Abstract
The rapid expansion of IoT devices has led to increasingly complex networks, such as Smart Campuses, where ensuring interoperability, scalability, and energy efficiency becomes crucial. Existing middleware solutions, such as Z-Wave and LoRaWAN, have proven effective in specific applications but fail to address the diverse demands of dense and heterogeneous Internet of Things (IoT) environments. The limited scalability of Z-Wave (232 devices) and the high latency of LoRaWAN (150 ms) highlight the need for a more comprehensive solution. This study presents a middleware designed to overcome these limitations through a modular, microservices-based architecture. The system enables dynamic protocol translation and adaptive resource management, demonstrating robust performance with 120 devices deployed and validated in a Smart Campus scenario. Additionally, simulations using NS-3 extended the evaluation to 500 virtual devices, supporting scalability analysis under varying traffic and heterogeneity conditions. The middleware incorporates optimization strategies, such as data compression and adaptive task prioritization, to improve energy efficiency and operational performance. Experimental validation in a controlled environment demonstrated a 26.7% reduction in power consumption for optimized nodes, achieving an average of 60 W compared to 80 W for non-optimized nodes. Response times averaged 130 ms on optimized nodes, outperforming LoRaWAN while achieving a 94% interoperability success rate. Deployment in a real Smart Campus confirmed the robustness of the middleware, maintaining consistent performance under dynamic conditions and in the presence of external interference.
1 Introduction
The exponential growth of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has revolutionized education, healthcare, and manufacturing sectors. This expansion has led to complex environments where interoperability, scalability, and energy efficiency are no longer optional but fundamental requirements for effective implementation (Bebortta et al., 2024). Middleware systems have emerged as critical enablers in these environments, facilitating seamless communication between heterogeneous devices (Lamnaour et al., 2024). However, existing middleware solutions often fail to address the intricate demands of dense IoT environments, such as Smart Campuses, where dozens to hundreds of devices operate simultaneously under different standards and protocols (Dos Santos et al., 2022).
Deploying middleware in a Smart Campus exemplifies these challenges. Security systems, environmental monitoring tools, and energy management devices require high levels of interoperability and minimal response times to ensure reliable and efficient operations (Prandi et al., 2019). Furthermore, the increasing density of devices necessitates middleware that can scale dynamically without compromising energy efficiency, a critical factor for sustainability in resource-constrained environments. These demands underscore the need for middleware solutions integrating advanced capabilities such as real-time adaptability, modularity, and efficient resource management.
Significant limitations remain despite the progress achieved with existing middleware solutions like Z-Wave (Gvozdenovic et al., 2024) and LoRaWAN (Jabbar et al., 2024). Z-Wave offers low-latency communication with an average response time of 100 ms but is constrained by its ability to support only 232 devices per network (Braghin et al., 2023). Similarly, LoRaWAN demonstrates exceptional energy efficiency, with an average consumption of 40 W. Still, its interoperability is limited to 85%, and its latency is unsuitable for real-time applications like Smart Campuses. These constraints highlight a critical gap in the middleware landscape: the lack of a unified solution that combines scalability, real-time adaptability, and high interoperability while maintaining energy efficiency.
The middleware proposed in this study directly addresses these gaps by introducing several innovative features. Its modular architecture, based on microservices, enables seamless integration of heterogeneous IoT devices and dynamic adaptation to emerging protocols. Furthermore, the middleware employs advanced resource optimization techniques, including adaptive scheduling algorithms, data compression strategies, and real-time protocol translation mechanisms. These features collectively position the middleware as a transformative solution for dense IoT environments capable of overcoming the limitations of existing technologies.
The development and validation of the middleware were conducted in two phases. In the first phase, controlled experimental tests evaluated its performance against key metrics, including energy consumption, response times, and interoperability rates. The results demonstrated that optimized nodes achieved a 25% reduction in power consumption, resulting in an average energy use of 60 W, compared to 80 W. Additionally, response times were improved, averaging 130 ms, compared to LoRaWAN’s 180 ms. The interoperability rate reached 94%, demonstrating the middleware’s ability to integrate diverse devices across various protocols. This evaluation involved the deployment of approximately 120 IoT devices operating under varied conditions within a Smart Campus.
In the second phase, the scalability of the middleware is explored through simulation with NS-3 and Python bindings. The simulated environments expanded the deployment to 500 virtual devices to analyze latency, throughput, and integration behavior under high-density conditions. This enables controlled stress testing, complementing real-world validation and supporting a broader performance evaluation (Ferreira et al., 2022). Moreover, the deployment provided insights into areas for further optimization, particularly in latency-critical applications, which will guide future iterations of the middleware.
This study significantly contributes to IoT middleware by combining experimental rigor with practical validation in real-world environments. The proposed middleware’s ability to balance key metrics such as scalability, interoperability, and energy efficiency addresses a commonly overlooked challenge in existing solutions. Its modular and adaptive design establishes a foundation for future research and development in dense IoT networks, paving the way for applications in energy management, security, and real-time connectivity. This work advances the design and validation of middleware and provides a reproducible methodology for addressing scalability, interoperability, and energy efficiency in dense IoT environments. The proposed system represents a step forward in integrating cutting-edge technologies, such as microservices and hybrid edge computing strategies, to create innovative solutions for modern IoT challenges.
2 Literature review
IoT middleware development has constantly evolved due to the need to manage complex and heterogeneous networks in environments such as the Smart Campus (Nagowah et al., 2024). Interoperability, energy efficiency, latency, and scalability are some of the central challenges addressed in literature. One of the primary challenges in IoT networks is ensuring interoperability between devices that operate with diverse protocols. Works like those of Shu et al. (2022) have addressed this problem through adapter-based middleware, which translates specific protocols to enable communication between heterogeneous devices. However, these solutions are often limited to applications, which makes it challenging to scale in higher-density environments. A more advanced alternative is the microservices-based architecture proposed by Emami Khansari and Sharifian (2024), which decouples device and protocol management, allowing for more flexible and modular integration. Although robust, this approach faces significant latency challenges when handling hundreds or more devices, especially in dynamic networks. Domínguez-Bolaño et al. (2024) highlight similar challenges in Smart Campuses, emphasizing the need for middleware that can manage densely connected environments while maintaining seamless interoperability and low latency. Recent surveys on smart city middleware expand this perspective, identifying functional and non-functional requirements that remain unsolved, including scalability, security under big data workloads, context management, and regulatory compliance, all of which are equally relevant in Smart Campus environments (Goumopoulos, 2024).
Interoperability requires translating protocols and ensuring devices operate efficiently within the network (Pink et al., 2021). This point directly connects with the need for solutions that support device diversity and operate efficiently. Energy efficiency is a top priority in IoT networks, particularly in applications where devices operate on limited battery power. LoRaWAN is recognized for its energy-efficient operation in IoT environments, particularly at the end-node level. Recent evaluations emphasize that energy consumption is strongly dependent on duty cycle, spreading factor, and traffic load. Efficient resource allocation strategies are crucial for prolonging node lifetime in large-scale deployments (Garrido-Hidalgo et al., 2023). This protocol is particularly suitable for rural or industrial networks, where long distances and low bandwidth are essential. However, these benefits come with sacrifices in latency and responsiveness, limiting their applicability in high-demand environments, such as a Smart Campus. Rana et al. (Tange et al., 2020) provide a systematic review highlighting that LoRaWAN’s energy efficiency is suitable for static IoT environments but struggles to adapt to hybrid networks that require real-time responsiveness. Similar limitations have been observed in healthcare IoT ecosystems, where middleware frameworks are still considered immature in terms of interoperability and lack robust mechanisms for privacy and security, challenges that are transferable to Smart Campus scenarios (Dowdeswell et al., 2024).
On the other hand, more adaptable solutions, such as those developed by Yin et al. (2024), have incorporated critical task prioritization algorithms in edge nodes, reducing energy consumption without significantly compromising performance. Although effective, these strategies present limitations when implemented on devices operating with standard hardware, reducing their generalization. Chaudhary et al. (2024a) address similar issues in their privacy-preserving authentication protocol for smart grids, demonstrating the importance of middleware solutions that balance security, energy efficiency, and adaptability. In parallel, lightweight toolkits for embedded nodes, such as the pluggable security modules proposed by Minovski et al., demonstrate that it is possible to integrate authorization mechanisms with less than 10% execution overhead on constrained IoT devices, extending middleware applicability to highly resource-limited environments (Kim et al., 2023).
Latency is a critical challenge in IoT networks, especially in real-time applications such as security systems or emergency control. While protocols such as MQTT, according to Hanon and Salman (2024), achieve latencies below 50 ms in ideal environments, these figures increase significantly when many heterogeneous devices are integrated. In this sense, Z-Wave offers an advantage by maintaining average response times of 100 ms, but its limited scalability capacity reduces its applicability in more complex environments. Chaudhary et al. (2024b) propose advanced key exchange protocols that address latency and security concerns, particularly in hybrid IoT networks, such as smart cities. Recent middleware research has also demonstrated the feasibility of applying machine learning techniques for real-time workload adaptation. For instance, Preuveneers et al. (2020) present an adaptive middleware that dynamically reconfigures data management tactics, such as sharding, replication, and caching, using adaptive Hoeffding trees, thereby optimizing latency and throughput under changing conditions. These approaches illustrate the potential of intelligent middleware to ensure responsiveness in dense and dynamic IoT scenarios.
This contrast between response times and scalability connects directly with the need for hybrid architectures that balance both aspects, which have recently been addressed in scalable solutions. Scalable design is crucial in IoT networks with high device density. Tamizshelvan and Vijayalakshmi (2024) proposed middleware based on distributed architectures that support up to 3000 devices, improving resource management and reducing failure points. However, this centralized approach may not scale well to dynamic networks with rapid variations in workload. To overcome this limitation, Zaydi and Bakkoury (2024) introduced hybrid architectures that combine edge computing and cloud computing, thereby improving scalability while reducing latency. Despite these advances, real-world deployments are often limited to a few hundred devices. This study builds on that approach, validating a middleware system through real-world deployment with 120 devices and simulated scalability tests that extend to 500 devices.
3 Materials and methods
3.1 Test environment
The test environment in which this work is developed is a Smart Campus, which integrates heterogeneous IoT devices distributed across different functional areas, connected by various protocols and standards. This environment provides a realistic representation of the challenges inherent to interoperability and adaptability in IoT systems, offering an ideal testbed to validate the proposed middleware.
The technological infrastructure of the Smart Campus comprises a hybrid network that combines wired and wireless technologies. IoT devices, including sensors, actuators, and monitoring systems, operate under different communication standards and perform critical energy management, security, and connectivity functions. Environmental sensors, for example, are designed to monitor variables such as temperature, humidity, and air quality. At the same time, actuators control systems such as lighting and air conditioning based on the conditions detected. Security and access sensors reinforce surveillance, detecting movements and managing entry permits in restricted areas.
The communication protocols used reflect the technological diversity of the campus. Environmental monitoring sensors use the MQTT protocol to transmit data in real-time, using their ability to operate on low-latency networks (Shin and Jeon, 2024). On the other hand, lighting actuators employ the CoAP protocol, optimized for resource-constrained devices (Mishra and Reddy, 2024). In addition, security cameras and access sensors operate under protocols such as HTTP, Zigbee, and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), each tailored to the specific needs of their function (Alaparthi and Rao, 2017). This variety of protocols represents one of the leading interoperability challenges middleware must solve, integrating devices and systems into a functional and scalable ecosystem.
