Abstract
Introduction:
The rapid growth of advanced networking causes a significant increase in malicious threats to website data for accessing user information via phishing attacks. For the detection of phishing attacks, many works are developed based on a single data source. But, detecting the phishing attacks of different web sources was not concentrated in any of the existing works. Thus, multiple data sources, including SMS, E-Mail, and URL links, are used in this paper to detect and mitigate phishing attacks.
Methods:
Initially, the input data is collected from the SMS, E-Mail, and URL datasets. The contents and URLs are extracted from the datasets. Next, the textual analysis, including behavioral analysis and structural analysis, is carried out on the extracted URL. Moreover, by utilizing the Entropy Macqueen-based Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (EM-BERT) algorithm, the contents extracted from SMS and E-Mail datasets and the textually analyzed characters of the URL are transformed into vector form. Simultaneously, the CSS files and images are obtained from the URL dataset. Then, by utilizing Spherical Principal Component Analysis (SPCA), the features are extracted. Further, the optimal features are chosen by using the Cauchy distribution-based Seagull Optimization Algorithm (CSOA). Next, the phishing attack is detected using the Explainable AI SERF CoLU Long Short Term Memory (EAI-SC-LSTM) model. The recognized phishing data and URL are updated to the Blacklist; hence, any new URL, which is already on Blacklist, is reported to the user.
Results:
As per the experimental outcomes, the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM attains accuracies of 99.627% for SSC, 99.645% for PEC, and 99.541% for WPD in phishing attack detection, which are higher than the existing works. Moreover, the proposed technique detects the phishing attack within a training time of 24417 ms (PEC Dataset).
Discussion:
Thus, cybersecurity is improved against the evolving phishing threats.
1 Introduction
In today’s digital age, the Internet has become a cornerstone of communication, information dissemination, and engagement across various sectors, including business, education, and banking. The Internet serves as a platform for exchanging diverse content, such as research papers, educational materials, and multimedia resources, which increases cybercriminal threats that seize users’ confidential information (Catal et al., 2022; Mahmoud et al., 2013). Among different threats, phishing is considered as a widespread attack, where the hackers can access the data without any complex cipher codes (Hannousse and Yahiouche, 2021). Such phishing attacks occur in various forms through Email, random SMS, social media, Quick Response codes, and URL links (Safi and Singh, 2023). Due to a lack of knowledge about URLs, blind trust in webpages or messages, and redirected webpage locations, the users are subjected to phishing attacks (Basit et al., 2021). The report of the Anti-Phishing Working Group stated that the number of phishing attacks increased to 2,50,000 within a month in 2021 and kept on increasing. Thus, it is essential to develop an effective system to detect phishing attacks for preventing further attacks in the future (Asiri et al., 2023).
For phishing detection, Meta-heuristic methods are developed to collect information, and the URL is verified with the blacklist to check its legitimacy (Odeh et al., 2021). As an efficient worldwide standard, Email networks are intruded on by cybercriminals for financial benefits. These phishing emails are detected by utilizing the Themis model, which deeply analyzes the structure of the mail (Atlam and Oluwatimilehin, 2023; Salloum et al., 2021). Due to the various ambiguities of the detection systems, phishing websites can also be tested and detected by utilizing a Fuzzy logic technique (Bhagwat et al., 2021). Similar to phishing emails, phishing SMS is created with some random phone numbers for making money transactions by users (Abdillah et al., 2022). Currently, to enhance the phishing detection process, Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) algorithms are being analyzed (Li et al., 2023).
The labeled datasets are utilized to recognize malicious and benign websites by using ML approaches. For the phishing detection, the supervised learning algorithms like Logistic Regression (LR), Support Vector Machines (SVM), Decision Tree (DT), Naïve Bayes (NB), and Random Forest (RF) are utilized (Tang and Mahmoud, 2021). Among these, the SVM classifier accurately detects phishing attacks along with the word embedding technique (Salloum et al., 2022). Furthermore, the DL models, including LSTM and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), efficiently detect phishing by learning the patterns and anomalies of the data (Thakur et al., 2023). These phishing detection systems contribute to mitigating attacks via software-based phishing tools and human-centric strategies (Naqvi et al., 2023). But, for phishing attack detection, multiple website sources, such as SMS, E-Mail, and URLs were not concentrated in any of the existing works.
The existing (Brezeanu et al., 2025) utilized the HyperText Markup Language (HTML) code to identify the phishing attack, helping in automatically updating the phishing indicators. Also, the prevailing (Sturman et al., 2024) detected the phishing attack based on the user knowledge and decision style. The traditional (Shombot et al., 2024) used SVM for attack detection and attained higher accuracy. Moreover, the prevailing (Sudar et al., 2024) improved the resilience against evasive phishing strategies. In the existing (Biswas et al., 2024), the transparent and interpretable models were utilized for the attack prediction. Yet, these prevailing models did not predict the phishing strategies in the multi-data source. Hence, this work detects phishing attacks in various sources, including SMS, E-Mail, and URL data, by analyzing the user behavior using EM-BERT and SPCA BASED EAI-SC-LSTM techniques.
1.1 Problem statement
Some of the issues in existing works of phishing attack detection are listed below,
• Existing works did not concentrate on the phishing attacks that occurred among various data sources, including SMS, E-Mail, and URL links.
• Based on the contents like sender, subject, body, or attachments, the phishing emails were detected in (Bu and Kim, 2022). But, the links and the Javascript features related to such phishing emails were not analyzed, leading to inaccurate attack detection.
• In (Aljofey et al., 2022), the URLs were examined via Hyperlinks, URLs, and Textual Content. Nevertheless, the behavior after clicking the links was not concentrated, restricting the information of phished URLs for future alerts to the user.
• The phishing URL was blocked and alerted to the user in (Yang et al., 2021). But, the reason behind the blocked URL was not intimated to the user for enhancing awareness.
This paper presents an effective multimodal framework for phishing detection to overcome the problems in existing works. The major contributions are given below,
• This proposed work focuses on different data sources like SMS, E-Mail, and URL links for detecting phishing attacks.
• Along with content features, the Javascript features and URL features are obtained from input datasets. Thus, the phishing attack is more accurately detected by using the EAI-SC-LSTM approach.
• To provide future alerts to the user, the behavior after clicking URL links is identified via the behavior analysis; also, the optimal features are selected by using CSOA.
• As the phishing URL is updated in the blacklist, the user is alerted with better awareness about the legitimacy of incoming new URLs.
The paper is structured as: In Section 2, the previous works related to the proposed system are explained. In Section 3, the proposed methodology is described. In Section 4, the performance attained by the proposed technique is analyzed. Lastly, Section 5 concludes the paper with future suggestions.
2 Literature survey
Aljofey et al. (2022) established an efficient technique to detect phishing websites. Primarily, the webpage dataset was created. From the URL and HTML, the textual contents and hyperlinks were extracted. In addition, by using eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGB), LR, NB, and RF classifiers, the phishing attack was detected. The detection result was improved with superior accuracy and precision. But, the overfitting issues and less interpretability were caused by the XGB classifier, which limited the detection efficiency.
Bu and Kim (2022) propounded the phishing detection model using DL approaches. Primarily, the domain-centric and script-centric URL features were extracted. Then, by utilizing the genetic algorithm, the significant features were selected. Next, the phishing and benign URLs were classified utilizing the Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network with improved accuracy and recall. Nevertheless, the utilized network did not recall the long-term dependency of the features, thus hindering effective training.
Yang et al. (2021) suggested the phishing detection technique via the extreme learning machine. Firstly, the website-related data was collected. Next, the surface feature, topological feature, and deep features were extracted. Then, by utilizing the Adaptive Synthetic Sampling (ASS) algorithm, the data was balanced. Hence, the performance was improved with higher accuracy and lower error. However, the used ASS approach did not produce the accurate minority class data samples as the synthetic samples.
Tang and Mahmoud (2022) presented a DL approach to detect phishing websites. Initially, the data was gathered from various websites. Next, the URL characteristics were extracted from the data. Then, by utilizing six different ML classifiers, the obtained features were trained. Subsequently, to detect the legitimacy of URLs, the Chrome browser extension was utilized. Therefore, the detection performance was improved with superior accuracy and f1-score. But, the used RF classifier was sensitive to hyperparameters and time series interpretability of data.
Karim et al. (2023) introduced a hybrid ML technique for website phishing detection. Initially, the URL-centric dataset in vector form was obtained and further preprocessed for removing the null values. Then, by utilizing a hybrid model, including LR, SVM, and DT classifiers, the features selected via the canopy technique were trained. By using the grid search optimization technique, the prediction outcomes were improved. Thus, the performance was increased with higher accuracy and precision. Nevertheless, the larger amount of data was not effectively learned by the adopted SVM.
Gupta et al. (2021) recommended a lexical-centric ML technique to detect phishing URLs. Primarily, from the dataset, the input data was collected and preprocessed. Next, the domain and lexical features of the URL were extracted. In addition, phishing URLs were detected by utilizing various ML classifiers, such as LR, SVM, and RF. Among them, the RF classified phishing data with enhanced accuracy. However, the user was not aware of phishing data, which threatened the user’s information.
Sanchez-Paniagua et al. (2022) propounded a phishing website detection system for real-time scenarios. The input data was obtained from the multipurpose dataset and further pre-processed by utilizing a three-filter system. Next, the URL feature, HTML feature, and technology-based features were extracted and vectorized. Lastly, by using a Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM) classifier, the phishing attack was detected with enhanced accuracy and F1-score. However, due to the complex structure, the GBM model was less interpretable and vulnerable to overfitting issues.
Opara et al. (2024) detected the phishing of web pages by utilizing Deep Neural Network (DNN). Initially, the data was obtained from the webpage datasets. Next, the URL and HTML characteristics were extracted and embedded into homologous dense vectors. Then, by utilizing a concatenation layer, the embedded matrices were merged. Finally, by utilizing CNN, the website phishing was identified with better precision and accuracy. But, the adopted CNN needed a lot of labeled data for training and had a gradient exploding problem.
Ariyadasa et al. (2022) established a hybrid convolutional network to detect phishing websites. Primarily, the URL and HTML content data were gathered from the webpage dataset and were individually preprocessed. Furthermore, by using Long Term recurrent network and the Graph Convolution Network (GCN), the gathered data was trained. Then, the phishing website was detected with enhanced f1-score and accuracy. Nevertheless, the GCN didn’t handle the directed graphs and had inferior scalability, thus degrading the performance.
Rao et al. (2021) suggested a heuristic approach to detect phishing websites. Primarily, the data was gathered from the login and home page of the website dataset. By using the Jaccardian similarity measure, the similarity among homepage features was evaluated and vectorized. Next, the URL and hyperlink features were extracted, and the feature vectors were generated. Then, the phishing website was identified using the Twin SVM classifier with enhanced accuracy. However, the irrelevant data was not ignored, thus complicating the detection process.
Alotaibi et al. (2025) integrated explainable artificial intelligence for the classification of web-based phishing. The web-based data were collected and pre-processed regarding data cleaning and normalization. Then, the Harris’ Hawks Optimization (HHO) method was used for selecting the optimal feature. Further, the Multi-Head Attention-based Long Short-Term Memory (MHA-LSTM) with Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanation (LIME) classified the phishing attack accurately. Yet, the accuracy was compromised due to the unrepresentative features.
Aljabri et al. (2024) developed phishing attack detection in the Internet of Things (IoT) environment. Here, from the gathered data, the important features were selected using the Dwarf Mongoose Optimization (DMO) technique. Next, by utilizing the Hybrid Stacked AutoEncoder (HSAE), the phishing attack was predicted. The data in the classifier was hyper-tuned using Jellyfish Search Optimizer (JSO). Thus, this model enhanced the classification task. However, in real-time, this model failed to analyze a large number of data.
Elberri et al. (2024) estimated a cyber-defense system against phishing attacks with deep learning. Initially, for the collected data, the synthetic samples were generated by using the Synthetic Minority Over-sampling TEchnique (SMOTE). The African Vulture Optimization Algorithm (AVOA) was then used for feature selection. Afterward, based on the combination of the CNN and LSTM techniques, the spatial features were extracted, temporal features were analyzed, and finally, the phishing attack was determined precisely. Yet, the computational complexity was increased, affecting the system’s overall performance.
Alsubaei et al. (2024) investigated phishing detection for cybercrime forensics. Here, the digital forensic data was collected. Then, the data imbalance was rectified using SMOTE analysis. Next, the Residual Networks Next (ResNeXt) and the Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) were embedded for accurate phishing attack classification. During the classification, the Jaya optimization was utilized for hyperparameter tuning. On the contrary, the diverse attack scenarios could not be handled by the model.
Sahingoz et al. (2024) deployed deep learning-based phishing detection system. Primarily, the webpages with URL data were collected. Next, the CNN, Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Networks (BRNN), and Attention Network were used for phishing attack detection. Among these classifiers, the CNN model predicted the phishing attack more efficiently. Yet, the model analyzed every data that was collected, leading to increased processing time during the analysis.
3 Proposed methodology for phishing attack detection
This framework adopts multiple sources for phishing detection using the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM method by analyzing various features, namely, contents, URL, behavior, and Javascript. Figure 1 represents the proposed phishing detection framework.
FIGURE 1

Block diagram of proposed methodology.
