- 1Department of Medicine, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China
- 2Department of Cardiology, The First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Kunming, China
Ceramides are components of sphingolipid metabolism and have been linked to cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors, including hypertension, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and chronic kidney disease. Ceramide expression has been extensively studied but individual variability, species differences and regulatory mechanisms characterizing underlying relationships remain unclear. The current review analyzes roles of ceramides in the onset and progression of CVD and its risk factors. Diverse ceramide expression profiles are highlighted and recommendations for standardization of ceramide studies given. Ceramides are multifunctional and contribute to organ damage through dysregulated homeostasis during pathological processes. The current work emphasizes the importance of detecting ceramide imbalance and accounting for individual differences as a novel approach to metabolic research. Such a focus may enhance CVD management and give insights into ceramide-related pathologies.
1 Introduction
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains a leading global cause of mortality, responsible for approximately 20.5 million deaths or one-third of total deaths annually (1). CVD prevalence and mortality are on the rise due to changing population age structure, dietary habits and other lifestyle factors (2) and represent a substantial impact on patient quality of life and burden on families and healthcare systems. CVD is thus a global public health concern, for which early identification and management of risk factors are essential for prevention. Hjermann et al. (1) introduced the concept of cardiovascular metabolic syndrome, linking CVD with metabolic disorders, such as obesity, fatty liver and diabetes. Metabolic diseases are now well-established as key risk factors for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and worsen patient prognosis. The American Heart Association expanded this concept in 2023, identifying “cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome”, a holistic interpretation of the shared pathophysiology underlying CVD, kidney dysfunction and metabolic abnormalities. The detrimental impact of dysregulated metabolism and circulation gives a theoretical framework to advance metabolic CVD treatment.
Sphingolipids, including ceramides (Cer), were discovered by Thudicum in the 19th century and identified as highly hydrophobic lipids with regulatory functions in nutrient metabolism and intracellular signal transduction. Sphingolipids have now been linked to the assessment, prediction and prognosis of adverse cardiovascular events and Cer are considered independent risk factors for CVD with abnormal Cer metabolism strongly associated with increased incidence of cardiovascular events (3, 4). An observational study involving 920 participants found elevated Cer to correlate with greater likelihood of adverse cardiovascular events (5) and Cer reduction has been shown to improve metabolic cardiovascular disease risk factors, such as diabetes and hypertension (6). The Coronary Event Risk Test (CERT 1/2) demonstrated the superiority of Cer over conventional biomarkers, such as low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and total cholesterol, in predicting major adverse cardiovascular events (7). A lipidomics study conducted by Hilvo and colleagues on three prospective coronary heart disease cohorts from Europe (WECAC, KAROLA) and Australia (LIPID) developed and validated a novel risk assessment score, CERT 2, which includes six lipid species in a rapid and reliable clinical test. CERT 2 may be used alongside pre-existing risk assessment models, such as SMART and TIMI, and shows good predictive performance in various patient populations (7).
A four-year follow-up study of 495 patients who underwent non-acute coronary angiography showed a high Cer score (CERT ≥10) to be associated with twofold increased risk of all-cause mortality compared with a low score (CERT ≤2) (8). Comparable results were obtained by Qing et al. with Chinese patients with coronary artery disease, supporting the view that Cer has potential as a biomarker for prevention, treatment and prognosis.
The current review addresses the growing burden presented by CVD and its risk factors by synthesizing mechanistic roles of Cer in hypertension, dyslipidemia/obesity, chronic kidney disease and diabetes mellitus, emphasizing contributions to lipotoxicity, inflammation and metabolic dysfunction. Therapeutic strategies targeting Cer metabolism are explored, including neutral sphingomyelinase inhibitors for hypertension, dietary DHA/EPA supplementation for dyslipidemia and the pharmacological approach of the anti-diabetic, metformin. The clinical utility of Cer risk scores, such as CERT 1/2, which enhance risk stratification for major adverse cardiovascular events and guide precision therapy development are examined. The aim was to construct a framework by which Cer-related pathologies may be understood and to advance CVD therapeutic strategies.
2 Ceramide metabolism
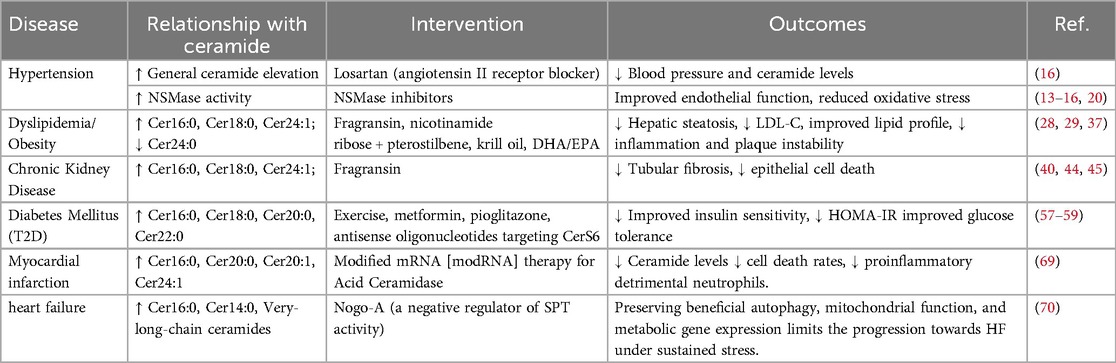
Cer are sphingolipids composed of long-chain sphingosine and saturated fatty acids attached to an amino group and are components of organelle and cell membranes. There are three synthetic pathways: de novo synthesis, sphingomyelin hydrolysis and salvage. De novo synthesis begins with the reaction of L-serine and palmitoyl-CoA, catalyzed by serine palmitoyl transferase (SPT), followed by reduction to dihydrosphingosine, catalyzed by Cer synthecerase (CerS) and condensation to generate a 3-ketotic dihydrosphingosine. The action of dihydroceramide desaturase then produces Cer (9). The sphingomyelin hydrolysis and salvage pathways involve hydrolysis by resolvase enzymes, such as the neutral sphingomyyelase (NSMase) in the cell membrane and the acid sphingomyyelase (ASMase), to produce intracellular Cer (10). Sphingosine and sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) are formed by ceramidase and ceramide kinase (9, 10). Cer is involved in the metabolism of many organs when synthesized primarily in the endoplasmic reticulum and degraded to maintain a dynamic sphingolipid balance (11). High Cer promotes inflammation, dyslipidemia, diabetes, atherosclerosis and vascular endothelial dysfunction and represent risk factors for CVD.