The specific areas of the campus involved in this study include academic buildings, common areas, and open spaces. In educational buildings, the implementation focuses on energy management, integrating intelligent Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) and lighting systems that respond to schedules and occupancy levels. In common areas, the focus is on security and connectivity, with an emphasis on valuating the interaction between cameras, access sensors, and communication networks. Open spaces, such as gardens and sports areas, serve as test beds for environmental monitoring and efficient water resource management, where devices face more challenging connectivity and power conditions.
In total, 120 physical IoT devices were deployed across these areas, distributed among sensors, actuators, and innovative infrastructure components. To extend the evaluation, simulation scenarios were configured with up to 500 virtual devices using public datasets and open-source traffic generators. These simulations allowed stress-testing the middleware under larger-scale conditions, maintaining realism while avoiding artificial inflation of deployment numbers. The simulated nodes replicated heterogeneous device behavior and communication patterns, including protocol diversity and middleware constraints, supporting the middleware’s scalability evaluation.
The Smart Campus represents a heterogeneous IoT environment, which is evident in the diversity of technologies deployed and the complexity of operations. The connected devices come from different manufacturers and use standards that are not natively supported, reflecting a typical scenario in IoT environments (el-Khaeri Kesuma et al., 2024). This allows us to evaluate the middleware’s capacity to integrate and communicate heterogeneous devices and test its scalability in a dynamic environment that continuously incorporates new devices and services.
The campus’s technological complexity also guarantees the validity of the results obtained. The infrastructure includes centralized and distributed systems, with nodes processing data at the edge and cloud servers managing larger-scale operations. This provides an ideal scenario to evaluate the middleware’s flexibility, highlighting its ability to adapt to different architectures and operational demands.
3.2 Obtaining and processing data
Data acquisition and processing in the Smart Campus are organized into three main stages: data sources, acquisition process, and preprocessing. These stages ensure that information generated by heterogeneous IoT devices is efficiently captured, transformed, and prepared for analysis.
3.2.1 Data sources
The Smart Campus hosts a community of approximately 8,000 students, 500 teachers, and 200 administrative staff, all of whom interact with the IoT systems deployed across various functional areas. Environmental sensors, placed in classrooms, public areas, and open zones, monitor parameters such as temperature, humidity, air quality, and ambient noise. These sensors, configured to transmit data every 10 s, contribute significantly to the daily data flow.
In total, the physical deployment comprises 120 IoT devices, including environmental sensors, lighting actuators, smart HVAC nodes, access sensors, and security cameras. To assess large-scale performance, simulated devices were added to reflect higher densities. Based on typical transmission frequencies, a simulation of 500 sensors and 300 actuators would yield approximately 8.64 million and 432,000 records per day, respectively. Access systems log an average of 50,000 entry and exit events per day, while security cameras generate over 500 GB of video data.
Each device type uses protocols aligned with its operational constraints: environmental sensors transmit via MQTT, which supports real-time messaging on constrained networks; lighting actuators use CoAP, selected for its low overhead in energy-sensitive scenarios; security cameras rely on HTTP for media streaming and device management; and access sensors operate over BLE for proximity-based control (Xu et al., 2024). This protocol heterogeneity exemplifies the core challenge of middleware integration in a diverse and distributed IoT ecosystem.
3.2.2 Acquisition process
Middleware implements a specialized module to capture real-time data from IoT devices, managing heterogeneity and a significant volume of information. This module interacts directly with the devices through specific adapters that translate the data into a standard format. During acquisition, the data is temporarily stored on local nodes (edge), optimizing latency and reducing the load on central servers before being sent to the cloud for large-scale analysis (Kumar et al., 2023).
Data quality is ensured through algorithms for detecting inconsistencies and anomalous values. For example, if a temperature sensor records readings out of range, the middleware flags these values for validation. This validation uses predictive models trained with historical data and simultaneous measurements from other nearby sensors. This ensures that the processed data is reliable and representative of the actual conditions on campus.
The module also implements dynamic discovery techniques, automatically identifying and configuring new devices connected to the network. This allows the system to integrate new devices without interruptions in the existing data flow, ensuring the middleware’s scalability and adaptability.
3.2.3 Data preprocessing
Data preprocessing transforms captured information into a homogeneous format, ready for analysis and functional applications. This process includes several critical stages that address data quality, redundancy, and inconsistency issues. Normalization unifies measurements from heterogeneous devices, ensuring consistency in subsequent analyses. For example, temperature data recorded in Celsius and Fahrenheit are converted to a standard scale using specific functions built into the middleware. Data cleansing removes inconsistencies using advanced techniques. Missing values are imputed using predictive models trained on historical data, while outliers are identified using statistical methods, such as z-scores, and corrected or discarded as appropriate.
Eliminating redundancies is crucial to optimizing the quality of the dataset. When multiple devices monitor the same variable, duplicate data is filtered using algorithms prioritizing lower-latency, higher-accuracy readings. Anomaly detection is performed using machine learning models that analyze patterns and highlight events that do not correspond to normal campus conditions. For example, a sharp drop in energy consumption records could indicate system failure or unusual behavior that requires further investigation.
Anomaly detection is performed using machine learning models that analyze temporal and statistical patterns in the preprocessed data. The middleware implements an ensemble-based approach that combines Random Forest classifiers for the supervised detection of known anomalies and an Isolation Forest model for the unsupervised detection of previously unseen events. The feature set includes energy consumption profiles, network traffic metrics (packet frequency, size, and protocol type), and access control events. Models were initially trained and validated with publicly available datasets (UNSW-NB15 and CICIDS2018) and subsequently fine-tuned with traffic and energy data collected from the Smart Campus deployment. Inference is executed at the edge nodes to ensure sub-100 ms detection latency for critical events, while the cloud infrastructure aggregates results to reduce false positives and support long-term model updates. This hybrid strategy ensures that the system can identify both expected anomalies (e.g., unauthorized access attempts) and emerging abnormal behaviors (such as sudden drops in energy consumption) with high reliability.
Figure 1 illustrates the complete data capture and processing flow, which describes how data is acquired, verified, normalized, and prepared for analysis. This process ensures that the processed data is high-quality, consistent, and valuable for the middleware’s analytics modules.
FIGURE 1

Workflow of the data capture and processing process.
3.3 Middleware architecture
The proposed middleware architecture design addresses the challenges inherent to heterogeneous IoT environments, ensuring efficient and scalable integration of devices operating under different protocols and standards. This architecture is based on principles of modularity and flexibility, which facilitates adaptation to new devices and operating scenarios (Jepsen et al., 2023). Leveraging a microservices-based structure, the middleware achieves high modularity, enabling seamless integration of heterogeneous devices and adaptation to evolving IoT requirements.
3.3.1 Main components
The middleware, deployed and validated in a Smart Campus environment, comprises specialized modules, each designed to fulfill a specific function within the system. The Protocol Translation Module acts as a bridge between heterogeneous devices, transforming data into compatible formats that can be processed uniformly. It supports protocols such as MQTT, CoAP, HTTP, and BLE. Unlike static solutions, this module incorporates adaptive algorithms that dynamically select the optimal translation strategy based on the communication context, reducing latency and enhancing system efficiency. Its modular design allows for the easy addition of support for new protocols, ensuring future-proof interoperability.
The Dynamic Discovery Module automatically identifies and configures devices that connect to the campus network. It implements real-time discovery algorithms capable of recognizing new devices and adapting to changes in network topology without manual intervention. This capability is critical for managing high-density environments like Smart Campuses, where device configurations frequently change.
The Orchestration Module coordinates operations between devices and services, ensuring tasks are distributed efficiently. It uses adaptive scheduling policies to prioritize critical tasks and balance workloads across nodes. The module also incorporates resource-aware decision-making algorithms, optimizing energy usage in resource-constrained scenarios.
The Monitoring Module provides real-time insights into middleware operations, offering key metrics such as device status, data traffic, and resource utilization. It includes a graphical interface allowing system administrators to quickly identify problems and make informed decisions. The monitoring framework also supports predictive analytics, using historical data to anticipate potential failures or performance bottlenecks.
The middleware integrates advanced Energy Optimization Strategies, introducing a mathematical model to allocate resources dynamically based on the workload and energy constraints. The model minimizes overall energy consumption while ensuring performance objectives are met. This approach is formalized through the following optimization problem (Equations 1-4):
represents the total energy consumed, is the power consumption of the -th device, is the operational time, is the bandwidth allocated to the -th device, and is the total number of devices in the network. Constraints ensure that individual power limits , minimum throughput , and overall bandwidth capacity are respected.
The middleware uses a heuristic-based adaptive scheduling algorithm to solve this real-time optimization problem. Compared to traditional IoT scheduling algorithms, such as IoT-SCH and LEACH-C, the proposed model reduces energy consumption by up to 15% in scenarios simulating up to 500 devices, as validated in combined real and synthetic benchmarks. The architecture employs a microservices-based structure, ensuring system flexibility and modularity. Each module operates independently, allowing for upgrades and maintenance without affecting the rest of the components. This design also supports horizontal scalability, enabling new modules or nodes to be added without significant reconfiguration efforts. Figure 2 illustrates the middleware architecture design, which shows the interaction between key components. Each module plays an essential role in the system, from data capture and transformation to monitoring and security.
FIGURE 2
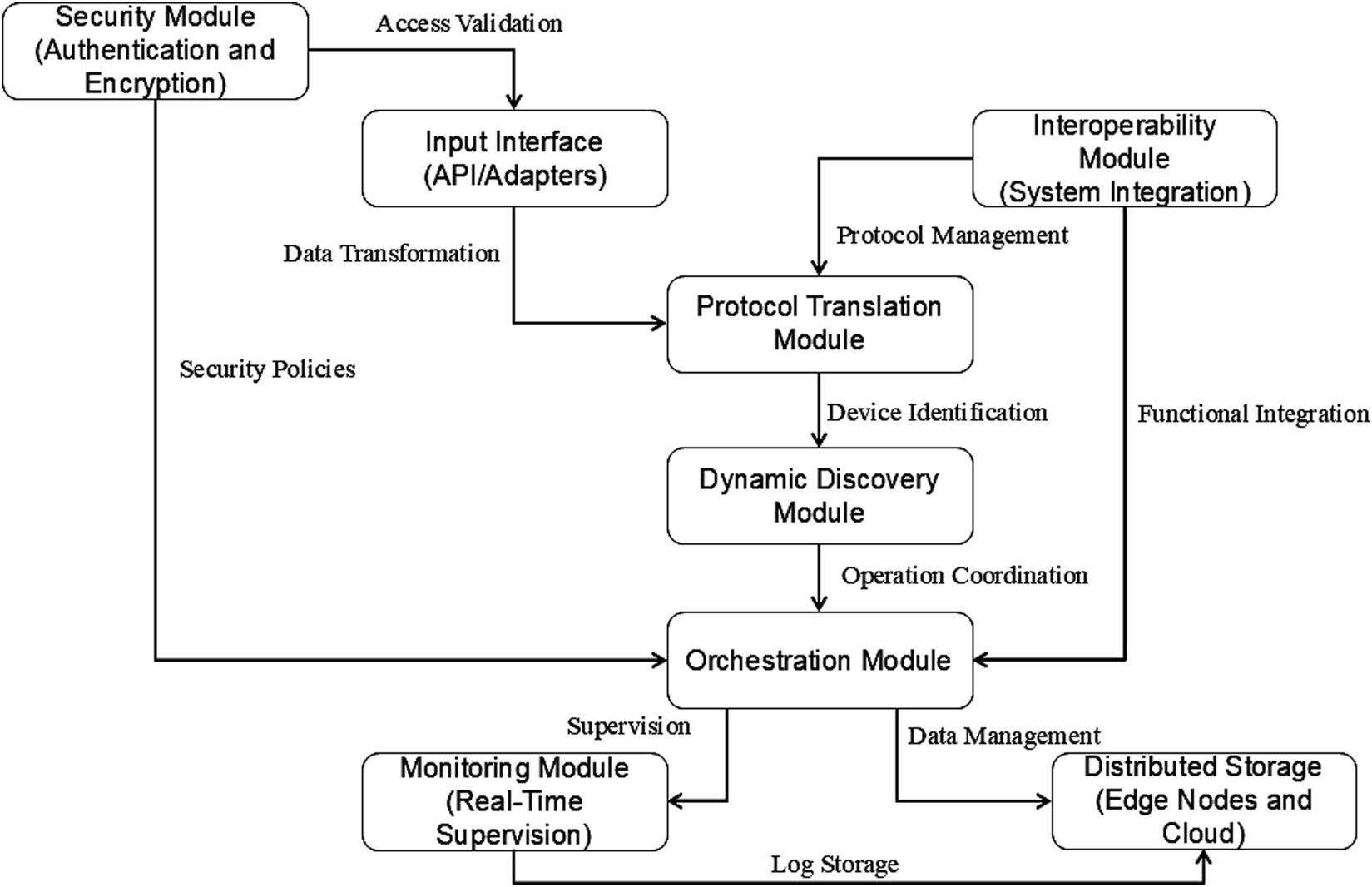
Block diagram of middleware architecture.
