategies for atherosclerotic plaque stabilization.
6.1 Therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), defined as multipotent stromal cells with tri-lineage differentiation capacity and immunomodulatory properties, have emerged as promising biotherapeutic agents for atherosclerosis intervention (99, 100). Their therapeutic efficacy stems from multimodal mechanisms: (1) Anti-inflammatory reprogramming: MSC-secreted paracrine factors (TSG-6, IL-10, TGF-β) induce macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype, attenuating pro-inflammatory cytokine storms in atherosclerotic lesions (101). (2) Plaque microenvironment modulation: Through dynamic crosstalk with plaque-resident cells, MSCs regulate immune cell infiltration profiles, reducing CD68+ macrophage density while increasing regulatory T-cell populations (102–104). (3) Endothelial homeostasis restoration: MSC-derived extracellular vesicles enhance eNOS recoupling via miR-126-3p delivery, counteracting oxidative stress-induced EC apoptosis (105).
These pleiotropic actions collectively stabilize vulnerable plaques by increasing fibrous cap thickness (>65% vs. controls) and reducing lipid core size (41.2% decrease, p < 0.01), as demonstrated in recent clinical-phase trials (102–105).
6.2 Functional mechanisms of MSCs
Emerging evidence has established an intricate link between small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) and the functional properties of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) (105, 106). These nanoscale vesicles, generated through the fusion of multivesicular bodies with the plasma membrane, serve as critical intercellular messengers containing bioactive cargo including mRNAs, microRNAs, proteins, and organelle components. Experimental evidence demonstrates that when MSCs are co-cultured with ox-LDL-stimulated endothelial cells, they significantly upregulate interleukin-8 (IL-8) and macrophage inflammatory protein-2 (MIP-2) expression, subsequently activating the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) system. This activation cascade enhances nitric oxide (NO) production and improves endothelial cell functionality (107).
Furthermore, MSC-derived Wnt proteins have been shown to activate the β-catenin-dependent Wnt signaling pathway, effectively mitigating endothelial cell apoptosis through reduction of oxidative stress (108). Notably, mechanistic studies utilizing MSCs derived from patients with atherosclerosis and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) have provided crucial insights into NF-κB-mediated immunoregulatory pathways (109).
While current research in stem cell therapy continues to reveal complex regulatory networks requiring further investigation, particularly regarding factors modulating stem cell biological functions, MSC-based approaches remain a promising therapeutic strategy for atherosclerosis management.
6.3 Key risks and limitations of MSCs
A major meta-analysis on MSC safety, integrating 62 randomized clinical trials (N = 3,546 participants), revealed significant risks including transient fever within 48 h post-administration (OR 3.65, 95% CI 2.05–6.49, p < 0.01) and increased incidence of administration-site adverse events such as bleeding, swelling, pruritus, pain, or local infection (OR 1.98, 95% CI 1.01–3.87, p = 0.05) (110). Furthermore, MSCs' high proliferative capacity and tumor-homing potential enable recruitment into tumor microenvironments in response to hypoxia or pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, TNF-α, IFN-γ). These tumor-associated MSCs differentiate into cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), which secrete pro-angiogenic and immunosuppressive factors, including PDGF, FGF, VEGF, IL-6, and IL-8, that promote cancer cell survival, angiogenesis, immunosuppression, tumor growth, and metastasis (111). Consequently, comprehensive risk assessment of MSC therapy requires further clinical evaluation.
7 Conclusion
As a predominant pathology in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems, atherosclerosis manifests through intricate and multifactorial pathogenic mechanisms. With advancing insights into its etiological complexity, contemporary research has yielded novel therapeutic strategies demonstrating superior efficacy to conventional approaches. These innovations encompass three primary domains: (1) optimization of existing treatment protocols, (2) development of next-generation pharmacological agents, and (3) exploration of cutting-edge interventions in gene therapy and regenerative medicine.
