Abstract
Within the set of risk factors that compromise the conservation of marine biodiversity, one of the least understood concerns is the noise produced by human operations at sea and from land. Many aspects of how noise and other forms of energy may impact the natural balance of the oceans are still unstudied. Substantial attention has been devoted in the last decades to determine the sensitivity to noise of marine mammals—especially cetaceans and pinnipeds—and fish because they are known to possess hearing organs. Recent studies have revealed that a wide diversity of invertebrates are also sensitive to sounds, especially via sensory organs whose original function is to allow maintaining equilibrium in the water column and to sense gravity. Marine invertebrates not only represent the largest proportion of marine biomass and are indicators of ocean health but many species also have important socio-economic values. This review presents the current scientific knowledge on invertebrate bioacoustics (sound production, reception, sensitivity), as well as on how marine invertebrates are affected by anthropogenic noises. It also critically revisits the literature to identify gaps that will frame future research investigating the tolerance to noise of marine ecosystems.
1 Introduction
Marine invertebrates represent a hugely diverse taxa, playing a central role in food webs and ecosystem services, as well as constituting an important economical resource. Invertebrates make essential contributions to global biodiversity and provide major ecosystem functions (e.g., water filtering, habitat creation, organic matter processing, carbon transfer through food webs and nutrient recycling) (Collier et al., 2016). Many marine invertebrate species also have important intrinsic value to human society, including as food resources (shellfish protein), for health purposes (protection form algae eutrophication), as coastal protection from natural disasters and ocean acidification, through ornamental and recreational value, and in tourism.
Some agents of biodiversity decline in marine ecosystems (e.g., water pollution, overexploitation, habitat degradation, invasive species and climate change) have been analysed extensively (Collier et al., 2016). However, it is only relatively recently that noise and other forms of energy, like anthropogenic electromagnetic fields, have been considered critical stressors of the natural balance of the oceans. These pressure elements can have detrimental impacts on the survival and reproduction of individuals, with consequences for entire populations and species (van der Graaf et al., 2012; Hutchison et al., 2020; Popper et al., 2020). Recent findings have shown that marine invertebrates can be sensitive to anthropogenic noise and indicated that this sensitivity may have influence ocean biodiversity (André et al., 2011; Aguilar de Soto, 2016; Edmonds et al., 2016; Sordello et al., 2020), placing them as direct indicators of ocean health.
Ocean soundscapes are composed of a combination of biological, geological and anthropogenic sounds produced from a variety of sources (Pijanowski et al., 2011; Lindseth and Lobel, 2018; Duarte et al., 2021). As with other marine species, invertebrates have evolved around the extraction of information from soundscapes. Invertebrates are mainly sensitive to the particle motion of sound, rather than the sound pressure. As many of them live close to the seabed they are often affected by substrate vibration, which usually involves particle motion (Hawkins et al., 2021). Changing soundscapes due to a decrease of sound-producing animals and the introduction of man-made noises may thus alter vital invertebrate sensory abilities. Sources of marine underwater anthropogenic noise that generate vibration, include shipping (fishing boats, recreational motorboats, jet skis, trade vessels), oil and gas exploration and operation, the construction and operation of offshore wind farms and other renewable energy devices, dredging, construction of bridges and harbours, commercial and military sonar, and underwater explosions for construction or ordnance disposal. There are some natural sources of substrate vibration, including volcanos, earthquakes and breaking waves, animal movements/interactions and objects falling or rolling onto the seabed. Seabed substrates can propagate some seismic interface waves well, with particle motion existing in both the water and the sediment. Underwater sound sources can extend over large periods of time (continuous; e.g., shipping (Van der Graaf et al., 2008) and result in an increase in low-level background noise, or can be short and intense (tonal/impulsive; e.g., sonar, pile driving, air guns (Rako-Gospić and Picciulin, 2019). Impulsive sounds have a fast rise time reaching a maximum value followed by a fast decay. Impulsive sounds may be much higher in amplitude near the source than continuous sounds, but their energy decreases faster with distance (Hawkins and Popper, 2016). It is important to note that sound is not limited to just the water column but that the near-surface seabed can respond vigorously to in-water sound and the seabed transmits low-frequency energy well (Nedelec, 2021).
Impulsive sounds can be expressed in terms of their peak levels, but in some cases (e.g., seismic airguns) that is not sufficient for characterizing the energy. An alternative is the sound exposure level (SEL) – the time integral of the pressure squared for a single event – a measure reflecting the total acoustic energy received by an organism (Slabbekoorn et al., 2010). The metrics applied for continuous sounds are the root-mean-square sound pressure (RMS) and the peak sound pressure (Hawkins and Popper, 2016; Hawkins and Popper, 2017). In general it is accepted that the assessment of the sound sources and its potential impact on marine fauna needs to consider cumulative (repetition of a particular source) and aggregate (combined effects of different type of sources (Hawkins and Popper, 2016).
Sound can affect marine organisms depending on sound pressure level at the source, the pitch (frequency) and the distance between source and receiver (Richardson et al., 1995). Table 1 provides a summary of the typical characteristics of different common anthropogenic sound sources in the marine environment.
Table 1
| Sound | Source level (dB re 1 μPa-m)* | Bandwidth (Hz) | Major amplitude (Hz) | Duration (ms) | Directionality | Sound type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TNT
(1-100 lbs) |
272–287
Peak |
2–1000 | 6–21 | ~ 1–10 | Omnidirectional |
Tonal/
impulsive |
| Pile driving |
228 Peak/
243–257 P-to-P |
20–>20 000 | 100–500 | 50 | Omnidirectional |
Tonal/
impulsive |
| Offshore industrial activities | ||||||
| Dredging |
168–186
rms |
30–>20 000 | 100 - 500 | Continuous | Omnidirectional | Continuous |
| Drilling |
145–190
rms** |
10–10 000 | < 100 | Continuous | Omnidirectional | Continuous |
| Wind turbine | 142 rms | 16–20 000 | 30 - 200 | Continuous | Omnidirectional | |
| Shipping | ||||||
| Small boats and ships |
160 –180
rms |
20–>10 000 | >1 000 | Continuous | Omnidirectional | Continuous |
| Large vessels |
180–190
rms |
6–>30 000 | >200 | Continuous | Omnidirectional | Continuous |
| Sonar | ||||||
| Military sonar low- frequency | 215 Peak | 100 –500 | _ | 600–1 000 | Horizontally focused |
Tonal/
impulsive |
| Military sonar mid-frequency |
223–235
Peak |
2800–8200 | 3 500 | 500–2 000 | Horizontally focused |
Tonal/
impulsive |
| Echosounders | 235 Peak | Variable | Variable 1500 – 36 000 | 5–10 ms | Vertically focused |
Tonal/
impulsive |
| Seismic surveys | ||||||
| Airgun array |
260–262
P-to-P |
10–100 000 | 10–120 | 30–60 | Vertically focused* |
Tonal/
impulsive |
| Other activities | ||||||
| Acoustic deterrent/harassment Devices |
132–200
Peak |
5 000–30 000 | 5 000–30 000 | Variable 15–500 ms | Omnidirectional |
Tonal/
impulsive |
|
Tidal and wave energy
devices*** |
165–175
rms*** |
10–50 000 | _ | Continuous | Omnidirectional | Continuous |
Acoustic properties of some anthropogenic noises.
* Nominal source, ** Higher source levels from drill ships use of bow thrusters, *** Projection based on literature data with levels back-calculated at 1 m (Modified from Götz, 2009).
Given the increasing introduction of anthropogenic noise to the oceans, it has become essential to design tools to monitor and regulate the effects of sounds on marine fauna. Anthropogenic noise is recognized as a major component of environmental change in the 21st Century and a pollutant of international concern, featuring prominently on international directives and agendas. Although additional scientific and technical progress is still required to support the further development of criteria related to acoustic impact on marine environment (including in relation to impacts of introduction of energy on marine life, relevant noise and frequency levels), two indicators were published for Descriptor 11 (Noise/energy) of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD EU, 2008) in the EC Decision 2010/477/EU on criteria and methodological standards on GES of marine waters (Dekeling et al., 2014):
Indicator 11.1 Distribution in time and place of loud, low and mid frequency impulsive sounds.
-
- Proportion of days and their distribution within a calendar year, over areas of a determined surface as well as their spatial distribution, in which anthropogenic sound sources exceed level that are likely to entail significant impact on marine animals, measured as Sound Exposure Level (in dB re 1μPa2.s) or as peak sound pressure level (in dB re 1μPa-peak) at one meter, measured over the frequency band 10 Hz to 10 kHz.
-
Indicator11.2 Continuous low frequency sound.
-
- Trends in the ambient noise level within the 1/3 octave bands 63 and 125 Hz (centre frequency) (re 1μPa2; average noise level in these octave bands over a year) measured by a statistical representative sets of observation stations and/or with the use of models if appropriate.
In this review, we provide a synthesis of the peer-reviewed literature published from the late 1960s to 2022 reporting marine invertebrate bioacoustics (detection and production of sound) and responses to anthropogenic noise in different life stages, in populations and ecosystems. This work documents prominent trends in research topics and methods, the kinds of noise sources that have been studied, the measurements used to characterise them, and the gaps and perspectives in research coverage that merit attention in future research. We outline the necessity/utility of existing scientific information concerning anthropogenic noise effects on marine invertebrates for predicting potential consequences of noise exposure. We also scale up to influences on ecological and evolutionary processes, and consider how this information is important for biodiversity conservation and the implementation of meaningful mitigation measures.
2 Marine invertebrate bioacoustics
Sound travels about five times faster in water (ca. 1500 m/s) than in air (ca. 340 m/s) because the density of water is greater, and also attenuates less over the same distance. This characteristic allows long-distance communication in water, but also implies a long-distance impact of noise on aquatic animals (Slabbekoorn et al., 2010). Particle motion is an important component of sounds travelling through the water and it is detected by invertebrates (Popper & Hawkins, 2019). Sound is an important sensory modality for marine organisms, especially because other senses (vision, smell or taste) may be limited due to information loss in marine ecosystems (Popper and Hawkins, 2019). The scientific knowledge of the biological significance of sound perception and production in marine invertebrates is scarce. Animals produce acoustic signals for communication about, for instance, predators, prey, territorial defence, social and sexual behaviour, and identity. They have evolved to detect sounds both as part of communication and to make use of acoustic cues in the environment, aiding in, for instance, settlement and habitat choice. In this section, we summarize the current knowledge regarding marine invertebrate bioacoustics including analysis methods, receptor organs, sound detection and production.
2.1 Measurements: Imaging, electrophysiology, respirometry, biochemistry
The different techniques used to study invertebrate bioacoustics are summarized and described below.
2.1.1 Imaging techniques
Scientific and diagnostic imaging allow visual representations of invertebrate sensory structures, organs or tissues for various purposes such as the study of normal anatomy and function, or the diagnosis of the effects of sound on these structures. Imaging techniques include Electron Microscopy and 3D imaging techniques (Figure 1).
Figure 1
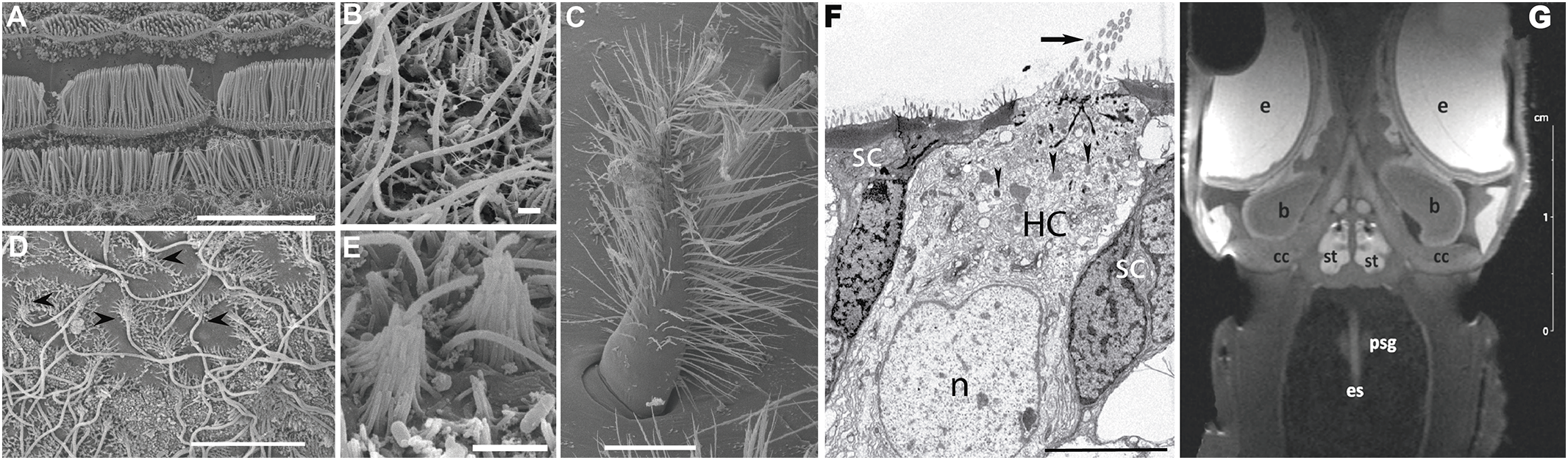
Imaging Techniques. (A–E): Scanning Electron Microscopy. (F): Transmission Electron Microscopy. (G): Magnetic Resonance Imaging. (A–F): Different types of sensory epithelia (hair cells) depending on the marine invertebrate group (A, F: Cephalopods. (B, E): Cnidarians. C: Crustaceans. D: Gastropods). (A): View of three rows of hair cells (bundle of kinocilia) in statocyst crista epithelium of Sepia officinalis. (B): Statocyst sensory epithelium of the jellyfish Cotylorhiza tuberculata. Hair cells carry an only nonmotile kinocilia surrounded by a short crown of stereocilia (Solé et al., 2016). (C): A seate (bearing hairs) of the medial group sensory epithelia in the hermit crab Dardanus calidus statocyst. Setae are typical hair cell on crustaceans. (D): Apple snail (Pomacea maculata) inner statocyst sensory epithelia. Arrowheads point to the hair cells exhibiting their lonely kinocilia surrounded by a crown of stereocilia. Between them microvilli of the supporting cells is visible (Solé et al., 2021a). (E): Statocyst sensory epithelia of the sea anemone Calliactis parasitica. Similarlly to other groups of cnidarians (B) their hair cells present a solitary kinocilia surrounded by a crown of stereocilia. (F): Apex of a S. officinalis hair cell (HC) in between two supporting cells (SC). The HC shows kinocilia (arrow), nucleus (n) and cytoplasmic mitochondria (arrowheads) (André et al., 2011). (G): Coronal view -anterior section- of squid (Loligo vulgaris) head (B: Brain, cc: cranial cartilage, e: eye, es: oesophagus, m: mouth, psg: posteror salivary gland, st: statocyst. (Solé et al., 2013b). Scale bar: (G) = 2 cm. (C) = 25 µm. (A) = 10 µm. (D, F) = 5 µm. (E) = 2 µm. (B) = 1 µm.
Electron microscopes have a higher resolution than light microscopes and are capable of a higher magnification (up to 2 million times) (Rudenberg and Rudenberg, 2010), allowing the visualization of structures that would not normally be visible by optical microscopy. There are two major types of electron microscopes used in invertebrate bioacoustics: Transmission Electron Microscopes and Scanning Electron Microscopes. Scanning Electron Microscopy produces images of a sample by scanning it with a focused beam of electrons that interact with atoms in the sample, providing information about its surface topography and composition (Butterfield et al., n.d.) and achieving resolution better than 1 nanometre (Suzuki, 2002). In invertebrates, this technique allows description of the surface of sensory epithelium and effects of noise upon it (Figures 1A–E) (Solé et al., 2013a; Solé et al., 2013b; Day et al., 2016; Solé et al., 2016; Solé et al., 2018; Day et al., 2019). In Transmission Electron Microscopy, a beam of electrons is passed through an ultrathin specimen and an image is formed from the interaction of the electrons transmitted through it. This technique is used in the description of invertebrate ultrastructural sensory epithelia, allowing the inner cellular organelles to be visualised and analysis of the effects of sound on them. (Figure 1F) (Solé et al., 2013b)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive imaging technique that allows creation of a 3D image of a body’s internal organs using powerful magnetic fields and radio waves. This technique has been used to construct models of the morphological structure of invertebrate sensory systems (Ziegler et al., 2018). Computer tomography (CT) relies on differences in X-ray attenuation of biological tissues to do a 3D reconstruction of them. Major molluscan organs have been visualized using CT techniques (Ziegler et al., 2018).
2.1.2 Electrophysiology
Auditory evoked potential recordings have been used in a variety of invertebrate taxa as a measurement of sound sensitivity (Figure 2A). The evoked potential technique for hearing was popularized by Hong Yan’s work on fishes before to spreading it among invertebrates (Yan, 2002). This method involves measuring responses from neurons associated with sound detection and the resulting conduction of responses toward a brain or central set of ganglia (Hall, 2007). Recording may be thus from nearby sensory organs, such as the statocyst, or if sound detection comes from more peripheral hair cells or organs, it may occur nearby the brain/central ganglia area (Jezequel et al., 2021). While evoked potential methods have been widely applied to measure hearing abilities in many aquatic vertebrates e.g., (Supin et al., 2001; Kastak et al., 2005; Nachtigall et al., 2007; Mooney et al., 2012; Piniak et al., 2016; Jones et al., 2021), it has only been sparingly applied to invertebrates, including squid (Mooney et al., 2010), prawns (Lovell et al., 2005), snapping shrimp (Dinh and Radford, 2021), lobsters (Jezequel et al., 2021) and other crustaceans (Hughes et al., 2014; Radford et al., 2016). Some of its advantages include that it can be applied to a variety of taxa, including wild caught animals, and it can be non-invasive. Although often times it is a more invasive method involving sedation, needle electrodes and surgery to access nerve structures. Evoked potential methods are generally cost-effective and permit to reach a relatively high animal sample size of (i.e. > 10), that is higher than psychophysical methods, and whole audiograms can be measured quickly (tens of minutes to a few hrs).
Figure 2
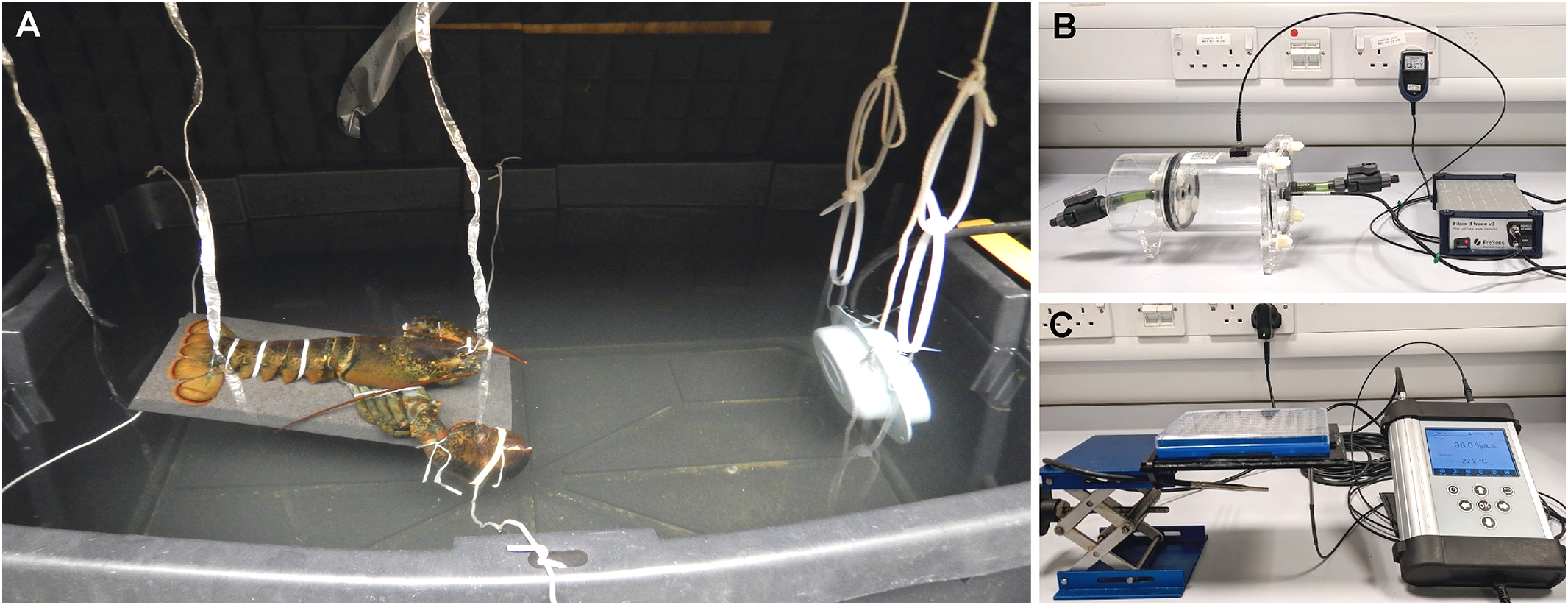
(A) Electrophysiology. (B, C): Respirometry. (A): Evoked potential hearing test of an American lobster (Homarus americanus) (B): Respiration set-up for adult invertebrates; calibrated volume sealed respiration chamber connected to a fibox 3 trace v3 fibre-optic trace oxygen meter (Presens – Precision Sensing, Regensburg, Germany) via fibre-optic cable to a PSt3 oxygen sensor spot (detection limit: 0.03% oxygen, 15ppb). (C): Plate set-up used for larvae and gametes; 64 well plate with PSt7 oxygen sensor spots (detection limit: 0.03% oxygen, 15ppb) attached to a fibox 4 trace hand held oxygen meter (Presens – Precision Sensing, Regensburg, Germany). Both (B, C use non-destructive oxygen measurements, measuring luminescence decay time by stimulating an immobilised luminophore with monochromic light.
2.1.3 Respirometry
There are a number of techniques used to assess the effects of a stimulus on the metabolic rate of an organism. One such method, respirometry, provides an indirect calorimetric approach to the measurement of metabolic heat changes through monitoring and measurement of variations in oxygen uptake (Figures 2B, C). For marine invertebrates, changes in respiration rate are observed indirectly through changes in the dissolved oxygen of the surrounding water. Animals are encapsulated in a sealed, water-filled chamber and dissolved oxygen is measured either at the start and end points of the exposure using an oxygen probe, or continuously throughout the exposure using an oxygen sensor. During long exposures, intermittent flow respirometry may be used (Steffensen et al., 1984; Steffensen, 1989) when periodic flushing of the respirometry chamber is performed to maintain sufficient oxygen saturation. In both static and intermittent-flow respirometry, oxygen consumption is calculated accounting for bacterial respiration, water volume, exposure time and environmental conditions, and calibrated against the animal’s mass to allow comparability between individuals and across species. Respirometry has been used to investigate the effects of anthropogenic noise on decapods (Regnault and Lagardere, 1983; Wale et al., 2013b; Ruiz-Ruiz et al., 2020), bivalves (Shi et al., 2019; Wale et al., 2019) and cephalopods (Woodcock et al., 2014).
2.1.4 Cellular–biochemical–molecular aspects
Several techniques for the assessment of invertebrate stress are based on cellular, biochemical and molecular aspects. It is possible to determine the physiological state of an animal using stress analysis after sound exposure. Stress bioindicators can be measured in invertebrate haemolymph. Total haemocyte count (THC), heat shock protein 27 (Hsp27) expression in haemocyte lysate, total protein concentration (PT) and phenoloxidase activity (PO) in cell-free haemolymph, were considered potential biomarkers of stress (Filiciotto et al., 2014; Celi et al., 2015).
In aquatic invertebrates, the homeostasis of total haemocyte density and composition may be considered an important well-being predictive parameter. Decreases of total haemocyte count (THC) under stressful conditions, usually carried out with cell counter chambers, have been reported for several aquatic crustacean species (Le Moullac et al., 1998; Sánchez et al., 2001; Mercier et al., 2006), suggesting the possibility of immune depletion as well as an increased risk of infection (Filiciotto et al., 2014; Celi et al., 2015). Although the variation in differential haemocyte count in the presence of different stressors is not well understood, it has been used as a stress indicator in crustaceans (Jussila et al., 1997; Johansson et al., 2000; Filiciotto et al., 2014) (Figure 3). The measurement of this parameter is easily feasible under the microscope after on slide cell fixation and stain.
