- 1Department of Medicine and Biosystemic Science, Kyushu University Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Fukuoka, Japan
- 2Department of Rheumatology, Shimonoseki City Hospital, Yamaguchi, Japan
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Kyushu University Beppu Hospital, Beppu, Japan
- 4Department of Medical Education, Kyushu University Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Fukuoka, Japan
Objectives: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), a cornerstone drug, is recommended for long-term use in treating systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). However, in cases where HCQ is unavailable, it is unclear which drugs should be prioritised for continuation. We aimed to clarify whether belimumab (BLM), which has recently been reported to have long-term safety and efficacy, could be a viable alternative to HCQ.
Methods: We retrospectively compared the efficacy, drug continuation rate and safety of HCQ and BLM in the maintenance phase in patients with SLE. The efficacy endpoints were the cumulative incidence of flares over 2 years, the increase in the damage index and the changes in the SLE Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI) score and prednisolone dose. The safety endpoint was the adverse event rates.
Results: Among 96 patients analysed, 15 out of 84 patients (17.9%) in the HCQ group and 1 out of 12 patients (8.3%) in the BLM group experienced a flare, with no significant difference in the cumulative incidence of flares between the two groups (p = 0.47). No differences were observed in the cumulative incidence of the increase in the damage index, changes in the SLEDAI score and prednisolone dose, drug continuation rates and adverse events.
Conclusions: The efficacy and safety of BLM were similar to those of HCQ. BLM could be a valuable treatment option for patients with SLE as an alternative for those who cannot tolerate HCQ.
Introduction
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease with a variable clinical course and prognosis (1, 2). According to the treat-to-target strategy in SLE, the long-term goals should be ensuring long-term survival, preventing organ damage and optimising the health-related quality of life (3). Given these goals, once clinical remission or the lowest possible disease activity has been achieved, the next step should be to prevent flares and minimise drug toxicities. While it is important to discontinue drugs when disease flares are absent in order to minimise drug toxicities, there are limited data on the withdrawal of glucocorticoids, immunosuppressive agents or biologic agents, and it has been suggested that discontinuing all agents increases flare risk (4). Additionally, the British Society for Rheumatology guidelines for the management of SLE in adults (5) recommends that, after stable remission is achieved, physicians should aim to reduce and stop drugs except for hydroxychloroquine (HCQ). However, the order of drug reduction or cessation is not specifically mentioned. Therefore, one of the current challenges is the exact method to reduce and stop drugs after achieving remission.
HCQ is a cornerstone drug in SLE treatment because of its multifaceted effectiveness in reducing SLE activity, preventing disease flares, increasing long-term survival and reducing the risk of infection (6–11). The 2023 EULAR recommendations strongly advocate for HCQ as the mainstay of treatment for patients with SLE (12). It is recommended for all SLE patients during the treatment period, from induction to maintenance, unless contraindicated and should be continued for as long as possible since an increased flare rate with HCQ withdrawal has been reported (13, 14). However, in clinical practice, approximately 20%–30% of patients cannot tolerate HCQ owing to adverse events, and retinal toxicity due to cumulative dosage during long-term use remains a concern (15–17). Therefore, although HCQ should be continued as the current treatment strategy for SLE, it is unclear which drugs should be prioritised for continuation in cases of HCQ unavailability.
Belimumab (BLM), the first biologic agent approved for SLE, has been reported effective in reducing disease activity, glucocorticoid dose and flare rate, preventing organ damage and having a long-term safety profile (18–21). Multiple randomised controlled trials have consistently shown that BLM does not increase infection risk compared to placebo or standard therapy (19, 20, 22), and a cohort study reported a lower risk of severe infection and infection-related hospitalisation with BLM compared to immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine, methotrexate and mycophenolate mofetil (23). Therefore, BLM may be considered appropriate for long-term use like HCQ or as an alternative when HCQ is unavailable, expanding the treatment options for patients with SLE.
This study aimed to determine whether BLM could be a viable alternative to HCQ and compared the efficacy and safety of BLM and HCQ in the maintenance phase in patients with SLE.
