- 1Rheumatology Unit, Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Pisana and Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy
- 2Department of Clinical and Translational Science, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy
Sjögren's disease (SjD) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are distinct autoimmune disorders and their clinical overlap presents a unique immunological entity with specific challenges. While the clinical manifestations of the SjD-SLE overlap have been extensively characterised, its underlying pathogenetic mechanisms remain less understood. This review underscores the immunological features of the overlap, highlighting the roles of genetic predisposition, interferon pathway activation and B-cell dysregulation. Key genetic factors, particularly those associated with HLA and cytokine signaling, underpin disease susceptibility by promoting aberrant immune responses. The consequent and persistent interferon pathway activation drives chronic inflammation and establishes a feedback loop with autoantibody production. Furthermore, Extrafollicular B-cell responses are central to generating hallmark autoantibodies, such as anti-dsDNA and rheumatoid factor, which are frequent in the overlap. Finally, the continuous activation of interferons and B-cells not only increase disease activity but also contributes to lymphoproliferative complications. Despite progress in elucidating these mechanisms, patients with SjD-SLE overlap remain underrepresented in clinical trials, limiting therapeutic advancements. Emerging strategies, including interferon receptor inhibitors, BAFF-blocking antibodies, and advanced B-cell depletion therapies, may offer promising options to hit the distinct immunological abnormalities of these patients.
Introduction
Sjögren's Disease (SjD) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) are systemic autoimmune disorders classified among connective tissue diseases. SjD and SLE are indeed distinct diseases; however, their possible coexistence and their pathogenetic similarities have always opened research questions about pathophysiological interplay between the two diseases. SjD is typically characterized by chronic inflammation of the salivary and lachrymal glands, leading to symptoms such as dry mouth and dry eyes (sicca symptoms) (1). Beyond glandular involvement, SjD encompasses a broad spectrum of extra-glandular manifestations including B cell lymphoma (2). SLE, on the other hand, is distinguished by its heterogeneous clinical presentation, with common involvement of the skin, joints and kidneys. Disease activity is often associated with hypocomplementemia, a result of the impaired clearance of immune complexes, which contributes to its immune-mediated manifestations (3). Intriguingly, both the diseases share common immunological abnormalities, particularly associated with B-cell hyperactivity, which can drive autoantibody production, tissue inflammation and damage (4, 5).
SjD occurring in patients with SLE has historically been defined as “secondary”. Recent literature has highlighted that the term “secondary Sjögren”s syndrome” is a misnomer, emphasizing the need to recognize the unique clinical manifestations that emerge when Sjögren's disease overlaps with other autoimmune diseases, such as SLE. Although SjD and SLE are clinically distinct entities, their coexistence is increasingly recognized as more than a simple overlap of features. Instead, the SjD-SLE overlap represents a unique clinical and immunological phenotype with specific implications for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic management. Rather than merely exhibiting features of both conditions, these patients represent a distinct clinical entity with specific characteristics that differ from the individual disease when considered separately (Figure 1) (6). Indeed, SjD-SLE are predominantly female and tend to be older than typical SLE patients but younger than those with isolated SjD (7, 8). Clinically, they are characterized by prominent salivary gland involvement, including parotid gland enlargement and sicca symptoms, alongside mucocutaneous manifestations, joint involvement, renal complications, and serositis. Laboratory tests demonstrate elevated IgG levels, frequent hypocomplementemia and a characteristic autoantibody profile, including SSA, SSB, dsDNA, and rheumatoid factor. Moreover, SjD-SLE patients often present with evidence of systemic inflammation and a higher disease activity compared to patients with either condition alone (9–11). Finally, it has been suggested that overlapping patients may have a higher risk of lymphoma when compared to SLE alone (12, 13).
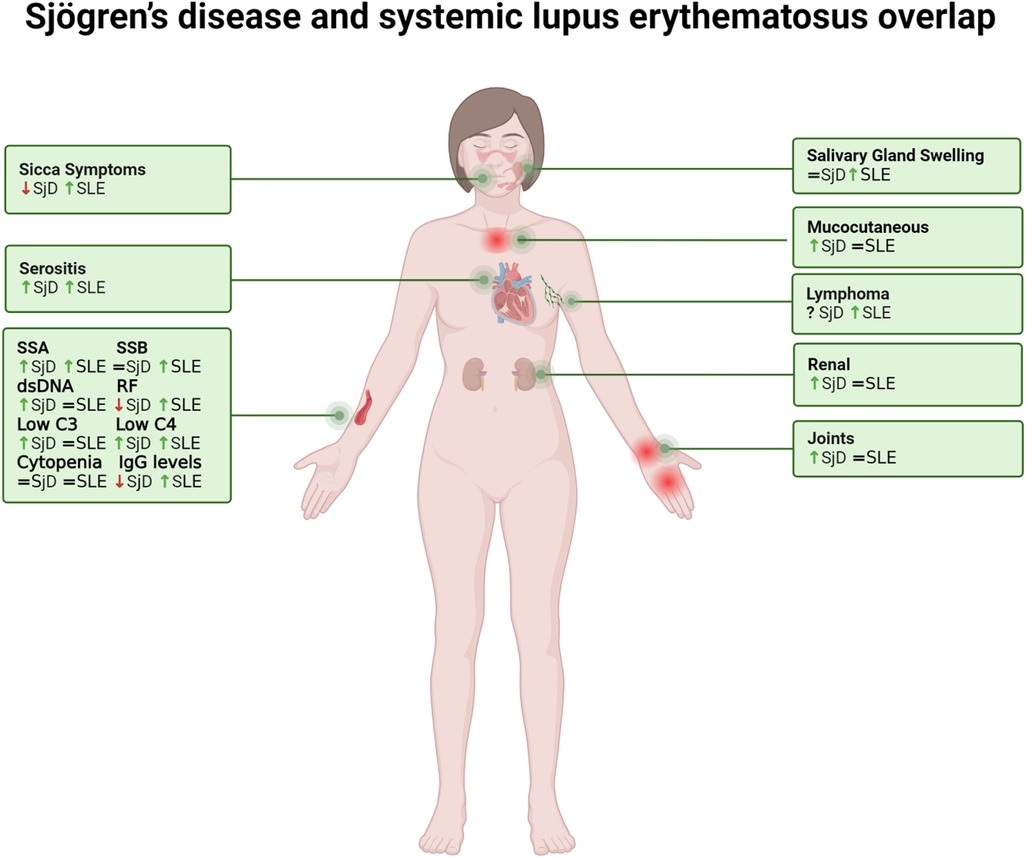
Figure 1. The figure illustrates the features of overlapping Sjögren's disease and systemic lupus erythematosus. Comparative symbols indicate manifestation levels relative to the diseases in isolation: an arrow up (↑) signifies higher prevalence in the overlap condition, an arrow down (↓) denotes lower prevalence, and an equal sign (=) indicates similar prevalence or intensity. SjD, Sjögren's disease; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus.
Despite its importance, the overlap phenotype remains under-recognized in clinical practice and is not adequately captured by current classification criteria. This under-recognition has important consequences. Diagnostic uncertainty can delay appropriate management, and the routine exclusion of overlap patients from clinical trials limits the applicability of emerging therapies to this subgroup. Furthermore, treatment decisions rarely account for the distinct immunopathological features of the overlap. Indeed, while the clinical phenotype of the SjD-SLE overlap is well-defined, research into its pathogenesis remains limited. Interestingly, emerging studies suggest that, despite differences in diagnosis, organ involvement, and disease presentation, autoimmune diseases often share common pathogenic mechanisms. However, these shared mechanisms alone are insufficient for differentiating between diseases, as a single disease can exhibit multiple molecular signatures, while distinct diseases may share similar ones (14). This complexity has led to growing interest in defining patient subgroups based on endotypes, biologically distinct mechanisms underlying similar clinical features. The SjD-SLE phenotype may represent an underlying unique endotype, emphasizing the need for targeted, personalized therapeutic strategies. However, specific studies focusing on the SjD-SLE overlap are rare, hence understanding pathogenetic information may also come from common pathways shared by the two diseases and their specific manifestations.
In this review, we investigate the pathogenetic basis of the SjD-SLE overlap, drawing insights from evidence specific to the overlap condition as well as shared mechanisms observed in SjD and SLE as separate disease. Specifically, we highlight recent advances in understanding the genetic background, interferon expression, and B-cell phenotypes. Finally, we also explore the potential for developing targeted therapies tailored to the unique SjD-SLE endotype, focusing on the specific pathogenetic processes that characterize this overlap.