As shown in Figure 1, dysregulation includes enhanced de novo synthesis via SPT or increased sphingomyelin hydrolysis by NSMase/ASMase and may cause Cer accumulation. Overactivation of these pathways contributes to oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in hypertension, lipid imbalances in dyslipidemia, mitochondrial damage in chronic kidney disease and insulin signaling impairment in diabetes (Figure 1). The use of SPT inhibitors or ceramidase modulators may thus have therapeutic potential.
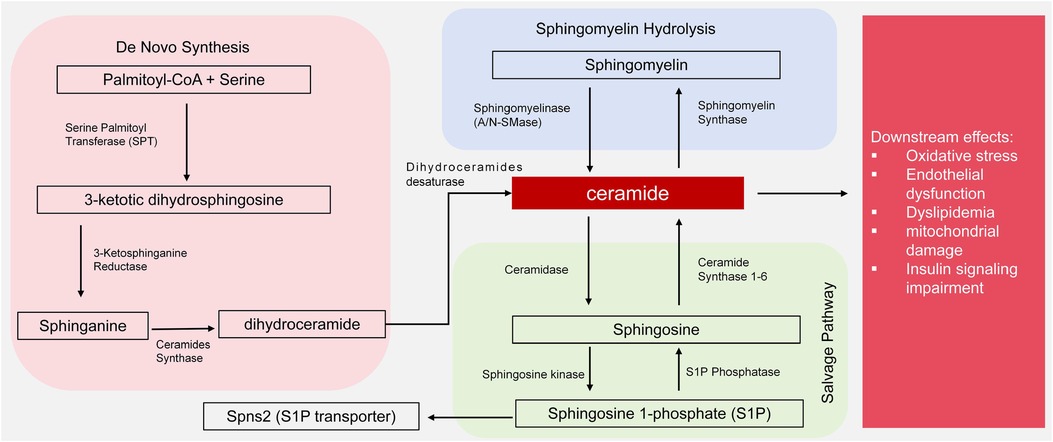
Figure 1. Ceramide synthesis by de novo, hydrolysis and salvage pathways and downstream effects of ceramide. de novo synthesis begins with palmitoyl-CoA and serine, catalyzed by serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT), leading to 3-ketodihydrosphingosine, dihydroceramide, and ceramide via subsequent enzymatic steps (reductase and dihydroceramide desaturase). Sphingomyelin hydrolysis, mediated by neutral sphingomyelinase (N-SMase) or acid sphingomyelinase (A-SMase), generates ceramide from sphingomyelin. The salvage pathway involves ceramidase converting ceramide to sphingosine, which can be further phosphorylated to sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) by ceramide kinase. Downstream effects of ceramide accumulation include oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, dyslipidemia, mitochondrial damage, and insulin signaling impairment.
3 Ceramides and cardiovascular risk factors
3.1 Ceramides and hypertension
3.1.1 Evidence of association
The etiology of hypertension is multifactorial, involving oxidative stress, vascular endothelial dysfunction and reduced mitochondrial function, and incidence has risen steadily with time (2). Antihypertensive drugs achieve control of blood pressure in only 30% patients, highlighting the limitations of traditional treatments in addressing complex molecular pathologies (12). Novel therapeutic targets are required to improve management outcomes.
Cer have been linked to hypertension by numerous studies and circulating Cer have been suggested as biomarkers for conditions such as isolated nocturnal hypertension (13). A positive correlation was observed among Cer levels, NSMase activity and blood pressure in ovariectomized rat models (14, 15). High Cer often arises due to increased sphingomyelin hydrolysis (via NSMase), leading to a cascade of oxidative stress and vascular dysfunction. The reduction of blood pressure with angiotensin II receptor antagonists, such as losartan, or vasodilators has decreased Cer levels in clinical studies. Similarly, Cer synthesis inhibitors have been shown to lower blood pressure (16). Patients with hypertension often have endothelial dysfunction, sphingolipid dysregulation and elevated oxidative stress (17).
3.1.2 Proposed mechanisms
Abnormal Cer production contributes to sustained vasoconstriction and increased oxidative stress, exacerbating endothelial dysfunction and elevating blood pressure (17–19). Cer promotes the conversion of nitric oxide (NO) into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), increasing levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), giving a self-reinforcing cycle of oxidative stress which stimulates Cer production, leading to endothelial dysfunction. NSMase inhibitors have been shown to reverse these deleterious effects (16, 20).
Spinster homolog 2 (Spns2) is an S1P transporter which is involved in lipid signaling cascades. Spns2 deficiency leads to Cer accumulation, impaired endothelial signal transduction, reduced respiratory capacity and mitochondrial dysfunction. Apoptosis is triggered and impaired vasodilation contributes to early-stage cardiovascular disease. Inhibition of de novo Cer synthesis has been found to improve mitochondrial function (21, 22) and S1P modulates the balance between NO and H2O2 with an impact on blood pressure regulation. These effects are dependent on the expression of S1PR receptor subtypes. Activation of endothelial S1PR1 promotes NO production, leading to vasodilation (23) but activation of S1PR2 and S1PR3 by Cer-mediated S1P signaling triggers stress fiber formation and adhesion junction disassembly via GTPase Rho activation in endothelial cells (Figure 2). This cascade increases endothelial permeability and activates the p38 SAPK and NF-κB pathways, contributing to vascular remodeling and inflammation. In addition, S1PR3 activation induces H2O2 production, promoting vascular smooth muscle contraction and vasoconstriction (23, 24).
