Abstract
This paper presents an intelligent multipath transmission method for multimodal data streams over wide area networks (WANs), addressing challenges such as network delay and packet loss in telemedicine scenarios. Utilizing a content-aware approach, the proposed method assigns transmission priorities to different types of data and selects optimal paths via an intelligent routing algorithm based on real-time network conditions. The system incorporates mechanisms for dynamic path switching, load balancing, and fault tolerance. Experimental results demonstrate that under conditions of link interruption and insufficient bandwidth, the proposed method achieves significantly better transmission quality compared to traditional approaches. For instance, in scenarios with 40% packet loss, the average network delay for high-priority data was reduced to 141.8 ms, compared to 297.2 ms and 318.2 ms for conventional methods. Additionally, with bandwidth reduced to 2 Mbps, the high-priority data stream’s average bit rate and frame rate were maintained at 2.67 Mbps and 29 FPS, respectively, ensuring reliable performance during critical operations.
1 Introduction
With the progress of science and technology, remote surgery has gradually come into reality, and people can present the remote surgery scene in a more natural way through electronic devices, that is, experienced surgeons can also control remote surgery robots through electronic devices to carry out surgical treatment for patients who are thousands of miles away (Singh et al., 2022; Anvari et al., 2005a; V et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2024). This will undoubtedly help people in developing countries, remote areas, or those who have limited medical means but still need corresponding medical services to offer people a more equitable and cost-effective medical environment. Although the current remote-controlled robotic surgery has been around for more than 20 years and has made amazing technological advances, the technology is still in its infancy (Sherif et al., 2023). The safety, cost, and delay issues all limit its further development. It is well known that delays can lead to serious degradation in task performance, and when surgeons work under delayed conditions, they take longer to complete and make more errors (Anvari et al., 2005b; Zanaboni and Wootton, 2012; Raison et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2015). Therefore, it is believed that the problem of signal delay is directly related to safety, which has also become a major obstacle to the development of remote surgery (Ta Kim and Chow, 2022; Li et al., 2024; Chu et al., 2025).
Therefore, dealing with the signal delay problem is worthy of further study. Previous studies have increased network connections by compromising image clarity, increasing bandwidth, optimized issues such as data compression and so on (Zy et al., 2025). However, compromising image clarity will inevitably compromise surgeons’ clear observation of the surgical area, so that it will increase the difficulty of the operation, and the risk of making mistakes. Furthermore, in most remote areas or emergency situations, adjustments to hardware conditions are also difficult to achieve. Therefore, there are still considerable research challenges in solving the delay problem.
To solve this problem, this paper proposes a solution: establish multiple transmission paths between the media transmission proxy server connected by the sender client and the media transmission proxy server connected by the receiver client to effectively avoid the problem of poor communication quality caused by the congestion of one link. The media stream data is sent to the connected media transmission proxy server by the sender client. By identifying the media type of the media data to be transmitted and assigning different priorities to the media, the data with higher priorities is sent through the path with the best quality to effectively improve the transmission quality of audio and video streams. However, we carried out a series of experimental verifications. It turns out that the multipath transmission method we proposed can effectively reduce the network delay (<200 ms) without damaging the image resolution and providing a more stringent equipment environment. Overall, the performance of the multipath transmission method is superior to the previous method.
2 The proposed methods
To address the shortcomings of existing technologies, this invention provides an intelligent content-aware method for multipath transmission of audio/video streams and data streams over WANs. By employing intelligent routing algorithms to select transmission links based on data importance, along with real-time network detection and feedback mechanisms, transmission path switching and load balancing mechanisms, and fault tolerance and error correction mechanisms, the quality and stability of real-time audio and video transmission are enhanced. This approach meets users’ demands for low-latency and high-reliability audio/video transmission. We will provide a comprehensive introduction to the proposed method, detailing each of its components and multipath transmission algorithm. Finally, we will explore the method’s fault tolerance and error correction mechanisms.
2.1 System architecture design
When the Wenchuan earthquake hit China on 12 May 2008, the Radiology Department of West China Hospital undoubtedly demonstrated the advantages of fully mobilizing medical staff from non-disaster areas to carry out telemedicine: They completed more than 100 cases of emergency X-ray on-site examination and remote imaging consultation in just 1 week and timely gave on-site medical treatment and referral suggestions, which not only won valuable rescue time for patients but also greatly improved the situation It has been 16 years since the incident, with the rapid development of science and technology, the idea of establishing temporary surgery sites in remote areas and mobilizing more national expert resources to carry out remote surgery has become a goal that people are striving to achieve. Imagine such a scenario: patients in disaster areas are critically ill, and it is difficult to transfer them, or there is no suitable medical environment to carry out the surgery they need, the skilled experts of various disciplines all over the country standing in their hospital surgery center control remote robots in the disaster area to carry out various emergency operations through the remote surgery service cloud platform. The realization of this vision can have enormous value for individual families, nations, and societies.
To provide a stable communication environment to effectively facilitate the implementation of telemedicine, this paper first proposes a content-aware multi-path transmission communication method for WANs. The network topology is shown in Figure 1. In this setup, S1 and S2 are Network Servers that periodically query the Network Routing Center for addresses of other servers. They perform small-traffic probing to measure packet loss rates and latency between each other and report these findings back to the Network Routing Center. When the sender generates different types of data, the Network Routing Center assigns the nearest accessible Network Servers (S1 and S2) for it to handle the data. Between S1 and S2, based on the link probing results regarding packet loss and network latency, the Network Routing Center establishes N virtual transmission paths composed of private net and open net connections.
FIGURE 1
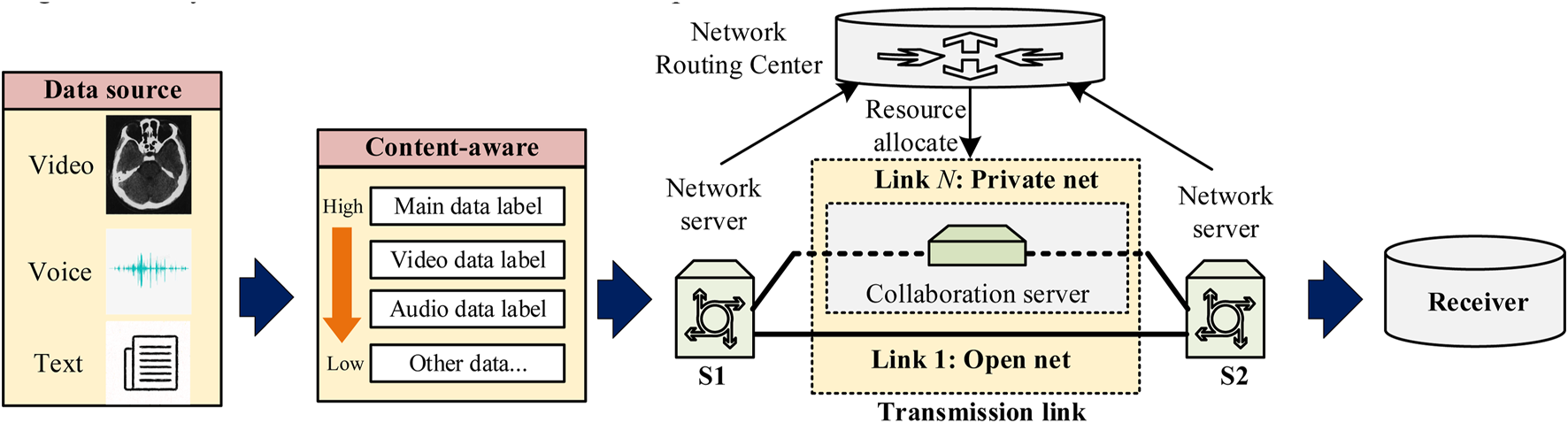
Topology for transmitting audio and video media over a wide area network.