3.1 Input data
Initially, the input data is collected from multiple sources, namely, the SMS dataset , Email dataset , and URL dataset to detect the phishing attack. It is given as in Equation 1,
Here, illustrates the input data.
3.2 Content extraction
Then, the contents are extracted from and . For further analysis of data, the URL is extracted from . It is expressed as in Equations 2, 3,
Here, signifies the extracted contents and depicts the extracted URL from input data.
3.3 Textual analysis
Here, is given as input to the textual analysis in which the textual features, including words, characters, and symbols of URL, are analyzed for the efficient identification of phishing attacks. For examining every character, behavior analysis, content-based features, Java script features, and URL features are considered under textual analysis.
3.3.1 Behavior analysis
The discriminative features of URLs like domain name , bag-of-words , generic Top-Level domains , IP address , and port number are used to predict the user’s behavior. It is expressed as in Equation 4,
Where, implies the analyzed features related to user behavior.
3.3.2 Content-based features
Then, to examine the contents of the data, the content-centric features like Anchor, U_request, Popup, Links_in_tags, Cookies, Iframe, Submit, IMG_Hyperlink, Susp_links, and Dest_port are extracted from . It is given as in Equation 5,
Here, is the extracted content-centered features, and is the number of .
3.3.3 Java script features
In addition, to analyze the events or actions performed by the user, the features of Javascript, including the length of characters, number of lines, number of strings, number of Unicode symbols, number of words, number of comments, the average length of strings, the average length of arguments, count of numbers in hex or octal, and number of methods, are considered. It is represented as in Equation 6,
Here, is the acquired features and signifies the number of Javascript features.
3.3.4 URL features
Subsequently, the URL features are gathered from for the accurate identification of phishing URLs. The URL features, namely, length_url, length_hostname, ip, domain_age, web_traffic, dns_record, google_index, page_rank, nb_www, and port are extracted from . It is expressed as in Equation 7,
Where, is the extracted URL features, and is the number of . Thus, the textual analysis is carried out on , which is declared as .
3.4 Structural analysis
Next, for analyzing the structural features of the URL, the CSS files and image files are chosen from . For analyzing the structure of , the features like sub-domain, scheme, subdirectory, path, port number, query string, top-level domain, parameter, second-level domain, fragment, and protocol are evaluated from and . It is given as in Equation 8,
Here, is the structurally analyzed characters of the URL.
3.5 Feature extraction
Here, is fed as input to the feature extraction phase. Principal component analysis, which identifies the principal features and aids in developing the predictive models, is utilized for extracting features. It is essential to reduce dimensions to effectively visualize the data before analyzing the significant features. However, feature extraction using PCA sometimes causes information loss, as it projects data into principal components that may not fully capture all the underlying structure of the data. Also, PCA assumes linearity in the data, which may not be suitable for datasets with non-linear relationships, potentially leading to suboptimal feature representations and reduced model performance. Thus, spherical-centric vectors are utilized to compute the covariance matrix of PCA and preserve the information while minimizing feature dimension. These vectors maintain the geometric relationships within the data by projecting it into a unit sphere, which reduces information loss and retains the crucial data characteristics. Also, this approach mitigates the impact of scaling differences between features, enhancing the dimensionality reduction process and resulting in a more robust feature representation. The feature extraction process using the proposed SPCA technique is explained below,
Step 1Primarily, the is initialized and signified as in Equation 9,Where, indicates the number of . Next, to avoid the biased outcome, the different structures in are standardized within the ‘0’ mean and a unit Standard Deviation (SD). It is expressed as in Equation 10,Here, is standardized , depicts each feature value, is the mean of features, and is the SD among the features.
Step 2Then, by computing the Covariance matrix , the correlations between and its mean are determined. For computing , a spherical-based vector is generated so that the information loss is prevented during dimension reduction. This is especially useful in phishing detection, where small changes in text or structure can indicate malicious intent. The representation of is given as in Equation 11,Here, is the functional characteristics of spherical space and is the random point on . Thus, is computed regarding for number of features and is given as in Equation 12,The sign of characters in identifies the correlation among features. The features are declared as correlated when is positive, and features are indirectly correlated when is negative. Moreover, there is no correlation between features when the feature value is zero.
Step 3Next, to identify the principal components, the Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors are computed. Such principal components are recognized by the Eigenvalue and the Eigenvector . Here, defines the maximum variation among and expresses the direction of maximum deviation among features. It is expressed as in Equation 13,Moreover, the Equation 13 is rewritten by utilizing the Identity matrix and is equated as in Equations 14, 15,
Step 4Next, for extracting features with reduced dimensions, the features that have lower are selected as the principal components . It is given as in Equation 16,Here, specifies the low of the feature.
Step 5Lastly, to attain maximum data information with reduced dimension, is transformed along the coordinates of . Hence, by using the SPCA method, the features are extracted from with minimum dimension, and it is mentioned as . The pseudo-code for the proposed SPCA technique is given below,
Algorithm 1.
Input: URL structure,
Output: Extracted features,
Begin
Initialize
Standardize using Equation 10
For
Define
Evaluate correlation
If is positive
is correlated
Else
Indirectly correlated
Or
Non-correlated
End if
End for
For extract features
Compute and
If
Select
Transform along
End if
End for
Return
End
Thus, the SPCA effectively extracts the features. Also, it differs from prior PCA variants in phishing detection by better capturing non-linear data structures, enhancing model performance and accuracy in detecting phishing through the preservation of complex, high-dimensional patterns. In the meantime, the contents extracted from and and the textual features of are converted into vector form for the better training of features. The word embedding process for vector conversion using the proposed method is explained further.
3.6 Word embedding
Here,
,
,
, and
are declared as
and are given to the embedding process using EM-BERT for enabling the classifier’s effective learning. The Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) algorithm is utilized for vector conversion, which is trained on a larger corpus and is suitable for well-defined Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. However, the training performance is influenced by random weight generation from the normal distribution of BERT. Thus, to solve this issue, an Entropy Macqueen (EM)-based weight initialization is utilized. This initialization improves the weights by considering the data distribution, leading to faster convergence and better model performance of the BERT algorithm. Hence, EM-BERT becomes more efficient, achieving higher accuracy and better results when fine-tuned for specific tasks. The word embedding process using EM-BERT is described below,
• Primarily, is converted into individual words via tokenization, which splits the text into smaller units and is signified as . This pre-processing step divides the words into meaningful tokens. Thus, the rare and out-of-vocabulary words are handled effectively. Afterwards, by using an embedded matrix , are transformed into high-dimensional vector form. It is given as in Equation 17,
Here,
signifies the vectorized tokens.
• Then, the relationship among words in is specified by calculating the self-attention score for each token. It is defined as in Equation 18,
Here,
is the softmax activation function,
is the query, the key matrix of words with dimension is signified as
, and
is the transpose function.
• Then, the tokens are activated by utilizing along with Euler’s value, and it is expressed as in Equation 19,
Where,
is the Euler’s value,
is the
th element of
,
is the index iterating over all the elements in
, and
depicts the total number of elements in
.
• As the random weight creation from the normal distribution limits the training process, the weights are generated among BERT layers by utilizing the EM technique for improving the model training. The EM-based weight initialization enhances the model’s training by improving the weight distribution, and it is equated as in Equation 20,
Here,
refers to the length of the embedded matrix,
demonstrates the similarity function between
and
, and
represents the logarithmic function. Therefore, by applying the linear transformation
and residual connection
to
, the final output
is obtained. It is signified as in
Equation 21,
• Next, some tokens in are randomly masked to examine the missing words related to the nearby words. Also, the model is trained to predict the masked token by the embedding process. The probability of exactly predicting the masked tokens is expressed as in Equation 22,
Here,
represents masked tokens, and
is the prediction probability.
• Lastly, to enhance the embedding performance, the predicted are fine-tuned based on the pre-trained parameters . It is given as in Equation 23,
Here, is the fine-tuned output of the proposed BERT model.
Hence, the context information of is encoded via the word embedding process by utilizing EM-BERT, and it is signified as . The pseudocode for EM-BERT is demonstrated below.
Algorithm 2.
Input: Combined Inputs from , , , and
Output: Word Embedded Features
Begin
Initialize , , , iteration , maximum iteration
Set
While
For each do
Convert into
Use embedded matrix to obtain
Compute for each # self-attention score.
Activate tokens using with
Evaluate #EM-based weight initialization.
Calculate by applying and to
Mask a few tokens randomly in
Train the model to predict
Compute probability
Fine-tune based on
Perform encoding of
End for
End while
Return
End
Thus, the proposed EM-BERT effectively enhances word embedding by utilizing EM-based weight initialization and capturing rich contextual relationships. Also, the model’s use of entropy-based methods ensures better handling of uncertainty in the data, further refining the detection accuracy and robustness in identifying phishing threats. Therefore, EM-BERT enhances phishing detection by improving BERT’s ability to understand phishing-specific patterns.
3.7 Feature selection
Subsequently, URL features and extracted features from are considered as and are fed as input to the feature selection phase. The Seagull Optimization Algorithm (SOA) is utilized for selecting the optimal features because of its supreme migration and attacking behavior for attaining prey. But, due to the usage of random values for position updation, the SOA suffers from premature convergence issues. For solving this problem, the Cauchy Distribution Function (CDF) is utilized to update the seagull position with less computational time. The CDF enables a better exploration of the search space, leading to a more diverse set of potential solutions and avoiding premature convergence. This allows for a more precise and efficient feature selection process. The processes performed for feature selection by utilizing the proposed CSOA are described below.
3.7.1 Initialization
Initially, the acquired features are inputted to the SOA. Next, , which is assumed to be the population of the Seagull, is initialized. It is given as in Equation 24,
Here, depicts the number of features in .
3.7.2 Fitness function
In this, the maximum classification accuracy is considered as the fitness function to achieve the optimal solution for feature selection. It is given as in Equation 25,
Here, is the fitness function, and is the classification accuracy of features.
3.7.3 Migration behavior
Based on migration and attacking behavior, the exploration capability and exploitation capability of the seagull population are analyzed. The seagull should satisfy three basic rules, such as preventing collisions, moving toward the direction of the best neighbor, and remaining closer to the best search agent for moving from one location to another.
• To prevent collision with neighboring seagulls, the position of the seagull is adjusted using a parameter named , which represents the non-colliding migration behavior of seagulls. It is given as in Equation 26,
Here, is the new location of the seagull, which does not lead to a collision with other seagulls, and is the current location of the seagull at the th iteration. Here, signifies the migration behavior of seagulls, which is determined as in Equation 27,
Here,
is the frequency control of
within
and
is the maximum iteration.
• After fulfilling the non-collision condition, the seagulls move towards the position of the best seagull to search for the prey. It is represented as in Equation 28,
Where, is the position of the optimal seagull, is the current position of the seagull towards the , and is the random value that balances the exploration and exploitation phases, which is given as in Equation 29,
Here, is the random value ranges between . Then, based on the best agent, the position of the seagull is updated to reach the prey location. It is given as in Equation 30,
Here, is the new position of the seagull towards the optimal position.
3.7.4 Attacking behavior
Here, although the attacking angle and speed of seagulls keep on changing during the migration phase, they maintain their altitude through their wings and weight in the air. The seagulls perform attacks in a spiraling manner over the , , and plane in the air. Such attacking behavior is analytically given as in Equation 31–33,
Here, is the radius of spiral turns, and indicate the attacking angles of the seagull, and is the random value within . The spiral region in which the seagulls are involved in attacking is defined as in Equation 34,
Where, , depict the spiral shape and is the logarithm base function. Next, to grab the prey, the seagulls update their position. Nevertheless, updating the position using a random parameter leads to premature convergence and gets trapped in a sub-optimal solution while selecting the optimal solution. Thus, to update the seagulls’ position, CDF is introduced, which adaptively balances exploration and exploitation, thus helping the algorithm escape local optima. The CDF is equated as in Equation 35,
Here, is the location variable, and is the normalizing constant.
3.7.5 Optimal solution
Based on , the position of seagulls is updated to achieve . It is given as in Equation 36,
Here, is the updated position of the seagull. Further, if the updated position satisfies , then is attained for selecting optimal features. Or else, the process is repeated till is attained. Thus, by using the CSOA technique, the optimal features are selected and simply declared as . The pseudo-code for the proposed CSOA is provided below,
Algorithm 3.
Input: Acquired features,
Output: Optimal features,
Begin
Initialize features,
Evaluate fitness using Equation 25
While
Define ,
Adjust seagull position
Migrate towards
If
Update position,
Else
Original position,
Perform attack in
For
Evaluate using Equation 35
Update position
End for
End if
End while
Return
End
Furthermore, to recognize the phishing and legitimate data, the selected features are forwarded to the proposed classifier, and such a classification process is described in the further section.
3.8 Data classification
Then, to detect phishing and legitimate URL data, the selected features and word-embedded features are inputted into the classifier. It is given as in Equation 37,
Here, is the classifier input. In this, for training the features, the LSTM model is used owing to its ability to learn complex features and incorporate large volumes of data. But, LSTM suffers from a vanishing gradient issue while the gradients are repeatedly processed through recurrent connections. Hence, to overcome the aforementioned issue, a SERF CoLU (SC) activation function is used in the gating mechanism of LSTM. The SC function ensures that the gradient flow is maintained, preventing it from vanishing. Thus, the learning efficiency of the model is enhanced. Explainable AI (EAI) of the proposed LSTM refers to the process of making Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems more understandable and transparent to human users. This transparency allows users to interpret the model’s decision-making process and trust the results. By providing clear reasoning, EAI helps in identifying potential biases and improving the reliability of the model. Figure 2 exhibits the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM model for data classification.