Figure 3
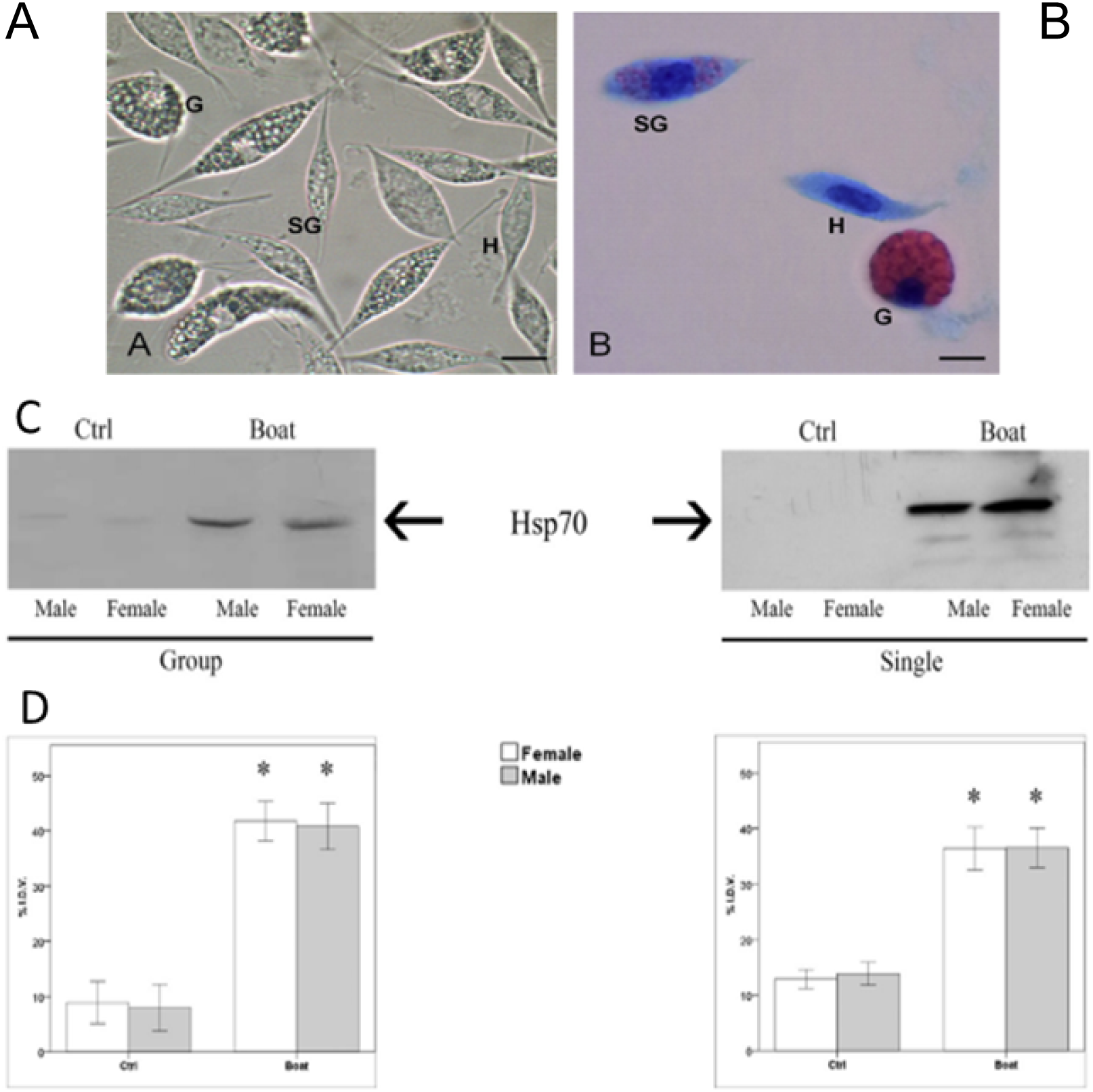
Light Microscopy. Haemocytes of the spiny lobster Palinurus elephas(A) no staining and (B) stained with May–Grünwald–Giemsa. H: hyalinocytes; SG: semigranulocytes; G: granulocytes. Scale bars: (A, B) = 8 µm. Effect of the acoustic stimuli on the expression levels of the protein Hsp70 in P. elephas; (C) Representative western blot of Hsp70 levels in single and grouped animals. (D) Integrated density value (% IDV) of the Hsp70 protein bands. Data are the means ± standard error (N = 18 control and N = 18 test specimens). Asterisks represent significant differences between CTRL and BOAT condition (*= p < 0.01). (Filiciotto et al., 2014).
Another parameter useful to evaluate the disturbance of the homeostatic balance of animals is the measurement of glucose haemolymphatic. Hyperglycemia is a primary response typical of many aquatic animals to different stressors (Lorenzon, 2005; Fazio et al., 2013; Faggio, 2014). Glucose haemolymphatic, which can be measured in haemolymph using commercial kits, increases in marine invertebrates under exposure to acoustic stimulu (Filiciotto et al., 2014; Vazzana et al., 2016). In the haemolymph, it is possible to measure the total protein concentration. This parameter is non-destructive, easy, cheap and measurable through fluorimetric methods. It can be used as a “warning” of poor environmental conditions such as noise (Filiciotto et al., 2014; Vazzana et al., 2016). A further indicator of the negative effect of altered conditions on invertebrates is a change in enzyme activities. There are still few studies on the variations of enzymes in stressed invertebrates, but some have shown a modulation of peroxidase, alkaline phosphatase and esterase activity measured through rapid colorimetric methods (Vazzana et al., 2016; Vazzana et al., 2020a; Vazzana et al., 2020b) after acoustic stimulus. Among bioindicators of stressful conditions in crustaceans is also included expression of heat shock proteins (Snyder and Mulder, 2001; Liberge and Barthelemy, 2007). Some authors showed, through the use of western blot analysis and Real-Time PCR (RT-PCR), that, in marine invertebrates exposed to acoustic stimuli, occurs a protein and gene overexpression of the Hsp70 (Filiciotto et al., 2014; 2016; Vazzana et al., 2016; 2020a). The latter aspect is useful to understand better the variations of the complex cellular–biochemical–molecular network of organism in stress condition.
2.1.5 Measurement of underwater sound
In a sound wave, particles of the medium (e.g., water) oscillate around a point of origin (‘particle motion’) causing local compressions and expansions (‘sound pressure’) that transfer the sound energy to neighbouring particles (ISO 18405:2017; Gray et al., 2016). Thus, all sound involves both pressure and particle motion fluctuations. The number of oscillations per second is the frequency in Hertz (Hz). Sound pressure fluctuations are omnidirectional and are measured as force per unit area in Pascals (Pa), typically using piezoelectric hydrophones, which have been readily available for many years (ISO 18405:2017, Robinson et al., 2014). Sound particle vibrations are directional and are described by displacement (m), velocity (ms-1) or acceleration (ms-2); three metrics that have a frequency-dependent relationship to one another (Nedelec et al., 2016, ISO 18405:2017). The directional information is described by angles relative to references such as magnetic north and gravity. Particle acceleration can be measured using capacitive, piezoresistive or piezoelectric accelerometers, while particle velocity can be measured using geophones, all of which are proof-mass instruments (a proof mass is a known quantity of mass used in a measuring instrument as a reference for the measurement of an unknown quantity) that are becoming more readily available (Nedelec, 2021). Particle acceleration can also be measured using a pressure gradient between hydrophone pairs (Chapuis et al., 2019). Finally, in simplified acoustic conditions (deep water and far from the source relative to wavelength), particle velocity magnitude but not direction can be estimated from pressure measured by a single hydrophone (Nedelec, 2021). Underwater sound is often reported in decibel units (dB), which are represented on a logarithmic scale relative to 1 µPa for pressure, 1 pm for displacement, 1 nm s-1 for velocity and 1 um s-2 for acceleration (ISO 18405:2017).
The statolith organs of many invertebrates measure the relative motion of the body of the animal to the dense statocyst, which moves with a lag due to its greater mass and inertia, creating a biological analogue of a proof-mass instrument (Packard et al., 1990; Kaifu et al., 2011). Therefore, measuring the whole-body vibration of animals is of interest because it links acoustic stimulus and sound detection. Piezoresistive accelerometers that measure acoustic vibrations of solid objects they are fixed to exist, however their scale relative to the bodies of aquatic invertebrates means that the accelerometers themselves would alter the vibration of the whole body. Recently, the availability of non-contact laser Doppler vibrometer techniques, that have already been applied to research on hearing in several amphibian, reptile and crustacean species (Hetherington and Lindquist, 1999; Hetherington, 2001), has opened the possibility of measuring whole-body vibration of aquatic animals. Whole-body vibrations of cephalopods and scallops that were exposed to air borne sound (<360 Hz) were successfully measured using a laser Doppler vibrometer, confirming the hypothesis that particle motion can vibrate the whole body of invertebrates (André et al., 2016). However, to report the particle motion levels measured by an instrument, it is necessary to calibrate the instrument for its coupling to the medium in which the sound is to be measured. The coupling of animal bodies to the water column remains poorly understood, thus measuring whole-body motion gives us a limited understanding of responses to particle motion levels in the water. Further advancement of measurement techniques on whole-body vibration of aquatic animals elicited by propagating acoustic waves will improve understanding of particle motion reception in invertebrates. This will involve calibrating the animals themselves as well as any accelerometers that are attached to them.
2.2 Detection of sound: Vibration, reception and sensitivity
2.2.1 Physical aspects: Acoustic pressure vs particle motion
The motion of the ‘particles’ that make the medium (e.g., air, water, or solid substrate) is an intrinsic aspect of sound. Sound pressure can be described by its magnitude and its temporal and frequency characteristics, but at a single point, sound pressure does not contain directional information. Particle motion can be described by its magnitude, temporal and frequency characteristics, but additionally it always contains directional information because of its inherent ‘back and forth’ action (Hawkins and Popper, 2017). Many aquatic invertebrates sense and use particle motion, including to detect the direction of the source, (André et al., 2016; Nedelec et al., 2016). Particle motion and sound pressure are proportional in ‘plane wave’ conditions (far from the source and from any boundaries that may cause reflections relative to the wavelength). Close to the source in the ‘near field’, particle motion is higher than would be expected from equivalent pressure in plane wave conditions in the ‘far field’ due to interactions between the wavelength, frequency and distance from the source. This interaction, which causes additional particle motion near to the source decreases with inverse proportion to the distance from the source until it can be treated as negligible after approximately one wavelength. A good rule of thumb is therefore that the boundary of the near field region with additional particle motion is one wavelength from the source. Therefore, particle motion is present wherever there is sound and a good rule of thumb is that the boundary of the near field region with additional particle motion is one wavelength from the source. Sensory hair cells in the sensory systems (see below) are stimulated by mechanisms that respond to particle motion and convert these motions to electrical signals that stimulate the nervous system. Because aquatic invertebrates lack gas-filled cavities, it seems that they mostly perceive the particle motion of the sound. But recent experiments put this statement in question: particle motion may not be the sole component implied in sound lesions in invertebrates (Solé et al., 2017).
2.2.2 Receptor systems
2.2.2.1 Cilia-based mechanosensory systems
Mechanoreceptors are sensory cells (hair cells) detecting mechanical forces that usually bear specialized cilia (Figure 1). These mechanosensory cells are the starting point of mechanotranduction processes in which the hair cells express transmembrane channels that convert force into cellular signal. Hearing, proprioception or gravity mechanisms are based in these mechanosensory cells (Bezares-Calderón et al., 2020). These receptor systems can be found on the body surface of animals or enclosed in fluid-filled cavities. Hair cells possess unique features including the presence of cilia (microtubule with a basal body which contains organelles) that can be motile or not and, a tuft of stereovilli (actin-filled microvilli). Unlike vertebrates that are characterized by the presence of a single cilia with a 9 + 2 axoneme and a group of stereovilli, invertebrates generally have kinocilia (with an internal structure of 9 x 2 + 2 microtubules in the axoneme) in their hair-cell-based receptor systems. The number of kinocilia per cell varies according to the group of invertebrates (e.g., cnidarians: monociliary cells with a concentric or eccentric bundle of stereovilli; cephalopods: multiciliary cells with microvilli; crustaceans: monociliary cells without microvilli; Figure 1). Some mechanosensory systems present accessory structures (statolith, statoconia, cupula) above the hair cells which stimulate the underlying sensory epithelia. The kinocilia are mechanically directly or indirectly (via a cupula) coupled with the surrounding fluid. An external stimulus causes the movement of an accessory structure or fluid which leads to the mechanical deflection of the cilia, and stimulates the sensory cells. These hair cells may appear in the form of primary (specialized neurons with an axon leaving the cell) or different types of secondary sensory cells (without an axon) that make afferent synaptic contacts with first-order afferent neurons. Hair cells and neurons receive numerous efferent endings (Budelmann, 1989) and are responsible from the information transmission to the nervous system. Depending on the direction of deflation of the kinocilia, the amount of neurotransmitter release will be different, causing an excitation or inhibition response and serving to regulate a wide range of behaviours.
Invertebrates can detect underwater sound (i.e., of mechanical disturbance of water) through three types of sensory systems: the body superficial receptor systems, the internal statocyst receptor system and the chordotonal organs (Budelmann, 1992b) (Figure 4).
Figure 4
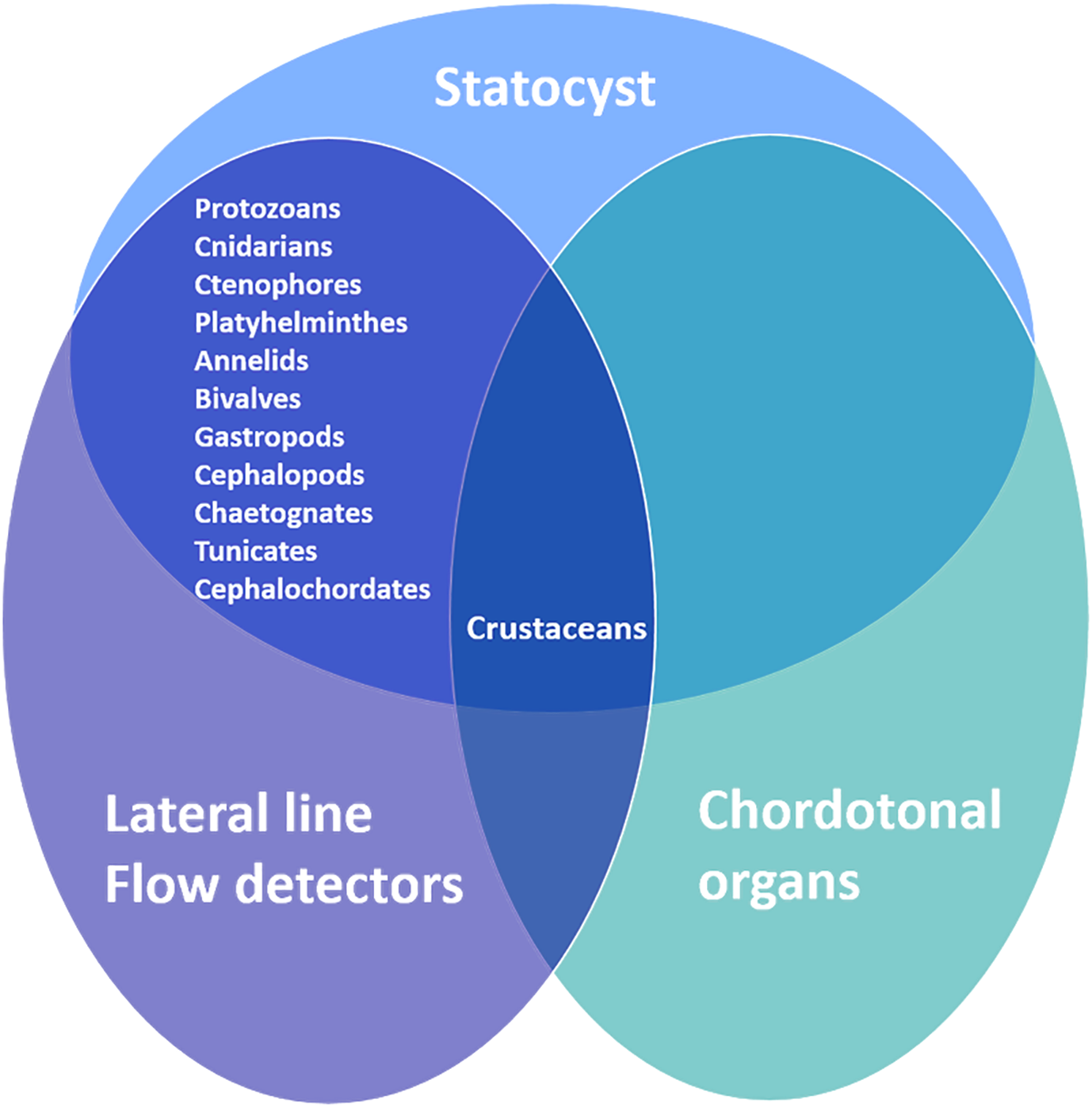
Marine Invertebrate sound sensory systems.
2.2.2.2 Superficial receptor systems
Epidermal detector systems for vibration and other local water movements known as “hydrodynamic receptor systems” are found all over the external body surface and are analogous structures to fish and amphibian lateral lines (Budelmann, 1992b) (Figure 5). Their receptor cells are epidermal sensory cells carrying kinocilia that can be mechanically deflected by local movements that occur relative to the animal’s body surface. In some cases, the cilia are embedded in an accessory cupula structure (Budelmann, 1989) (Figure 5).
Figure 5
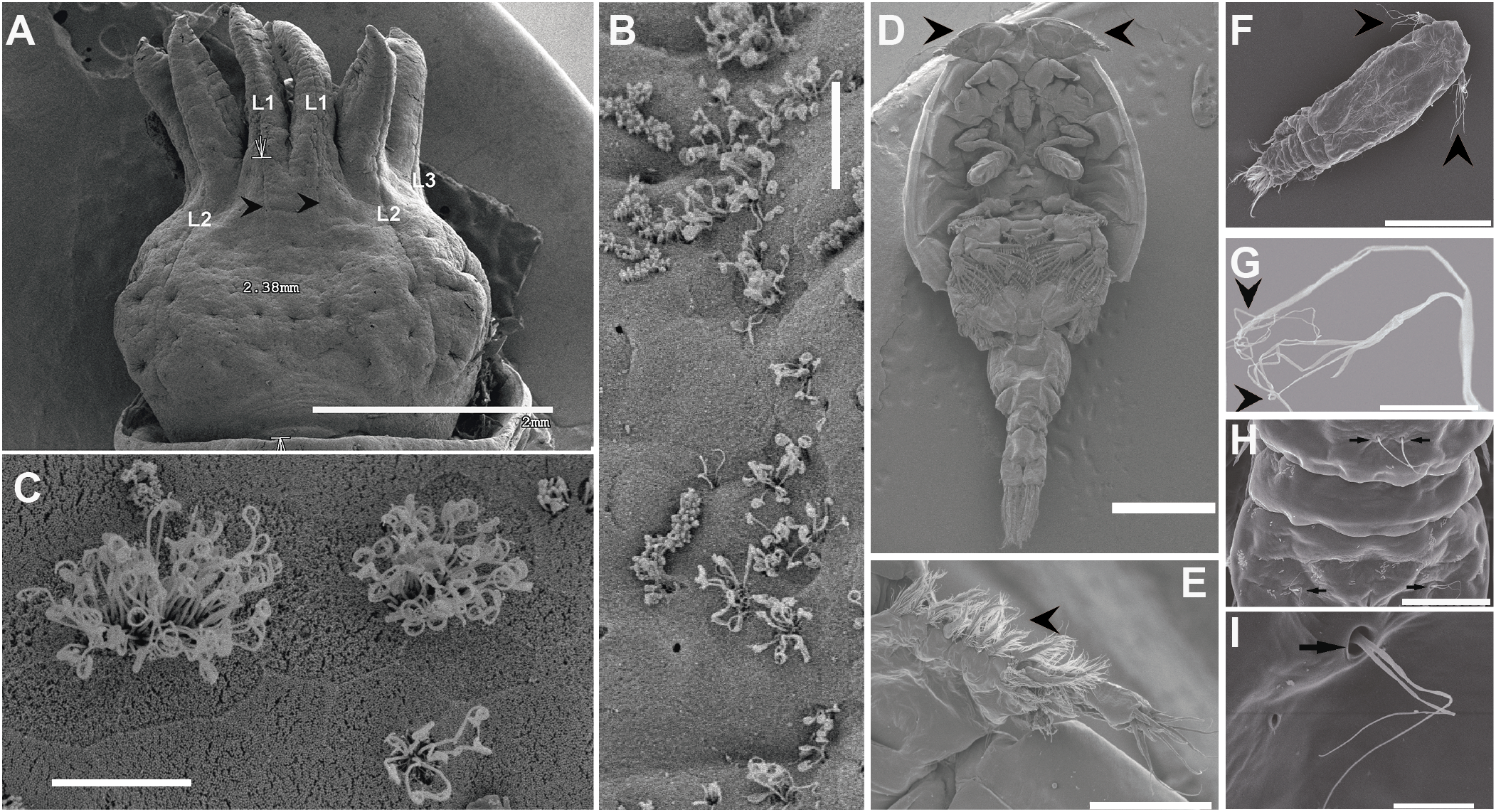
Scanning Electron Microscopy. (A–C: Cephalopod. D–I Crustacean). (A): Epidermal lines (lateral line analogue) on the head of Sepia officinalis larva. Lateral lines on three arms and above the eye (L1–L3) that run in anterior/posterior direction are visible. White arrows show the length of the lateral line L1 (black arrowheads). (B): Epidermal line L1. (C): Detail from (B). Hair cells’ kinocilia of L1. (D): Ventral view of an adult whole body of sea lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) showing the first antenna (arrowheads) responsible from the sound perception. (E): First antenna of an adult of L. salmonis.(F): Dorsal view of a L. salmonis copepodid showing the first antenna (arrowheads). (G): Detail from the first antenna setae showing their irregular branching tips. (H): Dorsal view of the L. salmonis copepodid abdomen showing some paired setae (arrows). (I): Detail from H showing the structure of a birrame setae (arrow). (A–C: Solé et al., 2022; D–I: (Solé et al., 2021b). Scale bar (A, D) = 2 mm. (F) = 300 µm. (E) = 100 µm. (H) = 30 µm. (B, C, G) = 10 µm. (I) = 5 µm.
Some species of protozoans respond to vibrations and water disturbances (Kolle-Kralik and Ruff, 1967). Unicellular organisms commonly respond to mechanical stimuli impinging upon them. Motor responses in ciliated cells result from alterations in motility of the cilia. The resulting behaviour is cellular contraction or alteration in locomotion (Budelmann, 1992b).
Cnidarians are sensitive to low-frequency water oscillations. Horridge (Horridge, 1966) showed sensitivity to low-frequency oscillations by the hydromedusa Eutonia. The sea anemone Sagartia reacts to water currents (Frings, 1967). The sensory structures are monociliary hair cells with a concentric bundle of stereovilli (Budelmann, 1989). Cnidarian’s polyp and medusa stages to detect vibrations in water associated with prey movement. Hydrozoan and Cubozoan polyps show mechanoreceptors bearing specialized cilia located in their tentacles (Golz and Thurm, 1993; Golz and Thurm, 1994; Bouillon et al., 2006; Tardent and Schmid, 1972) which inform the animals about surrounding environment changes. Albert (Albert, 2011) described light, touch, gravity, chemicals, sound pressure waves, direction, vibration and hydrostatic pressure receptors in medusa. Behavioural observations in Aurelia labiata under turbulent water evidenced its sensitivity to sound pressure waves and vibration mediated by sensory ciliary hairs (Albert, 2007).
Ctenophores possess sensory organs able to detect vibrations in water associated to prey movement (Tamm, 2014). The comb jelly Leucothea and the sea walnut Pleurobrachia are sensitive to water oscillations. The receptor cells are monociliary hair cells with a specialized basal body (Budelmann, 1992b).
Platyhelminthes have many sensory cells that sense local water movements. In flatworms, each cell has a single kinocilium surrounded by either a collar of eight separate stereovilli or a collar with eight columnar ridges, closely filled with microfilaments (Budelmann, 1989).
The receptor organs for water movements and vibrations on annelids are the “segmental sensilla” which are disk-like-sensory buds containing three types of ciliated epidermal cells distributed all over the body surface, tentacular cirri and palps (Budelmann, 1989). When low-frequency vibrations stimulate their tentacles, tube worms withdraw into their tubes (Laverack, 1968).
Among Mollusks, Cephalopods also have superficial receptor systems sensitive to local water movements. These receptors are analogous in structure and function to the amphibian and fish lateral lines. Late embryonic stages and hatchlings of cephalopods have epidermal lines (Villanueva and Norman, 2008), consisting of ciliated primary sensory hair cells that carry cilia (Hanlon and Budelmann, 1987) and non-ciliated accessory cells, running in anterior-posterior direction and located on the arms, head, anterior part of dorsal mantle and funnel (Figures 5A–C). Cuttlefish present eight, and squids ten, “epidermal lines” of ciliated sensory cells (Budelmann, 1992b; Solé et al., 2018) which are sensitive to local water oscillations (0.5–400 Hz) and are able to perceive hydrodynamic pressure. In addition to the epidermal lines in the head and arms, on cephalopods, there are others ciliated cells with shorter cilia that occur on the body surface, also involved in the detection of water movements (Budelmann, 1992b; Preuss and Budelmann, 1995).
In gastropods, several types of receptor endings were identified in the skin of the tentacles, lips, dorsal surface of the head and mouth region of the pond snails Lymnaea stagnalis and Vivipara viviparus (Zaitseva and Bocharova, 1981). The bivalve abdominal sense organ (ASO) of scallop Patinopecten yessoensis is highly sensitive to water-born vibrations (Zhadan and Semen’kov, 1984; Zhadan et al., 2004). It is the largest of the mechanosensory organs studied, containing about 4 million sensory cells (Haszprunar, 1983; 1985).
Chaetognathes are predators of marine plankton. They wait motionless until the water oscillation produced by a prey or another source of vibration arrives (Budelmann, 1992b; Feigenbaum, 2011). Chaetognates exhibit “ciliary fences” on the body surface, consisting of stiff kinocilia polarized in the same direction. All fences together are able to detect the direction of water movements (Horridge and Boulton, 1967; Budelmann, 1992b).