Participants and methods
Patients
Our retrospective study considered patients with SLE who were receiving HCQ or BLM in the maintenance phase at Kyushu University Hospital and Shimonoseki City Hospital in December 2020. Patients who had been diagnosed with SLE according to the 1997 American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for SLE (24) and were receiving maintenance treatment with prednisolone (PSL) ≤ 15 mg/day and/or immunosuppressive agents were included in the study. HCQ was administered at 200–400 mg doses based on ideal body weight (<6.5 mg/kg/day), while BLM was administered at 200 mg/week dose via subcutaneous injection. Concomitant immunosuppressive agents such as mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus, azathioprine, mizoribine, cyclosporine A and methotrexate were permitted at stable doses. Patients were excluded if they had received additional immunosuppressive agents or an increased dose of PSL within one month before the study, were receiving HCQ and BLM concomitantly at the start of the observation or were using a biologic agent other than BLM or a Janus kinase inhibitor. We obtained data for all consecutive patients who met the inclusion criteria.
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Kyushu University Hospital (approval number 22042-00) and conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. As this research had a retrospective design, we disclosed the study information at the relevant facilities. Patient consent was not required as per the committee's guidelines.
Clinical and laboratory assessment
This study involved the extraction of information from the medical records of patients with SLE, including demographic data, clinical characteristics, disease activity, medications, adverse events and outcomes. Organ manifestations were defined using the SLE Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI) (25). Disease activity was assessed using the SLEDAI (24). Lupus Low Disease Activity State was defined as a SLEDAI score of ≤4 with no major organ activity and no new disease activity, a Physician Global Assessment (PGA) score (scale, 0–3) of ≤1, a PSL dose of ≤7.5 mg/day and well-tolerated immunosuppressive dosages (26). Remission was defined as a clinical SLEDAI score of 0, a PGA score (scale, 0–3) of <0.5, a PSL dose of ≤5 mg/day and stable immunosuppressive agents, according to the 2021 DORIS definition (27). The serological activity was defined as meeting at least one of the relevant SLEDAI criteria (increased anti-dsDNA titres and low complement levels).
Outcomes
This analysis compared the efficacy, drug continuation rate and safety of HCQ and BLM. The primary endpoint was the cumulative incidence of flares, which was determined using the SLE Flare Index (28). The starting date of observation was fixed at 1 December 2020 for all cases. Patients were followed for up to 2 years until the date of a flare, drug discontinuation or 30 November 2022. Secondary efficacy endpoints were the cumulative incidence of the increase in the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics damage index (SDI) (29) and the changes in SLEDAI score and PSL dose between the beginning and end of the observation period. The drug continuation rate was defined as the time to discontinuation for any cause. The drug discontinuation rate due to a lack of efficacy was defined as the time from the beginning of the observation to a disease flare or an increased PSL dose or the addition of an immunosuppressive agent before a flare. The safety endpoint was the frequency of adverse events during the observation period. Serious adverse events were defined as those resulting in hospitalisation or leading to drug discontinuation.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables are presented as the mean ± standard deviation or the median with an interquartile range. Categorical variables are reported as frequencies and percentages. The two groups were compared using the Student t-test for normally distributed continuous variables, Mann–Whitney U-test for non-normally distributed continuous variables and Fisher exact test for categorical variables. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were used to analyse the cumulative rate of flares or SDI increase, drug continuation rates and drug discontinuation rates. Group comparisons were made using log-rank statistics. Multivariate Cox proportional-hazards analysis was conducted to adjust for potential confounders in the survival analysis. Statistical significance was set at a p-value of <0.05. The data analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 9 or EZR (Saitama Medical Centre, Jichi Medical University, Saitama, Japan), which is a graphical user interface for R (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). More precisely, it is a modified version of R commander designed to add statistical functions frequently used in biostatistics (30).