Network fluctuations and congestion within the WAN can cause real-time issues such as link latency and packet loss on some connections, thereby affecting the transmission quality of those links. Consequently, this paper proposes two methods to improve transmission performance in the context of telemedicine: content-aware processing and multipath transmission. Content-aware processing is used to prioritize multimodal data in telemedicine, while multipath transmission ensures that the resources of the links meet the transmission requirements. Both methods will be described in detail in the following sections.
2.2 The content-aware method
Telemedicine services include a variety of application scenarios such as remote outpatient clinic, remote surgery, and remote B-ultrasound, and different application scenarios generate various types of data streams. For example, remote outpatient scenarios include voice streams, conference background streams, doctor portrait streams, patient portrait streams, and patient inspection information streams. Remote surgery scenarios may include voice streams, control instruction streams, surgical scene streams, surgical field streams, doctor/patient portrait streams, and patient inspection information streams. The “Wireless Medical White Paper” issued by the Internet Healthcare Industry Alliance in 2018 clearly states that different telemedicine application scenarios have different requirements for internet bandwidth and latency (Internet Medical System and Application National Engineering Laboratory, 2018). In addition, for the same data stream, the priority of its transmission may also change under different application scenarios. The patient portrait stream is crucial for remote dermatology clinics, because the remote doctor needs to clearly observe the patient’s affected skin, so it needs a higher priority; for remote surgery scenarios, the patient portrait stream may appear less important, and the doctor will pay more attention to the change of the surgical field of view, so the patient portrait stream will have a lower priority in this scenario. Therefore, in order to quickly and accurately perceive the type of telemedicine flow and give a reasonable priority order, this study developed a perception strategy for medical content. The strategy mainly includes two parts: “Main data label” and “Additional data label”. We achieve content awareness by adding different fields to the data header. The introduction of the different data fields is shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| Index | Data field | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AppType | String | Telemedicine service scenarios |
| 2 | StreamID | Short | The identity number of the data stream automatically identified by the software |
| 3 | StreamType | Char | Types of Telemedicine Streams |
| 4 | StreamSN | Uint | Packet serial numbers for different data streams |
Introduction to each field of the stream protocol header.
Telemedicine includes plenty of different types of media data, such as text, pictures, phonetic matrix, video, etc. The transmission priority of different formats of data also needs to be treated differently. For example, Telemedicine must first ensure that doctors can obtain patients’ status information in real-time and can promptly implement medical measures as needed. On this foundation, telemedicine can also simultaneously provide certain online information to other healthcare professionals or the patient’s family members. The importance of the former far outweighs that of the latter. Therefore, we must configure appropriate priorities for different types of medical data, which could ensure high-quality intelligent transmission for higher-priority content by sacrificing lower-priority communication resources and giving priority to higher-priority transmission. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
Step 1. Perceiving the media type of the data to be sent and determine its transmission priority. Data from direct interaction between doctors and patients should be labeled as ‘Main data label,’ while other video and audio format data should be respectively labeled as ‘Additional data label’.
Step 2. After defining different data types, prioritize the data. If the data stream is labeled with the ‘Main data label,’ it is identified as the highest priority; if it is labeled with the ‘Additional data label,’ it is identified as the second priority.
Step 3. After selecting the priority of the packets to be sent, insert the pending data into the transmission queue in order of priority.
2.3 Multipath transmission method
Through real-time network monitoring and feedback mechanism, the performance indicators of each path on the WANs can be obtained in real time. These performance indicators can include bandwidth utilization, delay, packet loss rate, etc. Based on these indicators, a feedback mechanism is designed to feed back the real-time monitored network status information to the intelligent routing algorithm, so as to dynamically adjust the path selection. Media transmission proxy server is connected to the client side of the transmission of data packets in each link play independent packet sequence number, after receiving the media transmission proxy server connected to the client side receives the data, according to the data reception of each link, periodically calculating the packet loss rate of each link, and returns the packet loss rate of each link to the media transmission proxy server connected to the sender client side. The round-trip time of each transmission path and the transmission and reception traffic of each transmission link are obtained respectively according to the preset time interval, and the bidirectional delay and transmission effective reception rate of each transmission path are calculated. This invention provides an intelligent routing algorithm that can send high-priority data over links with better transmission quality. The specific method is as follows:
Step 1. Calculate the weight of each link based on the round-trip time (RTTn) and packet loss rate (Ln) for the n-th path. The calculation method is shown in the following Equation 1:
where
Lnrepresents the packet loss rate;
RTTnrepresents the round-trip time (bidirectional delay);
WLand
Wdare the weights assigned to consider the impact of packet loss rate and bidirectional delay, respectively.
Step 2. The server performs small traffic probing to measure the round-trip time (RTTn) and packet loss rate (Ln) for different links. If the packet loss rate Ln is higher or the round-trip delay RTTn is greater, the resulting link weight Wn will be lower. Here, WL is the weighting factor for packet loss in this algorithm, while Wd is the weighting factor for delay in this algorithm.
Step 3. Sort the links according to their weights, Links with larger weights are ranked higher.
Step 4. According to the sorted order of the links, periodically allocate the pending data to each link based on its estimated bandwidth. Assuming that the available bandwidth of the n-th link is Bn, each transmission cycle is T, the start timestamp of this transmission cycle is t1, the current timestamp is t2, and the number of bytes sent in this cycle is xn, then calculate the number of bytes that can be sent in this cycle for the n-th link using the following Equation 2.
Obtain a total byte count from the pending queue not exceeding bn with the highest priority, and send it through the nth link to the media transfer proxy server R2.
Step 5. Let V represent the volume of data traffic that needs to be sent by the sender if the total transmission bandwidth of all sending links is insufficient to send all the pending data, i.e., when the media transfer proxy server R1 requests the network routing center to add P new transmission links until (Here, P is a positive integer).
Due to problems of packet loss and transmission mistakes in the transmission process, the proposed method divides packets into different data streams according to different media types and assigns a unique ID to each packet in each stream for data error correction on the media transmission proxy server S2.
Periodically, the media transmission proxy server S2 checks the unreceived data to determine whether the unreceived data can be decoded through Forward Error Correction (FEC). If the FEC cannot decode the unreceived data, NACK packets (Negative Acknowledgment packets) will be generated for each stream and sent to the media transmission proxy server S1 through the link with the smallest RTT.
After receiving NACK packets, the media transmission proxy server S1 can acquire corresponding data packets from reissued cache data and add them to the pending data queue according to priority.
