- 1School of Computer Science and Information Systems, Pace University, New York, NY, United States
- 2Wu Ying College of Computing, New Jersey Institute of Technology, Newark, NJ, United States
Background: Extended reality (XR) technologies, which generally encompass virtual, augmented, and mixed reality, and realized through head-mounted devices, have been increasingly adopted to support Emergency Medical Services (EMS) training.
Objective: The objective of this review is to synthesize the current applications of immersive technologies in EMS training.
Methods: A systematic review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) framework. The studies were analyzed based on their objectives, methods, major findings, implemented technologies, and reported benefits and barriers.
Results: The majority of reviewed studies used virtual reality (VR) technologies for EMS training. Key system features identified as effective included interactive user interfaces, task performance recording, monitoring and feedback, scenario editor and control, realism and presence, and multi-user collaboration. The studies primarily assessed four aspects of the implemented immersive technologies: technical feasibility, training effectiveness (e.g., clinical performance, knowledge acquisition), cost-effectiveness (e.g., cost savings, business models), and user experience (e.g., immersion, presence, cognitive load, usability, acceptance). Notable benefits highlighted included enhanced engagement, accessibility, cost-efficiency, standardization, and teamwork. Despite these advantages, challenges persist, which are categorized as ergonomic and human factor issues, usability problems, and technical limitations.
Conclusion: Immersive technologies have demonstrated significant potential to enhance EMS training by improving skill acquisition and readiness for high-stakes scenarios, such as massive casualty incidents or disasters. However, research in this area remains limited, requiring further investigation to address persistent challenges and optimize implementation.
Introduction
Emergency medical services (EMS) clinicians operate in highly dynamic prehospital environments where rapid decision-making, precise interventions, and effective teamwork are essential (1). As the first point of contact for critically ill or injured patients, EMS clinicians must be well-versed in protocols, possess the necessary clinical expertise, and effectively manage the emotional challenges of high-pressure situations. Moreover, EMS clinicians face low-frequency, high-stakes emergency scenarios from time to time, such as natural disasters and major accidents (2, 3). Thus, providing effective training is critical to adequately prepare EMS clinicians for these demanding tasks.
Traditional EMS training methods, including tabletop exercises and high-fidelity simulations, are valuable for fostering knowledge, competence, and confidence among EMS clinicians (4, 5). However, these approaches face significant limitations as they not only require access to costly simulators, expert personnel, and dedicated physical spaces (e.g., simulation rooms) but also fail to replicate the full range of diverse clinical practice environments (6, 7). These barriers make traditional EMS training expensive and impractical to conduct on a regular basis, potentially leading to the decay of EMS clinicians' skills and competencies without repeated, hands-on training opportunities (8). Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensure that EMS clinicians are consistently prepared to deliver optimal care in high-stakes scenarios.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend in using extended reality (XR) technologies to support training in emergency medicine (9–12). XR encompasses virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). Specifically, VR allows users to fully immerse themselves in a virtual environment, while AR technology overlays digital elements onto real-world environments. MR technology, on the other hand, not only overlays digital elements but also enables users to interact seamlessly with physical and digital components. In this paper, we collectively refer to these technologies as XR.
XR technology is often implemented through head-mounted displays (HMDs) such as headsets. By leveraging XR-based HMDs, EMS clinicians can engage in safe yet visually immersive and interactive learning environment, eliminating adverse effects on patients and minimizing direct risks to participants (10). These technologies also offer a cost-effective, scalable alternative to traditional training methods as they enable repeated practice by overcoming the logistical and financial challenges associated with high-fidelity simulations (13, 14). With these innovative tools, EMS clinicians can refine their skills, acquire new knowledge, improve retention, and ultimately be better prepared for the increasingly technologically advanced workplace (10, 15).
Despite the growing interest in using XR technologies for EMS training, there remains a lack of comprehensive understanding regarding their applications, effectiveness, and challenges. Previous reviews have either broadly focused on emergency medicine, with much of the reviewed literature centering on training for hospital-based emergency department (ED) clinicians (9, 11), or have a narrow focus on specific technology such as AR (12). To address this gap, a systematic review of the literature was conducted to synthesize insights from existing studies to provide a roadmap for future research and offer practical guidance for leveraging XR-based HMDs to enhance EMS training outcomes and preparedness. Through this systematic review, we aim to answer the following research questions (RQs):
• RQ1: How are XR-based HMDs used in EMS training? This question examines the major use cases, as well as the types and features of XR technologies employed in EMS training.
• RQ2: What tools and metrics are used to evaluate the XR-based training? This question explores the methodologies and tools utilized to evaluate the XR technologies in EMS training.
• RQ3: What are the perceived benefits and challenges of using XR technology in EMS training? This question aims to uncover the advantages and limitations associated with adopting XR technology for EMS training from the perspectives of stakeholders.
Methods
Literature search
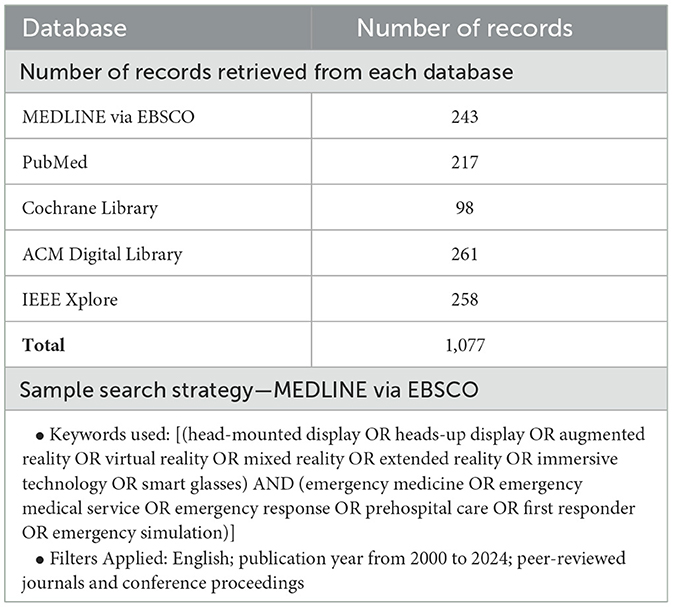
We conducted a comprehensive literature search to ensure a thorough exploration of relevant studies on XR technology for EMS training. The search was performed across five databases spanning healthcare and computer science domains: Medline via EBSCO, Cochrane Library, PubMed, ACM Digital Library, and IEEE Xplore. In collaboration with a research librarian, we developed a search strategy using two sets of keywords: one targeting XR technology and the other focused on the emergency medical services context. The keywords used are presented in Table 1. The search was limited to articles published between January 2000 and September 2024 in peer-reviewed journals and conference proceedings. Only articles written in English were included. Literature reviews, dissertations, posters, and extended abstracts were excluded. We managed all retrieved citations using EndNote (Version 20) for effective organization. The retrieved records for each database and a sample search strategy are presented in Table 1.
Article screening and selection
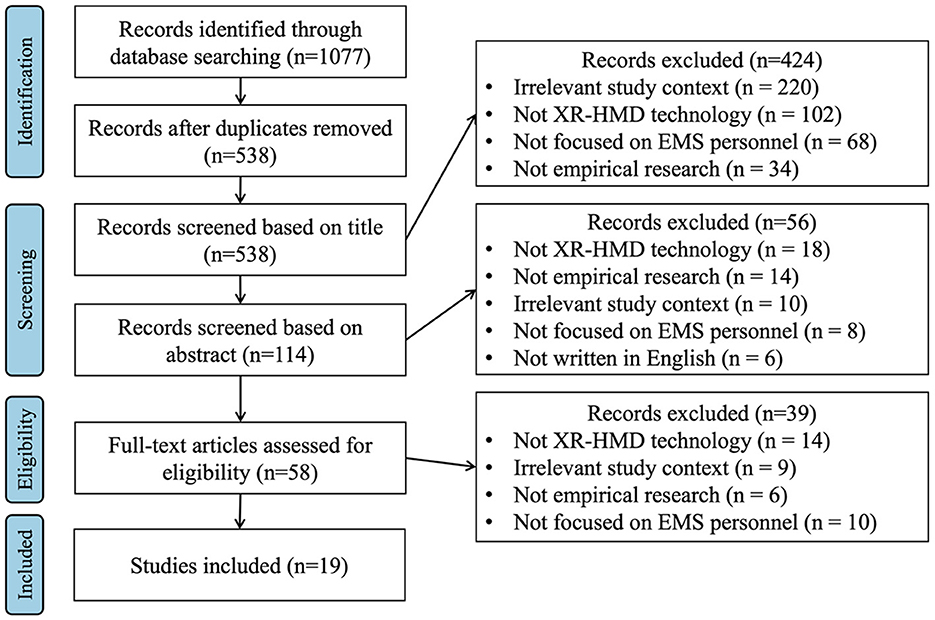
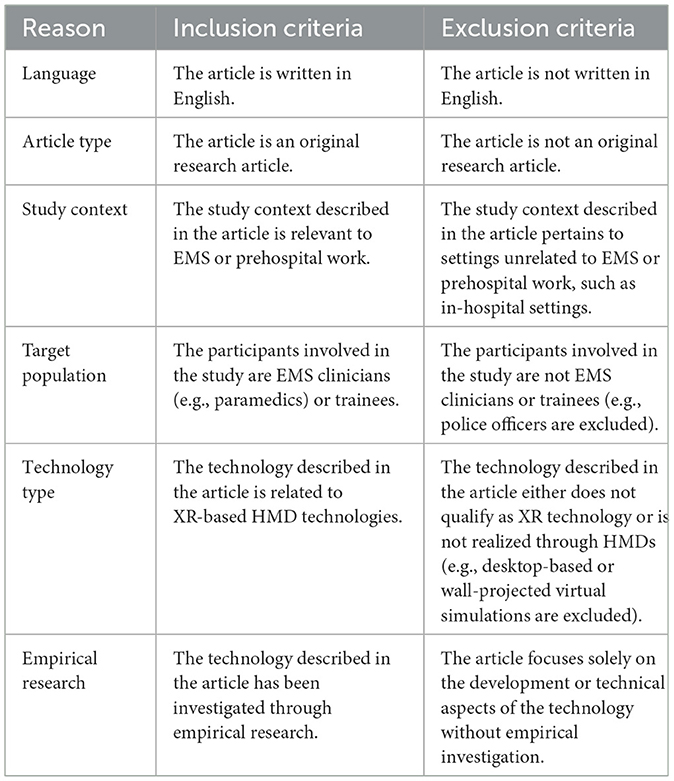
The selection process followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) (16). Figure 1 provides an overview of the records identified, included, and excluded during each stage. The inclusion and exclusion criteria are presented in Table 2.