The advent of nanotechnology has revolutionized pharmaceutical development through its capacity for site-specific drug delivery, significantly enhancing therapeutic targeting and bioavailability at lesion sites. Concurrently, microRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as promising therapeutic targets, given their regulatory functions in critical atherogenic processes including lipid homeostasis modulation, immunoinflammatory response coordination, and vascular endothelial remodeling.
This paradigm shift in atherosclerosis management reflects a progressive transition from traditional pharmacological interventions toward an integrated multidisciplinary therapeutic framework. Future clinical approaches will likely emphasize the synergistic integration of diverse treatment modalities, potentially offering optimized therapeutic outcomes through personalized combination therapies.
Author contributions
ZW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. WP: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. LH: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Investigation. YZ: Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JY: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. XC: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Writing – original draft. FL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Investigation. QZ: Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from Cultivating Project for Young Scholars at Hubei University of Medicine (2020QDJZR025); Provincial Advantage Characteristic Subject Group of University of Medicine (2023PHXKQ3); Hubei Provincial Department of Education project (B2023105); Educational Research Program at Hubei University of Medicine (YJ2024033,YHJ2024005, 2024022); Soft science project at Shiyan (202406); College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program at Hubei University of Medicine (X202110929005, X202110929007, S202310929007, YSRTP202106). The funders had no role in study design, data collection, and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Falk E. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2006) 47(8):C7–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.09.068
2. Al-Mallah MH, Sakr S, Al-Qunaibet A. Cardiorespiratory fitness and cardiovascular disease prevention: an update. Curr Atheroscler Rep. (2018) 20(1):e1. doi: 10.1007/s11883-018-0711-4
3. Frostegård J. Immunity, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. BMC Med. (2013) 11:117. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-117
4. Wolf D, Ley K. Immunity and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2019) 124(2):315–27. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313591
5. Singh B, Cui K, Eisa-Beygi S, Zhu B, Cowan DB, Shi J, et al. Elucidating the crosstalk between endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) and endothelial autophagy in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Vascul Pharmacol. (2024) 155:107368. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2024.107368
6. Kruth HS, Huang W, Ishii I, Zhang WY. Macrophage foam cell formation with native low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277(37):34573–80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205059200
7. Batty M, Bennett MR, Yu E. The role of oxidative stress in atherosclerosis. Cells. (2022) 11(23):e3843. doi: 10.3390/cells11233843
8. Carnevale R, Bartimoccia S, Nocella C, Di Santo S, Loffredo L, Illuminati G, et al. LDL oxidation by platelets propagates platelet activation via an oxidative stress-mediated mechanism. Atherosclerosis. (2014) 237(1):108–16. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.08.041
9. Binder CJ, Papac-Milicevic N, Witztum JL. Innate sensing of oxidation-specific epitopes in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2016) 16(8):485–97. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.63
10. Haberland ME, Mottino G, Le M, Frank JS. Sequestration of aggregated LDL by macrophages studied with freeze-etch electron microscopy. J Lipid Res. (2001) 42(4):605–19. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2275(20)31170-6
11. Palinski W, Rosenfeld ME, Ylä-Herttuala S, Gurtner GC, Socher SS, Butler SW, et al. Low density lipoprotein undergoes oxidative modification in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1989) 86(4):1372–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1372
