- 1Computer School, Beijing Information Science and Technology University, Beijing, China
- 2Shandong Changdao National Nature Reserve, Shandong, Yantai, China
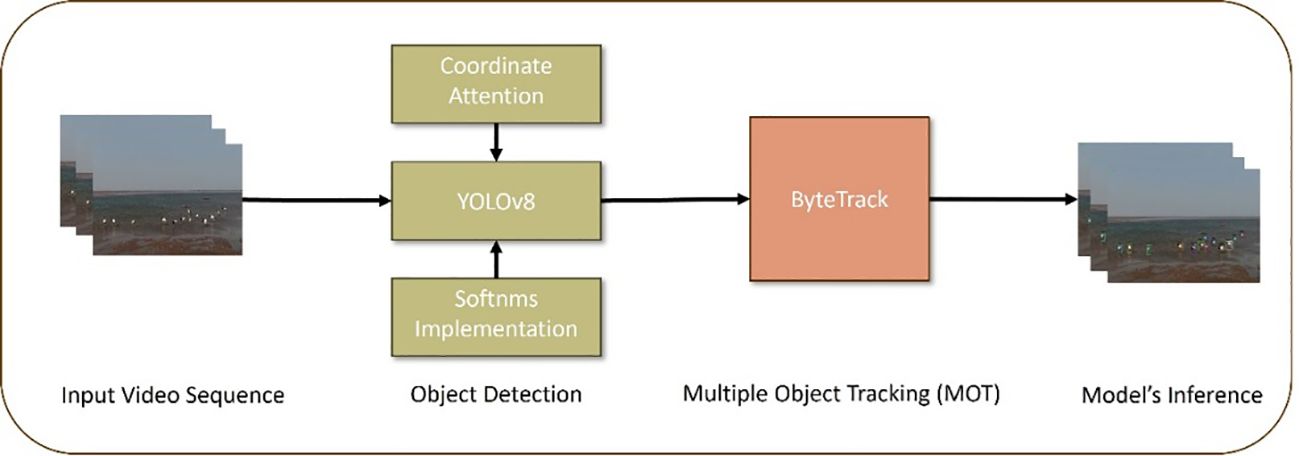
This study focuses on tracking cranes and storks to aid in wetland ecological protection. Multi-target tracking of these birds presents challenges such as frequent occlusions, sudden appearances, and disappearances. To tackle these issues, we propose a novel multi-target tracking algorithm, AviaryMOT, which utilizes a fusion technique that combines shallow and deep features to enhance tracking accuracy and effectiveness. We construct a dataset, BirdTrack, for cranes and storks tracking. In the detecting stage, we proposed Aviary Attention to effectively capture the features of birds, by integrating the Coordinate Attention into the YOLOv8 framework and applying Soft-NMS to improve detection in occluded scenarios. In the tracking stage, the BYTE data association method effectively utilizes similarities between low-score detection boxes and tracking trajectories, enabling the identification of true objects and filtering out background noise. Experimental results show that our method outperforms the state-of-art models, maintaining stable target trajectories while ensuring high-quality detection.
1 Introduction
Wetlands play a critical role in hydrological cycles, biodiversity conservation, and climate regulation, yet their ecological integrity in Pakistan is increasingly threatened by anthropogenic pressures and climate change (Aslam et al., 2023b; Aslam et al., 2024b). Remote sensing and machine learning techniques, including supervised classification, Tasseled Cap indices, and spectral analysis, have proven effective in monitoring wetland dynamics, revealing significant declines in water bodies across various regions (Aslam et al., 2023b; Aslam et al., 2024b; Aslam et al., 2024d). Studies employing advanced geospatial modeling techniques project further wetland degradation under scenarios of rising temperatures, groundwater depletion, and land-use changes (Aslam et al., 2024a; Aslam et al., 2024c). Currently, groundwater quality in urban centers faces serious challenges from industrial effluents, with contamination levels in some areas exceeding safe consumption standards; mitigation strategies involving wastewater treatment show potential to improve water quality (Naz et al., 2023; Naz et al., 2024). These findings highlight the need for integrated approaches that combine satellite data analysis, machine learning, and policy interventions to protect wetlands and water resources against increasing climatic and anthropogenic pressures (Aslam et al., 2023a; Aslam et al., 2024a; Aslam et al., 2024c).
The success of environmental monitoring through machine learning has catalyzed broader adoption of AI technologies in ecological management. This technological paradigm shift is particularly evident in advancements in computational technology and the increasing sophistication of artificial intelligence, where the trend of employing computer vision to analyze and interpret video data in place of human visual processing has become increasingly prominent. With advancements in computational technology and the increasing sophistication of artificial intelligence, the trend of employing computer vision to analyze and interpret video data in place of human visual processing has become increasingly prominent. Multi-object tracking (MOT) technology harnesses sophisticated methodologies from various domains, including pattern recognition, machine learning, computer vision, image processing, and computational applications, to enable precise localization and trajectory prediction of multiple targets. This technology holds significant promise and potential economic impact in a variety of applications, such as intelligent surveillance, behavioral analysis, human-computer interaction, sports analytics, and autonomous driving systems.
Although there has been significant development in deep learning-based multi-target tracking methods, they are all designed based on pedestrian datasets and still face some challenges when applied to multitarget tracking of crane and stork birds. The dynamic characteristics and significant deformations of birds present three main challenges for tracking. First, bird flocks exhibit higher maneuverability than ground objects due to their three-dimensional movement space and additional degrees of freedom. In addition, birds have relatively low inertia, allowing them to accelerate, decelerate, and change direction more flexibly. This, combined with complex aerodynamic effects, makes their motion even more difficult to predict. Second, birds often undergo frequent and drastic deformations during flight, primarily due to their flapping-wing locomotion. Finally, collective behavior is prevalent in bird flocks, further increasing the complexity of tracking. However, when the tracking scene switches to crane and stork bird habitats, due to the complexity of crane and stork bird movements and the ambiguity of their characteristics, these methods make it difficult to achieve good results in multi-target tracking of crane and stork birds.
To strengthen the ability of the tracking algorithm to associate inter-frame targets in complex environments and reduce mis-tracking caused by changes in crane and stork bird habitats, this paper introduces Coordinate Attention, which considers not only channel information but also direction-related positional information. Unlike 2D global pooling that transforms feature tensors into a single feature vector with channel attention, coordinate attention decomposes channel attention into two one-dimensional feature encoding processes, aggregating features along two spatial directions. In this way, remote dependency relationships can be captured along one spatial direction while precise positional information can be retained along the other spatial direction. The obtained feature maps are then separately encoded into a pair of direction-aware and position-sensitive attention maps, which can be complementary applied to input feature maps to enhance the representation of the objects of interest. Soft non-maximum suppression (soft-NMS) can be conveniently introduced into the algorithm without the need to retrain the original model, and the code implementation is easy without increasing computational overhead.
In summary, the main contributions of this paper are as follows:
1. We constructed the BirdTrack dataset for bird tracking, which is entirely sourced from real-world environments and meticulously annotated. The dataset comprises 20 video sequences, each containing an average of 16 target trajectories, and includes motion imagery of cranes and storks captured across diverse scenes, such as water surfaces, mudflats, and the sky.
2. We proposed Aviary Attention to effectively capture bird features by integrating Coordinate Attention and Soft-NMS. This led to the development of the multi-target tracking algorithm AviaryMOT, which enhances network performance. The algorithm employs a fusion technique that combines shallow and deep features to create a new feature detection layer, thereby improving the accuracy and effectiveness of convolutional neural networks in tracking bird targets.