Genetic
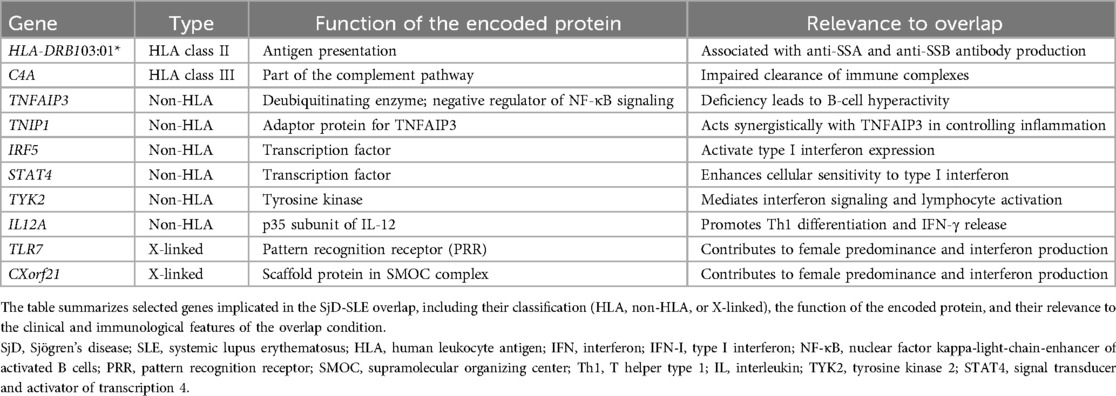
Few studies, often limited by small patient cohorts, have explored the genetic basis of the SjD-SLE overlap (15, 16). Despite limited direct evidence, a shared genetic predisposition is strongly supported by indirect findings. Indeed, in families where one member is affected by SLE, there is a higher incidence of SjD, and vice versa (17, 18). This phenomenon, known as co-aggregation, supports the concept of polygenic inheritance with condition-specific thresholds, rather than the existence rather than two entirely separate genetic backgrounds. Furthermore, there is considerable overlap in the genes identified as risk loci for Sjögren's Disease and for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (19, 20). Research has revealed genetic risk factors within the HLA locus and in non-HLA loci (21, 22). Variants associated with SjD and SLE predominantly influence pathways of the innate and adaptive immune responses, notably involving the antigen presentation, type I interferon pathway and cytokine-mediated signaling pathway (23) (Table 1).
HLA risk loci
Among HLA class II alleles, the most robust genetic association identified so far is HLA-DR3. This association has been confirmed by several studies and still represents the strongest genetic risk factor for these conditions (24, 25). Specifically, HLA-DRB103:01* (DR3) is strongly associated with the presence of anti-SSA and anti-SSB autoantibodies in both SjD and SLE. This variant affects antigen presentation and immune tolerance, fostering autoantibody production. Importantly, HLA-DRB103:01* is also associated with reduced copy number of complement component C4A, which compromises immune complex clearance. These links illustrate how genetic variation contributes to both immune activation and defective clearance mechanisms, central to SjD-SLE pathogenesis (25–28). Furthermore, C4 and its effector, C3, are typically found at lower levels in the plasma of women compared to men possibly contributing to the higher incidence of autoimmunity in females. These sex-linked differences in complement protein expression may thus help explain the marked female predominance observed in both SLE and SjD (29).
Non-HLA risk loci
Beyond the HLA region, several non-HLA genes also play crucial roles as modifiers of disease progression and severity in SLE and SjD. In this review, we will specifically examine the roles of the genes TNFAIP3, TNIP1, IRF-5, STAT4, TYK2, IL-12A, as well as the significance of genes located on the X-Chromosome (Figure 2) (21, 22, 24). TNFAIP3, encoding the A20 protein, and TNIP1, encoding the TNFAIP3-interacting protein 1, are both negative regulators of the NF-κB pathway, a crucial mediator of inflammation. This pathway is activated by several pattern recognition receptors (PRRs, such as Toll-like receptors), a key part of the innate immune response, and by the T-cell receptor (TCR) or B-cell receptor (BCR), vital for the adaptive immune response (30). A20 deficiency leads to profound effects on B cells, which exhibit a hyperactive phenotype characterized by enhanced proliferation and the excessive production of immunoglobulins. This results in the overproduction of autoantibodies, such as double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) antibodies (31, 32). Furthermore, A20 impairment has been linked with primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS) related lymphoma, suggesting that B cells continuously stimulated by autoimmunity may increase the risk of developing lymphoma (33).
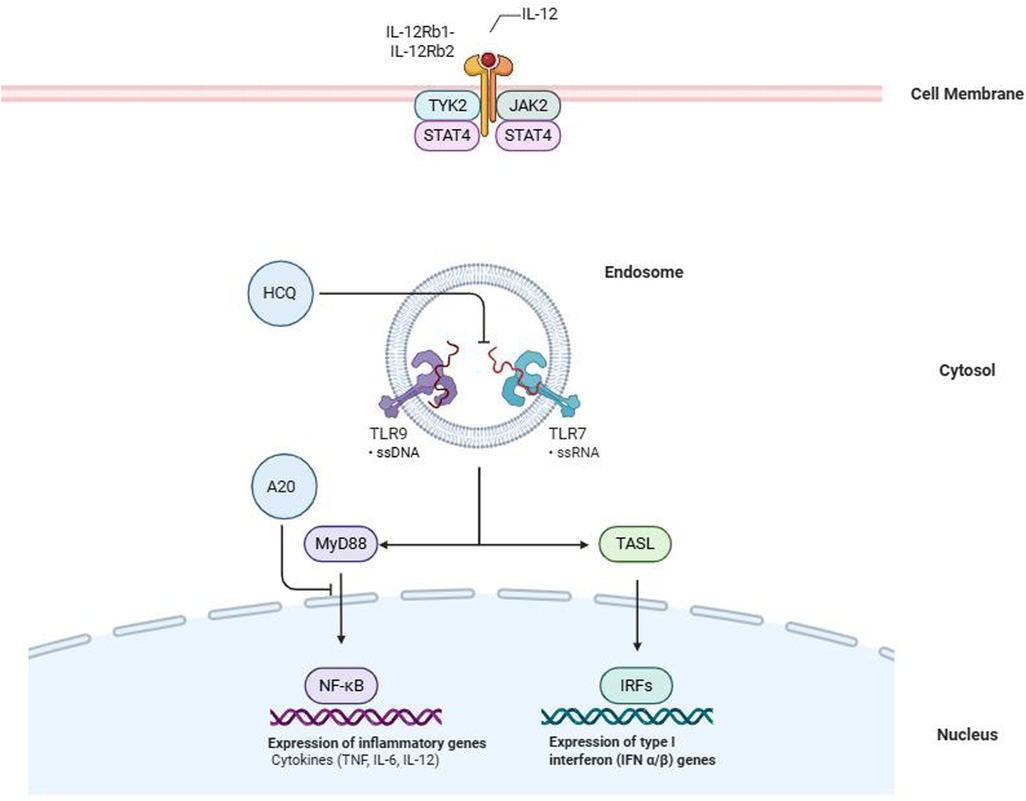
Figure 2. The image illustrates the intracellular signaling pathways involved in innate immune activation through Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and the interleukin-12 (IL-12) receptor. Within the endosome, TLR7 and TLR9 detect single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) and single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), respectively, triggering two downstream cascades: the MyD88-dependent NF-κB pathway, which promotes the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF, IL-6, IL-12), and the TASL-mediated IRF pathway, responsible for the induction of type I interferons (IFN-α/β). The regulatory molecule A20 inhibits NF-κB activation by targeting MyD88, while hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) blocks TLR activation, dampening both inflammatory and interferon responses. At the cell membrane level, IL-12 binds its receptor complex (IL-12Rb1/IL-12Rb2), initiating signaling via the kinases TYK2 and JAK2 and activating STAT4 to mediate transcriptional responses. HCQ, hydroxychloroquine; TLR, Toll-like receptor; ssRNA, single-stranded RNA; ssDNA, single-stranded DNA; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; IFN, interferon; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; TASL, TRAF3-interacting protein 2; IL, interleukin; TYK2, tyrosine kinase 2; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; STAT4, signal transducer and activator of transcription 4.
Additional susceptibility genes include IRF5 and STAT4, transcription factors essential for type I and type II interferon signaling. Overactivity of the IRF5 signaling pathway is a common observation across SLE and SjD and is intricately linked to Toll-like receptor pathways (24, 34, 35). Activation of IRF generally requires phosphorylation of IRF and its subsequent translocation to the nucleus. Once in the nucleus, IRF5 regulates the expression of various cytokines and its activity is associated with increased type I interferon (36). Another gene identified as a candidate for SjD and SLE development is STAT4 (37, 38). The gene encodes a transcription factor that functions downstream of IL-12 and type I interferon receptor, therefore mutations in STAT4 are linked to type I interferons (39, 40). Intriguingly, IRF5 and STAT4 combined risk alleles exhibit additive effects in promoting the SjD-SLE phenotype, especially in anti-dsDNA–positive individuals (36, 41–43).
Another shared gene that encode for a protein of intracellular signaling is TYK2 (21, 44). This gene encodes a tyrosine kinase is crucial for downstream signals of several cytokine receptors, including type I interferon and IL-12, and is therefore central in both interferon signaling and the activation of lymphocytes (45). IL12A, is another risk gene implicated in both SJD and encodes the p35 subunit of interleukin-12 (IL-12). This subunit signals through the Janus kinase (JAK)–STAT pathway, involving, as mentioned before, TYK2 and STAT4 (46, 47). IL-12 serves multiple functions but is particularly crucial for the differentiation of naive T cells into T helper type 1 (TH1) cells and is essential for the production of interferon-γ (IFNγ) by these cells (48).
X-linked genes
The most relevant X-linked genes implicated in the SjD-SLE overlap are TLR7 and CXorf21. Activation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) by nucleic acids initiates two primary transcriptional pathways: the NFκB pathway, which stimulates the production of cytokines like IL-6, TNF, and IL-12, and the interferon regulatory factor (IRF) pathway. IRF activation requires the assembly of a supramolecular organizing center (SMOC). In this context, TASL (encoded by CXorf21) acts as a scaffold protein within the SMOC downstream of TLR7, enabling IRF5 phosphorylation and translocation to the nucleus. This mechanism ultimately enhances type I interferon production. Importantly, increased expression or dysregulation of TASL has been associated with heightened interferon signatures, particularly in anti-SSA/SSB positive patients, suggesting a functional link between genetic risk, interferon amplification, and clinical phenotype (49). Finally, X-linked genes such as TLR7 and CXorf21 may escape X-chromosome inactivation, contributing to the well-known female predominance of both diseases (50–52). Skewed X-inactivation may also arise as a consequence of chronic interferon exposure, particularly in hematopoietic progenitor cells, suggesting a dynamic interplay between genetic susceptibility and disease environment (53).