FIGURE 2
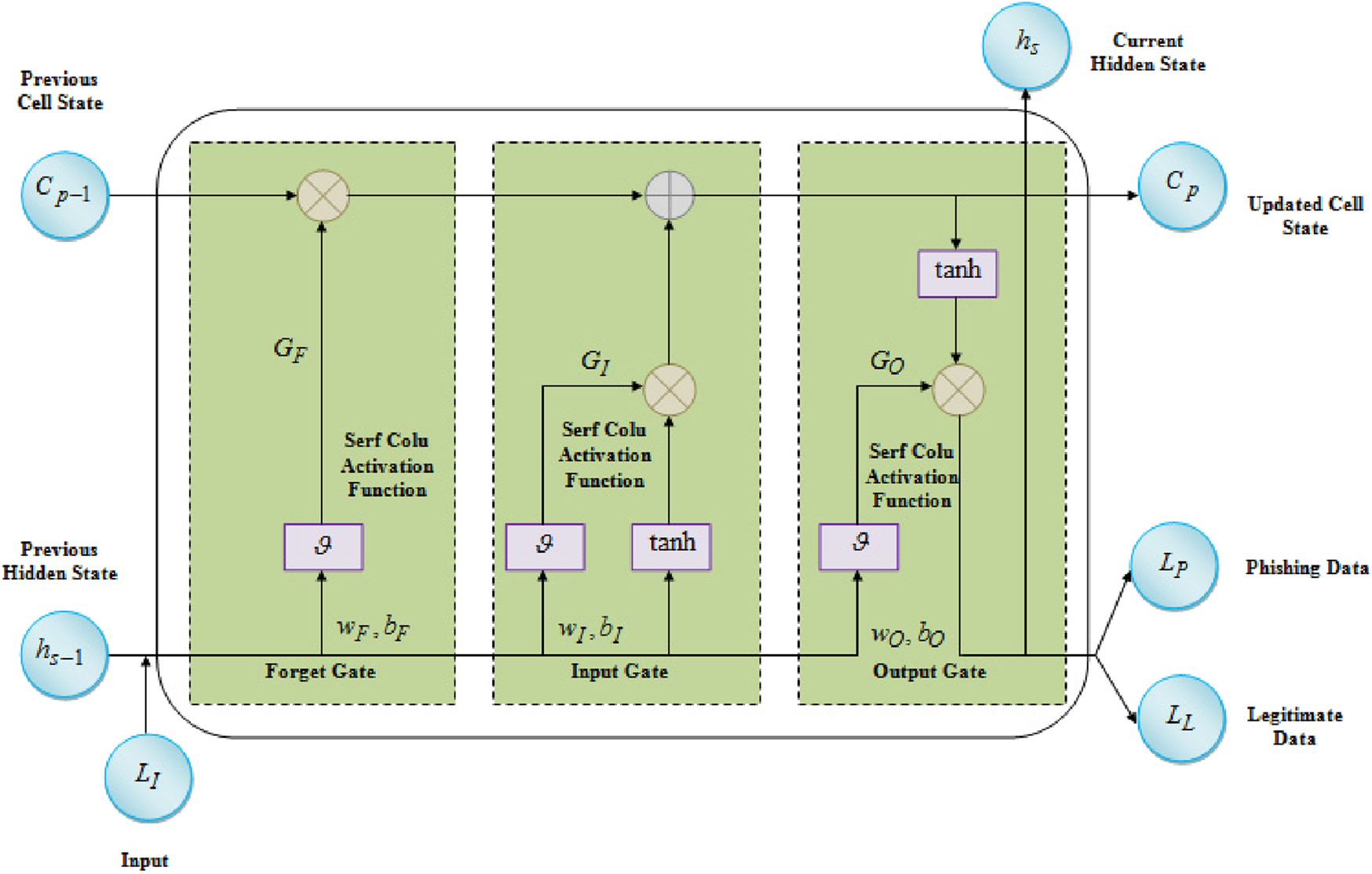
Architecture of proposed EAI-SC-LSTM network.
The is processed via three gates, namely, the forget gate , input gate , and output gate of the proposed classifier. The detection of phishing URLs using EAI-SC-LSTM is explained below,
3.8.1 Forget gate
Primarily, is integrated with the previous cell state , which acts as a memory unit and retains the network information. The information to be stored or neglected from the network is declared through the SC activation function. This allows the network to selectively “forget” unnecessary information, optimizing learning and memory flow. This selective forgetting helps prevent the network from overfitting irrelevant data, thus improving the model’s ability to generalize. Therefore, the forget gate is defined as in Equation 38,
Here, is the SC activation function, is the previous hidden state, and and are the weights and biases of , respectively. Here, is established by replacing the sigmoid function to suppress the gradient vanishing problem. It is given as in Equation 39,
Here, is the error function and is the natural logarithm operation. Thus, enhances the gate’s ability to filter out irrelevant information, improving model accuracy. By focusing on important patterns and information, the model becomes more efficient and trains faster. This results in better generalization, allowing the model to perform well on unseen data.
3.8.2 Input gate
Subsequently, the input gate determines the information to be reserved in the cell state . The output of , which is activated with , is defined as in Equation 40,
Then, to store the information, the candidate vector of is generated by the hyperbolic tangent function . It is determined as in Equation 41,
Here, and are the weights and biases of , correspondingly.
3.8.3 Cell state update
Next, the cell state is updated into a new cell state to regulate the essential information over time. It is updated by the scaling of with and forget gate with . The cell state updation is given as in Equation 42,
3.8.4 Output gate
In this, the phishing and legitimate data are predicted by passing the information through the proposed and . IIt is expressed as in Equation 43,
Here, and are the biases and weights of , correspondingly. Next, is scaled with a function to upgrade the current hidden state . Hence, it is expressed as in Equation 44,
In the meantime, Explainable AI (EAI) is utilized to interpret phishing detection and make the predicted outcome more transparent and understandable by human users. Thus, it is embedded with the predicted outcome of the proposed network, and it is given as in Equation 45,
Where, is the classifier outcome, and is the EAI scaled with the current . The complex learning of the network can be executed with relevant decision-making by using the EAI, which fulfills the user requirement. Thus, by using the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM model, the phishing data and legitimate data are detected and classified with more accurate interpretability.
3.9 User alert
After classifying and , the is updated to the blacklist for future reference. If any new URL enters the system, then the respective URL is checked inside the blacklist. A URL is reported to the user if it is already present in the blacklist. Or else, the new URL is processed by the proposed framework to detect the legitimacy of the URL.
4 Results and discussions
This section discusses the experimental outcome of the proposed work with respect to different metrics by comparing it with the prevailing approaches. To analyze the performance, the proposed technique is implemented in the PYTHON platform, which emphasizes code readability and possesses robust integration of the system. The hyperparameters used in the proposed classifier are depicted in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| Hyperparameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Hidden Size | 128 |
| Number of Layers | 3 |
| Batch Size | 128 |
| Dropout | 0.2 |
| Learning Rate | 0.001 |
| Epochs | 100 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Activation Function | SERF CoLU |
Hyperparameters of the proposed classifier.
The above Table 1 shows the hyperparameters of the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM classifier that are used in the proposed framework.
4.1 Dataset description
By using the “SMS Smishing Collection (SSC) Dataset”, “Phishing Email Curated (PEC) Dataset”, and “Webpage Phishing Detection (WPD) Dataset”, the performance of the proposed method is evaluated.
Table 2 depicts the dataset details utilized for training and testing the proposed model. The SSC dataset contains a total of 9654 messages after augmentation, consisting of 4827 normal SMS and 4827 smished SMS in the English language with URLs. The Zenodo open repository publishes the PEC dataset that comprises 9654 features, including 3,600 normal emails and 3,600 smished emails. Further, the WPD dataset includes 11,430 URL data with balanced phishing and legitimate data. From each dataset, 80% and 20% of data are used for training and testing the proposed model, correspondingly. The utilized dataset links to examine the proposed model are given below the reference list.
TABLE 2
| SSC dataset | PEC dataset | WPD dataset | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data | Original data | Augmented data | Training | Testing | Original data | Augmented data | Training | Testing | Original data | Training | Testing |
| Normal data | 4827 | 4827 | 3,861 | 966 | 3,600 | 3,600 | 2,880 | 720 | 5,715 | 4572 | 1,143 |
| Attacked data | 747 | 4827 | 3,861 | 966 | 2,209 | 3,600 | 2,880 | 720 | 5,715 | 4572 | 1,143 |
| Total data | 5,574 | 9654 | 7,722 | 1932 | 5,809 | 7,200 | 5,760 | 1,440 | 11,430 | 9144 | 2,286 |
Dataset description.
Table 3 describes the dataset features used in the proposed work. These features are utilized for training purposes regarding phishing attack detection.
TABLE 3
| Datasets | Features’ name | Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
| SSC | Message | The SMS text message content |
| Label | Classification of the message to be ham for legitimate data and spam for phishing data | |
| PEC | sender | The email address of the sender |
| receiver | The email address of the recipient | |
| subject | The subject line of the email | |
| body | The main content of the email | |
| label | The email is to be a legitimate class or a phishing class | |
| url | Other emails present in the main body of the email | |
| WPD | URL | Web address |
| length_url | The total number of characters in the URL. | |
| length_hostname | The number of characters present in the hostname of the URL. | |
| ip | Indicates the presence of the Internet Protocol (IP) address instead of the domain name | |
| nb_dots | The count of dot characters in the URL. | |
| http_in_path | Indicates the presence of HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) in the URL path | |
| port | Indicates the specification of the port number in the URL. | |
| abnormal_subdomain | Indication of the subdomain structure to be abnormal or excessively long | |
| phish_hints | It shows the webpage content with certain keywords, which are already associated with phishing attempts | |
| domain_age | Calculates the age of the domain | |
| web_traffic | Assessment of the web traffic ranking of each site | |
| dns_record | Checking the availability and validity of the Domain Name System (DNS) record | |
| google_index | Verification of the webpage to be indexed by Google | |
| page_rank | The rank of the webpage, which reflects the credibility of the site | |
| Status | Target variable that indicates the webpage to be phishing or legitimate |
Dataset feature description.
In Table 4, the parameters used for the analysis are given. Based on True Positive (TP), False Negative (FN), True Negative (TN), False Positive (FP), end time, and start time, the parameters utilized for the investigation of the proposed work are evaluated.
TABLE 4
| Parameters | Formulae |
|---|---|
| Recall | |
| Precision | |
| F-measure | |
| Accuracy | |
| Specificity | |
| Sensitivity | |
| TPR | |
| TNR | |
| FPR | |
| FNR | |
| PPV | |
| NPV | |
| Training Time | |
| Feature Selection Time |
Parameters formulae.
4.2 Performance assessment
The performance of the proposed method is evaluated and compared with existing approaches. The following results demonstrate its improved efficiency in phishing attack detection and mitigation.
4.2.1 Performance analysis of EAI-SC-LSTM
Initially, to detect phishing data, the performance of the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM classifier is examined by comparing it with the prevailing classifiers, namely, LSTM, Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), CNN, and DNN using the SSC Dataset, PEC Dataset, and the WPD Dataset.
4.2.1.1 Analysis with SSC dataset
The performance analysis of the proposed and existing classifiers is conducted using the SSC dataset as presented below,
In Figure 3, the performance comparison of EAI-SC-LSTM and the existing models regarding accuracy, precision, recall, f-measure, and Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) is estimated for the SSC dataset. Figure 3 displays that the proposed network attains 99.627% accuracy, 99.895% precision, 99.784% recall, 99.562% f-measure, and 99.564% MCC. This is because of tackling the gradient vanishing issue and enhancing the learning capability by utilizing the SERF CoLU activation function in the proposed classifier. Meanwhile, the prevailing networks, namely, LSTM, RNN, DNN, and CNN achieve average values of 95.332% accuracy, 95.562% recall, 97.043% precision, 96.025% f-measure, and 95.404% MCC, respectively, which are lower than the proposed approach. Hence, when compared to the traditional networks, the proposed model detects phishing data with enhanced performance.
