- 1Department of Endodontics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
- 2Department of Endodontics, School of Stomatology, Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
- 3NHC Key Laboratory of Cell Transplantation, The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
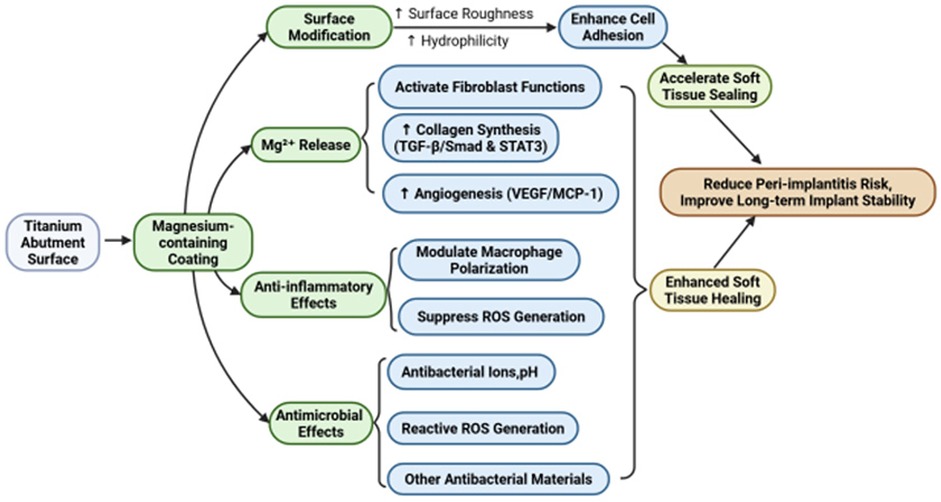
The inherent limitations of smooth titanium abutments—particularly inadequate soft tissue sealing that predisposes implants to infection and inflammation—underscore the need for surface modifications. This review synthesizes evidence on magnesium-containing coatings as a bioactive solution to enhance peri-implant soft tissue healing. Through 1) modifying the surface properties of the implant abutment to promote better cell adhesion and proliferation; 2) releasing Mg2+ to promote fibroblast migration, collagen synthesis, and angiogenesis; and 3) exerting antimicrobial effects and regulating inflammatory responses, these coatings establish a microenvironment conducive to robust tissue integration. This helps prevent peri-implant infections and inflammation, strengthens soft tissue attachment, and improves the long-term stability of dental implants, providing a new direction for the development of biomedical materials.
1 Introduction
Dental implants, since their advent in the 1960s, have become the primary solution for addressing tooth loss due to their efficiency, durability, and aesthetic benefits. Dental implants usually consist of three parts: an implant, the abutment, and the crown. The abutment is mainly in contact with the surrounding soft tissue. Critical to dental implant success is the peri-implant soft tissue barrier, formed by keratinized epithelium adherent to the abutment. This barrier effectively prevents bacteria and food debris in the mouth from entering the space between the implant and bone tissue, which can reduce the risk of inflammation and infection (1). However, the connective tissue around the implant is collagen fibers oriented parallel to the abutment; there are no fibers inserted into the abutment surface, which is different from the natural tooth, as shown in Figure 1 (2). As such, the soft tissue around the implant has low attachment strength, which facilitates peri-implant infection. Research has shown that the average prevalence of peri-implant inflammation in implant patients is 19.53% (3). Progressive chronic inflammation will eventually cause the implant to loosen and fall out. This fundamental biological limitation underscores the need for strategies to enhance soft tissue integration.
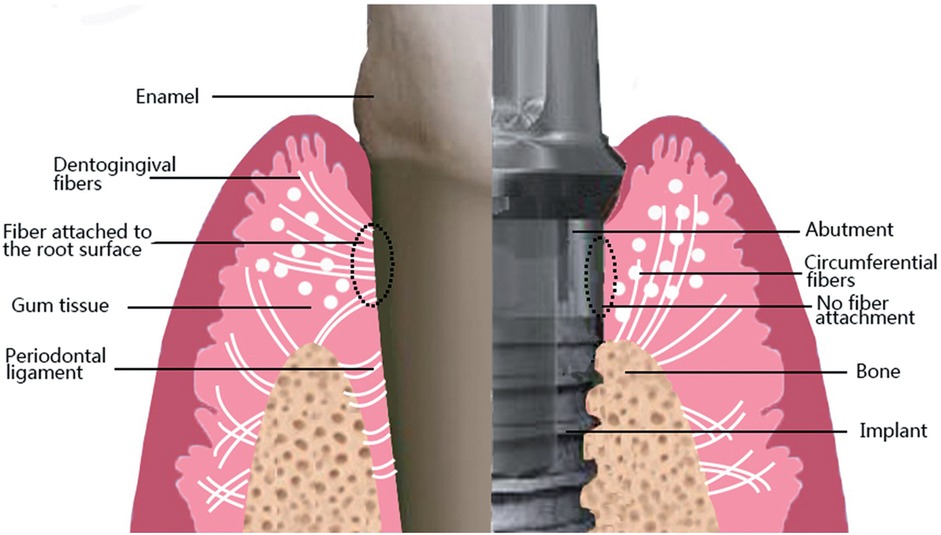
Figure 1. Differences between the connection of soft tissues to natural teeth and dental implants. Note the arrangement of gingival fibers in a parallel orientation on implant surfaces. This figure was adapted from Ref. (2) with permission.
Magnesium (Mg), the fourth most abundant element in humans, serves as a critical cofactor in cellular metabolism, membrane stability, signaling pathways, and so on (4). Mg-containing materials have been studied for various soft-tissue repair applications, such as skin wound healing (5) and periodontal tissue regeneration (6). Mg-containing coatings gradually degrade in vivo to release Mg2+. Mg2+ supports cell proliferation and migration and modulates intercellular signaling, which is conductive to tissue regeneration (7). Additionally, Mg2+ release has been found to promote angiogenesis; this process ensures the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen to healing tissue by enhancing the local blood supply, which can accelerate the healing process (8). Mg-containing coatings also exhibit excellent anti-inflammatory properties (9). Finally, Mg2+ regulates the immune response, reducing excessive inflammation to provide a more conducive environment for soft tissue healing.
Most titanium abutments are typically designed with a smooth surface. However, having a smooth surface alone is insufficient to establish a robust soft tissue seal (10). Mg-containing coatings offer a bioactive alternative by way of their unique surface properties and the release of therapeutic ions. This review synthesizes mechanistic and clinical evidence on how Mg-containing coatings enhance peri-implant soft tissue healing. We focus on their multifaceted impacts—from cellular interactions to antibacterial effects—and discuss unresolved translational barriers.
2 Physiological process and influencing factors of peri-implant soft tissue healing
The healing of peri-implant soft tissue is a complex and delicate physiological process. This physiological process and its main influencing factors are outlined below.
2.1 Physiological stages of soft tissue healing around implants
2.1.1 Initial blood clot formation
After implantation, blood clots quickly form around the wound (11). These clots provide a temporary matrix for cell migration and release a variety of growth factors, such as platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor–β [TGF-β]), which regulate subsequent cellular responses (12).
2.1.2 Inflammatory phase
Macrophages and neutrophils are recruited to the wound site to remove damaged tissue and bacteria (13). This phase is typically accompanied by the onset of localized inflammation, which plays a role in coordinating tissue repair processes.
2.1.3 Proliferative phase
Under the stimulation of growth factors, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and epithelial cells proliferate and migrate to the wound site. During this phase, fibroblasts synthesize extracellular matrix components, such as collagen, providing structural support for the regenerating tissue (14).