Epigenetic regulation
In addition to genetic variation, epigenetic regulation appears to be a key modulator of interferon activity. Hypomethylation of interferon-stimulated genes has been observed in both SLE and SjD, especially in patients with SSA/SSB autoantibodies, contributing to sustained interferon gene expression (54). These findings reinforce the view that genetic and epigenetic mechanisms converge to promote a self-perpetuating interferon-driven immune response in the SjD-SLE overlap.
In summary, both HLA and non-HLA loci—along with epigenetic and sex-linked mechanisms—converge to promote a pathogenic immune landscape in SjD-SLE overlap. These factors enhance B-cell activation, disrupt immune complex clearance, and amplify interferon signaling, providing a strong rationale for viewing this overlap as a biologically distinct entity.
Interferons
Interferon signaling is a well-known hallmark of both SLE and SjD and recent data indicate that patients with SjD-SLE overlap exhibit a stronger type I interferons and type II Interferon signature than those with either disease alone (11, 55).
Type I interferon (IFN-I)
An elevated type I Interferon (IFN-I) signature in SLE has been proposed as a predisposing factor for the development of overlapping SjD (56). While IFN-α is the dominant type I interferon in most autoimmune diseases differences in subtype-specific effects (e.g., IFN-α vs. IFN-β) have begun to emerge. For instance, IFN-β may exert more tolerogenic effects in certain contexts, while IFN-α is more potent in driving autoreactive B-cell responses (57). The specific IFN-I subtype distribution in SjD-SLE overlap remains to be fully characterized, but a higher total burden of IFN-I signaling may underlie the increased immunopathology observed in these patients.
As previously discussed, genetic risk variants contribute to this heightened interferon activity. There is a strong interplay between genetic risk factors, interferon signatures and specific autoantibodies, both in SjD and SLE. These genetic factors are closely linked to the production of autoantibodies such as anti-SSA/Ro, SSB/La, and dsDNA. However, in patients lacking an IFN signature, associations between HLA-DRB1*0301 and SSA disappear, further emphasizing the centrality of interferons in shaping the autoimmune phenotype. A similar observation can be made for IRF5, IFN-I and dsDNA, associations in SLE (14, 24, 58, 59). Indeed, type I interferons influence B-cell function through various mechanisms, driving autoreactive B-cell activation and the subsequent production of autoantibodies (60, 61). In turn, autoantibodies can induce type I interferon through several mechanisms. One key process involves Fcγ receptor (FcγR)-mediated internalization of immune complexes, where IgG antibodies potentially leak from phagolysosomes into the cytosol (62). These immune complexes deliver dsDNA and single-stranded RNA into endosomal compartments, activating TLR7 and TLR9, respectively (63–65). Additionally, autoantibodies can intensify innate immune responses, inhibiting TRIM21 (Ro52) and possibly Ro60 which are normally responsible for damping interferon responses. TRIM21 acts as a negative regulator of TLR signaling by ubiquitinating (inactivating) interferon-regulating factors (IRFs), whereas when Ro60 is deleted there is an increase in interferon-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine production (59, 66–69). Ultimately, SjD patients anti-Ro/SSA and/or anti-La/SSB positive pSS patients exhibited hypomethylation in type I interferon induced genes (54, 70). Collectively, these findings suggest a feed-forward loop where IFN-I induces B cell activation and autoantibody production, leading to immune complex formation and further escalation of IFN-I production (71). Clinically, patients with high interferon present with high levels of dsDNA and SSA autoantibodies, increased circulating free light chains, decreased C3 levels, reduced lymphocyte counts ultimately corresponding to increased disease activity (72–74).
Type II interferon (IFN-II)
Similar to IFN-I, IFN-γ (type II Interferon, IFN-II) also plays a significant and perhaps earlier role. Interestingly, temporal analyses reveal elevated IFN-γ levels in patients with preclinical SLE before the appearance of most autoantibodies and before increases in IFN-α activity (75). This suggests that IFN-γ may be an early factor in breaking immune tolerance, leading to autoreactive B-cell, autoantibody production and IFN-α activity. This cascade establishes a feedback loop between autoantibodies and IFN-α, ultimately contributing to the full development of an autoimmune disease. Indeed, there is significant crosstalk between type I and type II interferons and many signaling pathways and inducible genes are shared between them. Additionally, each type induces the other's production, leading to a mutual stimulation and a combined interferon signature (76). Despite this overlap, IFN-γ remains functionally distinct. IFN-γ is associated with specific genetic risks, notably with IL-12A, which drives its production, and with genes like STAT4, encoding a protein involved in shared interferon signaling pathways (46, 47, 77). Moreover, IFN-II significantly enhances MHC complex expression, as demonstrated on salivary gland epithelial cells (SGECs) (66, 78). Furthermore, IFN-γ has a profound impact on B cells by stimulating T cells and antigen-presenting cells (APCs) to produce B lymphocyte stimulating factor (BLyS), crucial for B cell activation (79). Within B cells, instead, IFN-γ and its downstream signaling molecules, STAT1 and T-bet, drive inflammatory cytokine production (80). IFN-γ-STAT1 signaling pathways activate critical processes in B cells, fostering their differentiation into autoreactive, antibody-producing cells, with type I IFN signalling providing only moderate support to these processes (80). Instead, T-bet is essential for antibody class switching, with IFN-γ promoting a shift toward more pathogenic IgG subclasses, such as IgG2a and IgG3 in mice (81). Elevated IFN-γ correlates with high anti-dsDNA and RF levels, as well as with higher disease activity scores in both SjD and SLE, as reflected in SLEDAI and ESSDAI scores (82, 83).
In summary, in the SjD-SLE overlap, simultaneous upregulation of both IFN-I and IFN-II pathways likely accounts for the co-occurrence of high-titer autoantibodies, severe systemic inflammation, and multi-organ involvement. Thus, while interferons contribute to pathogenesis in both diseases, their combined and sustained activity may define the unique clinical and immunological features of the overlap phenotype.
B-cell
B-cell activation is a prominent feature of the SjD-SLE overlap, and despite very few differences in immunological architecture, a recent study has demonstrated that patients with SjD-SLE overlap, SjD alone, and SLE alone share a similar immunological profile (84). However, unique features of B-cell subsets and activation pathways suggest a distinct pathogenic mechanism in the overlap condition. Historically, germinal centers (GCs) were considered the primary sites for generating pathogenetic somatically-mutated and high-affinity autoantibodies in autoimmune patients (85). However, more recent data challenge this view, pointing instead to extrafollicular (EF) B-cell responses as central drivers of autoimmunity (85–87). EF responses refer to antibody-producing pathways that occur outside GCs, typically in regions such as the red pulp of the spleen, the medullary cords of lymph nodes, and importantly, in tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS), ectopic lymphoid aggregates found in inflamed non-lymphoid tissues, such as the salivary glands of SjD patients (88). Notably, in this scenario, two distinct B-cell subsets have been identified: double-negative 2 (DN2) B cells in SLE and FcRL4+ intraepithelial B cells in SjD.
Double-negative 2 (DN2) B cells
DN2 B cells are characterized by a hyperactivated, proinflammatory phenotype and are expanded in active SLE. These cells are distinguished by the absence of both IgD and CD27 markers (IgD-, CD27-), differentiating them from conventional memory and naive B cell populations. Key markers for DN2 cells include T-bet, CD11c, FcRL5, along with the absence of CXCR5 (89). DN2 cells are characterized by the expression of the transcription factor T-bet, as well as high levels of CD11c (CD11chi), which guide their migration to inflammatory sites (90). Another marker of DN2 B cells is FcRL5, a member of the Fc receptor-like (FcRL) family, which shares structural similarities with the classical Fc gamma receptor I (FcγRI). FcRL5 binds IgG of all subclasses, with strongest binding by IgG1 and IgG2, and its interaction with IgG-containing immune complexes can mediate either stimulatory or inhibitory signaling (90). CXCR5, a chemokine receptor commonly expressed on B and T cell subsets, is notably absent in DN2 cells. The CXCR5-CXCL13 axis plays a pivotal role in recruiting immune cells to germinal centers and ectopic lymphoid structures further confirming the extrafollicular origin of DN2 cells (91, 92). Furthermore, unlike germinal center (GC) B cells, which depend on robust B cell receptor (BCR) signaling for survival and selection, DN2 cells are unresponsive to BCR-mediated survival signals and are instead highly responsive to TLR7 stimulation, reflecting a distinct mechanism of activation (86, 93–95). DN2 cells differentiate into autoantibody-secreting plasma cells under the influence of IFN-γ, IL-21, and IL-2, cytokines typically derived from Th1-skewed T cells (96). In lupus-prone mouse models, EF responses producing anti-dsDNA and RF autoantibodies rely heavily on TLR7/TLR9-mediated activation—confirming the pathological potential of DN2-like cells (63, 97, 98). These cells have been correlated with decreased complement levels and increased disease activity, and may contribute to tissue damage in organs such as kidneys and skin (90).