2 Related work
2.1 Multi-object tracking
The existing MOT works primarily fall into two main categories. The first category involves detection based tracking, wherein each frame begins with target detection, utilizing a pre-existing detector to capture objects within video frames. Subsequently, features are extracted to delineate target appearance and motion, facilitating similarity value computation. During data association, targets are partitioned into distinct groups, maintaining one-to-one association constraints while employing matching algorithms to resolve data association issues and maximize overall global similarity. With the rapid advancements in detection algorithms, many methods leverage robust detectors to enhance tracking performance. The YOLO series, renowned for its efficient target detection and real-time processing capabilities, is an appealing choice for integration into tracking systems. Noteworthy for its simplicity, efficiency, and ease of deployment, it has become the most favored detector. Its balance between accuracy and speed has led to its adoption by numerous tracking algorithms. WANG et al. introduced JDE (Wang et al., 2020), which utilizes the DarkNet’s YOLOv3 framework, incorporating a ReID branch parallel to the detection branch. This branch extracts feature vectors from the output feature map, utilizing the central points of positive anchor boxes as the target’s appearance feature vectors. ZHANG et al. proposed FairMOT (Zhang et al., 2021), building upon JDE by selecting feature extraction at estimated object centers, thereby mitigating alignment issues between features extracted from coarse anchor boxes and target centers, effectively enhancing tracking algorithm performance. ByteTrack (Zhang et al., 2022) presents a simple, effective, and versatile association method, tracking nearly all detection boxes instead of solely those with high scores. For low-scoring detection boxes, similarity is utilized to recover true targets while filtering out background detections. The SORT (Bewley et al., 2016) algorithm employs a simple Kalman filter for frame-by-frame data correlation and utilizes the Hungarian algorithm for association measurement. Its simplicity enables SORT to achieve commendable performance at high frame rates. However, due to its disregard for target appearance features, SORT’s accuracy is compromised when uncertainty in target state estimation is high. Consequently, the introduction of cascaded matching and other enhancements has yielded DeepSORT (Wojke et al., 2017), which exhibits superior performance over SORT’s basic framework.
The other category integrates detection and tracking modules into a single network for multitask learning, simultaneously accomplishing object detection and tracking. Joint detection and tracking algorithms typically detect two consecutive frames in a video, employing diverse strategies to assess the similarity between targets across frames, aiding in simultaneous tracking and prediction. Prominent examples in this category include FairMOT, CenterTrack (Zhou et al., 2020), and QDTrack (Pang et al., 2021). On the other hand, Transformer-based tracking integrates Transformer architectures into multi-object tracking. Currently, there are primarily two approaches: TransTrack (Sun et al., 2020) and TrackFormer (Meinhardt et al., 2022). In TransTrack, the feature mapping of the current frame serves as the Key, while the Query comprises the combination of target features from the previous frame and the current frame. These inputs drive the operation of the entire network.
2.2 The benchmark dataset for multi-object tracking
In recent years, numerous benchmarks have been proposed. PETS2009 (Ferryman and Shahrokni, 2009) stands as one of the earliest MOT benchmark tests, comprising three video sequences for pedestrian tracking. KITTI (Geiger et al., 2013), designed for autonomous driving, consists of 50 video sequences focusing on tracking pedestrians and vehicles in traffic scenes. In addition to 2D MOT, KITTI also supports 3D MOT. UA-DETRAC (Wen et al., 2020) comprises 100 challenging sequences captured from real-world traffic scenarios. This dataset provides rich annotations for multi-object tracking, including lighting conditions, occlusion, truncation ratios, vehicle types, and bounding boxes. MOTChallenge (Dendorfer et al., 2021) encompasses a series of benchmark tests. The initial version, MOT15 (Leal-Taixé, 2015), consisting of 22 sequences, was utilized for tracking. Due to the relatively low difficulty of MOT15 videos, MOT16 (Milan, 2016) compiled 14 new, more challenging sequences. MOT17 employed the same videos as MOT16 but enhanced annotations and applied different evaluation systems. Subsequently, MOT20 (Dendorfer, 2020) was introduced for MOT in crowded scenes, featuring new sequences. MOTS (Voigtlaender et al., 2019) is a newly introduced multi-object tracking dataset. In addition to 2D bounding boxes, MOTS provides pixel masks for each target, aiming to facilitate simultaneous tracking and segmentation. BDD100K (Yu et al., 2020), recently introduced for video understanding in traffic scenes, offers multiple tasks including multi-object tracking. AnimalTrack (Zhang et al., 2022) provides a new platform dedicated to studying animal MOT.
2.3 The mechanism of attention
The attention mechanism serves as a technique to enhance the performance of network models, enabling them to focus on crucial features. The theory of attention mechanisms has established a comprehensive and mature framework in the field of deep learning. (Hu et al., 2018). introduced a Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) block to obtain weights corresponding to each channel. This is achieved by compressing features to aggregate global channel information. When SE interacts with information, the correspondence between each channel and its weight is indirect. Therefore, they designed an Effective Channel Attention (ECA) (Wang et al., 2020) by replacing the fully connected (FC) layer in SE with one-dimensional convolution with adaptive kernel sizes. (Woo et al., 2018). proposed the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM), which combines channel attention and spatial attention.
As a plug-and-play module, it can be embedded into convolutional neural networks to enhance network performance. While SE and CBAM have improved network performance, there is still room for further exploration and refinement in attention mechanisms (Liu et al., 2023). (Hou et al., 2021). found that SE and CBAM’s compressed features lose too much information. Hence, they proposed Lightweight Coordinate Attention Blocks to address this issue. (Long et al., 2015). designed a spatial attention module and a channel attention module to extend Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN), modeling semantic interdependence in spatial and channel dimensions, respectively. (Zhang et al., 2023). generated feature maps at different scales in the channel to construct a more efficient channel attention mechanism.
3 The method
We introduced Aviary Attention by integrating Coordinate Attention into YOLOv8 and applying Soft-NMS to improve detection in occluded scenarios. In the tracking stage, we used the BYTE data association method to match low-confidence detections with tracking paths, helping to identify true objects and filter out background noise. The pipeline of the proposed AviaryMOT is shown in Figure 1.