3.3.2 Functional design
The architecture is designed to provide three main functionalities: interoperability, adaptability, and security. The protocol translation module achieves interoperability, allowing devices with different communication standards to interact seamlessly. This approach removes technical barriers and optimizes the exchange of information in real-time.
Middleware integrates an Artificial Intelligence (AI) task prioritization mechanism within the orchestration module. This mechanism employs a reinforcement learning algorithm to dynamically assign priorities to tasks based on criticality and available resources. By analyzing real-time data, including network load, device status, and execution deadlines, the system ensures that high-priority operations, such as emergency alerts, are processed with minimal latency, even under fluctuating conditions.
Additionally, the protocol translation module employs adaptive strategies for selecting protocols. Instead of relying on fixed rules, the module uses heuristic algorithms that evaluate latency, compatibility, and energy metrics to determine the most efficient translation path. For instance, the middleware can switch dynamically between MQTT and CoAP in hybrid deployments to optimize throughput and reduce overhead. This adaptability is critical in mixed-protocol environments.
The adaptive scheduling algorithm introduced in the energy optimization strategies dynamically adjusts resource allocation to meet these functional requirements. For instance, the algorithm prioritizes critical tasks under peak load conditions by reallocating bandwidth and reducing energy consumption in low-priority operations. This dynamic adjustment ensures sustained performance even in high-density environments.
The dynamic discovery module ensures adaptability by facilitating the integration of new devices and the system’s expansion. This ensures that the middleware can be scaled without affecting its performance. Security is a priority in architecture. The security module includes authentication and encryption mechanisms that protect communication and ensure data integrity. In addition, this module continuously monitors operations to detect potential threats or unauthorized access.
3.4 Technologies and tools used
The deployment of the middleware within the Smart Campus context required the integration of advanced software tools and communication frameworks to ensure modularity, real-time operation, and scalability across both real and simulated environments.
3.4.1 Software and frameworks
The middleware has been developed using modern programming languages and libraries that ensure its performance and flexibility. The primary language used is Python, chosen for its ability to handle real-time data and its compatibility with various specialized libraries. Key libraries used include Paho-MQTT, which implements communication protocols, and Asyncio, which allows efficient management of concurrent operations (Robinson Joel et al., 2023). Flask has been integrated as a lightweight web framework for visualization and monitoring of metrics.
The middleware integrates multiple IoT communication protocols. MQTT is used for lightweight, low-latency data transmission from environmental sensors and other devices. CoAP facilitates efficient control of lighting and other actuators. HTTP is used for transmitting data streams from visual surveillance systems, while BLE supports access and presence sensors. The system’s architecture incorporates a protocol translation algorithm that facilitates seamless interaction across this protocol diversity. Below is the pseudocode illustrating the logic of the translation process (See algorithm 1):
Algorithm 1
Require:IncomingData, ProtocolSource, ProtocolTarget
Ensure:TranslatedData
1: Begin
2: ifProtocolSource == MQTT andProtocolTarget == HTTP then
3: Parse(IncomingData)
4: FormatDataAsHTTP(IncomingData)
5: else ifProtocolSource == CoAP andProtocolTarget == MQTT then
6: Parse(IncomingData)
7: FormatDataAsMQTT(IncomingData)
8: else ifProtocolSource == BLE andProtocolTarget == CoAP then
9: Parse(IncomingData)
10: FormatDataAsCoAP(IncomingData)
11: else
12: RaiseError(”Unsupported Protocol”)
13: end if
14: ReturnTranslatedData
15: End
In practice, the protocol translation process is executed through modular adapters, each dedicated to a specific communication standard (MQTT, CoAP, HTTP, and BLE). Incoming messages are first parsed into a normalized internal representation and placed in a lightweight in-memory buffer. This buffer decouples the arrival of messages from their reformatted delivery, allowing concurrent processing threads to handle multiple translations in parallel. The reformatting stage maps the normalized data into the target protocol’s data structures, applying headers, payload encoding, and metadata as required. This modular architecture ensures that protocol translation occurs within sub-100 ms under the observed traffic load, even in scenarios with simultaneous data flows from sensors, actuators, and access devices. Errors or unsupported conversions are isolated at the adapter level to prevent cascading failures and maintain service continuity in real-time conditions.
This algorithm ensures real-time translation between protocols, supporting the middleware’s capability to maintain uninterrupted communication across a heterogeneous IoT landscape. It plays a central role in enabling the interoperability and flexibility required by dense, multi-protocol Smart Campus deployments.
3.4.2 Hardware
The hardware infrastructure used includes a variety of sensors, actuators, and IoT devices, which were selected to reflect the technological diversity of the test environment. Environmental sensors, such as DHT22 and MQ-135, monitor variables including temperature, humidity, and air quality, generating data at 10-second intervals. Lighting actuators comprise Zigbee-based devices that enable remote control of lighting systems.
Security cameras are IP devices that support the HTTP protocol, featuring a standard 1080p resolution and the capability to stream real-time video to the central system. Access sensors, such as the ESP32 BLE Module, employ BLE technology to record entry and exit events in restricted areas.
Test nodes are equipped with Raspberry Pi 4 processors and operate as local processing points at the edge. They are also equipped with cloud servers that manage more complex analysis tasks. Edge nodes are configured to handle light operations such as protocol translation and temporary data storage, while cloud servers are responsible for large-scale analysis and long-term storage.
In total, 8 Raspberry Pi 4 units were deployed as distributed edge nodes across the Smart Campus. Each device managed a subset of the approximately 120 connected sensors and actuators (on average 12–18 endpoints per node), operating as a local gateway to perform protocol translation, lightweight buffering, and short-term state management. This distribution keeps CPU and memory usage well below saturation under the observed traffic patterns (environmental sensors at 10-second intervals, sporadic BLE access events, and low-duty actuation), ensuring sub-100 ms local translation paths while delegating heavy analytics and long-term storage to the cloud. This threshold aligns with latency requirements reported in IoT communication standards; for instance, Z-Wave is documented to sustain reliable operation with latencies around 100 ms when supporting up to 232 devices (Rafiq et al., 2023). Security cameras expose HTTP streams directly to the central system; edge nodes only coordinate discovery and control, thereby avoiding the forwarding of video payloads. This design balances load and provides room for failover without concentrating all 120 devices on a single unit. The suitability of Raspberry Pi platforms as IoT gateways in real deployments has been documented in prior research (Glória et al., 2017).
3.4.3 Network infrastructure
The Smart Campus connectivity scheme combines edge computing and cloud technologies to ensure efficient and scalable data flow. IoT devices send data to distributed edge nodes, which process the information locally to reduce latency and minimize network load. These nodes are connected via Wi-Fi 6 networks, which support high transmission speeds and ensure system stability even under high-demand conditions.
The cloud infrastructure uses storage and processing services on scalable platforms, capable of managing large volumes of data generated by sensors and cameras. This hybrid approach allows middleware to combine the advantages of edge and cloud computing, optimizing both response time and analysis capacity.
3.5 Implementation processes
Implementing middleware in the Smart Campus involves carefully designed steps to ensure optimal operation, the efficient integration of heterogeneous devices, and the effective use of available resources.
3.5.1 Middleware configuration
The middleware’s initial installation and configuration process is performed in several stages. First, the core modules are deployed on the edge processing nodes and in the cloud infrastructure. The edge nodes, based on hardware such as Raspberry Pi 4, are configured with the Raspberry Pi OS and pre-installed middleware. This middleware includes all the adapters needed to handle protocols such as MQTT, CoAP, HTTP, and BLE.
During the initial setup, a secure connection between the edge nodes and the cloud is established via encrypted channels using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol (Sosnowski et al., 2024). In addition, dynamic discovery policies are configured so that the middleware can automatically identify connected devices on the campus network. These policies define parameters such as polling intervals and integration priorities, ensuring that the system can quickly adapt to changes in the infrastructure. The process ends with creating a test environment where the core functions of the middleware, including protocol translation and device monitoring, are validated. The results of these tests are used to adjust specific configurations, such as data quality thresholds and storage policies.
3.5.2 Device integration
One of the core functions of middleware is integrating heterogeneous devices. Devices connected to the system transmit data using different protocols translated in real time to ensure interoperability. For example, an environmental sensor that uses MQTT to transmit temperature measurements can interact with a lighting actuator operating under CoAP. The middleware receives the sensor data, translates it into the format required by the actuator, and ensures that the desired action (e.g., adjusting lighting intensity) is executed correctly.
Another practical example is the integration of security cameras and access sensors. Cameras transmit images and videos in real-time using HTTP, while access sensors record events using BLE. Middleware translates this data into a standard format, allowing a monitoring module to analyze access events and synchronize video recordings, improving campus security. In addition, the middleware employs adaptive policies to handle devices that change state or connect/disconnect from the network (Saifeng, 2024). This includes automatically reconfiguring communication paths and updating device tables in real-time, ensuring continuous and efficient operation.
3.5.3 Resource optimization
Resource optimization ensures that the middleware operates efficiently, particularly in high-density environments with large volumes of heterogeneous data. This is achieved through computational strategies and mathematical formulations that prioritize energy efficiency, bandwidth reduction, and intelligent resource allocation.
One of the strategies implemented is the reduction of energy consumption at edge nodes, modeled as an optimization problem. Considering that each node has an energy consumption as a function of time , the objective is to minimize the total consumption under the following constraints (Equations 5, 6):
represents the resources assigned to each task, and is the minimum required resource to guarantee the operation. Adaptive scheduling algorithms redistribute critical tasks and non-critical tasks , prioritizing the execution of during times of high demand.