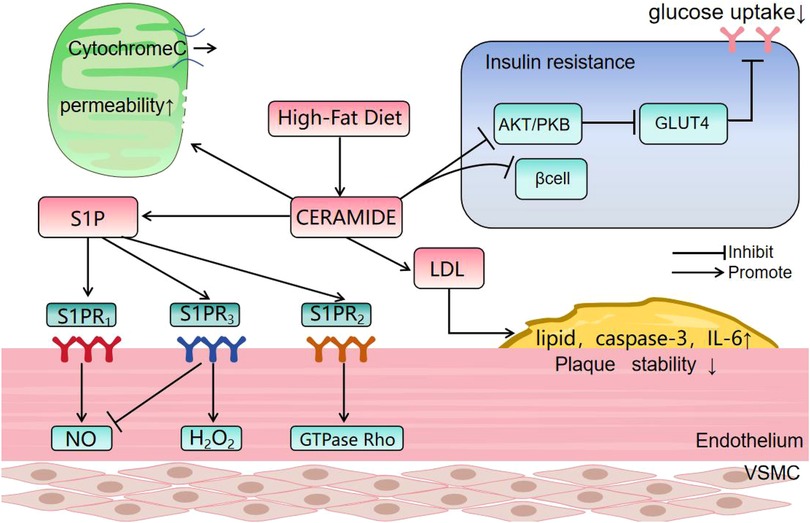
Figure 2. The effect of ceramide. PKB: Protein kinase B; GLUT4: Glucose transporter 4; S1PR: sphingosine −1-phosphate receptor; VSMC: Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. (1) Ceramide causes dephosphorylation and inactivation of protein kinase B (Akt) by stimulating the activity of protein phosphatase A2. The inactivation of Akt prevents translocation of GLUT4 to the plasma membrane, reducing glucose uptake. (2) Ceramide forms large, stable channels in the outer mitochondrial membrane, increasing permeability and facilitating release of respiratory factor, cytochrome c. CerS6-derived ceramide interacts with mitochondrial fission factors, initiating fission and breakage. (3) Ceramide promotes LDL aggregation and plaque formation, and levels show an inverse relationship with vascular smooth muscle cell numbers which normally stabilize atherosclerotic plaques. Cer levels correlate positively with plaque lipid and caspase-3 and with inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6. (4) Binding of S1P to S1PR1 enhances NO production and binding to S1PR2 may inhibit this effect and promote H2O2 production. Binding to S1PR3 activates the GTPase, Rho, and stimulates inflammatory responses.
3.1.3 Findings from intervention studies
Clinical studies have correlated decreased blood pressure with reduced Cer levels. Angiotensin II receptor antagonists, such as losartan, vasodilators or Cer synthesis inhibitors achieve the reduction of circulating Cer and of blood pressure (16). The Cer pathway has also been suggested to reduce blood pressure via smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation (18), although precise mechanisms remain unclear.
3.1.4 Potential therapeutic strategies
In summary, abnormal Cer synthesis has been associated with hypertension and vascular disease. Enzymes and receptor subtypes involved in Cer metabolism contribute to increased blood pressure via effects on oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. Inhibition of such pathways may reduce blood pressure and improve vascular endothelial function and further research may allow the development of innovative anti-hypertension therapeutic strategies.
3.2 Ceramides and dyslipidemia/obesity
3.2.1 Evidence of association
ASCVD accounted for 61% of China's CVD burden in 2019 and elevated LDL-C is the second-largest ASCVD risk factor (25). Statins are the primary treatment for dyslipidemia and ASCVD but improved therapeutic strategies are required to tackle rising prevalence and its increasing incidence in younger populations (2). Dyslipidemia describes a pathological imbalance in circulating lipids, characterized by elevated LDL-C and reduced high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). The imbalance often stems from increased fat intake and metabolic dysfunction, particularly the accumulation of saturated fatty acids in skeletal muscle and liver. Such imbalances promote insulin resistance, inflammation and increased Cer production (26).
Hyperlipidemia and elevated Cer are frequently concomitant. Saturated fatty acids stimulate Cer accumulation through upregulation of de novo synthesis and the sphingomyelin pathway (27, 28). Species-specific accumulation of Cer occurs, with Cer16:0, Cer18:0 and Cer24:1 increasing while Cer24:0 decreases, disrupting lipid homeostasis and promoting atherosclerosis (28, 29). Cer24:0 levels have been positively correlated with LDL-C in elderly patients with coronary heart disease and diabetes (30), perhaps reflecting disease-specific or genetic predispositions.
3.2.2 Proposed mechanisms
The liver is a central organ in lipid metabolism and the primary source of plasma Cer. Increased fatty acids may stimulate liver Cer synthesis and secretion, rather than increasing SPT activity, to protect against the harmful effects of intracellular Cer accumulation (31). Hepatocyte Cer promotes fatty acid uptake by an impact on the subcellular distribution of CD36 and induces triglyceride synthesis and lipid metabolism via an effect on Srebf1 expression. These effects mitigate dyslipidemia (32). However, excessive Cer production induces oxidative stress (18), mitochondrial dysfunction (22) and impaired respiratory function (21). These observations support the notion that plasma Cer correlate with liver fat content rather than causing liver dysfunction (33).
3.2.3 Findings from intervention studies
Fatty acids are precursors for sphingolipid synthesis and excessive intake results in elevated Cer. Experiments with high-fat diets have demonstrated that krill oil and DHA/EPA supplementation lower liver Cer16:0 and serum Cer18:0, Cer22:0 and Cer24:0 while increasing liver Cer22:0 and Cer24:0 (29). Such supplements may ameliorate metabolic disorders caused by high-fat diets by an impact on Cer metabolism. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) may be taken up by macrophages in the vascular endothelium, forming foam cells which contribute to lipid stripes and fibrous plaques during atherosclerotic progression. Cer is inversely proportional to the number of vascular smooth muscle cells and exacerbate plaque instability (34). Cer also correlates positively with the pro-inflammatory molecules, IL-6 and MCP-1, promoting plaque lipid and caspase-3 (35). The ASMase/Cer pathway also facilitates lipoprotein aggregation and foam cell formation, accelerating atherosclerosis (34). Cer have been incorporated into predictive tools, such as the CERT 2 score, and outperform the traditional LDL-C biomarker in forecasting major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease, illustrating clinical relevance in dyslipidemia (7). Cer profiling has the potential to inform targeted interventions for dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis.
HDL is protective, unlike LDL-C, and lowers Cer levels by promoting the release the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant NO. HDL binds scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) and affects Cer by a pathway that is independent of calcium phosphorylation or Akt kinase activation. Endothelial NO synthase is stimulated and NO released to mitigate atherosclerosis (36). Cer thus have a pleiotropic role in lipid metabolism with effects dependent on interactions with upstream regulators, such as LDL and HDL.
3.2.4 Potential therapeutic strategies
The targeting of Cer synthesis has potential for dyslipidemia treatment. The fragransin inhibitor of de novo Cer synthesis reduced hepatic steatosis, lobular inflammation and ballooning and improved dyslipidemia (37). The combination of nicotinamide ribose and pterostilbene enhanced liver function and lowered circulating Cer14:0 levels compared with a placebo (38). These findings suggest that regulation of Cer synthesis may slow the progression of dyslipidemia to atherosclerosis and alleviate pathological manifestations, giving additional therapeutic options for dyslipidemia patients.
3.3 Ceramides and chronic kidney disease
3.3.1 Evidence of association
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is characterized by the progressive impairment of renal function, manifesting as persistent urinary abnormalities, structural kidney damage or impaired excretory function. The global prevalence of CKD was 18.99 million in 2019, resulting in 41.54 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) (39). The economic burden associated with dialysis and other nephropathy treatments places substantial pressure on patients and healthcare systems and CKD prevention and mitigation remain the focus of research.