The sessile ascidians (Tunicates) are sensitive to water movements through cupular organs present in the exhalent siphon of the animal (Bone, and Ryan, 1978; Mackie and Singla, 2004). The cupular organ exhibit primary sensory cells embedded in a gelatinous cupula, structure considered an analogue of neuromasts in vertebrates. In ascidians, mechanoreceptors of the oral area are involved in monitoring the incoming water flow. In the coronal organ of the oral siphon, the sensory cells present different morphologies depending on the species (Enterogona order show multiciliate cells, Pleurogona present one or two cilia accompanied by stereovilli). The coronal organ presents a line of secondary sensory cells with a hair bundle also comprising graded stereovilli. These hair cells resemble vertebrate hair cells for morphology, embryonic origin and arrangement, and this organ is considered homologous to the vertebrate octavo-lateralis system (Burighel et al., 2011). Molgula socialis presents a coronal organ with a few associated rows of sensory cells running the whole length of the oral velum and the tentacles (Caicci et al., 2007). Oikopleura exhibit another organ sensitive to water oscillations, the Langerhans receptor (with monociliary cells that lack a cupula) on either side of the trunk (Bone and Ryan, 1979).
Two types of ciliated sensory cells sensitive to water movements are shown in the lancelet Branchiostoma (Amphioxus) (Cephalochordates) (Bone and Best, 1978). On the buccal cirri, the hair cells carry a normal kinocilium. On the velar tentacles, the sensitive cells bears a shorter and thicker modified cilium (Burighel et al., 2011).
Crustaceans exhibit superficial receptor systems sensitive to water disturbances over the body surface. The receptors systems can present a single cuticular hair (“sensillum”) or a group of hairs. The structure of the hair(s) consists of one to four sensory cells with a flexible basal joint. When the water oscillations bend the hairs the sensory cells are mechanically stimulated (Budelmann, 1992a). Decapod crustaceans, especially lobsters and crayfish, present cuticular cells on their carapace and over the body surface, on the two large and small antennae and on the telson (Budelmann, 1992a; Jezequel et al., 2021). In addition to sensory sensilla distributed around the body surface, some planktonic crustaceans present sensory sensilla responsible for the water disturbance and sound perception on the antenna (Solé et al., 2021b) (Figures 5D–I).
2.2.2.3 Statocyst receptor systems
Invertebrate statocysts can be defined as internal receptor systems, analogous to the vertebrate inner ear (otolith organ), that act as equilibrium receptor systems, although most are thought to be gravity receptor systems only (Anken and Rahmann, 2002). In addition, statocysts of cephalopods and decapod crustacea include angular acceleration detector systems (Budelmann, 1988; Budelmann, 1992a). In these groups, the statocyst as linear accelerometers can also detect acoustic particle motion (since the whole animal vibrates together with the water column) and are involved in underwater hearing (Budelmann 1992a; Budelmann 1992b).
Statocysts present different range of complexity from the simplest gravity receptor systems to the more complex organs of cephalopods which show receptor systems for linear and angular accelerations (Budelmann, 1992b). However, all these different systems have only two basic structural elements: a mass, the statolith or statoconia, the position of which varies as a function of the forces applied; and sensory elements (hair cells that carry kinocilia in contact with the mass) that are mechanically affected by the position of the mass (Figure 6). Changes in orientation cause the movement of the statolith into the statocyst and thereby the stimulation of different groups of hair cells. In some cases, the heavy mass is surrounded by, or included in, the sensory cell lacking kinocilia (Budelmann, 1992b).
Figure 6
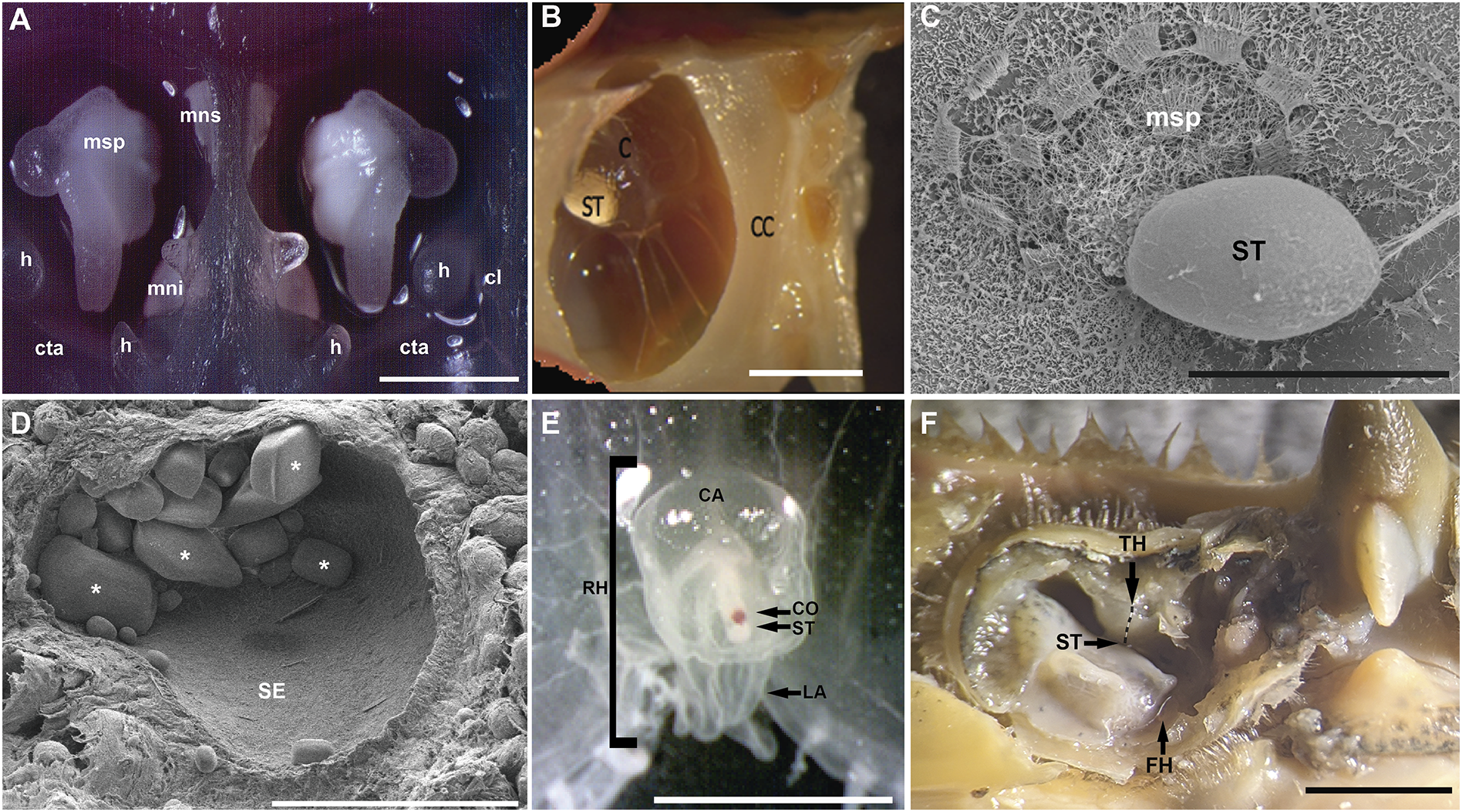
Invertebrate marine statocyst (A–C: Cephalopods. D: Gastropods. E: Cnidarians. F: Crustaceans). (A,B, E, F): Photomicrograps. (C, D): SEM. (A): epia officinalis statocyst cavities opened transversally (Anterior view). Each cavity shows the three macula-statolith systems (msp, mns, mni) and two of the crista-cupula systems (cta, cl)(Solé et al., 2017). (B): Lateral view of the interior of a Octopus vulgaris statocyst. The spherical inner sac is suspended in the cephalic cartilage cavity by fibrous strands. The statolith is attached to the macula. The crista lies on the inside wall of the sac-like structure (André et al., 2011). (C): Illex coindetii hatchling inner statocyst morphology. The transversally opened statocyst cavity shows the statolith attached to the macula statica princeps. Note the hair cell kinociliary groups arranged in nearly concentric rings around a center (Solé et al., 2018). (D): Inner cavity of apple snail (Pomacea maculate) statocyst covered by sensory epithelium. Some aragonite crystals are visible (asterisk) (Solé et al., 2021a). (E): Anterior view of the jellyfish Aurelia aurita rhopalium bell margin. There is a mass of sensory cells with a single layer of pigment cells (pigment-cup ocellus) on the oral side near the statocyst (Solé et al., 2016). (F): Transversally opened statocyst cavity of a blue crab (Callinectes sapidus). Arrows point to the location of the different ciliary areas (ST, TH, FH). TH hair cells run following a line distribution as it is shown in the image (Solé et al., 2023) (ca, rhopalar canal; C, Crista; CC, Cephalic cartilage; cl, crista longitudinalis; co, pigment-cup ocellus; cta, crista transversalis anterior; FH, Free-hook hairs; h, hamuli lobe; LA, lappet; mni, macula neglecta inferior; mns, macula neglecta superior; msp, macula statica princeps; RH, rhopalium; SE, Sensory epithelium; ST, statolith; TH, Thread hairs). Scale bars: (A, B) = 2 mm. (F) = 0,5 mm. (E) = 400 μm. (D) = 200 µm. (C) = 20 µm.
In cnidarians, statocysts can be external or internal pendulum-like projections bearing internally the mass (Budelmann, 1988; Solé et al., 2016). The position of the pendulum is monitored by one or several hair cells. Scyphozoan medusae shows marginal sense organs bearing statocysts (Werner, 1993). Numerous small crystals collected in sac-like statocyst are located at the distal ends of their rhopalia (sensory organs associated with pulsing, swimming, orientation and gravireception) (Passano, 1982) (Figure 6E). Statocysts lacking hair cells occur in cnidarian polyp Corymorpha (Campbell, 1972), in the nemertine worm Ototyphlonemertes (Brüggernann and Ehlers, 1981), and in some flatworms (Ferrero, 1973). The process of stimulus detection in the statocyst is mediated by the differential contact of the statolith and the surrounding sensory cell(s), or alternatively by membrane distortions (Budelmann, 1988).
Ctenophores have only a single statocyst containing a single large statolith in the aboral organ (apical organ). The frequencies of the eight locomotory comb rows are controlled by four compound motile mechanoresponsive cilia (balancers), which support the statolith, and consequently regulate the position of the animal respect to gravity perception (Budelmann, 1992b; Tamm, 2014).
Lacking on the sessile adults, the ascidian tunicateCiona present a unique statocyst in their its larvae, consisting in a single cell carrying a large pendulum-like projection without cilia (Budelmann, 1992b).
Bivalve, scaphopod mollusks and most gastropods exhibit the “typical” invertebrate statocyst. (Figure 6D) (Cragg and Nott, 1977; Budelmann, 1992b) that is shown from the pediveliger stage (Cragg and Nott, 1977). It is a sphere filled with endolymph which walls are lined by between 10 and 3,000 hair cells, each bearing kinocilia and contains either a single statolith or a mass of statoconia (Budelmann, 1988).
With the exception of the Nautiloids, which present a simplest statocyst that resemble gastropod and bivalve molluscs equilibrium organs, all cephalopods have a couple of statocysts generally located within the cephalic cartilage. The cephalopod statocysts are sophisticated balloon-shape bodies filled with endolymph that contain the sensory hair cells which lie on the inside wall of the inner sac and are grouped into two main areas of sensory epithelium (macula and crista). In octopods, the statocyst is a sphere-like sac. It contains a single gravity receptor system, the macula plate with a compact attached statolith. The angular acceleration receptor system is a ridge of cells that runs along the inside of the statocyst sac, divided into nine crista segments. Either a large or a small cupula is attached to each segment (Budelmann, 1988). In decapods, such as cuttlefish and squid, the statocysts are even more complex (Figures 6A–C). Its angular acceleration receptor system is subdivided into only four segments. Its gravity receptor system is subdivided into three systems. Each system has a unique pattern of morphological and physiological polarization of its hair cells, depending on the position of the basal foot structure and the internal tubuli content of its kinocilia (Budelmann, 1979). One of these three systems is covered by a large calcareous statolith, whereas the others are covered by statoconial layers. In cephalopods statocysts, the sensory hair cell organization is highly complex and receive a high degree of efferent innervation (Colmers, 1981).
Crustaceans are sensitive to low frequency acoustic stimuli (Salmon and Horch, 1972; Goodall et al., 1990; Roberts et al., 2016). Mechanical disturbances of water/sediment (associated to sound waves) are detected by a pair of statocysts (Figure 6F), chordotonal organs linked to joints of antenna or legs (Figure 7) and internal and external sensilla (Figure 5) (Popper et al., 2001; Breithaupt, 2002). The statocyst in crustaceans shows a similar basic structure among all species and can be located on the basal segment of the antennule (in decapods) and the uropod or telson of the tail (mysids and isopods). The statocyst presents cuticular sensory hairs polarized in one particular direction due to its asymmetric basal joint. They have an overlying statolith mechanically connected to the cuticular hair which stimulates three sensory hair cells. Depending on the species the cuticular hairs per statocyst is variable but in general they are arranged in two to four rows and are polarized towards the centre (Budelmann, 1992a; Rose and Stokes, 1981).
Figure 7
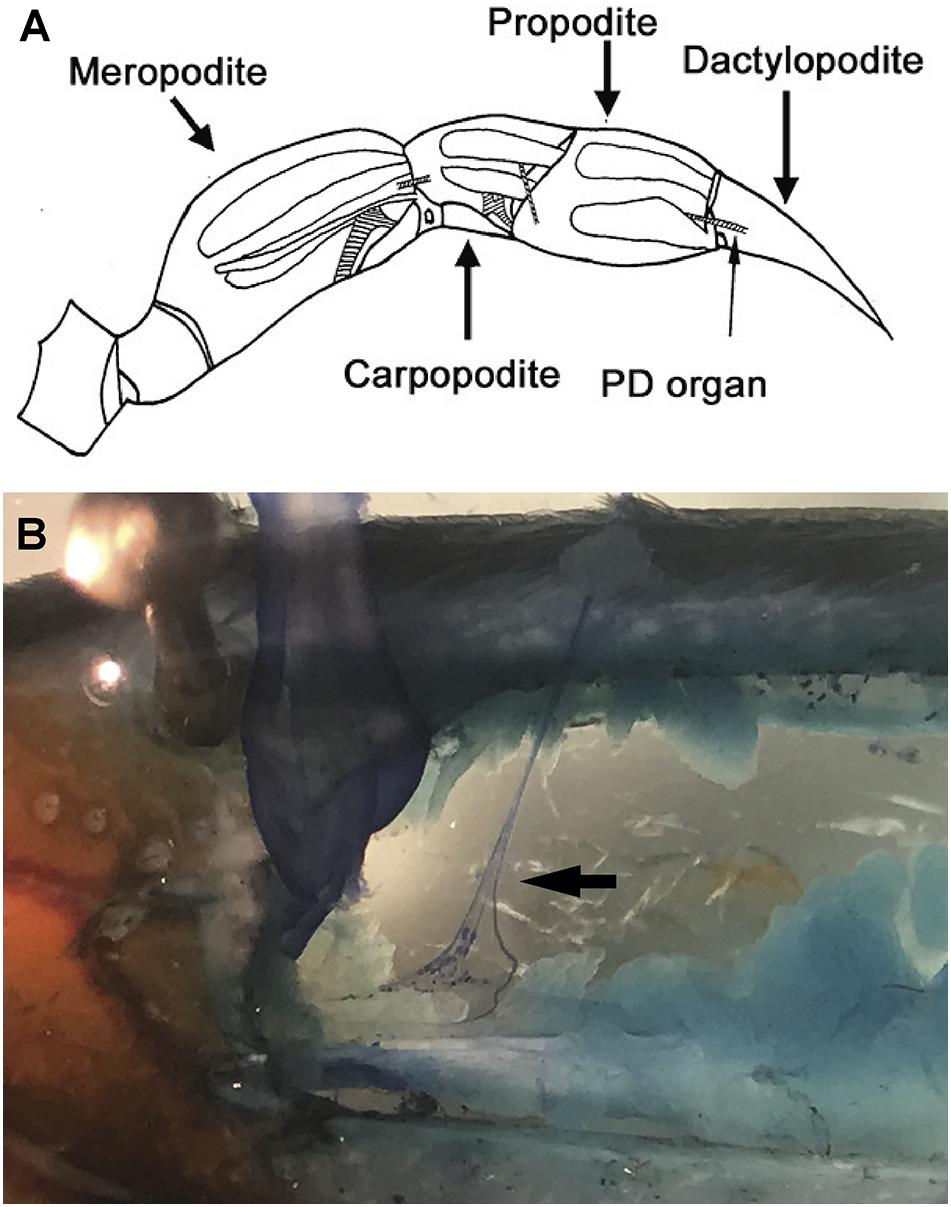
Crab chordotonal organ. (A): Drawing of the first walking leg of a crab showing the anatomical location of chordotonal organs (hatched regions). PD organ spans the most distal joint in the limb between the propodite and dactylopodite. (B): Innervation of chordotonal organs. Image of a dissected first walking leg of a blue crab (Callinectes sapidus). PD nerve dissected away from the main leg nerve (arrow). The individual neurons stained with methylene blue are visible. (PD: Propodite-dactylopodite chordotonal organ) (Image courtesy of Dr. Robin L. Cooper).
2.2.2.4 Chordotonal organs
Chordotonal organs which are associated with flexible articulations of the appendages, are common among crustaceans (Bush and Laverack, 1982; Cooper, 2008; Atkins et al., 2021) (Figure 7). The oscillations of the water column stimulate the chordotonal sensory cells sited in the appendages. The hermit crab Petroehirus exhibit chordotonal organs with sensory cells in the basal segment of the antennal flagellum. The rock and the spiny lobster present a similar organs in the large and small antenna and, the crayfish Astaeus in intersegmental joints of the first and second antenna (Laverack, 1964; Rossi-Durand and Vedel, 1982). The chordotonal organ is a proprioceptive organ that monitors joint movement, direction of movement and static position and in some cases could be related with sound perception (Figure 7). Fiddler and ghost crabs present specialized Barth’s myochordotonal organs (Bart’s MCO) located on each walking leg; these resembles a distinct, thin-walled “window” in the exoskeleton. The males of these species produce acoustic signals detected by their females. Thanks to Barth’s myochordotonal organs, ghost crabs are sensitive to both substrate-borne and airborne sounds and, fiddler crabs responds to substrate-born vibrations.
2.2.3 Acoustic sensitivity in molluscs and crustaceans
Using a broad definition – the reception of vibratory stimuli of any kind and nature, provided that the sound source is not in direct contact with the animal’s body (Budelmann, 1992b) – hearing is widespread among invertebrates. Although the research on invertebrate acoustic sensitivity is scarce, some studies on bivalves, cephalopods and crustaceans have determined some important aspects about the invertebrate threshold sensitivities.
Early studies on sound detection by bivalves reported induced burrowing behaviour in clam species (Mosher, 1972; Ellers, 1995). Recent work has quantified sensitivity of marine bivalves to substrate-borne vibration (Zhadan, 2005; Kastelein, 2008; Roberts et al., 2015). By exposure to vibration under controlled conditions using valve closure as the behavioural indicator of reception and response (Roberts et al., 2015), the thresholds were shown to be within the range of vibrations measured in the vicinity of anthropogenic operations such as pile-driving and blasting. Using pure-tone exposures and an accelerometer fixed to the shell to detect valve closure, Japanese oysters (Crassostrea gigas) were shown to have maximum sensitivity from 10 to 200 Hz (Charifi et al., 2017). The bivalve abdominal sense organ (ASO) is highly sensitive to water-born vibration in the range 20–1500 Hz (Zhadan and Semen’kov, 1984; Zhadan et al., 2004).
While there is uncertainty regarding the biological importance of particle motion sensitivity versus acoustic pressure, recent behavioural (including changes in ventilation rhythm) and electrophysiological studies confirmed cepaholopd sensitivity to frequencies under 400 Hz (Sepia officinalis, (Packard et al., 1990); Sepioteuthis lessoniana, (Hu et al., 2009); Octopus vulgaris (Packard et al., 1990; Kaifu et al., 2007; Kaifu et al., 2008; Hu et al., 2009; Kaifu et al., 2011), Loligo vulgaris, (Packard et al., 1990), Loligo pealeii, (Mooney et al., 2010). Whole body vibrations due to particle motion were detected in cuttlefish Sepia officinalis (André et al., 2016) through an experimental set-up based on laser Doppler vibrometer techniques (frequencies 60, 120 and 320 Hz). This work confirmed the hypothesis that particle motion can encompass the whole body of cephalopods and cause it to move with a similar phase and amplitude. Mantle movement (lengthened ventilation or jetting) has been used as an indicator of the sound perception to understand the perceptionmechanism (Kaifu et al., 2007; 2008Packard et al., 1990) or to understand the biological significance of their acoustical perception (Wilson et al., 2007; Samson et al., 2014; Mooney et al., 2016; Jones et al., 2021). In most cases, unconditioned animals were used to observe their baseline behavior. Mantle muscle movements were recorded using an electromyograph (Kaifu et al., 2007; Kaifu et al., 2008) or measurement of the changes of mantle muscle thickness based on impedance between two electrodes inside and outside the mantle (Packard et al., 1990). Cephalopod behavioural responses were then categorized to response type (e.g., inking, jetting, startle, colour change, fin movement, no response).
Among crustaceans, Lovell and colleagues studied the mechanism of the reception of sound and hearing abilities of the prawn Palaemon serratus using a combination of anatomical techniques, electron microscopy and electrophysiology (Lovell et al., 2005). They concluded that P. serratus is sensitive to sounds with frequencies ranging between 100 and 3000 Hz. The same authors (Lovell et al., 2006) demonstrated that all P. serratus individuals were able to hear sound with a frequency of 500 Hz, regardless of their size. Although data are not available on frequency-specific hearing/particle motion detection capability, preliminary experiments demonstrated Nephrops norvegicus postural responses to water vibrations (Goodall et al., 1990). The hermit crab (Pagurus berhnardus) showed antenna/maxilliped movement and forward locomotion in response to particle motion (Roberts et al., 2016). Auditory evoked potential (AEP) analyses of Panopeus sp. crabs evidenced their sensitivity to particle motion (Hughes et al., 2014). This response range overlaps with peak frequencies associated with airgun, pile-driving, sonar activities and biologically sources of underwater noise (Jeffs et al., 2003; Radford et al., 2007). Marine crustaceans present sensory hairs covering their bodies, which, when stimulated by water or substrate-borne vibrations associated with changes in acceleration hydrodynamic flow or sound, help animals sense nearby biological movements (Tautz and Sandeman, 1980; Radford et al., 2016). The American lobster Homarus americanus shows sensory hairs sensitives to low frequency (Derby, 1982) and ontogenic variations in AEP response up to 5 kHz (Pye and Watson, 2004; Jezequel et al., 2021). Crustacean chordotonal organs are stimulated by vibrations. One specialised organ, present on fiddler and ghost crabs, Barth’s myochordotonal organ (Barth’s MCO), is sensitive to frequencies above 300 Hz. All walking legs contain the sensory organ and if an individual loses a walking leg, it would still be able to detect vibrations through its other walking legs (Derby, 1982). Pelagic crab larva with capacity to detect specific underwater sounds/vibrations are able to use sound as an orientation cue to settle (Montgomery et al., 2006; Stanley et al., 2010; Stanley et al., 2012) (Jeffs et al., 2003; Radford et al., 2007).
Relevant studies on marine invertebrate acoustic sensitivity are detailed in Table 2.