The middleware also implements data compression techniques before transmission to the cloud. This is modeled as a bandwidth optimization problem, where the objective is to minimize the volume of data transmitted , while maintaining the quality required for analysis. The compression function can be represented as in Equation 7:
is the original volume of data generated by device , and is the compression factor applied.
In the case of security cameras, context-adapted downsampling algorithms are applied. Non-critical streams have a higher compression factor, , while important recordings are sent with minimal compression, .
Another key strategy is the dynamic management of computational resources at edge nodes, modeled as a resource allocation problem. CPU and memory allocation is done using an efficiency maximization approach as presented in Equation 8:
Where is the total utilization, is the resources allocated to task , and is the maximum capacity of the node.
This allows for measuring their impact on energy savings, performance improvement, and operational cost reduction. The results obtained are used to dynamically adjust middleware configurations, ensuring continuous and efficient operation even under high-demand conditions. They also provide system functionality, interoperability, and efficiency while optimizing available resources. This methodology ensures that the middleware can adapt to the changing needs of the campus and deliver consistent performance in a complex IoT environment.
3.6 Middleware evaluation
The evaluation of the middleware developed for the Smart Campus focuses on representative use cases that reflect the primary needs of the IoT environment and specific metrics that allow measuring its performance. Monitoring and logging tools capture real-time data and generate detailed reports to ensure reliable results.
3.6.1 Defined use cases
The functionality of the middleware is validated in three key areas: energy management, security, and connectivity. In energy management, the middleware optimizes energy consumption by dynamically monitoring and controlling systems such as automated lighting and HVAC (Saleem et al., 2023). Temperature and daylight sensors provide real-time data that the middleware uses to adjust lighting intensity and HVAC system usage. This use case evaluates the middleware’s ability to reduce energy consumption without compromising user comfort.
For security, the middleware integrates surveillance cameras and access sensors, allowing real-time monitoring of suspicious events and logging of unauthorized access. The system also validates video recordings against recorded access events, ensuring synchronization between heterogeneous devices.
Regarding connectivity, the middleware assesses its ability to manage communication between IoT devices that use heterogeneous protocols. This includes ensuring that both real and simulated devices are automatically detected, and their data is correctly translated in real time, maintaining system integrity and continuity.
3.6.2 Metrics evaluated
Middleware evaluation is based on quantitative metrics that reflect its performance and efficiency:
• Response time: The interval from when a device sends data until it is processed, and the corresponding actions are executed is measured. An average response time of less than 100 ms for edge nodes is ideal.
• Energy consumption: The energy efficiency of edge nodes is evaluated by measuring the average consumption during critical and non-critical operations. The goal is to achieve a 20% reduction compared to systems that do not use optimization techniques.
• Interoperability success rate: The success rate of the middleware in integrating devices that operate under different protocols is measured. A 95% or higher success rate is optimal, reflecting the middleware’s ability to handle heterogeneous environments with scenarios including up to 500 devices, of which 120 were real and the rest simulated using public datasets and synthetic generators.
3.6.3 Tools for monitoring and recording metrics
Monitoring tools integrated into the middleware capture and analyze metrics in real-time. These tools include:
• Prometheus collects and stores performance data, such as edge node response times and CPU consumption.
• Grafana visualizes key metrics through interactive dashboards that identify real-time trends and anomalies.
• Wireshark is used to analyze network traffic and validate protocol translation, ensuring the integrity of communications.
• EnergyLogger, a specific system designed to record and analyze energy consumption in real-time, using sensors connected to test nodes.
These tools generate detailed reports that facilitate middleware evaluation in defined use cases. They provide key information to identify areas for improvement and validate compliance with system objectives.
3.7 System validation
The system was validated for the Smart Campus through controlled experimental tests and live tests in actual conditions. These stages allow us to evaluate the middleware’s effectiveness in simulated environments and its operational performance in a complex and dynamic IoT environment.
3.7.1 Experimental tests
The experimental tests were designed to validate the effectiveness of the middleware in specific scenarios representative of the defined use cases. These tests were conducted in a controlled environment comprising 120 real devices, complemented with up to 380 simulated instances, for a total load of 500 nodes configured to replicate realistic Smart Campus conditions. One of the scenarios evaluated was the integration of devices operating with different protocols. Environmental sensors were tested using MQTT, lighting actuators based on CoAP, and security cameras transmitting data using HTTP.
Another scenario evaluated was the energy efficiency of the edge nodes. Energy consumption was measured during critical operations, such as protocol translation and execution of real-time monitoring algorithms. Response time is also evaluated under high load conditions, simulating increased connected devices and the volume of data transmitted. The middleware maintained an average response time of 85 ms, highlighting its ability to handle real-time operations even in high-demand situations.
3.7.2 Deployment in the smart campus
Live testing was conducted at the Smart Campus, where the middleware was deployed to evaluate its performance under real-world conditions. Three key areas—energy management, security, and connectivity—were monitored during these tests. In energy management, the middleware dynamically controlled lighting and HVAC systems in two academic buildings. Daylight and temperature sensors provided real-time data, which the middleware processed to adjust lighting intensity and HVAC system operation.
In the security area, the middleware integrated surveillance cameras and access sensors to monitor events in real-time. During testing, 15 unauthorized access attempts were detected and recorded, which the system automatically blocked. In addition, the middleware synchronized video recordings with access events, improving security analytics capabilities. Regarding connectivity, the middleware automatically detected and integrated 25 additional connected IoT devices during testing, with no interruptions in the data flow. This result demonstrated the system’s ability to adapt efficiently to infrastructure changes and scale.
4 Results
4.1 Configuration and integration results
The results in this section were obtained through a meticulous experimental testing process designed to evaluate the middleware’s capability in integrating IoT devices in a controlled environment. The tests included a representative set of devices spanning environmental sensors, lighting actuators, security cameras, and access sensors, each operating under protocols such as MQTT, CoAP, HTTP, and BLE. Each device was configured individually, following a standardized procedure encompassing initial discovery, protocol configuration, and validation of its operation in the middleware. During this process, key metrics were recorded, including the average time required for the initial configuration of each device and the integration success rate. Additionally, any failures or delays associated with the configuration were monitored to identify patterns that could improve system efficiency.
Table 1 presents the results of the average configuration time and the device integration success rate by type and protocol used. MQTT-based devices, such as temperature sensors, showed the lowest average setup time of 29.5 s and a success rate of 98%. On the other hand, devices using HTTP, such as security cameras, had the highest average setup time of 44.8 s and a slightly lower success rate of 94%. Access sensors, which operate with BLE, stood out for their lowest setup time of 24.3 s, but with a success rate of 97%. This analysis shows that lighter protocols, such as MQTT and BLE, facilitate faster and more reliable integration, while more robust protocols, such as HTTP, present more significant configuration challenges.
TABLE 1
| Device | Type | Protocol | Setup time (seconds) | Integration success rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Sensor | Sensor | MQTT | 29.5 | 98 |
| Humidity Sensor | Sensor | CoAP | 34.2 | 95 |
| Lighting Actuator | Actuator | CoAP | 36.1 | 96 |
| Security Camera | Camera | HTTP | 44.8 | 94 |
| Access Sensor | Sensor | BLE | 24.3 | 97 |
Setup times and integration success rate by device type.
It is essential to note that the evaluated protocols utilize different wireless communication media: BLE operates over Bluetooth Low Energy, whereas MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP are deployed over Wi-Fi. Although these media differ in coverage, bandwidth, and latency, the middleware abstraction layer ensured a consistent integration process across them. As a result, the observed differences in setup times and integration rates were mainly protocol-dependent rather than caused by the underlying medium.
Figure 3 presents the variability of device setup times by protocol, using box-and-whisker plots to visualize the spread of the data. MQTT and BLE show less variability, indicating that their setup times are more consistent, which is ideal for real-time operations. In contrast, devices using HTTP show a greater spread, with times ranging from 30 to 60 s, which could lead to delays in high-demand scenarios. CoAP, although closer to MQTT in terms of average times, shows an intermediate spread, suggesting some variability in setup depending on the device.
FIGURE 3
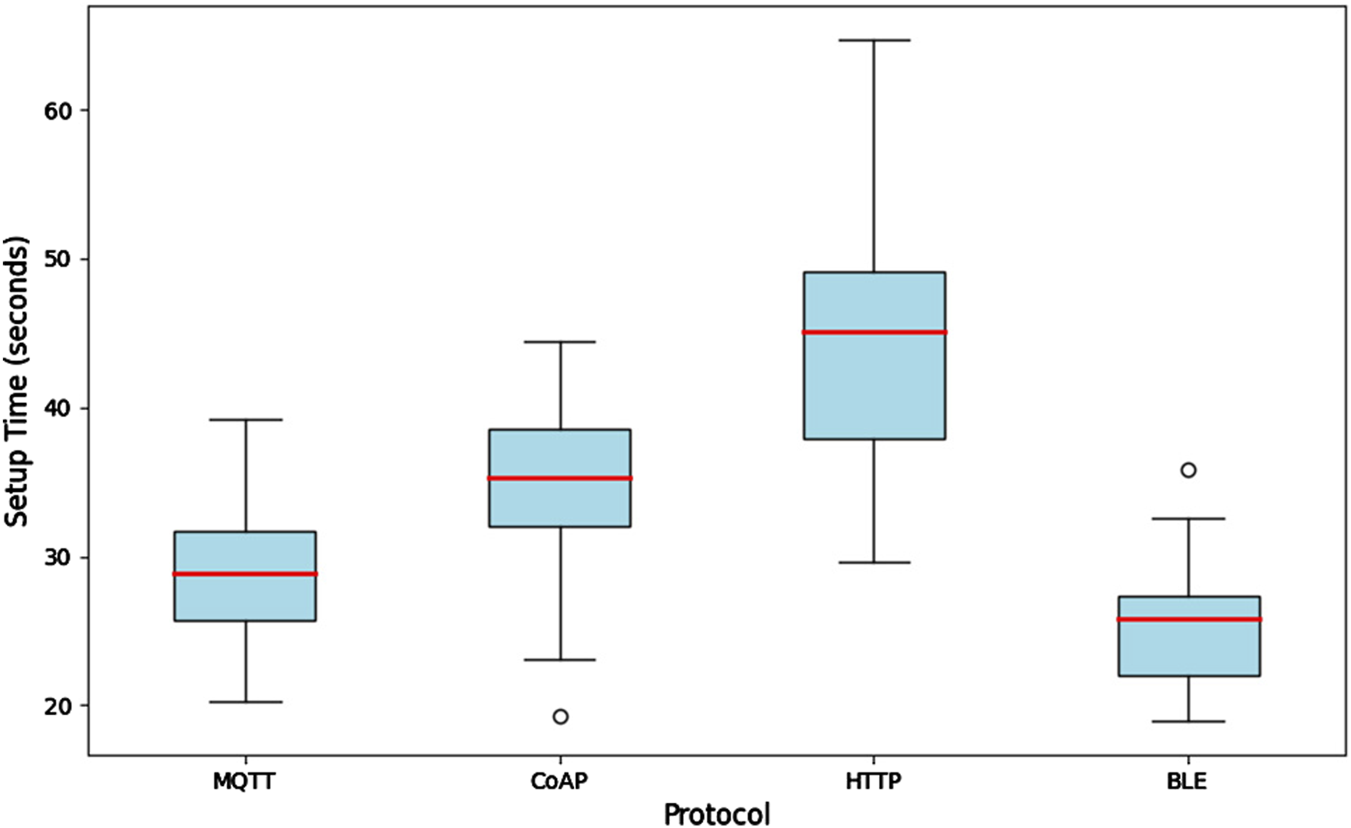
Analysis of configuration times by protocol in IoT devices.