2.1.4 Remodeling phase
Newly formed soft tissue undergoes maturation, with collagen fibers reorganizing to enhance tissue strength and functionality (15). The result is a stable soft tissue seal that protects the implant from external invasion.
2.2 Factors influencing peri-implant soft tissue healing
The healing of peri-implant soft tissue is influenced by multiple factors. Abutment materials [such as titanium, zirconia (16)], surface features of abutments [such as macro design, morphology (17)], loading protocols [such as immediate implantation and early or delayed implantation (18)], host conditions [such as diabetes, smoking, immune suppression, etc (19, 20).], and microbial factors all have different effects on the soft tissue. The following will analyze factors related to the Mg-containing coating.
2.2.1 Material factors
Surface characteristics of implant abutments, such as roughness, hydrophilicity, and chemical composition, directly affect soft tissue healing. Rough surfaces enhance cellular adhesion and tissue integration (21), while hydrophilic surfaces attract and retain blood proteins, promoting cell adhesion and expansion (22). Moreover, surface coatings, such as Mg-containing coatings, can release bioactive ions (e.g., Mg2+) to modulate cell behavior, facilitating soft tissue healing (23). The biocompatibility of the material directly affects the intensity and duration of the host's inflammatory response (24). Furthermore, the formation of new blood vessels ensures the supply of oxygen and nutrients required during the healing process. Materials design should consider promoting angiogenesis to support effective healing.
2.2.2 Microbial factors
After implant placement, oral microbes rapidly colonize its surface, forming a biofilm that includes bacteria and their secreted adhesive substances. This biofilm can resist both antimicrobial agents and the host immune system (25). Once established, this biofilm may become a source of chronic inflammation, potentially leading to peri-implantitis, which can compromise soft tissue integrity and lead to bone loss. Microbial colonization and infection with organisms such as Porphyromonas gingivalis and Aggregatibacter actinomy-cetemcomitans (26) can also trigger a local immune response, which can damage soft tissue and induce a stronger inflammatory response. To address microbial factors, the antimicrobial properties of materials have gradually become a focus of research.
Understanding these influencing factors and implementing appropriate design and management strategies are essential for achieving successful implant restoration. Mg-containing coatings can enhance peri-implant soft tissue healing by improving surface characteristics, releasing Mg2+ to promote cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation, modulating inflammatory responses, affecting fibroblast function, collagen synthesis, and angiogenesis, and providing antibacterial effects.
3 Mg-containing coatings modify the surface properties of abutments to promote soft tissue healing
Abutment surface characteristics play a crucial role in soft tissue healing, with surface roughness, hydrophilicity, and chemical composition directly impacting cellular adhesion, proliferation, migration, and integration. Below, we explore how Mg-containing coatings alter abutment surface characteristics to promote soft tissue healing.
3.1 Increased surface roughness of abutments promotes cell adhesion
Rough surfaces mimic the natural extracellular matrix environment, facilitating directed cell migration and promoting tissue integration with the abutment surface (27). This integration accelerates the healing process and enhances the mechanical strength and functionality of the new tissue. The surface characteristics may be adjusted by flame carbonization and oxygen plasma treatment (22). The results showed that moderate roughness (roughness ratio r ≈ 2) is best for cell adhesion, growth, and proliferation, while too high or too low roughness can inhibit cell adhesion.
When Mg-containing coatings are prepared with different surface treatment techniques, they can alter the nanoscale morphology of the titanium surface of the abutment to increase its roughness. A nanostructured surface provides more adhesion sites for cells, allowing cells to attach more securely to the material surface (28). This modulation is particularly important for orderly tissue regeneration and effective wound repair. Changes in surface roughness can also be sensed by integrins associated with cell adhesion, including the focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and Src family kinase pathway (29), the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase/Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase (MAPK/ERK) signaling pathway (30, 31), and the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B (PI3 K/AKT) signaling pathway (32). Studies have shown that dendritic cell adhesion influenced by titanium surface roughness is regulated via the β2 integrin–FAK–AKT signaling cascade (33). This further illustrates the notion that Mg-containing coatings enhance cell adhesion by increasing surface roughness.
3.2 Enhanced surface hydrophilicity of abutment promotes protein adsorption
A hydrophilic surface can facilitate better fluid transport at the abutment–soft tissue interface, enhancing the protein-adsorption capacity (34). Highly wettable hydrophilic abutment surfaces form a stable and uniform liquid film upon contact with biological fluids, which improves cell proliferation and differentiation (35). Yu et al. (36) used Mg plasma immersion ion implantation and deposition technology to fabricate Mg-containing coatings on the surface of abutments. They found that this treatment improved the hydrophilicity of the surface and enhanced the proliferation, adhesion, wound healing, and extracellular matrix formation of fibroblasts. With the addition of Mg, the hydrophilicity of the abutment surface is improved (37).
Hydrophilicity alone does not significantly increase protein adsorption, but combining hydrophilicity with nanostructures can maximize protein-adsorption levels. Nanostructures increase the surface area, providing more sites for protein adsorption, which can enhance the adsorption efficiency of protein (38). Research (37) has shown that preparing Mg-containing nanocoatings on titanium implants with wet chemical treatments enhanced the protein-adsorption capacity. By increasing adsorption of proteins like fibrinogen and platelets, a continuous protein layer is formed, which is essential for subsequent cell adhesion. Overall, Mg-containing nanocoatings increase protein adsorption, creating a favorable microenvironment for cell adhesion and expansion. Rapid cell expansion helps to cover the abutment surface, accelerating the healing process.
At present, there is a lack of detailed comparative studies on the effects of Mg-containing coatings prepared by different methods on the surface properties of abutment. Controversy persists about which surface properties are the key factors affecting the healing of peri-implant soft tissue. In addition to hydrophilicity and roughness, it is important to analyze the effects of physicochemical properties such as surface tension and surface energy on soft tissue closure.
4 Mg2+ release influences fibroblast function, promoting collagen synthesis and angiogenesis
The connective tissue surrounding implants consists of collagen fibers, matrix, cells, and blood vessels. Among these, fibroblasts and blood vessels are less distributed. They form a weak, closed area of soft tissue with collagen fibers on the abutment surface. In particular, fibroblasts are the main cell type in soft tissue repair and regeneration, which are responsible for the generation and maintenance of the extracellular matrix. Therefore, improving the number and biological activity of fibroblasts is very important to promote the healing of peri-implant soft tissue.
4.1 Mg2+ promotes fibroblast proliferation, differentiation, and migration
4.1.1 Mg2+ promotes fibroblast proliferation and adhesion
The trigger for cell proliferation originates from the action of growth factors. After binding growth factors to the cell surface, Mg2+ quickly enters the cell interior through transporters such as TRPM7 and MagT1 (39). On the one hand, Mg2+ is directly involved in the construction of integrins and regulates cell motility and adhesion by activating the widespread expression of adhesion molecules such as Vinculin (VCL) and FAK. On the other hand, Mg2+ activates signal-transduction pathways such as PI3 K/AKT or PI3 K/mTOR (Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin), thereby playing a regulatory role in cell proliferation, migration, and extracellular matrix secretion, increasing the number of fibroblasts. Zhen et al. (40) studied the effects of pure Mg extract on mouse fibroblasts by proteomic methods and found that Mg extract significantly enhanced the expression of cell cycle–related proteins, which suggests that Mg extract plays a positive role in the cell cycle pathway (Figure 2). The upregulation of key cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks), such as Cdk1 and Cdk6, indicates that Mg2+ accelerates the transition from the G1 to S phase and promotes the DNA replication and division of cells, which suggests the role of Mg2+ in promoting fibroblast proliferation. Protein synthesis is also important for cell proliferation. Mg extracts contribute to the overall process of cellular protein synthesis by regulating multiple links such as splicing, RNA trafficking, ribosome translation, and folding and glycosylation of the endoplasmic reticulum. At the same time, Mg extract also enhances ATP production by affecting the oxidative phosphorylation process of mitochondria (40) to provide energy for cell proliferation and metabolic activities.