Table 2
| Species | Common name | Acoustic Perception | Method | Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bivalves | ||||
| Donax variabilis | coquina | Sounds below 4096 Hz | Burrowing behaviour responses to sound |
(Ellers, 1995) |
| Macoma balthica | Baltic clam | Digging movements after vibratory stimulation | (Mosher, 1972) | |
| Mytilus edulis | blue mussel | Vibration stimulus (Sinusoidal excitation -tonal signals (5–410 Hz). Thresholds 0.06–0.55 m/s2 (RMS) | Behavioural changes (valve closure) | (Roberts et al., 2015) |
| Crassostrea gigas | Japanese oyster | 10–200 Hz pure tones | Valve closure (accelerometer oyster shell) | (Charifi et al., 2017) |
| Mizuhopecten yessoensis | Japanese scallop | 30–1000 Hz | Behavioural (shell oscillations) directional sensitivity of ASO to water-borne vibrations. | (Zhadan, 2005) |
| Chlamys swifti | swifti scallop | 30–1000 Hz | Behavioural (shell oscillations) directional sensitivity of ASO to water-borne vibrations. | (Zhadan, 2005) |
| Patinopecten yessoensis | Ezo giant scallop | ASO Fibres I: 20–1000 Hz (max 250–300 Hz) ASO Fibres II: 20–340 Hz |
Electrophysiological study ASO | (Zhadan and Semen’kov, 1984) |
| Cephalopods | ||||
| Sepia officinalis | European common cuttlefish | Particle motion (acceleration) <4x 10-3 m/s2 | Behavioural changes in breathing and jetting activity | (Packard et al., 1990 |
| Sepia officinalis | European common cuttlefish | Fit the frequency dependence of particle motion sensitivity model | Physical model of the sensory system | (Kaifu et al., 2011) |
| Sepia officinalis | European common cuttlefish |
PM encompass the whole body of cephalopods and cause it to move with same phase and amplitude |
Experimental set based on laser Doppler vibrometer techniques |
(André et al., 2016) |
| Sepioteuthis lessoniana | oval squid | 400–1500 Hz | Auditory brainstem response (ABR) approach | (Hu et al., 2009) |
| Octopus vulgaris | common octopus | 400–1000 Hz | Auditory brainstem response (ABR) approach | (Hu et al., 2009) |
| Octopus vulgaris | common octopus | Fit the frequency dependence of particle motion sensitivity model | Physical model of the sensory system | (Kaifu et al., 2011) |
| Octopus vulgaris | common octopus | Particle motion (acceleration) <4x 10-3 m/s2 | Behavioural changes in breathing and jetting activity | (Packard et al., 1990) |
| Amphioctopus fangsiao/Octopus ocellatus1 | webfoot octopus | 50–150 Hz | Behavioural changes (respiratory activities) | (Kaifu et al., 2007) |
| Amphioctopus fangsiao/Octopus ocellatus1 | webfoot octopus | 141 Hz particle motion at particle accelerations below 1.3 × 10 -3 m/s2 | Behavioural changes (respiratory activities) | (Kaifu et al., 2008) |
| Amphioctopus fangsiao/Octopus ocellatus1 | webfoot octopus | Fit the frequency dependence of particle motion sensitivity model | Physical model of the sensory system | (Kaifu et al., 2011) |
| Loligo vulgaris | European squid | Particle motion (acceleration) <4x 10-3 m/s2 | Behavioural changes in breathing and jetting activity | (Packard et al., 1990) |
| Loligo pealeii | longfin squid | 30–500 Hz (lowest thresholds between 100–200 Hz) | Auditory evoked potentials (AEPs) with electrodes placed near the statocysts | (Mooney et al., 2010) |
| Crustaceans | ||||
| Palaemon serratus | common prawn | 100–3000 Hz | Anatomical techniques, electron microscopy and electrophysiology | (Lovell et al., 2005) (Lovell et al., 2006) |
| Neprhops norvegicus | Norway lobster | 20–180 Hz | Behaviour responses to water vibrations | (Goodall et al., 1990) |
| Pagur Panopeus sp.us berhnardus | hermit crab | [5–400 Hz at particle velocities of 0.03–0.044 m/s2 (RMS)] | Behavioural responses to particle motion | (Roberts et al., 2016) |
| Panopeus sp. | mud crabs | predatory fish sounds (or vibrations) 90–200 Hz, (vibrations <0.01 m/s2) |
Electrophysiological, auditory evoked potential (AEP) | (Hughes et al., 2014) |
| Cherax destructor | Australian freshwater crayfish | 150–300 Hz | Electrophysiological recordings (Sensory hairs located on the claws) |
(Tautz & Sandeman, 1980) |
| Ovalipes catharus | paddle crabs | 100–200 Hz | Medical imaging technology, microCT, and auditory evoked potentials (AEP) | (Radford et al., 2016) |
| Homarus americanus | American lobster | 20–300 Hz | Electrophysiological recordings (Sensory hairs, cuticular sensilla) |
(Derby, 1982) |
|
Uca sp. Ocypode sp. |
fiddler crab ghost crab |
≥300 Hz | Barth’s myochordotonal organs (Barth’s MCO) | (Popper et al., 2001) |
|
Alpheus
richardsoni |
snapping shrimp | ≥1500 Hz. (more sensitive: 80–100 Hz) |
Electrophysiological, auditory evoked potential (AEP) in response to only particle motion and to both particle motion and sound pressure. |
(Dinh & Radford, 2021) |
Relevant studies on marine invertebrate acoustic sensitivity.
(1Octopus ocellatus has been accounted as a junior synonym of Amphioctopus fangsiao (Norman and Hochberg, 2005).
2.3 Production of sound
Marine invertebrates can produce and use sounds to reveal their presence and for a broad variety of behaviours. They can generate the sound unintentionally during moving or feeding (Radford et al., 2008; Di Iorio et al., 2012) or deliberately for communication (Salmon, 1984; Popper et al., 2001; Chitre et al., 2012) (e.g. reproduction (Lucrezi and Schlacher, 2014) or defence (Patek, 2001; Buscaino et al., 2011). The capacity to produce sounds is known in only three groups of marine invertebrates: bivalves, echinoderms and crustaceans.
Many mussels (bivalves) produce snapping sound by stretching and breaking byssal threads, which the animals use to attach themselves to hard substrates. In addition, mussels can produce sound with the valve movements (Ubirajara Gonçalves et al., 2020).When expelling water and faeces from their central inner cavity, scallops “cough” by the contraction of the two valves of their shell. In this process, scallops produce a sharp “crack” followed by a long puffing noise as the two valves close (Di Iorio et al., 2012).
Among Echinodermata, there are some examples of sound producers. The long-spined sea urchin (Diadema antillarum) produces, during movement, crackling sounds by stridulation of its stiff spines and with a special feeding structure, the Aristotle’s lantern. This animal uses the five teeth of the lantern to scrape kelp or invertebrates from the substrate. In addition, sea urchin have a calcified test that act as a resonator. The sound originated by the feeding noises of sea urchins, which frequencies are in the range of 800 to 2800 Hz, are amplified by the ovoid calcareous skeleton of urchins acting as a Helmholtz resonator (Radford et al., 2008). There is noise associated with Kina (a sea urchin from New Zeland) caused by feeding apparatus and spines and by the fluid inside the Aristotle’s lantern that produces sound by resonance. Sounds associated with grazing Kina urchins contribute to the surrounding soundscape, increasing ambient sounds level 20– 30 dB during the sunrise/sunset periods (Radford et al., 2010).
Crustaceans are the only marine invertebrates in which communication via acoustic signals is well known (Aicher and Tautz, 1990; Budelmann, 1992a; Schmitz, 2002; Buscaino et al., 2011; Staaterman et al., 2011; Edmonds et al., 2016). In marine crustacea, the production of sound has been described only in two groups – barnacles (Cirripeda) and decapods (Decapoda) – but the detection of sound is widespread. In barnacles, the sound is produced incidentally when the chitinous appendages scrape on its shells during feeding (Fish, 1967). This movement produces rhythmic crackling (Budelmann, 1992a). In decapods, stridulatory movements during which several body parts are scratched against each other produce creaky sounds on spiny lobster, crayfish, shrimps and crabs (Budelmann, 1992a). These sounds may serve to scare off potential predators (Takemura, 1971; Patek, 2002). Patek showed the slip-stick mechanism (similar to bowing a violin) in the spiny lobsters (Patek, 2001). This was the first description of this mechanism in the animal kingdom, which is similar to the system underlying pectoral spine stridulation in blue catfish (Mohajer et al., 2015).
There is scarce knowledge about which sounds are incidentally produced or used for intra/extra-species communication. Snapping shrimp produce explosive clicks (Au and Banks, 1998; Versluis et al., 2000; Kim et al., 2009). These clicks have a fundamental role in the territorial behaviour of the shrimp and are used to stun prey or interspecific opponents (Au and Banks, 1998). Crustaceans produce acoustic signals that span a wide range of frequencies (Edmonds et al., 2016). Stomatopod mantis shrimp (Hemisquilla californiensis) and American lobsters (Homarus americanus) produce low-frequency rumblings. European spiny lobsters (Palinurus elephas) emit ultrasonic signals (Patek and Caldwell, 2006; Staaterman et al., 2011). P. elephas use a stridulating organ (plectrum) and rigid file to produce audible rasps associated with anti-predator responses (Buscaino et al., 2011). Jézérel experimentally investigated the propagation features of the sounds from various sizes of European spiny lobsters (Palinurus elephas) in natural conditions (Jézéquel et al., 2020a). The sound propagation and its attenuation with the distance on European spiny lobsters varied significantly with the body size. California spiny lobsters (Palinurus interruptus) produce pulsatile rasps using frictional structures located at the base of each antenna when interacting with potential predators (Patek et al., 2009). American lobsters produce carapace vibrations (Henninger and Watson, 2005), by simultaneously contracting the antagonistic remotor and promotor muscles located at the base of the second antenna. These sounds may serve in addition as a territorial or courtship role (Stocker, 2002). Red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) produce sound signals related to a territorial role (Buscaino et al., 2012). The sound-producing and acoustic behaviour of 11 large crustacean species of North East Atlantic such as moving, feeding, mandible rubbing, swimming, species-specific behaviour were analysed (Coquereau et al., 2016a; Coquereau et al., 2016b). The male of European lobsters (Homarus gammarus) use buzzingsounds for intraspecific communication during agonistic interactions (Jézéquel et al., 2018; 2020b).
Relevant studies on sound production are detailed in Table 3.
Table 3
| Species | Common Name | Sound Type | Sound Origin | Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bivalbes | ||||
| Perna perna | brown mussel | Impulsive activities: 4–6 kHz band with a max SPL between 43 to 105 dB re 1μPa | Valve movements | (Ubirajara Gonçalves et al., 2020) |
| Pecten maximus | great scallop | Coughing sounds: 20–27 kHz | Valve movements | (Di Iorio et al., 2012) |
| Echinoderms | ||||
| Diadema antillarum | long-spined sea urchin | Crackling sounds | Stridulation of its stiff spines and Aristotle’s lantern (calcified test act as a resonator) | (Radford et al., 2008) |
| Evechinus chloroticus | Kina | Grazing sounds (800 Hz–28 kHz) | Feeding apparatus and spines Fluid inside the Aristotle’s lantern (produces sound by resonance) |
(Radford et al., 2010) |
| Crustaceans | ||||
| Cirripeda | barnacle | 1–3 ms pulses peak amplitude 70 dB (measured at 50 cm of distance) |
Chitionous appendages scrape on its shell during feeding | (Fish, 1967) |
| Linuparus trigonus | spear lobster (spiny lobster) |
2 type series of pulses: A type; slow repetition rate (10–80 times/sec) - weak at the low frequency range below 3 kHz; B type sound, powerful at low frequency. Repetition rate very high | Creaky sounds by rubbing the protuberance of the antennal coxa against the white tubercle in front of its optic stalk | (Takemura, 1971) |
|
Palunirus argus
Palinurus elephas |
spiny lobsters | Stick-and-slip’ sounds | Rubbing the base of each antenna against the antennular plate | (Patek, 2002) |
| Synalpheus paraneomeris | snapping shrimp | Explosive clicks, source levels between~175–220 dB re 1 μPa (peak–peak) @ 1 m; frequency spectrum 2-200 kHz with (peak energy at 2 kHz)) | Forceful closing of the chela (in addition to a strong jet of water) | (Au and Banks, 1998) (Kim et al., 2009) (Versluis et al., 2000) |
| Hemisquilla californiensis | mantis shrimp | Low frequency rumblings (20–60 Hz) | Vibrating their posterior mandibular remoter muscles | (Edmonds et al., 2016) |
| Palinurus elephas | European spiny lobster | Ultrasonic signals (20–55 kHz) | Stridulating organ (plectrum) and rigid file | (Patek & Caldwell, 2006) (Staaterman et al., 2011) |
| Palinurus elephas | European spiny lobster | Audible rasps in the 2–75 kHz range (15 kHz peak frequency) | Stridulating organ (plectrum) and rigid file | (Buscaino et al., 2011) |
| Panulirus interruptus | California spiny lobster | Pulsatile rasps (150.4+/-2.0 dB re 1 microPa) at distances from 0.9 to 1.4 m. | Frictional structures located at the base of each antenna | (Patek, 2002) |
| Homarus americanus | American lobster | Mean frequency of 183.1·Hz (range 87–261·Hz), range in duration from 68 to 1720·ms (mean 277.1·ms) and lead to waterborne acoustic signals | Produce carapace vibrations, by simultaneously contracting the antagonistic remotor and promotor muscles located at the base of the second antenna | (Henninger & Watson, 2005) |
| Procambarus clarkii | red swamp crayfish | Sound signals [multi-pulsed, 0.4 ms duration, 128 dB re 1 μPa (zero-peak), mean bandwidth 20 kHz] | (Buscaino et al., 2012) | |
|
Cancer pagurus
Carcinus maenas Necora puber Pachygrapsus marmoratus Galathea squamifera Lophozozymus incisus |
11 large crustacean species of NE Atlantic | Single pulse and pulse train signals distributed across a peak frequency of 3 to 45 kHz with received levels between 93 and 142 dB re 1 μPa (peak to peak) | 34 sounds were associated with behaviours such as moving, feeding, mandible rubbing, swimming, species-specific behaviour and other unidentified behaviours | (Coquereau et al., 2016b) |
|
Alpheus heterochaelis
Alpheus angulosus Alpheus sp. |
Snapping shrimp | Snaps | collapse of a cavitation bubble upon the rapid closure of their specialized snapping claw |
(Lillis et al., 2017) (Lillis & Mooney, 2018) |
| Homarus gammarus | European lobster | “Rattles” |
Rattles when feeding
|
(Jézéquel et al., 2018) |
| Homarus gammarus | European lobster | Buzzing sounds | When stressed vibrated its carapace, producing a low-frequency sound similar to ‘buzzing’ sound of the American lobster | (Jézéquel et al., 2020b) |
| Palinurus elephas | European spiny lobster | SL, at one meter from the animals, varied with size (largest SLup to 167 dB re 1 μPa2) | (Jézéquel et al., 2020a) | |
Relevant studies on sound production on marine invertebrates.
3 Effects of anthropogenic noise in marine invertebrates
Acoustic impact generally refers to activities of anthropogenic origin that generate sounds with frequencies that overlap those of the auditory range of marine organisms (Richardson et al., 1995). The underwater sounds that can affect marine biota can be differentiated between acute and chronic effects. Acute effects are those that cause immediate hearing damage or body injuries due to intense sound sources. Chronic effects are produced by prolonged exposure to moderate pressure level sounds. In addition, sounds can be differentiated between intentional (produced by seismic surveys, navy sonar, etc.) and unintentional (associated to pile-driving, shipping, harbour construction, etc.) sources whose potential effects range from behaviour changes, immediate hearing damage, body injuries or physiological trauma due to intense sound sources, to habitat degradation or expulsion from preferred habitats for prolonged periods. Much of the damage comes from the vibration of the invertebrate body created by the particle motion travelling through the water or the substrate (André et al., 2016). These impacts can affect individuals, populations or even entire ecosystems to unpredictable levels.
Relevant studies on invertebrate effects of noise are detailed in Tables 4–7.
Table 4
| Bivalves | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Common name | Stage | Sound effects | Sound source | Received Levels | Reference |
| Pecten fumatus | Southern Australian scallop | Larva |
Impaired development
Significant under development Body malformations (D-veliger larva) |
Seismic pulses playback | SEL pulse 165 dB re 1 Y/μPa2 | (Aguilar et al., 2013) |
| Pecten fumatus | Southern Australian scallop | Larva |
High Mortality
Behaviour and reflex responses disruption Permanent Immunosuppression |
Seismic airgun | Max SELcum 198 dB re 1 μPa | (Day et al., 2017) |
| Perna canaliculus | New Zealand green-lipped mussel | Larva |
Behaviour
Faster settlement with decreased size of the settlers |
Ship noise | 126 and 100 dB re 1μParms | (Wilkens et al., 2012) |
| Mytilus edulis | blue mussel | Adult |
Physiology (stress)/Behaviour
Increased clearance rates/valve movement |
Pile driving playback | SELss 153,47 dB re 1μPa | (Spiga et al., 2016) |
| Mytilus edulis | blue mussel | Adult |
Physiology (stress)
Higher breaks in the DNA Lower algal clearance rates, higher oxygen-consumption rates |
Ship noise playbacks | (Wale et al., 2019) | |
| Mytilus edulis | blue mussel | Adult |
Physiology (stress)
Changes in biochemical and immunological parameters in digestive gland |
Playback | high frequency acoustic treatment (100–200 kHz) |
(Vazzana et al., 2020a) |
| Mytilus edulis | blue mussel | Larva | Larva settlement increase | Low frequency vessel noises | 127 ± 3 dB re 1 μ Pa between 100 and 1,000 Hz | (Jolivet et al., 2016) |
| Mytilus edulis | blue mussel | Adult |
Behaviour
Reduction responsiveness over sequential exposures Mostly respond to the onset of a pulse train. |
single pulses and pulse trains (laboratory conditions) | 150 and 300 Hz tones | (Hubert et al., 2021) |
| Mytilus galloprovincialis | Mediterranean mussel | Adult |
Physiology (stress)/Behaviour
No changes in behaviour Changes in plasma and tissue biochemical parameters (glucose, total proteins, total haemocyte number (THC), heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) expression, and Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity) |
Low frequency | linear chirp 0.1-5 kHz SPL 150 dB re 1μPa rms |
(Vazzana et al., 2016) |
| Mytilus galloprovincialis | Mediterranean mussel | Adult |
Physiology (stress)
Changes in biochemical and immunological parameters in digestive gland |
Linear chirp Playback |
SPL 145-160 dB 1μPa rms high frequency acoustic treatment (100–200 kHz) |
(Vazzana et al., 2020a) |
| Magallana gigas | Pacific oyster | Adult |
Physiology
Lower growth rate (2.6 time slower) Behaviour Decreased valve activity (lower metal contamination/decreased grow) |
Cargo ship noise (with trace metal contamination, Cd) | 150 dBrms re 1μPa | (Charifi et al., 2018) |
| Ruditapes philippinarum | Manila clam | Adult |
Behaviour
Reduced maximum depth of sediment particle redistribution Reduced valve activity Effects on benthic ecosystem Physiology Tissue biochemistry effects due to perturbations in the delivery of oxygen to tissues |
Continuous Broadband Noise (CBN) and Impulsive Broadband Noise (IBN) (similar offshore shipping and construction) |
SEL 135-150 dB re 1 μPa | (Solan et al., 2016) |
| Sinonovacula solanconstricta | razor clam | Adult |
Behaviour
Avoidance response: deeper digging Physiology (stress) Changes in metabolic activity (O:N ratios) Altered expression of metabolic genes Affected activity of Ca2+/Mg2+-ATPase |
White noise and sine wave | 80 dB re 1 μPa (induced gens expression) 100 dB re 1 μPa (repressed gens expression) |
(Peng et al., 2016) |
| Cardium edule | common cockle | Adult |
Behaviour
Cockles retracted their siphons and closed the shells |
Seismic operations | (Kastelein, 2008) | |
| Paphia aurea | golden carpet shell | Adult |
Physiology (stress)
Hydrocortisone, glucose and lactate Ievel increase |
Seismic operations | 210 dB re to 1µPa | (La Bella et al., 1996) |
| Crassostrea virginica | Eastern oyster | Larva |
Behaviour
Higher levels of oyster settlement in larval cultures |
Acoustic signatures ambient reef sound | 1.5–20 kHz | (Lillis et al., 2013) |
| Crassostrea gigas | Pacific oyster | Larva |
Behaviour
No response to sound on unfed larvae Increased swimming activity fed larvae |
Natural and anthropogenic sound (laboratory conditions) | (Stocks et al., 2012) | |
| Mytilus coruscus | Korean mussel | Adult |
Physiology
reduced byssal threads secretion mechanical performances (strength, extensibility, breaking stress, toughness and failure location) wakened |
Ambient underwater condition | ∼50 dB re 1 μPa | (Zhao et al., 2021) |
|
Physiology
reduced byssal threads secretion mechanical performances (strength, extensibility, breaking stress, toughness and failure location) wakened |
Playbacks of pile-driving | ∼70 or ∼100 dB re 1 μPa | ||||
|
Placopecten
magellanicus |
giant scallop | Adult/juveniles |
Behaviour
repeated valve closures (stronger effects for juveniles) |
Pile driving sounds in field experiments | single strike levels: VH (near site = 136.60 ± 4.98 dB re (1 μm·s-2)2s, far site = 116.20 ± 4.03 dB re (1 μm·s-2)2s) IH (near site = 94.39 ± 1.34 dB re (1 μm·s-2 )2s, far site = 72.48 ± 2.51 dB re(1 μm·s-2)2.s |
(Jézéquel et al., 2022) |
| Limecola balthica | Baltic macoma Baltic clam | Adult |
Behaviour
Potential anti-burrowing stress response |
“noise eggs” | low-frequency multi-tone ~ 100 Hz – 200 Hz | (Wang et al., 2022) |
| Pecten maximus | King scallop | Larva |
Mortality
<4% mortality rates without any noise influence Physiology/Growth Interactive impact on postlarval growth between trophic environment and noise level /spectra No change in fatty acid profiles |
Pile Driving playback Drilling playback |
Pile driving (increasing levels P1, P2, P3)
SPLpp 147.6 (P1) up to 187.6 dB (P3)re 1 mPa s SEL24h 186.9 (P1) up to 215.8 dB (P3) re 1 mPa s Drilling (increasing levels D1, D2, D3) SPLrms 107.0 (D1) up to 175.4 dB (D3) re 1 mPa s SEL24h 153.4 (D1) up to 221.7 dB (D3) re 1 mPa s |
(Olivier et al., 2023) |
Relevant studies on noise impact on bivalves.
Table 5
| Cephalopods | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Common name | Stage | Sound effects | Sound source | Levels | Reference |
| Loligo vulgaris | European squid | Adult |
Damage to sensory systems
substantial, permanent, cellular damage to the statocysts and neurons |
Sinusoidal wave sweeps | 157 dB re 1 μPa (peak levels up to 175 dB re 1 μPa | (André et al., 2011) (Solé et al., 2013a) |
| Loligo vulgaris | European or common squid | Larva |
Damage to sensory systems
cellular damage to the statocysts and lateral line system |
Sinusoidal wave sweeps | 157 dB re 1 μPa (peak levels up to 175 dB re 1 μPa | (Solé et al., 2018) |
| Illex coindetii | Southern shortfin squid | Adult |
Damage to sensory systems
substantial, permanent, cellular damage to the statocysts and neurons |
Sinusoidal wave sweeps | 157 dB re 1 μPa (peak levels up to 175 dB re 1 μPa | (André et al., 2011) (Solé et al., 2013a) |
| Illex coindetii | southern shortfin squid | Larva |
Damage to sensory systems
cellular damage to the statocysts and lateral line system |
Sinusoidal wave sweeps | 157 dB re 1 μPa (peak levels up to 175 dB re 1 μPa | (Solé et al., 2018) |
| Sepioteuthis australis | southern reef squid | Adult |
Stress
Alarm responses Aggression jetting |
Seismic airgun | 168-173 dB re 1 μPa | (Fewtrell & McCauley, 2012) |
| Architeuthis dux | giant squid | Adult |
Mortality
Damage to sensory systems Nine strandings Extensive damage to internal muscle fibres, and organs including statocysts |
Seismic airgun | (Guerra et al., 2004) | |
| Sepia officinalis | common Mediterranean cuttlefish | Adult |
Damage to sensory systems
Substantial, permanent, cellular damage to the statocysts and neurons |
Sinusoidal wave sweep | 157 dB re 1 μPa (peak levels up to 175 dB re 1 μPa | (André et al., 2011) (Solé et al., 2013b) |
| Sepia officinalis | common Mediterranean cuttlefish | Adult |
Damage to sensory systems
Injuries to the statocysts the severity of the injuries was greater, the closer the distance to the sound source |
Sinusoidal wave sweep | 139-142 dB re 1 μPa2 at 1/3 octave bands centred at 315 Hz and 400 Hz (off-shore experiments) |
(Solé et al., 2017) |
| Sepia officinalis | common Mediterranean cuttlefish | Larva |
Damage to sensory systems
Cellular damage to the statocysts and lateral line system |
Sinusoidal wave sweep | 157 dB re 1 μPa (peak levels up to 175 dB re 1 μPa | (Solé et al., 2018) |
| Sepia officinalis | common Mediterranean cuttlefish | Adult |
Physiology
Changes on the statocyst endolymph proteomic composition |
Sinusoidal wave sweep | 157 dB re 1 μPa (peak levels up to 175 dB re 1 μPa | (Solé et al., 2019) |
| Sepia officinalis | common Mediterranean cuttlefish | Adult |
Behaviour
Escape responses (inking, jetting) Body patterning changes and fin movements Sound habituation |
Pure-tone pips | Pure-tone pips from 80 to 300 Hz (> 140 dB re. 1 μPa rms and 0.01 m s−2) and (Solé et al., 2022)Part. accel. of 0–17.1 m s−2 80 and 300 Hz 200Hz |
(Samson et al., 2014) |
| Sepia officinalis | common Mediterranean cuttlefish | Adult/Larva/Eggs |
Damage to sensory systems
cellular damage to the statocysts and lateral line system (adult and larva) Decreased larva survival rate Decreased hatching success |
Pile-driving playback Drilling playback |
Max. 170 dB re 1 μPa2 Max: 167 dB re 1 μPa2, |
(Solé et al., 2022) |
| Octopus vulgaris | common octopus | Adult |
Damage to sensory systems
Substantial, permanent, cellular damage to the statocysts and neurons |
Sinusoidal wave sweeps | 157 dB re 1 μPa (peak levels up to 175 dB re 1 μPa | (André et al., 2011) (Solé et al.2013a) |
Relevant studies on noise impact on cephalopods.