FcRL4+ B cells
On the other hand, FcRL4+ B cells, found in salivary gland epithelium in SjD, exhibit a phenotype similar to DN2 cells (99). These FcRL4+ B cells exhibit an activated phenotype, characterized by elevated expression of T-bet, CD11c and TACI, along with reduced expression of CXCR5 and CD40. FcRL4 is an immunoregulatory receptor that belongs to the Fc receptor-like (FcRL) family. Evidence suggests that when soluble IgA binds to FcRL4, it triggers a functional switch in B cells from BCR-mediated activation to TLR-mediated activation, similar to what was observed for DN2 (100, 101). Unlike DN2 B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus, glandular FcRL4+ B cells in SjD do not express plasma cell markers, suggesting a distinct, possibly more regulatory or tissue-resident role. Their localization is guided by CXCR3, which responds to CXCL10, an IFN-induced chemokine produced by the inflamed ductal epithelium. Persistent stimulation by IFN-γ, IL-27, BAFF, and APRIL, as well as CD40-independent signals, supports their maintenance in situ. Notably, FcRL4+ cells are strongly associated with RF positivity and are believed to serve as a precursor pool for MALT lymphoma, given their activated and persistent phenotype (66, 102).
B cells in SjD-SLE overlap
Importantly, even though direct evidence is lacking, it is plausible that in the SjD-SLE overlap, elements of both DN2 and FcRL4+ B-cell pathways coexist. The frequent presence of both anti-dsDNA and RF autoantibodies in these patients suggests a broad extrafollicular response that may encompass both systemic and tissue-resident features. Moreover, given the high prevalence of TLS in the salivary glands of SjD patients, it is reasonable to speculate that such structures could support the persistence and expansion of these B-cell subsets in the overlap condition.
In summary, EF B-cell responses—occurring in both secondary lymphoid tissues and TLS—are likely to be key orchestrators of the SjD-SLE overlap phenotype. DN2 and FcRL4+ cells may represent two ends of an EF continuum, contributing to distinct but converging autoantibody profiles, tissue localization, and clinical manifestations. Their chronic activation and persistence may also underlie the increased lymphoproliferative risk observed in these patients.
Treatment
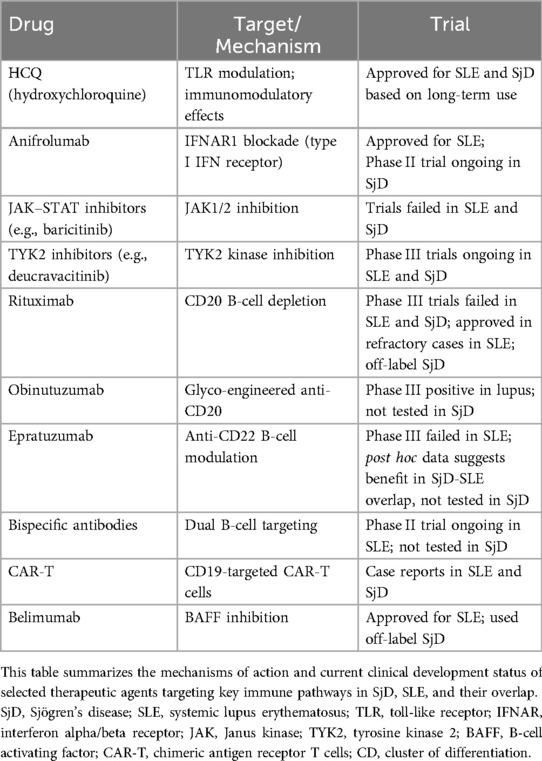
Therapeutic options for SLE and SjD remain limited despite extensive research in recent years (103–105) (Table 2). A significant barrier is patient heterogeneity, which has led to increasingly strict inclusion criteria in clinical trials. As a result, patients with overlapping SjD-SLE features are often excluded from studies of either disease, leaving them without evidence-based treatment options. To address this challenge, future trials should adopt more inclusive designs based on molecular signatures (e.g., interferon-high or BAFF-dependent endotypes) rather than rigid diagnostic categories. This approach would facilitate the enrolment of overlap patients and enhance the generalizability of trial results. Notably, only one trial—investigating epratuzumab, an anti-CD22 antibody—has demonstrated efficacy in this population, albeit based on post hoc analysis (106). However, given the distinct clinical profile of SjD-SLE overlap, including prominent inflammation, high interferon activity, and intense B-cell dysregulation, specific therapeutic approaches should be considered (Figure 3).
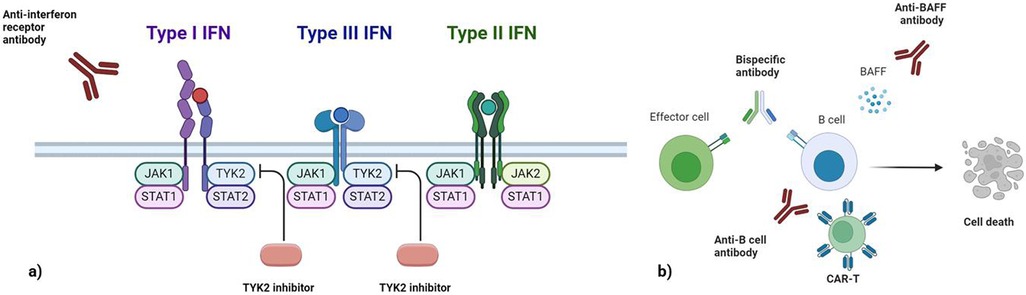
Figure 3. This image illustrates therapeutic approaches targeting interferon signaling and B cells. (a) Interferon-targeting strategies include anti-interferon receptor antibodies that block signaling for type I interferon. The associated signaling pathways involve TYK2, JAK1, and STAT transcription factors for type I and III IFNs, and JAK1/JAK2 for type II IFNs. TYK2 inhibitors specifically disrupt pathways shared by type I and III interferons, offering a selective approach to modulate their activity. (b) B-cell depletion strategies employ various mechanisms, such as anti-B-cell antibodies (e.g., anti-CD20), bispecific antibodies that engage effector cells to eliminate B cells, and CAR-T cells engineered to target B-cell-specific markers. Additionally, anti-BAFF antibodies inhibit BAFF-dependent B-cell survival, leading to cell death and suppression of pathogenic B-cell activity. IFN, Interferon; TYK2, Tyrosine Kinase 2; JAK, Janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; BAFF, B-cell activating factor; CAR-T, chimeric antigen receptor T-cell.
Several therapeutic strategies have been explored to target the activation of interferon pathways, including TLR inhibitors, interferon receptor blockers, and JAK-STAT signaling inhibitors (Figure 3a). Hydroxychloroquine, a TLR7 and TLR9 inhibitor, reduces type I interferon (IFN-I) levels and is widely used in clinical practice for both SjD and SLE (Figure 2). However, in these diseases results from randomized clinical trials of hydroxychloroquine remains contradictory (107, 108). Anifrolumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting type I interferon receptors, has been approved for SLE and is currently being evaluated in clinical trials for SjD (109, 110). Interestingly, Anifrolumab has shown greater efficacy in patients with a high interferon signature, making it a promising option for patients with this feature, including those with SjD-SLE overlap (111). JAK-STAT inhibitors, which interfere with interferon signaling, have also been investigated. However, multiple trials of JAK inhibitors in both SLE and SjD have not yet demonstrated consistent efficacy (112, 113). It is important to note that different interferons rely on distinct JAK signaling pathways. For instance, while type I and III interferons signal through TYK2 and JAK1, IFN-γ relies exclusively on JAK1 and JAK2 (114). Consequently, not all JAK inhibitors may have equal effectiveness across all interferon pathways. A novel drug, Deucravacitinib, a TYK2 inhibitor, is currently undergoing trials in both SLE and SjD (115, 116) (Figure 3a). TYK2 is a genetic risk factor for the SjD-SLE overlap and plays a pivotal role in IL-12 signaling, which impacts IFN-γ expression as well as IFN-I and IFN-III pathways.
B-cell–targeted therapies include direct depletion (e.g., anti-CD20/anti-CD19 antibodies, CAR-T cells, bispecific antibodies) and indirect modulation via BAFF inhibition (Figure 3b). Rituximab reduces dsDNA and RF levels and has been shown to deplete DN2 and FcRL4+ B cells in SLE and SjD, respectively (117–120). Despite its success in rheumatoid arthritis, randomised clinical trials for rituximab in SjD (TEARS and TRACTISS) and SLE (EXPLORER and LUNAR) failed to demonstrate significant efficacy (121–123). Indeed, a major challenge with B cell-depleting therapies lies in their inability to uniformly target all B cell subsets, allowing residual B cells to perpetuate autoimmunity. Two key reasons may explain this limitation. First, the kinetics of B cell depletion in tissues is slower than in peripheral blood, leaving tissue-resident subsets in the spleen, lymph nodes, and tertiary lymphoid tissues incompletely depleted (124). Second, certain pathogenic B cells or plasma cells may lack CD20 expression or express it at low levels, reducing their susceptibility to CD20-targeted therapies (63, 125). Moreover, as B cells differentiate into plasma cells, they sequentially downregulate CD20 and CD19, rendering long-lived plasma cells largely refractory to anti-CD20 treatment (124). Indeed, autoantibody production reflects multiple B-cell sources: long-lived plasma cells from germinal centers (resistant to CD20 therapies) vs. short-lived plasmablasts from extrafollicular pathways (sensitive to therapy) (63, 125). One promising approach is second-generation anti-CD20 agents, like obinutuzumab have shown promise in lupus nephritis and may provide more effective tissue depletion. Moreover, emerging B-cell-depleting therapies, such as CAR-T cells targeting CD19 and bispecific T-cell engagers (TCEs), are under active investigation and could offer deeper and more sustained B-cell depletion. These methods may overcome limitations seen with rituximab, particularly in depleting autoantibody-producing extrafollicular B cells and may offer additional therapeutic options for patients with SjD-SLE overlap (125–127).