The database search yielded 1,077 articles. After removing duplications, 538 records remained for further screening. Articles were screened based on their relevance to the study focus. Two reviewers (AI, MMM) independently assessed the titles and abstracts against predefined inclusion criteria (Table 2). Title screening excluded 424 records, leaving 114 articles for abstract review. Abstract screening led to the exclusion of 56 additional records. Finally, full-text reviews of the remaining 58 articles resulted in the inclusion of 19 studies that met all inclusion criteria for this systematic review. Discrepancies were resolved through group discussions with all researchers involved.
Data extraction and synthesis
Three researchers (AI, MMM, and LK) independently performed data extraction using a structured Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. The extraction was guided by the research questions and included information on the following: general study characteristics (e.g., publication year, country, and clinical context), study objectives and scope, device/system used (e.g., features), methods, outcomes, and metrics used for system assessment, and reported benefits, challenges, and limitations of the XR technology. In addition to this set of key information, the major findings of each study and the researchers' reflections on the study were also documented.
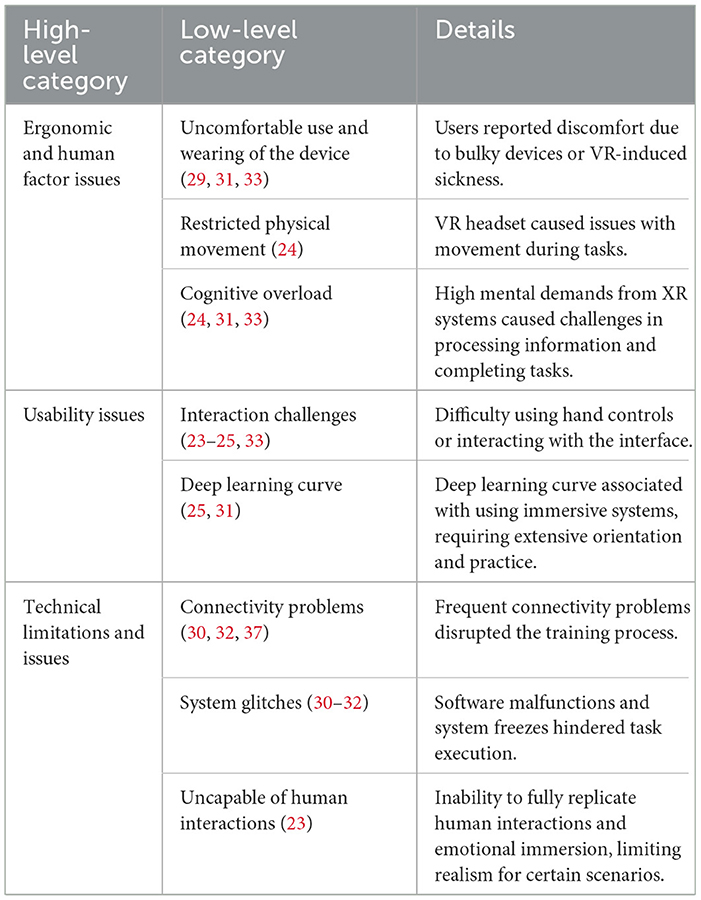
Upon completion of data extraction, the results were compared and synthesized. In particular, we thoroughly reviewed all extracted data to identify common themes. For instance, during the review, we found that participants highlighted a wide range of challenges with using XR-based HMDs. These challenges ranged from the bulkiness of the devices to the financial burden they could impose on organizations. The low-level categories identified were then grouped into broader high-level categories.
The senior researcher and corresponding author (ZZ) supervised the synthesis process and reviewed the extracted data as part of a validation step. Notably, the data extraction and synthesis process were iterative, allowing the research team to refine the analysis throughout the review and ensure that the data extraction was both comprehensive and accurate.
Methodological quality assessment of selected studies
The Meta-Quality Appraisal Tool (MetaQAT) was adopted as a study quality assessment tool (17). This assessment tool has been used in prior systematic literature review (10, 18). We chose this tool because it allows for the evaluation of individual studies regardless of their research design, ensuring a consistent methodological assessment across all included articles.
MetaQAT consists of eight items or questions designed to assess each study's relevance, reliability, validity, and applicability (17). For each question, the researchers used a rating scale to evaluate how well an individual study addressed the criteria. Given the need for extensive research expertise to conduct study quality assessment, the senior researcher (ZZ) and another researcher (MMM), who also holds a PhD and has undergone extensive research training, independently assessed each reviewed article. Any disagreements were resolved through thorough discussions.
Results
In this section, we report the main themes that are derived from the reviewed articles, including the general characteristics of selected studies, system features, system evaluation details, and perceived benefits and challenges. The main findings are reported in Table 3.
General characteristics
In this review, the 19 included articles were published between 2008 and 2024 (Figure 2A). Specifically, 18 of them were published after 2018, with four published in 2023 (19–22) and three each in 2020 (23–25), 2021 (26–28), and 2024 (29–31), respectively. This upward trend highlights an increasing focus on XR technologies in EMS training over the past few years. Most of the publications (n = 15) are journal articles, while only four studies were published as conference proceedings (20, 32–34) (Figure 2B).
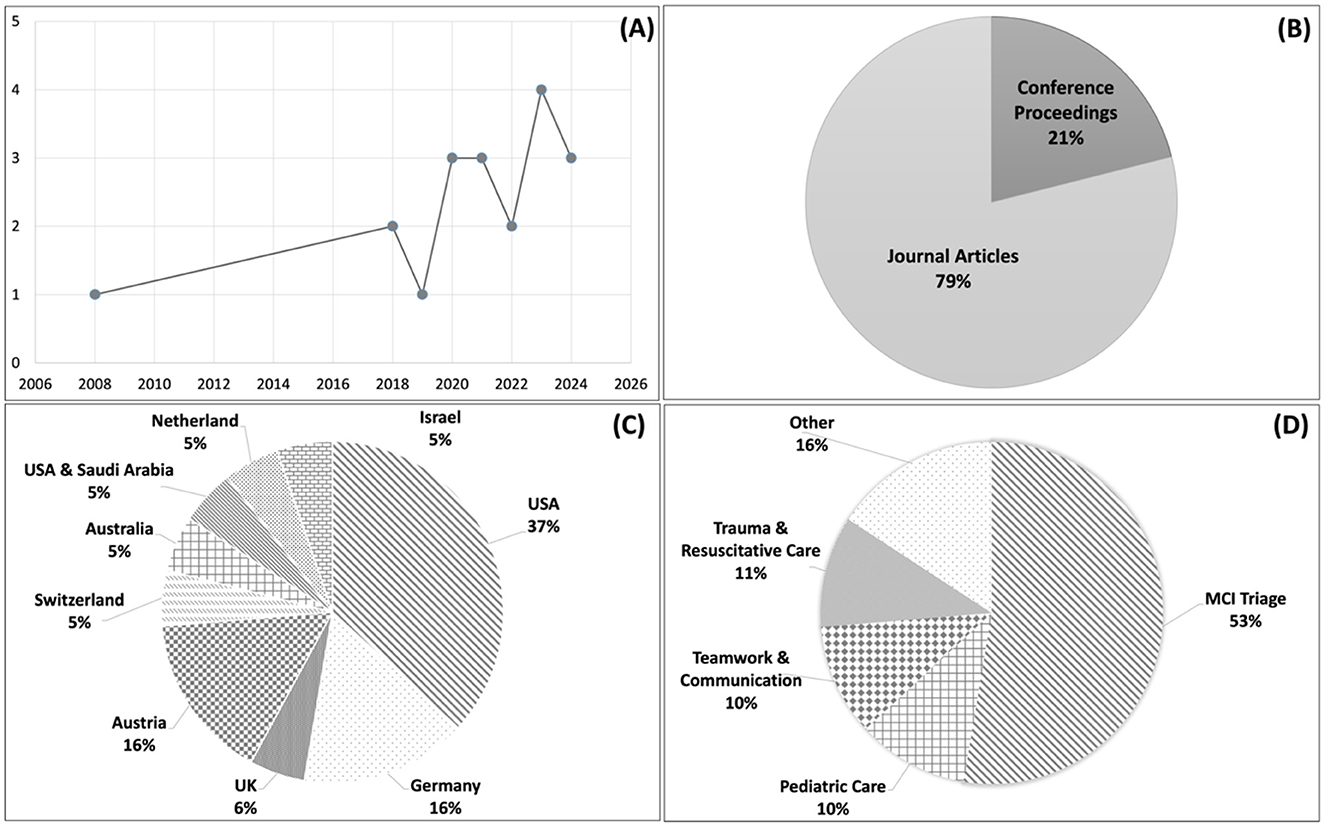
Figure 2. Overview of study characteristics across the reviewed literature. (A) Distribution of publication years. (B) Types of publication venues. (C) Countries where the studies were conducted. (D) Clinical focus of the studies.
As shown in Figure 2C, among the 19 studies reviewed, seven were conducted in the United States of America (USA) (25, 26, 30, 31, 33–35), three each in Germany (24, 29, 32) and Austria (19, 27, 36), and one each in Switzerland (22), Australia (23), Netherland (20), UK (21), Israel (28), and between the USA and Saudi Arabia (37).