3.1 The network architecture of adaptive multi-object tracking
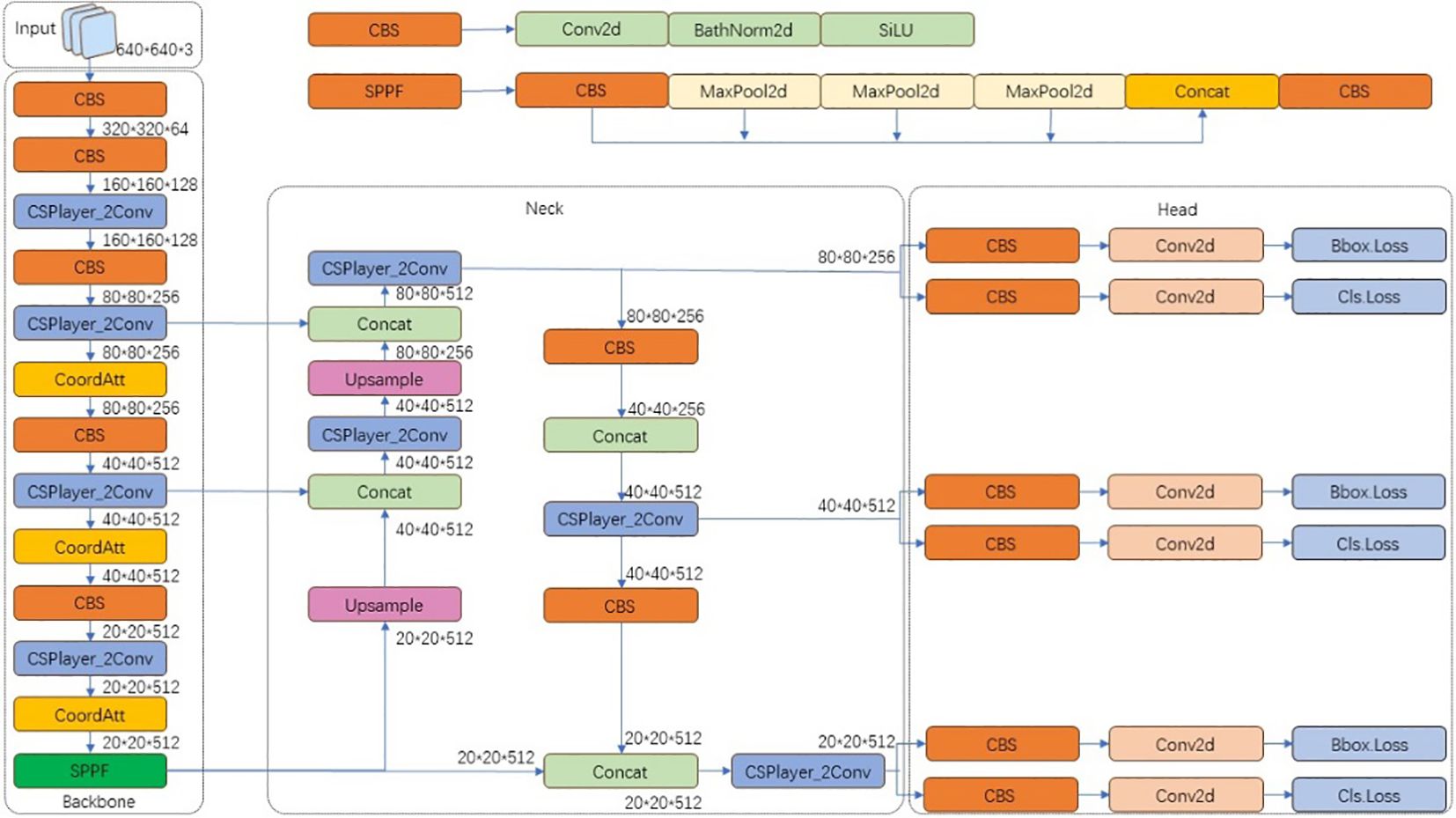
The YOLOv8 (Terven et al., 2023) detection algorithm represents a significant advancement in the YOLO series, integrating cutting-edge technologies and design principles to achieve precise and efficient object detection. Built upon the architecture of YOLOv5 (Jocher et al., 2022), YOLOv8 introduces important enhancements. The C3 module of YOLOv5 is replaced by the C2f module, drawing inspiration from the Cross Stage Partial (CSP) concept. This fusion leverages the advantages of the C3 module and the Efficient Lightweight Attention Network (ELAN) from YOLOv7 (Wang et al., 2023), resulting in fine-grained gradient insight and lightweight configuration. The backbone of YOLOv8 adopts the Spatial Pyramid Pooling Fusion (SPPF) module, employing three consecutive max-pooling layers with a size of 5 × 5. These pooled feature maps are then concatenated, effectively encompassing objects of different scales. This blueprint ensures accurate detection capability while maintaining computational efficiency. In the neck component, feature fusion is performed using the Path Aggregation Network and Feature Pyramid Network (PAN-FPN) approach. This method optimizes the integration and utilization of feature layers at different scales, thereby improving overall detection performance. The neck module seamlessly integrates two upsampling operations, multiple C2f modules, and a decoupled head structure inspired by YOLOX (Ge, 2021). This combination emphasizes target localization and classification accuracy.
YOLOv8 integrates functionalities such as pose estimation and rotated object detection by replacing the detection head while keeping the main network architecture unchanged. When adopting a two-branch detection head with shared parameters, the feature extraction capability tends to weaken. For decoupled heads, the improvement in feature extraction is more significant when detecting multiple object categories, whereas for single-class detection, a coupled head with shared parameters generally performs better since both classification and regression branches are category-dependent. To further enhance YOLOv8’s performance, our method incorporates a Coordinate Attention (CA) module into the network architecture, which strengthens multi-scale feature extraction by improving spatial awareness and emphasizing positional information, thereby optimizing the overall network structure.
To further enhance the performance of YOLOv8, this paper proposes an improved YOLOv8 algorithm that combines an attention mechanism module. This combination aims to enhance spatial awareness, focus on positional information, and optimize the network architecture. The network architecture of the proposed model is illustrated in Figure 2.
The synergistic attention mechanism consists of two consecutive steps: coordinate information embedding and coordinate attention generation. As illustrated in Figure 3, initially, two spatial ranges of the pooling kernel encode horizontal and vertical information for each channel. In the second step, a shared 1 × 1 convolutional transformation function is applied to the concatenated outputs of the two pooling layers. Subsequently, the coordinate attention divides the resulting tensor into two separate tensors, thereby generating attention vectors with the same number of channels for the input X in horizontal and vertical coordinates. This can be expressed by Equations 1–6.
where and denote pooling functions for vertical and horizontal coordinates, and and represent corresponding attention weights.
To embed positional information into channel attention, allowing the mobile network to engage in large areas while avoiding excessive computational overhead, the channel attention is decomposed into two parallel one-dimensional feature encoding processes. This effectively integrates spatial coordinate information into the generated attention map, alleviating positional information loss caused by 2D global pooling. Specifically, two one-dimensional global pooling operations are employed to aggregate input features in the vertical and horizontal directions into two independent direction-aware feature maps. These two feature maps, embedding direction-specific information, are then encoded into two attention maps, each capturing long-range spatial dependencies along one spatial direction of the input feature map. As a result, positional information is retained in the generated attention maps. Subsequently, the two attention maps are applied to the input feature map through multiplication to emphasize the representations of interest. This approach not only captures inter-channel information but also captures direction-aware and position-sensitive information, aiding the model in more accurately localizing and identifying objects of interest.
3.2 Aviary Attention Block
The Aviary Attention Block incorporates positional information into attention mechanisms, dynamically adjusting representation weights at different locations in feature maps to enhance the model’s sensitivity and modeling capability for spatial information. It introduces positional encoding to represent absolute positional information for each location in the input feature map, enabling better understanding of relative positional relationships.
The mechanism operates through two primary steps: attention weight computation and feature weighted summation. To capture precise positional attention across image dimensions, the input feature map undergoes width-wise and height-wise global average pooling:
where and . These pooled features are then concatenated and processed through a shared convolutional module with channel reduction ratio :
producing , where denotes batch normalization. The transformed features are then split and convolved to generate dimension-specific attention weights:
with representing the sigmoid activation function. The final output combines original features with these attention weights:
The comprehensive description of the Aviary Attention architecture is expressed by Equations 7-10. This architecture provides several advantages: (1) Enhanced spatial relationship modeling through explicit positional encoding, (2) Dynamic weight adjustment that improves perception of both local structures and global layouts, (3) Flexible integration requiring minimal architectural modifications, and (4) Increased model robustness by focusing computation on salient regions. The coordinate attention mechanism significantly boosts spatial representation throughout the network, improving performance across various vision tasks while maintaining parameter efficiency.