Nephropathy patients have dysregulated circulating Cer (40). Cer is abundant in the kidney and have been implicated in the pathogenesis of ischemia-reperfusion, toxic and acute kidney injuries driven by oxidative stress (41). CKD is a dynamic and multifaceted pathological process and renal tubular epithelial cells of the kidney parenchyma are involved in disease progression (42).
3.3.2 Proposed mechanisms
Excessive Cer affected glomerular filtration and promoted epithelial cell death in the renal proximal convoluted tubule in animal experiments (43). De novo synthesis may be upregulated or salvage pathways impaired in CKD, compromising mitochondrial integrity and accelerating renal fibrosis. Indeed, renal tubular atrophy and basement membrane thickening are frequently observed in the renal cortices of diabetic mice. Protein droplets, collagen deposition and increased expression of CerS6 mRNA, Cer (d18:1/14:0) and Cer (d18:1/16:0) are also present (44). Excessive fatty acid accumulation in the kidney impairs tubular uptake and fatty acid oxidation and Cer activate fatty acid esterification and storage to mitigate this effect (47). However, increased Cer are detrimental to mitochondrial function, forming large, stable channels in the outer membrane which affect the membrane platform and increase permeability, facilitating the release of cytochrome C (41). Cer also affects electron transport chain activity and those derived from CerS6 initiate mitochondrial fission and fragmentation (23).
3.3.3 Findings from intervention studies
NanoZnO treatment has been linked to increased death of renal juxtamedullary convoluted tubule epithelial cells due to elevated intracellular Cer. However, the ceramide synthetase inhibitor, fumarisin, reduced CerS6, reduced renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis and prolonged survival of diabetic mice (45). Cer24:0 has been suggested to protect against endoplasmic reticulum stress, consistent with findings that reduced Cer24:0 is associated with renal fibrosis (40, 46). By contrast, high levels of Cer16:0, Cer18:0 and Cer24:1 have been linked to a rapid decline in renal function (40).
3.3.4 Potential therapeutic strategies
Elevated Cer levels induced programmed cell death and fibrosis in damaged kidney, perhaps as an adaptation to prevent uncontrolled cell lysis. Harmful effects of Cer on the kidney are mediated through mitochondrial dysfunction, vascular endothelial dysfunction and excessive programmed cell death.
3.4 Ceramides and diabetes mellitus
3.4.1 Evidence of association
Diabetes mellitus is characterized by chronic hyperglycemia and microangiopathy and progression is linked to disturbed glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetic insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction increase the risk of CVD in addition to an impact on glycemic control. Data from the China National Hospital Quality Monitoring System show a 21% incidence of microvascular and 18.4% incidence of macrovascular lesions in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) (48). Thus, mitigation of insulin resistance is central to both diabetes management and reduction of CVD risk. Elevated plasma Cer16:0, Cer18:0, Cer20:0 and Cer22:0 correlate with higher HOMA-IR values, β-cell damage and an increased T2D risk. Lipidomic studies show increased Cer in T2D but decreased levels in type 1 diabetes (T1D), highlighting differences in disease mechanisms associated with risk (49–51).
3.4.2 Proposed mechanisms
The inhibition of insulin signaling by Cer leads to reduced skeletal muscle glucose uptake and increased hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis, impairing blood glucose regulation. Cer activates protein phosphatase A2 and inhibit the Akt/PKB phosphorylation necessary for insulin signaling. GLUT4 expression is reduced and β-cell apoptosis induced which reduces insulin secretion (52, 53). Cer accumulates due to increased de novo synthesis from saturated fatty acids or reduced breakdown by ceramidase, perpetuating insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction.
Abnormal Cer accumulates and impairs mitochondrial function, causing mitochondrial DNA damage (54) and lowering respiratory activity (21). A self-perpetuating cycle of Cer accumulation and metabolic dysfunction results. Plasma Cer increase significantly with excessive consumption of saturated fats, causing insulin resistance but not necessarily weight gain (55). The obesity which is often associated with dyslipidemia is another contributory factor and lipid accumulation facilitates the development of insulin resistance and T2D. Lipoproteins devoid of Cer fail to induce insulin resistance in muscle cells but approximately 98% circulating Cer are normally bound to lipoprotein subcomponents, evenly distributed in LDL and HDL cholesterol (56). Thus, Cer link saturated fatty acids to the inhibition of insulin signaling, indicating a significant role in metabolic regulation.
3.4.3 Findings from intervention studies
Genetically engineered C2C12 myocytes that converted Cer to sphingosine were used to demonstrate that acid ceramidase overexpression both prevented the accumulation of Cer and reduced the inhibition of insulin signaling due to saturated fatty acids (57). Exercise, metformin, pioglitazone and dietary modifications have been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce Cer levels (58). In addition, knockdown of CerS6 by antisense oligonucleotides decreased Cer(d18:1/18:0) and Cer16:0, reduced fat and improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in a mouse model (59).
3.4.4 Potential therapeutic strategies
Cer clearly play a role in diabetic pathophysiology, linking insulin resistance and CVD and mediating the inhibitory effects of saturated fatty acids on insulin signaling. Observed gender differences in Cer production may enable precision medicine tailored to individual patients.
3.5 Ceramides and cardiovascular events
3.5.1 Evidence of association
A clinical causal relationship between altered Cer profile and cardiovascular events has been shown. A prospective European cohort study (n = 495) showed an elevated Cer risk score (CERT ≥ 10) to double all-cause mortality. Predictive efficacy exceeded that of pre-existing coronary calcium scoring, giving a novel tool for early risk stratification (8, 15). A 1 μmol/L increase in Cer24:0 correlated with LDL-C levels in Chinese patients with coronary artery disease and diabetes, suggesting vasoprotective properties in Asian populations (30). Therapy targeted to acid ceramidase reduced mortality post-myocardial infarction, a benefit attributed to the suppression of Cer20:0/Cer24:1, indicating the clinical value of precision therapy (69). Lower plasma Cer18:0 levels have been demonstrated in male T2D patients compared with females, emphasizing the utility of sex-stratified management of CVD (51).