Table 6
| Crustaceans | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Common name | Stage | Sound effects | Sound source | Levels | Reference |
| Daphnia magna | water flea | Adult |
Behaviour
No effects on swimming speed or depth |
Ambient noise (continuous regular and irregular intermittent) | 122 dB re 1 μ Pa | (Sabet et al., 2015) |
| Palaemon serratus | common prawn | Adult |
Behaviour
Change in locomotor patterns Physiology (stress) Change in haemolymph and brain total protein content, DNA fragmentation Change in brain protein (HSP 27, HSP 70) level expression |
Boat noise (Laboratory experiments) |
Power spectrum peaks up to 140 dB re 1μPa rms in the frequency band 0.1-3 kHz | (Filiciotto et al., 2016) |
|
Litopenaeus schmitti
Farfantepenaeus subtilis Xyphopenaeus kroyeri |
southern white shrimp southern brown shrimp Atlantic Seabob |
Larva/Adult |
Catch rate
No significant deleterious impact |
Seismic survey | 635 cu. 196 dB peak re 1 μ Pa |
(Andriguetto-Filho et al., 2005) |
| Crangon crangon | southern brown shrimp | Adult |
Physiology (stress)
Significant growth and reproduction rates reduction Increased Mortality rate |
High ambient sound-level in tanks | 30 dB (25 to 400 Hz) | (Lagardère, 1982) |
| Crangon crangon | southern brown shrimp | Adult |
Behaviour
Increased cannibalism Increased food intake Physiology (stress) Increased ammonia excretion Increased O2 consumption |
High ambient sound-level in tanks | 105 dB re 1 μPa | (Regnault & Lagardere, 1983) |
| Balanus amphirite | barnacle | Larva |
Impaired development
Larva metamorphosis and settling reduction |
Low frequency sound (30Hz) | (Branscomb & Rittschof, 1984) | |
|
Jasus
edwardsii |
southern rock lobster | Larva | No effects on larva hatching and morphology | Airgun | >185 dB re 1 μPa2.s | (Day et al., 2016) |
|
Jasus
edwardsii |
southern rock lobster | Adult |
Physiology (stress) Suppressed total haemocyte count 120 days post-exposure, but biochemical haematological homeostasis resilient to seismic signals after 365days Chronic impairment of nutritional condition |
Air-gun seismic signals/controlled field experiments | (2000-40000 cu.in.) 185 dB re 1 μPa2.s at 20 m range |
(Fitzgibbon et al., 2017) |
| Nephrops norvegicus | Norway lobster | Adult |
Physiology
Tissue biochemistry effects due to perturbations in the delivery of oxygen to tissues Behaviour Reduced maximum depth of sediment particle redistribution reduced burying and bioirrigation |
Continuous Broadband Noise (CBN) and Impulsive Broadband Noise (IBN) |
135-150 dB re 1 μPa | (Solan et al., 2016) |
| Nephrops norvegicus | Norway lobster | Adult | No effects on catch or size | Air-gun seismic operations | 210 dB re to µPa/m. | (La Bella et al., 1996) |
| Homarus americanus | American lobster | Adult |
Behaviour
Increase in food intake Physiology Change in serum biochemistry Mortality No effect on delayed mortality No effects on catch |
Airgun sounds | 227 dB re 1 μPa (peak–peak) @ 1 m] at 144-169 dB re 1 μPa2/Hz average peak energy density 187 re 1 μPa2/Hz |
(Payne et al., 2008) |
|
No damage to equilibrium sensory systems
Physiology Sub-lethal physical changes in serum biochemistry and hepatopancreatic cells Behaviour changes in feeding level |
Airgun exposure on aquarium | [202 dB re 1 μPa ] at 144-169 dB re 1 μPa2/Hz | ||||
| No effects | Vessel noise | < 1kHz | ||||
|
Physiology
Increase haemolymph glucose |
Mid-frequency sonar | 1-s 1.67 kHz /2.5 to 4.0 kHz 1-s | ||||
| Palinurus elephas | European spiny lobster |
Adult |
Physiology (stress)
Total haemocyte count (THC), henoloxidase (PO) activity in cell-free haemolymph activity decreased significantly, total protein and Hsp27 expression increased significantly |
Ships noise (tank experiments) | Power spectrum peaks up to 120 dB below 10 kHz | (Celi et al., 2015) |
| Palinurus elephas | European spiny lobster |
Adult |
Behaviour
Increased locomotion Physiology Increased levels of haemolymph stress bio indicators (glucose, total protein, heat-shock proteins (HP 70), and total haemocyte count) |
Ship noise (tank experiment) | Power spectrum peaks up to 120 dB below 10 kHz | (Filiciotto et al., 2014) |
| Carcinus maenas | shore crab | Adult |
Physiology (stress)
Size-dependent response as oxygen consumption (higher metabolic rate and potentially greater stress) Behaviour Effects on feeding Behaviour (remaining immobile). Slower to retreat to shelter. Faster righting reflex |
Ship noise playback | 148–155 dB re 1 μPa Rms |
(Wale et al., 2013a) (Wale et al., 2013b) |
| Carcinus maenas | shore crab | Adult | Reduced food aggregation in crabs and released competition for shrimp | Playback of a broadband artificial sound | 129.5 to 142.0 dB re 1 μPa depending on the location | (Hubert et al., 2018) |
|
Coenobita
clypeatus |
Caribbean hermit crab | Adult |
Behaviour
Delayed response to predator risk |
Boat motor playback | 98.1 dB SPL re 1 μPa at 1 m range |
(Chan et al., 2010) |
| Pagurus bernhardus | common hermit crab | Adult |
Behaviour
Faster shell selection (critical for reproduction and survival) |
Anthropogenic noise/ playback experiments | 165 dB re 1 μPa | (Walsh et al., 2017) |
| Cancer magister | dungeness crab | Larva |
Mortality
For immediate and long-term survival and time to molting, the field experiment revealed no statistically significant effects |
Air guns (controlled field experiments) | Mean sound pressure 231 dB re 1 μPa cumulative energy density up to 251 J/M2 |
(Pearson et al., 1994) |
| Chionoecetes opilio | snow crab | Adult |
Catch rates
No change in catch (limited statistical power) |
Airgun seismic array | Max 155–163 dB re 1 μPa at 1m | (Morris et al., 2018) |
| Jasus edwardsii | rock lobster | Adult |
Behaviour
Impaired righting reflex Damage to sensory systems Damaged statocyst |
Airgun seismic array | 109–125 dB re 1 μPa | (Day et al., 2019) |
| Callinectes sapidus | blue crab | Adult |
Mortality
No effects |
Underwater explosions Vessel noise |
< 1kHz | (Moriyasu et al., 2004) |
| Callinectes sapidus | blue crab | Adult |
Behaviour
Changes competitive behaviour Physiology Increase haemolymph glucose |
Mid-frequency sonar | 1-s 1.67 kHz /2.5 to 4.0 kHz 1-s | (Hudson et al., 2022) |
| Chionoecetes opilio | snow crab | Adult |
Physiology
No significant acute effects upon adult snow crabs (haemolymph, hepatopancreas, heart, and statocysts) |
Seismic airgun | [broadband received levels 197–220 dB re 1 μPa (zero-peak)] | (Christian et al., 2003) |
| Larva | Slower developmental rates and higher mortality or abnormality rates in larvae of crabs | Seismic airgun | [224–227 dB re 1 μPa (zero-peak) @ 1 m]. peak sound levels of 216 dB re 1 μPa every 10 s for 33 min |
|||
| Chionoecetes opilio | snow crab | Adult |
Physiology
Bruised hepatopancreas and ovaries on adult crabs resultant larvae of exposed eggs were smaller than controls |
Seismic survey | (Christian et al., 2004) | |
| Austrohelice crassa | tunnelling mud crab | Larva |
Physiology
Delayed due to interference with natural sound associated with mudflats which has been shown to mediate crab metamorphosis |
Wind and tidal | 125–245 dB re 1 μPa, up to 10 kHz | (Stanley et al., 2012) |
| Hemigrapsus crenulatus | hairy-handed crab or papaka huruhuru | Larva |
Physiology
Delayed due to interference with natural sound associated with mudflats which has been shown to mediate crab metamorphosis |
Wind and tidal | 125–245 dB re 1 μPa, up to 10 kHz | (Pine et al., 2012) (Pine et al., 2016) |
|
Hemigrapsus sexdentatus
Cyclograpsus lavaux Macrophthalmus hirtipes Grapsidae |
hairy-handed crab smooth shore crab stalk-eyed mud crab |
Larva | Reductions between 34–60% metamorphosis time | Exposure to underwater reef noise | (Stanley et al., 2010) | |
| Amphibalanus amphitrite | Acorn barnacle | Larva |
Behaviour
Fails on primary settlement Physiology Delays in metamorphosis up to nearly 2 weeks |
Exposure to low frequency noise | 30 Hz but no specified level | (Branscomb & Rittschof, 1984) |
| Amphibalanus amphitrite | Acorn barnacle | Larva |
Behaviour
significantly reduced cyprid settlement |
Exposure to ultrasound (antifouling treatment) | (ultrasound - continuous sound at 23 kHz) - discontinuous sound: 5 min at 20-25 kHz/20 min pause). |
(Guo et al., 2012) |
|
Amphibalanus Amphitrite
Elminius sp. |
Acorn barnacle | Larva |
Behaviour
significantly reduced fixation rates above 260 Hz |
Exposure to low frequency sounds (fouling study) | 70-445Hz | (Choi et al., 2013) |
| Carcinus maenas | Shore crab | Adult |
Behaviour
increase in activity and antennae beats (males higher activity than females) Physiology No effects on oxygen consumption |
Geophones supported on a softly sprung frame to induce a seabed vibration | 20 Hz | (Aimon et al., 2021) |
| Lepeophtheirus salmonis | Sea lice | Adult Larva (copepodids, chalimus and pre-adults) |
Damage to sensory systems
Damaged sensory setae of the first antenna Damaged cells involved in frontal filament production Damaged nervous system |
Continuous acoustic signals (SEL at a level that induces sufficient lesions in the sensory organs to disrupt vital functions) |
Laboratory experiments: Discrete frequencies 100Hz - 1kHz Field experiments: continuous exposure to individual 350 Hz and 500 Hz signals) during, respectively, a cumulative cycle of 2 h and 1 h, played back every 4 h |
(Solé et al., 2021b) |
| Homarus gammarus | European lobster | Adult (young-of-year) |
Behaviour
Increased exploring time and decreased hiding time |
“noise eggs” | low-frequency multi-tone ~ 100 Hz | (Leiva et al., 2021) |
| Nephrops norvegicus | Norway lobster | Larva/Juvenile |
Mortality
Larval mortality, antagonistic to cadmium toxicity. Physiology Delays in larval development Behaviour differences in swimming behaviour juvenile stage. |
combination of pile driving playbacks and cadmium combined synergistically at concentrations >9.62 μg[Cd] L-1 | 170 dBpk-pk re 1 μPa |
(Stenton et al., 2022) |
| Corophium volutator | Adult |
Behaviour
lower bioturbation rates and shallower luminophore burial depths |
“noise eggs” | low-frequency multi-tone ~ 100 Hz – 200 Hz | (Wang et al., 2022) | |
| Callinectes sapidus | Blue crab | Adult |
Behaviour
No impact on olfactory-mediated foraging No cross-modal effects |
Natural sounds of predators and soundscape | Atlantic croaker (Micropogonias undulates) and red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) and marine background sounds | (Solé et al., 2023) |
|
Behaviour
No impact on olfactory-mediated foraging No cross-modal effects Physiology Righting reflex Damaged sensory statocyst epithelia No damaged antennule or eye sensory epithelia |
Sinusoidal wave sweep | 171 dB of 1 μPa2 ; max 180 dB of 1 μPa2 |
||||
Relevant studies on noise impact on crustaceans.
Table 7
| Other taxa | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Taxa | Common name | Stage | Sound effects | Sound source | Levels | Reference |
| Stylocheilus striatus | Gastropod | sea hare | Larva |
Impaired development
Reduced embryos development Increased larva mortality |
Boat noise playback (field experiment) | (Nedelec et al., 2014) | |
| Bolinus brandaris | Gastropod | purple dye murex | Adult |
Behaviour
Reduction of Motility No mortality |
Air-gun seismic operations | 210 dB re 1 µPa/m. | (La Bella et al., 1996) |
| Bembicium nanum | Gastropod | striped-mouth conniwink | Larva |
Behaviour
Increased swimming activity |
Natural and anthropogenic sound (laboratory conditions) | (Stocks et al., 2012) | |
| Pomacea maculata | Gastropod | apple snail | Adult |
Damage to sensory systems
Cellular damage to the statocysts |
Sinusoidal wave sweep | 157 dB re 1 μPa (peak levels up to 175 dB re 1 μPa | (Solé et al., 2021a) |
| Ciona intestinalis | Tunicate | sea squirt | Larva |
Physiology
Increase rate of settlement, metamorphosis and survival |
Vessel generator noise (biofouling study) | 127.5-140.6 dB re 1 μ Pa | (McDonald et al., 2014) |
| Zooplankton (copepods, Cladocera, krill) | Multiple taxa | Larva/Adult |
Mortality
Increase in dead zooplankton All immature krill (shrimp-like zooplankton) killed |
Airgun | 156 dB re 1 μ Pa2 s−1 sound exposure levels and 183 dB re 1 μ Pa peak-to-peak |
(McCauley et al., 2017) | |
| Zooplankton (Calanus sp.) | Multiple taxa | Larva/Adult |
Mortality
Increase in dead zooplankton |
Airgun | 1363 kPa, yielding SEL 221 dB re 1 mPa2 s, and 25 kPa yielding SEL 183 dB re 1 mPa2 s | (Fields et al., 2019) | |
| Bugula neritina | Bryozoan | brown bryozoan | Larva |
Behaviour
Decrease swim activities |
Boat noise (laboratory conditions) | (Stocks et al., 2012) | |
|
Amphiura
filiformis |
Echinoderm | brittle star | Adult |
Physiology
Tissue biochemistry effects due to perturbations in the delivery of oxygen to tissues Behaviour Reduced maximum depth of sediment particle redistribution |
Continuous Broadband Noise (CBN) and Impulsive Broadband Noise (IBN) |
135-150 dB re 1 μPa | (Solan et al., 2016) |
| Heliocidaris erythrogramma | Echinoderm | Australian sea urchin |
Behaviour
No differences on swimming behaviour |
Natural and anthropogenic sound (laboratory conditions) | (Stocks et al., 2012) | ||
| Arbacia lixula | Echinoderm | Black sea urchin | Adult |
Physiology
Changes in enzyme activity, expression of the HSP70 gene and protein |
Laboratory condition, linear chirp 100-200 kHz |
145-160 dB re 1 μPa rms | (Vazzana et al., 2020b) |
| Cotylorhiza tuberculate | Cnidarian | fried egg jellyfish | Adult |
Damage to sensory systems
Extruded or missing hair cells Bent, flaccid or missing kinocilia |
Sinusoidal wave sweeps | 157 dB re 1 μPa (peak levels up to 175 dB re 1 μPa | (Solé et al., 2016) |
| Rhizostoma pulmo | Cnidarian | barrel jellyfish | Adult |
Damage to sensory systems
Extruded or missing hair cells Bent, flaccid or missing kinocilia |
Sinusoidal wave sweeps | 157 dB re 1 μPa (peak levels up to 175 dB re 1 μPa | (Solé et al., 2016) |
| Styela plicata | Ascidian | pleated sea squirt | Adult |
Behaviour
increased the frequency and longevity of siphon closure events |
3 separate stimuli: boat motor, song recording, water current to simulate turbulence. | (White et al., 2021) | |
| Arenicola marina | Polychaete | lugworm sandworm | Adult |
Behaviour
Increased shallower particle burial dephts |
“noise eggs” | low-frequency multi-tone ~ 100 Hz – 200 Hz | (Wang et al., 2022) |
Relevant studies on noise impact on Gastropods, Bryozoa, Echinoderms, Cnidarians, Tunicates and zooplankton.
3.1 Early life stages
There are few scientific studies which have directly investigated the effects of low-frequency sound on larvae and other early life stages of invertebrates. Acoustic impacts can be expressed throughout the life cycle of marine invertebrates, 2/3 of whose species have a bentho-planktonic life cycle (Thorson, 1964), i.e., they have a pelagic larval stage of variable duration. This section focuses on the larval, paralarval and juvenile stages, which can exhibit developmental impact (body malformations, higher hatchlings mortality, lower hatch rate and immature hatchlings and slower growth rate) after sound exposure.
Anthropogenic sound exposure resulted in delayed hatching and development of crustaceans eggs, and impaired embryonic development or significantly increase larvae abnormality and mortality rates in crustaceans, bivalve and gastropod (Christian et al., 2003; Courtenay et al., 2009; Stanley et al., 2010; Aguilar et al., 2013; Nedelec et al., 2014). Nedelec et al. (2014) showed negative effects on sea hare Stylocheilus striatus larvae of exposure to boat noise, whilst Aguilar de Soto, 2013 found a negative impact of exposure to high levels of seismic air gun noise on Pecten novaezelandiae larvae.
Two more general studies focused on the impacts of anthropogenic noise on zooplankton or some of its permanent components (copepods, krill) as invertebrate larvae are temporarily found there (meroplankton). Fields et al. conducted an in situ experiment on seismic air gun impacts on Calanus spp. showing low mortality (Fields et al., 2019). McCauley et al. through an in situ sampling strategy estimated major impacts on zooplankton (copepods, cladocera in particular; mass mortality for krill larvae) after seismic surveys (McCauley et al., 2017). Although the results of these two works could seem contradictory, the opposite results can be explained by the size of the plankton species. McCauley et al. (2017) showed that seismic mostly affected small copepod species, while Calanus finmarchicus, the species assessed by Fields et al. (2019) is a very large species. This reinforces the idea that the effects on one species is not applicable on taxonomically near species.
A recent study suggests a critical period of increased sensitivity to acoustic trauma in three species of cephalopod hatchlings (Sepia officinalis, Loligo vulgaris and Illex coindetii) after sound exposure (Solé et al., 2018). This is the first analysis of noise damaged sensory epithelia in the statocyst and lateral line system on cephalopod hatchlings.
For decades, barnacles have been a study model of choice for research in larval ecology, particularly because of their major role in the ‘fouling’ of ship hulls. More than three decades ago, Branscomb and Rittschof (1984) demonstrated that the primary settlement of young cypris stages of Amphibalanus amphitrite fails when exposed to low-frequency noise (Branscomb & Rittschof, 1984). Testing the impact of continuous ultrasound on their larvae collected from plankton there were delays in metamorphosis, which highly reduces primary settlement of cypris larvae (Guo et al., 2012; Choi et al., 2013). This last study further reveals that the other classical components of sessile epibiosis (polychaetes, bryozoans, ascidians and algae) are not affected by these low-frequency, low intensity ultrasound. Mussel larvae could use low-frequency sounds to select the natural habitat of mussel adults in a high-energy coastal area as suggested after exposure of Mytilus edulis to boat sounds (Jolivet et al., 2016).
Many other benthic invertebrates have a free-swimming larval stage and use biotic sounds for orientation, habitat selection and settlement (Jeffs et al., 2003; Montgomery et al., 2006; Lillis et al., 2013). Anthropogenic can lead to developmental delays during the metamorphosis and settlement stages after tidal and wind turbines sound exposure (Pine et al., 2016). In this study, the times to metamorphosis of megalope larvae of the crabs Austrohelice crassa and Hemigrapsus crenulatus decreased in ambient sound recorded in a natural estuarine environment and tidal and wind turbine sounds treatments. This reduction classically corresponds to a positive effect in larval ecology but the authors also suggest that spectral composition rather than sound level is more relevant to explain the observed results.
Whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei exposed to aquaculture production system soundscapes (sound recordings of a commercial recirculating aquaculture system, RAS) showed no effects on early stages of this species probably due to a rapid habituation or higher hearing thresholds of hatchery-produced individuals, (Slater et al., 2020).
3.2 Adults
Animals under exposure to low-frequency sounds may suffer physical damage such as changes in the hearing threshold or barotraumatic ruptures. Morphological or histological analysis allows detection of physical trauma (internal injuries, sensory cell damage of statocysts, epidermal sensory cells and neurons) that can lead to death. This trauma can affect structures involved in sound perception. Invertebrates can behaviourally respond to sound (increased aggressiveness, alarm responses, predator defence, orientation, habitat selection which could have consequences for reproduction and survival). Stress bioindicators such as hormones, immune responses, heat shock proteins, cardiac physiology and overall degraded body condition are the main physiological responses. Metabolic rate, which is the most direct indicator of stress, can be measured from respiration, oxygen consumption or feeding rate. In some cases, irreversible DNA damages has been reported.
3.2.1 Physical effects
In bivalves, field studies of airgun exposure found no evidence of increased mortality in adult scallops and clams (La Bella et al., 1996; Parry et al., 2002; Harrington et al., 2010). In another field study, a dose-dependent increase scallop mortality was found four months after exposure to an airgun (Day et al., 2016). In addition, scallops exhibited abnormal reflexes that may indicate damage to mechanosensory organs (Day et al., 2017). The opposite results of these works could be explained by the time of monitoring. Harrington et al. (2010) only monitored scallops for two months, whereas Day et al. (2016) showed that significantly higher mortality rates only occurred towards the end of the 4-month period. Parry and Gason (2006) also stated that to detect mortality in such studies, very significant mortality level would be needed.
Low-frequency noise exposure causes anatomical damage in cephalopods. After an increase in the frequency of strandings in North Spain (Guerra et al., 2004), recent findings showed that exposure to artificial noise had a direct consequence on the functionality and physiology of cephalopod statocysts, which are the sensory organs responsible for equilibrium and movements in the water column (André et al., 2011; Solé et al., 2013a; Solé et al., 2013b; Solé et al., 2017). Exposure to noise was challenging the life of exposed individuals in laboratory and offshore conditions (feeding and mating cancellation and irregular swimming). Lesions present on the exposed animals were consistent with a manifestation of a massive acoustic trauma observed in vertebrate species.
Cnidarians and ctenophores, both in the polyp and the medusa stage, possess sensory organs located in their tentacles, able to detect vibration in water associated to prey movement and changes in their surrounding environment. A study described morphological effects (severe damages to the statocyst sensory epithelia) after noise exposure on two species of Mediterranean Scyphozoan medusa, Cotylorhiza tuberculata and Rhizostoma pulmo (Solé et al., 2016).
Among crustaceans, blue crabs (Callinectes sapidus) suffer mortality as a result of underwater explosions (Moriyasu et al., 2004). Although no lethal effects of underwater noise have been described for C. pagurus, Homarus gammarus or Nephrops norvegicus, sub-lethal effects of continuous, low-frequency anthropogenic noise have been reported among the Decapoda (Edmonds et al., 2016).
Although no significant effects were detected in snow crabs after exposure (Christian et al., 2003), airgun exposure caused ultrastructural statocyst damages in rock lobsters up to a year later (Day et al., 2016). In a recent study, lobsters showed impaired righting and significant damage to the sensory hairs of the statocyst after exposure equivalent to a full-scale commercial assay passing within 100–500 m (Day et al., 2019). Reflex impairment and statocyst damage persisted over the course of the experiment – up to 365 days post-exposure – and did not improve following moulting.
3.2.2 Behavioural effects
Behavioural responses, not necessarily associated with startle responses, has been observed in bivalves (e.g., valve closure and recessing reflex behaviour). These responses were used to establish thresholds of sound detection (Roberts et al., 2015). In addition to classic behavioural patterns (i.e., persistent alterations in recessing reflex behaviour), a novel flinching behaviour (a rapid retraction of the velum and then returned to position) was observed on commercial scallops (Pecten fumatus) after exposure to a seismic survey. This behaviour was observed before the acoustic wave reached the animal, suggesting that it was a response to the faster traveling ground roll wave (Day et al., 2016). Changes in scallop behaviour and reflex responses disruption were observed at least 120 days after seismic survey exposure (Day et al., 2017).
Among cephalopods, behavioural startling responses (jetting and inking) were observed in squids during seismic surveys (Fewtrell & McCauley, 2012) and in response to noise in laboratory conditionss (Samson et al., 2014). Squid show fewer alarm responses with subsequent exposure to noise from seismic surveys (Fewtrell & McCauley, 2012). This process of habituation has been observed in different species of cephalopods (McCauley et al., 2000; Samson et al., 2014; Mooney et al., 2016). While other studies also reported behavioural response to acoustic stimuli in a context of anti-predator defence (Hanlon and Budelmann, 1987; Kaifu et al., 2007); the capture of Todarodes pacificus reportedly increased in the presence of underwater sound (Maniwa, 1976). Feeding and foraging behaviour has been shown to be altered in response to different noise stimuli in cephalopods (Jones et al., 2021).
Decapod crustaceans exposed to seismic sound exhibited alarm behaviour (startle responses) when they were very near from the sound source (Goodall et al., 1990; Christian et al., 2003). Carcinus maenas subjected to boat noise were more likely to suspend their search for food, although their ability to find food was not affected (Wale et al., 2013a). Crabs subjected to boat noise took longer to find refuge than when subjected to ambient noise (Wale et al., 2013a). Increased respiration, decreasing escape responses and reduction on foraging activity in the presence of sound from its predatory species suggests that crustaceans use sound as a sensory cue for the presence of fish (Regnault and Lagardere, 1983; Hughes et al., 2014). Nephrops norvegicus showed a reduced activity, bury less deeply and flush their burrows less regularly under impulsive anthropogenic noise (Solan et al., 2016). Anthropogenic noise can modify foraging interactions, reducing food aggregation in crabs (C. maenas) and thereby release competition for shrimps (C. crangon) (Hubert et al., 2018).