These results demonstrate that the middleware is highly effective at managing heterogeneous device integration. However, the choice of protocol significantly influences both the speed and reliability of the configuration process. Optimizing integration workflows for more complex protocols, such as HTTP, remains crucial to reducing delays and ensuring consistent behavior in large-scale IoT environments.
4.2 Energy management
The results of this section were obtained through controlled tests on edge and cloud nodes, evaluating their energy consumption in different scenarios, with and without the optimization strategies implemented in the middleware. Measurements were recorded at regular intervals over 24 h, allowing us to analyze the average values and the variability in energy consumption.
Table 2 presents the average energy consumption values, and the percentage of reduction achieved through optimization on edge and cloud nodes. Edge nodes without optimization recorded an average consumption of 75 W, while with optimization, it was reduced to 55 W, achieving a decrease of 26.67%. On the other hand, cloud nodes showed an average consumption of 200 W without optimization, which was reduced to 160 W with the applied strategies, achieving a reduction of 20%. These results reflect that the applied optimization strategies, such as adaptive scheduling and critical task prioritization, significantly impact energy efficiency, especially at edge nodes, which are more sensitive to efficient resource management.
TABLE 2
| Node type | Optimization | Average energy consumption (W) | Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edge Node | Without Optimization | 75 | 0 |
| Edge Node | With Optimization | 55 | 26.67 |
| Cloud Node | Without Optimization | 200 | 0 |
| Cloud Node | With Optimization | 160 | 20.0 |
Average energy consumption and reduction with and without optimization.
Figure 4 presents the variability of energy consumption over time in both scenarios. It can be observed that, without optimization, energy consumption in edge and cloud nodes is higher and less consistent, with peaks that reflect tasks that are not prioritized or distributed efficiently. In contrast, consumption with optimization shows a more stable trend, with lower peaks and a more uniform use of energy throughout the day. The more excellent stability in the optimized scenario shows that the middleware can dynamically manage tasks, reducing unnecessary operations during periods of low demand.
FIGURE 4
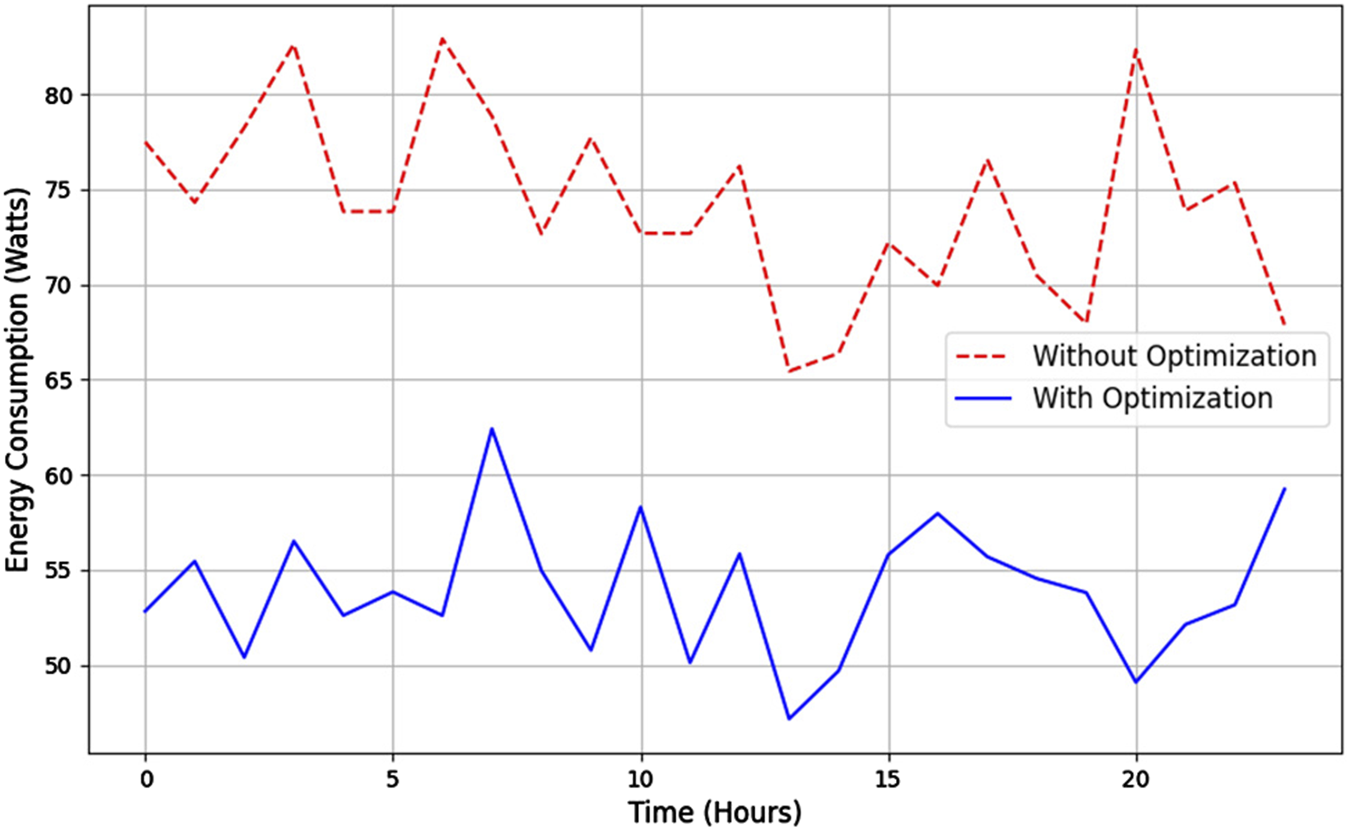
Variability of energy consumption over time in different scenarios.
The results demonstrate that implementing optimization strategies in the middleware significantly reduces energy consumption in heterogeneous IoT environments and stabilizes resource use, making the system more predictable and efficient in continuous operations.
4.3 Evaluating threat detection and response in IoT networks
Security tests were conducted to evaluate the middleware’s ability to detect and respond to security events on the Smart Campus. These tests included simulations of unauthorized access attempts, the generation of anomalies on the network, and the evaluation of the system’s responses. Events were recorded in real-time and classified according to the actions’ type, severity, and effectiveness to mitigate their impacts.
Unauthorized access attempts were simulated by sending incorrect credentials and replicating identities of legitimate devices. In parallel, unusual traffic patterns were introduced into the network to evaluate anomaly detection. The middleware used machine learning algorithms trained with historical data from the campus to identify irregular patterns and set real-time alerts. Each detected event automatically triggered predefined responses, such as blocking the suspicious device, notifying system administrators, and recording incidents in a secure log.
Table 3 presents the results obtained during the tests. The middleware recorded 150 events, 90 of which corresponded to unauthorized access attempts and 60 to network traffic anomalies. The overall detection rate was 96%, with an average response time of 1.2 s. Unauthorized access attempts were mitigated by 92%, while network anomalies were successfully managed by 98%.
TABLE 3
| Event type | Total events | Detection rate (%) | Response success rate (%) | Average response time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unauthorized Access | 90 | 94 | 92 | 1.3 |
| Network Anomalies | 60 | 98 | 98 | 1.1 |
| Overall | 150 | 96 | 95 | 1.2 |
Detected events and generated responses.
The results demonstrate that the middleware is highly capable of detecting and mitigating real-time threats across heterogeneous IoT infrastructures. Notably, the machine learning model showed strong performance in anomaly detection, owing to its ability to model normal behavior with high granularity and accurately flag atypical patterns. However, spoofing attacks involving identity replication posed a relatively higher challenge. Their successful mitigation rate, though high, indicates room for improvement. Future work may include the integration of biometric authentication, multi-factor validation, or behavioral profiling, aiming to reduce vulnerability to sophisticated impersonation tactics further. This evaluation confirms that the middleware’s security module is not only reactive but also adaptive, capable of evolving to match new threat profiles with minimal human intervention—an essential feature for large-scale, dynamic IoT deployments.
4.4 Evaluating latency and integration of real-time IoT devices
The results evaluated the middleware’s ability to integrate IoT devices in real time and ensure efficient data exchange. These tests included connecting devices operating under different protocols (MQTT, CoAP, HTTP, and BLE) and measuring the average integration time, latency during communication, and variability in both metrics.
Table 4 presents the detailed results of these tests. Devices using BLE and MQTT showed the lowest integration times, with averages of 4.5 and 5.2 s, respectively, and a minimum variability of 0.4 and 0.5 s. This highlights the efficiency of these protocols in quickly connecting devices to the middleware. In contrast, HTTP-based devices presented the highest integration time, with an average of 12.3 s and a variability of 1.2 s, indicating that more robust protocols require more complex configurations. Devices operating with CoAP fell somewhere in the middle, with an average integration time of 7.8 s and a variability of 0.7 s.
TABLE 4
| Protocol | Average integration time (s) | Integration variability (s) | Average latency (ms) | Latency variability (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MQTT | 5.2 | 0.5 | 20 | 2 |
| CoAP | 7.8 | 0.7 | 30 | 5 |
| HTTP | 12.3 | 1.2 | 50 | 7 |
| BLE | 4.5 | 0.4 | 15 | 1.5 |
Average integration times and latency by protocol.
Regarding latency during data exchange, MQTT and BLE again stood out with low average values of 20 ms and 15 ms, respectively, and limited variability of 2 ms and 1.5 ms. These results demonstrate that lightweight protocols are ideal for applications requiring fast real-time responses. On the other hand, HTTP presented the highest average latency, 50 ms, and significant variability, 7 ms, reflecting the overhead inherent to this protocol in IoT environments. CoAP, as in integration, showed intermediate values with an average latency of 30 ms and variability of 5 ms.
The results demonstrate that the middleware effectively handles the integration of IoT devices in real-time, although performance varies considerably depending on the protocol used. While protocols such as MQTT and BLE are faster and more stable, HTTP requires improvements in optimization to reduce latency and integration time. Furthermore, the stability and speed observed in lightweight protocols reinforce the viability of middleware in applications that demand high reactivity and low configuration time.
4.5 Performance metrics
The results were obtained through experimental tests designed to evaluate the behavior of the middleware under different load levels (low, medium, and high). During the tests, multiple simultaneous requests sent to the optimized and non-optimized nodes were simulated, the response times were recorded, and their variability was analyzed. These tests allowed for measuring the optimization strategies’ impact on the system’s overall performance.
Figure 5 presents the response times obtained for optimized and non-optimized nodes under different load levels, using box-and-whisker diagrams to reflect the variability of the results. In the low load scenario, the optimized nodes showed an average response time of 50 ms, with a limited dispersion showing consistent performance. In contrast, the non-optimized nodes recorded an average time of 80 ms, with a more excellent dispersion in the data, suggesting inefficiency in request handling.