The clinical focus of the reviewed studies is shown in Figure 2D. The articles primarily focused on the training of patient triage and intervention during MCIs (n = 10) (19–21, 23, 25, 30, 32, 35–37). The rationales cited by most articles for focusing on MCIs in training are: (1) The infrequent nature of MCIs limits the exposure of EMS clinicians to these events, leading to many lacking the necessary skills to ensure an effective and safe response (e.g., managing the sheer number of casualties and the allocation of resources) (23, 25). (2) Traditional training methods (e.g., large-scale simulations) are costly to implement in the physical world (20, 21, 30) and are often scarce or entirely absent in many regions around the world (37), highlighting the need for innovative, cost-effective pedagogical approaches. The remaining articles focused on other types of EMS training, including pediatric care (24, 31), teamwork and communication (29, 36), trauma and resuscitative care (22, 34), and other [e.g., finding equipment inside an ambulance bus (26), hazardous materials (hazmat) incidences (33), and chest thoracotomy (28)]. In summary, the reviewed studies primarily focused on training for low-frequency, high-stakes clinical scenarios.
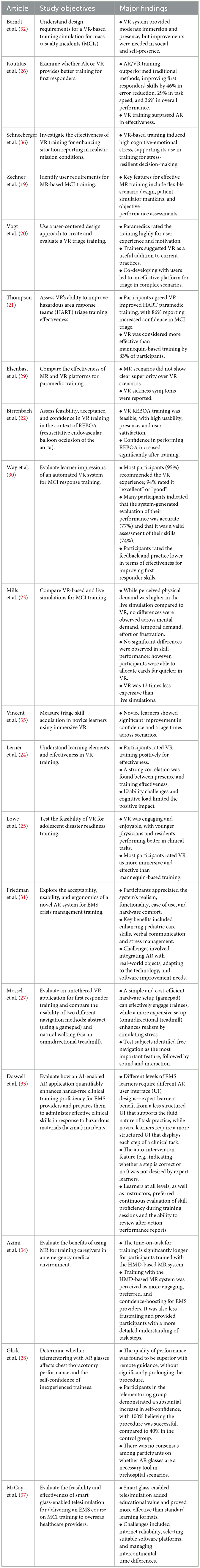
The study objectives of the reviewed articles are summarized in Table 3. Most studies focused on evaluating the implemented immersive platforms in terms of their acceptability, feasibility, effectiveness, and user perceptions. Two noteworthy observations should be highlighted. First, among the 19 reviewed articles, only four studies (19, 20, 27, 32) adopted a human-centered design approach to investigate user requirements for designing immersive training technologies by engaging end-users, such as EMS providers or trainers. Second, two studies (26, 29) conducted comparative evaluations of immersive technologies, i.e., between VR and MR.
Devices and features
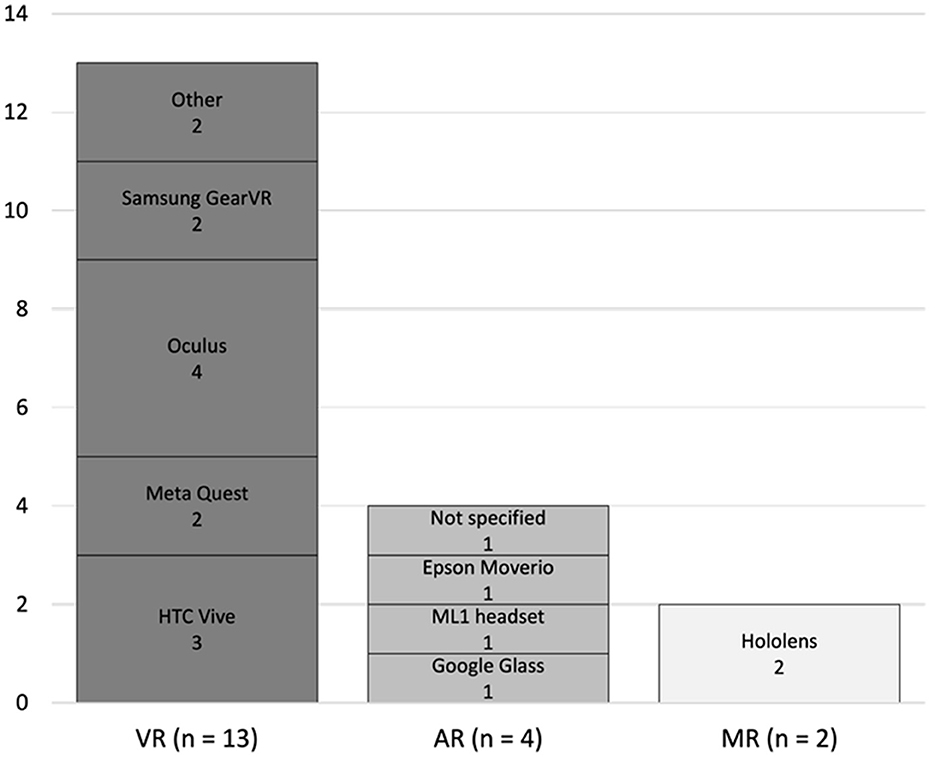
To answer RQ1, we analyzed the types and features of XR technologies employed in EMS training. Our analysis found that most of the studies (n = 13) used VR devices, including HTC (HTC Corporation, Taiwan) (19, 23, 24), Meta Quest (Meta Platforms, Inc., Menlo Park, California) (21, 30), Oculus (now part of Meta Platforms, Inc., Menlo Park, California) (22, 25, 26, 32), and Samsung GearVR (Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., South Korea) (27, 36). Four studies used AR devices, including the ML1 headset (Magic Leap, Inc., Plantation, FL) (31), Google Glass (Google, Mountain View, California) (37), and Epson Moverio (Seiko Epson Corporation, Suwa, Japan) (33). Finally, two studies used MR technologies, both of which used HoloLens (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA) (26, 34). The used devices are summarized and presented in Figure 3.
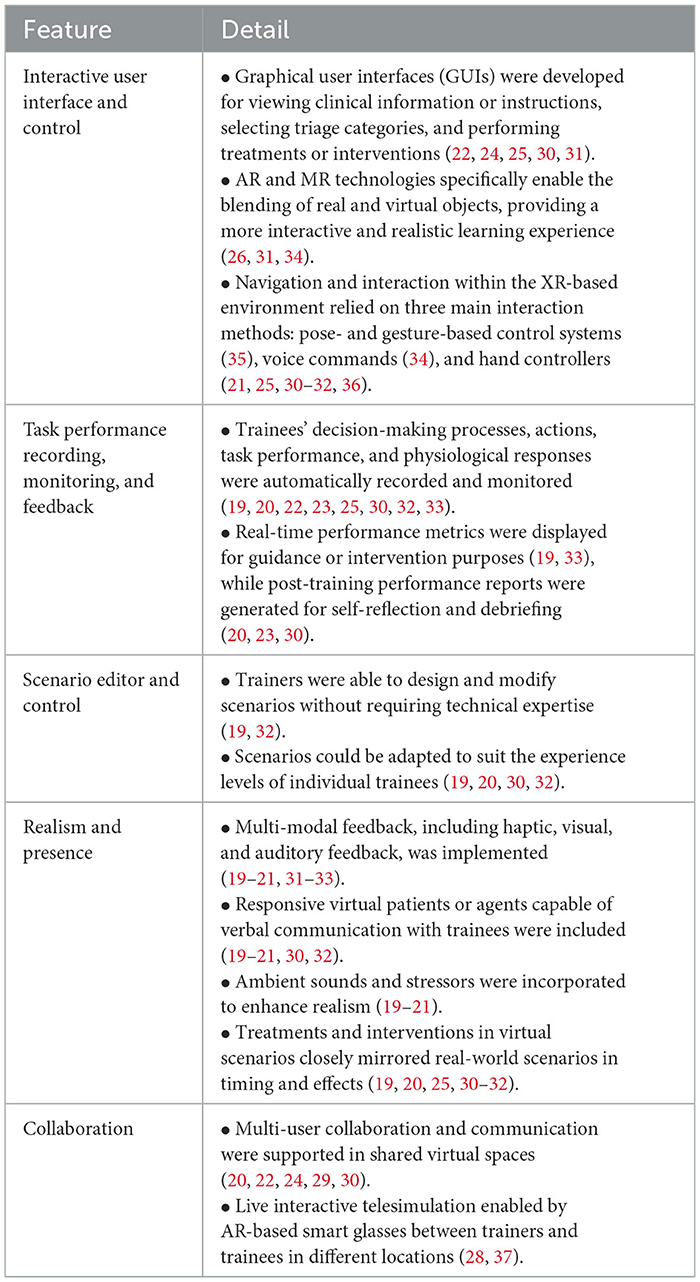
The reviewed studies highlighted a diverse range of system features that were deemed useful or effective for EMS training (Table 4). These features can be categorized into five key areas: (1) interactive user interface and control, (2) task performance recording, monitoring, and feedback, (3) smart scenario editor and control, (4) realism and presence, and (5) collaboration.
Interactive user interface and control
Many systems provided user-friendly, interactive graphical user interfaces (GUI) for viewing clinical information or instructions, selecting triage categories, and performing treatments or interventions (22, 24, 25, 30, 31). For example, one study (30) on MCI triage training implemented a virtual medical kit within the VR system, which contained different medical tools and equipment that could be selected by participants to perform lifesaving interventions such as controlling major hemorrhage with a tourniquet or wound packing. In another example (23), participants could click on designated icons attached to each patient within the virtual environment to gather and view basic clinical information (e.g., airway, respiratory rate and pulse rate), and also allocate an appropriate triage card.
In AR-enabled environments, trainers were able to interact not only with virtual images of patients and objects (e.g., virtual cardiac monitors, bag-valve masks, intravenous fluid poles, etc.) but also with real-world objects, such as length-based resuscitation tapes and tangible airway devices, which could be overlaid on the AR patient (31). In MR-based environments, trainers could operate in a blended real and virtual setting, allowing them to work with real patient mannequins while performing interventions using virtual elements overlaid on the mannequins (26, 34).