FIGURE 3
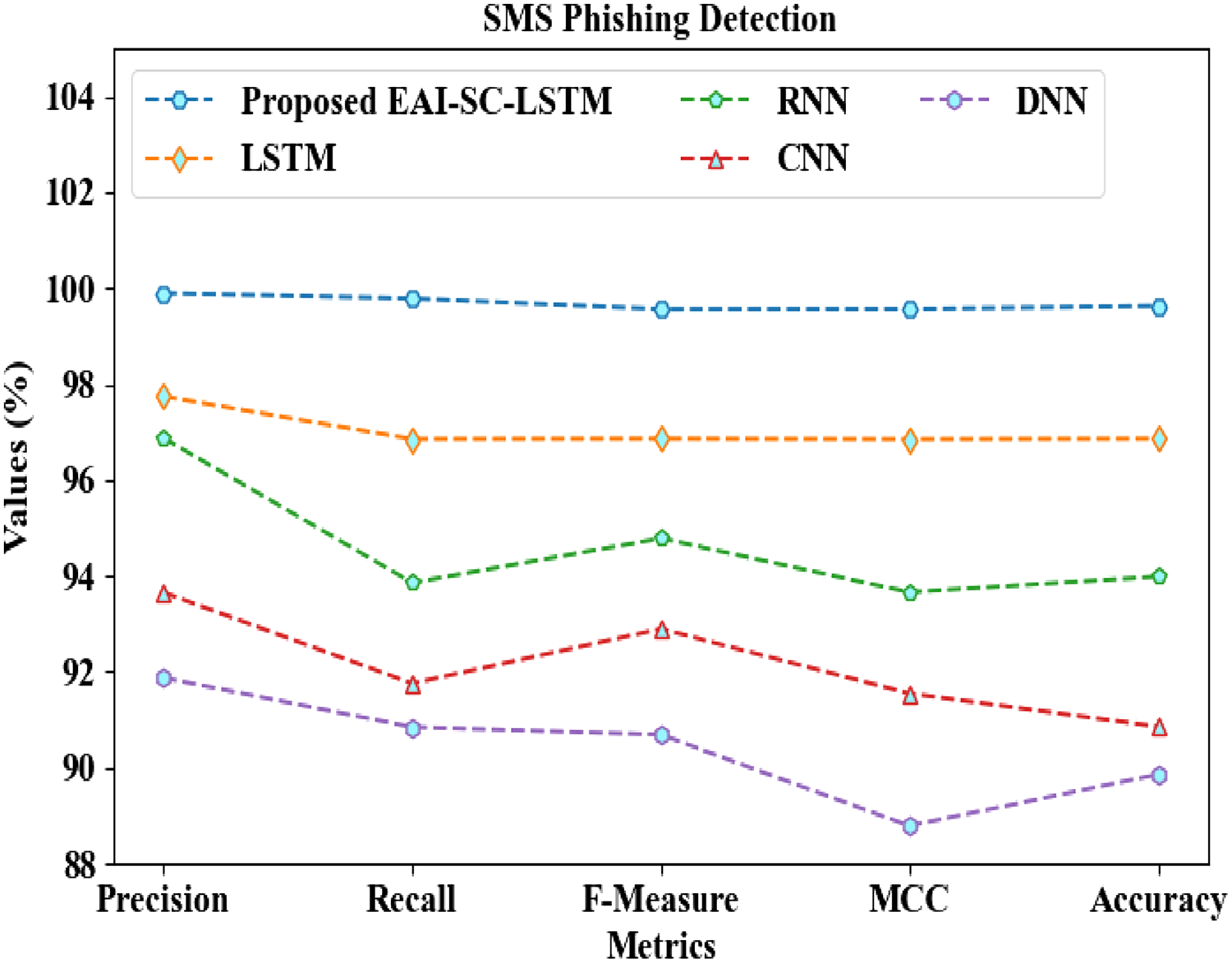
Graphical analysis of EAI-SC-LSTM.
Table 5 illustrates the training time performance of the proposed and existing techniques on the SSC dataset. The Proposed EAI-SC-LSTM attained the lowest training time of 34692 ms, followed by LSTM at 40158 ms, RNN and CNN both at 44127 ms and 50236 ms, respectively, and DNN with the highest at 50236 ms, confirming the model’s efficiency in training duration.
TABLE 5
| Techniques | Training time (ms) |
|---|---|
| Proposed EAI-SC-LSTM | 34692 |
| LSTM | 40158 |
| RNN | 44127 |
| CNN | 50236 |
| DNN | 44127 |
Analysis of Proposed EAI-SC-LSTM and Existing Techniques in SSC Dataset based on Training Time.
As shown in Figure 4, the Area Under Curve (AUC) comparison for SMS phishing detection demonstrates that the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM model achieves the highest performance with an AUC of 0.99. It outperforms traditional models, such as LSTM (0.96), RNN (0.94), CNN (0.90), and DNN (0.89), highlighting its superior capability in distinguishing phishing messages with high true positive rates.
FIGURE 4
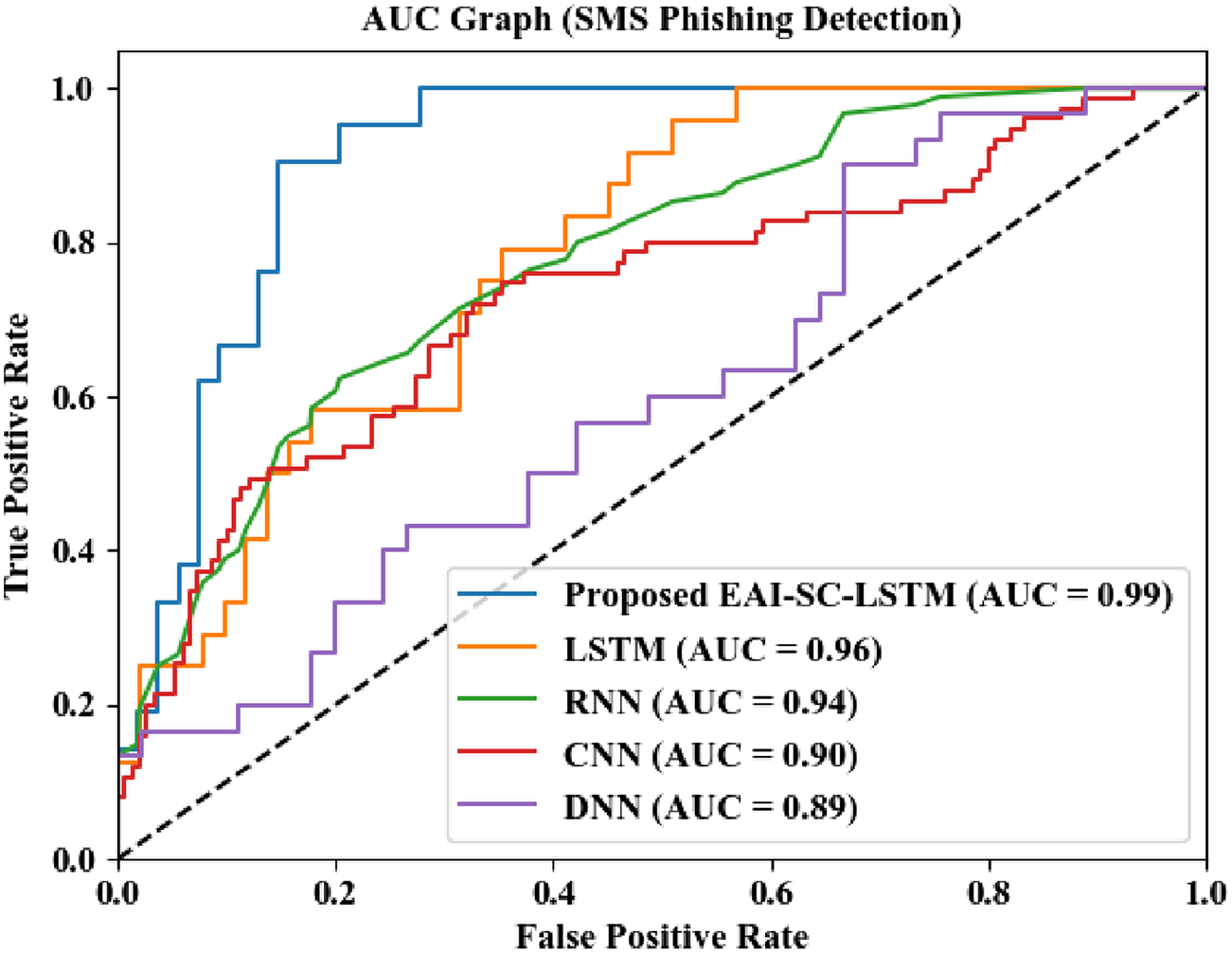
AUC graph analysis for the SMS phishing detection.
Figure 5 represents a shape often seen in data visualization, symbolizing cycles or flow. In the SPCA Variance Graph for SMS Phishing Detection, individual variance (blue line) starts high but declines, while cumulative variance (orange line) increases, reaching 1.0 by the 4th principal component. This shows how SPCA reduces dimensions while preserving crucial data for detecting phishing patterns efficiently.
FIGURE 5
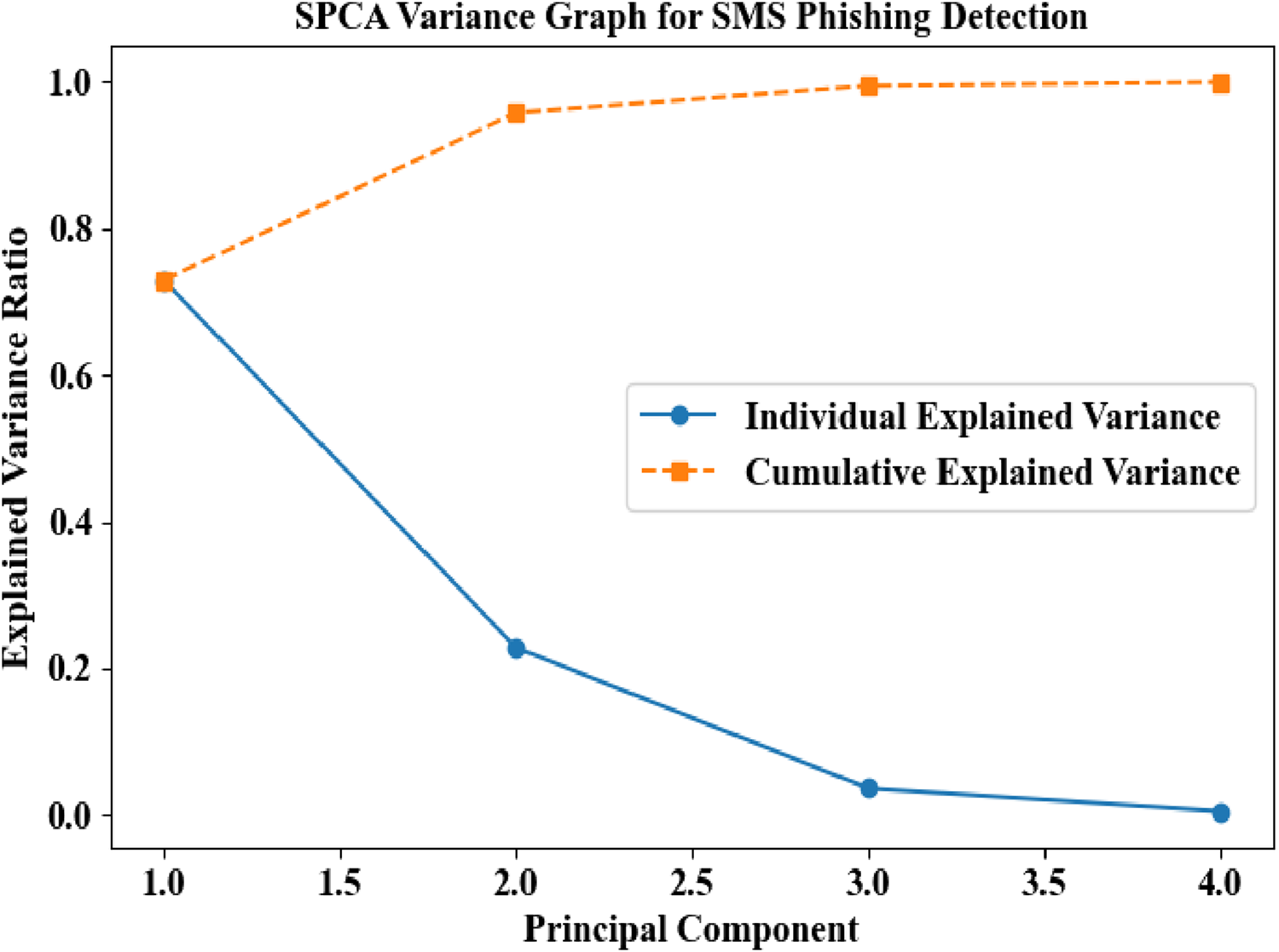
Variance graph analysis for the proposed SPCA in SMS phishing detection.
4.2.1.2 Analysis with PEC dataset
The performance of both the proposed and existing classifiers is evaluated using the PEC dataset, which is detailed below.
In Figure 6, the assessment of the proposed classifier on the PEC dataset is presented, showcasing its performance regarding Positive Predictive Value (PPV), Negative Predictive Value (NPV), sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for classifying phishing and legitimate data. By minimizing the gradient explosion problem via the introduced SERF CoLU activation function, the proposed model learns the complex data features. Figure 6 shows that the EAI-SC-LSTM attains 99.652% PPV, 99.326% NPV, 99.874% sensitivity, 99.857% specificity, and 99.645% accuracy, which are higher than the prevailing networks. Simultaneously, the existing networks like RNN achieve 96.857% PPV and 93.845% accuracy, CNN obtains 87.847% NPV and 91.689% sensitivity, and DNN attains 91.987% PPV and 88.9655 specificity. Hence, it is verified that when compared to other conventional techniques, the proposed classifier provides increased performance.