3.3 Soft-NMS implementation for Aviary Attention
In the original YOLOv8 framework, non-maximum suppression (NMS) (Neubeck and Van Gool, 2006) is utilized to refine candidate boxes. However, the selection of the NMS threshold significantly impacts the accuracy of crane and stork bird detection. An overly conservative threshold may suppress valid positive instances, while an overly lenient threshold may lead to an increase in false positive instances. Given the common occlusion issues in crane and stork bird detection, traditional NMS often results in missed detections. To overcome this limitation, we integrated Soft-NMS (Bodla et al., 2017) to enhance the detection performance of crane and stork birds in occluded scenes. Soft-NMS is tailored for closed datasets, and its mathematical expression is as follows:
Where Sirepresents the score of the i th candidate box, M and birespectively denote the coordinates of the highest scoring candidate box and the i th candidate box, the function iou(M,bi) quantifies the intersection over union ratio between the i th candidate box and M, Ntrepresents the predetermined threshold. However, Equation 11 is not a continuous function. When a bounding box overlaps with M by an iou exceeding the threshold Nt, its score undergoes a discontinuous change, resulting in significant fluctuations in the detection results. Therefore, Soft-NMS ultimately provides a more stable and continuous score resetting function as follows:
Soft-NMS improves upon the hard suppression mechanism of traditional NMS by adopting a dynamic decay strategy for overlapping bounding boxes. The process involves: first sorting detection boxes by confidence score, then adding the highest-scoring box to the result set. Instead of directly discarding remaining boxes, their scores are decayed based on IoU (Intersection over Union) with the current highest-scoring box, using either linear or Gaussian weighting.
By employing this score decay approach in Equation 12, for certain highly-scored bounding boxes, they may still be considered as correct detection boxes in subsequent computations, unlike NMS, which essentially “eliminates” them. Thus, this method can effectively enhance the model’s recall rate. The computational complexity of Soft-NMS is equivalent to that of NMS, making it a more versatile non maximum suppression method. NMS can be viewed as a binary special case of Soft-NMS.
4 Experiment
4.1 The dataset
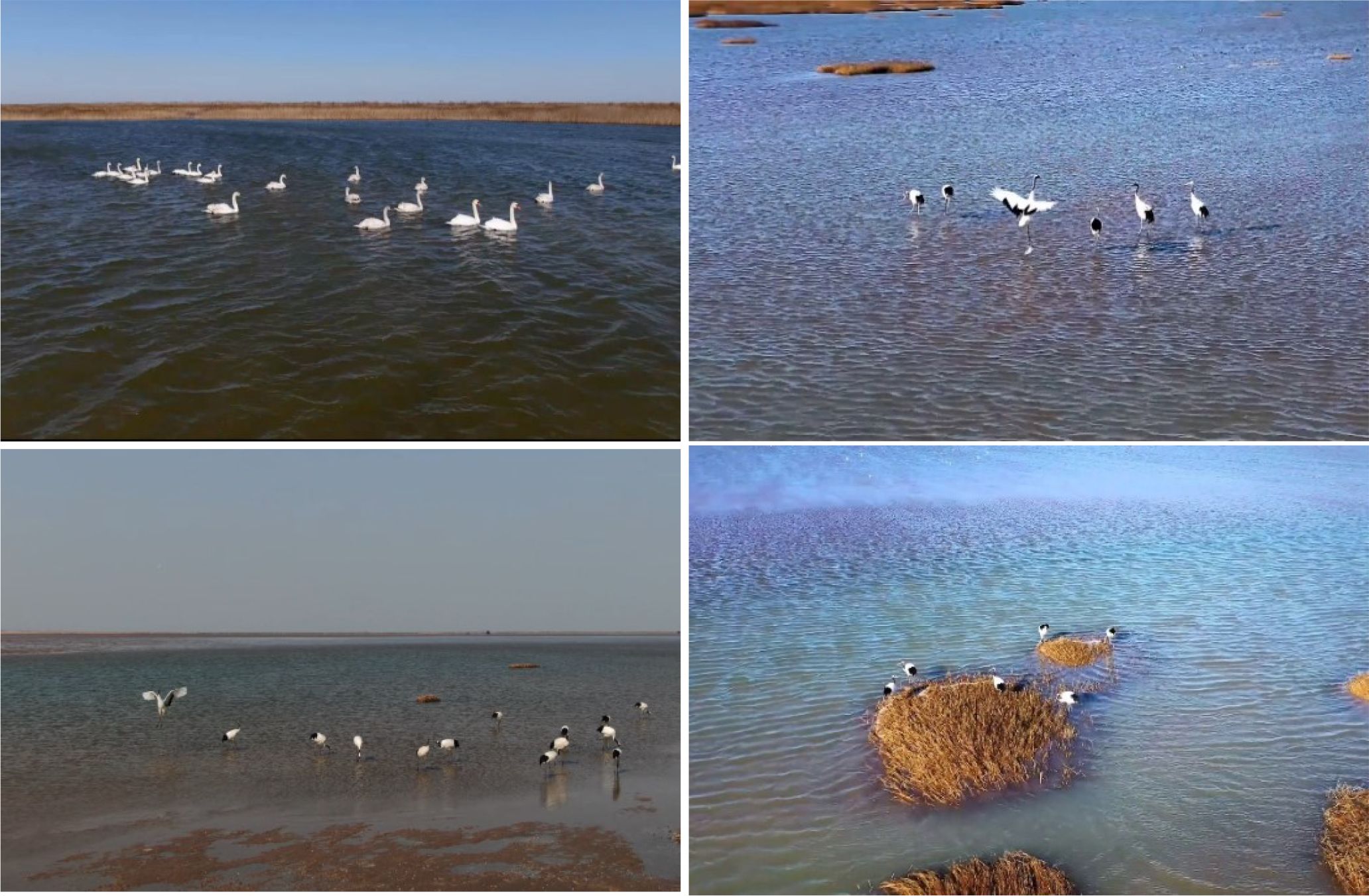
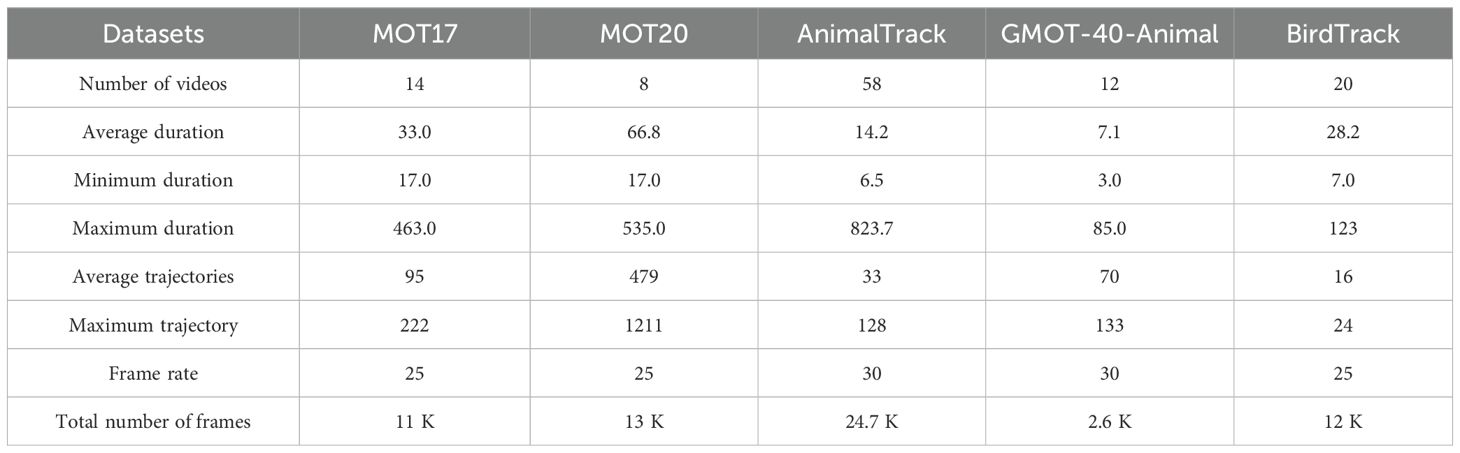
To comprehensively evaluate the multi-object tracking capabilities of the model, we conducted experiments on both our custom-built BirdTrack dataset and the publicly available MOT17 dataset. MOT17 is a representative dataset in the MOT challenge, comprising data collected from the real world and annotated. It consists of 7 training subsets and 7 validation subsets. The BirdTrack dataset is a dataset created and proposed by our team, focusing on multi-object tracking of crane and stork bird species. When constructing the dataset, BirdTrack selected videos containing a large number of crane and stork bird activities. Unlike other multi-object tracking datasets, the BirdTrack dataset aims to include only crane and stork bird species as tracking targets in the videos, excluding other objects that could be used for tracking (Luo et al., 2021). The dataset includes species of crane and stork from the Yellow River Delta, captured in their natural habitat, with no requirement for specifying the exact number of stork species. And the dataset covers field environments across different seasons and time periods, without annotations for species, age, or movement patterns.