Results
Patients
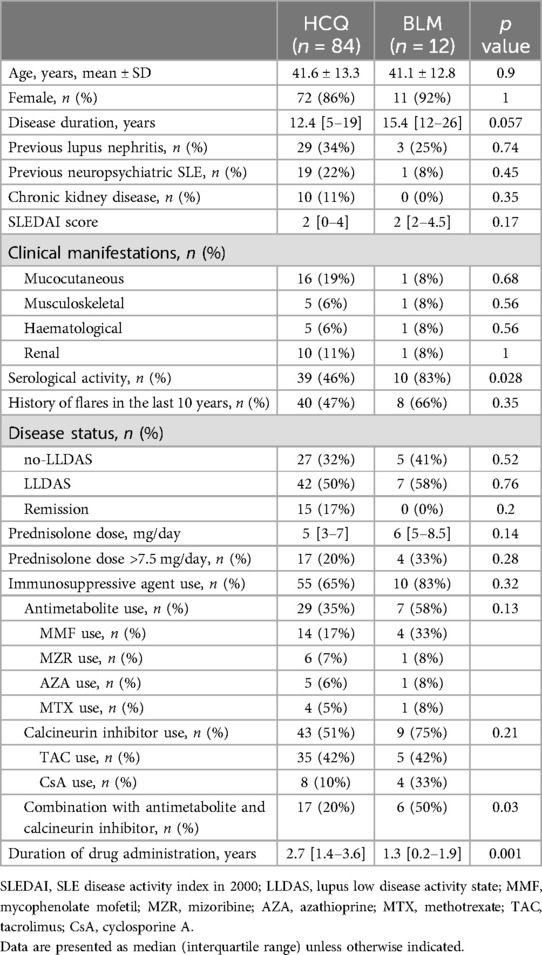
The study included 125 patients with SLE who were receiving HCQ or BLM at study entry. Twenty-nine patients were excluded because they were receiving HCQ and BLM concomitantly (n = 24), were using a biologic agent other than BLM or a Janus kinase inhibitor (n = 3) or had a treatment change within one month before the study (n = 2) (Figure 1). Therefore, 96 patients were analysed in this study; 84 and 12 were classified into the HCQ and BLM groups, respectively (Figure 1). The mean ± standard deviation age of the patients was 41.5 ± 13.2 years, and 83 patients (86.5%) were female. The median (interquartile range) disease duration was 14 (6–20) years. As noted in Table 1, except for serological activity and disease duration, the baseline clinical characteristics of the two groups were similar. The serological activity was significantly higher in the BLM group than in the HCQ group (p = 0.028). Disease duration tended to be slightly longer in the BLM group than in the HCQ group. Regarding concomitant medications, the median PSL dose was 6 mg, and 55 (65%) and 10 (83%) patients received immunosuppressive agents in the HCQ and BLM groups, respectively. Combination with antimetabolites and calcineurin inhibitors was more common in the BLM group compared to the HCQ group. The duration of drug administration differed between the two groups, reflecting the difference in when the drugs were approved in Japan. The reasons for not receiving HCQ concomitantly in the BLM group varied, including discontinuation due to adverse events, such as skin rash (n = 5), and gastrointestinal symptoms (n = 1); concerns about potential complications, such as retinopathy (n = 3) and cardiotoxicity (n = 1); and the discretion of the treating physician (n = 1). The median ± interquartile range of the observation period was similar between the two groups, with the HCQ group at 24.0 [22.1–24.0] months and the BLM group at 24.0 [22.8–24.0] months.
Efficacy
Fifteen patients (17.9%) in the HCQ group and 1 patient (8.3%) in the BLM group experienced a flare during the 2-year observation period, with no significant difference in the cumulative incidence of flares between the two groups (p = 0.47) (Figure 2A). Similar results were obtained after adjusting for a history of flares in the last 10 years and serological activity as covariates of flare risk factors in the multivariable Cox proportional-hazards analysis.

Figure 2. The cumulative incidence of flares (A) the adjusted hazard ratio was calculated after adjusting for a history of flares in the last 10 years and serological activity in the multivariable Cox proportional-hazard analysis. The cumulative incidence of the SDI increase (B) the changes in SLEDAI score (C) and PSL dose (D) during the observation period. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
Four patients (4.7%) in the HCQ group and none in the BLM group experienced an SDI increase. Events associated with the increased SDI score in the HCQ group included one case each of myelitis, peripheral neuropathy, compression fracture and malignancy. No significant difference in the cumulative incidence of the SDI increase was found between the two groups (p = 0.45) (Figure 2B).
The changes in SLEDAI score and PSL dose from the beginning to the end of the observation are shown in Figures 2C,D. PSL doses could be reduced in both groups without worsening SLEDAI scores.