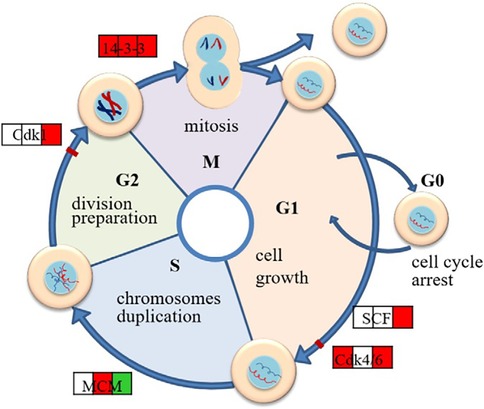
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of regulated cell cycle pathways in L929 exposed to Mg extract.where the three squares stand for the protein expression in 8, 24 and 48 h respectively,and red color shows that at this time point the protein is up-regulated, while green color stands for down-regulation and the blank square means no change of the expression. This figure was adapted from Ref. (40) with permission.
4.1.2 Mg2+ promotes fibroblast migration and differentiation
Fibroblasts migrate to the wound site and begin repairing the damaged tissue. During cell migration, cytoskeletal reorganization plays a critical role, particularly the polymerization and depolymerization of filamentous actin (41). This process is associated with a Mg2+-dependent pathway involving RhoA, a GTP-binding protein (40). RhoA (42) regulates actin–myosin contraction by influencing myosin light chain phosphatase, facilitating stress fiber assembly and promoting cytoskeletal reorganization.Additionally, Mg2+ can promote fibroblast endocytosis (40). By upregulating proteins such as clathrin and adaptor protein 2, Mg2+ enhances the capacity of fibroblasts to uptake external signaling factors. This enables fibroblasts to respond to changes in the microenvironment during migration and to regulate cytoskeletal reorganization.
Myofibroblasts play a key role in the advanced stages of wound healing, promoting wound closure and tissue reconstruction. Yang et al. (43) showed that Mg and zinc (Zn) ions can facilitate the differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, a process achieved through activation of the STAT3 signaling pathway. Mg2+ upregulates the expression of ZIP6 and ZIP10 and promotes Zn2+ entry into fibroblasts. Increasing intracellular Zn2+ concentration effectively promotes STAT3 phosphorylation, which induces fibroblast differentiation into myofibroblasts and accelerates extracellular matrix deposition, as shown in Figure 3. Recent research showed that connective tissue growth factor mediates the proliferation and migration of mouse fibroblasts through the STAT3 signaling pathway (44). Myofibroblasts not only contract the wound but also synthesize proteins, including collagen and fibronectin, and remodel the extracellular matrix, thereby accelerating peri-implant soft tissue healing.
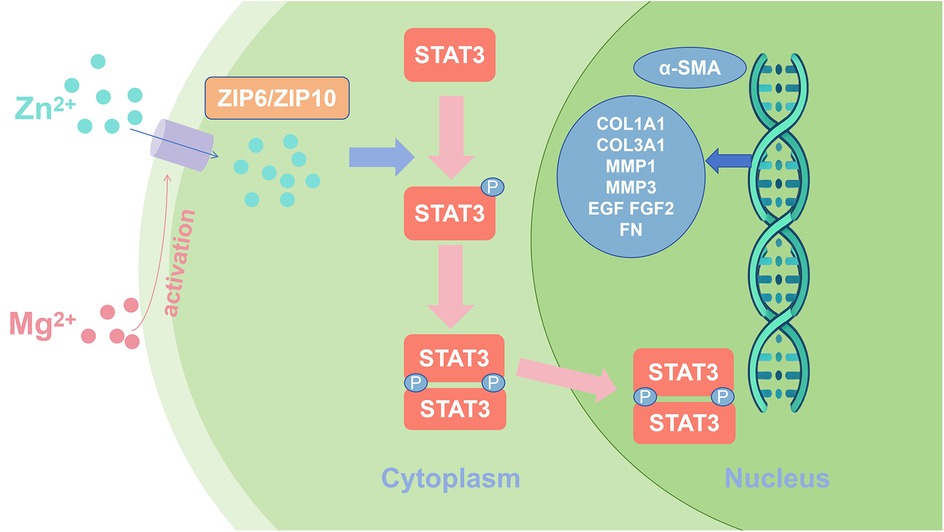
Figure 3. Schematic representation of magnesium and zinc ions promoting fibroblast differentiation through activation of STAT3 signaling.
4.2 Mg2+ enhances collagen synthesis in peri-implant soft tissue
Collagen is a major component of the extracellular matrix, providing structural support in wound healing and tissue repair. The release of Mg2+ promotes collagen synthesis in peri-implant soft tissue through various mechanisms. On the one hand, Mg2+ enhances the collagen-synthesis capacity of fibroblasts by activating signaling pathways related to extracellular matrix synthesis, such as the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway (45). On the other hand, Mg2+ clears old collagen fibers by activating matrix metalloproteinases (e.g., MMP-7) (46), promoting the degradation and reorganization of the extracellular matrix and creating a framework for the generation and arrangement of new fibers. Besides, Mg2+ regulates the recombination of actin and other cytoskeletal proteins by activating the ERK1/2 signaling pathway (46, 47). Further, it can enhance the migration and collagen-secretion capacity of fibroblasts. This helps the newly generated collagen fibers to be more orderly and closely arranged, improving the mechanical strength and functionality of the new tissue.
4.3 Mg2+ promotes angiogenesis in peri-implant soft tissue
Angiogenesis is a critical process in soft tissue repair, supplying new tissue with oxygen and nutrients. Mg2+ enhances the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells (48), which are fundamental steps in angiogenesis. Mg2+ primarily interacts with G-protein–coupled receptors and calcium-sensing receptors on cell surfaces to initiate downstream signal-transduction pathways (49). Activation of these receptors raises intracellular calcium levels, which triggers a series of processes related to cytoskeletal reorganization and focal adhesion protein disassembly. This disassembly reduces cell adhesion to the matrix, making cells more “loosened” and thus more mobile. Furthermore, Mg2+ supports directed cell migration by increasing the expression of certain chemokines, such as monocyte chemoattractant protein–1 and interleukin (IL)-8 (36, 50). Mg2+ also promotes the expression of angiogenic factors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (49), which stimulates endothelial cell proliferation and induces new blood vessel formation, both crucial to accelerate soft tissue healing.
It is worth mentioning that diabetes mellitus has been recognized as a risk factor for unsuccessful implant therapy. Liu et al. (51) established a diabetic mouse model and developed an Mg-coated implant by hydrothermal synthesis. These implants were found to successfully improve vascularization and osseointegration in the diabetic state. Mechanismally, Mg2+ promotes the degradation of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 and the nucleation of nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 by up-regulating the expression of sestrin 2 in endothelial cells, which can reduce elevated oxidative stress levels in mitochondria and alleviate endothelial cell dysfunction under hyperglycemic conditions.