On the media transmission proxy server S2, the media transmission proxy server R1 periodically checks the final packet loss rate of each stream. If the final packet loss rate of a stream is non-zero, the media transmission proxy server R1 is notified to increase the FEC redundant packet ratio of the stream.
2.4 The reliability calculation of the proposed method
Suppose there are N transmission paths between two media transmission servers R1 and R2, and the transmission reliability of the i-th path is Qi, where 1≤i≤N and 0≤Qi≤1. If only the path k (1≤k≤N) is selected between the media transmission servers R1 and R2 for single-path transmission, the transmission reliability Qmulti between R1 and R2 is shown in Equation 3:
If N paths are selected between media servers R1 and R2 for multipath transmission, the overall transmission reliability between R1 and R2 is shown in Equation 4:
Since , and , so it could be confirmed as Equation 5
Therefore, it can be seen that the reliability of multi-path transmission is greater than that of single-path transmission.
3 Experiment
In telemedicine scenarios, wireless networks in operating rooms may suffer from intermittent packet loss due to signal shielding (e.g., lead-lined walls), base station congestion from high patient volumes, or electromagnetic interference from medical equipment. While typical packet loss rates in stable networks remain below 5%, extreme conditions (e.g., 40% loss) can occur in rare but critical situations such as natural disasters or infrastructure failures. To validate the method’s resilience under worst-case conditions, we simulated 40% packet loss using a network impairment generator, exceeding normal thresholds to stress-test the system’s fault tolerance.
3.1 Experimental setup
The data sources are generated by two kinds of data streams. One data stream is encoded by remote acquisition of surgical robot pictures and control commands. The other data stream is encoded by the operating room panorama shot by the camera.
We named the former data stream “Main data” and the latter data stream “Additional data”. During the transmission process, different data have different priorities. In telesurgery, doctors perform surgery by controlling the surgical robot remotely, which means that timely feedback is needed. The “Additional data” stream is only used for spectator’s learning, so the “Main data” stream has higher precedence than the “Additional data” stream. Thus, in this paper, we set up three different network transmission schemes to transmit the data presented above and verify the effectiveness of the proposed method by comparing transmission results, as shown in the following figure:
The “Additional data” stream is only used to communicate with the remote doctor for use, so the priority of the shared data is higher compared to the video communication data. Therefore, in this thesis, we set up three different network transmission schemes to transmit the above data and verify the effectiveness of the proposed method by comparing transmission results. The process is shown in the figure below (Figure 2). Among them, the first transmission scheme is to use point-to-point direct connection (DC) to deploy audio and video collaboration server schemes in a centralized manner. The second transmission scheme is to implement a distributed audio and video collaboration server to achieve a cascading network scheme named public connection (PC). The third transmission scheme is the method we proposed in this paper, which is to deploy a distributed audio and video collaboration server to construct a multipath transmission cascading network.
FIGURE 2
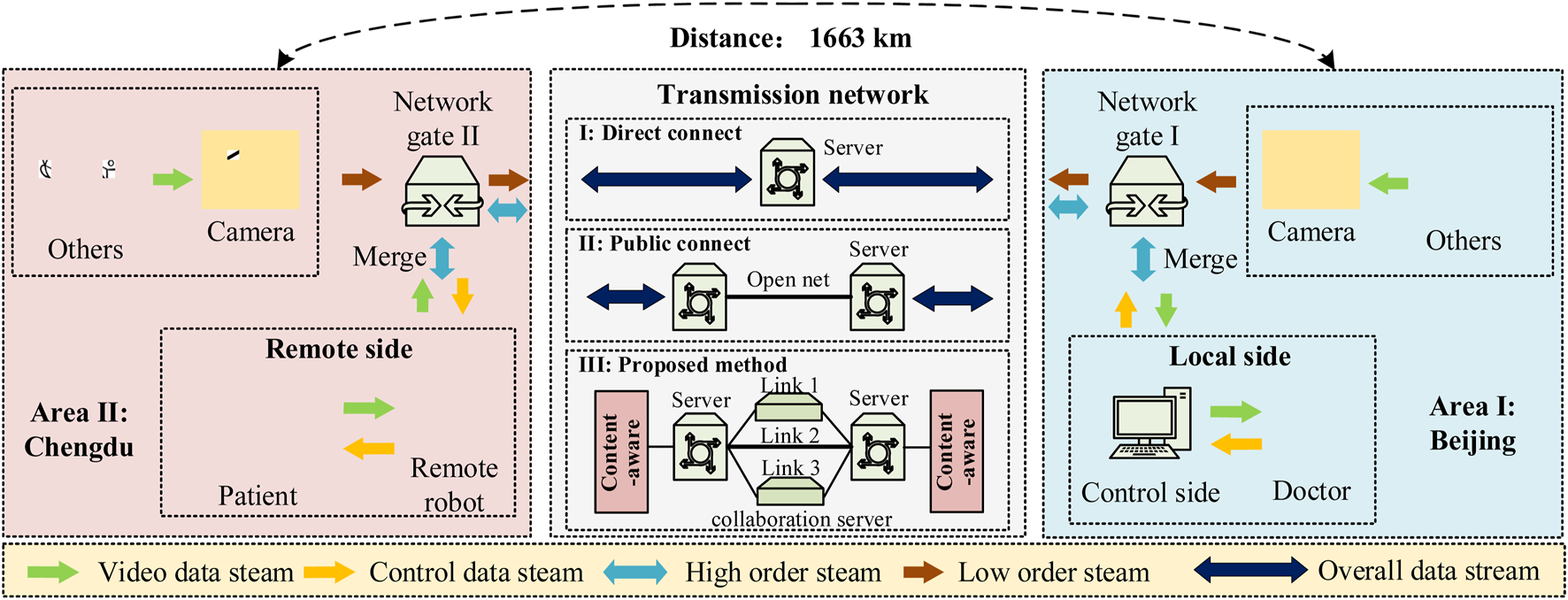
Experimental platform.
To compare the network performances of different transmission schemes, we used three different evaluation indicators, including the change of bit rate and frame rate of the receiver of network information. The time delay is obtained to determine the link delay by recording the response delay of the robotic operation at the receiving and transmitting ends. The calculating formula of time delay is as Equation 6where tman is the local operation time, and the trobot is the remote robot operation time.