12. Zheng D, Liu J, Piao H, Zhu Z, Wei R, Liu K. ROS-triggered endothelial cell death mechanisms: focus on pyroptosis, parthanatos, and ferroptosis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1039241. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1039241
13. Gimbrone MA Jr., García-Cardeña G. Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2016) 118(4):620–36. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306301
14. Tamargo IA, Baek KI, Kim Y, Park C, Jo H. Flow-induced reprogramming of endothelial cells in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2023) 20(11):738–53. doi: 10.1038/s41569-023-00883-1
15. Schwartz SM, Virmani R, Rosenfeld ME. The good smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. (2000) 2(5):422–9. doi: 10.1007/s11883-000-0081-5
16. Sirtori CR. The pharmacology of statins. Pharmacol Res. (2014) 88:3–11. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2014.03.002
17. Tomaszewski M, Stępień KM, Tomaszewska J, Czuczwar SJ. Statin-induced myopathies. Pharmacol Rep. (2011) 63(4):859–66. doi: 10.1016/S1734-1140(11)70601-6
18. Kosmas CE, Skavdis A, Sourlas A, Papakonstantinou EJ, Peña Genao E, Echavarria Uceta R, et al. Safety and tolerability of PCSK9 inhibitors: current insights. Clin Pharmacol Adv Appl. (2020) 12:191–202. doi: 10.2147/cpaa.s288831
19. Endo A, Kuroda M, Tsujita Y. ML-236A, ML-236B, and ML-236C, new inhibitors of cholesterogenesis produced by penicillium citrinium. J Antibiot (Tokyo). (1976) 29(12):1346–8. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.1346
20. Kuroda M, Endo A. Inhibition of in vitro cholesterol synthesis by fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. (1976) 486(1):70–81.12837
21. Zhao L, Ma D, Wang L, Su X, Feng L, Zhu L, et al. Metabolic changes with the occurrence of atherosclerotic plaques and the effects of statins. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1301051. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1301051
22. Tiwari R, Pathak K. Statins therapy: a review on conventional and novel formulation approaches. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2011) 63(8):983–98. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01273.x
23. Kosmas CE, Frishman WH. New and emerging LDL cholesterol-lowering drugs. Am J Ther. (2015) 22(3):234–41. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000063
24. Flores AM, Ye J, Jarr KU, Hosseini-Nassab N, Smith BR, Leeper NJ. Nanoparticle therapy for vascular diseases. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2019) 39(4):635–46. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311569
25. Duivenvoorden R, Tang J, Cormode DP, Mieszawska AJ, Izquierdo-Garcia D, Ozcan C, et al. A statin-loaded reconstituted high-density lipoprotein nanoparticle inhibits atherosclerotic plaque inflammation. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:3065. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4065
26. Gao C, Huang Q, Liu C, Kwong CHT, Yue L, Wan JB, et al. Treatment of atherosclerosis by macrophage-biomimetic nanoparticles via targeted pharmacotherapy and sequestration of proinflammatory cytokines. Nat Commun. (2020) 11(1):2622. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16439-7
27. Rayner KJ, Sheedy FJ, Esau CC, Hussain FN, Temel RE, Parathath S, et al. Antagonism of miR-33 in mice promotes reverse cholesterol transport and regression of atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. (2011) 121(7):2921–31. doi: 10.1172/JCI57275
28. Li C, Dou Y, Chen Y, Qi Y, Li L, Han S, et al. Site-specific MicroRNA-33 antagonism by pH-responsive nanotherapies for treatment of atherosclerosis via regulating cholesterol efflux and adaptive immunity. Adv Funct Mater. (2020) 30(42):e2002131. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202002131
29. Jiang T, Xu L, Zhao M, Kong F, Lu X, Tang C, et al. Dual targeted delivery of statins and nucleic acids by chitosan-based nanoparticles for enhanced antiatherosclerotic efficacy. Biomaterials. (2022) 280:121324. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121324
30. Chen W, Schilperoort M, Cao Y, Shi J, Tabas I, Tao W. Macrophage-targeted nanomedicine for the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2022) 19(4):228–49. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00629-x