To interact with the GUI, virtual patients, or overlaid objects, three interaction methods were employed. One study (35) explored a pose- and gesture-based control system to offer a more naturalistic interaction experience, while another study (34) relied on voice commands. However, nearly all other studies relied on hand controllers for navigation and interaction within the virtual environment (21, 25, 30–32, 36). Hand controllers, in particular, improved navigation efficiency through the “teleport” feature, allowing participants to point to a desired location and click to move there without physical walking. This feature was especially valuable in MCI training scenarios, where large physical spaces are typically required; by using hand controllers, the need for extensive physical space was significantly reduced (30).
Task performance recording, monitoring, and feedback
Several studies incorporated methods to record and monitor trainees' decision-making processes, actions, and task performance, including metrics such as task completion time, errors, triage accuracy, and physiological responses like stress levels (19, 20, 22, 23, 25, 30, 32, 33). Using this real-time data, the system could automatically assess and quantify various aspects of trainee performance, such as distinguishing correct vs. incorrect triage categories and evaluating the order and timeliness of triage assignments.
These advanced analytics and performance metrics were often displayed to trainers or simulation experts, enabling them to intervene or provide guidance in real-time as training scenarios progressed (19). For example, trainers could increase the complexity of an exercise by introducing distractions or additional challenges to create a more realistic and engaging training environment. They could also adjust the difficulty level if trainees were not sufficiently challenged. Additionally, the system itself could automatically identify correct or incomplete procedural steps and intervene when a step was performed incorrectly (33).
Beyond real-time adjustments, systems also generated comprehensive performance reports post-training (20, 23, 30). These reports provided opportunities for trainees to engage in self-reflection and facilitated debriefing sessions between trainers and trainees to discuss strengths, areas for improvement, and actionable strategies for better performance. The ability to monitor and adapt training based on real-time data, combined with post-training feedback, was found to enhance the overall effectiveness of XR-based training systems (20).
Scenario editor and control
Two studies (19, 32) highlighted that it is useful to allow trainers to design and modify scenarios before or even during training sessions without needing technical expertise from application developers. For example, to facilitate the creation and modification of the scenarios, a study (19) developed a scenario editor that included an asset library and drag-and-drop functionality to adapt training scenarios. This feature allows for content customization, quick development, and shortened learning curve for trainers.
Additionally, being able to modify and control the scenarios, trainers can adapt scenarios to suit the experience levels of individual trainees (19, 20, 30, 32). This feature leverages real-time trainees' performance data, such as triage accuracy and physiological markers, to create a tailored and responsive training environment. For example, if a trainee exhibits low stress, the system can increase the scenario's complexity by introducing stress-inducing elements, such as barking dogs or wandering children (19). This adaptive approach ensures trainees are consistently engaged and challenged.
Realism and presence
Realism and presence are highlighted as perhaps the most essential and critical features in XR-based training. Under this theme, several aspects were discussed in the reviewed articles, including multi-modal feedback, responsive virtual patients, ambient sounds and stressors, and the capability to perform interventions. Each feature is described in greater detail below.
Multi-modal feedback, encompassing haptic, visual, and auditory feedback, plays a crucial role in enhancing the sense of realism and presence in XR training environments. Several studies (19–21, 31–33) have explored the integration of haptic feedback in hand controllers, allowing trainees to practice performing physical assessments, such as checking a patient's pulse or monitoring their breathing rate, without the need for a live patient. Furthermore, auditory and visual feedback, such as hearing the patient's breathing or observing physical signs like chest movements that indicate respiratory effort, was also considered critical (20, 31). By engaging multiple senses, these capabilities foster an increased sense of presence within the virtual environment.
The inclusion of responsive virtual patients or agents capable of verbal communication with trainees further enhances the realism and interactivity of immersive training systems, as demonstrated by several studies (19–21, 30, 32). For instance, one study (20) illustrates how responsive virtual agents are programmed to exhibit emotional reactions, challenging trainees to adapt their communication style based on the situation. Two additional studies (21, 32) note that such interactions improve the realism of training by simulating the complexities of human behavior under stress.
Ambient sounds and stressors are integral to creating immersive training environments that replicate the chaotic nature of real-world emergencies. Three studies (19–21) highlight how incorporating environmental sounds, such as sirens, crowd noise, or even a barking dog, can elevate the intensity and authenticity of training scenarios, preparing trainees to manage distractions effectively amidst the sensory overload of actual emergencies.
Finally, the ability to perform or select treatments and interventions is a cornerstone of immersive EMS training. Six studies (19, 20, 25, 30–32) discuss how trainees can interact with virtual medical kits or equipment to simulate life-saving interventions, such as applying tourniquets, defibrillating the patient, or performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Additionally, as noted in (19), the timing of virtual medical equipment application and its effects should closely mirror real-world scenarios. For instance, a wound should not stop bleeding immediately after the application of a tourniquet; instead, there should be a delayed response to reflect real-world physiological processes.
Collaboration
Five studies (20, 22, 24, 29, 30) developed features to support multi-user collaboration in a shared virtual space, enabling trainees to simulate real-world emergency scenarios that require coordinated efforts, such as performing synchronized interventions during resuscitation efforts. By participating in a collaborative task, trainees not only practiced their individual skills but also enhanced their ability to communicate, coordinate, and operate effectively as a team under high-pressure conditions.
Another two studies (28, 37) utilized AR-enabled smart glasses for telesimulation and telementoring between remote trainers and trainees. The AR glasses facilitated live, video-based communication through a “see-what-I-see” first-person point of view. Additionally, mentors could access trainees' surroundings via their computer screens and annotate visual aids directly onto the display of smart glasses to provide precise comments and instructions (28).
System evaluation
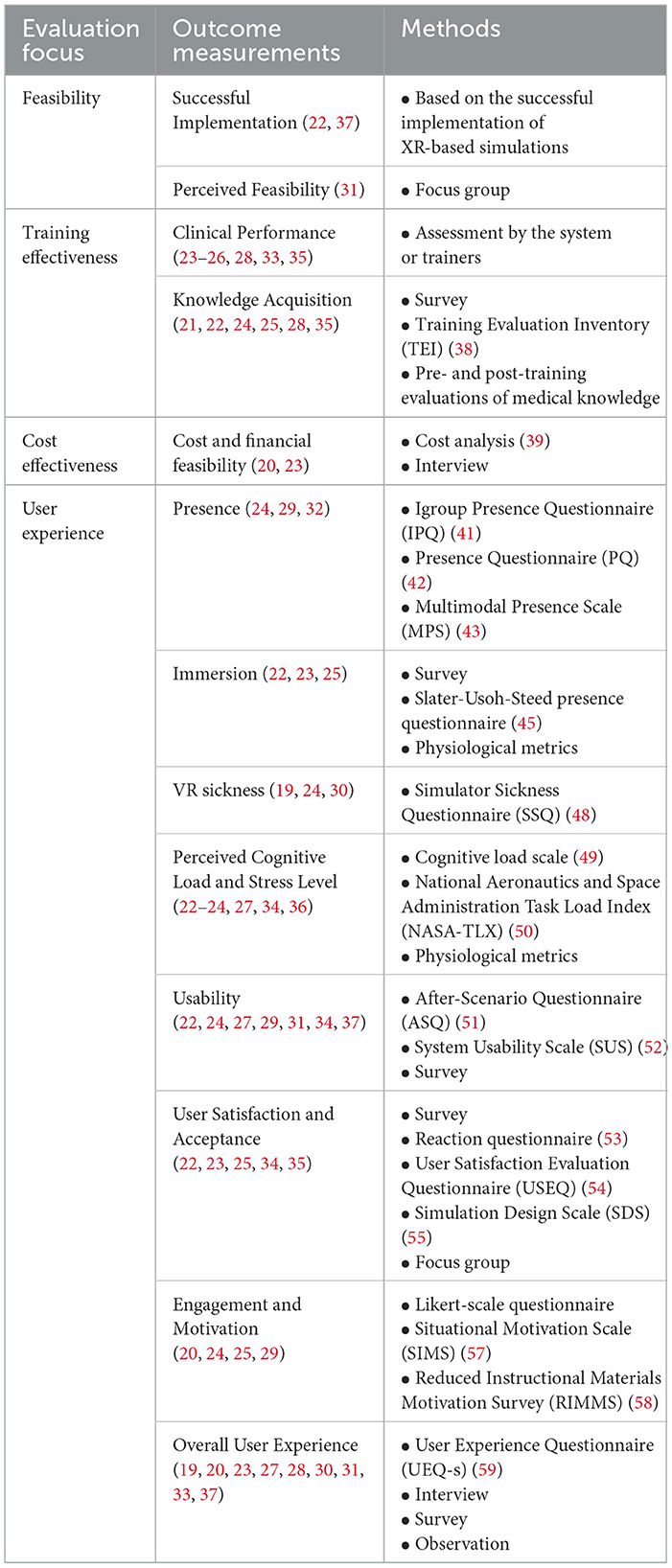
To address RQ2, we analyzed the evaluation focuses, as well as the methodologies and tools used to evaluate XR technologies in EMS training. Based on this analysis, we organized the evaluation focus into four categories: feasibility, training effectiveness, cost-effectiveness, and user experience. Within each category, we describe how the system was evaluated. The outcome measurements and methods used for evaluating each aspect are summarized in Table 5.
Technical feasibility
Three studies (22, 31, 37) examined the technical feasibility of implementing XR-based technology to support EMS training, with a particular focus on its ability to deliver effective training with minimal setup requirements, disruptions, and technical glitches. For instance, two studies (22, 37) explored whether an XR-based training platform could be successfully implemented and executed, while another study (31) conducted interviews to explicitly assess trainees' perceptions of the feasibility of integrating real-world objects with AR imagery during simulation training.
Training effectiveness
Training effectiveness is a core evaluation focus for XR training systems, focusing on how well they improve the knowledge, skills, and preparedness of trainees. This critical aspect primarily focused on clinical performance and knowledge acquisition.
Clinical performance
Seven studies (23–26, 28, 33, 35) focused on assessing clinical performance and reasoning skills by analyzing the completeness of medical procedures, as well as the accuracy and timing of decisions and intervention choices. These metrics provided quantitative data to evaluate trainees' ability to make critical decisions under pressure and to identify specific areas where they excelled or required further improvement.