3.2 Experiment 1: the impact of link damage
In practical applications, the link is flexible and encounters external interference, interruption, and packet loss. Considering the characteristic of the flexibility of the link, the transmission network performance is also far from constant. So, we took the first step of simulating the fluctuation of network delay by unplugging the network cable or 4G/5G SIM card. For the control variable, we consider that the link bandwidth at this time is sufficient to transmit the required content. The proposed method consists of three different carrier networks and server connections. To control for variables, we assume that the link bandwidth is sufficient to transmit the required content at this point. The method proposed herein involves connections between servers and three different networks of Internet service providers. We collected video bit rates in stable or unstable transmissions for evaluating the link stability by video bit rate changes. We recorded the rate data when the link was stable 10 times consecutively, and before the 11th collection, we randomly disconnected a transmission link and repeated the data collection 10 times. The result is shown in Figure 3 below:
FIGURE 3
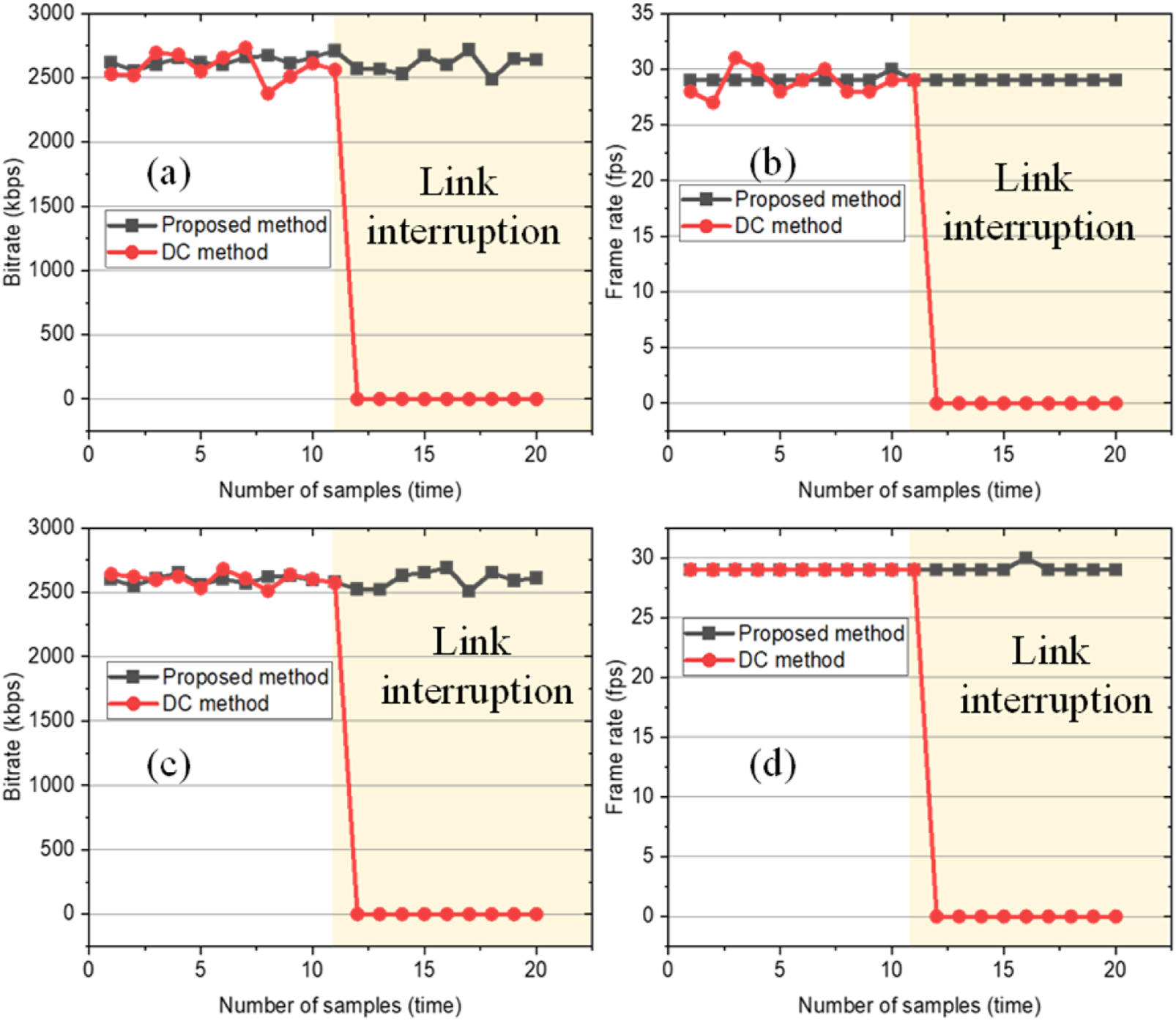
Network transmission performance results during link interruption. (a) Bitrate of the main data stream. (b) The frame rate of the main data stream. (c) The bitrate of the additional data stream. (d) The frame rate of the additional data stream.
As we can see from the results above, before the change of network delay, two network transmission schemes both maintain normal performance, and the bit rate and frame rate of the two schemes are approximately the same, which remains at about 2500 kbps and the frame rate is stable at 30 frame per second (FPS). When one link failed, the bit rate and frame rate of Scheme 2 dropped to 0, indicating that Scheme 2 could not provide effective network transmission at that time, while the bit rate and frame rate of the proposed method ensured stable data transmission.
Secondly, we use an impairment generator of the network to simulate signal impairments. A link is randomly selected, and the packet loss rate is set to 40% to simulate the actual application scenario. The recordings of network delay are shown in Figure 4 as follows.
FIGURE 4
Network transmission performance results with link packet loss.
Figure 4 shows the transmission performance of the proposed method versus the direct connection method for the main data stream and the additional data stream before and after a link interruption, where the yellow area represents the scenario during which the link interruption occurs.
As shown in the figure above, it can be seen from the above figure that the performance of the proposed method for data transmission of the “Main data” stream and “Additional data” stream is better than the other two methods, while the performance of the remaining two methods is close to that of the other two methods. The average network delay of the “Main data” stream is 141.8 ms, and the average network delay of the “Additional data” stream is 154.7 ms. The average network delay of control group 1 is 297.2 ms for the “Main data” stream and 327.5 ms for the “Additional data” stream. The average network delay of control group 2 is 318.2 ms for the “Main data” stream and 318.4 ms for the “Additional data” stream. It is proved that the proposed method can effectively reduce network delay when packet loss occurs.
3.3 Experiment 2: the effect of insufficient bandwidth impact
Subsequently, we verified the scenario with insufficient bandwidth. Different kinds of data are generated in the process of remote surgery, and different types of data have different requirements for the quality of the required transmission. Doctors perform surgery by controlling surgical robots remotely, so they need to receive timely feedback. The “Additional data” stream is only used to communicate with the remote doctor for use, so the priority of the shared data is higher compared to the video communication data. When the link bandwidth cannot support all the data to be transmitted normally, some of the data will not be transmitted.