31. Talev J, Kanwar JR. Iron oxide nanoparticles as imaging and therapeutic agents for atherosclerosis. Semin Thromb Hemost. (2020) 46(5):553–62. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-3400247
32. Yu M, Ortega CA, Si K, Molinaro R, Schoen FJ, Leitao RFC, et al. Nanoparticles targeting extra domain B of fibronectin-specific to the atherosclerotic lesion types III, IV, and V-enhance plaque detection and cargo delivery. Theranostics. (2018) 8(21):6008–24. doi: 10.7150/thno.24365
33. Tu Y, Sun Y, Fan Y, Cheng Z, Yu B. Multimodality molecular imaging of cardiovascular disease based on nanoprobes. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2018) 48(4):1401–15. doi: 10.1159/000492251
34. Berry C, L'Allier PL, Grégoire J, Lespérance J, Levesque S, Ibrahim R, et al. Comparison of intravascular ultrasound and quantitative coronary angiography for the assessment of coronary artery disease progression. Circulation. (2007) 115(14):1851–7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.655654
35. Zhu N, Ji H, Yu P, Niu J, Farooq MU, Akram MW, et al. Surface modification of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanomaterials (Basel). (2018) 8(10):e810. doi: 10.3390/nano8100810
36. Zhang W, Liu L, Chen H, Hu K, Delahunty I, Gao S, et al. Surface impact on nanoparticle-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Theranostics. (2018) 8(9):2521–48. doi: 10.7150/thno.23789
37. Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association joint committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. (2022) 145(18):e895–1032. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063
38. Khakoo AY, Yurgin NR, Eisenberg PR, Fonarow GC. Overcoming barriers to development of novel therapies for cardiovascular disease: insights from the oncology drug development experience. JACC Basic Transl Sci. (2019) 4(2):269–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2019.01.011
39. Martelli F, Mishra PK, Caporali A. Editorial: nucleic acid-based therapies for cardiovascular diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2024) 11:e1392073. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1392073
40. Hummelgaard S, Vilstrup JP, Gustafsen C, Glerup S, Weyer K. Targeting PCSK9 to tackle cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol Ther. (2023) 249:108480. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108480
41. Benjannet S, Rhainds D, Essalmani R, Mayne J, Wickham L, Jin W, et al. NARC-1/PCSK9 and its natural mutants: zymogen cleavage and effects on the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor and LDL cholesterol. J Biol Chem. (2004) 279(47):48865–75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409699200
42. Barale C, Melchionda E, Morotti A, Russo I. PCSK9 Biology and its role in atherothrombosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(11):e5880. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115880
43. Santos RD, Gidding SS, Hegele RA, Cuchel MA, Barter PJ, Watts GF, et al. Defining severe familial hypercholesterolaemia and the implications for clinical management: a consensus statement from the international atherosclerosis society severe familial hypercholesterolemia panel. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2016) 4(10):850–61. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(16)30041-9
44. Südhof TC, Van der Westhuyzen DR, Goldstein JL, Brown MS, Russell DW. Three direct repeats and a TATA-like sequence are required for regulated expression of the human low density lipoprotein receptor gene. J Biol Chem. (1987) 262(22):10773–9. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)61030-0
45. Davis CG, Elhammer A, Russell DW, Schneider WJ, Kornfeld S, Brown MS, et al. Deletion of clustered O-linked carbohydrates does not impair function of low density lipoprotein receptor in transfected fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. (1986) 261(6):2828–38. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)35862-3
46. Norata GD, Tibolla G, Catapano AL. Targeting PCSK9 for hypercholesterolemia. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2014) 54:273–93. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011613-140025
47. Cameron J, Holla ØL, Ranheim T, Kulseth MA, Berge KE, Leren TP. Effect of mutations in the PCSK9 gene on the cell surface LDL receptors. Hum Mol Genet. (2006) 15(9):1551–8. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl077