Knowledge acquisition
The effectiveness of XR training systems in improving knowledge gain has been demonstrated across multiple studies (21, 22, 24, 25, 28, 35). For example, four studies (21, 22, 25, 28) conducted survey to assess trainees' perceived readiness and confidence for performing critical procedures after completing immersive training, while another study (24) utilized an existing instrument, Training Evaluation Inventory (TEI) (38), to assess trainees‘ perceptions of the content quality and relevance of the XR-based learning environments.
Pre- and post-training evaluations of medical knowledge were employed in two studies (22, 24) to objectively measure knowledge acquisition. In another study (35), trainees completed a survey before and after the training to rate their perceived self-efficacy. These pre- and post-training evaluations allowed researchers to directly compare their learning outcomes.
Cost effectiveness
Cost analysis is an essential aspect of evaluating XR training systems, as it helps determine their financial feasibility and potential for adoption. Two studies (20, 23) focused on this area, using different approaches to assess the cost-effectiveness of implementing XR technologies in EMS training programs. Specifically, one study (23) used methods from prior research (39) to conduct a detailed analysis of the direct and indirect costs associated with setting up and maintaining XR training systems, such as hardware acquisition, software development, and personnel training. Another study (20) adopted a qualitative approach by interviewing EMS program representatives to explore the business models associated with adopting XR training systems. These interviews provided insights into how organizations could justify the initial investment and ongoing expenses by aligning the training technology with organizational goals, such as improving staff readiness and reducing errors in high-stakes scenarios.
User experience
The reviewed articles evaluated different aspects of the user experience of XR technologies, as explained below.
Presence
The experience of presence refers to users' subjective sensation of “being there” within a virtual environment, despite knowing it is not real (40). This is a critical measure of user experience with XR technology, as it significantly influences engagement and realism. To evaluate this aspect, two studies (24, 29) utilized the Igroup Presence Questionnaire (IPQ) (41), while one study (32) used the Presence Questionnaire (PQ) (42) and the Multimodal Presence Scale (MPS) (43). Higher scores on these instruments indicate a stronger sense of presence.
Immersion
Immersion reflects the degree to which a virtual environment provides a sense of inclusion and engagement in the virtual experience (44). It was assessed using various methods across different studies (22, 23, 25). For instance, surveys and the Slater-Usoh-Steed presence questionnaire (45) were utilized in Lowe et al. (25) and Birrenbach et al. (22), respectively. Conversely, Mills et al. (23) employed physiological metrics, such as heart rate, to provide objective insights into participants' level of involvement.
VR sickness
VR sickness, also known as simulator sickness, is a condition characterized by symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, fatigue, and disorientation experienced by some users while interacting with XR-based HMDs (46). These symptoms are often caused by sensory conflicts, such as discrepancies between visual and vestibular cues, or by frame rate inconsistencies within the virtual environment (47). VR sickness can negatively impact user comfort and the overall training experience, making it a critical aspect of system evaluation. The reviewed studies (19, 24, 30) primarily used the Simulator Sickness Questionnaire (SSQ) (48)—a standardized tool for quantifying the negative physical effects of using VR—to assess the extent of VR sickness among participants.
Perceived cognitive load and stress level
The cognitive load and stress levels experienced by participants in XR training programs were key factors evaluated in six studies (22–24, 27, 34, 36). Perceived cognitive load, which refers to the mental effort required to complete tasks, was assessed using different methods. Specifically, one study (24) measured the perceived cognitive load with the scale by Klepsch et al. (49), while four other studies (22, 23, 27, 34) utilized the National Aeronautics and Space Administration Task Load Index (NASA-TLX) (50). These measures offered valuable insights into whether the training tasks were appropriately challenging without overwhelming participants.
Given that EMS clinicians often work in high-stress, time-critical environments, training programs should replicate these conditions. To address this, one study (36) specifically focused on assessing stress levels through physiological metrics, including electrodermal activity (EDA), electrocardiogram (ECG) readings, and respiratory data. These objective measures could provide a deeper understanding of how XR-based training influenced emotional and physiological states.
Usability
A system with poor usability may hinder participants' ability to navigate virtual environments, complete tasks, or focus on training objectives. Therefore, usability was a primary focus of evaluation in at least seven studies (22, 24, 27, 29, 31, 34, 37). The tools used for the usability evaluation included the After-Scenario Questionnaire (ASQ) (51) and the System Usability Scale (SUS) (52).
User satisfaction and acceptance
Five studies (22, 23, 25, 34, 35) focused on evaluating user satisfaction and acceptance, which are key metrics that directly impact the likelihood of users adopting immersive technologies in EMS training programs. Survey, including established questionnaires such as the Reaction Questionnaire (53), the User Satisfaction Evaluation Questionnaire (USEQ) (54), and the Simulation Design Scale (SDS) (55), were the primary methods for assessing these aspects. Additionally, one study (23) conducted focus groups to gain in-depth insights into participants' satisfaction and openness to adopting the technology.
Engagement and motivation
Engagement and motivation are critical factors in the success of any training program (56). High levels of engagement and motivation ensure that participants remain focused and actively involved, which enhances learning retention and skill acquisition. Engagement was assessed in one study using Likert-scale questionnaire (25), while intrinsic motivation was evaluated in three studies (20, 24, 29), where the Situational Motivation Scale (SIMS) (57) and the Reduced Instructional Materials Motivation Survey (RIMMS) (58) were used.
Overall user experience
Nine studies (19, 20, 23, 27, 28, 30, 31, 33, 37) explored participants' general experiences, thoughts, feelings, attitudes, and suggestions. Commonly used methods included interviews (19, 20, 31), focus groups (23, 33), survey (19, 20, 27, 28, 30, 31, 37), and observations (19). It is worth noting that the reviewed studies usually combined qualitative and quantitative methods to obtain comprehensive insights into participants' perspectives. For example, one study (20) administered the User Experience Questionnaire (UEQ-s) (59) with trainees and conducted interviews with trainers to explore their experiences with the XR training program. In another study (19), the researchers combined interviews, surveys, and observations to gain a holistic understanding of participants' experiences with the training system.
Perceived benefits and challenges
To address RQ3, we analyzed and synthesized the benefits and challenges of using XR technologies for EMS training and education as reported in the reviewed articles, which are outlined in this section.
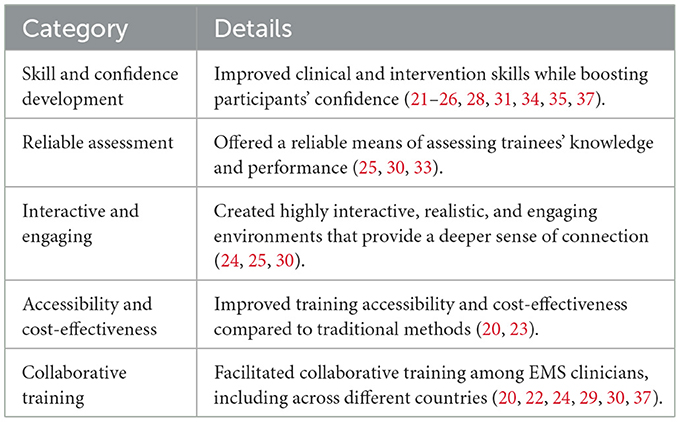
Benefits
As detailed below and summarized in Table 6, the reviewed articles highlight that integrating XR technology into EMS training offers numerous advantages, including enhancing clinical skills, engagement, accessibility, cost-efficiency, and promoting training standardization and teamwork.
First and foremost, the majority of the reviewed articles suggested that XR-based training can enhance clinical and intervention skills while boosting EMS clinicians' confidence in handling low-frequency, high-stakes scenarios (21–26, 28, 31, 34, 35, 37). For example, novice learners reported significant improvements in performance, speed, and self-efficacy (35), while another study (26) revealed a 46% increase in accuracy and a 29% boost in task execution speed. Additionally, confidence—a critical factor in EMS work—was enhanced through XR training, as highlighted by three studies (21, 22, 35).
Second, in addition to practicing clinical skills, XR technology provides a robust and reliable means of assessing trainees‘ knowledge and performance to identify areas requiring improvement or more training (25, 30, 33). For instance, one study (30) illustrated that the XR training system was a valid method for evaluating first responders' skills, with 77% of participants affirming that the system's generated evaluations were accurate and served as a valid assessment of their abilities. Additionally, the automatic identification of inaccurate or incomplete tasks, along with the provision of feedback to trainees, may reduce or even eliminate the need for additional trainers (33).
Third, XR technologies were praised for their ability to create highly interactive, realistic, and engaging environments, offering a deeper sense of connection compared to traditional training methods (24, 25, 30). For instance, as Lowe et al. (25) pointed out, VR could foster a higher level of connection that can be delivered globally and without restrictions to bridge the gap between trainees and real-world scenarios.
Fourth, these technologies significantly improve accessibility and cost-effectiveness (20, 23). Unlike traditional simulation-based training, which often requires substantial resources, XR technologies make training more accessible by democratizing access to training for EMS clinicians. The study conducted by Mills et al. (23) underscored this benefit, showing that a VR platform costing $712.04 was substantially less expensive than live simulation training, which cost $9,413.71. This cost efficiency makes XR technology an economical solution for broad-scale EMS training programs.
Finally, XR-based training platforms facilitate collaborative training (20, 22, 24, 29, 30, 37). For instance, Lerner et al. (24) developed a VR application that allowed participants to interact and perform tasks collaboratively in a shared virtual environment, simulating the coordination and communication challenges they might encounter in real-life emergency situations. Another study (37) focused on delivering training between two countries (USA and Saudi Arabia), which focused on delivering training between USA and Saudi Arabia, highlighted the successful implementation of telesimulation using AR-enabled smart glasses to connect participants across different regions and countries.
Challenges and barriers
The reviewed articles also pointed out several challenges in the adoption and implementation of immersive systems in EMS training. The challenges are summarized in Table 7.