Another indirect depletion of B cells involves BAFF-blocking antibodies. Transitional and naive B cells rely heavily on BAFF (B cell–activating factor of the tumor necrosis factor family) for survival and are effectively targeted by BAFF-blocking therapies (66, 124, 126). Targeting BAFF with belimumab may be particularly useful in SjD-SLE overlap, especially given the BAFF-dependence of DN2 and FcRL4+ cells (66, 126). Accordingly, belimumab, a BAFF inhibitor, has demonstrated efficacy in SLE and has shown potential when used in combination with rituximab for the treatment of SjD (127–130). Given the complementary mechanisms of action, combining B-cell depletion with BAFF inhibition—such as rituximab followed by belimumab—has shown synergistic effects in depleting both mature B cells and their precursors (131). This approach may be particularly relevant in SjD-SLE overlap, where extrafollicular and tissue-resident B cells are simultaneously active.
Despite these advances, SjD-SLE overlap patients remain systematically excluded from most trials. To address this, future clinical studies should incorporate dedicated overlap subgroups, stratify patients by immunological endotype (e.g., IFN-high, BAFF-high), and explore combination regimens tailored to dual interferon/B-cell axis dysregulation. In conclusion, targeting interferons and B cells remains the cornerstone of therapy in SjD-SLE overlap. However, the heterogeneity and dual-pathway activation in these patients necessitate personalised strategies. Emerging therapies, including interferon receptor antagonists, next-generation B-cell depletors, CAR-T cells, and BAFF inhibitors, offer new hope for this challenging subgroup.
Conclusions
The SjD-SLE overlap represents a distinct clinical and immunological phenotype that cannot be fully explained by either disease alone. Genetic predisposition—particularly involving somatic HLA alleles and non-HLA variants affecting interferon and cytokine signalling—creates a permissive background that shapes the immunological landscape. This is further amplified by epigenetic dysregulation and X-linked gene activity, which together enhance interferon responsiveness and female predominance.
A common pathogenic axis emerges in this overlap condition, where aberrant extrafollicular B-cell activation intersects with heightened interferon signalling. These mechanisms reinforce each other, contributing to autoantibody production (e.g., anti-dsDNA, RF, SSA/SSB) and sustained inflammation in both systemic and tissue-specific compartments. Integrating these pathways provides a more cohesive model of disease pathogenesis and opens the door for a precision medicine approach.
Despite these insights, overlap patients remain systematically underrepresented in clinical trials, limiting the evidence base for effective treatments. Addressing this gap requires both the inclusion of immunologically stratified overlap cohorts in future studies and the development of diagnostic criteria that reflect their unique biology.
Promising therapies—such as interferon receptor inhibitors, BAFF-blocking agents, and next-generation B cell–targeted strategies—may yield synergistic effects when used in combination. Ultimately, the integration of genetic, molecular, and cellular findings into clinical practice could enable earlier diagnosis, better risk stratification, and more personalised treatment of patients with SjD-SLE overlap.
Author contributions
GF: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GL: Writing – review & editing. CT: Writing – review & editing. MM: Writing – review & editing. CB: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Baldini C, Chatzis LG, Fulvio G, La Rocca G, Pontarini E, Bombardieri M. Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s disease: one year in review 2024. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2024) 42(12):2336–43. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/i8iszc
2. Goules AV, Chatzis L, Pezoulas VC, Patsouras M, Mavragani C, Quartuccio L, et al. Identification and evolution of predictors of Sjögren’s disease-associated mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma development over time: a case-control study. Lancet Rheumatol. (2024) 6(10):e693–702. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00183-8
3. Schilirò D, Silvagni E, Ciribè B, Fattorini F, Maccarrone V, Elefante E, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus: one year in review 2024. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2024) 42(3):583–92. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/mnvmvo
4. Baldini C, Ferro F, Elefante E, Bombardieri S. Biomarkers for Sjögren’s syndrome. Biomark Med. (2018) 12(3):275–86. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2017-0297
5. Yap DYH, Chan TM. B cell abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis-role in pathogenesis and effect of immunosuppressive treatments. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(24):6231. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246231
6. Kollert F, Fisher BA. Equal rights in autoimmunity: is Sjögren’s syndrome ever ’secondary’? Rheumatology. (2020) 59(6):1218–25. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa009
7. Fulvio G, La Rocca G, Chatzis LG, Ferro F, Navarro Garcia IC, Cafaro G, et al. Impact of gender and age at onset on Sjögren’s syndrome presentation and outcome: state of the art. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2023) 41(12):2547–54. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/lygrzv
8. Ambrose N, Morgan TA, Galloway J, Ionnoau Y, Beresford MW, Isenberg DA. Differences in disease phenotype and severity in SLE across age groups. Lupus. (2016) 25(14):1542–50. doi: 10.1177/0961203316644333
9. De Marchi G, Nano A, Fulvio G, Manfrè V, Navarro Garcia IC, Zabotti A, et al. Sjögren’s disease and systemic lupus erythematosus overlap syndrome as distinct entity at crossroads of two autoimmune disorders: clinical characterisation from two Italian reference centres for both the diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2024) 42(12):2453–8. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/7v6qht
10. Baldini C, Arnaud L, Avčin T, Beretta L, Bellocchi C, Bouillot C, et al. Sjögren’s syndrome and other rare and complex connective tissue diseases: an intriguing liaison. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2022) 40(5):103–12. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/3y0hqs
11. Ruacho G, Kvarnström M, Zickert A, Oke V, Rönnelid J, Eketjäll S, et al. Sjögren syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus: a subset characterized by a systemic inflammatory state. J Rheumatol. (2020) 47(6):865–75. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.190250
12. Löfström B, Backlin C, Sundström C, Ekbom A, Lundberg IE. A closer look at non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma cases in a national Swedish systemic lupus erythematosus cohort: a nested case-control study. Ann Rheum Dis. (2007) 66(12):1627–32. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.067108
13. Bernatsky S, Ramsey-Goldman R, Joseph L, Boivin J-F, Costenbader KH, Urowitz MB, et al. Lymphoma risk in systemic lupus: effects of disease activity versus treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. (2014) 73(1):138–42. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202099
14. Barturen G, Babaei S, Català-Moll F, Martínez-Bueno M, Makowska Z, Martorell-Marugán J, et al. Integrative analysis reveals a molecular stratification of systemic autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheum. (2021) 73(6):1073–85. doi: 10.1002/art.41610
15. Szanto A, Szodoray P, Kiss E, Kapitany A, Szegedi G, Zeher M. Clinical, serologic, and genetic profiles of patients with associated Sjögren’s syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Immunol. (2006) 67(11):924–30. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2006.06.006
16. Provost TT, Talal N, Bias W, Harley JB, Reichlin M, Alexander EL. Ro(SS-A) positive Sjogren’s/lupus erythematosus (SC/LE) overlap patients are associated with the HLA-DR3 and/or DRw6 phenotypes. J Invest Dermatol. (1988) 91(4):369–71. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12476204
17. Kuo C, Grainge MJ, Valdes AM, See L, Luo S, Yu K, et al. Familial risk of Sjögren’s syndrome and co-aggregation of autoimmune diseases in affected families: a nationwide population study. Arthritis Rheum. (2015) 67(7):1904–12. doi: 10.1002/art.39127
18. Aggarwal R, Anaya JM, Koelsch KA, Kurien BT, Scofield RH. Association between secondary and primary Sjögren’s syndrome in a large collection of lupus families. Autoimmune Dis. (2015) 2015:1–4. doi: 10.1155/2015/298506
19. Toro-Domínguez D, Carmona-Sáez P, Alarcón-Riquelme ME. Shared signatures between rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren’s syndrome uncovered through gene expression meta-analysis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2014) 16(6):489. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0489-x
20. Chau K, Raksadawan Y, Allison K, Ice JA, Scofield RH, Chepelev I, et al. Pervasive sharing of causal genetic risk factors contributes to clinical and molecular overlap between Sjögren’s disease and systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(19):14449. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914449
21. Thorlacius GE, Björk A, Wahren-Herlenius M. Genetics and epigenetics of primary Sjögren syndrome: implications for future therapies. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2023) 19(5):288–306. doi: 10.1038/s41584-023-00932-6
22. Ghodke-Puranik Y, Olferiev M, Crow MK. Systemic lupus erythematosus genetics: insights into pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2024) 20(10):635–48. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01152-2
23. Cui Y, Zhang H, Wang Z, Gong B, Al-Ward H, Deng Y, et al. Exploring the shared molecular mechanisms between systemic lupus erythematosus and primary Sjögren’s syndrome based on integrated bioinformatics and single-cell RNA-seq analysis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1212330. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1212330
24. Ortíz-Fernández L, Martín J, Alarcón-Riquelme ME. A summary on the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic sclerosis, and Sjögren’s syndrome. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol. (2022) 64(3):392–411. doi: 10.1007/s12016-022-08951-z