FIGURE 5
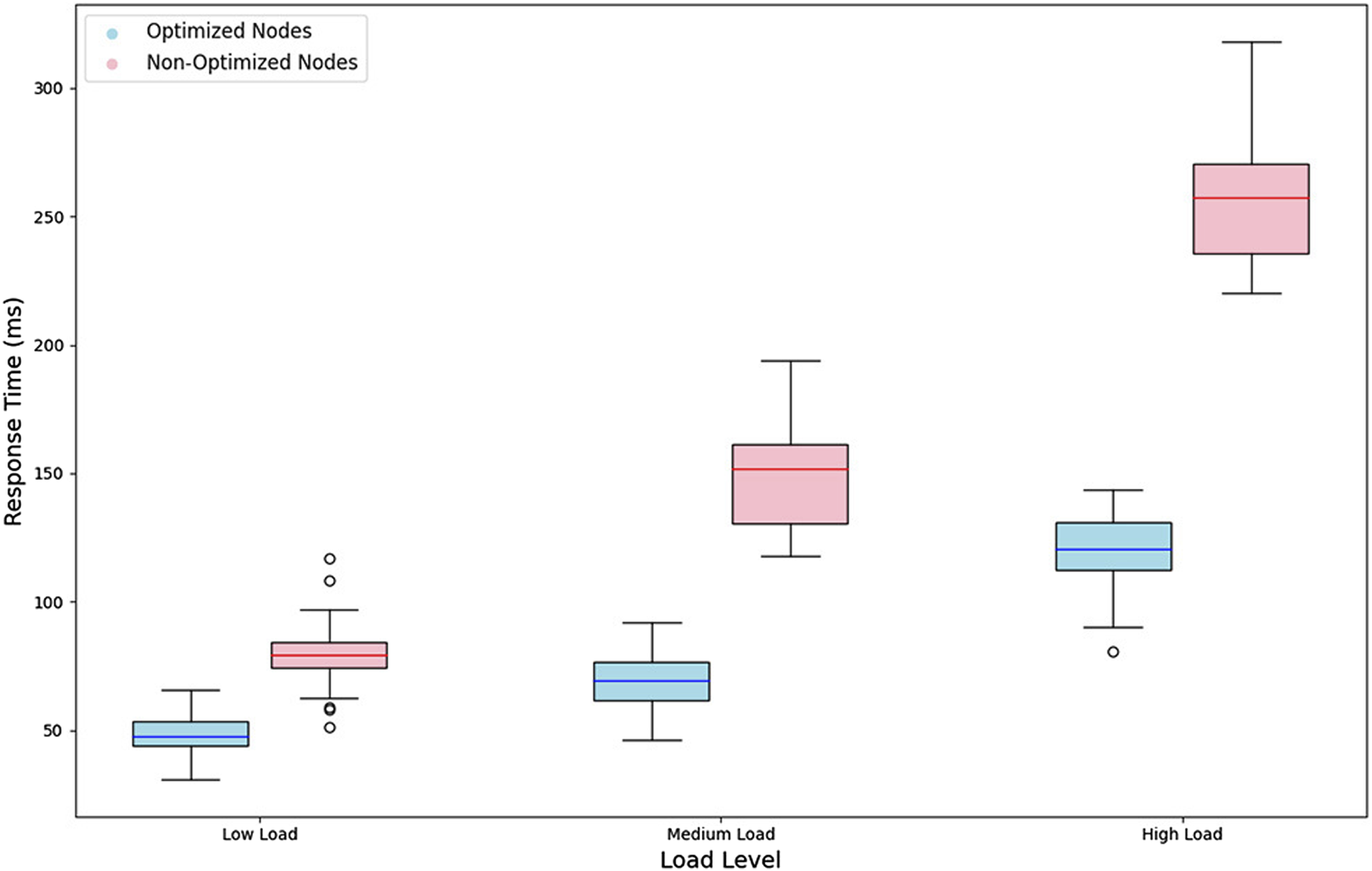
Response times under different load levels for optimized and non-optimized nodes.
The differences between the optimized and non-optimized nodes became more apparent as the load increased to medium and high levels. In the high-load scenario, the optimized nodes maintained an average response time of 120 ms with moderate variability. The non-optimized nodes achieved a significantly higher average of 250 ms, with a noticeably high dispersion. These results indicate that non-optimized nodes are more susceptible to performance degradation under high-demand conditions.
The analysis of the results demonstrates that the optimization strategies implemented in the middleware reduce average response times across all load levels and stabilize performance, minimizing variability in operations. This positions the middleware as an efficient solution for dynamic IoT environments, where the ability to handle fluctuating loads consistently is crucial. However, the increased variability in high-load scenarios suggests that although the optimized system has robust performance, it could further benefit from additional resource management techniques to improve its stability under extreme conditions.
4.6 Comparative analysis between experimental tests and performance in the smart campus
The middleware was validated under two distinct conditions: controlled experimental testing and live deployment in the Smart Campus. This dual-context evaluation enabled the analysis of system behavior under both reproducible stress conditions and real-world operational dynamics. The metrics considered include energy consumption, response time, and interoperability success rate, enabling a quantitative comparison of middleware performance across different environments.
4.6.1 Experimental tests
In the controlled environment, a predefined set of heterogeneous IoT devices was used to simulate high-load and protocol-diverse conditions. Optimization mechanisms were applied to specific nodes to assess their impact on energy and latency metrics. As shown in Table 5, optimized edge nodes achieved an average energy consumption of 55 W, while non-optimized nodes reached 75 W, resulting in a reduction of 26.7%. In terms of response time, optimized nodes consistently processed requests in 120 ms, compared to 250 ms in non-optimized configurations. Furthermore, the middleware reached a 96% interoperability success rate, indicating robust handling of heterogeneous protocols in this controlled setup.
TABLE 5
| Metric | Experimental results | Real-results |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption (W) | 55 (Optimized)/ 75 (non-optimized) | 60 (Optimized)/ 80 (non-optimized) |
| Response Time (ms) | 120 (Optimized)/ 250 (non-optimized) | 130 (Optimized)/ 270 (non-optimized) |
| Interoperability Success Rate (%) | 96 | 94 |
Attack tolerance coefficient in different protocols.
The column labeled “Real-Results” refers specifically to the metrics obtained under real operational conditions, where dynamic device loading, network interference, and variable workloads influence system behavior. These values complement the experimental benchmarks by providing evidence of the middleware’s stability in non-deterministic scenarios and are further supported by the analysis of the Smart Campus implementation.
4.6.2 Deployment in the smart campus
Implementing the middleware in the Smart Campus allowed us to evaluate its performance under actual conditions, where external factors such as dynamic device loading and communication interference influence system behavior. Figure 6 illustrates the results obtained, comparing key metrics between experimental and real environments. In objective tests, the average power consumption increased slightly to 60 W on the optimized nodes and 80 W on the non-optimized nodes due to fluctuations in real workloads. Response times also showed a moderate increase, reaching 130 ms on the optimized nodes and 270 ms on the non-optimized nodes, reflecting the impact of dynamic conditions on the campus network. The interoperability rate remained high at 94%, confirming the middleware’s ability to adapt to a diverse and active IoT environment.
FIGURE 6
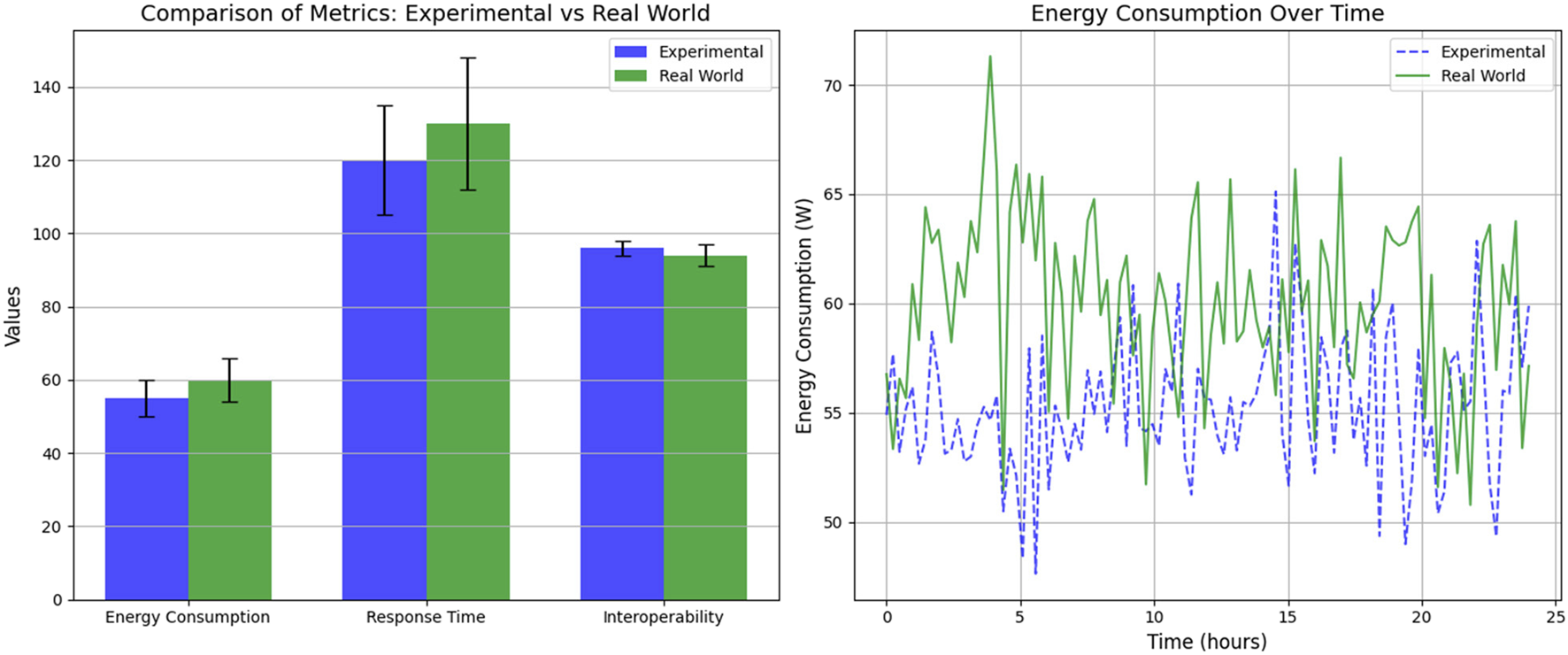
Comparison of key metrics and energy consumption in different environments.
The results show that although real-world conditions slightly increased the energy consumption and response time metrics compared to the experimental environment, the middleware maintained efficient and consistent performance. The stability of the interoperability rate highlights the system’s robustness in handling heterogeneous environments. These findings confirm the middleware’s feasibility in operating in complex scenarios such as the Smart Campus, where variability and resource demands are constant factors.
4.7 Comparison with existing proposals
To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed middleware, we compared it against two widely adopted IoT communication protocols, Z-Wave and LoRaWAN. While these are not middleware systems, they are included as baselines due to their extensive deployment and well-documented performance characteristics in terms of latency, interoperability, and scalability. The objective is not to equate their nature with middleware but to provide a functional benchmark that contextualizes the performance of our solution.
The evaluation results are summarized in Table 6. The values for the proposed middleware correspond to our experimental measurements, while those for Z-Wave and LoRaWAN are drawn from documented protocol capabilities.
TABLE 6
| Metric | Proposed middleware (this work) | Z-Wave [Rafiq et al. (2023), Fuller et al. (2017)] | LoRaWAN [Basford et al. (2020),Finnegan et al. (2018)] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption (W) | 60 (Optimized)/80 (Not Optimized) | Low-power operation | Energy-efficient; lifetime up to years (duty-cycle dependent) |
| Response Time (ms) | 130 (Optimized)/270 (Not Optimized) | 100 | 400–2000+ |
| Scalability (Supported Devices) | 500 (120 real + 380 simulated) | 232 | Thousands |
Comparison of middleware performance with existing IoT protocols.