3.5.2 Proposed mechanisms
The axis by which Cer increase cardiovascular risk begins with the de novo synthesis (SPT/CerS-regulated) and sphingomyelin hydrolysis (NSMase/ASMase-mediated) promoted by saturated fatty acids which leads to an altered circulating profile (Cer16:0/Cer18:0↑, Cer24:0↓) that triggers mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction and oxidative stress (9, 22, 54). Cer accumulation within the vasculature leads to conversion of NO to H2O2, activation of the S1PR2/3-Rho axis and vascular smooth muscle contraction (16, 23). Hepatic Cer16:0 upregulates CD36 membrane translocation, promoting fatty acid uptake and oxidized LDL deposition (32, 34). Renal CerS6 derivatives form mitochondrial channels, releasing cytochrome c and inducing tubular epithelial apoptosis and fibrosis (44, 47). Cer inhibit Akt phosphorylation in pancreatic β-cells, disrupting insulin signaling and acting synergistically with mitochondrial DNA damage to exacerbate insulin resistance (53, 54). Increased inflammatory cytokines (IL-6/MMP-9↑), lipotoxicity and fibrotic cascades are stimulated by multi-tissue damage and promote atherosclerotic plaque rupture and cardiorenal metabolic syndrome (35, 42).
3.5.3 Findings from intervention studies
The angiotensin II receptor antagonist, losartan, and NSMase inhibitors reduced circulating Cer and improved systolic pressure and endothelial function for hypertension management (16, 20). In addition, DHA/EPA supplementation decreased serum Cer18:0/Cer24:0 and increased hepatic Cer22:0 in a synergistic action with the fragransin-mediated inhibition of de novo lipid synthesis to ameliorate dyslipidemia (29, 37). Reduction of Cer(d18:1/18:0) by CerS6 antisense oligonucleotides blocked Akt phosphorylation and alleviated diabetic insulin resistance (59). Targeted acid ceramidase therapy also reduced post-MI mortality and Nogo-A-preserved mitophagy delayed progression to heart failure (69, 70).
3.5.4 Potential therapeutic strategies
Therapies targeting Cer metabolism dysregulation might adopt an integrated approach of pathway modulation, subtype-specific targeting and individualized clinical application to reduce cardiovascular risk. Pharmacological inhibition of de novo synthesis and sphingomyelin hydrolysis may alleviate lipotoxicity, enhance insulin sensitivity and restore mitochondrial integrity. The concurrent stimulation of Cer degradation would facilitate conversion to the protective S1P, improving endothelial function.
The reduction of pathogenic short-chain Cer variants, Cer16:0, Cer18:0, combined with elevation of the cardioprotective long-chain, Cer24:0, is likely to optimize organ-specific outcomes. It has been shown that inhibition of CerS6 alleviated renal fibrosis and modulation of the Cer24:0/Cer24:1 ratio stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques.
3.5.5 Individual ceramide differences
Differences in Cer levels due to racial, gender and age cause variability in CVD susceptibility and progression (Sections 2.1–2.4). Higher baseline Cer may amplify risks, such as dyslipidemia or diabetes, and influence responses to Cer synthesis inhibitors. The tailoring of CVD prevention and treatment must take account of these differences, emphasizing the significance of a personalized approach. Ethnic and gender-based differences have received little attention in previous studies of Cer levels but cross-sectional analyses by high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC/MS-MS) have revealed racial variations. Total Cer was higher in African Americans compared with Caucasians but Cer16:0, Cer20:0, Cer24:0 and Cer24:1 were elevated in Caucasians with metabolic disorders (MetD) compared with African Americans (p < 0.05) (60). Chinese subjects had reported plasma levels of 0.28 μmol/L Cer16:0 (p < 0.01), 0.075 μmol/L Cer18:0 (p < 0.01), 10.785 μmol/L Cer24:0 (p < 0.03) and 3.435 μmol/L Cer24:1 (p < 0.01), all of which were higher than in African Americans or Caucasians (30).
A study of 71 healthy student volunteers found Asians to have the highest ceramide-to-cholesterol ratio with no significant differences among Cer subgroups (61). These findings suggest higher plasma Cer levels in Asians than in other groups but further research with larger sample sizes is needed to confirm and evaluate therapeutic implications.
Impacts of gender and age on Cer levels are less well understood. Plasma Cer(d18:1/24:0) and Cer(d18:1/24:1) have been observed to increase with age in women and plasma Cer(d18:1/24:1) correlated inversely with plasma estradiol levels across all female age groups (61). In vitro experiments with human estrogen receptor positive cancer cells have demonstrated that estradiol inhibited Cer biosynthesis and promoted degradation, reducing total Cer level (62).
Elevated Cer in muscle tissue was associated with increased risk of diabetes, higher body fat ratio and lower insulin sensitivity in men. By contrast, adipose tissue shows a more complex relationship with Cer in women, perhaps influenced by estrogen regulation. Changes in Cer metabolism linked to type 1 diabetes (T1D) appear more pronounced in males with lower Cer(d18:1/20:0) and Cer(d18:1/18:0) observed. In addition, 1-deoxyceramides (m18:1/20:0) were associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D) in women but not in men. Gender may thus be an independent factor influencing Cer metabolism and its role in diabetes (51).
A review of patients with coronary endothelial dysfunction (CFR > 2) between 1992 and 2019 produced contrary results and no relationship of plasma Cer with sex or correlation with age was found (63). However, substantial age and sex-related differences have been reported elsewhere. For instance, sphingolipid concentrations were lower in females than males at ages 18–39 but higher in females at ages 56–70 (64). A cohort study of 164 participants aged 19–80 showed a positive correlation of age with Cer(d18:1/24:0) (p = 0.0198) and Cer(d18:1/24:1) (p < 0.0001). Cer(d18:1/24:1) was positively associated with age in males (p = 0.0179) but negatively correlated with plasma estradiol in females (p = 0.007) (63).
4 Summary and outlook
The association between Cer and CVD is well-established and plasma Cer risk scores, such as CERT 1, have been used for clinical prediction (64). Cer is known to mediate lipotoxicity, contributing to inflammation, impaired insulin signaling and apoptosis, which promotes CVD risk factors, such as hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia and kidney disease (Table 1). Cer has an impact throughout CVD progression. A Mayo Clinic cohort study identified Cer score as a robust predictor of CVD risk stratification and major adverse cardiovascular events (65). Cer levels remained a statistically significant predictive marker even after clinical treatment. CERT 1/2 scores integrate Cer species, Cer16:0, Cer18:0 and Cer24:1, into a practical clinical tool to stratify CVD risk and monitor therapeutic responses, particularly in patients with dyslipidemia and diabetes. Elevated Cer levels inform the use of targeted interventions, such as inhibitors of ceramide synthesis or dietary modifications, to mitigate cardiovascular risk. Disruption of de novo synthesis, sphingomyelin hydrolysis and salvage mechanisms allow Cer to drive risk factors, underscoring the need for therapies that restore sphingolipid balance, including pathway-specific inhibitors and lifestyle interventions.