25. Khatri B, Tessneer KL, Rasmussen A, Aghakhanian F, Reksten TR, Adler A, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies Sjögren’s risk loci with functional implications in immune and glandular cells. Nat Commun. (2022) 13(1):4287. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30773-y
26. Morris DL, Fernando MMA, Taylor KE, Chung SA, Nititham J, Alarcón-Riquelme ME, et al. MHC Associations with clinical and autoantibody manifestations in European SLE. Genes Immun. (2014) 15(4):210–7. doi: 10.1038/gene.2014.6
27. Zhou D, King EH, Rothwell S, Krystufkova O, Notarnicola A, Coss S, et al. Low copy numbers of complement C4 and C4A deficiency are risk factors for myositis, its subgroups and autoantibodies. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82(2):235–45. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-222935
28. Lundtoft C, Pucholt P, Martin M, Bianchi M, Lundström E, Eloranta M, et al. Complement C4 copy number variation is linked to SSA/Ro and SSB/La autoantibodies in systemic inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheum. (2022) 74(8):1440–50. doi: 10.1002/art.42122
29. Kamitaki N, Sekar A, Handsaker RE, de Rivera H, Tooley K, Morris DL, et al. Complement genes contribute sex-biased vulnerability in diverse disorders. Nature. (2020) 582(7813):577–81. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2277-x
30. Das T, Chen Z, Hendriks RW, Kool M. A20/tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 3 in immune cells controls development of autoinflammation and autoimmunity: lessons from mouse models. Front Immunol. (2018) 9, 104. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00104
31. Hövelmeyer N, Reissig S, Xuan NT, Adams-Quack P, Lukas D, Nikolaev A, et al. A20 deficiency in B cells enhances B-cell proliferation and results in the development of autoantibodies. Eur J Immunol. (2011) 41(3):595–601. doi: 10.1002/eji.201041313
32. Tavares RM, Turer EE, Liu CL, Advincula R, Scapini P, Rhee L, et al. The ubiquitin modifying enzyme A20 restricts B cell survival and prevents autoimmunity. Immunity. (2010) 33(2):181–91. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.07.017
33. Nocturne G, Tarn J, Boudaoud S, Locke J, Miceli-Richard C, Hachulla E, et al. Germline variation of TNFAIP3 in primary Sjögren’s syndrome-associated lymphoma. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75(4):780–3. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207731
34. Lazzari E, Jefferies CA. IRF5-mediated Signaling and implications for SLE. Clin Immunol. (2014) 153(2):343–52. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2014.06.001
35. Miceli-Richard C, Comets E, Loiseau P, Puechal X, Hachulla E, Mariette X. Association of an IRF5 gene functional polymorphism with Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. (2007) 56(12):3989–94. doi: 10.1002/art.23142
36. Niewold TB, Kelly JA, Kariuki SN, Franek BS, Kumar AA, Kaufman KM, et al. IRF5 Haplotypes demonstrate diverse serological associations which predict serum interferon alpha activity and explain the majority of the genetic association with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. (2012) 71(3):463–8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200463
37. Taylor KE, Wong Q, Levine DM, McHugh C, Laurie C, Doheny K, et al. Genome-wide association analysis reveals genetic heterogeneity of Sjögren’s yndrome according to ancestry. Arthritis Rheum. (2017) 69(6):1294–305. doi: 10.1002/art.40040
38. Patel ZH, Lu X, Miller D, Forney CR, Lee J, Lynch A, et al. A plausibly causal functional lupus-associated risk variant in the STAT1–STAT4 locus. Hum Mol Genet. (2018) 27(13):2392. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy140
39. Hagberg N, Joelsson M, Leonard D, Reid S, Eloranta M-L, Mo J, et al. The STAT4 SLE risk allele rs7574865[T] is associated with increased IL-12-induced IFN-γ production in T cells from patients with SLE. Ann Rheum Dis. (2018) 77(7):1070–7. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212794
40. Kariuki SN, Kirou KA, MacDermott EJ, Barillas-Arias L, Crow MK, Niewold TB. Cutting edge: autoimmune disease risk variant of STAT4 confers increased sensitivity to IFN-α in lupus patients in vivo. J Immunol. (2009) 182(1):34–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.1.34
41. Nordmark G, Kristjansdottir G, Theander E, Eriksson P, Brun JG, Wang C, et al. Additive effects of the major risk alleles of IRF5 and STAT4 in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Genes Immun. (2009) 10(1):68–76. doi: 10.1038/gene.2008.94
42. Bianchi M, Kozyrev SV, Notarnicola A, Sandling JK, Pettersson M, Leonard D, et al. Unraveling the genetics of shared clinical and serological manifestations in systemic inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheum. (2024) 77:212–225. doi: 10.1002/art.42988
43. Chung SA, Taylor KE, Graham RR, Nititham J, Lee AT, Ortmann WA, et al. Differential genetic associations for systemic lupus erythematosus based on anti–dsDNA autoantibody production. PLoS Genet. (2011) 7(3):e1001323. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001323
44. Cunninghame Graham DS, Morris DL, Bhangale TR, Criswell LA, Syvänen A-C, Rönnblom L, et al. Association of NCF2, IKZF1, IRF8, IFIH1, and TYK2 with systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS Genet (2011) 7(10):e1002341. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002341
45. Liang Y, Zhu Y, Xia Y, Peng H, Yang X-K, Liu Y-Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of tyrosine kinase 2 in autoimmunity. Expert Opin Ther Targets. (2014) 18(5):571–80. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.892925
46. Fogel O, Rivière E, Seror R, Nocturne G, Boudaoud S, Ly B, et al. Role of the IL-12/IL-35 balance in patients with Sjögren syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2018) 142(1):258–68.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.07.041
47. Gao Y, Zhou Y, Lin Z, Chen F, Wu H, Peng C, et al. Prioritizing drug targets in systemic lupus erythematosus from a genetic perspective: a druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization study. Clin Rheumatol. (2024) 43(9):2843–56. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07059-3
48. Ueno H. The IL-12-STAT4 axis in the pathogenesis of human systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur J Immunol. (2020) 50(1):10–6. doi: 10.1002/eji.201948134
49. Elkon KB, Briggs TA. The (Orf)ull truth about IRF5 and type I interferons in SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2020) 16(10):543–4. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0472-7
50. Harris VM, Harley ITW, Kurien BT, Koelsch KA, Scofield RH. Lysosomal pH is regulated in a sex dependent manner in immune cells expressing CXorf21. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:578. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00578
51. Souyris M, Cenac C, Azar P, Daviaud D, Canivet A, Grunenwald S, et al. TLR7 escapes X chromosome inactivation in immune cells. Sci Immunol. (2018) 3(19):eaap8855. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aap8855
52. Huret C, Ferrayé L, David A, Mohamed M, Valentin N, Charlotte F, et al. Altered X-chromosome inactivation predisposes to autoimmunity. Sci Adv. (2024) 10(18):eadn6537. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adn6537
53. Roberts AL, Morea A, Amar A, West M, Karrar S, Lehane R, et al. Haematopoietic stem cell-derived immune cells have reduced X chromosome inactivation skewing in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. (2024) 83(10):1315–21. doi: 10.1136/ard-2024-225585
54. Imgenberg-Kreuz J, Almlöf JC, Leonard D, Sjöwall C, Syvänen A-C, Rönnblom L, et al. Shared and unique patterns of DNA methylation in systemic lupus erythematosus and primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1686. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01686
55. Idborg H, Zandian A, Sandberg AS, Nilsson B, Elvin K, Truedsson L, et al. Two subgroups in systemic lupus erythematosus with features of antiphospholipid or Sjögren’s syndrome differ in molecular signatures and treatment perspectives. Arthritis Res Ther. (2019) 21(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1836-8
56. Mi X, Lai K, Yan L, Wu H, Wei S. A comprehensive analysis of type 1 interferon gene signatures in systematic lupus erythematosus and prediction of the crucial susceptible factor for Sjögren syndrome. Clin Exp Med. (2023) 23(8):4731–43. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01154-6
57. Psarras A, Wittmann M, Vital EM. Emerging concepts of type I interferons in SLE pathogenesis and therapy. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2022) 18(10):575-90 doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00826-z.36097207
58. Teruel M, Barturen G, Martínez-Bueno M, Castellini-Pérez O, Barroso-Gil M, Povedano E, et al. Integrative epigenomics in Sjögreńs syndrome reveals novel pathways and a strong interaction between the HLA, autoantibodies and the interferon signature. Sci Rep. (2021) 11(1):23292. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01324-0
59. Foulquier N, Le Dantec C, Bettacchioli E, Jamin C, Alarcón-Riquelme ME, Pers J. Machine learning for the identification of a common signature for Anti–SSA/Ro 60 antibody expression across autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheum. (2022) 74(10):1706–19. doi: 10.1002/art.42243
60. Kiefer K, Oropallo MA, Cancro MP, Marshak-Rothstein A. Role of type I interferons in the activation of autoreactive B cells. Immunol Cell Biol. (2012) 90(5):498–504. doi: 10.1038/icb.2012.10
61. Sjöstrand M, Johansson A, Aqrawi L, Olsson T, Wahren-Herlenius M, Espinosa A. The expression of BAFF is controlled by IRF transcription factors. J Immunol. (2016) 196(1):91–6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501061
62. Monteith AJ, Kang S, Scott E, Hillman K, Rajfur Z, Jacobson K, et al. Defects in lysosomal maturation facilitate the activation of innate sensors in systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2016) 113(15):E2142–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1513943113
63. Caielli S, Wan Z, Pascual V. Systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis: interferon and beyond. Annu Rev Immunol. (2023) 41(1):533–60. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-101921-042422