48. DeVay RM, Yamamoto L, Shelton DL, Liang H. Common proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) epitopes mediate multiple routes for internalization and function. PLoS One. (2015) 10(4):e0125127. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125127
49. Holla ØL, Laerdahl JK, Strøm TB, Tveten K, Cameron J, Berge KE, et al. Removal of acidic residues of the prodomain of PCSK9 increases its activity towards the LDL receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2011) 406(2):234–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.02.023
50. Fisher TS, Lo Surdo P, Pandit S, Mattu M, Santoro JC, Wisniewski D, et al. Effects of pH and low density lipoprotein (LDL) on PCSK9-dependent LDL receptor regulation. J Biol Chem. (2007) 282(28):20502–12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701634200
51. Tveten K, Holla ØL, Cameron J, Strøm TB, Berge KE, Laerdahl JK, et al. Interaction between the ligand-binding domain of the LDL receptor and the C-terminal domain of PCSK9 is required for PCSK9 to remain bound to the LDL receptor during endosomal acidification. Hum Mol Genet. (2012) 21(6):1402–9. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr578
52. Yamamoto T, Lu C, Ryan RO. A two-step binding model of PCSK9 interaction with the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. (2011) 286(7):5464–70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.199042
53. Khvorova A. Oligonucleotide therapeutics — a new class of cholesterol-lowering drugs. N Engl J Med. (2017) 376(1):4–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1614154
54. Furtado RHM, Giugliano RP. What lessons have we learned and what remains to be clarified for PCSK9 inhibitors? A review of FOURIER and ODYSSEY outcomes trials. Cardiol Ther. (2020) 9(1):59–73. doi: 10.1007/s40119-020-00163-w
55. Gallego-Colon E, Daum A, Yosefy C. Statins and PCSK9 inhibitors: a new lipid-lowering therapy. Eur J Pharmacol. (2020) 878:173114. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173114
56. Jeswani BM, Sharma S, Rathore SS, Nazir A, Bhatheja R, Kapoor K. PCSK9 inhibitors: the evolving future. Health Sci Rep. (2024) 7(11):e70174. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70174
57. Lee RG, Mazzola AM, Braun MC, Platt C, Vafai SB, Kathiresan S, et al. Efficacy and safety of an investigational single-course CRISPR base-editing therapy targeting PCSK9 in nonhuman primate and mouse models. Circulation. (2023) 147(3):242–53. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.062132
58. Kumar R, Krishnaperumal G, Vellapandian C. Innovative mRNA vaccine approaches in targeting atherosclerosis: a new era in cardiovascular therapy. Cureus. (2024) 16(11):e74141. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74141
59. Murray PJ, Smale ST. Restraint of inflammatory signaling by interdependent strata of negative regulatory pathways. Nat Immunol. (2012) 13(10):916–24. doi: 10.1038/ni.2391
60. Kabat AM, Pearce EJ. Inflammation by way of macrophage metabolism. Science. (2017) 356(6337):488–9. doi: 10.1126/science.aan2691
61. Gao M, Tang M, Ho W, Teng Y, Chen Q, Bu L, et al. Modulating plaque inflammation via targeted mRNA nanoparticles for the treatment of atherosclerosis. ACS Nano. (2023) 17(18):17721–39. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c00958
62. Blom DJ, Hala T, Bolognese M, Lillestol MJ, Toth PD, Burgess L, et al. A 52-week placebo-controlled trial of evolocumab in hyperlipidemia. N Engl J Med. (2014) 370(19):1809–19. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1316222
63. Raal FJ, Honarpour N, Blom DJ, Hovingh GK, Xu F, Scott R, et al. Inhibition of PCSK9 with evolocumab in homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia (TESLA part B): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. (2015) 385(9965):341–50. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61374-X
64. Moriarty PM, Jacobson TA, Bruckert E, Thompson PD, Guyton JR, Baccara-Dinet MT, et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab, a monoclonal antibody to PCSK9, in statin-intolerant patients: design and rationale of ODYSSEY ALTERNATIVE, a randomized phase 3 trial. J Clin Lipidol. (2014) 8(6):554–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2014.09.007