Future studies should prioritize the evaluation of population differences and the standardization of Cer measurement in different tissues to allow assessment of potential organ damage. Dietary fat intake should be carefully monitored during research. C22:0, C24:0 and C18:0 Cer have been negatively correlated with vegetable intake (r = −0.679, p < 0.05; r = −0.711, p < 0.05; r = −0.808, p < 0.01) and C24:0 with soy intake (r = −0.736, p < 0.05) (61, 66). Mechanisms causing racial and gender differences in Cer levels remain unclear. The integration of racial and gender variations in Cer profile into CVD management is essential, since increased susceptibility to diabetes and dyslipidemia in Asian males is an example that affects both risk and treatment response, including that to NSMase blockers or dietary interventions. Large-scale, diverse cohorts should be investigated to standardize Cer measurement, account for differences in CERT 1/2 and develop tailored therapies to optimize outcomes.
Cer represents promising therapeutic targets for reducing CVD risk, but limitations remain. Changes to downstream metabolites in the sphingolipid pathway may disrupt protective functions. For instance, lactosylceramides (LacCer) are glycosylated Cer species with an inverse association with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes in human cohort studies. LacCer 14:0, 16:0 and 24:1 were linked to reduced diabetes risk, perhaps due to anti-inflammatory or insulin-sensitizing effects (67). Reduced Cer synthesis may lower beneficial LacCer species, exacerbating metabolic dysfunction or offsetting therapeutic gains in diabetes and dyslipidemia. In addition, S1P promotes vasodilation and endothelial protection via S1PR1 and may be reduced if Cer levels are lowered. Over-suppression may lead to the vasoconstriction, increased oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction observed in animal models where LacCer accumulation contributed to diabetic mitochondrial impairment (68). Broader metabolic implications include potential off-target effects on lipid homeostasis, inflammation or apoptosis, particularly given species and individual differences in Cer metabolism. These potential risks highlight the need for selective inhibitors to target pathogenic Cer species, Cer16:0 and Cer18:0, without broader pathway effects and incorporation of CERT scores for monitoring of efficacy and safety. Future studies should prioritize randomized controlled trials to evaluate adverse effects, dose-response relationships and interactions with comorbidities to ensure net benefits for Cer modulation in CVD management.
Author contributions
SY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Cesare MD, Bixby H, Gaziano T, Hadeed L, Kabudula C, McGhie DV, et al. World Heart Report 2023: Confronting the World’s Number One Killer. Geneva: World Heart Federation (2023).
2. Wang Z, Ma L, Liu M, Fan J, Hu S, Writing Committee of the Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China. Summary of the 2022 report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China. Chin Med J (Engl). (2023) 136(24):2899–908. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002927
3. Liu Y, Qu Y, Li SQ, Liu B, Li HS, Liu YX. Predictive value of ceramide levels detected by tandem MS analysis by HPLC analysis for the occurrence of cardiovascular events. Clin J Med Off. (2021) 49(10):1150–4. doi: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2021.10.23
4. Anroedh S, Hilvo M, Akkerhuis KM, Kauhanen D, Koistinen K, Oemrawsingh R, et al. Plasma concentrations of molecular lipid species predict long-term clinical outcome in coronary artery disease patients. J Lipid Res. (2018) 59(9):1729–37. doi: 10.1194/jlr.P081281
5. Yin W, Li F, Tan X, Wang H, Jiang W, Wang X, et al. Plasma ceramides and ceramide scores for risk stratification in hypertensive patients at high cardiovascular risk. Am J Hypertens. (2021) 34(11):1209–16. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpab105
6. Chaurasia B, Summers SA. Ceramides in metabolism: key lipotoxic players. Annu Rev Physiol. (2021) 83:303–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-031620-093815
7. Hilvo M, Meikle PJ, Pedersen ER, Tell GS, Dhar I, Brenner H, et al. Development and validation of a ceramide- and phospholipid-based cardiovascular risk estimation score for coronary artery disease patients. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41(3):371–80. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz387
8. Meeusen JW, Donato LJ, Bryant SC, Baudhuin LM, Berger PB, Jaffe AS. Plasma ceramides: a novel predictor of major adverse cardiovascular events after coronary angiography. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2018) 38(8):1933–9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311199
9. Du Y, Zhang XF, Zeng M. Progress in studying the role of ceramide in inflammatory response and related diseases. Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol. (2023) 37(05):376–82.
10. Kogot-Levin A, Saada A. Ceramide and the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Biochimie. (2014) 100:88–94. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.07.027
11. Zelnik ID, Rozman B, Rosenfeld-Gur E, Ben-Dor S, Futerman AH. A stroll down the CerS lane. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2019) 1159:49–63. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-21162-2_4
12. Mehanna M, McDonough CW, Smith SM, Gong Y, Gums JG, Chapman AB, et al. Integrated metabolomics analysis reveals mechanistic insights into variability in blood pressure response to thiazide diuretics and beta blockers. Clin Transl Sci. (2024) 17(5):e13816. doi: 10.1111/cts.13816
13. Zhang D, Guo Q, Cheng Y, Wang J, Li Y. Circulating ceramide as a potential biomarker for isolated nocturnal hypertension. J Hypertens. (2021) 39(1):e106. doi: 10.16098/j.issn.0529-1356.2021.01.024
14. Li Y, Li JL, Sun YR, Yang QY, Wang WJ, Wang K, et al. Advances in the relationship between sphingolipid metabolism and cardiovascular diseases. Acta Anat Sin. (2021) 52(1):146–51. doi: 10.16098/j.issn.0529-1356.2021.01.024
15. Turner DGP, De Lange WJ, Zhu Y, Coe CL, Simcox J, Ge Y, et al. Neutral sphingomyelinase regulates mechanotransduction in human engineered cardiac tissues and mouse hearts. J Physiol. (2023) 602(18):4387–407. doi: 10.1113/JP284807
16. Freed JK, Beyer AM, LoGiudice JA, Hockenberry JC, Gutterman DD. Ceramide changes the mediator of flow-induced vasodilation from nitric oxide to hydrogen peroxide in the human microcirculation. Circ Res. (2014) 115(5):525–32. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.303881
17. Varzideh F, Jankauskas SS, Kansakar U, Mone P, Gambardella J, Santulli G. Sortilin drives hypertension by modulating sphingolipid/ceramide homeostasis and by triggering oxidative stress. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132(3):e156624. doi: 10.1172/JCI156624