64. Marketos N, Cinoku I, Rapti A, Mavragani CP. Type I interferon signature in Sjögren’s syndrome: pathophysiological and clinical implications. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2019) 37(118):185–91. Available online at: https://www.clinexprheumatol.org/abstract.asp?a=1441631376268
65. Eloranta ML, Barbasso Helmers S, Ulfgren AK, Rönnblom L, Alm GV, Lundberg IE. A possible mechanism for endogenous activation of the type I interferon system in myositis patients with anti-Jo-1 or anti-Ro 52/anti-Ro 60 autoantibodies. Arthritis Rheum. (2007) 56(9):3112–24. doi: 10.1002/art.22860
66. Verstappen GM, Pringle S, Bootsma H, Kroese FGM. Epithelial–immune cell interplay in primary Sjögren syndrome salivary gland pathogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2021) 17(6):333–48. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00605-2
67. Espinosa A, Hennig J, Ambrosi A, Anandapadmanaban M, Abelius MS, Sheng Y, et al. Anti-Ro52 autoantibodies from patients with Sjögren’s syndrome inhibit the Ro52 E3 ligase activity by blocking the E3/E2 interface. J Biol Chem. (2011) 286(42):36478–91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.241786
68. Bettacchioli E, Saraux A, Tison A, Cornec D, Dueymes M, Foulquier N, et al. Association of combined anti-Ro52/TRIM21 and anti-Ro60/SSA antibodies with increased Sjögren disease severity through interferon pathway activation. Arthritis Rheum. (2024) 76(5):751–62. doi: 10.1002/art.42789
69. Kunishita Y, Yoshimi R, Kamiyama R, Kishimoto D, Komiya T, Sakurai N, et al. Anti-TRIM21 antibody is associated with aberrant B-cell function and type I interferon production in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2021) 30(13):2054–65. doi: 10.1177/09612033211042293
70. Bombardieri M, Argyropoulou OD, Ferro F, Coleby R, Pontarini E, Governato G, et al. One year in review 2020: pathogenesis of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2021) 38(4):S3–9. Available online at: https://www.clinexprheumatol.org/abstract.asp?a=16428
71. Bodewes ILA, Björk A, Versnel MA, Wahren-Herlenius M. Innate immunity and interferons in the pathogenesis of Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology. (2021) 60(6):2561–73. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key360
72. Kirou KA, Lee C, George S, Louca K, Peterson MGE, Crow MK. Activation of the interferon-alpha pathway identifies a subgroup of systemic lupus erythematosus patients with distinct serologic features and active disease. Arthritis Rheum. (2005) 52(5):1491–503. doi: 10.1002/art.21031
73. Li QZ, Zhou J, Lian Y, Zhang B, Branch VK, Carr-Johnson F, et al. Interferon signature gene expression is correlated with autoantibody profiles in patients with incomplete lupus syndromes. Clin Exp Immunol. (2010) 159(3):281–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04057.x
74. Weckerle CE, Franek BS, Kelly JA, Kumabe M, Mikolaitis RA, Green SL, et al. Network analysis of associations between serum interferon-α activity, autoantibodies, and clinical features in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. (2011) 63(4):1044–53. doi: 10.1002/art.30187
75. Munroe ME, Lu R, Zhao YD, Fife DA, Robertson JM, Guthridge JM, et al. Altered type II interferon precedes autoantibody accrual and elevated type I interferon activity prior to systemic lupus erythematosus classification. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75(11):2014–21. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208140
76. Liu W, Zhang S, Wang J. IFN-γ, should not be ignored in SLE. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:954706. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.954706
77. Madera-Salcedo IK, Ramírez-Sánchez AL, Rodríguez-Rodríguez N, García-Quintero R, Rubio RM, Morales-Montes de Oca G, et al. Down-regulation-resistant STAT4 risk haplotype contributes to lupus nephritis through CD4+ T cell interferon-γ production. Arthritis Rheum. (2023) 75(6):961–72. doi: 10.1002/art.42435
78. Schoenborn JR, Wilson CB. Regulation of interferon-gamma during innate and adaptive immune responses. Adv Immunol. (2007) 96:41–101. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(07)96002-2
79. Harigai M, Kawamoto M, Hara M, Kubota T, Kamatani N, Miyasaka N. Excessive production of IFN-gamma in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and its contribution to induction of B lymphocyte stimulator/B cell-activating factor/TNF ligand superfamily-13B. J Immunol. (2008) 181(3):2211–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.3.2211
80. Chodisetti SB, Fike AJ, Domeier PP, Singh H, Choi NM, Corradetti C, et al. Type II but not type I IFN signaling is indispensable for TLR7-promoted development of autoreactive B cells and systemic autoimmunity. J Immunol. (2020) 204(4):796–809. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901175
81. Xu W, Zhang JJ. Stat1-dependent synergistic activation of T-bet for IgG2a production during early stage of B cell activation. J Immunol. (2005) 175(11):7419–24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.11.7419
82. Liu M, Liu J, Hao S, Wu P, Zhang X, Xiao Y, et al. Higher activation of the interferon-gamma signaling pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with a high type I IFN score: relation to disease activity. Clin Rheumatol. (2018) 37(10):2675–84. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4138-7
83. Sebastian A, Madej M, Sebastian M, Łuczak A, Gajdanowicz P, Zemelka-Wiącek M, et al. The clinical and immunological activity depending on the presence of interferon γ in primary Sjögren’s syndrome-A pilot study. J Clin Med. (2022) 11(1):3. doi: 10.3390/jcm11010003
84. Martin-Gutierrez L, Peng J, Thompson NL, Robinson GA, Naja M, Peckham H, et al. Stratification of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus according to two shared immune cell signatures, with potential therapeutic implications. Arthritis Rheum. (2021) 73(9):1626–37. doi: 10.1002/art.41708
85. He Y, Vinuesa CG. Germinal center versus extrafollicular responses in systemic autoimmunity: who turns the blade on self? Adv Immunol. (2024) 162:109–33. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2024.02.002
86. Brown GJ, Cañete PF, Wang H, Medhavy A, Bones J, Roco JA, et al. TLR7 gain-of-function genetic variation causes human lupus. Nature. (2022) 605(7909):349–56. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04642-z
87. Voss LF, Howarth AJ, Wittenborn TR, Hummelgaard S, Juul-Madsen K, Kastberg KS, et al. The extrafollicular response is sufficient to drive initiation of autoimmunity and early disease hallmarks of lupus. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1021370. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1021370
88. MacLennan ICM, Toellner KM, Cunningham AF, Serre K, Sze DM-Y, Zúñiga E, et al. Extrafollicular antibody responses. Immunol Rev. (2003) 194:8–18. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2003.00058.x
89. Sanz I, Wei C, Jenks SA, Cashman KS, Tipton C, Woodruff MC, et al. Challenges and opportunities for consistent classification of human B cell and plasma cell populations. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2458. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02458
90. Wang S, Wang J, Kumar V, Karnell JL, Naiman B, Gross PS, et al. IL-21 drives expansion and plasma cell differentiation of autoreactive CD11chiT-bet+ B cells in SLE. Nat Commun. (2018) 9(1):1758. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03750-7
91. Wiener A, Schippers A, Wagner N, Tacke F, Ostendorf T, Honke N, et al. CXCR5 is critically involved in progression of lupus through regulation of B cell and double-negative T cell trafficking. Clin Exp Immunol. (2016) 185(1):22–32. doi: 10.1111/cei.12791
92. Amft N, Curnow SJ, Scheel-Toellner D, Devadas A, Oates J, Crocker J, et al. Ectopic expression of the B cell-attracting chemokine BCA-1 (CXCL13) on endothelial cells and within lymphoid follicles contributes to the establishment of germinal center-like structures in Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. (2001) 44(11):2633–41. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200111)44:11%3C2633::aid-art443%3E3.0.co;2-9
93. Chen ST, Oliveira TY, Gazumyan A, Cipolla M, Nussenzweig MC. B cell receptor signaling in germinal centers prolongs survival and primes B cells for selection. Immunity. (2023) 56(3):547–561.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.02.003
94. Dörner T, Szelinski F, Lino AC, Lipsky PE. Therapeutic implications of the anergic/postactivated status of B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. RMD Open. (2020) 6(2):e001258. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001258
95. Jenks SA, Cashman KS, Zumaquero E, Marigorta UM, Patel AV, Wang X, et al. Distinct effector B cells induced by unregulated toll-like receptor 7 contribute to pathogenic responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity. (2018) 49(4):725–739.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.08.015
96. Zumaquero E, Stone SL, Scharer CD, Jenks SA, Nellore A, Mousseau B, et al. IFNγ induces epigenetic programming of human T-bethi B cells and promotes TLR7/8 and IL-21 induced differentiation. eLife. (2019) 8:e41641. doi: 10.7554/eLife.41641
97. Soni C, Perez OA, Voss WN, Pucella JN, Serpas L, Mehl J, et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells and type I interferon promote extrafollicular B cell responses to extracellular self-DNA. Immunity. (2020) 52(6):1022–38.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.04.015
98. Sang A, Niu H, Cullen J, Choi SC, Zheng YY, Wang H, et al. Activation of rheumatoid factor-specific B cells is antigen dependent and occurs preferentially outside of germinal centers in the lupus-prone NZM2410 mouse model. J Immunol. (2014) 193(4):1609–21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1303000
99. Haacke EA, Bootsma H, Spijkervet FKL, Visser A, Vissink A, Kluin PM, et al. FcRL4+ B-cells in salivary glands of primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients. J Autoimmun. (2017) 81:90–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.03.012
100. Jourdan M, Robert N, Cren M, Thibaut C, Duperray C, Kassambara A, et al. Characterization of human FCRL4-positive B cells. PLoS One. (2017) 12(6):e0179793. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179793
101. Sohn HW, Krueger PD, Davis RS, Pierce SK. FcRL4 acts as an adaptive to innate molecular switch dampening BCR signaling and enhancing TLR signaling. Blood. (2011) 118(24):6332–41. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-05-353102