FIGURE 6
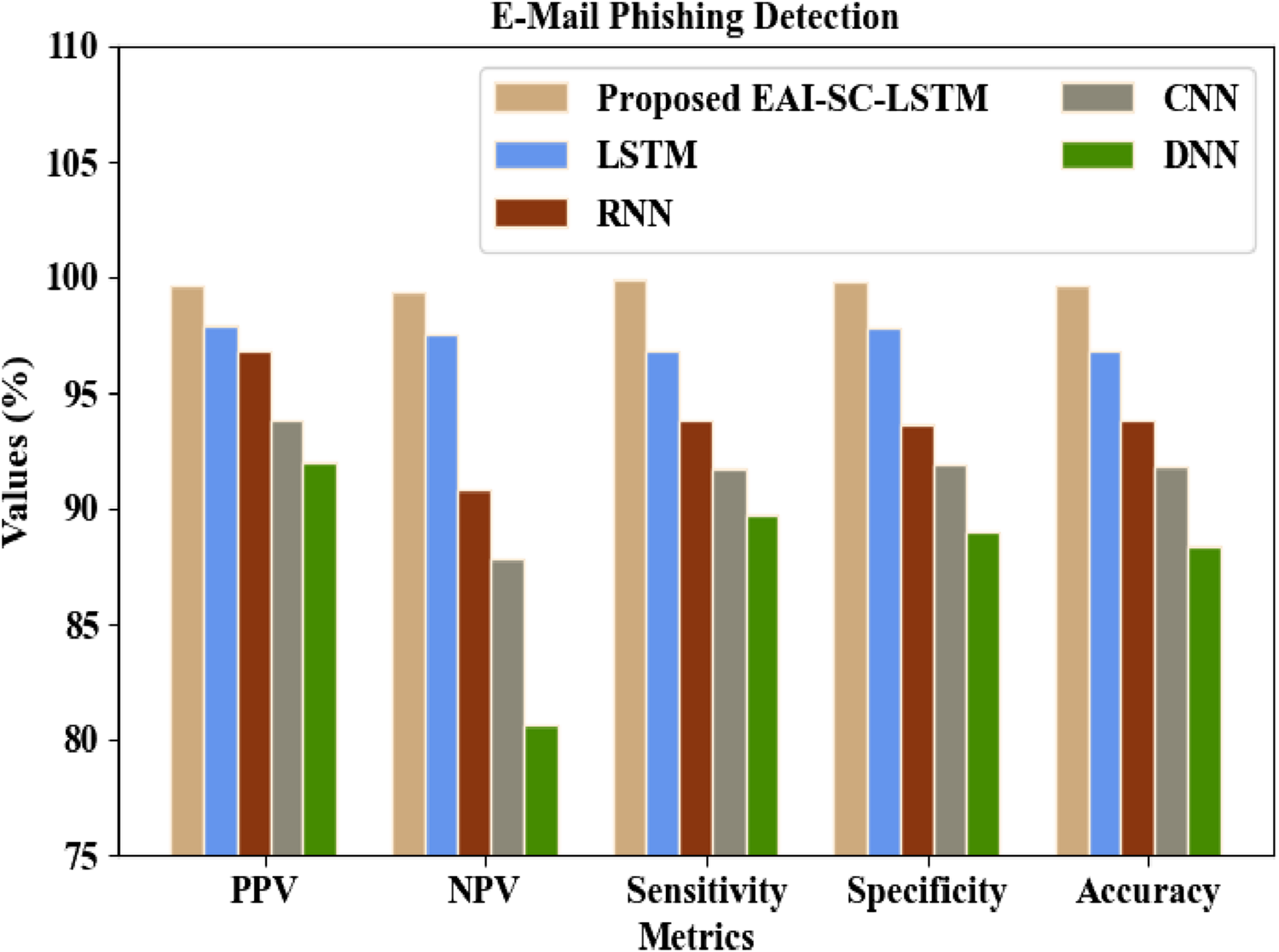
Performance assessment of the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM and existing techniques for detecting the phishing attacks.
Table 6 upresents the training time analysis of the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM on the PEC dataset. The Proposed EAI-SC-LSTM achieved the lowest training time of 24417 ms, outperforming LSTM (30265 ms), RNN (35265 ms), CNN (40157 ms), and DNN (44784 ms). This reduction is due to the use of the efficient SERF-CoLU activation function, which accelerates convergence in the proposed classifier.
TABLE 6
| Techniques | Training time (ms) |
|---|---|
| Proposed EAI-SC-LSTM | 24417 |
| LSTM | 30265 |
| RNN | 35265 |
| CNN | 40157 |
| DNN | 44784 |
Training time analysis for the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM and existing techniques in the PEC dataset.
As depicted in Figure 7, for E-Mail phishing detection, the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM model attains the highest AUC value of 0.99, indicating excellent classification ability. In comparison, LSTM attained an AUC of 0.96, RNN at 0.93, CNN at 0.91, and DNN at 0.88, showing that the proposed method significantly improves detection performance over conventional approaches.
FIGURE 7
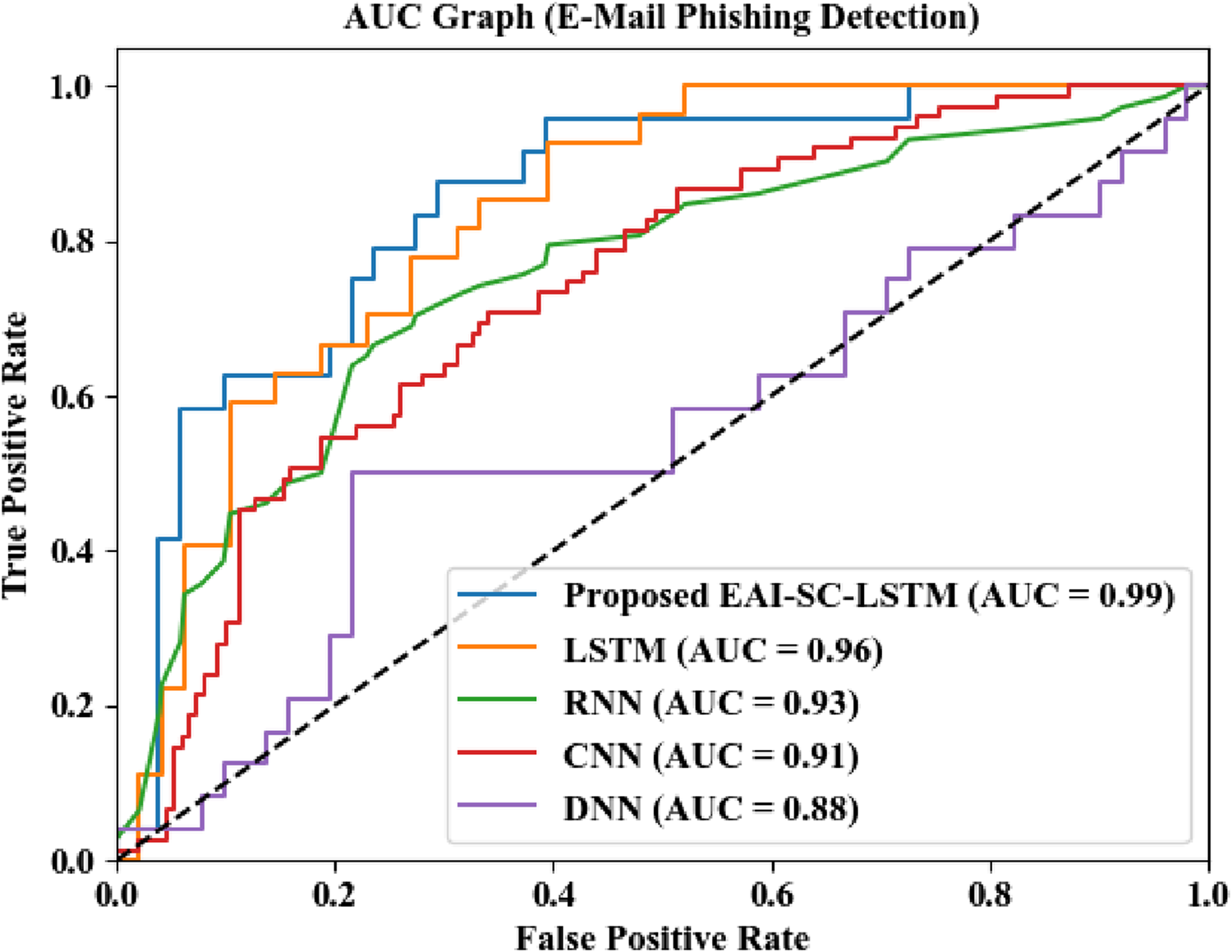
Graphical analysis of AUC for the PEC dataset.
Figure 8 represents a graph that helps analyze variance in data. In the SPCA Variance Graph for E-Mail Phishing Detection, individual variance is highest for the first principal component and gradually decreases, while cumulative variance rises steadily, approaching 1.0 by nearly the 14th principal component. This demonstrates how SPCA effectively reduces dimensions while retaining key information for accurate phishing detection.
FIGURE 8
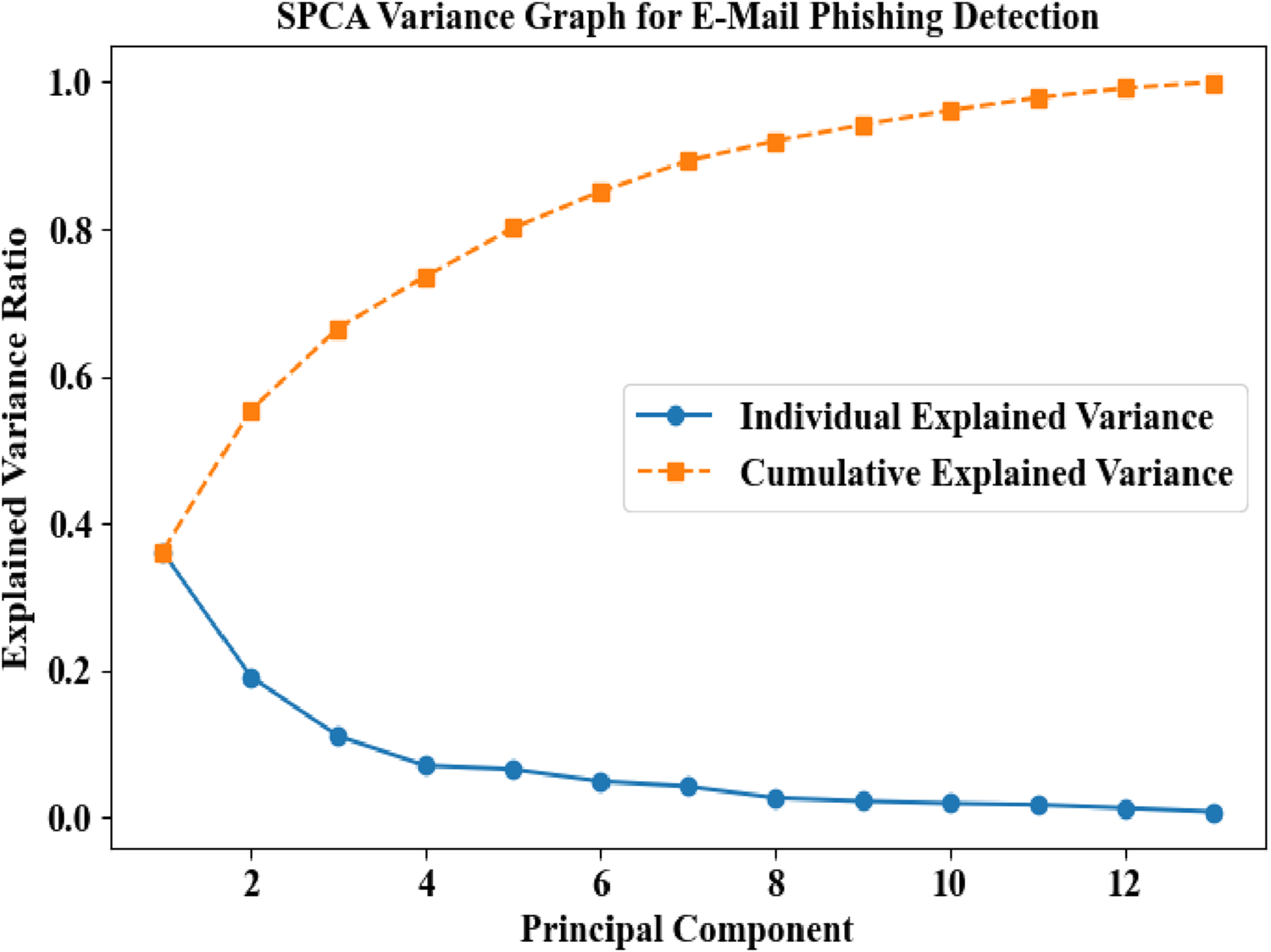
Variance graph analysis for the proposed SPCA in E-mails phishing detection.
4.2.1.3 Analysis with WPD dataset
An evaluation of the proposed and existing classifiers is conducted using the WPD dataset, as outlined below.
Regarding accuracy, True Positive Rate (TPR), True Negative Rate (TNR), False Positive Rate (FPR), and False Negative Rate (FNR), the performance of EAI-SC-LSTM is analyzed for the WPD dataset, which is displayed in Table 7. The proposed approach achieves 99.541% accuracy, 99.865% TPR, 99.562% TNR, 0.587% FPR, and 0.635% FNR. Meanwhile, the prevailing techniques attain an average accuracy, TNR, TPR, FPR, and FNR of 96.156%, 95.903%, 95.055%, 5.616%, and 5.387%, correspondingly, which are better than the proposed technique. Since various features, including user behavior, are analyzed and embedded prior to classification, the EAI-SC-LSTM detects phishing data with better performance than the prevailing approaches.