18. Zhang D. Clinical study of occult hypertension (Phd thesis). Shanghai Jiao Tong University (2020).
19. Birk M, Baum E, Zadeh JK, Manicam C, Pfeiffer N, Patzak A, et al. Angiotensin II induces oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in mouse ophthalmic arteries via involvement of AT1 receptors and NOX2. Antioxidants. (2021) 10(8):1238. doi: 10.3390/antiox10081238
20. Cogolludo A, Villamor E, Perez-Vizcaino F, Moreno L. Ceramide and regulation of vascular tone. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(2):411. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020411
21. Sasset L, Chowdhury KH, Manzo OL, Rubinelli L, Konrad C, Maschek JA, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate controls endothelial sphingolipid homeostasis via ORMDL. EMBO Rep. (2023) 24(1):e54689. doi: 10.15252/embr.202254689
22. Lima TI, Laurila PP, Wohlwend M, Morel JD, Goeminne LJE, Li H, et al. Inhibiting de novo ceramide synthesis restores mitochondrial and protein homeostasis in muscle aging. Sci Transl Med. (2023) 15(696):eade6509. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.ade6509
23. Katunaric B, SenthilKumar G, Schulz ME, De Oliveira N, Freed JK. S1p (Sphingosine-1-Phosphate)-induced vasodilation in human resistance arterioles during health and disease. Hypertension. (2022) 79(10):2250–61. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.19862
24. Zhang G, Yang L, Kim GS, Ryan K, Lu S, O'Donnell RK, et al. Critical role of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 (S1PR2) in acute vascular inflammation. Blood. (2013) 122(3):443–55. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-11-467191
25. Zhang MN, Li MT, Zhi XY, Zhu H, Zhang X, Xie J. Trends of a burden on atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and its related risk factors in China, 1990 to 2019. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. (2021) 42(10):1797–803. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20201208-01390
26. Walchuk C, Wang Y, Suh M. The impact of EPA and DHA on ceramide lipotoxicity in the metabolic syndrome. Br J Nutr. (2021) 125(8):863–75. doi: 10.1017/S0007114520003177
27. Arndt L, Hernandez-Resendiz I, Moos D, Dokas J, Müller S, Jeruschke S, et al. Trib1 deficiency promotes hyperlipidemia, inflammation, and atherosclerosis in LDL receptor knockout mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2023) 43(6):979–94. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.122.318137
28. Sambolín-Escobales L, Tirado-Castro L, Suarez C, Pacheco-Cruz D, Fonseca-Ferrer W, Deme P, et al. High-fat diet and short-term unpredictable stress increase long-chain ceramides without enhancing behavioral despair. Front Mol Biosci. (2022) 9:859760. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.859760
29. Chen YF, Fan ZK, Gao X, Zhou F, Guo XF, Sinclair AJ, et al. n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in phospholipid or triacylglycerol form attenuate nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via mediating cannabinoid receptor 1/adiponectin/ceramide pathway. J Nutr Biochem. (2024) 123:109484. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109484
30. Cao R, Fang Z, Zhang J, Hu W, Lu T, Fan L, et al. Correlation of circulating ceramide and LDL-C in elderly patients with coronary heart disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin J Geriatr Heart Brain Vessel Dis. (2023) 25(7):676–9.
31. Watt MJ, Barnett AC, Bruce CR, Schenk S, Horowitz JF, Hoy AJ. Regulation of plasma ceramide levels with fatty acid oversupply: evidence that the liver detects and secretes de novo synthesised ceramide. Diabetologia. (2012) 55(10):2741–6. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2649-3
32. Chaurasia B, Tippetts TS, Mayoral Monibas R, Liu J, Li Y, Wang L, et al. Targeting a ceramide double bond improves insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. Science. (2019) 365(6451):386–92. doi: 10.1126/science.aav3722
33. Denimal D, Béland-Bonenfant S, Pais-de-Barros JP, Rouland A, Bouillet B, Duvillard L, et al. Plasma ceramides are associated with MRI-based liver fat content but not with noninvasive scores of liver fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02049-2
34. Piccoli M, Cirillo F, Ghiroldi A, Rota P, Coviello S, Tarantino A, et al. Sphingolipids and atherosclerosis: the dual role of ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate. Antioxidants. (2023) 12(1):143. doi: 10.3390/antiox12010143
35. Edsfeldt A, Dunér P, Ståhlman M, Mollet IG, Asciutto G, Grufman H, et al. Sphingolipids contribute to human atherosclerotic plaque inflammation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2016) 36(6):1132–40. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.305675
36. Li XA, Titlow WB, Jackson BA, Giltiay N, Nikolova-Karakashian M, Uittenbogaard A, et al. High density lipoprotein binding to scavenger receptor, class B, type I activates endothelial nitric-oxide synthase in a ceramide-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277(13):11058–63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110985200
37. Yang RX, Pan Q, Liu XL, Zhou D, Xin FZ, Zhao ZH, et al. Therapeutic effect and autophagy regulation of myriocin in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Lipids Health Dis. (2019) 18(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1118-0
38. Dellinger RW, Holmes HE, Hu-Seliger T, Butt RW, Harrison SA, Mozaffarian D, et al. Nicotinamide riboside and pterostilbene reduces markers of hepatic inflammation in NAFLD: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Hepatology. (2023) 78(3):863–77. doi: 10.1002/hep.32778
39. Ying M, Shao X, Qin H, Yin P, Lin Y, Li J, et al. Disease burden and epidemiological trends of chronic kidney disease at the global, regional, national levels from 1990 to 2019. Nephron. (2024) 148(2):113–23. doi: 10.1159/000534071
40. Gurung RL, Yiamunaa M, Tham WK, Liu S, Zeng H, Lee J, et al. Association of plasma ceramide with decline in kidney function in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Lipid Res. (2024) 65(6):100552. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100552
41. Nicholson RJ, Holland WL, Summers SA. Ceramides and acute kidney injury. Semin Nephrol. (2022) 42(3):151281. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2022.10.007
42. Liu X. The role and mechanism of LAPTM5-mediated tubular epithelial cell senescence in kidney fibrosis (Master’s thesis). Shandong University (2023).