Variables related to locomotion such as distance travelled, linear and angular velocity, or single events such alarm responses, intraspecific aggressive encounters and sheltering behaviour were found in crustacean species exposed to underwater noise (Celi et al., 2013; Filiciotto et al., 2014; De Vincenzi et al., 2015). Lobsters and common prawn exposed to boat noises modified their locomotor activities (distance moved, velocity, proximity with conspecific) when exposed to ship noise (Filiciotto et al., 2014; Filiciotto et al., 2016). Roberts et al. showed modification on the hermit crab (Pagurus bernardus) antennae movement under sound exposure (Roberts et al., 2016). Righting reflex (time to right itself) of the rock lobster (Jasus edwardsii) was delayed after exposure to airguns (Day et al., 2016). Shrimp Procrambarus clarkii showed decreased agonistic behaviour under frequencies between 100 and 25,000 Hz (Celi et al., 2013).
Behavioural effects on movement of snow crabs (Chionoecetes opilio) after 2D seismic noise exposure, analysed by positioning telemetry, were similar to natural vibrations, and smaller than the responses of crabs to handling, temperature and time of day (Morris et al., 2020a). Habituation to vibrations in crabs has been shown and crabs maintained in captivity for short periods of time presented greatest sensitivity to particle motion (Roberts et al., 2016).
Hermit crabs (Pagurus bernhardus show interaction of ship noise exposure with predator presence reaction, shell size and the mean duration to accept or reject the optimal empty shell (Tidau and Briffa, 2019b). Ship noise, but not loud natural ambient noise, causes adverse effects on the shore crabs (C.maenas) capacity to change the carapace colour to improve camouflage and predator escape responses (Carter et al., 2019). Bioturbation may affect intra and inter-specific behaviour on lobster (Nephrops norvegicus) and after exposure to continuous and impulsive low-frequency noise (Solan et al., 2016).
3.2.3 Physiological effects
A few studies conducted on marine bivalves exposed to sound have highlighted its effects on physiological and molecular mechanisms. Increased sound intensity result in an alteration in metabolism related genes (Peng et al., 2016) or increases in the levels of biochemical stress parameters measured in their plasma and tissues (La Bella et al., 1996; Vazzana et al., 2016; Vazzana et al., 2020a). The long-term capability of scallops to maintain homeostasis was reduced after airgun exposure (Day et al., 2016).
Among cephalopods, analysis of statocyst endolymph of the Mediterranean common cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) showed changes in the protein content immediately and 24 h after sound exposure (Solé et al., 2019). The affected proteins were mostly related to stress and cytoskeletal structure. Hemocyanin isoforms, tubulin alpha chain and intermediate filament protein were down-regulated after exposure.
Among crustaceans sub-lethal physiological changes (serum biochemistry and hepatopancreatic cells) were observed in American lobsters (H. americanus) after one month of sound exposure (Payne et al., 2007). Permanent high-level exposure to sound caused a significant reduction in the rate of growth and reproduction, an increase in the level of aggressiveness (cannibalism) and the mortality rate, and a reduction in feed intake of shrimp Crangon crangon (Lagardère, 1982; Regnault and Lagardere, 1983). Reduced growth and reproductive rates are known tertiary effects of stress response (Barton, 2002). Some crustaceans show alterations on respiration (increase on metabolic rate) in high ambient noise conditions (Regnault and Lagardere, 1983; Wale et al., 2013b). European spiny lobsters are affected by noise in both cellular and biochemical parameters. Filiciotto et al. (Filiciotto et al., 2016) found in laboratory experiments that the common prawn Palaemon serratus exhibits stress responses to playback of boat noise. In particular, noise exposure produced alterations in total protein concentrations in the haemolymph and brain, in DNA integrity, in the expression protein levels of HSP 27 and 70 in brain tissues.
Respiratory responses to noise exposure are often species-specific with some animals, such as the shore crab Carcinus maenas (Wale et al., 2013b), displaying an increased oxygen consumption in response to noise exposure, whilst others, such as the blue mussel Mytilus edulis (Wale et al., 2019) and the blood clam Tegillarca granosa (Shi et al., 2019), showing decreased respiration during noise exposure. Among the echinoderms, brittle stars (Amphiura filiformis) showed signs of physiological stress after low-frequency noise exposure (Solan et al., 2016) and in the sea urchin Arbacia lixula significant change was found in enzyme activity and in gene and protein expression of the HSP70 (Vazzana et al., 2020b).
3.3 Effects on populations and ecosystems
Noise exposure could have an enormous impact on the regional population structure of a species because of the induced emigration, unbalanced prey–predator relation, and the effects on larva development that leads to a reduced recruitment (Peng et al., 2015). Physical, behavioural and physiological effects may result in a reduction of the population within a given area that leads to a decline in the fisheries catch. Some studies analysed the effects of seismic noise exposure on regional catch rates (snow crabs in Canada (Christian et al., 2004) and rock lobsters and scallops in Australia (Parry and Gason, 2006; Harrington et al., 2010). A recent study found no negative effects on catch rates of snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio) after 3D seismic noise exposure (Morris et al., 2020b). No statistical significance was found on catch rate of different marine invertebrate groups after seismic exposure (cephalopods (La Bella et al., 1996), bivalves (Parry et al., 2002; Harrington et al., 2010), gastropods (La Bella et al., 1996; Christian et al., 2003; Parry and Gason, 2006; Boudreu et al., 2009), and stomatopods (La Bella et al., 1996).
Acoustic noise pollution can disrupt the antagonistic behaviour, the communication, the social grouping and associations (including their dominance hierarchies and mating systems) and consequently their capacity to act collectively or mate normally by altering the medium through which signals are transmitted or directly altering physiology (Fisher et al., 2021).Changes in mating behaviour and grouping behaviour are shown in crustaceans (Ruiz-Ruiz et al., 2020; Tidau and Briffa, 2019a) demonstrating noise-induced changes in social interaction. Population level could be compromise due to changes in predator avoidance behaviours, if sound exposure induces behavioural changes in prey (i.e. recessing reflex, or decreasing the time of shell selection (Walsh et al., 2017) and consequently, the predation rates increase (Chan et al., 2010). Avoidance behaviours have a greater impact than startling responses on populations that migrate from the areas where seismic surveys are conducted. More research is needed to determine if marine invertebrates avoid other types of noise or can modify their sound characteristics (e.g. amplitude, frequency, and signal timing) in the presence of noise as in some terrestrial invertebrate species, which have shown the physical ability to adjust the frequencies of their courtship signals to avoid anthropogenic masking (Cator et al., 2009) limiting the effects on their population.
4 Gaps and perspectives: The responses to noise
This review provides the current information concerning marine invertebrate bioacoustics and effects of anthropogenic noise. This effort can assist scientists, natural resource managers, industries and policy-makers to predict potential consequences of noise exposure on marine ecosystems and may allow implementing mitigation measures and define a successful strategy for a complete marine noise risk management. On the basis of this review, we identified gaps in our current knowledge on the potential effects that noise exposure may trigger in marine invertebrates:
-
(1) The biological mechanisms of sound detection and production lack of descriptive data for most species.
-
(2) Some marine invertebrate groups are very poorly investigated (i.e., annelids and echinoderms). Expanding taxonomic sampling will provide tools to identify species that are especially vulnerable to noise, including those that play an important role in local ecosystems. Priority should be devoted to biological productivity, vulnerability and sensitivity to noise exposure in addition to legal protection aspects and commercially importance of target species.
-
(3) The physical and physiological variables related to stress, energy metabolism and hormones responses need to be improved (including proteomic and metabolomics methods), especially how these changes may influence individual and population health.
-
(4) Sound impacts in populations, communities and ecosystems involves referring to sensory systems and auditory capabilities, social structure, life history, ecological role, and evolutionary adaptation. Gathering more information will help predicting noise responses of understudied species or species that could be presumably unaffected by noise because they survive in noisy habitats or possess lower hearing sensitivity to noise sources.
-
(5) There is a need to undertake and compare large-scale/long-term field and laboratory studies. Very few research studies have explored the effects of noise at large scales or over long periods of time (e.g. seasonal, yearly) due to the logistical and experimental challenges that they represent. Large-scale studies can provide interesting outputs on cumulative effects of noise exposure related to population persistence, ecological integrity, and evolutionary processes. In addition, it is necessary to increase the number of opportunities to investigate the effects of exposure to a gradient noise in contrast to the traditional research that compares quiet/noisy treatments. This would allow to determine the levels of noise at which a response is initiated and the changes in response when increasing noise levels. In laboratory studies, it is necessary to work in an acoustic environment that would be as close as possible as the invertebrate’s natural environment, particularly to what concerns particle motion effects.
-
(6) Given the short life cycle of most invertebrates, adaptation and habituation to long-term noise exposure or a potential recovery from chronic noise exposure effects are not likely to occur but this has not been investigated.
-
(7) Current literature references mostly lack of detailed metrics to interpret results. A standardised protocol in future publications should always include duration, frequency range, weighting filters applied, reference pressure used, source and received levels, distance and duration of recordings, including data on the magnitude and direction of particle motion respect to the source.
-
(8) When performing field studies, particularly under Controlled Exposure Experiments, a previous characterisation of the local soundscapes should be provided to extract the contribution of noise exposure to potential effects.
-
(9) Changes in environmental factors do not usually occur independently from other stressors. Different changes can operate simultaneously and have antagonistic or synergistic effects (in addition to noise introduction, artificial light, habitat fragmentation, global warming, acidification, etc.). The interactions between these different stressors (multistressors) must be considered when describing noise effects.
-
(10) Dose-response data is necessary to provide regulators and decision-makers with proper information.
5 Conclusions
-
(1) We reported on the current scientific knowledge on marine invertebrate bioacoustics (detection and production of sound) and their responses (physical, physiological and behavioural effects) to anthropogenic noise at different life stages, population and ecosystem levels. Although the impact of noise pollution in marine invertebrates is understudied, an exhaustive and systematic revision of literature provided evidence that anthropogenic noise is detrimental not only to these species but also to the natural ecosystems they inhabit.
-
(2) Considering that the effects of noise can be elicited from cellular to ecosystems level, the understanding of noise impact requires an interdisciplinary expertise to embrace a holistic vision of the problem.
-
(3) Further research must include a detailed protocol that would ideally provide not only accurate acoustic metrics and methods, but also long-term experiments, cumulative effects, gradients of noise exposure, potential recovery from chronic noise in a variety of taxonomic groups and noise sources.
-
(4) Multiple stressors effects have to be considered when assessing potential impacts of noise exposure.
-
(5) This review represents a valuable reference to provides guidance to natural resource managers when evaluating anthropogenic noise effects and developing future operations at temporal and spatial scales that are relevant to oceanic ecosystems.
Statements
Author contributions
MS and MA wrote a first version of the manuscript that was completed and significantly improved with the expert input of all co-authors. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Prof. Robin Cooper (Department of Biology. University of Kentucky), for kindly provide the images of Figure 5 and Dr. Youenn Jézéquel (Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution) for the 2A picture.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Aguilar de Soto N. (2016). Peer-reviewed studies on the effects of anthropogenic noise on marine invertebrates: From scallop larvae to giant squid. In Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.875, 17–26. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2981-8_3
2
Aguilar de Soto N. Delorme N. Atkins J. Howard S. Williams J. Johnson M. (2013). Anthropogenic noise causes body malformations and delays development in marine larvae. Sci. Rep.3, 1–5. doi: 10.1038/srep02831
3
Aicher B. Tautz J. (1990). Vibrational communication in the fiddler crab, Uca pugilator. J. Comp. Physiol. A166, 345–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00204807
4
Aimon C. Simpson S. D. Hazelwood R. A. Bruintjes R. Urbina M. A. (2021). Anthropogenic underwater vibrations are sensed and stressful for the shore crab Carcinus maenas. Environ. pollut.285 (April). doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117148
5
Albert D. J. (2007). Aurelia labiata medusae (Scyphozoa) in Roscoe bay avoid tidal dispersion by vertical migration. J. Sea Res.57 (4), 281–287. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2006.11.002
6
Albert D. J. (2011). What’s on the mind of a jellyfish? a review of behavioural observations on aurelia sp. jellyfish. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev.35 (3), 474–482. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.06.001
7
Akamatsu T Balastegui A Sánchez AM Castell JV . (2016). Contribution to the understanding of particle motion perception in marine invertebrates. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.875, 47–55. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2981-8_6
8
André M. Solé M. Lenoir M. Durfort M. Quero C. Mas A. et al . (2011). Low-frequency sounds induce acoustic trauma in cephalopods. Front. Ecol. Environ.9 (9). doi: 10.1890/100124
9
André M. Kaifu K. Solé M. van der Schaar M. Akamatsu T (2016). “Contribution to the understanding of particle motion perception in marine invertebrates,” In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life II. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Eds PopperA. N.HawkinsA. (New York: Springer). p. 47–55.
10
Andriguetto-Filho J. M. Ostrensky A. Pie M. R. Silva U. A. Boeger W. A. (2005). Evaluating the impact of seismic prospecting on artisanal shrimp fisheries. Continental Shelf Res.25 (14), 1720–1727. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2005.05.003
11
Anken R. H. Rahmann H. (2002). “Gravitational zoology: How animals use and cope with gravity,” in Astrobiology; the quest for the conditions of life. Eds. Horneck.G.Baumstark-KhanC. (Berlin: Springer-Verlag), 315–333.
12
Atkins D. E. Bosh K. L. Breakfield G. W. Daniels S. E. Devore M. J. Fite H. E. et al . (2021). The effect of calcium ions on mechanosensation and neuronal activity in proprioceptive neurons. NeuroSci2, 353–371. doi: 10.3390/neurosci2040026
13
Au W. W. L. Banks K. (1998). The acoustics of the snapping shrimp Synalpheus parneomeris in kaneohe bay. J. Acoust. Soc Am.103, 41–47. doi: 10.1121/1.423234
14
Barton B. A. (2002). Stress in fishes: A diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integr. Comp. Biol.42 (3), 517–525. doi: 10.1093/icb/42.3.517
15
Bezares-Calderón L. A. Berger J. Jékely G. (2020). Diversity of cilia-based mechanosensory systems and their functions in marine animal behaviour. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci.375 (1792), 65–75. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0376
16
Bone Q. Best A. C. G. (1978). Ciliated sensory cells in amphioxus (Branchiostomastoma). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K.58 (2), 479–486. doi: 10.1017/S0025315400028137
17
Bone Q. Ryan. K. (1978). Cupular sense organs in ciona (Tunicata: Ascidiacea). J. Zool.186 (3), 417–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7998.1978.tb03931.x
18
Bone Q. Ryan K. P. (1979). The langerhans receptor of oikopleura (Tunicata, larvacea). J. Mar. BioI Assoc. U. K.59, 69–75. doi: 10.1017/S002531540004618X
19
Boudreu M. Courtenay S. C. Lee K. (2009). Potential impacts of seismic energy on snow crab: An update to the September 2004 peer review. Environ. Stud. Res.178, 181.
20
Bouillon J. Philippe G. Betsch J. Bouchet P. Érard C. Ohler A. et al . (2006). An intruction to hydrozoa. MÉmoires du muséum national d’Histoire naturelle (Paris: Publications Scientifiques du Muséu).
21
Branscomb E. S. Rittschof D. (1984). An investigation of low frequency sound waves as a means of inhibiting barnacle settlement. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol.79, 149–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-0981(84)90215-6
22
Breithaupt T. (2002). Sound perception in aquatic crustaceans. Crustacean Nervous System, 548–558. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-04843-6_41
23
Brüggernann J. Ehlers U. (1981). Ultrastruktur der statocyste von Ototyphlonemertes pallida (Keferstein 1862) (Nemertini). Zoomorphology97, 75–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00310103
24
Budelmann B. V. (1979). Hair cell polarization in the gravity receptor systems of the statocysts of the cephalopods Sepia officinalis and Loligo vulgaris. Brain Res.160, 261–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90423-2
25
Budelmann B. U. (1988). “Morphological diversity of equilibrium receptor systems in aquatic invertebrates,” in Sensory biology of aquatic animals. Eds. AtemaJ.FayR. R.PopperA. N.TovalgaW. N.New York, NY: Springer, 757–782. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3714-3_30
26
Budelmann B. U. (1989). “Hydrodynamic receptor systems in invertebrates,” in The mechanosensory lateral line: Neurobiology and evolution. Eds. CoombsS.GomerP.MiinzH. (New York: Springer- Verlag).
27
Budelmann B. U. (1992). “Hearing in Crustacea,” in The evolutionary biology of hearing. Eds. PopperA. N.WebsterD. B.FayR. R.New York, NY: Springer, 131–139. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-2784-7_9
28
Budelmann B. U. (1992b). “Hearing in n onarthropod invertebrates,” in The evolutionary biology of hearing. Eds. PopperA. N.WebsterD. B.FayR. R. (New York: Springer-Verlag), 141–155.
29
Burighel P. Caicci F. Manni L. (2011). Hair cells in non-vertebrate models: Lower chordates and molluscs. Hearing Res.273 (1–2), 14–24. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2010.03.087
30
Buscaino G. Filiciotto F. Buffa G. Di Stefano V. Maccarrone V. Buscaino C. et al . (2012). The underwater acoustic activities of the red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. J. Acoustical Soc. America132 (3), 1792–1798. doi: 10.1121/1.4742744
31
Buscaino G. Filiciotto F. Gristina M. Bellante A. Buffa G. Di Stefano V. et al . (2011). Acoustic behaviour of the European spiny lobster Palinurus elephas. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.441 (November), 177–184. doi: 10.3354/meps09404
32
Bush B. M. H. Laverack M. S. (1982). “Mechanoreception,” in The biology of crustacea. , vol. 3_ neurobiology: Structure and function. Eds. SandemanD.AtwoodH. L. (New York: Academic Press), 399–468.
33
Butterfield N. Rowe P. M. Stewart E. Roesel D. Neshyba S. (2017). Quantitative three-dimensional ice roughness from scanning electron microscopy. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos.122, 3023–3041. doi: 10.1002/2016JD026094
34
Caicci F. Burighel P. Manni L. (2007). Hair cells in an ascidian (Tunicata) and their evolution in chordates. Hearing Res.231 (1–2), 63–72. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2007.05.007
35
Campbell R. D. (1972). Statocyst lacking cilia in the coelenterate Corymorpha palma. Nature238, 49–51. doi: 10.1038/238049a0
36
Carter E. E. Tregenza T. Stevens M. (2020). Ship noise inhibits colour change, camouflage, and anti-predator behaviour in shore crabs. Curr. Biol30 (5), R211–R212. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.01.014
37
Cator L. J. Arthur B. J. Harrington L. C. Hoy R. R. (2009). Harmonic convergence in the love songs of the dengue vector mosquito. Science323 (5917), 1077–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1166541
38
Celi M. Filiciotto F. Parrinello D. Buscaino G. Damiano M. A. Cuttitta A. et al . (2013). Physiological and agonistic behavioural response of Procambarus clarkii to an acoustic stimulus. J. Exp. Biol.216 (4), 709–718. doi: 10.1242/jeb.078865
39
Celi M. Filiciotto F. Vazzana M. Arizza V. Maccarrone V. Ceraulo M. et al . (2015). Shipping noise affecting immune responses of European spiny lobster (Palinurus elephas). Can. J. Zoology93 (2), 113–122. doi: 10.1139/cjz-2014-0219
40
Chan A. A. Y. H. Giraldo-Perez P. Smith S. Blumstein D. T. (2010). Anthropogenic noise affects risk assessment and attention: The distracted prey hypothesis. Biol. Lett.6 (4), 458–461. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2009.1081
41
Chapuis L. Kerr C. C. Collin S. P. Hart N. S. Sanders K. L. (2019). Underwater hearing in sea snakes (Hydrophiinae): First evidence of auditory evoked potential thresholds. J. Exp. Biol.222 (14), jeb198184. doi: 10.1242/jeb.198184
42
Charifi M. Miserazzi A. Sow M. Perrigault M. Gonzalez P. Ciret P. et al . (2018). Noise pollution limits metal bioaccumulation and growth rate in a filter feeder, the pacific oyster Magallana gigas. PloS One13 (4), 1–21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194174
43
Charifi M. Sow M. Ciret P. Benomar S. Massabuau J. C. (2017). The sense of hearing in the pacific oyster, Magallana gigas. PloS One12 (10), 1–19. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185353
44
Chitre M. Legg M. Koay T. (2012). Snapping shrimp dominated natural soundscape in Singapore waters. Contributions to Mar. Sci.2012, 127–134. Available at: https://www.tmsi.nus.edu.sg/wp-content/uploads/14_Chitre_Pg%20127-134.pdf.
45
Choi C. H. Scardino A. J. Dylejko P. G. Fletcher L. E. Juniper R. (2013). The effect of vibration frequency and amplitude on biofouling deterrence. Biofouling29 (2), 195–202. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2012.760125
46
Christian J. R. Mathieub A. Thomson D. H. White D. Buchanana R.-A. (2003). Effects of seismic energy on snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio). Environmental Research Funds Report No. 144. Calgary. 106 p. Available at: https://www.pge.com/includes/docs/pdfs/shared/edusafety/systemworks/dcpp/christian_et_al_2003_effect_of_seismic_energy_on_snow_crab.pdf.
47
Christian J. R. Mathieu A. Thomson D. H. White D. Buchanan A. (2004). Chronic effects of seismic energy on snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio). Environmental Studies Research Funds Report No. 158, Calgary, AB. Available at: https://www.esrfunds.org/sites/www.esrfunds.org/files/publications/ESRF158-ChristianMathieuBuchanan.pdf.
48
Collier K. J. Probert P. K. Jeffries M. (2016). Conservation of aquatic invertebrates: concerns, challenges and conundrums. Aquat. Conservation: Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst.26 (5), 817–837. doi: 10.1002/aqc.2710
49
Colmers W. F. (1981). Afferent synaptic connections between hair cells and the somata of intrarnacu- alar neurons in the gravity receptor system of the statocyst of Octopus vulgaris. J. Comp. Neurol.197, 385–394. doi: 10.1002/cne.901970303
50
Cooper R. L. (2008). Proprioceptive neurons of chordotonal organs in the crab, Cancer magister Dana (Decapoda, brachyura). Crustaceana81 (4), 447–475. doi: 10.1163/156854008783797499
51
Coquereau L. Grall J. Chauvaud L. Gervaise C. Clavier J. Jolivet A. et al . (2016a). Sound production and associated behaviours of benthic invertebrates from a coastal habitat in the north-east Atlantic. Mar. Biol.163 (5), 127. doi: 10.1007/s00227-016-2902-2
52
Coquereau L. Grall J. Clavier J. Jolivet A. Chauvaud L. (2016b). Acoustic behaviours of large crustaceans in NE Atlantic coastal habitats. Aquat. Biol.25, 151–163. doi: 10.3354/ab00665
53
Courtenay S. C. Boudreu M. Lee K. (2009). Potential impacts of seismic energy on snow crab: An update to the September 2004 peer review. Environ. Stud. Res. Funds Rep. No. 178, 181. Available at: https://publications.gc.ca/site/eng/9.811363/publication.html.
54
Cragg S. M. Nott J. A. (1977). Ultrastructure of statocysts in pediveliger larvae of Pecten maximus (L)-(Bivalvia). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol.27 (1), 23–36. doi: 10.1016/0022-0981(77)90051-X
55
Day R. D. McCauley R. D. Fitzgibbon Q. P. Hartmann K. Semmens J. M. (2016). Assessing the impact of marine seismic surveys on southeast Australian scallop and lobster fisheries. Australia: Fisheries Research and Development Corporation.
56
Day R. D. McCauley R. D. Fitzgibbon Q. P. Hartmann K. Semmens J. M. (2017). Exposure to seismic air gun signals causes physiological harm and alters behavior in the scallop Pecten fumatus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.114 (40), E8537–E8546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1700564114
57
Day R. D. McCauley R. D. Fitzgibbon Q. P. Hartmann K. Semmens J. M. (2019). Seismic air guns damage rock lobster mechanosensory organs and impair righting reflex. Proc. R. Soc. B.2862019142420191424. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2019.1424
58
Dekeling R. P. A. Tasker M. L. van der Graaf A. J. Ainslie M. Andersson M. H. André M. et al . (2014). Monitoring guidance noise in European common implementation strategy framework directive. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union. doi: 10.2788/27158
59
Derby C. D. (1982). Structure and function of cuticular sensilla of the lobster Homarus americanus. J. Crustacean Biol.2 (1), 1–21. doi: 10.2307/1548106
60
De Vincenzi G. Maccarrone V. Filiciotto F. Buscaino G. Mazzola S. (2015). Behavioural responses of the European spiny lobster, Palinurus elephas (Fabricius 1787), to conspecific and synthetic sounds. Crustaceana88 (5), 523–540. doi: 10.1163/15685403-00003430
61
Di Iorio L. Gervaise C. Jaud V. Robson A. A. Chauvaud L. (2012). Hydrophone detects cracking sounds: Non-intrusive monitoring of bivalve movement. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol.432–433 (November), 9–16. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2012.07.010
62
Dinh J. Radford C. (2021). Acoustic particle motion detection in the snapping shrimp (Alpheus richardsoni). J. Comp. Physiol. A207 (5), 641–655. doi: 10.1007/s00359-021-01503-4
63
Duarte C. M. Chapuis L. Collin S. P. Costa D. P. Devassy R. P. Eguiluz V. M. et al . (2021). The soundscape of the anthropocene ocean. Science371 (6529), eaba4658. doi: 10.1126/science.aba4658
64
Edmonds N. J. Firmin C. J. Goldsmith D. Faulkner R. C. Wood D. T. (2016). A review of crustacean sensitivity to high amplitude underwater noise: Data needs for effective risk assessment in relation to UK commercial species. Mar. Pollut. Bull.108 (1–2), 5–11. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.05.006
65
Ellers O. (1995). Discrimination among wave-generated sounds by a swash-riding clam. Biol. Bull.189 (2), 128–137. doi: 10.2307/1542463
66
Faggio C. (2014). Haematological and biochemical response of Mugil cephalus after acclimation to captivity. Cah. Biol. Mar.55, 31–36. Available at: https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20143079604.