Additionally, although this study excluded patients receiving HCQ and BLM concomitantly from the main analysis, the efficacy for the concomitant group was comparable to that of the HCQ or BLM monotherapy groups (Supplementary Figure S1).
Drug continuation rate
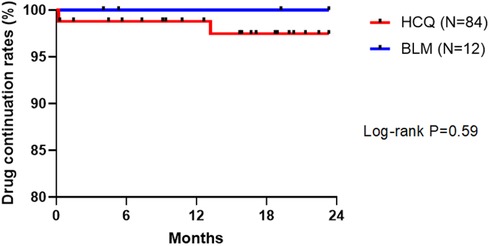
Of 84 patients in the HCQ group, 2 discontinued the drug due to adverse events during the observation period; the reasons for HCQ discontinuation were suspected drug eruption and gastrointestinal symptoms. In contrast, all 12 patients in the BLM group could continue the drug. Neither group recorded drug discontinuation due to a lack of efficacy. No significant difference in drug continuation rate was found between the two groups (Figure 3).
Safety
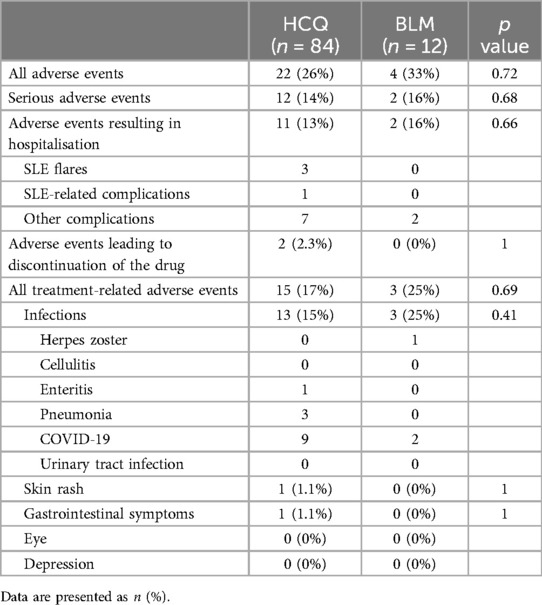
The frequency of adverse events showed no clear difference between the two groups (Table 2). Infections were the most common adverse events in both groups. Serious adverse events were also similar between the two groups. Retinopathy or depression was not observed in either group.
Discussion
This study demonstrated no significant differences in the efficacy and safety of HCQ and BLM regarding the cumulative incidences of flares and the SDI increase, the changes in the SLEDAI score and PSL dose, drug continuation rates and adverse events. These results indicate that BLM could serve as an alternative to HCQ when HCQ is unavailable due to adverse events or concerns about cumulative dosage.
This study compared the efficacy and safety of BLM with those of HCQ, a cornerstone drug in the treatment of SLE. The concept of disease modification is established in the field of SLE, referring to drugs that can positively affect the natural course of a disease. Based on the disease modification framework in other areas, disease modification in SLE has been proposed to require minimising disease activity with the fewest drug toxicities and slowing or preventing organ damage (31). HCQ is considered the leading candidate drug for disease modification because it is positioned as the background SLE treatment and data have confirmed its multifaceted benefits. Additionally, recent reports on the long-term efficacy and safety of BLM suggest that it could also be a candidate drug. Nonetheless, it is crucial to reiterate that, as stated in the 2023 EULAR recommendations (12), HCQ remains the mainstay of treatment for patients with SLE. BLM is approved for use as an add-on therapy in patients with moderate-to-severe SLE and refractory mild SLE, in combination with HCQ, glucocorticoids, and possibly immunosuppressive agents (12). This study, on the other hand, investigates an alternative, exploratory use of BLM as a maintenance treatment for patients who have achieved a response, particularly when HCQ cannot be used due to adverse effects or concerns about cumulative dosage. Given that many patients receiving BLM are already taking HCQ, the efficacy and safety of BLM and HCQ have not been directly compared. Therefore, the findings of the present study seem valuable for validating BLM as a candidate drug for disease modification or as an alternative to HCQ. Moreover, the results may be clinically significant when considering treatment strategies after achieving remission and alternative treatment for patients with SLE who cannot tolerate HCQ.