The proposed method can identify different transmission data in the process of transmission and allocate link resources to meet the needs of remote surgery intelligently. The settings of experiments are as follows:
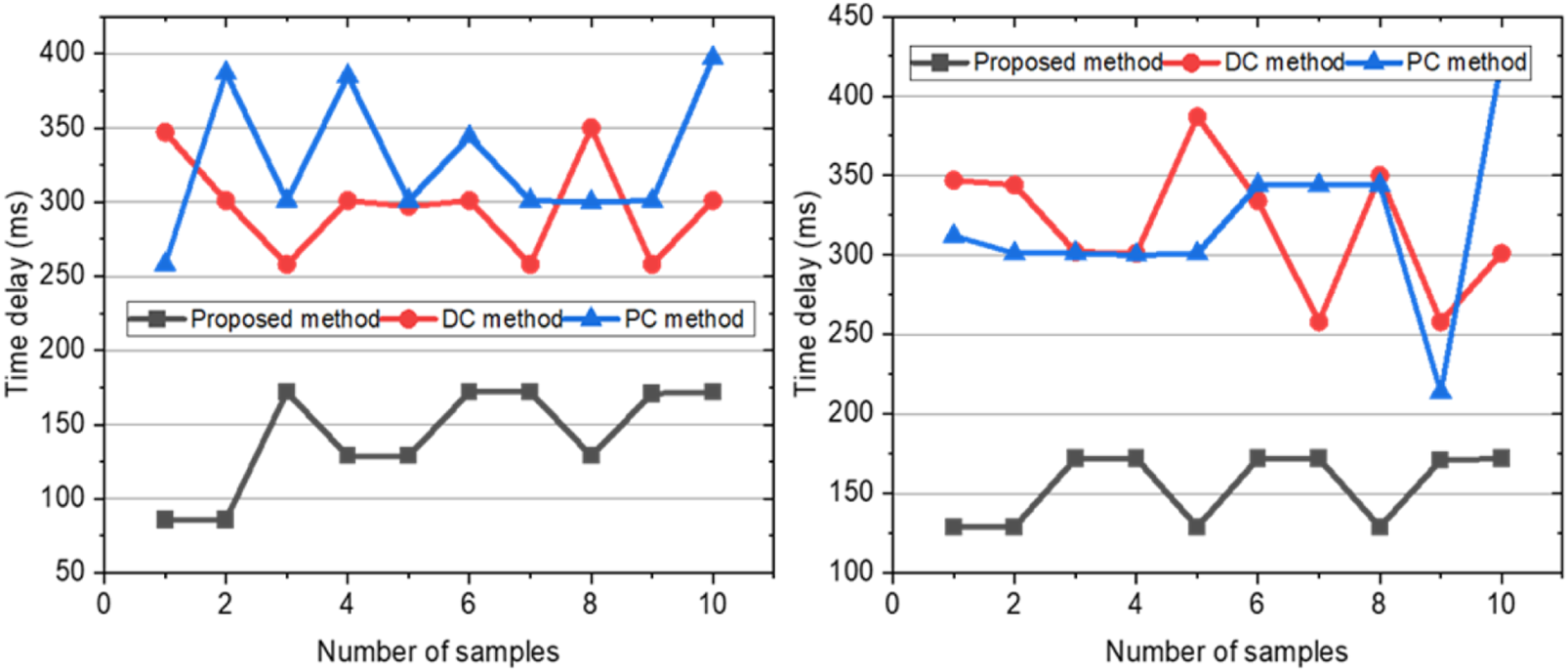
From the Table 2 above, we can infer that the total bandwidth needs to be 6 Mbps. When the bandwidth of each link was insufficient to send all the data, the network property of data transmission would be affected. Therefore, we set up the signal impairment generator to create extra delay and packet loss on each link, mimicking real-world usage scenarios. The result is shown in Figure 5.
TABLE 2
| Parameters | Main data stream | Additional data stream |
|---|---|---|
| Bit rate | 3M bps | 3M bps |
| Resolution | 1920*1080 | 1920*1080 |
| Frame rate | 30 FPS | 30 FPS |
The parameters of the main data stream and additional data stream.
FIGURE 5
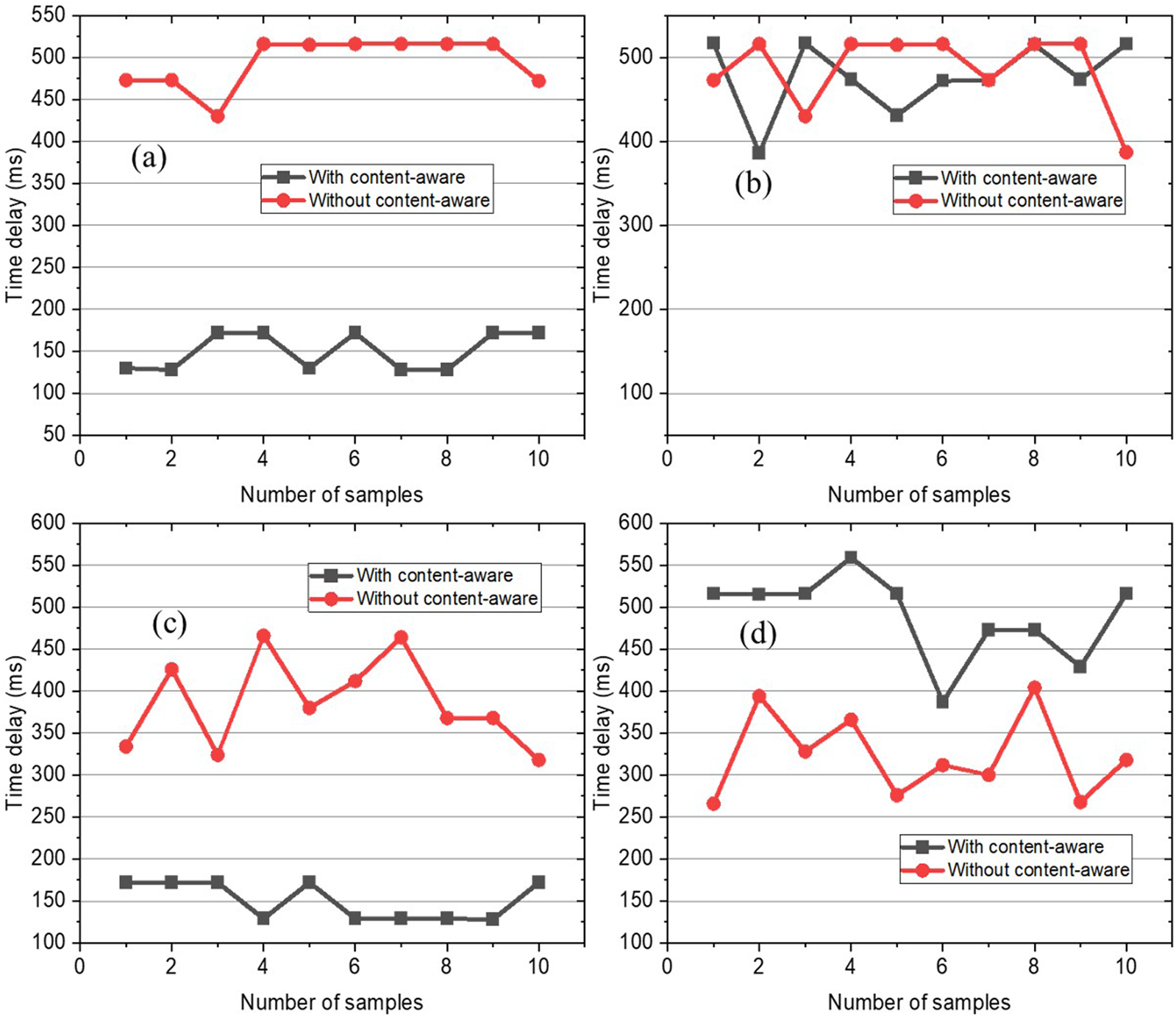
Time delay results when bandwidth is insufficient. (a) Differences in link latency (sufficient bandwidth). (b) Differences in link packet loss (sufficient bandwidth). (c) Differences in link latency (insufficient bandwidth). (d) Differences in link packet loss (insufficient bandwidth).