Ergonomic and human factor issues
One of the primary challenges in adopting XR technology is the discomfort associated with its use, often caused by bulky devices (31, 33), incompatibility with spectacles (e.g., eyeglasses) (33), or VR-induced sickness (29). Elsenbast et al. (29) highlighted that such discomfort significantly hinders participants' engagement and may limit their ability to effectively complete training sessions. Additionally, physical limitations caused by headset cables were highlighted in (24), where participants experienced difficulties performing tasks due to restricted movement. Finally, cognitive overload, resulting from the mental demands of operating complex XR systems, was noted in (24, 31, 33). Participants reported difficulties in processing information and completing tasks simultaneously, emphasizing the importance of streamlined designs to minimize mental strain.
Usability issues
Interface and usability challenges were identified across multiple studies. For example, participants struggled with navigating XR interfaces and controls, such as pressing incorrect buttons on the controls or being unable to log and enter data during simulations (23–25). Issues related to information clarity and display readability also contributed to a negative user experience when interacting with XR systems (33). Additionally, two studies (25, 31) specifically pointed out the learning curve associated with using immersive systems, as participants' unfamiliarity with the technology often led to inefficiencies during training.
Technical limitations and issues
Technical challenges, such as connectivity problems, were noted in three studies (30, 32, 37). These disruptions, including devices losing connection during simulations, impacted participants' ability to complete tasks effectively. This was particularly problematic during live, interactive telesimulations conducted between distributed locations, such as different countries or regions (37). Software malfunctions also posed significant challenges, as highlighted in (30–32). Examples included system freezing and system glitches, which not only disrupted the learning process but also undermined confidence in the technology. Finally, Mills et al. (23) noted the inability of immersive systems to fully replicate human interactions and emotional immersion, which are essential for EMS training scenarios requiring interpersonal communication and empathy.
Risk of bias
The relevance, reliability, validity, and applicability of all reviewed studies were thoroughly evaluated by the research team, as described in the method section. The overall quality of the studies was categorized as high in 15 studies and medium in 4, with none being classified as low. However, three notable issues emerged during the appraisal process. First, only six studies addressed issues related to potential confounders, with the remaining 13 studies failed to adequately account for possible biases in their methodologies. For instance, variations in trainees' prior knowledge and experience were not consistently controlled for, which may have influenced the reported training effects and hindered direct comparison across studies. Second, eight studies did not clearly describe their ethical approval or related procedures, such as obtaining informed consent from participants or getting study approval from an ethics review board. This lack of information raises concerns about the adherence to ethical standards and the transparency of these studies. Third, a significant disparity in participant numbers was observed across the studies, ranging from as few as 10 participants in one study (32, 33) to as many as 375 in another (30). This variance could affect the generalizability of findings, as smaller sample sizes may lead to less representative results compared to studies with larger, more diverse participant pools.
Discussion
In this section, we discuss the implications derived from this systematic review of the existing literature. We focus on three key aspects: methodological implications, design implications, and practical implications.
Methodological implications
With one exception (34), almost all of the reviewed studies primarily focused on short-term outcomes, such as immediate performance during or after the training, user satisfaction, and perceived usability. While these metrics are valuable for understanding the initial effectiveness of a training platform, they do not provide insights into how well the knowledge and skills are retained over time or how effectively trainees perform in actual emergency situations. For instance, while participants may demonstrate improved triage scores or reduced error rates through XR-based training, it remains unclear whether these gains translate into better performance weeks or months later in high-pressure, real-world scenarios. To address this gap, future studies should incorporate longitudinal designs to evaluate the long-term impact of immersive training. This could involve follow-up assessments weeks or months after the initial training to measure knowledge retention and skill decay, as demonstrated in one reviewed study (34). Moreover, tracking how trainees apply their training in real-world emergencies could offer more meaningful insights into the practical value of these technologies. For example, studies could examine whether EMS clinicians trained with XR-based platforms demonstrate faster response times, better decision-making under pressure, or improved patient outcomes in real incidents compared to those trained with traditional methods. Overall, longitudinal evaluations that extend beyond the training period are essential to assess the durability of learning outcomes, monitor performance over time, and ensure that XR interventions deliver sustained benefits in clinical practice.
Another interesting observation is the use of user-centered design in four studies (19, 20, 27, 32) to investigate user requirements for the development of XR-based training systems. User-centered design ensures that the needs, preferences, and challenges of end-users are integrated into the system from the outset, resulting in more intuitive interfaces and effective training experiences (60, 61). Without such involvement, there is a risk of creating systems that fail to address critical pain points or that introduce additional cognitive and physical burdens (62). Future research should prioritize co-designing systems with EMS clinicians to ensure alignment with their training needs to enhance the usability and acceptance of XR training systems.
Third, it is worth noting the geographic distribution of the reviewed studies. The majority were conducted in high-income countries, particularly the United States and European nations. This geographic concentration raises concerns about the generalizability of findings to low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), where EMS systems often operate under different constraints, including limited funding, understaffing, and reduced access to advanced technologies such as XR. The implementation and outcomes of XR-based training programs may vary significantly in these settings due to differences in technological infrastructure, educational resources, and healthcare priorities (63, 64). Future research should explicitly consider these contextual differences and evaluate how XR solutions can be adapted to better serve the needs of diverse EMS environments globally.
Finally, one of the significant challenges in evaluating the effectiveness of XR-based training technologies for EMS is the lack of standardized evaluation frameworks. As seen in the reviewed studies, researchers used a wide variety of tools, metrics, and methodologies to assess outcomes. Additionally, there was substantial variation in the number of participants, the consideration of compounding factors, and the reporting of ethical procedures. This diversity makes it challenging to compare results across studies, draw generalized conclusions, and identify best practices for the development and implementation of these systems. Notably, these challenges are not unique to the EMS training domain. XR technologies have also been broadly applied in other areas of healthcare education—such as surgical training, nursing, and medical school curricula—where similarly diverse evaluation methods are employed, ranging from technical performance metrics (e.g., surgical accuracy, task completion time) to cognitive and behavioral outcomes (e.g., decision-making, communication, empathy) (65–67). Drawing from these broader applications, the EMS community could benefit from adopting validated instruments and multi-dimensional assessment strategies that extend beyond user satisfaction and short-term performance. Specifically, integrating behavioral, affective, and situational awareness measures—commonly used in other healthcare XR evaluations—may offer a richer understanding of how immersive training influences readiness and clinical competence in EMS settings. Additionally, developing standardized evaluation frameworks would enable the field to move toward more rigorous, comparable, and actionable evaluations. We hope this systematic review serves as a starting point toward achieving this goal.
Design implications
The majority of studies reviewed focused on virtual reality (VR) as the primary immersive technology for EMS training. VR's ability to create realistic, fully immersive environments makes it a natural choice for replicating high-pressure emergency scenarios. Several factors contribute to the predominant use of VR in the reviewed literature. First, VR technologies were developed and adopted earlier than other XR technologies such as AR or MR, leading to a head start in their exploration and application. This early adoption likely paved the way for more research and practical implementations of VR systems. Second, comparative studies examining the effectiveness of VR against other technologies, such as AR or MR, further confirm its effectiveness in EMS training. For instance, Koutitas, et al. (26) found that VR training surpassed AR in effectiveness, improving performance in critical areas such as error reduction and task completion speed. Similarly, Elsenbast et al. (29) concluded that MR scenarios did not demonstrate clear superiority over VR scenarios in EMS training. While AR and MR offer unique advantages, such as the ability to overlay critical information onto real-world environments, these technologies have yet to show consistent benefits over VR in EMS training contexts. Given VR's current dominance and its proven capabilities, it is understandable why it has become the focal point of research in immersive EMS training. However, with recent advancements in AR and MR technologies, expanding future research to compare the most advanced AR and MR systems against VR could uncover additional insights and help determine the most effective applications for each type of technology.
The reviewed studies highlighted several critical features deemed highly useful or effective through evaluations or requirement gathering. One such feature is “smart scenario editors”, identified as essential for minimizing reliance on developers for customization (19, 32). These tools allow trainers to independently design, modify, and adapt training scenarios using a plug-and-play approach in the backend, without requiring technical expertise. This capability not only promotes greater flexibility and adaptability but also enhances the cost-efficiency of immersive training systems by enabling EMS agencies to save on development costs while maintaining relevant and engaging training content. Additionally, several reviewed studies suggested that the integration of responsive virtual patients is a valuable feature that should be incorporated into XR systems (19–21, 30, 32). With the exponential development and advancement of large language models (LLMs), there is significant potential to enhance virtual patients by leveraging LLMs to simulate realistic patient interactions, communicate dynamically with trainees, and adapt to various scenarios in real-time—capabilities that were not feasible just a few years ago (68, 69). This approach could also help address current technical limitations in XR training applications, such as the inability to fully replicate human interactions and emotional immersion (23). Future research is needed to evaluate the feasibility and effectiveness of LLM-powered virtual patients in EMS training.
The reviewed studies also noted several challenges that must be addressed to ensure their effective adoption. VR sickness, characterized by symptoms like dizziness, nausea, and fatigue, remains a significant barrier. Such symptoms can hinder participants‘ ability to complete training sessions and may reduce the overall acceptance of VR-based systems (46, 47). Researchers and developers must explore strategies to minimize VR sickness, such as optimizing frame rates, reducing sensory conflicts, and providing breaks during training (70, 71). Cognitive workload is another critical challenge, as operating complex VR systems while processing training scenarios can overwhelm participants. High cognitive demands can detract from learning outcomes and impede performance during simulations. To address this, training systems should have adaptive difficulty levels that align with trainees' expertise. Providing pre-training sessions and adequate user support to familiarize users with the technology can help mitigate cognitive overload by allowing trainees to focus on skill development rather than system navigation (25).
Practical implications
One of the most critical considerations for EMS agencies in adopting XR-based HMDs for training purposes is the associated costs and financial burden. EMS agencies often operate under constrained budgets, making it essential for training solutions to be affordable and sustainable. XR technologies have demonstrated their potential to deliver high-quality training at a fraction of the cost of traditional live simulations. For example, as highlighted in one reviewed study (23), a VR platform costing $712.04 was significantly less expensive than live simulation training, which required $9,413.71 to execute. This large difference in cost indicates the financial feasibility of VR-based solutions. To further support adoption, XR training platforms should prioritize cost efficiency, including low-cost hardware, affordable software licensing, and minimal ongoing maintenance expenses. Such accessibility ensures that resource-limited EMS agencies, including those in low- and middle-income countries, can implement these technologies to enhance their training programs without compromising other critical operational needs.