The release of Mg2+ significantly accelerates soft tissue repair and regeneration by promoting fibroblast proliferation, migration, differentiation, collagen synthesis, and angiogenesis. Through the activation of multiple key biological signaling pathways, Mg2+ not only supports extracellular matrix formation and tissue reconstruction but also ensures the long-term survival and functionality of new tissue by improving blood supply. Future studies can further optimize the release behavior of Mg-containing coatings to make more effective use of these mechanisms in clinical applications and improve the effect of soft tissue repair.
5 Mg-containing coatings modulate the inflammatory response to enhance peri-implant soft tissue healing
The inflammatory response plays a dual role in peri-implant soft tissue healing. A moderate inflammatory response can clear debris and initiate tissue regeneration, while excessive or prolonged inflammation may hinder healing and implant stability. Effective inflammation regulation creates an optimal healing environment to promote recovery. Below, we discuss the mechanisms by which Mg-containing coatings regulate inflammation.
5.1 Regulation of immune cell behavior
Mg-containing coatings gradually degrade in vivo and release Mg2+. With an appropriate concentration, Mg2+ exhibits significant anti-inflammatory properties, which is reflected in the regulation of immune cell behavior, especially macrophage polarization. Macrophages are categorized into pro-inflammatory M1 and anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes based on their functions. During the acute inflammatory phase, M1 macrophages secrete cytokines like tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and IL-6 to eliminate pathogens and clear damaged tissue. However, a prolonged M1 response can lead to chronic inflammation and tissue damage (52). Separately, M2 macrophages promote tissue repair and regeneration by secreting anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β. Cerqueira et al. (50) successfully developed a sol-gel coating containing Mg and found that Mg2 + significantly reduced the level of TNF-α secreted by cells with an appropriate concentration while enhancing the expression of anti-inflammatory factors (TGF-β, IL-4). Qiao et al. (53) found via in vitro experiments in which THP1, a human monocyte line that can differentiate into macrophages, was exposed to different Mg2+ concentrations that increasing the Mg2+ concentration significantly promoted the maturation of THP1-derived macrophages from suspension monocytes to adherent macrophages and enhanced their activity. Gene-expression analysis showed that Mg2+ up-regulates M2 macrophage marker genes (such as CD163 and CD206) and regulates osteoblast growth–related cytokine genes (such as CCL5, IL-1ra, and TGF-β1) while down-regulating osteoclast-promoting inflammatory factors (such as TNF-α and IL-1β). Cytokine array and Western blot analysis further confirmed that Mg2+ promotes the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1ra, IL-8, and CCL5 and inhibits the expression of IL-1β (as shown in Figure 4). Therefore, Mg-containing coatings can facilitate the shift from M1 to M2 macrophages through the release of Mg2+ (54), effectively reducing the duration of the inflammatory response and accelerating the healing process.
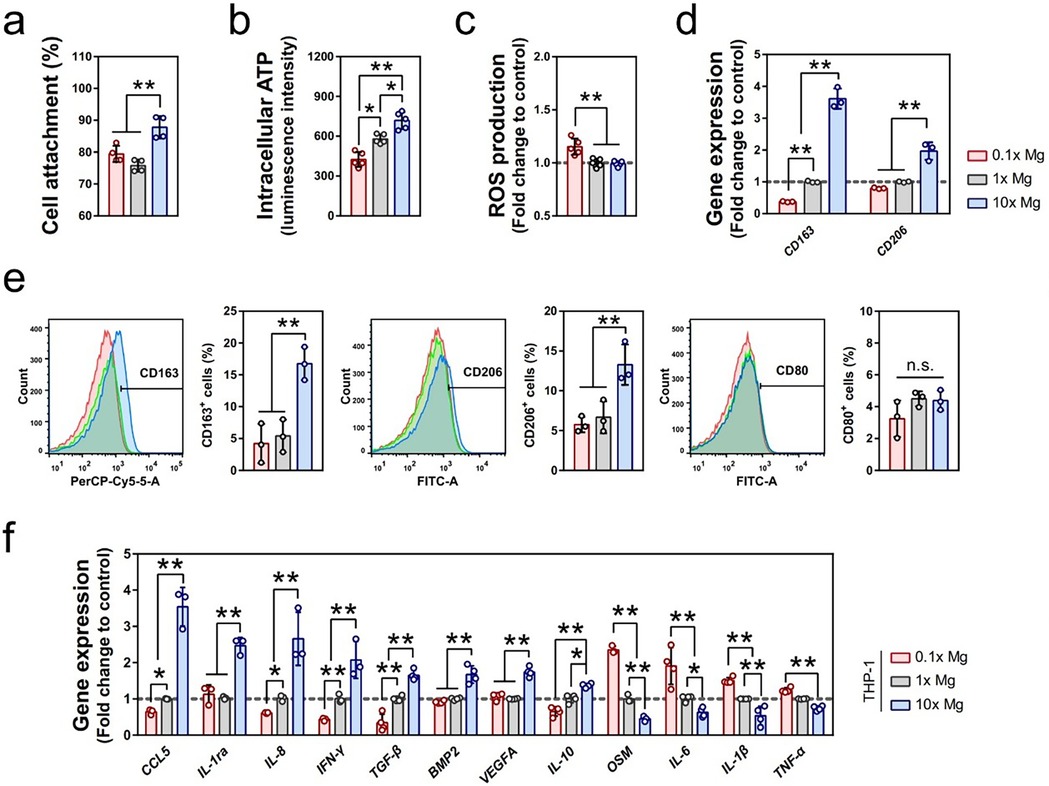
Figure 4. Mg2+ regulated the inflammatory microenvironment through the immunomodulation of macrophages. (a–c) The effects of different concentrations of Mg2+ on the cell attachment (a, n = 4), intracellular ATP level (b, n = 5), and ROS production (c, n = 4) of macrophages differentiated from suspension THP1 monocytes. The data for cell attachment was expressed as a percentage of initially seeded THP-1 cells. (d) The effect of different concentrations of Mg2+ on the gene expression of CD163 and CD206 in THP1-derived macrophages as evaluated by RT-qPCR (n = 3). (e) The effect of different concentrations of Mg2+ on the polarization of macrophages was evaluated by the expression of CD163, CD206, and CD80 using flow cytometry (n = 3). (f) The relative expression of inflammatory-related genes regulated by the stimulation of Mg2+ in THP1-derived macrophages (n = 3). Cited from Qiao W et al. (53) under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY4.0).
The specific effects of Mg2+ on macrophages have also been a recent research focus. Jin et al. (55) found that, under liposaccharide stimulation, Mg2+ can inhibit the TLR4–NFκB pathway and promote anti-inflammatory cytokine secretion via activation of the TRPM7–PI3K–AKT pathway. Qiao et al. (53) further studied the role of TRPM7 in macrophages, showing that the regulatory effect of Mg2+ on pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion was significantly weakened when TRPM7 expression was inhibited using TRPM7 siRNA. This suggests that macrophages may sense and respond to Mg2+ through TRPM7.
In addition to macrophage polarization, Mg-containing coatings also regulate the behavior of other immune cells. Dendritic cells activate effector T-cells or regulatory T-cells via the uptake of antigens and cooperate with other immune cells such as macrophages to participate in tissue regeneration and barrier formation around the implant. Dai et al. (56) treated mice with bone defects with chitosan- and hyaluronic acid–coated Mg ion carriers and demonstrated that Mg2+ enters dendritic cells through the TRPM7 ion channel. The activation of the MAPK signaling pathway up-regulates the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and further promotes the secretion of TGF-β. Separately, TGF-β can inhibit the activation of effector T-cells (CD4+, CD8+) and increase the proportion of regulatory T-cells, thereby forming an immunosuppressive microenvironment and limiting the excessive immune response.