We simulate the scenario where the sum of all link bandwidths between the medical collaboration gateway and the audio-video collaboration server is insufficient to meet the scenario where the medical collaboration gateway receives all data. Compared with the content-aware multi-link transmission and the content-aware single-link transmission characteristics, the resolution and frame rate of the remote surgical data sharing stream and the camera stream received by the medical collaboration gateway are compared. The results in Figure 5a show that the proposed method achieves the lowest network delay when the bandwidth is insufficient, with an average network delay of transmission of 150.4 ms for “Main data” stream and an average network delay of transmission of 477.5 ms for “Additional data” stream. In control group 3, the average network delay of the “Main data” stream is 494.3 ms, and the average network delay of the “Additional data” stream is 477.5 ms. Because the experimental group uses a low-latency link to forward “Main data” and a high-latency link to forward “Additional data”, the network delay of “Main data” is much lower than the “Additional data”. The control group does not have content-aware processing, so it cannot select low-latency links for data transmission, resulting in high latency for both “Main data” and “Additional data”. The results from Figure 6b above are similar to those from Figure 6a, and the network delay of the “Main data” stream in the experimental group is much lower than both the delay of the “Additional data” stream in the experimental group and the delay of “Main data” stream or “Additional data” stream in the control group 2. The detailed results are shown in the Table 3. The Figures 6c,d show the frame rates of image transmission in both cases. From the frame rate results, it can also be seen that “Main data” can achieve stable transmission through content awareness, and the frame rate is maintained at around 30 frames, while the frame rate of “Additional data” is 0.
FIGURE 6
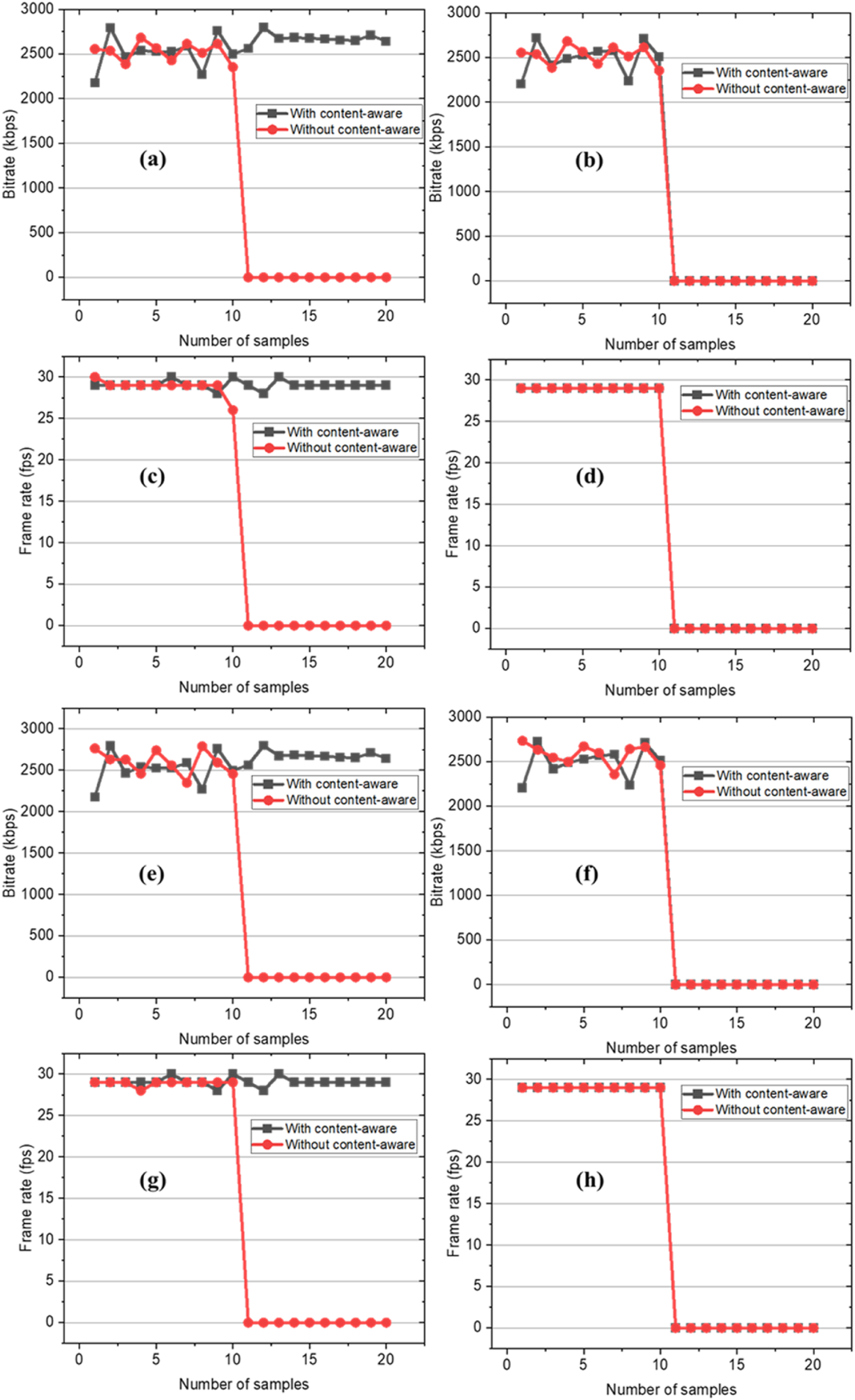
Changes in transmission performance of different methods (content-aware vs. content-unaware) for Main data and Additional data when the total link bandwidth is insufficient. (a) The bitrate of Main data (single link). (b) The bitrate of Additional data (single link). (c) The frame rate of Main data (single link). (d) The frame rate of Additional data (single link). (e) The bitrate of Main data (multi link). (f) The bitrate of Additional data (multi link). (g) The frame rate of Main data (multi link). (h) The frame rate of Additional data (multi link).
TABLE 3
| Scenario | Main data | Additional data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitrate | Frame rate | Bitrate | Frame rate | |
| Sufficient bandwidth | 2672 kbps | 29 FPS | 2469 kbps | 29 FPS |
| Insufficient bandwidth | 2510 kbps | 29 FPS | 0 kbps | 0 FPS |
The bitrate and frame rate of main data and additional data (sufficient bandwidth/insufficient bandwidth).
We use an impairment generator of the network to set the bandwidth of links to 2M, 2M, and 1.5M to simulate that the total bandwidth is not enough to receive all the data. Collect the bit rate and frame rate data before and after setting bandwidths. Figures 6e–h between the analog medical synergy gateway and the audio-video synergy server, the same use of aggregated multi-link network for the analog medical synergy gateway, the sum of all the link bandwidth is not sufficient to meet the medical synergy gateway receives all the data in the scene, compared with the content-aware transmission and no content-aware transmission characteristics, the medical synergy gateway receives the remote surgical data sharing stream and camera stream resolution and frame rate. The results show that in multi-path, if the transmission bandwidth still cannot transmit all the data, the high-priority data after content awareness can be transmitted smoothly, while the low-priority data cannot be transmitted. The above results show that the content-aware method can ensure the accurate transmission of high-priority data under limited bandwidth conditions, which proves the effectiveness of the proposed method. The results are shown in the Figure 7.