65. Coumau C, Gaspar F, Terrier J, Schulthess-Lisibach A, Lutters M, Le Pogam MA, et al. Drug-drug interactions with oral anticoagulants: information consistency assessment of three commonly used online drug interactions databases in Switzerland. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1332147. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1332147
66. Duarte JD, Cavallari LH. Pharmacogenetics to guide cardiovascular drug therapy. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2021) 18(9):649–65. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00549-w
67. Liu H, Wang L, Wang H, Hao X, Du Z, Li C, et al. The association of triglyceride-glucose index with major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events after acute myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Nutr Diabetes. (2024) 14(1):39. doi: 10.1038/s41387-024-00295-1
68. McFarland MS, Buck ML, Crannage E, Armistead LT, Ourth H, Finks SW, et al. Assessing the impact of comprehensive medication management on achievement of the quadruple aim. Am J Med. (2021) 134(4):456–61. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.12.008
69. Grześk G, Dorota B, Wołowiec Ł, Wołowiec A, Osiak J, Kozakiewicz M, et al. Safety of PCSK9 inhibitors. Biomed Pharmacother. (2022) 156:113957. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113957
70. Burnett JR, Hooper AJ. MK-0616: an oral PCSK9 inhibitor for hypercholesterolemia treatment. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. (2023) 32(10):873–8. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2023.2267972
71. Johns DG, Campeau LC, Banka P, Bautmans A, Bueters T, Bianchi E, et al. Orally bioavailable macrocyclic peptide that inhibits binding of PCSK9 to the low density lipoprotein receptor. Circulation. (2023) 148(2):144–58. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.063372
72. Liu M, Gomez D. Smooth muscle cell phenotypic diversity. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2019) 39(9):1715–23. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312131
73. Papadopoulos N, Lennartsson J. The PDGF/PDGFR pathway as a drug target. Mol Aspects Med. (2018) 62:75–88. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2017.11.007
74. Karvinen H, Rutanen J, Leppänen O, Lach R, Levonen AL, Eriksson U, et al. PDGF-C and -D and their receptors PDGFR-alpha and PDGFR-beta in atherosclerotic human arteries. Eur J Clin Invest. (2009) 39(4):320–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2009.02095.x
75. Raines EW. PDGF and cardiovascular disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2004) 15(4):237–54. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2004.03.004
76. Chang Y, Ceacareanu B, Zhuang D, Zhang C, Pu Q, Ceacareanu AC, et al. Counter-regulatory function of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B in platelet-derived growth factor- or fibroblast growth factor-induced motility and proliferation of cultured smooth muscle cells and in neointima formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2006) 26(3):501–7. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000201070.71787.b8
77. Markova B, Herrlich P, Rönnstrand L, Böhmer FD. Identification of protein tyrosine phosphatases associating with the PDGF receptor. Biochemistry. (2003) 42(9):2691–9. doi: 10.1021/bi0265574
78. He C, Medley SC, Hu T, Hinsdale ME, Lupu F, Virmani R, et al. PDGFRβ signalling regulates local inflammation and synergizes with hypercholesterolaemia to promote atherosclerosis. Nat Commun. (2015) 6:7770. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8770
79. Shimizu H, Shiota M, Yamada N, Miyazaki K, Ishida N, Kim S, et al. Low M(r) protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibits growth and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells induced by platelet-derived growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2001) 289(2):602–7. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.6007
80. Thompson D, Morrice N, Grant L, Le Sommer S, Ziegler K, Whitfield P, et al. Myeloid protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) deficiency protects against atherosclerotic plaque formation in the ApoE(-/-) mouse model of atherosclerosis with alterations in IL10/AMPKα pathway. Mol Metab. (2017) 6(8):845–53. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.06.003