After determining the requirements for the initial screening data, we began selecting the original video sequences that met the criteria. The main sources of video data include two aspects: one is from online sources, mainly selecting crane and stork bird activity videos from the internet with clear video quality but potential post-processing artifacts. The other is from protected area monitoring; the data collection work received strong support from the Yellow River Delta Protected Area. The protected area provided some original monitoring videos, which the production team screened and cropped to extract the required video sequences. Although the data from protected area monitoring is more authentic and reflects the natural activity patterns of crane and stork birds, the video quality is relatively poor due to limitations in the image acquisition capabilities of the monitoring equipment, with low resolution. Ultimately, the entire dataset comprises 12 video sequences, with an average length of 600 frames per video and no fewer than 10 targets appearing in each video. Table 1 compares the specific parameter details of BirdTrack with other general multi-object tracking datasets.
The dataset originates from the wetlands, collected entirely from crane and stork birds and annotated following the standard MOT dataset format, mainly detailing basic information such as video frame rate and resolution, as shown in Figure 4. It comprises a total of 16 training subsets and 4 testing subsets. In the realm of deep learning, the objective of multi-object tracking tasks is to train and evaluate deep trackers. BirdTrack focuses on multi-object tracking of crane and stork birds. When constructing the dataset, BirdTrack selected videos containing a large number of crane and stork bird activity scenes. Unlike other multi-object tracking datasets mentioned earlier, BirdTrack’s videos strive to include only crane and stork birds as tracking targets, excluding other objects that could be used for tracking. This approach not only reduces the difficulty of dataset creation but also ensures the dataset’s specialization in crane and stork bird tracking. The BirdTrack dataset is constructed to provide a dedicated benchmark for tracking crane and stork species. The following principles are adhered to in the dataset construction process:
1. Specialized Benchmark: The primary goal of BirdTrack is to offer a specialized benchmark for tracking crane and stork species. The dataset should ensure the continuity of video sequences and consistency between frames to enable accurate target tracking. Appropriate strategies should be in place to handle cases of target occlusion, disappearance, and reappearance.
2. Annotation Quality and Completeness: The quality of annotations directly affects model training outcomes and performance evaluation. Every target in the dataset should be accurately and fully annotated, including key information such as bounding boxes, categories, and IDs.
3. Diversity and Representativeness: The movement scenarios of crane and stork species are much more varied than those of humans, so the dataset should include video sequences from diverse scenes to ensure model generalization. Additionally, the dataset should be representative of typical real-world applications.
4.2 Evaluation metrics
To better compare our model’s performance with existing methods, we employ evaluation metrics identical to those used in the MOT challenge. Specifically, the metrics used include High-Order Tracking Accuracy (HOTA), Multi-Object Tracking Accuracy (MOTA), Identity Switches (IDS), Identity F1 Score (IDF1), False Positives (FP), and False Negatives (FN). Among these metrics, MOTA is the most widely used and closely represents human visual assessment. A higher MOTA indicates that the proposed method has the ability to balance various factors. HOTA comprehensively evaluates the performance of detection and data association. IDF1 focuses more on association performance, with a higher IDF1 score indicating that most of an object’s images are mapped to the same identity. FP and FN are defined as the number of incorrect targets and missed correct targets, respectively.