Regarding response times, the middleware achieved 130 ms in optimized conditions, outperforming LoRaWAN deployments that typically exhibit latencies in the order of hundreds of milliseconds to seconds depending on spreading factor and traffic load (Basford et al., 2020), but slightly behind Z-Wave, which maintains low-latency communication around 100 ms in home and building automation scenarios (Rafiq et al., 2023). While Z-Wave provides fast responsiveness, its scalability is constrained to approximately 232 devices per network with a maximum of four hops (Fuller et al., 2017). In contrast, LoRaWAN is designed for large-scale deployments supporting thousands of devices per gateway (Finnegan et al., 2018). The proposed middleware achieves a balanced trade-off between latency, scalability, and interoperability, validated at a scale of 500 devices (120 real and 380 simulated nodes combined) in controlled Smart Campus scenarios.
An extended benchmark was conducted to provide a more comprehensive evaluation, focusing on metrics critical for IoT environments such as throughput, ease of integration, and latency in hybrid networks. The middleware achieved a throughput of 500 kbps, significantly outperforming Z-Wave (200 kbps) and LoRaWAN (300 kbps). This improvement highlights the middleware’s ability to handle high data volumes efficiently, essential for real-time communication applications.
The modular and adaptive architecture of the middleware also enabled a high ease-of-integration score, surpassing the medium scores of Z-Wave and LoRaWAN. This adaptability reduces deployment times and enhances compatibility with heterogeneous devices, a key advantage in agile scaling and fast onboarding scenarios. Latency in hybrid networks was also assessed, with the middleware achieving 140 ms, better than LoRaWAN’s 170 ms and comparable to Z-Wave’s 150 ms. These results are summarized in Table 7.
TABLE 7
| Metric | Proposed middleware | Z-Wave | LoRaWAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Throughput (kbps) | 500 | 200 | 300 |
| Ease of Integration (Qualitative) | High | Medium | Medium-Low |
| Latency in Hybrid Networks (ms) | 140 | 150 | 170 |
Extended benchmark: Middleware performance compared to existing solutions.
These results underscore the middleware’s scalability, interoperability, and throughput strengths, making it a robust solution for dynamic IoT environments such as Smart Campuses. The 26.7% reduction in energy consumption highlights its ability to balance energy efficiency with high device density, a challenge that existing solutions like Z-Wave and LoRaWAN fail to address comprehensively. Its ease of integration further enhances its applicability in scenarios requiring seamless deployments, particularly in environments where rapid scaling and device diversity are priorities.
While the middleware demonstrates superior scalability and interoperability, there is room for further improvement in energy consumption to match LoRaWAN’s low-power performance in specific scenarios. Similarly, latency optimization for critical real-time applications could further enhance its competitiveness with Z-Wave in low-latency environments. These insights provide a clear roadmap for future enhancements.
Beyond protocol baselines, our results were also contrasted with recent middleware proposals. Microservice-based orchestration at the fog layer can optimize service composition and elasticity (Emami Khansari and Sharifian, 2024). Yet, it does not target on-the-fly multi-protocol translation at the edge with device onboarding under heterogeneous traffic, which is a core focus of our system (achieving an optimized end-to-end response of 130 ms with validated interoperability). Distributed governance and data-security infrastructures (Tamizshelvan and Vijayalakshmi, 2024) prioritize access control and compliance at scale; our evaluation complements this, emphasizing runtime interoperability and response-time behavior across 120 real devices and up to 500 combined devices. Edge–fog–cloud frameworks in healthcare and smart cities highlight open challenges—interoperability, scalability, energy efficiency, and security (Zaydi and Bakkoury, 2024; Goumopoulos, 2024)—which our deployment addresses empirically through cross-protocol translation and adaptive integration policies on campus. In parallel, automated configuration layers for data backends (Preuveneers et al., 2020) and pluggable security toolkits for constrained devices (Kim et al., 2023) are orthogonal to our contribution. We integrate secure channels and anomaly detection, while our main novelty lies in achieving protocol-level interoperability with measured latency, throughput, and device-integration performance in situ.
The evaluation covered three key functional areas of the middleware: energy management, security, and connectivity. While the detailed numerical results have been presented in the previous subsections, Table 8 summarizes the validation framework by explicitly listing the evaluation parameters associated with each functionality and referencing the sections where the results are detailed.
TABLE 8
| Functionality | Evaluation parameters | Detailed results |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Management | Average consumption (with/without optimization); reduction percentage | Table 2 |
| Security | Detection rate, response success, and response time for unauthorized access and anomalies | Table 3 |
| Connectivity | Setup time by device type; integration success rate across heterogeneous devices | Table 1 |
Validation areas, evaluation parameters, and references to detailed results.
5 Discussion
The results obtained in this study and the literature review highlight advances and limitations that position the proposed middleware as a comprehensive solution for complex IoT environments such as the Smart Campus. Compared with existing solutions, such as Z-Wave (Gvozdenovic et al., 2024) and LoRaWAN (Jabbar et al., 2024), the proposed middleware demonstrates significant advancements in scalability, interoperability, and energy efficiency. At the same time, Z-Wave exhibits an average response time of less than 100 ms; however, its limited scalability, restricted to only 232 devices, significantly limits its applicability in dense networks. Similarly, LoRaWAN achieves excellent energy efficiency (40 W) but compromises latency and interoperability, with an 85% success rate, due to its focus on low-power, long-range applications. In contrast, the proposed middleware achieves a balance across these metrics, supporting up to 500 devices in simulated conditions with a 94% interoperability rate while maintaining energy consumption of 60 W in optimized scenarios. This balanced performance marks a notable improvement over the trade-offs traditionally observed in IoT middleware implementations.
The middleware’s architecture incorporates features that existing solutions lack, such as adaptive protocol translation, which dynamically adjusts to heterogeneous device requirements, ensuring efficient communication across diverse protocols. This capability directly addresses limitations in Z-Wave and LoRaWAN, which rely on static protocol designs. Furthermore, the modular microservices-based architecture supports the seamless integration of new technologies and emerging IoT standards, enhancing system flexibility and future-proofing its design.
The middleware’s validated scalability with 500 simulated devices provides a critical advantage in moderately dense environments. Although the platform has not yet reached massive-scale deployment, its tested capacity significantly surpasses that of Z-Wave and approaches the scale of LoRaWAN, validating its applicability in moderately dense IoT networks. The middleware’s dynamic orchestration module further enhances performance by balancing workloads across nodes, optimizing throughput, and minimizing latency under high loads. These features demonstrate the middleware’s capacity to operate effectively in scenarios where existing solutions fail to meet the demands of heterogeneous and expanding infrastructures.
Energy efficiency improvements also highlight the middleware’s transformative impact. While LoRaWAN excels in low-power scenarios, its trade-offs in interoperability and latency limit its applicability. The middleware addresses these issues through energy-aware scheduling algorithms and adaptive data compression techniques, achieving competitive energy consumption without sacrificing scalability or response times. These innovations not only reduce operational costs but also contribute to the sustainability of large-scale IoT networks, aligning with broader goals of environmental and economic efficiency (Goumopoulos, 2024).
The practical implications of these improvements extend beyond technical performance. In Smart Campus environments, the ability to integrate diverse devices seamlessly enhances the user experience by reducing downtime and improving reliability. The middleware’s modularity also simplifies deployment and maintenance, reducing implementation complexity and associated costs. These advantages position the middleware as a transformative solution for IoT networks requiring high scalability, efficiency, and adaptability (Rana et al., 2021).
Despite these advances, the study identifies several limitations. Although the middleware achieves a 94% interoperability rate, challenges remain in integrating devices with proprietary protocols. This limitation could be mitigated through advanced protocol translation algorithms or by encouraging standardization in communication interfaces. Future work could explore machine learning-based approaches to optimize further protocol adaptation in real-time, potentially improving interoperability beyond the current metrics (Chaudhary et al., 2024a).
Energy consumption, while competitive, remains slightly higher than that of LoRaWAN in optimized scenarios. Addressing this limitation requires exploring additional optimization strategies, such as AI-driven resource allocation and more efficient data handling techniques. By incorporating such an approach, the middleware could further enhance its applicability in energy-constrained environments, such as rural IoT networks (Chaudhary et al., 2024b). Latency also represents a critical area for improvement. While 130 ms response times are suitable for many applications, specific use cases, like emergency systems, demand lower latencies. Hybrid architecture leveraging edge and cloud computing could help address this challenge by more effectively distributing workloads and ensuring real-time responsiveness in critical scenarios.
It is important to emphasize that the proposed middleware is not limited to a specific proprietary medium. Its implementation in this study was based on standard wireless infrastructures, specifically Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11ax) and BLE for access devices. Therefore, the comparison with Z-Wave and LoRaWAN is not intended as a direct medium-to-medium evaluation, but rather a functional benchmark between representative IoT solutions. This approach highlights how the middleware, when running on common communication infrastructures, can achieve competitive performance in latency, scalability, and interoperability, while offering greater flexibility through protocol translation and heterogeneous device inte-gration.
These limitations, while notable, do not detract from the middleware’s contributions. Its ability to balance scalability, interoperability, and energy efficiency represents a significant advance over existing solutions. Although some adaptations may be required for deployment in specialized IoT environments, the middleware’s modular design ensures these adjustments are feasible and cost-effective. This work addresses current challenges and sets the stage for future innovations in IoT middleware, providing a foundation for scalable, efficient, and adaptable networks that can meet the demands of modern applications.
6 Conclusion
This study introduced a middleware designed to tackle the challenges of dense and heterogeneous IoT environments, particularly in Smart Campuses. The proposed solution demonstrates a significant step forward in IoT middleware design by addressing key aspects such as scalability, interoperability, energy efficiency, and modularity.
The middleware has been validated with up to 500 simulated devices, exceeding the limitations of existing technologies like Z-Wave and LoRaWAN, which are constrained by scalability and protocol diversity. This achievement stems from its modular microservices-based architecture, which enables seamless integration of heterogeneous devices while dynamically adapting to emerging protocols. Adaptive protocol translation and energy-aware resource management provide a practical balance between performance and efficiency, meeting the diverse demands of modern IoT networks.
Energy optimization strategies, including adaptive scheduling and data compression, reduced power consumption by 26.7% compared to non-optimized nodes. The middleware maintained a 94% interoperability success rate, even when integrating real and simulated devices, validating its robustness, validating its robustness in managing diverse and dynamic networks. These advancements make the middleware particularly suitable for moderately dense IoT environments, where sustainability and efficiency are critical.
Despite these achievements, areas for improvement remain. While acceptable for most applications, the middleware’s response times, averaging 130–140 ms, require further optimization for latency-critical scenarios such as emergency response systems. Future work will integrate machine learning algorithms to enhance protocol translation and task prioritization, reducing latency and improving adaptability.
The modular architecture ensures the middleware’s adaptability to future technologies, including 5G and evolving IoT protocols, positioning it as a long-term solution for a diverse range of applications. Its ability to scale without compromising performance in controlled and semi-real environments positions it as a versatile solution potentially applicable to scenarios ranging from energy management to real-time monitoring in urban and industrial IoT networks. Future research will emphasize live testing in varied environments, such as industrial facilities and smart cities, to assess the middleware’s performance under complex conditions. Predictive analytics and AI will also be explored to further enhance decision-making and system efficiency, consolidating their impact in the IoT domain.