81. Luo J, Zheng M, Jiang B, Li C, Guo S, Wang L, et al. Antidiabetic activity in vitro and in vivo of BDB, a selective inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, from rhodomela confervoides. Br J Pharmacol. (2020) 177(19):4464–80. doi: 10.1111/bph.15195
82. Phong NV, Oanh VT, Yang SY, Choi JS, Min BS, Kim JA. PTP1B inhibition studies of biological active phloroglucinols from the rhizomes of Dryopteris crassirhizoma: kinetic properties and molecular docking simulation. Int J Biol Macromol. (2021) 188:719–28. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.091
83. Krishnan N, Konidaris KF, Gasser G, Tonks NK. A potent, selective, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B improves insulin and leptin signaling in animal models. J Biol Chem. (2018) 293(5):1517–25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C117.819110
84. Liu R, Mathieu C, Berthelet J, Zhang W, Dupret J-M, Rodrigues Lima F. Human protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B): from structure to clinical inhibitor perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(13):7027. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137027
85. Gunasekaran T, Haile T, Nigusse T, Dhanaraju MD. Nanotechnology: an effective tool for enhancing bioavailability and bioactivity of phytomedicine. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. (2014) 4:S1–7. doi: 10.12980/APJTB.4.2014C980
86. Feng B, Dong Y, Shang B, Zhang B, Crans DC, Yang X. Convergent protein phosphatase inhibitor design for PTP1B and TCPTP: exchangeable vanadium coordination complexes on graphene quantum dots. Adv Funct Mater. (2021) 32(5):e08645. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202108645
87. Jinek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I, Hauer M, Doudna JA, Charpentier E. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science. (2012) 337(6096):816–21. doi: 10.1126/science.1225829
88. Clow PA, Du M, Jillette N, Taghbalout A, Zhu JJ, Cheng AW. CRISPR-mediated multiplexed live cell imaging of nonrepetitive genomic loci with one guide RNA per locus. Nat Commun. (2022) 13(1):1871. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29343-z
89. Bonowicz K, Jerka D, Piekarska K, Olagbaju J, Stapleton L, Shobowale M, et al. CRISPR-Cas9 in cardiovascular medicine: unlocking new potential for treatment. Cells. (2025) 14(2):e131. doi: 10.3390/cells14020131
90. Magadán AH, Dupuis M, Villion M, Moineau S. Cleavage of phage DNA by the Streptococcus thermophilus CRISPR3-cas system. PLoS One. (2012) 7(7):e40913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040913
91. Zhao H, Li Y, He L, Pu W, Yu W, Li Y, et al. In vivo AAV-CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing ameliorates atherosclerosis in familial hypercholesterolemia. Circulation. (2020) 141(1):67–79. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.042476
92. Demetz E, Tymoszuk P, Hilbe R, Volani C, Haschka D, Heim C, et al. The haemochromatosis gene Hfe and Kupffer cells control LDL cholesterol homeostasis and impact on atherosclerosis development. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41(40):3949–59. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa140
93. Soubeyrand S, Nikpay M, Turner A, Dang AT, Herfkens M, Lau P, et al. Regulation of MFGE8 by the intergenic coronary artery disease locus on 15q26.1. Atherosclerosis. (2019) 284:11–7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.02.012
94. Thakore PI, Kwon JB, Nelson CE, Rouse DC, Gemberling MP, Oliver ML, et al. RNA-guided transcriptional silencing in vivo with S. aureus CRISPR-Cas9 repressors. Nat Commun. (2018) 9(1):1674. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04048-4
95. Lee EC, Desai U, Gololobov G, Hong S, Feng X, Yu XC, et al. Identification of a new functional domain in angiopoietin-like 3 (ANGPTL3) and angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4) involved in binding and inhibition of lipoprotein lipase (LPL). J Biol Chem. (2009) 284(20):13735–45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807899200
96. Xu YX, Redon V, Yu H, Querbes W, Pirruccello J, Liebow A, et al. Role of angiopoietin-like 3 (ANGPTL3) in regulating plasma level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Atherosclerosis. (2018) 268:196–206. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.08.031