Another critical aspect of successfully implementing XR training technologies in EMS is securing buy-in from end users, particularly those who may be skeptical or resistant to the adoption of new technologies. Resistance often stems from concerns about the learning curve, perceived complexity, or fear that technology may replace traditional training methods rather than complement them. To address these concerns, EMS organizations must actively involve end users—both trainers and trainees—in the development and implementation process.
Study limitations
As with any research project, our study presents several limitations. First, the included studies varied significantly in terms of sample size, technologies, study designs, and evaluation tools, which makes direct comparisons and generalizations challenging. Second, the review excluded non-English studies, theses, and posters, which may have led to the omission of valuable insights from other regions or works that were not part of a journal or conference. Lastly, the reliance on reported data in the reviewed studies may have introduced biases, as some studies lacked transparency in describing inclusion criteria, ethical approvals, and potential confounding factors. Future research should address these gaps by adopting standardized frameworks and conducting larger-scale, multi-center evaluations.
Conclusion
This systematic review highlights the potential of XR-based HMDs to transform EMS training by providing immersive, interactive, and cost-effective alternatives to traditional methods. The reviewed studies demonstrated that XR technologies can enhance clinical skills, boost confidence, and promote collaborative learning, especially for low-frequency, high-stakes scenarios. However, the findings also underscore significant challenges, including issues with ergonomics, usability, and technical limitations. Building on these insights, our work outlines the methodological, design, and practical implications to guide future research and development of XR-based EMS training systems.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZZ: Software, Visualization, Formal analysis, Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Project administration, Validation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Supervision, Investigation. MM: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Validation, Visualization, Formal analysis, Methodology. AI: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology. LK: Methodology, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. MV: Writing – review & editing, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Science Foundation (1948292).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
EMS, emergency medical service; MCIs, mass casualty incidents; XR, extended reality; VR, virtual reality; AR, augmented reality; MR, mixed reality; HMDs, head-mounted displays; LLM, large language models.
References
1. Delbridge TR, Bailey B, Chew JL, Conn AK, Krakeel JJ, Manz D, et al. EMS agenda for the future: where we are… where we want to be. Prehosp Emerg Care. (1998) 2:1–12. doi: 10.1080/10903129808958832
2. Klassen AB, Marshall M, Dai M, Mann NC, Sztajnkrycer MD. Emergency medical services response to mass shooting and active shooter incidents, United States, 2014–2015. Prehosp Emerg Care. (2019) 23:159–66. doi: 10.1080/10903127.2018.1484970
3. Schultz CH Koenig KL Whiteside M Murray R National Standardized All-Hazard Disaster Core Competencies Task Force. Development of national standardized all-hazard disaster core competencies for acute care physicians, nurses, EMS professionals. Ann Emerg Med. (2012) 59:196–208. e191. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2011.09.003
4. Abelsson A, Rystedt I, Suserud BO, Lindwall L. Learning by simulation in prehospital emergency care–an integrative literature review. Scand J Caring Sci. (2016) 30:234–40. doi: 10.1111/scs.12252
5. Farrell C, Dorney K, Mathews B, Boyle T, Kitchen A, Doyle J, et al. A statewide collaboration to deliver and evaluate a pediatric critical care simulation curriculum for Emergency Medical Services. Front Pediat. (2022) 10:903950. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.903950
6. Hssain I, Souaiby N, Benmiloud K, Zumbiehl F, Schoettker P, Bellou A. Benefits and limitations of medical simulation in emergency medicine. Med Emergency. (2012) 10:09–14.
7. McFetrich J. A structured literature review on the use of high fidelity patient simulators for teaching in emergency medicine. Emerg Med J. (2006)23:509–11. doi: 10.1136/emj.2005.030544
8. Wolfram RW, Warren CM, Doyle CR, Kerns R, Frye S. Retention of pediatric advanced life support (PALS) course concepts. J Emerg Med. (2003) 25:475–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2003.06.001
9. Wu TC, Ho CB. A scoping review of metaverse in emergency medicine. Australas Emerg Care. (2023) 26:75–83. doi: 10.1016/j.auec.2022.08.002
10. del Carmen Cardós-Alonso M, Otero-Varela L, Redondo M, Uzuriaga M, González M, Vazquez T, et al. Extended reality training for mass casualty incidents: a systematic review on effectiveness and experience of medical first responders. Int J Emerg Med. (2024) 17:99. doi: 10.1186/s12245-024-00685-3
11. Munzer BW, Khan MM, Shipman B, Mahajan P. Augmented reality in emergency medicine: a scoping review. J Med Internet Res. (2019) 21:e12368. doi: 10.2196/12368
12. Harari RE, Schulwolf SL, Borges P, Salmani H, Hosseini F, Bailey SKT, et al. Applications of augmented reality for prehospital emergency care: systematic review of randomized controlled trials. JMIR XR Spatial Comput. (2025) 2:e66222. doi: 10.2196/66222
13. Pantelidis P, Chorti A, Papagiouvanni I, Paparoidamis G, Drosos C, Panagiotakopoulos T, et al. Virtual and augmented reality in medical education. Med Surg Educ-Past, Present Future. (2018) 26:77–97. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.71963
14. Barteit S, Lanfermann L, Bärnighausen T, Neuhann F, Beiersmann C. Augmented, mixed, and virtual reality-based head-mounted devices for medical education: systematic review. JMIR Serious Games. (2021) 9:e29080. doi: 10.2196/29080
15. Gunshin M, Doi K, Morimura N. Use of high-fidelity simulation technology in disasters: an integrative literature review. Acute Med Surg. (2020) 7:e596. doi: 10.1002/ams2.596
16. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. (2010) 8:336–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007
17. Rosella L, Bowman C, Pach B, Morgan S, Fitzpatrick T, Goel V. The development and validation of a meta-tool for quality appraisal of public health evidence: Meta Quality Appraisal Tool (MetaQAT). Public Health. (2016) 136:57–65. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2015.10.027
18. Boudewijns EA, Vermond D, van der Kleij RM, Chavannes NH, van Schayck OC, Kirenga B, et al. Factors critical to implementation success of cleaner cooking interventions in low-income and middle-income countries: protocol for an umbrella review. BMJ Open. (2020) 10:e041821. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-041821
19. Zechner O, García Guirao D, Schrom-Feiertag H, Regal G, Uhl JC, Gyllencreutz L, et al. NextGen training for medical first responders: advancing mass-casualty incident preparedness through mixed reality technology. Multimodal Technol Interact. (2023) 7:113. doi: 10.3390/mti7120113
20. Vogt P R. Boer, de Boer M, Prins H, Smit J, Tuinstra D, Degens N, Hettinga M, Paans W. Designing and evaluating a Virtual Reality training for paramedics to practice triage in complex situations. In: International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction. Cham: Springer. (2023). p. 503–522.
21. Thompson S. Mass casualty triage: using virtual reality in hazardous area response teams training. J Paramedic Pract. (2023) 15:418–27. doi: 10.12968/jpar.2023.15.10.418
22. Birrenbach T, Wespi R, Hautz W, Berger J, Schwab PR, Papagiannakis G, et al. Development and usability testing of a fully immersive VR simulation for REBOA training. Int J Emerg Med. (2023) 16:67. doi: 10.1186/s12245-023-00545-6
23. Mills B, Dykstra P, Hansen S, Miles A, Rankin T, Hopper L, et al. Virtual reality triage training can provide comparable simulation efficacy for paramedicine students compared to live simulation-based scenarios. Prehosp Emerg Care. (2020) 24:525–36. doi: 10.1080/10903127.2019.1676345
24. Lerner D, Mohr S, Schild J, Göring M, Luiz T. An immersive multi-user virtual reality for emergency simulation training: usability study. JMIR Serious Games. (2020) 8:e18822. doi: 10.2196/18822
25. Lowe J, Peng C, Winstead-Derlega C, Curtis H. 360 virtual reality pediatric mass casualty incident: A cross sectional observational study of triage and out-of-hospital intervention accuracy at a national conference. J Am College Emerg Physicians Open. (2020) 1:974–80. doi: 10.1002/emp2.12214
26. Koutitas G, Smith S, Lawrence G. Performance evaluation of AR/VR training technologies for EMS first responders. Virtual Real. (2021) 25:83–94. doi: 10.1007/s10055-020-00436-8
27. Mossel A, Schoenauer C, Froeschl M, Peer A, Goellner J, Kaufmann H. Immersive training of first responder squad leaders in untethered virtual reality. Virtual Real. (2021) 25:745–59. doi: 10.1007/s10055-020-00487-x
28. Glick Y, Avital B, Oppenheimer J, Nahman D, Wagnert-Avraham L, Eisenkraft A, et al. Augmenting prehospital care. BMJ Mil Health. (2021) 167:158–62. doi: 10.1136/jramc-2019-001320
29. Elsenbast C, Dahlmann P, Schnier D. Virtual team training with Mixed Reality and Virtual Reality–benefits and limitations illustrated on the example of two paramedic classes. Multimedia Tools Appl. (2024) 2:1–25. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-17878-2
30. Way DP, Panchal AR, Price A, Berezina-Blackburn V, Patterson J, McGrath J, et al. Learner evaluation of an immersive virtual reality mass casualty incident simulator for triage training. BMC Digital Health. (2024) 2:56. doi: 10.1186/s44247-024-00117-5
31. Friedman N, Zuniga-Hernandez M, Titzler J, Suen MY, Wang E, Rosales O, et al. Prehospital pediatric emergency training using augmented reality simulation: a prospective, mixed methods study. Prehosp Emerg Care. (2024) 28:271–81. doi: 10.1080/10903127.2023.2224876
32. Berndt H, Wessel D, Mentler T, Herczeg M. Human-centered design of a virtual reality training simulation for mass casualty incidents. In: 2018 10th International Conference on Virtual Worlds and Games for Serious Applications (VS-Games). Würzburg: IEEE, 1–8.