FIGURE 7
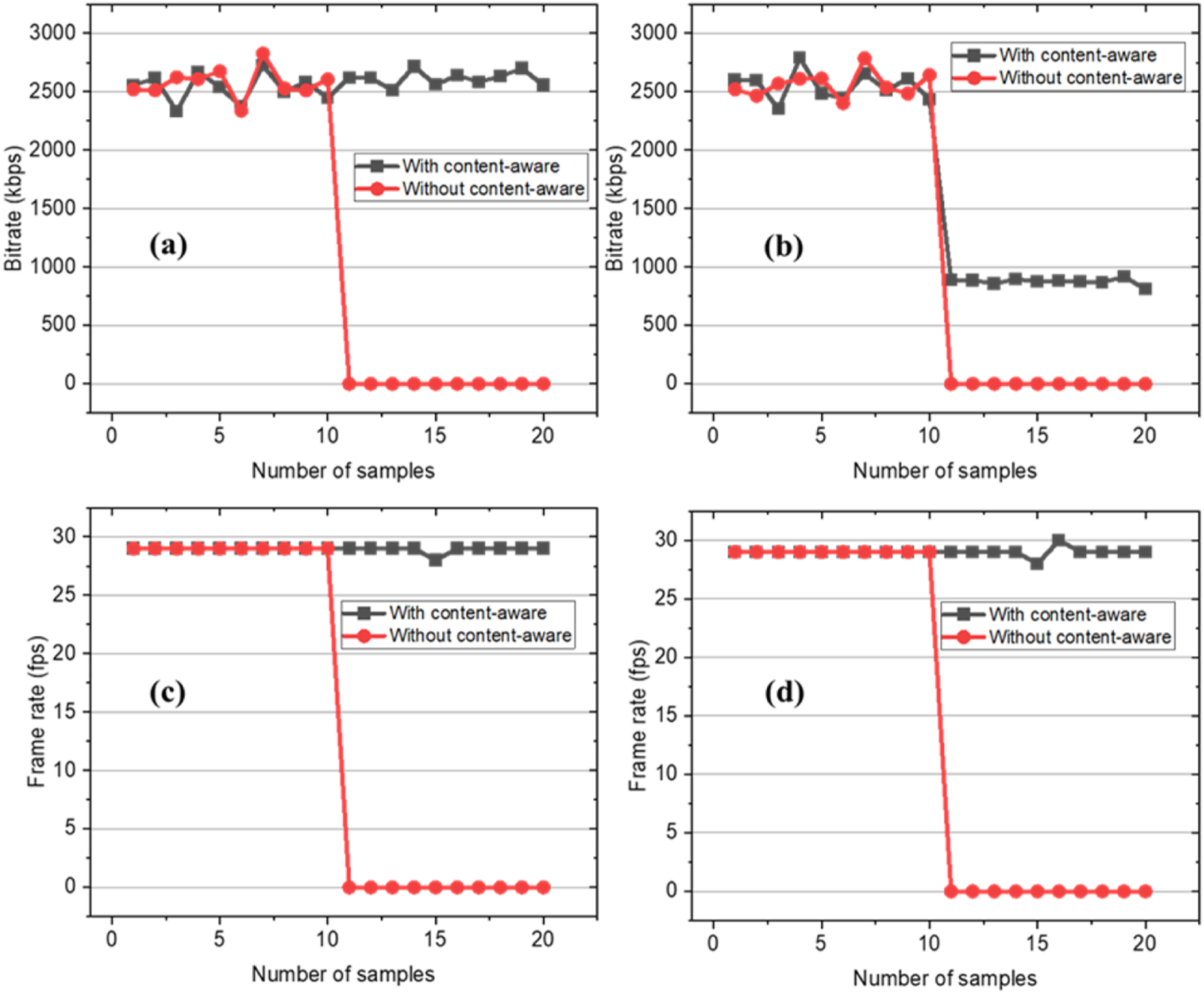
Variation of Main data and Additional data transmission performance of different methods (content-aware vs. non-content-aware) in the scenario where the sum of bandwidths is not sufficient for receiving all data. (a) Main data code rate. (b) Additional data code rate (c) Main data frame rate. (d) Additional data frame rate.
As we can see from the figure above, the average bit rate of the proposed shared stream is 2.67 Mbps, and the average frame rate is 29 frames. When the bandwidths of the link in control groups 2 and 3 are insufficient, the frame rate of the shared stream and video stream both drop to 0, indicating that their links cannot guarantee normal transmission.
Through performing theoretical analysis, we can see that if we only need to transmit the shared stream data, the bandwidth still could have a certain margin. Therefore, we can reduce the bit rate of the “Additional data” stream to reduce the bandwidth that a successful transmission requires. We decreased the resolution ratio of the original “Additional data” stream from 1920*1080 to 1280*720. The experimental results show as follows:
Compared with previous results, it could be seen that when the link bandwidth mentioned above was insufficient, the proposed method could decrease the bit rate by reducing the resolution of the “Additional data” stream. In this case, the average bit rate of the “Additional data” stream was 875 kbps, and the average frame rate was 29 frames, while the bit rate of the “Main data” stream remained unchanged. The results showed that the proposed method could maintain the average frame rate of 30 frames to ensure a successful implementation of remote surgery, while the other methods could not transmit “Main data” and “Additional data” successfully when the bandwidth was insufficient. The results described in the Table 4 showed that the method we proposed could recognize the transmission content more effectively and ensure the quality of transmission according to the priority of data required for the telemedicine scenario, along with limited bandwidth.
TABLE 4
| Scenario | Main data | Additional data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitrate | Frame rate | Bitrate | Frame rate | |
| No link interruption | 2601 kbps | 29 FPS | 2641 kbps | 29 FPS |
| Link interruption | 2612 kbps | 30 FPS | 0 kbps | 0 FPS |
| Sufficient bandwidth | 2672 kbps | 29 FPS | 2469 kbps | 29 FPS |
| Lower bandwidth | 2510 kbps | 29 FPS | 0 kbps | 0 FPS |
| Insufficient bandwidth | 809 kbps | 10 FPS | 0 kbps | 0 FPS |
The bitrate and frame rate of main data and additional data.
4 Discussion
This study introduces a content-aware multipath transmission method tailored to the demands of telemedicine. By intelligently prioritizing data streams based on the type and importance of data, the proposed method demonstrably ensures the quality of high-priority data transmission, even under adverse network condition such as network instability or bandwidth insufficiency. Our experimental evaluations reveal that:
1. Robustness to Packet Loss: Under a simulated 40% packet loss condition, the proposed method achieved an average delay of 141.8 ms for the “Main data” stream, compared to 297.2 ms and 318.2 ms for traditional direct connection and distributed server methods, respectively.
2. Adaptability to Bandwidth Scarcity: In bandwidth-constrained environments (total bandwidth <6 Mbps), the proposed method maintained an average bit rate of 2.67 Mbps and frame rate of 29 FPS for high-priority data while adapting low-priority data transmission by reducing resolution.
These results highlight the method’s capability to prioritize critical data, ensuring the smooth execution of remote surgeries where real-time feedback is essential. The content-aware mechanism dynamically allocates bandwidth and route critical data (like surgical control signals and real-time video) through the lowest-latency available paths, while intelligently offloading less critical data to higher-latency available links without disrupting the operation. This ensures the continuity and quality of operations demanding immediate feedback, such as telesurgery.