67
Fazio F. Faggio C. Torre A. Sanfilippo M. Piccione G. (2013). Effect of water quality on hematological and biochemical parameters of gobius niger caught in faro lake (Sicily). Iranian J. Fisheries Sci.12 (1), 219–231. Available at: https://jifro.ir/article-1-884-en.pdf.
68
Feigenbaum D. L. (2011). Hair-fan patterns in the Chaetognatha. Can. J. Zoology56 (4), 536–546. doi: 10.1139/z78-077
69
Ferrero E. (1973). A fine structural analysis of the statocyst in Turbellaria acoeola. Zool Scr2, 5–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-6409.1973.tb00793.x
70
Fewtrell J. L. McCauley R. D. (2012). Impact of air gun noise on the behaviour of marine fish and squid. Mar. Pollut. Bull.64 (5), 984–993. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.02.009
71
Fields D. M. Handegard N. O. Dalen J. Eichner C. Malde K. Karlsen Ø. et al . (2019). Airgun blasts used in marine seismic surveys have limited effects on mortality, and no sublethal effects on behaviour or gene expression, in the copepod Calanus finmarchicus. ICES J. Mar. Sci.76 (7), 2033–2044. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsz126
72
Filiciotto F. Vazzana M. Celi M. Maccarrone V. Ceraulo M. Buffa G. et al . (2016). Underwater noise from boats: Measurement of its influence on the behaviour and biochemistry of the common prawn (Palaemon serratus, pennant 1777). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol.478 (May), 24–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2016.01.014
73
Filiciotto F. Vazzana M. Celi M. Maccarrone V. Ceraulo M. Buffa G. et al . (2014). Behavioural and biochemical stress responses of Palinurus elephas after exposure to boat noise pollution in tank. Mar. Pollut. Bull.84 (1–2), 104–114. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.05.029
74
Fish M. P. (1967). “Biological source of sustained ambient sea noise,” in Marine bio-acoustics. Ed. TavolgaW. N. (Oxford, U.K.: Pergamon Press), 175–194.
75
Fisher D. N. Kilgour R. J. Siracusa E. R. Foote J. R. Hobson E. A. Montiglio P. O. et al . (2021). Anticipated effects of abiotic environmental change on intraspecific social interactions. Biol. Rev.96 (6), 2661–2693. doi: 10.1111/brv.12772
76
Fitzgibbon Q. P. Day R. D. McCauley R. D. Simon C. J. Semmens J. M. Bulletin M. P. (2017). The impact of seismic air gun exposure on the haemolymph physiology and nutritional condition of spiny lobster lobster Jasus edwardsii. Mar. Pollut. Bull.125 (1–2), 146–156. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.08.004.%0A
77
Frings H. Frings M. (1967). “Underwater sound fields and behavior of marine invertebrates,” in Marine Bio-Acoustics. Ed. TavolgaW. N. (Oxford, U.K.: Pergamon Press), 261–282.
78
Golz R. Thurm U. (1993). Ultrastructural evidence for the occurrence of three types of mechanosensitive cells in the tentacles of the cubozoan polyp Carybdea marsupialis. Protoplasma173 (1–2), 13–22. doi: 10.1007/BF01378858
79
Golz R. Thurm U. (1994). The ciliated sensory cell of stauridiosarsia producta (Cnidaria, hydrozoa) - a nematocyst-free nematocyte? Zoomorphology114 (3), 185–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00403266
80
Goodall C. Chapman C. Neil D. (1990). “The acoustic response threshold of the Norway lobster, Nephrops norvegicus (L.) in a free sound field. In: Eds. WieseK.KrenzW. D.TautzJ.ReichertH.MulloneyB.Frontiers in Crustacean Neurobiology. Advances in Life Sciences. Birkhäuser, Basel. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-5689-8_11
81
Götz T. Hastie G. Hatch L.T. et al (2009). Overview of the impacts of anthropogenic underwater sound in the marine environment. OSPAR Commission, 134. Available at: https://tethys.pnnl.gov/sites/default/files/publications/Anthropogenic_Underwater_Sound_in_the_Marine_Environment.pdf.
82
Gray M. D. Rogers P. H. Zeddies D. G. (2016). Acoustic particle motion measurement for bioacousticians: Principles and pitfalls. Proc. Meetings Acoustics27 (1). doi: 10.1121/2.0000290
83
Guerra A. González A. F. Rocha F. (2004). “A review of the records of giant squid in the north-eastern Atlantic and severe injuries in Architeuthis dux stranded after acoustic explorations,” in ICES Annual Science Conference, Vigo, Spain, 22–25.
84
Guo S. Lee H. P. Teo S. L. M. Khoo B. C. (2012). Inhibition of barnacle cyprid settlement using low frequency and intensity ultrasound. Biofouling28 (2), 131–141. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2012.658511
85
Hall J. W. (2007). New handbook of auditory evoked responses (Boston: Pearson Education), 171–211.
86
Hanlon R. T. Budelmann B. U. (1987). Why cephalopods are probably not “Deaf ”. Am. Nat, vol. 129 (2), 312–317. doi: 10.1086/284637
87
Harrington J. J. McAllister J. Semmens J. M. (2010). Assessing the short-term impact of seismic surveys on adult commercial scallops (Pecten fumatus) in Bass Strait, Australian Fisheries Management Authority. [Contract Report] http://ecite.utas.edu.au/95126.
88
Haszprunar G. (1983). Comparative analysis of the abdominal sense organs of Pteriomorpha (Bivalvia). J. Molluscan Stud.12A, 47–50. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.mollus.a065765
89
Haszprunar G. (1985). The fine structure of the abdominal sense organs of Pteriomorpha (Mollusca, Bivalvia). J. Molluscan Stud.51, 315–319. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.mollus.a065922
90
Hawkins A. D. Hazelwood R. A. Popper A. N. Macey P. C. (2021). Substrate vibrations and their potential effects upon fishes and invertebrates. J. Acoustical Soc. America149, 2782–2790. doi: 10.1121/10.0004773
91
Hawkins A. D. Popper A. (2016). “Developing sound exposure criteria for fishes,” in PopperA. N. ed. The effects of noise on aquatic life II. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology875, 431–439. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2981-8_51
92
Hawkins A. D. Popper A. N. (2017). A sound approach to assessing the impact of underwater noise on marine fishes and invertebrates. ICES J. Mar. Sci.74 (3), 635–651. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsw205
93
Henninger H. P. Watson W. H. (2005). Mechanisms underlying the production of carapace vibrations and associated waterborne sounds in the American lobster, Homarus americanus. J. Exp. Biol.208 (17), 3421–3429. doi: 10.1242/jeb.01771
94
Hetherington T. E. (2001). Laser vibrometric studies of sound-induced motion of the body walls and lungs of salamanders and lizards: implications for lung-based hearing. J. Comp. Physiol.187, 499–507. doi: 10.1007/s003590100220
95
Hetherington T. Lindquist E. (1999). Lung-based hearing in an “earless“ anuran amphibian.” J. Comp. Physiol. A184, 395–401. doi: 10.1007/s003590050338
96
Horridge G. A. (1966). “Some recently discovered under- water vibration receptors in invertebrates,” in Some contemporary studies in marine science. Ed. BarnesH. (London: Allen and Unwin), 395–405.
97
Horridge G. A. Boulton P. S. (1967). Prey detection by Chaetognatha via a vibration sense. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci.168 (1013), 413–419. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0072
98
Hubert J. Campbell J. van der Beek J. G. den Haan M. F. Verhave R. Verkade L. S. et al . (2018). Effects of broadband sound exposure on the interaction between foraging crab and shrimp – a field study. Environ. Pollut.243 (September), 1923–1929. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.076
99
Hubert J. van Bemmelen J. J. Slabbekoorn H. (2021). No negative effects of boat sound playbacks on olfactory-mediated food finding behaviour of shore crabs in a T-maze. Environ. Pollut.270, 116184. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116184
100
Hudson D. M. Krumholz J. S. Pochtar D. L. Dickenson N. C. Dossot G. Phillips G. et al . (2022). Potential impacts from simulated vessel noise and sonar on commercially important invertebrates. PeerJ10, 1–19. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12841
101
Hughes A. R. Mann D. A. Kimbro D. L. (2014). Predatory fish sounds can alter crab foraging behaviour and influence bivalve abundance. Proc Biol Sci.281 (1788), 20140715. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2014.0715
102
Hutchison Z. L. Gill A. B. Sigray P. He H. King J. W. (2020). Anthropogenic electromagnetic fields (EMF) influence the behaviour of bottom-dwelling marine species. Sci. Rep.10 (1), 4219. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60793-x
103
Hu M. Y. Yan H. Y. Chung W. S. Shiao J. C. Hwang P. P. (2009). Acoustically evoked potentials in two cephalopods inferred using the auditory brainstem response (ABR) approach. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. - A Mol. Integr. Physiol.153 (3), 278–283. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.02.040
104
ISO/DIS (2016). 8405.2 underwater acoustics–terminology. Available at: https://www.iso.org/standard/62406.html.
105
ISO, 18405:2017 Underwater acoustics —, T . (2017) ISO 18405:2017 underwater acoustics — terminology. Available at: https://www.iso.org/standard/62406.html.
106
Jeffs A. Tolimieri N. Montgomery J. C. (2003). Crabs on cue for the coast: the use of underwater sound for orientation by pelagic stages. Mar. Freshw. Res.54, 841–845. doi: 10.1071/MF03007
107
Jézéquel Y. Bonnel J. Coston-Guarini J. Guarini J. M. Chauvaud L. (2018). Sound characterization of the European lobster Homarus gammarus in tanks. Aquat. Biol.27 (October), 13–23. doi: 10.3354/ab00692
108
Jézéquel Y. Chauvaud L. Bonnel J. (2020a). Spiny lobster sounds can be detectable over kilometres underwater. Sci. Rep.10 (1), 7943. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64830-7
109
Jézéquel Y. Cones S. Jensen F. H. Brewer H. Collins J. Mooney T. A. (2022). Pile driving repeatedly impacts the giant scallop (Placopecten magellanicus ). Sci Rep12, 15380. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19838-6
110
Jézéquel Y. Coston-Guarini J. Chauvaud L. Bonnel J. (2020b). Acoustic behaviour of male European lobsters (Homarus gammarus) during agonistic encounters. J. Exp. Biol.223 (4), jeb211276. doi: 10.1242/jeb.211276
111
Jezequel Y. Jones I. T. Bonnel J. Chauvaud L. Atema J. Mooney T. A. (2021). Sound detection by the American lobster (Homarus americanus). J. Exp. Biol.224 (6), jeb240747. doi: 10.1242/jeb.240747
112
Johansson M. W. Keyser P. Sritunyalucksana K. Söderhäll K. (2000). Crustacean haemocytes and haematopoiesis. Aquaculture191 (1–3), 45–52. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00418-X
113
Jolivet A. Tremblay R. Olivier F. Gervaise C. Sonier R. Genard B. et al . (2016). Validation of trophic and anthropic underwater noise as settlement trigger in blue mussels. Sci. Rep.6 (October 2015), 1–8. doi: 10.1038/srep33829
114
Jones I. Peyla J. Clark H. Song Z. Stanley J. Mooney T. (2021). Changes in feeding behavior of longfin squid (Doryteuthis pealeii) during laboratory exposure to pile driving noise. Mar. Environ. Res.165, 105250. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2020.105250
115
Jussila J. Jago J. Tsvetnenko E. Dunstan B. Evans L. H. (1997). Total and differential haemocyte counts in western rock lobsters (Panulirus cygnus George) under post-harvest stress. Mar. Freshw. Res.48 (8), 863–868. doi: 10.1071/MF97216
116
Kaifu K. Akamatsu T. Segawa S. (2008). Underwater sound detection by cephalopod statocyst. Fisheries Sci.74 (4), 781–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-2906.2008.01589.x
117
Kaifu K. Akamatsu T. Segawa S. (2011). Preliminary evaluation of underwater sound detection by the cephalopod statocyst using a forced oscillation model. Acoustical Sci. Technol.32 (6), 255–260. doi: 10.1250/ast.32.255
118
Kaifu K. Segawa S. Tsuchiya K. (2007). Behavioral responses to underwater sound in the small benthic octopus Octopus ocellatus. J. Mar. Acoustics Soc. Japan34 (4), 266–273. doi: 10.3135/jmasj.34.266
119
Kastak C. Kastak D. Finneran J. Houser D. Supin A. (2005). Electrophysiological methods for hearing assessment in pinnipeds. J Acoust Soc Am117 (4), 2408–2408. doi: 10.1121/1.4786197
120
Kastelein R. A. (2008). Effects of vibrations on the behaviour of cockles (bivalve molluscs). Bioacoustics17 (1–3), 74–75. doi: 10.1080/09524622.2008.9753770
121
Kim B. N. Hahn J. Choi B. K. Kim B. C. Park Y. Jung S. K. et al . (2009). Acoustic characteristics of the snapping shrimp sound observed in the coastal sea of Korea. Jpn.J. Appl. Phys.5 (7), 07. Available at: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Acoustic-Characteristics-of-Pure-Snapping-Shrimp-Kim-Hahn/2b4b7402f3a711f002aa0969cd6ac09f85bb47dd.
122
Kolle-Kralik V. Ruff P. W. (1967). Vibrotaxis von Amoeba proteus (Pallas) im vergleich mit der zilienschlagfre- quenz der beutetiere. Protistologica3, 319–323.
123
La Bella G. Cannata S. Froglia C. Ratti S. Rivas G. (1996). “First assessment of effects of air-gun seismic shooting on marine resources in the central Adriatic Sea,” in Paper presented at the SPE Health, Safety and Environment in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production Conference, New Orleans, Louisiana. Vol. 1. 227–238. doi: 10.2118/35782-MS
124
Lagardère J. P. (1982). Effects of noise on growth and reproduction of Crangon crangon in rearing tanks. Mar. Biol.71, 177–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00394627
125
Laverack M. S. (1964). The antennular sense organs of Panulirus argus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.13 (4), 301–321. doi: 10.1016/0010-406X(64)90026-X
126
Laverack M. S. (1968). On the receptors of marine invertebrates. Oceanogr Mar. Bioi Annu. Rev.6.
127
Leiva L. Scholz S. Giménez L. Boersma M. Torres G. Krone R. et al . (2021). Noisy waters can influence young-of-year lobsters ’ substrate choice and their antipredatory responses noisy waters can influence young-of-year lobsters ’ substrate choice and their antipredatory responses ☆. Environ. Pollut.291, 118108. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118108
128
Le Moullac G. Soyez C. Saulnier D. Ansquer D. Avarre J. C. Levy P. (1998). Effect of hypoxic stress on the immune response and the resistance to vibriosis of the shrimp Penaeus stylirostris. Fish Shellfish Immunol.8 (8), 621–629. doi: 10.1006/fsim.1998.0166
129
Liberge M. Barthelemy R. M. (2007). Localization of metallothionein, heat shock protein (Hsp70), and superoxide dismutase expression in Hemidiaptomus roubaui (Copepoda, Crustacea) exposed to cadmium and heat stress. Can. J. Zoology85 (3), 362–371. doi: 10.1139/Z07-009
130
Lillis A. Eggleston D. B. Bohnenstiehl D. R. (2013). Oyster larvae settle in response to habitat-associated underwater sounds. PloS One8 (10), 21–23. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079337
131
Lillis A. Mooney T. (2018). Snapping shrimp sound production patterns on Caribbean coral reefs: relationships with celestial cycles and environmental variables. Coral Reefs.7 (2), 567–607. doi: 10.1007/s00338-018-1684-z
132
Lillis A. Perelman J. N. Panyi A. Aran Mooney T. (2017). Sound production patterns of big-clawed snapping shrimp (Alpheus spp.) are influenced by time-of-day and social context. J. Acoustical Soc. Am.142 (5), 3311–3320. doi: 10.1121/1.5012751
133
Lindseth A. V. Lobel P. S. (2018). Underwater soundscape monitoring and fish bioacoustics: A review. Fishes3 (3). doi: 10.3390/fishes3030036
134
Lorenzon S. (2005). Hyperglycemic stress response in Crustacea. Invertebrate Survival J.2 (2), 132–141.
135
Lovell J. M. Findlay M. M. Moate R. M. Yan H. Y. (2005). The hearing abilities of the prawn Palaemon serratus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. - A Mol. Integr. Physiol.140 (1), 89–100. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2004.11.003
136
Lovell J. M. Moate R. M. Christiansen L. Findlay M. M. (2006). The relationship between body size and evoked potentials from the statocysts of the prawn Palaemon serratus. J. Exp. Biol.209 (13), 2480–2485. doi: 10.1242/jeb.02211
137
Lucrezi S. Schlacher T. (2014). The ecology of ghost crabs. Oceanogr Mar. Biol.52, 201–256. doi: 10.1201/b17143-5
138
Mackie G. O. Singla C. L. (2004). Cupular organs in two species of Corella (Tunicata: Ascidiacea). Invertebrate Biol.123 (3), 269–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7410.2004.tb00161.x
139
Maniwa Y. (1976). “Attraction of bony fish, squid and crab by sound,” in Sound Perception in Fish, 271–283.
140
McCauley R. D. Day R. D. Swadling K. M. Fitzgibbon Q. P. Watson R. A. Semmens J. M. (2017). Widely used marine seismic survey air gun operations negatively impact zooplankton. Nat. Ecol. Evol.1 (7), 1–8. doi: 10.1038/s41559-017-0195
141
McCauley R. D. Fewtrell J. Duncan A. J. Jenner C. Jenner M.-N. Penrose J. D. et al . (2000). Marine seismic surveys— a study of environmental implications. APPEA J.40 (1), 692. doi: 10.1071/aj99048
142
McDonald J. I. Wilkens S. L. Stanley J. A. Jeffs A. G. (2014). Vessel generator noise as a settlement cue for marine biofouling species. Biofouling30 (6), 741–749. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2014.919630
143
Mercier L. Palacios E. Campa-Córdova Á. I. Tovar-Ramírez D. Hernández-Herrera R. Racotta I. S. (2006). Metabolic and immune responses in pacific whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei exposed to a repeated handling stress. Aquaculture258 (1–4), 633–640. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.04.036
144
Mohajer Y. Ghahramani Z. Fine M. L. (2015). Pectoral sound generation in the blue catfish Ictalurus furcatus. J. Comp. Physiol. A201, 305–315. doi: 10.1007/s00359-014-0970-7
145
Montgomery J. C. Jeffs A. G. Simpson S. D. Meekan M. G. Tindle C. T. (2006). Sound as an orientation cue for the pelagic larvae of reef fish and crustaceans. Adv. Mar. Biol.51, 143–196. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2881(06)51003-X
146
Mooney T. A. Hanlon R. T. Christensen-Dalsgaard J. Madsen P. T. Ketten D. R. Nachtigall P. E. (2010). Sound detection by the longfin squid (Loligo pealeii) studied with auditory evoked potentials: Sensitivity to low-frequency particle motion and not pressure. J. Exp. Biol.213 (21), 3748–3759. doi: 10.1242/jeb.048348
147
Mooney T. A. Samson J. E. Schlunk A. D. Zacarias S. (2016). Loudness-dependent behavioral responses and habituation to sound by the longfin squid (Doryteuthis pealeii). J. Comp. Physiol. A: Neuroethology Sensory Neural Behav. Physiol.202 (7), 489–501. doi: 10.1007/s00359-016-1092-1
148
Mooney T. Yamato M. Branstetter B. (2012). Hearing in cetaceans: From natural history to experimental biology. Adv. Mar. Biol.63, 197–246. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394282-1.00004-1
149
Moriyasu M. Allain R. Benhalima K. Claytor R. Region G. Branch S. et al . (2004) Effects of seismic and marine noise on invertebrates: A literature review. Available at: https://www.mendeley.com/catalogue/6d242464-faca-3148-a3a9-3a5936920c9a/?utm_source=desktop.
150
Morris C. J. Cote D. Martin B. Kehler D. (2018). Effects of 2D seismic on the snow crab fishery. Fisheries Res.197 (September), 67–77. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2017.09.012
151
Morris C. J. Cote D. Martin S. B. Mullowney D. (2020a). Effects of 2D seismic surveying on snow crab fishery. Fisheries Res.232, 105719. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2020.105719
152
Morris C. J. Cote D. Martin S. B. Mullowney D. (2020b). Effects of 3D seismic surveying on snow crab fishery. Fisheries Res.232 (December). doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2020.105719
153
Mosher J. I. (1972). The responses of macoma balthica (bivalvia) to vibrations. Proc. Malacological Soc. London40, 125–131.
154
MSFD EU (2008). DIRECTIVE 2008/56/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 17 June 2008 establishing a framework for community action in the field of marine environmental policy (MarineStrategy framework Directive).25.6.2008. J. Eur. Union.
155
Nachtigall P. Supin A. Amundin M. Roken B. Moller T. Mooney T. et al . (2007). Polar bear Ursus maritimus hearing measured with auditory evoked potentials. J. Exp. Biol.210, 1116–1122. doi: 10.1242/jeb.02734
156
Nedelec S. L. Ainslie M. A. Andersson M. H. Cheong S-H. Halvorsen M. B. Linné M. et al (2021). Best practice guide for measurement of underwater particle motion for biological applications. Exeter, UK: University of Exeter for the IOGP Marine Sound and Life Joint Industry Programme, 89pp. & Appendices. doi: 10.25607/OBP-1726
157
Nedelec S. L. Campbell J. Radford A. N. Simpson S. D. Merchant N. D. (2016). Particle motion: the missing link in underwater acoustic ecology. Methods Ecol. Evol.7 (7), 836–842. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.12544
158
Nedelec S. L. Radford A. N. Simpson S. D. Nedelec B. Lecchini D. Mills S. C. (2014). Anthropogenic noise playback impairs embryonic development and increases mortality in a marine invertebrate. Sci. Rep.4 (Figure 1), 13–16. doi: 10.1038/srep05891
159
Norman M. D. Hochberg F. G. (2005). THE CURRENT STATE OF OCTOPUS TAXONOMY. Phuket Mar. Biol. Cent. Res. Bull.154, 127–154.
160
Olivier F. Gigot M. Mathias D. Jezequel Y. Meziane T. L'Her C. et al (2023). Assessing the impacts of anthropogenic sounds on early stages of benthic invertebrates: The “Larvosonic system”. Limnol Oceanogr Methods. doi: 10.1002/lom3.10527
161
Packard A. Karlsen H. E. Sand O. (1990). Low frequency hearing in cephalopods. J. Comp. Physiol. A166 (4), 501–505. doi: 10.1007/BF00192020
162
Parry G. D. Gason A. (2006). The effect of seismic surveys on catch rates of rock lobsters in western Victoria, Australia. Fish. Res.79, 272–284. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2006.03.023
163
Parry G. D. Heislers S. Werner G. F. Asplin M. D. Gason A. (2002). Assessment of environmental effects of seismic testing on scallop fisheries in bass strait. Victoria: Marine and Freshwater Resources Institute, 31.
164
Passano L. M. (1982). “Scyphozoa and cubozoa,” in Electrical conduction and behaviour in “Simple“ invertebrates. Ed. SheltonG. A. B.Oxford: Clarendon Press, pp. 73–148.
165
Patek S. (2001). Spiny lobsters stick and slip to make sound. Nature411, 153–154. doi: 10.1038/35075656
166
Patek S. N. (2002). Squeaking with a sliding joint: Mechanics and motor control of sound production in palinurid lobsters. J. Exp. Biol.205 (16), 2375–2385. doi: 10.1242/jeb.205.16.2375
167
Patek S. N. Caldwell R. L. (2006). The stomatopod rumble: Low frequency sound production in Hemisquilla californiensis. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol.39 (2), 99–111. doi: 10.1080/10236240600563289
168
Patek S. N. Shipp L. E. Staaterman E. R. (2009). The acoustics and acoustic behavior of the California spiny lobster (Panulirus interruptus). J. Acoustical Soc. America125 (5), 3434. doi: 10.1121/1.3097760
169
Payne J. F. Andrews C. A. Cook A. L. Christian J. R. Branch S. Canada O. (2007). Pilot study on the effects of seismic air gun noise on lobster (Homarus americanus) (St. John's Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences No. 2712).