4.3 Experimental details
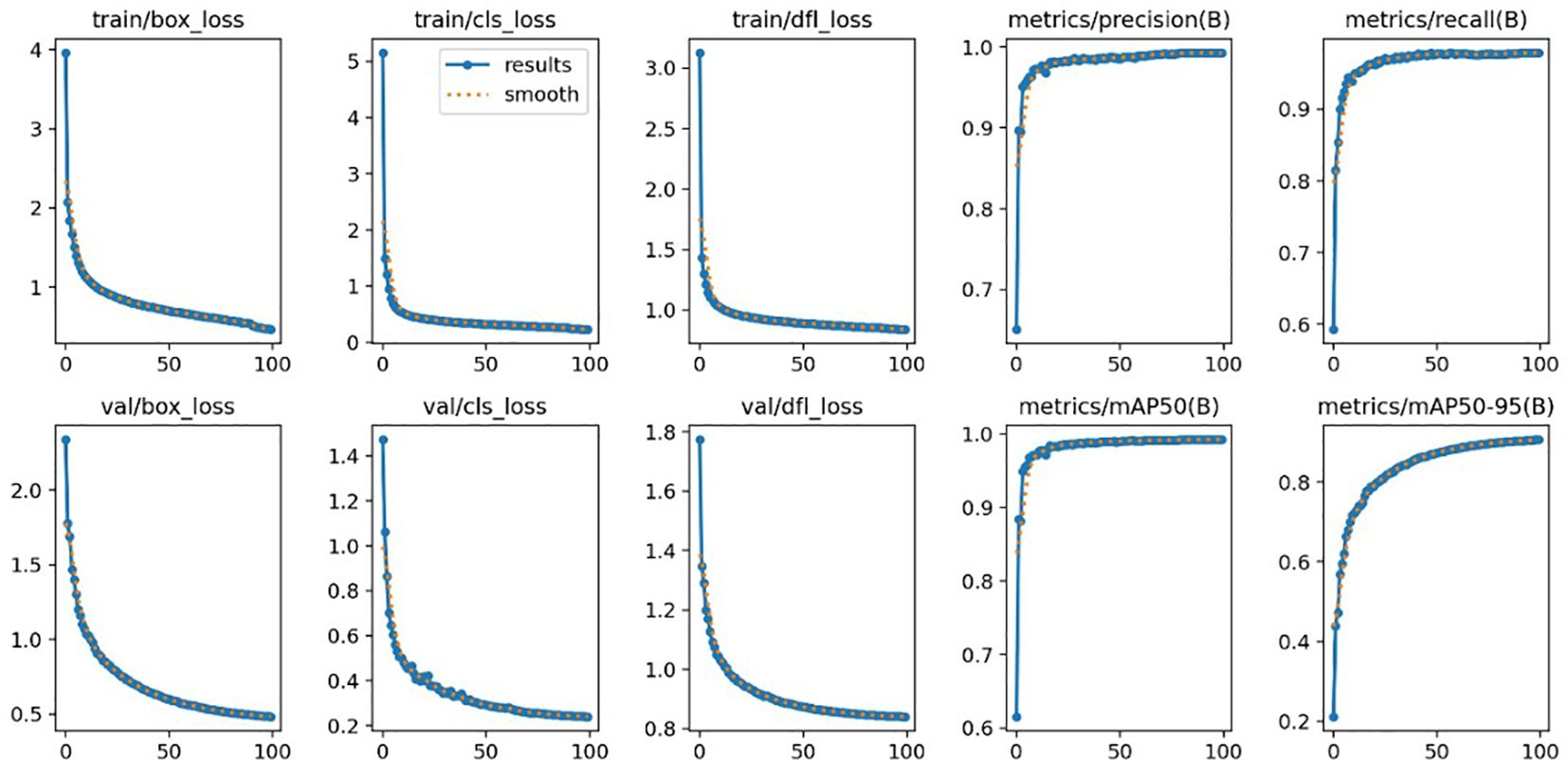
The method proposed in this paper is implemented based on the PyTorch 1.9.0 framework. The model runs on a Linux 18.04 system and is trained from scratch using two NVIDIA GTX 3090 GPUs. The batch size for the DataLoader is set to 16, and the SGD optimization method is chosen. CUDA v11.1 is utilized to accelerate computations, with a batch size of 8 and an initial learning rate of 0.01. We employ the Warmup strategy to gradually increase the learning rate during training. The model is initially trained for 100 epochs on the MOT17 dataset, followed by fine-tuning for 40 epochs, with a training duration of approximately 56 hours. Similarly, on the BirdTrack dataset, the model is trained for 100 epochs initially, followed by 40 epochs of fine-tuning, with a training duration of about 49 hours. During fine-tuning, the learning rate starts from the initial value and decreases after 10 epochs. Due to variations in the total number of tracks per frame in trajectory tracking, to align the lengths of tracking results across all frames, we pad empty tracking results in each frame’s output when stacking multi-frame results into batches. The training results of the improved YOLOv8 mode are shown in Figure 5.
4.4 Compare the improved method with attention mechanism
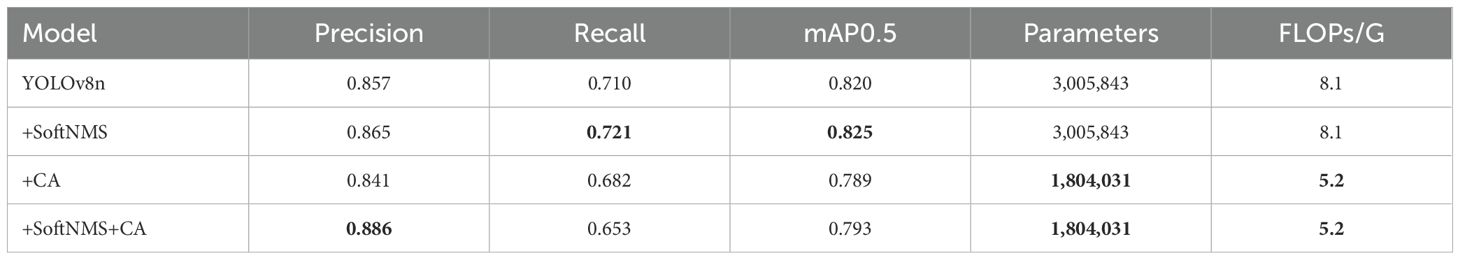
As shown in Table 2, we evaluated our proposed model based on the YOLOv8 baseline network. The integration of Soft-NMS technology resulted in significant improvements across various performance metrics. Notably, we observed an increase in precision by 0.93%, recall by 1.55%, and mAP0.5 by 0.61%. Furthermore, we achieved a reduction in parameter count by 39.98% and a decrease in FLOPs by 35.8%. When combined with Coordinate Attention, the precision improved by 3.38%. These findings underscore the effectiveness of these enhancement techniques in optimizing the YOLOv8 model, enhancing object detection capabilities while maintaining a balance between accuracy and lightweight design.
Although the individual performance may decrease after incorporating CA, the combination of Soft-NMS and Coordinate Attention can improve performance compared to the baseline, owing to the complementary nature of these two techniques. Soft-NMS suppresses redundant detections, compensating for the slight performance decrease caused by Coordinate Attention. Additionally, the integration of Coordinate Attention provides benefits such as reducing complexity and computational costs, enhancing feature representation, and increasing receptive fields, which contribute to overall performance improvement.
4.5 Compare the improved method on different datasets
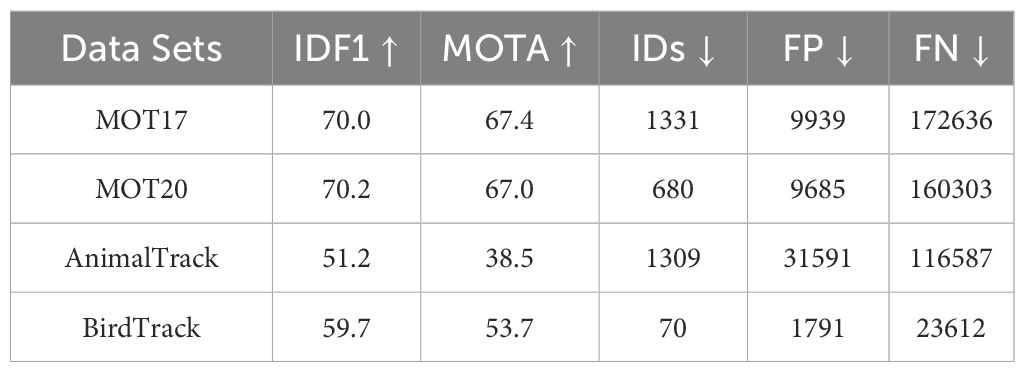
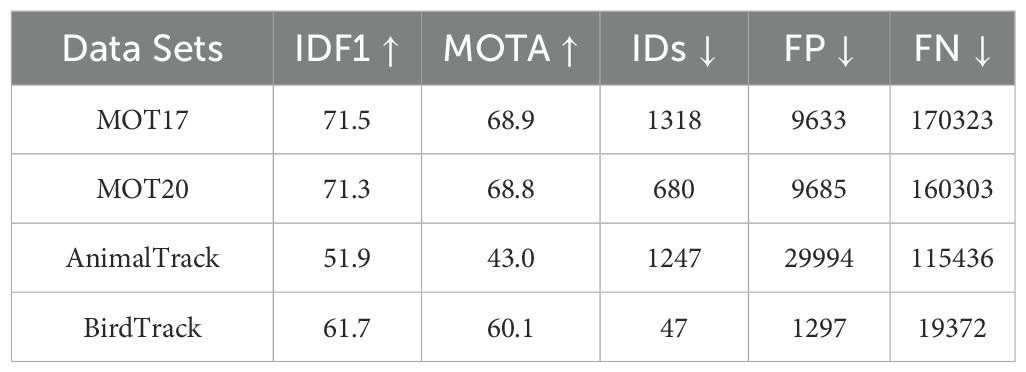
We employed a straightforward yet effective multi-object tracking data association method called BYTE. With the improved YOLOv8 detector, AviaryMOT, compared to the original ByteTrack, achieved an increase of 1.5 MOTA and 1.8 IDF1 on the MOT17 test set at a speed of 30 FPS. For the original ByteTrack algorithm, as shown in Table 3, MOTA scores recorded on four different datasets were (67.4,67.0,38.5,53.7), indicating high accuracy and effectiveness in tracking multiple targets. On the other hand, when used in conjunction with the YOLOv8 detector, as shown in Table 4, MOTA increased to 67.9%, and IDF 1 score increased to 71.5%, demonstrating improved detection and tracking precision. False positives (FP) and false negatives (FN) values were 9633 and 170323 respectively. A comprehensive improvement over ByteTrack is evident. Overall, both algorithms demonstrate their capability to effectively track targets within the given data. These results provide valuable insights into the tracking performance of each algorithm and aid in selecting the most suitable algorithm based on specific tracking requirements and dataset characteristics.