5.2 Regulation of the oxidative stress response
Oxidative stress is a key mechanism that initiates and sustains inflammation. During inflammation, immune cells like macrophages and neutrophils produce reactive oxygen species (ROS), which further amplify inflammation through pathways such as NADPH oxidase activation (57). However, excessive ROS can damage surrounding tissues and delay healing (58). Mg2+ effectively reduces oxidative stress levels by inhibiting ROS production, thereby alleviating tissue damage (57, 59). Mg2+ can also suppress inflammatory responses by regulating oxidative stress–related signaling pathways such as NF-κB (60). NF-κB is an important transcription factor that activates multiple genes associated with inflammation, so inhibiting the NF-κB pathway can effectively reduce the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This mechanism not only reduces the initial inflammatory response but also helps prevent chronic inflammation in the long term.
Overall, Mg-containing coatings regulate the inflammatory response through multiple mechanisms. On the one hand, they achieve precise control of the inflammatory response by modulating immune cell behavior, particularly macrophage polarization; on the other hand, they reduce the intensity of inflammation by inhibiting oxidative stress. These anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects demonstrate the broad potential of Mg-containing coatings in tissue repair and anti-inflammatory applications.
6 Mg-containing coatings enhance the antimicrobial properties of the abutment surface
In discussing the antimicrobial mechanisms of Mg-containing coatings, we analyze four primary mechanisms that contribute to their effectiveness and propose directions for future research.
6.1 Antibacterial ions release and pH modification
The primary antibacterial mechanism of Mg-containing coatings is the release of Mg2+. Higher concentrations of Mg2+ create greater osmotic pressure on bacteria, disrupting their physiological activities and inhibiting their growth and reproduction (61). The alkaline microenvironment created by Mg-containing coatings is another important factor contributing to their antibacterial properties. Most bacteria, especially anaerobes, struggle to survive and proliferate under high-pH conditions (62). This local alkaline environment not only inhibits bacterial growth but also prevents bacterial adhesion to the abutment surface, reducing biofilm formation (63). This is crucial for preventing postoperative infections and improving the long-term success rate of implants. The sustained ion release allows the coating to provide long-term antimicrobial protection for the abutment.
6.2 ROS generation
Mg2+ can promote the generation of ROS, especially hydroxyl radicals (•OH) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), through redox reactions (58). ROS can directly damage bacterial cell membranes and cause lipid peroxidation, ultimately resulting in bacterial death. Bacterial DNA can be oxidatively damaged by ROS, which will accelerate bacterial death. Also, ROS can oxidize proteins within cells, such as cysteine and methionine, causing protein denaturation or inactivation, which further inhibits bacterial growth and survival (64). The generation of ROS is a key mechanism in the antibacterial efficacy of Mg-containing coatings.
Tan et al. (65) used magnetron sputtering to deposit MgO film on biomedical titanium. Through their experiments, it was confirmed that MgO film would cause a lack of nutrients and ATP in bacteria, induce oxidative stress and death of said bacteria. This method only needs to increase the thickness of the MgO film to enhance its antibacterial effect. The specific mechanism is as follows: An appropriate transmembrane electrochemical proton gradient is necessary for the bacteria to pull extracellular H+ into the body by an F-type proton pump to produce ATP. Once the bacteria contact the MgO film, the extracellular H+ will be consumed and the proton gradient will be weakened, which will inhibit the synthesis of ATP and lead to a decrease in bacterial activity (65). The weakened proton gradient will interfere with the transmembrane transport of bacterial nutrients (66) and further affect bacterial metabolism. Oxygen is normally reduced to water by terminal oxidases in the respiratory electron transport chain that react on the bacterial membrane. However, due to the lack of protons in the alkaline microenvironment of bacteria, many oxygen molecules cannot obtain enough protons and eventually become ROS through the reaction. When the surface alkaline of MgO films is enhanced, bacteria will produce more ROS, which can damage bacterial enzymes, lipids and DNA, and other biomolecules, eventually leading to bacterial death. Although bacteria can regulate the acid–base balance inside and outside the cell through some ion channels, with the increase of MgO film thickness, the surface alkalinity rises beyond the threshold of the bacterial regulatory capacity, eventually leading to bacterial death.
6.3 Synergistic effects with other antibacterial materials
Mg-containing coatings can be combined with other antibacterial materials to enhance their antimicrobial efficacy. For instance, combining Mg with antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) has shown promising results. AMPs (67) primarily kill bacteria by disrupting bacterial cell membranes. A synergistic effect has been observed between Mg2+ and AMPs in the coating. Co-culture experiments with Escherichia coli (68) revealed that the coating maintained significant antibacterial efficacy even at low AMP concentrations, achieving a bactericidal rate of over 99%. Particularly, Mg oxide layers formed by electrodeposition combined with AMPs exhibited the most pronounced antibacterial effect. Kasi et al. (69) found that Mg-containing coatings combined with silver markedly enhanced antibacterial properties through multiple mechanisms, including metal ion release, ROS generation, and membrane disruption. This synergy also contributes to broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against various microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. These composite coatings have demonstrated excellent antibacterial properties in vitro and in animal studies. In addition, research has explored the synergistic effects of Mg with other elements, such as iron (70) and Zn (71), to further enhance abutment coating antibacterial properties.
7 Challenges and future directions
Despite the promising effects of Mg-containing coatings in promoting soft tissue healing and providing antimicrobial properties, there are still several challenges in current research that require further exploration and optimization.
7.1 Ensuring long-term stability and controlled degradation
Controlling degradation kinetics and preventing cytotoxic Mg2+ bursts remain critical. Excessive Mg2+ concentrations may lead to dose-dependent cytotoxicity and genotoxicity (72), which could negatively impact the soft-tissue healing process. The oral microenvironment—characterized by dynamic masticatory forces, salivary flow, and pH fluctuations—accelerates coating degradation and complicates release predictability. While techniques like plasma immersion ion implantation enhance corrosion resistance, validation gaps persist, particularly in long-term (>6 months) in vivo models under oral-mimicking conditions. To bridge this, future studies must quantify real-time Mg2+ release profiles under mechanical stress and salivary exposure, establish epithelial/fibroblast viability thresholds, and comparatively evaluate degradation kinetics across key Mg compounds.
7.2 Advancing multifunctional composite coatings
Single Mg-containing coatings often struggle to simultaneously meet the requirements for antibacterial, corrosion-resistant, and bioactive properties. To address this, researchers are exploring multifunctional composite coatings by combining Mg with other materials. For instance, one study shows incorporating Mg and iron on a titanium substrate enhances fibroblast adhesion and promotes soft tissue healing (70). Similarly, co-implanting Mg2+ and Zn2+ ions into titanium substrates using plasma-implantation techniques has been shown to significantly promote the adhesion, migration, and proliferation of gingival fibroblasts (71). However, the clinical translation of such findings is hindered by undefined optimal formulations and species-specific dosing. Critically, current antimicrobial evaluations oversimplify oral ecology, focusing on single-pathogen models while neglecting complex polymicrobial biofilms. Future work should therefore prioritize three pillars: (1) screening broad-spectrum efficacy against multispecies biofilms, (2) quantifying epithelial sealing quality through hemidesmosome formation assays, and (3) systematically comparing adhesion strength across different multifunctional composite coatings.
7.3 Optimizing fabrication for clinical translation
Improving coating-fabrication techniques is another critical direction for future research. Currently, several methods for producing Mg-containing coatings, such as sol-gel, thermal spraying, and electrochemical deposition, face challenges, including technical complexity, high costs, and potential pollution. These issues limit the widespread clinical application of Mg-containing coatings. Therefore, next-generation techniques must concurrently achieve wear-resistant architectures able to sustain clinical function under masticatory stress for at least 5 years, low-energy consumption manufacturing processes, and eco-friendly deposition by eliminating toxic byproducts.