170
Payne J. F. Andrews C. D. Fancey L. L. Guiney J. Cook A. Christian J. R. (2008). Are seismic surveys an important risk factor for fish and shellfish? Bioacoustics17, 262–265. doi: 10.1080/09524622.2008.9753842
171
Pearson W. H. Skalski J. R. Skulkin S. D. Malme C. I. (1994). Effects of seismic energy releases on the survival and development of zoeal larvae of dungeness crab (Cancer magister). Mar. Environ. Res.38 (2), 93–113. doi: 10.1016/0141-1136(94)90003-5
172
Peng C. Zhao X. Liu G. (2015). Noise in the sea and its impacts on marine organisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health12 (10), 12304–12323. doi: 10.3390/ijerph121012304
173
Peng C. Zhao X. Liu S. Shi W. Han Y. Guo C. et al . (2016). Effects of anthropogenic sound on digging behavior, metabolism, Ca 2+ /Mg 2+ ATPase activity, and metabolism-related gene expression of the bivalve sinonovacula constricta. Sci. Rep.6 (April), 1–12. doi: 10.1038/srep24266
174
Pijanowski B. C. Villanueva-Rivera L. J. Dumyahn S. L. Farina A. Krause B. L. Napoletano B. M. et al . (2011). Soundscape ecology: The science of sound in the landscape. BioScience61 (3), 203–216. doi: 10.1525/bio.2011.61.3.6
175
Pine M. K. Jeffs A. G. Radford C. A. (2012). T. sound may influence the metamorphosis behaviour of estuarine crab megalopae. P. O. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.005179
176
Pine M. K. Jeffs A. G. Radford C. A. (2016). Effects of underwater turbine noise on crab larval metamorphosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.875, 847–852. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2981-8_104
177
Piniak W. E. D. Mann D. A. Harms C. A. Jones T. T. Eckert S. A. (2016). Hearing in the juvenile green sea turtle (Chelonia mydas): A comparison of underwater and aerial hearing using auditory evoked potentials. PloS One11 (10), 1–14. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159711
178
Popper A. N. Hawkins A. D. (2019). An overview of fish bioacoustics and the impacts of anthropogenic sounds on fishes. J. Fish Biol.94 (5), 692–713. doi: 10.1111/jfb.13948
179
Popper A. N. Hawkins A. D. Thomsen F. (2020). Taking the animals’ perspective regarding anthropogenic underwater sound. Trends Ecol. Evol.35 (9), 787–794. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2020.05.002
180
Popper A. N. Salmon M. Horch K. W. (2001). Acoustic detection and communication by decapod crustaceans. J. Comp. Physiol. - A Sensory Neural Behav. Physiol.187 (2), 83–89. doi: 10.1007/s003590100184
181
Preuss T. Budelmann B. U. (1995). Proprioceptive hair cells on the neck of the squid Lolliguncula brevis:a sense organ in cephalopods for the control of head-to-body position. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci.349 (1328), 153–78. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1995.0101
182
Pye H. J. Watson W. H. (2004). Sound detection and production in the American lobster, Homarus americanus: Sensitivity range and behavioral implications. J. Acoust. Soc. Am.115, 2486–2486. doi: 10.1121/1.4782805
183
Radford C. A. Jeffs A. G. Montgomery J. C. (2007). Directional swimming behavior by five species of crab postlarvae in response to reef sound. Bull. Mar. Sci.80 (2), 369–378. Available at: https://researchspace.auckland.ac.nz/handle/2292/21315.
184
Radford C. Jeffs A. Tindle C. Montgomery J. C. (2008). Resonating sea urchin skeletons create coastal choruses. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.362 (March 2014), 37–43. doi: 10.3354/meps07444
185
Radford C. A. Stanley J. A. Tindle C. T. Montgomery J. C. Jeffs A. G. (2010). Localised coastal habitats have distinct underwater sound signatures. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.401, 21–29. doi: 10.3354/meps08451
186
Radford C. A. Tay K. Goeritz M. L. (2016). Hearing in the paddle crab, Ovalipes catharus. Proc. Mtgs. Acoust.27 (1), 010013. doi: 10.1121/2.0000259
187
Rako-Gospić N. Picciulin M. (2019). “Underwater noise: Sources and effects on marine life,” in World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation (Second Edition) Volume III: Ecological Issues and Environmental Impacts. (Elsevier Ltd), 367–389.
188
Regnault N. Lagardere J.-P. (1983). Effects of ambient noise on the metabolic level of Crangon crangon (Decapoda, natantia). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.11, 71–78. doi: 10.3354/meps011071
189
Richardson W. J. Greene C. R. Jr. Malme C. I. Thomson D. H. (1995). Marine mammals and noise (San Diego CA: Academic Press), 576 pp.
190
Roberts L. Cheesman S. Breithaupt T. Elliott M. (2015). Sensitivity of the mussel Mytilus edulis to substrate-borne vibration in relation to anthropogenically generated noise. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.538 (October), 185–195. doi: 10.3354/meps11468
191
Roberts L. Cheesman S. Elliott M. Breithaupt T. (2016). Sensitivity of Pagurus bernhardus (L.) to substrate-borne vibration and anthropogenic noise. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol.474, 185–194. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2015.09.014
192
Robinson S. P. Lepper P. A. Hazelwood R. A. (2014). Good Practice Guide for Underwater Noise Measurement, National Measurement Office, Marine Scotland. In RobinsonS. P.LepperP. A.HazelwoodR. A. Eds. The Crown Estate. NPL Good Practice Guide No. 133.
193
Rose R. D. Stokes D. R. (1981). A crustacean statocyst with only three hairs: Light and scanning electron microscopy. J. Morphology169 (1), 21–28. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051690103
194
Rossi-Durand C. Vedel J. P. (1982). Antennal proprioception in the rock lobster Palinurus vulgaris: Anatomy t."l and physiology of a bi-articular chordotonal organ. J. Comp. Physiol. A145, 505–516. doi: 10.1007/BF00612816
195
Rudenberg H. G. Rudenberg P. G. (2010). Origin and background of the invention of the electron microscope: Commentary and expanded notes on memoir of Reinhold rüdenberg. Advances in Imaging and Electron Physics160, 207–286. doi: 10.1016/S1076-5670(10)60006-7
196
Ruiz-Ruiz P. A. Hinojosa I. A. Urzua A. Urbina M. A. (2020). Anthropogenic noise disrupts mating behavior and metabolic rate in a marine invertebrate. Proc. Meetings Acoustics . Acoustical Soc. America37 (1), 040006. doi: 10.1121/2.0001302
197
Sabet S. S. Neo Y. Y. Slabbekoorn H. (2015). The effect of temporal variation in sound exposure on swimming and foraging behaviour of captive zebrafish. Anim. Behav.107, 49–60. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2015.05.022
198
Salmon M. (1984). Acoustic “calling” by fiddler and ghost crabs. Aust. Museum Memoir18 (5), 63–76. doi: 10.3853/j.0067-1967.18.1984.372
199
Salmon M. Horch K. (1972). “Sound production and acoustic detection by ocypodid crabs,” in Recent advances in the behavior of marine organisms. Eds. WinnH.Olla.B. (New York: Plenum Press), 60–96.
200
Samson J. E. Mooney T. A. Gussekloo S. W. S. Hanlon R. T. (2014). Graded behavioral responses and habituation to sound in the common cuttlefish Sepia officinalis. J. Exp. Biol.217 (24), 4347–4355. doi: 10.1242/jeb.113365
201
Sánchez A. Pascual C. Sánchez A. Vargas-Albores F. Le Moullac G. Rosas C. (2001). Hemolymph metabolic variables and immune response in litopenaeus setiferus adult males: the effect of acclimation. Aquaculture198 (1–2), 13–28. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00576-7
202
Schmitz B. (2002). “Sound production in Crustacea with special reference to the Alpheidae,” in The crustacean nervous system. Ed. WieseK. (Berlin: Springer).
203
Shi W. Han Y. Guan X. Rong J. Du X. Zha S. et al . (2019). Anthropogenic noise aggravates the toxicity of cadmium on some physiological characteristics of the blood clam Tegillarca granosa. Front. Physiol.10, 1–10. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00377
204
Slabbekoorn H. Bouton N. van Opzeeland I. Coers A. ten Cate C. Popper A. N. (2010). A noisy spring: The impact of globally rising underwater sound levels on fish. Trends Ecol. Evol.25 (7), 419–427. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2010.04.005
205
Slater M. Fricke E. Weiss M. Rebelein A. Bögner M. Preece M. et al . (2020). The impact of aquaculture soundscapes on whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and Atlantic salmon Salmo salar. Aquaculture Environ. Interacctons12, 167–177. doi: 10.3354/aei00355
206
Snyder M. J. Mulder E. P. (2001). Environmental endocrine disruption in decapod crustacean larvae: hormone titers, cytochrome P450, and stress protein responses to heptachlor exposure. Aquat. Toxicol.55 (3–4), 177–190. doi: 10.1016/S0166-445X(01)00173-4
207
Solan M. Hauton C. Godbold J. A. Wood C. L. Leighton T. G. White P. (2016). Anthropogenic sources of underwater sound can modify how sediment-dwelling invertebrates mediate ecosystem properties. Sci. Rep.6 (January), 1–9. doi: 10.1038/srep20540
208
Solé M. De Vreese S. Fortuño J.-M. van der Schaar M. Sanchez A. André M. (2022). Commercial cuttlefish exposed to noise from offshore windmill construction show short-range acoustic trauma. Environ. Pollut.312, 119853. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119853
209
Solé M. Fortuño J. M. van der Schaar M. André M. (2021a). An acoustic treatment to mitigate the effects of the apple snail on agriculture and natural ecosystems. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.9, 969. doi: 10.3390/jmse9090969
210
Solé M. Lenoir M. Durfort M. López-Bejar M. Lombarte A. André M. (2013a). Ultrastructural damage of Loligo vulgaris and Illex coindetii statocysts after low frequency sound exposure. PloS One8 (10), 1–12. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078825
211
Solé M. Lenoir M. Durfort M. López-Bejar M. Lombarte A. van der Schaar M. et al . (2013b). Does exposure to noise from human activities compromise sensory information from cephalopod statocysts? Deep-Sea Res. Part II: Topical Stud. Oceanography95, 160–181. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2012.10.006
212
Solé M. Lenoir M. Fontuño J. M. Durfort M. van der Schaar M. André M. (2016). Evidence of cnidarians sensitivity to sound after exposure to low frequency noise underwater sources. Sci. Rep.6, 37979. doi: 10.1038/srep37979
213
Solé M. Lenoir M. Fortuño J. M. De Vreese S. van der Schaar M. André M. (2021b). Sea Lice are sensitive to low frequency sounds. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.9 (7), 765. doi: 10.3390/jmse9070765
214
Solé M. Lenoir M. Fortuño J.-M. van der Schaar M. André M. (2018). A critical period of susceptibility to sound in the sensory cells of cephalopod hatchlings. Biol. Open7 (10), bio033860. doi: 10.1242/bio.033860
215
Solé M. Monge M. André M. Quero C. (2019). A proteomic analysis of the statocyst endolymph in common cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis): An assessment of acoustic trauma after exposure to sound. Sci. Rep.9 (1), 9340. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45646-6
216
Solé M. Sigray P. Lenoir M. van der Schaar M. Lalander E. André M. (2017). Offshore exposure experiments on cuttlefish indicate received sound pressure and particle motion levels associated with acoustic trauma. Sci. Rep.7, 45899. doi: 10.1038/srep45899
217
Solé M. De Vreese S. Sánchez A. M. Fortuño J. -M. van der Schaar M. Sancho N. et al (2023). Cross-sensory interference assessment after exposure to noise shows different effects in the blue crab olfactory and sound sensing capabilities. Sci. Tot Env.873, 162260. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162260
218
Sordello R. Ratel O. Flamerie De Lachapelle F. Leger C. Dambry A. (2020). Evidence of the impact of noise pollution on biodiversity: A systematic map. Environ. Evidence9, 1–27. doi: 10.1186/s13750-020-00202-y
219
Spiga I. Caldwell G. S. Bruintjes R. (2016). Influence of pile driving on the clearance rate of the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.). Proc. Meetings Acoustics27 (1). doi: 10.1121/2.0000277
220
Staaterman E. R. Clark C. W. Gallagher A. J. de Vries M. S. Claverie T. Patek S. N. (2011). Rumbling in the benthos: Acoustic ecology of the California mantis shrimp Hemisquilla californiensis. Aquat. Biol.13 (2), 97–105. doi: 10.3354/ab00361
221
Stanley J. A. Radford C. A. Jeffs A. G. (2010). Induction of settlement in crab megalopae by ambient underwater reef sound. Behav. Ecol.21 (1), 113–120. doi: 10.1093/beheco/arp159
222
Stanley J. A. Radford C. A. Jeffs A. G. (2012). Effects of underwater noise on larval settlement. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.730, 371–374. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-7311-5_84
223
Steffensen J. F. (1989). Some errors in respirometry of aquatic breathers - how to avoid and correct for them. Fish Physiol. Biochem.6, 49–59. doi: 10.1007/BF02995809
224
Steffensen J. F. Johansen K. Bushnell P. G. (1984). An automated swimming respirometer. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. - Physiol.79, 437–440. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(84)90541-3
225
Stenton C. A. Bolger E. L. Michenot M. Dodd J. A. Wale M. A. Briers R. A. et al . (2022). Effects of pile driving sound playbacks and cadmium co-exposure on the early life stage development of the Norway lobster, Nephrops norvegicus effects of pile driving sound playbacks and cadmium co-exposure on the early life stage development of the norw. Mar. Pollut. Bull.179, 113667. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113667
226
Stocker M. (2002). Fish, mollusks and other sea animals’ use of sound, and the impact of anthropogenic noise in the marine acoustic environment. J. Acoustical Soc. America112 (5), 2431–2431. doi: 10.1121/1.4779979
227
Stocks J. R. Broad A. Radford C. Minchinton T. E. Davis A. R. (2012). Response of marine invertebrate larvae to natural and anthropogenic sound: A pilot study. Open Mar. Biol. J.6 (1), 57–61. doi: 10.2174/1874450801206010057
228
Supin A. Popov V. Mass A. (2001). The sensory physiology of aquatic mammals (Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers).
229
Suzuki E. (2002). High-resolution scanning electron microscopy of immunogold-labelled cells by the use of thin plasma coating of osmium. J. Microscopy.208, 153–157. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2818.2002.01082.x
230
Takemura A. (1971). Studies on underwater sounds III. on the mechanism of sound production and the underwater sounds produced by Linuparus trigonus. Mar. Biol.9, 87. doi: 10.1007/BF00348247
231
Tamm S. L. (2014). Formation of the statolith in the ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi. Biol. Bull.227 (1), 7–18. doi: 10.1086/BBLv227n1p7
232
Tardent P. Schmid V. (1972). Ultrastructure of mechano- receptors of the polyp Coryne pintneri (Hydrozoa, athecata). Exp. Cell Res.72, 265–275. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90589-7
233
Tautz J. Sandeman D. C. (1980). The detection of waterborne vibration by sensory hairs on the chelae of the crayfish. J. Exp. Biol.88 (1), 351–356. doi: 10.1242/jeb.88.1.351
234
Thorson G. (1964). Light as an ecological factor in the dispersal and settlement of larvae of marine bottom invertebrates. Ophelia1, 167–208. doi: 10.1080/00785326.1964.10416277
235
Tidau S. Briffa M. (2019a). Anthropogenic noise pollution reverses grouping behaviour in hermit crabs. Anim. Behav.151, 113–120. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2019.03.010
236
Tidau S. Briffa M. (2019b). Distracted decision makers: Ship noise and predation risk change shell choice in hermit crabs. Behav. Ecol.30 (4), 1157–1167. doi: 10.1093/beheco/arz064
237
Ubirajara Gonçalves J. de M. Campbell D. Silveira N. Versiani L. Cumplido R. et al . (2020). Characterization of the acoustic activity of Perna perna (bivalve mollusc) under laboratory conditions. 2019 Int. Congress Ultrasonics38 (June 2020), 010010. doi: 10.1121/2.0001254
238
van der Graaf A. J. Ainslie M. A. André M. Brensing K. Dalen J. Dekeling R. P. A. et al . (2012). European Marine strategy framework directive good environmental status (MSFD-GES). Rep. Tech. Subgroup Underwater Noise Other Forms Energy, 1–75. Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/marine/pdf/MSFD_reportTSG_Noise.pdf.
239
Van der Graaf A. J. Ainslie M. A. André M. Brensing K. Dalen J. Dekeling R. P. A. et al . (2012). European Marine Strategy Framework Directive - Good Environmental Status (MSFD GES): Report of the Technical Subgroup on Underwater noise and other forms of energy.
240
Vazzana M. Celi M. Maricchiolo G. Genovese L. Corrias V. Quinci E. M. et al . (2016). Are mussels able to distinguish underwater sounds? assessment of the reactions of Mytilus galloprovincialis after exposure to lab-generated acoustic signals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A. Mol. Integr. Physiol.201, 61–70. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.06.029
241
Vazzana M. Ceraulo M. Mauro M. Papale E. Dioguardi M. Mazzola S. et al . (2020a). Effects of acoustic stimulation on biochemical parameters in the digestive gland of Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck 1819). J. Acoustical Soc. America147 (4), 2414–2422. doi: 10.1121/10.0001034
242
Vazzana M. Mauro M. Ceraulo M. Dioguardi M. Papale E. Mazzola S. et al . (2020b). Underwater high frequency noise: Biological responses in sea urchin Arbacia lixula (Linnaeus 1758). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A. Mol. Integr. Physiol.242, 110650. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2020.110650
243
Versluis M. Schmitz B. Von der Heydt A. Lohse D. (2000). How snapping shrimp snap: Through cavitating bubbles. Science289 (5487), 2114–2117. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5487.2114
244
Villanueva R. Norman M. D. (2008). “Biology of the planktonic stages of benthic octopuses,” in Oceanography and Marine Biology; An Annual Review46, 105–202. doi: 10.1201/9781420065756.ch4
245
Wale M. A. Briers R. A. Hartl M. G. J. Bryson D. Diele K. (2019). From DNA to ecological performance: Effects of anthropogenic noise on a reef-building mussel. Sci. Total Environ.689, 126–132. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.380
246
Wale M. A. Simpson S. D. Radford A. N. (2013a). Noise negatively affects foraging and antipredator behaviour in shore crabs. Anim. Behav.86 (1), 111–118. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2013.05.001
247
Wale M. A. Simpson S. D. Radford A. N. (2013b). Size-dependent physiological responses of shore crabs to single and repeated playback of ship noise. Biol. Lett.9 (2), 20121194. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2012.1194
248
Walsh E. P. Arnott G. Kunc H. P. (2017). Noise affects resource assessment in an invertebrate. Biol. Lett.13 (4). doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2017.0098
249
Wang S. V. Wrede A. Tremblay N. Beermann J. (2022). Low-frequency noise pollution impairs burrowing activities of marine benthic invertebrates low-frequency noise pollution impairs burrowing activities of marine. Environ. pollut.310 (August), 119899. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119899
250
Werner B. S. (1993). “Stamm Cnidaria, Nesseltiere,” in Lehrbuch der speziellen zoologie. Ed. KaestnerA. Fischer, Stuttgart. 734, 11–305.
251
White K. N. L. Ambrosio J. Edwards G. (2021). Anthropogenic sound in the Sea: Are ascidians affected? Gulf Caribbean Res.32 (1), 1–7. doi: 10.18785/gcr.3201.02
252
Wilkens S. Stanley J. A. Jeffs A. (2012). Induction of settlement in mussel (Perna canaliculus) larvae by vessel noise. Biofouling28 (1), 65–72. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2011.651717
253
Wilson M. Hanlon R. T. Tyack P. L. Madsen P. T. (2007). Intense ultrasonic clicks from echolocating toothed whales do not elicit anti-predator responses or debilitate the squid Loligo pelaeii. Biol. Lett.3 (3), 225–227. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2007.0005
254
Woodcock S. H. Johansen J. L. Steer M. A. Gaylard S. G. Prowse TAA Gillanders. BM (2014). Regional sustainability planning in the upper Spencer gulf investigating potential impacts of shipping on giant Australian cuttlefish. Department of the Environment, 54. Available at: https://www.adelaide.edu.au/environment/ua/media/726/investigating-potential-impacts.pdf.
255
Yan H. Y. (2002). The use of acoustically evoked potentials for the study of hearing in fishes. Bioacoustics12 (2–3), 324–328. doi: 10.1080/09524622.2002.9753736
256
Zaitseva O. V. Bocharova L. S. (1981). Sensory cells in the head skin of pond snails - fine structure of sensory endings. Cell Tissue Res.220 (4), 797–807. doi: 10.1007/BF00210463
257
Zhadan P. M. (2005). Directional sensitivity of the Japanese scallop Mizuhopecten yessoensis and swift scallop Chlamys swifti to water-borne vibrations. Russian J. Mar. Biol.31 (1), 28–35. doi: 10.1007/s11179-005-0040-7
258
Zhadan P. M. Semen’kov P. G. (1984). An electrophysiological study of the mechanoreceptory function of the abdominal sense organ of the scallop Patinopecten yessoensis (Jay). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Ser. A.78, 865–870. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(84)90647-9
259
Zhadan P. M. Sizov A. V. Dautov S. S. (2004). Ultrastructure of the abdominal sense organ of the scallop Mizuchopecten yessoensis (Jay). Cell Tissue Res.318 (3), 617–629. doi: 10.1007/s00441-004-0926-2
260
Zhao X. Sun S. Shi W. Sun X. Zhang Y. Zhu L. et al . (2021). Mussel byssal attachment weakened by anthropogenic noise. Front. Mar. Sci.8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.821019
261
Ziegler A. Bock C. Ketten D. R. Mair R. W. Mueller S. Nagelmann N. et al . (2018). Digital three-dimensional imaging techniques provide new analytical pathways for malacological research. Am. Malacological Bull.36 (2), 248–273. doi: 10.4003/006.036.0205.
Glossary
|
GLOSSARY OF TERMS 1
Marine noise pollution: Noise produced by human activities which can potentially damage marine organisms by interfering with or masking biological relevant signals, causing physiological stress, physical damage on sensory systems or behavioural reactions Vibration: Mechanical oscillation able to propagate in an elastic medium (air, water, etc.). Impulsive sound: Sound of short duration and wide frequency bandwidth reaching a rapid maximum value followed by a fast decay. (e. g. explosions, military sonar, pile driving, airgun arrays, cetacean echolocation signals). Continuous sound: Sound of a narrow frequency range that extends over long periods of time (e.g. dredging, drilling, wind turbines, tidal and wave energy devices, ships, etc.). Sound Pressure: component of the underwater sound waves consisting on the pressure fluctuations of the local hydrostatic pressure in the medium (ISO/DIS, 2016) . Particle motion: component of the underwater sound waves consisting on the back-and-forth motion of particles in the medium (ISO/DIS, 2016) |
|
GLOSSARY OF TERMS 2
Statocyst: Invertebrates internal sensory receptor that act as an equilibrium and sound/vibration perceptor system. Hydrodynamic receptor systems: Invertebrate epidermal sensory systems located all over external body surface that are used to detect movement and vibration. Lateral line system: sensory organ (analogous to fish lateral line) used to detect movement and vibration in some invertebrate larvae. Usually they are ciliated cell lines running over the head and arms. Chordotonal organs: proprioceptive organs associated with flexible articulations on the crustacean appendages that monitor joint movement, direction of movement, static position and sound perception. Stridulation: Mechanism of sound-production where the vibrations are produced by rubbing two rigid structures against each other. Dose–response: Relationship between the sound exposure level and the magnitude of the response. Physical effects: damage produced after noise exposure consisting in barotraumatic ruptures, massive internal injuries, statocyst sensory cell ultrastructural damages, epidermal sensory cells and neurons that can lead to death. Behavioural effects: changes produced in the species normal behaviour after noise exposure related to reproduction and survival, increased aggressiveness, alarm responses or predator defence. Physiological effects: changes in physiological parameters after noise exposure. Stress bioindicators such as hormones, immune responses, heat shock proteins, cardiac physiology and metabolic rate are main physiological responses to noise exposure. Cortisol (stress hormone): corticosteroid hormone or glucocorticoid involved in response to stress after sound exposure. Masking: Situation where a biological signal occurs at the same time as noise, leading to an increase of the threshold for detection by the receiver. Mitigation: Procedure to reduce harmful effects, in this case from exposure to underwater sound. |
Summary
Keywords
marine invertebrates, marine noise pollution, sound production, sound detection, noise effects, statocyst, sound pressure, particle motion
Citation
Solé M, Kaifu K, Mooney TA, Nedelec SL, Olivier F, Radford AN, Vazzana M, Wale MA, Semmens JM, Simpson SD, Buscaino G, Hawkins A, Aguilar de Soto N, Akamatsu T, Chauvaud L, Day RD, Fitzgibbon Q, McCauley RD and André M (2023) Marine invertebrates and noise. Front. Mar. Sci. 10:1129057. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1129057
Received
21 December 2022
Accepted
23 January 2023
Published
07 March 2023
Volume
10 - 2023
Edited by
Caterina Longo, University of Bari Aldo Moro, Italy
Reviewed by
José Pedro Andradem, University of Algarve, Portugal; Michael L. Fine, Virginia Commonwealth University, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2023 Solé, Kaifu, Mooney, Nedelec, Olivier, Radford, Vazzana, Wale, Semmens, Simpson, Buscaino, Hawkins, Aguilar de Soto, Akamatsu, Chauvaud, Day, Fitzgibbon, McCauley and André.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Marta Solé, marta.sole@upc.edu
This article was submitted to Marine Biology, a section of the journal Frontiers in Marine Science
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.