TABLE 7
| Methods | TPR(%) | TNR(%) | Accuracy (%) | FPR(%) | FNR(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed EAI-SC-LSTM | 99.8653 | 99.5621 | 99.5412 | 0.5874 | 0.6359 |
| LSTM | 96.8574 | 97.8451 | 97.8457 | 3.6574 | 3.5241 |
| RNN | 93.6524 | 93.6589 | 94.6532 | 7.6358 | 7.1254 |
| CNN | 91.8451 | 92.5478 | 92.5847 | 10.5847 | 10.2658 |
| DNN | 89.8475 | 87.6532 | 89.6523 | 16.3256 | 12.6598 |
Performance analysis of TPR, TNR, accuracy, FPR, and FNR for the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM and the existing techniques.
Figure 9 analyzes the AUC measure of the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM and the prevailing networks. The capability of the network is determined by the AUC to accurately categorize the phishing and legitimate data. Figure 9 displays that the proposed network attains a higher AUC value (0.99) than the prevailing networks. The existing networks like LSTM, RNN, CNN, and DNN attain lower AUC measures of 0.97, 0.94, 0.92, and 0.89, respectively. Since different features that comprise user behavior, contents, Javascript, and URL structures are analyzed for training the classifier, the proposed model more accurately detects the legitimate and phishing classes than the prevalent networks.
FIGURE 9
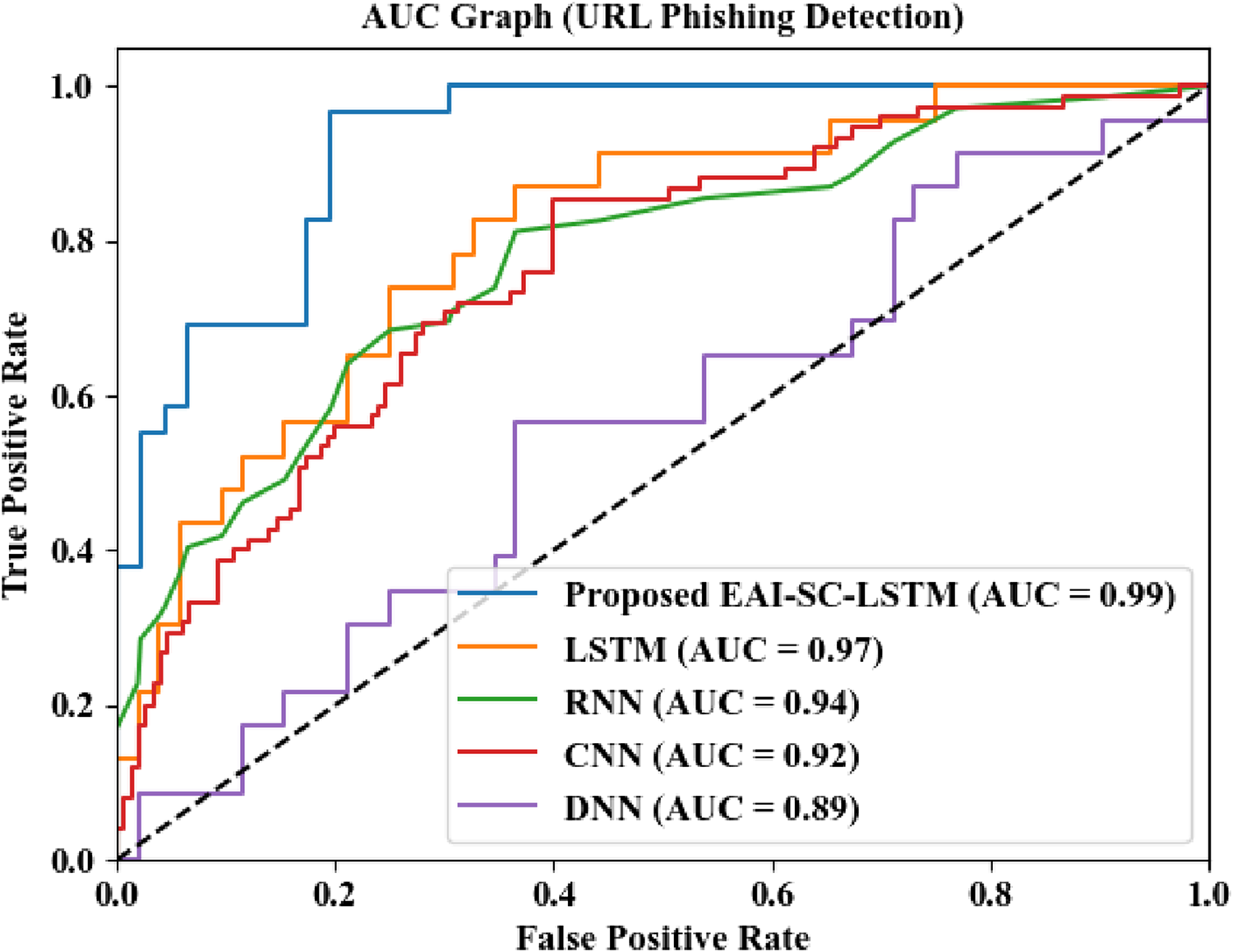
AUC analysis of the proposed classifier for the WPD dataset.
In Table 8, the supremacy of the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM model regarding training time for phishing detection is depicted. Table 8 exhibits that the proposed model takes a lesser duration (38965 ms) for training. However, the prevailing approaches, namely, LSTM, RNN, CNN, and DNN take 45712 ms, 50698 ms, 55847 ms, and 60254 ms for training, respectively. Thus, they consume more time than the proposed classifier. As the optimal features are chosen centered on maximum accuracy before training the model, they help in faster training of the classifier. Therefore, the proposed model attains enhanced performance than other existing methods.
TABLE 8
| Techniques | Training time (ms) |
|---|---|
| Proposed EAI-SC-LSTM | 38965 |
| LSTM | 45712 |
| RNN | 50698 |
| CNN | 55847 |
| DNN | 60254 |
Analysis of the Proposed EAI-SC-LSTM and the Existing Techniques in terms of Training Time.
Figure 10 represents a graph that visualizes variance distribution in data. In the SPCA Variance Graph for URL Phishing Detection, individual variance (blue circles) decreases across principal components, while cumulative variance (orange squares) steadily rises, approaching 1.0 by the 10th component. This highlights how SPCA efficiently reduces dimensions and maintains critical information for detecting phishing threats.
FIGURE 10
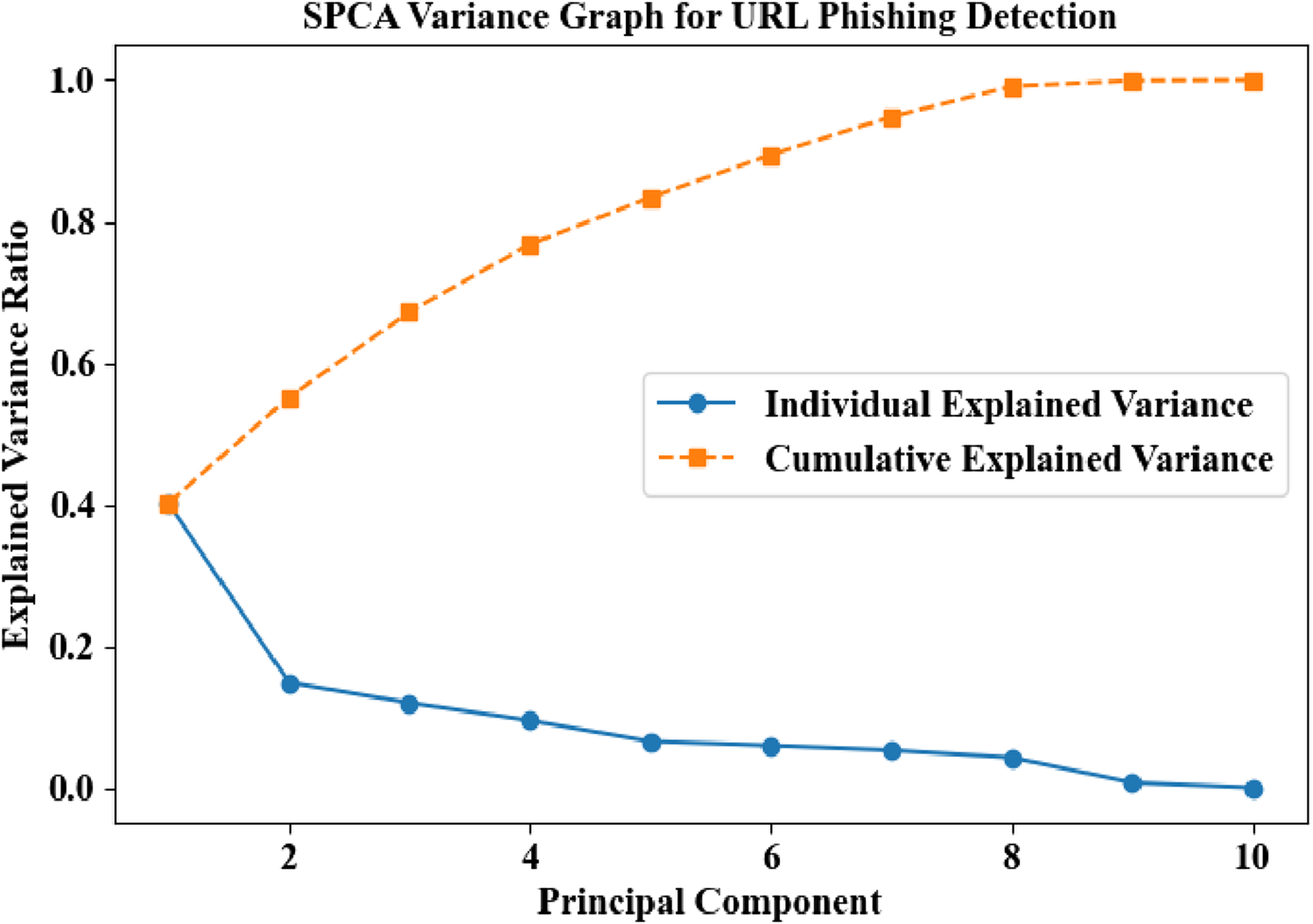
Variance graph analysis for the proposed SPCA in url phishing detection.
4.2.2 Performance evaluation of CSOA
The performance of the proposed CSOA is evaluated with existing approaches for feature selection.
Table 9 evaluates the performance of CSOA in selecting the important features with respect to the feature selection time. The performance of CSOA is examined by comparing it with other algorithms, namely, SOA, Fish Swarm Optimization Algorithm (FSOA), Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA), and Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm (PSOA). It is observed that the proposed CSOA chooses optimal features within 3625 ms for 10 iterations and 12874 ms for 40 iterations, which are lesser than the prevailing algorithms. In the meantime, the prevailing FSOA takes 11784 ms, WOA consumes 15639 ms, and PSOA takes 19865 ms for 10 iterations. Moreover, during feature selection, the prevailing FSOA and WOA take 20685 ms and 24865 ms for 40 iterations, correspondingly. The proposed algorithm takes minimal time to choose the optimal features since the premature convergence problem of SOA is resolved by updating the seagull position using CDF. Hence, when compared to other traditional algorithms, the proposed CSOA attains enhanced performance.
TABLE 9
| No. of<Iterations | Feature selection time (ms) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed CSOA | SOA | FSOA | WOA | PSOA | |
| 10 | 3625 | 7856 | 11784 | 15639 | 19865 |
| 20 | 6985 | 10856 | 14785 | 18759 | 22874 |
| 30 | 9874 | 13965 | 17685 | 21874 | 25847 |
| 40 | 12874 | 16885 | 20685 | 24865 | 28695 |
| 50 | 15698 | 19865 | 23784 | 27846 | 31698 |
Performance evaluation of proposed CSOA.
4.3 Comparative analysis with related works
Based on accuracy, precision, and recall, the proposed phishing detection framework is compared with some existing works for validating the enhanced performance.
Table 10 displays the comparison of the performance of phishing detection using the proposed technique and other related works. It is found that the proposed model achieves accuracies of 99.625% on the SSC dataset, 99.645% on the PEC dataset, and 99.541% on the WPD dataset. Also, the SSC dataset attains a precision of 99.895% and an F-measure of 99.541%, demonstrating high overall performance. In the meantime, the prevailing approaches, namely, RF achieves 98.90% accuracy, Functional Tree-based Meta-Learning (FTML) attains 98.50% f-measure, LSTM-CNN obtains 98.02% precision, Multistage Detection based on Different Features (MDDF) achieves 96.59% f-measure, ML algorithms attain 96.30% accuracy, AntiPhishStack-LSTM model achieved 98.01 precision, Decision Tree and Random Forest (DT+RF) achieved 97.44 accuracy, and Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) obtained 98.8 f-measure. These prevailing works don’t examine the multiple data sources as well as the user behavior for phishing detection. However, the proposed work considers user behavior and Java script features of various data sources for phishing detection. Also, the proposed model included the integration of SMS, email, and URL data. Further, in the proposed system, the phishing attack was detected with transparency and interpretability. Hence, when compared to the prevailing works, the proposed system attains enhanced performance regarding phishing attack detection.