97. Chadwick AC, Evitt NH, Lv W, Musunuru K. Reduced blood lipid levels with in vivo CRISPR-Cas9 base editing of ANGPTL3. Circulation. (2018) 137(9):975–7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031335
98. Lin Y, Zhu W, Chen X. The involving progress of MSCs based therapy in atherosclerosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 11(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01728-1
99. Colmegna I, Stochaj U. MSC—targets for atherosclerosis therapy. Aging (Albany NY). (2018) 11(2):285–6. doi: 10.18632/aging.101735
100. Si YL, Zhao YL, Hao HJ, Fu XB, Han WD. MSCs: biological characteristics, clinical applications and their outstanding concerns. Ageing Res Rev. (2011) 10(1):93–103. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2010.08.005
101. Zhang B, Zhao N, Zhang J, Liu Y, Zhu D, Kong Y. Mesenchymal stem cells rejuvenate cardiac muscle through regulating macrophage polarization. Aging (Albany NY). (2019) 11(12):3900–8. doi: 10.18632/aging.102009
102. Takafuji Y, Hori M, Mizuno T, Harada-Shiba M. Humoral factors secreted from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate atherosclerosis in ldlr-/- mice. Cardiovasc Res. (2019) 115(6):1041–51. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy271
103. Wang ZX, Wang CQ, Li XY, Feng GK, Zhu HL, Ding Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate atherosclerosis by elevating number and function of CD4(+)CD25 (+)FOXP3 (+) regulatory T-cells and inhibiting macrophage foam cell formation. Mol Cell Biochem. (2015) 400(1–2):163–72. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2272-3
104. Kusuma GD, Carthew J, Lim R, Frith JE. Effect of the microenvironment on mesenchymal stem cell paracrine signaling: opportunities to engineer the therapeutic effect. Stem Cells Dev. (2017) 26(9):617–31. doi: 10.1089/scd.2016.0349
105. Phinney DG, Di Giuseppe M, Njah J, Sala E, Shiva S, St Croix CM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat Commun. (2015) 6:8472. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9472
106. Casado-Díaz A, Quesada-Gómez JM, Dorado G. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in regenerative medicine: applications in skin wound healing. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2020) 8:146. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00146
107. Lin YL, Yet SF, Hsu YT, Wang GJ, Hung SC. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate atherosclerotic lesions via restoring endothelial function. Stem Cells Transl Med. (2015) 4(1):44–55. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2014-0091
108. Wang L, Qing L, Liu H, Liu N, Qiao J, Cui C, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate oxidative stress-induced islet endothelium apoptosis and functional impairment via Wnt4-β-catenin signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2017) 8(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0640-0
109. Kizilay Mancini O, Huynh DN, Menard L, Shum-Tim D, Ong H, Marleau S, et al. Ex vivo ikkβ ablation rescues the immunopotency of mesenchymal stromal cells from diabetics with advanced atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res. (2021) 117(3):756–66. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa118
110. Wang Y, Yi H, Song Y. The safety of MSC therapy over the past 15 years: a meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12(1):545. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02609-x
Keywords: atherosclerosis, PCSK9, nanoparticles, statin, MSCs
Citation: Wang Z, Peng W, Huang L, Zhang Y, Yang J, Chen X, Liu X, Li F and Zhang Q (2025) Innovative molecular intervention and precision therapy for atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1652933. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1652933
Received: 26 June 2025; Accepted: 4 September 2025;
Published: 15 October 2025.
Edited by:
DeLisa Fairweather, Mayo Clinic Florida, United StatesReviewed by:
Leiming Zhang, Binzhou Medical University, ChinaIbrahim Alradwan, King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology, Saudi Arabia
Copyright: © 2025 Wang, Peng, Huang, Zhang, Yang, Chen, Liu, Li and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Feifeng Li, MjAyMDA1MTBAaGJtdS5lZHUuY24=; Qiong Zhang, anVhbmJpbmcxOTgwQDE2My5jb20=; Xiang Liu, NTYyMzYxNTAzQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Zhijie Wang
Zhijie Wang Wei Peng3
Wei Peng3 Linsheng Huang
Linsheng Huang Feifeng Li
Feifeng Li