4.6 Ablation study
As shown in Table 5, the integration of Soft-NMS technology resulted in significant improvements across various performance metrics. The experiments observed a 0.93% increase in precision, 1.55% improvement in recall, and 0.61% enhancement in mAP0.5. Additionally, the improved method achieved a 39.98% reduction in parameter count and 35.8% decrease in FLOPs.
The individual performance with CA alone shows degradation compared to the baseline. However, the combination of Soft-NMS and Coordinate Attention improves performance due to their complementary nature. Soft-NMS suppresses duplicate detections, compensating for the slight performance drop caused by Coordinate Attention. Furthermore, the integration of Coordinate Attention provides benefits such as reduced complexity and computational costs, enhanced feature representation, and increased receptive field, contributing to improved overall performance while maintaining a balance between accuracy and lightweight design.
4.7 Compare different methods on BirdTrack
Table 6 presents the results of our method and other tracking approaches on the BirdTrack dataset, including DeepSORT, CenterTrack, TrackFormer, GSDT, and MOTR. Since these methods have not been previously evaluated on our custom BirdTrack dataset, we implemented them on our experimental setup to obtain their results. Each indicator in the table is accompanied by an arrow, where “ ↑ “ indicates higher values are preferred, and “ ↓ “ indicates lower values are desired.
From Table 6, it is evident that our algorithm achieves outstanding results on the BirdTrack dataset in terms of MOTA and IDF1, with scores of 60.1% and 61.7% respectively, leading the second-best by 6.3% and 0.5% respectively. Apart from MOTA and IDF1, other metrics also show some improvement with our proposed method. However, the performance of our method on FP and FN is not the best, which may be attributed to the similarity between falsely detected and correctly identified targets, leading to false positives.
The excellent results of MOTA and IDF1 demonstrate that our model exhibits robust tracking performance, maintaining stable trajectories. This is mainly due to the utilization of the advanced YOLOv8 detection algorithm and the incorporation of the improved attention mechanism, Coordinate Attention, which enhances the extraction of receptive field features. Figure 6 illustrates the tracking results of the improved model on samples of bird images. These images depict various scenes, including sky, water, and land scenarios. The bounding boxes along with the corresponding class labels and confidence scores indicate the detected birds and their associated levels of certainty. The improved model can detect more birds, including those in densely populated areas with complex backgrounds. The bounding boxes can accurately localize the birds, even in complex scenes with dense bird populations. Furthermore, the improved model demonstrates increased sensitivity to birds of various sizes. It can successfully detect and track birds of different sizes and distances, thereby comprehensively covering birds of different scales. This capability is particularly important in real-world scenarios where birds may appear at different scales. The examples of Crane stork bird tracking results are shown in Figure 6.
5 Discussion
ByteTrack exhibits strong robustness to occlusion due to its accurate detection performance and the assistance of low-scoring detection boxes. The primary goal of multi-object tracking is to assign IDs to detected objects and maintain consistent IDs for the same objects across subsequent frames. Most existing work in this field is based on pedestrian datasets, where challenges such as occlusion, background clutter, and motion blur are less prevalent. However, in complex environments like those involving stork and heron birds, these adverse conditions occur more frequently, making it exceedingly difficult to maintain stable tracking.
This paper proposes a novel multi-object tracking algorithm, AviaryMOT, based on YOLOv8. AviaryMOT introduces an improved attention mechanism module called Coordinate Attention and Soft-NMS into the YOLOv8 detector compared to other methods. AviaryMOT can enhance network performance, strengthen the model’s feature extraction capabilities, maintain stable tracking in complex environments, and achieve better results by weighting channel and spatial attention. Experimental results on a stork and heron bird multi-object tracking dataset demonstrate that AviaryMOT performs excellently in tracking these birds. Several evaluation metrics reach optimal performance, validating the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
6 Conclusion
In bird multi-object tracking scenarios, challenges such as frequent occlusions, multiple appearances and disappearances of targets, and high visual similarity among birds are commonly encountered. To address these issues, we proposed a bird multi-object tracking algorithm called AviaryMOT, which utilizes a fusion technique of shallow and deep features to construct a new feature detection layer, thereby enhancing the accuracy and effectiveness of convolutional neural networks in tracking bird targets. The AviaryMOT algorithm integrates the Coordinate Attention module into the YOLOv8 architecture and incorporates SoftNMS to improve the detection performance of crane and stork species in occluded scenarios. Additionally, it employs the BYTE data association method, effectively leveraging the similarity between low-confidence detection boxes and tracking trajectories to extract actual targets from low-confidence boxes while filtering out the background.
Based on YOLOv8 as the object detector, this algorithm combines an improved non-maximum suppression (NMS) approach to significantly enhance detection performance for crane and stork species in complex scenes. Evaluation experiments conducted on multiple public datasets demonstrate that the proposed AviaryMOT algorithm outperforms existing models overall, maintaining the stability of target trajectories while ensuring high-quality detection.
Our approach exhibits good versatility and can adapt to various complex application scenarios, including but not limited to those involving stork and heron birds. Particularly in outdoor scenarios involving wildlife, AviaryMOT demonstrates highly competitive performance. In the future, we believe that our model can be used for multi-object tracking in important complex scenarios involving stork and heron birds and for exploring their activities.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
CL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XM: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. NS: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HL: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (under Grant Nos. 61931003, 62171044), the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (Grants No. 4222004).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aslam R. W., Naz I., Shu H., Yan J., Quddoos A., Tariq A., et al. (2024a). Multi-temporal image analysis of wetland dynamics using machine learning algorithms. J. Environ. Manage. 371, 123123. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.123123
Aslam R. W., Shu H., Javid K., Pervaiz S., Mustafa F., Raza D., et al. (2024b). Wetland identification through remote sensing: insights into wetness, greenness, turbidity, temperature, and changing landscapes. Big Data Res. 35, 100416. doi: 10.1016/j.bdr.2023.100416
Aslam R. W., Shu H., Naz I., Quddoos A., Yaseen A., Gulshad K., et al. (2024c). Machine learning-based wetland vulnerability assessment in the sindh province ramsar site using remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 16, 928. doi: 10.3390/rs16050928
Aslam R. W., Shu H., Tariq A., Naz I., Ahmad M. N., Quddoos A., et al. (2024d). Monitoring landuse change in uchhali and khabeki wetland lakes, Pakistan using remote sensing data. Gondwana Res. 129, 252–267. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2023.12.015
Aslam R. W., Shu H., and Yaseen A. (2023a). Monitoring the population change and urban growth of four major Pakistan cities through spatial analysis of open source data. Ann. GIS 29, 355–367. doi: 10.1080/19475683.2023.2166989
Aslam R. W., Shu H., Yaseen A., Sajjad A., and Abidin S. Z. U. (2023b). Identification of timevarying wetlands neglected in Pakistan through remote sensing techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollution Res. 30, 74031–74044. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-27554-5
Bewley A., Ge Z., Ott L., Ramos F., and Upcroft B. (2016). “Simple online and realtime tracking,” in 2016 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP) (IEEE). 3464–3468.