TABLE 10
| References | Techniques used | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | F-measure (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed | EAI-SC-LSTM | 99.625-SSC, 99.645-PEC, and 99.541-WPD Dataset. | 99.895-SSC Dataset. | 99.541-SSC Dataset. |
| Kara et al. (2022) | RF classifier | 98.90 | - | - |
| Balogun et al. (2021) | FTML | 98.51 | - | 98.50 |
| Al-Ahmadi et al. (2022) | LSTM-CNN | 97.58 | 98.02 | 97.64 |
| Liu et al. (2021) | MDDF | - | 98.92 | 96.59 |
| Akour et al. (2021) | ML algorithms | 96.30 | 96.20 | 96.30 |
| Aslam et al. (2024) | AntiPhishStack-LSTM | 96.04 | 98.01 | 95.91 |
| van Geest et al. (2024) | DT+RF | 97.44 | - | 96.56 |
| Alsubaei et al. (2024) | GRU | 98 | 97.8 | 98.8 |
Comparative analysis.
4.4 Comparative analysis with dataset
The comparison of similar studies regarding phishing attack detection with the dataset used in the proposed work is shown in Table 11.
TABLE 11
| Studies | Datasets | Methods | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F-measure (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed Work | SSC, PEC, and WPD | EAI-SC-LSTM | 99.625-SSC, 99.645-PEC, and 99.541-WPD Dataset. | 99.895-SSC Dataset. | 99.541-SSC Dataset. | 99.562-SSC Dataset. |
| Mehmood et al. (2024) | SSC | LSTM | 98.58 | 96 | 95 | 96 |
| Champa et al. (2024b) | PEC | ADB | 98.25 | 98.23 | 98.25 | 98.24 |
| Champa et al. (2024a) | PEC | XGB | 98.95 | 98.96 | 98.95 | 98.93 |
| Rashid and Abdullah (2023) | WPD | XGB | 96.413 | 97.086 | 96.44 | 95.802 |
| Shafin (2024) | WPD | XGB | 96.8 | 97 | 97 | 97 |
Dataset based Comparison.
As shown in Table 11, the proposed model achieves high accuracy across datasets like 99.625% (SSC), 99.645% (PEC), and 99.541% (WPD) with an F-measure of 99.562% on the SSC dataset, confirming its effective phishing detection. This is because of the utilization of selected features, SC activation function, and EAI technique. However, the existing studies that use a similar dataset with classifier models like LSTM, AdaBoost (ADB), and eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGB) show poor performance than the proposed system. The traditional techniques fail to analyze the important features or depend on one source, leading to lower accuracy, precision, recall, and F-measure. Thus, the proposed research work effectively detects the phishing attacks than the prevailing studies.
4.5 Computational Complexity Analysis
The time spent for the purpose of phishing attack detection is analyzed and depicted in Figure 11. Mostly, the Big O notation is used to describe the time complexity of the proposed model and the prevailing models regarding the performance characteristics while dealing with the input data.
FIGURE 11
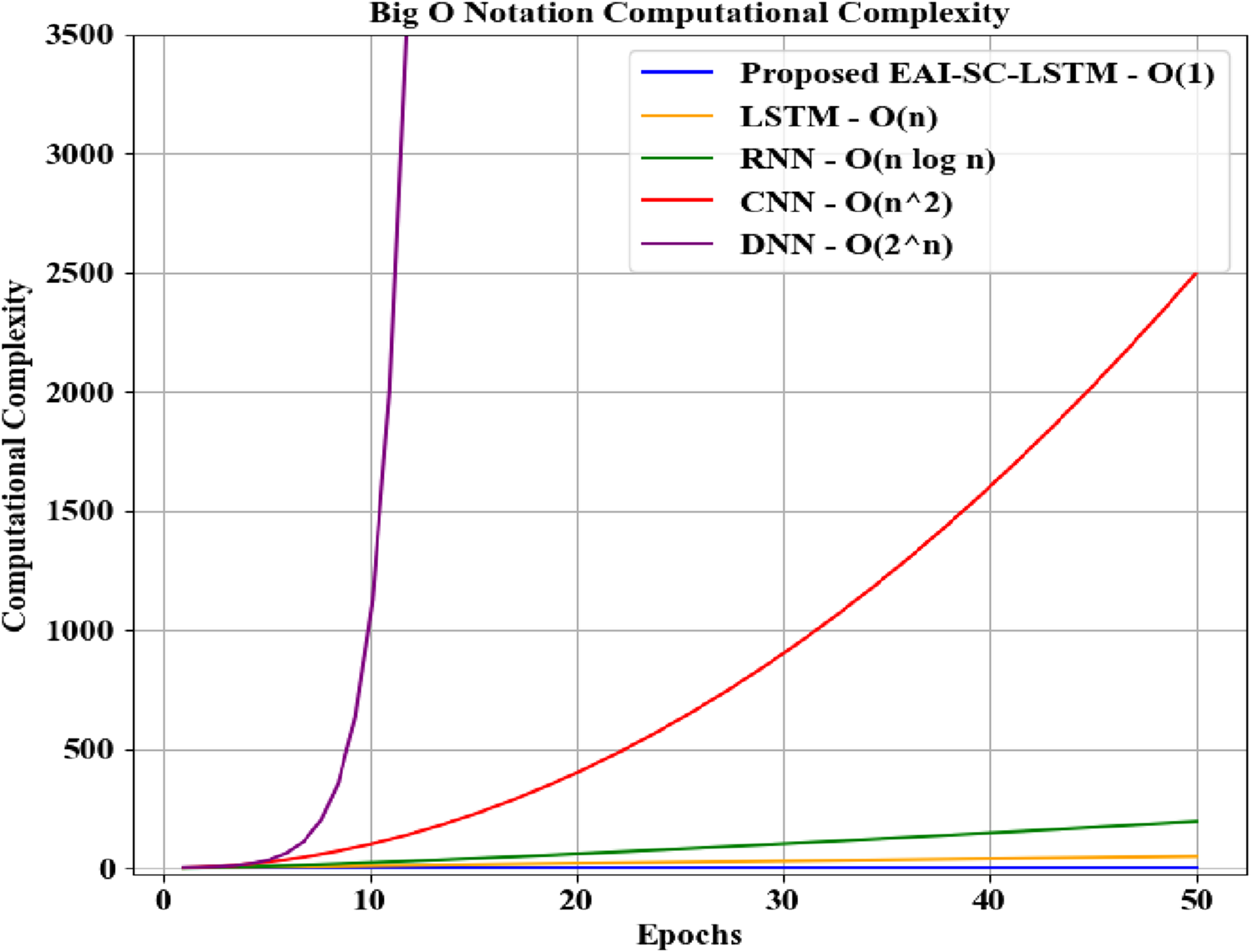
Computational complexity analysis of EAI-SC-LSTM.
As the SC activation function and the EAI are used by the proposed classifier, effective phishing attack detection in the multimodal data is done, thus avoiding the vanishing gradient problem. Hence, the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM classifier achieves a Big O notation of O(1), which shows that phishing attack detection is effective and quick. But, the existing LSTM attains O(n), the RNN achieves O(n log n), the CNN obtains O(n^2), and the DNN achieves O(2^n) Big O notation during phishing attack prediction. This proves that the runtime of the proposed classifier is lower than the existing classifiers. Hence, the usage of SC and the EAI technique in the proposed work does not produce computational complexity.
4.6 Discussion
As per the performance assessment of the proposed model, the phishing attacks in the multiple data sources were analyzed precisely. The features of the input data were converted to vector form using EM-BERT. Then, the important features were selected using CSOA, which attained a feature selection time of 3625 ms for 10 iterations and 15698 ms for 50 iterations. With the help of the extracted feature and the vector form data, the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM classified the phishing attack with an accuracy of 99.645% (PEC) and a precision of 99.895% (SSC). However, the existing models, as mentioned in the performance assessment, could not attain more effective results than the proposed models. Also, in the comparison of the proposed work and the prevailing works regarding phishing attack detection, the proposed work attained better results. Hence, the proposed work played an effective role in phishing attack detection for multiple data sources.
4.7 T-test analysis
The T-test analysis of the dataset distribution for the proposed framework that addresses the statistical significance is illustrated in Figure 12.
FIGURE 12
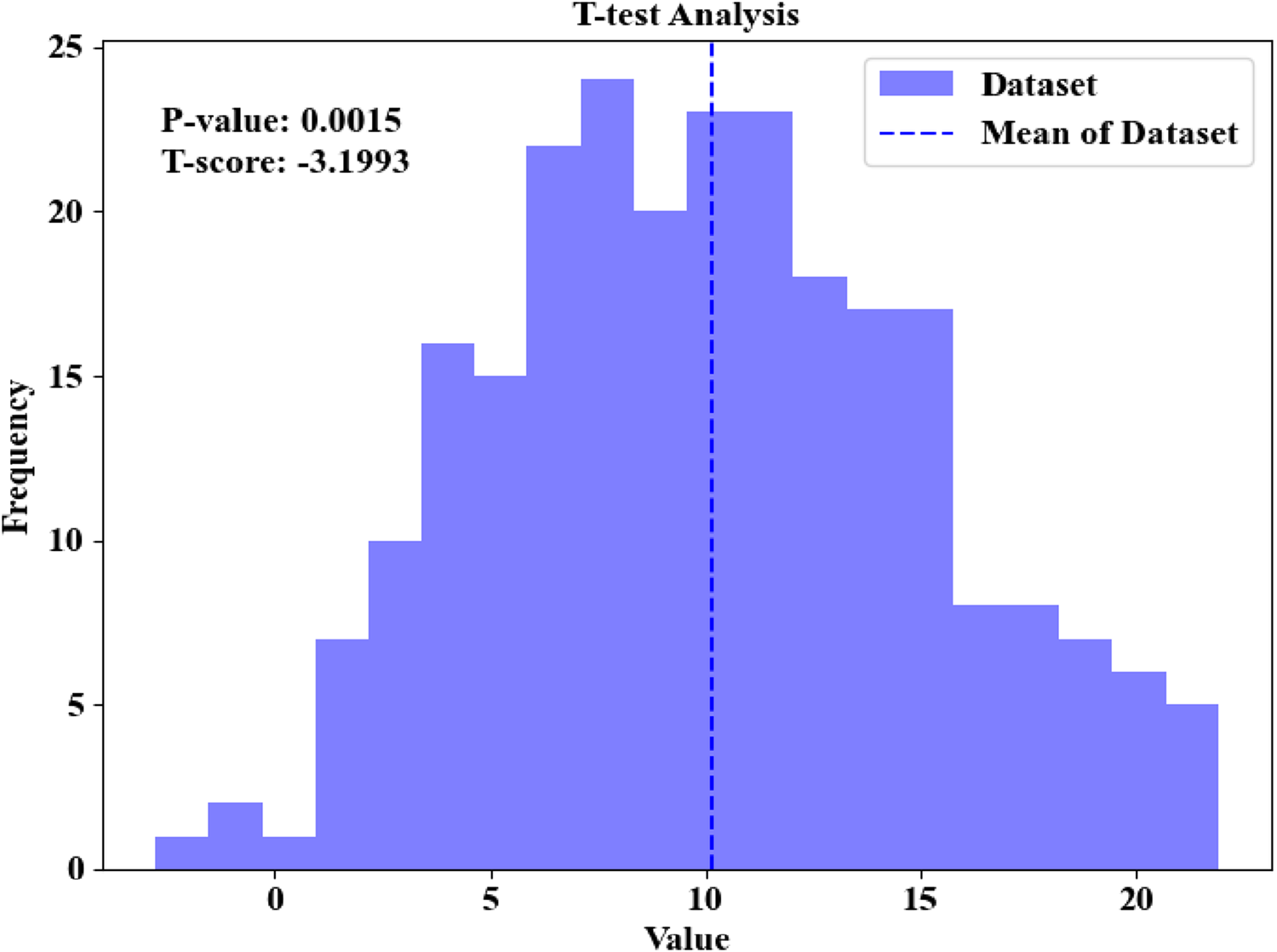
T-test analysis.
The above Figure 12 visualizes the distribution of values within the dataset. Here, the vertical dashed line indicates the sample mean. A one-sample-based T-test was conducted to check the deviation of the sample mean from the expected baseline. Thus, the T-test attained a T-score of −3.1993 and a P-value of 0.0015, showing statistically significant differences at the level of 0.05. Thus, it proves that the observed dataset values have occurred effectively and not by random chance. Thereby, this supports the hypothesis that the datasets used in the proposed work exhibit meaningful deviation concerning the assumed baseline. Hence, the robustness of the observed values is achieved.
4.8 Limitation
Although the proposed work efficiently analyzed the phishing attack in sources like SMS, email, and web page URLs, it failed to perform the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate analysis. The attacker uses this SSL certificate and makes the phishing site appear to be a secured one.