The efficacy endpoints of this study were the cumulative incidence of flares and SDI increase in the HCQ and BLM groups. The importance of maintaining remission and preventing flares as a therapeutic goal for reducing damage accumulation has been emphasised in the treat-to-target strategy (1). The SDI score, associated with a poor prognosis and increased mortality, is an important indicator for achieving long-term goals in SLE treatment. In the present work, we found that the cumulative incidences of flares and SDI increase in both groups were similar. Although the small sample size and retrospective design may have prevented adequate correction, the results suggest that BLM is at least as effective as HCQ in preventing flares and SDI increase.
The present study also compared the frequency of adverse events during the observation period of up to 2 years and revealed no significant differences in the frequency of infections or serious adverse events between the HCQ and BLM groups. Although this study was not conducted immediately after drug initiation, and thus adverse events caused by the drugs, such as skin rashes and gastrointestinal symptoms, were rarely noted, the safety profile of BLM was not less than that of HCQ. In a post hoc analysis of a large multicentre randomised controlled trial of BLM (32), adverse event rates between patients not receiving HCQ in the BLM group and those receiving HCQ in the placebo group were similar, although the comparison cannot be simply made due to the different patient backgrounds, which is comparable to the findings of our study. Moreover, adverse events stemming from the long-term use of the drugs, such as retinopathy with HCQ and depressive symptoms with BLM, should be further investigated. Longer-term and well-designed observational studies are required to provide more detailed safety considerations between the two groups.
Our results also showed similar drug continuation rates between the two groups. Notably, no discontinuation due to a lack of efficacy was observed in both groups, suggesting that BLM may have characteristics similar to HCQ. The current findings indicate that BLM has a high safety profile, as noted in a previous study (19, 20, 33). While similar comparisons need to be made for immunosuppressive agents and other biologic agents, at this stage, BLM seems the most reasonable treatment alternative for patients who cannot tolerate HCQ because of adverse effects or concerns about cumulative dosage.
The present study has several limitations that may affect the generalizability of the results. First, the sample size was small, and the number of patients in the BLM group was extremely small. It would be difficult to equalize the sample sizes of the two groups, given that many patients receiving BLM are already taking HCQ. Due to the small sample size, we limited the covariates to the two most significant flare risk factors, namely a history of flares in the last 10 years and serological activity. Therefore, to ensure a more accurate analysis, it is ideal to adjust for additional variables in a larger, multicentre, multiracial study for more precise results. Second, the retrospective analysis of clinical data and the lack of a standardised protocol for the use of concomitant immunosuppressive agents or glucocorticoids may have introduced bias. More rigorous comparisons using randomised controlled trials or prospective studies are needed to confirm the results. Third, because the time the target drug was added was not used as the starting point for analysis, it was impossible to determine whether the target drug directly affected efficacy or whether other factors influenced the results. Therefore, a study with a different design, in which the baseline is set at the starting date of both drugs, is necessary to compare the direct effect of the target drug. Fourth, the two drugs were not evaluated from a pharmacoeconomic perspective, which is a critical consideration in clinical decision-making (12). In this context, it is important to note that BLM is more expensive than HCQ in most countries; in Japan, for example, it costs approximately 6 times as much. Therefore, while BLM may be considered an alternative when HCQ cannot be used, careful consideration of the significant cost differential is necessary. Future studies should incorporate cost analyses to facilitate more informed treatment decisions.
In summary, this study demonstrates that BLM is as effective and safe as HCQ, suggesting BLM could be a valuable treatment option for SLE as an alternative for those who cannot tolerate HCQ because of adverse effects or concerns about cumulative dosage. BLM could also be considered for continuation in accordance with HCQ in a treat-to-target strategy to minimise the risk of disease flares and drug toxicities.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Review Committee for Observational Research, Department of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because as this research had a retrospective design, we disclosed the study information at the relevant facilities. Patient consent was not required as per the committee's guidelines.
Author contributions
KoK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MA: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. S-IO: Resources, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. KaK: Resources, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YK: Resources, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HM: Resources, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. NO: Resources, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YA: Resources, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. KA: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. TH: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HN: Resources, Supervision, Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The authors declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI under Grant number JP23K06868.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Enago for the English language review.