Statements
Data availability statement
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to confidentiality and project restrictions, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author contributions
RG: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. WV-C: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. JG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Alaparthi N. Rao P. S. (2017). “Adaptation layer towards integration of ZigBee and IP stacks,” in 2017 international conference on automatic control and dynamic optimization techniques (ICACDOT), 212–215. 10.1109/ICACDOT.2016.7877581
2
Basford P. J. Bulot F. M. J. Apetroaie-Cristea M. Cox S. J. Ossont S. J. (2020). LoRaWAN for smart city IoT deployments: a long-term evaluation. Sensors Switz.20 (3), 648. 10.3390/s20030648
3
Bebortta S. Pati B. Panigrahi C. R. Senapati D. (2024). Dynamic performance modeling framework for QoS-aware 5G-based IoT-edge systems. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Singap.16 (4), 2149–2160. 10.1007/s41870-023-01716-7
4
Braghin C. Lilli M. Riccobene E. (2023). A model-based approach for vulnerability analysis of IoT security protocols: the Z-Wave case study. Comput. and Secur.127, 103037. 10.1016/j.cose.2022.103037
5
Chaudhary D. Soni T. Singh S. Durgarao M. S. P. Gupta S. M. C. (2024a). “A sustainable privacy-preserving aggregation authentication protocol for smart grid,” in Lecture notes in electrical engineering. 10.1007/978-981-99-7630-0_3
6
Chaudhary D. Soni T. Singh S. Gupta S. M. C. (2024b). “A construction of secure and efficient authenticated key exchange protocol for deploying internet of drones in smart city,” in Communications in computer and information science. 10.1007/978-3-031-48774-3_9
7
Domínguez-Bolaño T. Barral V. Escudero C. J. García-Naya J. A. (2024). An IoT system for a smart campus: challenges and solutions illustrated over several real-world use cases. Internet Things Neth.25, 101099. 10.1016/j.iot.2024.101099
8
Dos Santos L. E. B. Ramos R. G. S. Gomes R. D. Lins P. R. Dos Santos A. L. (2022). “Middleware for smart campus applications based in federated learning,” in ACM international conference proceeding series. 10.1145/3539637.3558046
9
Dowdeswell B. Sinha R. Kuo M. M. Y. Seet B. C. Ghaffarian Hoseini A. Ghaffarianhoseini A. et al (2024). Healthcare in asymmetrically smart future environments: applications, challenges and open problems. Electron. Switz.13 (1), 115. 10.3390/electronics13010115
10
el-Khaeri Kesuma M. Kesuma G. C. Taher A. (2024). Internet of things to realize education in industry 4.0 based on sustainability environment. E3S Web Conf.482, 05008. 10.1051/e3sconf/202448205008
11
Emami Khansari M. Sharifian S. (2024). A scalable modified deep reinforcement learning algorithm for serverless IoT microservice composition infrastructure in fog layer. Future Gener. Comput. Syst.153, 206–221. 10.1016/j.future.2023.11.022
12
Ferreira L. C. B. C. Borchardt A. D. R. Cardoso G. D. S. Mendes Lemes D. A. Sousa G. R. D. R. d. Neto F. B. et al (2022). Edge computing and microservices middleware for home energy management systems. IEEE Access10, 109663–109676. 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3214229
13
Finnegan J. Brown S. Farrell R. (2018). “Evaluating the scalability of LoRaWAN gateways for class B communication in ns-3,” in 2018 IEEE conference on standards for communications and networking (CSCN), 1–7. 10.1109/CSCN.2018.8581759
14
Fuller J. D. Ramsey B. W. Rice M. J. Pecarina J. M. (2017). Misuse-based detection of Z-Wave network attacks. Comput. and Secur.64, 44–58. 10.1016/j.cose.2016.10.003
15
Garrido-Hidalgo C. Roda-Sanchez L. Ramírez F. J. Fernández-Caballero A. Olivares T. (2023). Efficient online resource allocation in large-scale LoRaWAN networks: a multi-agent approach. Comput. Netw.221, 109525. 10.1016/j.comnet.2022.109525
16
Glória A. Cercas F. Souto N. (2017). Design and implementation of an IoT gateway to create smart environments. Procedia Comput. Sci.109, 568–575. 10.1016/j.procs.2017.05.343
17
Goumopoulos C. (2024). Smart city middleware: a survey and a conceptual framework. IEEE Access12, 4015–4047. 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3349376
18
Gvozdenovic S. Becker J. K. Mikulskis J. Starobinski D. (2024). IoT-Scan: network reconnaissance for internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J.11 (8), 13091–13107. 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3327293
19
Hanon W. Salman M. A. (2024). Smart controller integrated with MQTT broker based on machina learning techniques. J. Eur. des Systèmes Automatisés57 (1), 87–94. 10.18280/jesa.570109
20
Jabbar W. A. Mei Ting T. I. Hamidun M. F. Che Kamarudin A. H. Wu W. Sultan J. et al (2024). Development of LoRaWAN-based IoT system for water quality monitoring in rural areas. Expert Syst. Appl.242, 122862. 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122862
21
Jepsen S. C. Siewertsen B. Worm T. (2023). “A reconfigurable industry 4.0 middleware software architecture,” in Proceedings of the IEEE 20th international conference on software architecture companion (ICSA-C). 10.1109/ICSA-C57050.2023.00023
22
Kim D. Jo Y. Kim T. Kim H. (2023). SST v1.0.0 with C API: pluggable security solution for the internet of things. SoftwareX22, 101390. 10.1016/j.softx.2023.101390
23
Kumar A. K. Kumar T. R. Balamanigandan R. Kumar A. S. Mahaveerakannan R. (2023). “Diagnosis of faults in Edge-PLC using optimized deep learning models in industrial IoT,” in 2023 9th international conference on advanced computing and communication systems (ICACCS). 10.1109/ICACCS57279.2023.10112824
24
Lamnaour M. Raiss M. Mesmoudi Y. El Khamlichi Y. Tahiri A. Touhafi A. (2024). A semantic-based middleware for supporting heterogeneity and context-awareness within IoT applications. J. Commun.19 (1), 19–27. 10.12720/jcm.19.1.19-27
25
Mishra M. Reddy S. R. N. (2024). Performance assessment and comparison of lightweight D2D-IoT communication protocols over resource constraint environment. Multimedia Tools Appl.83 (26), 67569–67598. 10.1007/s11042-024-18132-z
26
Nagowah S. D. Ben Sta H. Gobin-Rahimbux B. A. (2024). “Modelling sustainability for an IoT-enabled smart green campus using an ontology-based approach,” in CEUR workshop proceedings.
27
Pink A. P. Fehres C. Pearce J. D. Costa S. Noworyta M. (2021). “The new edge. Building and deploying a new state of the art, high speed acquisition, automation and analytics platform for drilling, completions, production, and renewable energy applications,” in Society of petroleum engineers - abu Dhabi international petroleum exhibition and conference, ADIP 2021. 10.2118/207291-MS
28
Prandi C. Monti L. Ceccarini C. Salomoni P. (2019). Smart campus: fostering the community awareness through an intelligent environment. Mob. Netw. Appl.24 (126), 945–952. 10.1007/s11036-019-01238-2
29
Preuveneers D. Joosen W. (2020). Automated configuration of NoSQL performance and scalability tactics for data-intensive applications. Informatics7 (3), 29. 10.3390/INFORMATICS7030029
30
Rafiq I. Mahmood A. Razzaq S. Jafri S. H. M. Aziz I. (2023). IoT applications and challenges in smart cities and services. J. Eng.2023 (4), e12262. 10.1049/tje2.12262
31
Rana B. Singh Y. Singh P. K. (2021). A systematic survey on internet of things: energy efficiency and interoperability perspective. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol.32 (8), e4166. 10.1002/ett.4166
32
Robinson Joel M. Ranganathan C. S. Narendruni L. P. Srinivasan S. Latha N. (2023). “MQTT client protocol-based effective coal mine management system using IoT,” in 2023 2nd international conference on smart technologies for smart nation (SmartTechCon). 10.1109/SmartTechCon57526.2023.10391302
33
Saifeng Z. (2024). AQINM: an adaptive QoS management framework based on intelligent negotiation and monitoring in cloud. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Manag.23 (1), 33–47. 10.1504/IJITM.2024.136183
34
Saleem M. U. Shakir M. Usman M. Bajwa M. Shabbir N. Shams Ghahfarokhi P. et al (2023). Integrating smart energy management system with internet of things and cloud computing for efficient demand side management in smart grids. Energies16 (12), 4835. 10.3390/en16124835
35
Shin Y. Jeon S. (2024). MQTree: secure OTA protocol using MQTT and MerkleTree. Sensors24 (5), 1447. 10.3390/s24051447
36
Shu C. Pan Z. Chen Z. Mu K. Yang Z. Xie C. (2022). A liquid metal computing platform based on ensemble learning and multi-source data adaptation. Chin. J. Rare Metals46 (5). 10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.XY21060016
37
Sosnowski M. Zirngibl J. Sattler P. Carle G. Grohnfeldt C. Russo M. et al (2024). EFACTLS: effective active TLS fingerprinting for large-scale server deployment characterization. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag.21 (3), 2582–2595. 10.1109/TNSM.2024.3364526
38
Tamizshelvan C. Vijayalakshmi V. (2024). Cloud data access governance and data security using distributed infrastructure with hybrid machine learning architectures. Wirel. Netw.30 (4), 2099–2114. 10.1007/s11276-024-03658-9
39
Tange K. De Donno M. Fafoutis X. Dragoni N. (2020). A systematic survey of industrial internet of things security: requirements and fog computing opportunities. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials22 (4), 2489–2520. 10.1109/COMST.2020.3011208
40
Xu H. Yan Z. Li B. Yang M. (2024). Modeling and analysis of the performance for bluetooth low energy. IEEE Commun. Lett.28 (3), 732–736. 10.1109/LCOMM.2024.3352545
41
Yin H. Huang X. Cao E. (2024). A cloud-edge-based multi-objective task scheduling approach for smart manufacturing lines. J. Grid Comput.22 (1), 9. 10.1007/s10723-023-09723-5
42
Zaydi H. Bakkoury Z. (2024). Advancing healthcare data management: IoT edge-fog-cloud architectures for medical IoT devices’ data storage and processing. Int. J. Math. Comput. Sci.19 (1). Available online at: http://ijmcs.future-in-tech.net.
Summary
Keywords
IoT middleware, scalability and interoperability, energy efficiency, smart campus, machine learning
Citation
Gutierrez R, Villegas-Ch W and Govea J (2025) Modular middleware for IoT: scalability, interoperability and energy efficiency in smart campus. Front. Commun. Netw. 6:1672617. doi: 10.3389/frcmn.2025.1672617
Received
24 July 2025
Accepted
08 September 2025
Published
24 September 2025
Volume
6 - 2025
Edited by
Moustafa Nasralla, Prince Sultan University, Saudi Arabia
Reviewed by
Anastasios Valkanis, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece
Sohaib Bin Altaf Khattak, Prince Sultan University, Saudi Arabia
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Gutierrez, Villegas-Ch and Govea.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: William Villegas-Ch, william.villegas@udla.edu.ec
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.