5 Conclusion
This work proposed an effective multimodal framework for phishing detection using EAI-SC-LSTM, CSOA, and SPCA approaches. The proposed approach used multiple data sources and examined various features like user behavior of the data. In addition, by using the proposed EM-BERT algorithm, the vector conversion of features enhanced the classifier learning. Then, by utilizing the presented CSOA, the optimal features of the URL were selected with a suitable fitness of 99.68% for 50 iterations. Hence, by using the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM model, the phishing and legitimate data were detected with an accuracy of 99.645% (PEC), a precision of 99.895% (SSC), recall of 99.784% (SSC), PPV of 99.652% (PEC), FNR of 0.6359, and training time of 24417 ms (PEC). Thus, the proposed model provided an enhanced system for phishing detection and mitigation of multisource data. This implied that the proposed EAI-SC-LSTM technique surpassed the traditional phishing detection models. The integration of the real-time blacklist update mechanism into the proposed system enhanced the system’s reliability in adapting to the evolving phishing attack. The results attained by the proposed system made the model to be a promising solution for real-time cybersecurity applications.
5.1 Future work
Although the behavior features are efficiently used for phishing detection, there is a possibility of developing Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates for the malicious domains by the attackers. This is a limitation of this research. So, in the future, SSL certificate analysis will be incorporated to improve the phishing attack detection accuracy and to enhance the security of the system against other sophisticated attacks. Hence, the proposed work will further improve the robustness in real-world scenarios.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
MM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. GN: Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank the referees for their useful suggestions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frcmn.2025.1587654/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Abdillah R. Shukur Z. Mohd M. Murah T. M. Z. (2022). Phishing classification techniques: a systematic literature review. IEEE Access10, 41574–41591. 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3166474
2
Akour I. Alnazzawi N. Aburayya A. Alfaisal R. Salloum S. A. (2021). Using Classical Machine Learning for phishing websites detection form URLS. J. Manag. Inf. Decis. Sci.24 (6), 1–9.
3
Al-Ahmadi S. Alotaibi A. Alsaleh O. (2022). PDGAN: phishing detection with generative adversarial networks. IEEE Access10, 42459–42468. 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3168235
4
Aljabri J. Alzaben N. Nemri N. Alahmari S. Alotaibi S. D. Alazwari S. et al (2024). Hybrid stacked autoencoder with dwarf mongoose optimization for Phishing attack detection in internet of things environment. Alexandria Eng. J.106, 164–171. 10.1016/j.aej.2024.06.070
5
Aljofey A. Jiang Q. Rasool A. Chen H. Liu W. Qu Q. et al (2022). An effective detection approach for phishing websites using URL and HTML features. Sci. Rep.12 (1), 8842–19. 10.1038/s41598-022-10841-5
6
Alotaibi S. R. Alkahtani H. K. Aljebreen M. Alshuhail A. Saeed M. K. Ebad S. A. et al (2025). Explainable artificial intelligence in web phishing classification on secure IoT with cloud-based cyber-physical systems. Alexandria Eng. J.110, 490–505. 10.1016/j.aej.2024.09.115
7
Alsubaei F. S. Almazroi A. A. Ayub N. (2024). Enhancing phishing detection: a novel hybrid deep learning framework for cybercrime forensics. IEEE Access12, 8373–8389. 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3351946
8
Ariyadasa S. Fernando S. Fernando S. (2022). Combining long-term recurrent convolutional and graph convolutional networks to detect phishing sites using URL and HTML. IEEE Access10, 82355–82375. 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3196018
9
Asiri S. Xiao Y. Alzahrani S. Li S. Li T. (2023). A survey of intelligent detection designs of HTML URL phishing attacks. IEEE Access11, 6421–6443. 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3237798
10
Aslam S. Aslam H. Manzoor A. Chen H. Rasool A. (2024). AntiPhishStack: LSTM-based stacked generalization model for optimized phishing URL detection. Symmetry16 (2), 248–25. 10.3390/sym16020248
11
Atlam H. F. Oluwatimilehin O. (2023). Business email compromise phishing detection based on machine learning: a systematic literature review. Electron. Switz.12 (1), 42–28. 10.3390/electronics12010042
12
Balogun A. O. Adewole K. S. Raheem M. O. Akande O. N. Usman-Hamza F. E. Mabayoje M. A. et al (2021). Improving the phishing website detection using empirical analysis of Function Tree and its variants. Heliyon7 (7), e07437–14. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07437
13
Basit A. Zafar M. Liu X. Javed A. R. Jalil Z. Kifayat K. (2021). A comprehensive survey of AI-enabled phishing attacks detection techniques. Telecommun. Syst.76 (1), 139–154. 10.1007/s11235-020-00733-2
14
Bhagwat M. D. Patil P. H. Vishawanath T. S. (2021). “A methodical overview on detection identification and proactive prevention of phishing websites,” in Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Communication Technologies and Virtual Mobile Networks, 1505–1508. 10.1109/ICICV50876.2021.9388441
15
Biswas B. Mukhopadhyay A. Kumar A. Delen D. (2024). A hybrid framework using explainable AI (XAI) in cyber-risk management for defence and recovery against phishing attacks. Decis. Support Syst.177, 114102. 10.1016/j.dss.2023.114102
16
Brezeanu G. Archip A. Artene C. G. (2025). Phish fighter: self updating machine learning shield against phishing kits based on HTML code analysis. IEEE Access13, 4460–4486. 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3525998
17
Bu S. J. Kim H. J. (2022). Optimized URL feature selection based on genetic-algorithm-embedded deep learning for phishing website detection. Electron. Switz.11 (7), 1090–12. 10.3390/electronics11071090
18
Catal C. Giray G. Tekinerdogan B. Kumar S. Shukla S. (2022). Applications of deep learning for phishing detection: a systematic literature review. Knowl. Inf. Syst.64 (6). 1457-1500. 10.1007/s10115-022-01672-x
19
Champa A. I. Rabbi F. Zibran M. F. (2024a). “Why phishing emails escape detection: a closer look at the failure points,” in 2024 12th international symposium on digital forensics and security (ISDFS) (IEEE), 1–6. Available online at: https://www2.cose.isu.edu/∼minhazzibran/resources/MyPapers/Champa_ISDFS24_Published.pdf.
20
Champa A. I. Rabbi M. F. Zibran M. F. (2024b). “Curated datasets and feature analysis for phishing email detection with machine learning,” in IEEE 3rd International Conference on Computing and Machine Intelligence (ICMI) (IEEE), 1–7. Available online at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10585821/.
21
Elberri M. A. Tokeşer Ü. Rahebi J. Lopez-Guede J. M. (2024). A cyber defense system against phishing attacks with deep learning game theory and LSTM-CNN with African vulture optimization algorithm (AVOA). Int. J. Inf. Secur.23, 2583–2606. 10.1007/s10207-024-00851-x
22
Gupta B. B. Yadav K. Razzak I. Psannis K. Castiglione A. Chang X. (2021). A novel approach for phishing URLs detection using lexical based machine learning in a real-time environment. Comput. Commun.175, 47–57. 10.1016/j.comcom.2021.04.023
23
Hannousse A. Yahiouche S. (2021). Towards benchmark datasets for machine learning based website phishing detection: an experimental study. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell.104, 104347–17. 10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104347
24
Kara I. Ok M. Ozaday A. (2022). Characteristics of understanding URLs and domain names features: the detection of phishing websites with machine learning methods. IEEE Access10, 124420–124428. 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3223111
25
Karim A. Shahroz M. Mustofa K. Belhaouari S. B. Joga S. R. K. (2023). Phishing detection system through hybrid machine learning based on URL. IEEE Access11, 36805–36822. 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3252366
26
Li W. Manickam S. Laghari S. U. A. Chong Y. W. (2023). Uncovering the cloak: a systematic review of techniques used to conceal phishing websites. IEEE Access11, 71925–71939. 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3293063
27
Liu D. J. Geng G. G. Jin X. B. Wang W. (2021). An efficient multistage phishing website detection model based on the CASE feature framework: aiming at the real web environment. Comput. Secur.110, 102421–14. 10.1016/j.cose.2021.102421
28
Mahmoud T. M. Abd-El-Hafeez T. Badawy A. (2013). A framework for an E-learning system based on semantic web. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng.5 (8), 698.
29
Mehmood M. K. Arshad H. Alawida M. Mehmood A. (2024). Enhancing smishing detection: a deep learning approach for improved accuracy and reduced False positives. IEEE Access12, 137176–137193. 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3463871
30
Naqvi B. Perova K. Farooq A. Makhdoom I. Oyedeji S. Porras J. (2023). Mitigation strategies against the phishing attacks: a systematic literature review. Comput. Secur.132, 103387–25. 10.1016/j.cose.2023.103387
31
Odeh A. Keshta I. Abdelfattah E. (2021). “Machine LearningTechniquesfor detection of website phishing: a review for promises and challenges,” in 11th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference, 0813–0818. 10.1109/CCWC51732.2021.9375997
32
Opara C. Chen Y. Wei B. (2024). Look before you leap: detecting phishing web pages by exploiting raw URL and HTML characteristics. Expert Syst. Appl.236, 121183–13. 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121183
33
Rao R. S. Pais A. R. Anand P. (2021). A heuristic technique to detect phishing websites using TWSVM classifier. Neural Comput. Appl.33 (11), 5733–5752. 10.1007/s00521-020-05354-z
34
Rashid S. H. Abdullah W. D. (2023). Cloud-based machine learning approach for accurate detection of website phishing. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng.11, 451–460. Available online at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/373659846_Cloud-Based_Machine_Learning_Approach_for_Accurate_Detection_of_Website_Phishing?enrichId=rgreq-c5186a18cbf358037766b257b86e931f-XXX&enrichSource=Y292ZXJQYWdlOzM3MzY1OTg0NjtBUzoxMTQzMTI4MTE4NjM3NTg0OUAxNjkzOTA1MzMxNjM3&el=1_x_3&_esc=publicationCoverPdf
35
Safi A. Singh S. (2023). A systematic literature review on phishing website detection techniques. J. King Saud Univ. - Comput. Inf. Sci.35 (2), 590–611. 10.1016/j.jksuci.2023.01.004
36
Sahingoz O. K. Bube E. Kugu E. (2024). Dephides: deep learning based phishing detection system. IEEE Access12, 8052–8070. 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3352629
37
Salloum S. Gaber T. Vadera S. Shaalan K. (2021). Phishing email detection using Natural Language Processing techniques: a literature survey. Procedia Comput. Sci.189, 19–28. 10.1016/j.procs.2021.05.077
38
Salloum S. Gaber T. Vadera S. Shaalan K. (2022). A systematic literature review on phishing email detection using Natural Language Processing techniques. IEEE Access10, 65703–65727. 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3183083
39
Sanchez-Paniagua M. Fidalgo E. Alegre E. Alaiz-Rodriguez R. (2022). Phishing websites detection using a novel multipurpose dataset and web technologies features. Expert Syst. Appl.207, 118010–118016. 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118010
40
Shafin S. S. (2024). An explainable feature selection framework for web phishing detection with machine learning. Data Sci. Manag.8, 127–136. 10.1016/j.dsm.2024.08.004
41
Shombot E. S. Dusserre G. Bestak R. Ahmed N. B. (2024). An application for predicting phishing attacks: a case of implementing a support vector machine learning model. Cyber Secur. Appl.2, 100036. 10.1016/j.csa.2024.100036
42
Sturman D. Auton J. C. Morrison B. W. (2024). Security awareness, decision style, knowledge, and phishing email detection: moderated mediation analyses. Comput. & Secur.148, 104129. 10.1016/j.cose.2024.104129
43
Sudar K. M. Rohan M. Vignesh K. (2024). Detection of adversarial phishing attack using machine learning techniques. Sādhanā49 (3), 232. 10.1007/s12046024025820
44
Tang L. Mahmoud Q. H. (2021). A survey of machine learning-based solutions for phishing website detection. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr.3 (3), 672–694. 10.3390/make3030034
45
Tang L. Mahmoud Q. H. (2022). A deep learning-based framework for phishing website detection. IEEE Access10, 1509–1521. 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3137636
46
Thakur K. Ali M. L. Obaidat M. A. Kamruzzaman A. (2023). A systematic review on deep-learning-based phishing email detection. Electron. Switz.12 (21), 4545–26. 10.3390/electronics12214545
47
van Geest R. J. Cascavilla G. Hulstijn J. Zannone N. (2024). The applicability of a hybrid framework for automated phishing detection. Comput. Secur.139, 103736–17. 10.1016/j.cose.2024.103736
48
Yang L. Zhang J. Wang X. Li Z. Li Z. He Y. (2021). An improved ELM-based and data preprocessing integrated approach for phishing detection considering comprehensive features. Expert Syst. Appl.165, 113863–18. 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113863
Summary
Keywords
short message service (SMS), java script, electronic mail (e-mail), user behavior, uniform resource locator (URL), cascading style sheets (CSS), phishing attack, and artificial
Citation
Murhej M and Nallasivan G (2025) Multimodal framework for phishing attack detection and mitigation through behavior analysis using EM-BERT and SPCA-BASED EAI-SC-LSTM. Front. Commun. Netw. 6:1587654. doi: 10.3389/frcmn.2025.1587654
Received
06 March 2025
Accepted
05 June 2025
Published
08 July 2025
Volume
6 - 2025
Edited by
Kuo-Hui Yeh, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Taiwan
Reviewed by
Abdur Rasool, University of Hawaii at Manoa, United States
Revathi S, VIT University, India
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Murhej and Nallasivan.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mahmoud Murhej, mahmoudmrhej@gmail.com; G. Nallasivan, drnallasivang@veltech.edu.in
ORCID: Mahmoud Murhej, orcid.org/0009-0004-8330-0128; G. Nallasivan, orcid.org/0000-0001-7852-6713
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.