Conflict of interest
M.A., S.O. and H.N. have received speaker's fees from Asahi Kasei Pharma and GlaxoSmithKline.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/flupu.2024.1459949/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Fanouriakis A, Tziolos N, Bertsias G, Boumpas DT. Update οn the diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. (2021) 80:14–25. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218272
2. Dörner T, Furie R. Novel paradigms in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. (2019) 393:2344–58. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30546-X
3. van Vollenhoven RF, Mosca M, Bertsias G, Isenberg D, Kuhn A, Lerstrøm K, et al. Treat-to-target in systemic lupus erythematosus: recommendations from an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis. (2014) 73:958–67. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-205139
4. Hanaoka H, Iida H, Kiyokawa T, Takakuwa Y, Kawahata K. Glucocorticoid, immunosuppressant, hydroxychloroquine monotherapy, or no therapy for maintenance treatment in systemic lupus erythematosus without major organ manifestations. Clin Rheumatol. (2019) 38:2785–91. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04633-y
5. Gordon C, Amissah-Arthur MB, Gayed M, Brown S, Bruce IN, D'Cruz D, et al. The British Society for Rheumatology guideline for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus in adults: executive summary. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2018) 57:14–8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex291
6. Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Alunno A, Aringer M, Bajema I, Boletis JN, et al. 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. (2019) 78:736–45. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215089
7. Fava A, Petri M. Systemic lupus erythematosus: diagnosis and clinical management. J Autoimmun. (2019) 96:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.11.001
8. Ruiz-Irastorza G, Khamashta MA. Hydroxychloroquine: the cornerstone of lupus therapy. Lupus. (2008) 17:271–3. doi: 10.1177/0961203307086643
9. Ruiz-Irastorza G, Bertsias G. Treating systemic lupus erythematosus in the 21st century: new drugs and new perspectives on old drugs. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2020) 59:v69–81. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa403
10. Ruiz-Irastorza G, Martín-Iglesias D, Soto-Peleteiro A. Update on antimalarials and systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2020) 32:572–82. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000743
11. Ruiz-Irastorza G, Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zeron P, Khamashta MA. Clinical efficacy and side effects of antimalarials in systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis. (2010) 69:20–8. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.101766
12. Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Andersen J, Aringer M, Arnaud L, Bae SC, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus: 2023 update. Ann Rheum Dis. (2024) 83:15–29. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-224762
13. Almeida-Brasil CC, Hanly JG, Urowitz M, Clarke AE, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Gordon C, et al. Flares after hydroxychloroquine reduction or discontinuation: results from the systemic lupus international collaborating clinics (SLICC) inception cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. (2022) 81:370–8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221295
14. Fernandez-Ruiz R, Bornkamp N, Kim MY, Askanase A, Zezon A, Tseng CE, et al. Discontinuation of hydroxychloroquine in older patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a multicenter retrospective study. Arthritis Res Ther. (2020) 22:191. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02282-0
15. Elfving P, Puolakka K, Kautiainen H, Virta LJ, Pohjolainen T, Kaipiainen-Seppänen O. Drugs used in incident systemic lupus erythematosus - results from the finnish nationwide register 2000–2007. Lupus. (2016) 25:666–70. doi: 10.1177/0961203316628998
16. Bruce IN, O'Keeffe AG, Farewell V, Hanly JG, Manzi S, Su L, et al. Factors associated with damage accrual in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from the systemic lupus international collaborating clinics (SLICC) inception cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. (2015) 74:1706–13. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-205171
17. Lenfant T, Salah S, Leroux G, Bousquet E, Le Guern V, Chasset F, et al. Risk factors for hydroxychloroquine retinopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus: a case-control study with hydroxychloroquine blood-level analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2020) 59:3807–16. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa157