7.4 Bridging the translational Gap
The limited translatability of preclinical models necessitates prioritizing human clinical validation, starting with randomized controlled trials to assess (1) gingival seal integrity quantified via transmucosal resistance measurements and (2) 3–5-year peri-implantitis incidence rates. Concurrently, advanced in vitro models co-culturing human gingival fibroblasts with epithelial cells should be developed to predict mucosal responses. Crucially, clinical outcomes must be correlated with histological evidence of epithelial attachment integrity—particularly basal lamina continuity and hemidesmosome density—to resolve soft-tissue specificity gaps identified in preclinical studies.
8 Conclusion
Mg-containing coatings exhibit compelling preclinical potential for enhancing peri-implant soft tissue integration via multifaceted mechanisms, including surface modification promoting fibroblast/epithelial adhesion, Mg2+ release accelerating collagen synthesis and angiogenesis while modulating pro-healing macrophage polarization, and inherent antimicrobial activity combating biofilm formation,as shown in Figure 5. Critically, however, translational barriers impede clinical adoption. Key limitations include unresolved long-term coating stability under dynamic oral stresses, insufficient validation of epithelial sealing integrity (e.g., hemidesmosome formation at the abutment–mucosa interface), and variable bioactivity across Mg compounds. Future research must prioritize human randomized trials assessing mucosal seal durability and 3–5-year peri-implantitis rates, complemented by standardized degradation kinetics profiling under clinically relevant conditions. Concurrently, optimizing Mg formulation dosing and developing polymicrobial biofilm models will strengthen therapeutic generalizability. Resolving these gaps—particularly through histological confirmation of epithelial attachment structures and wear-resistant coating designs—will position Mg-coated abutments as transformative tools for preventing peri-implant complications and improving implant longevity.
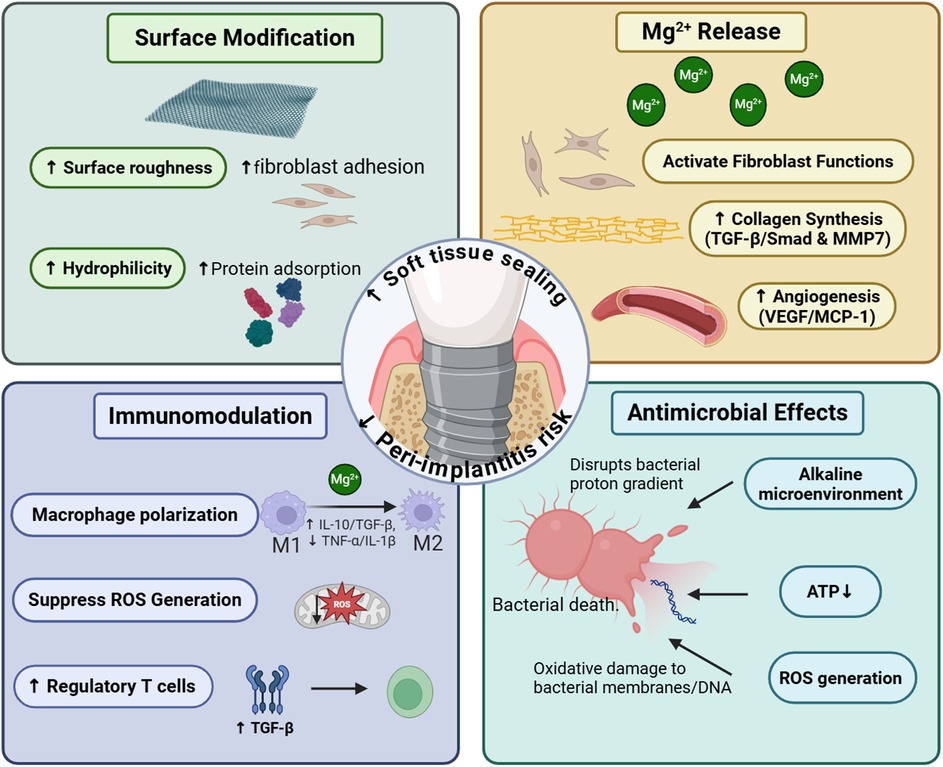
Figure 5. This figure summarizes the four cardinal functions of Mg-containing coatings in accelerating soft tissue healing around dental implants. This figure was created by the authors using licensed materials from https://BioRender.com.
Author contributions
HZ: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. CS: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. PL: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. WZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YN: Writing – review & editing. SP: Writing – review & editing. SZ: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M693820).
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support from Harbin Medical University for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Boynueğri D, Nemli SK, Kasko YA. Significance of keratinized mucosa around dental implants: a prospective comparative study. Clin Oral Implants Res. (2013) 24:928–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02475.x
2. Wang Y, Zhang Y, Miron RJ. Health, maintenance, and recovery of soft tissues around implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. (2016) 18:618–34. doi: 10.1111/cid.12343
3. Diaz P, Gonzalo E, Villagra LJG, Miegimolle B, Suarez MJ. What is the prevalence of peri-implantitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health. (2022) 22(449):1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02493-8
4. Fiorentini D, Cappadone C, Farruggia G, Prata C. Magnesium: biochemistry, nutrition, detection, and social impact of diseases linked to its deficiency. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1136. doi: 10.3390/nu13041136
5. Gupta S, Dutta P, Acharya V, Prasad P, Roy A, Bit A. Accelerating skin barrier repair using novel bioactive magnesium-doped nanofibers of non-mulberry silk fibroin during wound healing. J Bioact Compat Polym. (2021) 37:38–52. doi: 10.1177/08839115211061737
6. Liu X, He X, Jin D, Wu S, Wang H, Yin M, et al. A biodegradable multifunctional nanofibrous membrane for periodontal tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. (2020) 108:207–22. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.03.044
7. Wang J, Ma XY, Feng YF, Ma ZS, Ma TC, Zhang Y, et al. Magnesium ions promote the biological behaviour of rat calvarial osteoblasts by activating the PI3 K/akt signalling pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2017) 179:284–93. doi: 10.1007/s12011-017-0948-8
8. Pan SC, Huang YJ, Wang CH, Hsu CK, Yeh ML. Novel magnesium- and silver-loaded dressing promotes tissue regeneration in cutaneous wounds. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:9311. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179311
9. Su NY, Peng TC, Tsai PS, Huang CJ. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/akt pathway is involved in mediating the anti-inflammation effects of magnesium sulfate. J Surg Res. (2013) 185:726–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.06.030
10. De Oliveira DP, Ottria L, Gargari M, Candotto V, Silvestre FJ, Lauritano D. Surface modification of titanium alloys for biomedical application: from macro to nano scale. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. (2017) 31:221–32.