Bodla N., Singh B., Chellappa R., and Davis L. S. (2017). “Soft-nms–improving object detection with one line of code,” in Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 5561–5569.
Dendorfer P. (2020). Mot20: A benchmark for multi object tracking in crowded scenes. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.09003. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2003.09003
Dendorfer P., Osep A., Milan A., Schindler K., Cremers D., Reid I., et al. (2021). Motchallenge: A benchmark for single-camera multiple target tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vision 129, 845–881. doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01393-0
Ferryman J. and Shahrokni A. (2009). “Pets2009: dataset and challenge,” in 2009 Twelfth IEEE international workshop on performance evaluation of tracking and surveillance (IEEE). 1–6.
Ge Z. (2021). Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.08430. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2107.08430
Geiger A., Lenz P., Stiller C., and Urtasun R. (2013). Vision meets robotics: The kitti dataset. Int. J. Robotics Res. 32, 1231–1237. doi: 10.1177/0278364913491297
Hou Q., Zhou D., and Feng J. (2021). “Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 13713–13722.
Hu J., Shen L., and Sun G. (2018). “Squeeze-and-excitation networks,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 7132–7141.
Jocher G., Chaurasia A., Stoken A., Borovec J., Kwon Y., Michael K., et al. (2022). ultralytics/yolov5: v7. 0-yolov5 sota realtime instance segmentation. Zenodo. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.7347926
Leal-Taixé L. (2015). Motchallenge 2015: Towards a benchmark for multi-target tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:1504.01942. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1504.01942
Liu H., Liu C., Hao Z., Zhou Z., and Qiu J. (2023). “Global multi-object transformer tracking with detecting and attention mechanism,” in 2023 IEEE 13th International Conference on CYBER Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems (CYBER) (IEEE). 1068–1072.
Long J., Shelhamer E., and Darrell T. (2015). “Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 3431–3440.
Luo W., Xing J., Milan A., Zhang X., Liu W., and Kim T.-K. (2021). Multiple object tracking: A literature review. Artif. Intell. 293, 103448. doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2020.103448
Meinhardt T., Kirillov A., Leal-Taixe L., and Feichtenhofer C. (2022). “Trackformer: Multi-object tracking with transformers,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 8844–8854.
Milan A. (2016). Mot16: A benchmark for multi-object tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.00831. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1603.00831
Naz I., Ahmad I., Aslam R. W., Quddoos A., and Yaseen A. (2023). Integrated assessment and geostatistical evaluation of groundwater quality through water quality indices. Water 16, 63. doi: 10.3390/w16010063
Naz I., Fan H., Aslam R. W., Tariq A., Quddoos A., Sajjad A., et al. (2024). Integrated geospatial and geostatistical multi-criteria evaluation of urban groundwater quality using water quality indices. Water 16, 2549. doi: 10.3390/w16172549
Neubeck A. and Van Gool L. (2006). “Efficient non-maximum suppression,” in 18th international conference on pattern recognition (ICPR’06) (IEEE), Vol. 3. 850–855.
Pang J., Qiu L., Li X., Chen H., Li Q., Darrell T., et al. (2021). “Quasi-dense similarity learning for multiple object tracking,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 164–173.
Sun P., Cao J., Jiang Y., Zhang R., Xie E., Yuan Z., et al. (2020). Transtrack: Multiple object tracking with transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.15460. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2012.15460
Terven J., Córdova-Esparza D.-M., and Romero-González J.-A. (2023). A comprehensive review of yolo architectures in computer vision: From yolov1 to yolov8 and yolo-nas. Mach. Learn. Knowledge Extraction 5, 1680–1716. doi: 10.3390/make5040083
Voigtlaender P., Krause M., Osep A., Luiten J., Sekar B. B. G., Geiger A., et al. (2019). “Mots: Multi-object tracking and segmentation,” in Proceedings of the ieee/cvf conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 7942–7951.
Wang C.-Y., Bochkovskiy A., and Liao H.-Y. M. (2023). “Yolov7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 7464–7475.
Wang Q., Wu B., Zhu P., Li P., Zuo W., and Hu Q. (2020). “Eca-net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 11534–11542.
Wang Z., Zheng L., Liu Y., Li Y., and Wang S. (2020). “Towards real-time multi-object tracking,” in European conference on computer vision. 107–122 (Springer).
Wen L., Du D., Cai Z., Lei Z., Chang M.-C., Qi H., et al. (2020). Ua-detrac: A new benchmark and protocol for multi-object detection and tracking. Comput. Vision Image Understanding 193, 102907. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2020.102907
Wojke N., Bewley A., and Paulus D. (2017). “Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric,” in 2017 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP) (IEEE). 3645–3649.
Woo S., Park J., Lee J.-Y., and Kweon I. S. (2018). “Cbam: Convolutional block attention module,” in Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV). 3–19.
Yu F., Chen H., Wang X., Xian W., Chen Y., Liu F., et al. (2020). “Bdd100k: A diverse driving dataset for heterogeneous multitask learning,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. (Springer). 2636–2645.
Zhang L., Gao J., Xiao Z., and Fan H. (2022). Animaltrack: A large-scale benchmark for multi-animal tracking in the wild. (Springer). arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.00158.
Zhang X., Liu C., Yang D., Song T., Ye Y., Li K., et al. (2023). Rfaconv: Innovating spatial attention and standard convolutional operation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.03198. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2304.03198
Zhang Y., Sun P., Jiang Y., Yu D., Weng F., Yuan Z., et al. (2022). “Bytetrack: Multi-object tracking by associating every detection box,” in In European conference on computer vision. 1–21. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2110.06864
Zhang Y., Wang C., Wang X., Zeng W., and Liu W. (2021). Fairmot: On the fairness of detection and re-identification in multiple object tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vision 129, 3069–3087. doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01513-4
Keywords: multiple object tracking, Aviary Attention, YOLOv framework, ByteTrack, wetlands protection
Citation: Liu C, Ma X, Zhou J, Sun N and Liu H (2025) AviaryMOT: Aviary Attention-based adaptive multi-object tracking of cranes and storks in wetlands. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1524134. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1524134
Received: 07 November 2024; Accepted: 06 May 2025;
Published: 02 June 2025.
Edited by:
Hui Zhao, Guangdong Ocean University, ChinaReviewed by:
Rana Waqar Aslam, Wuhan University, ChinaPetros Karvelis, University of Ioannina, Greece
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Ma, Zhou, Sun and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chang Liu, bGl1LmNoYW5nLmNuQGllZWUub3Jn
 Chang Liu
Chang Liu Xuran Ma2
Xuran Ma2 Hengming Liu
Hengming Liu