18. Urowitz MB, Ohsfeldt RL, Wielage RC, Kelton KA, Asukai Y, Ramachandran S. Organ damage in patients treated with belimumab versus standard of care: a propensity score-matched comparative analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2019) 78:372–9. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214043
19. Furie RA, Wallace DJ, Aranow C, Fettiplace J, Wilson B, Mistry P, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of belimumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a continuation of a seventy-six-week phase III parent study in the United States. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2018) 70:868–77. doi: 10.1002/art.40439
20. Wallace DJ, Ginzler EM, Merrill JT, Furie RA, Stohl W, Chatham WW, et al. Safety and efficacy of belimumab plus standard therapy for up to thirteen years in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2019) 71:1125–34. doi: 10.1002/art.40861
21. Tanaka Y, Curtis P, DeRose K, Kurrasch R, Kinoshita K, Tanaka R, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of belimumab in Japanese patients with SLE: a 7-year open-label continuation study. Mod Rheumatol. (2023) 33:122–33. doi: 10.1093/mr/roab125
22. Steiger S, Ehreiser L, Anders J, Anders HJ. Biological drugs for systemic lupus erythematosus or active lupus nephritis and rates of infectious complications. Evidence from large clinical trials. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:999704. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.999704
23. Materne E, Choi H, Zhou B, Costenbader KH, Zhang Y, Jorge A. Comparative risks of infection with belimumab versus oral immunosuppressants in patients with non-renal systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2023) 75:19994–2002. doi: 10.1002/art.42620
24. Hochberg MC. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. (1997) 40:1725. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400928
25. Gladman DD, Ibañez D, Urowitz MB. Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol. (2002) 29:288–91.11838846
26. Franklyn K, Lau CS, Navarra SV, Louthrenoo W, Lateef A, Hamijoyo L, et al. Definition and initial validation of a lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS). Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:1615–21. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207726
27. van Vollenhoven RF, Bertsias G, Doria A, Isenberg D, Morand E, Petri MA, et al. 2021 DORIS definition of remission in SLE: final recommendations from an international task force. Lupus Sci Med. (2021) 8:e000538. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2021-000538
28. Petri M, Buyon J, Kim M. Classification and definition of major flares in SLE clinical trials. Lupus. (1999) 8:685–91. doi: 10.1191/096120399680411281
29. Gladman D, Ginzler E, Goldsmith C, Fortin P, Liang M, Urowitz M, et al. The development and initial validation of the systemic lupus international collaborating clinics/American College of Rheumatology damage index for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. (1996) 39:363–9. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390303
30. Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. (2013) 48:452–8. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2012.244
31. van Vollenhoven R, Askanase AD, Bomback AS, Bruce IN, Carroll A, Dall'Era M, et al. Conceptual framework for defining disease modification in systemic lupus erythematosus: a call for formal criteria. Lupus Sci Med. (2022) 9:e000634. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2021-000634
32. Schwarting A, Dooley MA, Roth DA, Edwards L, Thompson A, Wilson B, et al. Impact of concomitant medication use on belimumab efficacy and safety in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2016) 25:1587–96. doi: 10.1177/0961203316655215
Keywords: systemic lupus erythematosus, hydroxychloroquine, belimumab, flare, maintenance
Citation: Kimura K, Ayano M, Ota S-I, Kushimoto K, Kimoto Y, Mitoma H, Ono N, Arinobu Y, Akashi K, Horiuchi T and Niiro H (2024) Comparative efficacy and safety of belimumab and hydroxychloroquine in the maintenance phase in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a retrospective cohort study. Front. Lupus 2:1459949. doi: 10.3389/flupu.2024.1459949
Received: 5 July 2024; Accepted: 30 August 2024;
Published: 12 September 2024.
Edited by:
Luís Pedro Sousa Inês, Coimbra Hospital and University Center, PortugalReviewed by:
Yusuke Miyazaki, University of Occupational and Environmental Health Japan, JapanChen Au Peh, Royal Adelaide Hospital, Australia
Copyright: © 2024 Kimura, Ayano, Ota, Kushimoto, Kimoto, Mitoma, Ono, Arinobu, Akashi, Horiuchi and Niiro. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Masahiro Ayano, YXlhbm8ubWFzYWhpcm8uODExQG0ua3l1c2h1LXUuYWMuanA=
 Koichi Kimura
Koichi Kimura Masahiro Ayano
Masahiro Ayano Shun-Ichiro Ota2
Shun-Ichiro Ota2 Hiroki Mitoma
Hiroki Mitoma Hiroaki Niiro
Hiroaki Niiro