11. Li J, Zhao J, Xu Y, Xu A, He F. Titanium surface interacting with blood clot enhanced migration and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2023) 11:1136406. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1136406
12. Yamakawa S, Hayashida K. Advances in surgical applications of growth factors for wound healing. Burns Trauma. (2019) 7:10. doi: 10.1186/s41038-019-0148-1
13. Koh TJ, DiPietro LA. Inflammation and wound healing: the role of the macrophage. Expert Rev Mol Med. (2011) 13:e23. doi: 10.1017/s1462399411001943
14. Cialdai F, Risaliti C, Monici M. Role of fibroblasts in wound healing and tissue remodeling on earth and in space. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2022) 10:958381. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.958381
15. Diller RB, Tabor AJ. The role of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in wound healing: a review. Biomimetics. (2022) 7:87. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics7030087
16. Enkling N, Marder M, Bayer S, Götz W, Stoilov M, Kraus D. Soft tissue response to different abutment materials: a controlled and randomized human study using an experimental model. Clin Oral Implants Res. (2022) 33:667–79. doi: 10.1111/clr.13932
17. Li X, Qi M, Sun X, Weir MD, Tay FR, Oates TW, et al. Surface treatments on titanium implants via nanostructured ceria for antibacterial and anti-inflammatory capabilities. Acta Biomater. (2019) 94:627–43. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.06.023
18. Qian X, Vánkos B, Kelemen K, Gede N, Varga G, Hegyi P, et al. Comparison of implant placement and loading protocols for single anterior maxillary implants: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Prosthet Dent. (2024) 133:677–88. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2024.05.033
19. Zhang Q, Guo S, Li Y, Li Z, Wang D, Zhang K. Analysis of risk indicators for implant failure in patients with chronic periodontitis. BMC Oral Health. (2024) 24:1051. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04806-5
20. Zhang Z, Ji C, Wang D, Wang M, Song D, Xu X, et al. The burden of diabetes on the soft tissue seal surrounding the dental implants. Front Physiol. (2023) 14:1136973. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1136973
21. Osman MA, Alamoush RA, Kushnerev E, Seymour KG, Watts DC, Yates JM. Biological response of epithelial and connective tissue cells to titanium surfaces with different ranges of roughness: an in vitro study. Dent Mater. (2022) 38:1777–88. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2022.09.010
22. Majhy B, Priyadarshini P, Sen AK. Effect of surface energy and roughness on cell adhesion and growth—facile surface modification for enhanced cell culture. RSC Adv. (2021) 11:15467–76. doi: 10.1039/d1ra02402g
23. Rahman M, Dutta NK, Roy Choudhury N. Magnesium alloys with tunable interfaces as bone implant materials. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2020) 8:564. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00564
24. Zhou G, Groth T. Host responses to biomaterials and anti-inflammatory design-a brief review. Macromol Biosci. (2018) 18:e1800112. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201800112
25. Ng E, Tay JRH, Mattheos N, Bostanci N, Belibasakis GN, Seneviratne CJ. A mapping review of the pathogenesis of peri-implantitis: the biofilm-mediated inflammation and bone dysregulation (BIND) hypothesis. Cells. (2024) 13:315. doi: 10.3390/cells13040315
26. Persson GR, Renvert S. Cluster of bacteria associated with peri-implantitis. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. (2014) 16:783–93. doi: 10.1111/cid.12052
27. Zhukova Y, Hiepen C, Knaus P, Osterland M, Prohaska S, Dunlop JWC, et al. The role of titanium surface nanostructuring on preosteoblast morphology, adhesion, and migration. Adv Healthc Mater. (2017) 6:1601244. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201601244
28. Decuzzi P, Ferrari M. Modulating cellular adhesion through nanotopography. Biomaterials. (2010) 31:173–9. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.09.018
29. Skoog SA, Kumar G, Narayan RJ, Goering PL. Biological responses to immobilized microscale and nanoscale surface topographies. Pharmacol Ther. (2018) 182:33–55. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.07.009
30. Shen MJ, Wang GG, Wang YZ, Xie J, Ding X. Nell-1 enhances osteogenic differentiation of pre-osteoblasts on titanium surfaces via the MAPK-ERK signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2018) 50:1522–34. doi: 10.1159/000494651
31. Liu L, Zeng D, Chen Y, Zhou J, Liao Y, Shi B. Microarc oxidation surface of titanium implants promote osteogenic differentiation by activating ERK1/2-miR-1827-osterix. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. (2020) 56:296–306. doi: 10.1007/s11626-020-00444-7
32. Gu YX, Du J, Si MS, Mo JJ, Qiao SC, Lai HC. The roles of PI3 K/akt signaling pathway in regulating MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast proliferation and differentiation on SLA and SLActive titanium surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A. (2013) 101:748–54. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34377
33. Yang Y, Lin Y, Xu R, Zhang Z, Zeng W, Xu Q, et al. Micro/nanostructured topography on titanium orchestrates dendritic cell adhesion and activation via β2 integrin-FAK signals. Int J Nanomedicine. (2022) 17:5117–36. doi: 10.2147/ijn.s381222
34. Kopf BS, Ruch S, Berner S, Spencer ND, Maniura-Weber K. The role of nanostructures and hydrophilicity in osseointegration: in-vitroprotein-adsorption and blood-interaction studies. J Biomed Mater Res A. (2015) 103:2661–72. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.35401
35. Toffoli A, Parisi L, Tatti R, Lorenzi A, Verucchi R, Manfredi E, et al. Thermal-induced hydrophilicity enhancement of titanium dental implant surfaces. J Oral Sci. (2020) 62:217–21. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.19-0235
36. Yu Y, Jin G, Xue Y, Wang D, Liu X, Sun J. Multifunctions of dual Zn/Mg ion co-implanted titanium on osteogenesis, angiogenesis and bacteria inhibition for dental implants. Acta Biomater. (2017) 49:590–603. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.067
37. Park JW, Hanawa T, Chung JH. The relative effects of Ca and Mg ions on MSC osteogenesis in the surface modification of microrough Ti implants. Int J Nanomedicine. (2019) 14:5697–711. doi: 10.2147/ijn.s214363
38. Lotz EM, Olivares-Navarrete R, Berner S, Boyan BD, Schwartz Z. Osteogenic response of human MSCs and osteoblasts to hydrophilic and hydrophobic nanostructured titanium implant surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res. (2016) 104:3137–48. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.35852
39. Zhang X, Zu H, Zhao D, Yang K, Tian S, Yu X, et al. Ion channel functional protein kinase TRPM7 regulates Mg ions to promote the osteoinduction of human osteoblast via PI3 K pathway: in vitro simulation of the bone-repairing effect of Mg-based alloy implant. Acta Biomater. (2017) 63:369–82. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.08.051
40. Zhen Z, Luthringer B, Yang L, Xi T, Zheng Y, Feyerabend F, et al. Proteomic profile of mouse fibroblasts exposed to pure magnesium extract. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. (2016) 69:522–31. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.06.100
41. Gardel ML, Schneider IC, Aratyn-Schaus Y, Waterman CM. Mechanical integration of actin and adhesion dynamics in cell migration. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. (2010) 26:315–33. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.011209.122036
42. Reffay M, Parrini MC, Cochet-Escartin O, Ladoux B, Buguin A, Coscoy S, et al. Interplay of RhoA and mechanical forces in collective cell migration driven by leader cells. Nat Cell Biol. (2014) 16:217–23. doi: 10.1038/ncb2917
43. Yang F, Xue Y, Wang F, Guo D, He Y, Zhao X, et al. Sustained release of magnesium and zinc ions synergistically accelerates wound healing. Bioact Mater. (2023) 26:88–101. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.02.019