Future work will focus on refining the algorithm for more complex network conditions and extending its applications to other real-time domains, such as industrial automation and real-time video conferencing. In summary, the proposed method significantly enhances the reliability and efficiency of telemedicine communications, paving the way for broader adoption of remote healthcare technologies.
5 Challenges and limitations
Although our method shows significant promise, its practical implementation in diverse real-world telemedicine should be considered discreetly. For example, current hospital IT infrastructure may be insufficient, integrating various medical devices (endoscopes, robotic arms, vital signs monitors) and Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems could present integration challenges, and the need for standardized interfaces and intermediary components requires consideration. Moreover, the implementation of multi-path architectures may increase vulnerability to cyberattacks. Consequently, robust end-to-end encryption must be enforced across all paths, coupled with the establishment of comprehensive authentication mechanisms.
6 Future work
Based on our previous study and the promising directions, there are several working parts for future research:
1. Algorithm Enhancement for Complex Environments:
We could develop machine learning-based models to predict path quality fluctuations and proactively manage path switching to minimize disruptions.
2. Integration and Collaboration Focus:
We could conduct pilot deployments in live clinical settings to collect valuable data on real-world usability, workflow integration, and performance under actual operational loads and diverse network conditions. In the meantime, we should actively establish partnerships with medical device manufacturers to develop standardized APIs or interfaces, enabling the priority-based mechanism to be seamlessly integrated into medical devices and telemedicine platforms.
7 Conclusion
In conclusion, the proposed content-aware multipath transmission method has made significant progress in improving the reliability and efficiency of telemedicine communication, especially for delay-sensitive applications such as remote surgery. By ensuring the quality of key data streams under challenging network conditions, it directly addresses the main obstacles to the wide adoption and success of telemedicine interventions. Although acknowledging the complexity of implementation and the challenges discussed, the convincing experimental results and the overview roadmap of future research provide a solid foundation for further development and ultimate clinical translation. Addressing the identified limitations and pursuing specific future directions will help realize the full potential of this technology in transforming telemedicine services.
Statements
Author’s note
We confirm that we have thoroughly read and understood the terms of use for TikTok, YouTube, Instagram, and X regarding social media research. We ensured that our study adhered to all relevant policies and standards.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
YT: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. LL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. LW: Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. JM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review and editing. TL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. KH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Science and Technology Innovation 2030-Major Project, No. 2021ZD0140401 and No. 2021ZD0140410.
Conflict of interest
Author JM was employed by Beijing RedCDN Technology Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Anvari M. Broderick T. Stein H. Chapman T. Ghodoussi M. Birch D. W. et al (2005b). The impact of latency on surgical precision and task completion during robotic-assisted remote telepresence surgery. Comput. Aided Surg.10, 93–99. 10.3109/10929080500228654
2
Anvari M. McKinley C. Stein H. (2005a). Establishment of the world’s first telerobotic remote surgical service: for provision of advanced laparoscopic surgery in a rural community. Ann. Surg.241, 460–464. 10.1097/01.sla.0000154456.69815.ee
3
Chu G. Yang X. Zhang X. Guan B. Zhao J. Gao Y. et al (2025). Innovative integration of robotic-assisted laparoscopic telesurgery and quantum cryptography communication in urology: clinical application and initial experience. Int. J. Med. Robotics Comput. Assisted Surg.21, e70028. 10.1002/rcs.70028
4
Internet Medical System and Application National Engineering Laboratory (2018). Wireless medical white paper. Internet Healthc. Ind. Alliance. Available online at: https://m.wnwk.com/doc/3067093.html (Accessed May 30, 2025).
5
Li Y. Raison N. Ourselin S. Mahmoodi T. Dasgupta P. Granados A. (2024). AI solutions for overcoming delays in telesurgery and telementoring to enhance surgical practice and education. J. Robot. Surg.18, 403. 10.1007/s11701-024-02153-9
6
Raison N. Khan M. S. Challacombe B. (2015). Telemedicine in surgery: what are the opportunities and hurdles to realising the potential?Curr. Urol. Rep.16, 43–48. 10.1007/s11934-015-0522-x
7
Sherif Y. A. Adam M. A. Imana A. Erdene S. Davis R. W. (2023). Remote robotic surgery and virtual education platforms: how advanced surgical technologies can increase access to surgical care in resource-limited settings. Semin. Plast. Surg.37, 217–222. 10.1055/s-0043-1771301
8
Singh S. K. Sharma J Joshua L. M. Huda F. Kumar N. Basu S. et al (2022). “Telesurgery and robotics: current status and future perspectives,” in Telehealth and telemedicine - the far-reaching medicine for everyone and everywhere (IntechOpen). 10.5772/intechopen.107465
9
Ta Kim D. Chow D. (2022). The effect of latency on surgical performance and usability in a three-dimensional heads-up display visualization system for vitreoretinal surgery. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol.260, 471–476. 10.1007/s00417-021-05388-6
10
V P. J M. M C. M. (2024). The humanitarian impact of telesurgery and remote surgery in global medicine. Eur. Urol.86, 88–89. 10.1016/j.eururo.2024.04.029
11
Xu L. Shen C. Li X. Zhao F. Huang W. Yang K. et al (2024). Feasibility and safety of dual-console telesurgery with the KangDuo Surgical Robot-1500 System using fifth-generation and wired networks: an animal experiment and sea-spanning clinical study. Minerva Urology Nephrol.76, 241–246. 10.23736/s2724-6051.24.05808-7
12
Xu S. Perez M. Yang K. Perrenot C. Felblinger J. Hubert J. (2015). Effect of latency training on surgical performance in simulated robotic telesurgery procedures: latency training. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg.11, 290–295. 10.1002/rcs.1623
13
Zanaboni P. Wootton R. (2012). Adoption of telemedicine: from pilot stage to routine delivery. BMC Med. Inf. Decis. Mak.12, 1. 10.1186/1472-6947-12-1
14
Zy M. Desai A. Bisht R. Lathkar S. Misra S. Carbin D. D. (2025). Telesurgery: current status and strategies for latency reduction. J. robotic Surg.19, 153. 10.1007/s11701-025-02333-1
Summary
Keywords
intelligent transmission method, multimodal data streams, multi-path transmission, wide area network, telemedicine
Citation
Tong Y, Li L, Li S, Wang L, Ma J, Lyu T and He K (2025) An intelligent transmission method for multimodal data streams in telemedicine based on multi-path transmission over wide area network. Front. Commun. Netw. 6:1566554. doi: 10.3389/frcmn.2025.1566554
Received
21 February 2025
Accepted
05 June 2025
Published
19 June 2025
Volume
6 - 2025
Edited by
Constantinos Psomas, University of Cyprus, Cyprus
Reviewed by
Giovanni Pau, Kore University of Enna, Italy
Kapila W. S. Palitharathna, University of Cyprus, Cyprus
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Tong, Li, Li, Wang, Ma, Lyu and He.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ting Lyu, 77113432@163.com; Kunlun He, kunlunhe@plagh.org
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.