102. Pringle S, Verstappen GM, Van Ginkel MS, Nakshbandi U, Girigoria Z, Bootsma H, et al. Lymphoepithelial lesions in the salivary glands of primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients: the perfect storm? Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2022) 40(12):2434–42. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/06an99
103. Ruscitti P, Allanore Y, Baldini C, Barilaro G, Bartoloni Bocci E, Bearzi P, et al. Tailoring the treatment of inflammatory rheumatic diseases by a better stratification and characterization of the clinical patient heterogeneity. Findings from a systematic literature review and experts’ consensus. Autoimmun Rev. (2024) 23(7–8):103581. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103581
104. Giacomelli R, Afeltra A, Alunno A, Baldini C, Bartoloni-Bocci E, Berardicurti O, et al. International consensus: what else can we do to improve diagnosis and therapeutic strategies in patients affected by autoimmune rheumatic diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritides, systemic sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, antiphospholipid syndrome and Sjogren’s syndrome)?: the unmet needs and the clinical grey zone in autoimmune disease management. Autoimmun Rev. (2017) 16(9):911–24. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.07.012
105. Romão VC, Talarico R, Scirè CA, Vieira A, Alexander T, Baldini C, et al. Sjögren’s syndrome: state of the art on clinical practice guidelines. RMD Open. (2018) 4(1):e000789. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000789
106. Gottenberg J, Dörner T, Bootsma H, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Bowman SJ, Mariette X, et al. Efficacy of epratuzumab, an anti- CD 22 monoclonal IgG antibody, in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with associated Sjögren’s syndrome: post hoc analyses from the EMBODY trials. Arthritis Rheum. (2018) 70(5):763–73. doi: 10.1002/art.40425
107. Dima A, Jurcut C, Chasset F, Felten R, Arnaud L. Hydroxychloroquine in systemic lupus erythematosus: overview of current knowledge. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. (2022) 14:1759720X211073001. doi: 10.1177/1759720X211073001
108. Sandino-Bermúdez MJ, Hernández-Molina G. Hydroxychloroquine and Sjögren’s disease: current evidences for its use. Joint Bone Spine. (2024) 92(1):105799. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2024.105799
109. Morand EF, Furie RA, Bruce IN, Vital EM, Dall'Era M, Maho E, et al. Efficacy of anifrolumab across organ domains in patients with moderate-to-severe systemic lupus erythematosus: a post-hoc analysis of pooled data from the TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 trials. Lancet Rheumatol. (2022) 4(4):e282–92. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00317-9
110. University Medical Center Groningen. ANIfrolumab treatment for 24 weeks in patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome - efficacy and safety assessment in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase-iia proof-of-concept trial (ANISE-II). clinicaltrials.gov. (2022). Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05383677 (Accessed December 28, 2024).
111. Vital EM, Merrill JT, Morand EF, Furie RA, Bruce IN, Tanaka Y, et al. Anifrolumab efficacy and safety by type I interferon gene signature and clinical subgroups in patients with SLE: post hoc analysis of pooled data from two phase III trials. Ann Rheum Dis. (2022) 81(7):951–61. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221425
112. Baldini C, Fulvio G, La Rocca G, Ferro F. Update on the pathophysiology and treatment of primary Sjögren syndrome. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2024) 20(8):473–91. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01135-3
113. Amer BE, Afifi E, Mouffokes A, Hamad AA, Amin AM, Abdelwahab OA. Does baricitinib reduce disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Rheumatol. (2024) 43(2):579–89. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06731-4
114. Virtanen A, Spinelli FR, Telliez JB, O’Shea JJ, Silvennoinen O, Gadina M. JAK Inhibitor selectivity: new opportunities, better drugs? Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2024) 20(10):649–65. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01153-1
115. Bristol-Myers Squibb. A Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of deucravacitinib in adults with active Sjögren’s syndrome (POETYK SjS-1). clinicaltrials.gov. (2024). Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05946941 (Accessed December 28, 2024).
116. Bristol-Myers Squibb. A multi-center study to characterize the long-term safety and efficacy of BMS-986165 in subjects with systemic lupus erythematosus. clinicaltrials.gov. (2024). Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03920267 (Accessed December 28, 2024).
117. Merrill JT, Neuwelt CM, Wallace DJ, Shanahan JC, Latinis KM, Oates JC, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in moderately-to-severely active systemic lupus erythematosus: the randomized, double-blind, phase II/III systemic lupus erythematosus evaluation of rituximab trial. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62(1):222–33. doi: 10.1002/art.27233
118. Meijer JM, Meiners PM, Vissink A, Spijkervet FKL, Abdulahad W, Kamminga N, et al. Effectiveness of rituximab treatment in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62(4):960–8. doi: 10.1002/art.27314
119. Faustini F, Sippl N, Stålesen R, Chemin K, Dunn N, Fogdell-Hahn A, et al. Rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus: transient effects on autoimmunity associated lymphocyte phenotypes and implications for immunogenicity. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:826152. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.826152
120. Delli K, Haacke EA, Kroese FGM, Pollard RP, Ihrler S, van der Vegt B, et al. Towards personalised treatment in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: baseline parotid histopathology predicts responsiveness to rituximab treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75(11):1933–8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208304
121. Edwards JCW, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Emery P, Close DR, et al. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. (2004) 350(25):2572–81. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa032534
122. Mo S, Li Y, He J, Lin L. Progress of rituximab in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Front Med (Lausanne). (2024) 11:1472019. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1472019
123. Grigoriadou S, Chowdhury F, Pontarini E, Tappuni A, Bowman SJ, Bombardieri M. B cell depletion with rituximab in the treatment of primary Sjögren’s syndrome: what have we learnt? Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2019) 37(118):217–24. Available online at: https://www.clinexprheumatol.org/abstract.asp?a=1443331464681
124. Abeles I, Palma C, Meednu N, Payne AS, Looney RJ, Anolik JH. B cell–directed therapy in autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. (2024) 42(1):103–26. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-083122-044829
125. McCune WJ, Golbus J, Zeldes W, Bohlke P, Dunne R, Fox DA. Clinical and immunologic effects of monthly administration of intravenous cyclophosphamide in severe systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. (1988) 318(22):1423–31. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806023182203
126. Álvarez Gómez JA, Salazar-Camarena DC, Román-Fernández IV, Ortiz-Lazareno PC, Cruz A, Muñoz-Valle JF, et al. BAFF system expression in double negative 2, activated naïve and activated memory B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1235937. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1235937
127. Furie R, Petri M, Zamani O, Cervera R, Wallace DJ, Tegzová D, et al. A phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of belimumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits B lymphocyte stimulator, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. (2011) 63(12):3918–30. doi: 10.1002/art.30613
128. Furie R, Rovin BH, Houssiau F, Malvar A, Teng YKO, Contreras G, et al. Two-year, randomized, controlled trial of belimumab in lupus nephritis. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383(12):1117–28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001180
129. De Vita S, Quartuccio L, Salvin S, Picco L, Scott CA, Rupolo M, et al. Sequential therapy with belimumab followed by rituximab in Sjögren’s syndrome associated with B-cell lymphoproliferation and overexpression of BAFF: evidence for long-term efficacy. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2014) 32(4):490–4. Available online at: https://www.clinexprheumatol.org/abstract.asp?a=785224802131
130. Mariette X, Barone F, Baldini C, Bootsma H, Clark KL, De Vita S, et al. A randomized, phase II study of sequential belimumab and rituximab in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. JCI Insight. (2022) 7(23):e163030. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.163030
131. Gualtierotti R, Borghi MO, Gerosa M, Schioppo T, Larghi P, Geginat J, et al. Successful sequential therapy with rituximab and belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: a case series. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2018) 36(4):643–7. Available online at: https://www.clinexprheumatol.org/abstract.asp?a=1206629533753
Keywords: Sjögren's disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, overlap syndrome, genetic predisposition, interferon pathway, B-cell activation, extrafollicular B-cell response, targeted therapy
Citation: Fulvio G, La Rocca G, Tani C, Mosca M and Baldini C (2025) Sjögren's disease and systemic lupus erythematosus overlap: immunological insights and therapeutic implications. Front. Lupus 3:1600768. doi: 10.3389/flupu.2025.1600768
Received: 26 March 2025; Accepted: 12 August 2025;
Published: 1 September 2025.
Edited by:
Vasco C. Romão, Universidade de Lisboa, PortugalReviewed by:
Kristin Andreassen Fenton, UiT The Arctic University of Norway, NorwayHong Zan, Prellis Biologics, United States
Copyright: © 2025 Fulvio, La Rocca, Tani, Mosca and Baldini. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Giovanni Fulvio, Z2lvdmFubmkuZnVsdmlvOTJAZ21haWwuY29t
 Giovanni Fulvio
Giovanni Fulvio Gaetano La Rocca1,2
Gaetano La Rocca1,2 Chiara Tani
Chiara Tani Chiara Baldini
Chiara Baldini