43. Lopes-Virella MF, Baker NL, Hunt KJ, Hammad SM, Arthur J, Virella G, et al. Glycosylated sphingolipids and progression to kidney dysfunction in type 1 diabetes. J Clin Lipidol. (2019) 13(3):481–491.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2019.03.005
44. Wang X, Song M, Li X, Su C, Yang Y, Wang K, et al. CERS6-derived Ceramides aggravate kidney fibrosis by inhibiting PINK1-mediated mitophagy in diabetic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2023) 325(2):C538–49. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00144.2023
45. Kim B, Kim G, Jeon HP, Jung J. Lipidomics analysis unravels aberrant lipid species and pathways induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles in kidney cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25(8):4285. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084285
46. Eckes T, Trautmann S, Djudjaj S, Beyer S, Patyna S, Schwalm S, et al. Consistent alteration of chain length-specific ceramides in human and mouse fibrotic kidneys. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. (2021) 1866(1):158821. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158821
47. Nicholson RJ, Norris MK, Poss AM, Holland WL, Summers SA. The lard works in mysterious ways: ceramides in nutrition-linked chronic disease. Annu Rev Nutr. (2022) 42:115–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-062220-112920
48. Liu Y, Ning X, Zhang L, Long J, Liang R, Peng S, et al. Prevalence of long-term complications in inpatients with diabetes mellitus in China: a nationwide tertiary hospital-based study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. (2022) 10(3):e002720. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2021-002720
49. Morze J, Wittenbecher C, Schwingshackl L, Danielewicz A, Rynkiewicz A, Hu FB, et al. Metabolomics and type 2 diabetes risk: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Care. (2022) 45(4):1013–24. doi: 10.2337/dc21-1705
50. Yun H, Sun L, Wu Q, Zong G, Qi Q, Li H, et al. Associations among circulating sphingolipids, β-cell function, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes: a population-based cohort study in China. PLoS Med. (2020) 17(12):e1003451. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003451
51. Barranco-Altirriba M, Alonso N, Weber RJM, Lloyd GR, Hernandez M, Yanes O, et al. Lipidome characterisation and sex-specific differences in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02202-5
52. Sokolowska E, Blachnio-Zabielska A. The role of ceramides in insulin resistance. Front Endocrinol. (2019) 10:577. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00577
53. Xia QS, Lu FE, Wu F, Huang ZY, Dong H, Xu LJ, et al. New role for ceramide in hypoxia and insulin resistance. World J Gastroenterol. (2020) 26(18):2177–86. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i18.2177
54. Sergi D, Naumovski N, Heilbronn LK, Abeywardena M, O'Callaghan N, Lionetti L, et al. Mitochondrial (dys)function and insulin resistance: from pathophysiological molecular mechanisms to the impact of diet. Front Physiol. (2019) 10:532. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00532
55. Luukkonen PK, Sädevirta S, Zhou Y, Kayser B, Ali A, Ahonen L, et al. Saturated fat is more metabolically harmful for the human liver than unsaturated fat or simple sugars. Diabetes Care. (2018) 41(8):1732–9. doi: 10.2337/dc18-0071
56. Chavez JA, Holland WL, Bär J, Sandhoff K, Summers SA. Acid ceramidase overexpression prevents the inhibitory effects of saturated fatty acids on insulin signaling. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280(20):20148–53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M412769200
57. Olson E, Suh JH, Schwarz JM, Noworolski SM, Jones GM, Barber JR, et al. Effects of isocaloric fructose restriction on ceramide levels in children with obesity and cardiometabolic risk: relation to hepatic de novo lipogenesis and insulin sensitivity. Nutrients. (2022) 14(7):1432. doi: 10.3390/nu14071432
58. Turpin-Nolan SM, Hammerschmidt P, Chen W, Jais A, Timper K, Awazawa M, et al. CerS1-derived C18:0 ceramide in skeletal muscle promotes obesity-induced insulin resistance. Cell Rep. (2019) 26(1):1–10.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.12.031
59. Buie JNJ, Hammad SM, Nietert PJ, Magwood G, Adams RJ, Bonilha L, et al. Differences in plasma levels of long chain and very long chain ceramides between African Americans and whites: an observational study. PLoS One. (2019) 14(5):e0216213. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216213
60. Jungersted JM, Høgh JK, Hellgren LI, Jemec GBE, Agner T. Ethnicity and stratum corneum ceramides. Br J Dermatol. (2010) 163(6):1169–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.10080.x
61. Vozella V, Basit A, Piras F, Realini N, Armirotti A, Bossù P, et al. Elevated plasma ceramide levels in post-menopausal women: a cross-sectional study. Aging. (2019) 11(1):73–88. doi: 10.18632/aging.101719
62. Akhiyat N, Vasile V, Ahmad A, Sara JD, Nardi V, Lerman LO, et al. Plasma ceramide levels are elevated in patients with early coronary atherosclerosis and endothelial dysfunction. J Am Heart Assoc. (2022) 11(7):e022852. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.022852
63. Muilwijk M, Callender N, Goorden S, Vaz FM, van Valkengoed IGM. Sex differences in the association of sphingolipids with age in Dutch and South-Asian Surinamese living in Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Biol Sex Differ. (2021) 12(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13293-020-00353-0
64. Summers SA. Could ceramides become the new cholesterol? Cell Metab. (2018) 27(2):276–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.12.003
65. Vasile VC, Meeusen JW, Medina Inojosa JR, Donato LJ, Scott CG, Hyun MS, et al. Ceramide scores predict cardiovascular risk in the community. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2021) 41(4):1558–69. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315530
66. He J, Fang Z, Yang Y, Liu J, Ma W, Huo Y, et al. Relationship between lipid metabolism molecules in plasma and carotid atherosclerotic plaques, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and dietary factors. J Peiking Uni Health Sci. (2024) 56(4):722–8. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.028
67. Berkowitz L, Razquin C, Salazar C, Biancardi F, Estruch R, Ros E, et al. Sphingolipid profiling as a biomarker of type 2 diabetes risk: evidence from the MIDUS and PREDIMED studies. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23(1):446. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02505-7
68. Novgorodov SA, Riley CL, Yu J, Keffler JA, Clarke CJ, Van Laer AO, et al. Lactosylceramide contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetes. J Lipid Res. (2016) 57(4):546–62. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M060061
69. Hadas Y, Vincek AS, Youssef E, Zak MM, Chepurko E, Sultan A, et al. Altering sphingolipid metabolism attenuates cell death and inflammatory response after myocardial infarction. Circulation. (2020) 141(11):916–30. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.041882
Keywords: cardiovascular risk factors, ceramides, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, chronic kidney disease
Citation: Yang S and Wu Y (2025) Ceramide metabolism and cardiovascular risk factors: insights into therapeutic strategies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 12:1656113. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1656113
Received: 30 June 2025; Accepted: 11 August 2025;
Published: 4 September 2025.
Edited by:
Hyoung Kyu Kim, Inje University, Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
Loni Berkowitz, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, ChileMotohiro Nishida, National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS), Japan
Copyright: © 2025 Yang and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongxin Wu, eWFuZ3R1cGVsb0AxNjMuY29t
 Shouyi Yang
Shouyi Yang Yongxin Wu2*
Yongxin Wu2*