33. Doswell JT, Jolmson J, Brockingon B, Mosby A, Salaam S, Chinery A. Juxtopia® CAMMRAD prepare: a wearable ai-ar platform for clinical training emergency first response teams. In: 2020 22nd Symposium on Virtual and Augmented Reality (SVR). Porto de Galinhas: IEEE (2020). p. 164–168.
34. Azimi E, Winkler A, Tucker E, Qian L, Doswell J, Navab N, et al. Can mixed-reality improve the training of medical procedures? In: 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). Honolulu, HI: IEEE (2018). p. 4065–4068.
35. Vincent DS, Sherstyuk A, Burgess L, Connolly KK. Teaching mass casualty triage skills using immersive three-dimensional virtual reality. Academic Emerg Med. (2008) 15:1160–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2008.00191.x
36. Schneeberger M, Paletta L, Wolfgang Kallus K, Reim L, Schönauer C, Peer A, et al. First responder situation reporting in virtual reality training with evaluation of cognitive-emotional stress using psychophysiological measures. Cogn Comput Internet Things. (2022) 43:73. doi: 10.54941/ahfe1001841
37. McCoy CE, Alrabah R, Weichmann W, Langdorf MI, Ricks C, Chakravarthy B, et al. Feasibility of telesimulation and google glass for mass casualty triage education and training. West J Emerg Med. (2019) 20:512. doi: 10.5811/westjem.2019.3.40805
38. Ritzmann S, Hagemann V, Kluge A. The Training Evaluation Inventory (TEI)-evaluation of training design and measurement of training outcomes for predicting training success. Vocat Learn. (2014) 7:41–73. doi: 10.1007/s12186-013-9106-4
39. Maloney S, Haines T. Issues of cost-benefit and cost-effectiveness for simulation in health professions education. Adv Simulat. (2016) 1:1–6. doi: 10.1186/s41077-016-0020-3
40. Heater C. Being there: The subjective experience of presence. Presence Teleoperat Virtual Environ. (1992) 1:262–71. doi: 10.1162/pres.1992.1.2.262
41. Schubert T, Friedmann F, Regenbrecht H. The experience of presence: Factor analytic insights. Presence: Teleop Virtual Environm. (2001) 10:266–81. doi: 10.1162/105474601300343603
42. Witmer BG, Jerome CJ, Singer MJ. The factor structure of the presence questionnaire. Presence: Teleoperat Virtual Environm. (2005) 14:298–312. doi: 10.1162/105474605323384654
43. Makransky G, Lilleholt L, Aaby A. Development and validation of the Multimodal Presence Scale for virtual reality environments: A confirmatory factor analysis and item response theory approach. Comput Human Behav. (2017) 72:276–85. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2017.02.066
44. Nilsson NC, Nordahl R, Serafin S. Immersion revisited: a review of existing definitions of immersion and their relation to different theories of presence. Human Technol. (2016) 12:108–34. doi: 10.17011/ht/urn.201611174652
45. Slater M, Usoh M, Steed A. Depth of presence in virtual environments. Presence: Teleoperators Virtual Environm. (1994) 3:130–44. doi: 10.1162/pres.1994.3.2.130
46. Saredakis D, Szpak A, Birckhead B, Keage HA, Rizzo A, Loetscher T. Factors associated with virtual reality sickness in head-mounted displays: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Hum Neurosci. (2020) 14:96. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.00096
47. Chang E, Kim HT, Yoo B. Virtual reality sickness: a review of causes and measurements. Int J Human–Comp Interact. (2020) 36:1658–82. doi: 10.1080/10447318.2020.1778351
48. Kennedy RS, Lane NE, Berbaum KS, Lilienthal MG. Simulator sickness questionnaire: an enhanced method for quantifying simulator sickness. Int J Aviat Psychol. (1993) 3:203–20. doi: 10.1207/s15327108ijap0303_3
49. Klepsch M, Schmitz F, Seufert T. Development and validation of two instruments measuring intrinsic, extraneous, and germane cognitive load. Front Psychol. (2017) 8:1997. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01997
50. Hart S. Development of NASA-TLX (Task Load Index): Results of empirical and theoretical research. In: Human Mental Workload. London: Elsevier (1988).
51. Lewis JR. Psychometric evaluation of an after-scenario questionnaire for computer usability studies: the ASQ. ACM Sigchi Bullet. (1991) 23:78–81. doi: 10.1145/122672.122692
52. Brooke J. SUS-A quick and dirty usability scale. In: Usability Evaluation in Industry. (1996). p. 4–7.
53. Block EF, Lottenberg L, Flint L, Jakobsen J, Liebnitzky D. Use of a human patient simulator for the advanced trauma life support course. Am Surg. (2002) 68:648–51. doi: 10.1177/000313480206800720
54. Gil-Gómez J-A, Manzano-Hernández P, Albiol-Pérez S, Aula-Valero C, Gil-Gómez H, Lozano-Quilis JA. USEQ: a short questionnaire for satisfaction evaluation of virtual rehabilitation systems. Sensors. (2017) 17:1589. doi: 10.3390/s17071589
55. Franklin AE, Burns P, Lee CS. Psychometric testing on the NLN student satisfaction and self-confidence in learning, simulation design scale, and educational practices questionnaire using a sample of pre-licensure novice nurses. Nurse Educ Today. (2014) 34:1298–304. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2014.06.011
56. Saeed S, Zyngier D. How motivation influences student engagement: a qualitative case study. J Educ Learn. (2012) 1:252–67. doi: 10.5539/jel.v1n2p252
57. Guay F, Vallerand RJ, Blanchard C. On the assessment of situational intrinsic and extrinsic motivation: the Situational Motivation Scale (SIMS). Motiv Emot. (2000) 24:175–213. doi: 10.1023/A:1005614228250
58. Loorbach N, Peters O, Karreman J, Steehouder M. Validation of the Instructional Materials Motivation Survey (IMMS) in a self-directed instructional setting aimed at working with technology. Br J Educ Technol. (2015) 46:204–18. doi: 10.1111/bjet.12138
59. Schrepp M, Hinderks A, Thomaschewski J. Applying the user experience questionnaire (UEQ) in different evaluation scenarios. In: Design, User Experience, and Usability Theories, Methods, and Tools for Designing the User Experience: Third International Conference, DUXU 2014 Held as Part of HCI International 2014. Heraklion: Springer (2014). p. 383–392.
60. Yen P-Y, Bakken S. Review of health information technology usability study methodologies. J Am Med Inform Assoc. (2012) 19:413–22. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2010-000020
61. Carayon P, Hoonakker P. Human factors and usability for health information technology: old and new challenges. Yearb Med Inform. (2019) 28:071–7. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1677907
62. Göttgens I, Oertelt-Prigione S. The application of human-centered design approaches in health research and innovation: a narrative review of current practices. JMIR mHealth and uHealth. (2021) 9:e28102. doi: 10.2196/28102
63. Rybarczyk MM, Ludmer N, Broccoli MC, Kivlehan SM, Niescierenko M, Bisanzo M, et al. Emergency medicine training programs in low-and middle-income countries: a systematic review. Ann Global Health. (2020) 86:60. doi: 10.5334/aogh.2681
64. M. Faizan Siddiqui Jabeen S, Alwazzan A, Vacca S, Dalal L, Al-Haddad B, Jaber A, et al. Integration of augmented reality, virtual reality, and extended reality in healthcare and medical education: a glimpse into the emerging horizon in LMICs—a systematic review. J Med Educ Curricul Dev. (2025) 12:23821205251342315. doi: 10.1177/23821205251342315
65. Kyaw BM, Saxena N, Posadzki P, Vseteckova J, Nikolaou CK, George PP, et al. Virtual reality for health professions education: systematic review and meta-analysis by the digital health education collaboration. J Med Internet Res. (2019) 21:e12959. doi: 10.2196/12959
66. Foronda CL, Fernandez-Burgos M, Nadeau C, Kelley CN, Henry MN. Virtual simulation in nursing education: a systematic review spanning 1996 to (2018). Simulat Healthc. (2020) 15:46–54. doi: 10.1097/SIH.0000000000000411
67. R. De Ponti Marazzato J, Maresca AM, Rovera F, Carcano G, Ferrario MM. Pre-graduation medical training including virtual reality during COVID-19 pandemic: a report on students' perception. BMC Med Educ. (2020) 20:1–7. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02245-8
68. R. Gutiérrez Maquilón Uhl J, Schrom-Feiertag H, Tscheligi M. Integrating GPT-Based AI into virtual patients to facilitate communication training among medical first responders: usability study of mixed reality simulation. JMIR Format Res. (2024) 8:e58623. doi: 10.2196/58623
69. Kapadia N, Gokhale S, Nepomuceno A, Cheng W, Bothwell S, Mathews M, et al. Evaluation of large language model generated dialogues for an AI based VR nurse training simulator. In: International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction. Cham: Springer (2024). p. 200–212.
70. Shi R, Liang H-N, Wu Y, Yu D, Xu W. Virtual reality sickness mitigation methods: A comparative study in a racing game. In: Proceedings of the ACM on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques. (2021). p. 1–16. doi: 10.1145/3451255
Keywords: immersive technology, head-mounted display, emergency medical services, simulation, medical training
Citation: Zhang Z, Meybodi MM, Ingale A, Karimova L and Vinnikov M (2025) Extended reality technology for emergency medical service training: systematic review. Front. Disaster Emerg. Med. 3:1630167. doi: 10.3389/femer.2025.1630167
Received: 17 May 2025; Accepted: 04 July 2025;
Published: 22 July 2025.
Edited by:
Robert Wunderlich, University of Tübingen, GermanyReviewed by:
Tamorish Kole, University of South Wales, United KingdomMarc Lazarovici, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, Germany
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Meybodi, Ingale, Karimova and Vinnikov. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhan Zhang, enpoYW5nQHBhY2UuZWR1
 Zhan Zhang
Zhan Zhang Maryam Moeini Meybodi1
Maryam Moeini Meybodi1