44. Yang M, Bao D, Shi A, Yuan H, Wang J, He W, et al. Zinc promotes patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cell neural differentiation via ERK-STAT signaling. Stem Cells Dev. (2020) 29:863–75. doi: 10.1089/scd.2020.0016
45. Wang X, Zhang L, Zhang X, Zhang S, Yan J. Mg-6Zn alloys promote the healing of intestinal anastomosis via TGF-β/smad signaling pathway in regulation of collagen metabolism as compared with titanium alloys. J Biomater Appl. (2022) 36:1540–9. doi: 10.1177/08853282211066555
46. Yoshino Y, Teruya T, Miyamoto C, Hirose M, Endo S, Ikari A. Unraveling the mechanisms involved in the beneficial effects of magnesium treatment on skin wound healing. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:4994. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094994
47. Sano T, Kobayashi T, Ogawa O, Matsuda M. Gliding basal cell migration of the urothelium during wound healing. Am J Pathol. (2018) 188:2564–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.07.010
48. Sreenivasamurthy SA, Akhter FF, Akhter A, Su Y, Zhu D. Cellular mechanisms of biodegradable zinc and magnesium materials on promoting angiogenesis. Biomater Adv. (2022) 139:213023. doi: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2022.213023
49. Ben Amara H, Martinez DC, Shah FA, Loo AJ, Emanuelsson L, Norlindh B, et al. Magnesium implant degradation provides immunomodulatory and proangiogenic effects and attenuates peri-implant fibrosis in soft tissues. Bioact Mater. (2023) 26:353–69. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.02.014
50. Cerqueira A, Romero-Gavilán F, García-Arnáez I, Martinez-Ramos C, Ozturan S, Izquierdo R, et al. Characterization of magnesium doped sol-gel biomaterial for bone tissue regeneration: the effect of Mg ion in protein adsorption. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. (2021) 125:112114. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2021.112114
51. Liu L, Wang F, Song W, Zhang D, Lin W, Yin Q, et al. Magnesium promotes vascularization and osseointegration in diabetic states. Int J Oral Sci. (2024) 16:10. doi: 10.1038/s41368-023-00271-y
52. O'Brien EM, Risser GE, Spiller KL. Sequential drug delivery to modulate macrophage behavior and enhance implant integration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. (2019) 149:85–94. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2019.05.005
53. Qiao W, Wong KHM, Shen J, Wang W, Wu J, Li J, et al. TRPM7 kinase-mediated immunomodulation in macrophage plays a central role in magnesium ion-induced bone regeneration. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:2885. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23005-2
54. Li B, Cao H, Zhao Y, Cheng M, Qin H, Cheng T, et al. In vitro and in vivo responses of macrophages to magnesium-doped titanium. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:42707. doi: 10.1038/srep42707
55. Jin L, Chen C, Jia G, Li Y, Zhang J, Huang H, et al. The bioeffects of degradable products derived from a biodegradable Mg-based alloy in macrophages via heterophagy. Acta Biomater. (2020) 106:428–38. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.02.002
56. Dai Y, Wu J, Wang J, Wang H, Guo B, Jiang T, et al. Magnesium ions promote the induction of immunosuppressive bone microenvironment and bone repair through HIF-1α-TGF-β axis in dendritic cells. Small. (2024) 20:e2311344. doi: 10.1002/smll.202311344
57. Kwesiga MP, Gillette AA, Razaviamri F, Plank ME, Canull AL, Alesch Z, et al. Biodegradable magnesium materials regulate ROS-RNS balance in pro-inflammatory macrophage environment. Bioact Mater. (2023) 23:261–73. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.10.017
58. Bhattacharya P, Neogi S. Antibacterial properties of doped nanoparticles. Rev Chem Eng. (2019) 35:861–76. doi: 10.1515/revce-2017-0116
59. Zhao J, Wu H, Wang L, Jiang D, Wang W, Yuan G, et al. The beneficial potential of magnesium-based scaffolds to promote chondrogenesis through controlled Mg(2+) release in eliminating the destructive effect of activated macrophages on chondrocytes. Biomater Adv. (2022) 134:112719. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2022.112719
60. Zhou X, Li X, Yi K, Liang C, Geng S, Zhu J, et al. Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury by upregulating autophagy and inhibiting inflammation via IL-22 expression. Bioorg Chem. (2022) 128:106034. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106034
61. Rodríguez-Sánchez J, Pacha-Olivenza MÁ, González-Martín ML. Bactericidal effect of magnesium ions over planktonic and sessile Staphylococcus epidermidis and Escherichia coli. Mater Chem Phys. (2019) 221:342–8. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.09.050
62. Tan X, Wang Z, Yang X, Yu P, Sun M, Zhao Y, et al. Enhancing cell adhesive and antibacterial activities of glass-fibre-reinforced polyetherketoneketone through Mg and Ag PIII. Regen Biomater. (2023) 10:66. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbad066
63. Andrés NC, Sieben JM, Baldini M, Rodríguez CH, Famiglietti Á, Messina PV. Electroactive Mg(2+)-hydroxyapatite nanostructured networks against drug-resistant bone infection strains. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. (2018) 10:19534–44. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b06055
64. Bhattacharya P, Dey A, Neogi S. An insight into the mechanism of antibacterial activity by magnesium oxide nanoparticles. J Mater Chem B. (2021) 9:5329–39. doi: 10.1039/d1tb00875g
65. Tan J, Liu Z, Wang D, Zhang X, Qian S, Liu X. A facile and universal strategy to endow implant materials with antibacterial ability via alkalinity disturbing bacterial respiration. Biomater Sci. (2020) 8:1815–29. doi: 10.1039/c9bm01793c
66. Cai Z, Jitkaew S, Zhao J, Chiang HC, Choksi S, Liu J, et al. Plasma membrane translocation of trimerized MLKL protein is required for TNF-induced necroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. (2014) 16:55–65. doi: 10.1038/ncb2883
67. Yu Q, Wu Z, Chen H. Dual-function antibacterial surfaces for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. (2015) 16:1–3. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.01.018
68. Zhou W, Yan J, Li Y, Wang L, Jing L, Li M, et al. Based on the synergistic effect of Mg(2+) and antibacterial peptides to improve the corrosion resistance, antibacterial ability and osteogenic activity of magnesium-based degradable metals. Biomater Sci. (2021) 9:807–25. doi: 10.1039/d0bm01584a
69. Kasi G, Thanakkasaranee S, Stalin N, Arumugam A, Jantanasakulwong K, Panyathip R, et al. Enhancement of antimicrobial properties and cytocompatibility through silver and magnesium doping strategies on copper oxide nanocomposites. J Alloys Compd. (2024) 1007:176481. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2024.176481
70. Yin Y, Jian L, Li B, Liang C, Han X, Zhao X, et al. Mg-Fe layered double hydroxides modified titanium enhanced the adhesion of human gingival fibroblasts through regulation of local pH level. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. (2021) 131:112485. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2021.112485
71. Wang L, Luo Q, Zhang X, Qiu J, Qian S, Liu X. Co-implantation of magnesium and zinc ions into titanium regulates the behaviors of human gingival fibroblasts. Bioact Mater. (2021) 6:64–74. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.07.012
Keywords: magnesium-containing coating, magnesium, dental implants, soft tissue healing, abutments
Citation: Zheng H, Shang C, Li P, Zhao W, Niu Y, Pan S and Zhang S (2025) The effects of magnesium-containing coatings on the healing of soft tissues surrounding oral titanium abutments: a narrative review. Front. Dent. Med. 6:1638027. doi: 10.3389/fdmed.2025.1638027
Received: 30 May 2025; Accepted: 9 September 2025;
Published: 25 September 2025.
Edited by:
Maria Maddalena Marrapodi, University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, ItalyReviewed by:
Morena Petrini, University of Studies G. d'Annunzio Chieti and Pescara, ItalyFahad Bakitian, Umm al-Qura University, Saudi Arabia
Copyright: © 2025 Zheng, Shang, Li, Zhao, Niu, Pan and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shuang Zhang, aGFwcHl6czIwMTJAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Hongya Zheng1,2
Hongya Zheng1,2 Yumei Niu
Yumei Niu Shuang Zhang
Shuang Zhang